1. Introduction
Various climate extremes brought on by climate change have significantly impacted the growth of the human economy and society. With green development being deeply ingrained in people's minds, countries are constantly and thoroughly researching environmental governance to deal with the increasingly severe climate change. China, among other countries, actively participates in global governance through its ongoing reform and opening up [
1]. The agricultural sector is a key driver of national economic growth and social development, as well as a significant carbon source and sink system that is crucial for climate change mitigation [
2]. The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) of the United Nations also link four of the 17 global development goals to agriculture, highlighting the significance of green development in agriculture. Therefore, as a largely agricultural country, China is not only responsible for ensuring food security, but is also obligated to conduct environmental management.
Along with China's agricultural modernization, the agricultural economy has grown quickly in recent years. However, this growth is currently at a standstill due to the challenge of dynamic optimization operation under the dual constraints of the serious dependence of agricultural economic growth on resources and the environment and the need to reduce emissions and increase the efficiency of agricultural production in the context of the transition to a greener economy [
3]. The growth of a moderate agricultural scale and directing the orderly transfer of land management rights have become crucial pillars for optimizing resource allocation, maintaining food security, and enhancing production efficiency [
4]. Industrial agglomeration reflects the degree of convergence of agriculture in a particular region; it is a crucial indicator of scale, as well as a prerequisite for the intensive use of local resources, and it is more and more linked to the development of environmentally friendly agriculture [
5]. In a time when China's agricultural green development is rapidly advancing, industrial agglomeration offers a solution for promoting agricultural production in order to lower emissions and increase efficiency, coordinate the relationship between agricultural economic development and environmental protection, and promote land transfer in order to realize moderate-scale operation to ultimately achieve the goal of green development. So, is there a relationship among land transfers, industrial agglomeration, and agricultural green production efficiency? Can land transfers by industrial agglomerations help increase agricultural green production efficiency? Does the promotive effect of an industrial agglomeration on agricultural green production efficiency change at different levels of land transfer? These are the primary issues that this study aims to addressed. Therefore, the scientific measurement of agricultural green production efficiency, analysis of the characteristics of its spatial and temporal evolution and core power sources of growth, exploration of the driving role of industrial agglomeration on agricultural green production efficiency, and clarification of its mechanism of action and the differential characteristics of the impacts’ effects are of great theoretical and practical significance for promoting agricultural green development.
Existing research has three primary opposing viewpoints regarding how industrial agglomeration affects agricultural green production efficiency: First, industrial agglomeration promotes agricultural green production efficiency [
6]; that is, industrial agglomerations have effects such as scale and knowledge spillover, which can continuously stimulate the endogenous momentum of agricultural green development by improving technological innovation, boosting regional competitiveness, optimizing resource allocation, and specializing the division of labor, among other things. Second, industrial agglomeration prevents increases in agricultural green production efficiency [
7]. The congestion effect, which occurs when resource consumption exceeds the environment's capacity, is triggered by excessive industrial agglomeration. This effect impedes economic development, causes environmental pollution, and ultimately impedes the development of green agriculture. Areas with more developed industrial clusters frequently have more serious environmental damage. Third, there is a nonlinear "U-" [
8] or "inverted "U-" [
9] shaped effect of industrial agglomeration on agricultural green production efficiency. The impact of industrial agglomeration on agricultural green production efficiency changes with the degree of agglomeration, i.e., at the early stage of industrial agglomeration, there is both the effect of capacity expansion, which aggravates resource use and environmental damage, and the possibility of the scale effect, which reduces pollution. In contrast, at the later stage of industrial agglomeration, there is not only the effect of green technological innovation, which reduces resources, but also the effect of scale, which reduces pollution. Existing research has also demonstrated that land transfer is a significant element influencing agricultural green production efficiency. According to some researchers, land transfer and agricultural green production efficiency are positively correlated, meaning that achieving large-scale operations through land transfer can directly optimize resource utilization and indirectly promote green agricultural development by supporting inclusive digital finance and digital village development [
10]. Some scholars have also argued that inflows and outflows in land transfer have the opposite effects on agricultural green production efficiency [
11]. Additionally, other researchers have discovered that elements such as the degree of financial support for agriculture [
12], environmental regulation [
13], and the degree of marketization [
14] all have varying degrees of substantial effects on agricultural green production efficiency.
There are abundant studies on industrial agglomeration and agricultural green production efficiency, but only some studies have included land transfer to explore the intrinsic correlation among the three. As a result, this study elaborates on the following principal aspects: First, the study's focus is widened, and Chinese provincial panel data from the years 2006–2020 were used as the research sample to measure and analyze the current traits of geographical and temporal evolution, as well as the primary driving forces behind agricultural green production efficiency in China. Second, the interrelationships between industrial agglomeration, land transfer, and agricultural green production efficiency are clarified, the direct impact of industrial agglomeration on agricultural green production efficiency is examined, and the mediating effect of land transfer in this process is explored. The third goal is to determine whether different levels of land transfer differently affect industrial agglomeration's effects on agricultural green production efficiency. This study aims to establish a scientific foundation for the green development of Chinese agriculture by expanding on the aspects mentioned above and then suggesting corresponding countermeasures.
2. Theoretical Analysis and Research Hypothesis
2.1. Industrial Agglomeration Promotes Land Circulation
Following the theory of external economies of scale, the expansion of scale results in an incremental return to scale for regional production operators, meaning that a region with a larger industrial scale is more productive than a region with a smaller scale. This result further encourages the continuous extension of the regional industrial chain and the formation of industrial agglomerations [
15]. It is shown that industrial agglomeration reflects the process of aggregating agricultural production resources on a spatial scale and depicts the characteristics of the concentration of agricultural industry in a particular region. Industrial agglomeration, based on regional resource endowments, fosters intraregional organization and collaboration by developing leading enterprises and branding to form intensive and effective whole-industry-chain agglomerations, thereby enhancing the comprehensive agricultural benefits [
8]. Moreover, land transfer provides for the concentration of agricultural industries in specific areas.
On the one hand, due to the optimal allocation of land resources serving as the foundation and key component of industrial agglomeration, land transfer is necessary for its formation and growth. At the same time, by encouraging land transfer, production operators revitalize underutilized and abandoned land, raise the scale and standardization of agricultural production, and increase the scale of production, thereby realizing economic benefits. Additionally, as a result of the collaboration of many participants, different scales of operating modes are developed during the process of industrial chain extension, which further develops and consolidates the level of industrial agglomeration. On the other hand, the modes of land transfer have improved due to industrial agglomeration. Differences in resource endowment, environmental regulation, and market level have resulted in obvious regional distinctions in the kinds of land transfer supported by industrial agglomeration, and these have been used to promote agricultural industrialization and modest-scale operation in each region. Each region also develops various transfer methods, such as home-base reform and "share + cooperation", according to local conditions, and these play a significant role in local agricultural development, in addition to the main transfer methods that are already in use, such as subcontracting, leasing, transfer, swapping, and loans [
16]. Industrial agglomeration gives land transfer an intrinsic incentive. Thus, the following hypothesis is put forth:
H1.
Land transfer is aided by industrial agglomeration.
2.2. Land Transfer Enhances the Agricultural Green Production Efficiency
The rural collective land contract management system encouraged changes in agricultural production techniques. It significantly increased production efficiency in the early stages of China's reform and opening up. However, the consequences of its rural land fragmentation also forced Chinese agriculture into the dilemma of smallholder production, thus severely limiting further improvements in production efficiency [
17]. Land transfer refers to the transfer of land contracted by farmers to a third party under the principle of equal, paid, and voluntary ownership. Land transfer provides a way to revitalize land resources and break the longstanding smallholder production method [
18].
On the one hand, resource allocation theory suggests that under market-complete conditions, the scarcity of land resources leads to their rational allocation to various areas of agricultural production to achieve the best use thereof, i.e., production operators with higher green production efficiency will expand their production operations by obtaining transferred land to achieve more and more efficient output, while production operators with lower green production efficiency, because they are disadvantaged in this competition, prefer to transfer land away to reduce production costs,, obtain higher output, and free up agricultural labor resources to obtain more non-farm income. On the other hand, for a long time, due to the uncertainty of the policy, some farmers have been worried about the loss of land rights and interests after the expiration of their land contracts. Thus, they have adopted such methods as abandonment or sloppy management to protect their land rights and interests. According to the land property rights theory, in most cases, clear land property rights can systematically protect farmers' rights and interests. Long-term and stable property rights prompt farmers to increase their investment in land, agricultural production materials, and technology in order to improve the efficiency of land resource utilization, i.e., land transfer consolidates land contractors' land rights and interests, fundamentally changes farmers' rough production and operation modes, and improves agricultural green production efficiency. It can be seen that land transfer optimizes resource allocation, transforms production methods, increases green technology and material inputs, and reduces arable land abandonment, thus improving agricultural resource utilization and, ultimately, enhancing agricultural green production efficiency. Accordingly, hypothesis H1 is combined with the following hypothesis:
H2.
Industrial agglomeration can improve agricultural green production efficiency by promoting land transfer.
2.3. Nonlinear Relationship among Industrial Agglomeration, Land Transfer, and Agricultural Green Production Efficiency
The degree of industrial agglomeration is a crucial indicator of agricultural modernization because it may effectively encourage the green development of agriculture and, to a certain extent, reflect the size of arable land operations and the current activity of the land-transfer market. However, on the one hand, from the perspective of the theory of economies of scale, the expansion of the production scale enables production operators to use advanced technology and materials and other factors of production, as well as to specialize in the division of labor and management, thus saving costs and improving production efficiency; economies of scale in production are some of the necessary steps for maximizing profits. However, the effect of economies of scale is not absolute, and when the continuous expansion of scale causes the excessive concentration of industry, it may lead to external diseconomies, making it difficult to coordinate all aspects of production and, thus, significantly increasing production and distribution costs, causing waste of resources and environmental pollution, impacting the industrial structure, and ultimately inhibiting agricultural green production efficiency. On the other hand, since land transfer in China still primarily occurs among friends with little difference in their land-use efficiency, it is challenging for land to flow into production operators with higher green production efficiency; this not only cannot play the role of optimizing resource allocation, but even further causes the fragmentation of land resources, thereby reducing green production efficiency; at the same time, land transfer may simultaneously affect the original, refined production model while increasing the scale of operation due to the disparities in resource endowment between each location. Frequent land transfers are ineffective in stabilizing agricultural output considering the long-cycle characteristics of agricultural production, which ultimately prevents an increase in agricultural green production efficiency. Therefore, industrial agglomeration may have varied effects on agricultural green production efficiency due to the rising amount of land transfer. In general, the boosting effect of industrial agglomeration on agricultural green production efficiency often diminishes over time while land-transfer frequency increases. Consequently, the following hypothesis is put forth:
H3.
Under various levels of land transfer, industrial agglomeration has a diverse impact on agricultural green production efficiency.
3. Study Design, Models, and Data
3.1. Study Design
3.1.1. Super-Efficient EBM Model
Agricultural green production efficiency is a crucial benchmark for determining green agricultural development because it incorporates pollution emissions into a measurement framework to fully assess the state of agricultural development while achieving the maximum output under the assumption of established resource factor inputs. This approach assesses the degree of economic development and highlights the value of resource utilization and environmental protection [
19]. The super-efficient EBM model suggested by Tone and Tsutsui [
20] is a viable option for assessing agricultural green production efficiency because it considers the coexistence of radial and non-radial relationships, resource inputs, and both desired and unintended outcomes. Referring to a study by Qu et al. [
21], this study constructs a non-oriented global super-efficient EBM model with non-desired outputs as follows:
In Eq. (1), the letters , , and stand for the weights of the input factors, the desired outcomes, and the undesirable outcomes, respectively. Input redundancy variables are denoted by , while and , respectively, denote the desired output deficiency variables and undesirable output redundancy variables. represents the radial and non-radial slack combination degree and accepts values between 0 and 1. Weights were applied to the data in this research by using the MaxDEA ULTRA 9 software, which can more accurately reflect the weights of each input element and outcome, thus avoiding subjectivity when defining weights in the model.
3.1.2. Global Malmquist–Luenberger (GML) Index
The GML index was utilized to examine the number of changes in agricultural green production efficiency across the reporting periods to better understand the dynamics of agricultural green production efficiency. Because the GML index has greater transferability and continuity than the ML index, thus allowing the potential issue of the ML index's lack of a workable solution to be overcome and permitting technological regression, it is frequently used to quantify green production efficiency [
22,
23]. Referring to a related study by Oh et al. [
24], the GML index was constructed as follows:
In Eq. (2),
was derived from the global benchmark production possibility set. If
> 1, this indicates that agricultural green production efficiency increased; otherwise, it indicates that agricultural green production efficiency decreased. Eq. (3) illustrates how the GML index is divided into two parts—the green technical efficiency index (GEC) and the green technical change index (GTC)—in order to investigate the fundamental driving force behind agricultural green production efficiency.
3.2. Model Setting
3.2.1. Benchmark Regression Model
Based on a prior theoretical study, a fixed-effects model was utilized for empirical testing to confirm the direct impact of industrial agglomeration on agricultural green production efficiency. The fixed-effects model is established as follows:
In Eq. (4), represents agricultural green production efficiency; is the region; is the year; is the intercept term; represents industrial agglomeration, and is its coefficient that is to be estimated; represents the control variable, and is its coefficient vector; is an individual effect; is a random error term. Furthermore, because the model configuration for Eq. (4) and the investigation of the impacts of industrial agglomeration on green technical efficiency (GEC) and green technical change (GTC) are essentially the same, they are not reproduced here.
3.2.2. Mechanism of Action Test Model
This research employed a panel mediating effect model to investigate the mediating effect of land transfer in order to determine if industrial agglomeration can improve agricultural green production efficiency through the promotion of land transfer. Based on equation (4) and relevant studies [
25], the mediating effect model was created as follows.
In Equations (5) and (6), is the mediating variable for land transfer; and are the coefficients for industrial agglomeration that are required to be estimated; is the coefficient for land transfer that needs be estimated; the remaining variables all have definitions that are compatible with those in Eq. (4). The coefficient in Eq. (4) represents the total effect of industrial agglomeration on agricultural green production efficiency; coefficient in Eq. (5) represents the impact of industrial agglomeration on land transfer; coefficient in Eq. (6) represents the direct impact of industrial agglomeration on agricultural green production efficiency. The indirect impact is significant when the coefficients and are significant. Additionally, if the coefficient is significant and has the same sign as , a partial mediating effect with an effect value of is recognized.
3.2.3. Threshold Effect Model
Based on the aforementioned theoretical study, it is necessary to determine if industrial agglomeration has a variable impact on agricultural green production efficiency. Following the pertinent study by Hansen et al. [
26], the threshold effect of land transfer was tested by using land transfer as a threshold variable to create a segmental function of industrial agglomeration with respect to agricultural green production efficiency. Equation (4) and the panel threshold effect model were configured as follows:
In Eq. (7), and are the coefficients to be estimated for the corresponding threshold intervals; is the indicative function, taking the value of 1 if the expression in parentheses is true and 0 otherwise; is the threshold value to be determined; the remaining variables have meanings consistent with those in Eq. (4).
3.3. Variable Setting
3.3.1. Explained Variable
This study’s explanatory variable is agricultural green production efficiency, which is the global index calculated with the super-effective EBM-GML model. The following are some of the illustrations of the input and output indicators utilized for the measurement.
Regarding related studies [
2,
14,
27], in this study, the total sown area of agricultural works (thousand hectares), agricultural employment (ten thousand people), agricultural fertilizer application (converted) (tons), pesticide use (tons), agricultural plastic film use (tons), the total power of agricultural machinery (ten thousand kilowatts), agricultural diesel fuel use (tons), rural electricity consumption (billion-kilowatt hours), and effective irrigation area (thousand hectares) were used as input indicators. Because the number of individuals in agricultural employment is not directly published in the statistical yearbooks, this study referred to the method of Liu et al. [
28] and used the number of individuals employed in the primary sector multiplied by the ratio of total agricultural output value to total agricultural, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery output value in order to derive this value. The total agricultural output value (billion yuan) was used as the desired output indicator, and the base period of 2006 was used as a deflator to eliminate the effect of the price level; agricultural carbon emission (tons) and agricultural surface pollution were utilized as non-desired output indicators. The total agricultural carbon emissions were computed using
, where
represents each carbon source's carbon emissions,
represents each source's carbon usage, and
represents each source's carbon emission coefficient. The main agricultural carbon sources and coefficients were the following: agricultural tillage (3.126 kg/hm
2), according to a study conducted by the Institute of Biology and Technology, China Agricultural University; agricultural fertilizer (0.8956 kg/kg) and pesticide (4.9341 kg/kg), according to a study conducted by Oak Ridge National Laboratory; agricultural plastic film (5.18 kg/kg), according to a study conducted by Institute of Agricultural Resources and Ecological Environment, Nanjing Agricultural University, China; agricultural diesel (0.5927 kg/kg), according to a relevant study by the IPCC UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; agricultural irrigation (20.476 kg/hm
2), according to a relevant study by Wang et al. [
29]. Pesticide loss or residue, agricultural plastic film, and fertilizer use are the main causes of agricultural surface source pollution. Each source's pollution output is a function of its usage amount and pollution coefficient. According to the First National Pollution Source Census's Handbook of Pollution Coefficients for Agricultural Surface Source Pollution Sources and a study by Lu et al. [
30], the coefficient of pesticide loss was determined to be 50%, that of agricultural plastic films was determined to be 10%, and that of fertilizer residues was determined to be 75%. However, because the pollutants from each source differ and cannot simply be statistically added up, a relevant study by Zhou et al. [
31] was referred to. The amount of pollution from each pollutant was standardized by using the entropy value method before being finally integrated into a comprehensive index through objective assignment, thus avoiding the measurement error caused by inconsistency in the measurement scale.
3.3.2. Core Explanatory Variable
The main explanatory factor in this study was industrial agglomeration, which was calculated by using locational entropy [
32,
33], and this eliminated the effects of regional-scale differences and other effects and allowed the level of agricultural agglomeration to be calculated more precisely; the specific measurement formula is as follows:
In Eq. (8), stands for region 's industrial agglomeration in year , and its industrial agglomeration is proportional to the value; and stand for region 's total agricultural output value and regional GDP in year , respectively; and stand for the country's total agricultural output value and GDP in year , respectively.
3.3.3. Intermediate Variable
Land transfer served as the mediating variable in this study. It was represented by the ratio of the total area of farmland under a family contract that had been transferred to the entire area of farmland under a family contract in the area [
34,
35]. The total area of transfer included the areas of leasing (subcontracting), shareholding, and other forms, as well as the areas transferred to farmers, family farms, professional cooperatives, enterprises, and other subjects.
3.3.4. Control Variables
Because of the vulnerability of agricultural green production efficiency to many factors, the following variables were considered as control variables to improve the findings' external validity [
11,
21,
36,
37]:
The level of financial support for agriculture (Sup), which was characterized by the ratio of the local financial expenditure on agriculture, forestry, and water affairs to the regional GDP;
Environmental regulation (Reg), which was characterized by the ratio of completed investments in industrial pollution control to the added value of the industry;
R&D intensity (R&D) was characterized by using the ratio of internal expenditure on R&D funding to the regional GDP;
Foreign direct investment (For), which was characterized by using the total foreign direct investment multiplied by the current USD/CNH exchange rate and then divided by the regional GDP;
The level of transportation infrastructure (Tra), which was characterized by using the number of road miles;
The proportion of affected area (Dis), which was characterized by using the ratio of the affected area to total crop-sowing area;
The level of marketization (Mar), which was characterized by the Fan Gang marketization index, which was derived from a related study by Xie et al. [
38];
The technology market development (Tmd) level was characterized by using the technology market turnover with respect to the regional GDP.
3.4. Data Source
The sample period for this article was chosen as 2006–2020 in consideration of each indicator's availability, and the panel data of 30 Chinese provinces (excluding Tibet, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan) were the subject of the examination. The China Rural Statistical Yearbook, China Statistical Yearbook, EPS database, and the statistical yearbooks and bulletins of each province and city in the corresponding years were the primary sources of data on agricultural green production efficiency and industrial agglomeration. The data on land transfer were obtained from the China Rural Management Statistical Annual Report and China Agricultural Statistics; for some missing values, linear interpolation was used to fill in the gaps. Because this study depended more on weight and other percentage data, logarithmic processing of the data and descriptive statistics of variables were used, as stated in
Table 1, to lessen the impacts of heteroskedasticity and extreme values.
4. Analysis and Discussion of the Results
4.1. Analysis of the Agricultural Green Production Efficiency Measurement Results
4.1.1. Time-series Evolutionary Feature Analysis
First, the agricultural green production efficiency (AGPE) was measured while taking non-desired outputs into account and the agricultural production efficiency (APE) was measured without taking non-desired outputs into account by using the super-efficient EBM model. Second, the average production efficiency values were obtained by adding the efficiency values of each province by year and taking the mean values (
Figure 1). The results demonstrated an overall increase in green production efficiency in Chinese agriculture, which was generally in agreement with the conclusions of Zhou et al. [
31] and Peng et al. [
39]. Specifically, agricultural green production efficiency rose from 0.312 in 2006 to 0.848 in 2020 with an average annual growth rate of 11.45%, while agricultural production efficiency rose from 0.335 to 0.868 with an average annual growth rate of 10.60%. However, when non-desired outputs were considered, the value of agricultural green production efficiency was significantly lower than the previous value over the same period. Using the agricultural green production efficiency index to gauge the state of agricultural development is more logical. China's agricultural green growth has produced impressive results as green development has become more popular, agricultural surface pollution is avoided, and low-carbon production systems are continuously improved.
Eq. (2) and (3) were used to measure the agricultural green production efficiency index and its decomposition term index. Since the measured values of agricultural green production efficiency were chain growth indices, to more intuitively portray the time-series evolutionary characteristics of agricultural green production efficiency and its core sources of dynamics, the indices were treated as cumulative change indices with 2006 as the base period, i.e., each index was a continuous-chain product index from the base period to the reporting period (see
Figure 1), as was suggested in a study by Hang et al. [
14]. The findings demonstrated a strong correlation between the GTC and agricultural green production efficiency indexes. However, the GEC index showed fewer significant changes and even declined in some years. This indicated that the GTC’s “single-core drive” was an essential factor contributing to the green production efficiency of Chinese agriculture throughout the study period. China has been innovating and introducing advanced green technologies in recent years, which has been driven by the idea of “green development”. The expansion of the scale of agricultural green technologies has resulted in a continuous rise in agricultural modernization, a continuous transformation and upgrading of the agricultural production model towards sustainable development, and a steady increase in the efficiency of agricultural green production.
4.1.2. Analysis of the Spatial Variation Characteristics
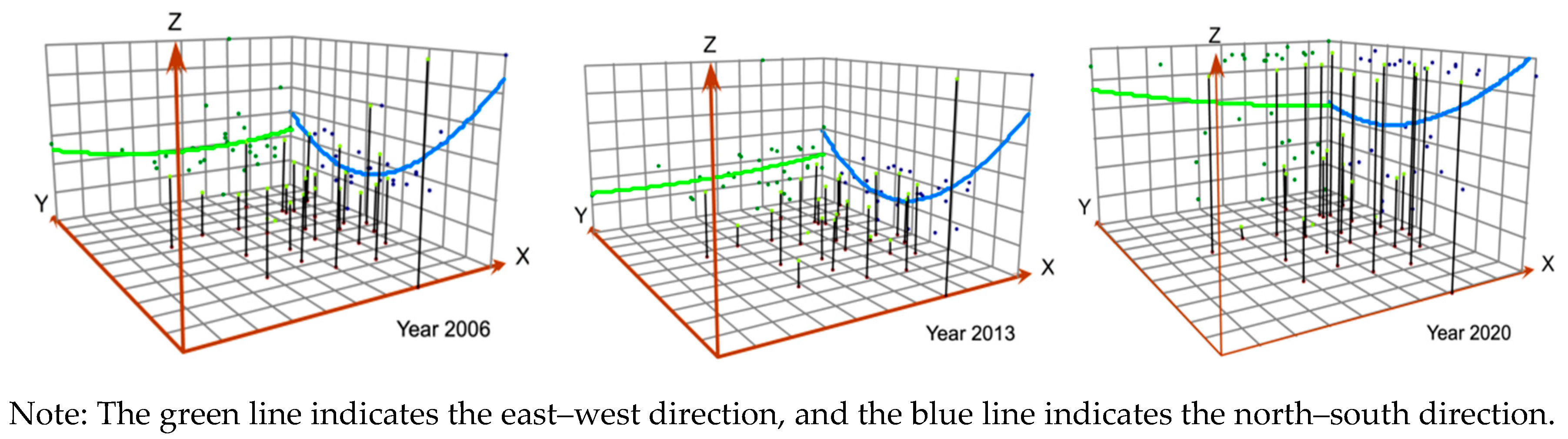
Clarifying the spatial differences in agricultural green production efficiency helps to grasp the regional evolution pattern of China's agricultural green development. This study created a spatial trend surface fit of green production efficiency in Chinese agriculture from 2006 to 2020 by using the ArcGIS 10.2 software (
Figure 2). As observed in
Figure 2, generally, the regional distribution of green production efficiency in Chinese agriculture varied greatly. Still, all levels rose throughout the study period. Specifically, in the north–south direction, in 2006, agricultural green production efficiency displayed a "U"-shaped distribution pattern with the characteristics of being low in the middle and high on both sides; by 2020, the efficiency level of the central region had significantly improved and was essentially the same as that of the northern region, while the agricultural green production efficiency of the southern region was lower. Due to its superior natural resources (land, water, and climate) compared to those of other regions, the southern region still had a high degree of green production efficiency. The efficiency levels of the various regions differed less in the east–west direction. Still, during the sample period, the western region's efficiency levels improved more quickly than those of the central and eastern regions. The result was primarily because the western region had many biological species, a wide distribution, and a high economic utilization value, which are a crucial foundation and material guarantee for the development of a green agricultural economy [
40]. These findings show that the spatial evolution of agricultural green production efficiency, an important measure of the regional green development level, is closely related to the spatial differences in the characteristics of the regional agricultural resource factor endowment, green technology development level, and economic development level.
4.2. Analysis of the Baseline Model’s Regression Results
The “variance inflation factor” method was used to test for multicollinearity to avoid distorted model estimates due to excessive inter-variable correlation. According to the results of multicollinearity, the Mean-VIF was 3.16 and the Max-VIF was 5.74, which were both below the crucial number of 10, proving that multicollinearity did not exist. As a result, Eq. (4) was used in this study to examine the impact of industrial agglomeration on the index of agricultural green production efficiency (
Table 2).
As shown in
Table 2, industrial agglomeration passed the positive significance test at the 5% level for the agricultural green production efficiency index, indicating that industrial agglomeration could significantly promote agricultural green production efficiency. These results are consistent with those of previous studies showing that agricultural industrial agglomeration can improve agricultural income [
41], improve agricultural surface pollution [
9], and optimize industrial processes. The effects of industrial agglomeration on the GEC and GTC were further investigated, and the findings demonstrated that industrial agglomeration continued to significantly contribute to green technical efficiency and change. The findings demonstrated that, on the one hand, as agricultural industry agglomeration rose, the industrial chain was enhanced. The gradual development of the agglomeration economy intensified healthy competition and cooperation among business organizations in the regions, forcing business organizations to continuously innovate in green production technology or improve the efficiency of green technology applications, prompting them to engage in energy-saving activities and, thus, achieve optimal resource allocation and reductions in environmental pollution, which promoted agricultural green production efficiency. The implementation of centralized government oversight and environmental regulation policies, on the other hand, was facilitated by industrial agglomeration, which also encouraged the spread of green production technologies, increased their coverage and radiation, significantly lowered the mismatch between resource factors and pollution emissions, and enhanced agricultural green production efficiency.
Additionally, among the control factors, Sup, R&d, Tra, Mar, and Tmd all significantly improved agricultural green production efficiency for the following reasons:
Sup: With the scale of financial support for agriculture steadily growing, the method of providing that support evolved from straightforward direct subsidies to the use of financial policies to direct and leverage financial and social capital to invest in the development of modern agriculture, thereby promoting agricultural green production efficiency [
42].
R&d: Agricultural green production efficiency could be increased by increasing R&D investments in green technology for agriculture and improving resource utilization efficiency, which played a vital role in raising crop yields and lowering production costs [
43].
Tra: Transport infrastructure not only made it easier for investors to invest in rural areas and improved the conditions for rural transportation, but it also helped modernize these areas and disseminate information, which increased agricultural green production efficiency [
31].
Mar and Tmd: One way in which the development of the technology market advanced was by encouraging the growth of low-carbon and green industries. On the other hand, the level of marketization advanced the market-based system for allocating resources and the environment. It hastened the adoption of advanced energy conservation and carbon reduction technologies, thereby enhancing agricultural green production efficiency [
38].
In contrast, Reg, For, and Dis all significantly inhibited agricultural green production efficiency for the following respective reasons:
Reg: With the development of the economy, the increase in environmental regulations directly led to an increase in the internal costs of investing in enterprises, which, to some extent, reduced the incentive to invest and hindered the further development of technology, thus inhibiting agricultural green production efficiency [
39].
For: The inflow of foreign capital had a constraining effect on China's economic development, leading to an increasingly pronounced low-performance ecological contradiction in the Chinese market in terms of the distortion of factor resources and resource depletion, which ultimately inhibited agricultural green production efficiency [
36].
The expansion of the impacted area resulted in not only a reduction in the desired output, but also increases in pesticides, fertilizers, and other inputs for resilience operations, resulting in a rise in undesirable output, which prevented the increase in agricultural green production efficiency [
28].
4.3. Robustness Tests
Robustness tests were performed by using
Table 3 to ensure that the findings of the estimation were reliable. The explanatory variables were changed first. To assess the agricultural green production efficiency, the super-efficient SBM model was used again instead of the super-efficient EBM model. The new variable was designated as “AGPE#”. The regression results are shown in column (1). Second, the core explanatory variables were substituted. The total agricultural, forestry, livestock, and fishery output value was substituted for the total agricultural output value in Eq. (8) to remeasure industrial agglomeration. The new variable was designated as “AGG#”, and the regression results are shown in column (2). Third, the sample period was adjusted to cover 2006 through 2019. Because the COVID-19 pandemic, which affected agricultural production in 2020, would have a significant impact, only samples taken before 2020 were kept for the analysis to exclude the effects of this significant environmental change. The regression results are shown in column (3). The findings on the impact of industrial agglomeration on agricultural green production efficiency were robust, as can be seen from the results in
Table 3. This is because the direction and significance of the coefficients of the industrial agglomeration variables for each test did not significantly change when compared to the results of the benchmark regression in
Table 2.
4.4. Endogeneity Test
Omitted variables and two-way causation may cause endogeneity issues in a model. Because of this, this study employed the panel instrumental variable method and lagged core explanatory variables to reduce the estimation bias brought on by endogeneity problems.
4.4.1. Lagged One-period Core Explanatory Variables
The results from when the industrial agglomeration variable was lagged by one period to examine its impact on agricultural green production efficiency are shown in column (1) of
Table 4. The results indicate that, after a one-period lag, industrial agglomeration passed the positive significance test at the 10% level for agricultural green production efficiency. After a one-period lag, the results showed that industrial agglomeration still significantly improved agricultural green production efficiency.
4.4.2. Instrumental Variable Method for Panel Data
In this study, the employment density (Den) and the delayed second period of industrial agglomeration were chosen as instrumental factors for industrial agglomeration, and endogeneity was examined by using two-stage least squares (2SLS) in reference to a related study by Jin et al. [
44]. For the second phase of industrial agglomeration lag, the industrial agglomeration in the earlier phase had a significant impact on the depth, breadth, and rate of development of industrial agglomeration in the later phase, thus satisfying the requirement of correlation; however, the industrial agglomeration in the second phase of lag had a weak correlation on agricultural green production efficiency in the current period, thus satisfying the requirement of the exogeneity of variables. The employment density was measured by using the ratio of the number of persons employed in the primary industry to the area of the regional administrative district. Employment density reflects, to a certain extent, the dependence of the agricultural industry on labor in a region, while industrial agglomeration highlights the adoption of innovative technologies, which has a strong substitution effect on labor-intensive industries and satisfies the requirement of correlation; at the same time, employment density is not significantly associated with agricultural green production efficiency, thus satisfying the requirement for homogeneity in the explanatory variables. The second period of lagged industrial agglomeration and employment density, therefore, satisfied the necessary conditions for the instrumental variables.
The results of the two-stage least squares approach are displayed in columns (2) and (3) of
Table 5. The results in column (2) demonstrate that employment density and the second stage of industrial agglomeration lag passed the significance tests at the 5% and 1% levels, respectively, for industrial agglomeration, thus satisfying the correlation requirement. The results in column (3) show that after applying the two-stage least squares method to alleviate the endogeneity problem, the effect of industrial agglomeration on agricultural green production efficiency still passed the positive significance test at the 1% level. Additionally, the test results for weak instrumental variables revealed that the F-statistic was 391.173, which was significantly higher than the critical value, indicating that there was no problem with weak instrumental variables. Similarly, the test results for over-identification revealed that the p-value was 0.280, so the original hypothesis of exogenous instrumental variables was accepted, indicating that there was no problem with over-identification. As a result, this demonstrated that industrial agglomeration did increase agricultural green production efficiency.
4.5. Regional Heterogeneity Analysis
China is enormous, and agricultural green development varies greatly from region to province. Industrial agglomeration revealed glaring regional disparities in agricultural green production efficiency, which were influenced by natural resources, cultural traditions, and industrial structures. To this end, this study divided China into three parts according to topographical and other characteristics—western (Chongqing, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan, Shaanxi, Gansu, Qinghai, Ningxia, and Xinjiang), central (Shanxi, Inner Mongolia, Jilin, Heilongjiang, Anhui, Jiangxi, Henan, Hubei, and Hunan), and eastern (Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Liaoning, Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Fujian, Shandong, Guangdong, Guangxi, and Hainan) China—to further investigate the inter-regional heterogeneity, and the regression results are shown in
Table 5.
Table 5 demonstrates that the central and western regions both passed the positive significance test at the 1% level for industrial agglomeration in terms of agricultural green production efficiency, whereas the eastern region passed the negative significance test at the 1% level. One explanation could be that the eastern region had a more developed economy and a greater industrial agglomeration than the central and western regions did. The high level of industrial agglomeration caused resource consumption to outpace the environmental carrying capacity, and the expansion of the production scale increased the input of pesticides, chemical fertilizers, and other factors, thus increasing the pressure on the agricultural ecology and environment. Additionally, the marginal benefit of industrial agglomeration was gradually diminished, thus impeding the improvement of agricultural green production efficacy. Therefore, the central and western regions should continue to play an innovative role in industrial agglomeration. In contrast, the eastern regions should concentrate on improving the efficiency of and technological changes in agricultural green technology in the industrial agglomeration and avoid heedlessly expanding the scale of industrial agglomeration.
5. Mechanism of Action and Threshold Effect Analysis
5.1. Analysis of the Mechanism of Action
According to theory, industrial agglomeration could promote land transfer in boosting agricultural green production efficiency. The mediating effect of land transfer was tested by using equations (4) to (6). The same fixed-effects model was utilized in the regression analysis in order to assure the comparability of the test results, and the results are displayed in
Table 6.
Table 6 demonstrates that the effect of industrial agglomeration on land transfer in column (1) passed the positive significance test at the 5% level. This showed that industrial agglomeration could encourage the intensive input of production factors, large-scale operation, and stimulation of the land-transfer market's activity. With a mediating effect value of 28.48%, land transfer played a mediating role in the influence of industrial agglomeration on agricultural green production efficiency, as shown in column (2), where both industrial agglomeration and land transfer passed the positive significance test at the 1% level for agricultural green production efficiency. Industrial agglomeration encouraged the growth of the land-transfer market, which optimized the allocation of resources and factors, increased the utilization rate of resources and factors, and, thus, encouraged the improvement of agricultural green production efficiency. The mediating effect values for the impact of industrial agglomeration on GEC and GTC were 27.91% and 47.75%, respectively, as shown in columns (3) and (4). On the one hand, land transfer boosted green technical efficiency by maximizing the distribution of production resource components, such as land, labor, and capital, and raising the utilization rate of resource factors under the same level of resource factor inputs. On the other hand, land transfer sped up the industrialization and scale of agricultural production by transferring farmers’ land into new agricultural business entities with more advanced technology. This increased the competitiveness of the agricultural market, improved agricultural innovation, and, ultimately, fostered the advancement of green technology. Accordingly, hypotheses H1 and H2 were verified.
5.2. Threshold Effect Analysis
According to theory, industrial agglomeration could promote land transfer in boosting the efficiency of agricultural green production. However, with increasing levels of land transfer, it is necessary to examine whether there are differences in the promotive effect of industrial agglomeration on agricultural green production efficiency. Therefore, the threshold effect test was performed by using Eq. (7), and the results are shown in
Table 7.
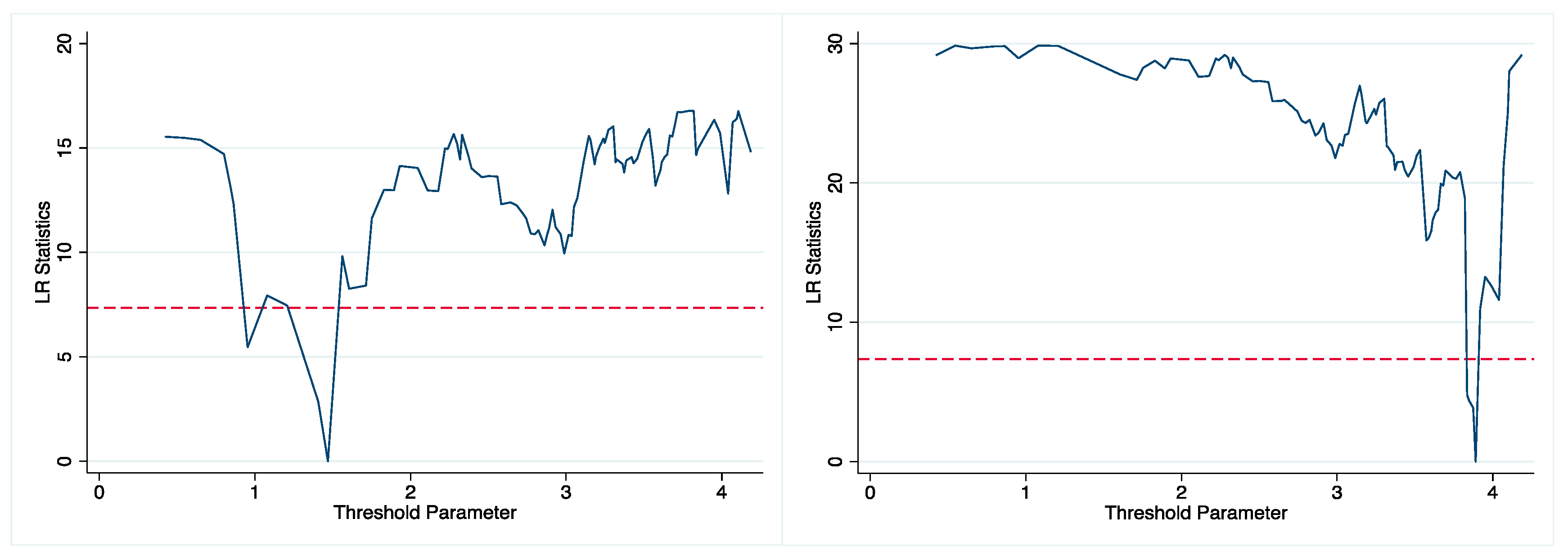
With land transfer serving as the threshold variable, the results in
Table 7 demonstrate that both the single and double thresholds passed significant positive tests, thus proving the existence of a double-threshold effect with threshold values of 1.468 and 3.891, respectively. There was a significant nonlinear relationship between industrial agglomeration and agricultural green production efficiency, as shown by the likelihood ratio function plot in
Figure 3, which corresponded to the threshold values, showing that both thresholds' corresponding LR values were less than the critical values at the 5% significance level.
The threshold effect of land transfer was tested next by using the double-threshold model, and the outcomes are displayed in
Table 8.
Table 8 demonstrates that when the logarithm of land transfer increased, the coefficient value of industrial agglomeration for agricultural green production efficiency declined from 0.611 to 0.218, and the t-value was reduced from 4.92 to 2.53, which indicated that there was a characteristic of a diminishing marginal effect of industrial agglomeration on the promotion of agricultural green production efficiency. A possible reason is that, on the one hand, the development of industrial agglomeration required continuous adjustment of the industrial structure to meet the market competition, and smooth land transfer is a necessary condition for bringing into play the effect of industrial agglomeration; however, frequent land transfer leads to an excessive adjustment of the planting structure, and production operators, out of the pursuit of profit maximization, turn from food crops to cash-crop planting, which relies more on chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and other chemicals, thus changing the original intensive production method and leading to a weakening of the effect of industrial agglomeration on the enhancement of agricultural green production efficiency through land transfer [
45]. On the other hand, with the deepening of land transfer, land resources and production may be controlled by capital. Even the phenomenon of “land enclosure movement” will lead to the distortion of the land-transfer market. The price of land transfer will rise sharply, driven by the profit-seeking nature of capital, which will influence the price and supply of agricultural products, thus causing a mismatch of resources such as land and, ultimately, inhibiting the development of green agriculture. This will lead to a distortion in the land-transfer market, leading to a sharp increase in land-transfer price driven by capital profit and influencing the price and supply of agricultural products. Accordingly, hypothesis H3 was verified.
6. Conclusions and Policy Recommendations
This study used panel data from 30 provinces in China from 2006 to 2020 as research samples and used the super-efficient EBM model combined with the GML index to measure and explore the green production efficiency of Chinese agriculture, the characteristics of its spatial and temporal evolution, and its core power sources. A fixed-effect model was used to test the influence of industrial agglomeration on the green production efficiency of agriculture, and the influence of regional heterogeneity was analyzed. A model of mediating effects was constructed to clarify the transmission mechanism of land transfer in industrial agglomeration with respect to agricultural green production efficiency; a model of threshold effects was constructed to explore the heterogeneous effects of industrial agglomeration on agricultural green production efficiency with different levels of land transfer. The results showed the following: (1) China’s agricultural green production efficiency showed stable growth over time. Its growth mainly relied on the “single-track drive” of green technological change, with an average annual growth rate of 11.45% from 2006 to 2020; the green development of agriculture was steadily promoted, and the construction of an ecological civilization achieved remarkable results. (2) Industrial agglomeration had a significant positive effect on agricultural green production efficiency, and the findings still held after testing the robustness of the sample; furthermore, there was regional heterogeneity in the effect of industrial agglomeration on agricultural green production efficiency, with the western and central regions having a facilitating effect, while the eastern region showed an inhibiting effect. (3) Industrial agglomeration could enhance agricultural green production efficiency by promoting land transfer and still had a significant contribution to the enhancement of green technological efficiency and green technological change, with mediating effect values of 28.48%, 27.91, and 47.75%, respectively. This was driven by industrial agglomeration, the revitalization of land and other resources, the release of agricultural capacity, and the acceleration of green production technology promotion and transformation, thus promoting the green development of agriculture. (4) Land transfer had a double-threshold effect on the effect of industrial agglomeration on agricultural green production efficiency. With different levels of land transfer, the influence of industrial agglomeration on agricultural green production efficiency was heterogeneous. When the land-transfer level crossed the threshold value, the intensity of the effect of industrial agglomeration on agricultural green production efficiency was weakened; the land-transfer mode should be innovated to carry out moderate-scale operation in order to maximize the role of industrial agglomeration in promoting agricultural green development. Accordingly, the following policy recommendations are put forward:
One should adhere to the idea of synergistic development and push for sustainable agricultural growth. There are differences in agricultural green development among regions in China due to differences in resource endowment, geographical location, and policy implementation. The specific manifestation is that at this stage, China’s agricultural green development relies more on the “single-track drive” of green technological change, and the green technological efficiency is not obvious. On the one hand, we should continue to guarantee investment in agricultural green technology research and development and expand the coverage and radiation of green technology by improving the green technology promotion system; at the same time, we should increase the government’s support for green technology, speed up the transfer and transformation of the results of innovation, industrialization, and development, and solve problems such as the difficulty of creating green technology. On the other hand, we should pay more attention to the enhancement of the effectiveness of green technology, increase training in green technology and improve green technological literacy in order to optimize resource allocation, improve resource utilization efficiency, and realize the dual benefits of economic and ecological improvements. In addition, as there are spatial and temporal differences in agricultural green production efficiency, it is necessary to formulate policies for promoting the coordinated development of green agriculture according to local conditions. For the less efficient eastern and northern regions, it is necessary to accelerate the pace of transformation and upgrading of green agricultural production, strengthen the development of regional linkages, encourage the proper flow of resources such as technology, capital, and labor to high-efficiency regions, and promote the formation of a synergistic mechanism of agricultural economy and ecology.
The development of industrial clusters should be bolstered and the standards and effectiveness of industries should be advanced. Industrial clustering has a significant role in the enhancement of the green development of agriculture, and the government should strengthen its supervision and leadership in this process. On the one hand, finance should enhance economic support for industrial agglomeration, comprehensively strengthen infrastructure construction, enhance market-oriented development, and attract upstream and downstream production operators to agglomerate and develop; at the same time, it is also necessary to strengthen the science and technology innovation drive, implement major innovation projects in areas with regional characteristics and advantages, increase R&D investment and the construction of science and technology innovation talents, improve the transformation and industrialization of scientific and technological achievements, and release new momentum for industrial agglomeration. On the other hand, a production safety responsibility system should be should strictly implemented, risk prevention capabilities should be enhanced, risk supervision should be strengthened, and safe and orderly agricultural production should be guaranteed; at the same time, a good development environment should be created, the focus should be on building a market-oriented system, the rule of law, and the international business environment, and foreign investment should be attracted while also optimizing the investment structure, improving financial literacy, avoiding mismatch of resource elements, and focusing on agricultural-scale operation. We will focus on the transformation of agricultural-scale operation from “quantity” to “quality”, enhance the quality and efficiency of industrial development with multiple channels and initiatives, and gradually form a green and sustainable regional agricultural development pattern.
The land-transfer system should be enhanced, and there should be a concentration on increasing resource efficiency. This study’s results prove that land transfer plays a mediating role in the process of industrial agglomeration with respect to the efficiency of green production in agriculture. Thus, each region should follow the overall spatial development strategy requirements based on the current reality of industrial agglomeration development and the scientific planning for industrial agglomerations, and the layout should be optimized. At the same time, we should encourage the development of various forms of moderate-scale operation according to local conditions, promote the development of the linkage of multiple subjects, promote innovative land-transfer methods, solve the problem of contracted land fragmentation, and fully stimulate the potential of rural production resources. However, since the role of industrial agglomeration in improving agricultural green production efficiency has weakened with the increase in the level of land transfer, it is necessary to stop the one-sided pursuit of scale when transferring land, effectively implement and improve the system of the “separation of three rights” of agricultural land, build a platform for rural property rights trading, regulate land transfer and mortgages, etc. At the same time, we should avoid the phenomena of non-agriculturalization and the lack of grain on agricultural land, strictly adhere to the “red line of arable land”, ensure food security, improve the supervision system for rural land transfer, restrain rent-seeking behavior on land through laws and regulations, improve the management and service mechanisms for land transfer, enhance agricultural green production efficiency, and realize green agricultural development.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.K. and B.L.; data curation, Z.W. and H.L.; formal analysis, Z.W.; funding acquisition, Z.W., X.K. and B.L.; methodology, H.L.; software, Z.W. and H.L.; visualization, Z.W.; writing—original draft, Z.W. and H.L.; writing—review and editing, Z.W., X.K. and B.L.; Z.W. and H.L. contributed equally to this work and should be regarded as co-first authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.71563016), Key Research base Project of Humanities and Social Sciences in colleges and universities of Jiangxi Province (JD21080) and the Jiangxi Postgraduate Innovation Special Fund Project (YC2022-s415).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Some or all of the data, models, and codes that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sicard, P.; Agathokleous, E.; Anenberg, S.C.; De Marco, A.; Paoletti, E.; Calatayud, V. Trends in Urban Air Pollution over the Last Two Decades: A Global Perspective. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2023, 858, 160064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, J.; Kwek, K. The Impact of Climate Change on China’s Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity. Tec. For. Socia. Chan. 2022, 185, 122054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Huang, M.; Hu, M.; Bai, Y. How Does Agricultural Production Agglomeration Affect Green Total Factor Productivity?: Empirical Evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 67865–67879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Qiao, C. Spatial spillover effects of agricultural industry agglomeration on agricultural carbon productivity: based on the regulatory role of fiscal decentralization. China Pop. Res. Environ. 2023, 33, 92–101. [Google Scholar]
- Picard, P.M.; Zeng, D.-Z. Agricultural Sector and Industrial Agglomeration. J. Dev. Econ. 2005, 77, 75–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Jin, Z.; Tang, H. Influence Paths and Spillover Effects of Agricultural Agglomeration on Agricultural Green Development. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Hamzah, H.Z.; Yin, J.; Wu, D.; Cao, J.; Mao, X.; Zhuang, Q. Impacts of Industrial Agglomeration and Energy Intensity on Industrial Eco-Efficiency-Analysis Based on Spatial Correlation and Mediating Effect. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 954252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Song, J. Analysis of the Threshold Effect of Agricultural Industrial Agglomeration and Industrial Structure Upgrading on Sustainable Agricultural Development in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 341, 130818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Xiong, L.; Wang, F. The Spatial Spillover Effect and Impact Paths of Agricultural Industry Agglomeration on Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution: A Case Study in Yangtze River Delta, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 401, 136600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; An, M.; Zhang, Z.; He, N. Unveiling the Impact of Digital Financial Inclusion on Low-Carbon Green Utilization of Farmland: The Roles of Farmland Transfer and Management Scale. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, D.; Yang, S.; Li, F. The Relationship between Land Transfer and Agricultural Green Production: A Collaborative Test Based on Theory and Data. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, J.; Wang, L.; Zhong, S. The Inhibitory Effect of Agricultural Fiscal Expenditure on Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Lv, D.; Luo, Y.; Jiang, T. Environmental Regulation, Urban-Rural Income Gap and Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Feng, C.; Qin, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T. Measuring China’s Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity and Its Drivers during 1998–2019. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2022, 829, 154477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Roest, K.; Ferrari, P.; Knickel, K. Specialisation and Economies of Scale or Diversification and Economies of Scope? Assessing Different Agricultural Development Pathways. J. Rural. Stu. 2018, 59, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Rural Land System Reforms in China: History, Issues, Measures and Prospects. Land Use Policy 2020, 91, 104330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Li, G. How Do Land Transfers Affect Agricultural Resource Allocation Efficiency :A Heterogeneous Analysis. J. Agro. Econo. 2023, 4, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L; Li, M; Shi, Y. Farmland Rights Confirmation, Land Transfer and Maximum Land Utilization Efficiency of Farmers. West Forum 2022, 32, 111–122. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Miao, J.; Zhu, Z. Measuring Green Total Factor Productivity of China’s Agricultural Sector: A Three-Stage SBM-DEA Model with Non-Point Source Pollution and CO2 Emissions. J. Cle. Produ. 2021, 318, 128543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K.; Tsutsui, M. An Epsilon-Based Measure of Efficiency in DEA – A Third Pole of Technical Efficiency. Europ. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 207, 1554–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Lyu, X.; Peng, W.; Xin, Z. How to Evaluate the Green Utilization Efficiency of Cultivated Land in a Farming Household? A Case Study of Shandong Province, China. Land 2021, 10, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhu, P.; Tang, L. Agricultural Services: Another Way of Farmland Utilization and Its Effect on Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity in China. Land 2022, 11, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myeki, L.W.; Matthews, N.; Bahta, Y.T. Decomposition of Green Agriculture Productivity for Policy in Africa: An Application of Global Malmquist–Luenberger Index. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.H.; Heshmati, A. A Sequential Malmquist-Luenberger Productivity Index: Environmentally Sensitive Productivity Growth Considering the Progressive Nature of Technology. Ener. Eco. 2010, 32, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.; Kang, X.; Liang, X.; Xie, F. The Impact of Rural Households’ Part-Time Farming on Grain Output: Promotion or Inhibition? Agriculture 2023, 13, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.E. Threshold Effects in Non-Dynamic Panels: Estimation, Testing, and Inference. J. Econ. 1999, 93, 345–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Cheng, C.; Sun, G.; Li, J. The Impact of Digital Inclusive Finance on Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity: Evidence from China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 905644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Y. China’s Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity Based on Carbon Emission: An Analysis of Evolution Trend and Influencing Factors. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B. Structural Characteristics and Spatial and Temporal Differences of Agricultural Carbon Emissions in China. Worl. Sur. Res. 2016, 5, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Xiong, J. Rural Finance, Agricultural Land Scale Management and Agricultural Green Efficiency. J. Sou. China Agr. Uni. (Soc. Sci. Edi.) 2021, 20, 63–75. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, T.; Zhang, B. Research on the Impact of Digital Agriculture Development on Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity. Land 2023, 12, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Wu, Q.; Wei, Y.D. How Does Industrial Agglomeration Affect Urban Land Use Efficiency? A Spatial Analysis of Chinese Cities. Land Use Pol. 2022, 119, 106178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ma, S.; Zheng, Y.; Xiao, X. Integrated Regional Development: Comparison of Urban Agglomeration Policies in China. Land Use Pol. 2022, 114, 105939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, R.; Lin, Z.; Chunga, J. How Land Transfer Affects Agricultural Land Use Efficiency: Evidence from China’s Agricultural Sector. Land Use Pol. 2021, 103, 105300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Huang, K.; Deng, X.; Xu, D. Livelihood Capital and Land Transfer of Different Types of Farmers: Evidence from Panel Data in Sichuan Province, China. Land 2021, 10, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rihui, T. a. N.; Huimin, L.I.U. Characteristic Evolution and Influencing Factors of the Spatial Correlation Network of Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity in China. zgstnyxb 2022, 30, 2011–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fu, W.; Wang, J. Evaluation and Influencing Factors of China’s Agricultural Productivity from the Perspective of Environmental Constraints. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie,X. ; Zhu, Q. How Can Green Innovation Solve the Dilemmas of “Harmonious Coexistence”? J. Mana. World 2021, 37, 128–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X. Environmental Regulation and Agricultural Green Productivity Growth in China: A Retest Based on ‘Porter Hypothesis.’ Environ. Tech. 2023, 1–15. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Luo, X. Agricultural green technical efficiency and its affecting factors in China. J. China Agric. Univ. 2017, 22, 203–212. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Zeng, Y. Impact of Agricultural Industry Agglomeration on Income Growth: Spatial Effects and Clustering Clustering Differences. Transform. Bus. Econ. 2020, 19, 486–507. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, H.; Zheng, W.; Shen, Z.; Štreimikienė, D. Does Fiscal Expenditure Promote Green Agricultural Productivity Gains: An Investigation on Corn Production. Applied Energy 2023, 334, 120666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebre, S.L.; Van Orshoven, J.; Cattrysse, D. Optimizing the Combined Allocation of Land and Water to Agriculture in the Omo-Gibe River Basin Considering the Water-Energy-Food-Nexus and Environmental Constraints. Land 2023, 12, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S; Ren, Z. The Impact of Rural Digitalization on Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity. Reform 2022, 12, 102–118. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Liu, X.; Ge, D.; Liu, B. Research on Spatial-Temporal Characteristics and Affecting Factors of Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity in Jiangxi Province. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).