Submitted:
21 June 2023
Posted:
27 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cells
2.3. Transfection of SiRNA and Reporter Gene Assays
2.4. RT-PCR Analysis
2.5. Immunoblotting
2.6. Real-Time Cell Migration Assays
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. TAp73 Up-Regulates ECAD and SMAD4 in in Human PDAC Cells
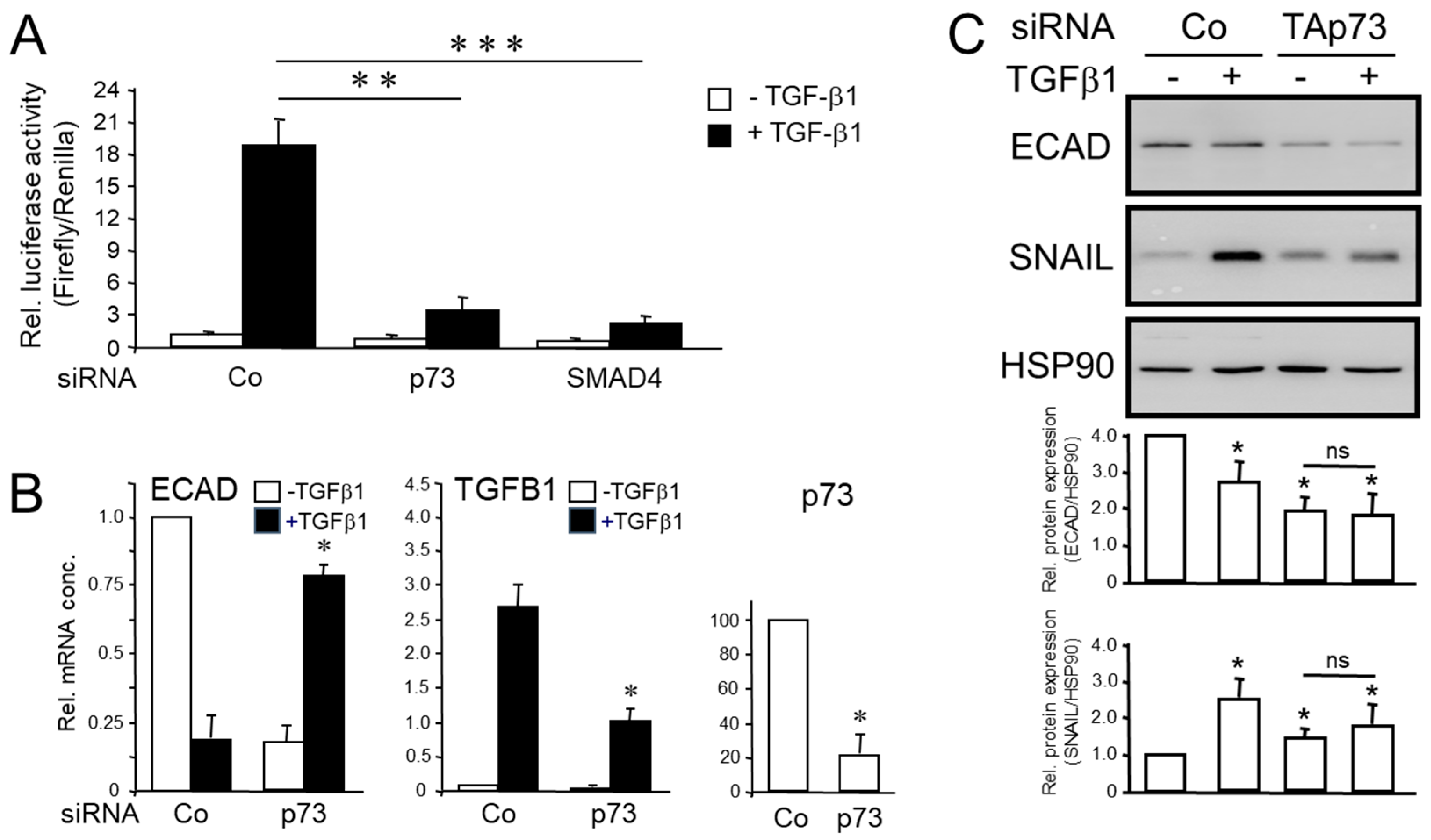
3.2. Knockdown of TAp73 Interfered with TGF-β1-induced Luciferase Activity on a SMAD-Responsive Promoter and Regulation of TGF-β/SMAD Target Genes in Human PDAC Cells
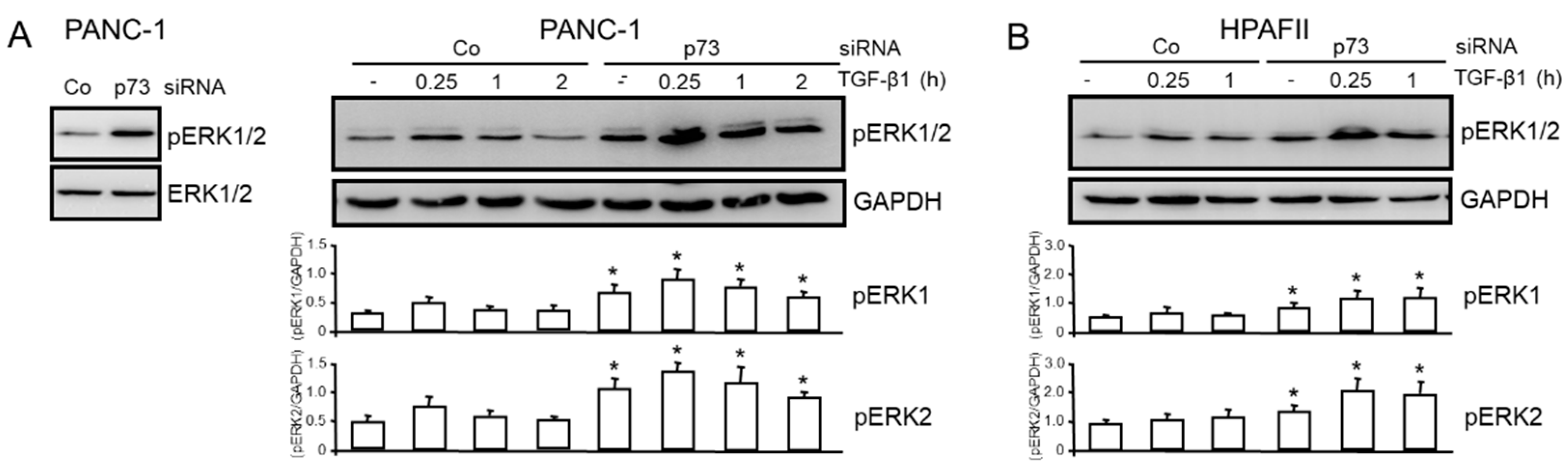
3.3. TAp73 Inhibits Basal and TGF-β1-induced ERK Activation
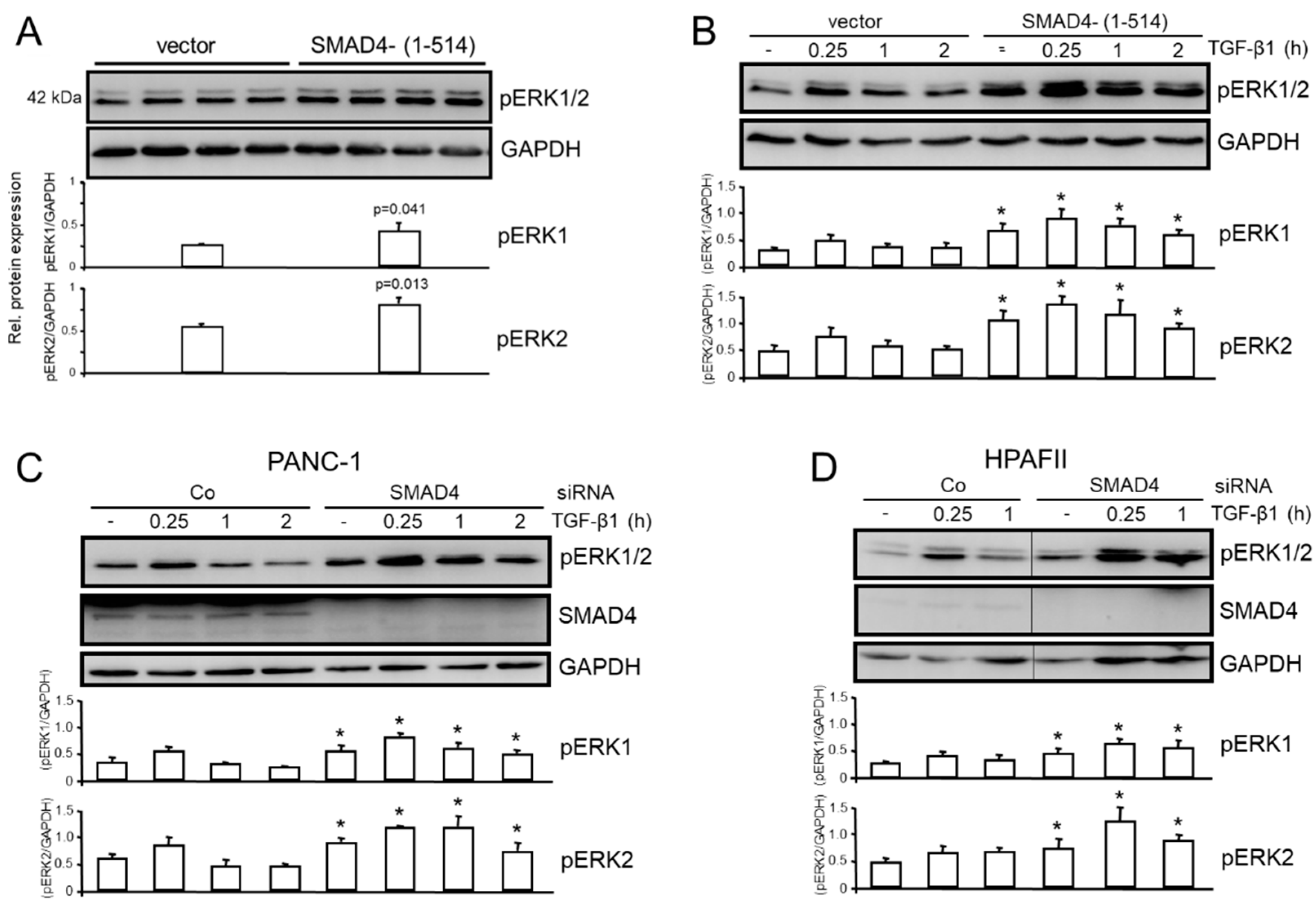
3.4. The Inhibitory Effect of TAp73 on ERK Activation is Mediated via SMAD4
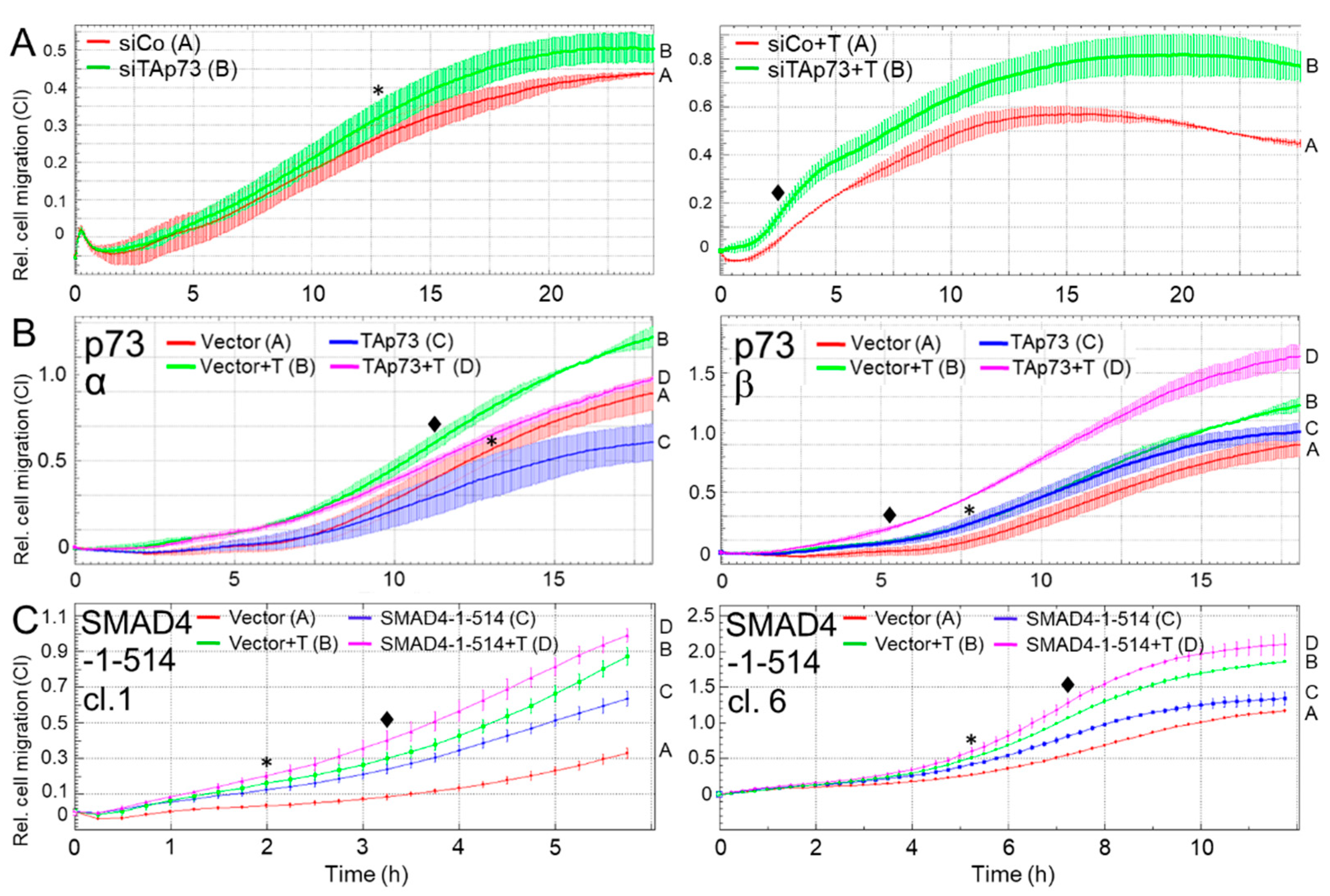
3.5. TAp73α and SMAD4 Mediate Inhibition of Cell Migration in Human PDAC Cells
4. Discussion
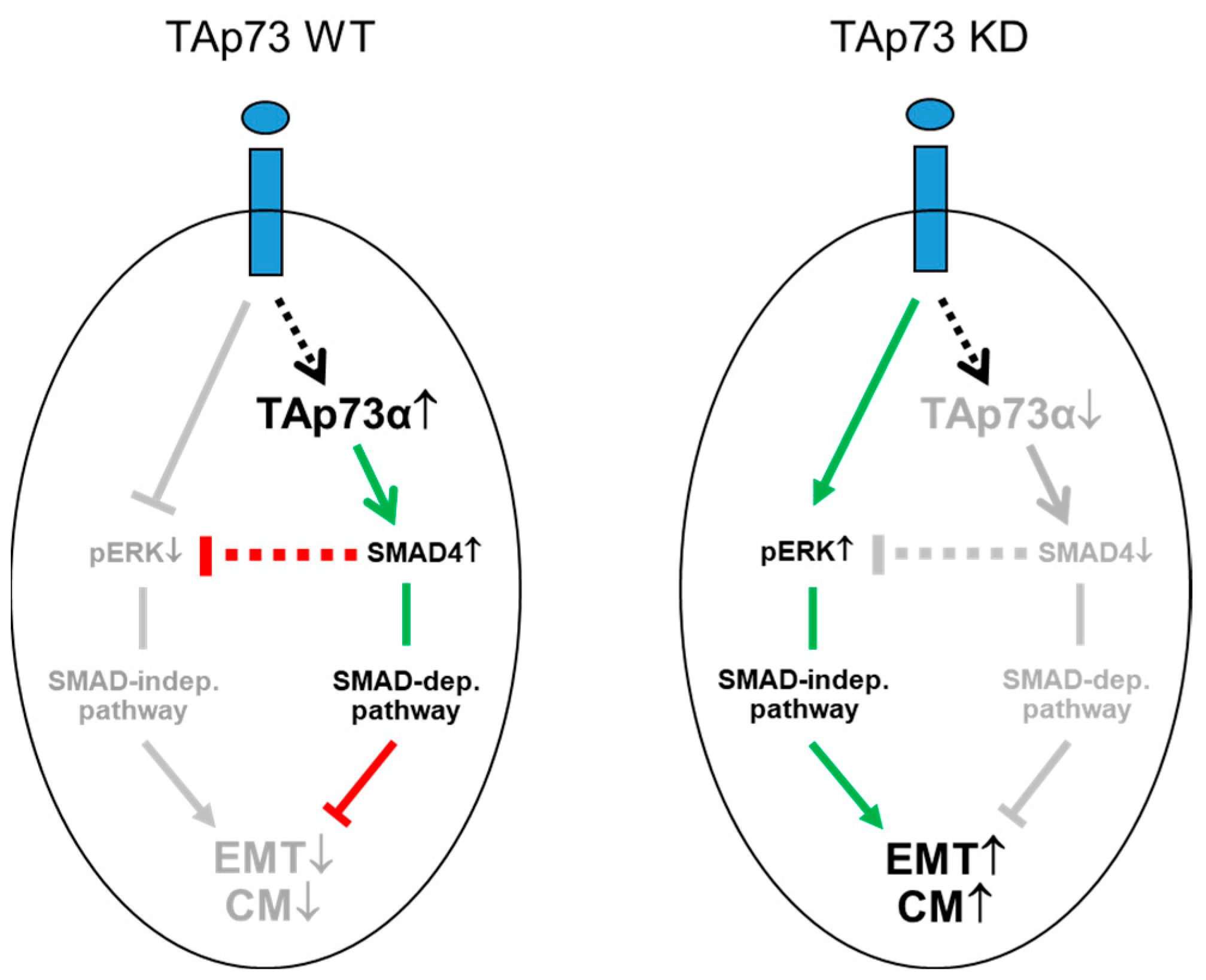
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalthoff, H. How open is the therapeutic horizon for pancreatic cancer patients? Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 2022, 21, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamska, A.; Domenichini, A.; Falasca, M. Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Current and Evolving Therapies. Int J Mol Sci 2017, 18, pii: E1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, K.C.; Yeh, C.N.; Ueng, S.H.; Hsu, J.T.; Yeh, T.S.; Jan, Y.Y.; Hwang, T.L.; Chen, M.F. Clinicodemographic aspect of resectable pancreatic cancer and prognostic factors for resectable cancer. World J Surg Oncol 2012, 10, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, G.; Siveke, J.T.; Eckel, F.; Schmid, R.M. Pancreatic cancer: basic and clinical aspects. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 1606–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Pothula, S.P.; Wilson, J.S.; Apte, M.V. Pancreatic cancer and its stroma: a conspiracy theory. World J Gastroenterol 2014, 20, 11216–11229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, S.; Masamune, A.; Shimosegawa, T. Novel therapeutic strategies targeting tumor stromal interactions in pancreatic cancer. Front Physiol 2013, 4, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.B.; Lenschow, W.; Tiede, K.; Fischer, J.W.; Kalthoff, H.; Ungefroren, H. Smad4/DPC4-dependent regulation of biglycan gene expression by transforming growth factor-beta in pancreatic tumor cells. J Biol Chem 2002, 277, 36118–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inman, G.J. Switching TGFbeta from a tumor suppressor to a tumor promoter. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2011, 21, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, C.; Kong, Y.; Huang, H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H. TGFbeta signaling in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Tumour Biol 2015, 36, 1613–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.E. Non-Smad pathways in TGF-beta signaling. Cell Res 2009, 19, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Law, B.K.; Chytil, A.M.; Brown, K.A.; Aakre, M.E.; Moses, H.L. Activation of the Erk pathway is required for TGF-beta1-induced EMT in vitro. Neoplasia 2004, 6, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellenrieder, V.; Hendler, S.F.; Boeck, W.; Seufferlein, T.; Menke, A.; Ruhland, C.; Adler, G.; Gress, T.M. Transforming growth factor beta1 treatment leads to an epithelial-mesenchymal transdifferentiation of pancreatic cancer cells requiring extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 activation. Cancer Res 2001, 61, 4222–4228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thakur, A.K.; Nigri, J.; Lac, S.; Leca, J.; Bressy, C.; Berthezene, P.; Bartholin, L.; Chan, P.; Calvo, E.; Iovanna, J.L.; et al. TAp73 loss favors Smad-independent TGF-β signaling that drives EMT in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Differ 2016, 23, 1358–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasini, R.; Tsuchihara, K.; Wilhelm, M.; Fujitani, M.; Rufini, A.; Cheung, C.C.; Khan, F.; Itie-Youten, A.; Wakeham, A.; Tsao, M.S.; et al. TAp73 knockout shows genomic instability with infertility and tumor suppressor functions. Genes Dev 2008, 22, 2677–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Semba, S.; Abe, T.; Makino, N.; Furukawa, T.; Fukushige, S.; Takahashi, H.; Sakurada, A.; Sato, M.; Shiiba, K.; et al. Infrequent somatic mutations of the p73 gene in various human cancers. Eur J Surg Oncol 1999, 25, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Kim, S.H.; Chen, C.Y. Sensitization of human pancreatic cancer cells harboring mutated K-ras to apoptosis. PLoS One 2012, 7, e40435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, A.S.; Ali, S.; Banerjee, S.; Bao, B.; Maitah, M.N.; Padhye, S.; Philip, P.A.; Mohammad, R.M.; Sarkar, F.H. Network modeling of CDF treated pancreatic cancer cells reveals a novel c-myc-p73 dependent apoptotic mechanism. Am J Transl Res 2011, 3, 374–382. [Google Scholar]
- Witte, D.; Otterbein, H.; Förster, M.; Giehl, K.; Zeiser, R.; Lehnert, H.; Ungefroren, H. Negative regulation of TGF-β1-induced MKK6-p38 and MEK-ERK signalling and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by Rac1b. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 17313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurice, D.; Pierreux, C.E.; Howell, M.; Wilentz, R.E.; Owen, M.J.; Hill, C.S. Loss of Smad4 function in pancreatic tumors: C-terminal truncation leads to decreased stability. J Biol Chem. 2001, 16, 43175–43181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungefroren, H.; Thürling, I.; Färber, B.; Kowalke, T.; Fischer, T.; De Assis, L.V.M.; Braun, R.; Castven, D.; Oster, H.; Konukiewitz, B.; et al. The Quasimesenchymal Pancreatic Ductal Epithelial Cell Line PANC-1-A Useful Model to Study Clonal Heterogeneity and EMT Subtype Shifting. Cancers 2022, 14, 2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.G.; Costanzo, A.; Yang, H.Q.; Melino, G.; Kaelin, W.G., Jr.; Levrero, M.; Wang, J.Y. The tyrosine kinase c-Abl regulates p73 in apoptotic response to cisplatin-induced DNA damage. Nature 1999, 399, 806–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vikhreva, P.; Melino, G.; Amelio, I. p73 Alternative Splicing: Exploring a Biological Role for the C-Terminal Isoforms. J Mol Biol 2018, 430, 1829–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennler, S.; Huet, S.; Gauthier, J.M. A short amino-acid sequence in MH1 domain is responsible for functional differences between Smad2 and Smad3. Oncogene 1999, 18, 1643–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, E.J.; Newton, C.C.; Silverman, D.T.; Nogueira, L.M.; Albanes, D.; Männistö, S.; Pollak, M.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.Z. Serum transforming growth factor-β1 and risk of pancreatic cancer in three prospective cohort studies. Cancer Causes Control 2014, 25, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Guix, M.; Rinehart, C.; Dugger, T.C.; Chytil, A.; Moses, H.L.; Freeman, M.L.; Arteaga, C.L. Inhibition of TGF-beta with neutralizing antibodies prevents radiation-induced acceleration of metastatic cancer progression. J Clin Invest 2007, 117, 1305–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, W.; Jung, Y.S.; Chen, X. Mammary epithelial cell polarity is regulated differentially by p73 isoforms via epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem 2012, 287, 17746–17753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemajerova, A.; Moll, U.M. Tissue-specific roles of p73 in development and homeostasis. J Cell Sci 2019, 132, jcs233338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemajerova, A.; Amelio, I.; Gebel, J.; Dötsch, V.; Melino, G.; Moll, U.M. Non-oncogenic roles of TAp73: from multiciliogenesis to metabolism. Cell Death Differ 2018, 25, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Laurenzi, V.; Raschella, G.; Barcaroli, D.; Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli, M.; Ranalli, M.; Catani, M.V.; Tanno, B.; Costanzo, A.; Levrero, M.; Melino, G. Induction of neuronal differentiation by p73 in a neuroblastoma cell line. J Biol Chem 2000, 275, 15226–15231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullerton, P.T., Jr.; Creighton, C.J.; Matzuk, M.M. Insights Into SMAD4 Loss in Pancreatic Cancer From Inducible Restoration of TGF-β Signaling. Mol Endocrinol 2015, 29, 1440–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Zhang, K.; Cen, G.; Jiang, T.; Cao, J.; Huang, K.; Huang, C.; Zhao, Q.; Qiu, Z. MicroRNA-301a-3p promotes pancreatic cancer progression via negative regulation of SMAD4. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 21046–21063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungefroren, H.; Witte, D.; Fiedler, C.; Gädeken, T.; Kaufmann, R.; Lehnert, H.; Gieseler, F.; Rauch, B.H. The Role of PAR2 in TGF-β1-Induced ERK Activation and Cell Motility. Int J Mol Sci 2017, 18, 2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, Y.; He, W.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Gao, J.; Wang, W.; Cheng, T.; Liu, B.; Yang, X. Endothelial Smad4 restrains the transition to hematopoietic progenitors via suppression of ERK activation. Blood 2014, 123, 2161–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, C.J.; Huang, Y.H.; Chen, M.; Su, J.; Zou, Y.; Bardeesy, N.; Iacobuzio-Donahue, C.A.; Massagué, J. TGF-β Tumor Suppression through a Lethal EMT. Cell 2016, 164, 1015–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melisi, D.; Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Macarulla, T.; Pezet, D.; Deplanque, G.; Fuchs, M.; Trojan, J.; Kozloff, M.; Simionato, F.; Cleverly, A.; et al. TGFβ receptor inhibitor galunisertib is linked to inflammation- and remodeling-related proteins in patients with pancreatic cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2019, 83, 975–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




