Submitted:
29 June 2023
Posted:
29 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Background on respiratory infections
1. Practical management
1. The relevance of mucus hyperproduction in respiratory infections
1. Muco-active drugs
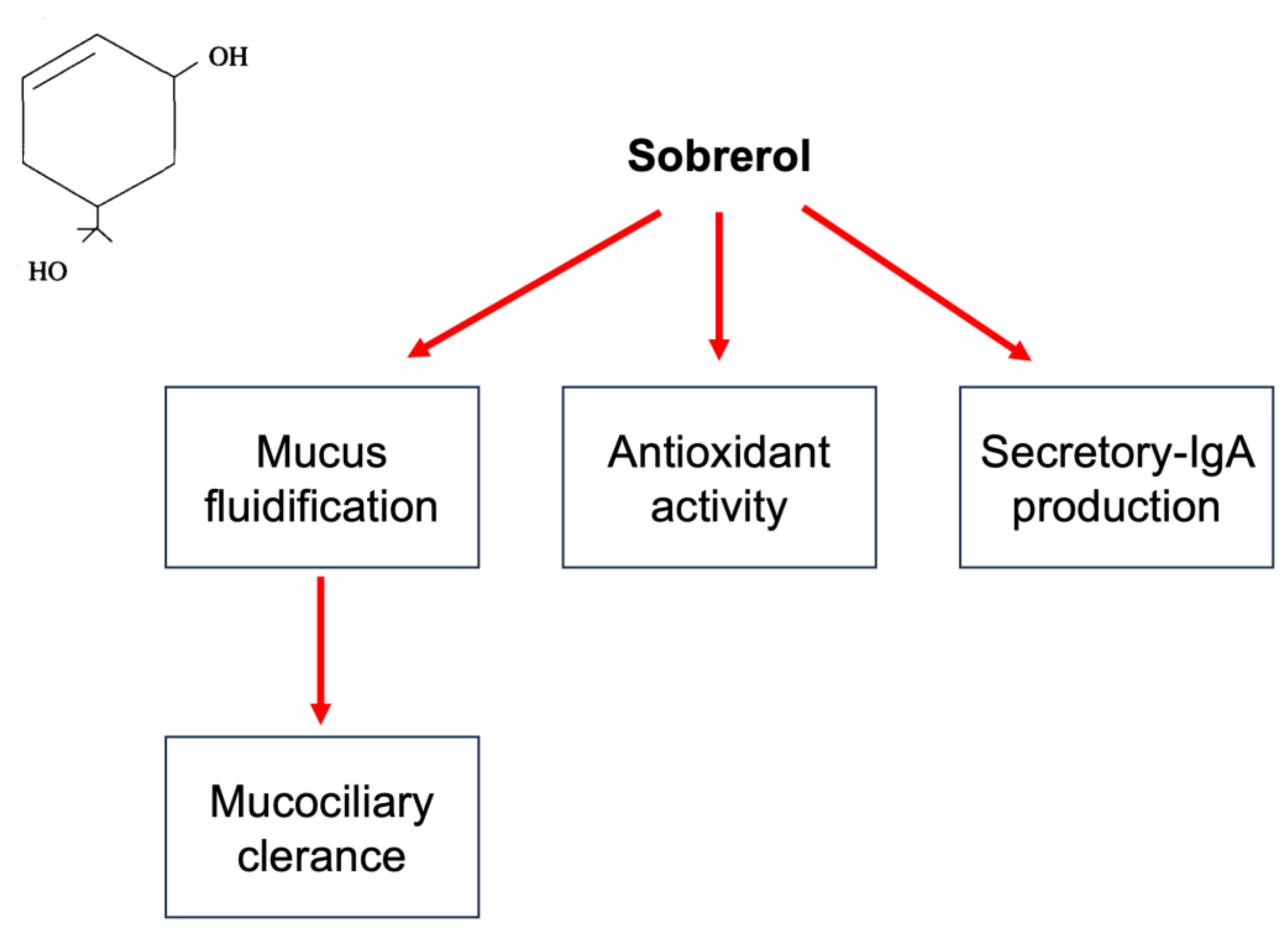
1. Sobrerol
1. Future perspectives
1. Conclusive remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Finley, C.R.; Chan, D.S.; Garrison, S.; Korownyk, C.; Kolber, M.R.; Campbell, S. What are the most common conditions in primary care? Systematic review. Can Fam Physician 2018, 64(11), 832–840. [Google Scholar]
- Murgia, V.; Manti, S.; Licari, A.; De Filippo, M.; Ciprandi, G.; Marseglia, G.L. Upper Respiratory Tract Infection-Associated Acute Cough and the Urge to Cough: New Insights for Clinical Practice. Pediatr Allergy Immunol Pulmonol 2020, 33(1), 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esneau, C.; Duff, A.C.; Bartlett, N.W. Understanding Rhinovirus Circulation and Impact on Illness. Viruses 2022, 14(1), 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Fan, Y.; Lai, Y.; Han, T.; Li, Z.; Zhou, P.; Pan, P.; Wang, W.; Hu, D.; Liu, X.; et al. Coronavirus infections and immune responses. J Med Virol 2020, 92(4), 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, E.C. Influenza Virus. Trends Microbiol 2018, 26(9), 809–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branche, A.R.; Falsey, A.R. Parainfluenza Virus Infection. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 2016, 37(4), 538–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Vecchio, A.; Ferrara, T.; Maglione, M.; Capasso, L.; Raimondi, F. New perspectives in Respiratory Syncitial Virus infection. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2013, 26 Suppl 2, 55–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, J.E.; Williams, J.V. Emerging Respiratory Viruses in Children. Infect Dis Clin North Am 2018, 32(1), 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriyama, M.; Hugentobler, W.J.; Iwasaki, A. Seasonality of Respiratory Viral Infections. Annu Rev Virol 2020, 7(1), 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eccles, R.; Wilkinson, J.E. Exposure to cold and acute upper respiratory tract infection. Rhinology 2015, 53, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humiston, S.G.; Pham, T.N. Influenza-Like Illness Diagnosis and Management in the Acute Care Setting. Pediatr Emerg Care 2016, 32(12), 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, J.A.; Shutt, D.P.; Moser, S.K.; Clegg, H.; Wearing, H.J.; Mukundan, H.; Manore, C.A. Distinguishing viruses responsible for influenza-like illness. J Theor Biol 2022, 545, 111145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzner, J.; Qasmieh, S.; Mounts, A.W.; Alexander, B.; Besselaar, T.; Briand, S.; Brown, C.; Clark, S.; Dueger, E.; Gross, D.; et al. Revision of clinical case definitions: influenza-like illness and severe acute respiratory infection. Bull World Health Organ 2018, 96(2), 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkinen, T.; Järvinen, A. The common cold. Lancet 2003, 361(9351), 51–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kardos, P.; Malek, F.A. Common Cold - an Umbrella Term for Acute Infections of Nose, Throat, Larynx and Bronchi. Pneumologie 2017, 71(4), 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passioti, M.; Maggina, P.; Megremis, S.; Papadopoulos, N.G. The common cold: potential for future prevention or cure. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 2014, 14(2), 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Common cold. https://www.cdc.gov/dotw/common- cold/index.html.
- DeGeorge, K.C.; Ring, D.J.; Dalrymple, S.N. Treatment of the common cold. Am Fam Physic 2019, 100, 281–9. [Google Scholar]
- Fokkens, W.; Lund, V.; Hopkins, C.; Hellings, P.; Kern, R.; Reitsma, S.; Toppila-salmi, S.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Mullol, J.; Alobid, I.; et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2020. Rhinology 2020, 58 (Suppl S29), 1–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degeorge, K.C.; Ring, D.J.; Dalrymple, S.N. Treatment of the common cold. Am Fam Physician 2019, 100, 281–9. [Google Scholar]
- Chiappini, E.; Parretti, A.; Becherucci, P.; Pierattelli, M.; Bonsignori, F.; Galli, L.; de Martino, M. Parental and medical knowledge and management of fever in Italian pre-school children. BMC Pediatrics 2012, 12, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciprandi, G.; Tosca, M.A. Non-pharmacological remedies for post-viral acute cough. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 2021, 9(1). [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Antibiotic use in the United States, 2023: progress and opportunities. Accessed June, 22, 2023.
- Jaume, F.; Valls-Mateus, M.; Mullol, J. Common Cold and Acute Rhinosinusitis: Up-to-Date Management in 2020. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 2020, 20(7), 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forchette, L.; Sebastian, W. , Liu T. A Comprehensive Review of COVID-19 Virology, Vaccines, Variants, and Therapeutics. Curr Med Sci. 2021, 41(6), 1037–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Anka, A.U; Tahir, M.I.; Abubakar, S.D.; Alsabbagh, M.; Zian, Z.; Hamedifar, H.; Sabzevari, A. , Azizi, G. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): An overview of the immunopathology, serological diagnosis and management. Scand J Immunol. 2021, 93(4), e12998. [Google Scholar]
- Van Brusselen, D.; De Troeyer, K.; Ter Haar, E.; Vander Auwera, A.; Poschet, K.; Van Nuijs, S.; Bael, A.; Stobbelaar, K.; Verhulst, S. , Van Herendael, B. , et al. Bronchiolitis in COVID-19 times: a nearly absent disease? Eur J Pediatr 2021, 180(6), 1969–1973. [Google Scholar]
- Cardenas, J.; Pringle, C.; Filipp, S.L.; Gurka, M.J.; Ryan, K.A.; Avery, K.L. Changes in Critical Bronchiolitis After COVID-19 Lockdown. Cureus 2022, 14(5), e25064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krumbein, H.; Kümmel, L.S.; Fragkou, P.C.; Thölken, C.; Hünerbein, B.L.; Reiter, R.; Papathanasiou, K.A.; Renz, H. , Skevaki, C. Respiratory viral co-infections in patients with COVID-19 and associated outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev Med Virol. 2023, 33(1), e2365. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, N.; Bosco-Levy, P.; Thurin, N.; Blin, P.; Droz-Perroteau, C. NSAIDs and COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Drug Saf 2021, 44(9), 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahy, J.V.; Dickey, B.F. Airway mucus function and dysfunction. N Engl J Med 2010, 363(23), 2233–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Rubin, B.K.; Voynow, J.A. Mucins, Mucus, and Goblet Cells. Chest 2018, 154(1), 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Schans, C.P. Bronchial mucus transport. Respir Care 2007, 52, 1150–6. [Google Scholar]
- Widdicombe, J. H. Regulation of the depth and composition of airways surface liquid. J Anat 2002, 201, 313–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansil, R.; Turner, B.S. The biology of mucus: Composition, synthesis and organization. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2018, 124, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, T.L.; Lock, J.Y.; Carrier, R.L. Engineering the Mucus Barrier. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 2018, 20, 197–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, R.J.; Chatterjee, B.; Loges, N.T.; Zentgraf, H.; Omran, H.; Lo, C.W. Initiation and maturation of cilia-generated flow in newborn and postnatal mouse airway. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2009, 296, 1067–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, C.M.; Koo, J.S. Airway mucus: the good, the bad, the sticky. Pharmacol Ther 2009, 121, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randell, S.H.; Boucher, R.C. Effective mucus clearance is essential for respiratory health. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2006, 35, 20–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaglione, F.; Petrini, O. Mucoactive Agents in the Therapy of Upper Respiratory Airways Infections: Fair to Describe Them Just as Mucoactive? Clin Med Insights Ear Nose Throat 2019, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, D.F. Mucoactive agents for airway mucus hypersecretory diseases. Respir Care 2007, 52, 1176–1193. [Google Scholar]
- Braga, P.C.; Allegra, L.; Bossi, R.; Scuri, R.; Castiglioni, C.L.; Romandini, S. Review on sobrerol as a muco-modifying drug: experimental data and clinical findings in hypersecretory bronchopulmonary diseases. Int J Clin Pharmacol Res 1987, 7, 381–400. [Google Scholar]
- Dalla Valle, V. L’impiego in terapie del dl-sobrerolo. Boll Chim Farm 1970, 109, 761–765. [Google Scholar]
- Braga, P.C.; Culici, M. Dal Sasso, M.; Falch, M.; Spallino, A. Antiradical activity of sobrerol investigated by electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR). Giorn It Mal Tor, 2009; 63, 263–267. [Google Scholar]
- Braga, P.C.; Allegra, L.; Bossi, R.; Scuri, R.; Castiglioni, C.L.; Romandini, S. Review on sobrerol as a muco-modifying drug: experimental data and clinical findings in hypersecretory bronchopulmonary diseases. Int J Clin Pharmacol Res 1987, 7, 381–400. [Google Scholar]
- Seidita, F.; Deiana, M.; Careddu, P. Acute bronchial diseases in paediatrics: therapeutic approach with sobrerol granules. G Ital Mal Torace 1984, 38, 191–194. [Google Scholar]
- Finiguerra, M.; De Martini, S.; Negri, L.; Simonelli, A. Clinical and functional effects of domiodol and sobrerol in hypersecretory bronchopneumonias. Minerva Med 1981, 72, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar]
- Medici, T.C.; Shang, H.; Grosgurin, P.; Berg, P.; Achermann, R.; Wehrli, R. No demonstrable effect of sobrerol as an expectorant in patients with stable chronic bronchial diseases. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir 1985, 21, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meyer-Shang, H.; Grosgurin, P.; Medici, T.C. Sobrerol as an expectorant in patients with stable chronic airway diseases: a controlled study. Prax Klin Pneumol 1983, 37, 936–938. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shang, H.; Grosgurin, P.; Medici, T.C. Sobrerol as expectorant in patients with stable chronic respiratory tract infections. A controlled study. Schweiz Med Wochenschr 1982, 112, 1846–1848. [Google Scholar]
- Pulerà, N.; Santolicandro, A.; Bernard, P. , Solfanelli, S.; Giuntini, C. Monodisperse labeled aerosol to visualize airflow redistribution in the lung after a mucokinetic drug. J Nucl Med Allied Sci 1989, 33, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Castiglioni, C.L.; Gramolini, C. Effect of long-term treatment with sobrerol on the exacerbations of chronic bronchitis. Respiration 1986, 50, 202–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellussi, L.; Manini, G.; Buccella, M.G.; Cacchi, R. Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of sobrerol granules in patients suffering from chronic rhinosinusitis. J Int Med Res 1990, 18, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distefano, S.M.; Palermo, F.; Crimi, N.; Mistretta, A.; Pamparana, F.; Messa, A. Evaluation of the activity of the carbocysteine-sobrerol combination on mucus spinnability. Int J Clin Pharmacol Res 1988, 8, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Milvio, C.; Di Tommaso, G.; Mader, R. Traitement des hypersécretions bronchiques dans les bronchopneumopathies aiguës et chroniques—étude contrôlée d’un nouveau composé à action mucolytique. Acta Ther 1981, 7, 243–260. [Google Scholar]
- Miraglia del Giudice, M.; Capristo, A.F.; Mirra, G.; Maiello, N.; Coppola, T. Controlled double-blind study on the efficacy of clofedanol-sobrerol in the treatment of pediatric pertussis. Minerva Pediatr 1984, 36, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar]
- Azzollini, E.; Bosi, M.; Mantegazza, M.; Piceci, E.; Careddu, P. Sobrerol (Sobrepim) administered dropwise to children with acute hypersecretory bronchopulmonary disease — a controlled trial v bromhexine. Clin Trials J 1990, 27, 241–249. [Google Scholar]
- Balzano, E.; De Gaetani, G. D1-sobrerol in the treatment of acute and chronic bronchopulmonary phlogoses. Minerva Med 1973, 64, 1995–2002. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Monzali, G.; Marchioni, C.F. Utilità di una nuova sostanza, il sobrerolo, nella terapia delle sequele della tubercolosi polmonare. Riv Pat Clin Tuberc 1970, 43, 562–563. [Google Scholar]
- Dotta, F.; Bianchi, A. Sobrerol for the treatment of chronic obstructive bronchopneumopathies (clinical and functional observations). Policlin Med 1971, 78, 82–90. [Google Scholar]
- Morandini, G.; Finiguerra, M.; Conti, P.; Bernocchi, D.; Manini, G. Treatment of chronic bronchitis—combined therapy with sustained-release theophylline (Teonova) and a mucoactive drug sobrerol (Sobrepin). Clin Trials J 1989, 26, 163–174. [Google Scholar]
- Morandini, G.C.; Finiguerra, M.; Messa, A.; Pamparana, F. L’associazione carbocisteina-sobrerolo nel trattamento della patologia cronico-ostruttiva dell’apparato respiratorio. Min Pneum 1986, 25, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Catena, E.; Marcatili, S.; Ciaccia, A. L’associazione carbocisteina-sobrerolo — studio clinico long-term nella profilassi delle riacutizzazioni da bronchite cronica. Med Toracica 1989, 11, 83–100. [Google Scholar]
- Gramiccioni, E.; Pamparana, F.; Messa, A. Mucolytic agents. Polycentric study of a carbocysteine-sobrerol combination. Arch Monaldi Mal Torace, 1989; 44, 791–793. [Google Scholar]
- Zanasi, A.; Cazzato, S.; Aprile, A.; Mazzolini, M.; Zenezini, C.; Pandolfi, P. Are antibiotics effective in treating children with acute moist cough? a retrospective study vs symptomatic therapy. Multidiscip Respir Med 2012, 7, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zanasi, A.; Lecchi, M.; Mazzolini, M.; Mastroroberto, M.; Nardi, E.; Morselli-Labate, A. Observational prospective study comparing mucoactive and antibiotic treatment in the management of acute cough from upper respiratory tract infections. Minerva Med 2015, 106, 239–246. [Google Scholar]
- Fadda, G. Oral neltenexine in patients with obstructive airways diseases: an open, randomised, controlled comparison versus sobrerol. Minerva Med 2001, 92, 269–275. [Google Scholar]
- Bellussi, L.; Bernocchi, D.; Ciferri, G.; Manini, G.; Passali, D. Sobrerol in the treatment of secretory otitis media in childhood. J Int Med Res 1989, 17, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milder, H.; Massari, M. Étude clinique d’un nouveau composé à activité mucolytique dans les bronchopneumopathies aiguës et chroniques. Acta Ther 1981, 7, 391–408. [Google Scholar]
- Crosca, V.; Ajello, A.; Crosca, C.; Minniti, A. Salbutamol combined with erythromycin and sobrerol in the therapy of pertussis. Arch Sci Med (Torino) 1982, 139, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Direct action |
Drugs depolymerizing mucins | - Thiolics - Enzymes - Other molecules |
- Cysteine - Methylciytein - Ethylciytein - Acetylcysteine - Erdostein - Ludostein - Stepronin - Thipronin - Mesna - Trypsin - Streptokinase - Serratiopeptidase - Stericase - Urea - Ascorbic acid - Hypertonic saline - Inorganic iodures |
| Indirect action |
Drugs modifying mucus secretion Drugs modifying adhesivity of gel layer Drugs modifying the sol layer Volatile and balsamic agents Drugs stimulating gastric reflex (cough inducing) Drugs modifying secretion |
• S-carbossimethylcystein • Sobrerol • Domiodol • Hydropropylidenglycerol • Ambroxol • Bromexine • Propylene-glycol • Etasulphate sodic • Bicarbonate sodic • H2O • Potassium salts • Sodium salts • Pinanes - Terpenes - Methanes - Phenol derivates - Ammonium chloride - Sodium citrate - Guaifenesin - Ipecap • -adrenergic agents - cholinergic agents - corticosteroids • - antihistamines |
| Authors (ref) | Study design | Disease | Patients number (age) | Primary outcomes | Treatments (dosage and duration) |
Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seidita et al. (46) | RCT | Acute respiratory infections | 20/20 (3-12 years) |
Clinical signs Expectorate Biological data |
Oral sobrerol (100mgx3/day) Oral N-Acteylcysteine (100mgx3/day) One week |
Sobrerol significantly reduced mucus viscosity |
| Milvio et al. (55) | RCT | Acute and chronic infections | 50/50 (12-74 years) |
Lung function Expectorate |
Oral sobrerol (260mg) + carbocysteine (375mg)x4/day Placebo 14-21 days |
Active treatment significantly improved all outcomes |
| Miraglia del Giudice et al. (56) | RCT | Pertussis | 15/15 (10 months-12 years) |
Clinical signs Lung function |
Clofedanol (1.62mg/kg/d)+oral sobrerol (6mg/kg/d) Placebo 15 days |
Active treatment improved parameters more quickly |
| Azzolini et al. (57) | Open | Acute and recurrent bronchitis | 40 (< 5 years) |
Improvement rate | Oral sobrerol (50-100mgx2/d) Oral brohexine (2-4x3/d) 2 weeks |
No difference |
| Zanasi et al. (65) | Open | Acute upper respiratory infections with wet cough | 59 (3-14 years) |
Severity, frequency, and duration of cough | Antibiotics (amoxicillin or erythromycic) Nebulized sobrerol or N-Acetylcysteine. |
Mucolytics improved cough |
| Bellussi et al. (68) | Open | Secretory otitis media | 30 (5-10 years) |
Nasal obstruction, earache, deafness | Nbulized sobrerol (40mg/d) 10 days |
Significant reduction of all outcomes |
| Crosca et al. (70) | Open | Pertussis | 20 (6 months-2 years) |
Time to resolution | Oral or rectal sobrerol Salbutamol Erythromycin Until resolution |
Better outcomes in comparison with historical records |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





