Submitted:
03 July 2023
Posted:
03 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Impact of Fermentation on Micronutrients
Effect of fermentation on Non-nutrient/Bioactive Compounds
Non-Digestible Carbohydrate
Prebiotics - Fructooligosaccharide (FOS) and Galactooligosaccharides (GOS)
Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs) and Conjugated Fatty Acids (CLA)
Conclusion and Future Prospects
Acknowledgement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huizar, M.I.; Arena, R.; Laddu, D.R. The Global Food Syndemic: The Impact of Food Insecurity, Malnutrition and Obesity on the Healthspan amid the COVID-19 Pandemic. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemu, E.A. Malnutrition and Its Implications on Food Security. 2020, 509–518. [CrossRef]
- Chadare, F.J.; Idohou, R.; Nago, E.; Affonfere, M.; Agossadou, J.; Fassinou, T.K.; Kénou, C.; Honfo, S.; Azokpota, P.; Linnemann, A.R.; et al. Conventional and Food-to-Food Fortification: An Appraisal of Past Practices and Lessons Learned. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 2781–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellies, W.; Rolfes, S. Understanding Nutrition; 15th, *!!! REPLACE !!!* (Eds.) 2019.
- Rahim, M.H.A.; Hazrin-Chong, N.H.; Harith, H.H.; Wan-Mohtar, W.A.A.Q.I.; Sukor, R. Roles of Fermented Plant-, Dairy- and Meat-Based Foods in the Modulation of Allergic Responses. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedelazeez, K.J.D.; Solehah, M.Z.N.; Jaafar, A.H.; Meor Hussin, A.S.; Wan-Mohtar, W.A.A.Q.I.; Abd Rahim, M.H. Production, Organoleptic, and Biological Activities of Belacan (Shrimp Paste) and Pekasam (Fermented Freshwater Fish), the Ethnic Food from the Malay Archipelago. Sains Malaysiana 2023, 52, 1217–1230. [Google Scholar]
- Faizal, F.A.; Ahmad, N.H.; Yaacob, J.S.; Abdul-Halim Lim, S.; Yaacob, J.S.; Abd Rahim, M.H. Food Processing to Reduce Anti-Nutrients in Plant-Based Food. Int. Food Res. J. 2023, 30, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan-Mohtar, W.A.A.Q.I.; Ab Kadir, S.; Halim-Lim, S.A.; Ilham, Z.; Hajar-Azhari, S.; Saari, N. Vital Parameters for High Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) Production by an Industrial Soy Sauce Koji Aspergillus Oryzae NSK in Submerged-Liquid Fermentation. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 28, 1747–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan-Mohtar, W.A.A.Q.I.; Ab Kadir, S.; Saari, N. The Morphology of Ganoderma Lucidum Mycelium in a Repeated-Batch Fermentation for Exopolysaccharide Production. Biotechnol. Reports 2016, 11, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajar-Azhari, S.; Wan-Mohtar, W.A.A.Q.I.; Ab Kadir, S.; Rahim, M.H.A.; Saari, N. Evaluation of a Malaysian Soy Sauce Koji Strain Aspergillus Oryzae NSK for γ-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) Production Using Different Native Sugars. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 27, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin Yee, C.; Sohedein, M.N.A.; Poh Suan, O.; Weng Loen, A.W.; Abd Rahim, M.H.; Soumaya, S.; Ilham, Z.; Wan-Mohtar, W.A.A.Q.I. The Production of Functional γ-Aminobutyric Acid Malaysian Soy Sauce Koji and Moromi Using the Trio of Aspergillus Oryzae NSK, Bacillus Cereus KBC, and the Newly Identified Tetragenococcus Halophilus KBC in Liquid-State Fermentation. Futur. Foods 2021, 4, 100055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Rahim, M.H. Production Of Lovastatin, (+)-Geodin And Sulochrin By Aspergillus Terreus ATCC 20542 Using Pure And Crude Glycerol, The University of Sydney, 2015.
- LeBlanc, J.G.; Milani, C.; de Giori, G.S.; Sesma, F.; van Sinderen, D.; Ventura, M. Bacteria as Vitamin Suppliers to Their Host: A Gut Microbiota Perspective. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gombart, A.F.; Pierre, A.; Maggini, S. A Review of Micronutrients and the Immune System–Working in Harmony to Reduce the Risk of Infection. Nutrients 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadh, P.K.; Kumar, S.; Chawla, P.; Duhan, J.S. Fermentation: A Boon for Production of Bioactive Compounds by Processing of Food Industries Wastes (By-Products); 2018; Vol. 23; ISBN 9116662431.
- Zhang, Z.; Xia, L.; Wang, F.; Lv, P.; Zhu, M.; Li, J.; Chen, K. Lignin Degradation in Corn Stalk by Combined Method of H2O2 Hydrolysis and Aspergillus Oryzae CGMCC5992 Liquid-State Fermentation. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2015, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarte, C.E.; Vargas, M.; Granfeldt, Y. Zinc Bioavailability in Rats Fed a Plant-Based Diet: A Study of Fermentation and Zinc Supplementation. Food Nutr. Res. 2015, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, S.; Rezaei Mokarram, R.; Sowti Khiabani, M.; Rezazadeh Bari, M.; Alizadeh Khaledabad, M. In Situ Production of Conjugated Linoleic Acid by Bifidobacterium Lactis BB12 and Lactobacillus Acidophilus LA5 in Milk Model Medium. Lwt 2020, 132, 109933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagas Junior, G.C.A.; Ferreira, N.R.; Gloria, M.B.A.; Martins, L.H. da S.; Lopes, A.S. Chemical Implications and Time Reduction of On-Farm Cocoa Fermentation by Saccharomyces Cerevisiae and Pichia Kudriavzevii. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 127834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, H.O.; Önning, G.; Holmgren, K.; Strandler, H.S.; Hultberg, M. Fermentation of Cauliflower and White Beans with Lactobacillus Plantarum – Impact on Levels of Riboflavin, Folate, Vitamin B12, and Amino Acid Composition. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2020, 75, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrizo, S.L.; de Moreno de LeBlanc, A.; LeBlanc, J.G.; Rollán, G.C. Quinoa Pasta Fermented with Lactic Acid Bacteria Prevents Nutritional Deficiencies in Mice. Food Res. Int. 2020, 127, 108735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Wang, W.; Shen, M.; Kang, Z.; Wang, J.; Quan, Z.; Xiao, J.; Zhao, S.; Liu, D.; Cao, L. Effect of Natural Fermentation of Sorghum on Resistant Starch Molecular Structure and Fermentation Property. J. Chem. 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laiño, J.E.; Juarez del Valle, M.; Savoy de Giori, G.; LeBlanc, J.G.J. Development of a High Folate Concentration Yogurt Naturally Bio-Enriched Using Selected Lactic Acid Bacteria. LWT - Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 54, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innate, T.; Cells, L. Streptococcus Thermophilus 1131 Induce the Expression of the REG3 Family in the Small Intestine of Mice via the Stimulation of Dendritic Cells And. 2019, 1–11.
- Clara, A.; Silvetti, T.; Milena, B. Folate Production by LAB and Their Potential for Dairy Product Bio-Enrichment by Fermentation.
- Fang, H.; Kang, J.; Zhang, D. Microbial Production of Vitamin B12: A Review and Future Perspectives. Microb. Cell Fact. 2017, 16, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, F.; Vera, J.L.; van der Heijden, R.; Valdez, G.; de Vos, W.M.; Sesma, F.; Hugenholtz, J. The Complete Coenzyme B12 Biosynthesis Gene Cluster of Lactobacillus Reuteri CRL1098. Microbiology 2008, 154, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Coda, R.; Chamlagain, B.; Varmanen, P.; Piironen, V.; Katina, K. Co-Fermentation of Propionibacterium Freudenreichiiand Lactobacillus Brevisin Wheat Bran for in Situproduction of Vitamin B12. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deptula, P.; Chamlagain, B.; Edelmann, M.; Sangsuwan, P.; Nyman, T.A.; Savijoki, K.; Piironen, V.; Varmanen, P. Food-like Growth Conditions Support Production of Active Vitamin B12 by Propionibacterium Freudenreichii 2067 without DMBI, the Lower Ligand Base, or Cobalt Supplementation. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolkers – Rooijackers, J.C.M.; Endika, M.F.; Smid, E.J. Enhancing Vitamin B12 in Lupin Tempeh by in Situ Fortification. LWT 2018, 96, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piwowarek, K.; Lipińska, E.; Hać-Szymańczuk, E.; Kieliszek, M.; Ścibisz, I. Propionibacterium Spp.—Source of Propionic Acid, Vitamin B12, and Other Metabolites Important for the Industry. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 515–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, B.; Karl, J.P.; Booth, S.L.; Boyaval, P. Menaquinones, Bacteria, and the Food Supply: The Relevance of Dairy and Fermented Food Products to Vitamin K Requirements. Adv. Nutr. 2013, 4, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pateiro, M.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Tsatsanis, C.; Domínguez, R.; Zhang, W.; Barba, F.J.; Lorenzo, J.M. Evaluation of the Protein and Bioactive Compound Bioaccessibility/Bioavailability and Cytotoxicity of the Extracts Obtained from Aquaculture and Fisheries by-Products. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2020, 92, 97–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, N.M.; Martha, G.S.; Harohally, N. V.; Murthy, P.S. Non-Digestible Oligosaccharides of Green Coffee Spent and Their Prebiotic Efficiency. Lwt 2020, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Rani, K.; Datt, C. Molecular Link between Dietary Fibre, Gut Microbiota and Health. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 6229–6237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Khan, I.; Li, X. ang; Huang, G.; Yu, Z.; Leong, W.K.; Han, R.; Ho, L.T.; Wendy Hsiao, W.L. Adaptogenic Flower Buds Exert Cancer Preventive Effects by Enhancing the SCFA-Producers, Strengthening the Epithelial Tight Junction Complex and Immune Responses. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 159, 104809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaprasob, R.; Kerdchoechuen, O.; Laohakunjit, N.; Somboonpanyakul, P. B Vitamins and Prebiotic Fructooligosaccharides of Cashew Apple Fermented with Probiotic Strains Lactobacillus Spp., Leuconostoc Mesenteroides and Bifidobacterium Longum. Process Biochem. 2018, 70, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, M.A.C.; Bedani, R.; LeBlanc, J.G.; Saad, S.M.I. Passion Fruit By-Product and Fructooligosaccharides Stimulate the Growth and Folate Production by Starter and Probiotic Cultures in Fermented Soymilk. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 261, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajar-Azhari, S.; Hafiz Abd Rahim, M.; Razid Sarbini, S.; Muhialdin, B.J.; Olusegun, L.; Saari, N. Enzymatically Synthesised Fructooligosaccharides from Sugarcane Syrup Modulate the Composition and Short-Chain Fatty Acid Production of the Human Intestinal Microbiota. Food Res. Int. 2021, 149, 110677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajar-Azhari, S.; Rahim, M.H.A.; Wan-Mohtar, W.A.A.Q.I.; Sarbini, S.R.; Saari, N. Novel Fructooligosaccharide Conversion from Sugarcane Syrup Using a Specialised Enzymatic PH-Stat Bioreactor. Process Biochem. 2020, 95, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadra, S.; Chettri, D.; Verma, A.K. Microbes in Fructooligosaccharides Production. Bioresour. Technol. Reports 2022, 20, 101159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Martínez, M.J.; Soto-Jover, S.; Antolinos, V.; Martínez-Hernández, G.B.; López-Gómez, A. Manufacturing of Short-Chain Fructooligosaccharides: From Laboratory to Industrial Scale. Food Eng. Rev. 2020, 12, 149–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celligoi, M.A.; Baratella, P. Optimization of High Production of Fructooligosaccharides by Sucrose Fermentation of Bacillus Subtilis Natto CCT 7712. Am. J. Food Technol. 2014, 9, 144. [Google Scholar]
- Tezgel, N.; Kırtel, O.; Van den Ende, W.; Toksoy Oner, E. Fructosyltransferase Enzymes for Microbial Fructan Production. Microb. Enzym. Roles Appl. Ind. 2020, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Zhou, H.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, N.; Zhao, Z.; Sun, G.; Zhong, Y. A Molasses Habitat-Derived Fungus Aspergillus Tubingensis XG21 with High β-Fructofuranosidase Activity and Its Potential Use for Fructooligosaccharides Production. AMB Express 2017, 7, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, L.; Ureta, M.; Romanini, D.; Woitovich, N.; Gómez-Zavaglia, A.; Clementz, A. Enzymatic Synthesis of Fructooligosaccharides: From Carrot Discards to Prebiotic Juice. Food Res. Int. 2023, 170, 112991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jesus, L.F.M.C.; Guimarães, L.H.S. Production of β-Galactosidase by Trichoderma Sp. through Solid-State Fermentation Targeting the Recovery of Galactooligosaccharides from Whey Cheese. J. Appl. Microbiol. [CrossRef]
- Bassetto, R.Z.; Cabral, P.S.; Silveira, M.H.L.; Almeida, M.M.; Chiquetto, N.C. Optimization of β-Galactosidase Production from Penicillium Sp. for Synthesis of Galactooligosaccharides. Int. Food Res. J. 2017, 24, 1793–1798. [Google Scholar]
- Fara, A.; Sabater, C.; Palacios, J.; Requena, T.; Montilla, A.; Zárate, G. Prebiotic Galactooligosaccharides Production from Lactose and Lactulose by: Lactobacillus Delbrueckii Subsp. Bulgaricus CRL450. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 5875–5886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zokaityte, E.; Cernauskas, D.; Klupsaite, D.; Lele, V.; Starkute, V.; Zavistanaviciute, P.; Ruzauskas, M.; Gruzauskas, R.; Juodeikiene, G.; Rocha, J.M.; et al. Bioconversion of Milk Permeate with Selected Lactic Acid Bacteria Strains and Apple By-Products into Beverages with Antimicrobial Properties and Enriched with Galactooligosaccharides. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, N.S.; Kim, K.; Oh, S.; Kim, Y. Enhanced Production of Galactooligosaccharides Enriched Skim Milk and Applied to Potentially Synbiotic Fermented Milk with <italic>Lactobacillus Rhamnosus</Italic> 4B15. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2019, 39, 725–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vénica, C.I.; Bergamini, C. V; Rebechi, S.R.; Perotti, M.C. Galacto-Oligosaccharides Formation during Manufacture of Different Varieties of Yogurt. Stability through Storage. LWT - Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yañez-Ñeco, C. V; Rodriguez-Colinas, B.; Amaya-Delgado, L.; Ballesteros, A.O.; Gschaedler, A.; Plou, F.J.; Arrizon, J. Galactooligosaccharide Production from Pantoea Anthophila Strains Isolated from “Tejuino”, a Mexican Traditional Fermented Beverage. Catalysts 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, C.; Kleinschmidt, T. Valorisation of Sweet Whey by Fermentation with Mixed Yoghurt Starter Cultures with Focus on Galactooligosaccharide Synthesis. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 119, 105068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Rosa, O.; Múñiz-Marquez, D.B.; Contreras-Esquivel, J.C.; Wong-Paz, J.E.; Rodríguez-Herrera, R.; Aguilar, C.N. Improving the Fructooligosaccharides Production by Solid-State Fermentation. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 27, 101704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganaie, M.A.; Soni, H.; Naikoo, G.A.; Santos Oliveira, L.T.; Rawat, H.K.; Mehta, P.K.; Narain, N. Screening of Low Cost Agricultural Wastes to Maximize the Fructosyltransferase Production and Its Applicability in Generation of Fructooligosaccharides by Solid State Fermentation. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 118, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.L. de; Silva, M.F. da; Converti, A.; Porto, T.S. Production of β-Fructofuranosidase with Transfructosylating Activity by Aspergillus Tamarii URM4634 Solid-State Fermentation on Agroindustrial by-Products. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohara, A.; Soares de Castro, R.J.; Goia Nishide, T.; Gonçalves Dias, F.F.; Pavan Bagagli, M.; Harumi Sato, H. Invertase Production by Aspergillus Niger under Solid State Fermentation: Focus on Physical-Chemical Parameters, Synergistic and Antagonistic Effects Using Agro-Industrial Wastes. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2015, 4, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davani-Davari, D.; Negahdaripour, M.; Karimzadeh, I.; Seifan, M.; Mohkam, M.; Masoumi, S.J.; Berenjian, A.; Ghasemi, Y. Prebiotics: Definition, Types, Sources, Mechanisms, and Clinical Applications. Foods 2019, 8, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanalia, P.; Gandhi, D.; Attri, P.; Dhanda, S. Purification and Characterization of β-Galactosidase from Probiotic Pediococcus Acidilactici and Its Use in Milk Lactose Hydrolysis and Galactooligosaccharide Synthesis. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 77, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, M.; Aida, R.; Saito, K.; Ochiai, A.; Takesono, S.; Saitoh, E.; Tanaka, T. Identi Fi Cation and Characterization of Multifunctional Cationic Peptides from Traditional Japanese Fermented Soybean Natto Extracts. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2018, xx. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raveschot, C.; Cudennec, B.; Coutte, F.; Flahaut, C.; Fremont, M.; Drider, D.; Dhulster, P. Production of Bioactive Peptides by Lactobacillus Species: From Gene to Application. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayyash, M.; Al-Dhaheri, A.S.; Al Mahadin, S.; Kizhakkayil, J.; Abushelaibi, A. In Vitro Investigation of Anticancer, Antihypertensive, Antidiabetic, and Antioxidant Activities of Camel Milk Fermented with Camel Milk Probiotic: A Comparative Study with Fermented Bovine Milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 900–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Medellín, S.A.; Camacho-Ruiz, R.M.; Guízar-González, C.; Rivera-Leon, E.A.; Llamas-Covarrubias, I.M.; Mojica, L. Protein Hydrolysates and Phenolic Compounds from Fermented Black Beans Inhibit Markers Related to Obesity and Type-2 Diabetes. Legum. Sci. 2020, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhao, J.; Yang, R.; Zhao, W. Bioactive Peptides with Antidiabetic Properties: A Review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 1909–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazorra-Manzano, M.A.; Robles-Porchas, G.R.; González-Velázquez, D.A.; Torres-Llanez, M.J.; Martínez-Porchas, M.; García-Sifuentes, C.O.; González-Córdova, A.F.; Vallejo-Córdoba, B. Cheese Whey Fermentation by Its Native Microbiota: Proteolysis and Bioactive Peptides Release with ACE-Inhibitory Activity. Fermentation 2020, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liao, W.; Udenigwe, C.C. Revisiting the Mechanisms of ACE Inhibitory Peptides from Food Proteins. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 69, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafian, L.; Babji, A.S. Fractionation and Identification of Novel Antioxidant Peptides from Fermented Fish (Pekasam). J. Food Meas. Charact. 2018, 12, 2174–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Chen, L.; Liu, D.; Huang, J.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, X.; Lei, M.; Chen, Y.; He, H. Preparation of Antioxidant Peptides from Salmon Byproducts with Bacterial Extracellular Proteases. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Sharma, D.; Kaur, S.; Borah, A. Optimization of Flaxseed Milk Fermentation for the Production of Functional Peptides and Estimation of Their Bioactivities. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Chen, Z.; Shao, J.; Wang, C.; Zhan, C. Effect of Fermentation on the Peptide Content, Phenolics and Antioxidant Activity of Defatted Wheat Germ. Food Biosci. 2017, 20, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, A.; Voo, H. Bioactive Peptides from Food Fermentation : A Comprehensive Review of Their Sources, Bioactivities, Applications, and Future Development. 2020, 1–61. [CrossRef]
- Maffioli, E.; Jiang, Z.; Nonnis, S.; Negri, A.; Romeo, V.; Lietz, C.B.; Hook, V.; Ristagno, G.; Baselli, G.; Kistler, E.B.; et al. High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry-Based Approaches for the Detection and Quantification of Peptidase Activity in Plasma. Molecules 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchal, G.; Hati, S.; Sakure, A. Characterization and Production of Novel Antioxidative Peptides Derived from Fermented Goat Milk by L. Fermentum; Elsevier Ltd, 2020; Vol. 119; ISBN 9409669561.
- Peres, C.M.; Peres, C.; Garcia, H.S. Assessment of Multifunctional Activity of Bioactive Peptides Derived from Fermented Milk by Specific Lactobacillus Plantarum Strains. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, H.; Masujima, Y.; Ushiroda, C.; Mizushima, R.; Taira, S.; Ohue-Kitano, R.; Kimura, I. Dietary Short-Chain Fatty Acid Intake Improves the Hepatic Metabolic Condition via FFAR3. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Chen, H.; Chen, H.; Ding, W. Effects of Fermentation with Lactobacillus Rhamnosus GG on Product Quality and Fatty Acids of Goat Milk Yogurt. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, R.; Zeng, F.; Wu, L.; Wan, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, B. Fermented Carrot Juice Attenuates Type 2 Diabetes by Mediating Gut Microbiota in Rats. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 2935–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yang, S.; Sun, S.; Si, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Lactobacillus Rhamnosus Strains Relieve Loperamide-Induced Constipation via Different Pathways Independent of Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Ha, J.S.; Park, H.Y.; Lee, E. Alteration of Gut Microbiota Composition by Short-Term Low-Dose Alcohol Intake Is Restored by Fermented Rice Liquor in Mice. Food Res. Int. 2020, 128, 108800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Burillo, S.; Mehta, T.; Pastoriza, S.; Kramer, D.L.; Paliy, O.; Rufián-Henares, J.Á. Potential Probiotic Salami with Dietary Fiber Modulates Antioxidant Capacity, Short Chain Fatty Acid Production and Gut Microbiota Community Structure. Lwt 2019, 105, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhao, J. biao; Tao, S. yu; Zhou, X. jian; Pi, Y.; Gerrits, W.J.J.; Johnston, L.J.; Zhang, S. yi; Yang, H. jian; Liu, L.; et al. Effect of Dietary Fiber Fermentation on Short-Chain Fatty Acid Production and Microbial Composition in Vitro. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 4282–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, C.; Swanson, K.S.; Fahey, G.C.; Garleb, K.A. Perspective : Physiologic Importance of Short-Chain Fatty Acids from Nondigestible Carbohydrate Fermentation. 2019, 576–589.
- Erik, K.; Knudsen, B.; Lærke, H.N.; Hedemann, M.S.; Nielsen, T.S.; Ingerslev, A.K.; Søvsø, D.; Nielsen, G.; Theil, P.K.; Purup, S.; et al. Intestinal Barrier Function and Inflammation. [CrossRef]
- Salsinha, A.S.; Pimentel, L.L.; Fontes, A.L.; Gomes, A.M.; Rodríguez-Alcalá, L.M. Microbial Production of Conjugated Linoleic Acid and Conjugated Linolenic Acid Relies on a Multienzymatic System. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2018, 82, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purba, R.A.P.; Paengkoum, P.; Paengkoum, S. The Links between Supplementary Tannin Levels and Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA) Formation in Ruminants: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS One 2020, 15, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, C.E.; Kim, S.C.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Suh, H.K.; Cho, K.M.; Lee, J.H. Enhancement of Isoflavone Aglycone, Amino Acid, and CLA Contents in Fermented Soybean Yogurts Using Different Strains: Screening of Antioxidant and Digestive Enzyme Inhibition Properties. Food Chem. 2021, 340, 128199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özer, C.O.; Kılıç, B. Optimization of PH, Time, Temperature, Variety and Concentration of the Added Fatty Acid and the Initial Count of Added Lactic Acid Bacteria Strains to Improve Microbial Conjugated Linoleic Acid Production in Fermented Ground Beef. Meat Sci. 2021, 171, 108303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palachum, W.; Choorit, W.; Manurakchinakorn, S.; Chisti, Y. Guava Pulp Fermentation and Processing to a Vitamin B12-Enriched Product. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 44, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, A.; Safari, M.; Khodaiyan, F.; Gharibzahedi, S.M.T. Bioconversion Enhancement of Conjugated Linoleic Acid by Lactobacillus Plantarum Using the Culture Media Manipulation and Numerical Optimization. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 5781–5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, C.; Soto, C. Lactobacillus Plantarum as Source of Conjugated Linoleic Acid: Effect of PH, Incubation Temperature and Inulin Incorporation. J. Biochem. Technol. 2013, 5, 649–653. [Google Scholar]
- Van Nieuwenhove, C.P.; Teran, V.; Nelina, S. Conjugated Linoleic and Linolenic Acid Production by Bacteria: Development of Functional Foods. Probiotics 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
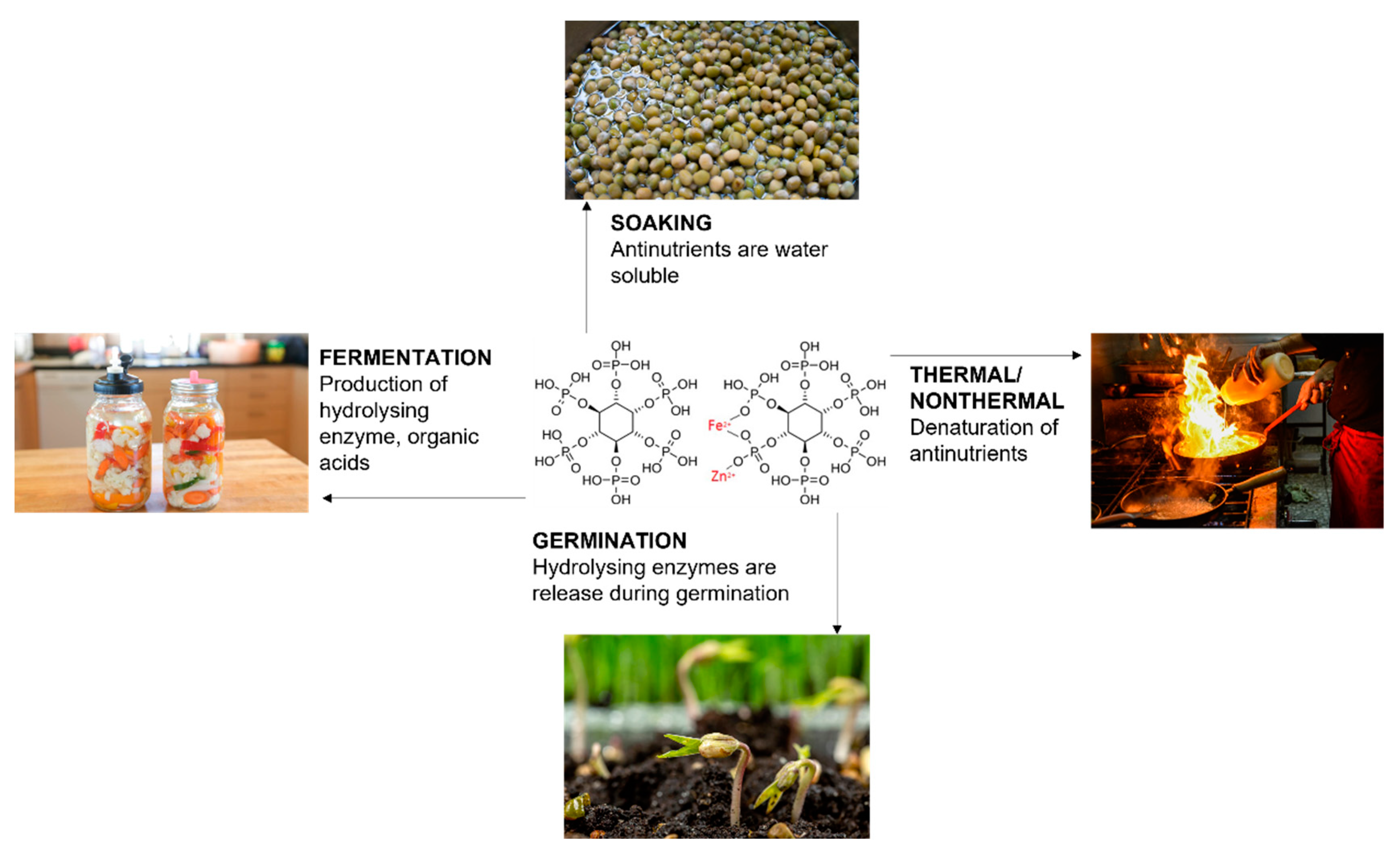
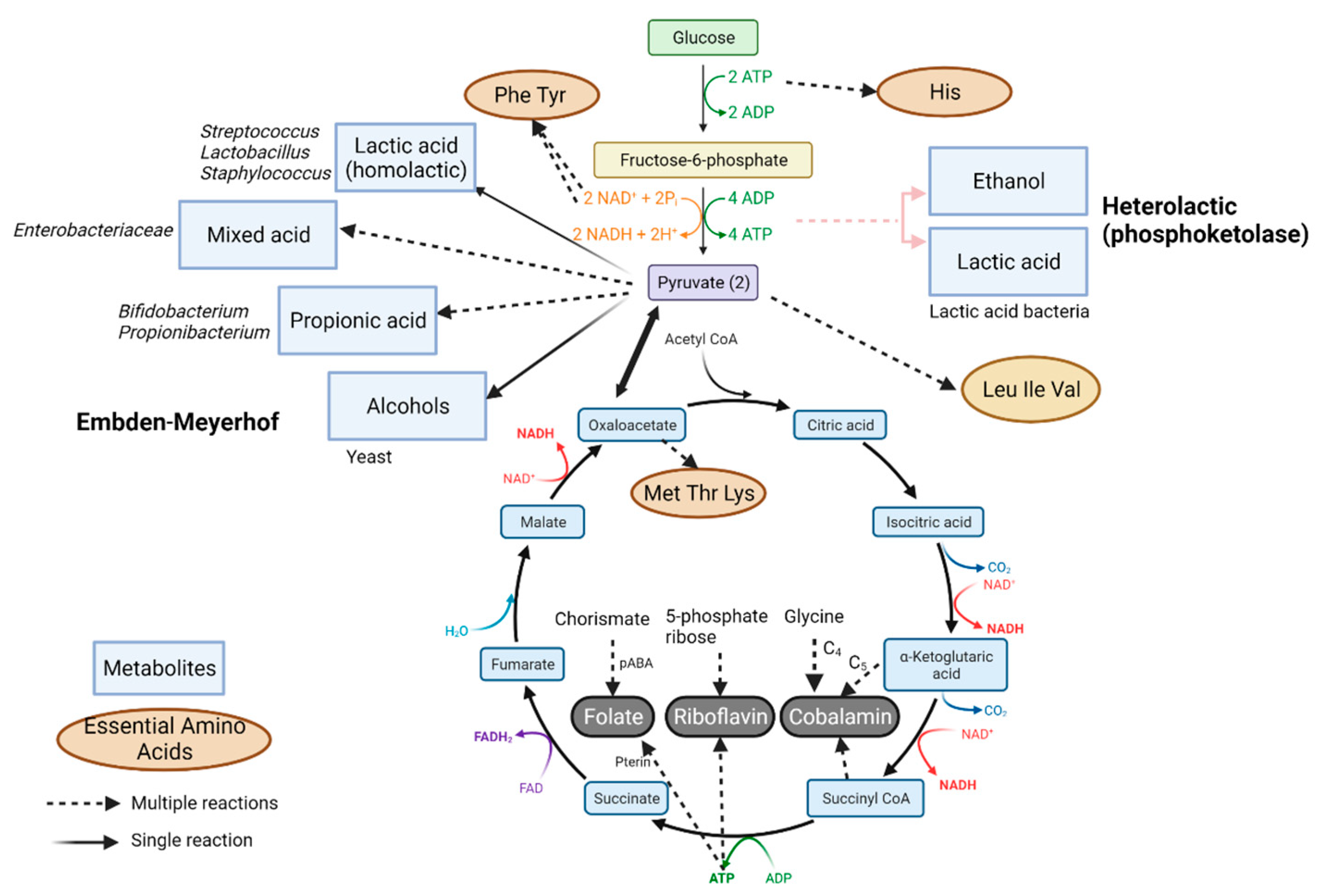
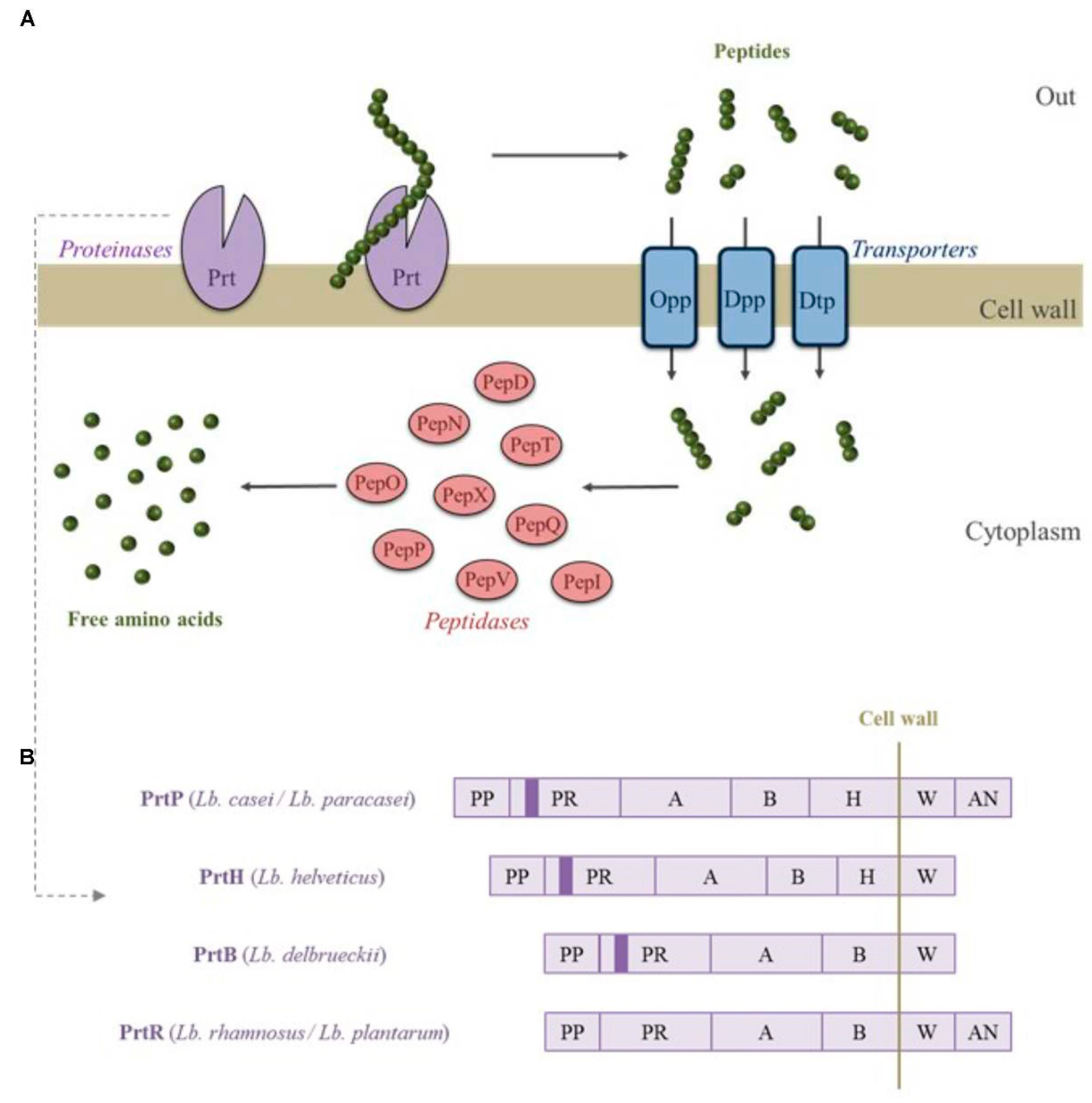
| Food item(s) | Microorganisms | Finding (s) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fructooligosaccharides (FOS) | |||
| Cashew apple juice | L. acidophilus, L. casei, L. plantarum, Leuconostoc mesenteroides, and Bifidobacterium longum | The juice contains increased vitamin B-complex and prebiotics like FOS and oligosaccharides | [37] |
| Natto | Bacillus subtilis natto CCT 7712 | The optimal conditions for FOS formation ( 98.86 g/L) were a sucrose concentration of 300 g/L, pH 7.7, and agitation at 234 rpm | [43] |
| Sugarcane syrup | None (enzymatic synthesis) | Sucrose-rich sugarcane syrup have a prebiotic effect by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria (Bifidobacterium) and the production of short-chain fatty acids | [39,40] |
| Fermented foods | Lactic acid bacteria and fungi | Inulosucrase catalyzes the biosynthesis of FOS by elongating fructan chains through the addition of fructosyl units, forming β-2,1-glycosidic bonds | [44] |
| Sugarcane Molasses | Aspergillus tubingensis XG21 | High fructofuranosidase (FFase) activity and the ability to synthesize FOS from sugarcane molasses | [45] |
| Carrot juice | A. niger | Carrot juice was utilized as a matrix for producing FOS through the use of a fructosyltransferase enzyme from A. niger | [46] |
| Galactooligosaccharides (GOS) | |||
| Whey cheese | Trichoderma sp. | The highest β-galactosidase activity at 550C | [47] |
| Wheat bran | Penicillium sp. | Highest β-galactosidase activity at the temperature 500C (1.60 IU.mL-1) | [48] |
| Yoghurt | L.bulgaricus CRL450 | Highest GOS production (41.3 %) at fermentation 450C | [49] |
| Fermented milk permeates with apple) | Pediococcus acidilactici | Highest GOS production production (26.80 mg/100mL) at fermentation 30 ◦C for 48 h | [50] |
| Skim milk | Lactobacillus | Direct transformation of lactose into GOS in skim milk Lactobacillus, and utilisation of GOS by Bifidobacterium spp. that lead to the enhanced fermentation and nutritional characteristics | [51] |
| Fermented foods (of Argentina) | Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus CRL450 | Out of 20 strains tested, 15 were able to grow on lactose and exhibited β-galactosidase activity, while 11 of them synthesized GOS | [49] |
| Yogurt | Kluyveromyces lactis (YNL-2, GODO) and Lactobacillus acidophilus La-5 | Different types of yogurts with reduced lactose content and enriched with GOS were successfully developed | [52] |
| Tejuino | Pantoea anthophila | The β-galactosidases demonstrated significant transgalactosylation activity, predominantly forming β(1 → 3) and β(1 → 6) linkages | [53] |
| Sweet whey | L. acidophilus, Streptococcus thermophilus, Bifidobacterium lactis, L. delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus and S. thermophilus | Transgalactosylation was higher in sweet whey compared to control and L. bulgaricus and S. thermophilus showed highest GOS yield | [54] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




