Quantitative data were extracted from LimeSurvey and imported into IBM SPSS Statistics 28, where they were pre-processed and subjected to descriptive statistics and parametric statistical tests, namely the t-Student test for two independent samples and One-way ANOVA for tests with more than two samples. A significance level of less than 0.05 was considered for the tests. Qualitative data were imported to MaxQDA and submitted to inductive content analysis.
5.3. Actual use and usefulness
The professionals were asked about the frequency of use of two of the most relevant AI technologies used on the job – NMT and LLM -and their motivations to use them. Regarding the frequency of use (
Table 6), NMT (x̄=3.32) is almost two times more frequent than LLM (x̄=1.86). This may be explained by how LLM have recently become popular (e.g., ChatGPT in 2023), while NMT has been available for longer.
The overall frequency of use of Artificial Intelligence technologies falls under the “Sometimes” interval, with professionals using them about 25% to 50% of the time.
A One-way ANOVA test confirms that men (x̄=2.00) use Language Models more frequently than women (x̄=1.72) (F(10.643)=8.969; p<0.0001). A series of One-way ANOVA tests also confirms that the frequency of use of NMT, Language Models and AI technologies overall is higher for professionals whose level of familiarity is also higher (“Very familiar” and “Extremely familiar”). No significant differences were found between age groups or years of experience on the job.
When asked about the reasons why professionals use NMT, the top five reasons reside in saving time (“Speed”, 55.7%), serving as a starting point for the translation of texts (35.4%), which allows professionals to focus on post-editing tasks (25.3%). Being useful for short texts (26.6%) and allowing generic understanding of the text is also referred to (22.8%), as depicted in
Table 7.
On top of the suggested list of potential motivations, professionals also refer to the larger variety of vocabulary provided by NMT and its ability to save costs for the client. There is one case in which it consists of a company requisite.
Concerning the usefulness of LLM, the reasons for their use are in line with the general motivation to use NMT (
Table 8). The most common utility resides in saving time in research (16.5%) and providing more translation options (12.7%). On top of the provided list of potential reasons, the professionals also refer to its ability to verify the clarity of the translated text in more complex sentences and to reduce costs for the client. Additionally, some, at present time, are using the tool to evaluate the potential of the technology or out of curiosity.
The professionals were also asked if they felt the AI technologies, in general, were useful in their specific job attributions. Results, in
Figure 3, show that only about 34% of professionals consider the technologies as very or extremely useful, and 15,19% find them not useful at all.
A series of t-test and One-way ANOVA tests reveal that there are no significant differences in the distribution of the usefulness averages among professionals with more or less years of experience. However, there are substantial differences among age groups and among the level of familiarity with AI, as shown in
Figure 4.
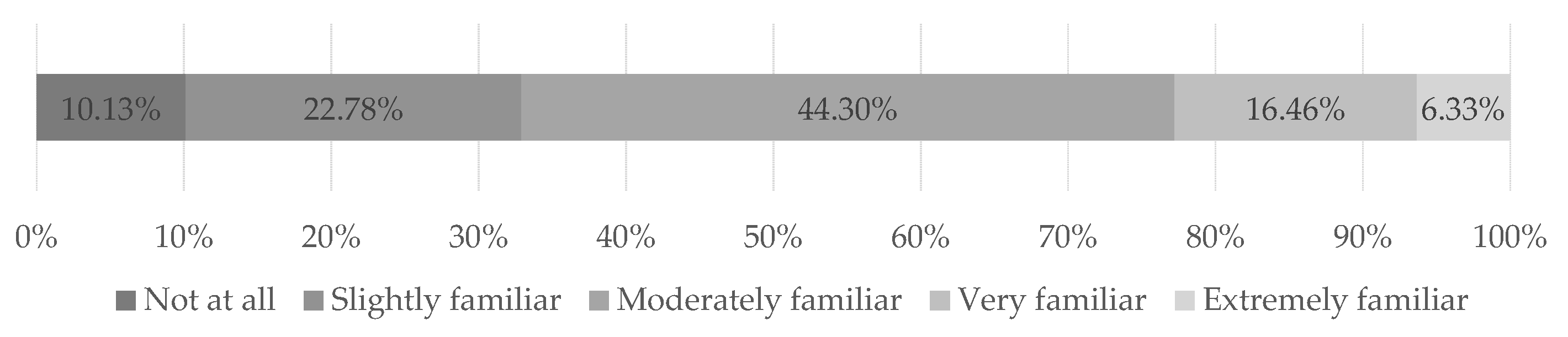
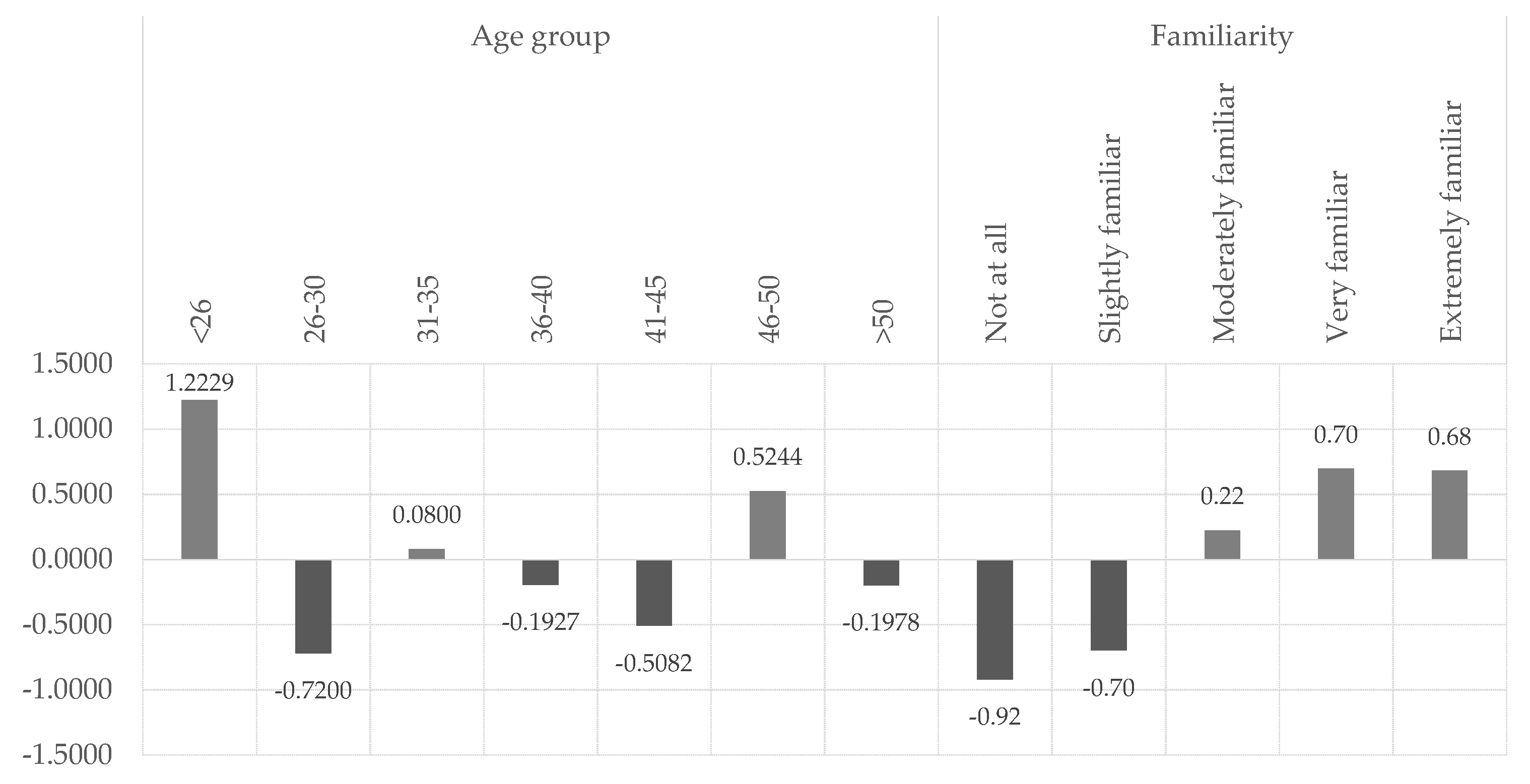
Professionals aged < 26 years and between 46 to 50 years old recognize higher levels of usefulness in AI (F(3.922)=3.069; p<0.005). Usefulness is also higher to the professionals who are very or extremely familiar with AI (F(6.468)=5,337; p<0.05). As mentioned, AI technologies have become more popular recently, and, in our sample, 44% of professionals are only moderately familiar with it and 33% are only slightly or not familiar with it at all. We believe that as the professionals become more familiarized with AI, they tend to see more usefulness in it. In fact, a One-way ANOVA test confirms that the participants who scored poorer in the quiz about AI and automation also reveal lower averages of perceived usefulness of AI in the performance of their work (F(2.625)=2.154; p<0.05).
For the participants who stated that AI is, at least, slightly useful (n=67), the most relevant reasons among the provided list consist of “Speed” and “Efficiency” (
Table 9).
For the participants who stated that AI is not useful at all (n=12), the most relevant reasons, among the provided list, consist of “Lack of contextual understanding” (inability of the tool to understand the context of the texts) and “Lack of precision and quality” (
Table 10).
Overall, we observe that the professionals are not very familiar with the use of AI in the profession and that their knowledge regarding these technologies and tools is low to very low. As a result, their perceived level of usefulness of AI is essentially low to moderate and those who are less familiar, know less and recognize less usefulness also demonstrate a lack of trust in AI, as observed in the reasons depicted in
Table 8.
5.4. Influence on work performance and the labour market
To evaluate the influence of AI on the work performance, the professionals were asked what they thought was the influence of the technology on specific job tasks in the present and the language services market in the future.
Concerning the influence of AI on job-specific tasks, the results are presented in
Table 11.
The tasks the professionals believe benefit more from AI are “Transcription”, “Translation of general topics”, “Terminology management” and “Technical/specific translations”. Those with less positive effects of AI consist of “Interpreting” and “Subtitling”, probably due to the particular characteristics of these tasks. In interpretation, there are many variables that may influence the correct understanding of what is being said (tone, pronunciation, noise, etc.) and in subtitling, there are a set of rules that are also important to convey in the message, namely the number of characters and lines. It is worth noting that the overall average for all tasks is relatively moderate (x̄=2.11), falling in the “Negatively” to “Both” interval.
After a series of t-tests and One-way ANOVA tests, we found no significant differences in the distribution of averages between genders, age, work experience, familiarity with AI, frequency of use of NMT and Language Models, and usefulness and frequency of use of AI.
Concerning the influence of AI on the language services market in the future, the professionals were provided with the following answer options:
- 1)
Very negatively: I believe that AI will have a highly negative impact on the language services market, which may include the devaluation of language professionals, the loss of linguistic nuance, or an erosion of the human touch in language services.
- 2)
Negatively: I foresee potential drawbacks, such as displacement of jobs, reduced demand for human translators and interpreters, or a decrease in the quality of language services.
- 3)
Both: It can bring both opportunities and challenges to the market.
- 4)
Positively: I foresee benefits such as increased productivity, streamlined processes, and the ability to handle larger volumes of content.
- 5)
Very positively: I believe it will bring significant advances, such as greater efficiency, better quality, and more opportunities for language professionals.
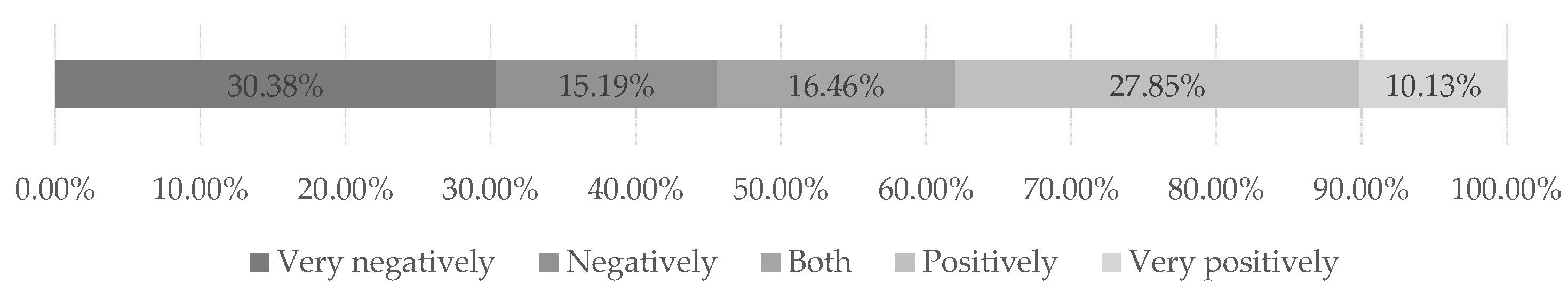
Only 38% of the professionals estimate a positive or very positive outcome, against a fraction of 46% who estimates a negative or very negative one, and an additional portion of 16% who estimates it can turn out either positive or negative (
Figure 5).
These results are fundamentally different from those obtained in Bulgaria [
17], which reports that only about one tenth of respondents (12%) are of the opinion that translators would become redundant.
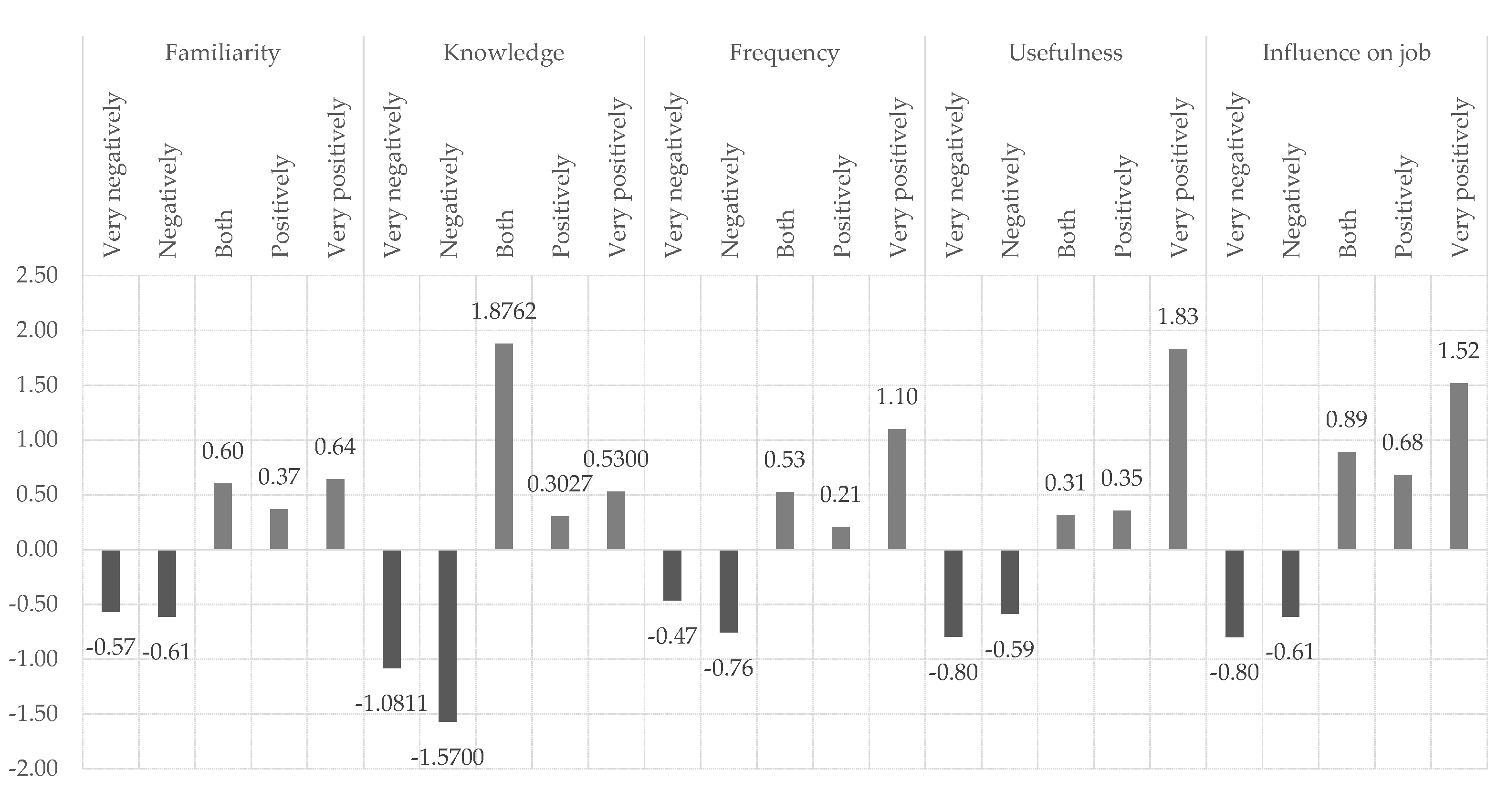
A series of One-way ANOVA tests (standardized values illustrated in
Figure 6), allowed us to identify that this overall negative tendency is essentially voiced by the professionals with below-average familiarity with AI in the provision of language services (
F(5.791)=7.351;
p<0.001), below-average knowledge regarding the incorporation of AI and automation in language tools (
F(5.064)=5.537;
p<0.001), below-average frequency of use of AI technologies on the job (
F(6.553)=7.274;
p<0.001), below-average perceived usefulness of AI in the provision of language services (
F(12.520)=14.153;
p<0.05) and perceived negative influence of AI on job-related tasks (
F(1.942)=11.358;
p<0.05).
The professionals were also asked about their perspective concerning the future of the language services market in Portugal. They were presented with the following open-ended question: “According to a recent study [
2], artificial intelligence (AI)-based tools such as ChatGPT may have implications for the language services market. This study identified interpreters and translators as some of the top professions with the greatest exposure to AI in the US labour market (76.5%), noting that AI could save professionals a significant amount of time in getting work done and/or lead to a high portion of work being automated and replaced by technology. According to your experience in the field of language services, what do you think about this issue for Portugal?”.
A total of 44 documents (answers) obtained from the experts were submitted to induction-based quantitative content analysis in MaxQDA. The total number of answers were provided by experts that had chosen the following answers regarding the influence of AI in the language service market (
Table 12).
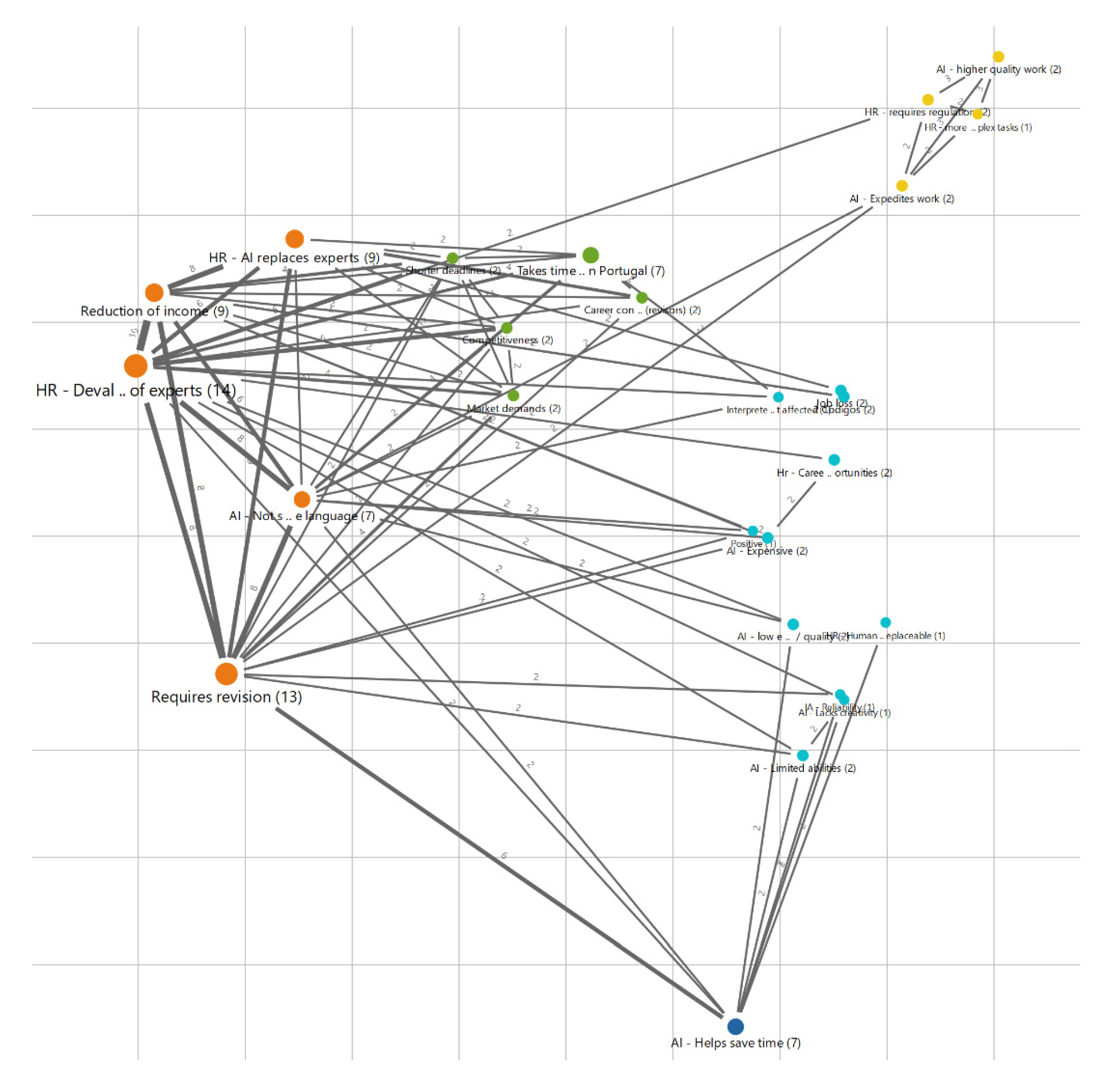
There are eighteen answers on the positive side (“Positive” + “Very positive”) and eighteen on the negative side (“Very negative” + “Negative”). The codes’ map obtained from MaxQDA is presented in
Figure 7, where the most frequent categories are and its relations are shown.
The codes with the highest degree of saturation consist of those in the orange cluster, which refers to the most critical negative influences that experts foresee for the Portuguese language market. These are depicted in
Table 13.
Even though the answers were obtained from a balanced sample of experts, regarding the positive or negative orientation on the influences of AI in the langue services market, when considering the effects on the Portuguese market, the negative outcomes appear as more relevant. This happens because, even for those experts that believe that the influences will be, in general, more positive, they also voice more general or more specific concerns with a non-positive outset, which translate, somewhat, into a negationist orientation. The devaluation of experts and their career is at the top of these concerns and appears, sometimes, linked to the lack of formal regulation of the career, but not only. This concern is frequently linked to other concerns, which we depict on
Table 14.
The lack or formal regulation to sustain the relevance of the experts on the market and ensure the quality of the translated texts appears as one of the reasons why they anticipate the devaluation of the profession. Regarding this, some experts foresee a shift in the career to become “mere text editors” (VN10, Pos. 1), which is also linked to the second most critical negative influence expected (“Automatic translation requires revision”, in
Table 13), as the clients tend to lower or adjust quality standards to incorporate machine translations. This appears both as a risk and as justification to sustain the role of the experts in the language services market (
Table 15), as is in line with [
17], who reports that 88% of Bulgarian translators think that AI will not be able to perform better translations than humans.
This line of reasoning is also frequently associated with the AI not being fully equipped to deal with the European Portuguese (more efficient in Brazilian Portuguese), not being able to identify cultural references and ineffective in specialized texts (such as literary). Some domains also appear to be more prone to be replaced by AI, such as the translation for subtitling (according to (VN03, Pos. 1)). However, it is not unanimous because, as seen on
Table 11, subtitling is one of the job tasks that, on average, is considered to be least influenced by AI. A residual number of experts, namely those with a more positive orientation towards the future of the career, foresee that this shift will turn AI into a resource that will strengthen the career, by providing experts with tools that allow them to work faster and increase their competitiveness.
However, the transition of the role of experts to mere reviewers is one of the critical and more voiced concerns, that, together with the lowering of quality standards and increased speed of translation, will cause a severe reduction of the prices. It is evident that machine translation leads to a shift in the market dynamics and in the labour market, depreciating the perceived value of the language services and the value of the experts, as voiced in the excerpts of
Table 16. This, however, is contrary to the report of [
17], according to which 59% of Bulgarian translators believe that their services will not become cheaper because of AI.
Ultimately, some experts expect AI and automation to fully replace translators, leading to the disappearance of the career, as visible in the excerpts of
Table 17. It is worth noting that these concerns are voiced both by experts with a more negative and uncertain foresight of the future of the language services market in Portugal. This means that, even though the potential of AI is recognized as a competitive factor for experts providing language services, namely in the expediency of the services provided and in the richness of the vocabulary, the experts fear they might end up being completely dispensable.
The study conducted on Bulgaria [
17] had also identified that most of the professionals perceive artificial intelligence and automatization as threats to the profession, believing that AI will modify the profession by relieving human translators of the routine, technical part of the job, while moving translators to predominantly edit machine-translated texts, and teach artificial intelligence to perform machine translation. However, in Bulgaria, the pessimistic scenarios about mass jobs destruction are reported as unjustified.
The apprehension and concerns regarding the downfall of the career appear to be somewhat eased by the argument that the penetration of AI in the Portuguese language market has not reached its full potential yet and should be slower than for other countries (English speaking, for instance), as stated by one of the experts “
It will take years to have a negative effect on our business” (B08, Pos. 1). This refers to the incorporation of technology in the market and to AI’s efficacy for dealing with the Portuguese language specifically, which experts indicate to be limited and questionable, as shown in
Table 18.
We have, therefore, identified two delayers: cultural (adoption of AI) and technological (perceived efficacy). From the previous excerpts, we have also identified a sense of hope regarding the maintenance of the human intervention in the provision of language services or to exalt it, as depicted in
Table 19, and they ask for protective regulation, as seen in
Table 14.
These refer mainly to human qualities that the experts believe AI cannot offer and to technical abilities acquired with experience on the job, specifically those related to cultural aspects.
There are very few opportunities identified by the experts regarding AI’s influence on the provision of language services in Portugal. The expediency of the services is the most relevant one, together with AI’s ability to provide prompt and more diversified vocabulary options/alternatives. It is worthy of note that Portuguese translators tend to value AI’s creative features regarding the diversity of vocabulary it provides to enrich their texts. In contrast, 96% of Bulgarian translators agree that AI will never replace human creativity [
17].
Concerning the overall scenario in Portugal, and according to the professionals’ views, there are severe concerns regarding a significant reconfiguration of the career and loss of income and/or jobs, justified by automation and mainly by AI, which works at the operational and creative levels. In Bulgaria, results point out AI, together with other digital technology, as becoming an “organiser of new activities within the profession”, with translators becoming the system’s teachers and not leaving the profession. Routine translations are automated and absorbed by AI, and new jobs are simultaneously created with the increase in the demand for editors of AI translated texts, as well as teachers of AI [
17]. This is seen as a positive outcome of the penetration of AI in the career. However, Portuguese translators view the reconfiguration of the profession into reviewers or post-editors as a depreciation of the profession, leading to a reduction of income and volume of work. Thus, they do believe that AI will negatively impact the quality of work or employment conditions in their professional activities. Moreover, within the qualitative data collected, none of the professionals envision themselves having a tutoring or teaching role over AI, such as reported by [
17], in the sense of perfecting it to improve it. What is commonly recognized is the increased expediency of the provision of services, facilitated by AI and automation.
Among the perspectives of experts with a more positive attitude, some mitigation strategies for professionals are suggested, as depicted in
Table 20.
The experts refer to the need of keeping up with the technological trends and invest in continuous training to help professionals incorporate AI as a competitive tool, allowing them to remain competitive and relevant. To this purpose, raising awareness regarding the poor quality of automated or AI-based translations among clients and companies is also believed to be necessary.