1. Introduction
A coronavirus infection that first emerged in Wuhan, China, is responsible for the respiratory illness known as COVID-19, which has quickly spread across the globe.
As of June 19, 2023, according to the World Health Organization official website, 767.984.989 confirmed COVID-19 cases have been reported [
1]. In Italy, the total number of cases registered as positive is more than 25 million, with 190.706 deaths [
2]
Italy was the first country in Europe to experience the impact of COVID-19 and has had one of the highest clinical burdens compared to other countries [
3].
In March 2020, Italy was also the first country to enforce a nation-wide stay-at-home order to mitigate the spread of the virus. This lockdown confined over 60 million people within their homes for almost three months.
The COVID-19 pandemic and the subsequent implementation of lockdown measures have exerted a significant influence on the mental health and psychological well-being of individuals not only within Italy but also across the globe. In this vein, the literature [
4] has widely documented a worldwide increase in the incidence of psychiatric disorders. Specifically, the COVID-19 pandemic has profoundly affected individuals' psychological well-being, leading to an increase in anxiety, fear and distress [
5,
6,
7]. The pandemic has disrupted individuals’ daily routines, resulting in emotions of powerlessness and seclusion [
8]. Multiple studies [
9,
10] have demonstrated that the fear of contracting the virus, the loss of loved ones, and financial instability were the most contributing factors to elevated levels of psychological distress.
Therefore, the heightened levels of concern for personal health and economic consequences, along with increased levels of stress and a reduction in alternative activities, have significantly affected people's lifestyle habits.
1.1. COVID-19 anxiety predictors
Although the long-term effects of the pandemic on mental health are yet to be fully understood, it has become increasingly clear that the psychological aftermath of COVID-19 will continue to be a significant public health issue for years to come.
For this reason, it appears crucial to ascertain the primary factors involved in the development of anxiety related to COVID-19. Research [
11] has shown that perceived threat of the virus, encompassing apprehensions regarding virus contraction, the gravity of the illness, and the potential repercussions at both individual and societal levels, indeed play a significant role in this regard. Other predictors include financial concerns, social isolation, loneliness, pre-existing mental health conditions, and exposure to misinformation or conflicting information about the pandemic [
12,
13,
14]. Additionally, demographic factors such as age, gender, and ethnicity have been found to influence the level of anxiety experienced during the pandemic [
15,
16].
1.2. Resilience and anxiety
On the opposite hand, psychological resilience, coping behaviors and social support have become crucial tools in managing COVID-19 impact on mental health in healthcare workers [
17,
18], in hospitalized patients [
19] and in the general population [
20]. In particular, the relationship between resilience and anxiety has been extensively studied in the scientific literature. Resilience can be defined as the ability to adapt to stress and adversity and bounce back from difficult situations [
21], whereas anxiety can be generally considered a psychological state characterized by feelings of apprehension, worry, and fear [
22]. Research [
23,
24] has demonstrated that individuals who display high levels of resilience tend to have lower levels of anxiety, as they are better able to cope with stress and challenges. Conversely, those with lower levels of resilience tend to experience higher levels of anxiety in response to stressors. Thus, resilience may serve as a protective factor against anxiety and other negative mental health outcomes [
25,
26] and interventions aimed at increasing resilience may be effective in reducing anxiety symptoms [
27]
In recent studies conducted during the COVID-19 pandemic, researcher [
28] have revealed a negative association between resilience and anxiety among physicians. Similar findings have been obtained in a Chinese sample of patients experiencing COVID-19 symptoms [
29]. Specifically, these results indicated that resilience was inversely related with anxiety, serving as a protective factor against its development. Similarly, among the general population, it has been found that resilience negatively predicted COVID-19 anxiety and this relationship was mediated by persistent dysfunctional thinking about COVID-19 [
30]. Furthermore, it has been shown [
31] that individuals exhibiting higher levels of resilience, as opposed to those with lower levels, demonstrated a reduced susceptibility to the perceived threat of COVID-19, resulting in lower levels of future anxiety.
Locomotion regulatory mode
1.3. Locomotion regulatory mode
Taken together, these findings highlight the extensive research conducted to examine the influence of risk and protective factors in relation to psychological distress and anxiety associated with the pandemic. Nevertheless, the role of regulatory modes in this context remains largely unexplored to date.
Based on the regulatory mode theory proposed by [
32], there are two regulatory mode orientations, namely assessment and locomotion. The present paper primarily focuses on the locomotion mode, which is defined as the self-regulatory aspect that involves transitioning from one state to another and directing psychological resources towards initiating and maintaining progress towards goals with minimal interference or delay. Individuals with high levels of locomotion mode are inclined to prioritize rapid action and uninterrupted movement, rather than engaging in critical appraisal, as suggested by [
33].
Research has established a positive association between high levels of locomotion and various positive psychological states, including optimism, increased self-esteem, achievement orientation, positive affect, and psychological well-being [
32,
34]. High levels of locomotion are also associated with increased job satisfaction, work engagement, and workaholism[
35,
36,
37,
38].
On the other hand, locomotion has also been negatively associated with social anxiety and depression [
32]. In addition, it has been demonstrated that individuals with high levels of locomotion tend to exhibit lower levels of hopelessness, psychological strain, stress, burnout, turnover intentions and withdrawal behaviors [
36,
39,
40].
Furthermore, locomotion has found to be positively associated with harmonious passion, which, in turn, is linked to better psychological adjustment and less stress in the workplace [
41]. Likewise, within the realm of sports, the locomotion regulatory mode has been identified as a predictor of harmonious passion, leading to a subsequent reduction in athletes' stress levels [
42].
Finally, when examining the predominance of regulatory mode (determined by subtracting assessment from locomotion scores), it has been observed as a predictive factor for work-related stress in a two-wave longitudinal design [
43].
1.4. Locomotion and resilience
Locomotion can be considered a significant empowering element and predictor of positive affect that supports the resilience process [
44]. This association can be explained by the inclination of individuals with such regulatory mode to prioritize progress and movement, consequently reducing their propensity to ruminate on negative aspects of their past or present circumstances [
45].
More in details, research has identified locomotion orientation as a significant predictor [
46] of resilient reintegration, which refers to the coping process involving personal growth, self-awareness, and development of resilient characteristics. In this vein, it has been proposed that when recovery resources are inadequate for the demands of the situation, a negative cycle of increased anxiety levels may occur causing a rupture of the body’s homeostasis [
47].
Based on previous scientific literature emphasizing internal resources and energy of individuals exhibiting high levels of locomotion [
32,
42,
48,
49], it is suggested that resilience is fostered through the resources of individuals who are proactive and maintain a steadfast focus on their goals. Therefore, this mechanism is expected to effectively contribute to preventing the escalation of anxiety.
In line with these notions, we hypothesize that locomotion should be positively related to resilience, whereas it should be negatively associated with COVID-19 anxiety. Furthermore, it is hypothesized that locomotion effect on COVID-19 anxiety could be mediated by individuals’ resilience.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
Two hundred and forty-three participants (44 males) were recruited using snowball sampling. Participants were thoroughly informed about the study and provided informed consent for the anonymous use of their data. They completed a web-mediated survey on a voluntary basis and did not receive any compensation in exchange for their participation. The original sample consisted of 262 participants, but 19 of them were excluded from further analysis as they failed to provide a correct response to a control question. Participants’ mean age was 31.24 (SD = 10.92). 6.6% of participants held a post-graduate specialization, 37.9% held a university degree, 55.1% held a high school degree and 0.4 % held a middle school diploma. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
2.2. Procedure and Materials
The survey, firstly, consisted of several questions about socio-demographic data. This was followed by a second section concerning Covid-19 information, locomotion regulatory mode, and resilience. Lastly COVID-19 anxiety was measured.
COVID-19 Vaccination. Participants had to respond to a question regarding their COVID-19 vaccination status. They were required to indicate whether they had received a COVID-19 vaccine by selecting either the response option "yes" or "no".
COVID-19 Infection. Participants were instructed to respond to an inquiry regarding COVID-19 infection, in which they were required to select one of three options: "yes "no", or "do not know" to indicate whether they had contracted COVID-19 in the past month. Subsequently, to facilitate additional analyses, the responses "no" and "do not know" have been combined.
Locomotion Scale. The Italian version of this scale, as designed by [
32], contains 12 self-reported items aimed at evaluating the differences in locomotion tendency among individuals. Specifically, respondents rate the extent to which they agree with self-descriptive statements, both in positive (e.g., “I enjoy actively doing things, more than just watching and observing.”) and negative wordings (e.g., “When I finish one project, I often wait a while before getting started on a new one.”). The responses were recorded on a 6-point Likert scale, ranging from "strongly disagree" (1) to "strongly agree" (6). The negative statements were reversed before analysis, and a final score was determined by taking the average of all responses. In this sample, Cronbach's α for the locomotion scale was .80 (
M = 4.74,
SD = .63).
Resilience. The Brief Resilience Scale [
50] consists of six items that are designed to assess an individual's level of resilience. The scale features three positively worded items and three negatively worded items. An example of positive item is “I tend to bounce back quickly after hard times.” Conversely, an example of negative item is “I have a hard time making it through stressful events.” Participants were asked to rate their agreement with each of the six statements using a 5-point Likert scale, ranging from 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree). In the present sample, Cronbach’s α was .87 for the resilience scale (
M = 3.15,
SD = .81).
Covid anxiety scale. COVID-19 anxiety scale [
51] was developed to assess COVID-19 related anxiety. The scale is composed of 7 items designed to assess individual differences. Specifically, participants had to rate the extent to which each item (e.g., “I feel heart racing when I read about COVID-19”) reflected their behavior in the last days. The responses were recorded on a 4-point Likert scale, ranging from 0 (not applicable to me) to 3 (very applicable to me). In this sample, Cronbach’s α was .92 (
M = .66,
SD = .67).
3. Results
Out of the total 243 participants, 13 reported that they had not received anti-COVID-19 vaccination. Additionally, only 8 participants reported with certainty that they had contracted COVID-19 within the past 30 days.
3.1. Correlation analyses
Table 1 presents correlations between the study variables. As can be seen, there is a positive and significant correlation between locomotion and resilience. On the other hand, COVID-19 anxiety was negatively related with resilience and with gender (females exhibited a higher level of COVID-19 anxiety in comparison to males).
3.2. Regression model
To test the hypothesis that resilience mediated the relationship between locomotion and COVID-19 anxiety, we used the PROCESS macro Model 4 [
52], which utilizes the bootstrapping method to extrapolate estimates of direct and indirect effects. Following the recommendation of [
53], predictor variables were centered. Gender (dummy coded as Male = 0 and Female = 1), age, education, COVID-19 vaccination (dummy coded as No = 0 and Yes = 1) and COVID-19 infection (dummy coded as No and Do not Know = 0 and Yes = 1) were entered as control variables. A summary of the results of these analyses is reported in
Table 2.
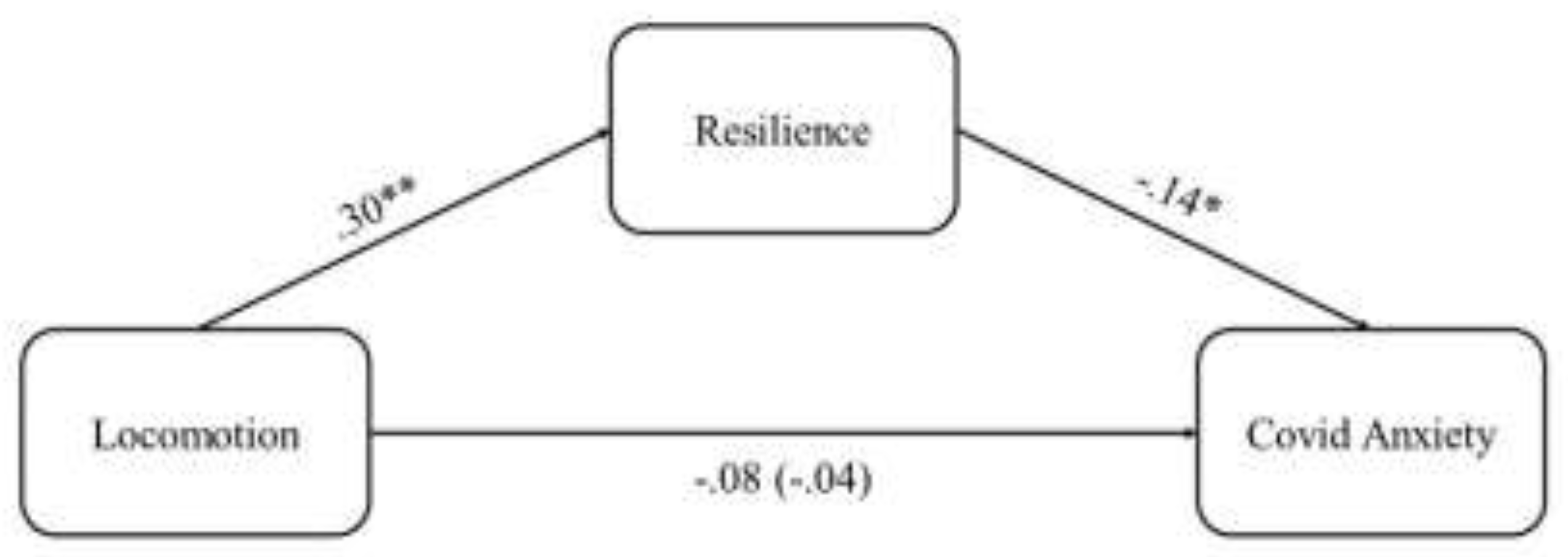
As can be seen, the results showed that locomotion had a positive and significant effect (
B = .38,
SE = .08,
p < .001) on resilience, which, in turn, had a significant and negative effect on COVID-19 anxiety (
B = -.12,
SE = .06,
p = .038). The association between locomotion and COVID-19 anxiety was non-significant when controlling for resilience, indicating that such relationship is fully mediated (See
Figure 1). Accordingly, the indirect effect of locomotion on COVID-19 anxiety through resilience was significant (
B = -.04,
BootSE = .02; bootstrapping CI = [-.09, -.01]).
4. Discussion
The COVID-19 pandemic has dramatically changed people's lives worldwide, causing unique levels of anxiety and stress. The long-lasting effects of the virus and its related stressors have made it challenging for individuals to maintain effective coping strategies, leading to persistent psychological challenges for many. In response to such crisis, researchers have been working to investigate the main factors influencing people's ability to be resilient while facing COVID-19 emergency. On the same vein, understanding COVID-19 anxiety predictors seems essential for identifying those most at risk, developing effective interventions to reduce anxiety symptoms and promote resilience during this challenging time.
In this regard, the present study aimed at examining the role of locomotion regulatory mode in the relationship between resilience and COVID-19 anxiety. In line with the hypotheses, this research demonstrated that locomotion regulatory mode was negatively, although not directly, related to COVID-19 anxiety and positively associated with resilience, suggesting that people with a goal-oriented approach to life were more able to face challenging circumstances and less likely to experience anxiety related to the pandemic. Additionally, the study found that resilience was negatively associated with COVID-19 anxiety. This suggests that people who are more resilient are better able to cope with anxiety related to the pandemic.
Importantly, the study found that resilience mediated the relationship between locomotion regulatory mode and COVID-19 anxiety. This means that the positive relationship between locomotion regulatory mode and resilience partially explains why people with a goal-oriented approach to life are less likely to experience anxiety related to the pandemic. In other words, individuals high on locomotion for their nature display high level of internal resources, are proactive and maintain a steadfast focus on their goals. Hence, they are more likely to be resilient and, this helps them to better cope with anxiety caused by the pandemic.
Our findings are consistent with prior research showing an association between locomotion and positive well-being [
32,
34]. They are also in line with previous works that have demonstrated how personality and motivational dispositions can predict a maladaptive adjustment to stressor in both personal and professional life [
54,
55]. In this vein, it has been suggested that certain types of individuals are more resilient to chronic stress than are other and locomotion seems to play a fundamental role in this process [
46].
Therefore, the present findings provide a unique insight into the basic mechanisms of locomotion regulatory mode by revealing its direct and indirect effects on COVID-19 anxiety. Specifically, this work focuses on locomotion protective role, helping understand how individuals who exhibit locomotion tendencies are equipped to cope with the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic. With this regard, understanding the factors that influence people's ability to cope with the pandemic can help interventions and support strategies to promote resilience and mental health during these challenging times.
Specifically, the peculiarity of locomotion orientation points to the importance of targeting these aspects to alleviate the harmful psychological consequences of COVID-19 pandemic. Since locomotion regulatory mode can be situationally induced [
56,
57], it could be possible to design health campaigns oriented at inducing locomotion motivation. This approach could be helpful in taking advantage of locomotion strengths to sustain people in finding a more adaptive ways to manage very difficult circumstances (such as a pandemic). More broadly, the present work increases awareness of the strengths and vulnerabilities associated with locomotion regulatory mode orientations in challenging circumstances, allowing people to be prepared for future global crisis.
Several factors limit the generalizability of these findings. Specifically, first aspect is related to the cross-sectional nature of the research that impede longitudinal assumption, allowing only for testing of relationships between predictor and outcomes at a specific point in time. Furthermore, it should be reported the use of a convenience sample (i.e., recruited using snowball sampling) and the imbalance of the sample (i.e., 82% female). Another limitation pertains to the use of self-report measures. In fact, data derived from the same source are potentially subject to common method/source bias. For this reason, it would be beneficial to have, for instance, a physiological measure of anxiety.
Additionally, it should be addressed that such data are limited to responses from individuals living in Italy during a specific phase of the COVID-19 pandemic. With this regard, it is important to note that many aspects of life in Italy have changed during the pandemic. In this vein, we could not be sure the pattern of our results could have been similar in the first phase of the pandemic. However, due to the nature of the relationship and the high level of anxiety experienced at the beginning of the pandemic, it is possible to hypothesize such relationship could be even stronger at that time.
As previously reported, data were collected using a web-mediated survey. Although such procedure may lead to self-selected and potentially biased samples [
58], in the case of COVID-19 and in presence of a scenario changing very quickly it allows to collect data with an extreme rapidity. With this regard, it has also been showed that psychometric properties of online surveys seem to be equivalent to those of paper-and-pencil formats in terms of both internal validity and reliability [
58,
59].
Yet another limitation of the present research pertains to the lack of assessment mode measure, which do not allow to identify its effects on COVID-19 anxiety and the possible interaction effects with locomotion mode. With this regard, a recent work [
60] has highlighted the detrimental impact of assessment regulatory mode vulnerabilities in response to COVID-19 pandemic. Specifically, these vulnerabilities have found to be indirectly linked to heightened psychological distress manifested through fear of missing out, challenges in engaging in activities, and involvement in negative behaviors. Hence, future studies would do well to examine the relationship between both regulatory modes, resilience and COVID-19 anxiety.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, this work provides valuable insights into the relationship between locomotion regulatory mode, resilience, and COVID-19 anxiety. The findings suggest that resilience mediates the relationship between locomotion and anxiety, highlighting the importance of being resilient when coping with worry and concern caused by the pandemic. These findings have important implications for mental health interventions and support strategies during the COVID-19 pandemic and beyond.
Author Contributions
“Conceptualization, Calogero Lo Destro and Alberto Costa; methodology, Calogero Lo Destro and Alberto Costa; formal analysis, Calogero Lo Destro; writing—original draft preparation, Calogero Lo Destro; writing—review and editing, Alberto Costa. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.”
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Research Board of the Niccolò Cusano University.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard Available online: https://covid19.who.int (accessed on 21 June 2023).
- COVID-19 Italia - Desktop Available online: https://opendatamds.maps.arcgis.com/apps/dashboards/0f1c9a02467b45a7b4ca12d8ba296596 (accessed on 21 June 2023).
- Onder, G.; Rezza, G.; Brusaferro, S. Case-Fatality Rate and Characteristics of Patients Dying in Relation to COVID-19 in Italy. Jama 2020, 323, 1775–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czeisler, M.É.; Lane, R.I.; Petrosky, E.; Wiley, J.F.; Christensen, A.; Njai, R.; Weaver, M.D.; Robbins, R.; Facer-Childs, E.R.; Barger, L.K. Mental Health, Substance Use, and Suicidal Ideation during the COVID-19 Pandemic—United States, June 24–30, 2020. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K. Psychological Distress Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic Among Adults in the United Kingdom Based on Coordinated Analyses of 11 Longitudinal Studies | Anxiety Disorders | JAMA Network Open | JAMA Network Available online: https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/article-abstract/2791456 (accessed on 21 June 2023).
- Schafer, K.M.; Lieberman, A.; Sever, A.C.; Joiner, T. Prevalence Rates of Anxiety, Depressive, and Eating Pathology Symptoms between the Pre- and Peri-COVID-19 Eras: A Meta-Analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 298, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; Ding, L.; Wang, L.; Deng, Y. Fear of COVID-19 Among College Students: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 846894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Zoghby, S.M.; Soltan, E.M.; Salama, H.M. Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Mental Health and Social Support among Adult Egyptians. J. Community Health 2020, 45, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Crosta, A.; Palumbo, R.; Marchetti, D.; Ceccato, I.; La Malva, P.; Maiella, R.; Cipi, M.; Roma, P.; Mammarella, N.; Verrocchio, M.C. Individual Differences, Economic Stability, and Fear of Contagion as Risk Factors for PTSD Symptoms in the COVID-19 Emergency. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 567367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Morstead, T.; Sin, N.; Klaiber, P.; Umberson, D.; Kamble, S.; DeLongis, A. Psychological Distress in North America during COVID-19: The Role of Pandemic-Related Stressors. Soc. Sci. Med. 2021, 270, 113687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, N.A.; Nazri, M.A.; Ali, M.H.; Alam, S.S. The Panic Buying Behavior of Consumers during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Examining the Influences of Uncertainty, Perceptions of Severity, Perceptions of Scarcity, and Anxiety. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2021, 62, 102600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Coninck, D.; Frissen, T.; Matthijs, K.; d’Haenens, L.; Lits, G.; Champagne-Poirier, O.; Carignan, M.-E.; David, M.D.; Pignard-Cheynel, N.; Salerno, S.; et al. Beliefs in Conspiracy Theories and Misinformation About COVID-19: Comparative Perspectives on the Role of Anxiety, Depression and Exposure to and Trust in Information Sources. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, F.D.; Krueger, R.F.; Vohs, K.D. Personal Economic Anxiety in Response to COVID-19. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2020, 167, 110233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkialis, L.; Rodrigues, N.B.; Cha, D.S.; Siegel, A.; Majeed, A.; Lui, L.M.W.; Tamura, J.K.; Gill, B.; Teopiz, K.; McIntyre, R.S. Social Isolation, Loneliness and Generalized Anxiety: Implications and Associations during the COVID-19 Quarantine. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, M.; Burch, A.E. Anxiety during the Pandemic: Racial and Ethnic Differences in the Trajectory of Fear. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 292, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlapani, E.; Holeva, V.; Nikopoulou, V.A.; Kaprinis, S.; Nouskas, I.; Diakogiannis, I. A Review on the COVID-19-Related Psychological Impact on Older Adults: Vulnerable or Not. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2021, 33, 1729–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrague, L.J. Psychological Resilience, Coping Behaviours and Social Support among Health Care Workers during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review of Quantitative Studies. J. Nurs. Manag. 2021, 29, 1893–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Destro, C.; Gasparini, C. COVID-19 Psychological Impact during the Italian Lockdown: A Study on Healthcare Professional. J. Workplace Behav. Health 2021, 36, 222–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandeğer, A.; Aydın, M.; Altınbaş, K.; Cansız, A.; Tan, Ö.; Tomar Bozkurt, H.; Eğilmez, Ü.; Tekdemir, R.; Şen, B.; Aktuğ Demir, N. Evaluation of the Relationship between Perceived Social Support, Coping Strategies, Anxiety, and Depression Symptoms among Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients. Int. J. Psychiatry Med. 2021, 56, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Li, M.; Li, Z.; Xiang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Xiong, Z. Coping Style, Social Support and Psychological Distress in the General Chinese Population in the Early Stages of the COVID-19 Epidemic. BMC Psychiatry 2020, 20, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnes, M. Webster’s New College Dictionary; Wiley Pub., 2007; ISBN 0-470-17777-2.
- Grillon, C. Models and Mechanisms of Anxiety: Evidence from Startle Studies. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 2008, 199, 421–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjemdal, O.; Vogel, P.A.; Solem, S.; Hagen, K.; Stiles, T.C. The Relationship between Resilience and Levels of Anxiety, Depression, and Obsessive–Compulsive Symptoms in Adolescents. Clin. Psychol. Psychother. 2011, 18, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leys, C.; Kotsou, I.; Shankland, R.; Firmin, M.; Péneau, S.; Fossion, P. Resilience Predicts Lower Anxiety and Depression and Greater Recovery after a Vicarious Trauma. IJERPH 2021, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiola, T.; Udofia, O. Psychometric Assessment of the Wagnild and Young’s Resilience Scale in Kano, Nigeria. BMC Res. Notes 2011, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredrickson, B.L.; Tugade, M.M.; Waugh, C.E.; Larkin, G.R. What Good Are Positive Emotions in Crisis? A Prospective Study of Resilience and Emotions Following the Terrorist Attacks on the United States on September 11th, 2001. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 2003, 84, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydov, D.M.; Stewart, R.; Ritchie, K.; Chaudieu, I. Resilience and Mental Health. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2010, 30, 479–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosheva, M.; Hertz-Palmor, N.; Dorman Ilan, S.; Matalon, N.; Pessach, I.M.; Afek, A.; Ziv, A.; Kreiss, Y.; Gross, R.; Gothelf, D. Anxiety, Pandemic-Related Stress and Resilience among Physicians during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Depress. Anxiety 2020, 37, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Dong, L.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Wei, R.; Zhang, J. The Relationship between Resilience, Anxiety and Depression among Patients with Mild Symptoms of COVID-19 in China: A Cross-Sectional Study. J Clin Nurs 2020, 4020–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalski, S.B.; Konaszewski, K.; Büssing, A.; Surzykiewicz, J. Resilience and Mental Well-Being During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Serial Mediation by Persistent Thinking and Anxiety About Coronavirus. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 810274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes, M.R.; Apaolaza, V.; Fernandez-Robin, C.; Hartmann, P.; Yañez-Martinez, D. The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Subjective Mental Well-Being: The Interplay of Perceived Threat, Future Anxiety and Resilience. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2021, 170, 110455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruglanski, A.W.; Thompson, E.P.; Higgins, E.T.; Atash, M.N.; Pierro, A.; Shah, J.Y.; Spiegel, S. To “Do the Right Thing” or to “Just Do It”: Locomotion and Assessment as Distinct Self-Regulatory Imperatives. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 2000, 79, 793–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, E.T.; Kruglanski, A.W.; Pierro, A. Regulatory Mode: Locomotion and Assessment as Distinct Orientations. 2003. [CrossRef]
- Garcia, D.; Jimmefors, A.; Mousavi, F.; Adrianson, L.; Rosenberg, P.; Archer, T. Self-Regulatory Mode (Locomotion and Assessment), Well-Being (Subjective and Psychological), and Exercise Behavior (Frequency and Intensity) in Relation to High School Pupils’ Academic Achievement. PeerJ 2015, 3, e847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bélanger, J.J.; Pierro, A.; Mauro, R.; Falco, A.; De Carlo, N.; Kruglanski, A.W. It’s about Time: The Role of Locomotion in Withdrawal Behavior. J. Bus. Psychol. 2016, 31, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carlo, N.A.; Falco, A.; Pierro, A.; Dugas, M.; Kruglanski, A.W.; Higgins, E.T. Regulatory Mode Orientations and Well-being in an Organizational Setting: The Differential Mediating Roles of Workaholism and Work Engagement. J. Appl. Soc. Psychol. 2014, 44, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Destro, C.; Di Santo, D.; Pierro, A.; Talamo, A.; Alessandri, G.; Caprara, G.-V. How People Feel about Their Job: Effects of Regulatory Mode on Positivity and Job Satisfaction ( ¿Cómo Se Sienten Las Personas Sobre Su Trabajo?: Los Efectos Del Modo Regulatorio En La Positividad y La Satisfacción Laboral ). Int. J. Soc. Psychol. 2021, 36, 487–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierro, A.; Giacomantonio, M.; Pica, G.; Kruglanski, A.W.; Higgins, E.T. Locomotion and the Preference for Multi-Tasking: Implications for Well-Being. Motiv. Emot. 2013, 37, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Santo, D.; Baldner, C.; Pierro, A.; Kruglanski, A.W. A “Bridge” over Troubled Water: Implications of the Effect of Locomotion Mode on Hopelessness. J. Appl. Soc. Psychol. 2018, 48, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Destro, C.; Chernikova, M.; Aiello, A.; Pierro, A. Who’s Most Likely to Get Stressed and Leave the Company? Effects of Regulatory Mode on Work Stress and Turnover Intentions. TPM - Test. Psychom. Methodol. Appl. Psychol. 2017, 543–555. [CrossRef]
- Bélanger, J.J.; Pierro, A.; Kruglanski, A.W.; Vallerand, R.J.; De Carlo, N.; Falco, A. On Feeling Good at Work: The Role of Regulatory Mode and Passion in Psychological Adjustment. J. Appl. Soc. Psychol. 2015, 45, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucidi, F.; Pica, G.; Mallia, L.; Castrucci, E.; Manganelli, S.; Bélanger, J.J.; Pierro, A. Running Away from Stress: How Regulatory Modes Prospectively Affect Athletes’ Stress through Passion. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2016, 26, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Destro, C.; Di Santo, D.; Pierro, A. Work-Related Stress among Nurses: The Effect of Regulatory Mode. Rassegna Psicol. 2018, 35, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, D.; Archer, T. Empowerment (Character, Motivation, and Regulatory Mode), Positive Affect, and Resilience. J. Happiness Well-Being 2016, 4, 212–225. [Google Scholar]
- Kruglanski, A.W.; Pierro, A.; Higgins, E.T. Experience of Time by People on the Go: A Theory of the Locomotion–Temporality Interface. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Rev. 2016, 20, 100–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diotaiuti, P.; Mancone, S.; Corrado, S. Using Sports Tracker: Evidences on Dependence, Self-Regulatory Modes and Resilience in a Sample of Competitive Runners. Psychology 2020, 11, 54–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Secades, X.; Molinero, O.R.; Ruiz-Barquín, R.; Salguero, A.; De la Vega, R.; Márquez, S. Resilience and Recovery-Stress in Competitive Athletes. Cuad. Psicol. Deporte 2017, 17, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Pierro, A.; Kruglanski, A.W.; Higgins, E.T. Regulatory mode and the joys of doing: effects of ‘locomotion’ and ‘assessment’ on intrinsic and extrinsic task-motivation. Eur. J. Personal. 2006, 20, 355–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholer, A.A.; Tory Higgins, E. Commitment to Change from Locomotion Motivation during Deliberation. Motiv. Emot. 2012, 36, 114–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.W.; Dalen, J.; Wiggins, K.; Tooley, E.; Christopher, P.; Bernard, J. The Brief Resilience Scale: Assessing the Ability to Bounce Back. Int. J. Behav. Med. 2008, 15, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, W.A.D.; de Sampaio Brito, T.R.; Pereira, C.R. COVID-19 Anxiety Scale (CAS): Development and Psychometric Properties. Curr. Psychol. 2022, 41, 5693–5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.F. Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis: Methodology in the Social Sciences. Kindle Ed. 2013, 193. [Google Scholar]
- Aiken, L.S.; West, S.G.; Reno, R.R. Multiple Regression: Testing and Interpreting Interactions; sage, 1991; ISBN 0-7619-0712-2.
- Grant, S.; Langan-Fox, J. Personality and the Occupational Stressor-Strain Relationship: The Role of the Big Five. J. Occup. Health Psychol. 2007, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swider, B.W.; Zimmerman, R.D. Born to Burnout: A Meta-Analytic Path Model of Personality, Job Burnout, and Work Outcomes. J. Vocat. Behav. 2010, 76, 487–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avnet, T.; Higgins, E.T. Locomotion, Assessment, and Regulatory Fit: Value Transfer from “How” to “What”. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 2003, 39, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauro, R.; Pierro, A.; Mannetti, L.; Higgins, E.T.; Kruglanski, A.W. The Perfect Mix: Regulatory Complementarity and the Speed-Accuracy Balance in Group Performance. Psychol. Sci. 2009, 20, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraut, R.; Olson, J.; Banaji, M.; Bruckman, A.; Cohen, J.; Couper, M. Psychological Research Online: Report of Board of Scientific Affairs’ Advisory Group on the Conduct of Research on the Internet. Am. Psychol. 2004, 59, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewson, C. Conducting Research on the Internet. Psychol.-Leic.- 2003, 16, 290–293.
- Jansen, E.J.; Danckert, J.; Seli, P.; Scholer, A.A. Under Pressure: Locomotion and Assessment in the COVID-19 Pandemic. Self Identity 2022, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).