Submitted:
26 June 2023
Posted:
27 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract

Keywords:
Introduction
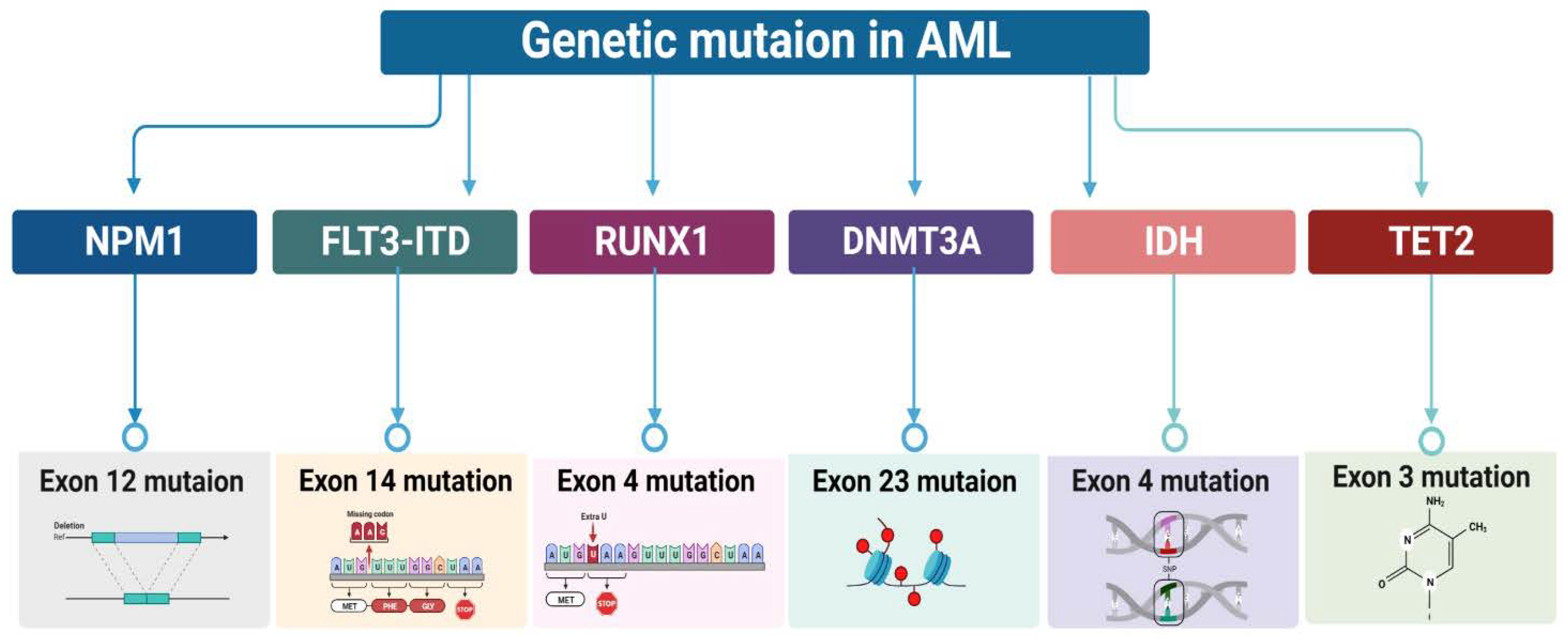
Characterization of Genetic mutation in AML
Significance of the phenomenon caused by HSC and AML’s initial interaction

Epigenetic modification of the LSC Microenvironment

Intelligent application: let the fat out and use it as fuel

Herbal Treatment Strategies for AML Employing System Biology

Clinical research and AML treatment

Conclusions and Perspectives
Funding
References
- Li, S.; Mason, C.E.; Melnick, A. Genetic and epigenetic heterogeneity in acute myeloid leukemia. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2016, 36, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcucci, G.; Haferlach, T.; Döhner, H. Molecular genetics of adult acute myeloid leukemia: Prognostic and therapeutic implications. J Clin Oncol 2011, 29, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, J. Precision therapy for acute myeloid leukemia. J Hematol Oncol 2018, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thol, F.; Ganser, A. Treatment of Relapsed Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Curr Treat Options Oncol 2020, 21, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andresen, V.; Gjertsen, B.T. Clinical Trials of Repurposing Medicines in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Limitations and Possibilities in the Age of Precision Therapy. Cancer J 2019, 25, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeijlemaker, W.; Gratama, J.W.; Schuurhuis, G.J. Tumor heterogeneity makes AML a "moving target" for detection of residual disease. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2014, 86, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCulloch, E.A. Stem cells in normal and leukemic hemopoiesis (Henry Stratton Lecture, 1982). Blood 1983, 62, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, D. Normal and leukaemic stem cells. Br J Haematol 2005, 130, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfons, L.M.; Tomblyn, M.; Rocha, V.; Lazarus, H.M. Second hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in myeloid malignancies. Curr Opin Hematol 2009, 16, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorror, M.L.; Maris, M.B.; Storb, R.; Baron, F.; Sandmaier, B.M.; Maloney, D.G.; Storer, B. Hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT)-specific comorbidity index: A new tool for risk assessment before allogeneic HCT. Blood 2005, 106, 2912–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, A.K.; Russell, N.H.; Hills, R.K.; Kell, J.; Freeman, S.; Kjeldsen, L.; Hunter, A.E.; Yin, J.; Craddock, C.F.; Dufva, I.H.; et al. Addition of gemtuzumab ozogamicin to induction chemotherapy improves survival in older patients with acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2012, 30, 3924–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, P.; Hills, R.K.; Grech, A.; Betteridge, S.; Kjeldsen, L.; Dennis, M.; Vyas, P.; Goldstone, A.H.; Milligan, D.; Clark, R.E.; et al. An operational definition of primary refractory acute myeloid leukemia allowing early identification of patients who may benefit from allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Haematologica 2016, 101, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dombret, H.; Seymour, J.F.; Butrym, A.; Wierzbowska, A.; Selleslag, D.; Jang, J.H.; Kumar, R.; Cavenagh, J.; Schuh, A.C.; Candoni, A.; et al. International phase 3 study of azacitidine vs conventional care regimens in older patients with newly diagnosed AML with >30% blasts. Blood 2015, 126, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantarjian, H.; O'Brien, S.; Cortes, J.; Giles, F.; Faderl, S.; Jabbour, E.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Wierda, W.; Pierce, S.; Shan, J.; et al. Results of intensive chemotherapy in 998 patients age 65 years or older with acute myeloid leukemia or high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome: Predictive prognostic models for outcome. Cancer 2006, 106, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burd, A.; Levine, R.L.; Ruppert, A.S.; Mims, A.S.; Borate, U.; Stein, E.M.; Patel, P.; Baer, M.R.; Stock, W.; Deininger, M.; et al. Precision medicine treatment in acute myeloid leukemia using prospective genomic profiling: Feasibility and preliminary efficacy of the Beat AML Master Trial. Nat Med 2020, 26, 1852–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, S.; Eiring, A.M.; Khorashad, J.S. Genomic Abnormalities as Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancers 2021, 13, 5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papaemmanuil, E.; Gerstung, M.; Bullinger, L.; Gaidzik, V.I.; Paschka, P.; Roberts, N.D.; Potter, N.E.; Heuser, M.; Thol, F.; Bolli, N.; et al. Genomic Classification and Prognosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N Engl J Med 2016, 374, 2209–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angenendt, L.; Röllig, C.; Montesinos, P.; Martínez-Cuadrón, D.; Barragan, E.; García, R.; Botella, C.; Martínez, P.; Ravandi, F.; Kadia, T.; et al. Chromosomal Abnormalities and Prognosis in NPM1-Mutated Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Pooled Analysis of Individual Patient Data From Nine International Cohorts. J Clin Oncol 2019, 37, 2632–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard-Carpentier, G.; DiNardo, C.D. Single-agent and combination biologics in acute myeloid leukemia. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2019, 2019, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falini, B.; Mecucci, C.; Tiacci, E.; Alcalay, M.; Rosati, R.; Pasqualucci, L.; La Starza, R.; Diverio, D.; Colombo, E.; Santucci, A. Cytoplasmic nucleophosmin in acute myelogenous leukemia with a normal karyotype. New England Journal of Medicine 2005, 352, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Pisani, L.A.; Shires, K. Development of a flow cytometric method to detect the presence of mutated nucleophosmin 1 in acute myeloid leukemia. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther 2015, 8, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renneville, A.; Roumier, C.; Biggio, V.; Nibourel, O.; Boissel, N.; Fenaux, P.; Preudhomme, C. Cooperating gene mutations in acute myeloid leukemia: A review of the literature. leukemia 2008, 22, 915–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratcorona, M.; Brunet, S.; Nomdedéu, J.; Ribera, J.M.; Tormo, M.; Duarte, R.; Escoda, L.; Guàrdia, R.; Queipo de Llano, M.P.; Salamero, O.; et al. Favorable outcome of patients with acute myeloid leukemia harboring a low-allelic burden FLT3-ITD mutation and concomitant NPM1 mutation: Relevance to post-remission therapy. Blood 2013, 121, 2734–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, A.D.; Schetelig, J.; Bochtler, T.; Schaich, M.; Schäfer-Eckart, K.; Hänel, M.; Rösler, W.; Einsele, H.; Kaufmann, M.; Serve, H.; et al. Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation Improves Survival in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia Characterized by a High Allelic Ratio of Mutant FLT3-ITD. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2016, 22, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Döhner, H.; Estey, E.; Grimwade, D.; Amadori, S.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Büchner, T.; Dombret, H.; Ebert, B.L.; Fenaux, P.; Larson, R.A.; et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2017 ELN recommendations from an international expert panel. Blood 2017, 129, 424–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruserud, O.; Hovland, R.; Wergeland, L.; Huang, T.-s.; Gjertsen, B.T. Flt3-mediated signaling in human acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) blasts: A functional characterization of Flt3-ligand effects in AML cell populations with and without genetic Flt3 abnormalities. haematologica 2003, 88, 416–428. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gilliland, D.G.; Griffin, J.D. The roles of FLT3 in hematopoiesis and leukemia. Blood 2002, 100, 1532–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, R.B.; Othus, M.; Burnett, A.K.; Löwenberg, B.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Ossenkoppele, G.J.; Hills, R.K.; Van Montfort, K.G.; Ravandi, F.; Evans, A. Significance of FAB subclassification of “acute myeloid leukemia, NOS” in the 2008 WHO classification: Analysis of 5848 newly diagnosed patients. Blood, The Journal of the American Society of Hematology 2013, 121, 2424–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arber, D.A.; Orazi, A.; Hasserjian, R.; Thiele, J.; Borowitz, M.J.; Le Beau, M.M.; Bloomfield, C.D.; Cazzola, M.; Vardiman, J.W. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood 2016, 127, 2391–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osato, M. Point mutations in the RUNX1/AML1 gene: Another actor in RUNX leukemia. Oncogene 2004, 23, 4284–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagata, T.; Maki, K.; Mitani, K. Runx1/AML1 in normal and abnormal hematopoiesis. International journal of hematology 2005, 82, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunadt, D.; Herold, S.; Poitz, D.; Wagenführ, L.; Kretschmann, T.; Sockel, K.; Ruhnke, L.; Brückner, S.; Sommer, U.; Meier, F.; et al. Spatial heterogeneity and differential treatment response of acute myeloid leukemia and relapsed/refractory extramedullary disease after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Ther Adv Hematol 2022, 13, 20406207221115005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saultz, J.N.; Garzon, R. Acute myeloid leukemia: A concise review. Journal of clinical medicine 2016, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, A.F.T.; Pratcorona, M.; Erpelinck-Verschueren, C.; Rockova, V.; Sanders, M.; Abbas, S.; Figueroa, M.E.; Zeilemaker, A.; Melnick, A.; Löwenberg, B. Mutant DNMT3A: A marker of poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood, The Journal of the American Society of Hematology 2012, 119, 5824–5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.J.; Kwon, A.; Cho, B.S.; Kim, H.J.; Hwang, K.A.; Kim, M.; Kim, Y. Characteristics of DNMT3A mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Res 2020, 55, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitman, Z.J.; Yan, H. Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 and 2 mutations in cancer: Alterations at a crossroads of cellular metabolism. J Natl Cancer Inst 2010, 102, 932–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, D.W.; Jones, S.; Zhang, X.; Lin, J.C.; Leary, R.J.; Angenendt, P.; Mankoo, P.; Carter, H.; Siu, I.M.; Gallia, G.L.; et al. An integrated genomic analysis of human glioblastoma multiforme. Science 2008, 321, 1807–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Parsons, D.W.; Jin, G.; McLendon, R.; Rasheed, B.A.; Yuan, W.; Kos, I.; Batinic-Haberle, I.; Jones, S.; Riggins, G.J.; et al. IDH1 and IDH2 mutations in gliomas. N Engl J Med 2009, 360, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Gong, Y. Isocitrate dehydrogenase inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia. Biomarker Research 2019, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcucci, G.; Maharry, K.; Wu, Y.Z.; Radmacher, M.D.; Mrózek, K.; Margeson, D.; Holland, K.B.; Whitman, S.P.; Becker, H.; Schwind, S.; et al. IDH1 and IDH2 gene mutations identify novel molecular subsets within de novo cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia: A Cancer and Leukemia Group B study. J Clin Oncol 2010, 28, 2348–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willander, K.; Falk, I.J.; Chaireti, R.; Paul, E.; Hermansson, M.; Gréen, H.; Lotfi, K.; Söderkvist, P. Mutations in the isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 gene and IDH1 SNP 105C > T have a prognostic value in acute myeloid leukemia. Biomark Res 2014, 2, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, K.; Damm, F.; Göhring, G.; Görlich, K.; Heuser, M.; Schäfer, I.; Ottmann, O.; Lübbert, M.; Heit, W.; Kanz, L.; et al. Impact of IDH1 R132 mutations and an IDH1 single nucleotide polymorphism in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia: SNP rs11554137 is an adverse prognostic factor. J Clin Oncol 2010, 28, 2356–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalban-Bravo, G.; DiNardo, C.D. The role of IDH mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. Future Oncology 2018, 14, 979–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, W.; Lei, W.; Ko, B.; Hou, H.; Chen, C.; Tang, J.; Yao, M.; Tsay, W.; Wu, S.; Huang, S. The prognostic impact and stability of Isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 mutation in adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2011, 25, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.B.; Smith-Díaz, C.C.; Vissers, M.C.M. Emerging epigenetic therapeutics for myeloid leukemia: Modulating demethylase activity with ascorbate. Haematologica 2021, 106, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonson, P.; Xanthopoulos, K.G. Molecular cloning, sequence, and expression patterns of the human gene encoding CCAAT/enhancer binding protein α (C/EBPα). Biochemical and biophysical research communications 1995, 215, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravandi, F.; Burnett, A.K.; Agura, E.D.; Kantarjian, H.M. Progress in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer 2007, 110, 1900–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, F.; Yoshida, S.; Saito, Y.; Hijikata, A.; Kitamura, H.; Tanaka, S.; Nakamura, R.; Tanaka, T.; Tomiyama, H.; Saito, N.; et al. Chemotherapy-resistant human AML stem cells home to and engraft within the bone-marrow endosteal region. Nat Biotechnol 2007, 25, 1315–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döhner, H.; Estey, E.H.; Amadori, S.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Büchner, T.; Burnett, A.K.; Dombret, H.; Fenaux, P.; Grimwade, D.; Larson, R.A.; et al. Diagnosis and management of acute myeloid leukemia in adults: Recommendations from an international expert panel, on behalf of the European LeukemiaNet. Blood 2010, 115, 453–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Reilly, E.; Zeinabad, H.A.; Nolan, C.; Sefy, J.; Williams, T.; Tarunina, M.; Hernandez, D.; Choo, Y.; Szegezdi, E. Recreating the Bone Marrow Microenvironment to Model Leukemic Stem Cell Quiescence. Front Cell Dev Biol 2021, 9, 662868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.C.; Li, S.C.; Wu, Y.C.; Wang, L.M.; Chao, K.S.; Liao, H.F. Resveratrol downregulates interleukin-6-stimulated sonic hedgehog signaling in human acute myeloid leukemia. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013, 2013, 547430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.T.; Hernandez, D.; Alonso, S.; Gao, M.; Su, M.; Ghiaur, G.; Levis, M.J.; Jones, R.J. Role of CYP3A4 in bone marrow microenvironment-mediated protection of FLT3/ITD AML from tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Blood Adv 2019, 3, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, G.; Kong, L.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.; Dong, M. Leukemia-derived exosomes induced IL-8 production in bone marrow stromal cells to protect the leukemia cells against chemotherapy. Life Sci 2019, 221, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.M.; Campbell, P. FLT3 inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia: Current and future. J Oncol Pharm Pract 2019, 25, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terwijn, M.; Zeijlemaker, W.; Kelder, A.; Rutten, A.P.; Snel, A.N.; Scholten, W.J.; Pabst, T.; Verhoef, G.; Löwenberg, B.; Zweegman, S.; et al. Leukemic stem cell frequency: A strong biomarker for clinical outcome in acute myeloid leukemia. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollyea, D.A.; Jordan, C.T. Therapeutic targeting of acute myeloid leukemia stem cells. Blood 2017, 129, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeijlemaker, W.; Grob, T.; Meijer, R.; Hanekamp, D.; Kelder, A.; Carbaat-Ham, J.C.; Oussoren-Brockhoff, Y.J.M.; Snel, A.N.; Veldhuizen, D.; Scholten, W.J.; et al. CD34(+)CD38(-) leukemic stem cell frequency to predict outcome in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2019, 33, 1102–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiozawa, Y.; Pedersen, E.A.; Havens, A.M.; Jung, Y.; Mishra, A.; Joseph, J.; Kim, J.K.; Patel, L.R.; Ying, C.; Ziegler, A.M.; et al. Human prostate cancer metastases target the hematopoietic stem cell niche to establish footholds in mouse bone marrow. J Clin Invest 2011, 121, 1298–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.; Wang, J.; Song, J.; Shiozawa, Y.; Wang, J.; Havens, A.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.X.; Emerson, S.G.; Krebsbach, P.H.; et al. Annexin II expressed by osteoblasts and endothelial cells regulates stem cell adhesion, homing, and engraftment following transplantation. Blood 2007, 110, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwajei, F.; Konopleva, M. The bone marrow microenvironment as niche retreats for hematopoietic and leukemic stem cells. Adv Hematol 2013, 2013, 953982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabe, Y.; Konopleva, M. Role of Microenvironment in Resistance to Therapy in AML. Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2015, 10, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepers, K.; Campbell, T.B.; Passegué, E. Normal and leukemic stem cell niches: Insights and therapeutic opportunities. Cell Stem Cell 2015, 16, 254–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linde, N.; Fluegen, G.; Aguirre-Ghiso, J.A. The Relationship Between Dormant Cancer Cells and Their Microenvironment. Adv Cancer Res 2016, 132, 45–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesbahi, Y.; Trahair, T.N.; Lock, R.B.; Connerty, P. Exploring the metabolic landscape of AML: From haematopoietic stem cells to myeloblasts and leukaemic stem cells. Frontiers in Oncology 2022, 12, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Chen, N.; Wang, J.; Siu, C.H. Transendothelial migration of melanoma cells involves N-cadherin-mediated adhesion and activation of the beta-catenin signaling pathway. Mol Biol Cell 2005, 16, 4386–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, S.E.; Kay, E.J.; Neilson, L.J.; Henze, A.T.; Serneels, J.; McGhee, E.J.; Dhayade, S.; Nixon, C.; Mackey, J.B.; Santi, A.; et al. Tumor matrix stiffness promotes metastatic cancer cell interaction with the endothelium. Embo j 2017, 36, 2373–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sistigu, A.; Musella, M.; Galassi, C.; Vitale, I.; De Maria, R. Tuning Cancer Fate: Tumor Microenvironment's Role in Cancer Stem Cell Quiescence and Reawakening. Front Immunol 2020, 11, 2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasi, R.; Evangelista, M.L.; Buccisano, F.; Venditti, A.; Amadori, S. Gemtuzumab ozogamicin in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer treatment reviews 2008, 34, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Lee, E.M.; Ramshaw, H.S.; Busfield, S.J.; Peoppl, A.G.; Wilkinson, L.; Guthridge, M.A.; Thomas, D.; Barry, E.F.; Boyd, A. Monoclonal antibody-mediated targeting of CD123, IL-3 receptor α chain, eliminates human acute myeloid leukemic stem cells. Cell stem cell 2009, 5, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rhenen, A.; Van Dongen, G.A.; Kelder, A.; Rombouts, E.J.; Feller, N.; Moshaver, B.; Walsum, M.S.-v.; Zweegman, S.; Ossenkoppele, G.J.; Jan Schuurhuis, G. The novel AML stem cell–associated antigen CLL-1 aids in discrimination between normal and leukemic stem cells. Blood, The Journal of the American Society of Hematology 2007, 110, 2659–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Hope, K.J.; Zhai, Q.; Smadja-Joffe, F.; Dick, J.E. Targeting of CD44 eradicates human acute myeloid leukemic stem cells. Nature medicine 2006, 12, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, S.; Jamieson, C.H.; Pang, W.W.; Park, C.Y.; Chao, M.P.; Majeti, R.; Traver, D.; van Rooijen, N.; Weissman, I.L. CD47 is upregulated on circulating hematopoietic stem cells and leukemia cells to avoid phagocytosis. Cell 2009, 138, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosen, N.; Park, C.Y.; Tatsumi, N.; Oji, Y.; Sugiyama, H.; Gramatzki, M.; Krensky, A.M.; Weissman, I.L. CD96 is a leukemic stem cell-specific marker in human acute myeloid leukemia. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2007, 104, 11008–11013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.M.I.; Aref, S.; Agdar, M.A.; Mabed, M.; El-Sokkary, A.M.A. Leukemic Stem Cell (CD34+/CD38–/TIM3+) Frequency in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Clinical Implications. Clinical Lymphoma Myeloma and Leukemia 2021, 21, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corces, M.R.; Buenrostro, J.D.; Wu, B.; Greenside, P.G.; Chan, S.M.; Koenig, J.L.; Snyder, M.P.; Pritchard, J.K.; Kundaje, A.; Greenleaf, W.J.; et al. Lineage-specific and single-cell chromatin accessibility charts human hematopoiesis and leukemia evolution. Nature Genetics 2016, 48, 1193–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, G.J.; Casasnovas, J.M.; Umetsu, D.T.; DeKruyff, R.H. TIM genes: A family of cell surface phosphatidylserine receptors that regulate innate and adaptive immunity. Immunological reviews 2010, 235, 172–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikushige, Y.; Shima, T.; Takayanagi, S.-i.; Urata, S.; Miyamoto, T.; Iwasaki, H.; Takenaka, K.; Teshima, T.; Tanaka, T.; Inagaki, Y. TIM-3 is a promising target to selectively kill acute myeloid leukemia stem cells. Cell stem cell 2010, 7, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, M.; Chao, M.P.; Cha, A.C.; Alizadeh, A.A.; Gentles, A.J.; Weissman, I.L.; Majeti, R. Prospective separation of normal and leukemic stem cells based on differential expression of TIM3, a human acute myeloid leukemia stem cell marker. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2011, 108, 5009–5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikushige, Y.; Miyamoto, T. TIM-3 as a novel therapeutic target for eradicating acute myelogenous leukemia stem cells. International journal of hematology 2013, 98, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Anderson, A.C.; Schubart, A.; Xiong, H.; Imitola, J.; Khoury, S.J.; Zheng, X.X.; Strom, T.B.; Kuchroo, V.K. The Tim-3 ligand galectin-9 negatively regulates T helper type 1 immunity. Nature immunology 2005, 6, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monney, L.; Sabatos, C.A.; Gaglia, J.L.; Ryu, A.; Waldner, H.; Chernova, T.; Manning, S.; Greenfield, E.A.; Coyle, A.J.; Sobel, R.A. Th1-specific cell surface protein Tim-3 regulates macrophage activation and severity of an autoimmune disease. Nature 2002, 415, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Yu, X.; Gu, C.; Ma, C.; Liu, H.; Tong, W.; Zou, Q.; Ye, L.; Chen, X.; Depei, W. The expression and mechanism of Tim3 and PD-1 in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. American Society of Hematology Washington, DC: 2015.
- de Almeida, M.J.; Luchsinger, L.L.; Corrigan, D.J.; Williams, L.J.; Snoeck, H.W. Dye-Independent Methods Reveal Elevated Mitochondrial Mass in Hematopoietic Stem Cells. Cell Stem Cell 2017, 21, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Pollyea, D.A. Shutting Down Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndrome with BCL-2 Family Protein Inhibition. Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2018, 13, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, I.; Sistigu, A.; Manic, G.; Rudqvist, N.P.; Trajanoski, Z.; Galluzzi, L. Mutational and Antigenic Landscape in Tumor Progression and Cancer Immunotherapy. Trends Cell Biol 2019, 29, 396–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tormin, A.; Li, O.; Brune, J.; Walsh, S.; Ehinger, M.; Ditzel, N.; Kassem, M.; Scheding, S. Human Primary CD271+/CD45−/CD146−/Low and CD271+/CD45−/CD146+ Bone Marrow Cells Are Developmentally Closely-Related Stroma Stem Cells with Similar Functional Properties but Different In-Situ Localization. Blood 2010, 116, 2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, Y.; Nakatsuka, R.; Sumide, K.; Kawamura, H.; Takahashi, M.; Fujioka, T.; Uemura, Y.; Asano, H.; Sasaki, Y.; Inoue, M.; et al. Prospectively Isolated Human Bone Marrow Cell-Derived MSCs Support Primitive Human CD34-Negative Hematopoietic Stem Cells. Stem Cells 2015, 33, 1554–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkness, L.; Zaher, W.; Ditzel, N.; Isa, A.; Kassem, M. CD146/MCAM defines functionality of human bone marrow stromal stem cell populations. Stem Cell Res Ther 2016, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumbly, V.; Landry, I.; Sneed, C.; Iqbal, Q.; Verma, A.; Dhokhar, T.; Masood, A.; Amaraneni, A. Leukemic stem cells and advances in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia: A narrative review of clinical trials. Stem Cell Investig 2022, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiozawa, Y.; Berry, J.E.; Eber, M.R.; Jung, Y.; Yumoto, K.; Cackowski, F.C.; Yoon, H.J.; Parsana, P.; Mehra, R.; Wang, J.; et al. The marrow niche controls the cancer stem cell phenotype of disseminated prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 41217–41232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malanchi, I.; Santamaria-Martínez, A.; Susanto, E.; Peng, H.; Lehr, H.-A.; Delaloye, J.-F.; Huelsken, J. Interactions between cancer stem cells and their niche govern metastatic colonization. Nature 2012, 481, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oskarsson, T.; Batlle, E.; Massagué, J. Metastatic stem cells: Sources, niches, and vital pathways. Cell stem cell 2014, 14, 306–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sendker, S.; Reinhardt, D.; Niktoreh, N. Redirecting the immune microenvironment in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancers 2021, 13, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghajar, C.M.; Peinado, H.; Mori, H.; Matei, I.R.; Evason, K.J.; Brazier, H.; Almeida, D.; Koller, A.; Hajjar, K.A.; Stainier, D.Y.; et al. The perivascular niche regulates breast tumour dormancy. Nat Cell Biol 2013, 15, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kienast, Y.; von Baumgarten, L.; Fuhrmann, M.; Klinkert, W.E.; Goldbrunner, R.; Herms, J.; Winkler, F. Real-time imaging reveals the single steps of brain metastasis formation. Nat Med 2010, 16, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Ding, B.S.; Guo, P.; Lee, S.B.; Butler, J.M.; Casey, S.C.; Simons, M.; Tam, W.; Felsher, D.W.; Shido, K.; et al. Angiocrine factors deployed by tumor vascular niche induce B cell lymphoma invasiveness and chemoresistance. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 350–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, T.T.; Burness, M.L.; Sivan, A.; Warner, M.J.; Cheng, R.; Lee, C.H.; Olivere, L.; Comatas, K.; Magnani, J.; Kim Lyerly, H.; et al. Dormant breast cancer micrometastases reside in specific bone marrow niches that regulate their transit to and from bone. Sci Transl Med 2016, 8, 340ra373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.M.; Kobayashi, H.; Rafii, S. Instructive role of the vascular niche in promoting tumour growth and tissue repair by angiocrine factors. Nat Rev Cancer 2010, 10, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fessler, E.; Dijkgraaf, F.E.; De Sousa, E.M.F.; Medema, J.P. Cancer stem cell dynamics in tumor progression and metastasis: Is the microenvironment to blame? Cancer Lett 2013, 341, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrader, J.; Gordon-Walker, T.T.; Aucott, R.L.; van Deemter, M.; Quaas, A.; Walsh, S.; Benten, D.; Forbes, S.J.; Wells, R.G.; Iredale, J.P. Matrix stiffness modulates proliferation, chemotherapeutic response, and dormancy in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1192–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukdar, S.; Bhoopathi, P.; Emdad, L.; Das, S.; Sarkar, D.; Fisher, P.B. Dormancy and cancer stem cells: An enigma for cancer therapeutic targeting. Adv Cancer Res 2019, 141, 43–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crea, F.; Nur Saidy, N.R.; Collins, C.C.; Wang, Y. The epigenetic/noncoding origin of tumor dormancy. Trends Mol Med 2015, 21, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansoori, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Davudian, S.; Shirjang, S.; Baradaran, B. The Different Mechanisms of Cancer Drug Resistance: A Brief Review. Adv Pharm Bull 2017, 7, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnet, D.; Dick, J.E. Human acute myeloid leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a primitive hematopoietic cell. Nat Med 1997, 3, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapidot, T.; Sirard, C.; Vormoor, J.; Murdoch, B.; Hoang, T.; Caceres-Cortes, J.; Minden, M.; Paterson, B.; Caligiuri, M.A.; Dick, J.E. A cell initiating human acute myeloid leukaemia after transplantation into SCID mice. Nature 1994, 367, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowie, M.B.; Kent, D.G.; Dykstra, B.; McKnight, K.D.; McCaffrey, L.; Hoodless, P.A.; Eaves, C.J. Identification of a new intrinsically timed developmental checkpoint that reprograms key hematopoietic stem cell properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007, 104, 5878–5882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Peng, C.; Li, S. Loss of the Alox5 gene impairs leukemia stem cells and prevents chronic myeloid leukemia. Nat Genet 2009, 41, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardal, R.; Clarke, M.F.; Morrison, S.J. Applying the principles of stem-cell biology to cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2003, 3, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reya, T.; Morrison, S.J.; Clarke, M.F.; Weissman, I.L. Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature 2001, 414, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molofsky, A.V.; Pardal, R.; Morrison, S.J. Diverse mechanisms regulate stem cell self-renewal. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2004, 16, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Blum, J.; Chen, A.; Kwon, H.Y.; Jung, S.H.; Cook, J.M.; Lagoo, A.; Reya, T. Loss of beta-catenin impairs the renewal of normal and CML stem cells in vivo. Cancer Cell 2007, 12, 528–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardal, R.; Clarke, M.F.; Morrison, S.J. Applying the principles of stem-cell biology to cancer. Nature Reviews Cancer 2003, 3, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molofsky, A.V.; Pardal, R.; Morrison, S.J. Diverse mechanisms regulate stem cell self-renewal. Current Opinion in Cell Biology 2004, 16, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molofsky, A.V.; He, S.; Bydon, M.; Morrison, S.J.; Pardal, R. Bmi-1 promotes neural stem cell self-renewal and neural development but not mouse growth and survival by repressing the p16Ink4a and p19Arf senescence pathways. Genes Dev 2005, 19, 1432–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, S.W.; Sherr, C.J. Tumor suppression by Ink4a–Arf: Progress and puzzles. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development 2003, 13, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cristofano, A.; Pandolfi, P.P. The multiple roles of PTEN in tumor suppression. Cell 2000, 100, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggerholm, A.; Grønbaek, K.; Guldberg, P.; Hokland, P. Mutational analysis of the tumour suppressor gene MMAC1/PTEN in malignant myeloid disorders. Eur J Haematol 2000, 65, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahia, P.L.; Aguiar, R.C.; Alberta, J.; Kum, J.B.; Caron, S.; Sill, H.; Marsh, D.J.; Ritz, J.; Freedman, A.; Stiles, C.; et al. PTEN is inversely correlated with the cell survival factor Akt/PKB and is inactivated via multiple mechanismsin haematological malignancies. Hum Mol Genet 1999, 8, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, J.W.; Eom, J.I.; Maeng, H.Y.; Lee, S.T.; Hahn, J.S.; Ko, Y.W.; Min, Y.H. Phosphatase and tensin homologue phosphorylation in the C-terminal regulatory domain is frequently observed in acute myeloid leukaemia and associated with poor clinical outcome. Br J Haematol 2003, 122, 454–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisfeld, A.K.; Kohlschmidt, J.; Mims, A.; Nicolet, D.; Walker, C.J.; Blachly, J.S.; Carroll, A.J.; Papaioannou, D.; Kolitz, J.E.; Powell, B.E.; et al. Additional gene mutations may refine the 2017 European LeukemiaNet classification in adult patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia aged <60 years. Leukemia 2020, 34, 3215–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullinger, L.; Döhner, K.; Döhner, H. Genomics of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Diagnosis and Pathways. J Clin Oncol 2017, 35, 934–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, T.J.; Miller, C.; Ding, L.; Raphael, B.J.; Mungall, A.J.; Robertson, A.; Hoadley, K.; Triche, T.J., Jr.; Laird, P.W.; Baty, J.D.; et al. Genomic and epigenomic landscapes of adult de novo acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2013, 368, 2059–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wong, M.P.M.; Ng, R.K. Aberrant DNA Methylation in Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Its Clinical Implications. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celik, H.; Kramer, A.; Challen, G.A. DNA methylation in normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Int J Hematol 2016, 103, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexheimer, G.M.; Alves, J.; Reckziegel, L.; Lazzaretti, G.; Abujamra, A.L. DNA Methylation Events as Markers for Diagnosis and Management of Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndrome. Dis Markers 2017, 2017, 5472893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varley, K.E.; Gertz, J.; Bowling, K.M.; Parker, S.L.; Reddy, T.E.; Pauli-Behn, F.; Cross, M.K.; Williams, B.A.; Stamatoyannopoulos, J.A.; Crawford, G.E.; et al. Dynamic DNA methylation across diverse human cell lines and tissues. Genome Res 2013, 23, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, U.; Hasemeier, B.; Christgen, M.; Müller, M.; Römermann, D.; Länger, F.; Kreipe, H. Epigenetic inactivation of microRNA gene hsa-mir-9-1 in human breast cancer. J Pathol 2008, 214, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fard, A.A.; Rahimi, H.; Shams, Z.; Ghoraeian, P. Screening and in Silico Functional Analysis of MiRNAs Associated with Acute Myeloid Leukemia Relapse. Microrna 2022, 11, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baer, C.; Claus, R.; Plass, C. Genome-wide epigenetic regulation of miRNAs in cancer. Cancer Res 2013, 73, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasheva, P.; Grossniklaus, U. Differentially Methylated Region-Representational Difference Analysis (DMR-RDA): A Powerful Method to Identify DMRs in Uncharacterized Genomes. Methods Mol Biol 2017, 1456, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, T.L. lncRNA express delivery. Nature Chemical Biology 2014, 10, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yang, L.; Zhong, T.; Mueller, M.; Men, Y.; Zhang, N.; Xie, J.; Giang, K.; Chung, H.; Sun, X.; et al. H19 lncRNA alters DNA methylation genome wide by regulating S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase. Nat Commun 2015, 6, 10221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taube, J.H.; Malouf, G.G.; Lu, E.; Sphyris, N.; Vijay, V.; Ramachandran, P.P.; Ueno, K.R.; Gaur, S.; Nicoloso, M.S.; Rossi, S.; et al. Epigenetic silencing of microRNA-203 is required for EMT and cancer stem cell properties. Sci Rep 2013, 3, 2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwak, J.M.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, E.J.; Chung, Y.R.; Yun, S.; Seo, A.N.; Lee, H.J.; Park, S.Y. MicroRNA-9 is associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition, breast cancer stem cell phenotype, and tumor progression in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2014, 147, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Sauer, M.A.; Hussein, S.G.; Yang, J.; Tenen, D.G.; Chai, L. SALL4 and microRNA: The Role of Let-7. Genes (Basel) 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves, R.; Scheel, C.; Weinhold, S.; Honisch, E.; Iwaniuk, K.M.; Trompeter, H.I.; Niederacher, D.; Wernet, P.; Santourlidis, S.; Uhrberg, M. Role of DNA methylation in miR-200c/141 cluster silencing in invasive breast cancer cells. BMC Res Notes 2010, 3, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrba, L.; Muñoz-Rodríguez, J.L.; Stampfer, M.R.; Futscher, B.W. miRNA gene promoters are frequent targets of aberrant DNA methylation in human breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payton, J.E.; Grieselhuber, N.R.; Chang, L.W.; Murakami, M.; Geiss, G.K.; Link, D.C.; Nagarajan, R.; Watson, M.A.; Ley, T.J. High throughput digital quantification of mRNA abundance in primary human acute myeloid leukemia samples. J Clin Invest 2009, 119, 1714–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Croce, L.; Raker, V.A.; Corsaro, M.; Fazi, F.; Fanelli, M.; Faretta, M.; Fuks, F.; Lo Coco, F.; Kouzarides, T.; Nervi, C.; et al. Methyltransferase recruitment and DNA hypermethylation of target promoters by an oncogenic transcription factor. Science 2002, 295, 1079–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Jacobsen, S.E.; Reik, W. Epigenetic reprogramming in plant and animal development. Science 2010, 330, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.C.; Zhang, Y. Active DNA demethylation: Many roads lead to Rome. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2010, 11, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, J.A.; Jacobsen, S.E. Establishing, maintaining and modifying DNA methylation patterns in plants and animals. Nat Rev Genet 2010, 11, 204–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babaei, G.; Aziz, S.G.; Jaghi, N.Z.Z. EMT, cancer stem cells and autophagy; The three main axes of metastasis. Biomed Pharmacother 2021, 133, 110909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elenbaas, B.; Spirio, L.; Koerner, F.; Fleming, M.D.; Zimonjic, D.B.; Donaher, J.L.; Popescu, N.C.; Hahn, W.C.; Weinberg, R.A. Human breast cancer cells generated by oncogenic transformation of primary mammary epithelial cells. Genes Dev 2001, 15, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, P.; Li, Z.W.; Fang, T.Y.; Jian, W.; Zhuan, Z.; Mei, L.X.; Yan, W.S.; Jian, N. Retinoic acid induces HL-60 cell differentiation via the upregulation of miR-663. J Hematol Oncol 2011, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, H.; Gao, P. Metabolic reprogramming and epigenetic modifications on the path to cancer. Protein Cell 2022, 13, 877–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagadinou, E.D.; Sach, A.; Callahan, K.; Rossi, R.M.; Neering, S.J.; Minhajuddin, M.; Ashton, J.M.; Pei, S.; Grose, V.; O'Dwyer, K.M.; et al. BCL-2 inhibition targets oxidative phosphorylation and selectively eradicates quiescent human leukemia stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2013, 12, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarry, J.E.; Murphy, K.; Perry, R.; Sanchez, P.V.; Secreto, A.; Keefer, C.; Swider, C.R.; Strzelecki, A.C.; Cavelier, C.; Récher, C.; et al. Human acute myelogenous leukemia stem cells are rare and heterogeneous when assayed in NOD/SCID/IL2Rγc-deficient mice. J Clin Invest 2011, 121, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Gerhard, B.; Hogge, D.E. Detection, isolation, and stimulation of quiescent primitive leukemic progenitor cells from patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Blood 2003, 101, 3142–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, K.; Okada, M.; Suzuki, S.; Seino, M.; Seino, S.; Takeda, H.; Kitanaka, C. Targeting the facilitative glucose transporter GLUT1 inhibits the self-renewal and tumor-initiating capacity of cancer stem cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.L.; Stevens, B.M.; D'Alessandro, A.; Reisz, J.A.; Culp-Hill, R.; Nemkov, T.; Pei, S.; Khan, N.; Adane, B.; Ye, H. Inhibition of amino acid metabolism selectively targets human leukemia stem cells. Cancer cell 2018, 34, 724–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Reilly, E.; Zeinabad, H.A.; Szegezdi, E. Hematopoietic versus leukemic stem cell quiescence: Challenges and therapeutic opportunities. Blood Reviews 2021, 50, 100850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuringa, J.J. Smart niche usage: Release its fat and burn it! Blood 2017, 129, 1239–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anselmi, L.; Bertuccio, S.N.; Lonetti, A.; Prete, A.; Masetti, R.; Pession, A. Insights on the interplay between cells metabolism and signaling: A therapeutic perspective in pediatric acute leukemias. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2020, 21, 6251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrtić, M.; Sriskanthadevan, S.; Jhas, B.; Gebbia, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Hurren, R.; Jitkova, Y.; Gronda, M.; Maclean, N.; et al. Inhibition of mitochondrial translation as a therapeutic strategy for human acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 674–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farge, T.; Saland, E.; de Toni, F.; Aroua, N.; Hosseini, M.; Perry, R.; Bosc, C.; Sugita, M.; Stuani, L.; Fraisse, M.; et al. Chemotherapy-Resistant Human Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells Are Not Enriched for Leukemic Stem Cells but Require Oxidative Metabolism. Cancer Discov 2017, 7, 716–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samudio, I.; Harmancey, R.; Fiegl, M.; Kantarjian, H.; Konopleva, M.; Korchin, B.; Kaluarachchi, K.; Bornmann, W.; Duvvuri, S.; Taegtmeyer, H.; et al. Pharmacologic inhibition of fatty acid oxidation sensitizes human leukemia cells to apoptosis induction. J Clin Invest 2010, 120, 142–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhajda, F.P. Fatty-acid synthase and human cancer: New perspectives on its role in tumor biology. Nutrition 2000, 16, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashima, T.; Seimiya, H.; Tsuruo, T. De novo fatty-acid synthesis and related pathways as molecular targets for cancer therapy. Br J Cancer 2009, 100, 1369–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, A.; Rodilossi, S.; Caprari, P.; Coppola, V.; Procopio, A. 5-Lipoxygenase regulates senescence-like growth arrest by promoting ROS-dependent p53 activation. Embo j 2005, 24, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wymann, M.P.; Schneiter, R. Lipid signalling in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2008, 9, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, O.H.; Valdez, R.; Theisen, B.K.; Guo, W.; Ferguson, D.O.; Wu, H.; Morrison, S.J. Pten dependence distinguishes haematopoietic stem cells from leukaemia-initiating cells. Nature 2006, 441, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomlinson, I.P.; Alam, N.A.; Rowan, A.J.; Barclay, E.; Jaeger, E.E.; Kelsell, D.; Leigh, I.; Gorman, P.; Lamlum, H.; Rahman, S.; et al. Germline mutations in FH predispose to dominantly inherited uterine fibroids, skin leiomyomata and papillary renal cell cancer. Nat Genet 2002, 30, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baysal, B.E.; Ferrell, R.E.; Willett-Brozick, J.E.; Lawrence, E.C.; Myssiorek, D.; Bosch, A.; van der Mey, A.; Taschner, P.E.; Rubinstein, W.S.; Myers, E.N.; et al. Mutations in SDHD, a mitochondrial complex II gene, in hereditary paraganglioma. Science 2000, 287, 848–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Yang, J.; Ku, M.; Kim, N.; Park, Y.; Park, C.; Suh, J.; Park, E.; Yook, J.; Mills, G. Metabolic stress induces a Wnt-dependent cancer stem cell-like state transition. Cell death & disease 2015, 6, e1805. [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs, J.S.; Jung, Y.J.; Mole, D.R.; Lee, S.; Torres-Cabala, C.; Chung, Y.L.; Merino, M.; Trepel, J.; Zbar, B.; Toro, J.; et al. HIF overexpression correlates with biallelic loss of fumarate hydratase in renal cancer: Novel role of fumarate in regulation of HIF stability. Cancer Cell 2005, 8, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollard, P.J.; Brière, J.J.; Alam, N.A.; Barwell, J.; Barclay, E.; Wortham, N.C.; Hunt, T.; Mitchell, M.; Olpin, S.; Moat, S.J.; et al. Accumulation of Krebs cycle intermediates and over-expression of HIF1alpha in tumours which result from germline FH and SDH mutations. Hum Mol Genet 2005, 14, 2231–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasmim, M.; Janji, B.; Khaled, M.; Noman, M.Z.; Louache, F.; Bordereaux, D.; Abderamane, A.; Baud, V.; Mami-Chouaib, F.; Chouaib, S. Cutting Edge: NANOG Activates Autophagy under Hypoxic Stress by Binding to BNIP3L Promoter. The Journal of Immunology 2017, 198, 1423–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockard, B.; Garrett, T.; Guingab-Cagmat, J.; Meshinchi, S.; Lamba, J. Distinct metabolic features differentiating FLT3-ITD AML from FLT3-WT childhood acute myeloid leukemia. Scientific reports 2018, 8, 5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdzisińska, B.; Żurek, A.; Kandefer-Szerszeń, M. Alpha-Ketoglutarate as a Molecule with Pleiotropic Activity: Well-Known and Novel Possibilities of Therapeutic Use. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 2017, 65, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Yang, H.; Xu, W.; Ma, S.; Lin, H.; Zhu, H.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; Xu, Y.; et al. Inhibition of α-KG-dependent histone and DNA demethylases by fumarate and succinate that are accumulated in mutations of FH and SDH tumor suppressors. Genes Dev 2012, 26, 1326–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, J.L. Metabolic mechanisms of epigenetic regulation. ACS Chem Biol 2013, 8, 2607–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, S.; Hausinger, R.P. Catalytic Mechanisms of Fe(II)- and 2-Oxoglutarate-dependent Oxygenases. J Biol Chem 2015, 290, 20702–20711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Deng, P.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, X.; Zhou, L.; Liu, W.; et al. Alpha-ketoglutarate ameliorates age-related osteoporosis via regulating histone methylations. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 5596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Zeng, L.; Yao, K.; Kong, X.; Wu, G.; Yin, Y. The glutamine-alpha-ketoglutarate (AKG) metabolism and its nutritional implications. Amino Acids 2016, 48, 2067–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.A.; Hong, J.; Asaka, R.; Asaka, S.; Hsu, F.C.; Suryo Rahmanto, Y.; Jung, J.G.; Chen, Y.W.; Yen, T.T.; Tomaszewski, A.; et al. Inhibition of the MYC-Regulated Glutaminase Metabolic Axis Is an Effective Synthetic Lethal Approach for Treating Chemoresistant Ovarian Cancers. Cancer Res 2020, 80, 4514–4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, N.J.; Yoon, H.; Yusuf, R.Z.; Murphy, J.P.; Finley, L.W.; Laurent, G.; Haas, W.; Satterstrom, F.K.; Guarnerio, J.; Zaganjor, E. PHD3 loss in cancer enables metabolic reliance on fatty acid oxidation via deactivation of ACC2. Molecular cell 2016, 63, 1006–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabe, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Saitoh, K.; Sekihara, K.; Monma, N.; Ikeo, K.; Mogushi, K.; Shikami, M.; Ruvolo, V.; Ishizawa, J. Bone marrow adipocytes facilitate fatty acid oxidation activating AMPK and a transcriptional network supporting survival of acute monocytic leukemia cells. Cancer research 2017, 77, 1453–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, I.; Kohno, B. 18FDG-PET/CT: 21st century approach to leukemic tumors in 124 cases. American journal of hematology 2016, 91, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.-L.; Wang, J.-H.; Zhao, A.-H.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.-H.; Chen, T.-L.; Li, J.-M.; Mi, J.-Q.; Zhu, Y.-M.; Liu, Y.-F. A distinct glucose metabolism signature of acute myeloid leukemia with prognostic value. Blood, The Journal of the American Society of Hematology 2014, 124, 1645–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Adane, B.; Khan, N.; Alexeev, E.; Nusbacher, N.; Minhajuddin, M.; Stevens, B.M.; Winters, A.C.; Lin, X.; Ashton, J.M. Subversion of systemic glucose metabolism as a mechanism to support the growth of leukemia cells. Cancer cell 2018, 34, 659–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreitz, J.; Schönfeld, C.; Seibert, M.; Stolp, V.; Alshamleh, I.; Oellerich, T.; Steffen, B.; Schwalbe, H.; Schnütgen, F.; Kurrle, N. Metabolic plasticity of acute myeloid leukemia. Cells 2019, 8, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallogly, M.M.; Lazarus, H.M.; Cooper, B.W. Midostaurin: A novel therapeutic agent for patients with FLT3-mutated acute myeloid leukemia and systemic mastocytosis. Ther Adv Hematol 2017, 8, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonas, B.A.; Pollyea, D.A. How we use venetoclax with hypomethylating agents for the treatment of newly diagnosed patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2019, 33, 2795–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulaklak, K.; Gersbach, C.A. The once and future gene therapy. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 5820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, B.; Wang, Q.; Mao, X.; Hu, S. Saponins From Paris forrestii (Takht.) H. Li Display Potent Activity Against Acute Myeloid Leukemia by Suppressing the RNF6/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Front Pharmacol 2018, 9, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Hui, H.; Yang, H.; Zhao, K.; Qin, Y.; Gu, C.; Wang, X.; Lu, N.; Guo, Q. Wogonoside induces cell cycle arrest and differentiation by affecting expression and subcellular localization of PLSCR1 in AML cells. Blood 2013, 121, 3682–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Perez, C.; Tamborero, D.; Schroeder, M.P.; Antolín, A.A.; Deu-Pons, J.; Perez-Llamas, C.; Mestres, J.; Gonzalez-Perez, A.; Lopez-Bigas, N. In silico prescription of anticancer drugs to cohorts of 28 tumor types reveals targeting opportunities. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.Z.; Yu, S.J.; Bai, H.; Ning, K. TCM-Mesh: The database and analytical system for network pharmacology analysis for TCM preparations. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lv, D.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ye, G.; Chai, Y. Network pharmacology-based strategy for predicting active ingredients and potential targets of Yangxinshi tablet for treating heart failure. J Ethnopharmacol 2018, 219, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xing, C.; Zhou, B.; Ye, H.; Feng, J.; Wu, J.; Gao, S. A regulatory circuitry between miR-193a/miR-600 and WT1 enhances leukemogenesis in acute myeloid leukemia. Exp Hematol 2018, 61, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, L.; Zhou, B.; Li, H.; He, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Chen, M.; Gao, S. A novel miR-375-HOXB3-CDCA3/DNMT3B regulatory circuitry contributes to leukemogenesis in acute myeloid leukemia. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.N.; Um, E.S.; Rahman, M.A.; Kim, J.W.; Park, S.S.; Cho, Y.; Song, H.; Son, S.R.; Jang, D.S.; Kim, W.; et al. Leonurus japonicus Houttuyn induces reactive oxygen species-mediated apoptosis via regulation of miR-19a-3p/PTEN/PI3K/AKT in U937 and THP-1 cells. J Ethnopharmacol 2022, 291, 115129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.N.; Jeon, H.W.; Rahman, M.A.; Park, S.S.; Jeong, S.Y.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, W.; Kim, B. Daemonorops draco Blume Induces Apoptosis Against Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells via Regulation of the miR-216b/c-Jun. Front Oncol 2022, 12, 808174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.; Wang, J.; Hou, J.; Zhang, L.; Liang, H. miR-338-3p Plays a Significant Role in Casticin-Induced Suppression of Acute Myeloid Leukemia via Targeting PI3K/Akt Pathway. Biomed Res Int 2022, 2022, 9214130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.J.; Wu, M.; Zhang, H.; Wu, X.P.; Zhou, L.; Wan, N.; Wu, Z.H. Effects of Qinghuang Powder on Acute Myeloid Leukemia Based on Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and In Vitro Experiments. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2021, 2021, 6195174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, M.L.; Rossi, R.M.; Karnischky, L.; Li, X.; Peterson, D.R.; Howard, D.S.; Jordan, C.T. The sesquiterpene lactone parthenolide induces apoptosis of human acute myelogenous leukemia stem and progenitor cells. Blood 2005, 105, 4163–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelakantan, S.; Nasim, S.; Guzman, M.L.; Jordan, C.T.; Crooks, P.A. Aminoparthenolides as novel anti-leukemic agents: Discovery of the NF-kappaB inhibitor, DMAPT (LC-1). Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2009, 19, 4346–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, P.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, C.; Qi, J.; Qiao, Y.; Kuo, P.C.; Gao, C. NF-κB- and AP-1-mediated DNA looping regulates osteopontin transcription in endotoxin-stimulated murine macrophages. J Immunol 2011, 186, 3173–3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samant, R.S.; Clark, D.W.; Fillmore, R.A.; Cicek, M.; Metge, B.J.; Chandramouli, K.H.; Chambers, A.F.; Casey, G.; Welch, D.R.; Shevde, L.A. Breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 (BRMS1) inhibits osteopontin transcription by abrogating NF-kappaB activation. Mol Cancer 2007, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Sugiyama, H.; Ogawa, H.; Yamagami, T.; Azuma, T.; Oka, Y.; Miwa, H.; Kita, K.; Hiraoka, A.; Masaoka, T.; et al. Expression of the interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-6 receptor, and gp130 genes in acute leukemia. Blood 1994, 84, 2672–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libermann, T.A.; Baltimore, D. Activation of interleukin-6 gene expression through the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol 1990, 10, 2327–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.J.; Hsiao, M.; Chang, J.L.; Yang, S.F.; Tseng, T.H.; Cheng, C.W.; Chow, J.M.; Lin, K.H.; Lin, Y.W.; Liu, C.C.; et al. Quercetin induces mitochondrial-derived apoptosis via reactive oxygen species-mediated ERK activation in HL-60 leukemia cells and xenograft. Arch Toxicol 2015, 89, 1103–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Somasagara, R.R.; Hegde, M.; Nishana, M.; Tadi, S.K.; Srivastava, M.; Choudhary, B.; Raghavan, S.C. Quercetin, a Natural Flavonoid Interacts with DNA, Arrests Cell Cycle and Causes Tumor Regression by Activating Mitochondrial Pathway of Apoptosis. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 24049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.X.; Deng, X.H.; Ai, F.; Yuan, G.Y.; Song, H.Y. Effect of quercetin on the proliferation of the human ovarian cancer cell line SKOV-3 in vitro. Exp Ther Med 2015, 10, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.J.; Chen, Y.R.; Tseng, T.H. Quercetin induces FasL-related apoptosis, in part, through promotion of histone H3 acetylation in human leukemia HL-60 cells. Oncol Rep 2011, 25, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avci, C.B.; Yilmaz, S.; Dogan, Z.O.; Saydam, G.; Dodurga, Y.; Ekiz, H.A.; Kartal, M.; Sahin, F.; Baran, Y.; Gunduz, C. Quercetin-induced apoptosis involves increased hTERT enzyme activity of leukemic cells. Hematology 2011, 16, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Park, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Cho, S.H.; Jeong, M.S.; Kim, S.R.; Seo, J.B.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, K.N. 1-Cinnamoyltrichilinin from Melia azedarach Causes Apoptosis through the p38 MAPK Pathway in HL-60 Human Leukemia Cells. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.U.; Ryu, J.Y.; Lee, J.O.; Lee, S.Y. A systems approach to traditional oriental medicine. Nat Biotechnol 2015, 33, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, F. TCM: Made in China. Nature 2011, 480, S82–S83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, A.C.; Das, T.K.; Shokat, K.M.; Cagan, R.L. Chemical genetic discovery of targets and anti-targets for cancer polypharmacology. Nature 2012, 486, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujral, T.S.; Peshkin, L.; Kirschner, M.W. Exploiting polypharmacology for drug target deconvolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2014, 111, 5048–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stylianopoulos, T.; Munn, L.L.; Jain, R.K. Reengineering the Physical Microenvironment of Tumors to Improve Drug Delivery and Efficacy: From Mathematical Modeling to Bench to Bedside. Trends Cancer 2018, 4, 292–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, R.; Ma, Z. A network pharmacology study on the Tripteryguim wilfordii Hook for treatment of Crohn's disease. BMC Complement Med Ther 2020, 20, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, F.; Barosi, G.; Venditti, A.; Angelucci, E.; Gobbi, M.; Pane, F.; Tosi, P.; Zinzani, P.; Tura, S. Consensus-based definition of unfitness to intensive and non-intensive chemotherapy in acute myeloid leukemia: A project of SIE, SIES and GITMO group on a new tool for therapy decision making. Leukemia 2013, 27, 997–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnett, A.K.; Russell, N.H.; Hills, R.K.; Hunter, A.E.; Kjeldsen, L.; Yin, J.; Gibson, B.E.; Wheatley, K.; Milligan, D. Optimization of chemotherapy for younger patients with acute myeloid leukemia: Results of the medical research council AML15 trial. J Clin Oncol 2013, 31, 3360–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenaux, P.; Mufti, G.J.; Hellström-Lindberg, E.; Santini, V.; Gattermann, N.; Germing, U.; Sanz, G.; List, A.F.; Gore, S.; Seymour, J.F.; et al. Azacitidine prolongs overall survival compared with conventional care regimens in elderly patients with low bone marrow blast count acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2010, 28, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollyea, D.A.; Stevens, B.M.; Jones, C.L.; Winters, A.; Pei, S.; Minhajuddin, M.; D'Alessandro, A.; Culp-Hill, R.; Riemondy, K.A.; Gillen, A.E.; et al. Venetoclax with azacitidine disrupts energy metabolism and targets leukemia stem cells in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Nat Med 2018, 24, 1859–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falini, B.; Mecucci, C.; Tiacci, E.; Alcalay, M.; Rosati, R.; Pasqualucci, L.; La Starza, R.; Diverio, D.; Colombo, E.; Santucci, A.; et al. Cytoplasmic nucleophosmin in acute myelogenous leukemia with a normal karyotype. N Engl J Med 2005, 352, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, E.M.; Chan, S.M.; Minden, M.D.; Murphy, T.; Shlush, L.I.; Schimmer, A.D. Biological and clinical consequences of NPM1 mutations in AML. Leukemia 2017, 31, 798–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostronoff, F.; Othus, M.; Lazenby, M.; Estey, E.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Evans, A.; Godwin, J.; Gilkes, A.; Kopecky, K.J.; Burnett, A.; et al. Prognostic significance of NPM1 mutations in the absence of FLT3-internal tandem duplication in older patients with acute myeloid leukemia: A SWOG and UK National Cancer Research Institute/Medical Research Council report. J Clin Oncol 2015, 33, 1157–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapper, S. The clinical development of FLT3 inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2011, 20, 1377–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daver, N.; Schlenk, R.F.; Russell, N.H.; Levis, M.J. Targeting FLT3 mutations in AML: Review of current knowledge and evidence. Leukemia 2019, 33, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, K.; Konopleva, M. New Treatment Options for Older Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Curr Treat Options Oncol 2021, 22, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, A.S.; Faisal, A.; Gonzalez de Castro, D.; Bavetsias, V.; Sun, C.; Atrash, B.; Valenti, M.; de Haven Brandon, A.; Avery, S.; Mair, D.; et al. Selective FLT3 inhibition of FLT3-ITD+ acute myeloid leukaemia resulting in secondary D835Y mutation: A model for emerging clinical resistance patterns. Leukemia 2012, 26, 1462–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadia, T.M.; Ravandi, F.; Cortes, J.; Kantarjian, H. Toward Individualized Therapy in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Contemporary Review. JAMA Oncol 2015, 1, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovici-Muller, J.; Lemieux, R.M.; Artin, E.; Saunders, J.O.; Salituro, F.G.; Travins, J.; Cianchetta, G.; Cai, Z.; Zhou, D.; Cui, D. Discovery of AG-120 (Ivosidenib): A first-in-class mutant IDH1 inhibitor for the treatment of IDH1 mutant cancers. ACS medicinal chemistry letters 2018, 9, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, K.; Travins, J.; Wang, F.; David, M.D.; Artin, E.; Straley, K.; Padyana, A.; Gross, S.; DeLaBarre, B.; Tobin, E. AG-221, a First-in-Class Therapy Targeting Acute Myeloid Leukemia Harboring Oncogenic IDH2 MutationsAG-221 Therapy for IDH2-Mutant AML. Cancer discovery 2017, 7, 478–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, E.M.; DiNardo, C.D.; Pollyea, D.A.; Fathi, A.T.; Roboz, G.J.; Altman, J.K.; Stone, R.M.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Levine, R.L.; Flinn, I.W. Enasidenib in mutant IDH2 relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Blood, The Journal of the American Society of Hematology 2017, 130, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNardo, C.D.; Stein, E.M.; de Botton, S.; Roboz, G.J.; Altman, J.K.; Mims, A.S.; Swords, R.; Collins, R.H.; Mannis, G.N.; Pollyea, D.A.; et al. Durable Remissions with Ivosidenib in IDH1-Mutated Relapsed or Refractory AML. N Engl J Med 2018, 378, 2386–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantarjian, H.M.; Thomas, X.G.; Dmoszynska, A.; Wierzbowska, A.; Mazur, G.; Mayer, J.; Gau, J.P.; Chou, W.C.; Buckstein, R.; Cermak, J.; et al. Multicenter, randomized, open-label, phase III trial of decitabine versus patient choice, with physician advice, of either supportive care or low-dose cytarabine for the treatment of older patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2012, 30, 2670–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bykov, V.J.; Issaeva, N.; Shilov, A.; Hultcrantz, M.; Pugacheva, E.; Chumakov, P.; Bergman, J.; Wiman, K.G.; Selivanova, G. Restoration of the tumor suppressor function to mutant p53 by a low-molecular-weight compound. Nat Med 2002, 8, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Connor, P.M.; Jackman, J.; Bae, I.; Myers, T.G.; Fan, S.; Mutoh, M.; Scudiero, D.A.; Monks, A.; Sausville, E.A.; Weinstein, J.N.; et al. Characterization of the p53 tumor suppressor pathway in cell lines of the National Cancer Institute anticancer drug screen and correlations with the growth-inhibitory potency of 123 anticancer agents. Cancer Res 1997, 57, 4285–4300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- DiNardo, C.D.; Jonas, B.A.; Pullarkat, V.; Thirman, M.J.; Garcia, J.S.; Wei, A.H.; Konopleva, M.; Döhner, H.; Letai, A.; Fenaux, P.; et al. Azacitidine and Venetoclax in Previously Untreated Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N Engl J Med 2020, 383, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, A.H.; Döhner, H.; Pocock, C.; Montesinos, P.; Afanasyev, B.; Dombret, H.; Ravandi, F.; Sayar, H.; Jang, J.H.; Porkka, K.; et al. Oral Azacitidine Maintenance Therapy for Acute Myeloid Leukemia in First Remission. N Engl J Med 2020, 383, 2526–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, E.L. Antibody-targeted chemotherapy of acute myeloid leukemia using gemtuzumab ozogamicin (Mylotarg). Blood Cells, Molecules, and Diseases 2003, 31, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, J.L.; Hege, K.; Yang, J.; Kalpage, H.A.; Su, Y.; Edwards, H.; Hüttemann, M.; Taub, J.W.; Ge, Y. Targeting multiple signaling pathways: The new approach to acute myeloid leukemia therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2020, 5, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skopek, R.; Palusińska, M.; Kaczor-Keller, K.; Pingwara, R.; Papierniak-Wyglądała, A.; Schenk, T.; Lewicki, S.; Zelent, A.; Szymański, Ł. Choosing the Right Cell Line for Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Research. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.H.; Sun, X.B. [Network pharmacology: New opportunity for the modernization of traditional Chinese medicine]. Yao Xue Xue Bao 2012, 47, 696–703. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, T.; Liu, L.; Liu, W. Network pharmacology-based strategy for predicting therapy targets of Tripterygium wilfordii on acute myeloid leukemia. Medicine (Baltimore) 2020, 99, e23546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, W.; Kong, F.; Yi, P.; Huang, J.; Mao, D.; Peng, W.; Zhang, S. Network Pharmacology-Based Prediction and Verification of the Active Ingredients and Potential Targets of Zuojinwan for Treating Colorectal Cancer. Drug Des Devel Ther 2020, 14, 2725–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Fan, X.; Ma, W. Network pharmacology-based investigation and experimental validation of the mechanism of scutellarin in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Front Pharmacol 2022, 13, 952677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barretina, J.; Caponigro, G.; Stransky, N.; Venkatesan, K.; Margolin, A.A.; Kim, S.; Wilson, C.J.; Lehár, J.; Kryukov, G.V.; Sonkin, D.; et al. The Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia enables predictive modelling of anticancer drug sensitivity. Nature 2012, 483, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Angelo, D.; Schiffer, C.; Stone, R.; Amrein, P.; Fernandez, H.; Bradstock, K.; Tallman, M.; Foran, J.; Juliusson, G.; Liu, D. Interim analysis of a phase II study of the safety and efficacy of gemtuzumab ozogamicin (Mylotarg (R)) given in combination with cytarabine and daunorubicin to patients< 60 years old with untreated acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2002, 100, 745. [Google Scholar]
- Bassan, R.; Intermesoli, T.; Masciulli, A.; Pavoni, C.; Boschini, C.; Gianfaldoni, G.; Marmont, F.; Cavattoni, I.; Mattei, D.; Terruzzi, E.; et al. Randomized trial comparing standard vs sequential high-dose chemotherapy for inducing early CR in adult AML. Blood Adv 2019, 3, 1103–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, T.T.; Lu, Y.; Yan, S.K.; Xiao, X.; Rong, X.L.; Guo, J. Network Pharmacology in Research of Chinese Medicine Formula: Methodology, Application and Prospective. Chin J Integr Med 2020, 26, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haykal, T.; Younes, M.; El Khoury, M.; Ammoury, C.; Tannous, S.; Hodroj, M.H.; Sarkis, R.; Gasilova, N.; Menin, L.; Rizk, S. The pro-apoptotic properties of a phytonutrient rich infusion of A. cherimola leaf extract on AML cells. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2021, 140, 111592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




