Submitted:
25 June 2023
Posted:
26 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Elementary Results
2.1. Some Fundamental Results about the Model (1)
3. Existence Theory
- (C1)
- Let , such that then
- (C2)
- If and then
4. Numerical Scheme
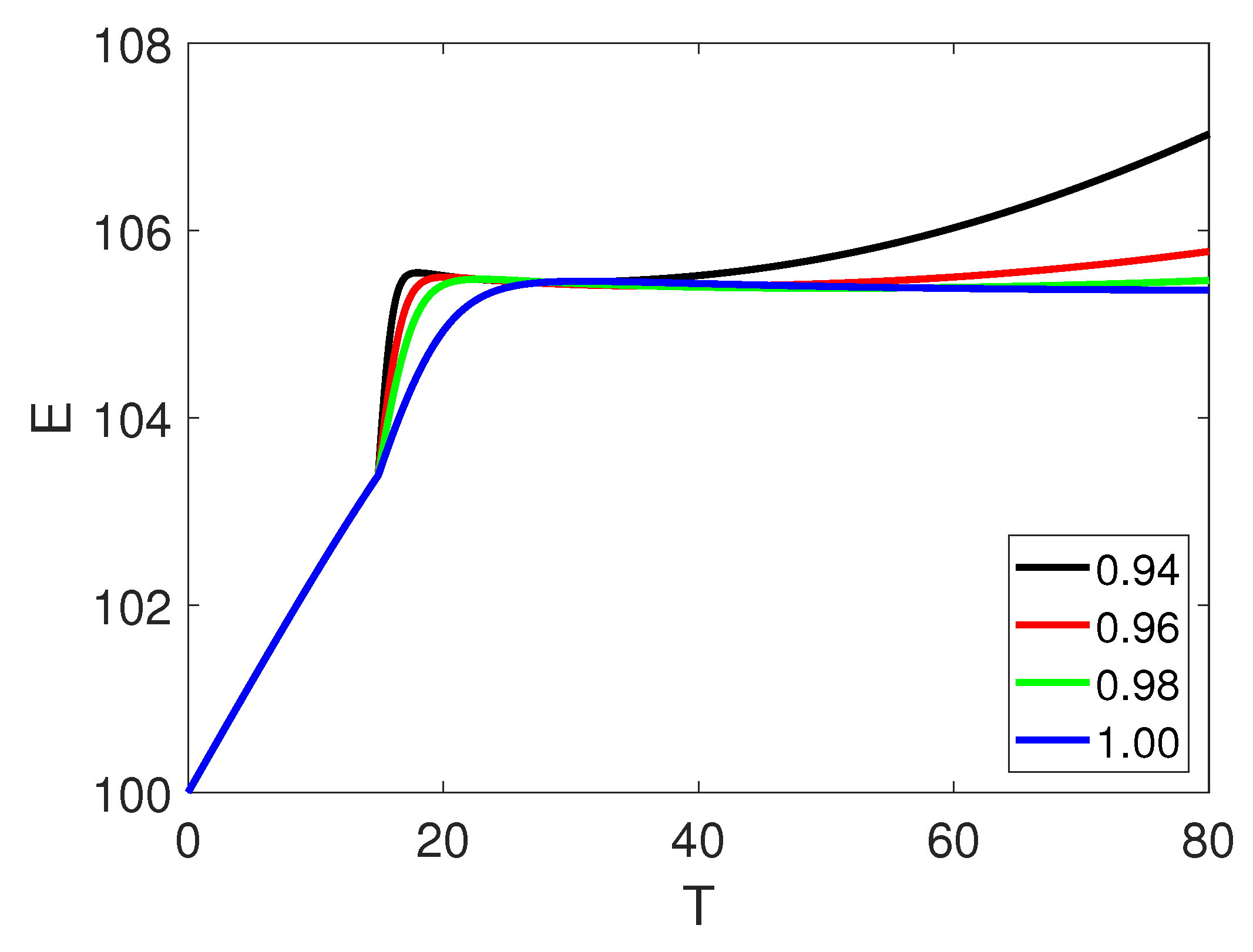
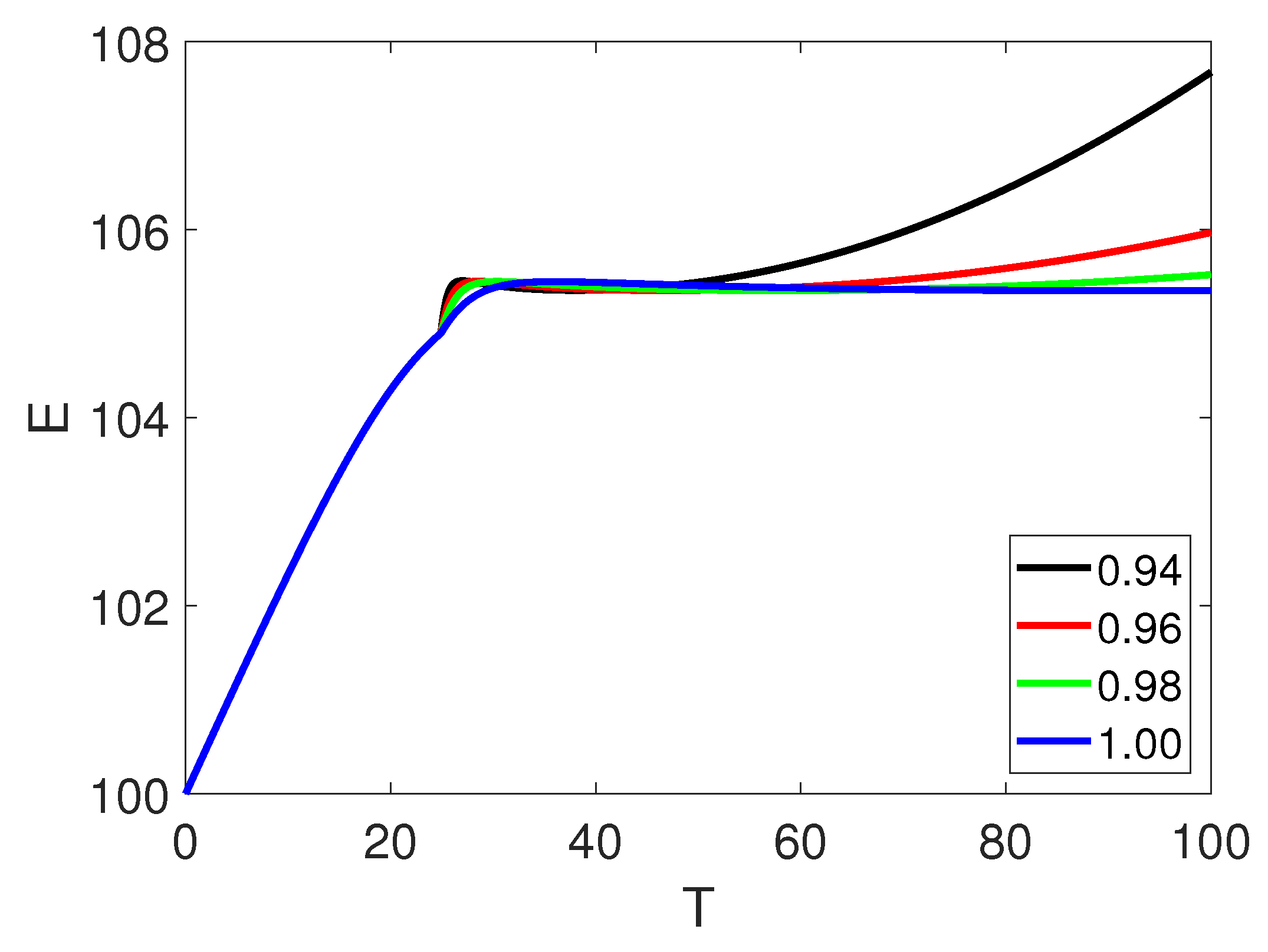
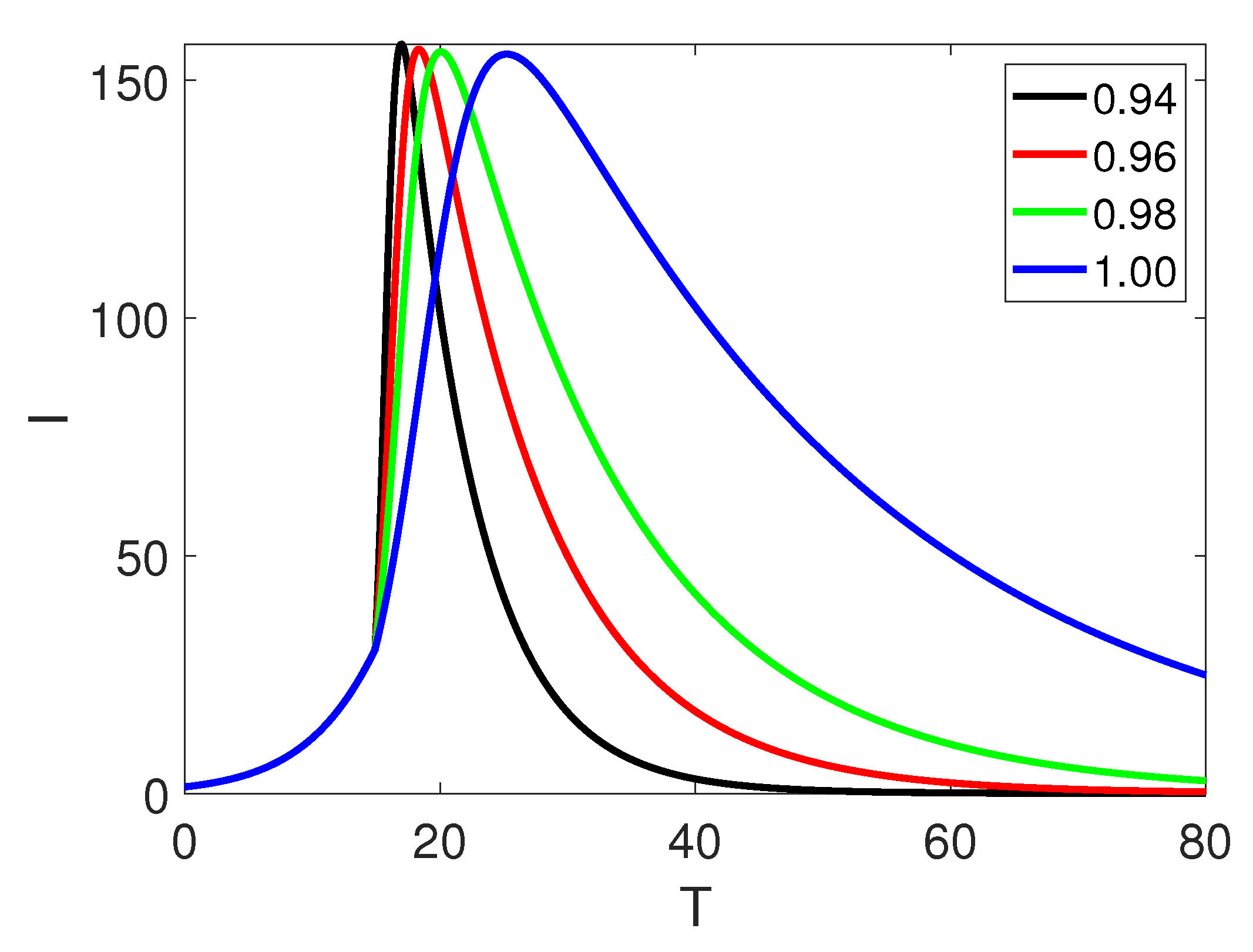
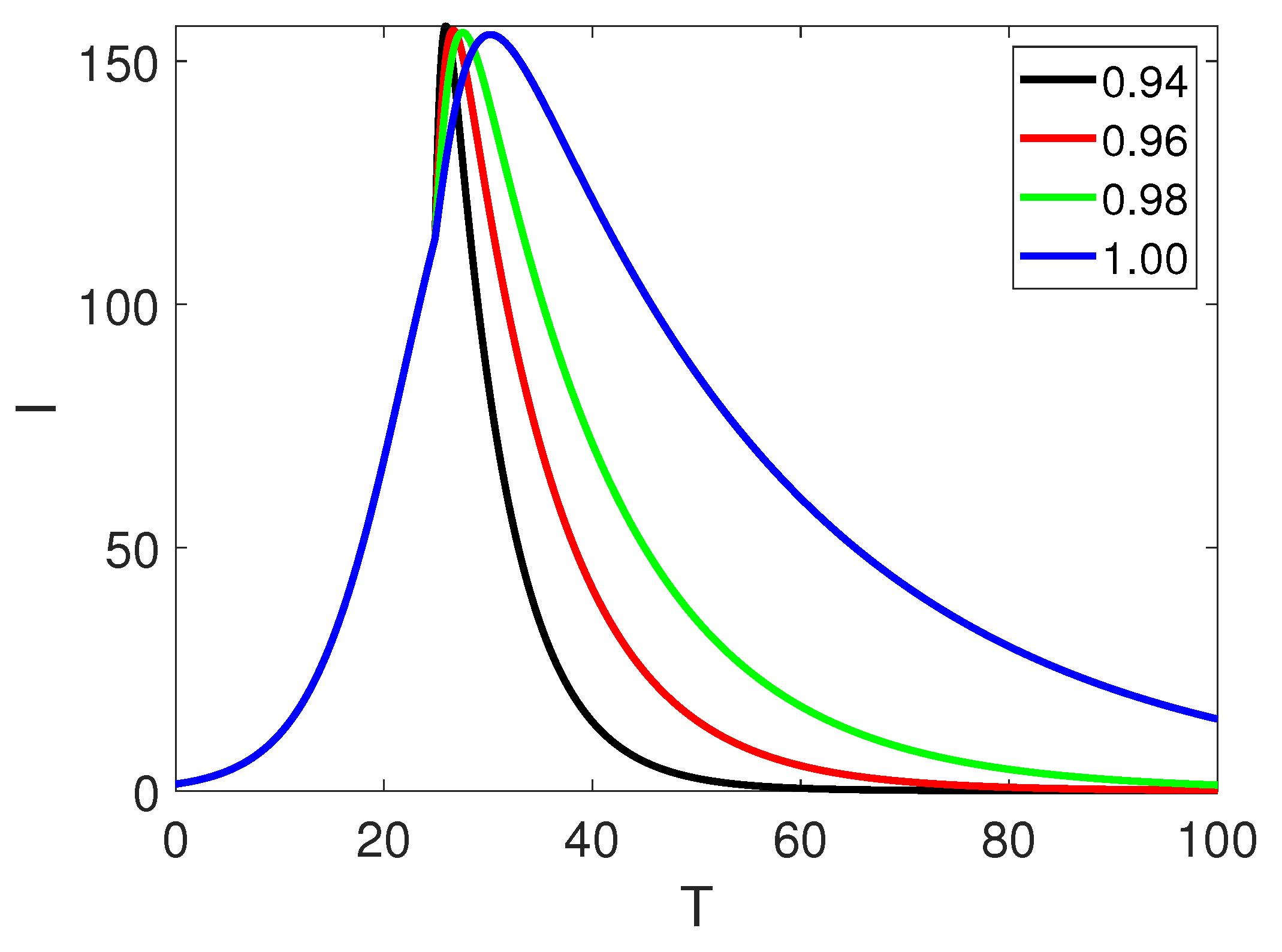
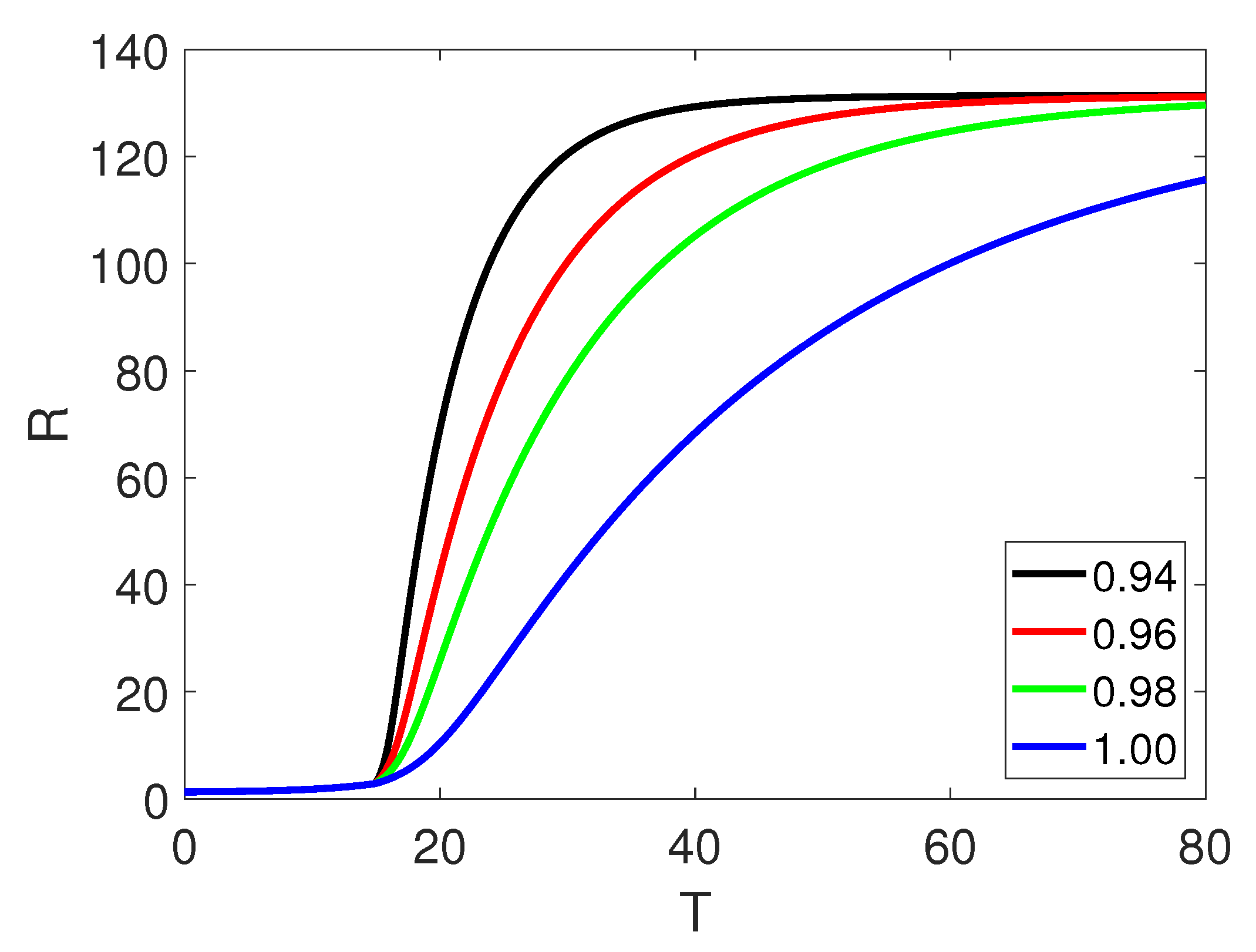
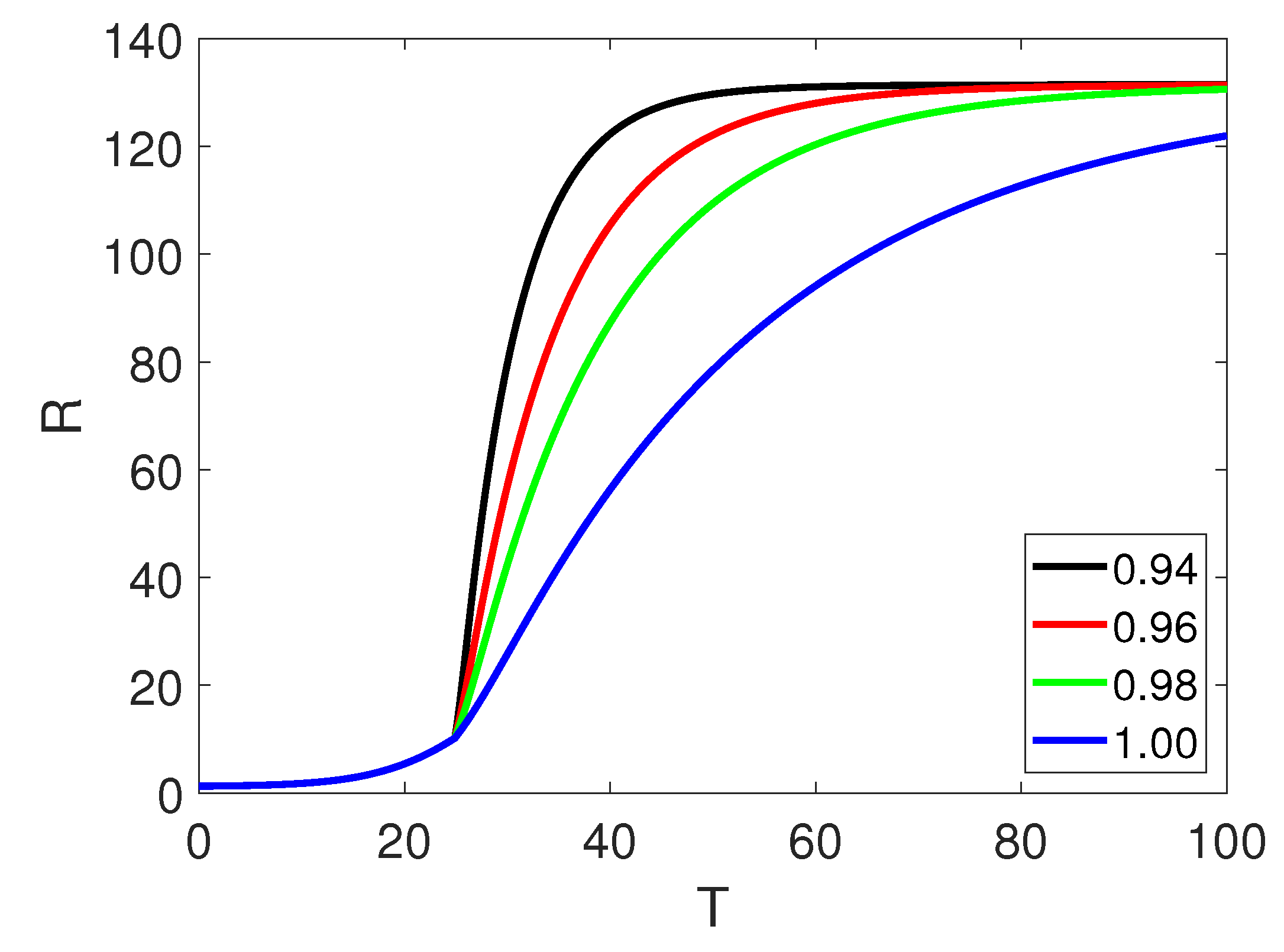
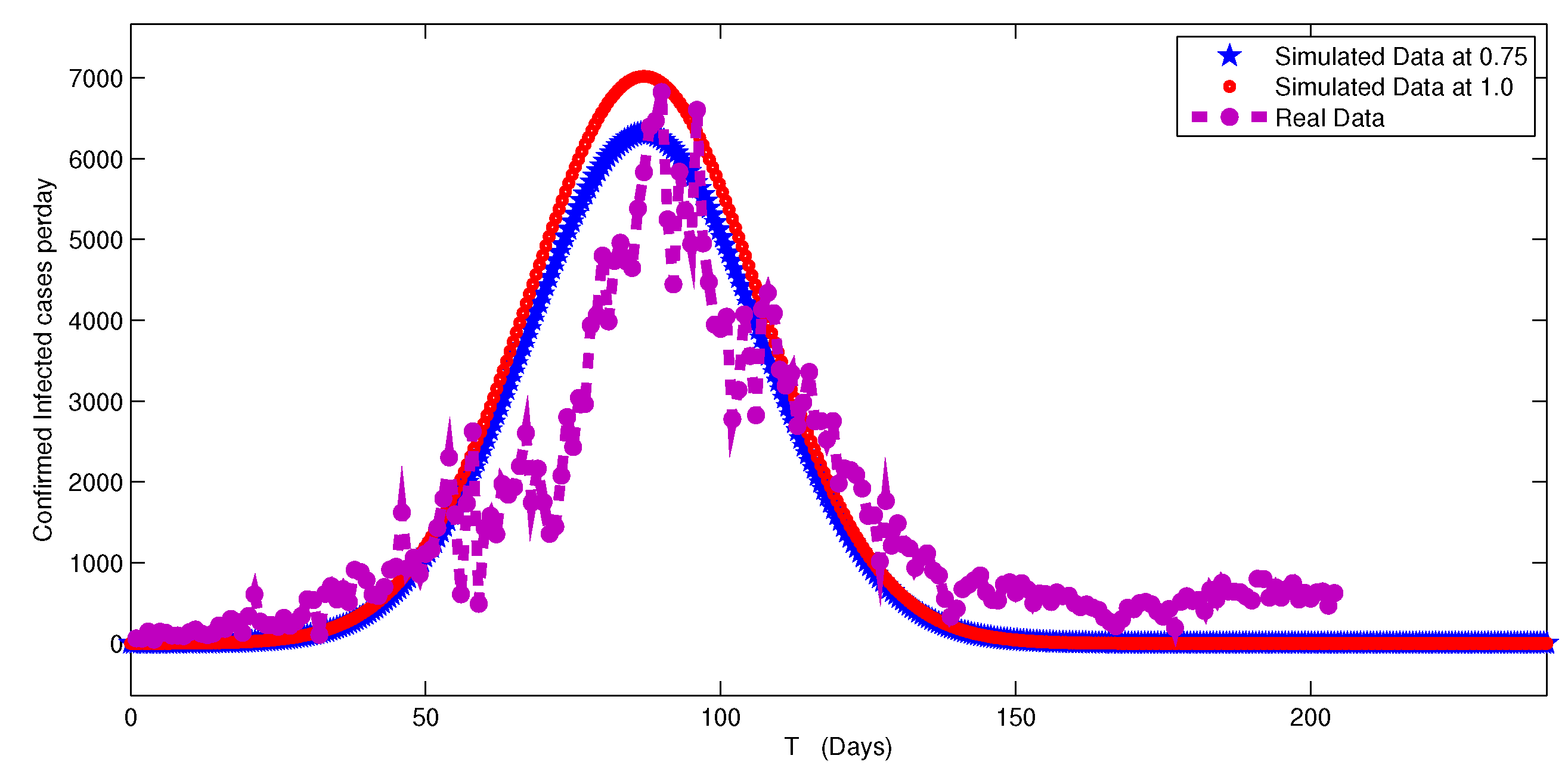
5. Numerical Simulation
6. Discussion and Conclusion
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO), Naming the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and the virus that causes it,Archived from the original on 28 February 2020. Retrieved 28 February, 2020.
- D. S. I.Hui, et.al., The continuing 2019-nCoV epidemic threat of novel coronaviruses to global health-The latest 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China, Bulletin of Mathematical Biology, 91(6) (2020) 264-66. [CrossRef]
- S.Zhao, et. al, Preliminary estimation of the basic reproduction number of novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in China International Journal of Infectious Diseases 92 (2020) 214-217. [CrossRef]
- S.Zhao, et.al., Estimating the unreported number of novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) cases in China in the first half of January 2020, a data-driven Modelling analysis of the early outbreak. J. Clin. Med., 9(2) (2020) 388. [CrossRef]
- I. Nesteruk, Statistics based predictions of coronavirus 2019-nCoV spreading in mainland China, MedRxiv, 4(1) (2020) 1988-1989. [CrossRef]
- K. Shah, R.U. Din, W. Deebani, P. Kumam, Z. Shah, On nonlinear classical and fractional order dynamical system addressing COVID-19, Results in Physics, 24 (2021) 104069. [CrossRef]
- J.A. Lotka, Contribution to the theory of periodic reactions, The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 14(3) (2002) 271-274. [CrossRef]
- N.S. Goel, S.C. Maitra, and E.W. Montroll, On the Volterra and other nonlinear models of interacting populations,Reviews of modern physics, 43(2) (1971) p.231. [CrossRef]
- M.M.Khalsaraei, An improvement on the positivity results for 2-stage explicit Runge-Kutta methods, J.Comput. Appl. Math., 235(1)(2010) 137-143. [CrossRef]
- P. Zhou, X.L. Yang, X.G. Wang, B. Hu, L. Zhang, W.Zhang, H.R.Si, Y. Zhu, B. Li, C.L. Huang, H.D.Chen, A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature, 579(7798) (2020) 270-273. [CrossRef]
- Q. Li, X. Guan, et.al., Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus infected pneumonia, New England Journal of Medicine, 382 (2020) 1199-1207. [CrossRef]
- I.I. Bogoch, et.al., Pneumonia of unknown aetiology in Wuhan, China: potential for international spread via commercial air travel. Journal of travel medicine, 27(2) (2020) taaa008. [CrossRef]
- A.B. Gumel, et al., Modelling strategies for controlling SARS out breaks, Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B, 271(1554) (2004) 2223–2232. [CrossRef]
- R. Kahn, I. Holmdahl, S. Reddy, J. Jernigan, M.J. Mina, R.B.Slayton, Mathematical Modeling to Inform Vaccination Strategies and Testing Approaches for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Nursing Homes, Clinical Infectious Diseases, 74(4) (2022) 597-603. [CrossRef]
- J. Mondal and S. Khajanchi, Mathematical modeling and optimal intervention strategies of the COVID-19 outbreak, Nonlinear Dynamics, 2022 (2022), 1-26. [CrossRef]
- S. Hussain, et.al., On the Stochastic Modeling of COVID-19 under the Environmental White Noise, Journal of Function Spaces, 2022 (2022), Article ID 4320865, 9 pages. [CrossRef]
- J.T. Wu, K. Leung, G.M. Leung, Nowcasting and forecasting the potential domestic and international spread of the 2019-nCoV outbreak originating in Wuhan, China: a modelling study, The Lancet, 395(10225) (2020) 689-697. [CrossRef]
- J.T.Machado, V. Kiryakova, F. Mainardi, Recent history of fractional calculus, Commun. Nonl. Sci. Numer. Simul., 16(3) (2011) 1140-1153. [CrossRef]
- F.C. Meral, T.J. Royston, R. Magin, Fractional calculus in viscoelasticity: an experimental study. Commun. Nonl. Sci. Numer. Simul., 15(4) (2010) 939-945. [CrossRef]
- L.M. Richard, Fractional calculus in bioengineering, part 1, Critical Reviews in Biomedical Engineering 32(1) (2004). [CrossRef]
- M. Dalir, M. Bashour, Applications of fractional calculus, Appl. Math. Sci., 4(21) (2010) 1021-1032. [CrossRef]
- L.M. Richard, Fractional Calculus in Bioengineering. Vol. 2. No. 6. Redding: Begell House, 2006. [CrossRef]
- A.Y.Rossikhin and M. V. Shitikova, Applications of fractional calculus to dynamic problems of linear and nonlinear hereditary mechanics of solids, (1997), 15-67. [CrossRef]
- F. Mainardi, Fractional calculus. In Fractals and fractional calculus in continuum mechanics, Springer, Vienna, 1997.
- M.M.Matar, M. I. Abbas, J. Alzabut, M.K.A. Kaabar, S. Etemad, S. Rezapour, Investigation of the p-Laplacian nonperiodic nonlinear boundary value problem via generalized Caputo fractional derivatives. Advances in Difference Equations, 2021(1) (2021) 1-18. [CrossRef]
- M.Shimizu and W. Zhang, Fractional calculus approach to dynamic problems of viscoelastic materials. JSME Int. J.Ser. C. Mech. Sys. Mach. Ele. Manuf., 42(4) (1999) 825-837. [CrossRef]
- F. Mainardi, An historical perspective on fractional calculus in linear viscoelasticity, Fractional Calculus and Applied Analysis,15(4) (2012) 712-717. [CrossRef]
- Z. Dai, et al., A model of lung parenchyma stress relaxation using fractional viscoelasticity, Medical Eng. Physics, 37(8) (2015) 752-758. [CrossRef]
- M. M. Amirian and Y.Jamali, The concepts and applications of fractional order differential calculus in modeling of viscoelastic systems: a primer, Critical Reviews in Biomedical Engineering 47( 4) (2019) 1-35. [CrossRef]
- H. Khan, J.F. Gómez-Aguilar, A. Alkhazzan, A. Khan, A fractional order HIV-TB coinfection model with nonsingular Mittag-Leffler Law, Mathematical Methods in the Applied Sciences, 43(6)(2020) 3786-3806. [CrossRef]
- C. Celauro, C. Fecarotti, A. Pirrotta, and A. C. Collop, Experimental validation of a fractional model for creep/recovery testing of asphalt mixtures, Construction and Building Materials, 36( 2012) 458-466. [CrossRef]
- G.C.Wu, M. Luo, L.L. Huang, S. Banerjee, Short memory fractional differential equations for new memristor and neural network design, Nonlinear Dynamics, 100(4) (2020) 3611-3623. [CrossRef]
- A. Atangana, D. Baleanu, New fractional derivatives with non-local and non-singular kernel. Theory Appl Heat Transf Model Therm Sci 20(2) (2016) 763-9. [CrossRef]
- E.F.D. Goufo, Application of the Caputo-Fabrizio fractional derivative without singular kernel to Korteweg-de Vries-Burgers equation, Math Model Anal, 21(2)(2016) 188-98. [CrossRef]
- E.F.D. Goufo, A bio mathematical view on the fractional dynamics of cellulose degradation, Fract. Calc. Appl. Anal., 18(3)(2015) 554-64. [CrossRef]
- R.Begum, O. Tunç, H. Khan, H. Gulzar, A. Khan, A fractional order Zika virus model with Mittag-Leffler kernel, Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 146 (2021) 110898. [CrossRef]
- A. Atangana, S.I.Araz, Nonlinear equations with global differential and integral operators:existence, uniqueness with application to epidemiology, Results in Phy., 20 (2021): 103593. [CrossRef]
- S.K. Kabunga, E.F.D.Goufo, V. H. Tuong. Analysis and simulation of a mathematical model of tuberculosis transmission in democratic Republic of the Congo, Adv. Differ. Equ., (1)(2020) 1-19. [CrossRef]
- A. Atangana, S.I. Araz, Mathematical model of COVID-19 spread in Turkey and South Africa: theory, methods and applications, Adv Differ Equ 2020 (2020):659. [CrossRef]
- A. Atangana, S. I. Araz, New concept in calculus:Piecewise differential and integral operators, Chaos Soliton. Fract., 145 (2021) 110638. [CrossRef]
- M.A. Khan and A. Atangana, Modeling the dynamics of novel coronavirus (2019-nCov) with fractional derivative, Alexandria Engineering Journal, 59(4) (2020) 2379-2389. [CrossRef]
- M.A. Khan, A. Atangana, E. Alzahrani, The dynamics of COVID-19 with quarantined and isolation, Advances in Difference Equations, 2020(1) (2020) 1-22. [CrossRef]
- S. Boccaletti, W. Ditto, G. Mindlin, A. Atangana, Modeling and forecasting of epidemic spreading: The case of Covid-19 and beyond, Chaos, Solitons, and Fractals, 135 (2020) 109794. [CrossRef]
- E. Atangana, A.Atangana, Facemasks simple but powerful weapons to protect against COVID-19 spread: Can they have sides effects?. Results in Physics, 19 (2020) 103425. [CrossRef]
- A.Zeb, A. Atangana, Z.A. Khan and S. Djillali, A robust study of a piecewise fractional order COVID-19 mathematical model. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 61(7) (2022), pp.5649-5665. [CrossRef]
- S. Boccaletti, D. William, G. Mindlin, and A. Atangana, Modeling and forecasting of epidemic spreading: The case of Covid-19 and beyond, Chaos, Solitons and Fractals, 135 (2020) 109794. [CrossRef]
- M.S.Arshad.et.al, A Novel 2-Stage Fractional Runge-Kutta Method for a Time Fractional Logistic Growth Model, Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society, 2020 (2020), Article ID 1020472, 8 pages. [CrossRef]
- F. Liu, K. Burrage, Novel techniques in parameter estimation for fractional dynamical models arising from biological systems, Comput. Math. Appl., 62(3) (2011) 822-833. [CrossRef]
- M.T.Hoang, O.F. Egbelowo, Dynamics of a fractional-order hepatitis B epidemic model and its solutions by nonstandard numerical schemes, Mathematical Modelling and Analysis of Infectious Diseases, 2020 (2020) 127-153. [CrossRef]
- F. Zhuo-Jia, et al. Numerical solutions of the coupled unsteady nonlinear convection-diffusion equations based on generalized finite difference method, The European Physical Journal Plus 134(6) (2019) 1-20. [CrossRef]
- B. Wang, L. Li, Y. Wang, An efficient nonstandard finite difference scheme for chaotic fractional-order Chen system. IEEE Access, 8 (2020) 98410-98421. [CrossRef]
- A.J.Arenas, G. González-Parra, B.M. Chen-Charpentier, Construction of nonstandard finite difference schemes for the SI and SIR epidemic models of fractional order, Math. Comput. Simul., 121 (2016) 48-63. [CrossRef]
- R. Lewandowski, and Z. Pawlak, Dynamic analysis of frames with viscoelastic dampers modelled by rheological models with fractional derivatives, Journal of sound and Vibration, 330(5) (2011) 923-936. [CrossRef]
- https://www.worldometers.info/world-population/pakistan-population/ 25 January 2022.
- https://www.coronatracker.com/country/pakistan/ 10 December 2021.
- www.worldometers.info, Current information about COVID-19 in Pakistan, 18 January, 2021.
- A Al Elaiw, F Hafeez, MB Jeelani, M Awadalla, K Abuasbeh .Existence and uniqueness results for mixed derivative involving fractional operatorsAIMS Mathematics 8 (3), 7377-7393.
- Jeelani, M. B. (2023). STABILITY AND COMPUTATIONAL ANALYSIS OF COVID-19 USING A HIGHER ORDER GALERKIN TIME DISCRETIZATION SCHEME. Advances and Applications in Statistics, 86(2), 167–206. https://doi.org/10.17654/0972361723022. [CrossRef]
- A Moumen, R Shafqat, A Alsinai, H Boulares, M Cancan, MB Jeelani ,Analysis of fractional stochastic evolution equations by using Hilfer derivative of finite approximate controllability. AIMS Math 8, 16094-16114. [CrossRef]
- K. Shah, T. Abdeljawad, R. Din, To study the transmission dynamic of SARS-CoV-2 using nonlinear saturated incidence rate, Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 604 (2022) 127915. [CrossRef]
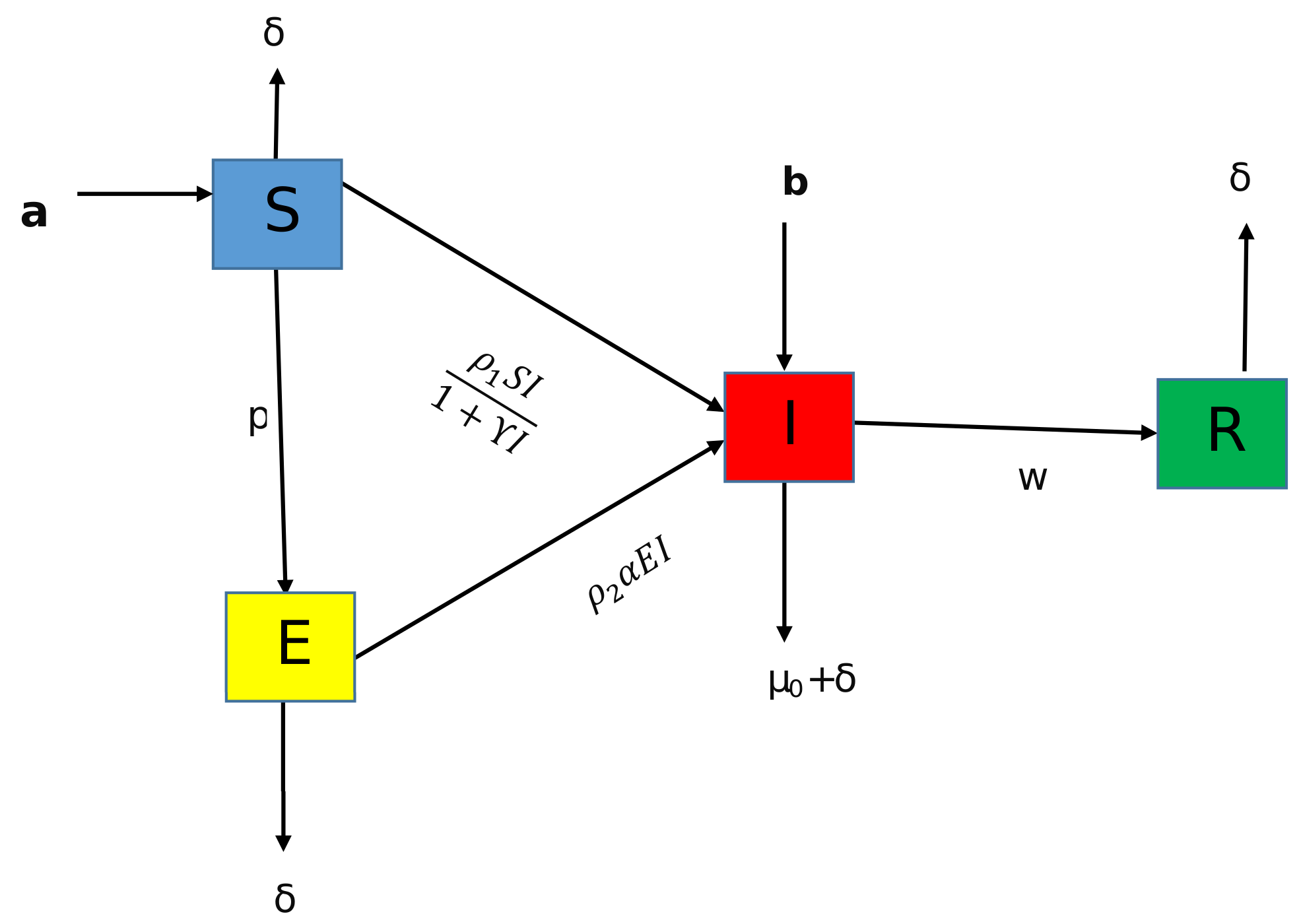
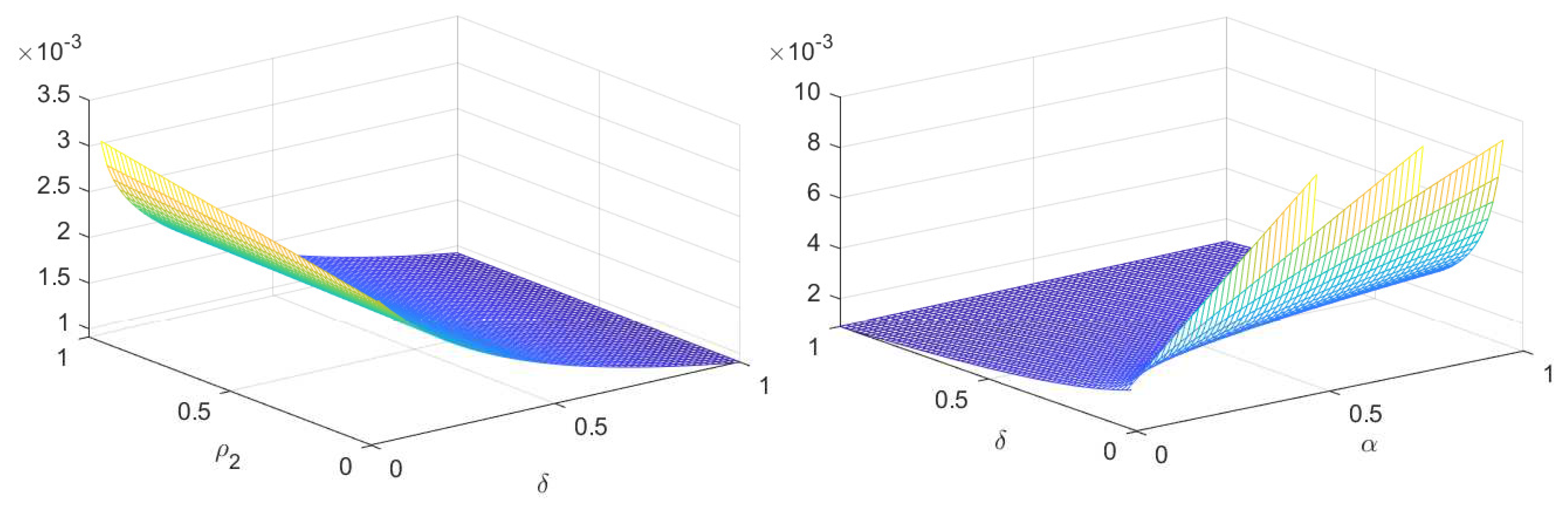
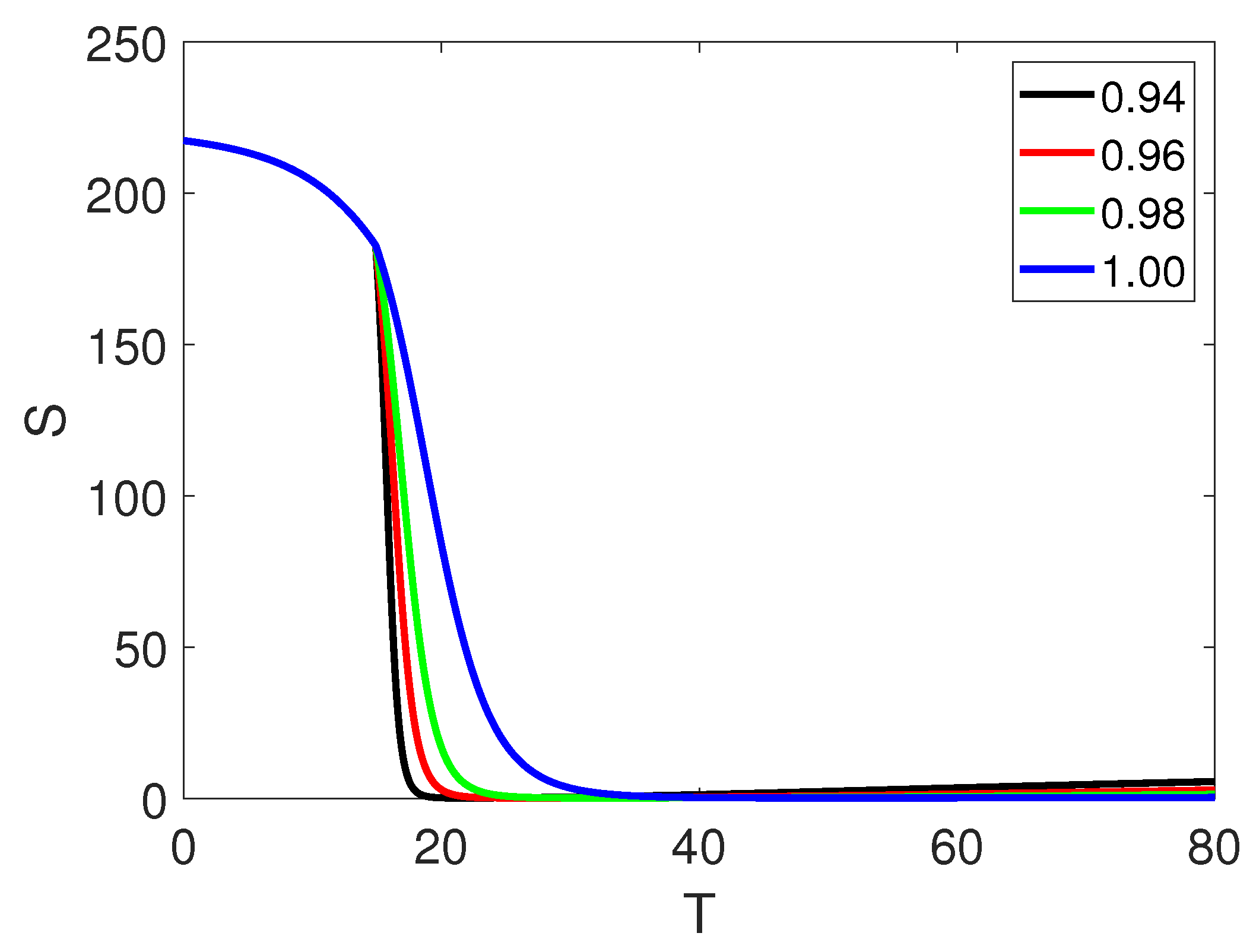
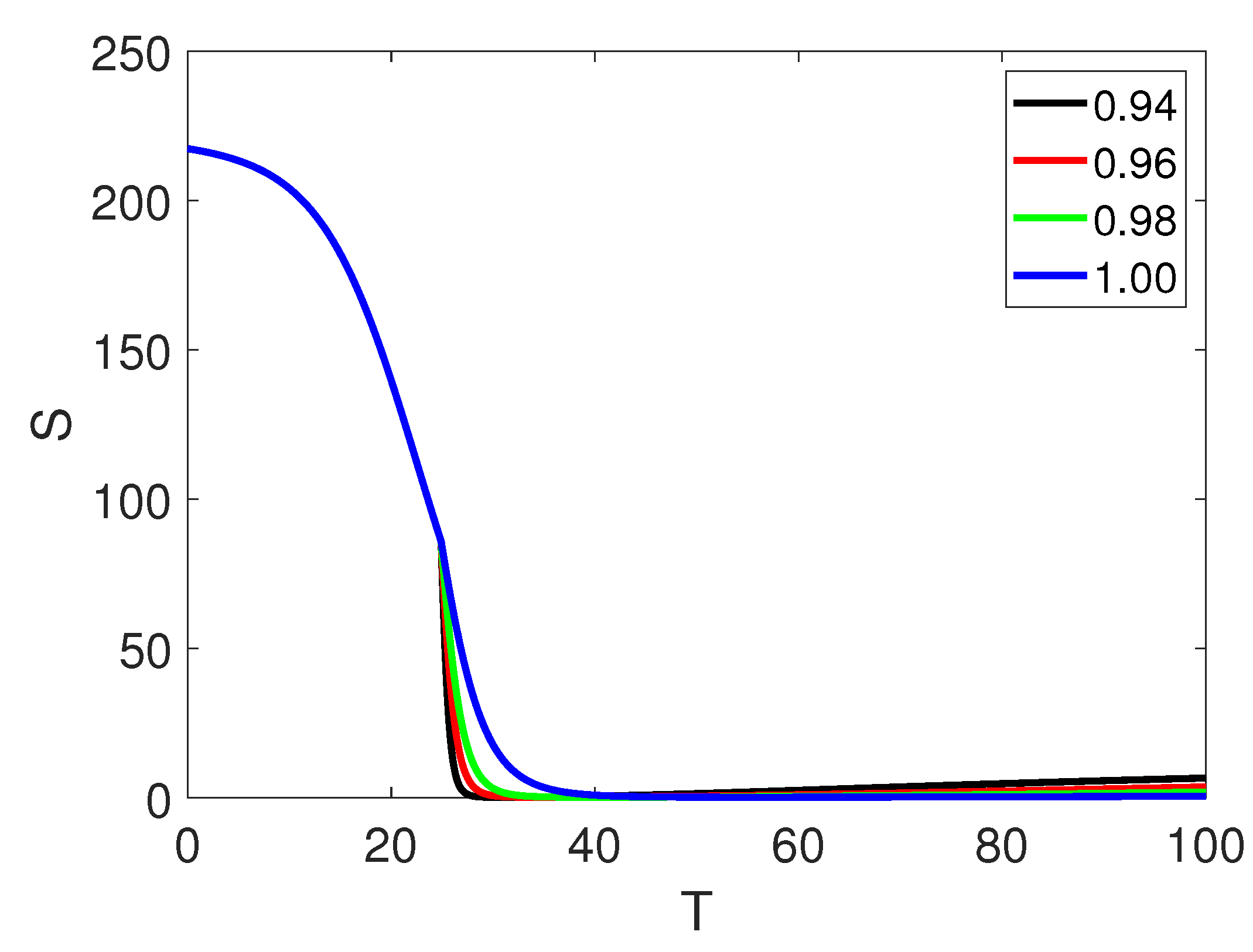
| Nomenclature | Representation |
|---|---|
| S | Susceptible class |
| E | Exposed class |
| I | Infected class |
| R | Recovered class |
| Total initial papulation | |
| Total population at time t | |
| Immigrant to I from E | |
| infection death rate | |
| death rate due to natural way | |
| Recruitment rate | |
| p | Migration rate from S to E |
| Saturation value of virus | |
| rate at which infection is reducing | |
| contact rate | |
| w | rate at which individual gets ride from infection |
| infection rate |
| Nomenclature | Numerical value |
|---|---|
| S | in millions[54] |
| E | 100 in million (assumed) |
| I | in million[54] |
| R | in million [54] |
| 0.135 (assumed) | |
| 0.19 [54] | |
| 0.000065 [54] | |
| 1.43 (assumed) | |
| p | 0.45 |
| 0.00019 (assumed) | |
| 0.0008601 (assumed) | |
| 0.10 (assumed) | |
| w | 0.98 (assumed) |
| 0.020 (assumed) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





