Submitted:
03 July 2023
Posted:
04 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Phytoplankton and zooplankton culture conditions
2.2. Phytoplankton biomass estimative and saxitoxin analysis
2.3. Life table experiments
2.4. Dietary exposure to STX-producing cyanobacteria under constant nutritious food
2.5. Dietary exposure to STX-producing cyanobacteria under variable nutritious food
2.6. Grazing assays
2.7. Data analysis
3. Results
3.1. Dietary exposure to STX-producing cyanobacteria under constant nutritious food
3.2. Dietary exposure to STX-producing cyanobacteria under variable nutritional food
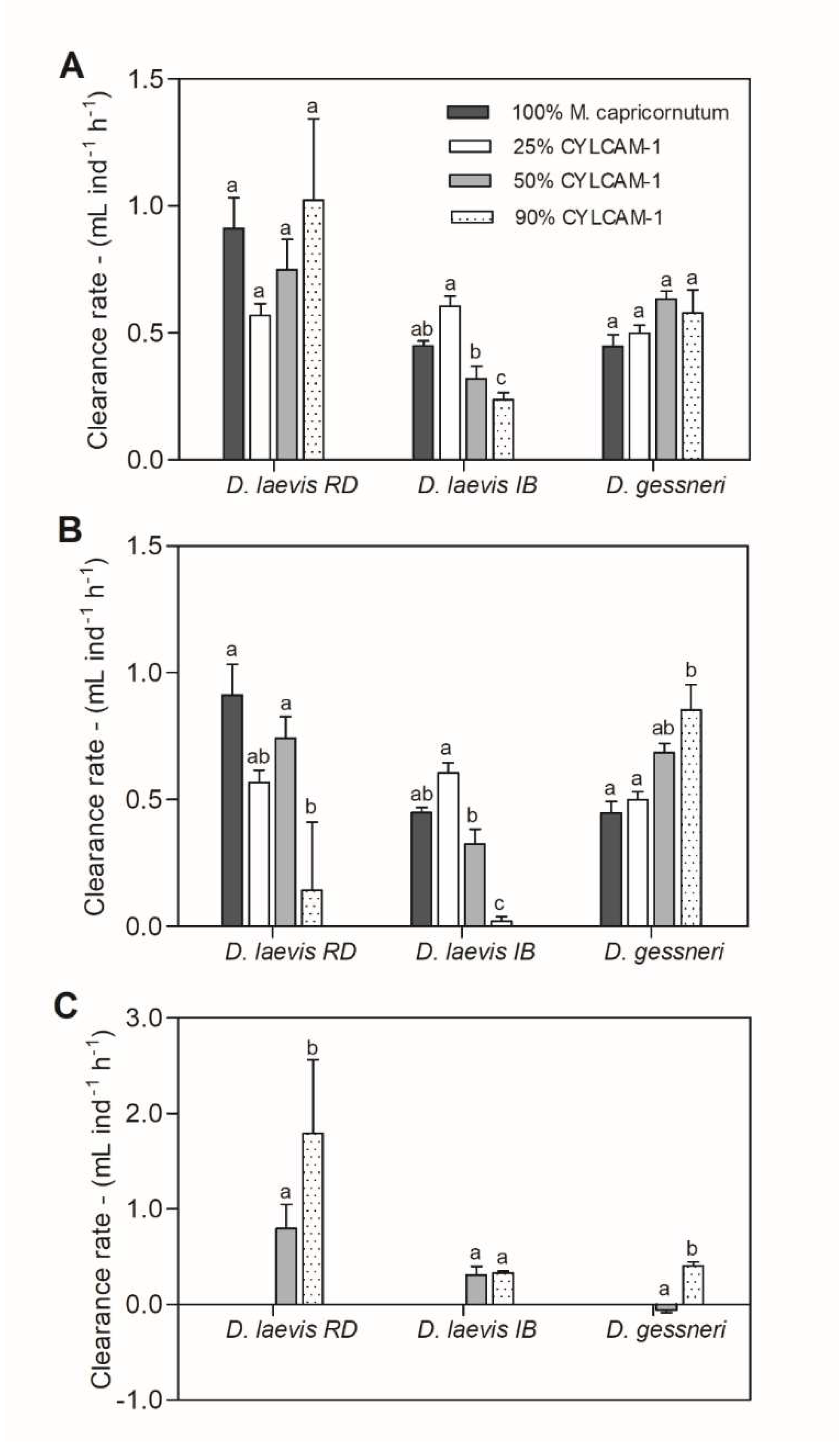
3.3. Cyanobacterial effects on feeding behavior
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- AFNOR - Association Française of Normalization (1980). Essais des eaux. Determination of inhibition of Scenedesmus subspicatus par une substance. Norme Experimentale T90-304.
- Aguilera, A.; Gómez, E.B.; Kaštovský, J.; Echenique, R.O.; Salerno, G.L. The polyphasic analysis of two native Raphidiopsis isolates supports the unification of the genera Raphidiopsis and Cylindrospermopsis (Nostocales, Cyanobacteria). Phycologia 2018, 57, 130–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, J.T.; Leã£O, P.N.; Vasconcelos, V.M. Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii: review of the distribution, phylogeography, and ecophysiology of a global invasive species. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bednarska, A.; Pietrzak, B.; Pijanowska, J. Effect of poor manageability and low nutritional value of cyanobacteria on Daphnia magna life history performance. J Plankton Res 2014, 36, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarska, A.; Slusarczyk, M. Effect of non-toxic, filamentous cyanobacteria on egg abortion in Daphnia under various thermal conditions. Hydrobiologia 2012, 715, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, S.; Aubriot, L.; Soares, M.C.S.; et al. What drives the distribution of the bloom-forming cyanobacteria Planktothrix agardhii and Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii? FEMS Microbiol Ecol 2012, 79, 594–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvy, M.; Falcão, D.; Marinho, M.; Pagano, M.; Moura, A. Occurrence of Cylindrospermopsis (Cyanobacteria) in 39 Brazilian tropical reservoirs during the 1998 drought. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2000, 23, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvy, M.; Molica, R.; Oliveira, S.; Marinho, M.; Becker, B. Dynamics of a toxic cyanobacterial bloom (Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii) in a shallow reservoir in the semi-arid region of Northeast Brazil. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 1999, 20, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunioto, T.C.; Arcifa, M.S. Effects of food limitation and temperature on cladocerans from a tropical Brazilian lake. Aquat Ecol 2007, 41, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burford, M.A.; Beardall, J.; Willis, A.; Orr, P.T.; Magalhaes, V.F.; Rangel, L.M.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O.E.; Neilan, B.A. Understanding the winning strategies used by the bloom-forming cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.M.; Ferrão-Filho, A.S.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O. Effects of saxitoxin- and non-saxitoxin-producing strains of the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii on the fitness of temperate and tropical cladocerans. Harmful Algae 2013, 28, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles S, Veber P, Delignette-Muller ML MOSAIC: a web-interface for statistical analyses in ecotoxicology. Env. Sci Pollut Res. 2018, 25, 11295. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chorus I, Bartram J. Toxic cyanobacteria in water: a guide to their public health consequences, monitoring and management, 3rd ed.; WHO - World Health Organization: Geneva, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- DeMott, W.R. Foraging strategies and growth inhibition in five daphnids feeding on mixtures of a toxic cyanobacterium and a green alga. Freshwat Biol 1999, 42, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMott, W.R.; Van Donk, E. Strong interactions between stoichiometric constraints and algal defenses: evidence from population dynamics of Daphnia and algae in phosphorus-limited microcosms. Oecologia 2013, 171, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeMott, W.R.; Gulati, R.D.; Van Donk, E. Daphnia food limitation in three hypereutrophic Dutch lakes: Evidence for exclusion of large-bodied species by interfering filaments of cyanobacteria. Limnol Ocean. 2001, 46, 2054–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabre, A.; Lacerot, G.; de Paiva, R.R.; Soares, M.C.S.; Magalhães, V.F.; Bonilla, S. South American PSP toxin-producing Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria) decreases clearance rates of cladocerans more than copepods. Hydrobiologia 2017, 785, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrão-Filho, A.S. Bioacumulação de cianotoxinas e seus efeitos em organismos aquáticos. Oecol. Bras. 2009, 13, 272–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrão-Filho, A.S.; Abreu, S.S.D.; Oliveira, T.; Magalhães, V.F.; Pflugmacher, S.; Silva, E.M. Single and combined effects of microcystin and saxitoxin producing cyanobacteria on the fitness and antioxidant defenses of cladocerans. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 9999, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrão-Filho, A.S.; Costa, S.M.; Ribeiro, M.G.L.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O. Effects of a saxitoxin-producer strain of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (cyanobacteria) on the swimming movements of cladocerans. Environ. Toxicol. 2008, 23, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrão-Filho, A.S.; Cunha, R.; Magalhães, V.F.; Soares, M.C.S.; Baptista, D.F. Evaluation of sub-lethal toxicity of Cyanobacteria on the swimming activity of aquatic organisms by image analysis. J. Braz. Soc. Ecotoxicol. 2007, 2, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrão-Filho, A.S.; Dias, T.M.; Pereira, U.J.; dos Santos, J.A.A.; Kozlowsky-Suzuki, B. Nutritional and toxicity constraints of phytoplankton from a Brazilian reservoir to the fitness of cladoceran species. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 12881–12893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrão-Filho AS, Koslowsky-Suzuki B Cyanotoxins: Bioaccumulation and Effects on Aquatic Animals. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2729–2772. [CrossRef]
- Ferrão-Filho, Soares MC, Magalhães VF, Azevedo SM. A rapid bioassay for detecting saxitoxins using a Daphnia acute toxicity test. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2084–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrão-Filho AS, Soares MCS, Lima RS, Magalhães VF Effects of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria) on the swimming behavior of Daphnia (Cladocera). Envirn Toxicol Chem 2014, 31, 223–229.
- Garcia FC, Barbosa FAR, Braz S, Petrucio MM, Faria B Water quality of an urban reservoir subjected to periodic applications of copper sulphate: the case of Ibirité reservoir, Southeast Brazil. Acta Limnol Bras 2009, 21, 235–243.
- Ghadouani, A.; Pinel-Alloul, B.; Plath, K. Effects of Microcystis aeruginosa and purified microcystin-LR on the feeding behavior of Daphnia pulicaria. Limnol Ocean. 2004, 49, 666–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ger, K.A.; Urrutia-Cordero, P.; Frost, P.C.; Hansson, L.-A.; Sarnelle, O.; Wilson, A.E.; Lürling, M. The interaction between cyanobacteria and zooplankton in a more eutrophic world. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ger, K.A.; Panosso, R.; Lürling, M. Consequences of acclimation to Microcystis on the selective feeding behavior of the calanoid copepod Eudiaptomus gracilis. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2011, 56, 2103–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliwicz, Z.M. Food thresholds and body size in cladocerans. Nature 1990, 343, 638–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillard, R.R. Cultures of phytoplankton for feeding of marine invertebrates. In Culture of Marine Invertebrate Animals; Smith, W.L., Chanley, M.H., Eds.; Plenum: New York, 1975; pp. 29–60. [Google Scholar]
- Hansson, L.; Gustafsson, S.; Rengefors, K.; Bomark, L. Cyanobacterial chemical warfare affects zooplankton community composition. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 1290–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, E. R.; Duncan, A. Food concentration and temperature effects on life-cycle characteristics of tropical Cladocera Daphnia gessneri Herbst, Diaphanosoma sarsi Richard, and Moina reticulata Daday. I. Development time. Acta Amaz. 1994, 24, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, R.C.; Bychek, E.A. Body syze in freshwater planktonic crustaceans: an overview of extrinsic determinants and modifying influences of bioctic interactions. Hydrobiologia 2011, 668, 61–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havens, K.E.; Hudnell, H.K. Cyanobacteria blooms: effects on aquatic ecosystems, Cyanobacterial Harmful Algal Blooms: State of the Science and Research Needs; Springer: New York, 2008; pp. 733–747. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins, P.R.; Chandrasena, N.R.; Jones, G.J.; Humpage, A.R.; Falconer, I.R. Isolation and toxicity of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii from an ornamental lake. Toxicon 1997, 35, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heathcote, A.J.; Filstrup, C.T.; Kendall, D.; Downing, J.A. Biomass pyramids in lake plankton: influence of Cyanobacteria size and abundance. Inland Waters 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillebrand, H.; Dürselen, C.D.; Kirschtel, D.; Pollingher, U.; Zohary, T. Biovolume calculation for pelagic and benthic microalgae. J. Phycol. 2002, 35, 403–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, J.; Codd, G.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Ibelings, B.W.; Verspagen, J.M.; Visser, P.M. Cyanobacterial blooms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huszar, V.L.M.; Silva, L.H.S.; Marinho, M.M.; Domingos, P.; Sant’Anna, C.L. Cyanoprokaryote assemblages in eight productive tropical Brazilian waters. Hydrobiologia 2000, 424, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jónasdóttir, S.H.; Kiørboe, T.; Tang, K.W.; St John, M.; Visser, A.W.; Saiz, E.; Dam, H.G. Role of diatoms in copepod production: good, harmlessor toxic? Mar Ecol Prog Ser 1998, 172, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagos, N.; Onodera, H.; Zagatto, P.A.; Andrinolo, D.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O.; Oshima, Y. The first evidence of paralytic shelfish toxins in the freshwater cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii, isolated from Brazil. Toxicon 1999, 37, 1359–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Peng, L.; Huang, X.; Han, B.P. Occurrence and dominance of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii and dissolved cylindrospermopsin in urban reservoirs used for drinking water supply. South China, Environ. Monit. 2014.
- Leonard, J.A.; Pearl, H.W. Zooplâncton community structure, micro-zooplâncton grazing impact, and seston energy content in the St. Johns river system, Florida as influenced by the toxic cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Hydrobiologia 2005, 537, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lürling, M.; Verschoor, A.M. FO-spectra of chlorophyll fluorescence for the determination of zooplankton grazing. Hydrobiologia 2003, 491, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagni, R.L.; de Falco, P.B.; dos Santos, A.C.A. Autecology of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Woloszynska) Seenayya et Subba Raju. Acta Limnol. Bras. 2020, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearl, H.; Huisman, J. Blooms Like It Hot. Science 2008, 320, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Creuzburg, D.; von Elert, E.; Hoffmann, K.H. Nutritional constraints at the cyanobacteria-Daphnia magna interface: The role of sterols. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, N.A.S.T.; Maia-Barbosa, P.M. Cyanobacteria bloom: selective filter for zooplankton? Braz J Biol 2015, 75, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesquita, M.; Lürling, M.; Dorr, F.; Pinto, E.; Marinho, M. Combined Effect of Light and Temperature on the Production of Saxitoxins in Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii Strains. Toxins 2019, 11, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, F.S.; Pinto-Coelho, R.M.; Gonzaga, A.V. Redução da riqueza de organismos do zooplâncton (com ênfase em Copepoda e Cladocera) nas lagoas do médio Rio Doce/MG. Rev. Bras. De Zoociências 2013, 15, 69–90. [Google Scholar]
- Miranda, C.T.; de Lima, D.V.N.; Atella, G.C.; de Aguiar, P.F.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O. Optimization of Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Salt for Lipid Accumulation of Microalgae: Towards the Viability of Microalgae Biodiesel. Nat. Sci. 2016, 08, 557–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molica, R.J.R.; Oliveira, E.J.A.; Carvalho, P.V.V.C.; Costa, A.P.N.S.F.; Cunha, M.C.C.; Melo, G.L. Ocurrence of saxitoxins and anatoxin-a(s)-like anticholinesterase in Brazilian drinking water supply. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustaka-Gouni, M.; Sommer, U. Effects of Harmful Blooms of Large-Sized and Colonial Cyanobacteria on Aquatic Food Webs. Water 2020, 12, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, I.C.; Lobo-Da-Cunha, A.; Vasconcelos, V.M. Effects of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii and Aphanizomenon ovalisporum (cyanobacteria) ingestion on Daphnia magna midgut and associated diverticula epithelium. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 80, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, I.C.G.; Saker, M.L.; Pflugmacher, S.; Wiegand, C.; Vasconcelos, V.M. Toxicity of the cyanobacteriumCylindrospermopsis raciborskii toDaphnia magna. Environ. Toxicol. 2004, 19, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panosso, R.; Carlsson, P.; Kozlowsky-Suzuki, B.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O.; Granéli, E. Effect of grazing by a neotropical copepod, Notodiaptomus, on a natural cyanobacterial assemblage and on toxic and non-toxic cyanobacterial strains. J. Plankton Res. 2003, 25, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccini, C.; Aubriot, L.; Fabre, A.; Amaral, V.; González-Piana, M.; Giani, A.; Figueredo, C.C.; Vidal, L.; Kruk, C.; Bonilla, S. Genetic and eco-physiological differences of South American Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii isolates support the hypothesis of multiple ecotypes. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto-Coelho, R.M.; Bezerra-Neto, J.F.; Giane, A.; Macedo, C.F.; Figueiredo, C.C.; Carvalho, E.A. The Collapse of a Daphnia laevis (Birge, 1878) population in Pampulha Resevoir, Brasil. Acta Limnol. Bras. 2003, 3, 53–70. [Google Scholar]
- Pomati, F.; Neilan, B.A.; Suzuki, T.; Manarolla, G.; Rossett, C. Enhancement of intracellular saxitoxin accumulation by lidocaine hydrocloride in the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii T3 (Nostocales). J. Phycol. 2003, 39, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, L.M.; Ger, K.A.; Silva, L.H.S.; Soares, M.C.S.; Faassen, E.J.; Lürling, M. Toxicity Overrides Morphology on Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii Grazing Resistance to the Calanoid Copepod Eudiaptomus gracilis. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 71, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, L.M.; Silva, L.H.S.; Faassen, E.J.; Lürling, M.; Ger, K.A. Copepod Prey Selection and Grazing Efficiency Mediated by Chemical and Morphological Defensive Traits of Cyanobacteria. Toxins 2020, 12, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restani, G.C.; Fonseca, A.L. Effects of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii strains (Woloszynska, 1912) Senayya & Subba Raju on the mobility of Daphnia laevis (Cladocera, Daphniidae). Braz. J. Biol. 2014, 74, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Rzymski, P.; Poniedziałek, B. In search of environmental role of cylindrospermopsin: a review on global distribution and ecology of its producers. Water Res. 2014, 66, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, O.; Duncan, A. The relationship between cell carbono and cell volume in freshwater algal species used in zooplanktonic studies. J Plankton Res. 1985, 7, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnelle, O.; Gustafsson, S.; Hansson, L.A. Effects of cyanobacteria on fitness components of the herbivore Daphnia. J. Plankton Res. 2010, 32, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, A.; Dawidowicz, P. Breakage of cyanobacterial filaments by small- and large-sized Daphnia: are there any temperature dependent differences? Hydrobiologia 2017, 798, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.C.S.; Lürling, M.; Panosso, R.; Huszar, V. Effects of the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii on feeding and life history characteristics of the grazer Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicol. Environ. 2009, 72, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.C.S.; Huszar, V.; Miranda, M.N.; Melo, M.M.; Roland, F.; Lürling, M. Cyanobacterial dominance in Brazil: distribution and environmental preferences. Hydrobiologia 2013, 717, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, D. Geometric models for calculating cell biovolume and surface area for phytoplankton. J. Plankton Res. 2003, 25, 1331–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taberner, A.; Castañera, P.; Silvertre, E.; Dopazo, J. Estimation of the intrinsic rate of natural increase and its error by both algebraic and resampling Approaches. Comput. Appl. Biosci. 1993, 9, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmanns, A.R.; Burton, S.K.; Pick, F.R. Daphnia Pre-Exposed to Toxic Microcystis Exhibit Feeding Selectivity. Hydrobiology 2011, 96, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmanns, A.R.; Wilson, A.E.; Pick, F.R.; Sarnelle, O. Meta-analysis of cyanobacterial effects on zooplankton population growth rate: species-specific responses. Hydrobiology 2008, 171/4, 285–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urabe, J.; Shimizu, Y.; Yamaguchi, T. Understanding the stoichiometric limitation of herbivore growth: the importance of feeding and assimilation flexibilities. Ecol. Lett. 2018, 21, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar, MCP. ; Rodrigues, TFCP.; Silva, LO; Pacheco, ABF; Ferrão-Filho, AS; Azevedo, SMFO. Ecophysiological Aspects and sxt Genes Expression Underlying Induced Chemical Defense in STX-Producing Raphidiopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria) against the Zooplankter Daphnia gessneri. Toxins 2021, 13, 406. [Google Scholar]
- Vilar, M.C.P.; Ferrão-Filho, A.d.S.; Azevedo, S.M. Single and mixed diets of the toxic Cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa and Raphidiopsis raciborskii differently affect Daphnia feeding behavior. Food Webs 2022, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson AE, Sarnelle O, Tillmanns AR Effects of cyanobacterial toxicity and morphology on the population growth of freshwater zooplankton: Meta-analyses of laboratory experiments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 1915–1924. [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.A.; Stirling, D.J. First identification of the cylindrospermopsin-producing cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in New Zealand. New Zeal. J. Mar. Fresh. Res. 2003, 37, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.R.; Hong, L.V.; Isabwe, A.; Liu, L.; Yu, X.; Chen, H.; Yang, J. Disturbance-induced phytoplankton regime shifts and recovery of cyanobacteria dominance in two subtropical reservoirs. Water Res. 2017, 120, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
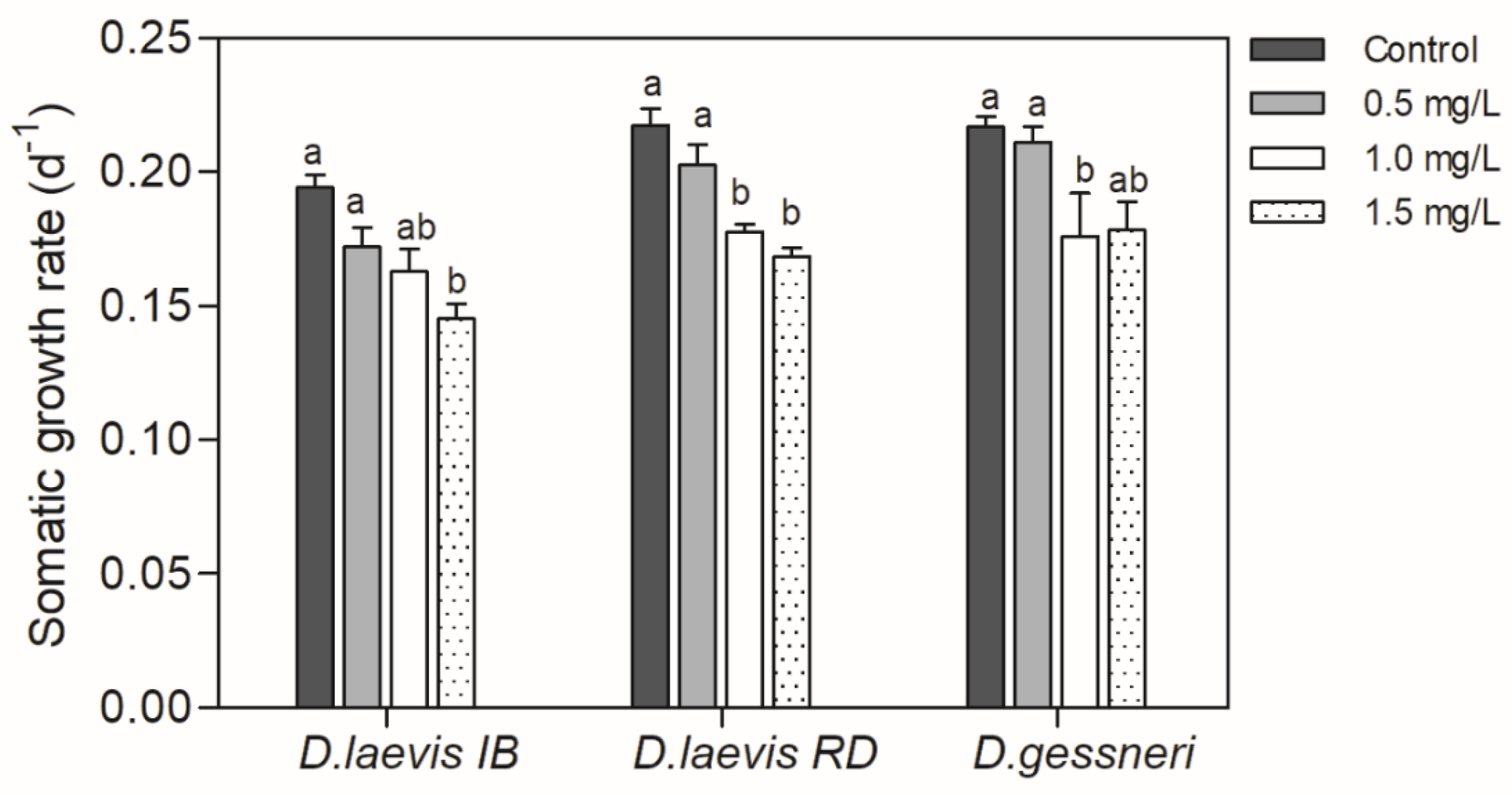
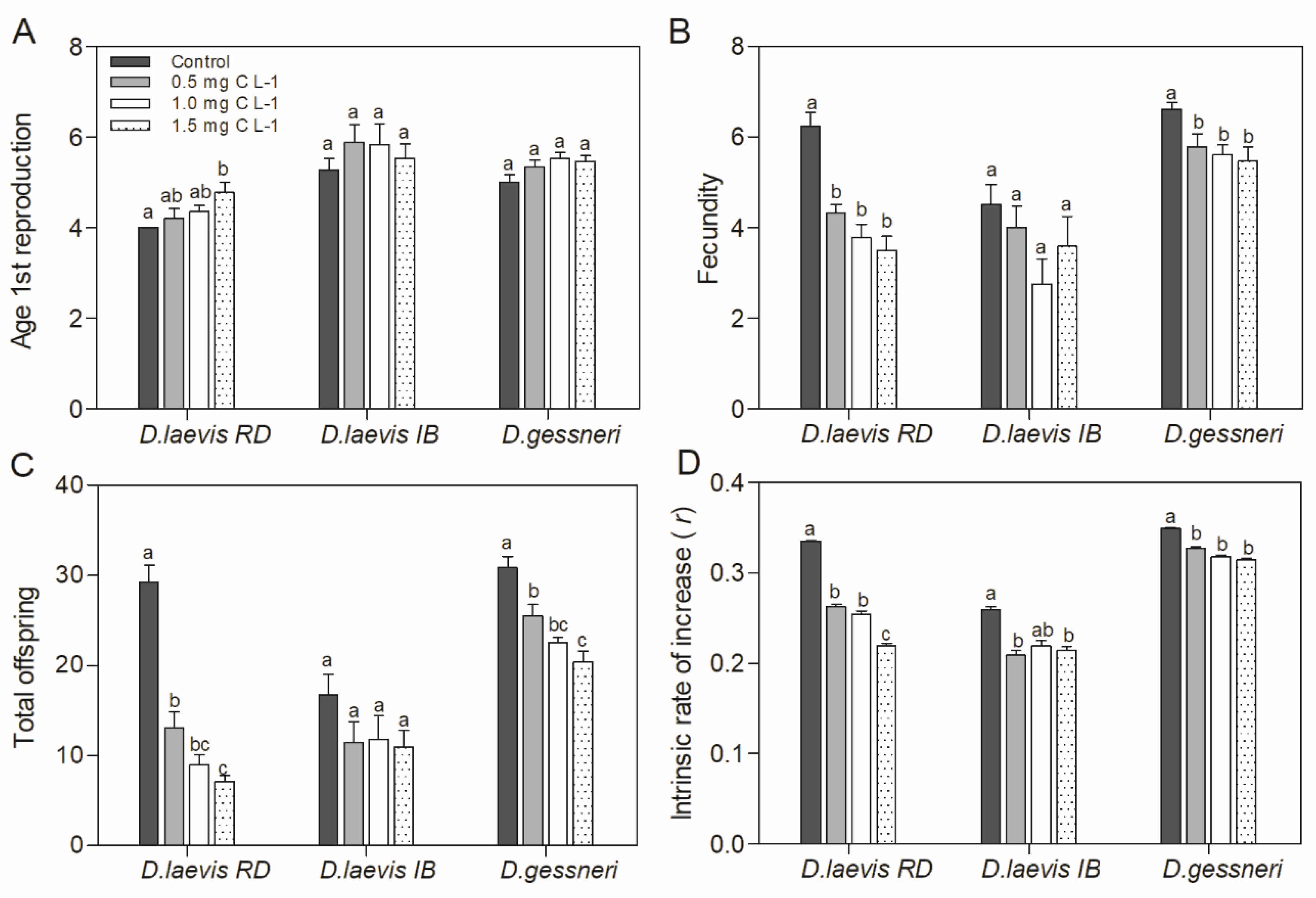
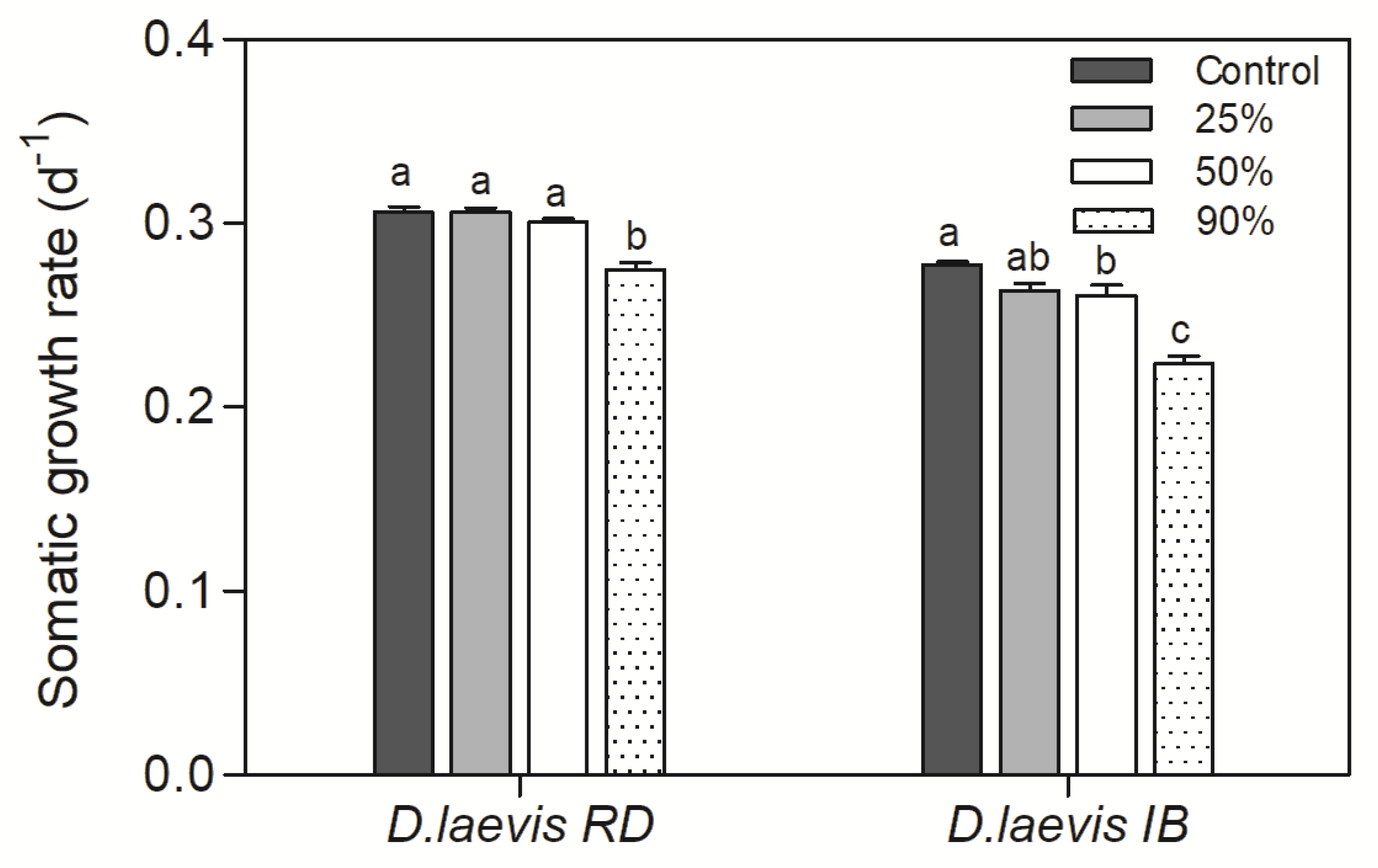
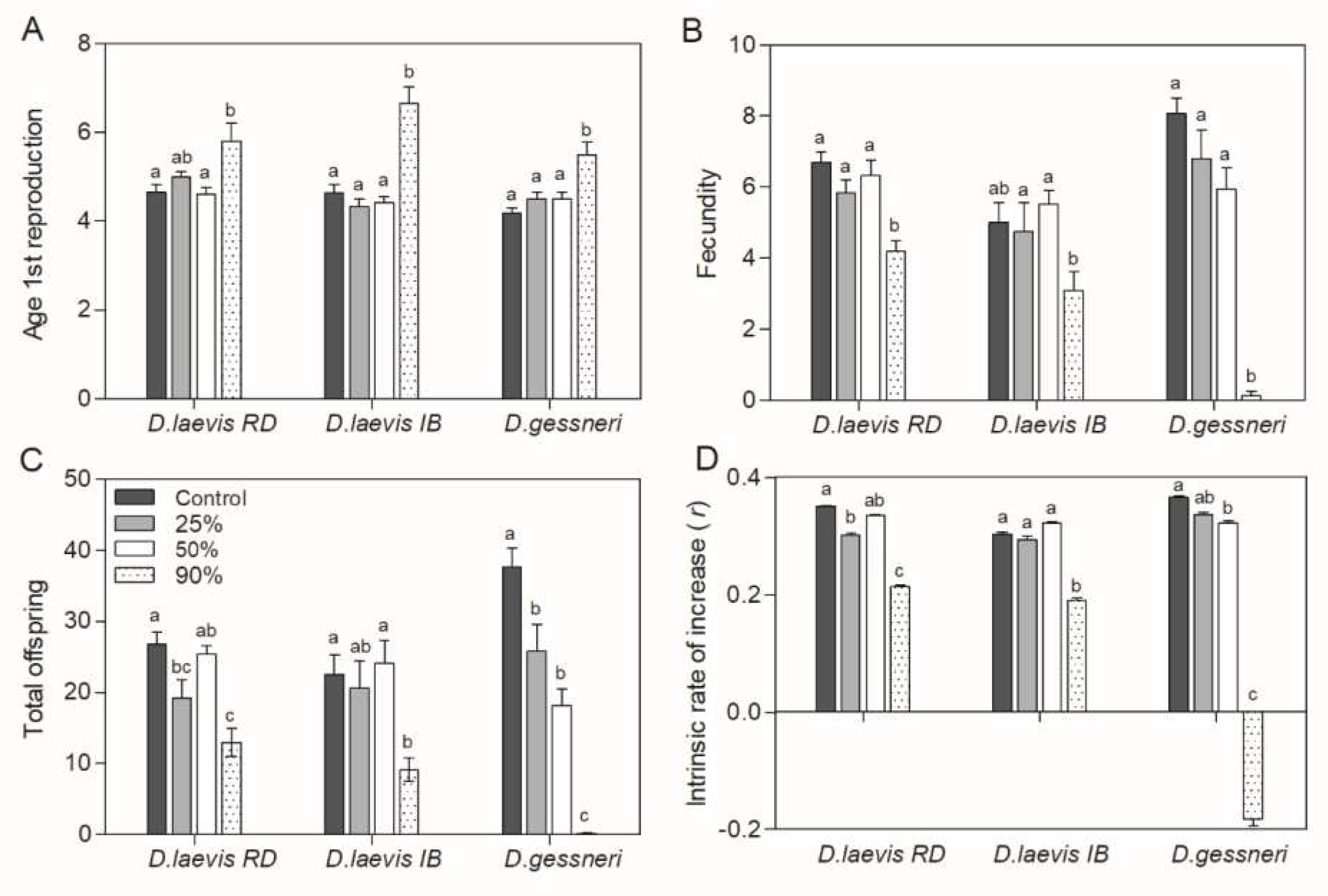
| Assay | Date | Cyanobacteria concentration (mg C L-1) | Green algae concentration (mg C L-1) | % nutritious food | STX (ng/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Life table (Constant nutritious food) | 16/05/2017 | 0.00 | 0.40 | 100.0 | --- |
| 0.50 | 0.40 | 44.4 | 1,5 | ||
| 1.00 | 0.40 | 28.6 | 3,0 | ||
| 1.50 | 0.40 | 21.1 | 4,5 | ||
| 2. Life table (Variable nutritious food) | 12/03/2018 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 100.0 | --- |
| 0.25 | 0.75 | 75.0 | 5,0 | ||
| 0.50 | 0.50 | 50.0 | 9,9 | ||
| 0.90 | 0.10 | 10.0 | 15,2 | ||
| 3. Grazing (Variable nutritious food) | 16/02/2018 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 100.0 | --- |
| 0.25 | 0.75 | 75.0 | 7,2 | ||
| 0.50 | 0.50 | 50.0 | 14,4 | ||
| 0.90 | 0.10 | 10.0 | 25,9 | ||
| 4. Grazing (Variable nutritious food) | 03/05/2018 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 100.0 | --- |
| 0.25 | 0.75 | 75.0 | 3,3 | ||
| 0.50 | 0.50 | 50.0 | 6,6 | ||
| 0.90 | 0.10 | 10.0 | 11,9 |
| Species | LC50 (mg C L-1) | EC50 (mg C L-1) |
|---|---|---|
| D. laevis (Ibirité) | - | 1,24 (1,02 - 1,52) |
| D. laevis (Rio Doce) | - | 0,98 (0,82 - 1,21) |
| D. gessneri | 1,33 (0,75 - 1,92) | 1,68 (1,47 - 1,92) |
| Factor | df | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age at first reproduction | |||
| Species | 6 | 35,42 | < 0,0001 |
| Treatment | 3 | 3,32 | 0,02 |
| Species x treatment | 6 | 0,74 | 0,60 |
| Fecundity | |||
| Species | 2 | 37,04 | < 0,001 |
| Treatment | 3 | 15,30 | < 0,001 |
| Species x treatment | 6 | 1,87 | 0,09 |
| Total offspring | |||
| Species | 2 | 67,35 | < 0,001 |
| Treatment | 3 | 15,30 | < 0,001 |
| Species x treatment | 6 | 1,87 | 0,09 |
| Species | LC50 (mg C L-1) | EC50 (mg C L-1) |
|---|---|---|
| D. laevis (Ibirité) | - | 0,81 (0,23 - 0,95) |
| D. laevis (Rio Doce) | - | 0,89 (0,76 - 0,97) |
| D. gessneri | 0,25 (0,17 - 0,34) | 0,56 (0,53 - 0,61) |
| Factor | df | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age at first reproduction | |||
| Species | 2 | 2,24 | 0,11 |
| Treatment | 3 | 20,45 | < 0,001 |
| Species x treatment | 6 | 2,19 | 0,04 |
| Fecundity | |||
| Species | 2 | 5,87 | 0,003 |
| Treatment | 3 | 38,33 | < 0,001 |
| Species x treatment | 6 | 7,54 | < 0,001 |
| Total offspring | |||
| Species | 2 | 0,68 | 0,50 |
| Treatment | 3 | 36,97 | < 0,001 |
| Species x treatment | 6 | 6,05 | < 0,001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





