Submitted:
30 June 2023
Posted:
30 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
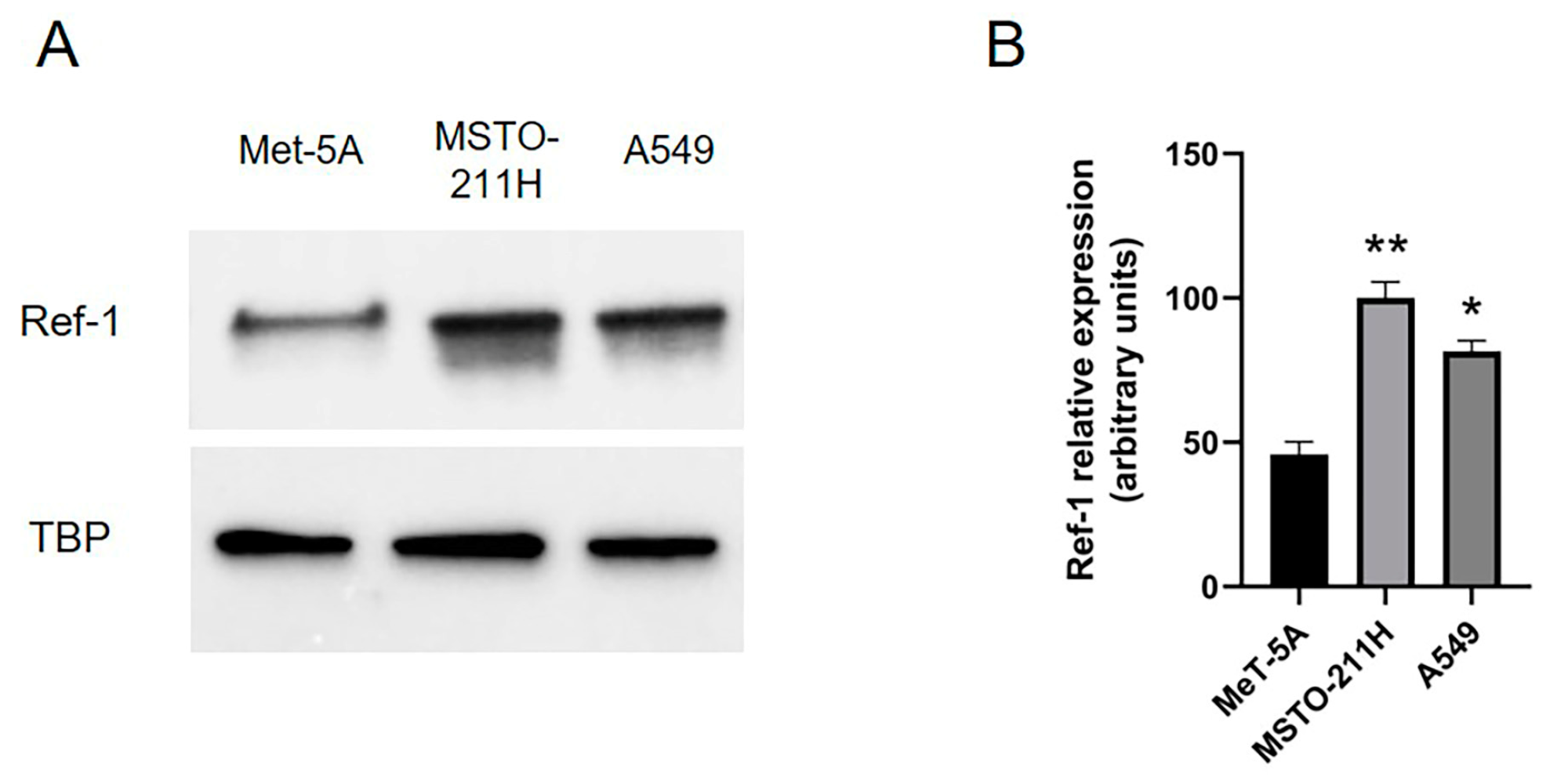
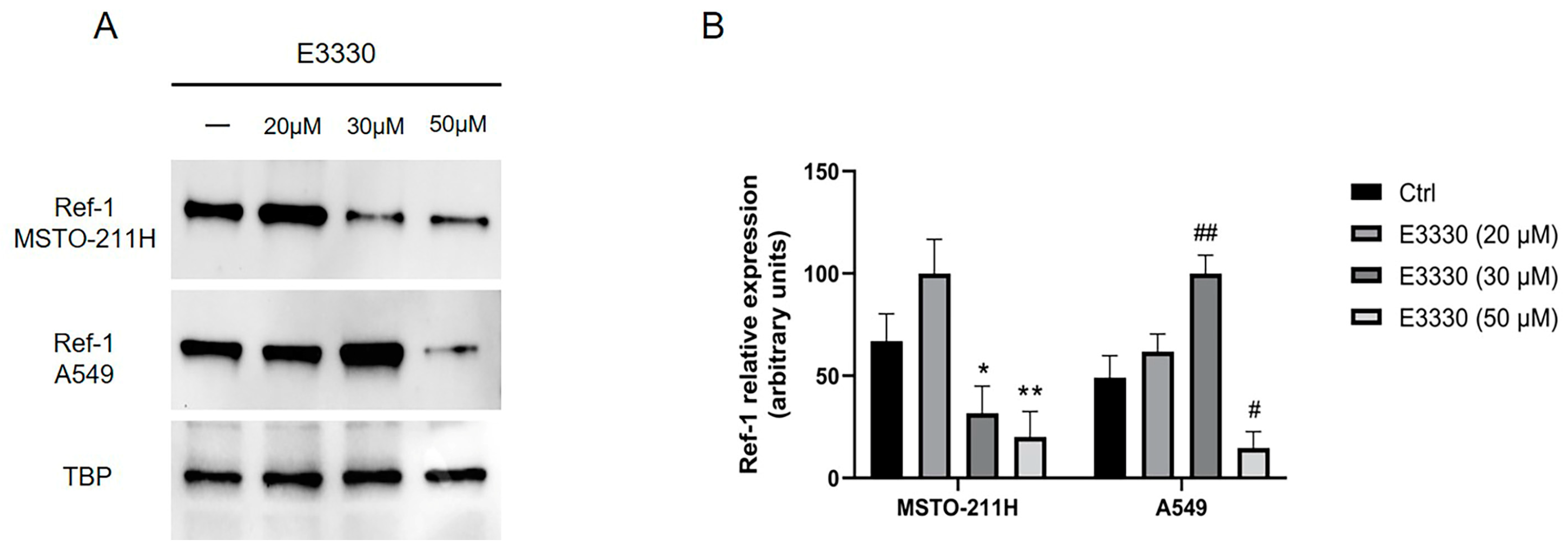
2.1. Overexpressed Ref-1 in MPM cells is downregulated after co-incubation with E3330 specific Ref-1 inhibitor.
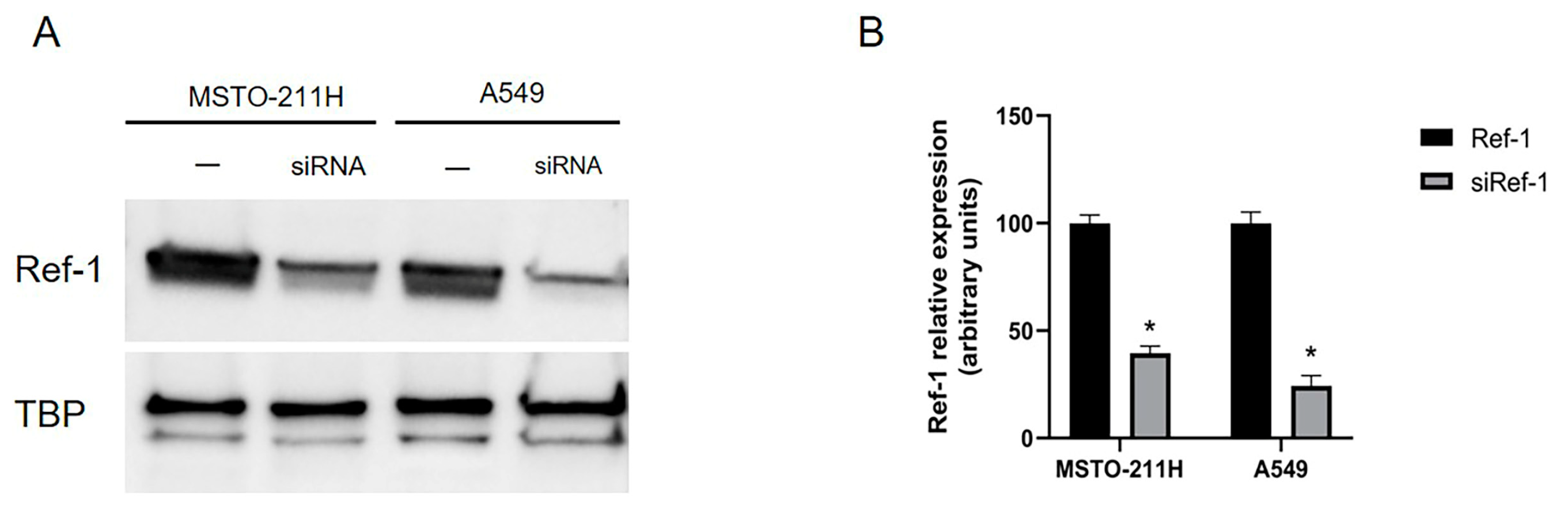
2.2. Overexpressed Ref-1 in MPM and A549 cells is downregulated after siRNA transfection.
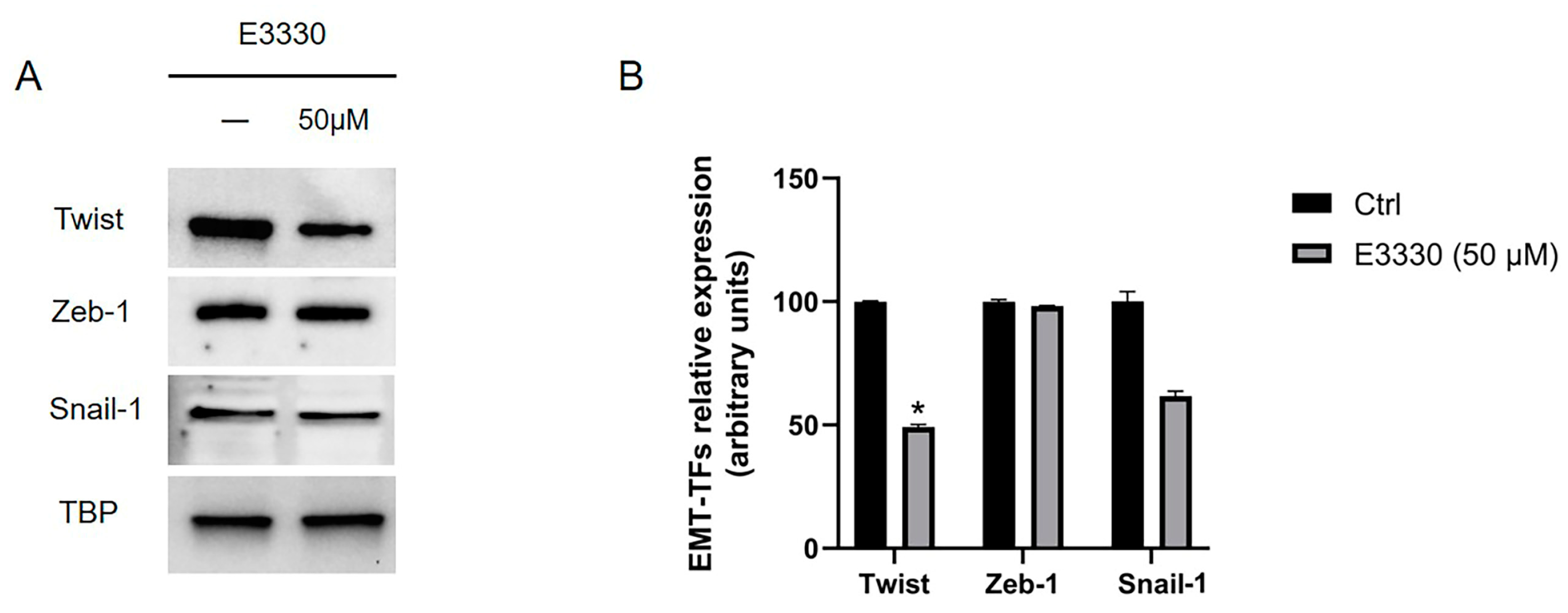
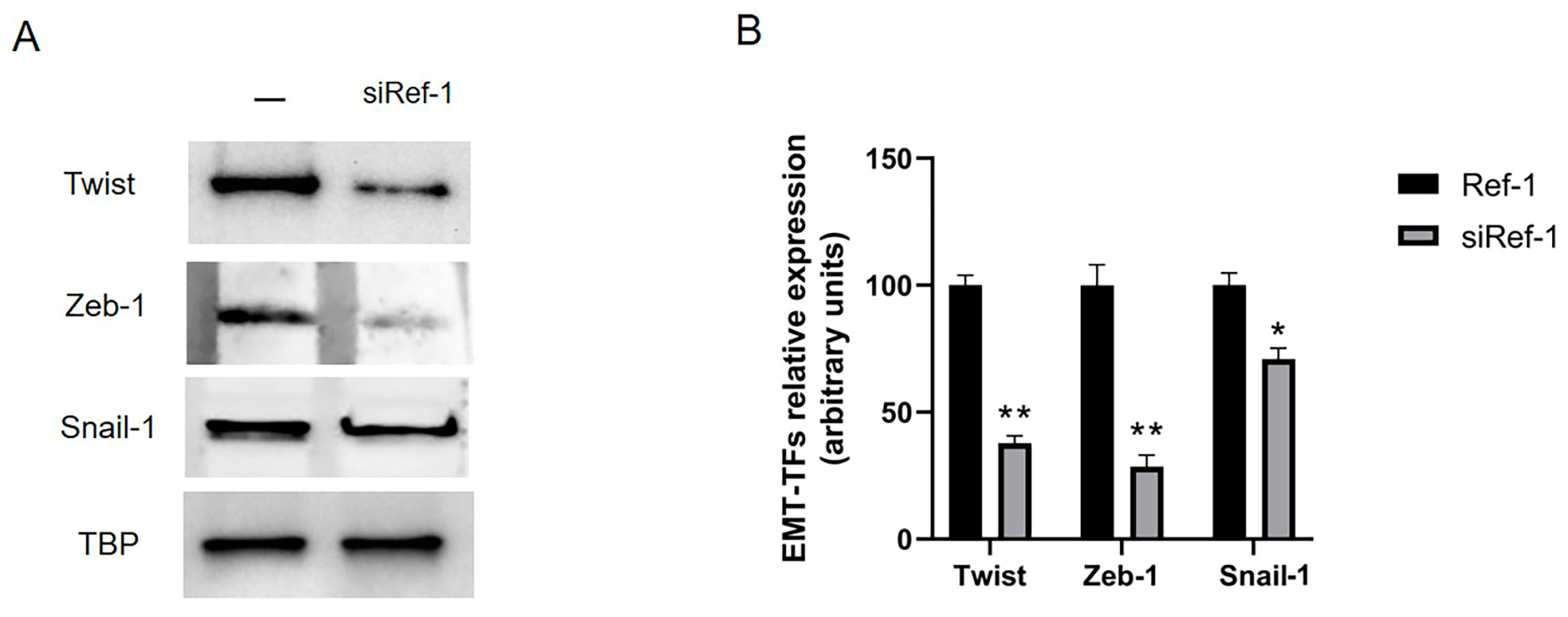
2.3. Overexpressed EMT-TFs in MPM are downregulated after both co-incubation with E3330 specific Ref-1 inhibitor and siRNA Ref-1.
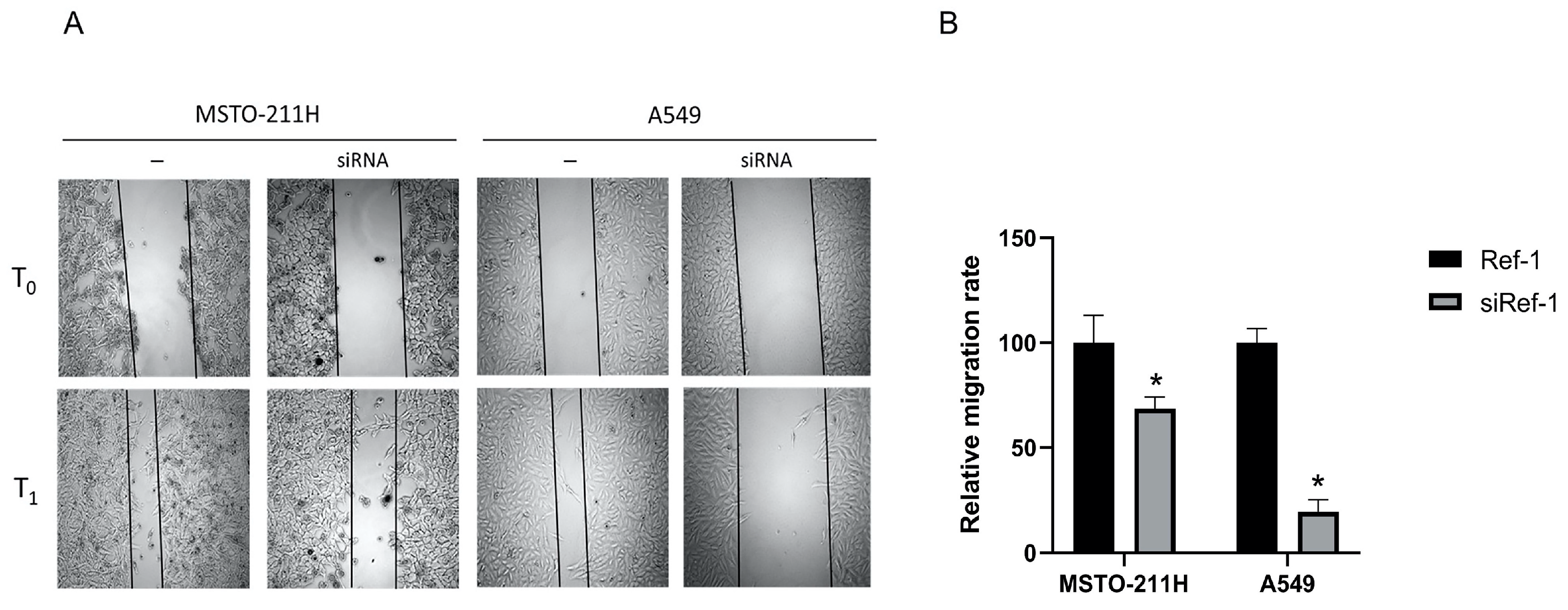
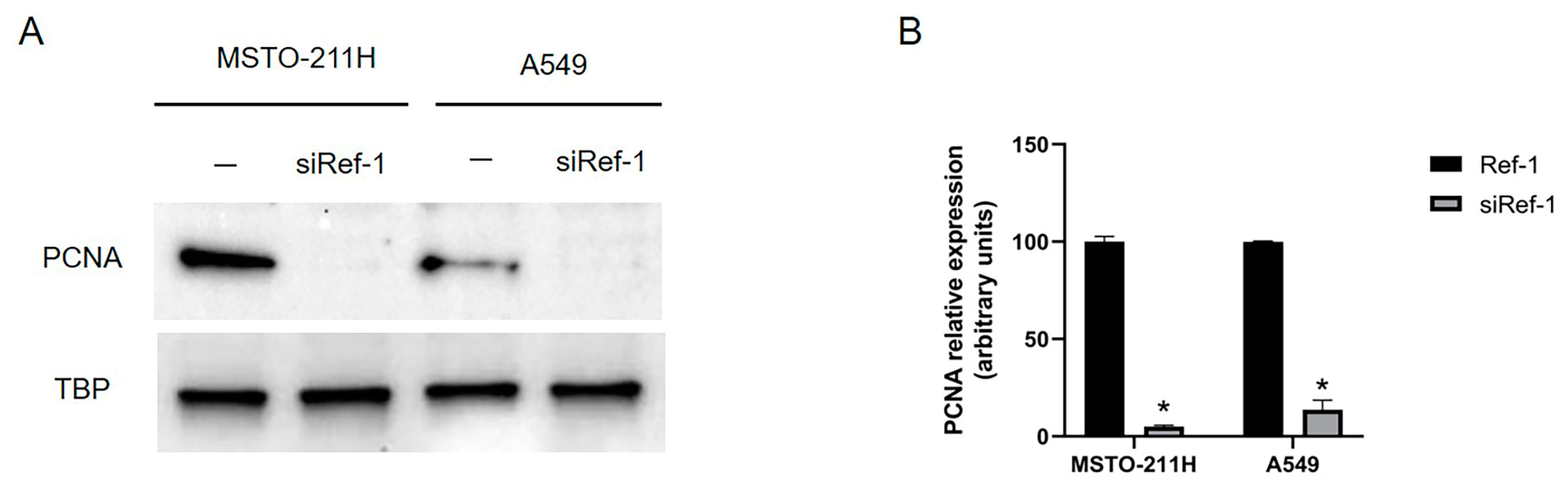
2.4. Effect of Ref-1 inhibition/knockdown on cellular proliferation.
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell cultures
4.2. E3330 Ref-1 inhibitor
4.3. siRNA Ref-1
4.4. Nuclear protein extraction
4.5. Western blot Analysis
4.6. Migration assay
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nicolini, F.; Bocchini, M.; Bronte, G.; Delmonte, A.; Guidoboni, M.; Crinò, L.; Mazza, M. Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: State-of-the-Art on Current Therapies and Promises for the Future. Frontiers in Oncology 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brcic, L.; Kern, I. Clinical Significance of Histologic Subtyping of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Transl Lung Cancer Res 2020, 9, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibby, A.C.; Tsim, S.; Kanellakis, N.; Ball, H.; Talbot, D.C.; Blyth, K.G.; Maskell, N.A.; Psallidas, I. Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: An Update on Investigation, Diagnosis and Treatment. Eur Respir Rev 2016, 25, 472–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamp, D.W. Asbestos-Induced Lung Diseases: An Update. Translational Research 2009, 153, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramundo, V.; Zanirato, G.; Aldieri, E. The Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in the Development and Metastasis of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. IJMS 2021, 22, 12216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, S.H.; Toyokuni, S. Malignant Mesothelioma as an Oxidative Stress-Induced Cancer: An Update. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 2015, 86, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffer, C.L.; San Juan, B.P.; Lim, E.; Weinberg, R.A. EMT, Cell Plasticity and Metastasis. Cancer and Metastasis Reviews 2016, 35, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongre, A.; Weinberg, R.A. New Insights into the Mechanisms of Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Implications for Cancer. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 2019, 20, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannito, S.; Novo, E.; di Bonzo, L.V.; Busletta, C.; Colombatto, S.; Parola, M. Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition: From Molecular Mechanisms, Redox Regulation to Implications in Human Health and Disease. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling 2010, 12, 1383–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; He, J. Epithelial mesenchymal transition and lung cancer. J Thorac Dis 2010, 2, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legras, A.; Pécuchet, N.; Imbeaud, S.; Pallier, K.; Didelot, A.; Roussel, H.; Gibault, L.; Fabre, E.; Le Pimpec-Barthes, F.; Laurent-Puig, P.; et al. Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and MicroRNAs in Lung Cancer. Cancers 2017, 9, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, M.Q.; Ward, C.; Muller, H.K.; Sohal, S.S.; Walters, E.H. Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) and Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): A Mutual Association with Airway Disease. Medical Oncology 2017, 34, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramm, A.; Opitz, I.; Thies, S.; Seifert, B.; Moch, H.; Weder, W.; Soltermann, A. Prognostic Significance of Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery 2010, 37, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Amjad, S.; Yun, H.; Mani, S.; de Perrot, M. A Panel of Emerging EMT Genes Identified in Malignant Mesothelioma. Scientific Reports 2022, 12, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turini, S.; Bergandi, L.; Gazzano, E.; Prato, M.; Aldieri, E. Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Human Mesothelial Cells Exposed to Asbestos Fibers: Role of TGF-β as Mediator of Malignant Mesothelioma Development or Metastasis via EMT Event. IJMS 2019, 20, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanami, T.; Uramoto, H.; Nakagawa, M.; Shimokawa, H.; Yamada, S.; Kohno, K.; Tanaka, F. Clinical Significance of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition-Associated Markers in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Oncology 2014, 86, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.-Y.; Zeng, Y.; Lei, Z.; Wang, L.; Yang, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.-T. JAK/STAT3 Signaling Is Required for TGF-β-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Lung Cancer Cells. Int J Oncol 2014, 44, 1643–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bao, J.; Hao, J.; Peng, Y.; Hong, F. HSP70 Inhibits High Glucose-Induced Smad3 Activation and Attenuates Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition of Peritoneal Mesothelial Cells. Mol Med Rep 2014, 10, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hydrogen Peroxide Promotes Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition and Stemness in Human Malignant Mesothelioma Cells. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention 2013, 14, 3625–3630. [CrossRef]
- Gorowiec, M.R.; Borthwick, L.A.; Parker, S.M.; Kirby, J.A.; Saretzki, G.C.; Fisher, A.J. Free Radical Generation Induces Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Lung Epithelium via a TGF-Β1-Dependent Mechanism. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 2012, 52, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavello, M.; Gazzano, E.; Bergandi, L.; Silvagno, F.; Libener, R.; Riganti, C.; Aldieri, E. Identification of Redox-Sensitive Transcription Factors as Markers of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Cancers 2021, 13, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Xiang, D.-B.; Yang, X.; Chen, L.-S.; Li, M.-X.; Zhong, Z.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-S. APE1 Overexpression Is Associated with Cisplatin Resistance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Targeted Inhibition of APE1 Enhances the Activity of Cisplatin in A549 Cells. Lung Cancer 2009, 66, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caston, R.A.; Gampala, S.; Armstrong, L.; Messmann, R.A.; Fishel, M.L.; Kelley, M.R. The Multifunctional APE1 DNA Repair–Redox Signaling Protein as a Drug Target in Human Disease. Drug Discovery Today 2021, 26, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, F.; Logsdon, D.; Messmann, R.A.; Fehrenbacher, J.C.; Fishel, M.L.; Kelley, M.R. Exploiting the Ref-1-APE1 Node in Cancer Signaling and Other Diseases: From Bench to Clinic. npj Precision Oncology 2017, 1, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Luo, M.; Kelley, M.R. Human Apurinic Endonuclease 1 (APE1) Expression and Prognostic Significance in Osteosarcoma: Enhanced Sensitivity of Osteosarcoma to DNA Damaging Agents Using Silencing RNA APE1 Expression Inhibition. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics 2004, 3, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.-B.; Chen, Z.-T.; Wang, D.; Li, M.-X.; Xie, J.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-S.; Qing, Y.; Li, Z.-P.; Xie, J. Chimeric Adenoviral Vector Ad5/F35-Mediated APE1 SiRNA Enhances Sensitivity of Human Colorectal Cancer Cells to Radiotherapy in Vitro and in Vivo. Cancer Gene Therapy 2008, 15, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.-Z.; Chen, X.-H.; Wang, D. Experimental Study Enhancing the Chemosensitivity of Multiple Myeloma to Melphalan by Using a Tissue-Specific APE1-Silencing RNA Expression Vector. Clinical Lymphoma and Myeloma 2007, 7, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassina, A.; Cappellesso, R.; Guzzardo, V.; Dalla Via, L.; Piccolo, S.; Ventura, L.; Fassan, M. Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Malignant Mesothelioma. Modern Pathology 2012, 25, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merikallio, H.; Pääkkö, P.; Salmenkivi, K.; Kinnula, V.; Harju, T.; Soini, Y. Expression of Snail, Twist, and Zeb1 in Malignant Mesothelioma. APMIS 2013, 121, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.; Dobersch, S.; Romero-Olmedo, A.J.; Barreto, G. Epigenetics in Lung Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy. Cancer and Metastasis Reviews 2015, 34, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, E.C.; Vousden, K.H. The Role of ROS in Tumour Development and Progression. Nature Reviews Cancer 2022, 22, 280–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Li, Y.; Kong, J.; Li, C. Apurinic/Apyrimidinic Endonuclease 1/Redox Factor-1 Could Serve as a Potential Serological Biomarker for the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 2019, 77, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gampala, S.; Shah, F.; Lu, X.; Moon, H.; Babb, O.; Umesh Ganesh, N.; Sandusky, G.; Hulsey, E.; Armstrong, L.; Mosely, A.L.; et al. Ref-1 Redox Activity Alters Cancer Cell Metabolism in Pancreatic Cancer: Exploiting This Novel Finding as a Potential Target. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2021, 40, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Zhen, P.; Niu, X.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, M. APE1 Promotes Proliferation and Migration of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Journal of Dermatological Science 2020, 100, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Peng, Y.; Jiang, X.; Lu, X.; Duan, W.; Zhang, S.; Dai, N.; Shan, J.; Feng, Y.; Li, X.; et al. The Regulatory Role of APE1 in Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and in Determining EGFR-TKI Responsiveness in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Medicine 2018, 7, 4406–4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menju, T.; Date, H. Lung Cancer and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. General Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery 2021, 69, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishel, M.L.; Xia, H.; McGeown, J.; McIlwain, D.W.; Elbanna, M.; Craft, A.A.; Kaimakliotis, H.Z.; Sandusky, G.E.; Zhang, C.; Pili, R.; et al. Antitumor Activity and Mechanistic Characterization of APE1/Ref-1 Inhibitors in Bladder Cancer. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics 2019, 18, 1947–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




