1. Introduction
With the full outbreak and spread of the COVID-19 pandemic, there have been numerous panic buying around the world. These events not only threaten the safety and property of consumers but also have a serious impact on social security and order. Panic buying typically refers to excessive behavior by individuals or groups in a certain social context to obtain specific goods, leading to phenomena such as shortage of supplies, price increases, and social disorder. Such events usually occur under certain specific circumstances, such as during a pandemic when people scramble to purchase protective equipment such as masks, disinfectants, and antigen tests; or during natural disasters when people scramble to purchase essential survival items such as food and water. The characteristic of such events is their large scale, strong impact and harm, and the behavior of the shoppers is easily extreme, such as fighting, shoving, and trampling.
In the situation of information asymmetry, some businesses take advantage of the opportunity to spread rumors, causing short-term price increases for related goods, seriously affecting normal purchasing orders in society, and causing serious harm to public safety. For example, during the SARS period in 2003, rumors appeared on some websites and social media claiming that Isatis Root [
1] was a drug that could prevent and treat SARS, leading to many citizens scrambling to buy it. In 2011, the nuclear leakage accident caused by the tsunami at the Fukushima nuclear power plant in Japan affected the Chinese salt market. Rumors claim that 'salt safety will be affected by nuclear radiation ', resulting in a large number of coastal residents hoarding salt [
2]. Similar events also occurred on January 31, 2020, when a rumor about 'Shuanghuanglian' [
3]is an effective drug for treating COVID-19 was spread on Internet social media, causing many citizens to rush to buy. In 2023, the Omicron variant XBB.1.5 [
4,
5] is spreading widely in the United States, causing rumors to spread urging people to stockpile diarrhea drugs such as montmorillonite powder [
6], norfloxacin, and intestinal micro-ecological agents. The above events demonstrate that the spread of rumors can cause sudden rushes and hoarding of goods by the public, resulting in a shortage of supplies and seriously affecting normal purchasing order in society. It is of great practical significance to explore the causes and evolution mechanism behind such events for the effective prevention and control of panic buying in sudden public crises.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 reviews the relevant literature in terms of the causes, influencing factors and evolutionary mechanisms of panic buying behavior.
Section 3 presents the basic assumptions and construction of the relevant game model in this article. The calculation and discussion of the three-party game in
Section 4. The analysis of the relevant equilibrium points according to the Jacobi equation of the game in
Section 5. The case study of the rumor-induced Montmorillonite powder panic buying in
Section 6. The MATLAB simulation in
Section 7. Finally, conclusions and recommendations are proposed for the sudden mass panic buying events.
2. Literature Review
Currently, research in the academic field on panic buying can be summarized into three main categories. The first category mainly studies the causes of panic buying events. For example, items are divided into categories such as medical drugs, personal protective equipment, and daily necessities. Panic buying occurs when items that have a good curative effect or can play a critical protective role in this sudden crisis event are widely publicized through various information channels, triggering large-scale panic buying by the public. Scholars such as He [
7], and Xu [
8] have analyzed the reasons behind the panic buying of Shuanghuanglian from the perspective of journalism and professional media, and sorted out the process of the entire event and its spread. Some news media have caused items to be madly snapped up just to gain more views and exposure by promoting false information. During the rampant COVID-19 pandemic, masks were the most effective way to block the spread of the virus and faced the situation of one mask is hard to find. Using the example of the Korean government's restrictive purchasing policy for masks during the COVID-19 pandemic, Paek et al. [
9] argued that the main cause of an excessive shortage of masks was due to people's panic buying and suppliers' hoarding of items. To more effectively solve this problem, it requires the cooperation of multiple stakeholders such as government departments, suppliers, retailers, and the public, and start with six key elements of product supply, price, promotion, distribution, cooperation, and policy. Similarly, edible salt as a necessary item for daily life is also sought after by the public. Wei et al. [
10] constructed an evolutionary dynamics theory model of panic buying behavior by introducing the theory of group behavior dynamics and analyzed the reason why the iodized salt was snapped up in coastal areas of China due to the nuclear leakage crisis caused by the earthquake in Japan. The study showed that during the COVID-19 pandemic, following expert guidance, spreading false information, creating panic, personal hoarding behavior, and caring for family and friends can indirectly trigger the occurrence of group panic buying behavior. During the COVID-19 pandemic, most products experienced a shortage to some extent. Chen et al. [
11] analyzed the reasons for this phenomenon. External environmental stimuli, home confinement measures, the intensity of pandemic information dissemination, perception of the crisis, and commodity prices can all cause the public to panic buy different types of items. Most scholars only focus on the reasons for the panic buying of physical products, and only a very few have realized the reasons for panic buying and digital hoarding of virtual products such as paid social Q&A during the COVID-19 pandemic. Wang et al. [
12] found through their study using the SOBC (Surprise, Opportunity, Belongingness, and Control) framework model that online paid Q&A can create emotional resonance among platform users, thereby stimulating their willingness to pay and ultimately lead to digital hoarding and panic buying behavior. From the above research, it can be seen that the causes of triggering buying frenzies include social media, dissemination of harmful information, public panic buying, supplier hoarding for profit, and conformity bias, among others.
The second type of research focuses on the influencing factors of panic buying and hoarding behavior, and many scholars have analyzed the influencing factors based on mathematical models. Sun et al. [
13] demonstrated through the construction of a binary logistic regression model using panic buying of masks as a case study that factors such as age, education level, occupation, reference group influence, and product scarcity all have a significant impact on panic buying behavior in crises. The research results indicate that in emergencies, people's consumption behavior may be different from usual, and non-economic factors may become the main influencing factors in purchasing decisions. Wang et al. [
14] analyzed and demonstrated that the actual demand for drugs by the public is the objective reason for the occurrence of panic buying behavior, and it will be influenced by other key factors such as public fear and herd mentality. Panic buying behavior has also been referred to as panic buying and competitive buying by other scholars. He and Hu [
15] analyzed the purchase of masks from an economic perspective and concluded that competitive buying during the COVID-19 pandemic is a kind of hoarding behavior taken when people's perception of the reserve value of the purchased item is higher than its retail price, and this behavior will ultimately lead to further tightening of medical resource supply. Panic buying behavior will also have a certain impact on the retail industry in the market and will affect the different behavioral strategy decisions of retail industry merchants. Kogan and Herbon [
16] assuming that the supply chain was disrupted globally, demonstrated from the perspective of the retail industry in the market the psychological and optimal behavioral strategy choices of corresponding retailers triggered by consumer panic buying during the COVID-19 pandemic. In the initial stage of panic buying, retailers will adopt a wait-and-see (intentional scarcity) strategy to suppress the inventory in the market, and ultimately, the price of retained products will increase based on the supply-demand relationship. The government can increase retail prices in the initial stage and then lower them to improve the supply efficiency of goods in the market. Yang and Ren [
17] taking the epidemic control policy adopted during the domestic Omicron variant period in China as an example, analyzed through the Protection-Adoption-Decision-Making (PADM) model and found that panic buying behavior is a stress response taken by the public in a dangerous situation, and society will implement coping behaviors based on the perception and decisions of policy decision-makers corresponding to their risks. They also believe that panic buying behavior will be influenced by factors such as media exposure, public protective cognition, public risk cognition, and stakeholders. When local governments adopt control policies, the public's freedom is often restricted. Xu et al. [
18] took the control policy adopted by the Chinese government in epidemic prevention and control as a case study and established a game model of evolution for both local governments and the public. They used the cost-benefit analysis method in economics to study the behavioral evolution trend of all parties in responding to sudden major public health events. When implementing a series of epidemic prevention and control measures, people's mental health can also be affected to a certain extent. Prolonged implementation of lockdown policies in a region often triggers a series of psychological illnesses. Some scholars have analyzed this phenomenon through online survey questionnaires. Using an online survey questionnaire as a source of quantitative data analysis, Niu et al. [
19] constructed a three-stage individual behavior decision-making model of information input-information processing-behavior output based on nearly 20,000 survey questionnaires, demonstrating that panic buying behavior during major public health events is influenced by education level, family background, gender, age, and many other factors. To further explore the factors behind panic buying behavior, Lavuri and Jaiswal [
20] demonstrated through sampling surveys based on the stimulus theory and the dual-factor theory that consumers' panic buying behavior during the COVID-19 pandemic is influenced by both internal factors (promotion activities and marketing environment) and external factors (hedonism and materialism). During the COVID-19 pandemic, consumers' income has a very important impact on their panic buying behavior. Based on sales data from 144 retail stores in the state of Sao Paulo, Brazil, de Brito and Yoshizaki [
21] compared sales data of various product categories before and after the epidemic, and combined them with regression models to analyze data on demographic information, actual sales, and per capita income. They found that panic buying behavior has a minimal impact on areas where per capita income is below average, but it will increase with the increase in per capita income. The GNPOs (government non-profit organization) played a crucial role in the supply chain during the COVID-19 pandemic and had unique advantages in resource mobilization, integration, and allocation [
22]. From an enterprise perspective, increasing research and development in green intelligent supply technology will enhance the efficiency of procurement and supply processes, thus reducing environmental pollution caused by the supply chain [
23]. Therefore, the government's policies during the epidemic should start with maintaining the basic daily life of the people, to alleviate consumer panic and ultimately reduce panic buying behavior. The above studies indicate that consumers' personal characteristics, payment willingness, product scarcity, supply chain congestion, and other factors can all affect panic buying behavior, but the above literature lacks consideration of the impact of the cost of public panic buying, the cost of rumor-mongering, and the cost of government intervention.
The third type of research focuses on the evolving mechanism behind the panic buying events. Most scholars explore the emergence, development, and evolutionary mechanisms of mass panic buying events by analyzing the game theory relationship between the participating entities in the panic buying events. Wang et al. [
24] took the edible iodized salt event caused by the 2011 Japanese nuclear leak as an example, constructed a two-party game model between the government and the public based on the prospect theory and the benchmark situation and the panic buying situation, and calculated the payoff matrices and stable equilibrium points for both parties based on considering public perception, and analyzed their stability. The government plays an indispensable leading role in sudden collective events and mainly exerts the macro-control function of the government through punishment or incentive means. With the increasingly complex social environment, sudden collective events occur from time to time. Luo et al. [
25] divided sudden collective events into six stages: pre-crisis, crisis, mid-crisis, end of the crisis, post-crisis, and termination of crisis, and constructed the static structural diagram and dynamic flow chart of the evolutionary mechanism based on the causes, participating entities, and conflicting points of the events, providing suggestions for the prevention and handling of collective sudden events. Some scholars have also studied the evolutionary laws and behavioral tendencies of collective sudden events. Wei et al. [
26] divided the process of mass panic buying into four stages: formation, reinforcement, implementation, and dissolution, each of which has different characteristics and performances. He believes that the behavior pattern of the participating group needs three elements, namely, activity is how participating entities express their personal demands in collective events, mutual influence is the interaction between different participating entities, and emotion reflects the psychological activities of participating entities. Some scholars have studied the mechanism of panic buying. Xu et al. [
27] regarded panic buying as a process of limited rationality-irrationality-returning to rationality, and combined with the emergency management operation modes of the United States, Russia, Japan, and other countries, analyzed the current situation of emergency management in China and put forward improvement suggestions. Wang and Li [
28] used the set description method to explore the phenomenon of looting in a truck accident. Based on the cumulative prospect theory and game theory, they constructed an evolutionary game model and calculated the corresponding payoff matrices and relevant equilibrium points. Based on this, they also verified their conclusions through simulation. Some scholars have summarized the mechanism, evolution process, and stages of sudden panic buying events. Xie et al. [
29] accurately defined the concept of sudden panic buying. Such sudden panic buying events have the characteristics of uncertainty, concentration, panic and abnormal purchasing, etc., and occur after the spread of information triggered by social events or natural disasters. The entire process goes through four stages: the occurrence period, development period, peak period, and subsiding period. Therefore, the earlier the government takes measures to intervene, the lower the peak of panic buying behavior, the duration of panic buying, and the harm caused to society can be reduced. Regarding the relationships between multiple stakeholders in a sudden public crisis event, Shufeng et al. [
30] found through research that when there are conflicting interests between the government, social organizations, and the public, a systematic approach should be taken to focus on the points of conflict of interest among multiple stakeholders and pay attention to the interaction between different stakeholders within the system. Shan et al. [
31] studied the possible impacts of panic buying behavior in public health emergencies, such as resource waste, price fluctuations, and unequal distribution of epidemic prevention materials. And applying evolutionary games theory to analyze the optimal strategic choices of different stakeholders (the public, government, and enterprises) can help reduce the likelihood of panic buying.
In summary, although the above-mentioned studies have studied the evolutionary process of large-scale panic buying events, they still lack the analysis of the subject of the rumor-monger and the analysis of real cases. Compared with the previous studies, the primary contributions of this thesis are as follows: (1) From the perspective of large-scale panic buying caused by online rumors, an evolutionary game model between local governments, rumor mongers and the public is constructed considering the analysis of rumor mongers; (2) The influence of various factors on strategy choice is analyzed, the evolutionary process of strategic choice of each game party under the government reward and punishment mechanism is considered, and the evolutionary stable equilibrium of the behavioral strategies of the three game parties is compared; (3) Through a case study of panic buying in Montelukast, the panic buying event is divided into different stages and verifies each stage in the evolutionary game process, and simulating the game evolution process using MATLAB software to analyze the impact of various factors on the choice of strategies.
3. Basic assumptions and model construction
The existence of rumor-mongers in sudden public health events who create and spread rumors can cause public panic and induce rush events, resulting in social disorder and affecting social stability. Active government intervention in crisis events is an effective measure that can solve sudden mass panic buying events. Therefore, the government and the rational public are the basic factors that promote social stability, while the existence of certain rumor-mongers becomes a negative factor that affects social security and stability. Therefore, this paper assumes that the three parties of the game in the analysis of the emergency public health event-related goods rush process are the local government, the rumor-monger, and the public who make panic buying or not. The specific variables that define the different behavioral choices of the relevant stakeholders are as follows shown in
Table 1:
Assumption 1. Relevant parameter settings regarding local government.
The local government weighs the advantages and disadvantages after the occurrence of a sudden mass purchase incident and considers whether to intervene, including the release and adjustment of policies, the regulation of drug prices, the disinformation of rumors, and the punishment of rumor-mongers.
The local government adopts the policy of intervention and non-intervention in response to the incident of sudden mass rush events. (1) The probability of adopting the intervention policy strategy is, and the main intervention behaviors are to dispel rumors and take a series of punishments against the rumor-monger. (2) The probability of adopting the no intervention policy is, meaning that the government does not regulate and adjust the rumor monger whether he chooses to make a rumor or not.
Where the assumptions about whether the local government intervenes are as follows: when the government intervenes in the rumor of disinformation, it will incur certain intervention costs related to human and material resources is. At the same time, the local government will give certain rewards to the higher government when it can carry out certain intervention behaviors in the event of disinformation, and the higher government will carry out certain penalties when the local government carries out inaction without intervention, and as the disinformation situation emergence will cause social instability and leads to social risk which government needs to bear the loss of is.
Assumption 2. Parameters related to whether the disinformation agent is a rumor monger or not.
Rumor mongers are people who consider whether to spread and pass on rumors in order to make profits in sudden mass buying events. They spread rumors on certain platforms and networks to gain attention and popularity in order to make profits. And their specific behaviors include exaggerating the effects and efficacy of the drugs concerned to trigger buying behavior, and taking further speculation in response to the adjustment of national policies.
It is assumed that the rumor-monger adopts the behavior of rumor without disinformation in response to the situation of the sudden mass rush event. (1) The probability of adopting the strategy of disinformation behavior is, which refers to the ability to distort the facts and further exaggerate the spread of the situation of the sudden public health event, to obtain certain attention and gain. (2) The probability of adopting a non-disinformation strategy is, which refers to the ability, to be honest, and trustworthy, abide by national policies, and consciously maintain a good network environment during emergencies.
Among them, the assumptions about whether the rumor monger creates a rumor are as follows: when the rumor monger makes a rumor, it will incur certain material resources such as time and financial resources related to the cost of the rumor is, but it will also gain certain traffic and fans and other benefits is At the same time, if the local government intervenes to dispel the rumor and punish the situation, the rumor-monger will have to pay the corresponding cost penalty , and because rumor-mongering may cause social risk problems, which is not conducive to social stability, and considering the problems related to the spread of rumors. It is assumed that the coefficient of social risk transmission is, , then the social risk of public panic buying due to rumor-mongering the rumor-monger needs to bear the responsibility for the loss is.
Assumption 3.
Relevant parameter settings for the social public.
The public mainly refers to the group of people who consider whether to purchase the relevant goods normally and cooperate with the government's relevant policies and measures due to external factors and cognitive level in the sudden mass purchasing event.
It is assumed that the social public adopts the behavior of panic buying and not panic buying in response to the situation of sudden mass rush events. (1) The probability of adopting the strategy of panic buying behavior is, which mainly refers to the behavior of snapping up a large number of items due to the wrong cognitive level of sudden rush events; (2) The probability of adopting the strategy of not snapping behavior is , which refers to the behavior of buying the relevant items normally.
The following assumptions are made about whether or not the public will rush to buy: the cost of the public's normal purchase of goods is; the cost of the public's purchase of goods under the panic of the emergency without rumors is ; the cost of the public's rush to buy goods in large quantities when the rumor-mongers start rumors is ; after the local government intervenes, the rush to buy is partially reduced in which the cost of public buying is . The parameter size relationship is. The parameter size relationship is.
Based on the above assumptions, the evolutionary game model among three types of subjects, namely, local government, rumor mongers, and the public is constructed, and the benefits of different strategy combinations of the three types of subjects are shown in Table 2.
5. The stability analysis of the hybrid strategy
The system of replication equations (4) is obtained from equations (1) (2) (3) above and analyzed by Jacobi matrix (5).
It is known that there are nine equilibrium points in the game process between the local government, the rumor-monger, and the public, which are:E
1 (0,0,0),E
2 (0,0,1),E
3 (0,1,0),E
4 (1,0,0),E
5 (1,1,0),E
6 (1,0,1),E
7 (0,1,1),E
8 (1,1,1),E
9 ; E
9 ∈V,V={
, for whether the nine equilibrium points of the above system of equations evolve stable, can be determined by the eigenvalues of the Jacobi matrix corresponding to each equilibrium point, when its eigenvalues are all less than 0, the equilibrium point is stable, and the Jacobi matrix of this game system is:
Taking the equilibrium point E
1 (0,0,0) as an example, its Jacobi matrix can be abbreviated as
The eigenvalues of this Jacobi matrix are.
Similarly, the eigenvalues of the other eight equilibrium points corresponding to the Jacobi matrix are shown in
Table 3; the eigenvalues of E
9 are the solutions of the replicated system of equations.
Based on the expressions of the eigenvalues of each equilibrium point corresponding to the Jacobi matrix in
Table 3, under the above assumptions
. Because considering
, the eigenvalues of E
1 (0,0,0), E
3 (0,1,0), E
4 (1,0,0), E
5 (1,1,0)
, while the other equilibrium points have
, so they are not involved in the discussion consideration. According to the range of values of each parameter in the expression, mainly are
and
, the stability of each equilibrium point can be discussed in the following four cases as
Table 4.
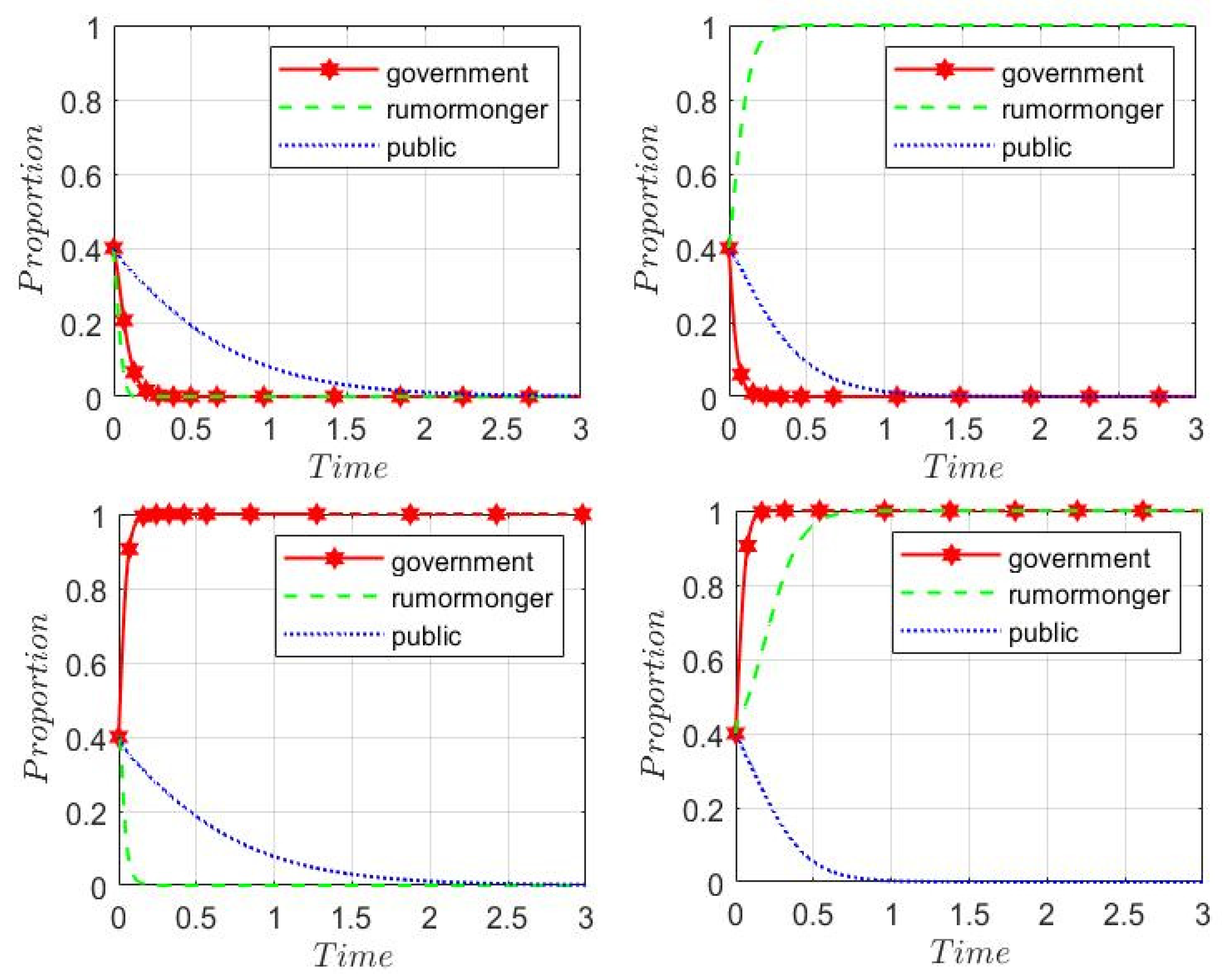
5.1. Scenario 1
If means that the payoff cost of government intervention is greater than the reward the government receives when it intervenes and the penalty the government receives when it does not intervene. Therefore,, then the eigenvalues of E1 (0,0,0) and E3 (0,1,0) are.
(1). If, the gain for the rumor monger is less than the cost and penalty for the rumor monger. Therefore,, then the eigenvalues of E1 (0,0,0) is, the corresponding eigenvalues of the Jacobi matrix meet the condition that all are less than 0. E1 (0,0,0) is the evolutionary stability point; At this time corresponds to the strategic combination of (no intervention, no rumor, no panic buying), similar to what happens in the normal state, in the public does not rush, the rumor monger disinformation gain is less than the cost and punishment when the choice of no rumor and government At this time, the cost of non-intervention is the lowest and the society is in a stable state.
(2). If means that when the gain of the rumor monger is greater than the cost paid by the rumor monger. Therefore,, then the eigenvalues of E3 (0,1,0) is, and the corresponding eigenvalues of Jacobi matrix satisfy the condition that all are less than 0. E3 (0,1,0) is the evolutionary stability point; at this time, it corresponds to the strategic combination of (no intervention, rumor, and no panic buying), in which the rumor will choose disinformation when the gain is greater than the cost paid. The public will not choose panic buying when the government the cost of intervention is greater than the sum of the rewards of intervention and the penalties of non-intervention In this strategy, the government chooses not to intervene because the cost of intervention is greater than the sum of the reward of intervention and the penalty of non-intervention, and the government chooses not to intervene because the society is still in a stable state and the cost is the lowest.
5.2. Scenario 2
If means that the payoff cost of government intervention is smaller than the reward the government receives when intervening and the penalty the government receives when not intervening. Therefore,, then the eigenvalues of E4(1,0,0) and E5(1,1,0) are.
(1). If, the gain for the rumor monger is less than the cost and penalty for the rumor monger. Therefore,, then the eigenvalues of E4 (1,0,0) is, the corresponding eigenvalues of the Jacobi matrix satisfy the condition that they are all less than 0. E4 (1,0,0) is the evolutionary stability point; At this time, corresponding to the strategic combination of (intervention, no rumor, and no panic buying), this strategy in which the rumor monger gains less than the cost and penalty paid by the rumor monger will choose not to create rumors, and the public chooses not to panic buy in the case of social stability in the cost of government intervention is less than the sum of the rewards of intervention and the penalties of non-intervention, and the government gets the highest benefit by choosing to intervene, thus strengthening the role of social stability as a stabilization strategy.
(2). If, the gain of the rumor monger is greater than the cost of the rumor monger and the penalty. Therefore,, then the eigenvalues of E5 (1,1,0) is , and the eigenvalues of the corresponding Jacobi matrix satisfy the condition that they are all less than 0. E5 (1,1,0) is the evolutionary stability point; At this time, it corresponds to the strategic combination of (intervention, rumor, no panic buying), in which the gain of disinformation is greater than the cost of disinformation and the penalty of disinformation will choose rumor, and the public will choose no panic buying when society is in a stable state. The cost of government intervention is less than the sum of the rewards of intervention and the penalties of non-intervention, and the government gets the highest benefit by choosing to intervene while avoiding the social risk loss caused by disinformation can strengthen social stability, which is a stabilization strategy.
In summary, according to the above research hypotheses, the stable points of scenario 1-(1), scenario 1-(2), scenario 2-(1), and scenario 2-(2) are E1 (0,0,0), E3 (0,1,0), E4 (1,0,0), and E5 (1,1,0), respectively, and the public chooses the strategic of no panic buying in the combination of these stable points, and the society is in a relatively stable state at this time. Rumor mongers will consider their own costs and benefits and penalties when they choose to create disinformation and will choose to create disinformation if the benefits of disinformation outweigh the costs and penalties, and vice versa. If the costs of government intervention are less than the benefits and penalties, the government will choose to intervene in order to enhance social stability by avoiding the possible social risks caused by disinformation, and vice versa. Therefore, the government's intervention strategy will be adjusted according to the different situations of public snapping and disinformation, and the dynamic game of the three-game subjects will be in the process of continuous adjustment.
6. Case Study
This section takes the panic-buying of Montmorillonite powder in China in 2023 as an example to verify the validity of the above theoretical study and analyzes the evolution of strategic choices between the government, the rumor monger, and the public in the context of the introduction of the XBB variant into China.
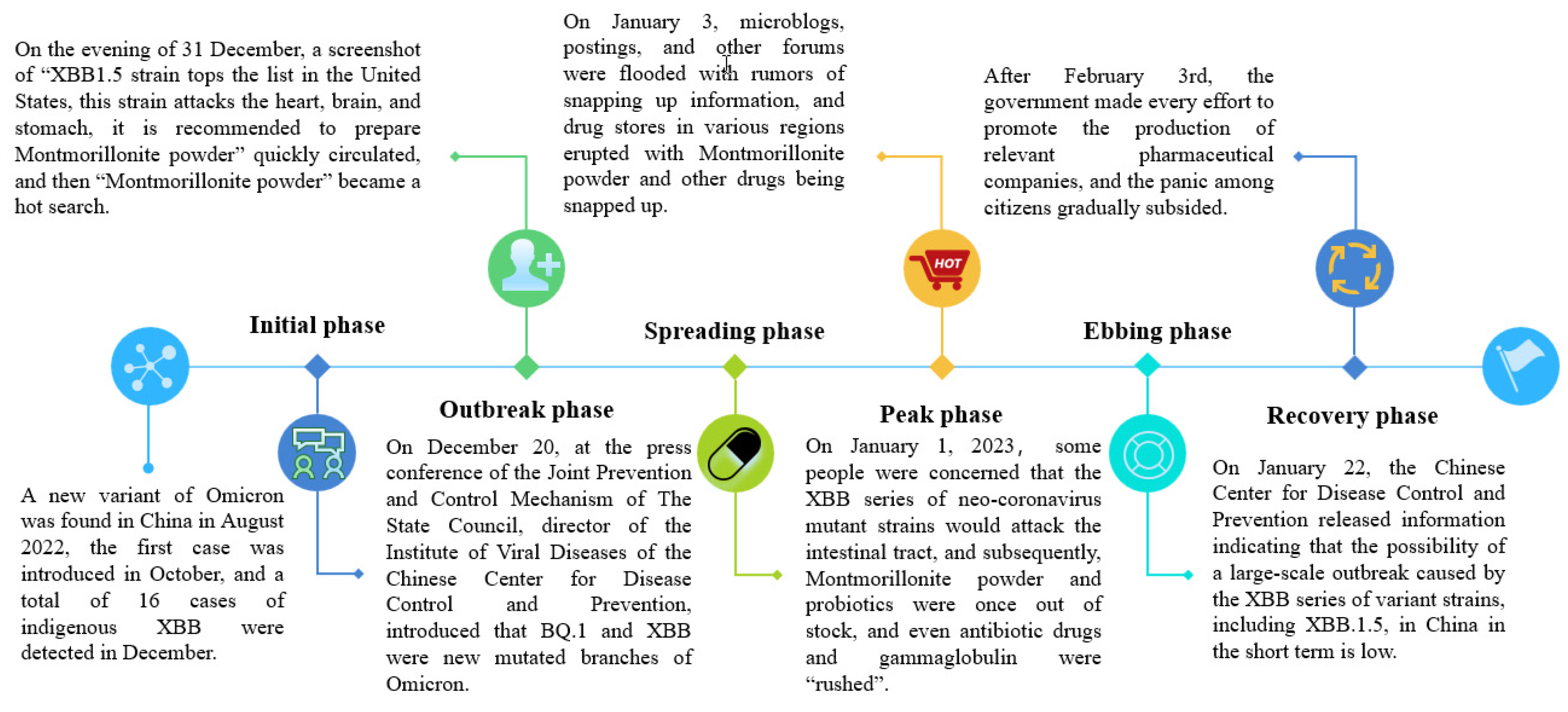
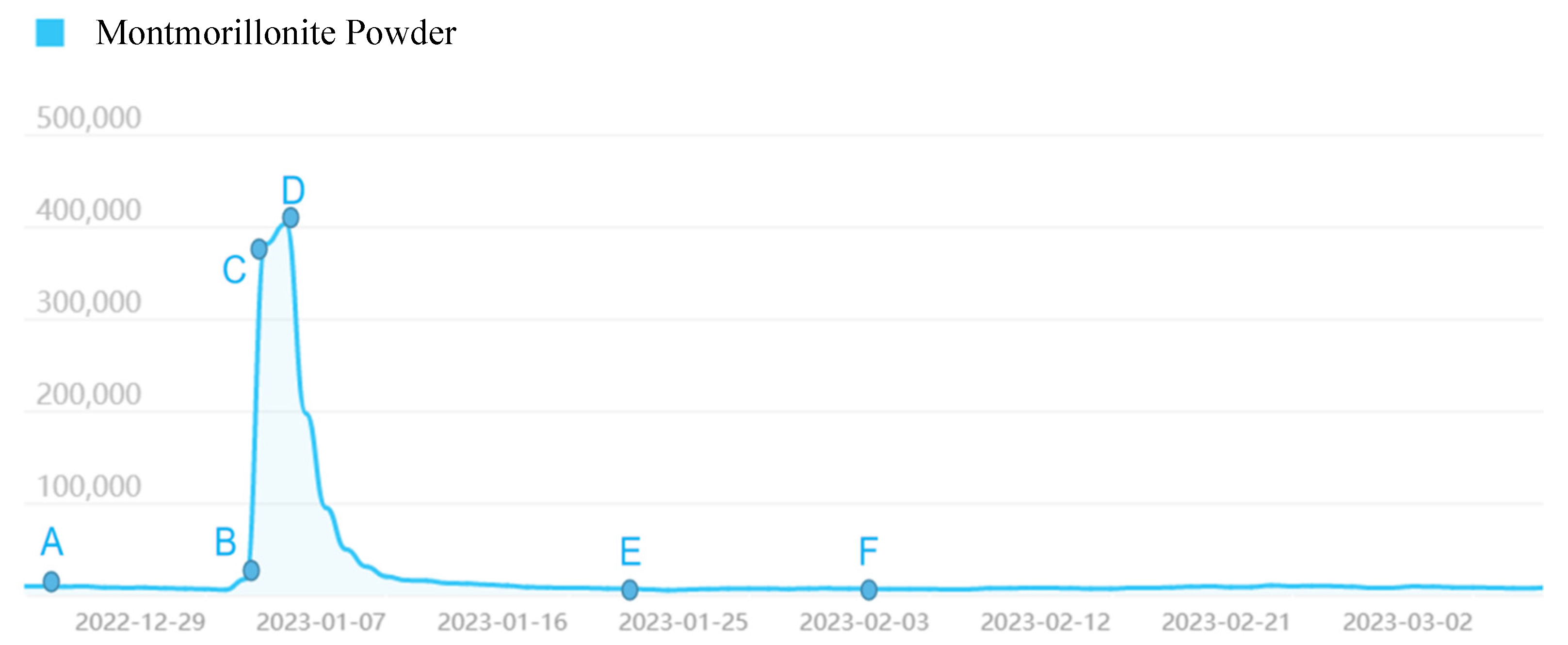
Since the beginning of 2020, due to the impact of the new coronavirus epidemic, countries have adopted certain prevention policies to curb the large-scale outbreak, and according to the coronavirus database, scientists determined that the first mutant strain of XBB1.5 was born in 2022.on August 3, 2022, XBB was first discovered in India and has now spread to more than 70 countries and become a major epidemic strain in Singapore. The earliest sample of the XBB1.5 variant was found in New York in October 2022, and XBB.1.5 has become the dominant strain in the United States by the end of 2022.A new variant of Omicron was found in China in August 2022, the first case was introduced in October, and a total of 16 cases of indigenous XBB were detected in December. On December 20, at the press conference of the Joint Prevention and Control Mechanism of The State Council, the director of the Institute of Viral Diseases of the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, introduced that BQ.1 and XBB were new mutated branches of Omicron, which opened the beginning of the panic-buying for Montmorillonite powder caused by XBB.1.5 strain.
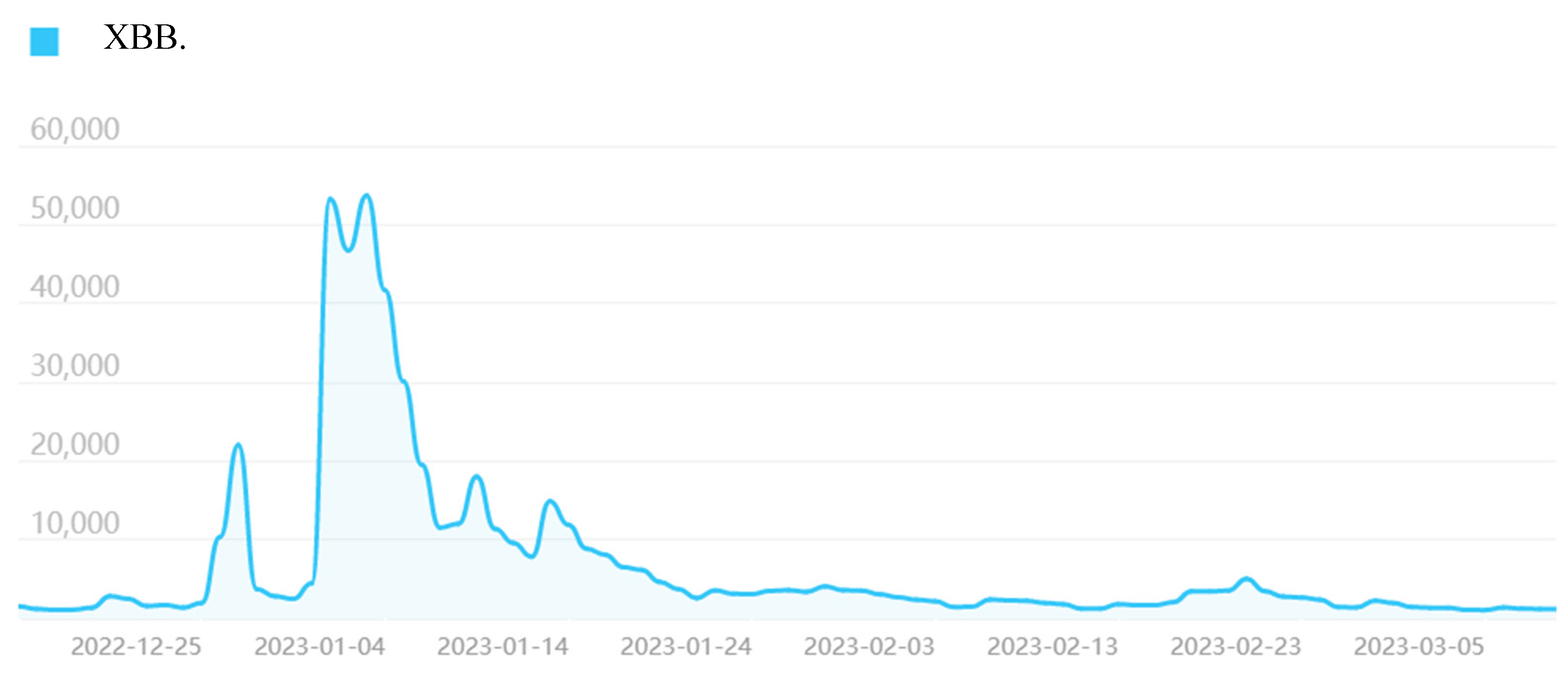
The panic-buying roughly went through the evolutionary process of "the beginning stage (December 20), the outbreak stage (December 31), the spread stage (January 1), the climax stage (January 3), the mitigation stage (January 22), and the recovery stage (after February 3)" (as shown in
Figure 3). Among them, the public's motivation for the snapping up of Montmorillonite powder and probiotics originated from a screenshot of a rumor that "The XBB1.5 strain is rampant in the United States, this strain mainly attacks the heart, brain, and stomach, it is recommended to prepare Montmorillonite powder", which began to arouse people's attention on XBB.1.5 strain and gradually subsided with time (as shown in
Figure 4.). In this panic buying wave, the government's emergency decision-making behavior evolved from no intervention to active intervention, the core reason is that it has the goal of maintaining social stability, and the rumor-mongering behavior of rumor-mongers also gradually evolved to no rumor under the government's active intervention, and the masses snapped up or not in the complex social environment to protect their own interests by choice. It can be seen that the case of the panic-buying satisfies the equilibrium points E
1 (0,0,0), E
3 (0,1,0), E
7 (0,1,1), E
8 (1,1,1), E
5 (1,1,0), and E
4 (1,0,0), respectively.
At the press conference of the joint prevention and control mechanism of the State Council on December 20, director of the Institute of Viral Diseases of the Chinese CDC, introduced that BQ.1 and XBB are new mutant branches of the Omicron mutation branch. During that period, the public trust in rumors is low in the face of a potentially abrupt change in the gain-loss situation (Point A in
Figure 5 is shown), while the government focuses on incident investigation and public opinion monitoring, so the payment pattern of the game satisfies the equilibrium point E
1 (0,0,0) and the game equilibrium outcome is (no intervention, no rumor, no panic buying).
On the evening of 31 December, a screenshot of "XBB1.5 strain tops the list in the United States, this strain attacks the heart, brain, and stomach, it is recommended to prepare Montmorillonite powder" quickly circulated, and then "Montmorillonite powder" became a hot search. During this period, the government did not intervene because the rumor had a small spread and the cost of the intervention was high, which led to the rumor and public opinion spreading, but the public's trust in the rumor was still relatively low (Point B in
Figure 5 is shown), so it did not lead to a large-scale rush to buy and the payment pattern of the game satisfied the equilibrium point E
3 (0,1,0), and the equilibrium result of the game was (no intervention, rumor, no panic buying).
On January 1 2023, some people were concerned that the XBB series of neo-coronavirus mutant strains would attack the intestinal tract, and subsequently Montmorillonite powder and probiotics were once out of stock, and even antibiotic drugs and gammaglobulinemia were "rushed" as some people feared that neo-coronavirus infections combined with bacterial infections would cause serious illness. And according to information released by the CDC, for XBB.1.5 evolutionary branch, although there is no evidence that it is more likely to cause severe diarrhea or other clinical manifestations of the gastrointestinal tract than other strains if infected with the new coronavirus, appropriate use of drugs such as Montmorillonite powder and flavivirid to relieve diarrhea symptoms, probiotics can also improve the intestinal flora, this information also exacerbated the rush phenomenon to a certain extent (Point C in
Figure 5 is shown). During that period, the public trust in rumors is high, so the payment pattern of the game satisfies the equilibrium point E
7 (0,1,1) and the equilibrium result of the game is (no intervention, rumor, panic buying).
On January 3, microblogs, postings, and other forums were flooded with rumors of snapping up information, and drug stores in various regions erupted with Montmorillonite powder and other drugs being snapped up. Although the local government began to hold press conferences and issued information to dispel the rumors, it still failed to effectively persuade the public to consume rationally (Point D in
Figure 5 is shown). The government had to actively intervene to avoid further deterioration of the situation. In this period, the payment pattern of the game satisfies the equilibrium point E
8 (1,1,1), and the equilibrium outcome of the game is (intervention, rumor, panic buying).
On January 22, the CDC released information showing that the population in China is generally susceptible to BA.5.2, BF.7 and XBB series of Omicron mutant strains, and BA.5.2 and BF.7 are dominant, and the antibodies produced by most people recently infected with BA.5.2 or BF.7 have a protective effect against XBB series of mutant strains in the short term. Therefore, at this stage, the XBB series variant strains will not cause a large-scale local epidemic. Meanwhile, medical experts and other kinds of scholars have dispelled rumors against the net rumors that the XBB strain will cause vomiting and diarrhea. Some people infected with the new coronavirus do have symptoms of vomiting and diarrhea, which can usually be relieved by themselves in 1-3 days, and medications for treating respiratory and digestive tract infections can be properly prepared, and there is no need to stock up in large quantities. During that period, public trust in rumors decreases because the government actively intervenes in social opinion and actively dispels rumors out of concern for maintaining social stability (Point E in
Figure 5 is shown). Therefore, the payment pattern of the game satisfies the equilibrium point E
5 (1,1,0) and the equilibrium outcome of the game is (intervention, rumor, no panic buying).
After 3 February, as the government stepped in to take measures to dispel the rumors, public trust in the local government was restored and rationality returned, with the level of trust in the rumors minimized (Point F in
Figure 5 is shown). At the same time, local governments at all levels start to increase their administrative penalties to avoid accountability and criticism from the central government, and the rumor-monger concerned have an increased cost of rumor-mongering and therefore stop doing so. At this point, the payment pattern of the game satisfies the equilibrium point E
4 (1,0,0), and the equilibrium outcome of the game is (intervention, no rumor, no panic buying).
8. Conclusions and recommendations
8.1. Conclusions
This paper presents a case study of a sudden public mass panic-buying event caused by a variant of the Omicron strain in the context of the New Crown Pneumonia epidemic. The findings are as follows:
8.1.1. The evolutionary process of mass rush events in the context of public health emergencies is expressed in six stages, and the evolutionary process is expressed in the starting stage E1 (no intervention, no rumor, no panic buying) - the outbreak stage E3 (no intervention, rumor, no panic buying) - the spreading stage E7 (no intervention, rumor, panic buying) - climax phase E8 (intervention, rumor, panic buying) - mitigation phase E5 (intervention, rumor, no panic buying) - recovery phase E4 (intervention, no rumor, no panic buying) six stages. The analytical discussion of the ESS equilibrium point leads to four evolutionary stabilization strategies, namely E1, E3, E4, and E5.
8.1.2. In the case of the initial three-party game model, when the conditions are satisfied that the cost of government intervention is less than the sum of the reward and punishment, the gain of the rumor monger is less than the cost and punishment, and the public chooses not to buying, the society is in a stable state at this time, and the three parties of the game can reach the optimal stable point E4 (1,0,0), when the government, the rumor-monger, and the public respectively choose the behavioral strategies of intervention, no rumor and no panic buying are conducive to building a harmonious and stable social environment and are optimal strategy.
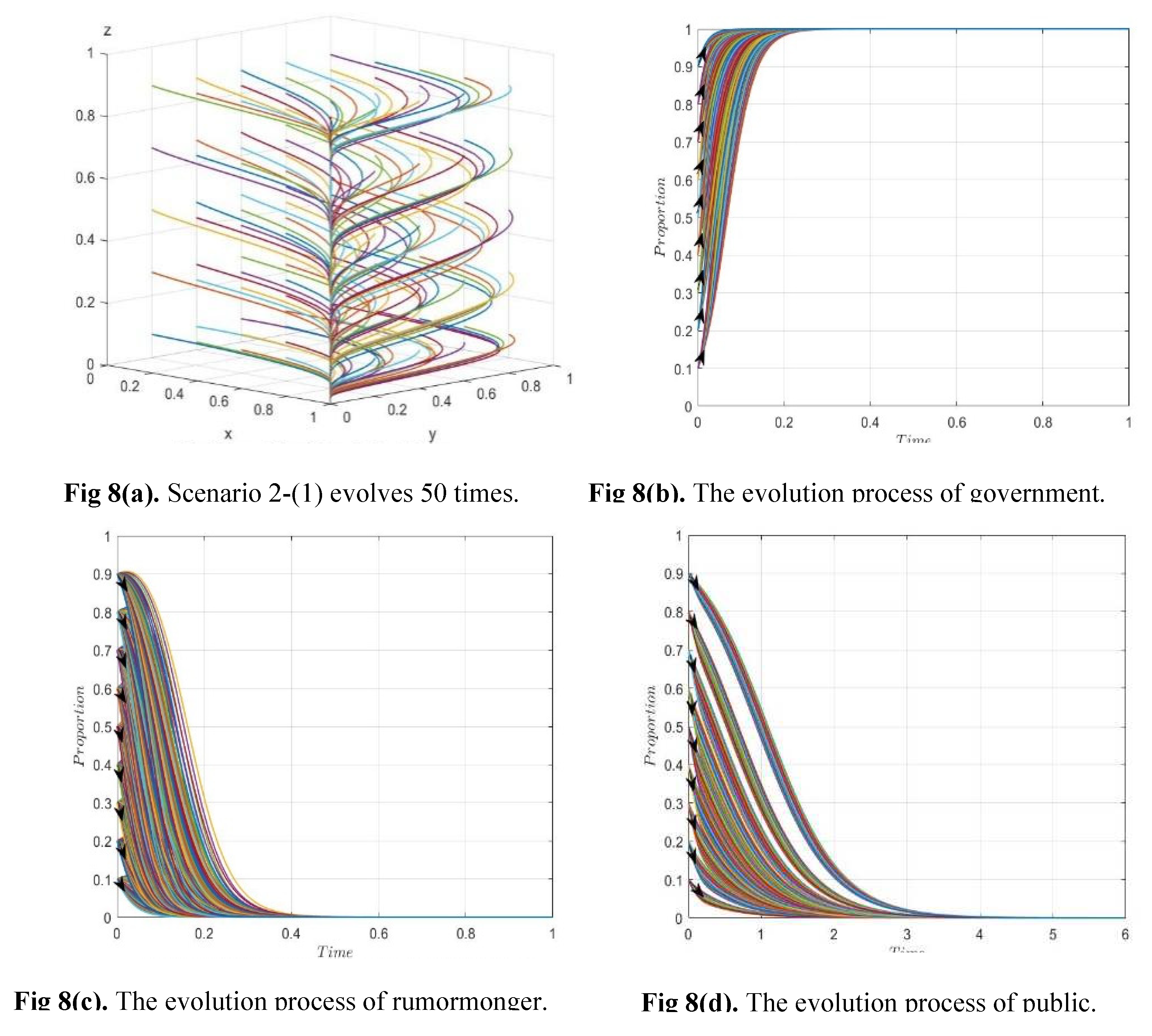
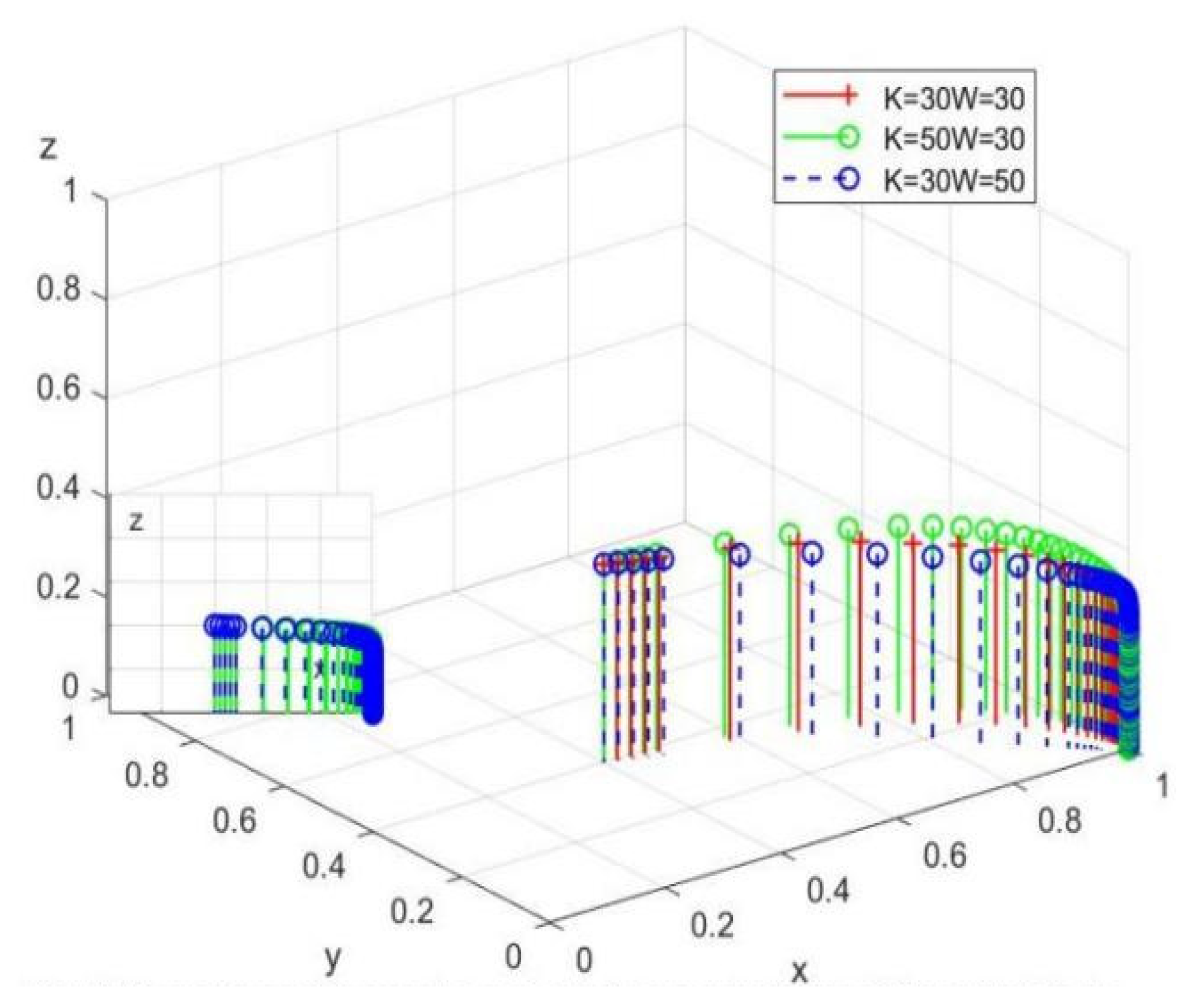
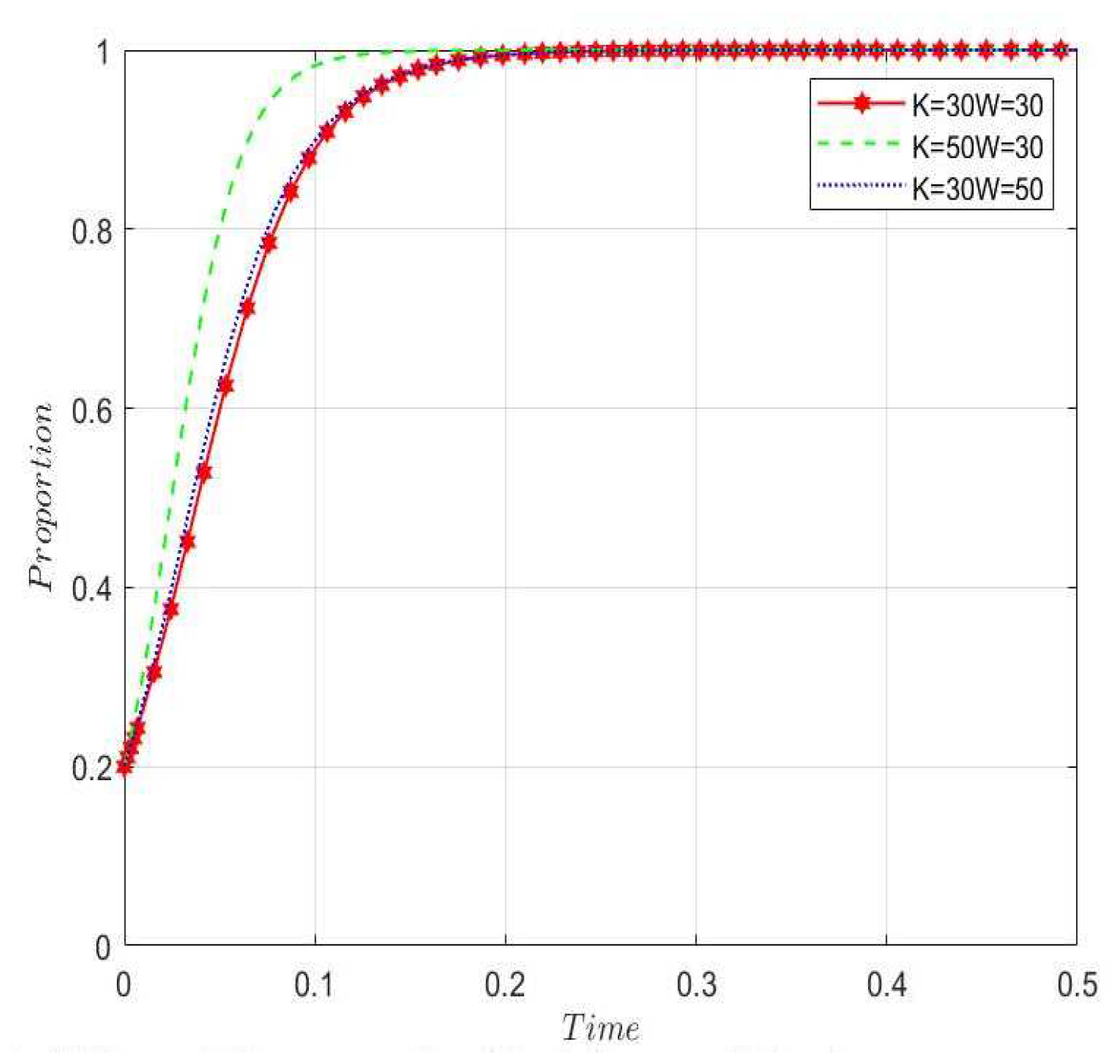
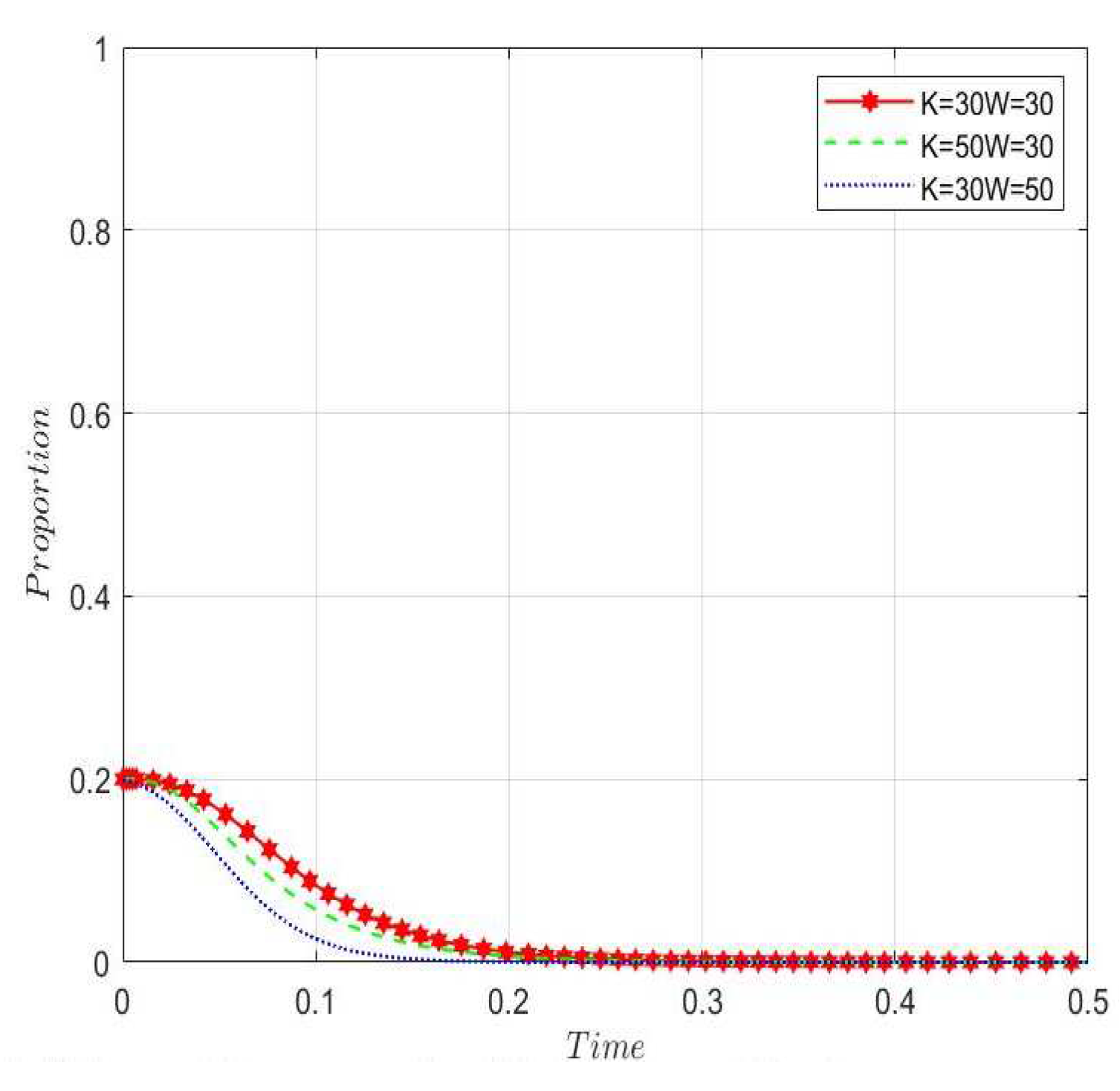
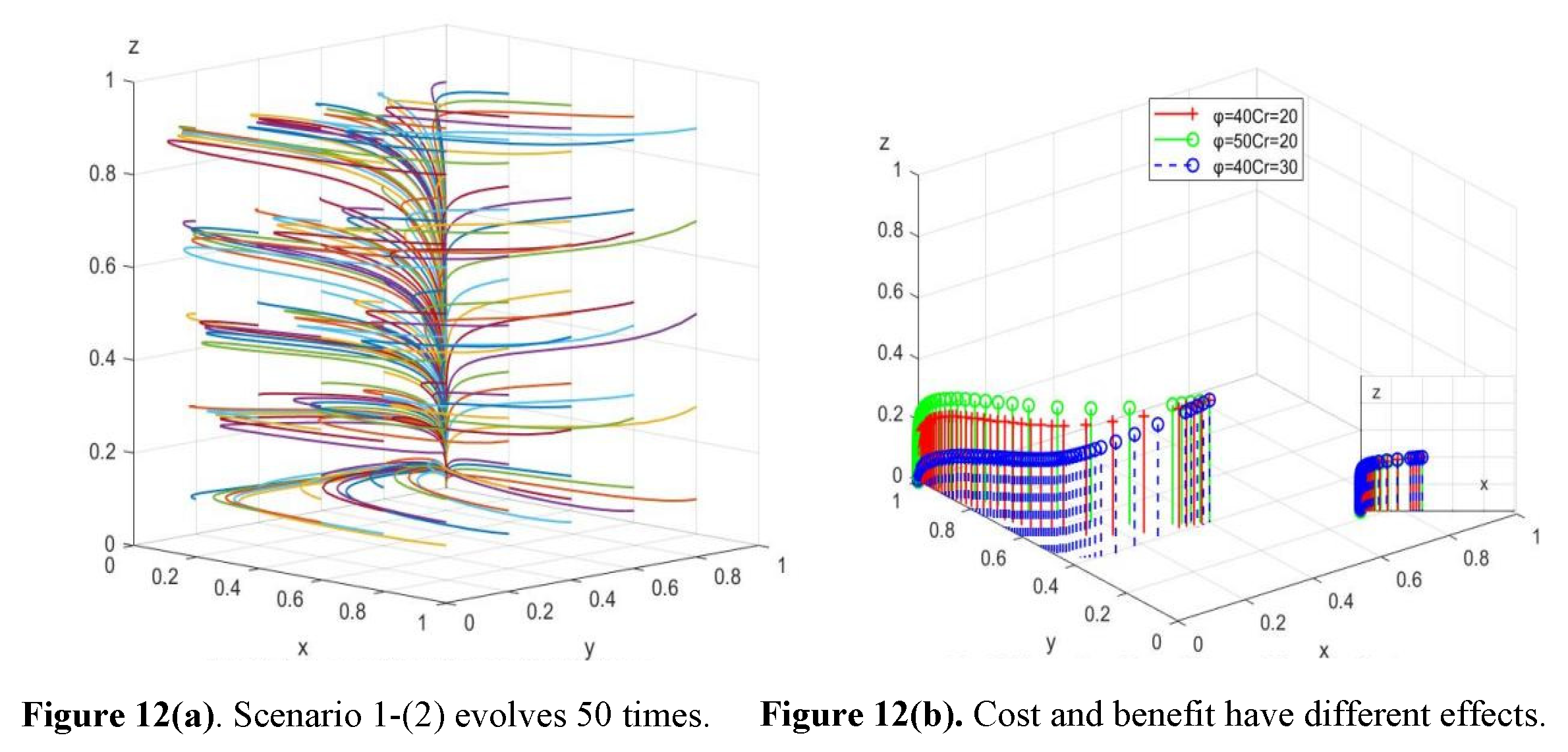
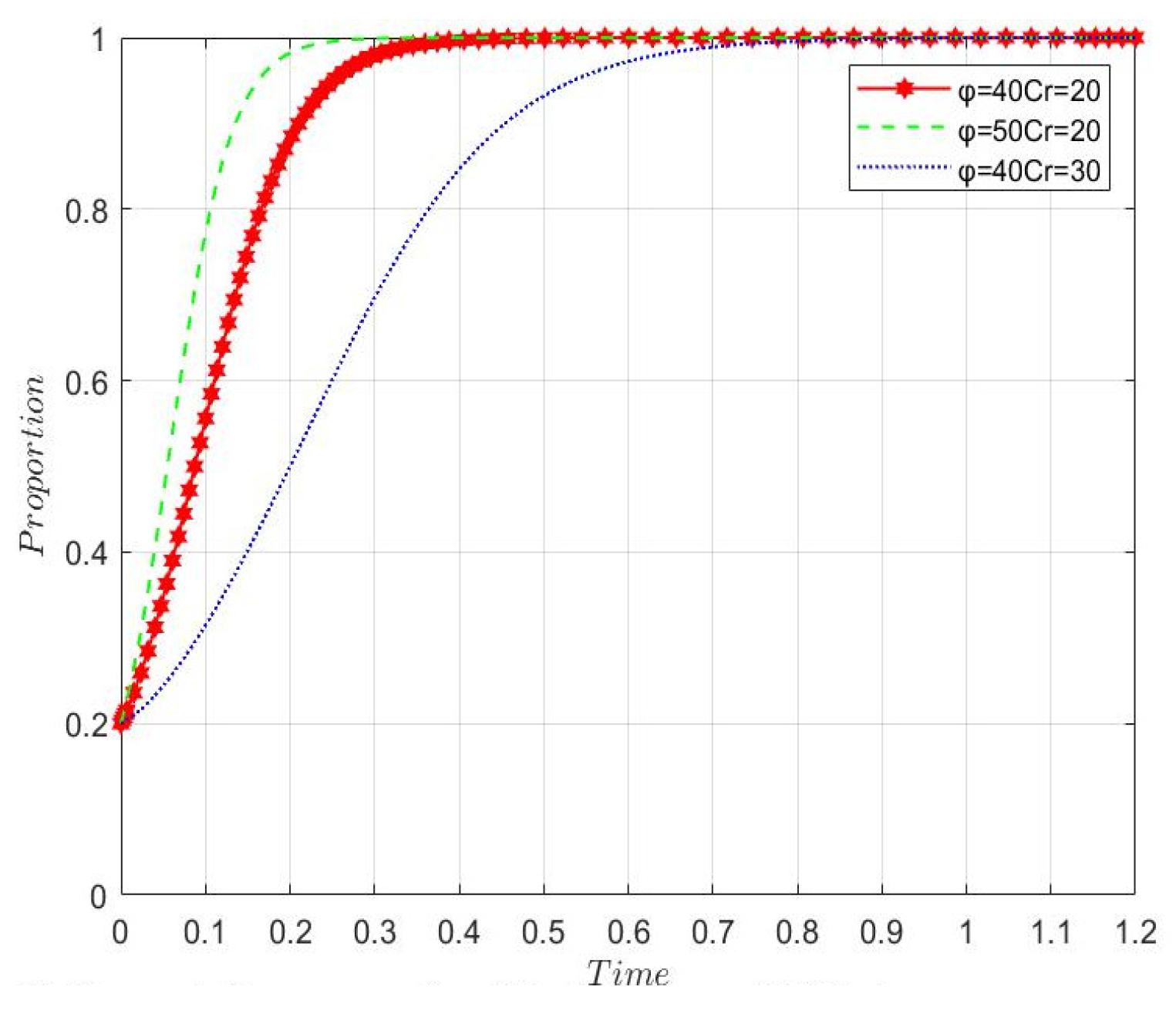
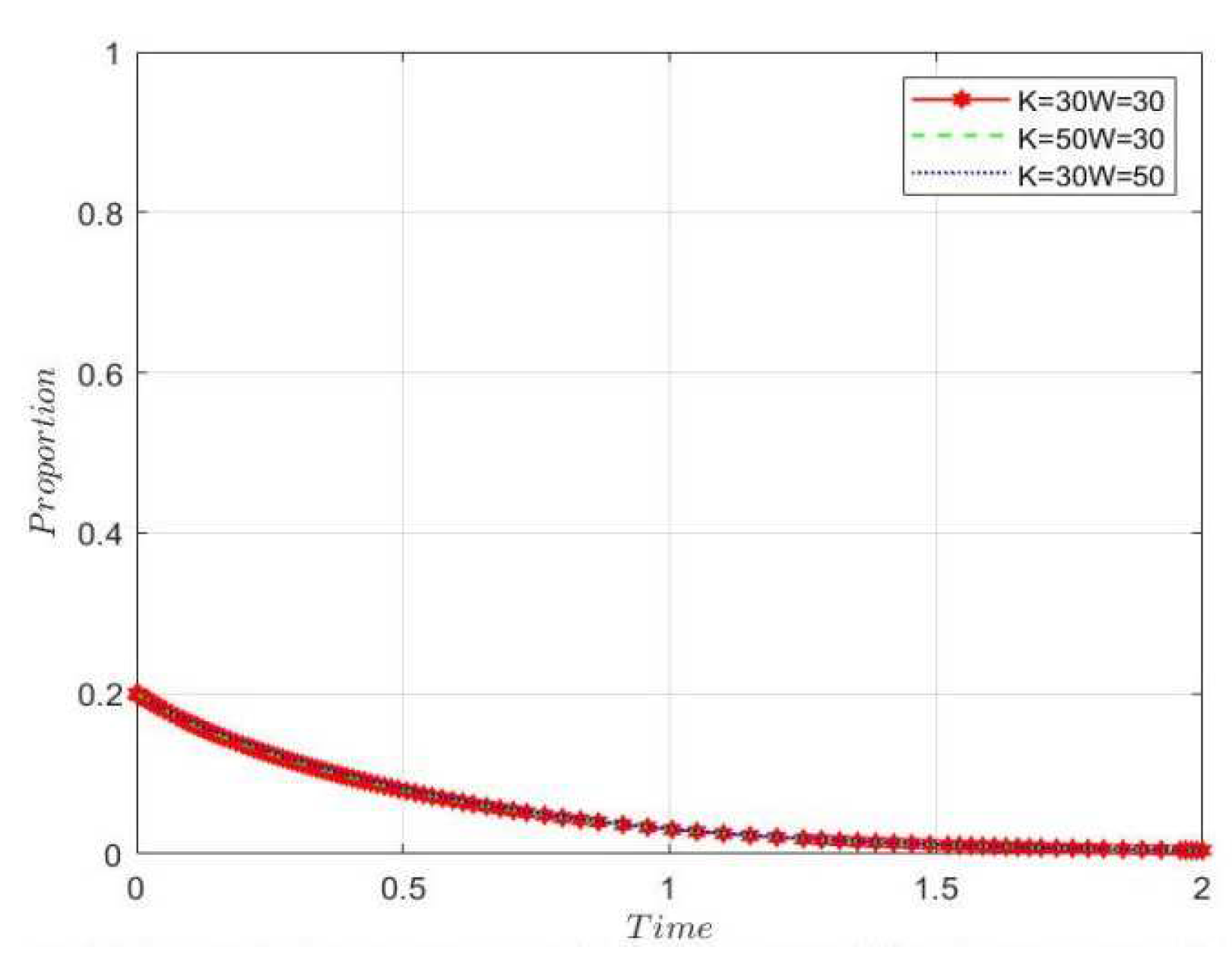
8.1.3. After simulating the three-party game model, we choose the optimal strategy option 2-(1) for analysis, and by adjusting the rewards and penalties for sensitivity analysis, we can conclude that both incentives and punishments from higher levels of government motivate local governments to accelerate their intervention of rumor-mongering, with incentives having a better effect than punishments. Therefore, the incentive behavior for local governments is the most effective.
8.1.4. In Scenario 2-(1), changes in rewards and punishments to the government have an impact on rumor mongers, the government will increase its intervention behavior and intensity under changes in rewards and punishments. Further increasing the cost of rumor for rumor mongers, and will increase the punishment for rumor mongers to maintain and improve their credibility, prompting rumor mongers to prefer non-rumor behavior. To compare the effects of the costs and benefits of rumor, discussing scenarios 1-(2), it is clear that under the condition of no government intervention, increasing the benefits will speed up the rumor, while increasing the costs will decrease the speed of rumor, which is more significant compared to the effects of costs. Therefore, controlling the cost of rumor for rumor mongers is an effective measure for conducting control.
8.2. Recommendations
According to the above conclusions, this paper analyzes the subjects and behaviors related to the sudden public mass rush events to realize the rumor control work in the context of the epidemic can form a joint action of up and down, active intervention, parallel rewards and punishments, mass supervision, mass self-regulation, and other multi-body participation and puts forward the following suggestions.
8.2.1. Broaden the information publication channels and improve the supervision mechanism
First, the government should attach great importance to information disclosure work, take information disclosure work as an important guarantee to boost rumor control work, continue to adhere to the concept of passive disclosure to active disclosure, from negative disclosure to active disclosure, and continuously improve the participation of various local governments and units of multiple parties to fundamentally avoid the spread of rumors caused by information asymmetry. Secondly, broaden information disclosure channels, establish and improve effective information filtering and screening system, and make full use of intelligent, modern, and technological mass communication media so that the government and the public can get real, scientific, and effective information in time and cut off the source of spreading online rumors. Finally, we encourage multiple parties to report rumor spreaders on time. At the same time, the public can be trained as "cyber police" to effectively strengthen the review and supervision of online information, and to stop online rumors in their bellies.
8.2.2. Strengthen the two-tier linkage mechanism between the higher-level and local government
Firstly, the roles of the higher government and local government should be rationalized. When emergencies occur, the higher government should focus on macro-control and policy guidance, and the local government should resolutely carry out the tasks explained by the higher level, but the scope of authority and responsibility of the higher level and the local level should be well defined, and they should not overstep their authority. Secondly, the higher government should strengthen the criminal legislation under sudden events and give legal protection to the local workers. The local government should strictly administer justice, but should not abuse its power and overdo it, and should guarantee the people's right to freedom of expression. Finally, local governments should strengthen their credibility, and as representatives of higher governments, they should work seriously and serve the people wholeheartedly.
8.2.3. Strengthen the construction of the reward and punishment system
In emergency handling emergencies not only need to strengthen supervision and monitoring but also needs a corresponding reward and punishment system to effectively mobilize enthusiasm. First, a reward and punishment mechanism should be set up for local governments and rumor-mongers. By rewarding and punishing local governments for effective intervention, local governments should pay attention to the control of rumors and take action. Secondly, by increasing the penalties and supervision for individuals or enterprises that create rumors, the costs and penalties for rumor-mongers can be further increased, so that rumor-mongers can be reduced or even dare not create rumors, and the existence and spread of rumors can be eliminated at the source. Finally, the higher government should guide the local government to carry out intervention activities with incentives to stimulate the local government public officials to work actively, grasp the principle of moderation, and avoid excessive harshness, leading to the local government to take action in fear, while triggering inaction and other bad behavior, while the local government should also respond positively to the requirements of the higher government, dare to act and dare to take charge.
8.2.4. Improve public information discernment
First, strengthen rumor prevention education for the public, guide the public to start from objective facts, and always keep rational thinking to avoid widespread rumors and their adverse effects on society. Second, cultivate the public's ability to think and discern, to be good at identifying rumors, digging out the truth, and pursuing the truth, and to avoid becoming rumor generators or spreaders from the scientific thinking of Marxism. Finally, to channel the public's psychology and avoid the existence of herd mentality that triggers sudden social snafus.