1. Introduction
In recent years, fiber optic sensors are becoming increasingly attractive for biomechanical researches[1-3], such as detection of skeletal strain[
4], monitoring of forces induced by tendons and ligaments[
1], stresses in intervertebral discs and in meniscus[1, 5], chest wall deformation[
2], biomechanical analysis of fracture healing[
2], wearable motion and respiratory monitoring[1, 3], and many measurement applications in dental biomechanics[6-9], etc. In dental biomechanics researches, fiber optic sensors have the advantages of being waterproof compared to electronic sensors, not afraid of being attacked by saliva, good biocompatibility, small sensor size, multiplexing capability and immunity to electromagnetic interference (EMI), providing a promising monitoring tool for dental biomechanics research.
Maxillary Transverse Deficiency (MTD) is one of the most common malocclusions at all ages, and its main treatment is maxillary skeletal expansion (MSE), routinely using a rapid palatal expansion (RPE) appliance. Traditionally, the use of RPE and surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion (SARPE) in late adolescent and adult patients has been considered to have some disadvantages[10-12]. To increase skeletal expansion and reduce the side effects of tooth-borne RPE, various types of boneborne RPE appliances have been developed. In recent years, miniscrew-assisted rapid palatal expansion (MARPE) has become a new treatment method for late adolescent and adult MTD patients due to its significant advantages[13-17], however, its device design, implantation site, expansion efficacy and complications are also controversial [18-20]. These appliances may produce different results based on their design and active protocol. The effective opening of the midpalatal suture is an important basis for evaluating the effectiveness of the expander. The existing research methods on the opening of the mid-palatal suture due to the excitation of the expander mainly include finite element analysis[20-23] and CT imaging[10, 17]. The finite element method is difficult to reproduce the fine structure of the complex jaw structure, of the zygomaticomaxillary complex (ZMC) and of the palatal expander structure, and the CT imaging is complicated and difficult to monitor the complete process of palatal suture opening dynamically in real time. In addition, there are often some differences in the results of the two studies. Therefore, it is necessary to be able to measure the dynamic changes of the opening process.
The use of fiber-optic sensors for biomechanical studies of MSE has been investigated in very recent years, e.g., strain measurement of the Hyrax appliance using fiber Bragg grating (FBG) sensors in a 3D printed human maxillary model [
24], in vitro validation of FBG sensors for rapid palatal expander suture expansion strain assessment [
25], etc. Due to their small size, implantability and on-line measurement, these sensors are able to reproduce the dynamic processes of the monitored parameters in RPE, providing important process parameters for diagnosis and evaluation of treatment effectiveness. However, their applications in the field of RPE monitoring are very recent and their practicality for full-scale implementation has not yet been fully established. Although the indirect response to the opening of the midpalatal suture through the monitoring of stress and strain parameters has been verified, no real-time monitoring of the opening displacement of the mid-palatal suture during MSE has been reported.
In this paper, we propose a new method to monitor the opening of the mid-palatal suture during RPE by mounting a pair of fiber optic Fabry-Perot (F-P) sensors on the palatal bases of a RPE appliance. As a demonstrative, we used a 3D printed scanned skull model fitted with a MARPE appliance to form a model simulation system for bone expansion simulation. F-P sensors were mounted on this model simulation system and while monitoring the opening distance of the midpalatal suture, we wanted to extrapolate the opening angle of the midpalatal suture from the comparison of the two sensors monitoring data. This model simulation system is more capable of simulating the complex structure of the ZMC than finite element simulation, and maintains the structural integrity of the MARPE appliance, and provides a new evaluation method for the biomechanical study of the maxillary skeletal expander with better economy and reproducibility than in vivo experiments. The advantages of miniaturization and good biocompatibility of the fiber optic sensor also offer the possibility of clinical monitoring applications.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sensor Concepts and Principles
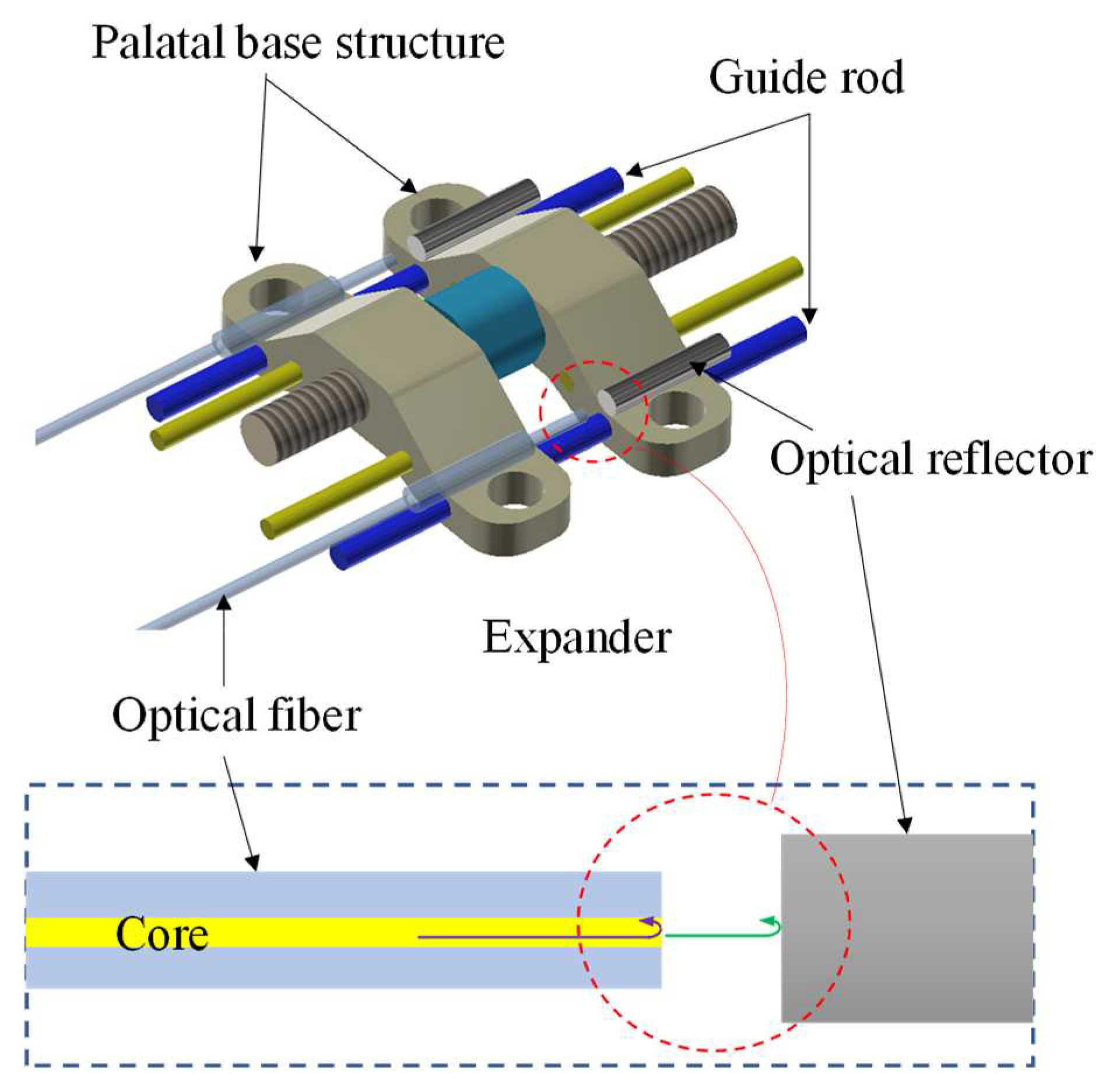
A fiber optic Fabry-Perot (F-P) sensor is a device that uses the variation of reflected light intensity caused by the interference of light waves between two parallel mirrors separated by a small gap to measure physical parameters such as displacement, pressure, temperature, or strain. A schematic diagram of our proposed fiber optic F-P sensor mounted on a MARPE appliance is shown in
Figure 1. The MARPE appliance used in this study was a helical arch expander (Type 9162-310E, Shinye, Hangzhou, China) that includes two palatal base structures for mounting miniscrews, a central folding helical screw for providing displacement for mechanical expansion, and two guide rods. Activation of the appliance consisted of turning the central folding helical screw one-sixth of a turn (hexagonal screw configuration), where one turn resulted in a 0.8 mm expansion. The fiber optic F-P sensor consists of an optical fiber and an optical reflector mounted on two base anchoring structures. The optical fiber (G657.A1, YOFC, China) was stripped of its coating at the end, has an outer diameter of 125 μm, has a cut flat end face with an optical reflectivity of approximately 0.04. For collimation, a quartz tube jacket with an outer diameter of 400 μm and an inner diameter of 200 μm is placed over the end of the fiber. The optical reflector is a custom-made quartz fiber with a diameter of 400 μm, polished on the end face and coated with reflective film, with an optical reflectivity of 99%. An epoxy resin adhesive (9005, LEAFTOP, China) was used for bonding the F-P sensors on the palatal base structures. The initial distance was about 0.3 mm between the two end surfaces of the sensor. The incident light in the optical fiber is reflected at the fiber end face and at the optical reflector, respectively, and forms an interference. The variation of the cavity length of the interference cavity reflects the variation of the opening distance of the palatal bases in the MARPE appliance.
The two reflections possess certain phase relationship determined by the optical path difference (OPD), defined as OPD=2nd, n is the refractive index of the dielectric (n=1 for air) and d is the physical cavity length, represents the monitored open distance of the midpalatal suture. The two beams are coupled back into the lead-in fiber and interfere. The interference spectrum is then obtained to calculate the OPD encoded and can be expressed as [
26]
where
R1 and
R2 are the reflectivities of the two fiber end faces, and
R1 =
R2 is 0.04 in the calculation of this paper,
Ii is the incident intensity,
q is the light coupling coefficient,
λ is the wavelength of incident light, and
φ0 is the additional phase.
Neglecting
φ0, the wavelength
λi of the
ith interference peak in the obtained optical spectrum is directly related to the cavity length d by
where
k is the corresponding interference order number of the first peek and should be an integer. Therefore,
k can be obtained from the first and the
ith peek as
Using the obtained
k, the cavity length can be obtained as
Multiple peaks in the spectrum can be used to calculate the fringe order by (4), avoiding the influence of the fringe order uncertainty, and the cavity length monitoring of large dynamic range can be realized.
The effect of temperature variation on the cavity length measurement is mainly caused by the mismatch in elongation due to the inconsistent coefficient of thermal expansion of different materials. If the coefficient of thermal expansion of the expander material is
α1 and the coefficient of thermal expansion of the fiber material is
α2, the cavity length temperature sensitivity of the sensor, defined as the ratio of the change in cavity length to the change in temperature, can be expressed as
where
l is the fixed length of the sensor. Using a fixed length of
l=600 μm, the thermal expansion coefficient of the expander material
α1=15×10
-6 /ºC and the thermal expansion coefficient of the optical fiber
α2=5.5×10
-7 /ºC, the cavity length temperature sensitivity of the sensor can be estimated to be 0.0088 μm/ºC. It can be seen that the sensor has a very low temperature sensitivity and the temperature effect in the experiment can be neglected. The sensor is therefore also suitable for applications in environments where there is some variation in temperature.
2.2. Preliminary Test
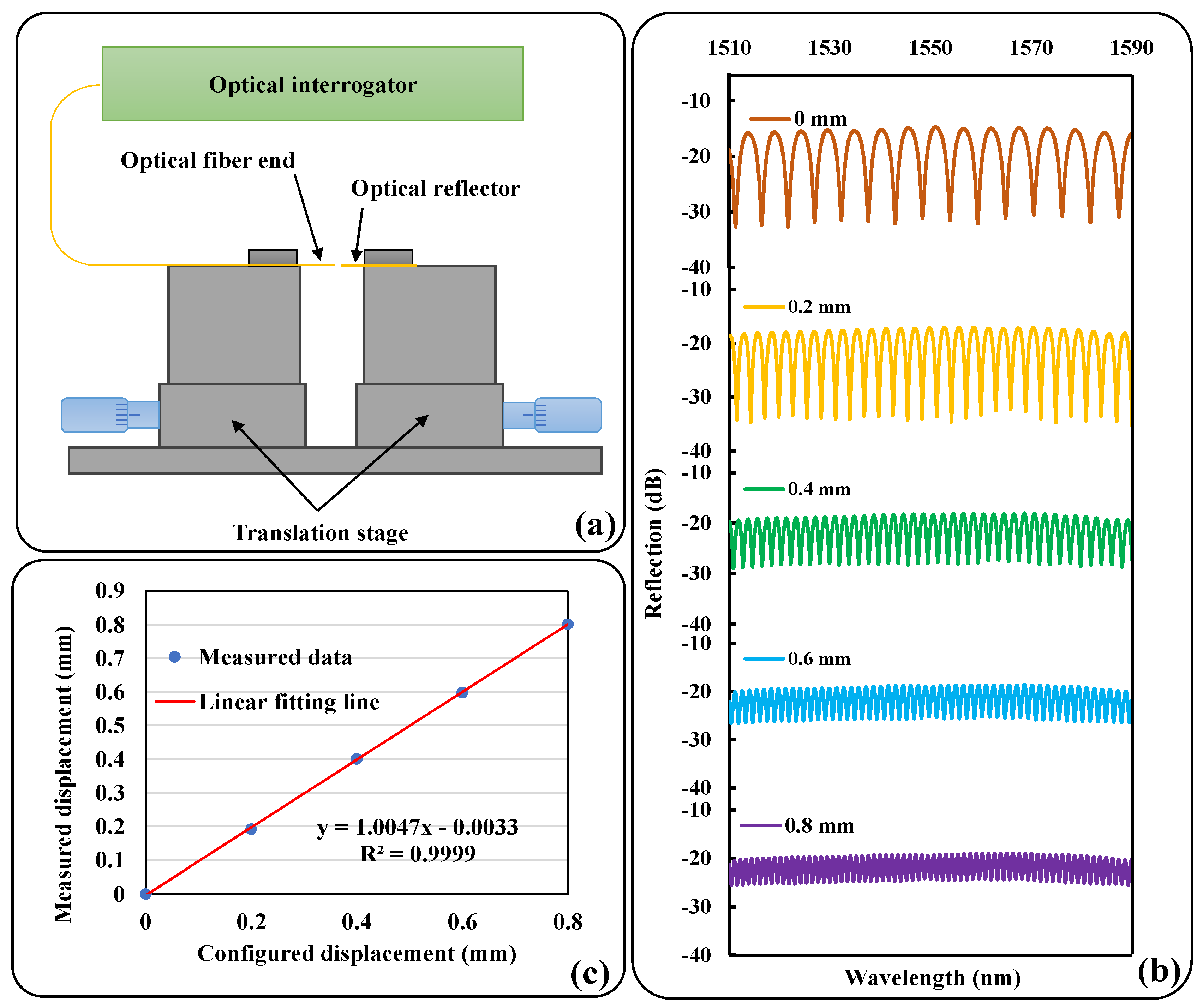
In order to evaluate the capability of the sensors to measure displacement, preliminary tests were carried out, which were achieved by generating displacement through a precision translation stage and verifying the agreement of the measurements with the configured displacement. The schematic diagram of experimental setup is shown in
Figure 2a. A fiber optic end and an optical reflector are mounted on two separate translation stages and the central axes are aligned to ensure that the two end faces are parallel. The fiber end is connected to the optical interrogator for testing. During the test, the cavity length was gradually changed from the initial distance at equal intervals of 0.2 mm by adjusting the translation table, and the reflection spectrum was recorded at each step as shown in
Figure 2b. The peaks in the spectrum were detected by the fiber interrogator and the measured displacements were derived from equations (4) and (5).
Figure 2c gives a linear relationship between the change in measured displacement and the configured displacement of the translation stage. As can be seen, there is an excellent agreement, demonstrating that the sensor can perform displacement measurements with high accuracy.
2.3. Simulation System Based on 3D Printed Model
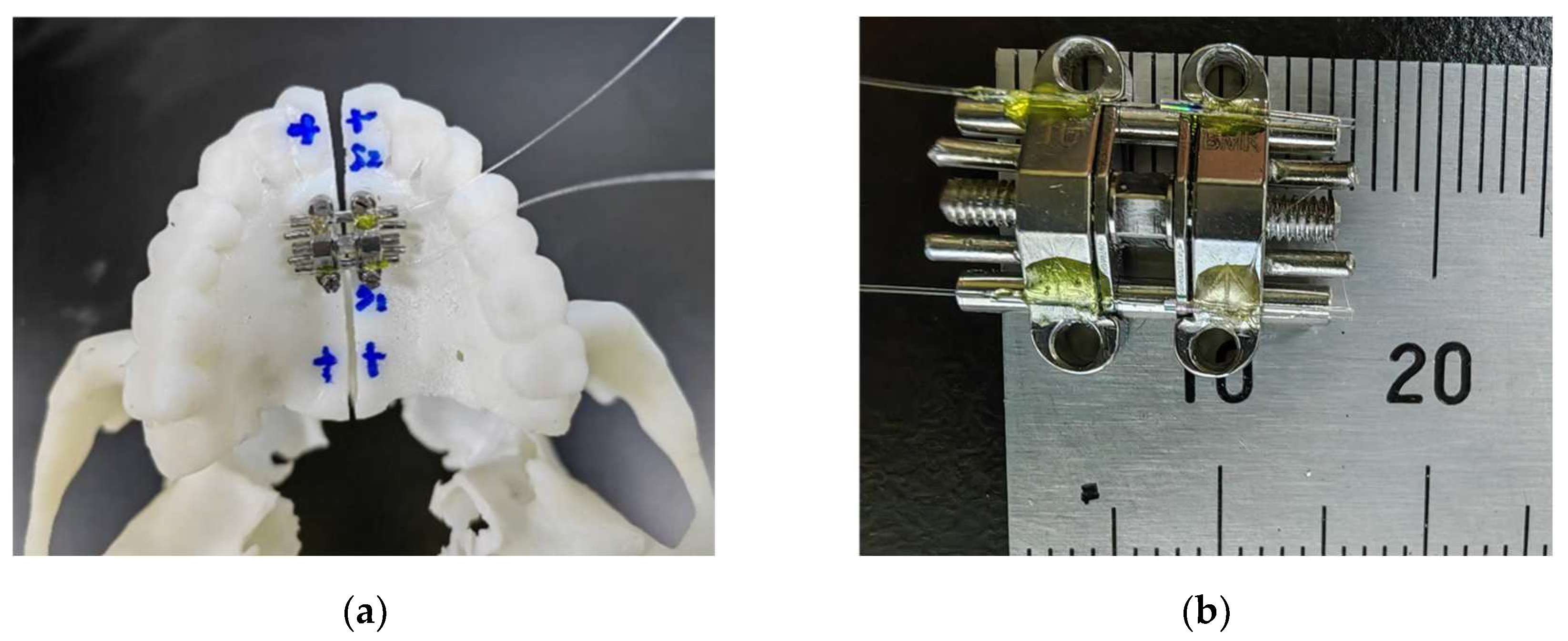
A human skull model, including ZMC, maxilla and teeth, was 3D printed from a digitized scan of a female patient in late adolescence. The patient was informed about this study and the study was ethically compliant. 8200 type photosensitive resin (WeNext Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, China) with a tensile modulus of 2.6 Gpa was used for the producing of 3D model. The modulus of elasticity of the model material is between that of cortical bone and cancellous bone (13.7 Gpa and 1.37 Gpa for cortical bone and cancellous bone, respectively [20, 21]). We reproduced the maxillary midline separation by cutting a suture approximately 1 mm wide along the midline with a medical hand drill. Four miniscrews (diameter: 1.6 mm, length: 11 mm, Cibei, Ningbo, China) were used to anchor the arch expander. The MARPE appliance was anchored by the mini-screws in the maxillary mesial suture at a distance of 22 mm from the upper anterior molar, with its center aligned with the midpalatal suture line, as shown in
Figure 3. The transverse mesial axis of the expander is located between the first premolar and the second premolar.
The MARPE appliance was opened with 3 activations, 1/6th of a turn each, by turning the hexagonal screw with a special wrench. This is generally considered to be the maximum amount of activation allowed to be applied in one operation. In clinical practice, a greater expansion rate would make the patient experience more discomfort, and increase the risk of causing side effects or failure. The opening distance of the two sensor positions was monitored in real time during the operation. After each activation, the next operation was carried out after about 1 minute in order to observe the change in the opening distance. A total of 1/2 turn was made and the opening distance was expected to be 0.4 mm according to the operating manual and experiences of operation.
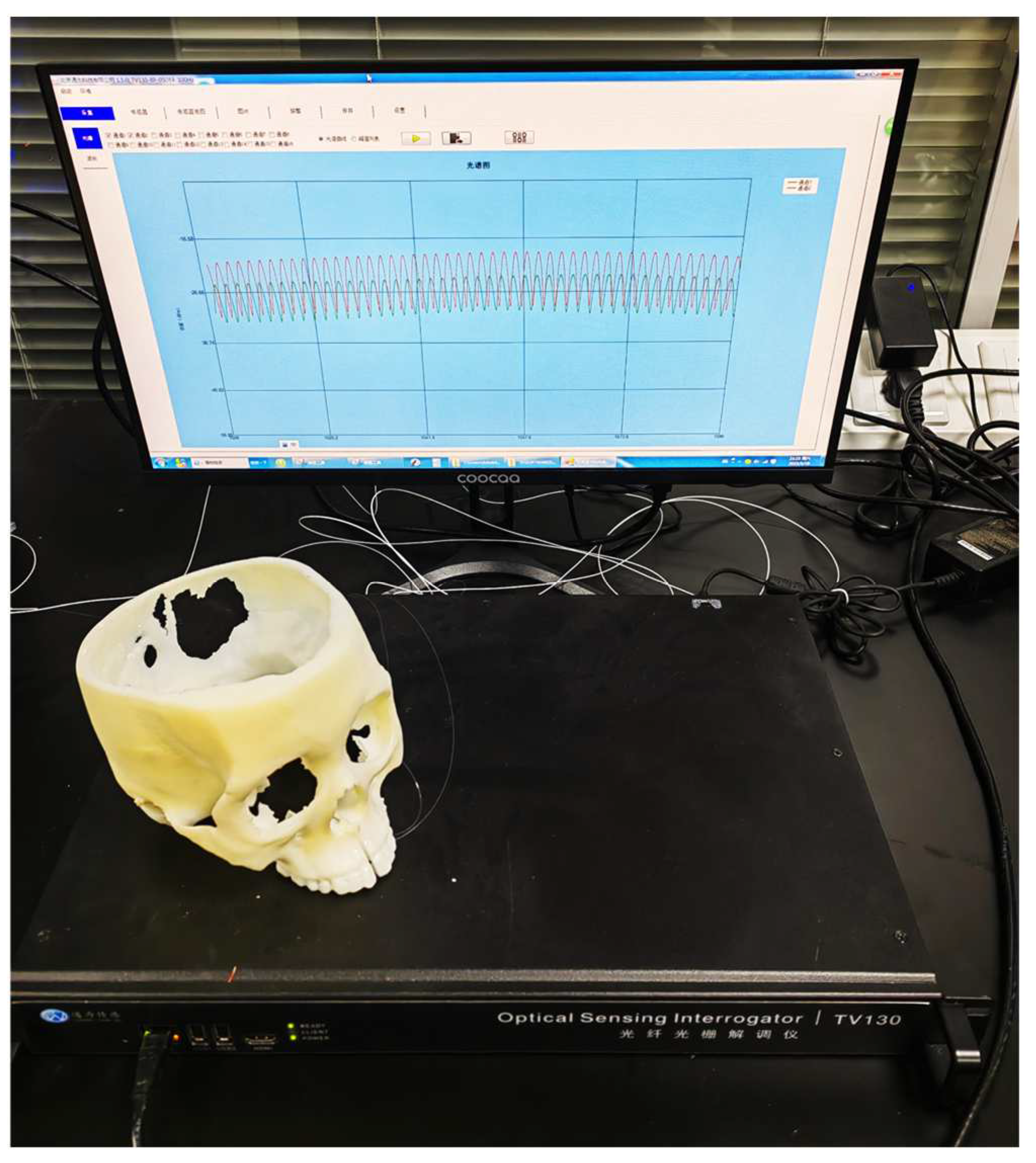
The reflected spectrums of the F-P sensors were acquired by an optical interrogator (TV130, Tongwei Sensing, Beijing, China), with a wavelength range of 1510 nm~1590 nm, a wavelength repeatability of 2 pm and an acquisition rate of 1 Hz, as shown in
Figure 4. The interrogator has 4 channels for each synchronous monitoring, of which 2 channels are used to monitor the two F-P sensors. The peaks of the F-P sensor reflected spectrum was monitored by the interrogator software. The first and the last peeks were used to calculate the cavity length of the sensors, according to (4) and (5), which reflects the opening distances of the midpalatal suture at the location of the sensor. Very high measurement accuracy can be achieved due to the detection of distance changes by interferometric spectroscopy. The measurement error mainly depends on the fitting accuracy of the interrogator to the spectral peak wavelength.
3. Results and Discussion
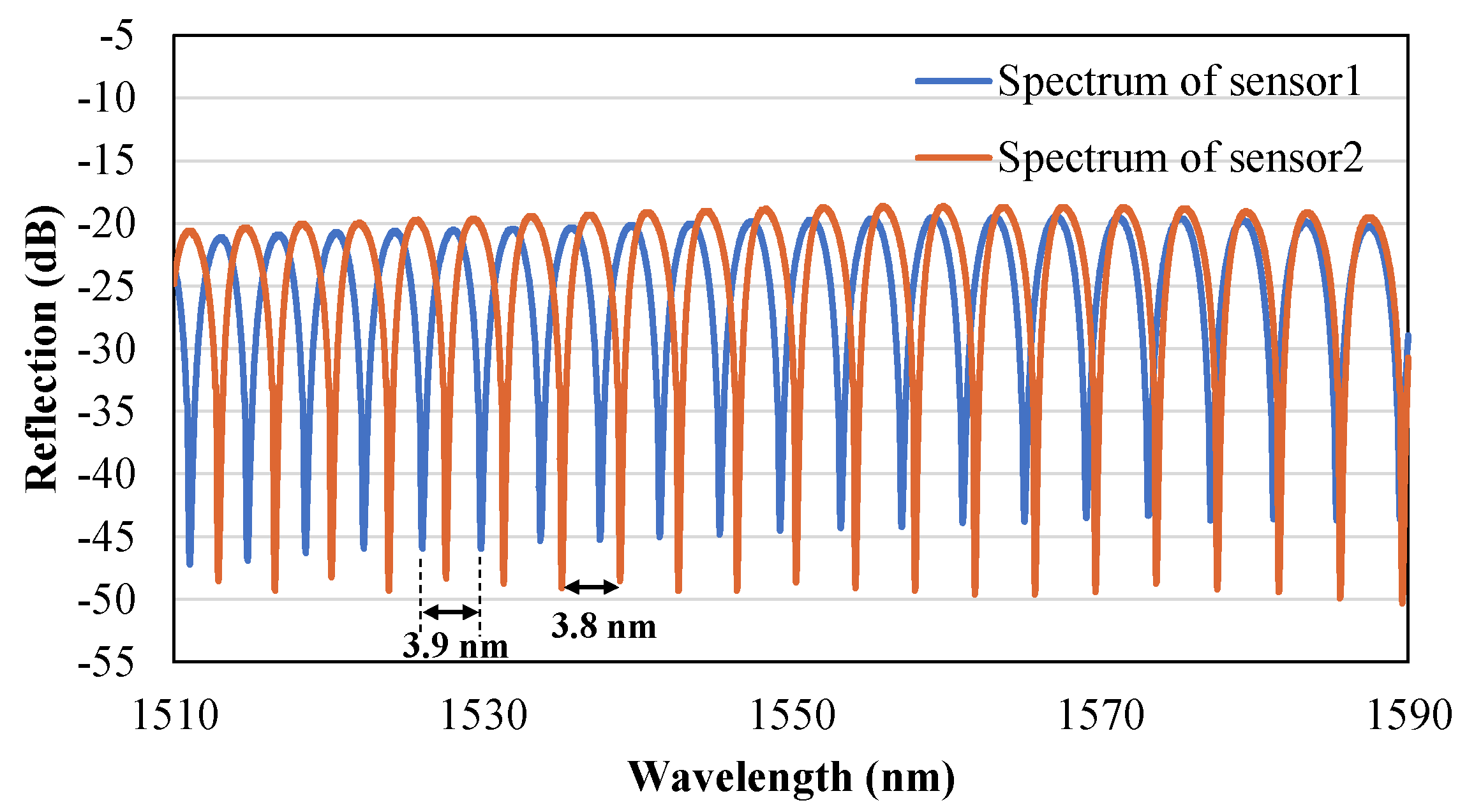
The reflected spectrums of the F-P sensors were observed when the expender with the sensors was mounted before operation, as shown in
Figure 5. The free spectral range (FSR), which is the distance between two adjacent wavelengths, was 3.9 nm for sensor1 and 3.8 nm for sensor2. The initial distances of the two sensors, can be calculated as 285 μm and 300 μm, respectively, according to (5).
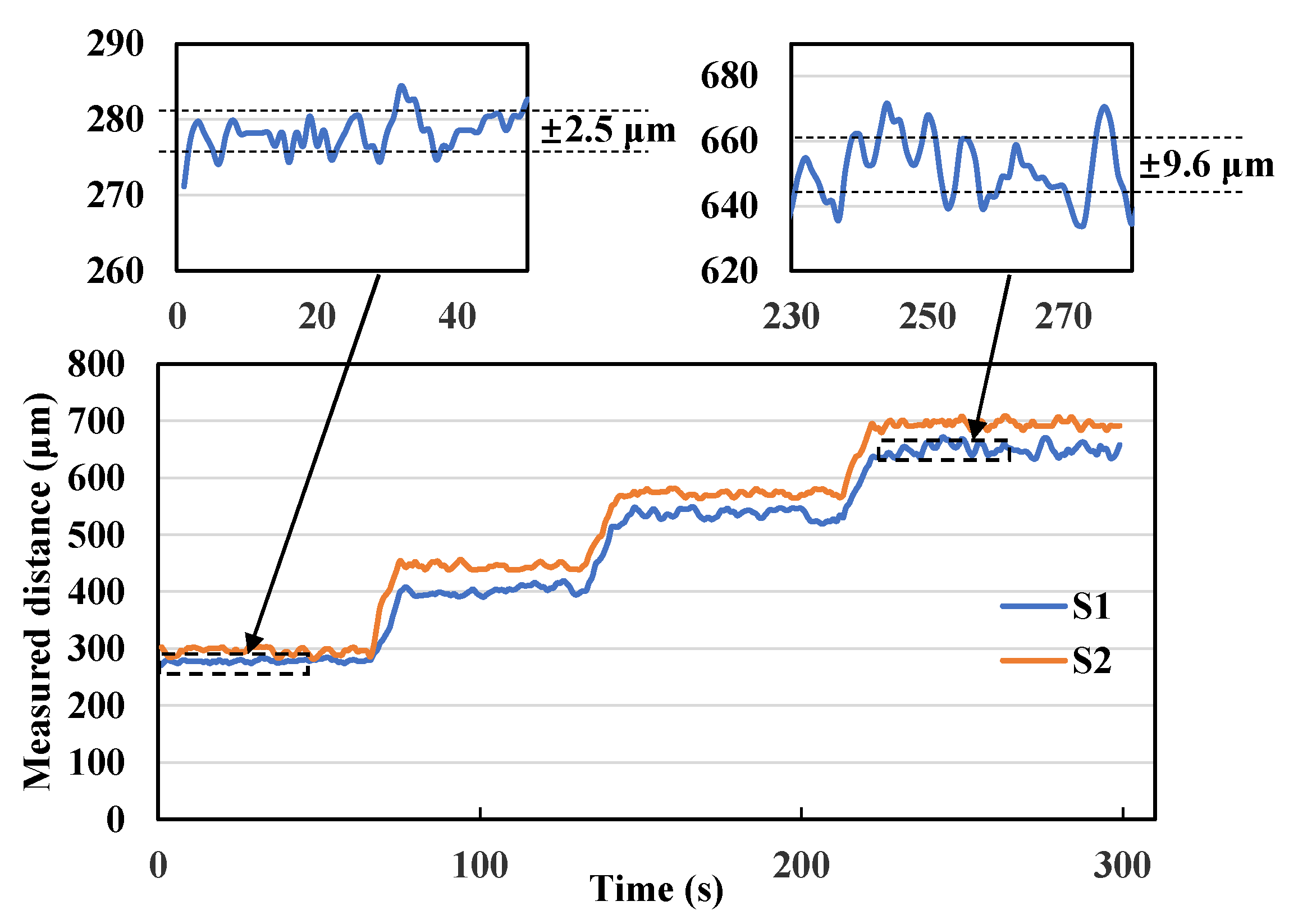
The time response of the distances measured by the two sensors during the activations of the expander mounted in the skull model is shown in
Figure 6. At first, the initial distance was acquired without operation. The measurement results fluctuated by ±2.5 μm (standard deviation value) when the expander was not activated, indicating that the sensor has a very high distance resolution.
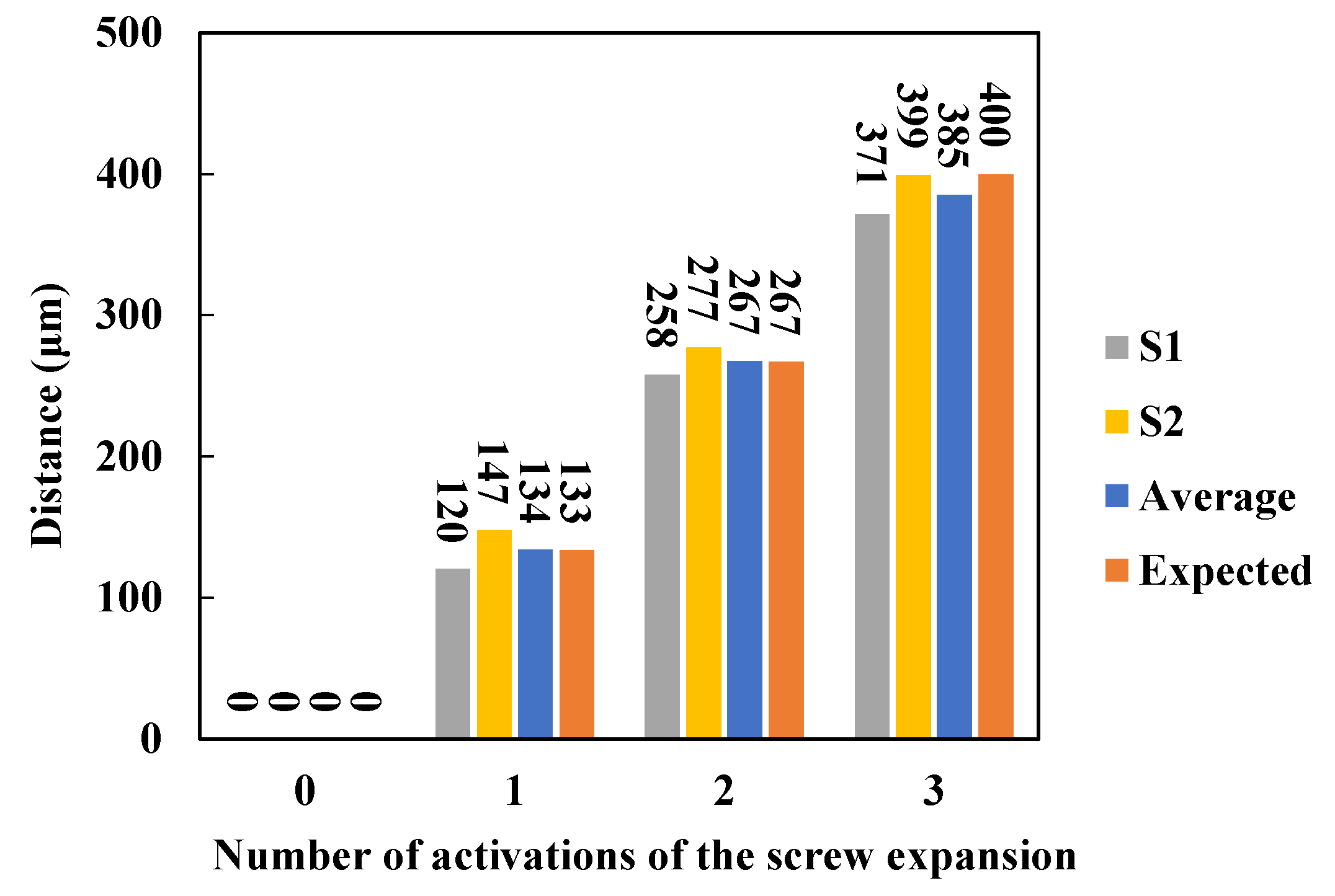
According to the dynamic changes in the opening distance of the midpalatal suture by the two sensors in
Figure 6, the amount of change from the initial distance monitored by each sensor (denoted by S1, S2) separately for each loading, the average value (denoted by average) of the change for the two sensors were calculated and compared with the expected value (denoted by expected) based on experience, as shown in
Figure 7. Where, based on experience, the expansion screw of the expander is considered to be activated for 1/6 turns each time, resulting in an expansion distance of 0.8/6≈0.13 mm. The results show that the average tested distance of the two sensors increases with the number of expansions, which agrees with the expected value. This indicates that the expansion simulation system has a very high loading efficiency and the sensor monitoring data are reliable and effective.
The fluctuation of the monitoring value during and after the opening operations in
Figure 6 was ±9.6 μm, indicating the high monitoring accuracy also in dynamic process of loading. The dynamic details of the loading process shows that distance change is done at once by each loading and the distance remains at a stable value without degradation. This result shows that the expander has good loadability and retention of the expansion amount.
At the same time, the skeletal expansion pattern can be quantitatively described by comparing the monitoring data from the two sensors. Based on the results in
Figure 6, for the first loading, the difference in the distance between the opening of the midpalatal suture monitored by the two sensors increased significantly, which suggests that a slightly type V expansion of the midpalatal suture has occurred. Sensor 2 monitored a greater distance of opening, indicating that the midpalatal suture opening was wider in the anterior region than in the posterior region. The angle of expansion of the midpalatal suture can be deduced as 27/900 =0.03 rad (1.72°) after the first loading, 0.021 rad (1.21°) after the second loading, and 0.031 rad (1.78°) after the third loading. The above analysis is based on the assumption of left-right symmetric expansion. For comparison, we calculated the angle of expansion using data reported in the previously published literatures on MARPE [17,27-32], as shown in
Table 1.
Previous studies have reported differences in the amount of expansion between the anterior and posterior regions after MARPE. Although the results have varied, the majority of studies suggest that expansion in the anterior region is greater than that in the posterior region. The clinical results of opening angle in [
17] are larger than the results of this study. Opening angles reported in [27-30] are smaller and varies from 0.19° to 0.8°. Although the opening angle is very small and close to parallel expansion, it still conforms to the trend of the anterior region being larger than the posterior region. The finite element simulation in [
31] also suggested a larger opening angle. The differences were generally attributed to the different relative positions of the center of resistance and the point of application of the force generated by the expander, as reported in [
31]. However, this does not seem to adequately explain why the guide rods of the expander did not function as expected. With the guide rods, the expander is expected to expand in a parallel pattern.
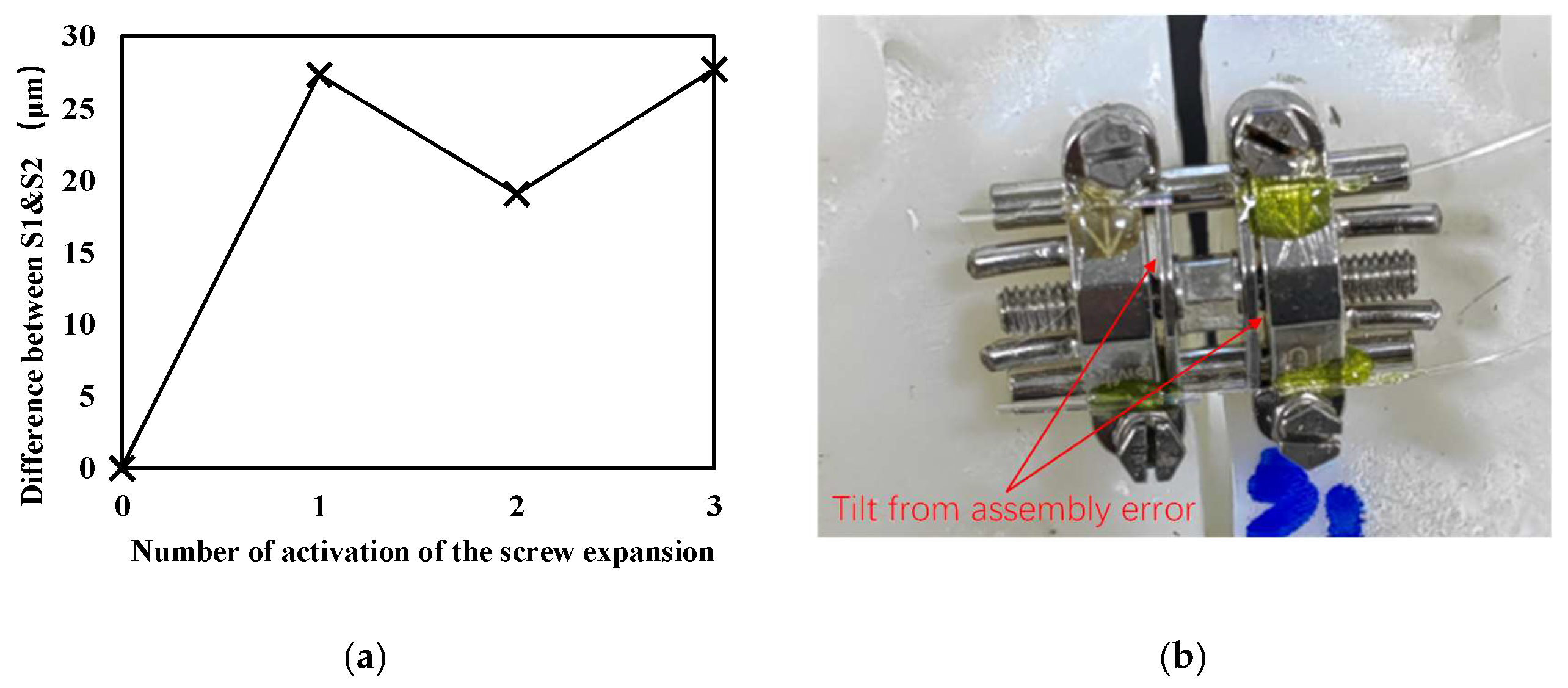
One interesting measurement result is that with the increase of loading times, the difference of the opening distance of the midpalatal suture monitored by the two sensors did not increase further (shown in
Figure 8), suggesting that the opening angle did not increase. This may be related to the restraining effect of the guide rod of the expander, which has not been seen discussed in the literatures. A reasonable explanation for this process is that during the initial loading, due to structural errors in the expander assembly (which is also corroborated by photograph of the expander after expansion activation, as shown in Figure 9, the guide bar did not fully function, which led to the onset of tilt with the overall mechanical properties of the jaw structure. During subsequent loading, the gradual expansion of the tilt was limited as the restraining effect of the guide rods took effect. The estimated opening angle at 1/2 turns of loading remained at approximately 0.031 rad (1.78°), indicating that the mechanically driven action leading to non-parallelism only occurred during the initial activation. This result suggests that in clinical practice, attention should be paid to each initial process during the expansion cycle of the arch expander. The operation of minimizing the proportion of the initial loading process in clinical may help to obtain a more parallel expansion. It also suggests that the guide rod should be modelled as a constraint when performing expander analysis and simulation with finite-element method, that the structural and assembly errors of the expander should not be ignored when performing small loading, and that the structural design of the expander guide rods should also be considered to reduce structural errors at smaller expansions.
Fiber optic sensor arrays can be used to measure the displacement of the appliance at multiple points simultaneously. In addition, it can be accompanied by strain, temperature, and other multiparameter measurements. Smaller appliances can be used by patients in clinical studies to help understand the biomechanical process of maxillary expansion. A biocompatible adhesive can be used to connect the FBG sensor to the application. The inherent safety of using light rather than current, as well as the biocompatibility of the fiber optic, can enable the application of the current appliance to be considered in more in vitro or clinical studies.
5. Conclusions
This section is not mandatory but can be added to the manuscript if the discussion is unusually long or complex.
A methodology based on a fiber optic F-P sensors to measure the multi-point opening of the expander during maxillary expansion is proposed to dynamically monitor the expansion process of a MARPE with guide rods on a 3D printed maxillary based model. The opening distance measurements of these sensors were in agreement with the operating manual and experiences of operation. The sensor was demonstrated to have a resolution of 2.5 μm and to be capable of monitoring the angle of expansion. A difference in the amount of opening between the two monitoring points at the first loading was monitored, suggesting the occurrence of a type V expansion, with an angle of 0.03 rad. The angle did not expand further with the subsequent expansion. This reveals that the mechanical action that leads to the expansion angle occurs at the initial loading. This provides a means to study the dynamic expansion process of the palatal expansion apparatus. In vitro testing is expected to contribute to the development of such mechanical structures and clinical procedures, such as the ability to better understand the process of RME expansion and to better control the amount of expansion and the angle of dilation required for RME treatment. Because of the advantages of miniaturization, high sensitivity, and good biocompatibility of fiber optic sensors, future research includes the study of dynamic dilation processes in more types of arch expanders and the evaluation of possibilities for clinical applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z. Z. and F.Z.; methodology, Z.Z. and F. Z; software, Z.D.; validation, Z.Z., F.Z. and Z.D.; formal analysis, Z.Z. and S. Z.; investigation, F.Z.; resources, Z.Z.; data curation, Z.D. and Y. W.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.Z. and F. Z.; writing—review and editing, S. Z.; visualization, Z.Z. and F. Z.; supervision, S. Z.; project administration, S. Z. and F. Z.; funding acquisition, S. Z., F. Z., and Y. W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded in part by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province under Grant ZR2020MH181 and ZR2021MF126, in part by the Jinan Science and Technology Bureau under Grant 2020GXRC010 and in part by the Basic Research Fund of Qilu University of Technology under Grant 2022PX074 and 2021JC02005.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent has been obtained from the patient(s) to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
Data of the laboratory tests carried out in this study are available upon request to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- P. Roriz, L. Carvalho, O. Frazão, J.L. Santos, José António Simões. From conventional sensors to fibre optic sensors for strain and force measurements in biomechanics applications: A review. J. Biomech. 2014, 47, 6, 1251-1261. [CrossRef]
- E. Al-Fakih, N. Osman, F. Adikan. The use of fiber bragg grating sensors in biomechanics and rehabilitation applications: The state-of-the-art and ongoing research topics. Sensors 2012, 12, 12890-12926. [CrossRef]
- M. Zaltieri, D. Presti, M. Bravi, M. Caponero, S. Sterzi, E. Schena, C. Massaroni. Assessment of a Multi-Sensor FBG-Based Wearable System in Sitting Postures Recognition and Respiratory Rate Evaluation of Office Workers. IEEE T. Bio-med. Eng. 2023, 70, 5, 1673-1682. [CrossRef]
- Kalinowski, L.Z. Karam, V. Pegorini, A.B.D. Renzo, C.S.R. Pitta, R. Cardoso, T.S. Assmann, H.J. Kalinowski, J.C.C.d. Silva. Optical Fiber Bragg Grating Strain Sensor for Bone Stress Analysis in Bovine During Masticatory Movements. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 8, 2385-2392. [CrossRef]
- P., C.R. Vakiel, Dennison, M. Shekarforoush, M. Scott, D.A. Hart, N.G. Shrive. Measuring the Internal Stress in Ovine Meniscus During Simulated In Vivo Gait Kinematics: A Novel Method Using Fibre Optic Technology. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 49,4, 1199-1208. [CrossRef]
- D.L. Romanyk, R. Guan, P.W. Major, C.R. Dennison. Repeatability of strain magnitude and strain rate measurements in the periodontal ligament using fibre Bragg gratings: An ex vivo study in a swine model. J. Biomech. 2017, 54, 117-122. [CrossRef]
- A.P.G.d.O. Franco, M.M.M. Costa, L.Z. Karam, O.M.M. Gomes and H.J. Kalinowski, “Dentistry Applications of Fiber Bragg Gratings: Irradiation Protocols for Bulk Fill Flow Dental Composites.” J. Lightwave Technol., vol. 37, pp. 4881-4887, Jul. 2019. [CrossRef]
- K.P. Houg, A.M. Camarillo, M.R.M. Doschak, P.W., T. Popowics, C.R. Dennison, D. Romanyk. Strain Measurement within an Intact Swine Periodontal Ligament. J. Dent. Res. 2022, 101, 12, 1474-1480. [CrossRef]
- W. Coimbra, P. Oliveira, C. Marques, A. Leal-Junior. Chirped Fiber Bragg Grating Sensors for Force Intensity and Location Assessment in Occlusal Splints: A Proof-of-Concept. IEEE T. Bio-med. Eng. 2023, 70, 4, 1189-1195. [CrossRef]
- J.J. Park, Y.C. Park, K.J. Lee, J.Y. Cha, J.H. Tahk, Y.J. Choi. Skeletal and dentoalveolar changes after miniscrew assisted rapid palatal expansion in young adults: A cone-beam computed tomography study. Korean J. Orthod. 2017, 47, 2, 77-86.. [CrossRef]
- M. Yildirim, M. Akin. Comparison of root resorption after bone-borne and tooth-borne rapid maxillary expansion evaluated with the use of microtomography. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofacial. Orthop. 2019, 155, 2, 182-190. [CrossRef]
- V. Ventura, J. Botelho, V. Machado, P. Mascarenhas, F.D. Pereira, J.J. Mendes, A.S. Delgado, P.M. Pereira. Miniscrew-Assisted Rapid Palatal Expansion (MARPE): An Umbrella Review. J Clin Med 2022, 11, 1287, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- S.H. Choi, K.K. Shi, J.Y. Cha, Y.C.P.J. Leee. Nonsurgical miniscrew-assistedrapid maxillary expansion results in acceptable stability in young adults. Angle Orthodontist 2016, 86, 5, 713-720, Mar. 2016. [CrossRef]
- C. Zong, B. Tang, F. Hua, H. He, P. Ngan. Skeletal and dentoalveolar changes in the transverse dimension using microimplant-assisted rapid palatal expansion (MARPE) appliances. Semin. Orthod.2019, 25, 1, 46-59. [CrossRef]
- Kapetanovic, C.I. Theodorou, S.J. Berge, J. Schols, T. Xi. Efficacy of Miniscrew-Assisted Rapid Palatal Expansion (MARPE) in late adolescents and adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Orthod 2021, 43, 3, 313-323. [CrossRef]
- R. Alcin, S. Malkoc. Does mini-implant-supported rapid maxillary expansion cause less root resorption than traditional approaches? A micro-computed tomography study. Korean J. Orthod 2021, 51, 4, pp. 241-249. [CrossRef]
- H. Jia, L. Zhuang, N. Zhang, Y. Bian, S. Li. Comparison of skeletal maxillary transverse deficiency treated by microimplant-assisted rapid palatal expansion and tooth-borne expansion during the post-pubertal growth spurt stage. Angle Orthod. 2021, 91, 1, 36-45. [CrossRef]
- T. M. Krusi, Eliades, S.N. Papageorgiou. Are there benefits from using bone-borne maxillary expansion instead of tooth-borne maxillary expansion? A systematic review with meta-analysis. Prog Orthod. 2019, 20, 1, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- C.B. Oliveira, P. Ayub, F. Angelieri, W.H. Murata, S.S. Suzuki, D.B. Ravelli, A. Santos-Pinto. Evaluation of factors related to the success of miniscrew-assisted rapid palatal expansion. Angle Orthod. 2021, 91, 2, 187-194. [CrossRef]
- S. Yoon, D.Y. Lee, S.K. Jung. Influence of changing various parameters in miniscrew-assisted rapid palatal expansion: A three-dimensional finite element analysis. Korean J. Orthod 2019, 49, 3, 150-160. [CrossRef]
- R.J. Lee, W. Moon, C. Hongb, Effects of monocortical and bicortical mini-implant anchorage on bone-borne palatal expansion using finite element analysis. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofacial Orthop. 2017, 151, 887-897. [CrossRef]
- V. Jain, T. Shyagali, P. Kambalyal, Y. Rajpara J. Doshi. Comparison and evaluation of stresses generated by rapid maxillary expansion and the implant-supported rapid maxillary expansion on the craniofacial structures using finite element method of stress analysis. Prog. Orthod. 2017, 18, 3, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- C.B. Andre, J. Rino-Neto, W. Iared, B.P.M. Pasqua, F.D. Nascimento. Stress distribution and displacement of three different types of micro-implant assisted rapid maxillary expansion (MARME): a three-dimensional finite element study. Prog Orthod. 2021, 22, 1, 1-201. [CrossRef]
- W. Coimbra, P. Oliveira, A. Theodosiou, C. Marques, K. Kalli, A. Leal-Junior. Strain Measurement in Hyrax Appliances Using FBG Sensors in a 3D-Printed Human Maxillary Model. IEEE Photonic. Tech. L. 2022, 34, 15, 811-814. [CrossRef]
- W. Coimbra, V. Campos, P.L.E. Oliveira, A. Frizera, E.F. Sant'Anna, M.T. Souza Araújo, R. Andrade, A. Leal-Junior. Fibre Bragg grating sensors for sutural expansion assessment in rapid palatal expanders: an ex-vivo validation. IET Optoelectron. 2020, 14, 6, 337-342. [CrossRef]
- F. Zhang, Z. Xu, S. Jiang, J. Ni, Q. Zhao, C. Wang. Ultrahigh-Resolution and Large-Dynamic-Range Temperature Sensor Based on Fiber-Optic EFPI Cavity. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 7, 6857-6863. [CrossRef]
- K.T. Song, J.H. Park, W. Moon, J.M. Chae, K.H. Kang. Three-dimensional changes of the zygomaticomaxillary complex after mini-implant assisted rapid maxillary expansion. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofacial Orthop. 2019, 156, 5, 653-662. [CrossRef]
- Elkenawy, L. Fijany, O. Colak, N.A. Paredes, A. Gargoum, S. Abedini, D. Cantarella, R. Dominguez-Mompell, L. Sfogliano, W. Moon. An assessment of the magnitude, parallelism, and asymmetry of micro-implant-assisted rapid maxillary expansion in non-growing patients. Prog Orthod. 2020, 21, no.42, 1-10.. [CrossRef]
- A.R. Cho, J.H. Park, W. Moon, J.M. Chae, K.H. Kang. Short-term effects of microimplant-assisted rapid palatal expansion on the circummaxillary sutures in skeletally mature patients: A cone-beam computed tomography study. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofacial Orthop. 2022, 161, 2, e187-e197. [CrossRef]
- Y.C. Liao, K.H. Ho, C.W. Wang, K.L. Wang, S.C. Hsieh, H.M. Chang. Skeletal and dental changes after microimplant-assisted rapid palatal expansion (MARPE) –a Cephalometric and Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) study. Clinical and Investigative Orthodontics 2022, 81,2, 84-92. [CrossRef]
- Lee R.J., W. Moon, C. Hong. Effects of monocortical and bicortical mini-implant anchorage on bone-borne palatal expansion using finite element analysis. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofacial Orthop. 2017, 151, 5, 887-897. [CrossRef]
- C. Chang, M. Chen, C. Chang, H. Chang. Investigation of the role of midpalatal and circummaxillary sutures in bone-anchored rapid maxillary expansion using a verified finite-element model. Am. J. of Orthod. and Dentofac. 2023, 163, 2, 198-209. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).