Submitted:
27 June 2023
Posted:
29 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Designing three possible prior level fusion scenarios of 3D semantic segmentation, each of which injects point clouds, aerial images, and a specific type of prior knowledge into the DL technique’s learning pipeline;
- Evaluate the performance of each scenario developed in terms of enhancing DL technique knowledge;
- Highlighting the smart fusion approach for a precise extraction of maximum urban fabric detail;
2. Related Works
2.1. Prior-Level Fusion Approaches
2.2. Point-Level Fusion Approaches
2.3. Feature-Level Fusion Approaches
2.4. Decision-Level Fusion Approaches
2.5. Summary
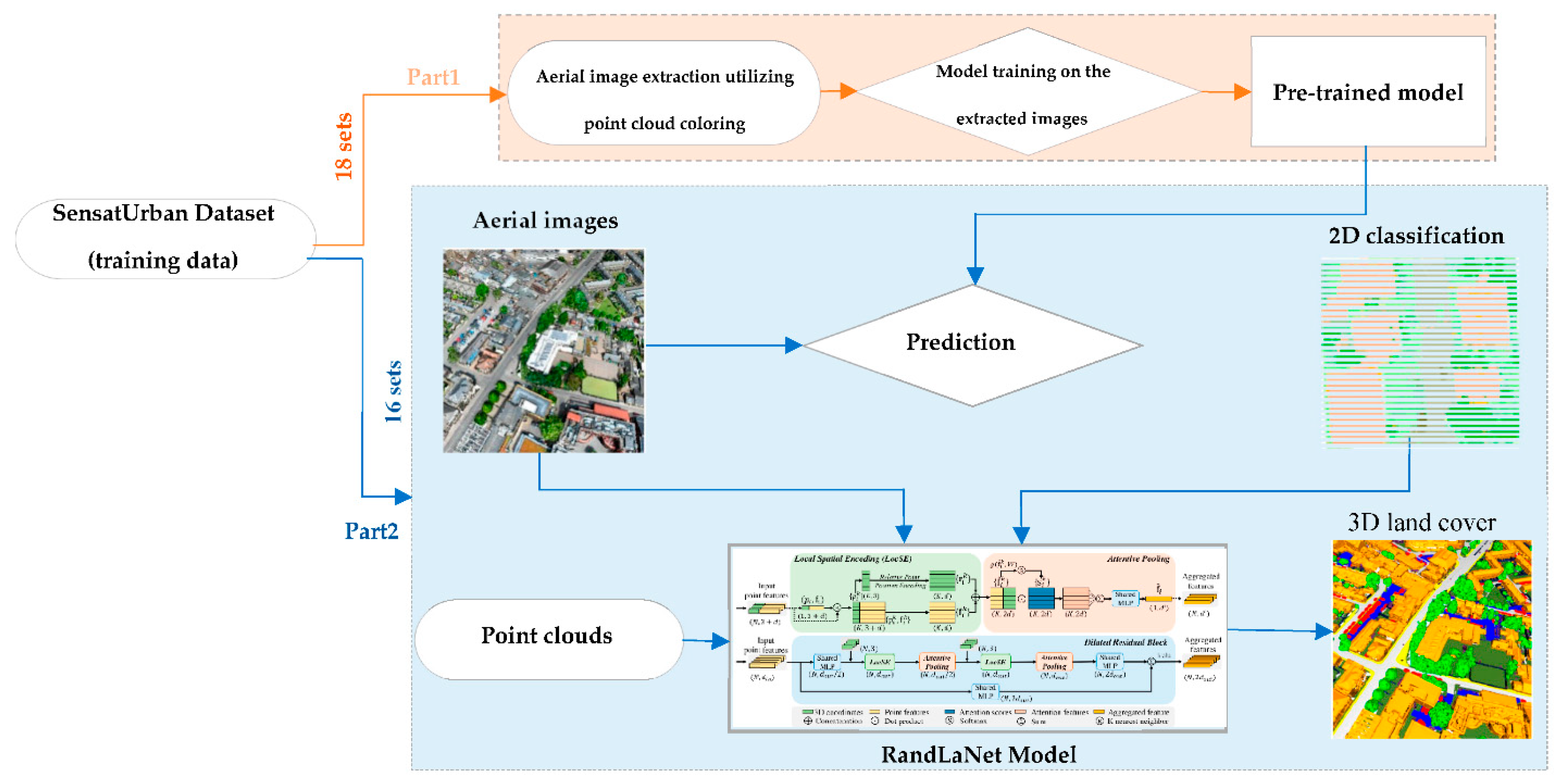
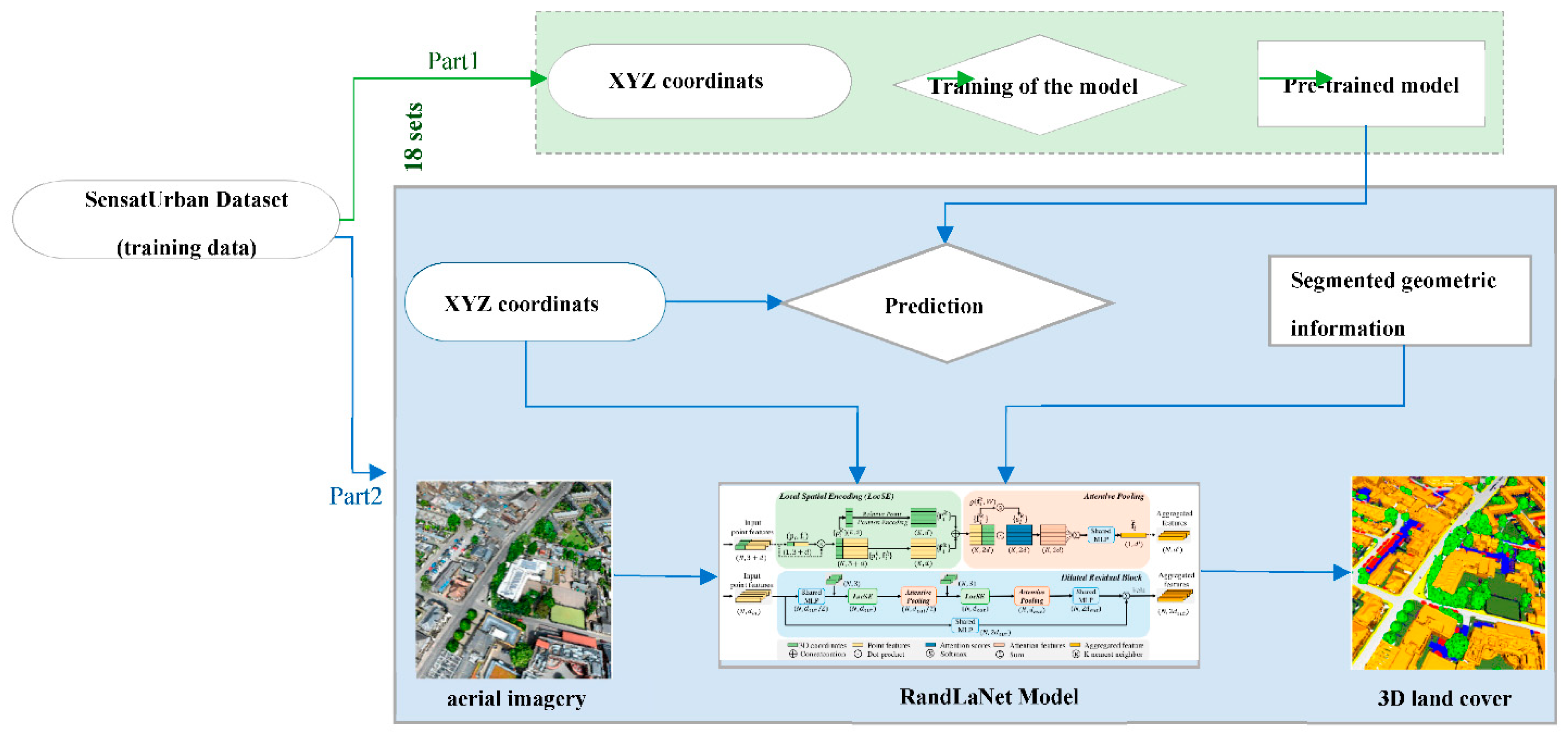
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Dataset
3.2. RandLaNet Deep Learning Algorithm
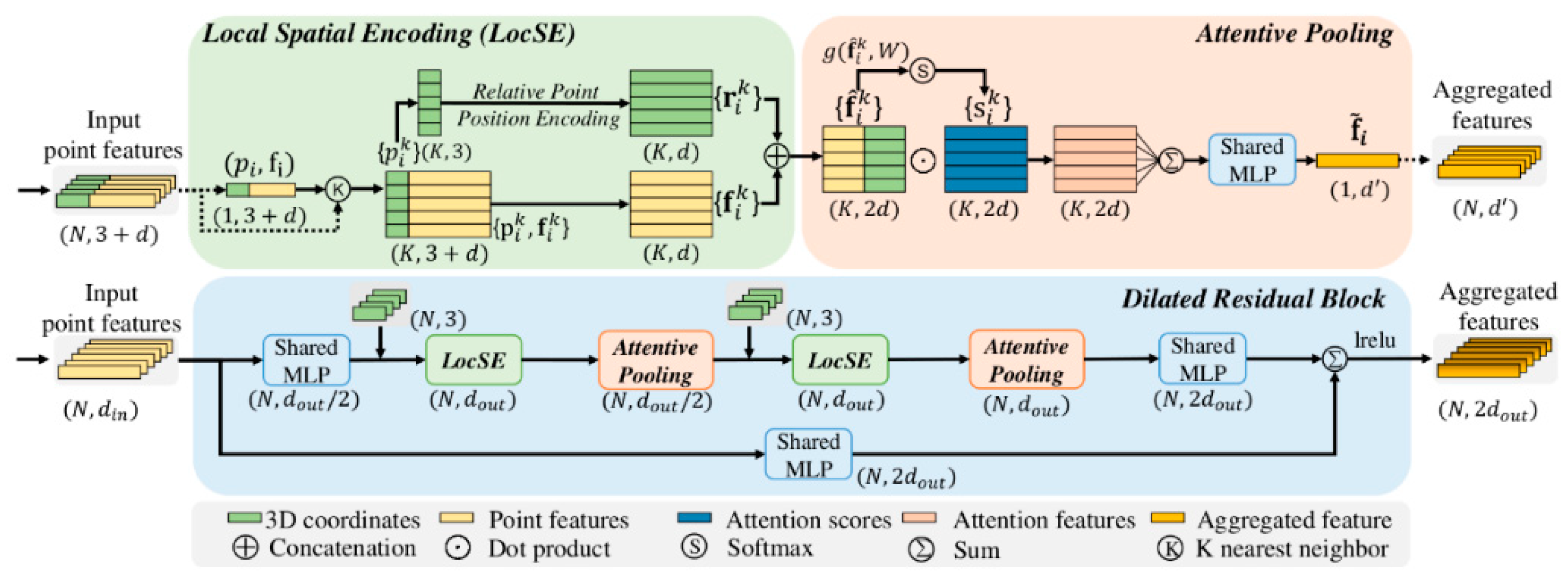
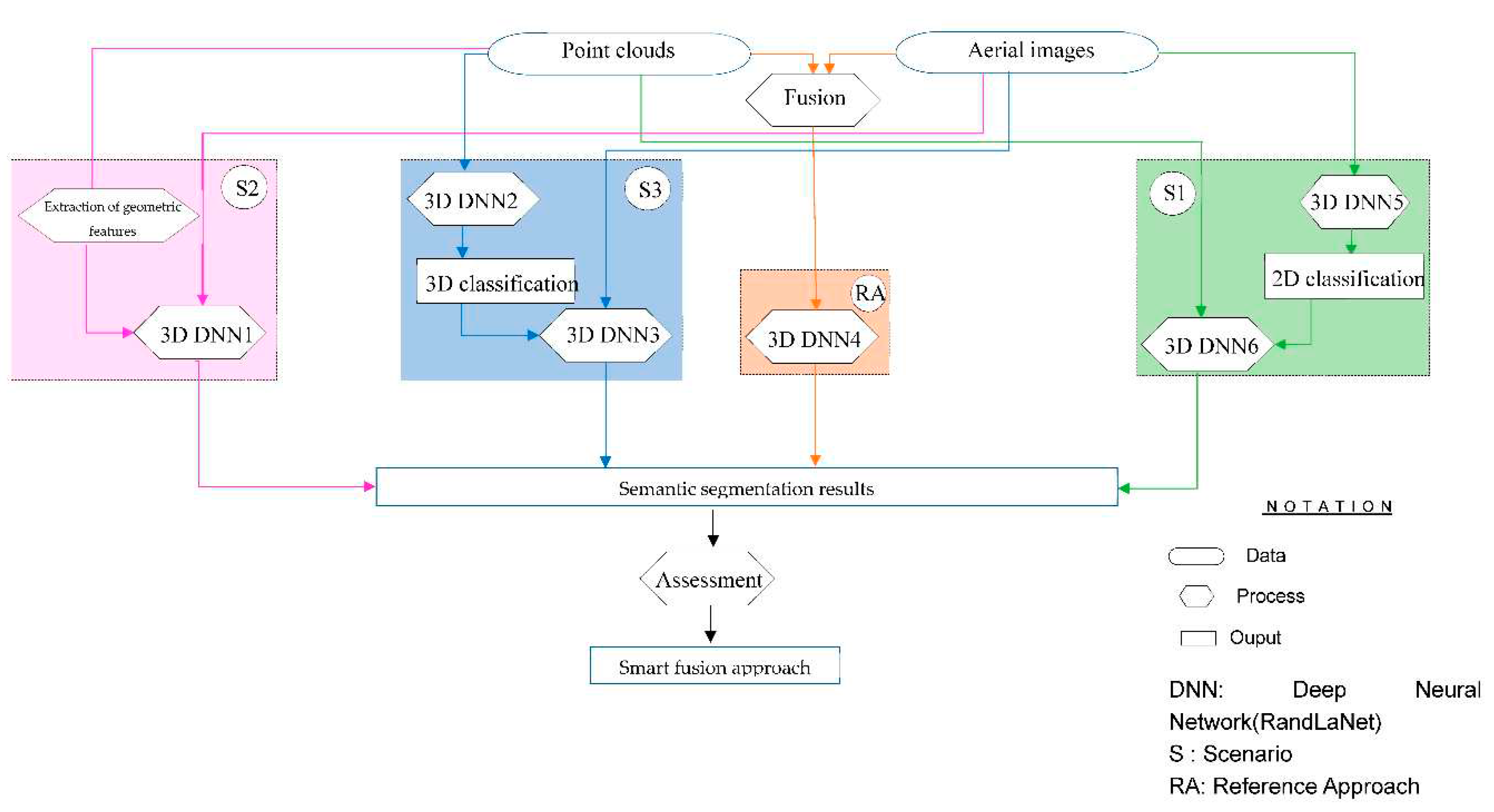
3.3. Methodology
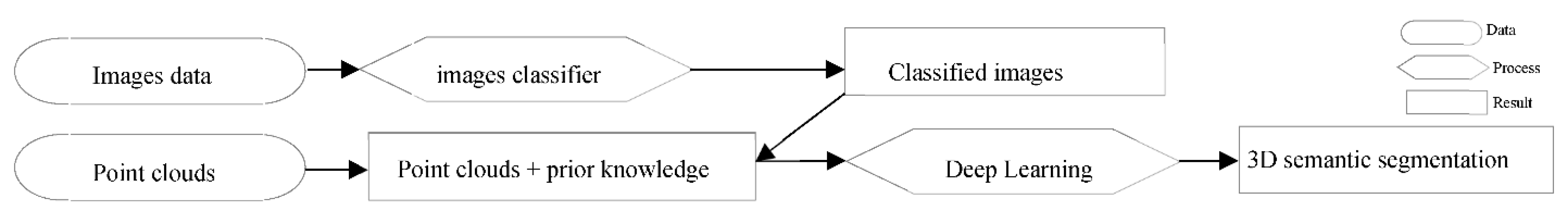
3.3.1. Classified Images and Point Clouds Based Scenario (S1)
3.3.2. Geometric Features, Point Clouds, and Aerial Images Based Scenario (S2)
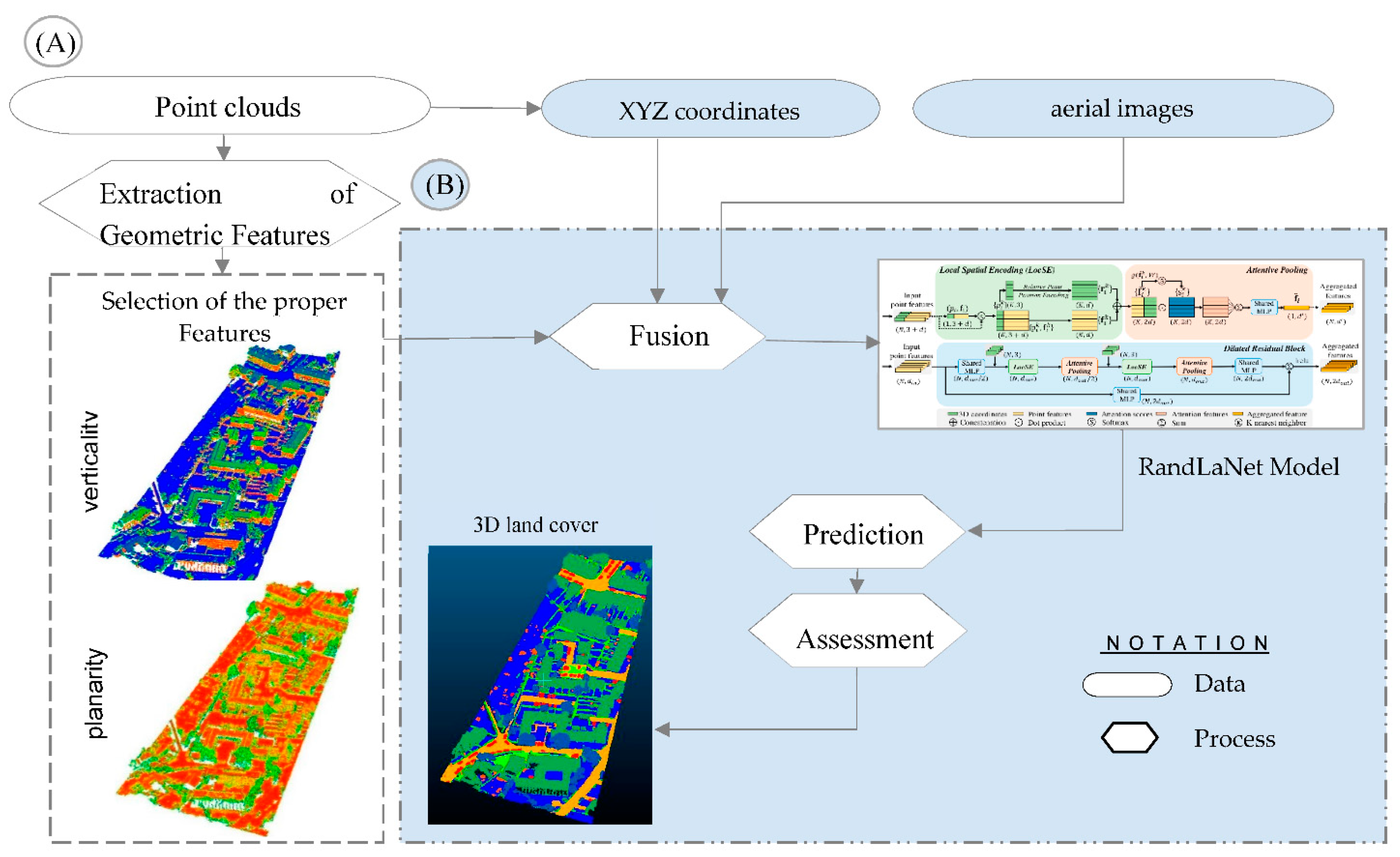
- Planarity is a characteristic that is obtained by fitting a plane to neighboring points and computing the average distance between those points and the plane (Özdemir and Remondino, 2019).
- Verticality: The angle between the xy-plane and the normal vector of each point is calculated using its 3D surface normal values (Özdemir and Remondino, 2019).

3.3.3. Classified Geometrical Information, Point Clouds, and Optical Images Based Scenario (S3)
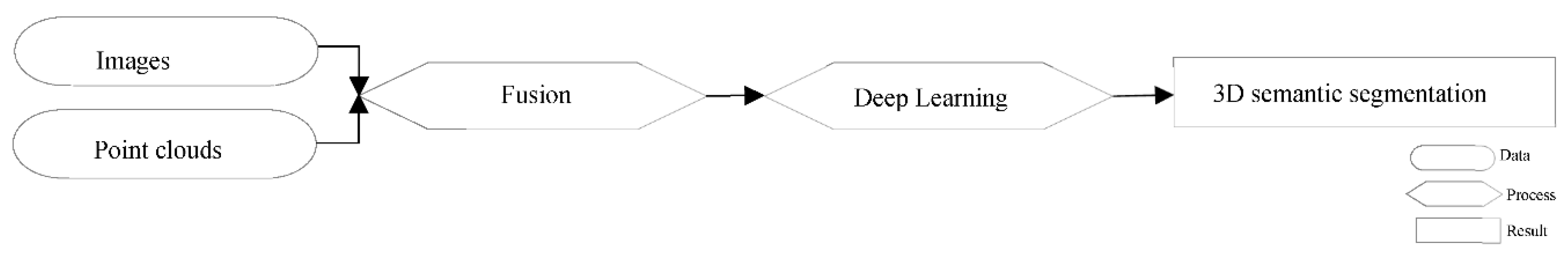
3.3.4. Reference Approach
4. Experiments and Results Analysis
4.1. Implementation
4.2. Results and Discussion
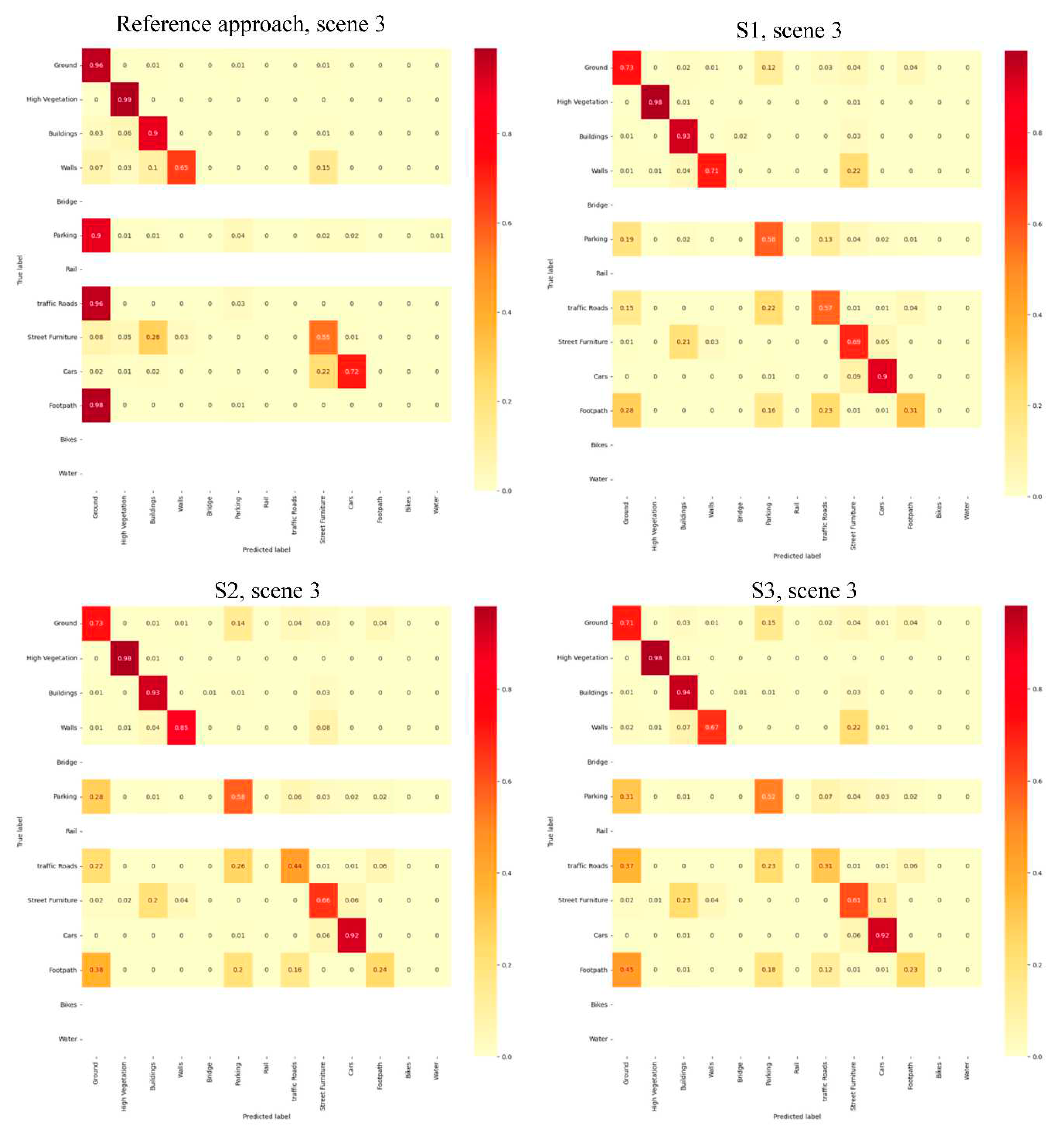
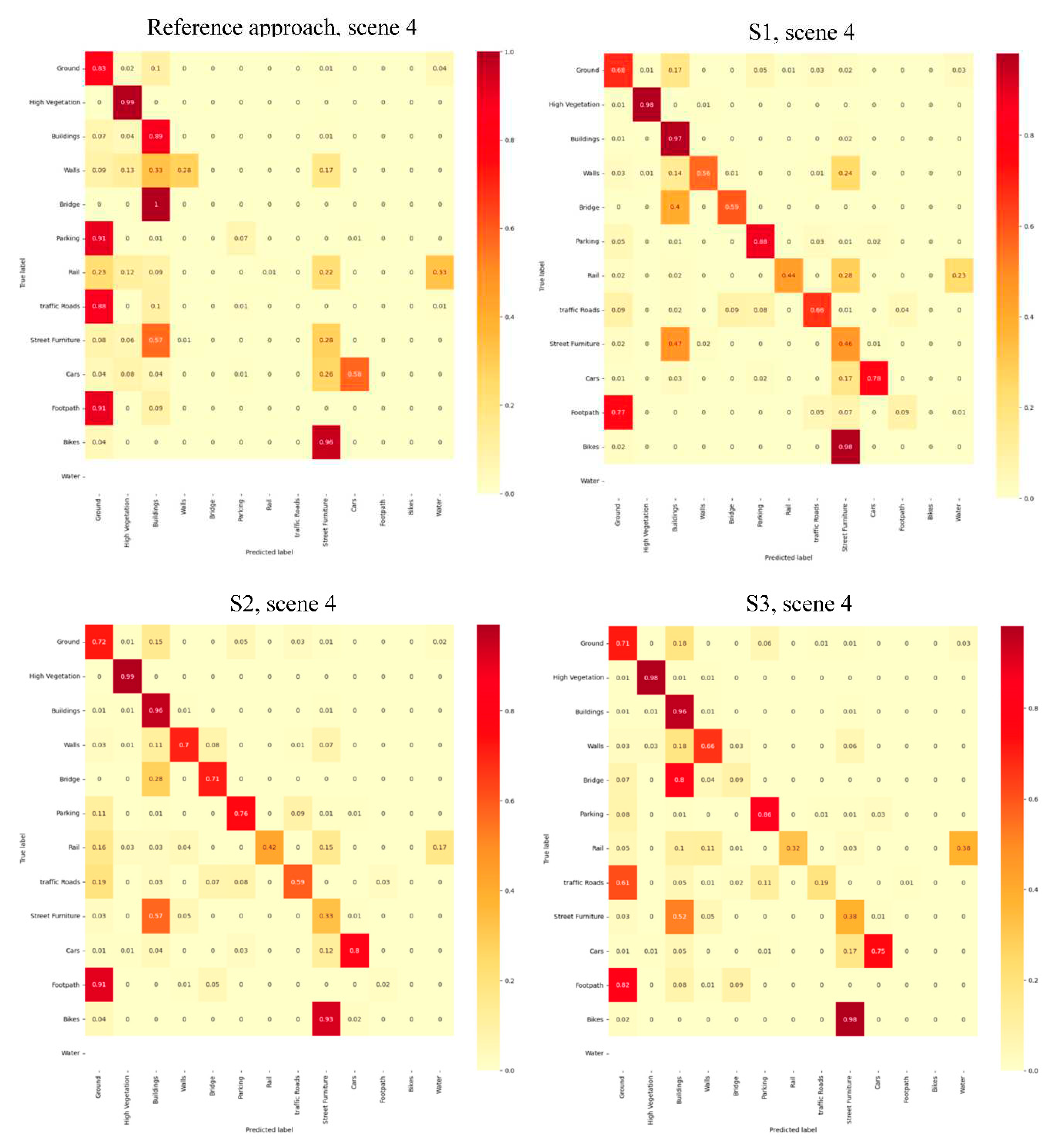
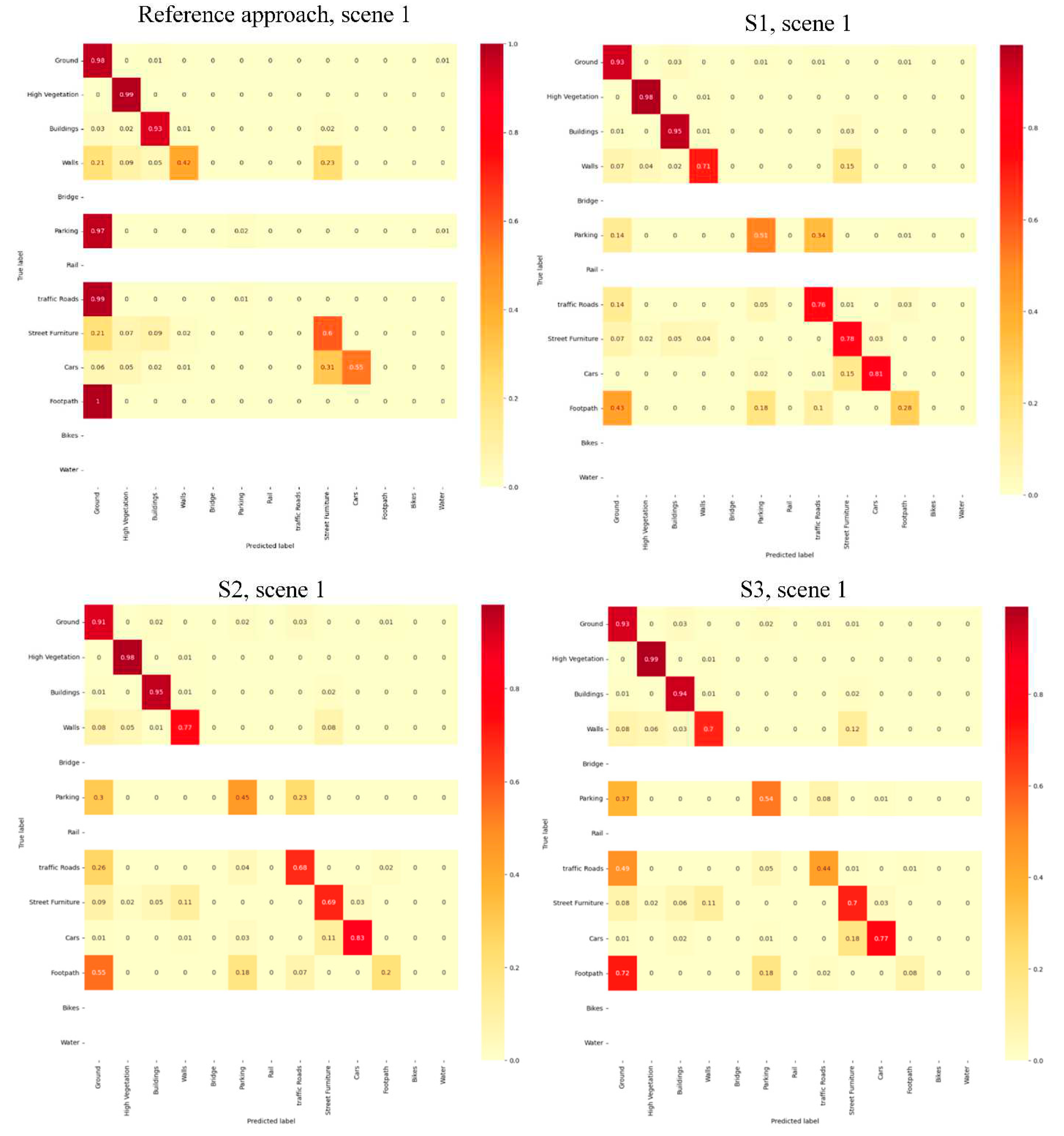
4.2.1. Quantitative Assessments
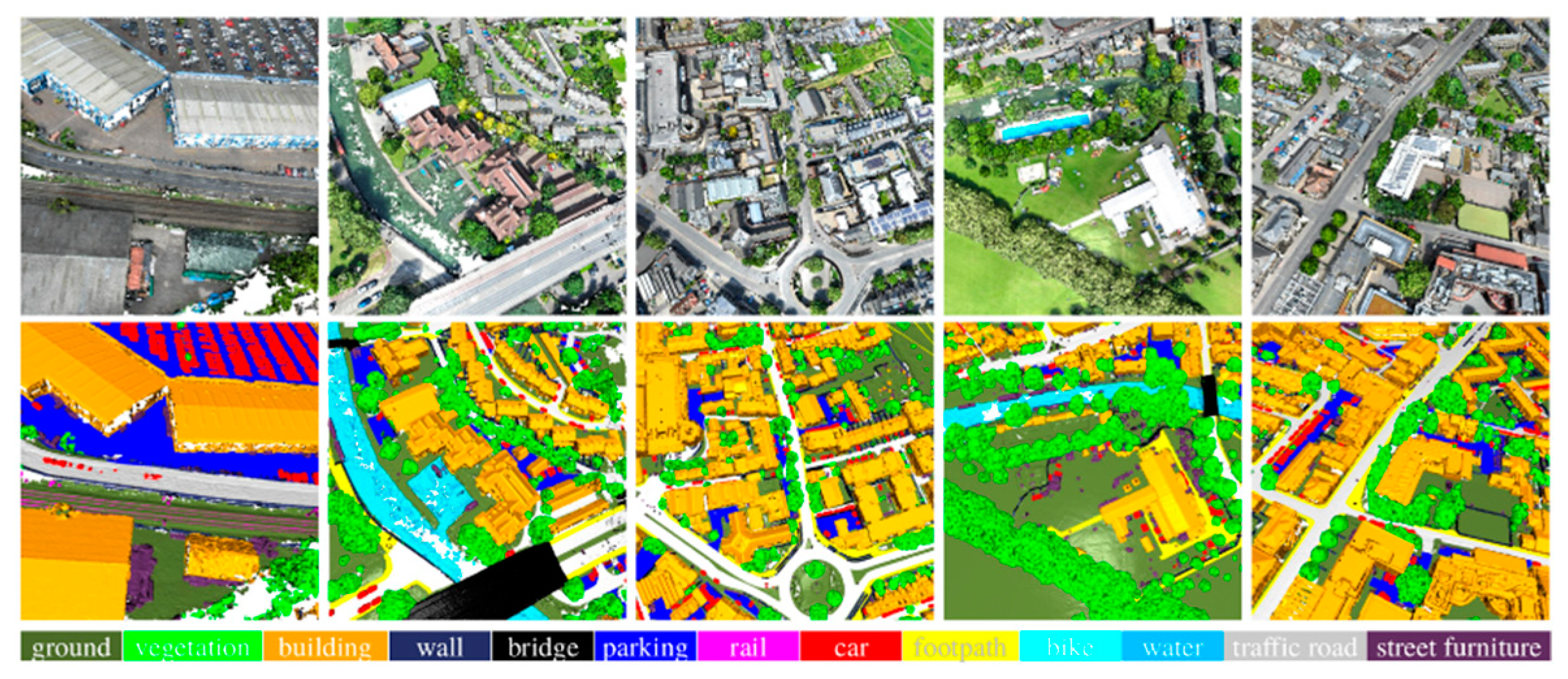
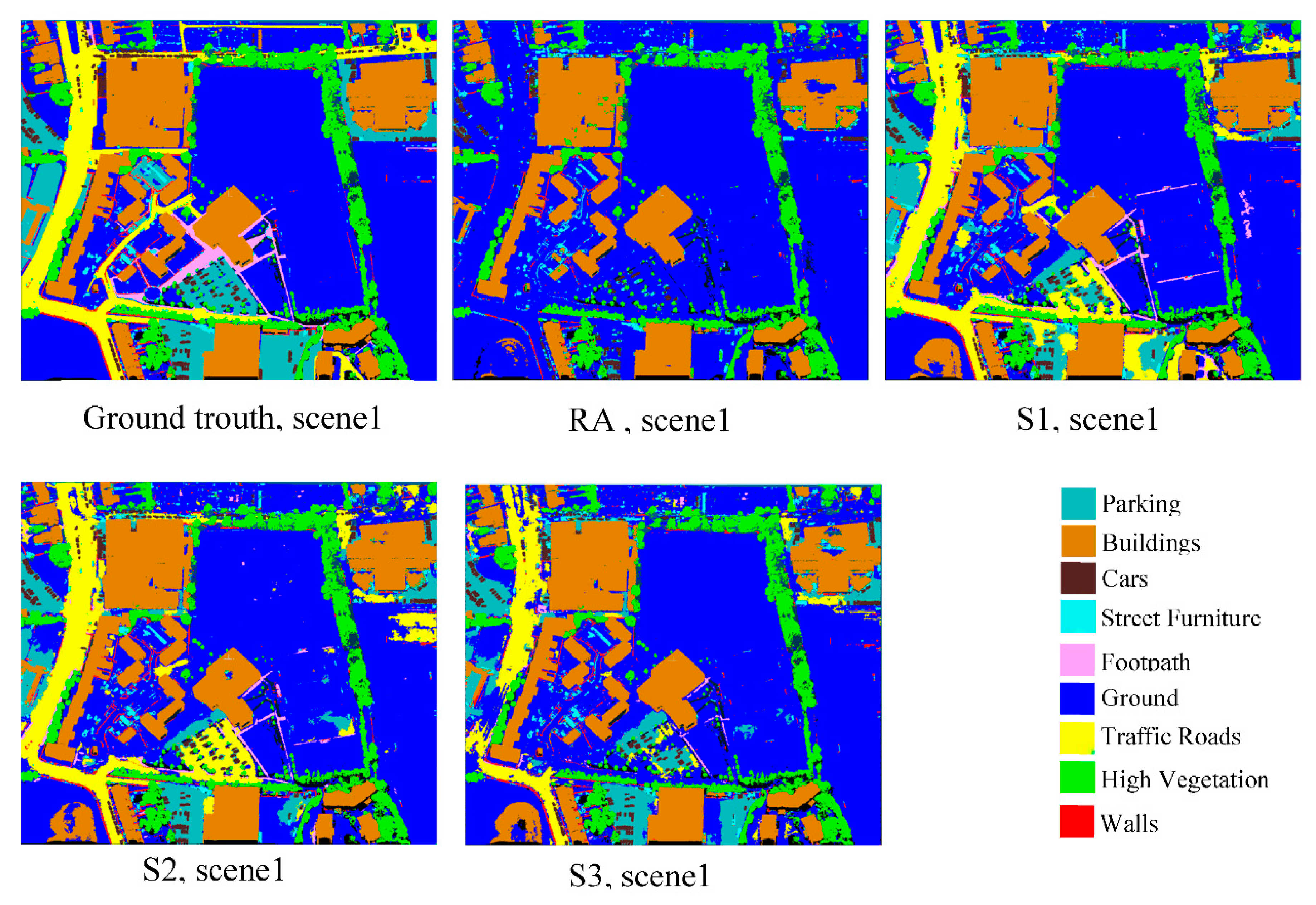
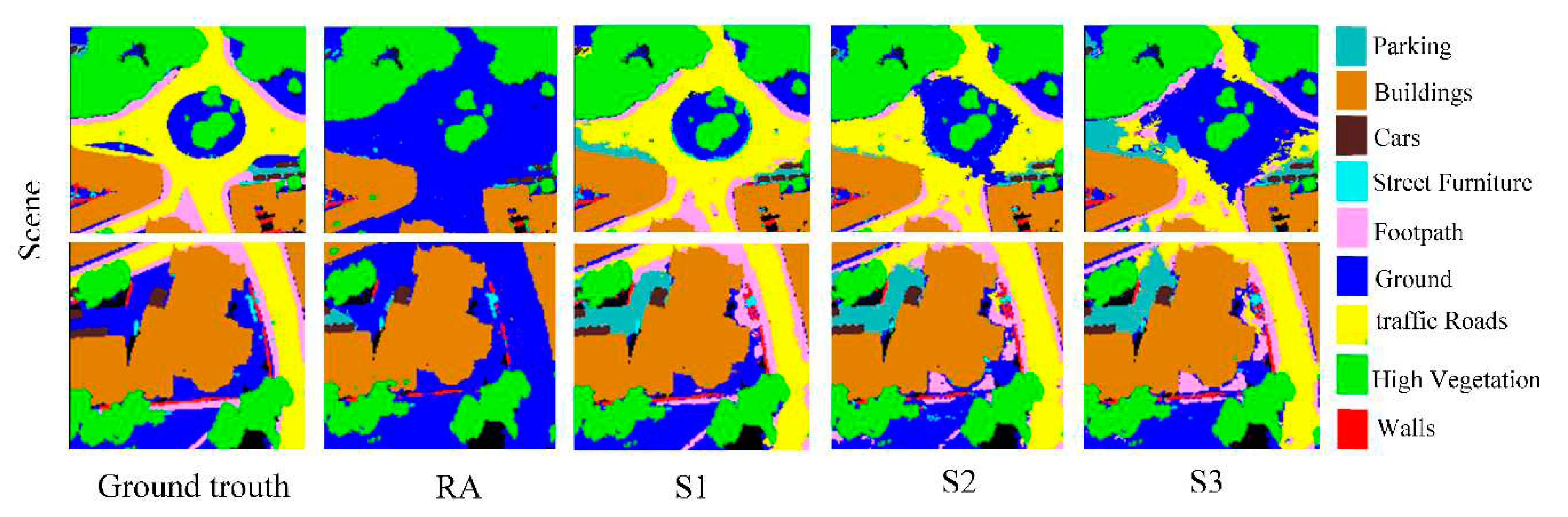
4.2.2. Qualitative Assessments
4.3. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Appendix A

References
- Atik, M.E. , Duran, Z., Seker, D.Z., 2021. Machine Learning-Based Supervised Classification of Point Clouds Using Multiscale Geometric Features. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 10, 187. [CrossRef]
- Bai, X. , Liu, C., Ren, P., Zhou, J., Zhao, H., Su, Y., 2015. Object Classification via Feature Fusion Based Marginalized Kernels. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters 12, 8–12. [CrossRef]
- Ballouch, Z. , Hajji, R., Ettarid, M., 2022a. Toward a Deep Learning Approach for Automatic Semantic Segmentation of 3D Lidar Point Clouds in Urban Areas, in: Barramou, F., El Brirchi, E.H., Mansouri, K., Dehbi, Y. (Eds.), Geospatial Intelligence: Applications and Future Trends. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp. 67–77. [CrossRef]
- Ballouch, Z. , Hajji, R., Ettarid, M., 2020. The contribution of Deep Learning to the semantic segmentation of 3D point-clouds in urban areas, in: 2020 IEEE International Conference of Moroccan Geomatics (Morgeo). Presented at the 2020 IEEE International conference of Moroccan Geomatics (Morgeo), pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Ballouch, Z. , Hajji, R., Poux, F., Kharroubi, A., Billen, R., 2022b. A Prior Level Fusion Approach for the Semantic Segmentation of 3D Point Clouds Using Deep Learning. Remote Sensing 14, 3415. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. , Liu, X., Xiao, Y., Zhao, Q., Wan, S., 2021. Three-Dimensional Urban Land Cover Classification by Prior-Level Fusion of LiDAR Point Cloud and Optical Imagery. Remote Sensing 13, 4928. [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y. , Zhang, L., Cui, X., Ai, H., Xu, B., 2018. Extraction of Buildings from Multiple-View Aerial Images Using a Feature-Level-Fusion Strategy. Remote Sensing 10, 1947. [CrossRef]
- Gao, W. , Nan, L., Boom, B., Ledoux, H., 2021. SUM: A benchmark dataset of Semantic Urban Meshes. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 179, 108–120. [CrossRef]
- Golipour, M. , Ghassemian, H., Mirzapour, F., 2016. Integrating Hierarchical Segmentation Maps With MRF Prior for Classification of Hyperspectral Images in a Bayesian Framework. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 54, 805–816. [CrossRef]
- Grilli, E. , Daniele, A., Bassier, M., Remondino, F., Serafini, L., 2023. Knowledge Enhanced Neural Networks for Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation. Remote Sensing 15, 2590. [CrossRef]
- Hackel, T. , Savinov, N., Ladicky, L., Wegner, J.D., Schindler, K., Pollefeys, M., 2017. Semantic3D.net: A new Large-scale Point Cloud Classification Benchmark. arXiv:1704.03847 [cs].
- Hu, Q. , Yang, B., Khalid, S., Xiao, W., Trigoni, N., Markham, A., 2021. Towards Semantic Segmentation of Urban-Scale 3D Point Clouds: A Dataset, Benchmarks and Challenges. Presented at the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4977–4987.
- Hu, Q. , Yang, B., Xie, L., Rosa, S., Guo, Y., Wang, Z., Trigoni, N., Markham, A., 2020. RandLA-Net: Efficient Semantic Segmentation of Large-Scale Point Clouds, in: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Presented at the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE, Seattle, WA, USA, pp. 11105–11114. [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J. , Song, H., Park, J., Resende, P., Bradaï, B., Jo, K., 2022. Fast and Lite Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation for Autonomous Driving Utilizing LiDAR Synthetic Training Data. IEEE Access 10, 78899–78909. [CrossRef]
- Landrieu, L. , Simonovsky, M., 2018. Large-Scale Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation With Superpoint Graphs. Presented at the Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4558–4567.
- Liu, C. , Zeng, D., Akbar, A., Wu, H., Jia, S., Xu, Z., Yue, H., 2022. Context-Aware Network for Semantic Segmentation Toward Large-Scale Point Clouds in Urban Environments. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 60, 1–15. [CrossRef]
- Luo, S. , Wang, C., Xi, X., Zeng, H., Li, D., Xia, S., Wang, P., 2016. Fusion of Airborne Discrete-Return LiDAR and Hyperspectral Data for Land Cover Classification. Remote Sensing 8, 3. [CrossRef]
- Man, Q. , Dong, P., Guo, H., 2015. Pixel- and feature-level fusion of hyperspectral and lidar data for urban land-use classification. International Journal of Remote Sensing 36, 1618–1644. [CrossRef]
- Megahed, Y. , Shaker, A., Yan, W.Y., 2021. Fusion of Airborne LiDAR Point Clouds and Aerial Images for Heterogeneous Land-Use Urban Mapping. Remote Sensing 13, 814. [CrossRef]
- Meyer, G.P. , Charland, J., Hegde, D., Laddha, A., Vallespi-Gonzalez, C., 2019. Sensor Fusion for Joint 3D Object Detection and Semantic Segmentation, in: 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). Presented at the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), IEEE, Long Beach, CA, USA, pp. 1230–1237. [CrossRef]
- Mirzapour, F. , Ghassemian, H., 2015. Improving hyperspectral image classification by combining spectral, texture, and shape features. International Journal of Remote Sensing 36, 1070–1096. [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.-I. , Kang, H.-B., 2017. Object Detection and Classification by Decision-Level Fusion for Intelligent Vehicle Systems. Sensors 17, 207. [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, E. , Remondino, F., 2019. CLASSIFICATION OF AERIAL POINT CLOUDS WITH DEEP LEARNING. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. XLII-2/W13, 103–110. [CrossRef]
- Poliyapram, V. , Wang, W., Nakamura, R., 2019. A Point-Wise LiDAR and Image Multimodal Fusion Network (PMNet) for Aerial Point Cloud 3D Semantic Segmentation. Remote Sensing 11, 2961. [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.R. , Yi, L., Su, H., Guibas, L.J., 2017. PointNet++: Deep Hierarchical Feature Learning on Point Sets in a Metric Space, in: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Curran Associates, Inc.
- Ruohomäki, T. , Airaksinen, E., Huuska, P., Kesäniemi, O., Martikka, M., Suomisto, J., 2018. Smart City Platform Enabling Digital Twin, in: 2018 International Conference on Intelligent Systems (IS). Presented at the 2018 International Conference on Intelligent Systems (IS), pp. 155–161. [CrossRef]
- Shahat, E. , Hyun, C.T., Yeom, C., 2021. City Digital Twin Potentials: A Review and Research Agenda. Sustainability 13, 3386. [CrossRef]
- Son, S.W. , Kim, D.W., Sung, W.G., Yu, J.J., 2020. Integrating UAV and TLS Approaches for Environmental Management: A Case Study of a Waste Stockpile Area. Remote Sensing 12, 1615. [CrossRef]
- Song, H. , Huang, B., Liu, Q., Zhang, K., 2015. Improving the Spatial Resolution of Landsat TM/ETM+ Through Fusion With SPOT5 Images via Learning-Based Super-Resolution. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 53, 1195–1204. [CrossRef]
- Tabib Mahmoudi, F. , Samadzadegan, F., Reinartz, P., 2015. Object Recognition Based on the Context Aware Decision-Level Fusion in Multiviews Imagery. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 8, 12–22. [CrossRef]
- Tan, W. , Qin, N., Ma, L., Li, Y., Du, J., Cai, G., Yang, K., Li, J., 2020. Toronto-3D: A Large-Scale Mobile LiDAR Dataset for Semantic Segmentation of Urban Roadways. Presented at the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 202–203.
- Weinmann, M. , Weinmann, M., 2019. FUSION OF HYPERSPECTRAL, MULTISPECTRAL, COLOR AND 3D POINT CLOUD INFORMATION FOR THE SEMANTIC INTERPRETATION OF URBAN ENVIRONMENTS. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. XLII-2/W13, 1899–1906. [CrossRef]
- White, G. , Zink, A., Codecá, L., Clarke, S., 2021. A digital twin smart city for citizen feedback. Cities 110, 103064. [CrossRef]
- Ye, C. , Pan, H., Yu, X., Gao, H., 2022. A spatially enhanced network with camera-lidar fusion for 3D semantic segmentation. Neurocomputing 484, 59–66. [CrossRef]
- Yousefhussien, M. , Kelbe, D.J., Ientilucci, E.J., Salvaggio, C., 2018. A multi-scale fully convolutional network for semantic labeling of 3D point clouds. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 143, 191–204. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. , Zhao, X., Chen, Z., Lu, Z., 2019. A Review of Deep Learning-Based Semantic Segmentation for Point Cloud. IEEE Access 7, 179118–179133. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R. , Li, G., Li, M., Wang, L., 2018. Fusion of images and point clouds for the semantic segmentation of large-scale 3D scenes based on deep learning. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 143, 85–96. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. , Chi, M., 2020. Mask-R-FCN: A Deep Fusion Network for Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Access 8, 155753–155765. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L. , Zhou, H., Zhu, X., Song, X., Li, H., Tao, W., 2021. LIF-Seg: LiDAR and Camera Image Fusion for 3D LiDAR Semantic Segmentation. arXiv:2108.07511 [cs].
- Zhou, T. , Ruan, S., Canu, S., 2019. A review: Deep learning for medical image segmentation using multi-modality fusion. Array 3–4, 100004. [CrossRef]


| Fusion approach | Performances | Limitations |
| Prior-level | -Direct use of semantic information from images -Fast convergence -Low loss function -High classification accuracy. |
-Problems of non-overlapping regions and uncertainties -Bit long process |
| Point-level | -Fast drive -Easy handling -No prior information is required. |
- High cost - Not able to classify diversified urban contexts - Relatively low classification accuracy |
| Feature-level | -Objective data compression -Retaining enough important information |
-Training loss higher -Features may not reflect the real objects. |
| Decision-level | -Non-interference of the two semantic segmentation processes -Good flexibility -Low-complexity -Learning the representation of independent features is allowed |
-Impacted by the shortcomings of both classifiers. - Additional parameters for layers are required - More memory requirement |
| ground truth | |||
| - | + | ||
| Predicted class | - | True Negatives | False Negatives |
| + | False Positives | True Positives | |
| Processes | F1-score | Recall | Precision | IoU | |
| Scene 1 | Reference approach | 0.71 | 0.77 | 0.71 | 0.63 |
| S1 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.88 | 0.80 | |
| S2 | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.85 | 0.77 | |
| S3 | 0.83 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.75 | |
| Scene 2 | Reference approach | 0.82 | 0.86 | 0.79 | 0.75 |
| S1 | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.94 | 0.88 | |
| S2 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.92 | 0.86 | |
| S3 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.91 | 0.85 | |
| Scene 3 | Reference approach | 0.75 | 0.78 | 0.74 | 0.67 |
| S1 | 0.86 | 0.85 | 0.88 | 0.79 | |
| S2 | 0.84 | 0.83 | 0.87 | 0.77 | |
| S3 | 0.83 | 0.82 | 0.86 | 0.76 | |
| Scene 4 | Reference approach | 0.61 | 0.68 | 0.58 | 0.50 |
| S1 | 0.80 | 0.78 | 0.84 | 0.68 | |
| S2 | 0.79 | 0.78 | 0.82 | 0.67 | |
| S3 | 0.70 | 0.72 | 0.76 | 0.57 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





