1. Introduction
Gilgit-Baltistan, formerly known as northern area, spreads over 7.25 million ha which hosts 1.49 million people (GoGB, 2020). Agriculture is main economic activity with which more than 90% population is engaged (IFAD, 2015). Within agriculture sector horticulture contributes 48%, followed by livestock 41% and forestry 11% (World Bank, 2011). With mean annual rainfall of 100-200 mm, approximately 95% of total cultivated area mainly depends on glacial meltwater from irrigation channels called khuls (IUCN, 2003; Velde, 1989). Meltwatert dependent agriculture sector has been facing challenges of limited arable land, climatic variabilities, water mismanagement and frequently reoccurring hazards. Glaciers in Gilgit-Baltistan have either lower retreat rates comparing to global average or are relatively stable (Bashir et. al., 2017). For instance, Batura, Passu and Gulmit glaciers located in central Karakorum have exhibited net frontal retreat of 680, 774 and 330 m respectively between period 1965 and 2018. Contrary to these glaciers, the Ghulkin glaciers kept retreating and advancing alternatively and now sit on the position as of 1958 showing almost zero net retreat (Nüsser et. al., 2019). Retreating of majority of glaciers has disconnected centuries old irrigation networks resulting in irrigation water shortages for already developed agriculture-base. Besides accelerated glacier melting, natural calamities including torrential rainfalls, landslides significantly impact the irrigation infrastructures and reducing the water carrying capacities (Nüsser, 2017). In most of the glacial water dependent hamlets, regular attempts with local wisdom and engineering approaches, had been made to reconnect the rehabilitate the irrigation supplies remained unsustain owing to glacial downwasting and water-induced hazards as result of climatic changes (Spies, 2016). Limited arable land, subsistence agricultural practices, weaker agriculture extension services and mismanagement of dwindling irrigation water has further worsen the situation. The overall scenario is resulting into lower land and water productivity consequently food insecurity.
Population of Gilgit Baltistan has increased from 0.884 to 1.49 million during period 1988 to 2017. While, cultivable area has increased from 0.86% to 1.2%, out of total cultivable (2%) area during period 2000 to 2020. Thus growing population has increased pressure on the existing agriculture system of the province (GoGB, 2020; IUCN, 2000; IFAD, 2015). For instance during 2012-13 provincial wheat requirement was 135 metric tonne out of which 90 metric tonne was produced locally and rest was imported (Anwar et. al., 2019). Government line agencies and development organizations have been assisting the local farming community in extending the agriculture livelihood base by sustaining and developing the glacial meltwater sources. A fair example of this is Economic Transformation Initiative (ETI) aiming to increase cultivated area by 20,000 ha mainly by harnessing available glacial meltwaters (IFAD, 2015). However these interventions are still prone to aforementioned challenges leading towards uncertainty in irrigation supplies (Dhakal et. al., 2021). Thus, there is a need to not only provide alternate irrigation supplies to cultivated area but also to tap remaining 1% cultivable land, located along river banks, having limited glacial or snow meltwater supplies.
Table 1.
Potential cultivable land in different districts of Gilgit Baltistan.
Table 1.
Potential cultivable land in different districts of Gilgit Baltistan.
| District |
Cultivated Land (ha) |
Barren Land (ha) |
Required Discharge |
| Cusecs |
(Cumecs) |
| Diamer |
13,216 |
31,210 |
435.40 |
12.33 |
| Astor |
5,476 |
5,652 |
180.40 |
5.11 |
| Ghizer |
11,280 |
2,370 |
371.60 |
10.52 |
| Ghanche |
1,109 |
13,806 |
36.50 |
1.03 |
| Hunza- Nager |
6,841 |
10,582 |
225.40 |
6.38 |
| Skardu |
29,235 |
22,037 |
963.20 |
27.27 |
| Gilgit |
6,968 |
7,973 |
229.60 |
6.5 |
| |
74,124 |
93,631 |
2,442 |
69.15 |
Water Management Directorate of Gilgit Baltistan has identified 43 potential glacial meltwater sources to irrigate 20,800 ha barren land in the province, out of which 5200 ha will be brought under cultivation through 23 schemes in Astor, Diamer, Ghanche and Ghizar districts under ETI programme (ETI, 2018). However, the glacial meltwater sources are insufficient to meet the requirement of province to bring all barren land under irrigation. Under these scenarios, river water lifting has become inevitable to extend the agriculture-base in the province.
To cope up with aforementioned challenges in sustainable irrigation water supplies, the International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) jointly with WWF-Pakistan and local partners conducted a detailed study on irrigation management in two villages (Morkhun and Khyber) in Gojal area of Hunza District. A project titled “Agricultural Water, Energy, and Hazard Management in the Upper Indus Basin for Improved Livelihoods and Resilience” was implemented in these villages. The project piloted options for alternate irrigation water supplies. The project interventions included river water lifting through solar and hydraulic ram pumps, uphill water tanks, and water distribution through drip irrigation system for high value horticultural practices. This project aimed to pilot and generate evidences of such solutions for scaling purposes.
The viability and scalability of any pilot depends on its performance and economic feasibility (ADB, 2017). Thus this study intends to evaluate the piloted schemes by estimating performance efficiencies and economic feasibilities. This study will provide strategic guidelines for selection of suitable irrigation scheme for wider upscaling.
1.1. Study area
The Hunza valley lies at altitude range of 4548 and 25669 feet having 1370104 ha catchment area (Qureshi et al., 2017; Immerzeel et al., 2012). It is divided into two zones, Lower Hunza and Upper Hunza usually called Gojal (Baig, 2018). The mean daily temperature falls in range 16 to 35.9 °C while mean annual rainfall is 5.36 inches (Qureshi et al. 2017). The soils in this valley are immature made up of river terraces, alluvial fans, glacial moraines and silt deposition by the irrigation water. These have shallow profiles upto maximum 2 feet, low water holding capacities and low fertility (IIMI, 1989)
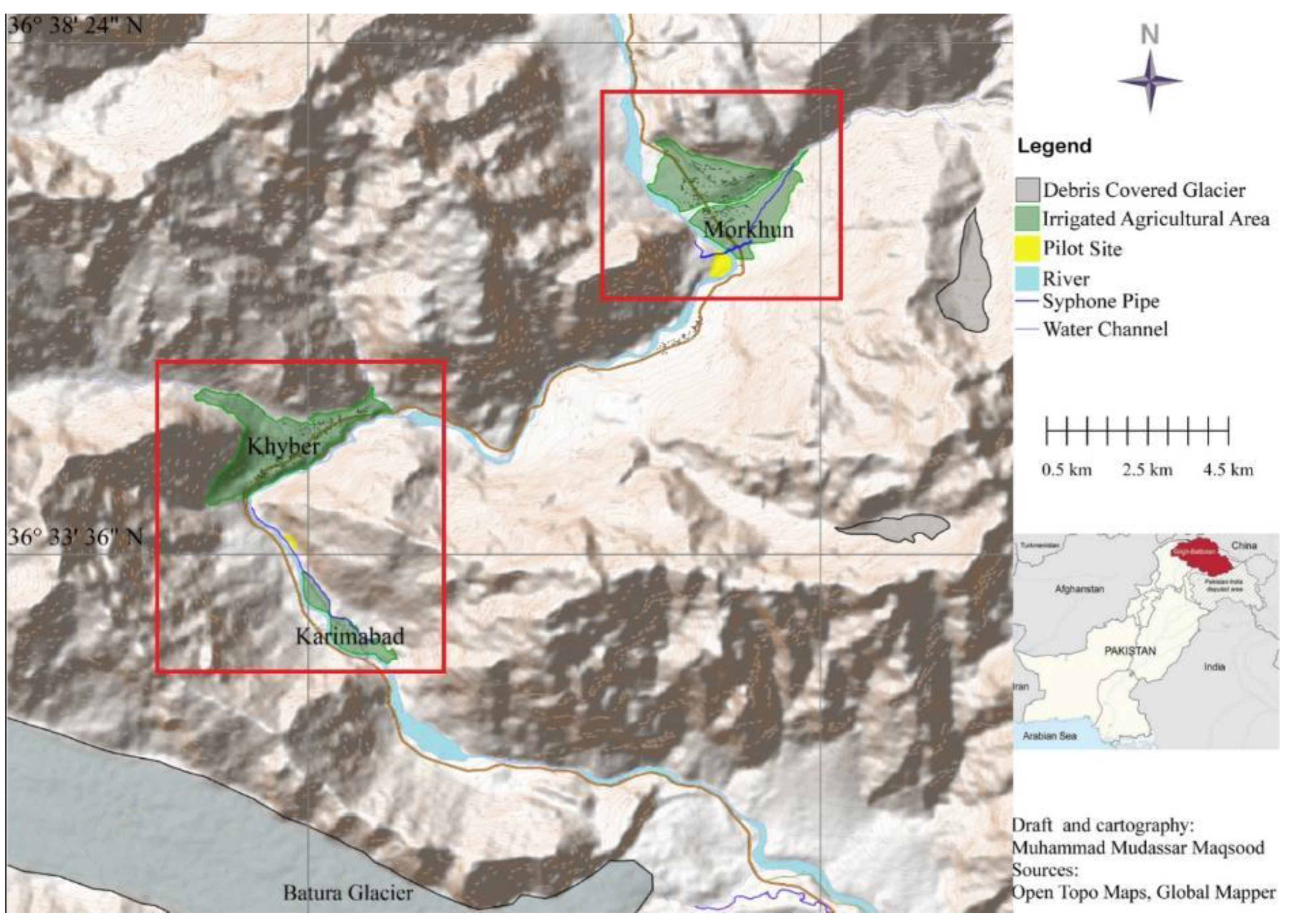
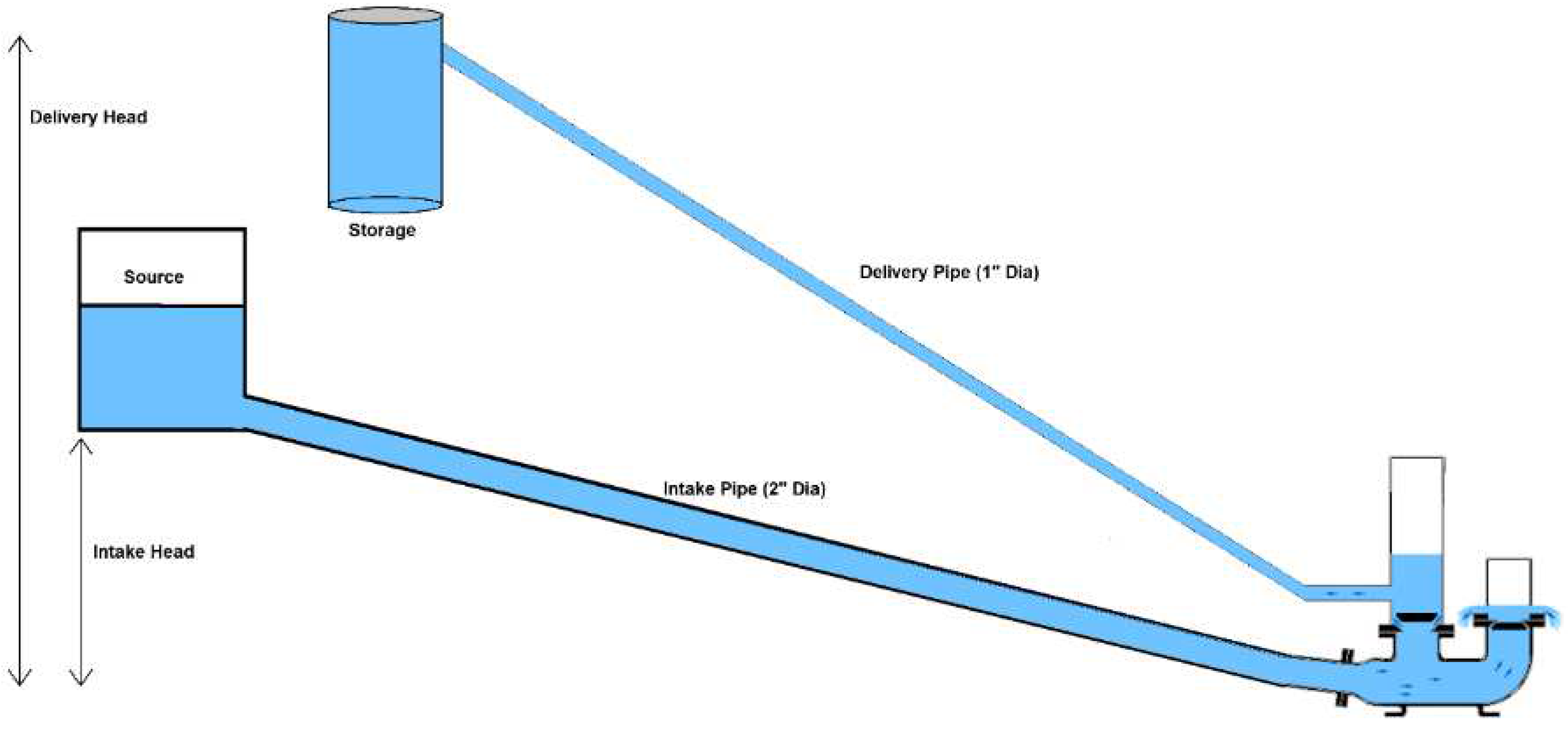
Keeping in view the objective of study, detailed site selection surveys were done. While selection of the pilot site the road accessibility, community interests and needs, and demonstration value of pilot interventions were considered. Based on the survey, sites were selected in Passu, Morkhun and Khyber for piloting water management interventions. This study covers two different technologies packages piloted in Morkhun and Khyber. The study area has been shown in the
Figure 1.
Khyber is a village of Gojal, stretching 11.18 miles from Passu to Ghalapan, covering a total area of 42.27 miles (Edwards, 2006). It is home of 1200 people (55% male and 45% female) residing in 150 houses. Majority of population is salaried followed by businessmen and farmers. The average landholding per household in Khyber is 1.4 ha, off which 0.9 ha is cultivated. These cultivated scattered fields are irrigated by six channels, out of which four originates from Shavjerab Nallah while one each from Keralgoz Nullah and Khunjrav River. Flood irrigation either through ridge and furrow or basin irrigation are common water application methods in Khyber village. The water management package, piloted at Khyber consisted of a Hydraulic Ram Pump, elevated storage tanks and drip irrigation for apple orchard at 2.5 acres. This pump operates 24 hours with minimal operation costs.
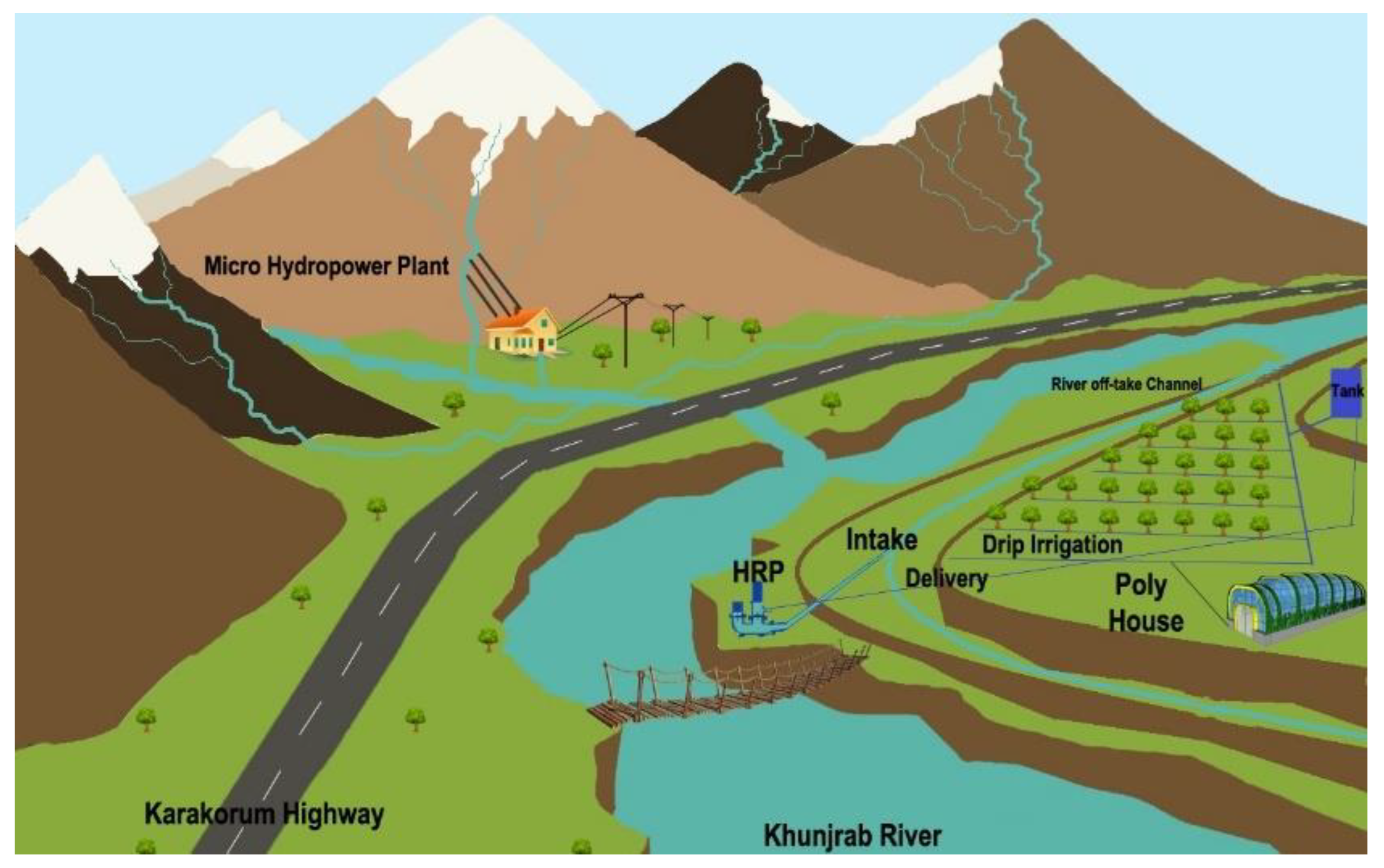
Figure 2.
Schematic Diagram of intervention package in Khyber.
Figure 2.
Schematic Diagram of intervention package in Khyber.
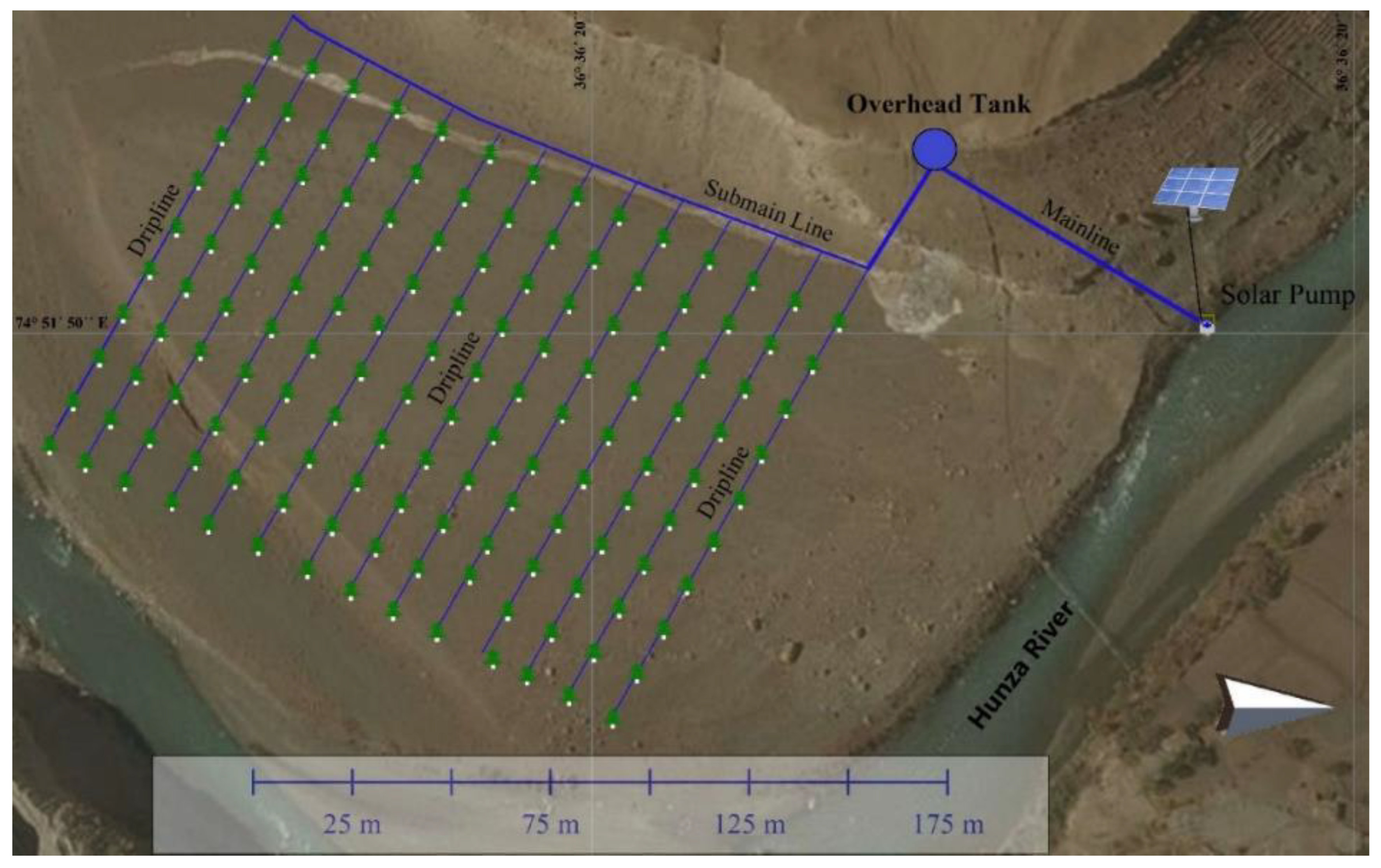
Morkhun consists of 86 households providing shelter to 652 individuals (51% male, 49% male), where 70% of households own up to 2 ha area per household, of which up to one ha is cultivated. Service sector, followed by business and farming, is the major means of earning. Major source of irrigation water supply are glacial melting at Tupopdon glaciers which is supplied through eight unlined channels to Jamal Abad and Morkhun. Improved surface and flood irrigation methods are common water application practices in Morkhun village. A solar pumping system consisting of 600 watt solar panels and 400 watts DC motor The lifted water is being stored in uphill storage tanks which is then distributed in a 5 acres apple orchard through drip irrigation under gravity action. However, in current study, only 2.5 area and corresponding cost of irrigation system piloting has been considered.
Figure 3.
Schematic Diagram of intervention package in Morkhun.
Figure 3.
Schematic Diagram of intervention package in Morkhun.
1.2. Methodology
The study involved piloting of packages and assessment through cost-benefit analysis and field investigations. After piloting the intervention packages, project team visited the field to collect the observation data to conduct performance evaluations of piloted systems. At the end, cost-benefit analysis studies were carried out to determine the economic viability of piloted irrigation packages respectively.
1.2.1. Performance Evaluation
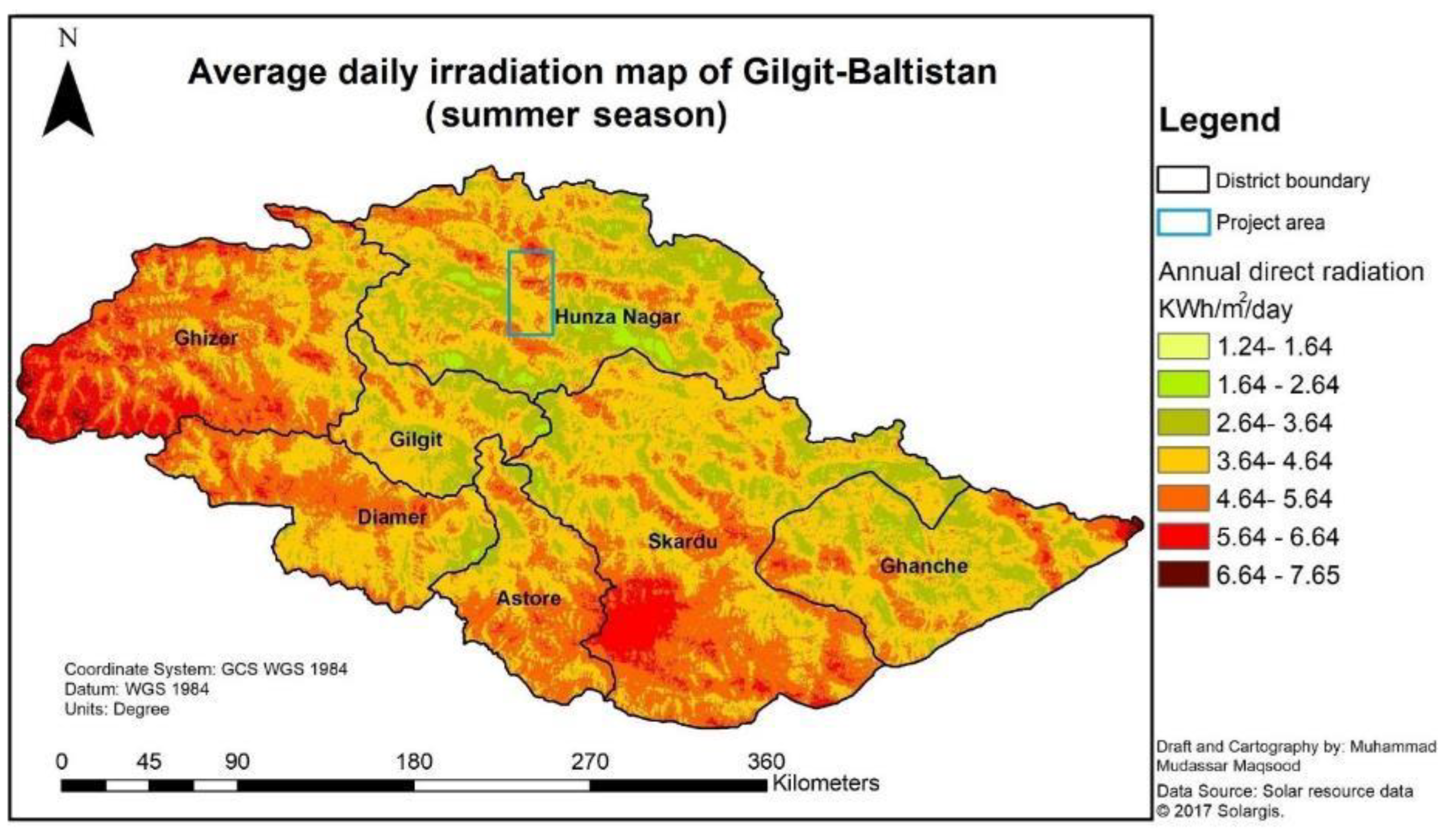
Performance evaluation of solar pumping and hydraulic ram pumping systems were carried out separately. The solar irradiation maps were developed using Solargis raster maps and extracted to Gilgit Baltistan boundary to assess the solar potential of the province. Daily sunshine hours’ data of the province was retrieved from research publication of Javed et al. (2020). Pump discharge was estimated by volumetric method. Daily pumped water volume was then calculated by multiplying the pump discharge with daily sunshine hours.
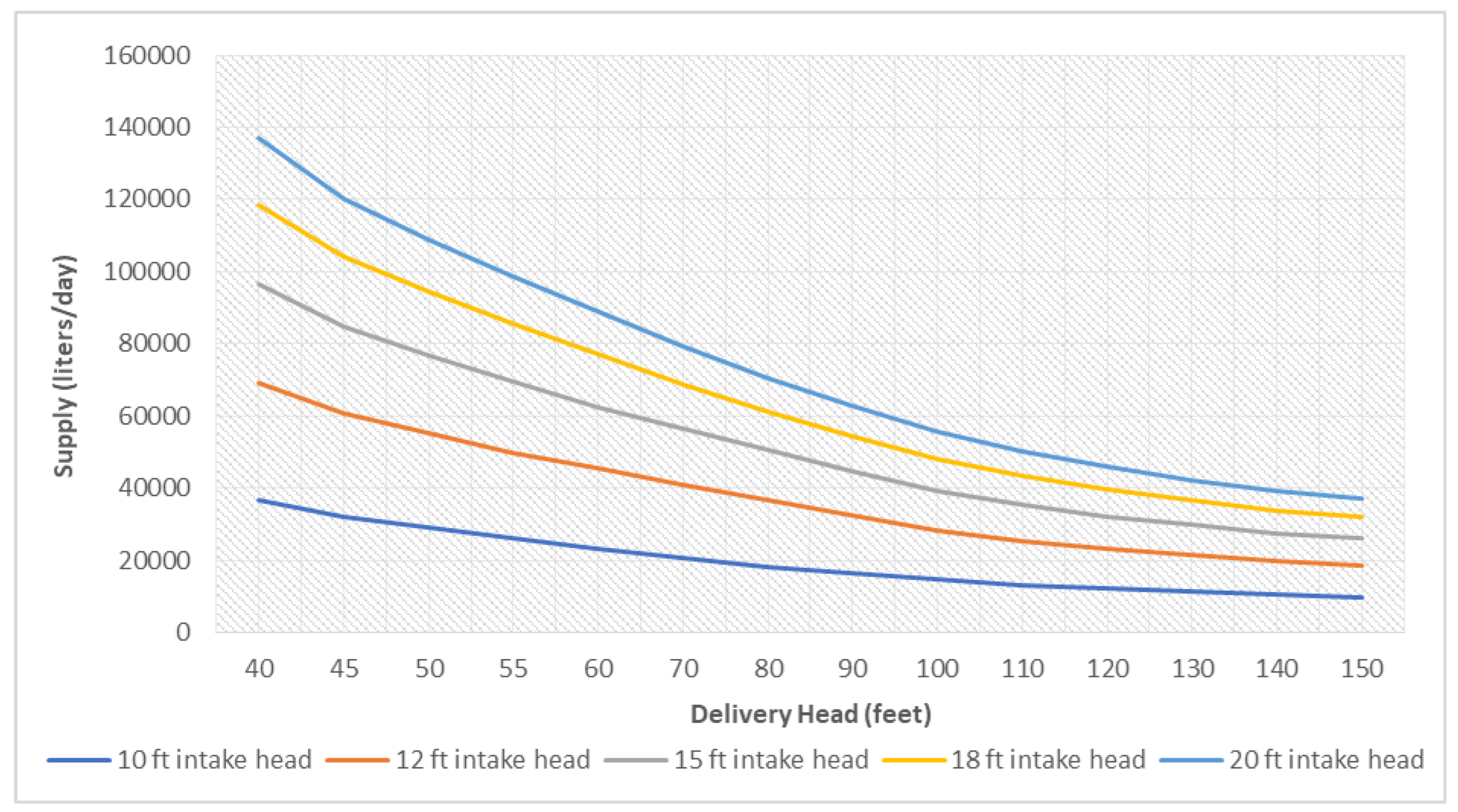
In case of hydraulic ram pump, discharge was estimated using volumetric method. Further investigations were made to access the pump performance against sites specific condition like intake head and delivery head which were plotted on a graph to represent the findings.
The performance evaluation of drip irrigation packages was done by field data measurements and calculation of uniformity coefficient (CU) (Equation 1), application efficiency (Ea) (Equation 2) and water saving as compared to flood irrigation methods. The coefficient of uniformity is an estimation of how equally the emitters supply water across the field. Water application efficiency is the ratio of the water applied to the root zone to the to the water quantity delivered. (Pair et. al., 1975).
The field data observations involved emitter discharge measurements at head, middle and tail of laterals using volumetric method (Equation 3). The measurements were taken for five minutes which were then used for estimation of CU and Ea parameters. Wu and Gitlin (1974) modified the equation of Christiansens (1942) to estimate the CU by replacing the depth of water with emitter discharge. Coefficient of Uniformity is the measure of uniform water application through the laterals in the drip irrigation.
where
CU = Uniformity Coefficient in percentage
D = Average absolute deviation from the average discharge (litre/hr)
M = mean discharge rate (litre/hr)
Qₙ = Emitter discharge (volume/time)
n = total measurements
The field application efficiency (Ea) is the ratio of total water quantity stored in root zone to total water applied. It was calculated using following equation used by Jamrey and Nigam (2018) as well as by Arya et al. (2017) with assumption that all water applied stored in root zone with no runoff and deep percolation.;
where
Ea = Field Application Efficiency in percentage
Qmin = Minimum emitter discharge (litre/hr)
Qavg = Average emitter discharge or emitter design discharge (litre/hr)
Emission uniformity is defined as the average discharge of 25% of the sampled emitters with the least discharge, divided by the average discharge of all sampled emitters. Field emission uniformity (EU
f) was estimated using Keller and Karmeli (1974) equation (5) given below;
where
Coefficient of variation was estimated using below standard equation (6) as;
where
Statistical Uniformity Coefficient was estimated by using following equation (7) as;
where
1.2.2. Economic Evaluation
In order to estimate the economic viability of the investment in solar and hydro ram drip irrigation systems, both Net Present Value (NPV) (Equation 5) and Benefit Cost Ratio (BCR) (Equation 6) have been used by discounting cash flow method.
where
The Internal Rate of Return (IRR) was estimated which is the most appropriate techniques to evaluate the economic efficiency of piloted irrigation systems (Asmon and Rothe, 2006). In IRR, the measurement of implied discount rate involves equitation of present value of benefits to the present value so that NPV of project becomes zero.
The NPV is one of the major criteria of project appraisal that has been widely used for estimation of economic viability of projects. This method accounts expected discounted costs and income earned during project life. While measuring NPV, assumptions are made that future cash flows are dependent on benefits and costs of project in future. The useful life of the systems, fruit harvesting time and variations in incomes, survival of plants, labour cost and increased discount rates were considered while calculations. To address the uncertainty of future cash flows, increasing the discount rate and comparing the pessimistic and optimistic future cash flows are considered (Gaspars and Wieloch, 2019).
2. Results and discussion
2.1. Economic Evaluation of Irrigation Systems
After detailed consultations with regional agricultural irrigation experts, the economic indicators of project interventions were calculated. The useful life of the systems, fruit harvesting time and variations in incomes, survival of plants, labour cost and increased discount rates were considered while calculations.
The total capital cost of solar driven drip coupled irrigation system, including equipment and maintenance costs, at Morkhun is 2,129,398 (US$13,354 as of July 2019). The local agricultural water experts suggested average maintenance costs for first five years as PKR 5 000 (USD$31.36), for years 6-10 as PKR10 000 (US $62.71), for years 11-15 as PKR15 000 (US$ 94.07), and for years 16–20 as PKR20 000 (US$125.43. The study also considered 20-year useful life of system, inflation, depreciation, maintenance and labour expenses.
Table 4. (US
$26,951) while Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is 23% greater than the discount rate 12.25%. The benefit to cost ratio of this package was calculated which is 2.96 with a payback period of 9.21 years which indicates that the estimated benefits of project will outweigh the total cost. Moreover, the project will expect 2.96 PKR in benefits for each 1 PKR cost.
Table 4.
Performance Evaluation of Drip Irrigation.
Table 4.
Performance Evaluation of Drip Irrigation.
| Village |
Qmean (lph) |
CU (%) |
Ea (%) |
EUf (%) |
Cv
|
SUC (%) |
| Khyber |
5.04 |
93.34 |
87.24 |
90.21 |
0.08 |
92.20 |
| Morkhun |
5.31 |
92.15 |
88.57 |
90.93 |
0.08 |
92.11 |
Table 5.
Estimated Economic Parameters of Both Intervention Packages.
Table 5.
Estimated Economic Parameters of Both Intervention Packages.
| Parameter |
Intervention Sites |
| Khyber (Hydro Ram Pump) |
Morkhun (Solar Pump) |
| Net Present Value |
PKR 6,898,005 (US$43,261) |
PKR 4,297,273 (US$26,951) |
| Internal Rate of Return |
31% |
23% |
| Cost Benefit Ratio |
4.21 |
2.96 |
| Payback Period |
8.25 |
9.21 |
In case of Hydraulic Ram Pump coupled drip irrigation system piloted at Khyber, the initial investment (including equipment and maintenance expenses) of 1,817,000 (US$11,395 as of July 2019). The average maintenance cost is presumed to be PKR 5 000 (USD$31.36) for each year. The study also account 20-year life cycle, amount for inflation, depreciation, maintenance and labour expenses.
The analysed economic parameters showed that the system is economically feasible with NPV of PKR 6,898,005 (US$43,261) having positive economy as the IRR is 31% which is more than the discount rate 12.25%. The benefit to cost ratio of project was calculated as 4.21 with payback period of 8.25 years.
3. Conclusions
The river water lifting and irrigation schemes piloted by ICIMOD has been proved vital in bringing the remaining cultivable lands under irrigation. Being environmentally, technically and economically viable, it can be replicated to bring the remaining cultivable area under irrigation in Gilgit Baltistan. Both systems have limitations, however detailed pre-feasibility and localized customization is essential for effective scaling of these systems.
Comparing to Solar Pumping Systems, the hydraulic ram pumps found lifting one third times more water to greater height even under heavy suspended solids and salts concentrations, thus these can irrigate more area. For higher discharges, hydraulic ram pumps can be installed in parallel on a same stream and connected to a common out-take for irrigating large areas. For proper selection of electric pump type, water quality analysis should be pre-requisite. Nevertheless, these systems have reduced labour work in the field, thus the farmers have enough time to take other chores. However, their initial capital costs and longer payback period are major constraints in upscaling these packages. For this, the provincial government and developing agencies could support the farming community for adaptation of these technologies.
Figure 8.
Barren land (left) converted into cultivated productive land (right) in Khyber.
Figure 8.
Barren land (left) converted into cultivated productive land (right) in Khyber.
The success of pilot studies has encouraged government and development agencies to upscale these technologies in other districts of Gilgit Baltistan. The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) with the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) has solar pump and Hydraulic Ram Pump assisted drip irrigation in 30 and 30 different sites in Gilgit-Baltistan respectively. The federal government has now launched a project to install 150 solar and 50 Hydraulic Ram Pump assisted irrigation systems 10 districts costing 150 million Pakistani rupees to bring 800 ha barren land (along river banks) under irrigation. These interventions would support the provincial government mandate to extend the irrigated area and to reduce poverty in the region.
Acknowledgement
The authors would like extend gratitude to the Indus Basin Initiative team of ICIMOD, the WWF Gilgit office, the Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resources (PCRWR), Mountain Agricultural Research Centre (MARC) and local community organizations for their assistance during field implementation of the technological packages in the project areas. We also acknowledge support of Mr. Rehmat Ullah Kundi for his support and dedication for successful piloting of hydraulic ram pump. This work was supported by the Indus Basin Initiative of ICIMOD, which contributes to the Sustainable Development Investment Portfolio and is supported by the Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade, Government of Australia. The study was partially supported by ICIMOD core funds (contributed by the governments of Afghanistan, Australia, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Myanmar, Nepal, Norway, Pakistan, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom).
References
- ADB (Asian Development Bank)., 2017. Kingdom of Bhutan: Adapting to Climate Change through Integrated Water Resources Management: Technical Assistance Completion Report, Project No. 46463. Manila, Philippines: Asian Development Bank (ADB). https://www.adb.org/sites/default/files/project-documents/46463/46463-002-tcr-en.pdf.
- Anwar, S., Khan, F.A. and Rahman, A., 2019. Impact of Karakorum Highway on land use and agricultural development of Gilgit-Baltistan, Pakistan. Sarhad Journal of Agriculture, 35(2), pp.417-431.
- Asmon, I.T.I.L. and Rothe, R.A.I.N.E.R., 2006. The economic feasibility of drip Irrigation in Afghanistan. Alternative Livelihoods Project-South (alp/s), February, 2.
- Arya, C.K., R.C. Purohit, L.K. Dashora, P.K. Singh and Mahesh Kothari. 2017., Performance Evaluation of Drip Irrigation Systems. Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci. 6(4): 2287-2292. doi: https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.604.266. [CrossRef]
- Baig, S.U., Khan, H. and Din, A., 2018. Spatio-temporal analysis of glacial ice area distribution of Hunza River Basin, Karakoram region of Pakistan. Hydrological Processes, 32(10), pp.1491-1501.
- Bashir, F., Zeng, X., Gupta, H. and Hazenberg, P., 2017. A hydrometeorological perspective on the Karakoram anomaly using unique valley-based synoptic weather observations. Geophysical Research Letters, 44(20), pp.10-470. [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, J.E., 1942. Irrigation by sprinkling. California agricultural experiment station bulletin 670. University of California, Berkeley, CA, 4275.
- Edwards, S.R., 2006. Saving biodiversity for human lives in northern Pakistan. IUCN.
- Gaspars-Wieloch, H., 2019. Project net present value estimation under uncertainty. Central European Journal of Operations Research, 27(1), pp.179-197. [CrossRef]
- Howell, T.A., 2003. Irrigation efficiency. p. 467–472. BA Stewart and TA Howell (ed.) Encyclopedia of water science. Marcel Dekker, New York. Irrigation efficiency. p. 467–472. In BA Stewart and TA Howell (ed.) Encyclopedia of water science. Marcel Dekker, New York.
- IFAD (International Fund for Agricultural Development)., 2015. Economic Transformation Initiative Gilgit-Baltistan Programme, Islamic Republic of Pakistan: Design Report, Gilgit, Pakistan. https://www.ifad.org/en/document detail/asset/40143518.
- Javed, Z.H., Khan, S., Wahid, A., Ranjha, A.N. and Hassan, M.U., 2020. Climate of the Gilgit-Baltistan Province, Pakistan. International Journal of Economic and Environmental Geology, 11(3), pp.16-21.
- Jamrey, P. K., & Nigam, G. K., 2018. Performance evaluation of drip irrigation systems. The Pharma Innovation Journal, 7(1), pp.346-348.
- Dhakal, M.P., Ali, A., Khan, M.Z., Wagle, N., Shah, G.M., Maqsood, M.M. and Ali, A., 2021. Agricultural water management challenges in the Hunza River Basin: Is a solar water pump an alternative option?. Irrigation and Drainage. [CrossRef]
- GoGB (Government of Gilgit-Baltistan). 2020., Gilgit-Baltistan at a Glance. Statistical & Research Cell (SRC), Planning and Development. Gilgit, Pakistan.
- Spies, M., 2016. Glacier thinning and adaptation assemblages in Nagar, northern Pakistan. Erdkunde, pp.125-140. [CrossRef]
- Pair, C.H., Hinz, W.W., Reid, C. and Frost, K.R., 1975. Sprinkler irrigation. Sprinkler Irrigation Assn.
- Nüsser, M., Dame, J., Parveen, S., Kraus, B., Baghel, R. and Schmidt, S., 2019. Cryosphere-fed irrigation networks in the northwestern Himalaya: Precarious livelihoods and adaptation strategies under the impact of climate change. Mountain Research and Development, 39(2), pp.R1-R11. [CrossRef]
- Nüsser, M., 2017. Socio-hydrology: a new perspective on mountain waterscapes at the nexus of natural and social processes. Mountain Research and Development, 37(4), pp.518-520. [CrossRef]
- Pakistan, I.I.M.I., 1989. Irrigation system performance in farmer-managed irrigation systems in Hunza-Gojal.
- Qureshi, M.A., Yi, C., Xu, X. and Li, Y., 2017. Glacier status during the period 1973–2014 in the Hunza Basin, Western Karakoram. Quaternary International, 444, pp.125-136.
- Velde, E.V., 1989. Irrigation Management in Pakistan Mountain Environment. [CrossRef]
- World Bank, 2011. Pakistan–Gilgit-Baltistan Economic Report: Broadening the Transformation.
- Wu, I.P. and Gitlin, H.M., 1973. Hydraulics and uniformity for drip irrigation. Journal of the Irrigation and Drainage Division, 99(2), pp.157-168.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).