1. Introduction
Environmental contamination is a serious issue that has to be addressed immediately. Pesticides, heavy metals, and organic pollutants can negatively influence considerable negative influence on ecosystems, wildlife, and human health (Briffa et al., 2020). For instance, pesticides can contaminate soil and water sources, leading to the decline of plant and animal populations (Alengebawy et al., 2021). Heavy metals can accumulate in the food chain, posing a threat to both wildlife and human consumers (Alengebawy et al., 2021). Organic pollutants can disrupt endocrine systems and cause reproductive and developmental problems in both animals and humans (Briffa et al., 2020). Bioremediation is a promising strategy for cleaning up contaminated areas, which uses microorganisms to break down or convert contaminants into less dangerous compounds. Bioremediation enzymes such as laccase are essential because they catalyze the degradation of contaminants. Since it can break down and change a wide variety of environmental contaminants, laccase is a versatile enzyme (Chandra & Chowdhary, 2015).
The oxidation of numerous organic and inorganic substances, including phenols, polyphenols, and aromatic amines, is catalyzed by laccases, and copper-containing enzymes. Many different organisms, including bacteria, fungi, and plants, have had their laccases separated (Dwivedi et al., 2011). However, nowadays, because of their great stability, a wide range of substrate specificity, and high activity, fungi laccases have been the subject of the majority of studies. Although the fungal laccases have a few drawbacks, such as limited yields and high manufacturing costs (Brugnari et al., 2021)which play a key role in the manufacturing of this enzyme. Therefore, as a result, alternate laccase sources are required to be studied for their use in bioremediation (Shraddha et al., 2011).
This systematic review is offered a detailed recent development on one of the most promising methods based on the latest technology for producing laccases which are known as “recombinant DNA technology”. Recombinant laccases are feasible for large-scale bioremediation applications since they can be manufactured in significant quantities using bacterial expression methods. Due to its effectiveness in dissolving pollutants such as phenolic compounds, dyes, and aromatic pollutants, the use of a recombinant bacterial enzyme (laccase) in bioremediation has drawn interest (Preethi et al., 2020). Recombinant laccases also differ from their native counterparts in that they are more stable, active, specific, and have higher expression levels. Therefore, it was an urgent need to get an update on recent development in the field (Preethi et al., 2020).
This review paper focused on the use of a recombinant bacterial enzyme (laccase) in bioremediation and covers the various kinds of bacteria that are utilized for expression, laccase production optimization, and the use of recombinant laccase in the breakdown of various types of contaminants. Future perspectives on this topic, as well as the difficulties and restrictions related to the use of recombinant laccase in bioremediation, are also highlighted. Overall, bioremediation using a recombinant bacterial enzyme (laccase) has tremendous promise for cleaning up contaminated settings, but more study is required to perfect its creation and use in real-world applications.
2. Selection of Bacterial Host for Optimum Production of Laccase
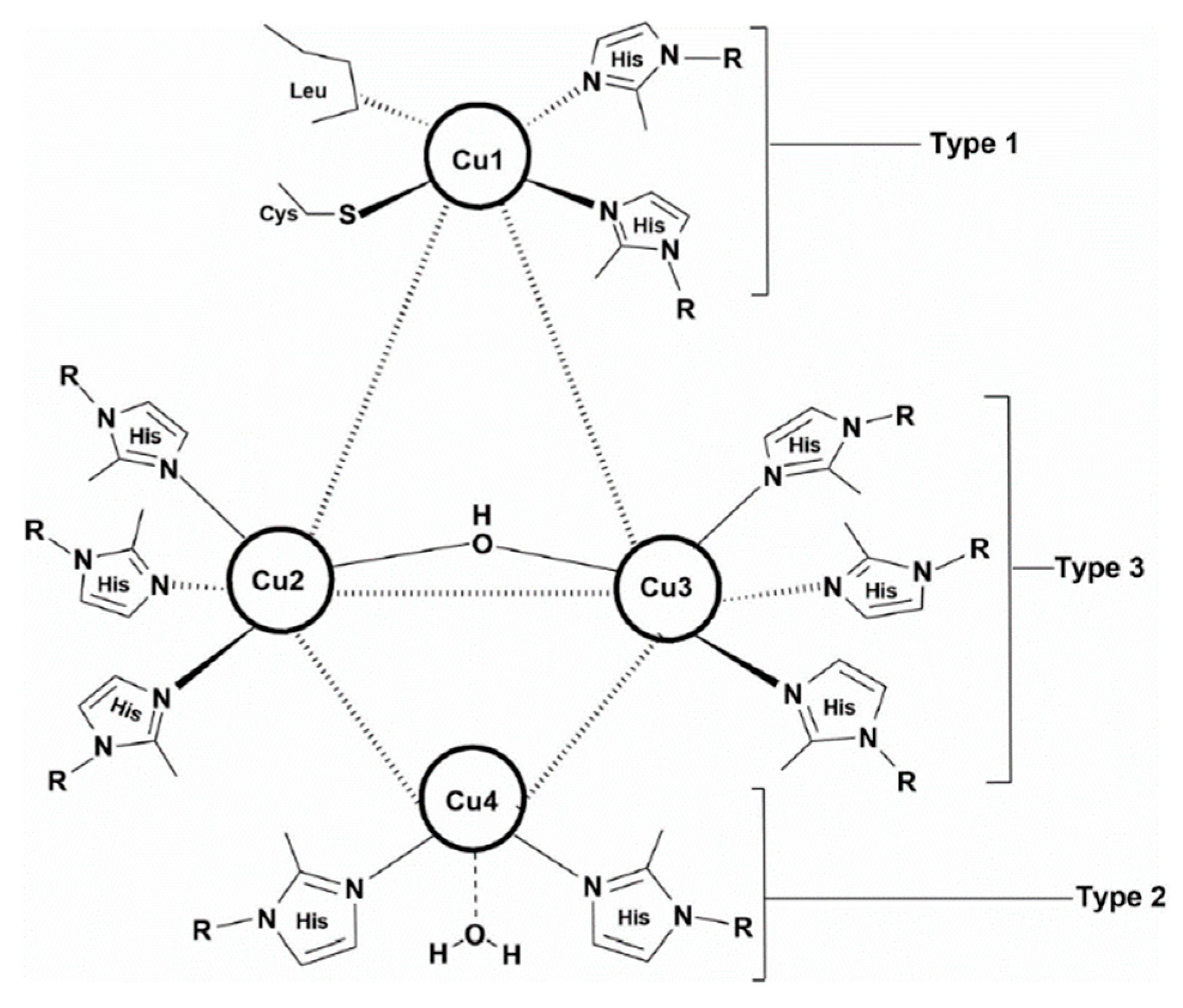
Figure 1.
Structure of laccase.
Figure 1.
Structure of laccase.
Recombinant laccase has been expressed using a variety of microorganisms. The selection of bacteria is typically based on aspects including handling simplicity, growth rate, genetic alteration, and output yields. Escherichia coli (Yang et al., 2021), Pseudomonas putida (Verma et al., 2015), Bacillus subtilis (Kumar et al., 2020), and Streptomyces lividans are a few of the frequently employed bacterial hosts for laccase expression.
2.1. Escherichia coli
In order to produce recombinant proteins, Escherichia coli is one of the most frequently employed bacterial hosts due to its quick growth, well-understood genetics, and simplicity of genetic modification (Jang et al., 2017; Yang et al., 2021). However, the development of inclusion bodies and low yields of soluble protein have made the expression of active laccases in E. coli difficult (Enayatizamir et al., 2020).
2.2. Pseudomonas putida
For the expression of recombinant laccases, Pseudomonas putida is another well-liked host. P. putida is a popular candidate for bioremediation applications because of its adaptable metabolism and capacity to use a variety of substrates (Verma et al., 2015). It has been demonstrated that P. putida laccase expression results in large amounts of active protein (Kuddus et al., 2013).
2.3. Bacillus subtilis
An assortment of enzymes and other proteins are produced by the Gram-positive bacteria Bacillus subtilis (Ahmed et al., 2020). It has been established that B. subtilis can produce significant amounts of active protein when laccases are expressed. However, optimizing growth conditions and expression systems is necessary for using B. subtilis for laccase synthesis (Allos & Hussein, 2015).
2.4. Streptomyces lividans
The synthesis of heterologous proteins is frequently carried out using the Gram-positive bacterium Streptomyces lividans. S. lividans is a viable option for bioremediation applications since it can secrete proteins into the extracellular environment and has been found to produce significant quantities of active protein when used for laccase expression (Berini et al., 2020).
3. Laccase Production Optimization
The selection of the expression host, growing conditions, induction techniques, and purification tactics are only a few of the variables that need to be optimized in order to produce recombinant laccases. To attain high yields of active protein and lower manufacturing costs, these parameters must be optimized. The choice of expression host is one of the main elements that affect laccase production. varied bacteria have varied genetic histories and metabolic processes, which can influence the quantity and quality of protein expression. Therefore, based on the intended production yields and protein quality, the choice of expression host should be carefully assessed (Callejón et al., 2017). The growth environment, including factors like temperature, pH, and the availability of nutrients, can also have a big impact on laccase production. For instance, P. putida and E. coli have distinct ideal growth temperatures and pHs for laccase synthesis. The availability of nutrients, such as carbon and nitrogen sources, can be optimized to increase laccase synthesis (Kuddus et al., 2013). Laccase synthesis can also be influenced by induction techniques like the use of inducers or promoters. Based on the expression host and the intended production yields, a detailed assessment of the inducer or promoter choice should be made. For instance, the use of IPTG as an inducer in E. coli can cause inclusion bodies to form as well as significant amounts of laccase synthesis (Kielkopf et al., 2021). To separate and purify active laccase from the bacterial culture, purification techniques including chromatography and ultrafiltration are required. The unique properties of the laccase and the required level of purity should be taken into consideration when selecting a purification approach (Ahmed et al., 2020). Laccase purification frequently involves the use of chromatography methods including affinity and ion exchange chromatography (Antecka et al., 2019). In conclusion, careful evaluation of a number of parameters, including the choice of expression host, growth circumstances, induction techniques, and purification procedures, is necessary to optimize laccase production.
4. Role of Recombinant Laccase in Various Types of Contaminants Breakdown
Recombinant laccase has shown great potential in the breakdown of various types of contaminants due to its ability to oxidize a wide range of substrates. For the treatment of a variety of contaminants, including dyes (Kesebir et al., 2021), phenolic chemicals, insecticides, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, laccase-mediated degradation has been researched. (PAHs).
Figure 2.
Bacterial laccase applications in industrial field; Source: (Chauhan et al., 2017.)
Figure 2.
Bacterial laccase applications in industrial field; Source: (Chauhan et al., 2017.)
4.1. Dyes
Recombinant laccase has been thoroughly investigated for the adsorption of azo, anthraquinone, and triphenylmethane dyes, among other dye types. The color molecules are oxidized by laccase, which transforms them into less complex chemicals that microbes can then further break down. An environmentally acceptable alternative to traditional dye degradation techniques that are frequently expensive and result in harmful consequences is laccase-mediated dye degradation (Vaithyanathan et al., 2022).
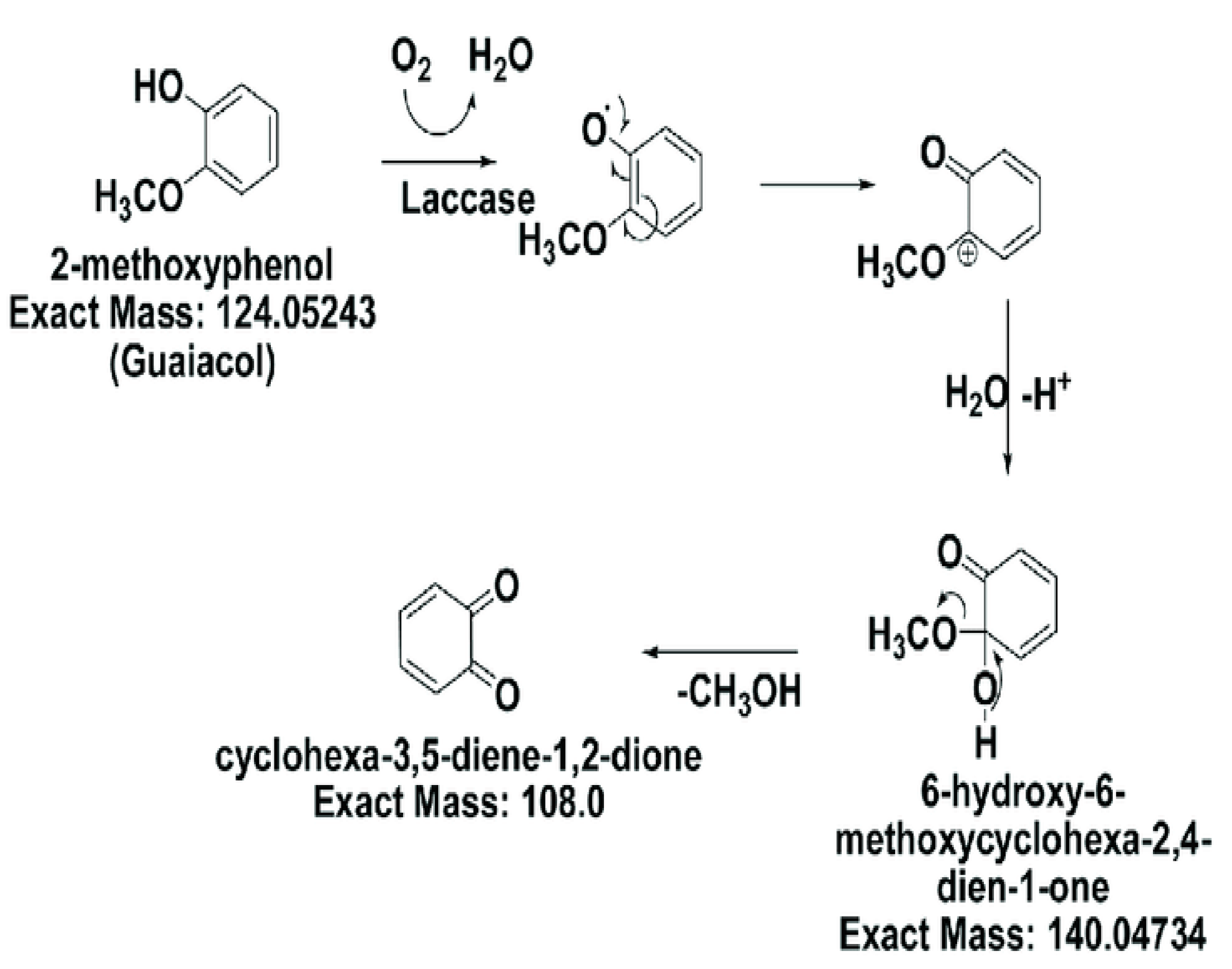
4.2. Phenolic Compounds
Figure 3.
Laccase activity on 2-methoxyphenol.
Figure 3.
Laccase activity on 2-methoxyphenol.
Phenolic compounds are typical wastewater contaminants, and it is crucial to prevent environmental harm by degrading them. Recombinant laccase has been demonstrated to efficiently break down a number of phenolic substances, including cresols, chlorophenols, and bisphenol A. Laccase degrades phenolic compounds by oxidizing them and generating reactive oxygen species that cause the chemical bonds to disintegrate (Asadgol et al., 2014).
4.3. Pesticides
Agricultural pesticides are frequently utilized and can contaminate the land and water. To avoid their buildup in the environment and potential harm to human health, pesticides must be degraded. Recombinant laccase has been demonstrated to efficiently break down a number of pesticides, including atrazine, diazinon, and chlorpyrifos. A promising method for treating contaminated soils and water is a laccase-mediated breakdown of pesticides (Vaithyanathan et al., 2022).
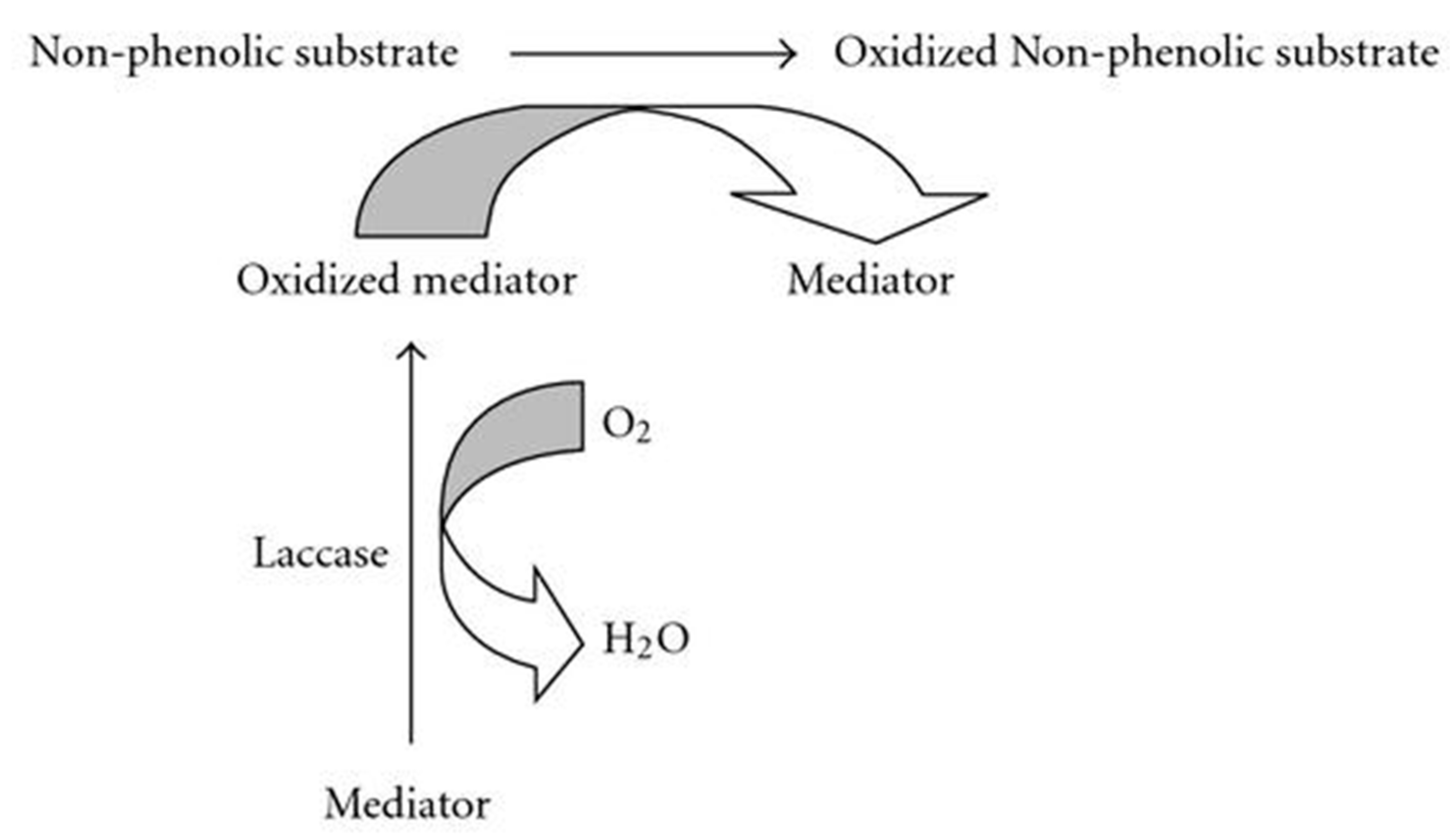
4.4. PAHs, or Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons
Figure 4.
Laccase activity on non-phenolic substrate.
Figure 4.
Laccase activity on non-phenolic substrate.
Organic chemicals known as PAHs are a persistent category that has the potential to harm the environment. It has been demonstrated that recombinant laccase can break down a variety of PAHs, including naphthalene, phenanthrene, and pyrene. The PAH molecules are oxidized by laccase, resulting in reactive oxygen species that weaken the chemical bonds and cause disintegration (L. Wang et al., 2022).
Recombinant laccase has also been demonstrated to break down a number of other pollutants, such as lignin, humic acids, and chlorinated compounds, in addition to these contaminants (Singh et al., 2021). Environmental applications for laccase-mediated degradation include the bioremediation of polluted soil and water, wastewater treatment, and detoxification of industrial effluents. Recombinant laccase is a promising method for environmental restoration because it can break down a variety of pollutants (Kesebir et al., 2021). To maximize laccase production and create effective and affordable application techniques for laccase-mediated degradation in environmental applications, more study is required.
5. Discussion
5.1. The Use of Laccase in Cleaning Up the Contaminated Environment
Cleaning up contaminated settings holds great potential when using the recombinant bacterial enzyme laccase. Recombinant laccase's capacity to target complex chemical compounds that are challenging to break down using standard techniques is one of its main benefits (Callejón et al., 2017).
Compared to conventional cleanup techniques, laccase-mediated degradation has a number of advantages (Nguyen et al., 2016). It is a practical strategy that doesn't generate any negative byproducts and is also environmentally beneficial. Furthermore, recombinant technology makes it possible to manufacture laccase in massive numbers, making it a feasible choice for extensive environmental remediation initiatives. Several research has effectively proven the usage of recombinant laccase. Recombinant laccase, for instance, was utilized to break down phenolic chemicals in contaminated soil, significantly reducing its toxicity (Bhardwaj et al., 2022). Recombinant laccase's potential for wastewater treatment was demonstrated in a different investigation where it was employed to decolorize a textile dye effluent (Aziz et al., 2023). The versatility of recombinant laccase, which may function under a variety of circumstances, is another benefit. Laccase is suitable for the cleanup of contaminated soils and water bodies with changing oxygen levels since it can work in both aerobic and anaerobic environments (Z. Wang et al., 2019; Zhao & Yi, 2010). Additionally, the stability, catalytic efficiency, and substrate specificity of laccase can be altered to increase, making it an even more powerful instrument for environmental cleanup. Protein engineering methods like directed evolution and rational design can be used to accomplish this.
Table 1.
Comparative table laccase-mediated degradation viruses conventional clean-up techniques.
Table 1.
Comparative table laccase-mediated degradation viruses conventional clean-up techniques.
| Aspect |
Laccase-mediated degradation |
Conventional clean-up techniques |
| By-products |
Doesn’t generate any negative by-products |
May generate negative by-products |
| Environmental impact |
Environmentally beneficial |
May have a negative environmental impact |
| Production |
Recombinant technology makes it possible to manufacture laccase in massive numbers |
May not be feasible for extensive environmental remediation initiatives |
| By product contamination |
Very low concentration after the processing |
Comparatively high concentration after the processing |
| Practicality |
Practical strategy |
May not be as practical |
5.2. Removal of Heavy Metals Using Laccase Enzymes
One of the main environmental pollutants that seriously endanger both human health and the ecosystem is heavy metal pollution. Precipitation, coagulation, and adsorption are examples of traditional heavy metal removal techniques (Sukmana et al., 2021). These techniques have some drawbacks, such as high cost, poor efficiency, and the production of secondary waste (Hussain et al., 2021; Torres, 2020). A viable alternative technique for removing heavy metals from contaminated water and soil is bioremediation using laccase enzymes. The heavy metal ions are changed from their soluble and toxic form to their insoluble and non-toxic form during laccase-mediated oxidation (Alengebawy et al., 2021; Hussain et al., 2021). Metal oxide/hydroxide precipitates, which may be easily removed from the environment, are formed in order to carry out this operation. Studies have shown that laccase enzymes are good at removing heavy metals like copper, lead, cadmium, zinc, and nickel. For instance, laccase was successfully utilized in one study to remove copper from aqueous solutions, with removal efficiencies reaching up to 98%. According to another study, the removal efficiency of lead and cadmium during laccase-mediated oxidation was up to 80% and 70%, respectively (Enayatizamir et al., 2020).
5.3. Limitations
Although in comparison to conventional techniques, laccase-mediated removal of heavy metals has a number of benefits (Dai et al., 2021), however, it also comes with several restrictions that must be addressed (Hussain et al., 2021). The low stability of laccase enzymes under specific environmental circumstances, such as high temperature and severe pH, is one of the major restrictions (Si et al., 2021). Another drawback is the potential toxicity of laccase enzymes to some environmental bacteria (Z. Wang et al., 2021).
6. Conclusions
Using recombinant bacterial enzyme (laccase) in bioremediation has thus far proven to be a successful method for decontaminating contaminated environments. Heavy metals and hazardous organic compounds are just two of the pollutants that laccase enzymes can break down into less dangerous byproducts. Recombinant laccase enzyme utilization has created new opportunities for improving the enzyme's effectiveness and stability under varied environmental factors. Recombinant laccase enzyme use in bioremediation has a number of benefits over conventional techniques, including affordability, environmental friendliness, and high efficiency. The limited enzyme stability and probable toxicity of some microbes are just two of the limitations that need to be addressed. Recombinant laccase enzymes have a lot of potential for cleaning up polluted locations, and with further study and development, this technology could become a commonly used method of environmental rehabilitation.
Author Contributions
Dr VC is working on the day of manuscript conceptualization, conceptualization, writing, reviewing, and editing the original draft. KA and AY has also contributed to writing - reviewing & editing the final manuscript VR and SP is contributed through Writing - Review & Editing. PY is contributed through manuscript formatting, revision and communicating to yet with all authors for writing and publications. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not Applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not Applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the contributions of individuals and institutions that have assisted in the completion of this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
References
- Ahmed, M. A., Shihata, A. M., & Elessawy, A. M. (2020). Optimization, Production, Purification of Laccase Enzyme from Bacillus sp. Journal of New Developments in Chemistry, 2(4), 35–43. [CrossRef]
- Alengebawy, A., Abdelkhalek, S. T., Qureshi, S. R., & Wang, M. Q. (2021). Heavy Metals and Pesticides Toxicity in Agricultural Soil and Plants: Ecological Risks and Human Health Implications. Toxics, 9(3), 1–34. [CrossRef]
- Allos, M. M., & Hussein, A. A. (2015). Optimum Conditions for Laccase Production by Local Isolate of Bacillus Cereus B5. Journal of Al-Nahrain University-Science, 18(2), 133–140. [CrossRef]
- Antecka, A., Blatkiewicz, M., Boruta, T., Górak, A., & Ledakowicz, S. (2019). Comparison of downstream processing methods in purification of highly active laccase. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 42(10), 1635–1645. [CrossRef]
- Asadgol, Z., Forootanfar, H., Rezaei, S., Mahvi, A. H., & Faramarzi, M. A. (2014). Removal of phenol and bisphenol-a catalyzed by laccase in aqueous solution. Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering, 12(1), 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Aziz, G. M., Hussein, S. I., M-Ridha, M. J., Mohammed, S. J., Abed, K. M., Muhamad, M. H., & Hasan, H. A. (2023). Activity of laccase enzyme extracted from Malva parviflora and its potential for degradation of reactive dyes in aqueous solution. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 50, 102671. [CrossRef]
- Berini, F., Marinelli, F., & Binda, E. (2020). Streptomycetes: Attractive Hosts for Recombinant Protein Production. Frontiers in Microbiology, 11, 1958. [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, P., Kaur, N., Selvaraj, M., Ghramh, H. A., Al-Shehri, B. M., Singh, G., Arya, S. K., Bhatt, K., Ghotekar, S., Mani, R., Chang, S. W., Ravindran, B., & Awasthi, M. K. (2022). Laccase-assisted degradation of emerging recalcitrant compounds – A review. Bioresource Technology, 364, 128031. [CrossRef]
- Briffa, J., Sinagra, E., & Blundell, R. (2020). Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon, 6(9), e04691. [CrossRef]
- Brugnari, T., Braga, D. M., dos Santos, C. S. A., Torres, B. H. C., Modkovski, T. A., Haminiuk, C. W. I., & Maciel, G. M. (2021). Laccases as green and versatile biocatalysts: from lab to enzyme market—an overview. Bioresources and Bioprocessing 2021 8:1, 8(1), 1–29. [CrossRef]
- Callejón, S., Sendra, R., Ferrer, S., & Pardo, I. (2017). Recombinant laccase from Pediococcus acidilactici CECT 5930 with ability to degrade tyramine. PloS One, 12(10). [CrossRef]
- Chandra, R., & Chowdhary, P. (2015). Properties of bacterial laccases and their application in bioremediation of industrial wastes. Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts, 17(2), 326–342. [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, P. S., Goradia, B., & Saxena, A. (2017). Bacterial laccase: recent update on production, properties and industrial applications. 3 Biotech, 7(5), 1–20. [CrossRef]
- Dai, X., Lv, J., Wei, W., & Guo, S. (2021). Effects of Adding Laccase to Bacterial Consortia Degrading Heavy Oil. Processes 2021, Vol. 9, Page 2025, 9(11), 2025. [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, U. N., Singh, P., Pandey, V. P., & Kumar, A. (2011). Structure–function relationship among bacterial, fungal and plant laccases. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 68(2), 117–128. [CrossRef]
- Enayatizamir, N., Liu, J., Wang, L., Lin, X., & Fu, P. (2020). Coupling Laccase production from Trametes pubescence with heavy metal removal for Economic Waste Water Treatment. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 37. [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A., Madan, S., Madan, R., Hussain, A., Madan, S., & Madan, R. (2021). Removal of Heavy Metals from Wastewater by Adsorption. Heavy Metals - Their Environmental Impacts and Mitigation. [CrossRef]
- Jang, J., Hur, H. G., Sadowsky, M. J., Byappanahalli, M. N., Yan, T., & Ishii, S. (2017). Environmental Escherichia coli: ecology and public health implications—a review. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 123(3), 570–581. [CrossRef]
- Kesebir, A. Ö., Kılıç, D., Şişecioğlu, M., Adıgüzel, A., & Küfrevioğlu, Ö. İ. (2021). Recombinant laccase production from Bacillus licheniformis O12: Characterization and its application for dye decolorization. Biologia, 76(11), 3429–3438. [CrossRef]
- Kielkopf, C. L., Bauer, W., & Urbatsch, I. L. (2021). Expression of Cloned Genes in E. coli Using IPTG-Inducible Promoters. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols, 2021(2), 70–84. [CrossRef]
- Kuddus, M., Joseph, B., & Wasudev Ramteke, P. (2013). Production of laccase from newly isolated Pseudomonas putida and its application in bioremediation of synthetic dyes and industrial effluents. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 2(4), 333–338. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A., Singh, A. K., Ahmad, S., & Chandra, R. (2020). Optimization of laccase production by Bacillus sp. Strain AKRC01 in Presence of Agro-waste as Effective Substrate using Response Surface Methodology. Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology, 14(1), 351–362. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L. N., van de Merwe, J. P., Hai, F. I., Leusch, F. D. L., Kang, J., Price, W. E., Roddick, F., Magram, S. F., & Nghiem, L. D. (2016). Laccase-syringaldehyde-mediated degradation of trace organic contaminants in an enzymatic membrane reactor: removal efficiency and effluent toxicity. Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences - Papers: Part A, 200, 477. [CrossRef]
- Preethi, P. S., Gomathi, A., Srinivasan, R., Pavan Kumar, J. G. S., Murugesan, K., & Kodiveri Muthukailannan, G. (2020). Laccase: Recombinant Expression, Engineering and Its Promising Applications. 63–85. [CrossRef]
- Shraddha, Shekher, R., Sehgal, S., Kamthania, M., & Kumar, A. (2011). Laccase: microbial sources, production, purification, and potential biotechnological applications. Enzyme Research, 2011(1). [CrossRef]
- Si, J., Wu, Y., Ma, H. F., Cao, Y. J., Sun, Y. F., & Cui, B. K. (2021). Selection of a pH- and temperature-stable laccase from Ganoderma australe and its application for bioremediation of textile dyes. Journal of Environmental Management, 299, 113619. [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. K., Bilal, M., Iqbal, H. M. N., Meyer, A. S., & Raj, A. (2021). Bioremediation of lignin derivatives and phenolics in wastewater with lignin modifying enzymes: Status, opportunities and challenges. Science of The Total Environment, 777, 145988. [CrossRef]
- Sukmana, H., Bellahsen, N., Pantoja, F., & Hodur, C. (2021). Adsorption and coagulation in wastewater treatment – Review. Progress in Agricultural Engineering Sciences, 17(1), 49–68. [CrossRef]
- Torres, E. (2020). Biosorption: A Review of the Latest Advances. Processes 2020, Vol. 8, Page 1584, 8(12), 1584. [CrossRef]
- Vaithyanathan, V. K., Vaidyanathan, V. K., & Cabana, H. (2022). Laccase-Driven Transformation of High Priority Pesticides Without Redox Mediators: Towards Bioremediation of Contaminated Wastewaters. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 9, 1434. [CrossRef]
- Verma, A., Dhiman Yashwant Singh Parmar, K., & Shirkot Yashwant Singh Parmar, P. (2015). Optimization for Laccase Production by Pseudomonas putida LUA15.1 using Response Surface Methodology. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/315809315.
- Wang, L., Tan, Y., Sun, S., Zhou, L., Wu, G., Shao, Y., Wang, M., & Xin, Z. (2022). Improving Degradation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons by Bacillus atrophaeus Laccase Fused with Vitreoscilla Hemoglobin and a Novel Strong Promoter Replacement. Biology, 11(8). [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z., Ren, D., Jiang, S., Yu, H., Cheng, Y., Zhang, S., Zhang, X., & Chen, W. (2021). The study of laccase immobilization optimization and stability improvement on CTAB-KOH modified biochar. BMC Biotechnology, 21(1), 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z., Ren, D., Zhao, Y., Huang, C., Zhang, S., Zhang, X., Kang, C., Deng, Z., & Guo, H. (2019). Remediation and improvement of 2,4-dichlorophenol contaminated soil by biochar-immobilized laccase. Https://Doi.Org/10.1080/09593330.2019.1677782, 42(11), 1679–1692. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J., Zhang, J., Zhu, Z., & Du, G. (2021). The challenges and prospects of Escherichia coli as an organic acid production host under acid stress. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 105(21–22), 8091–8107. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y., & Yi, X. (2010). Effects of Soil Oxygen Conditions and Soil pH on Remediation of DDT-contaminated Soil by Laccase from White Rot Fungi. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2010, Vol. 7, Pages 1612-1621, 7(4), 1612–1621. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).