Submitted:
29 June 2023
Posted:
30 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
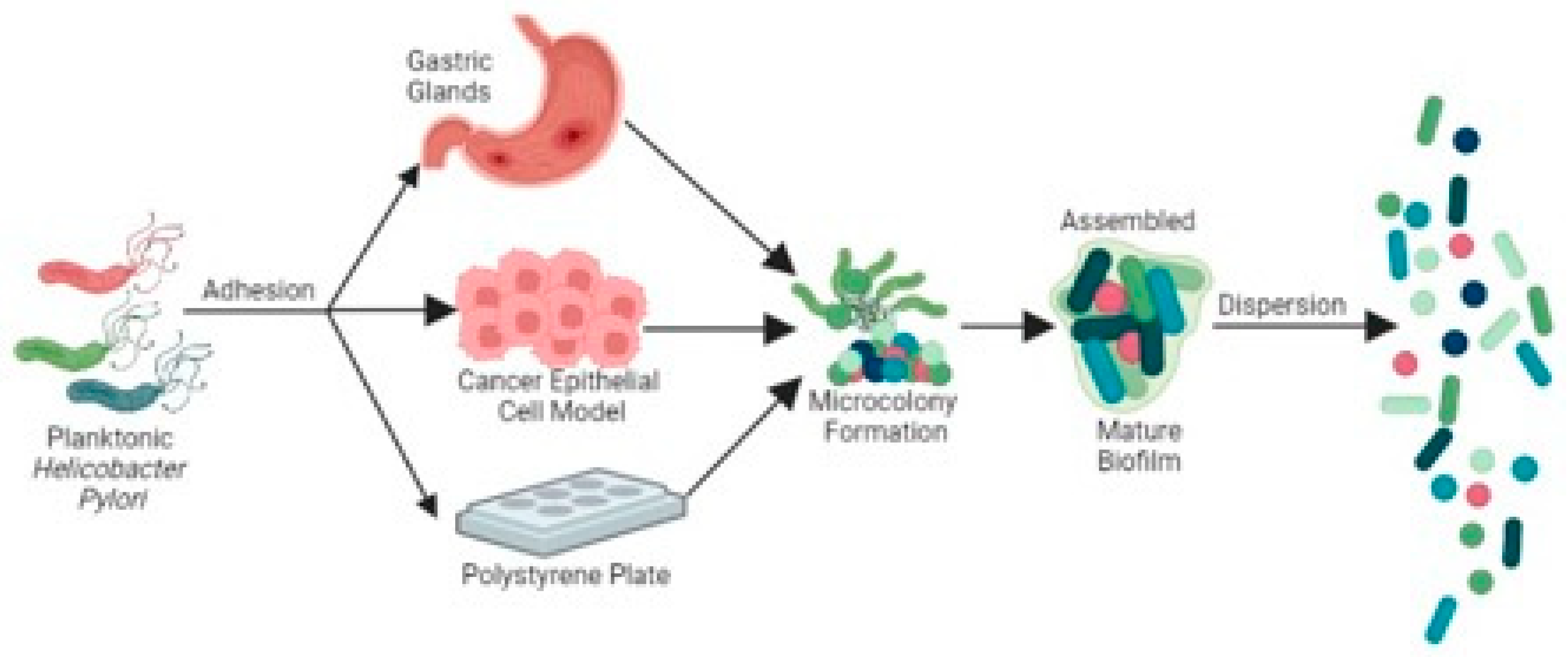
General features of H. pylori biofilms
Adherence
Assembly
Mature Phase
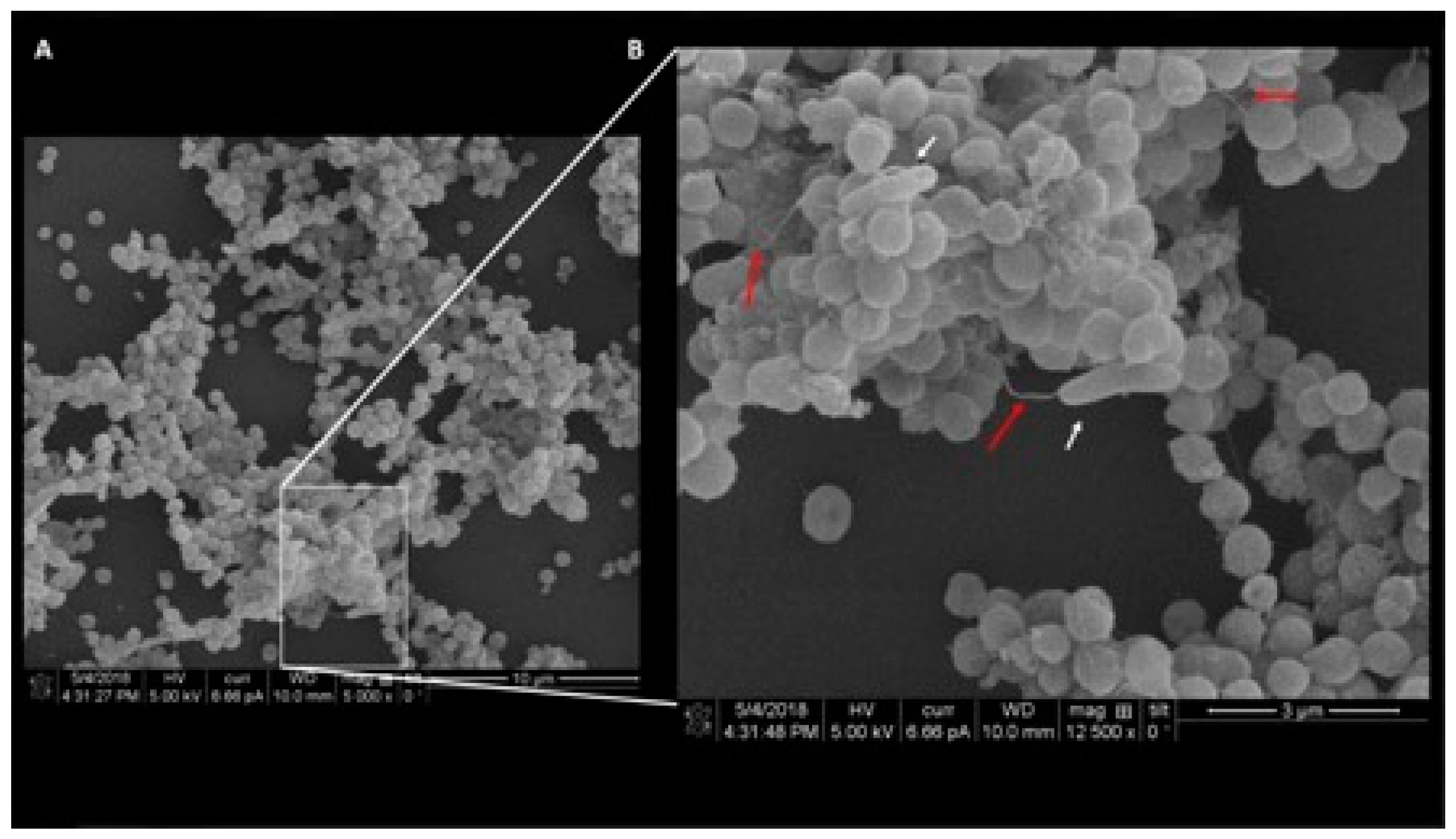
Dispersion
H. pylori clinical treatment strategies and the increasing prevalence of antibiotic resistance.
Approaches utilized in H. pylori antibiotic resistance detection and prediction.
Mechanisms of H. pylori biofilm-promoted antibiotic resistance.
Extracellular polymeric substance matrix reduces the efficacy of antibiotics
Coccoid Cellular morphology
Downregulated Metabolism in Biofilms
Efflux pumps involved drug external transportation
Anti-biofilm strategies
Antimicrobial peptides
Extracts from Natural Resources
Small Molecule Drug and Nanodrugs
Conclusion and Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cellini, L., Allocati, N., Angelucci, D., Iezzi, T., Campli, E. D., Marzio, L., & Dainelli, B. Coccoid Helicobacter pylori not culturable in vitro reverts in mice. Microbiology and immunology 1994, 38(11), 843–850.
- A Noach, L.; Rolf, T.M.; Tytgat, G.N. Electron microscopic study of association between Helicobacter pylori and gastric and duodenal mucosa. J. Clin. Pathol. 1994, 47, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, A.; Fiala, N.; Heman-Ackah, L.M.; Drazek, E.; Tarnawski, A.; Fishbein, W.N.; Perez-Perez, G.I.; Blaser, M.J. Natural gastric infection with Helicobacter pylori in monkeys: A model for spiral bacteria infection in humans. Gastroenterology 1994, 106, 1405–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malfertheiner, P., Camargo, M. C., El-Omar, E., Liou, J. M., Peek, R., Schulz, C., ... & Suerbaum, S. Helicobacter pylori infection. Nature Reviews Disease Primers 2023, 9(1), 19.
- Labenz, J.; Borsch, G. Evidence for the essential role of Helicobacter pylori in gastric ulcer disease. Gut 1994, 35, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.-I. Role ofHelicobacter pyloriin gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphomas. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 684–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaser, M.J. Helicobacter pyloriPhenotypes Associated with Peptic Ulceration. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1994, 29, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaka, M.; Kimura, T.; Kato, M.; Kudo, M.; Miki, K.; Ogoshi, K.; Kato, T.; Tatsuta, M.; Graham, D.Y. Possible role ofHelicobacter pylori infection in early gastric cancer development. Cancer 1994, 73, 2691–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldhuyzen van Zanten SJ, Sherman PM. Helicobacter pylori infection as a cause of gastritis, duodenal ulcer, gastric cancer and nonulcer dyspepsia: a systematic overview. CMAJ. PMID: 8287340; PMCID: PMC1486230. 1994, 150(2), 177–185.
- Isaacson, P.G. Gastric Lymphoma and Helicobacter pylori. New Engl. J. Med. 1994, 330, 1310–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yu, M.; Shao, Q.; Yu, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, L.; Qi, Y.; Hu, R.; Wei, P.; et al. Both family-basedHelicobacter pyloriinfection control and management strategy and screen-and-treat strategy are cost-effective for gastric cancer prevention. Helicobacter 2022, 27, e12911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, F.; Chi, W.; Ding, L.; Liu, T.; Zhu, F.; Ji, D.; Zhou, J.; Fang, Y.; et al. Antimicrobial resistance patterns and genetic elements associated with the antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori strains from Shanghai. Gut Pathog. 2022, 14, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbalaei, M.; Keikha, M.; Abadi, A.T.B. Prevalence of Primary Multidrug-resistant Helicobacter pylori in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Arch. Med Res. 2022, 53, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, H.; Cantrell, S.; Tang, H.; Epplein, M.; Garman, K.S. Racial Differences in Helicobacter pylori Prevalence in the US: A Systematic Review. Gastro Hep Adv. 2022, 1, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cellini, L.; Grande, R.; Di Campli, E.; Traini, T.; Di Giulio, M.; Lannutti, S.N.; Lattanzio, R. Dynamic colonizationof Helicobacter pyloriin human gastric mucosa. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 43, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackay, W.; Gribbon, L.; Barer, M.; Reid, D. Biofilms in drinking water systems: a possible reservoir for Helicobacter pylori. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1998, 85, 52S–59S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, R.M.; Gerwig, G.J.; Pitman, R.S.; Potts, L.F.; Williams, N.A.; Greenman, J.; Weinzweig, I.P.; Hirst, T.R.; Millar, M.R. Biofilm formation byHelicobacter pylori. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1999, 28, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carron, M.A.; Tran, V.R.; Sugawa, C.; Coticchia, J.M. Identification of Helicobacter pylori Biofilms in Human Gastric Mucosa. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2006, 10, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coticchia, J.M.; Sugawa, C.; Tran, V.R.; Gurrola, J.; Kowalski, E.; Carron, M.A. Presence and Density of Helicobacter pylori Biofilms in Human Gastric Mucosa in Patients With Peptic Ulcer Disease. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2006, 10, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windham, I.H.; Servetas, S.L.; Whitmire, J.M.; Pletzer, D.; Hancock, R.E.W.; Merrell, D.S. Helicobacter pylori Biofilm Formation Is Differentially Affected by Common Culture Conditions, and Proteins Play a Central Role in the Biofilm Matrix. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grande, R.; Di Giulio, M.; Bessa, L.; Di Campli, E.; Baffoni, M.; Guarnieri, S.; Cellini, L. Extracellular DNA in Helicobacter pylori biofilm: a backstairs rumour. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 110, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Chen, X.; Shen, Y.; Li, H.; Zou, Y.; Yuan, G.; Hu, P.; Hu, H. Mucus penetration enhanced lipid polymer nanoparticles improve the eradication rate of Helicobacter pylori biofilm. J. Control. Release 2019, 300, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, S.P.; Harwood, J.; Lee, R.; She, R.; Guiney, D.G. Characterization of Monospecies Biofilm Formation by Helicobacter pylori. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 3124–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hathroubi, S.; Hu, S.; Ottemann, K.M. Genetic requirements and transcriptomics of Helicobacter pylori biofilm formation on abiotic and biotic surfaces. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2020, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathroubi, S.; Zerebinski, J.; Ottemann, K.M. Helicobacter pylori Biofilm Involves a Multigene Stress-Biased Response, Including a Structural Role for Flagella. mBio 2018, 9, e01973–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.C.; McInnis, K.A.; Testerman, T.L. Adherence of Helicobacter pylori to Abiotic Surfaces Is Influenced by Serum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 1255–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Tompkins, L.S.; Amieva, M.R. Helicobacter pylori Usurps Cell Polarity to Turn the Cell Surface into a Replicative Niche. PLOS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.K.; Huang, J.Y.; Wreden, C.; Sweeney, E.G.; Goers, J.; Remington, S.J.; Guillemin, K. Chemorepulsion from the Quorum Signal Autoinducer-2 Promotes Helicobacter pylori Biofilm Dispersal. mBio 2015, 6, e00379–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigal, M.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Logan, C.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Honaker, R.W.; Cooper, R.L.; Passarelli, B.; Camorlinga, M.; Bouley, D.M.; Alvarez, G.; et al. Helicobacter pylori Activates and Expands Lgr5+ Stem Cells Through Direct Colonization of the Gastric Glands. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 1392–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellini, L., Grande, R., Di Campli, E., Di Bartolomeo, S., Di Giulio, M., Traini, T., & Trubiani, O. Characterization of an Helicobacter pylori environmental strain. Journal of applied microbiology 2008, 105(3), 761–769.
- Bugli, F., Palmieri, V., Torelli, R., Papi, M., De Spirito, M., Cacaci, M., ... & Sanguinetti, M. In vitro effect of clarithromycin and alginate lyase against Helicobacter pylori biofilm. Biotechnology Progress 2016, 32(6), 1584–1591.
- Azevedo, N.F.; Pinto, A.R.; Reis, N.M.; Vieira, M.J.; Keevil, C.W. Shear Stress, Temperature, and Inoculation Concentration Influence the Adhesion of Water-Stressed Helicobacter pylori to Stainless Steel 304 and Polypropylene. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 2936–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratthawongjirakul, P.; Thongkerd, V.; Chaicumpa, W. The impacts of a fliD mutation on the biofilm formation of Helicobacter pylori. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2016, 6, 1008–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessey, S.J.; Spencer, J.; I Wyatt, J.; Sobala, G.; Rathbone, B.J.; Axon, A.T.; Dixon, M.F. Bacterial adhesion and disease activity in Helicobacter associated chronic gastritis. Gut 1990, 31, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X., Baker, H., Hancock, W. S., Fawaz, F., McCaman, M., & Pungor Jr, E. Proteomic analysis for the assessment of different lots of fetal bovine serum as a raw material for cell culture. Part IV. Application of proteomics to the manufacture of biological drugs. Biotechnology progress 2006, 22(5), 1294–1300.
- Yonezawa, H.; Osaki, T.; Fukutomi, T.; Hanawa, T.; Kurata, S.; Zaman, C.; Hojo, F.; Kamiya, S. Diversification of the AlpB Outer Membrane Protein of Helicobacter pylori Affects Biofilm Formation and Cellular Adhesion. J. Bacteriol. 2017, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkovich, O.A.; Yin, J.; Ekshyyan, V.; Conant, C.; Traylor, J.; Adegboyega, P.; McGee, D.J.; Rhoads, R.E.; Slepenkov, S.; Testerman, T.L. Helicobacter pylori AlpA and AlpB Bind Host Laminin and Influence Gastric Inflammation in Gerbils. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 3106–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.W.; Kim, H.; Kim, K.H. Cell adhesion-related gene expression by Helicobacter pylori in gastric epithelial AGS cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2003, 35, 1284–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.H.J.; Ng, C.G.; Chua, E.G.; Tay, A.C.Y.; Peters, F.; Marshall, B.J.; Ho, B.; Goh, K.L.; Vadivelu, J.; Loke, M.F. Comparative Genomics Revealed Multiple Helicobacter pylori Genes Associated with Biofilm Formation In Vitro. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, e0166835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servetas, S.L.; Kim, A.; Su, H.; Cha, J.; Merrell, D.S. Comparative analysis of the Hom family of outer membrane proteins in isolates from two geographically distinct regions: The United States and South Korea. Helicobacter 2018, 23, e12461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleastro, M.; Monteiro, L.; Lehours, P.; Mégraud, F.; Ménard, A. Identification of Markers for Helicobacter pylori Strains Isolated from Children with Peptic Ulcer Disease by Suppressive Subtractive Hybridization. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 4064–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olofsson, A.; Vallström, A.; Petzold, K.; Tegtmeyer, N.; Schleucher, J.; Carlsson, S.; Haas, R.; Backert, S.; Wai, S.N.; Gröbner, G.; et al. Biochemical and functional characterization of Helicobacter pylori vesicles. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 77, 1539–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grande, R.; Di Marcantonio, M.C.; Robuffo, I.; Pompilio, A.; Celia, C.; Di Marzio, L.; Paolino, D.; Codagnone, M.; Muraro, R.; Stoodley, P.; et al. Helicobacter pylori ATCC 43629/NCTC 11639 Outer Membrane Vesicles (OMVs) from Biofilm and Planktonic Phase Associated with Extracellular DNA (eDNA). Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonezawa, H.; Osaki, T.; Kurata, S.; Fukuda, M.; Kawakami, H.; Ochiai, K.; Hanawa, T.; Kamiya, S. Outer Membrane Vesicles of Helicobacter pylori TK1402 are Involved in Biofilm Formation. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 197–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servetas, S. L. et al. ArsRS-dependent regulation of homB contributes to Helicobacter pylori biofilm formation. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 2(9), 1497.
- Oleastro, M.; Monteiro, L.; Lehours, P.; Mégraud, F.; Ménard, A. Identification of Markers for Helicobacter pylori Strains Isolated from Children with Peptic Ulcer Disease by Suppressive Subtractive Hybridization. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 4064–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadi, A.T.B.; Rafiei, A.; Ajami, A.; Hosseini, V.; Taghvaei, T.; Jones, K.R.; Merrell, D.S. Helicobacter pylori homB, but Not cagA, Is Associated with Gastric Cancer in Iran. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 3191–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zou, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, P.; Rao, Y.; Yang, X.; Sun, Y.; Hu, H. Antibacterial self-assembled nanodrugs composed of berberine derivatives and rhamnolipids against Helicobacter pylori. J. Control. Release 2020, 328, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadkhodaei, S.; Siavoshi, F.; Noghabi, K.A. Mucoid and coccoid Helicobacter pylori with fast growth and antibiotic resistance. Helicobacter 2019, 25, e12678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mortaji, Lamya, Alejandro Tejada-Arranz, Aline Rifflet, Ivo G. Boneca, Gérard Pehau-Arnaudet, J. Pablo Radicella, Stéphanie Marsin, and Hilde De Reuse. "A peptide of a type I toxin− antitoxin system induces Helicobacter pylori morphological transformation from spiral shape to coccoids". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2020, 117(49), 31398–31409.
- Krzyżek, P.; Migdał, P.; Grande, R.; Gościniak, G. Biofilm Formation of Helicobacter pylori in Both Static and Microfluidic Conditions Is Associated With Resistance to Clarithromycin. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 868905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzyżek, P.; Migdał, P.; Paluch, E.; Karwańska, M.; Wieliczko, A.; Gościniak, G. Myricetin as an Antivirulence Compound Interfering with a Morphological Transformation into Coccoid Forms and Potentiating Activity of Antibiotics against Helicobacter pylori. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cárdenas-Mondragón, M.G.; Ares, M.A.; Panunzi, L.G.; Pacheco, S.; Camorlinga-Ponce, M.; Girón, J.A.; Torres, J.; De la Cruz, M.A. Transcriptional Profiling of Type II Toxin–Antitoxin Genes of Helicobacter pylori under Different Environmental Conditions: Identification of HP0967–HP0968 System. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attaran, B.; Falsafi, T.; Kabiri, M. Biofilm Formation Capability of Clinical Helicobacter pylori Isolates on MKN-45 Cells. Jentashapir J. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rader, B.A.; Wreden, C.; Hicks, K.G.; Sweeney, E.G.; Ottemann, K.M.; Guillemin, K. Helicobacter pylori perceives the quorum-sensing molecule AI-2 as a chemorepellent via the chemoreceptor TlpB. Microbiology 2011, 157, 2445–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsyth, M.H.; Cover, T.L. Intercellular Communication in Helicobacter pylori : luxS Is Essential for the Production of an Extracellular Signaling Molecule. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 3193–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-K.; Ogura, K.; Loh, J.T.; Cover, T.L.; Berg, D.E. Quantitative Effect of luxS Gene Inactivation on the Fitness of Helicobacter pylori. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 6615–6622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.; Luo, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.C.; Huang, Y. Structural basis for lipopolysaccharide insertion in the bacterial outer membrane. Nature 2014, 511, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, A.J.F. Bacterial outer membrane constriction. Mol. Microbiol. 2018, 107, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alm, R.A.; Bina, J.; Andrews, B.M.; Doig, P.; Hancock, R.E.W.; Trust, T.J. Comparative Genomics of Helicobacter pylori : Analysis of the Outer Membrane Protein Families. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 4155–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonezawa, H.; Osaki, T.; Woo, T.; Kurata, S.; Zaman, C.; Hojo, F.; Hanawa, T.; Kato, S.; Kamiya, S. Analysis of outer membrane vesicle protein involved in biofilm formation of Helicobacter pylori. Anaerobe 2011, 17, 388–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamrakar, A.; Singh, R.; Kumar, A.; Makde, R.D.; Ashish; Kodgire, P. Biophysical characterization of the homodimers of HomA and HomB, outer membrane proteins of Helicobacter pylori. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.; Servetas, S.L.; Kang, J.; Kim, J.; Jang, S.; Choi, Y.H.; Su, H.; Jeon, Y.-E.; Hong, Y.A.; Yoo, Y.-J.; et al. Helicobacter pylori outer membrane protein, HomC, shows geographic dependent polymorphism that is influenced by the Bab family. J. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Shang, K.; Zhang, L.; Li, W.; Wang, X. A rapid anti-Helicobacter pylori biofilm drug screening biosensor based on AlpB outer membrane protein and colloidal gold/nanoporous gold framework. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 215, 114599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.Z.; Xie, Y.; Lu, H.; Cheng, H.; Zeng, Z.R.; Zhou, L.Y.; Chen, Y.; Bin Wang, J.; Du, Y.Q.; Lu, N.H.; et al. Fifth Chinese National Consensus Report on the management ofHelicobacter pyloriinfection. Helicobacter 2018, 23, e12475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miftahussurur, M.; Syam, A.F.; Nusi, I.A.; Makmun, D.; Waskito, L.A.; Zein, L.H.; Akil, F.; Uwan, W.B.; Simanjuntak, D.; Wibawa, I.D.N.; et al. Surveillance of Helicobacter pylori Antibiotic Susceptibility in Indonesia: Different Resistance Types among Regions and with Novel Genetic Mutations. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, e0166199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Megraud, F.; O’Morain, C.A.; Gisbert, J.P.; Kuipers, E.J.; Axon, A.T.; Bazzoli, F.; Gasbarrini, A.; Atherton, J.; Graham, D.Y.; et al. Management ofHelicobacter pyloriinfection—the Maastricht V/Florence Consensus Report. European Helicobacter and Microbiota Study Group and Consensus panel Gut 2017, 66, 6–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miftahussurur, M.; Shrestha, P.K.; Subsomwong, P.; Sharma, R.P.; Yamaoka, Y. Emerging Helicobacter pylori levofloxacin resistance and novel genetic mutation in Nepal. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauzia, K.A.; Miftahussurur, M.; Syam, A.F.; Waskito, L.A.; Doohan, D.; Rezkitha, Y.A.A.; Matsumoto, T.; Tuan, V.P.; Akada, J.; Yonezawa, H.; et al. Biofilm Formation and Antibiotic Resistance Phenotype of Helicobacter pylori Clinical Isolates. Toxins 2020, 12, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Shi, Z.; Lin, D.; Yang, N.; Meng, F.; Lin, L.; Jin, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. Is tailored therapy based on antibiotic susceptibility effective ? a multicenter, open-label, randomized trial. Front. Med. 2020, 14, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallone, C.A.; Chiba, N.; van Zanten, S.V.; Fischbach, L.; Gisbert, J.P.; Hunt, R.H.; Jones, N.L.; Render, C.; Leontiadis, G.I.; Moayyedi, P.; et al. The Toronto Consensus for the Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection in Adults. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 51–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Palma, G.Z.; Mendiondo, N.; Wonaga, A.; Viola, L.; Ibarra, D.; Campitelli, E.; Salim, N.; Corti, R.; Goldman, C.; Catalano, M. Occurrence of Mutations in the Antimicrobial Target Genes Related to Levofloxacin, Clarithromycin, and Amoxicillin Resistance inHelicobacter pyloriIsolates from Buenos Aires City. Microb. Drug Resist. 2017, 23, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Shen, Y.; Song, X.; Tang, X.; Hu, R.; Marshall, B.J.; Tang, H.; Benghezal, M. Need for standardization and harmonization of Helicobacter pylori antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Helicobacter 2022, 27, e12873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascellino, M.T.; Oliva, A.; De Angelis, M.; Pontone, S.; Porowska, B. Helicobacter pylori infection: antibiotic resistance and eradication rate in patients with gastritis showing previous treatment failures. new Microbiol. 2018, 41, 306–309. [Google Scholar]
- Redondo, J.J.; Keller, P.M.; Zbinden, R.; Wagner, K. A novel RT-PCR for the detection of Helicobacter pylori and identification of clarithromycin resistance mediated by mutations in the 23S rRNA gene. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 90, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Sun Min, Nayoung Kim, Yong Hwan Kwon, Ryoung Hee Nam, Jung Mogg Kim, Jong Youn Park, Yeon Suk Lee, and Dong Ho Lee. "rdxA, frxA, and efflux pump in metronidazole-resistant Helicobacter pylori: their relation to clinical outcomes". Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2018, 33(3), 681–688. [CrossRef]
- Hanafi, A.; Lee, W.C.; Loke, M.F.; Teh, X.; Shaari, A.; Dinarvand, M.; Lehours, P.; Mégraud, F.; Leow, A.H.R.; Vadivelu, J.; et al. Molecular and Proteomic Analysis of Levofloxacin and Metronidazole Resistant Helicobacter pylori. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attaran, Bahareh, and Tahereh Falsafi. "Identification of factors associated with biofilm formation ability in the clinical isolates of Helicobacter pylori". Iranian Journal of Biotechnology 2017, 15(1), 58. [CrossRef]
- Attaran, Bahareh, Tahereh Falsafi, and Nassim Ghorbanmehr. "Effect of biofilm formation by clinical isolates of Helicobacter pylori on the efflux-mediated resistance to commonly used antibiotics". World Journal of Gastroenterology 2017, 23(7), 1163. [CrossRef]
- Midolo, P.D.; Bell, J.M.; Lambert, J.R.; Turnidge, J.D.; Grayson, M.L. Antimicrobial resistance testing of Helicobacter pylori: A comparison of etest and disk diffusion methods. Pathology 1997, 29, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glupczynski, Y. O. U. R. I., Max Labbe, Willy Hansen, Françoise Crokaert, and Eugène Yourassowsky. "Evaluation of the E test for quantitative antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Helicobacter pylori". Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1991, 29(9), 2072–2075. [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Shen, Y.; Hu, R.; Yang, T.; Benghezal, M.; Li, H.; Tang, H. Re-assessment of the disk diffusion technique for routine antimicrobial susceptibility testing for Helicobacter pylori. Helicobacter 2020, 25, e12703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, K.K.; Srivastava, S.; Garg, A.; Ayyagari, A. Antibiotic Susceptibility of Helicobacter pylori Clinical Isolates: Comparative Evaluation of Disk-Diffusion and E-Test Methods. Curr. Microbiol. 2006, 53, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauzia, Kartika Afrida, Hafeza Aftab, Muhammad Miftahussurur, Langgeng Agung Waskito, Vo Phuoc Tuan, Takashi Matsumoto, Michiyuki Yurugi et al. "Genetic Determinants of Biofilm Formation and Antibiotic Resistance of Helicobacter Pylori using Whole Genome Sequencing." (2021). [CrossRef]
- Saruuljavkhlan, B.; Yamaoka, Y. Benefits of a Molecular-Based Method for the Detection of Clarithromycin-Resistant Helicobacter pylori. Gut Liver 2021, 15, 487–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tshibangu-Kabamba, E.; de Jesus Ngoma-Kisoko, P.; Tuan, V.P.; Matsumoto, T.; Akada, J.; Kido, Y.; Tshimpi-Wola, A.; Tshiamala-Kashala, P.; Ahuka-Mundeke, S.; Ngoyi, D.M.; et al. Next-Generation Sequencing of the Whole Bacterial Genome for Tracking Molecular Insight into the Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Resistance of Helicobacter pylori Clinical Isolates from the Democratic Republic of Congo. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.; Fowora, M.; Pellicano, R. Infections with Helicobacter pylori and challenges encountered in Africa. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 3183–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mégraud, F.; Lehours, P. Helicobacter pylori Detection and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 280–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Doorn, L.-J.; Glupczynski, Y.; Kusters, J.G.; Mégraud, F.; Midolo, P.; Maggi-Solcà, N.; Queiroz, D.M.M.; Nouhan, N.; Stet, E.; Quint, W.G.V. Accurate Prediction of Macrolide Resistance in Helicobacter pylori by a PCR Line Probe Assay for Detection of Mutations in the 23S rRNA Gene: Multicenter Validation Study. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 1500–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schabereiter-Gurtner, C.; Hirschl, A.M.; Dragosics, B.; Hufnagl, P.; Puz, S.; Kovách, Z.; Rotter, M.; Makristathis, A. Novel Real-Time PCR Assay for Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection and Simultaneous Clarithromycin Susceptibility Testing of Stool and Biopsy Specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 4512–4518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitui, M.; Patel, A.; Leos, N.K.; Doern, C.D.; Park, J.Y. Novel Helicobacter pylori Sequencing Test Identifies High Rate of Clarithromycin Resistance. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 59, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, T.; Suzuki, H. Mechanisms of Helicobacter pylori antibiotic resistance and molecular testing. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2014, 1, 19–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vital, J.S.; Tanoeiro, L.; Lopes-Oliveira, R.; Vale, F.F. Biomarker Characterization and Prediction of Virulence and Antibiotic Resistance from Helicobacter pylori Next Generation Sequencing Data. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Her, H.-L.; Wu, Y.-W. A pan-genome-based machine learning approach for predicting antimicrobial resistance activities of the Escherichia coli strains. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i89–i95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tshibangu-Kabamba, E.; Yamaoka, Y. Helicobacter pylori infection and antibiotic resistance — from biology to clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 613–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chen, X.; Shen, Y.; Li, H.; Zou, Y.; Yuan, G.; Hu, P.; Hu, H. Mucus penetration enhanced lipid polymer nanoparticles improve the eradication rate of Helicobacter pylori biofilm. J. Control. Release 2019, 300, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reshetnyak, V.I.; Reshetnyak, T.M. Significance of dormant forms ofHelicobacter pyloriin ulcerogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 4867–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, A.G.; Hazell, S.L.; Netting, A.G. Use of digoxigenin-labelled ampicillin in the identification of penicillin-binding proteins in Helicobacter pylori. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2000, 45, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, F.; Yokota, Y.; Mine, Y.; Tatsuta, M. Activity of cefixime against Helicobacter pylori and affinities for the penicillin-binding proteins. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1990, 34, 2426–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, K.; Bacher, G.; Allmaier, G.; Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Engstrand, L.; Falk, P.; de Pedro, M.A.; Portillo, F.G.-D. The Morphological Transition of Helicobacter pylori Cells from Spiral to Coccoid Is Preceded by a Substantial Modification of the Cell Wall. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 3710–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-J.; Guo, R.-T.; Lu, I.-L.; Liu, H.-G.; Wu, S.-Y.; Ko, T.-P.; Wang, A.H.-J.; Liang, P.-H. Crystal Structures and Computer Screened Inhibitors of Helicobacter pylori Undecaprenyl Pyrophosphate Synthase. 2007; 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modak, Joyanta K., Alexandra Tikhomirova, Rebecca J. Gorrell, Mohammad M. Rahman, Despina Kotsanas, Tony M. Korman, Jose Garcia-Bustos et al. "Anti-Helicobacter pylori activity of ethoxzolamide". Journal of enzyme inhibition and medicinal chemistry 2019, 34(1), 1660–1667.
- Rahman, M.M.; Tikhomirova, A.; Modak, J.K.; Hutton, M.L.; Supuran, C.T.; Roujeinikova, A. Antibacterial activity of ethoxzolamide against Helicobacter pylori strains SS1 and 26695. Gut Pathog. 2020, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Maier, S.E.; Lo, L.F.; Maier, G.; Dosi, S.; Maier, R.J. Peptidoglycan Deacetylation in Helicobacter pylori Contributes to Bacterial Survival by Mitigating Host Immune Responses. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 4660–4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y., Cai, Y., Chen, Z., Li, H., Xu, Z., Li, W.,... & Sun, Y. SpoT-mediated NapA upregulation promotes oxidative stress-induced Helicobacter pylori biofilm formation and confers multidrug resistance. Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy 2021, 65(5), e00152-21.
- Wang, G.; Lo, L.F.; Forsberg, L.S.; Maier, R.J. Helicobacter pylori Peptidoglycan Modifications Confer Lysozyme Resistance and Contribute to Survival in the Host. mBio 2012, 3, e00409–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, Feng-Pai, Chia-Tse Tsai, Ya-Sheng Chiou, Yi-Ju Chen, Meng-Erh Li, Ting-Wei Guo, Jason WenJay Lyu, Sheng-Hao Chou, and Tung-Kung Wu. "An enzymatic approach to configurationally rare trans-androsteronyl-α-glucoside and Its potential anticancer application". Chemical Biology & Drug Design 2017, 89(1), 61–66.
- Qaria, M. A., Kumar, N., Hussain, A., Qumar, S., Doddam, S. N., Sepe, L. P., & Ahmed, N. Roles of cholesteryl-α-glucoside transferase and cholesteryl glucosides in maintenance of Helicobacter pylori morphology, cell wall integrity, and resistance to antibiotics. MBio 2018, 9(6), e01523-18.
- Marcus EA et al. The effects of varying acidity on Helicobacter pylori growth and bactericidal efficacy of ampicillin. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2012, 36, 972. [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.H.J.; Ng, C.G.; Goh, K.L.; Vadivelu, J.; Ho, B.; Loke, M.F. Metabolomic analysis of low and high biofilm-forming Helicobacter pylori strains. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njume, C.; Afolayan, A.J.; Samie, A.; Ndip, R.N. Inhibitory and Bactericidal Potential of Crude Acetone Extracts of Combretum molle (Combretaceae) on Drug-resistant Strains of Helicobacter pylori. J. Heal. Popul. Nutr. 2011, 29, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, J.T.; Gupta, S.S.; Friedman, D.B.; Krezel, A.M.; Cover, T.L. Analysis of Protein Expression Regulated by the Helicobacter pylori ArsRS Two-Component Signal Transduction System. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 2034–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.G.; Bate, M.Y.; Tramonte, L.M.; Avalos, E.Y.; Loh, J.; Cover, T.L.; Forsyth, M.H. Regulation of Helicobacter pylori Urease and Acetone Carboxylase Genes by Nitric Oxide and the CrdRS Two-Component System. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0463322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmachary, P.; Wang, G.; Benoit, S.L.; Weinberg, M.V.; Maier, R.J.; Hoover, T.R. The human gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori has a potential acetone carboxylase that enhances its ability to colonize mice. BMC Microbiol. 2008, 8, 14–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Cruz, M.A.; Ares, M.; Von Bargen, K.; Panunzi, L.G.; Martínez-Cruz, J.; Valdez-Salazar, H.-A.; Jiménez-Galicia, C.; Torres, J. Gene Expression Profiling of Transcription Factors of Helicobacter pylori under Different Environmental Conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servetas, S.L.; Carpenter, B.M.; Haley, K.P.; Gilbreath, J.J.; Gaddy, J.A.; Merrell, D.S. Characterization of Key Helicobacter pylori Regulators Identifies a Role for ArsRS in Biofilm Formation. J. Bacteriol. 2016, 198, 2536–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, D.S.; Kesavan, D.K.; Muthusamy, N.; Umamaheswari, S. Efflux pumps potential drug targets to circumvent drug Resistance – Multi drug efflux pumps of Helicobacter pylori. Mater. Today: Proc. 2021, 45, 2976–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonezawa, H.; Osaki, T.; Hojo, F.; Kamiya, S. Effect of Helicobacter pylori biofilm formation on susceptibility to amoxicillin, metronidazole and clarithromycin. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 132, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.; Cai, Y.; Chen, Z.; Gao, S.; Geng, X.; Li, Y.; Jia, J.; Sun, Y. Bifunctional Enzyme SpoT Is Involved in Biofilm Formation of Helicobacter pylori with Multidrug Resistance by Upregulating Efflux Pump Hp1174 ( gluP ). Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e00957–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y., Wang, C., Chen, Z., Xu, Z., Li, H., Li, W., & Sun, Y. Transporters HP0939, HP0497, and HP0471 participate in intrinsic multidrug resistance and biofilm formation in Helicobacter pylori by enhancing drug efflux. Helicobacter 2020, 25(4), e12715.
- Hathroubi, S.; Zerebinski, J.; Clarke, A.; Ottemann, K.M. Helicobacter Pylori Biofilm Confers Antibiotic Tolerance in Part via A Protein-Dependent Mechanism. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolaiya, Tolulope Funbi, Muinah Adenike Fowora, Charles Onyekwere, Rose Ugiagbe, Ifeanyi Ifeoma Agbo, Olufunmilayo Lesi, Dennis Amojuayi Ndububa et al. "Gastroenterology and Hepatology Research". Journal of GHR 2020, 9(4), 3283–3289.
- Jiang, M.; Ma, L.; Huang, Y.; Wu, H.; Dou, J.; Zhou, C. Antimicrobial activities of peptide Cbf-K16 against drug-resistant Helicobacter pylori infection in vitro and in vivo. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 138, 103847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.-L.; Jiang, A.-M.; Ma, Z.-Y.; Li, X.-B.; Xiong, Y.-Y.; Dou, J.-F.; Wang, J.-F. The Synthetic Antimicrobial Peptide Pexiganan and Its Nanoparticles (PNPs) Exhibit the Anti-Helicobacter pylori Activity in Vitro and in Vivo. Molecules 2015, 20, 3972–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parreira, P.; Monteiro, C.; Graça, V.; Gomes, J.; Maia, S.; Gomes, P.; Gonçalves, I.C.; Martins, M.C.L. Surface Grafted MSI-78A Antimicrobial Peptide has High Potential for Gastric Infection Management. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Fuente-Núñez, C.; Reffuveille, F.; Mansour, S.C.; Reckseidler-Zenteno, S.L.; Hernández, D.; Brackman, G.; Coenye, T.; Hancock, R.E. D-Enantiomeric Peptides that Eradicate Wild-Type and Multidrug-Resistant Biofilms and Protect against Lethal Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections. Chem. Biol. 2015, 22, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, S.C.; de la Fuente-Núñez, C.; Hancock, R.E.W. Peptide IDR-1018: modulating the immune system and targeting bacterial biofilms to treat antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections. J. Pept. Sci. 2014, 21, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, D.H.; Gaynor, E.C. Helicobacter pylori Initiates the Stringent Response upon Nutrient and pH Downshift. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 3726–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Yang, H. In Vitro Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum LN66 and Antibiotics Used Alone or in Combination on Helicobacter pylori Mature Biofilm. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas-Jara, M.J.; Sanhueza, E.A.; Retamal-Díaz, A.; González, C.; Urrutia, H.; García, A. Probiotic Lactobacillus fermentum UCO-979C biofilm formation on AGS and Caco-2 cells and Helicobacter pylori inhibition. Biofouling 2016, 32, 1245–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Yang, H. Effects of Lactobacillus salivarius LN12 in Combination with Amoxicillin and Clarithromycin on Helicobacter pylori Biofilm In Vitro. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, C.; Wink, J.; Kurz, M.; Kogler, H.; Olivan, H.; Sablé, S.; Heyse, W.; Gerlitz, M.; Toti, L.; Nußer, A.; et al. Isolation and Structural Elucidation of Armeniaspirols A-C: Potent Antibiotics against Gram-Positive Pathogens. Chem. – A Eur. J. 2012, 18, 16123–16128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J., Zhang, C., Liu, Y., Huang, Y., Bai, Y., Hang, X.,... & Bi, H. Armeniaspirol A: a novel anti-Helicobacter pylori agent. Microbial biotechnology 2022, 15(2), 442–454.
- Yu, M.; Wang, X.; Ling, F.; Wang, H.; Zhang, P.; Shao, S. Atractylodes lancea volatile oils attenuated helicobacter pylori NCTC11637 growth and biofilm. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 135, 103641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wylie, M.R.; Windham, I.H.; Blum, F.C.; Wu, H.; Merrell, D.S. In vitro antibacterial activity of nimbolide against Helicobacter pylori. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 285, 114828–114828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.; Devi, A.T.; Prasad, M.N.N.; Zameer, F.; Shruthi, G.; Shivamallu, C. Phyto anti-biofilm elicitors as potential inhibitors ofHelicobacter pylori. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, P.; Huang, Y.; Hang, X.; Tong, Q.; Zeng, L.; Jia, J.; Zhang, G.; Bi, H. Dihydrotanshinone I Is Effective against Drug-Resistant Helicobacter pylori In Vitro and In Vivo. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran Trung, H.; Truong Thi Huynh, H.; Nguyen Thi Thuy, L.; Nguyen Van Minh, H.; Thi Nguyen, M.N.; Luong Thi, M.N. Growth-Inhibiting, Bactericidal, Antibiofilm, and Urease Inhibitory Activities of Hibiscus rosa sinensis L. Flower Constituents toward Antibiotic Sensitive- and Resistant-Strains of Helicobacter pylori. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 20080–20089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, R.; Carradori, S.; Puca, V.; Vitale, I.; Angeli, A.; Nocentini, A.; Bonardi, A.; Gratteri, P.; Lanuti, P.; Bologna, G.; et al. Selective Inhibition of Helicobacter pylori Carbonic Anhydrases by Carvacrol and Thymol Could Impair Biofilm Production and the Release of Outer Membrane Vesicles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, V.; Masanam, E.; Ramkumar, V.S.; Baskaraligam, V.; Selvaraj, G. Influence of N -acylhomoserine lactonase silver nanoparticles on the quorum sensing system of Helicobacter pylori : A potential strategy to combat biofilm formation. J. Basic Microbiol. 2020, 60, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande R, Sisto F, Puca V, et al. Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities of new synthesized silver Ultra-NanoClusters (SUNCs) against helicobacter pylori. Front Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1705. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, R.; Dai, Y.; Qin, C.; He, J.; Yang, S.; Wang, T.; Su, Y.; Jia, L.; Zhao, W. Rhamnolipid-assisted black phosphorus nanosheets with efficient isolinderalactone loading against drug resistant Helicobacter pylori. Mater. Des. 2022, 216, 110536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.; Ahmad, R.; Sharaf, M.; Samreen; Muhammad, J. ; Abdalla, M.; Eltayb, W.A.; Liu, C.-G. Antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of mannose-modified chitosan/PMLA nanoparticles against multidrug-resistant Helicobacter pylori. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 223, 418–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parreira, P.; Monteiro, C.; Graça, V.; Gomes, J.; Maia, S.; Gomes, P.; Gonçalves, I.C.; Martins, M.C.L. Surface Grafted MSI-78A Antimicrobial Peptide has High Potential for Gastric Infection Management. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




