Submitted:
22 June 2023
Posted:
29 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
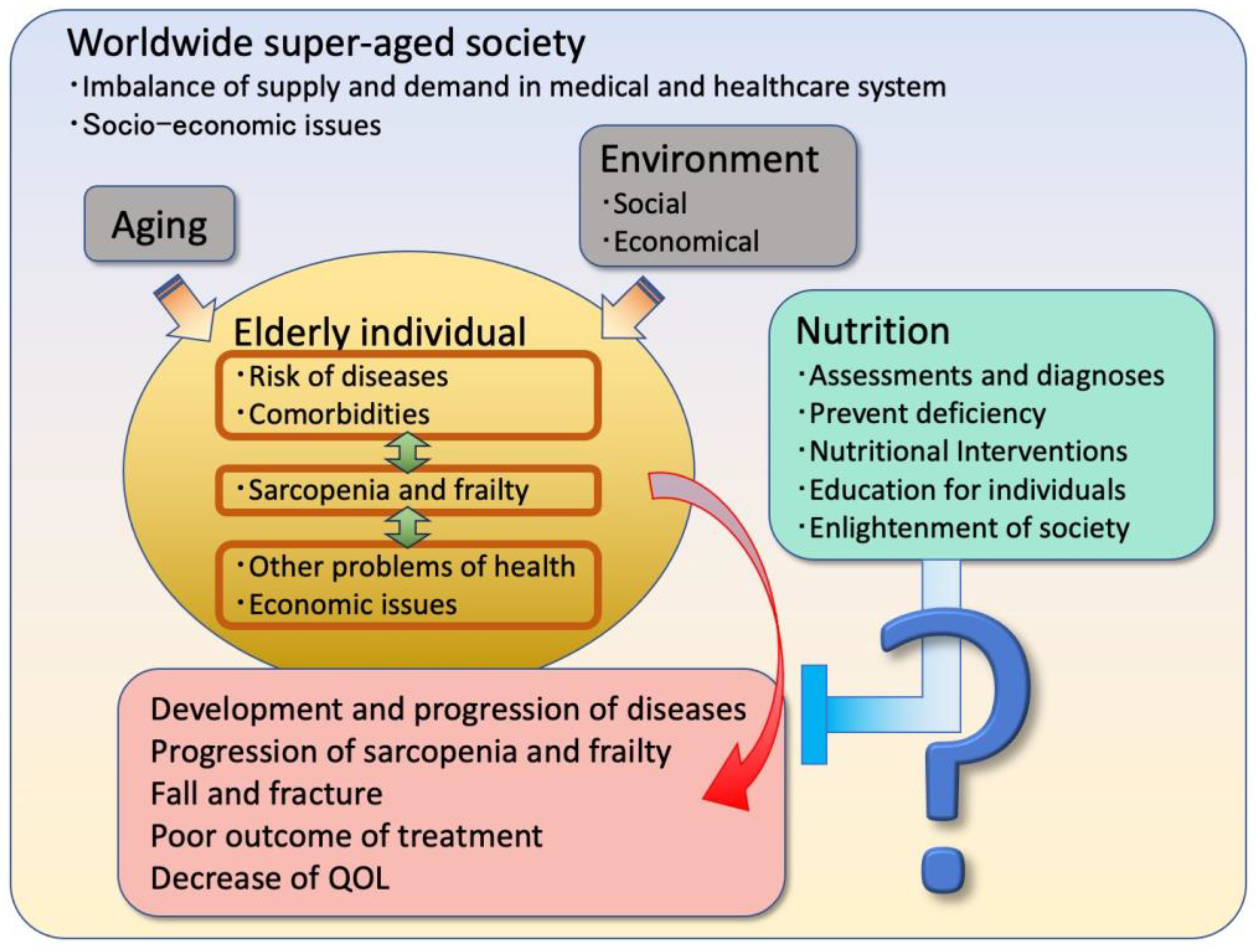
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
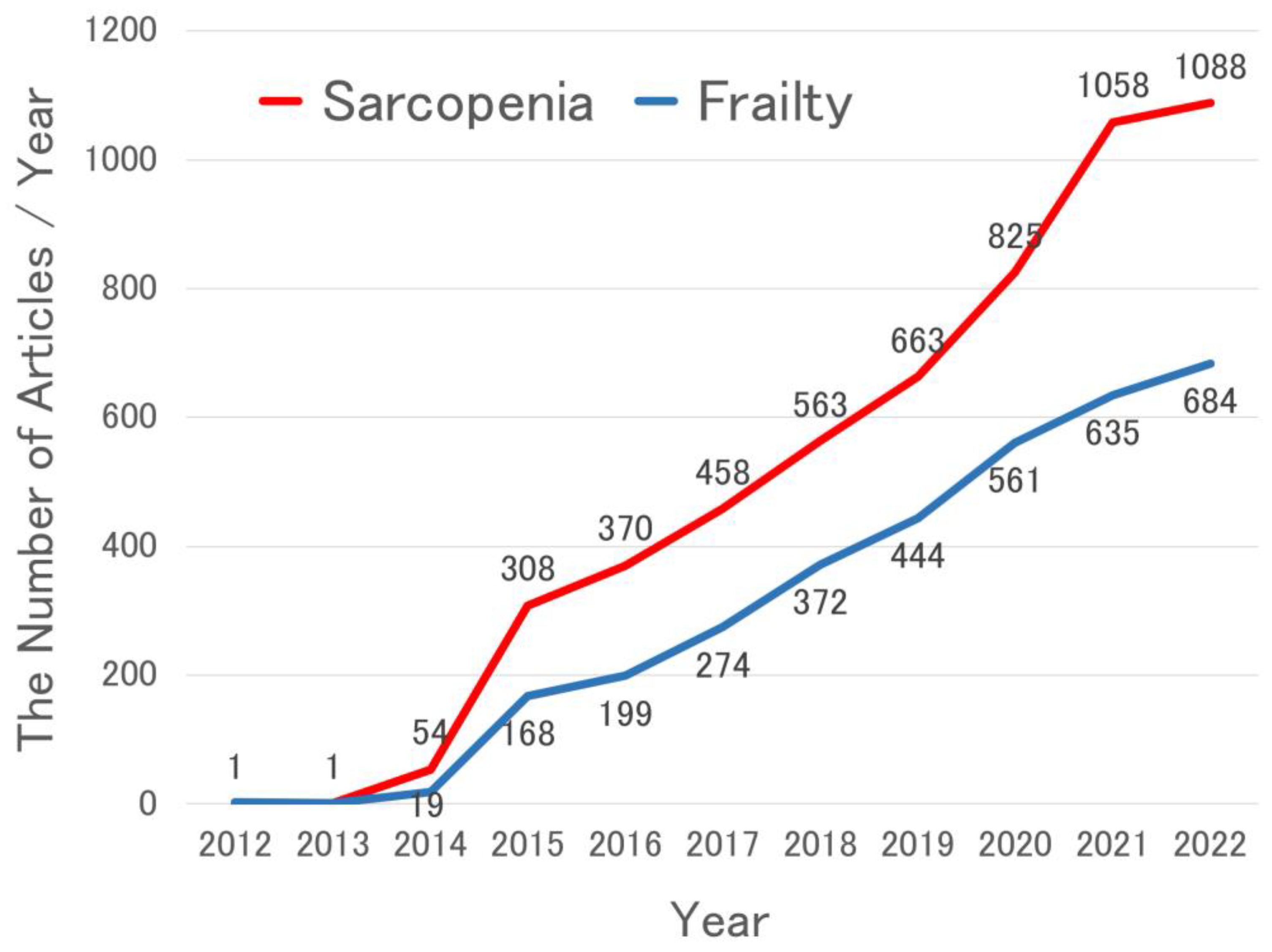
3.1. The Number of retrieved articles
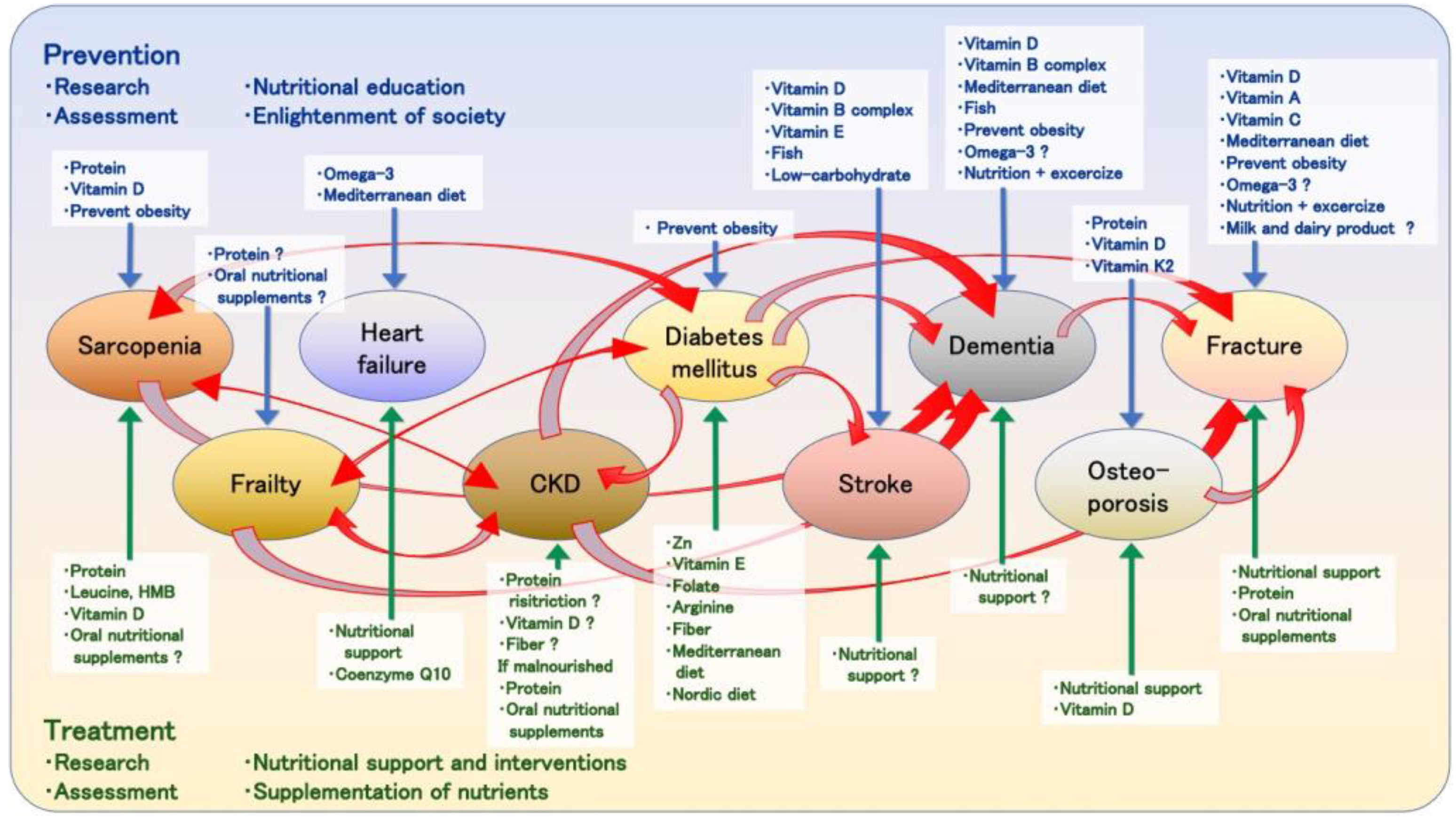
3.2. The Analysis of retrieved articles
3.2.1. Sarcopenia and nutrition
3.2.2. Frailty and nutrition
3.2.3. Heart failure and nutrition
3.2.4. CKD and nutrition
3.2.5. Diabetes and nutrition
3.2.6. Stroke and nutrition
3.2.7. Dementia and nutrition
3.2.8. Osteoporosis and nutrition
3.2.9. Fracture and nutrition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- The Department of Economic and Social Affairs of the United Nations. World Social Report 2023: Leaving No One behind in an Aging World. 2023.
- The World Bank. Population Ages 65 and above (% of Total). Available Online: Http://Data.Worldbank.Org/Indicator/SP.POP.65UP.TO.ZS (Accessed on 16/05/2023).
- American Diabetes Association. Older Adults: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2019. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, S139–S147. [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, Regional and Country-Level Diabetes Prevalence Estimates for 2021 and Projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2022, 183, 109119. [CrossRef]
- van Riet, E.E.S.; Hoes, A.W.; Wagenaar, K.P.; Limburg, A.; Landman, M.A.J.; Rutten, F.H. Epidemiology of Heart Failure: The Prevalence of Heart Failure and Ventricular Dysfunction in Older Adults over Time. A Systematic Review. Eur J Heart Fail 2016, 18, 242–252. [CrossRef]
- Emmons-Bell, S.; Johnson, C.; Roth, G. Prevalence, Incidence and Survival of Heart Failure: A Systematic Review. Heart 2022, 108, 1351–1360. [CrossRef]
- Ohno, Y.; Ishimura, E.; Naganuma, T.; Kondo, K.; Fukushima, W.; Mui, K.; Inaba, M.; Hirota, Y. Prevalence of and Factors Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) in Japanese Subjects without Notable Chronic Diseases, Undergoing an Annual Health Checkup. Kidney Blood Press Res 2012, 36, 139–148. [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.; McCulloch, C.E.; Lin, F.; Banerjee, T.; Bragg-Gresham, J.L.; Eberhardt, M.S.; Morgenstern, H.; Pavkov, M.E.; Saran, R.; Powe, N.R.; et al. Trends in Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease in the United States. Ann Intern Med 2016, 165, 473–481. [CrossRef]
- Betzler, B.K.; Sultana, R.; He, F.; Tham, Y.C.; Lim, C.C.; Wang, Y.X.; Nangia, V.; Tai, E.S.; Rim, T.H.; Bikbov, M.M.; et al. Impact of Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) GFR Estimating Equations on CKD Prevalence and Classification Among Asians. Front Med (Lausanne) 2022, 9, 957437. [CrossRef]
- Zemedikun, D.T.; Gray, L.J.; Khunti, K.; Davies, M.J.; Dhalwani, N.N. Patterns of Multimorbidity in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: An Analysis of the UK Biobank Data. Mayo Clin Proc 2018, 93, 857–866. [CrossRef]
- Wafa, H.A.; Wolfe, C.D.A.; Emmett, E.; Roth, G.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Wang, Y. Burden of Stroke in Europe: Thirty-Year Projections of Incidence, Prevalence, Deaths, and Disability-Adjusted Life Years. Stroke 2020, 51, 2418–2427. [CrossRef]
- Avan, A.; Hachinski, V. Stroke and Dementia, Leading Causes of Neurological Disability and Death, Potential for Prevention. Alzheimers Dement 2021, 17, 1072–1076. [CrossRef]
- Tarvonen-Schröder, S.; Niemi, T.; Koivisto, M. Inpatient Rehabilitation After Acute Severe Stroke: Predictive Value of the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale Among Other Potential Predictors for Discharge Destination. Advances in rehabilitation science and practice 2023, 12, 27536351231157970. [CrossRef]
- Makovski, T.T.; Schmitz, S.; Zeegers, M.P.; Stranges, S.; van den Akker, M. Multimorbidity and Quality of Life: Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis. Ageing Res Rev 2019, 53, 100903. [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European Consensus on Definition and Diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [CrossRef]
- 16. Chen, L.K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.W.; Chou, M.Y.; Iijima, K.; Jang, H.C.; Kang, L.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus Update on Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Treatment. J Am Med Dir Assoc 2020, 21, 300-307.e2. [CrossRef]
- 17. Fried, L.P.; Tangen, C.M.; Walston, J.; Newman, A.B.; Hirsch, C.; Gottdiener, J.; Seeman, T.; Tracy, R.; Kop, W.J.; Burke, G.; et al. Frailty in Older Adults: Evidence for a Phenotype. Journals of Gerontology - Series A Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences 2001. [CrossRef]
- Bahat, G.; Ilhan, B. Sarcopenia and the Cardiometabolic Syndrome: A Narrative Review. Eur Geriatr Med 2016, 7, 220–223. [CrossRef]
- Stewart, R. Cardiovascular Disease and Frailty: What Are the Mechanistic Links? Clin Chem 2019, 65, 80–86. [CrossRef]
- Bone, A.E.; Hepgul, N.; Kon, S.; Maddocks, M. Sarcopenia and Frailty in Chronic Respiratory Disease: Lessons from Gerontology. Chron Respir Dis 2017, 14, 85–99. [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, A.J.; Abdelhafiz, A.H.; Rodríguez-Mañas, L. Frailty and Sarcopenia - Newly Emerging and High Impact Complications of Diabetes. J Diabetes Complications 2017, 31, 1465–1473. [CrossRef]
- Pacifico, J.; Geerlings, M.A.J.; Reijnierse, E.M.; Phassouliotis, C.; Lim, W.K.; Maier, A.B. Prevalence of Sarcopenia as a Comorbid Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Exp Gerontol 2020, 131. [CrossRef]
- Pacifico, J.; Reijnierse, E.M.; Lim, W.K.; Maier, A.B. The Association between Sarcopenia as a Comorbid Disease and Incidence of Institutionalisation and Mortality in Geriatric Rehabilitation Inpatients: REStORing Health of Acutely Unwell AdulTs (RESORT). Gerontology 2021, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Jeong, J.B.; Kang, J.; Ahn, D.-W.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, B.G.; Lee, K.L.; Oh, S.; Yoon, S.H.; Park, S.J.; et al. Association between Sarcopenia Level and Metabolic Syndrome. PLoS One 2021, 16, e0248856. [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, R.; Peel, N.M.; Krosch, M.; Hubbard, R.E. Frailty and Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 2017, 68, 135–142. [CrossRef]
- Sabatino, A.; Cuppari, L.; Stenvinkel, P.; Lindholm, B.; Avesani, C.M. Sarcopenia in Chronic Kidney Disease: What Have We Learned so Far? J Nephrol 2021, 34, 1347–1372. [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, H.S.; Neri, S.G.R.; Oliveira, J.S.; Bennett, P.N.; Viana, J.L.; Lima, R.M. Association between Sarcopenia and Clinical Outcomes in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin Nutr 2022, 41, 1131–1140. [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.C.; Chen, W.L.; Wu, L.W.; Chang, Y.W.; Kao, T.W. Sarcopenia and Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clinical Nutrition 2020, 39, 2695–2701. [CrossRef]
- Landi, F.; Liperoti, R.; Russo, A.; Giovannini, S.; Tosato, M.; Capoluongo, E.; Bernabei, R.; Onder, G. Sarcopenia as a Risk Factor for Falls in Elderly Individuals: Results from the IlSIRENTE Study. Clinical Nutrition 2012. [CrossRef]
- Yeung, S.S.Y.; Reijnierse, E.M.; Pham, V.K.; Trappenburg, M.C.; Lim, W.K.; Meskers, C.G.M.; Maier, A.B. Sarcopenia and Its Association with Falls and Fractures in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019, 10, 485–500.
- GBD 2019 Dementia Forecasting Collaborators Estimation of the Global Prevalence of Dementia in 2019 and Forecasted Prevalence in 2050: An Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Public Health 2022, 7, e105–e125. [CrossRef]
- Scheltens, P.; Blennow, K.; Breteler, M.M.B.; de Strooper, B.; Frisoni, G.B.; Salloway, S.; Van der Flier, W.M. Alzheimer’s Disease. Lancet 2016, 388, 505–517. [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.T.; Thomas, A. Vascular Dementia. Lancet 2015, 386, 1698–1706. [CrossRef]
- Vishwanath, S.; Qaderi, V.; Steves, C.J.; Reid, C.M.; Hopper, I.; Ryan, J. Cognitive Decline and Risk of Dementia in Individuals With Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Card Fail 2022, 28, 1337–1348. [CrossRef]
- Viggiano, D.; Wagner, C.A.; Martino, G.; Nedergaard, M.; Zoccali, C.; Unwin, R.; Capasso, G. Mechanisms of Cognitive Dysfunction in CKD. Nat Rev Nephrol 2020, 16, 452–469. [CrossRef]
- Bordier, L.; Doucet, J.; Boudet, J.; Bauduceau, B. Update on Cognitive Decline and Dementia in Elderly Patients with Diabetes. Diabetes Metab 2014, 40, 331–337. [CrossRef]
- Aranda, M.P.; Kremer, I.N.; Hinton, L.; Zissimopoulos, J.; Whitmer, R.A.; Hummel, C.H.; Trejo, L.; Fabius, C. Impact of Dementia: Health Disparities, Population Trends, Care Interventions, and Economic Costs. J Am Geriatr Soc 2021, 69, 1774–1783. [CrossRef]
- Burks, H.B.; des Bordes, J.K.A.; Chadha, R.; Holmes, H.M.; Rianon, N.J. Quality of Life Assessment in Older Adults with Dementia: A Systematic Review. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 2021, 50, 103–110. [CrossRef]
- Haagsma, J.A.; Olij, B.F.; Majdan, M.; van Beeck, E.F.; Vos, T.; Castle, C.D.; Dingels, Z. V; Fox, J.T.; Hamilton, E.B.; Liu, Z.; et al. Falls in Older Aged Adults in 22 European Countries: Incidence, Mortality and Burden of Disease from 1990 to 2017. Inj Prev 2020, 26, i67–i74. [CrossRef]
- Dyer, S.M.; Crotty, M.; Fairhall, N.; Magaziner, J.; Beaupre, L.A.; Cameron, I.D.; Sherrington, C.; Fragility Fracture Network (FFN) Rehabilitation Research Special Interest Group A Critical Review of the Long-Term Disability Outcomes Following Hip Fracture. BMC Geriatr 2016, 16, 158. [CrossRef]
- Guzon-Illescas, O.; Perez Fernandez, E.; Crespí Villarias, N.; Quirós Donate, F.J.; Peña, M.; Alonso-Blas, C.; García-Vadillo, A.; Mazzucchelli, R. Mortality after Osteoporotic Hip Fracture: Incidence, Trends, and Associated Factors. J Orthop Surg Res 2019, 14, 203. [CrossRef]
- Komar, B.; Schwingshackl, L.; Hoffmann, G. Effects of Leucine-Rich Protein Supplements on Anthropometric Parameter and Muscle Strength in the Elderly: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Nutr Health Aging 2015, 19, 437–446. [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Arnau, F.M.; Fonfría-Vivas, R.; Cauli, O. Beneficial Effects of Leucine Supplementation on Criteria for Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2019, 11. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Lim, J.-Y. Effects of Leucine-Rich Protein Supplements in Older Adults with Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 2022, 102, 104758. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Fu, X.; Hu, Q.; Chen, L.; Zuo, H. The Effect of Leucine Supplementation on Sarcopenia-Related Measures in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 17 Randomized Controlled Trials. Front Nutr 2022, 9, 929891. [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Xia, Y.; Jiang, J.; Du, H.; Guo, X.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Huang, G.; Niu, K. Effect of Beta-Hydroxy-Beta-Methylbutyrate Supplementation on Muscle Loss in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 2015, 61, 168–175. [CrossRef]
- Bear, D.E.; Langan, A.; Dimidi, E.; Wandrag, L.; Harridge, S.D.R.; Hart, N.; Connolly, B.; Whelan, K. β-Hydroxy-β-Methylbutyrate and Its Impact on Skeletal Muscle Mass and Physical Function in Clinical Practice: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am J Clin Nutr 2019, 109, 1119–1132. [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Zhao, A.; He, J. Effect of β-Hydroxy-β-Methylbutyrate (HMB) on the Muscle Strength in the Elderly Population: A Meta-Analysis. Front Nutr 2022, 9, 914866. [CrossRef]
- Zanini, B.; Simonetto, A.; Zubani, M.; Castellano, M.; Gilioli, G. The Effects of Cow-Milk Protein Supplementation in Elderly Population: Systematic Review and Narrative Synthesis. Nutrients 2020, 12. [CrossRef]
- Camargo, L. da R.; Doneda, D.; Oliveira, V.R. Whey Protein Ingestion in Elderly Diet and the Association with Physical, Performance and Clinical Outcomes. Exp Gerontol 2020, 137, 110936. [CrossRef]
- Martin-Cantero, A.; Reijnierse, E.M.; Gill, B.M.T.; Maier, A.B. Factors Influencing the Efficacy of Nutritional Interventions on Muscle Mass in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutr Rev 2021, 79, 315–330. [CrossRef]
- Gielen, E.; Beckwée, D.; Delaere, A.; De Breucker, S.; Vandewoude, M.; Bautmans, I.; Sarcopenia Guidelines Development Group of the Belgian Society of Gerontology and Geriatrics (BSGG) Nutritional Interventions to Improve Muscle Mass, Muscle Strength, and Physical Performance in Older People: An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses. Nutr Rev 2021, 79, 121–147. [CrossRef]
- Khor, P.Y.; Vearing, R.M.; Charlton, K.E. The Effectiveness of Nutrition Interventions in Improving Frailty and Its Associated Constructs Related to Malnutrition and Functional Decline among Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Systematic Review. J Hum Nutr Diet 2022, 35, 566–582. [CrossRef]
- Tieland, M.; Franssen, R.; Dullemeijer, C.; van Dronkelaar, C.; Kyung Kim, H.; Ispoglou, T.; Zhu, K.; Prince, R.L.; van Loon, L.J.C.; de Groot, L.C.P.G.M. The Impact of Dietary Protein or Amino Acid Supplementation on Muscle Mass and Strength in Elderly People: Individual Participant Data and Meta-Analysis of RCT’s. J Nutr Health Aging 2017, 21, 994–1001. [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.-Y.; Huang, K.-S.; Chen, K.-M.; Chou, C.-P.; Tu, Y.-K. Exercise, Nutrition, and Combined Exercise and Nutrition in Older Adults with Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Maturitas 2021, 145, 38–48. [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.-D.; Wu, Y.-T.; Tsauo, J.-Y.; Chen, P.-R.; Tu, Y.-K.; Chen, H.-C.; Liou, T.-H. Effects of Protein Supplementation Combined with Exercise Training on Muscle Mass and Function in Older Adults with Lower-Extremity Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials. Nutrients 2020, 12. [CrossRef]
- Conde Maldonado, E.; Marqués-Jiménez, D.; Casas-Agustench, P.; Bach-Faig, A. Effect of Supplementation with Leucine Alone, with Other Nutrients or with Physical Exercise in Older People with Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review. Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr 2022, 69, 601–613. [CrossRef]
- Kirwan, R.P.; Mazidi, M.; Rodríguez García, C.; Lane, K.E.; Jafari, A.; Butler, T.; Perez de Heredia, F.; Davies, I.G. Protein Interventions Augment the Effect of Resistance Exercise on Appendicular Lean Mass and Handgrip Strength in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am J Clin Nutr 2022, 115, 897–913. [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.; Kim, H.; Bae, J. Does the Combination of Resistance Training and a Nutritional Intervention Have a Synergic Effect on Muscle Mass, Strength, and Physical Function in Older Adults? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Geriatr 2021, 21, 639. [CrossRef]
- Beaudart, C.; Dawson, A.; Shaw, S.C.; Harvey, N.C.; Kanis, J.A.; Binkley, N.; Reginster, J.Y.; Chapurlat, R.; Chan, D.C.; Bruyère, O.; et al. Nutrition and Physical Activity in the Prevention and Treatment of Sarcopenia: Systematic Review. Osteoporos Int 2017, 28, 1817–1833. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.K.; Quinn, M.A.; Saunders, D.H.; Greig, C.A. Protein Supplementation Does Not Significantly Augment the Effects of Resistance Exercise Training in Older Adults: A Systematic Review. J Am Med Dir Assoc 2016, 17, 959.e1-9. [CrossRef]
- Courel-Ibáñez, J.; Vetrovsky, T.; Dadova, K.; Pallarés, J.G.; Steffl, M. Health Benefits of β-Hydroxy-β-Methylbutyrate (HMB) Supplementation in Addition to Physical Exercise in Older Adults: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2019, 11. [CrossRef]
- Theodorakopoulos, C.; Jones, J.; Bannerman, E.; Greig, C.A. Effectiveness of Nutritional and Exercise Interventions to Improve Body Composition and Muscle Strength or Function in Sarcopenic Obese Older Adults: A Systematic Review. Nutr Res 2017, 43, 3–15. [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.-H.; Liu, J.Y.W.; Välimäki, M. Effectiveness of Non-Pharmacological Interventions on the Management of Sarcopenic Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Exp Gerontol 2020, 135, 110937. [CrossRef]
- Antoniak, A.E.; Greig, C.A. The Effect of Combined Resistance Exercise Training and Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Musculoskeletal Health and Function in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e014619. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.-H.; Chen, K.-H.; Chen, C.; Chu, W.-C.; Kang, Y.-N. The Optimal Strategy of Vitamin D for Sarcopenia: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- Cintoni, M.; Grassi, F.; Palombaro, M.; Rinninella, E.; Pulcini, G.; Di Donato, A.; Salvatore, L.; Quero, G.; Tortora, G.; Alfieri, S.; et al. Nutritional Interventions during Chemotherapy for Pancreatic Cancer: A Systematic Review of Prospective Studies. Nutrients 2023, 15. [CrossRef]
- Bozzetti, F. Nutritional Interventions in Elderly Gastrointestinal Cancer Patients: The Evidence from Randomized Controlled Trials. Support Care Cancer 2019, 27, 721–727. [CrossRef]
- Johnston, H.E.; Takefala, T.G.; Kelly, J.T.; Keating, S.E.; Coombes, J.S.; Macdonald, G.A.; Hickman, I.J.; Mayr, H.L. The Effect of Diet and Exercise Interventions on Body Composition in Liver Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.-J.; Lu, Q. The Effect of Oral Nutritional Supplement on Muscle Fitness of Patients Undergoing Dialysis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Adv Nurs 2021, 77, 1716–1730. [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, S.C.; Bernal, W.; Dasarathy, S.; Merli, M.; Plank, L.D.; Schütz, T.; Plauth, M. ESPEN Practical Guideline: Clinical Nutrition in Liver Disease. Clin Nutr 2020, 39, 3533–3562. [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, S.C.; Barazzoni, R.; Busetto, L.; Campmans-Kuijpers, M.; Cardinale, V.; Chermesh, I.; Eshraghian, A.; Kani, H.T.; Khannoussi, W.; Lacaze, L.; et al. European Guideline on Obesity Care in Patients with Gastrointestinal and Liver Diseases - Joint ESPEN/UEG Guideline. Clin Nutr 2022, 41, 2364–2405. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xu, H.; Chen, L.; Zhu, M. Exercise and Nutritional Intervention for Physical Function of the Prefrail: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Am Med Dir Assoc 2022, 23, 1431.e1-1431.e19. [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Liu, W.; Gao, Y.; Qin, L.; Feng, H.; Tan, H.; Chen, Q.; Peng, L.; Wu, I.X.Y. Comparative Effectiveness of Non-Pharmacological Interventions for Frailty: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Age Ageing 2023, 52. [CrossRef]
- Moraes, M.B. de; Avgerinou, C.; Fukushima, F.B.; Vidal, E.I.O. Nutritional Interventions for the Management of Frailty in Older Adults: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Nutr Rev 2021, 79, 889–913. [CrossRef]
- Thomson, K.; Rice, S.; Arisa, O.; Johnson, E.; Tanner, L.; Marshall, C.; Sotire, T.; Richmond, C.; O’Keefe, H.; Mohammed, W.; et al. Oral Nutritional Interventions in Frail Older People Who Are Malnourished or at Risk of Malnutrition: A Systematic Review. Health Technol Assess 2022, 26, 1–112. [CrossRef]
- Han, C.Y.; Miller, M.; Yaxley, A.; Baldwin, C.; Woodman, R.; Sharma, Y. Effectiveness of Combined Exercise and Nutrition Interventions in Prefrail or Frail Older Hospitalised Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e040146. [CrossRef]
- Lorbergs, A.L.; Prorok, J.C.; Holroyd-Leduc, J.; Bouchard, D.R.; Giguere, A.; Gramlich, L.; Keller, H.; Tang, A.; Racey, M.; Ali, M.U.; et al. Nutrition and Physical Activity Clinical Practice Guidelines for Older Adults Living with Frailty. J Frailty Aging 2022, 11, 3–11. [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhang, H.; Lin, Z.; Li, X.; Kong, X.; Sun, G. Review of Nutritional Screening and Assessment Tools and Clinical Outcomes in Heart Failure. Heart Fail Rev 2016, 21, 549–565. [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Zou, C.; Ji, S.; Liang, T. Prediction of All-Cause Mortality with Malnutrition Assessed by Nutritional Screening and Assessment Tools in Patients with Heart Failure:a Systematic Review. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2022, 32, 1361–1374. [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.-H.; Chen, S.-Y.; Zeng, H.-L.; Yang, B.; Pan, J. Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index Predicts All-Cause Mortality in Patients with Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 2021, 76, e2258. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cen, K.; Sun, W.; Feng, B. Prognostic Value of Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index in Elderly Patients with Heart Failure: A Meta-Analysis. Aging Clin Exp Res 2021, 33, 1477–1486. [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X. Predicting Prognosis of Heart Failure Using Common Malnutrition Assessment Tools: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Scott Med J 2022, 67, 157–170. [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-W.; Luo, J.-J.; Baldinger, B. The Controlling Nutritional Status Score and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Heart Failure: Pool Analysis of Observational Studies. Front Cardiovasc Med 2022, 9, 961141. [CrossRef]
- Habaybeh, D.; de Moraes, M.B.; Slee, A.; Avgerinou, C. Nutritional Interventions for Heart Failure Patients Who Are Malnourished or at Risk of Malnutrition or Cachexia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Heart Fail Rev 2021, 26, 1103–1118. [CrossRef]
- Al Saadi, T.; Assaf, Y.; Farwati, M.; Turkmani, K.; Al-Mouakeh, A.; Shebli, B.; Khoja, M.; Essali, A.; Madmani, M.E. Coenzyme Q10 for Heart Failure. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2021, (2), CD008684. [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Khan, F.; Fonarow, G.C.; Sreenivasan, J.; Greene, S.J.; Khan, S.U.; Usman, M.S.; Vaduganathan, M.; Fudim, M.; Anker, S.D.; et al. Dietary Interventions and Nutritional Supplements for Heart Failure: A Systematic Appraisal and Evidence Map. Eur J Heart Fail 2021, 23, 1468–1476. [CrossRef]
- Bernasconi, A.A.; Wiest, M.M.; Lavie, C.J.; Milani, R. V; Laukkanen, J.A. Effect of Omega-3 Dosage on Cardiovascular Outcomes: An Updated Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression of Interventional Trials. Mayo Clin Proc 2021, 96, 304–313. [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, V.E. Nutrition in Chronic Heart Failure Patients: A Systematic Review. Heart Fail Rev 2020, 25, 1017–1026. [CrossRef]
- Rahimlu, M.; Shab-Bidar, S.; Djafarian, K. Body Mass Index and All-Cause Mortality in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. J Ren Nutr 2017, 27, 225–232. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Nie, L.; He, T.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Feng, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J. Association of Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index with Mortality in Hemodialysis Patients: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Kidney Blood Press Res 2018, 43, 1878–1889. [CrossRef]
- Carrero, J.J.; Thomas, F.; Nagy, K.; Arogundade, F.; Avesani, C.M.; Chan, M.; Chmielewski, M.; Cordeiro, A.C.; Espinosa-Cuevas, A.; Fiaccadori, E.; et al. Global Prevalence of Protein-Energy Wasting in Kidney Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Contemporary Observational Studies From the International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism. J Ren Nutr 2018, 28, 380–392. [CrossRef]
- Mihaescu, A.; Masood, E.; Zafran, M.; Khokhar, H.T.; Augustine, A.M.; Filippo, A.; Van Biesen, W.; Farrigton, K.; Carrero, J.J.; Covic, A.; et al. Nutritional Status Improvement in Elderly CKD Patients: A Systematic Review. Int Urol Nephrol 2021, 53, 1603–1621. [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.-H.; Lee, D.H.; Min, J.; Jeon, J.Y. Handgrip Strength as a Predictor of All-Cause Mortality in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease Undergoing Dialysis: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. J Ren Nutr 2019, 29, 471–479. [CrossRef]
- Santana Gomes, T.; Espirito Santo Silva, D. do; Xavier Junior, G.F.; de Farias Costa, P.R.; Gusmão Sena, M.H.L.; Barreto Medeiros, J.M. Sarcopenia and Mortality in Patients With Chronic Non-Dialytic Renal Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Ren Nutr 2022, 32, 135–143. [CrossRef]
- Kojima, G. Prevalence of Frailty in End-Stage Renal Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int Urol Nephrol 2017, 49, 1989–1997. [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Wei-Jie, Y. Effects of Soy Protein Containing Isoflavones in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin Nutr 2016, 35, 117–124. [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.J.; Ma, F.; Wang, Q.Y.; He, S.L. The Effects of Oral Nutritional Supplements in Patients with Maintenance Dialysis Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0203706. [CrossRef]
- Mah, J.Y.; Choy, S.W.; Roberts, M.A.; Desai, A.M.; Corken, M.; Gwini, S.M.; McMahon, L.P. Oral Protein-Based Supplements versus Placebo or No Treatment for People with Chronic Kidney Disease Requiring Dialysis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2020, 5, CD012616. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Li, Z.; Qin, W. Effect of Restricted Protein Diet Supplemented with Keto Analogues in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int Urol Nephrol 2016, 48, 409–418. [CrossRef]
- Rhee, C.M.; Ahmadi, S.-F.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Low-Protein Diet for Conservative Management of Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Controlled Trials. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2018, 9, 235–245. [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Su, X.; Xu, B.; Qiao, X.; Wang, L. Effect of Diet Protein Restriction on Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0206134. [CrossRef]
- Chewcharat, A.; Takkavatakarn, K.; Wongrattanagorn, S.; Panrong, K.; Kittiskulnam, P.; Eiam-Ong, S.; Susantitaphong, P. The Effects of Restricted Protein Diet Supplemented With Ketoanalogue on Renal Function, Blood Pressure, Nutritional Status, and Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Ren Nutr 2020, 30, 189–199. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Yang, L.; Mi, X.; Qin, W. Effect of Restricted Protein Diet Supplemented with Keto Analogues in End-Stage Renal Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int Urol Nephrol 2018, 50, 687–694. [CrossRef]
- Hahn, D.; Hodson, E.M.; Fouque, D. Low Protein Diets for Non-Diabetic Adults with Chronic Kidney Disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2018, 10, CD001892. [CrossRef]
- Hahn, D.; Hodson, E.M.; Fouque, D. Low Protein Diets for Non-Diabetic Adults with Chronic Kidney Disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2020, 10, CD001892. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Fang, J.; Li, W. Protein Restriction for Diabetic Kidney Disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2023, 1, CD014906. [CrossRef]
- Goto, N.A.; Weststrate, A.C.G.; Oosterlaan, F.M.; Verhaar, M.C.; Willems, H.C.; Emmelot-Vonk, M.H.; Hamaker, M.E. The Association between Chronic Kidney Disease, Falls, and Fractures: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Osteoporos Int 2020, 31, 13–29. [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.-C.; Lu, C.-L.; Lu, K.-C. Mineral Bone Disorders in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nephrology (Carlton) 2018, 23 Suppl 4, 88–94. [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-Y.; Chen, L.-R.; Chen, K.-H. Osteoporosis in Patients with Chronic Kidney Diseases: A Systemic Review. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, D.; Chitalia, N.; Ster, I.C.; Appelbaum, E.; Thadhani, R.; Kaski, J.C.; Goldsmith, D. Impact of Vitamin D on Cardiac Structure and Function in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients with Hypovitaminosis D: A Randomized Controlled Trial and Meta-Analysis. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother 2021, 7, 302–311. [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, M.; Aspray, T.J.; Schoenmakers, I. Vitamin D Supplementation for Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses of Trials Investigating the Response to Supplementation and an Overview of Guidelines. Calcif Tissue Int 2021, 109, 157–178. [CrossRef]
- Karimi, E.; Bitarafan, S.; Mousavi, S.M.; Zargarzadeh, N.; Mokhtari, P.; Hawkins, J.; Meysamie, A.; Koohdani, F. The Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Fibroblast Growth Factor-23 in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Phytother Res 2021, 35, 5339–5351. [CrossRef]
- Milajerdi, A.; Ostadmohammadi, V.; Amirjani, S.; Kolahdooz, F.; Asemi, Z. The Effects of Vitamin D Treatment on Glycemic Control, Serum Lipid Profiles, and C-Reactive Protein in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Int Urol Nephrol 2019, 51, 1567–1580. [CrossRef]
- Chiavaroli, L.; Mirrahimi, A.; Sievenpiper, J.L.; Jenkins, D.J.A.; Darling, P.B. Dietary Fiber Effects in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Controlled Feeding Trials. Eur J Clin Nutr 2015, 69, 761–768. [CrossRef]
- McFarlane, C.; Ramos, C.I.; Johnson, D.W.; Campbell, K.L. Prebiotic, Probiotic, and Synbiotic Supplementation in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Ren Nutr 2019, 29, 209–220. [CrossRef]
- Sanz-París, A.; Gómez-Candela, C.; Martín-Palmero, Á.; García-Almeida, J.M.; Burgos-Pelaez, R.; Matía-Martin, P.; Arbones-Mainar, J.M.; Study VIDA group Application of the New ESPEN Definition of Malnutrition in Geriatric Diabetic Patients during Hospitalization: A Multicentric Study. Clin Nutr 2016, 35, 1564–1567. [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Rodríguez, D.; Marco, E.; Ronquillo-Moreno, N.; Miralles, R.; Vázquez-Ibar, O.; Escalada, F.; Muniesa, J.M. Prevalence of Malnutrition and Sarcopenia in a Post-Acute Care Geriatric Unit: Applying the New ESPEN Definition and EWGSOP Criteria. Clin Nutr 2017, 36, 1339–1344. [CrossRef]
- Sanz-París, A.; Martín-Palmero, A.; Gomez-Candela, C.; García-Almeida, J.M.; Burgos-Pelaez, R.; Sanz-Arque, A.; Espina, S.; Arbones-Mainar, J.M.; Study VIDA group GLIM Criteria at Hospital Admission Predict 8-Year All-Cause Mortality in Elderly Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Results From VIDA Study. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 2020, 44, 1492–1500. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, D.; Xu, J. Association between the Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index, Bone Mineral Density and Osteoporosis in Type 2 Diabetes Patients. J Diabetes Investig 2020, 11, 956–963. [CrossRef]
- Çakmak, G.; Ganidağlı, S.; Efendioğlu, E.M.; Öztürk, E.; Öztürk, Z.A. Do Long-Term Complications of Type 2 Diabetes Increase Susceptibility to Geriatric Syndromes in Older Adults? Medicina (Kaunas) 2021, 57. [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, F.; Hashimoto, Y.; Kaji, A.; Sakai, R.; Kawate, Y.; Okamura, T.; Kitagawa, N.; Okada, H.; Nakanishi, N.; Majima, S.; et al. Association between Geriatric Nutrition Risk Index and The Presence of Sarcopenia in People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- López-Gómez, J.J.; Gutiérrez-Lora, C.; Izaola-Jauregui, O.; Primo-Martín, D.; Gómez-Hoyos, E.; Jiménez-Sahagún, R.; De Luis-Román, D.A. Real World Practice Study of the Effect of a Specific Oral Nutritional Supplement for Diabetes Mellitus on the Morphofunctional Assessment and Protein Energy Requirements. Nutrients 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, S.; Shibazaki, K.; Uchida, R.; Imai, Y.; Mukoyama, T.; Shibata, S.; Morita, H. Sarcopenia Is Associated with the Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index in Elderly Patients with Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J Diabetes Investig 2022, 13, 1366–1373. [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Tan, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wang, X.; Liao, Z.; Wei, P. Diabetes and Sarcopenic Obesity: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatments. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2020, 11, 568. [CrossRef]
- Petroni, M.L.; Brodosi, L.; Marchignoli, F.; Sasdelli, A.S.; Caraceni, P.; Marchesini, G.; Ravaioli, F. Nutrition in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Present Knowledge and Remaining Challenges. Nutrients 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- Izzo, A.; Massimino, E.; Riccardi, G.; Della Pepa, G. A Narrative Review on Sarcopenia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Prevalence and Associated Factors. Nutrients 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- Velázquez-Alva, M.C.; Irigoyen-Camacho, M.E.; Zepeda-Zepeda, M.A.; Lazarevich, I.; Arrieta-Cruz, I.; D’Hyver, C. Sarcopenia, Nutritional Status and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-Sectional Study in a Group of Mexican Women Residing in a Nursing Home. Nutr Diet 2020, 77, 515–522. [CrossRef]
- Shiroma, K.; Tanabe, H.; Takiguchi, Y.; Yamaguchi, M.; Sato, M.; Saito, H.; Tanaka, K.; Masuzaki, H.; Kazama, J.J.; Shimabukuro, M. A Nutritional Assessment Tool, GNRI, Predicts Sarcopenia and Its Components in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Japanese Cross-Sectional Study. Front Nutr 2023, 10, 1087471. [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Shu, D.; Meng, F.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Xiao, X.; Guo, W.; Chen, F. Higher Risk of Sarcopenia in Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: NHANES 1999-2018. Obes Facts 2023, 1. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, W.; Zheng, W.; Fang, X.; Chen, L.; Rink, L.; Min, J.; Wang, F. Zinc Supplementation Improves Glycemic Control for Diabetes Prevention and Management: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am J Clin Nutr 2019, 110, 76–90. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ronsmans, C.; Woolf, B. Triangulating Evidence for the Causal Impact of Single-Intervention Zinc Supplement on Glycaemic Control for Type 2 Diabetes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trial and Two-Sample Mendelian Randomisation. Br J Nutr 2023, 129, 1929–1944. [CrossRef]
- Asbaghi, O.; Nazarian, B.; Yousefi, M.; Anjom-Shoae, J.; Rasekhi, H.; Sadeghi, O. Effect of Vitamin E Intake on Glycemic Control and Insulin Resistance in Diabetic Patients: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutr J 2023, 22, 10. [CrossRef]
- Lind, M.V.; Lauritzen, L.; Kristensen, M.; Ross, A.B.; Eriksen, J.N. Effect of Folate Supplementation on Insulin Sensitivity and Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am J Clin Nutr 2019, 109, 29–42. [CrossRef]
- Yousefi Rad, E.; Nazarian, B.; Saboori, S.; Falahi, E.; Hekmatdoost, A. Effects of L-Arginine Supplementation on Glycemic Profile: Evidence from a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials. J Integr Med 2020, 18, 284–291. [CrossRef]
- Karimi, E.; Hatami, E.; Ghavami, A.; Hadi, A.; Darand, M.; Askari, G. Effects of L-Arginine Supplementation on Biomarkers of Glycemic Control: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Clinical Trials. Arch Physiol Biochem 2023, 129, 700–710. [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, A.N.; Akerman, A.P.; Mann, J. Dietary Fibre and Whole Grains in Diabetes Management: Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses. PLoS Med 2020, 17, e1003053. [CrossRef]
- Esposito, K.; Maiorino, M.I.; Bellastella, G.; Chiodini, P.; Panagiotakos, D.; Giugliano, D. A Journey into a Mediterranean Diet and Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analyses. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e008222. [CrossRef]
- Becerra-Tomás, N.; Blanco Mejía, S.; Viguiliouk, E.; Khan, T.; Kendall, C.W.C.; Kahleova, H.; Rahelić, D.; Sievenpiper, J.L.; Salas-Salvadó, J. Mediterranean Diet, Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality in Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies and Randomized Clinical Trials. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2020, 60, 1207–1227. [CrossRef]
- Zimorovat, A.; Mohammadi, M.; Ramezani-Jolfaie, N.; Salehi-Abargouei, A. The Healthy Nordic Diet for Blood Glucose Control: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials. Acta Diabetol 2020, 57, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Massara, P.; Zurbau, A.; Glenn, A.J.; Chiavaroli, L.; Khan, T.A.; Viguiliouk, E.; Mejia, S.B.; Comelli, E.M.; Chen, V.; Schwab, U.; et al. Nordic Dietary Patterns and Cardiometabolic Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies and Randomised Controlled Trials. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 2011–2031. [CrossRef]
- Diabetes and Nutrition Study Group (DNSG) of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) Evidence-Based European Recommendations for the Dietary Management of Diabetes. Diabetologia 2023, 66, 965–985. [CrossRef]
- Lauwers, P.; Dirinck, E.; Van Bouwel, S.; Verrijken, A.; Van Dessel, K.; Van Gils, C.; Sels, M.; Peiffer, F.; Van Schil, P.; De Block, C.; et al. Malnutrition and Its Relation with Diabetic Foot Ulcer Severity and Outcome: A Review. Acta Clin Belg 2022, 77, 79–85. [CrossRef]
- Bechara, N.; Gunton, J.E.; Flood, V.; Hng, T.-M.; McGloin, C. Associations between Nutrients and Foot Ulceration in Diabetes: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- Strazzullo, P.; D’Elia, L.; Cairella, G.; Garbagnati, F.; Cappuccio, F.P.; Scalfi, L. Excess Body Weight and Incidence of Stroke: Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies with 2 Million Participants. Stroke 2010, 41, e418-26. [CrossRef]
- Forlivesi, S.; Cappellari, M.; Bonetti, B. Obesity Paradox and Stroke: A Narrative Review. Eat Weight Disord 2021, 26, 417–423. [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Fu, K.; Xue, W.; Teng, W.; Tian, L. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Level, Vitamin D Intake, and Risk of Stroke: A Dose-Response Meta-Analysis. Clin Nutr 2020, 39, 2025–2034. [CrossRef]
- Vergatti, A.; Abate, V.; Zarrella, A.F.; Manganelli, F.; Tozza, S.; Iodice, R.; De Filippo, G.; D’Elia, L.; Strazzullo, P.; Rendina, D. 25-Hydroxy-Vitamin D and Risk of Recurrent Stroke: A Dose Response Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, Q.; Fang, X.; Wang, X.; Min, J.; Wang, F. Dietary Intake of Homocysteine Metabolism-Related B-Vitamins and the Risk of Stroke: A Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. Adv Nutr 2020, 11, 1510–1528. [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, Q.; Li, Q.; Guo, C.; Tian, G.; Qie, R.; Han, M.; Huang, S.; Li, Y.; et al. Association of Homocysteine Level with Risk of Stroke: A Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2020, 30, 1861–1869. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Wang, L.; Ning, S.; Liu, Z.; Lin, H.; Chen, S.; Zhu, J. Vitamin E Intake and Risk of Stroke: A Meta-Analysis. Br J Nutr 2018, 120, 1181–1188. [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.-Z.; Xu, J.-Y.; Chen, G.-C.; Ma, Y.-X.; Qin, L.-Q. Effects of Fatty and Lean Fish Intake on Stroke Risk: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Lipids Health Dis 2018, 17, 264. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Tang, H.; Yang, X.; Luo, X.; Wang, X.; Shao, C.; He, J. Fish Consumption and Stroke Risk: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2019, 28, 604–611. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Zhang, W. Sen; Jiang, C.Q.; Zhu, F.; Jin, Y.L.; Cheng, K.K.; Lam, T.H.; Xu, L. Low-Carbohydrate Diet Score and the Risk of Stroke in Older People: Guangzhou Biobank Cohort Study and Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Nutrition 2023, 105, 111844. [CrossRef]
- Balcerak, P.; Corbiere, S.; Zubal, R.; Kägi, G. Post-Stroke Dysphagia: Prognosis and Treatment-A Systematic Review of RCT on Interventional Treatments for Dysphagia Following Subacute Stroke. Front Neurol 2022, 13, 823189. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H.; Huo, M.; Qin, H.H.; Zhao, B.L. Critical Prognostic Factors for Poststroke Dysphagia: A Meta-Analysis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2022, 26, 610–622. [CrossRef]
- D’Netto, P.; Rumbach, A.; Dunn, K.; Finch, E. Clinical Predictors of Dysphagia Recovery After Stroke: A Systematic Review. Dysphagia 2023, 38, 1–22. [CrossRef]
- Huppertz, V.; Guida, S.; Holdoway, A.; Strilciuc, S.; Baijens, L.; Schols, J.M.G.A.; van Helvoort, A.; Lansink, M.; Muresanu, D.F. Impaired Nutritional Condition After Stroke From the Hyperacute to the Chronic Phase: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Neurol 2021, 12, 780080. [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Chen, T.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Lin, K.; Zhang, G.; Wu, J. Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index and the Prognosis of Patients with Stroke: A Meta-Analysis. Horm Metab Res 2022, 54, 736–746. [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.; De Paola, L.; Pana, T.A.; Carter, B.; Soiza, R.L.; Kafri, M.W.; Potter, J.F.; Mamas, M.A.; Myint, P.K. The Relationship between Nutritional Status at the Time of Stroke on Adverse Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Nutr Rev 2022, 80, 2275–2287. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dong, J.; Guo, J. The Effects of Nutrition Supplement on Rehabilitation for Patients with Stroke: Analysis Based on 16 Randomized Controlled Trials. Medicine 2022, 101, e29651. [CrossRef]
- Sakai, K.; Kinoshita, S.; Tsuboi, M.; Fukui, R.; Momosaki, R.; Wakabayashi, H. Effects of Nutrition Therapy in Older Stroke Patients Undergoing Rehabilitation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Nutr Health Aging 2019, 23, 21–26. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chu, J.; Zheng, J.; Cheng, X.; Li, X.; Long, J. Effect of Probiotics on the Nutritional Status of Severe Stroke Patients with Nasal Feeding That Receive Enteral Nutrition: A Protocol for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Medicine 2021, 100, e25657. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hu, Y.; Yuan, X.; Yang, J.; Ka Li Effect of Early Enteral Nutrition Combined with Probiotics in Patients with Stroke: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Eur J Clin Nutr 2022, 76, 592–603. [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Yuki, M.; Otsuki, M. Prevalence of Stroke-Related Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2020, 29, 105092. [CrossRef]
- Beckwée, D.; Cuypers, L.; Lefeber, N.; De Keersmaecker, E.; Scheys, E.; Van Hees, W.; Perkisas, S.; De Raedt, S.; Kerckhofs, E.; Bautmans, I.; et al. Skeletal Muscle Changes in the First Three Months of Stroke Recovery: A Systematic Review. J Rehabil Med 2022, 54, jrm00308. [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.M.; Woodward, M.; Batty, G.D.; Beiser, A.S.; Bell, S.; Berr, C.; Bjertness, E.; Chalmers, J.; Clarke, R.; Dartigues, J.-F.; et al. Association of Anthropometry and Weight Change with Risk of Dementia and Its Major Subtypes: A Meta-Analysis Consisting 2.8 Million Adults with 57 294 Cases of Dementia. Obes Rev 2020, 21, e12989. [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhao, W.; Lu, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, P.; Xin, Z.; Sun, R.; Tian, W.; Cardoso, M.A.; Yang, J.; et al. Relationship between Central Obesity and the Incidence of Cognitive Impairment and Dementia from Cohort Studies Involving 5,060,687 Participants. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2021, 130, 301–313. [CrossRef]
- Chai, B.; Gao, F.; Wu, R.; Dong, T.; Gu, C.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, Y. Vitamin D Deficiency as a Risk Factor for Dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease: An Updated Meta-Analysis. BMC Neurol 2019, 19, 284. [CrossRef]
- Jayedi, A.; Rashidy-Pour, A.; Shab-Bidar, S. Vitamin D Status and Risk of Dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Dose-Response †. Nutr Neurosci 2019, 22, 750–759. [CrossRef]
- Kalra, A.; Teixeira, A.L.; Diniz, B.S. Association of Vitamin D Levels with Incident All-Cause Dementia in Longitudinal Observational Studies: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Prev Alzheimers Dis 2020, 7, 14–20. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Luo, J.; Yuan, C.; Ding, D. Vitamin B12, B6, or Folate and Cognitive Function in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Alzheimers Dis 2020, 77, 781–794. [CrossRef]
- Gil Martínez, V.; Avedillo Salas, A.; Santander Ballestín, S. Vitamin Supplementation and Dementia: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Je, Y. Fish Consumption and the Risk of Dementia: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. Psychiatry Res 2022, 317, 114889. [CrossRef]
- Buckinx, F.; Aubertin-Leheudre, M. Nutrition to Prevent or Treat Cognitive Impairment in Older Adults: A GRADE Recommendation. J Prev Alzheimers Dis 2021, 8, 110–116. [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Tan, L.-J.; Lee, J.E.; Shin, S. Association between the Mediterranean Diet and Cognitive Health among Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Nutr 2022, 9, 946361. [CrossRef]
- Patch, C.S.; Hill-Yardin, E.L.; Ryan, L.; Daly, E.; Pearce, A.J. Long Chain Omega-3 Fatty Acid Intervention in Ageing Adults at Risk of Dementia Following Repeated Head Trauma. Low-Level Support or an Opportunity for an Unanswered Question? J Prev Alzheimers Dis 2021, 8, 29–32. [CrossRef]
- McGrattan, A.; van Aller, C.; Narytnyk, A.; Reidpath, D.; Keage, H.; Mohan, D.; Su, T.T.; Stephan, B.; Robinson, L.; Siervo, M.; et al. Nutritional Interventions for the Prevention of Cognitive Impairment and Dementia in Developing Economies in East-Asia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2022, 62, 1838–1855. [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhao, F.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.; Lu, Y. N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Elderly with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Alzheimers Dis 2023. [CrossRef]
- Burckhardt, M.; Watzke, S.; Wienke, A.; Langer, G.; Fink, A. Souvenaid for Alzheimer’s Disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2020, 12, CD011679. [CrossRef]
- Alam, J. Vitamins: A Nutritional Intervention to Modulate the Alzheimer’s Disease Progression. Nutr Neurosci 2022, 25, 945–962. [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, N.; Hou, Z.; Liu, L.; Gao, L.; Wang, L.; Tan, J. Nutrition and Exercise Interventions Could Ameliorate Age-Related Cognitive Decline: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Aging Clin Exp Res 2021, 33, 1799–1809. [CrossRef]
- Porter, J.; Thompson, H.; Tjahyo, A.S. Understanding Total Energy Expenditure in People with Dementia: A Systematic Review with Directions for Future Research. Australas J Ageing 2021, 40, 243–251. [CrossRef]
- Doorduijn, A.S.; van de Rest, O.; van der Flier, W.M.; Visser, M.; de van der Schueren, M.A.E. Energy and Protein Intake of Alzheimer’s Disease Patients Compared to Cognitively Normal Controls: Systematic Review. J Am Med Dir Assoc 2019, 20, 14–21. [CrossRef]
- Fetherstonhaugh, D.; Haesler, E.; Bauer, M. Promoting Mealtime Function in People with Dementia: A Systematic Review of Studies Undertaken in Residential Aged Care. Int J Nurs Stud 2019, 96, 99–118. [CrossRef]
- Borders, J.C.; Blanke, S.; Johnson, S.; Gilmore-Bykovskyi, A.; Rogus-Pulia, N. Efficacy of Mealtime Interventions for Malnutrition and Oral Intake in Persons With Dementia: A Systematic Review. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 2020, 34, 366–379. [CrossRef]
- Tangvik, R.J.; Bruvik, F.K.; Drageset, J.; Kyte, K.; Hunskår, I. Effects of Oral Nutrition Supplements in Persons with Dementia: A Systematic Review. Geriatr Nurs 2021, 42, 117–123. [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Galik, E.; Boltz, M.; Nahm, E.-S.; Resnick, B. Optimizing Eating Performance for Older Adults With Dementia Living in Long-Term Care: A Systematic Review. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs 2015, 12, 228–235. [CrossRef]
- Leah, V. Supporting People with Dementia to Eat. Nurs Older People 2016, 28, 33–39. [CrossRef]
- Mole, L.; Kent, B.; Abbott, R.; Wood, C.; Hickson, M. The Nutritional Care of People Living with Dementia at Home: A Scoping Review. Health Soc Care Community 2018, 26, e485–e496. [CrossRef]
- Davies, N.; Barrado-Martín, Y.; Vickerstaff, V.; Rait, G.; Fukui, A.; Candy, B.; Smith, C.H.; Manthorpe, J.; Moore, K.J.; Sampson, E.L. Enteral Tube Feeding for People with Severe Dementia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2021, 8, CD013503. [CrossRef]
- Anantapong, K.; Bruun, A.; Walford, A.; Smith, C.H.; Manthorpe, J.; Sampson, E.L.; Davies, N. Co-Design Development of a Decision Guide on Eating and Drinking for People with Severe Dementia during Acute Hospital Admissions. Health Expect 2023, 26, 613–629. [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.-C.; Lu, C.-L.; Lu, K.-C. Mineral Bone Disorders in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nephrology (Carlton) 2018, 23 Suppl 4, 88–94. [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-Y.; Chen, L.-R.; Chen, K.-H. Osteoporosis in Patients with Chronic Kidney Diseases: A Systemic Review. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, H.; Zhao, L.; Wang, J. Osteoporosis in COPD Patients: Risk Factors and Pulmonary Rehabilitation. Clin Respir J 2022, 16, 487–496. [CrossRef]
- Shams-White, M.M.; Chung, M.; Du, M.; Fu, Z.; Insogna, K.L.; Karlsen, M.C.; LeBoff, M.S.; Shapses, S.A.; Sackey, J.; Wallace, T.C.; et al. Dietary Protein and Bone Health: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis from the National Osteoporosis Foundation. Am J Clin Nutr 2017, 105, 1528–1543. [CrossRef]
- Zittermann, A.; Schmidt, A.; Haardt, J.; Kalotai, N.; Lehmann, A.; Egert, S.; Ellinger, S.; Kroke, A.; Lorkowski, S.; Louis, S.; et al. Protein Intake and Bone Health: An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews for the Evidence-Based Guideline of the German Nutrition Society. Osteoporos Int 2023. [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; McKenzie, J.E.; McDonald, S.; Baram, L.; Page, M.J.; Allman-Farinelli, M.; Raubenheimer, D.; Bero, L.A. Assessment of the Methods Used to Develop Vitamin D and Calcium Recommendations-A Systematic Review of Bone Health Guidelines. Nutrients 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- Montero-Odasso, M.M.; Kamkar, N.; Pieruccini-Faria, F.; Osman, A.; Sarquis-Adamson, Y.; Close, J.; Hogan, D.B.; Hunter, S.W.; Kenny, R.A.; Lipsitz, L.A.; et al. Evaluation of Clinical Practice Guidelines on Fall Prevention and Management for Older Adults: A Systematic Review. JAMA Netw Open 2021, 4, e2138911. [CrossRef]
- Bertoldo, F.; Cianferotti, L.; Di Monaco, M.; Falchetti, A.; Fassio, A.; Gatti, D.; Gennari, L.; Giannini, S.; Girasole, G.; Gonnelli, S.; et al. Definition, Assessment, and Management of Vitamin D Inadequacy: Suggestions, Recommendations, and Warnings from the Italian Society for Osteoporosis, Mineral Metabolism and Bone Diseases (SIOMMMS). Nutrients 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Kazemian, E.; Pourali, A.; Sedaghat, F.; Karimi, M.; Basirat, V.; Sajadi Hezaveh, Z.; Davoodi, S.H.; Holick, M.F. Effect of Supplemental Vitamin D3 on Bone Mineral Density: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutr Rev 2023, 81, 511–530. [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Zhang, S.; Niu, X.; Dai, S. Meta-Analysis of Effects of Nutritional Intervention Combined with Calcium Carbonate D3 Tablets on Bone Mineral Density, Bone Metabolism, and Curative Effect in Patients with Osteoporosis. Contrast Media Mol Imaging 2022, 2022, 3670007. [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.-L.; Ma, Z.-J.; He, Y.-L.; Sun, H.; Yang, B.; Ruan, B.-J.; Zhan, W.; Li, S.-X.; Dong, H.; Wang, Y.-X. Efficacy of Vitamin K2 in the Prevention and Treatment of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Front Public Health 2022, 10, 979649. [CrossRef]
- Denova-Gutiérrez, E.; Méndez-Sánchez, L.; Muñoz-Aguirre, P.; Tucker, K.L.; Clark, P. Dietary Patterns, Bone Mineral Density, and Risk of Fractures: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2018, 10. [CrossRef]
- Panahande, B.; Sadeghi, A.; Parohan, M. Alternative Healthy Eating Index and Risk of Hip Fracture: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis. J Hum Nutr Diet 2019, 32, 98–107. [CrossRef]
- Fabiani, R.; Naldini, G.; Chiavarini, M. Dietary Patterns in Relation to Low Bone Mineral Density and Fracture Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Adv Nutr 2019, 10, 219–236. [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.; Rycroft, C.E.; Greenwood, D.C.; Cade, J.E. Dietary Risk Factors for Hip Fracture in Adults: An Umbrella Review of Meta-Analyses of Prospective Cohort Studies. PLoS One 2021, 16, e0259144. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Wu, F.; Makin, J.K.; Oddy, W.H.; Wills, K.; Jones, G.; Winzenberg, T. Associations of Dietary Patterns with Bone Density and Fractures in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Aust J Gen Pract 2021, 50, 394–401. [CrossRef]
- Kunutsor, S.K.; Laukkanen, J.A.; Whitehouse, M.R.; Blom, A.W. Adherence to a Mediterranean-Style Diet and Incident Fractures: Pooled Analysis of Observational Evidence. Eur J Nutr 2018, 57, 1687–1700. [CrossRef]
- Malmir, H.; Saneei, P.; Larijani, B.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Adherence to Mediterranean Diet in Relation to Bone Mineral Density and Risk of Fracture: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Eur J Nutr 2018, 57, 2147–2160. [CrossRef]
- Bian, S.; Hu, J.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Yu, M.; Ma, J. Dairy Product Consumption and Risk of Hip Fracture: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 165. [CrossRef]
- Matía-Martín, P.; Torrego-Ellacuría, M.; Larrad-Sainz, A.; Fernández-Pérez, C.; Cuesta-Triana, F.; Rubio-Herrera, M.Á. Effects of Milk and Dairy Products on the Prevention of Osteoporosis and Osteoporotic Fractures in Europeans and Non-Hispanic Whites from North America: A Systematic Review and Updated Meta-Analysis. Adv Nutr 2019, 10, S120–S143. [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, K.; Du, X.; Shi, B.-M.; Qin, L.-Q. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Association between Dairy Consumption and the Risk of Hip Fracture: Critical Interpretation of the Currently Available Evidence. Osteoporos Int 2020, 31, 1411–1425. [CrossRef]
- Malmir, H.; Larijani, B.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Consumption of Milk and Dairy Products and Risk of Osteoporosis and Hip Fracture: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2020, 60, 1722–1737. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Moore, J.B.; Wang, Y.; Yan, H.; Wu, Y.; Tan, A.; Fu, J.; Shen, Z.; Qin, G.; et al. The Effect of Vitamin A on Fracture Risk: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2017, 14. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, C.; Bo, Y.; You, J.; Zhu, Y.; Duan, D.; Cui, H.; Lu, Q. Dietary Vitamin C Intake and the Risk of Hip Fracture: A Dose-Response Meta-Analysis. Osteoporos Int 2018, 29, 79–87. [CrossRef]
- Malmir, H.; Shab-Bidar, S.; Djafarian, K. Vitamin C Intake in Relation to Bone Mineral Density and Risk of Hip Fracture and Osteoporosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Br J Nutr 2018, 119, 847–858. [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Cheng, G.; Wang, H.; Chen, B. The Associations between Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Level and the Risk of Total Fracture and Hip Fracture. Osteoporos Int 2017, 28, 1641–1652. [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Chen, Y.; Ji, J.; Chang, J.; Yu, S.; Yu, B. The Relationship between Serum Vitamin D and Fracture Risk in the Elderly: A Meta-Analysis. J Orthop Surg Res 2020, 15, 81. [CrossRef]
- Habibi Ghahfarrokhi, S.; Mohammadian-Hafshejani, A.; Sherwin, C.M.T.; Heidari-Soureshjani, S. Relationship between Serum Vitamin D and Hip Fracture in the Elderly: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Bone Miner Metab 2022, 40, 541–553. [CrossRef]
- Weaver, C.M.; Alexander, D.D.; Boushey, C.J.; Dawson-Hughes, B.; Lappe, J.M.; LeBoff, M.S.; Liu, S.; Looker, A.C.; Wallace, T.C.; Wang, D.D. Calcium plus Vitamin D Supplementation and Risk of Fractures: An Updated Meta-Analysis from the National Osteoporosis Foundation. Osteoporos Int 2016, 27, 367–376. [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.H.; Jang, H.N.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.W.; Shin, C.S. Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Risk of Fractures and Falls According to Dosage and Interval: A Meta-Analysis. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul) 2022, 37, 344–358. [CrossRef]
- Manoj, P.; Derwin, R.; George, S. What Is the Impact of Daily Oral Supplementation of Vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol) plus Calcium on the Incidence of Hip Fracture in Older People? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int J Older People Nurs 2023, 18, e12492. [CrossRef]
- Mozaffari, H.; Djafarian, K.; Mofrad, M.D.; Shab-Bidar, S. Dietary Fat, Saturated Fatty Acid, and Monounsaturated Fatty Acid Intakes and Risk of Bone Fracture: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Osteoporos Int 2018, 29, 1949–1961. [CrossRef]
- Harvey, N.C.; Orwoll, E.; Kwok, T.; Karlsson, M.K.; Rosengren, B.E.; Ribom, E.; Cauley, J.A.; Cawthon, P.M.; Ensrud, K.; Liu, E.; et al. Sarcopenia Definitions as Predictors of Fracture Risk Independent of FRAX® , Falls, and BMD in the Osteoporotic Fractures in Men (MrOS) Study: A Meta-Analysis. J Bone Miner Res 2021, 36, 1235–1244. [CrossRef]
- Kunutsor, S.K.; Seidu, S.; Voutilainen, A.; Blom, A.W.; Laukkanen, J.A. Handgrip Strength-a Risk Indicator for Future Fractures in the General Population: Findings from a Prospective Study and Meta-Analysis of 19 Prospective Cohort Studies. Geroscience 2021, 43, 869–880. [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, O.; Saneei, P.; Nasiri, M.; Larijani, B.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Abdominal Obesity and Risk of Hip Fracture: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. Adv Nutr 2017, 8, 728–738. [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, H.; Atayie, F.; Samii Kondrud, F.; Balali, A.; Beyene, J.; Tahery, N.; Asadi, M.; Sadeghi, O. Associations of Abdominal Obesity with Different Types of Bone Fractures in Adults: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2023, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Gandham, A.; Mesinovic, J.; Jansons, P.; Zengin, A.; Bonham, M.P.; Ebeling, P.R.; Scott, D. Falls, Fractures, and Areal Bone Mineral Density in Older Adults with Sarcopenic Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes Rev 2021, 22, e13187. [CrossRef]
- Vilaca, T.; Schini, M.; Harnan, S.; Sutton, A.; Poku, E.; Allen, I.E.; Cummings, S.R.; Eastell, R. The Risk of Hip and Non-Vertebral Fractures in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Update. Bone 2020, 137, 115457. [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, K.; Fang, Q.-L.; Shi, B.-M.; Qin, L.-Q. Influence of Glycemic Control and Hypoglycemia on the Risk of Fracture in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Osteoporos Int 2021, 32, 1693–1704. [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Sun, T. Prognostic Role of Serum Albumin, Total Lymphocyte Count, and Mini Nutritional Assessment on Outcomes After Geriatric Hip Fracture Surgery: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. J Arthroplasty 2019, 34, 1287–1296. [CrossRef]
- Foo, M.X.E.; Wong, G.J.Y.; Lew, C.C.H. A Systematic Review of the Malnutrition Prevalence in Hospitalized Hip Fracture Patients and Its Associated Outcomes. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 2021, 45, 1141–1152. [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Lv, L.; Jiao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zuo, X.-L. Association between Nutritional Indices and Mortality after Hip Fracture: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2023, 27, 2297–2304. [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yang, J.; Yu, X.; Huang, X.; Vaidya, S.; Huang, F.; Xiang, Z. The Role of Perioperative Oral Nutritional Supplementation in Elderly Patients after Hip Surgery. Clin Interv Aging 2015, 10, 849–858. [CrossRef]
- Peeters, C.M.M.; Visser, E.; Van de Ree, C.L.P.; Gosens, T.; Den Oudsten, B.L.; De Vries, J. Quality of Life after Hip Fracture in the Elderly: A Systematic Literature Review. Injury 2016, 47, 1369–1382. [CrossRef]
- Ernst, A.; Wilson, J.M.; Ahn, J.; Shapiro, M.; Schenker, M.L. Malnutrition and the Orthopaedic Trauma Patient: A Systematic Review of the Literature. J Orthop Trauma 2018, 32, 491–499. [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Momosaki, R.; Yasufuku, Y.; Nakamura, N.; Maeda, K. Nutritional Therapy in Older Patients With Hip Fractures Undergoing Rehabilitation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Am Med Dir Assoc 2020, 21, 1364-1364.e6. [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.-Y.; Chiu, Y.-C.; Lu, K.-C.; Huang, I.-T.; Tsai, P.-S.; Huang, C.-J. Beneficial Effects of Preoperative Oral Nutrition Supplements on Postoperative Outcomes in Geriatric Hip Fracture Patients: A PRISMA-Compliant Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Studies. Medicine 2021, 100, e27755. [CrossRef]
- Szklarzewska, S.; Mottale, R.; Engelman, E.; De Breucker, S.; Preiser, J.-C. Nutritional Rehabilitation after Acute Illness among Older Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin Nutr 2023, 42, 309–336. [CrossRef]
- Volkert, D.; Beck, A.M.; Cederholm, T.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.; Goisser, S.; Hooper, L.; Kiesswetter, E.; Maggio, M.; Raynaud-Simon, A.; Sieber, C.C.; et al. ESPEN Guideline on Clinical Nutrition and Hydration in Geriatrics. Clinical Nutrition 2019, 38, 10–47. [CrossRef]
- De Gennaro Colonna, V.; Bianchi, M.; Pascale, V.; Ferrario, P.; Morelli, F.; Pascale, W.; Tomasoni, L.; Turiel, M. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine (ADMA): An Endogenous Inhibitor of Nitric Oxide Synthase and a Novel Cardiovascular Risk Molecule. Med Sci Monit 2009, 15, RA91-101.
- Liu, J.; Li, C.; Chen, W.; He, K.; Ma, H.; Ma, B.; Zhao, P.; Tian, L. Relationship between Serum Asymmetric Dimethylarginine Level and Microvascular Complications in Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis. Biomed Res Int 2019, 2019, 2941861. [CrossRef]
- Sener, A.; Lebrun, P.; Blachier, F.; Malaisse, W.J. Stimulus-Secretion Coupling of Arginine-Induced Insulin Release. Insulinotropic Action of Agmatine. Biochem Pharmacol 1989, 38, 327–330. [CrossRef]
- Global BMI Mortality Collaboration; Di Angelantonio, E.; Bhupathiraju, S.; Wormser, D.; Gao, P.; Kaptoge, S.; Berrington de Gonzalez, A.; Cairns, B.; Huxley, R.; Jackson, C.; et al. Body-Mass Index and All-Cause Mortality: Individual-Participant-Data Meta-Analysis of 239 Prospective Studies in Four Continents. Lancet 2016, 388, 776–786. [CrossRef]
- Powell-Wiley, T.M.; Poirier, P.; Burke, L.E.; Després, J.-P.; Gordon-Larsen, P.; Lavie, C.J.; Lear, S.A.; Ndumele, C.E.; Neeland, I.J.; Sanders, P.; et al. Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 143, e984–e1010. [CrossRef]
- Csige, I.; Ujvárosy, D.; Szabó, Z.; Lőrincz, I.; Paragh, G.; Harangi, M.; Somodi, S. The Impact of Obesity on the Cardiovascular System. J Diabetes Res 2018, 2018, 3407306. [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, M.J.; Bauer, J.M.; Rämsch, C.; Uter, W.; Guigoz, Y.; Cederholm, T.; Thomas, D.R.; Anthony, P.S.; Charlton, K.E.; Maggio, M.; et al. Frequency of Malnutrition in Older Adults: A Multinational Perspective Using the Mini Nutritional Assessment. J Am Geriatr Soc 2010, 58, 1734–1738. [CrossRef]
- Crichton, M.; Craven, D.; Mackay, H.; Marx, W.; de van der Schueren, M.; Marshall, S. A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression of the Prevalence of Protein-Energy Malnutrition: Associations with Geographical Region and Sex. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 38–48. [CrossRef]
- 250. Vellas, B.; Villars, H.; Abellan, G.; Soto, M.E.; Rolland, Y.; Guigoz, Y.; Morley, J.E.; Chumlea, W.; Salva, A.; Rubenstein, L.Z.; et al. Overview of the MNA--Its History and Challenges. J Nutr Health Aging 2006, 10, 456–463; discussion 463-5.
- Kaiser, M.J.; Bauer, J.M.; Ramsch, C.; Uter, W.; Guigoz, Y.; Cederholm, T.; Thomas, D.R.; Anthony, P.; Charlton, K.E.; Maggio, M.; et al. Validation of the Mini Nutritional Assessment Short-Form (MNA-SF): A Practical Tool for Identification of Nutritional Status. J Nutr Health Aging 2009, 13, 782–788. [CrossRef]
- Cederholm, T.; Jensen, G.L.; Correia, M.I.T.D.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Fukushima, R.; Higashiguchi, T.; Baptista, G.; Barazzoni, R.; Blaauw, R.; Coats, A.; et al. GLIM Criteria for the Diagnosis of Malnutrition – A Consensus Report from the Global Clinical Nutrition Community. Clinical Nutrition 2019, 38, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Barazzoni, R.; Jensen, G.L.; Correia, M.I.T.D.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Higashiguchi, T.; Shi, H.P.; Bischoff, S.C.; Boirie, Y.; Carrasco, F.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.; et al. Guidance for Assessment of the Muscle Mass Phenotypic Criterion for the Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition (GLIM) Diagnosis of Malnutrition. Clin Nutr 2022, 41, 1425–1433. [CrossRef]
- Compher, C.; Cederholm, T.; Correia, M.I.T.D.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Higashiguch, T.; Shi, H.P.; Bischoff, S.C.; Boirie, Y.; Carrasco, F.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.; et al. Guidance for Assessment of the Muscle Mass Phenotypic Criterion for the Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition Diagnosis of Malnutrition. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 2022, 46, 1232–1242. [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhang, P.; Shen, L.; Niu, L.; Tan, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, L.; Hao, X.; Li, X.; et al. Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Their Association with Signalling Pathways in Inflammation, Glucose and Lipid Metabolism. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [CrossRef]
- Huda, M.N.; Kim, M.; Bennett, B.J. Modulating the Microbiota as a Therapeutic Intervention for Type 2 Diabetes. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2021, 12, 632335. [CrossRef]
- Voroneanu, L.; Burlacu, A.; Brinza, C.; Covic, A.; Balan, G.G.; Nistor, I.; Popa, C.; Hogas, S.; Covic, A. Gut Microbiota in Chronic Kidney Disease: From Composition to Modulation towards Better Outcomes-A Systematic Review. J Clin Med 2023, 12. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Chen, X.; Kwan, T.K.; Loh, Y.W.; Singer, J.; Liu, Y.; Ma, J.; Tan, J.; Macia, L.; Mackay, C.R.; et al. Dietary Fiber Protects against Diabetic Nephropathy through Short-Chain Fatty Acid-Mediated Activation of G Protein-Coupled Receptors GPR43 and GPR109A. J Am Soc Nephrol 2020, 31, 1267–1281. [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, L.; Corbin, A.L.; Goveas, J.S. Depression and Frailty in Later Life: A Systematic Review. Clin Interv Aging 2015, 10, 1947–1958. [CrossRef]
| Query | Number of articles |
|---|---|
| #1 sarcopenia and (malnutrition or undernutrition or nutrition) and (ENGLISH[LA] and 2015:2023[DP] | 4,926 |
| #1 and (systematic review[PT] or meta-analysis[PT] or randomized controlled trial or cohort study or guideline) | 1,721 |
| #1 and systematic review[PT] | 201 |
| #1 and meta-analysis[PT] | 119 |
| #1 and randomized controlled trial | 396 |
| #1 and cohort study | 1,179 |
| #1 and Cochrane Database Syst Rev | 0 |
| #1 and guideline | 56 |
| #2 frailty and (malnutrition or undernutrition or nutrition) and (ENGLISH[LA] and 2015:2023[DP] | 3,134 |
| #2 and (systematic review[PT] or meta-analysis[PT] or randomized controlled trial or cohort study or guideline) | 1,279 |
| #2 and systematic review[PT] | 130 |
| #2 and meta-analysis[PT] | 77 |
| #2 and randomized controlled trial | 246 |
| #2 and cohort study | 943 |
| #2 and Cochrane Database Syst Rev | 0 |
| #2 and guideline | 48 |
| #3 heart failure and (malnutrition or undernutrition or nutrition) and (ENGLISH[LA] and 2015:2023[DP] | 3,609 |
| #3 and (systematic review[PT] or meta-analysis[PT] or randomized controlled trial or cohort study or guideline) | 1,427 |
| #3 and systematic review[PT] | 110 |
| #3 and meta-analysis[PT] | 104 |
| #3 and randomized controlled trial | 240 |
| #3 and cohort study | 1,090 |
| #3 and Cochrane Database Syst Rev | 7 |
| #3 and guideline | 115 |
| #4 chronic kidney disease and (malnutrition or undernutrition or nutrition) and (ENGLISH[LA] and 2015:2023[DP] | 6,080 |
| #4 and (systematic review[PT] or meta-analysis[PT] or randomized controlled trial or cohort study or guideline) | 2,221 |
| #4 and systematic review[PT] | 163 |
| #4 and meta-analysis[PT] | 138 |
| #4 and randomized controlled trial | 425 |
| #4 and cohort study | 1,633 |
| #4 and Cochrane Database Syst Rev | 16 |
| #4 and guideline | 185 |
| #5 diabetes and (malnutrition or undernutrition or nutrition) and (ENGLISH[LA] and 2015:2023[DP] | 46,363 |
| #5 and (systematic review[PT] or meta-analysis[PT] or randomized controlled trial or cohort study or guideline) | 14,932 |
| #5 and systematic review[PT] | 1,605 |
| #5 and meta-analysis[PT] | 1,411 |
| #5 and randomized controlled trial | 4,285 |
| #5 and cohort study | 9,561 |
| #5 and Cochrane Database Syst Rev | 38 |
| #5 and guideline | 838 |
| #6 stroke and (malnutrition or undernutrition or nutrition) and ENGLISH[LA] and 2015:2023[DP] | 5,356 |
| #6 and (systematic review[PT] or meta-analysis[PT] or randomized controlled trial or cohort study or guideline) | 2,132 |
| #6 and systematic review[PT] | 265 |
| #6 and meta-analysis[PT] | 283 |
| #6 and randomized controlled trial | 428 |
| #6 and cohort study | 1,807 |
| #6 and Cochrane Database Syst Rev | 18 |
| #6 and guideline | 145 |
| #7 dementia and (malnutrition or undernutrition or nutrition) and ENGLISH[LA] and 2015:2023[DP] | 4,348 |
| #7 and (systematic review[PT] or meta-analysis[PT] or randomized controlled trial or cohort study or guideline) | 1,396 |
| #7 and systematic review[PT] | 184 |
| #7 and meta-analysis[PT] | 149 |
| #7 and randomized controlled trial | 285 |
| #7 and cohort study | 975 |
| #7 and Cochrane Database Syst Rev | 13 |
| #7 and guideline | 48 |
| #8 osteoporosis and (malnutrition or undernutrition or nutrition) and ENGLISH[LA] and 2015:2023[DP] | 3,802 |
| #8 and (systematic review[PT] or meta-analysis[PT] or randomized controlled trial or cohort study or guideline) | 1,056 |
| #8 and systematic review[PT] | 118 |
| #8 and meta-analysis[PT] | 92 |
| #8 and randomized controlled trial | 223 |
| #8 and cohort study | 723 |
| #8 and Cochrane Database Syst Rev | 4 |
| #8 and guideline | 91 |
| #9 fracture and (malnutrition or undernutrition or nutrition) and ENGLISH[LA] and 2015:2023[DP] | 3,616 |
| #9 and (systematic review[PT] or meta-analysis[PT] or randomized controlled trial or cohort study or guideline) | 1,362 |
| #9 and systematic review[PT] | 154 |
| #9 and meta-analysis[PT] | 125 |
| #9 and randomized controlled trial | 232 |
| #9 and cohort study | 1,021 |
| #9 and Cochrane Database Syst Rev | 8 |
| #9 and guideline | 89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





