Submitted:
30 June 2023
Posted:
30 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Research gap
3. Materials and methods
3.1. Research materials
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Self-compacting paste, mortar and concrete rheological assessment
3.2.2. Plastic and mechanical properties of self-compacting paste, mortar and concrete
4. Results and discussion
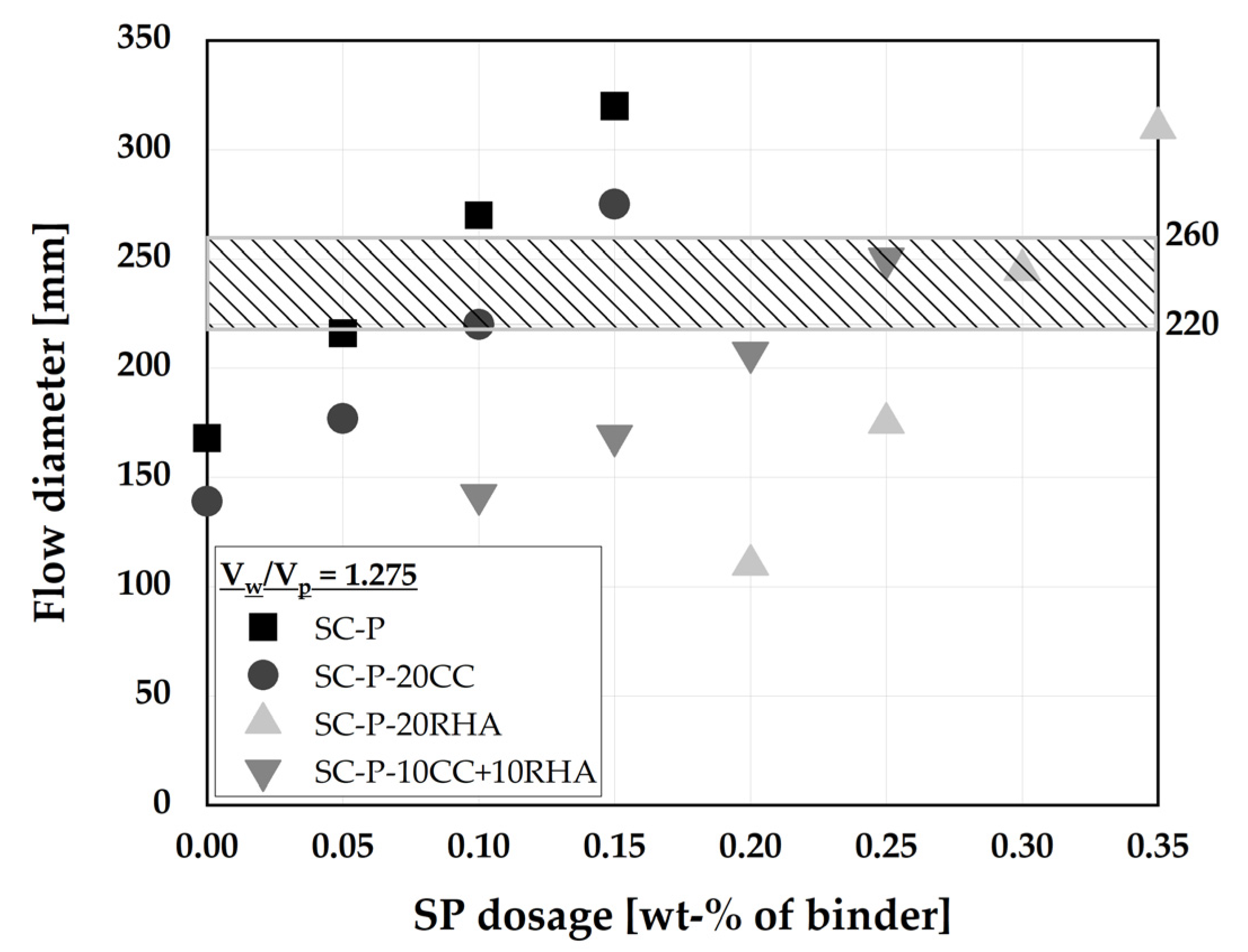
4.1. Optimization of SCC mix design with the blend of CC and RHA
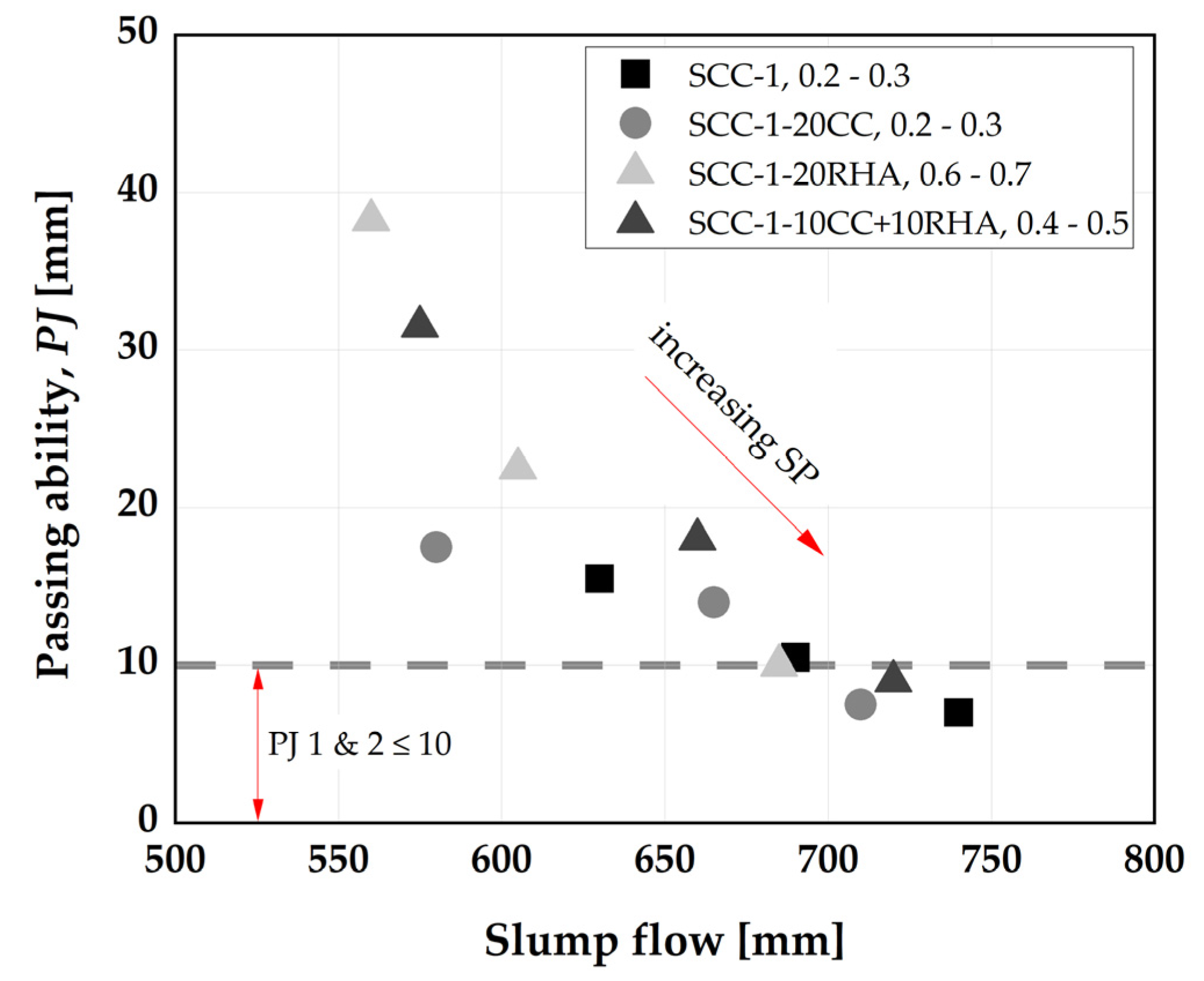
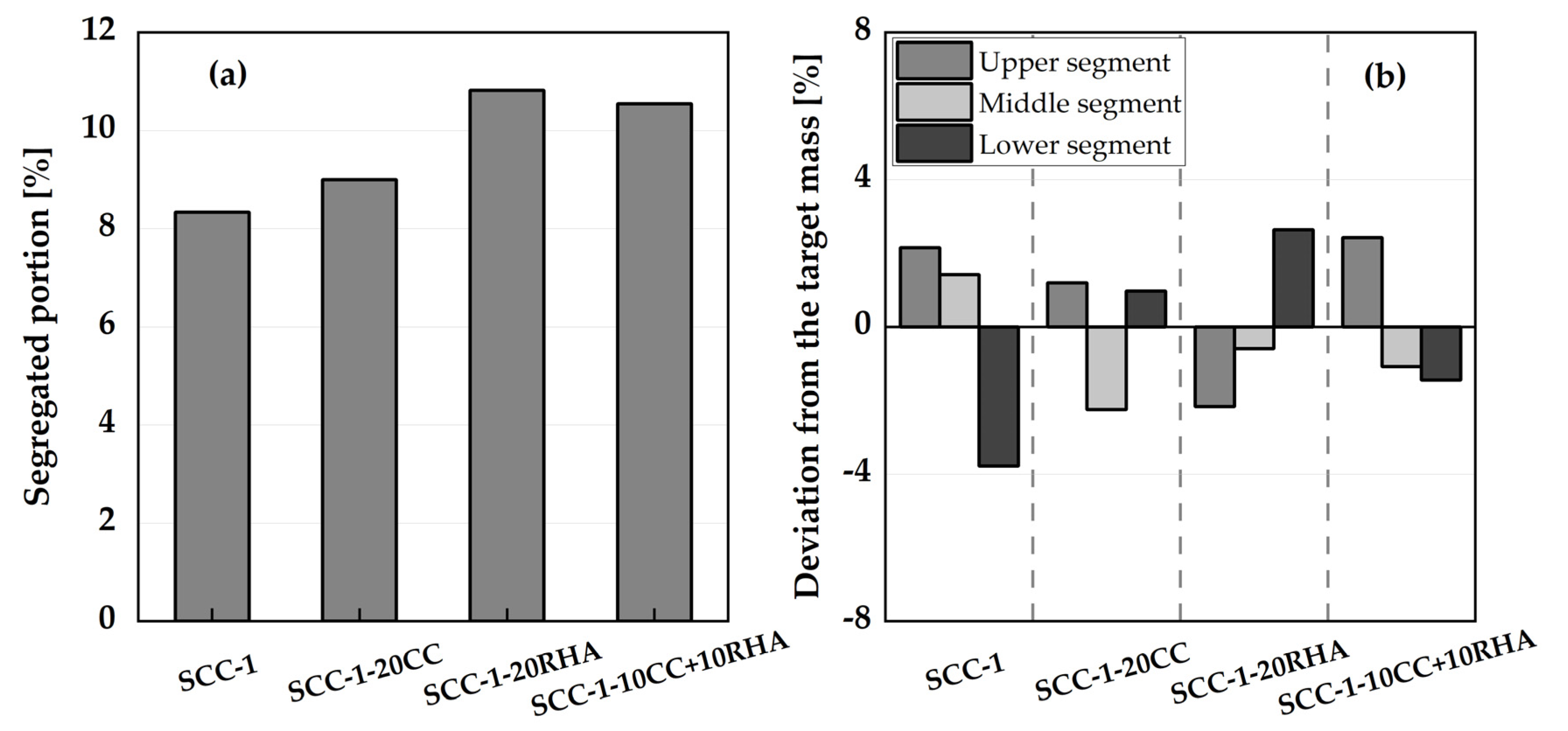
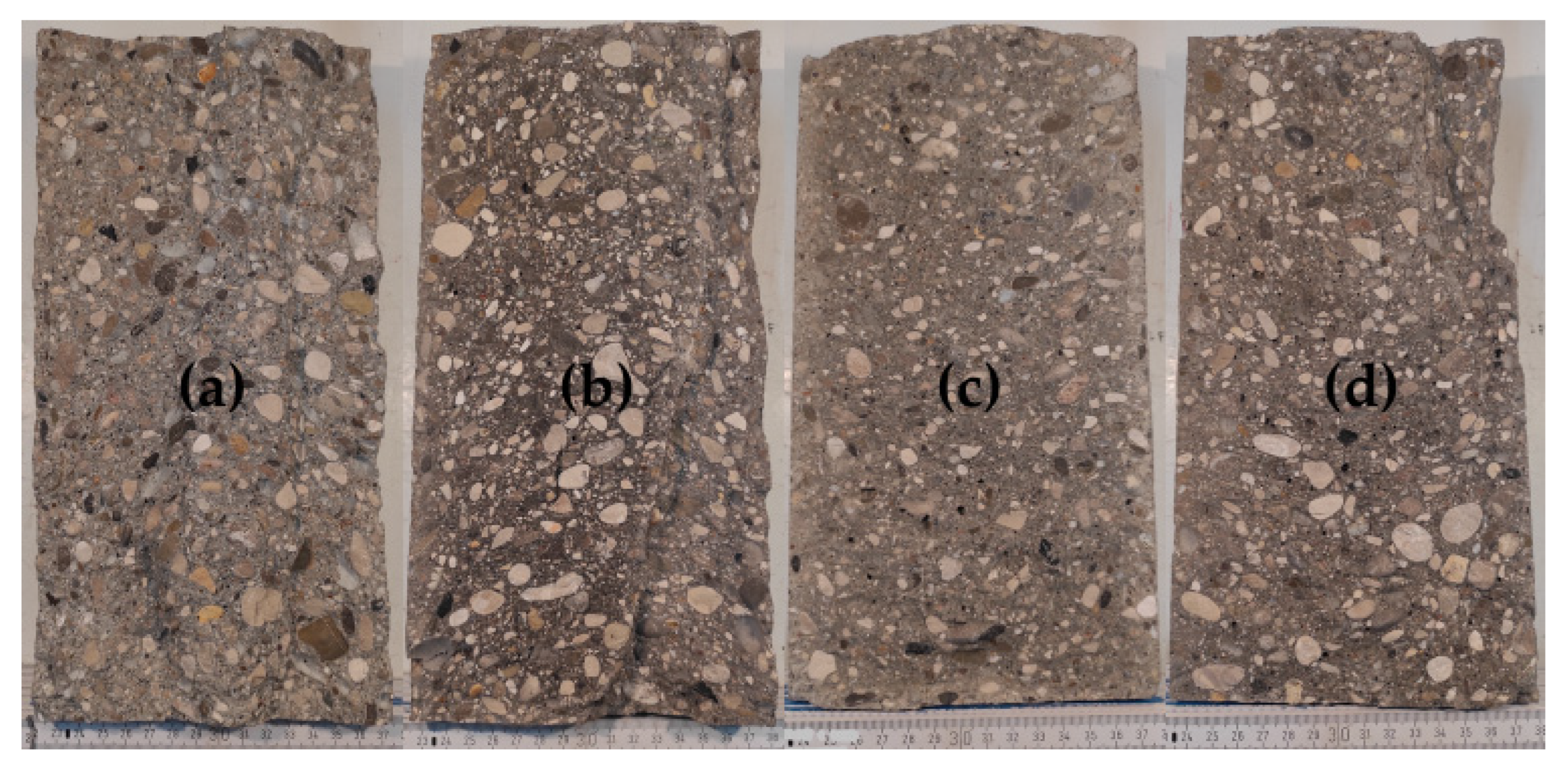
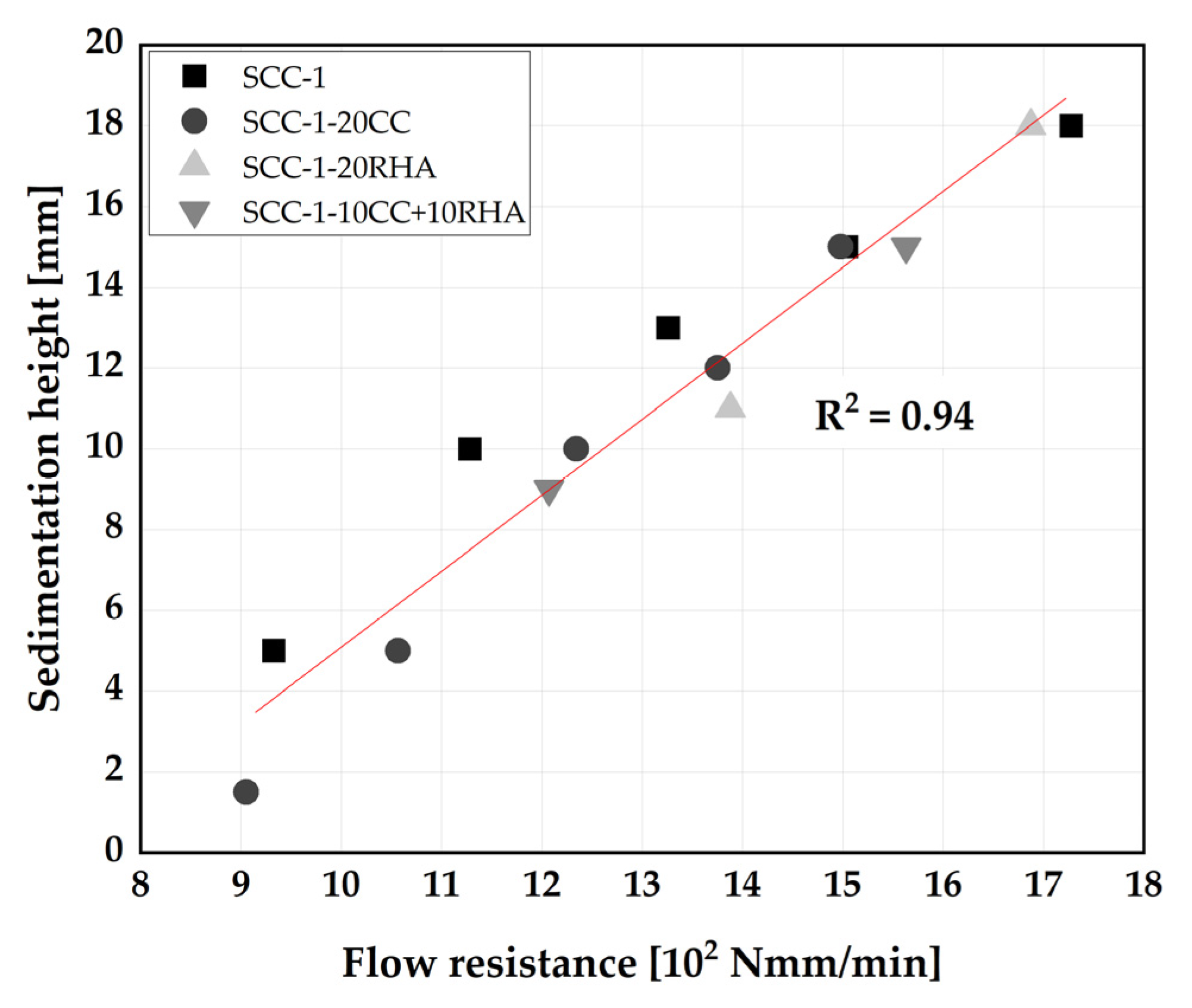
4.2. Influence of CC and RHA on the segregation resistance of SCC
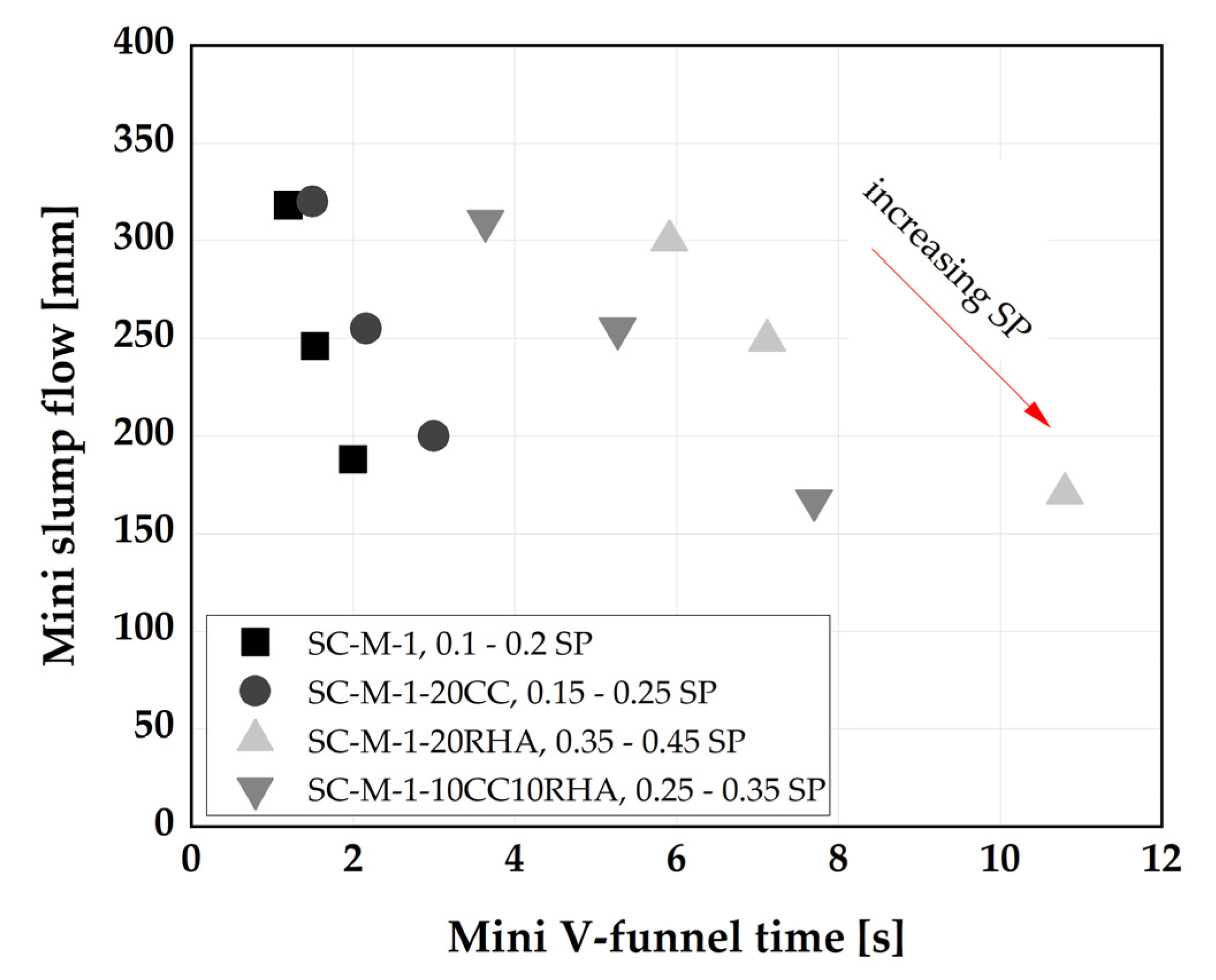
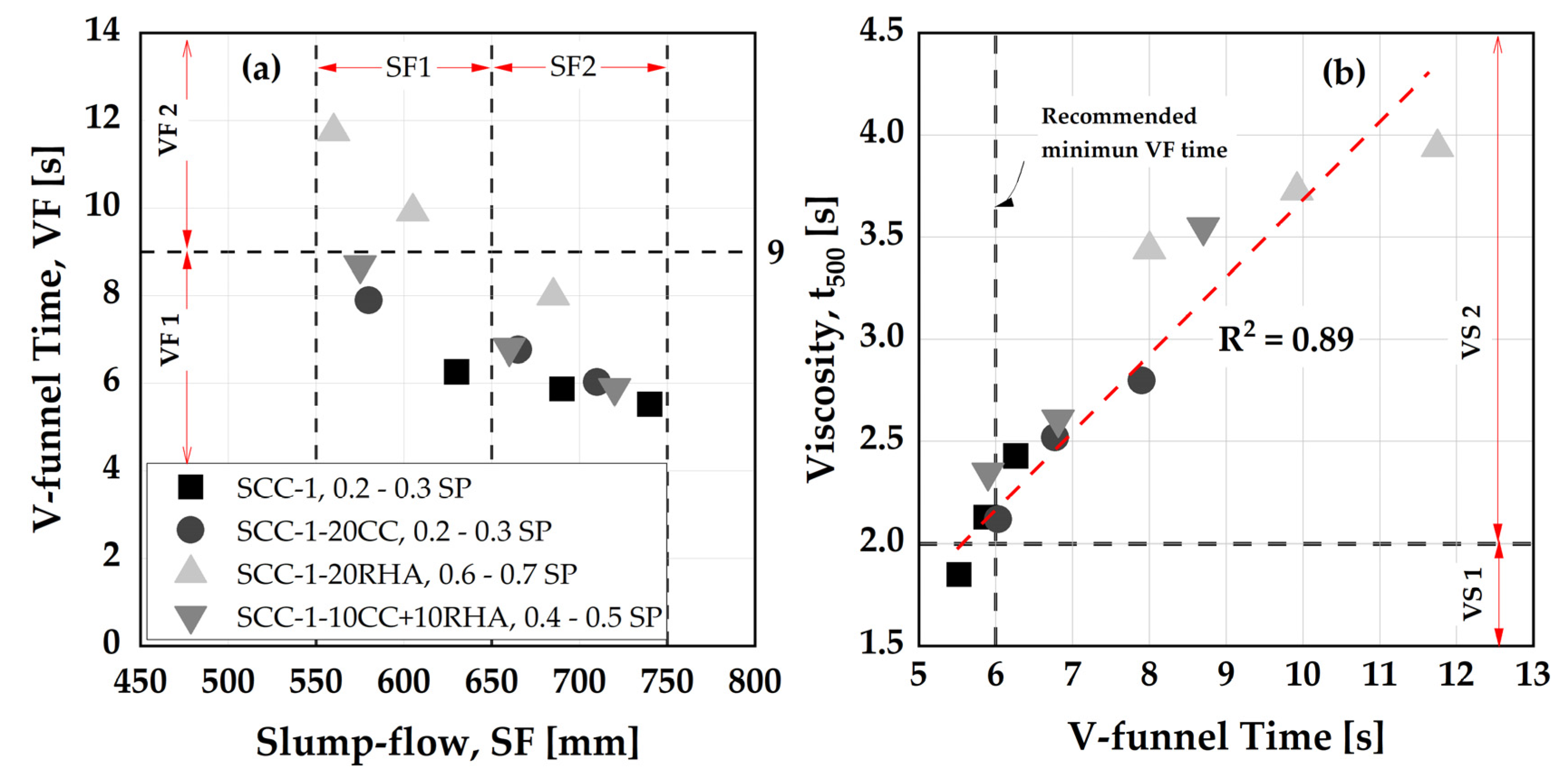
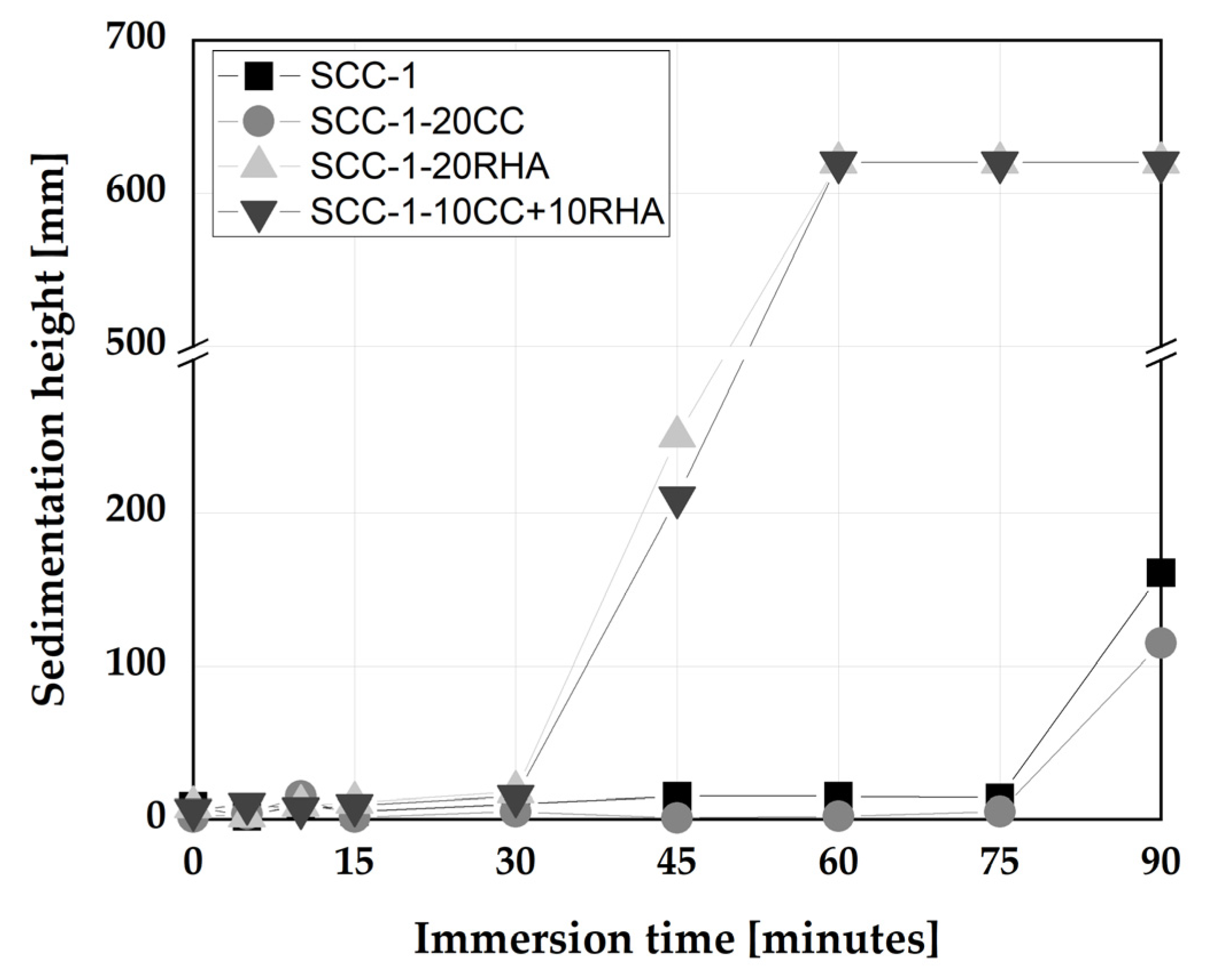
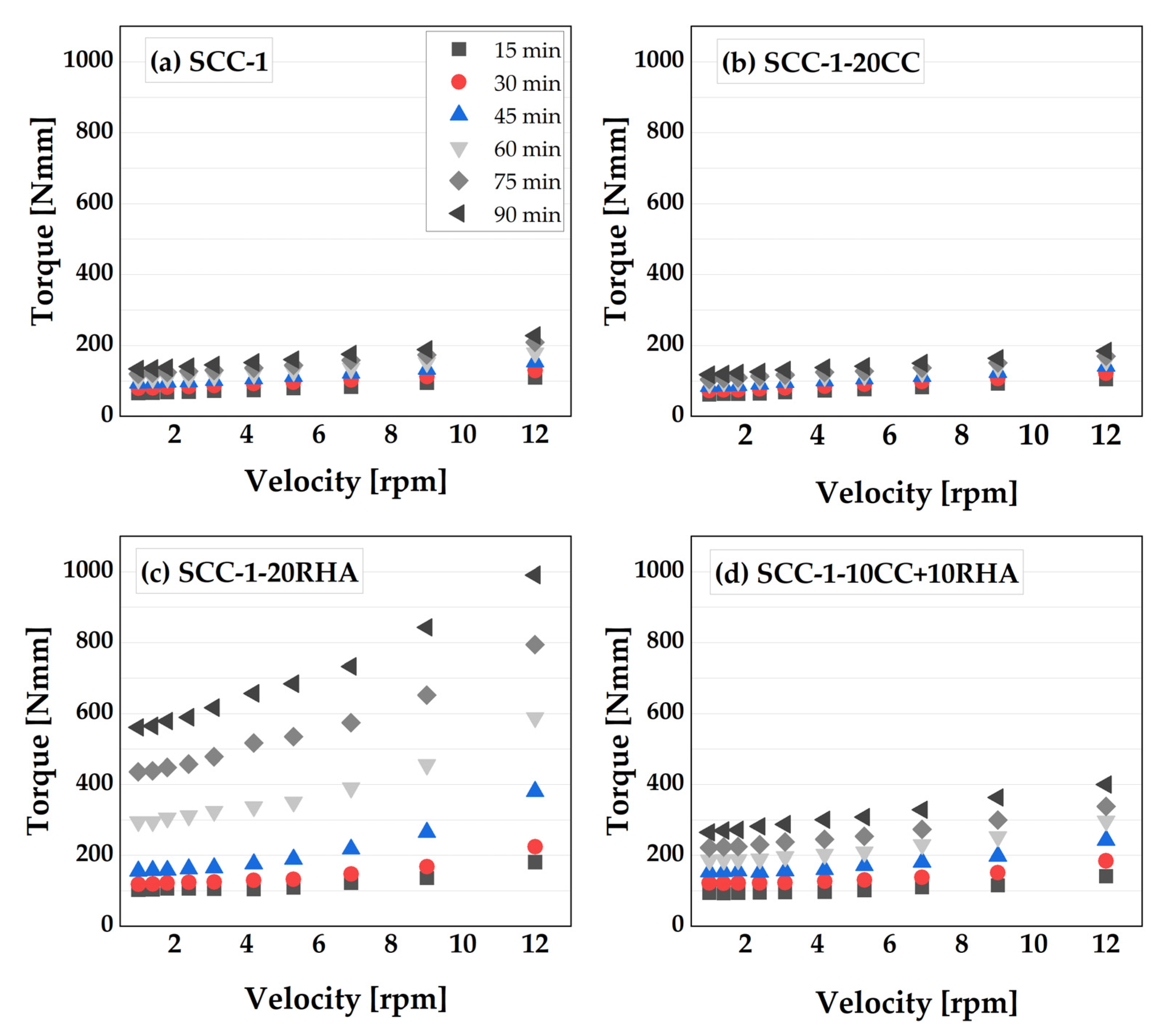
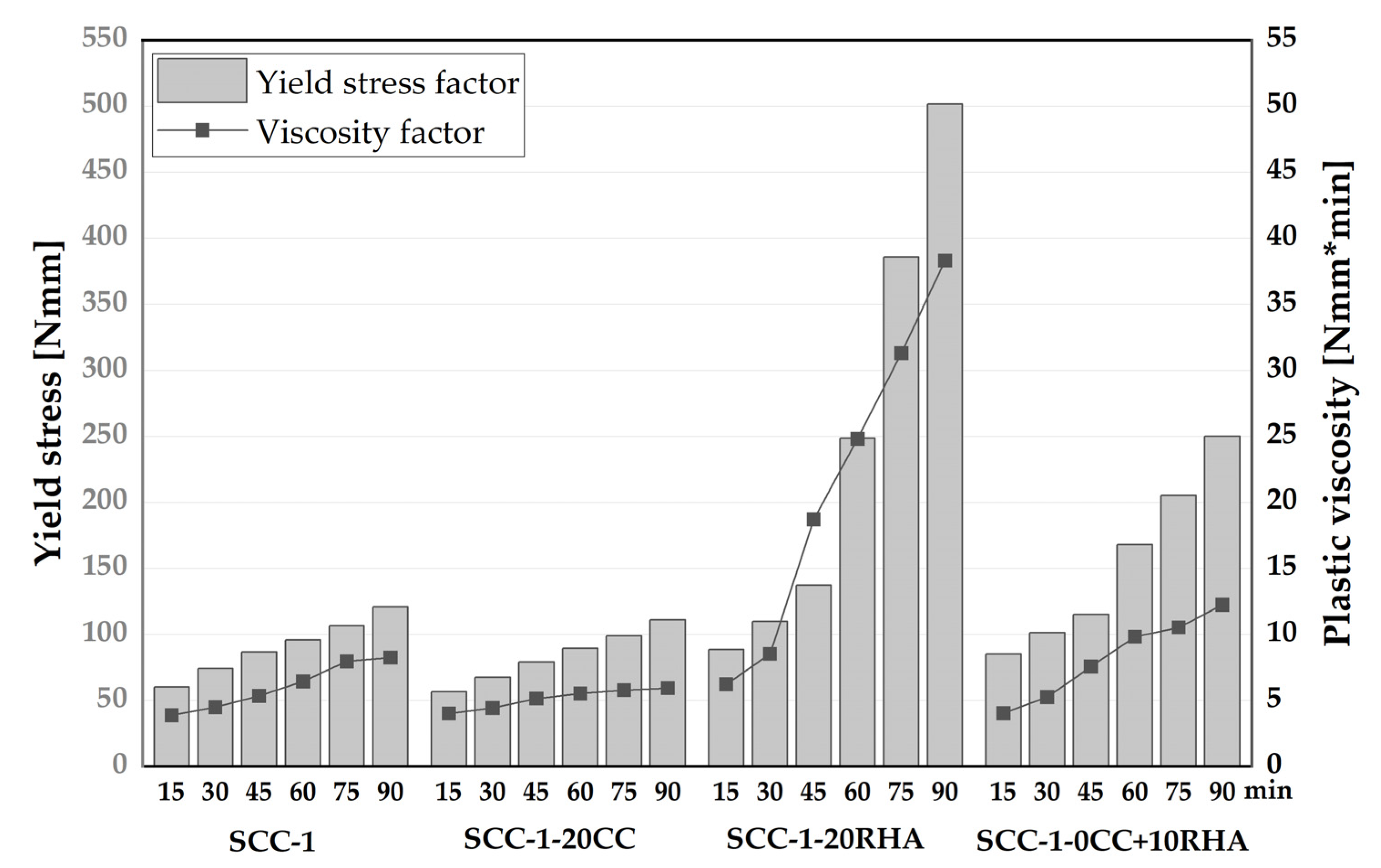
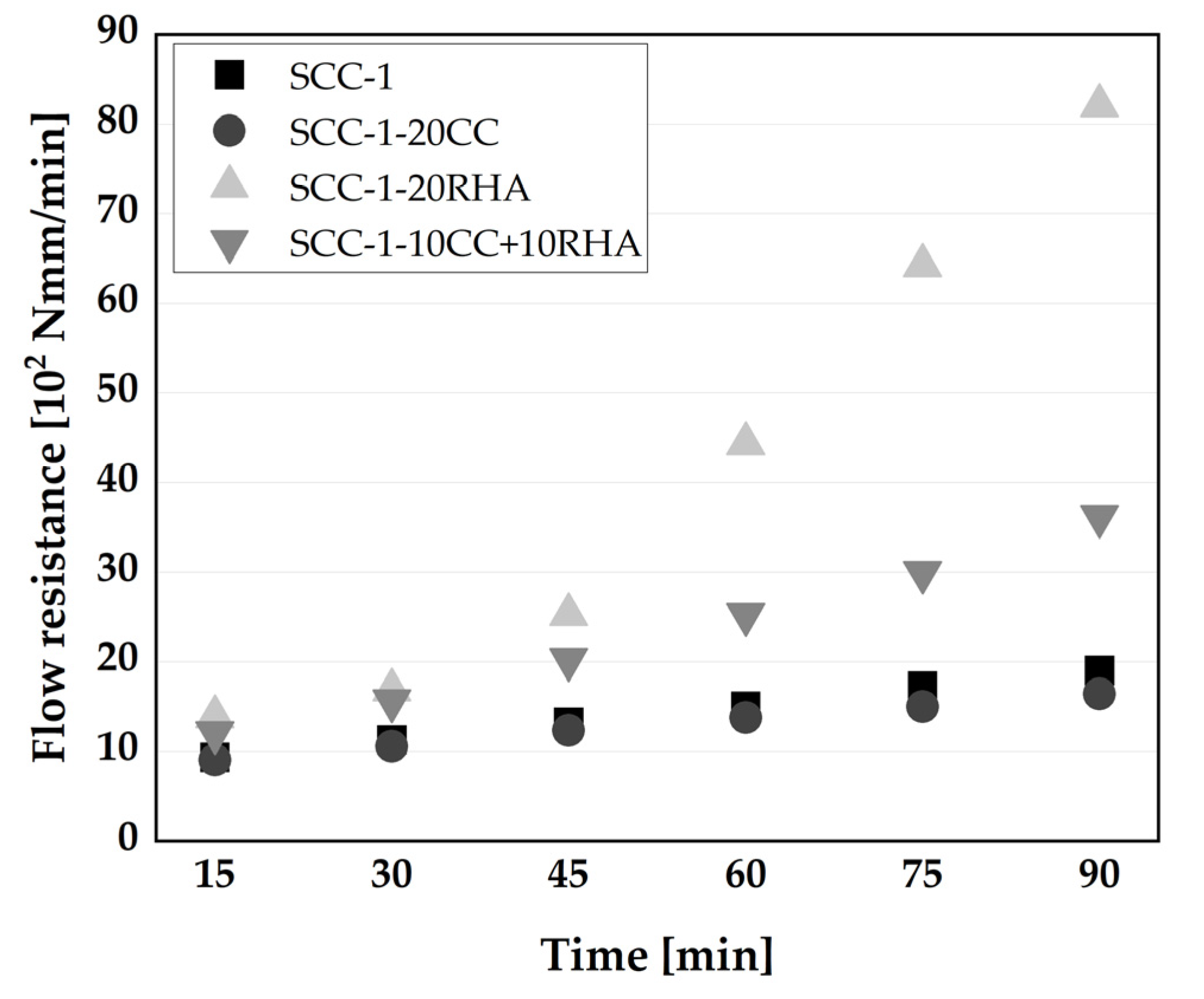
4.3. Rheological and time dependent workability retention of SCC
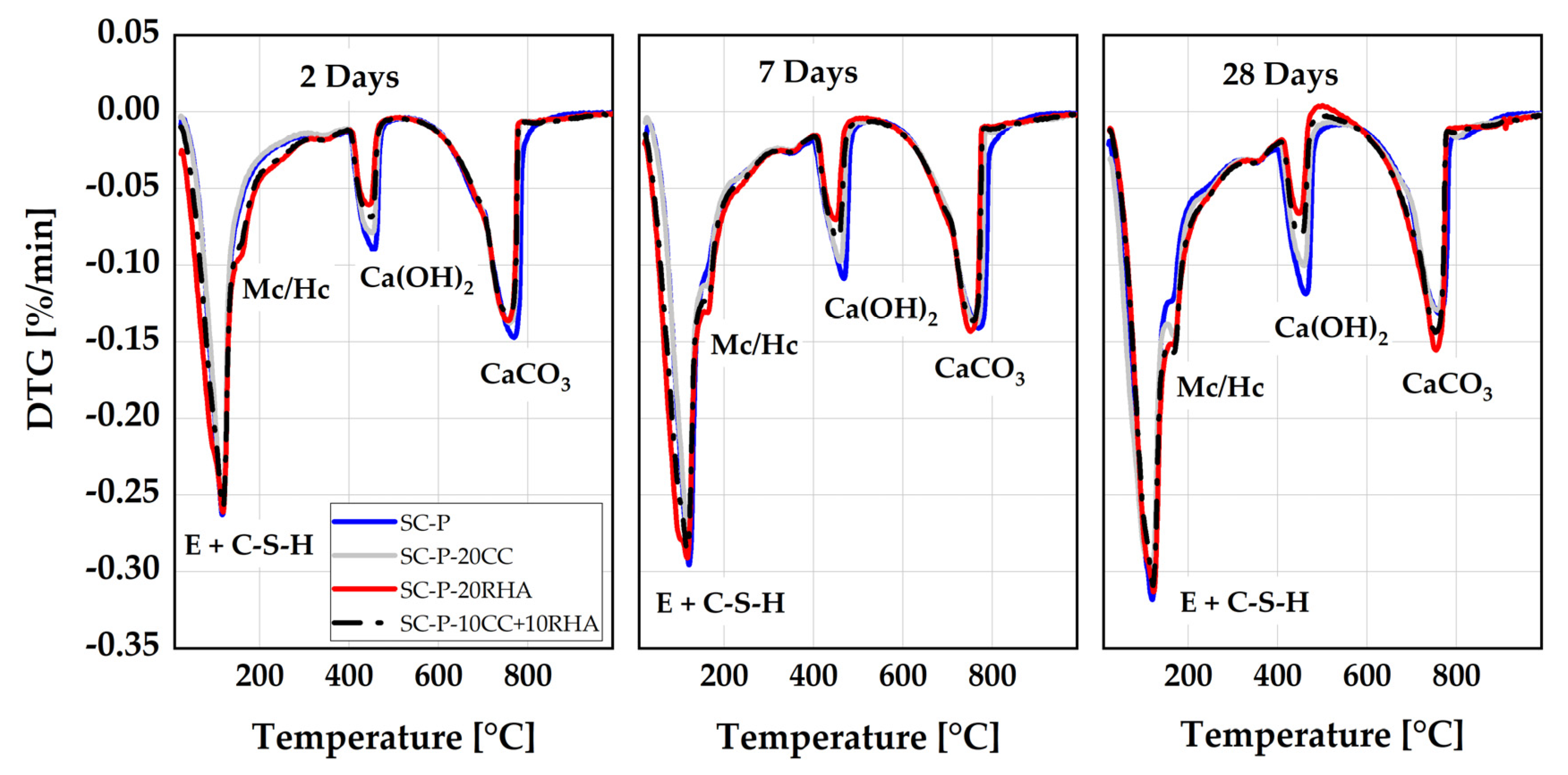
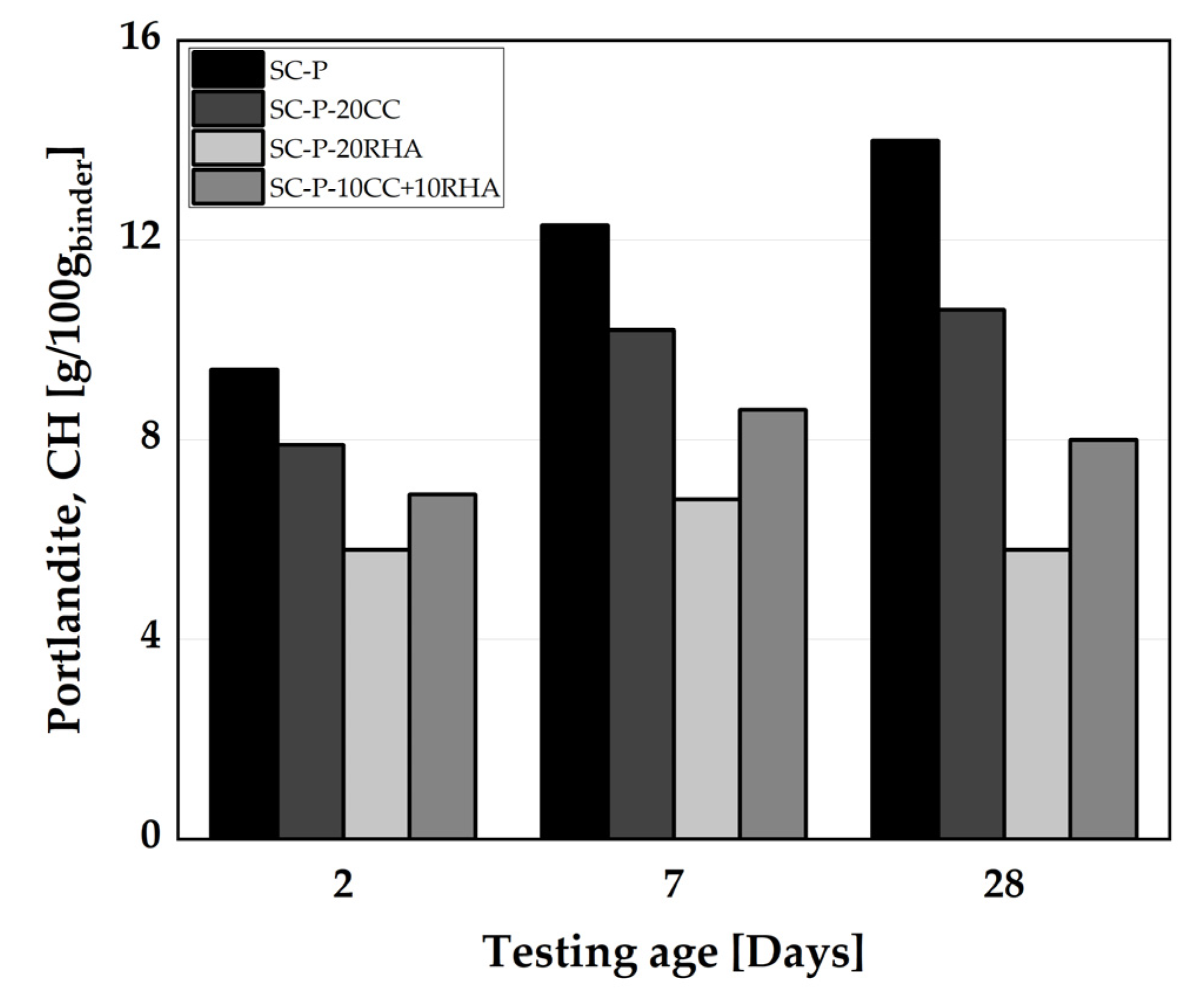
4.4. Formation of hydrate phases from the hardened SCP
4.5. Plastic and hardened properties of self-compacting mortar and concrete
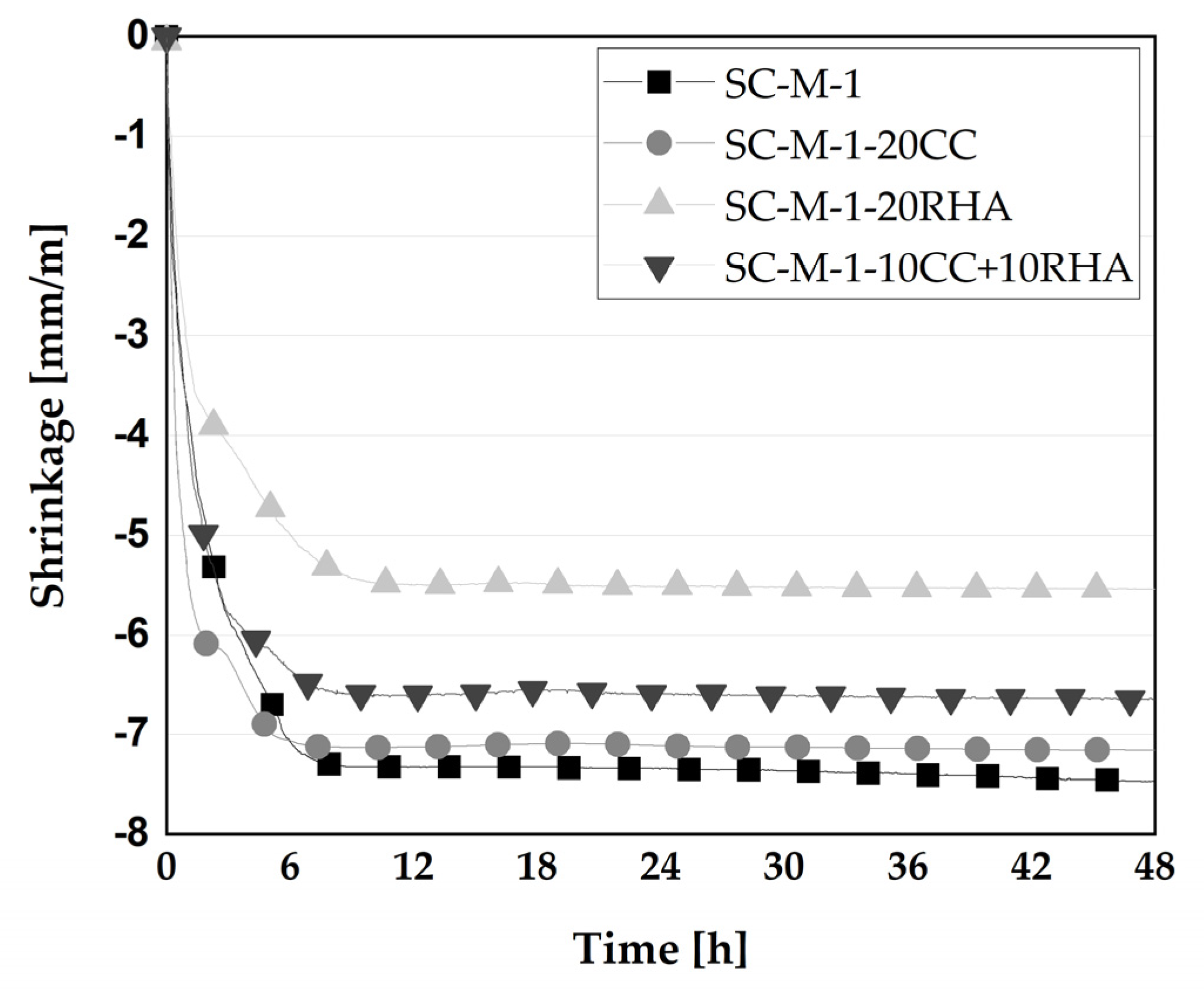
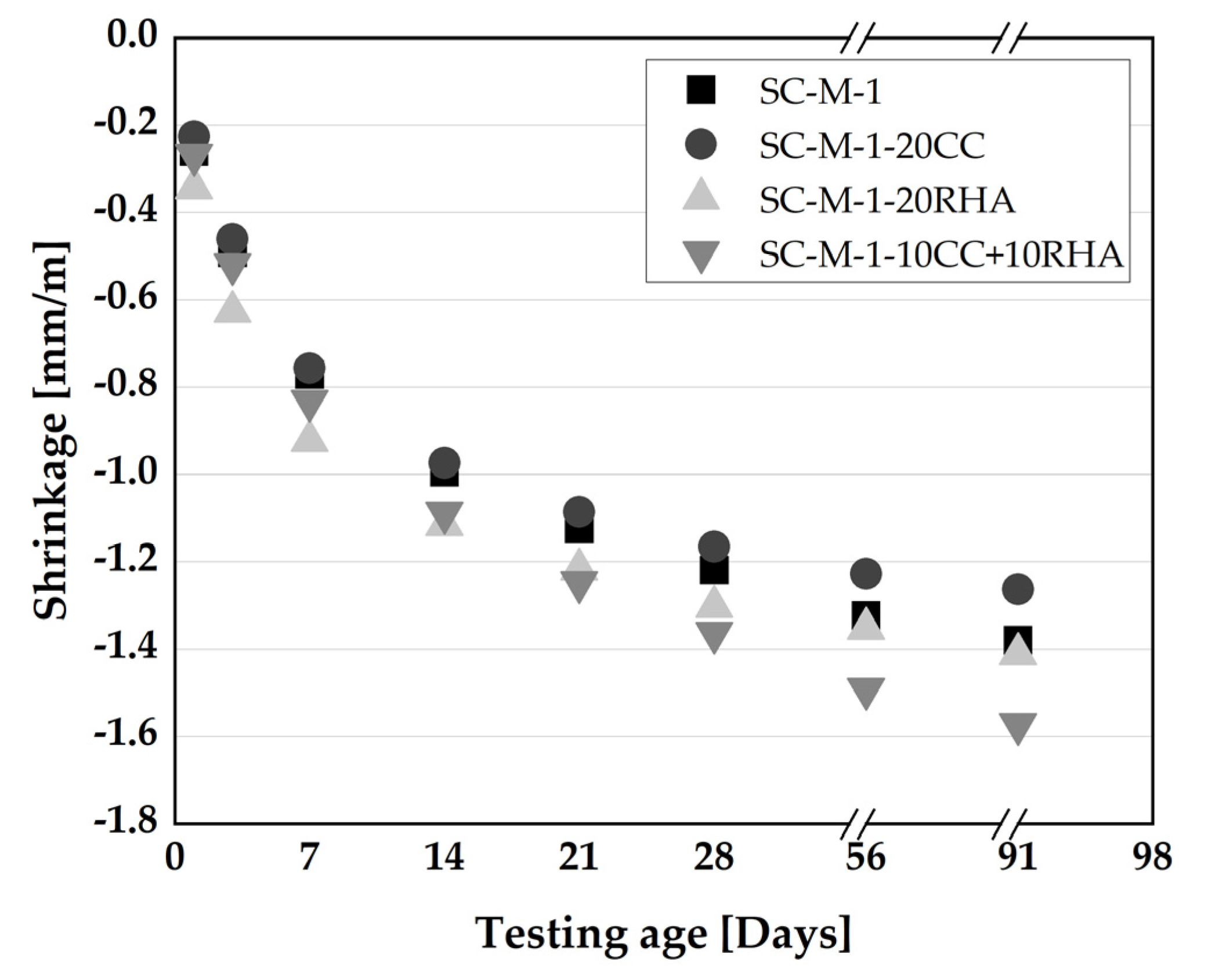
4.5.1. Effect of CC and RHA on plastic and total shrinkage of self-compacting mortar
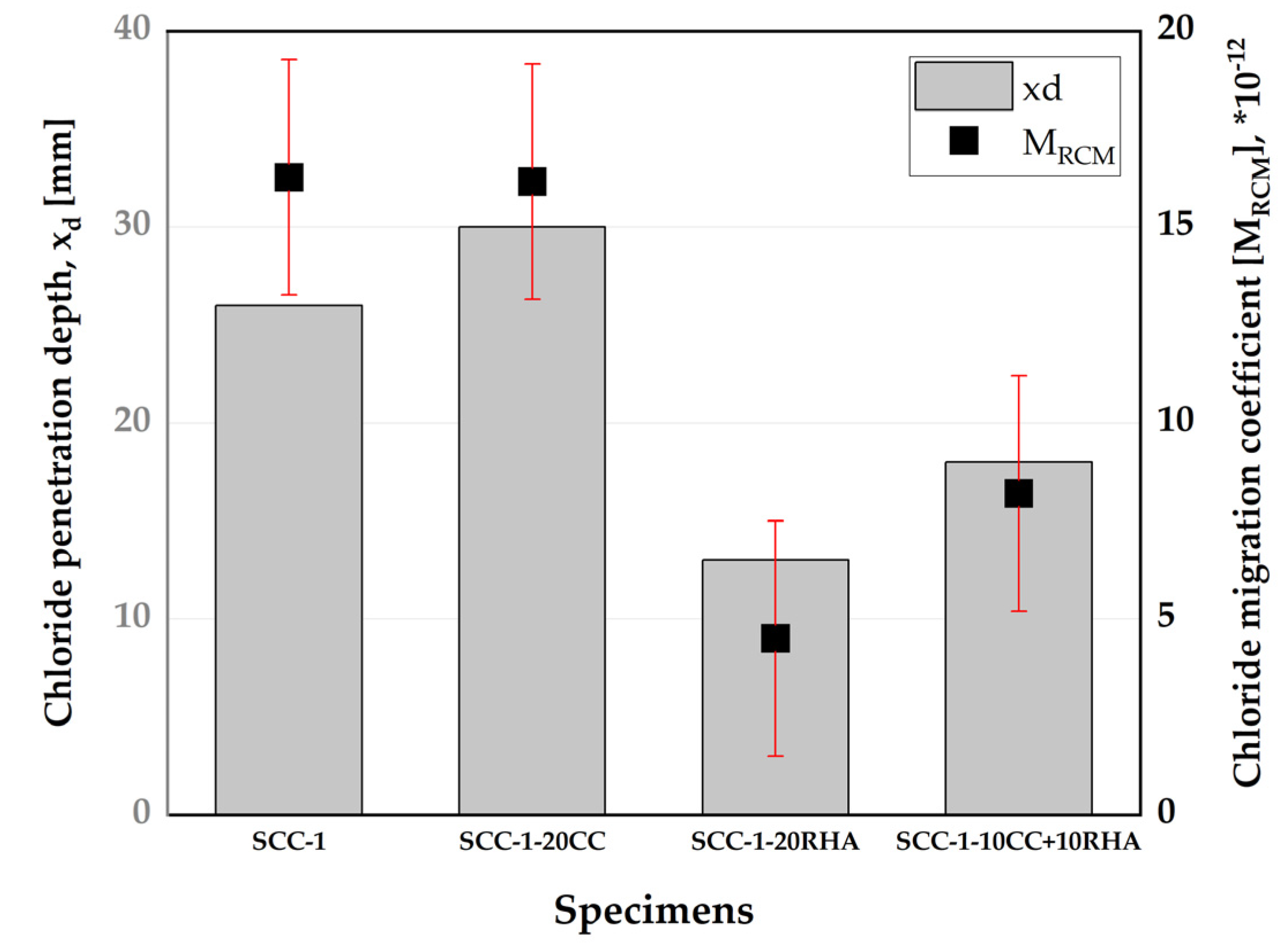
4.5.2. Compressive strength and rapid chloride migration assessment of SCC
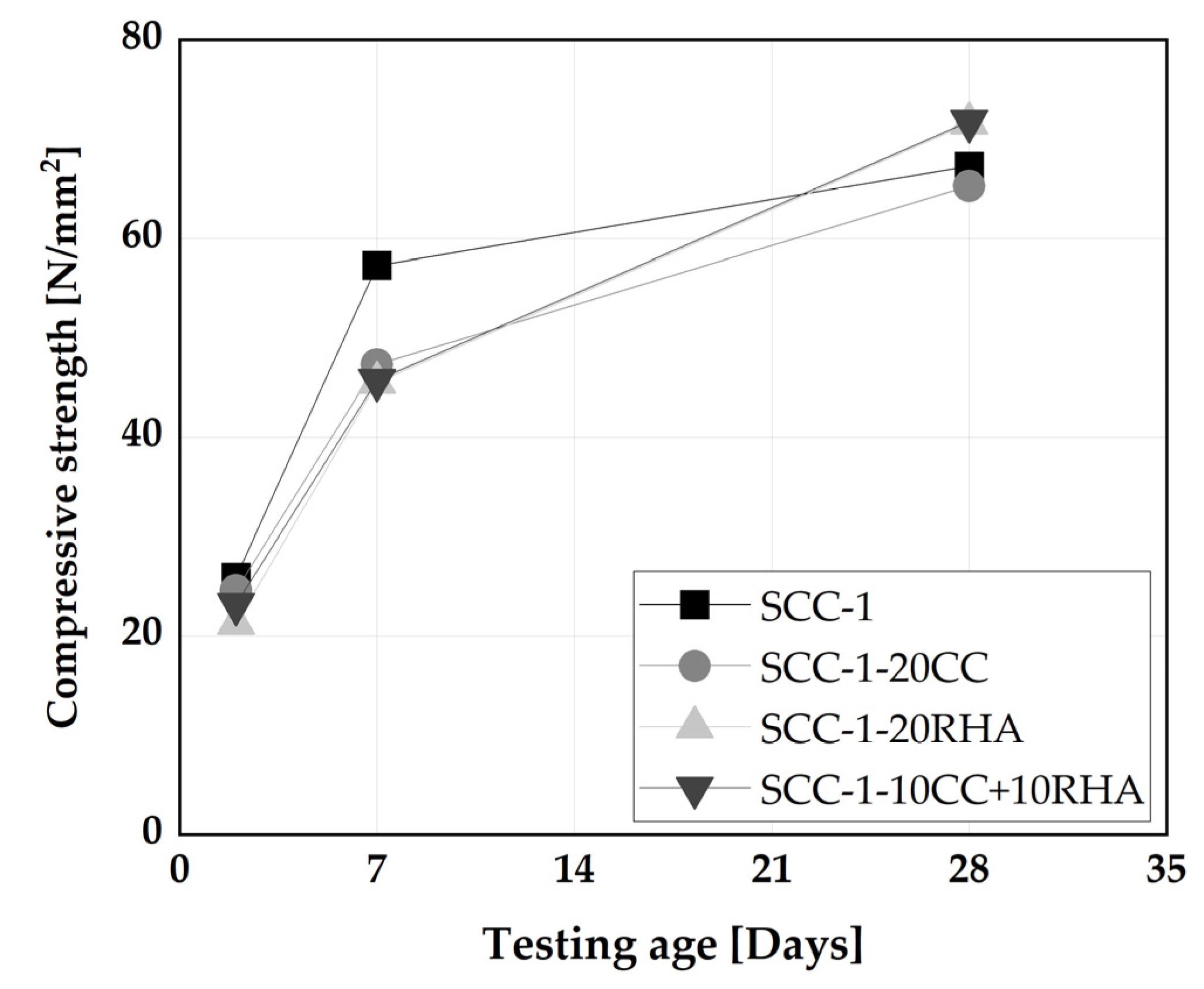
4.6. Rapid chloride resistance of SCC
5. Summary and conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aı̈tcin, P.-C. Cements of yesterday and today: Concrete of tomorrow. Cement Concrete Res 2000, 30, 1349–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Akhras, N.M. Durability of metakaolin concrete to sulfate attack. Cement Concrete Res 2006, 36, 1727–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, O.R.; Shanthi, V.M.; Arulraj, G.P.; Sivakumar, V.R. Microstructural studies on eco-friendly and durable Self-compacting concrete blended with metakaolin. Appl Clay Sci 2016, 124-125, 143-149. [CrossRef]
- Kannan, V. Strength and durability performance of self compacting concrete containing self-combusted rice husk ash and metakaolin. Constr Build Mater 2018, 160, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, H.; Ozawa, K. Mix-design for self-compacting concrete. Concrete Library of JSCE 1995, 107–120. [Google Scholar]
- Okamura, H. Self-Compacting High-Performance Concrete. Concrete International 1997, 19, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Su, N.; Hsu, K.C.; Chai, H.W. A simple mix design method for self-compacting concrete. Cement Concrete Res 2001, 31, 1799–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, P.; Baskar, I.; Muthupriya, P.; Venkatasubramani, R. Performance of self-compacting concrete containing different mineral admixtures. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering 2013, 17, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN EN 197-1. Zement - Teil 1: Zusammensetzung, Anforderungen und Konformitätskriterien von Normalzement (Cement - Part 1: Composition, specifications and conformity criteria for common cements). Beuth-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2011; p. 8. [CrossRef]
- Uysal, M.; Sumer, M. Performance of self-compacting concrete containing different mineral admixtures. Constr Build Mater 2011, 25, 4112–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahia, A.; Tanimura, M.; Shimoyama, Y. Rheological properties of highly flowable mortar containing limestone filler-effect of powder content and W/C ratio. Cement Concrete Res 2005, 35, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avet, F.; Scrivener, K. Hydration Study of Limestone Calcined Clay Cement (LC3) Using Various Grades of Calcined Kaolinitic Clays. In Calcined Clays for Sustainable Concrete - Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Calcined Clays for Sustainable Concrete, Martirena, F., Favier, A., Scrivener, K., Eds. Springer Nature: La Havanna, Cuba, 2018; pp. 35–40. [CrossRef]
- Scrivener, K.; Martirena, F.; Bishnoi, S.; Maity, S. Calcined clay limestone cements (LC3). Cement Concrete Res 2018, 114, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatib, J.M. Performance of self-compacting concrete containing fly ash. Constr Build Mater 2008, 22, 1963–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesoğlu, M.; Güneyisi, E.; Kocabağ, M.E.; Bayram, V.; Mermerdaş, K. Fresh and hardened characteristics of self compacting concretes made with combined use of marble powder, limestone filler, and fly ash. Constr Build Mater 2012, 37, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazici, H. The effect of silica fume and high-volume Class C fly ash on mechanical properties, chloride penetration and freeze-thaw resistance of self-compacting concrete. Constr Build Mater 2008, 22, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingöl, A.F.; Tohumcu, T. Effects of different curing regimes on the compressive strength properties of self compacting concrete incorporating fly ash and silica fume. Materials and Design 2013, 51, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parande, A.K.; Ramesh Babu, B.; Aswin Karthik, M.; Deepak Kumaar, K.K.; Palaniswamy, N. Study on strength and corrosion performance for steel embedded in metakaolin blended concrete/mortar. Constr Build Mater 2008, 22, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said-Mansour, M.; Kadri, E.-H.; Kenai, S.; Ghrici, M.; Bennaceur, R. Influence of calcined kaolin on mortar properties. Constr Build Mater 2011, 25, 2275–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.; Thienel, K.-C.; Sposito, R. Suitability of Blending Rice Husk Ash and Calcined Clay for the Production of Self-Compacting Concrete: A Review. Materials 2021, 14, 6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhandapani, Y.; Sakthivel, T.; Santhanam, M.; Gettu, R.; Pillai, R.G. Mechanical properties and durability performance of concretes with Limestone Calcined Clay Cement (LC3). Cement Concrete Res 2018, 107, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuntner, N.; Kustermann, A.; Thienel, K.-C. Pozzolanic potential of calcined clay in high-performance concrete. Proceedings of International Conference on Sustainable Materials, Systems and Structures – SMSS 2019 New Generation of Construction Materials, Rovinj, Croatia, 20-22 March; pp. 470–477.
- Kannan, V.; Ganesan, K. Chloride and chemical resistance of self compacting concrete containing rice husk ash and metakaolin. Constr Build Mater 2014, 51, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, A.S.; Siddique, R. Durability properties of self-compacting concrete incorporating metakaolin and rice husk ash. Constr Build Mater 2018, 176, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, S.A.; Shaikh, M.A.; Akbar, H. Utilization of Rice Husk Ash as viscosity modifying agent in Self Compacting Concrete. Constr Build Mater 2011, 25, 1044–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordts, S.; Grube, H. Steuerung der Verarbeitbarkeitseigenschaften von Selbstverdichtendem Beton als Transportbeton (Controlling the workability properties of self compacting concrete used as ready-mixed concrete). Beton 2002, 52, 217–223. [Google Scholar]
- DIN EN 12350-8. Prüfung von Frischbeton - Teil 8: Selbstverdichtender Beton – Setzfließversuch (Testing fresh concrete - Part 8: Self-compacting concrete – Slump-flow test). Beuth-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2019; p 8.
- DIN EN 12350-9. Prüfung von Frischbeton - Teil 9: Selbstverdichtender Beton – Auslauftrichterversuch (Testing fresh concrete - Part 9: Self-compacting concrete – V-funnel test). Beuth-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2010; p 8.
- DIN EN 12350-12. Prüfung von Frischbeton - Teil 12: Selbstverdichtender Beton – Blockierring-Versuch (Testing fresh concrete - Part 12: Self-compacting concrete – J-ring test). Beuth-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2010; p 11.
- Kordts, S.; Breit, W. Beurteilung der Frischbetoneigenschaften von Selbstverdichtendem Beton (Assessment of the fresh concrete properties of self compacting concrete). Beton 2003, 53, 565–571. [Google Scholar]
- Sposito, R.; Maier, M.; Beuntner, N.; Thienel, K.-C. Physical and mineralogical properties of calcined common clays as SCM and their impact on flow resistance and demand for superplasticizer. Cement Concrete Res 2022, 154, 106743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuntner, N.; Thienel, K.-C. Properties of Calcined Lias Delta Clay - Technological Effects, Physical Characteristics and Reactivity in Cement. In Calcined Clays for Sustainable Concrete - Proceedings of the 1ˢᵗ International Conference on Calcined Clays for Sustainable Concrete, Scrivener, K., Favier, A., Eds. Springer: Dordrecht, Netherlands, 2015; Vol. RILEM Bookseries Vol. 10, pp. 43-50. [CrossRef]
- DIN ISO 9277. Determination of the specific surface area of solids by gas adsorption - BET method. Beuth-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2003; p 19.
- Puntke, W. Wasseranspruch von feinen Kornhaufwerken. Beton 2002, 52, 242–248. [Google Scholar]
- DIN EN ISO 17892-3. Geotechnical investigation and testing - Laboratory testing of soil - Part 3: Determination of particle density. Beuth-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2015; p 21.
- Okamura, H.; Ouchi, M. Self-Compacting Concrete. Journal of Advanced Concrete Technology 2003, 1, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN EN 196-1. Prüfverfahren für Zement - Teil 1: Bestimmung der Festigkeit (Methods of testing cement - Part 1: Determination of strength). Beuth-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2016; p 31.
- DIN EN 12350-11. Prüfung von Frischbeton - Teil 11: Selbstverdichtender Beton – Bestimmung der Sedimentationsstabilität im Siebversuch (Testing fresh concrete - Part 11: Self-compacting concrete – Sieve segregation test). Beuth-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2010; p 11.
- Brameshuber, W.; Uebachs, S. Sedimentationsstabilität von Selbstverdichtenden Betonen (Sedimentation stability of self-compacting concretes). In Proceedings of Rheologische Messungen an mineralischen Baustoffen - Workshop 2003, Regensburg, Germany; p. 10.
- Feys, D.; Verhoeven, R.; De Schutter, G. Fresh self compacting concrete, a shear thickening material. Cement Concrete Res 2008, 38, 920–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, H.A.; Walters, K. The yield stress myth? Rheologica Acta 1985, 24, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackley, V.A.; Ferraris, C.F. Guide to Rheological Nomenclature - Measurements in Ceramic Particulate Systems. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST): Gaithersburg, Maryland, USA, 2001; pp III, 29.
- DIN EN 60825-1. Sicherheit von Lasereinrichtungen - Teil 1: Klassifizierung von Anlagen und Anforderungen (Safety of laser products - Part 1: Equipment classification and requirements). Beuth-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2015; p 115.
- DIN EN 12617-4. Produkte und Systeme für den Schutz und die Instandsetzung von Betontragwerken Prüfverfahren Teil 4: Bestimmung des Schwindens und Quellens (Products and systems for the protection and repair of concrete structures - Test methods - Part 4: Determination of shrinkage and expansion). Beuth-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2002; p 14.
- Snellings, R.; Chwast, J.; Cizer, Ö.; De Belie, N.; Dhandapani, Y.; Durdzinski, P.; Elsen, J.; Haufe, J.; Hooton, D.; Patapy, C.; et al. Report of TC 238-SCM: hydration stoppage methods for phase assemblage studies of blended cements—results of a round robin test. Mater Struct 2018, 51, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN EN 12390-3. Prüfung von Festbeton - Teil 3: Druckfestigkeit von Probekörpern (Testing hardened concrete - Part 3: Compressive strength of test specimens). Beuth-Verlag: Berlin, 2019; p 20.
- DIN EN 12390-18. Prüfung von Festbeton - Teil 18: Bestimmung des Chloridmigrationskoeffizienten (Testing hardened concrete Part 18: Determination of the chloride migration coefficient). Beuth-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2021; p 20.
- Muhammad, A.; Thienel, K.-C.; Sposito, R. Suitability of Clinker Replacement by a Calcined Common Clay in Self-Consolidating Mortar - Impact on Rheology and Early Age Properties. Minerals 2022, 12, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN 1045-2. Tragwerke aus Beton, Stahlbeton und Spannbeton – Teil 2: Beton – Festlegung, Eigenschaften, Herstellung und Konformität – Anwendungsregeln zu DIN EN 206-1 (Concrete, reinforced and prestressed concrete structures – Part 2: Concrete – Specification, properties, production and conformity – Application rules for DIN EN 206-1). Beuth-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2008; p 62.
- DIN EN 206. Beton – Festlegung, Eigenschaften, Herstellung und Konformität (Concrete - Specification, performance, production and conformity). Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2021; p. 105. [CrossRef]
- Le, H.T.; Kraus, M.; Siewert, K.; Ludwig, H.M. Effect of macro-mesoporous rice husk ash on rheological properties of mortar formulated from self-compacting high performance concrete. Constr Build Mater 2015, 80, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sua-iam, G.; Sokrai, P.; Makul, N. Novel ternary blends of Type 1 Portland cement, residual rice husk ash, and limestone powder to improve the properties of self-compacting concrete. Constr Build Mater 2016, 125, 1028–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, A.S.; Siddique, R. Strength and micro-structural properties of self-compacting concrete containing metakaolin and rice husk ash. Constr Build Mater 2017, 157, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molaei Raisi, E.; Vaseghi Amiri, J.; Davoodi, M.R. Mechanical performance of self-compacting concrete incorporating rice husk ash. Constr Build Mater 2018, 177, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, V. Relationship between ultrasonic pulse velocity and compressive strength of self compacting concrete incorporate rice husk ash and metakaolin. Asian J. Civ. Eng. 2015, 16, 1077–1088. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, A.; Thienel, K.-C. Performance of Calcined Common Clay as Partial Replacement to Cement in Selfcompacting Concrete. Proceedings of International Conference on Calcined Clays for Sustainable Concrete, Lausanne, Switzerland, 5 – 7 July 2022; pp. 102–103. [Google Scholar]
- Kundt, G.; Krentz, H.; Glass, Ä. Epidemiologie und Medizinische Biometrie (Epidemiology and Medical Biometry); Shaker Verlag: Aachen, 2011; p. 246. [Google Scholar]
- Diniz, H.A.A.; dos Anjos, M.A.S.; Rocha, A.K.A.; Ferreira, R.L.S. Effects of the use of agricultural ashes, metakaolin and hydrated-lime on the behavior of self-compacting concretes. Constr Build Mater 2022, 319, 126087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madandoust, R.; Mousavi, S.Y. Fresh and hardened properties of self-compacting concrete containing metakaolin. Constr Build Mater 2012, 35, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sposito, R.; Beuntner, N.; Thienel, K.-C. Characteristics of components in calcined clays and their influence on the efficiency of superplasticizers. Cement and Concrete Composites 2020, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belaidi, A.S.E.; Azzouz, L.; Kadri, E.; Kenai, S. Effect of natural pozzolana and marble powder on the properties of self-compacting concrete. Constr Build Mater 2012, 31, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, J.J.; Megat Johari, M.A. Effect of metakaolin on creep and shrinkage of concrete. Cement and Concrete Composites 2001, 23, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palou, M.; Boháč, M.; Kuzielová, E.; Novotný, R.; Žemlička, M.; Dragomirová, J. Use of calorimetry and thermal analysis to assess the heat of supplementary cementitious materials during the hydration of composite cementitious binders. J Therm Anal Calorim 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boháč, M.; Palou, M.; Novotný, R.; Másilko, J.; Všianský, D.; Staněk, T. Investigation on early hydration of ternary Portland cement-blast-furnace slag–metakaolin blends. Constr Build Mater 2014, 64, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berodier, E.; Scrivener, K. Understanding the Filler Effect on the Nucleation and Growth of C-S-H. J Am Ceram Soc 2014, 97, 3764–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliba, J.; Rozière, E.; Grondin, F.; Loukili, A. Influence of shrinkage-reducing admixtures on plastic and long-term shrinkage. Cement and Concrete Composites 2011, 33, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcry, P.; Loukil, A. Evaluation of plastic shrinkage cracking of self-consolidating concrete. ACI Materials Journal 2006, 103, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayahi, F.; Emborg, M.; Hedlund, H.; Cwirzen, A. Plastic shrinkage cracking of self-compacting concrete: influence of capillary pressure and dormant period. Nordic Concrete Research 2019, 60, 67–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, K.; Rajagopal, K.; Thangavel, K. Rice husk ash blended cement: Assessment of optimal level of replacement for strength and permeability properties of concrete. Constr Build Mater 2008, 22, 1675–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, Z.; Sun, T.; Fu, Z.; Wang, G. Dominant factors on the early hydration of metakaolin-cement paste. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed. 2010, 25, 849–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Ye, G.; Fehling, E.; Middendorf, B.; Thiemicke, J. Use of rice husk ash for mitigating the autogenous shrinkage of cement pastes at low water cement ratio. In Proceedings of Proceedings of the HiPerMat 2016 4th international symposium on ultra-high performance concrete and high performance construction materials, Kassel, Germany; pp. 9-11.
- Güneyisi, E.; Gesoğlu, M.; Özbay, E. Strength and drying shrinkage properties of self-compacting concretes incorporating multi-system blended mineral admixtures. Constr Build Mater 2010, 24, 1878–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechtcherine, V.; Gorges, M.; Schroefl, C.; Assmann, A.; Brameshuber, W.; Ribeiro, A.B.; Cusson, D.; Custódio, J.; da Silva, E.F.; Ichimiya, K.; et al. Effect of internal curing by using superabsorbent polymers (SAP) on autogenous shrinkage and other properties of a high-performance fine-grained concrete: results of a RILEM round-robin test. Mater Struct 2014, 47, 541–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Sun, W.; Wu, X.; Gao, B. The properties of the self-compacting concrete with fly ash and ground granulated blast furnace slag mineral admixtures. Journal of Cleaner Production 2015, 95, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongkeo, W.; Thongsanitgarn, P.; Ngamjarurojana, A.; Chaipanich, A. Compressive strength and chloride resistance of self-compacting concrete containing high level fly ash and silica fume. Mater Design 2014, 64, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, V.T.A.; Rößler, C.; Bui, D.D.; Ludwig, H.M. Mesoporous structure and pozzolanic reactivity of rice husk ash in cementitious system. Constr Build Mater 2013, 43, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C1202 - 19. Standard Test Method for Electrical Indication of Concrete’s Ability to Resist Chloride Ion Penetration. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, 2019; p 8.
- Bjegović, D.; Serdar, M.; Oslaković, I.; Jacobs, F.; Beushausen, H.; Andrade, C.; Monteiro, A.; Paulini, P.; Nanukuttan, S. Test methods for concrete durability indicators. In Performance-Based Specifications and Control of Concrete Durability: State-of-the-Art Report RILEM TC 230-PSC, Beushausen, H., Fernandez Luco, L., Eds. Springer, Dordrecht: 2016; Vol. 18, pp. 51-105. [CrossRef]
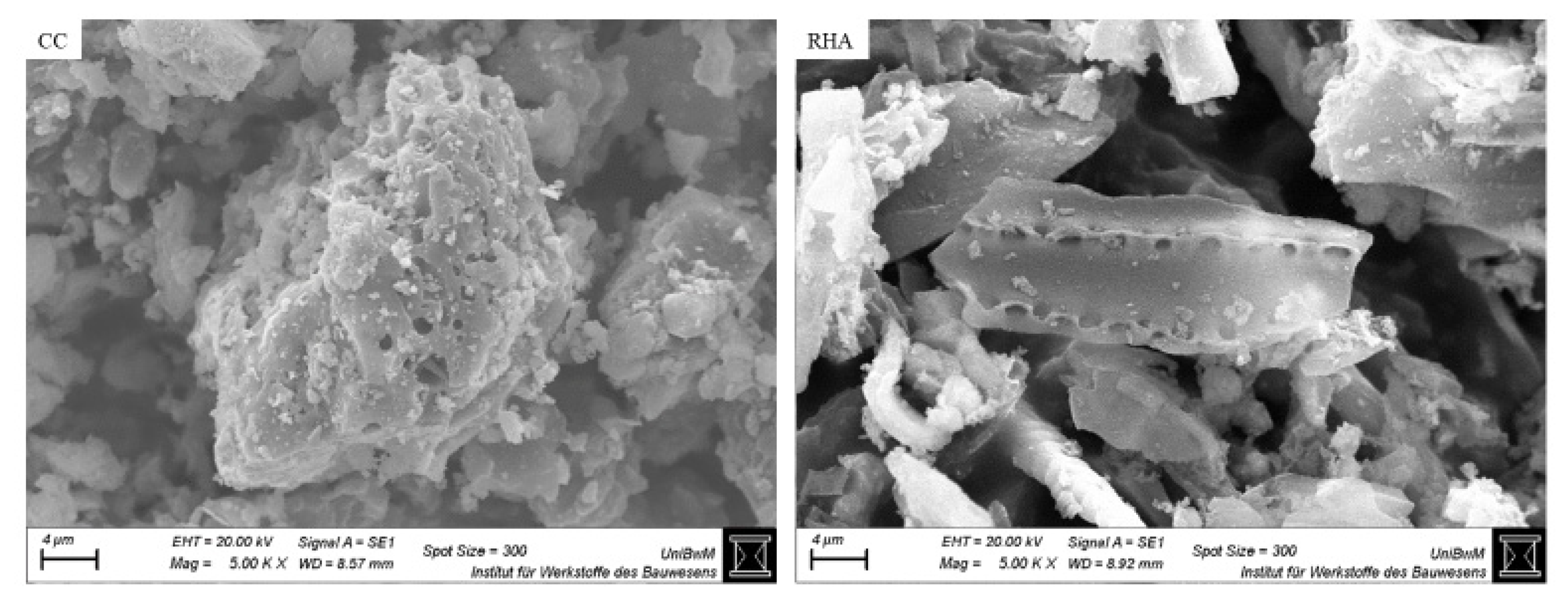
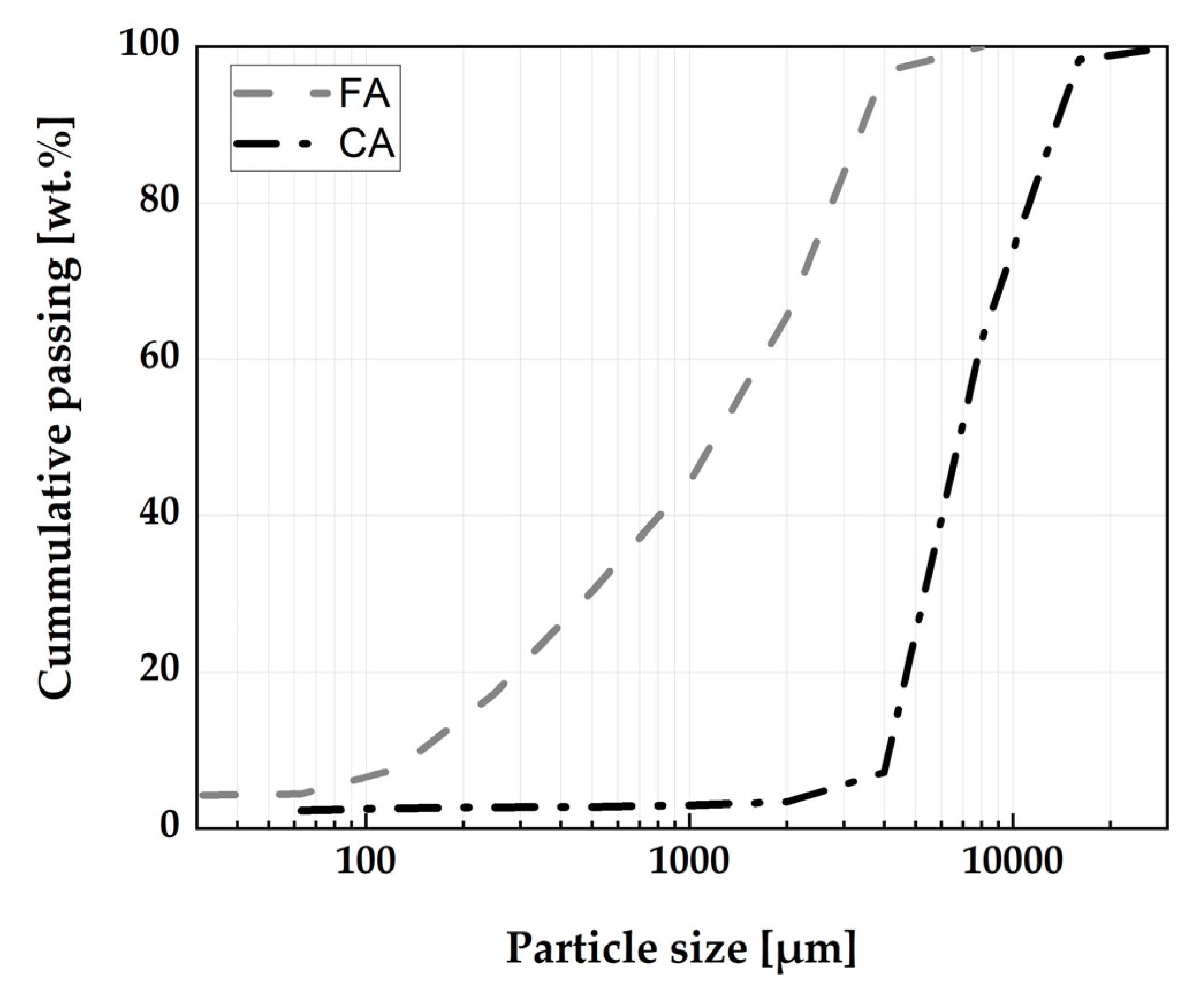

| Properties | Methodology | OPC | LP | CC | RHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specific surface area, m2/g | DIN ISO 9277 [33] | 1.0 | 1.6 | 3.9 | 160 |
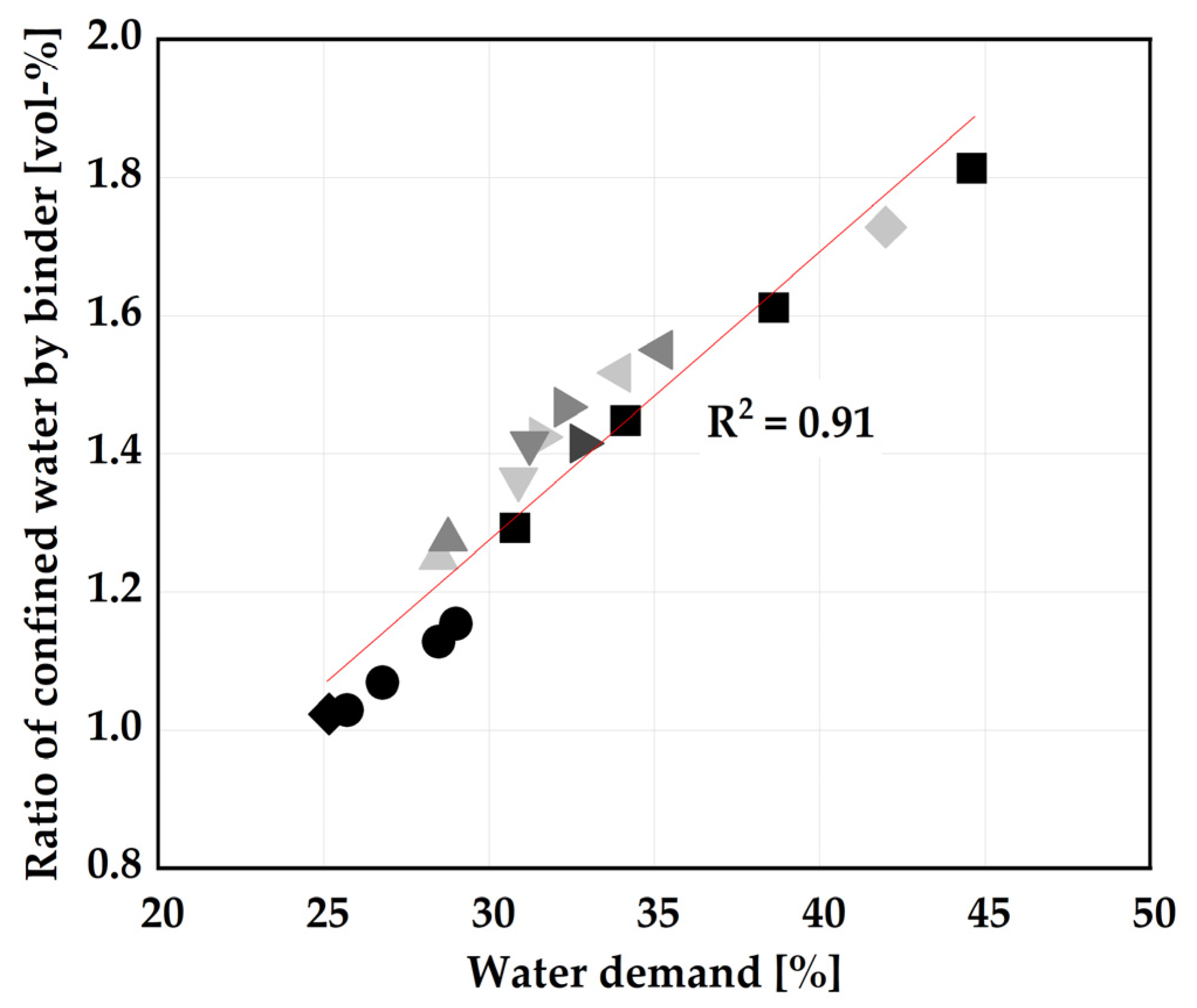
| Water demand, wt-% | Puntke method [34] | 29 | 20 | 38 | 96 |
| Particle density, g/cm3 | DIN EN ISO 17892-3 [35] | 3.29 | 2.81 | 2.65 | 2.4 |
| d10, µm | Bettersizer 3D instrument [31] | 2.6 | 0.8 | 1.9 | 5.4 |
| d50, µm | 16.0 | 4.6 | 12.7 | 23.7 | |
| d90, µm | 42.8 | 20.7 | 33.7 | 56.5 |
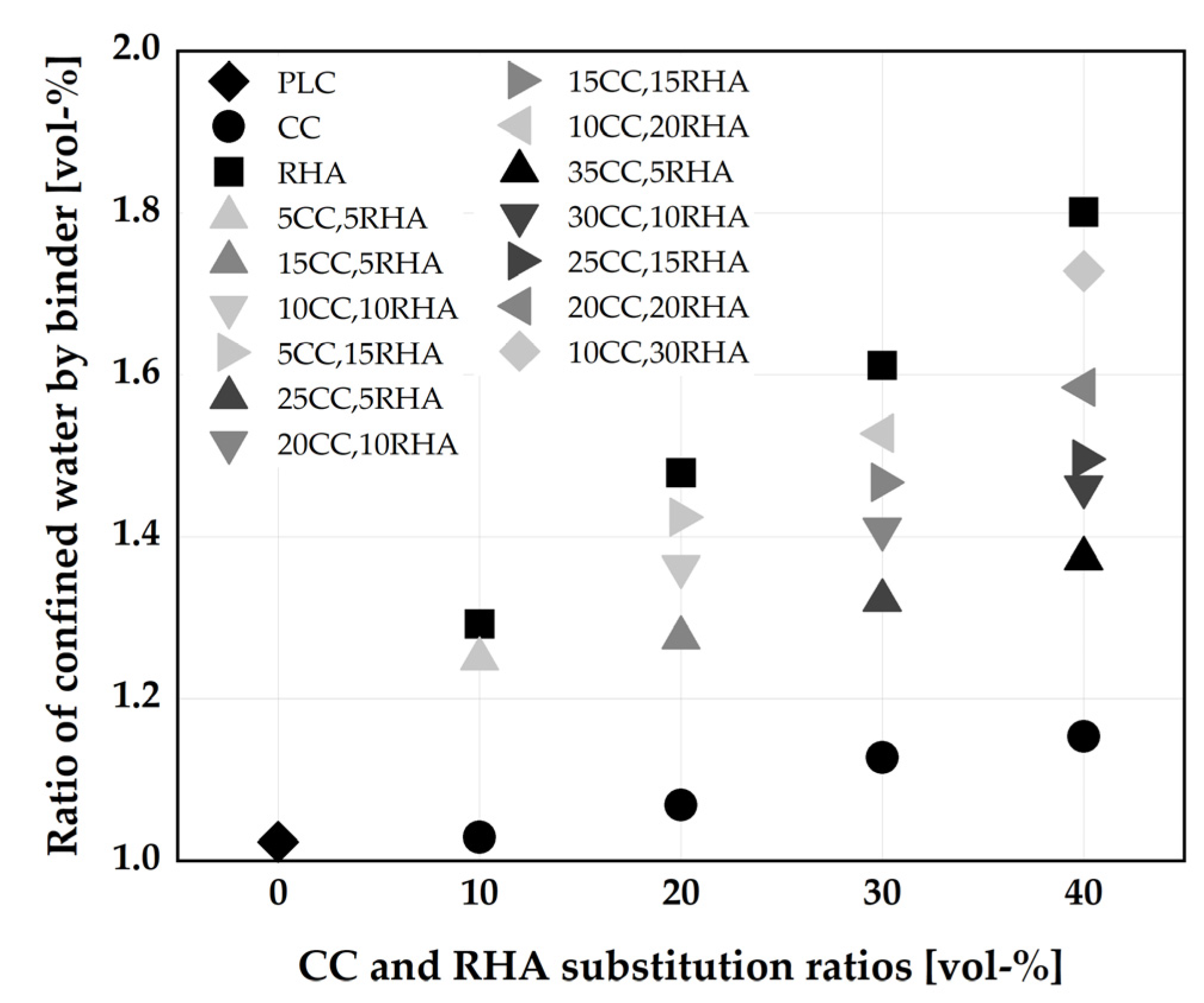
| CC | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RHA | ||||||||||
| 0 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.91 | 0.94 | 0.98 | |||||
| 5 | 1.1 | 1.08 | 1.12 | 1.17 | ||||||
| 10 | 1.10 | 1.16 | 1.2 | 1.24 | ||||||
| 15 | 1.21 | 1.25 | 1.27 | |||||||
| 20 | 1.26 | 1.3 | 1.35 | |||||||
| 25 | 1.34 | 1.42 | ||||||||
| 30 | 1.37 | 1.47 | ||||||||
| 35 | 1.50 | |||||||||
| 40 | 1.51 | |||||||||
| Mix designation | Constituent (measured in dm3/m3) |
Constituent (measured in kg/m3) |
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vw/Vp | OPC | LP | CC | RHA | Water | w/p | OPC | LP | CC | RHA | Water | SP [wt- %] |
|
| SC-P | 1.275 | 374 | 66 | - | - | 560 | 0.4 | 1231 | 185 | - | - | 560 | 0.05 |
| SC-P-20CC | 1.275 | 299 | 53 | 88 | - | 560 | 0.4 | 984 | 148 | 233 | - | 560 | 0.1 |
| SC-P-20RHA | 1.275 | 299 | 53 | - | 88 | 560 | 0.4 | 984 | 148 | - | 211 | 560 | 0.3 |
| SC-P-10CC+10RHA | 1.275 | 299 | 53 | 44 | 44 | 560 | 0.4 | 984 | 148 | 116 | 106 | 560 | 0.2 |
| Mix designation | Constituent (measured in dm3/m3) |
Constituent (measured in kg/m3) |
|||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vw/Vp | OPC | LP | CC | RHA | Water | FA | w/p | OPC | LP | CC | RHA | FA | Water | SP [wt- %] | |
| SC-M-1 | 1.275 | 224 | 40 | - | - | 336 | 400 | 0.4 | 738 | 111 | - | - | 1104 | 336 | 0.15 |
| SC-M-1-20CC | 1.275 | 179 | 32 | 53 | - | 336 | 400 | 0.4 | 591 | 89 | 140 | - | 1104 | 336 | 0.2 |
| SC-M-1-20RHA | 1.275 | 179 | 32 | - | 53 | 336 | 400 | 0.4 | 591 | 89 | - | 127 | 1104 | 336 | 0.4 |
| SC-M-1-10CC+10RHA | 1.275 | 179 | 32 | 26 | 26 | 336 | 400 | 0.4 | 591 | 89 | 70 | 63 | 1104 | 336 | 0.3 |
| Mix designation | Constituent (measured in dm3/m3) |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vw/Vp | OPC | LP | CC | RHA | Water | FA | CA | Va | |
| SCC-1 | 1.275 | 137 | 24 | - | - | 206 | 289 | 323 | 20 |
| SCC-1-20CC | 1.275 | 110 | 19 | 32 | - | 206 | 289 | 323 | 20 |
| SCC-1-20RHA | 1.275 | 110 | 19 | - | 32 | 206 | 289 | 323 | 20 |
| SCC-1-10CC+10RHA | 1.275 | 110 | 19 | 16 | 16 | 206 | 289 | 323 | 20 |
| Mix designation | Constituent (measured in kg/m3) |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w/p | OPC | LP | CC | RHA | Water | FA | CA | SP [wt- %] | |
| SCC-1 | 0.4 | 452 | 68 | - | - | 206 | 798 | 867 | 0.25 |
| SCC-1-20CC | 0.4 | 362 | 54 | 86 | - | 206 | 798 | 867 | 0.3 |
| SCC-1-20RHA | 0.4 | 362 | 54 | - | 78 | 206 | 798 | 867 | 0.7 |
| SCC-1-10CC+10RHA | 0.4 | 362 | 54 | 43 | 39 | 206 | 798 | 867 | 0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





