1. Introduction
Foveal hypoplasia is a retinal disorder in which there is a lack of a complete development of the morphology of the fovea. Several disorders are known to be associated with foveal hypoplasia including aniridia (OMIM 106210) and albinism (OMIM 203200) [
1]. It is known that mutations of the
PAX6 gene can cause aniridia. The product of this gene is a transcription factor that is essential for the development of the eyes of vertebrate and non-vertebrate species, and it is considered to be a master regulator for the development of the eye [
2]. This transcription factor is essential for the development of the normal structure of the retinal tissues as well as other eye tissues including the lens and corneal epithelium. It is also expressed in the central nervous system [
3].
There are numerous isoforms of the PAX6 genes of which two major isoforms, canonical PAX6 and PAX6(5a), play a pivotal role in the genesis of the eye.
The canonical PAX6 protein encodes a protein of approximately 46 kDa consisting of 422 amino acids. The PAX6(5a) has an additionally 14 amino acids inserted between exons 5 and 6. The PAX6(5a) isoform is highly expressed in the fovea, and it is associated with the formation of the fovea by interacting with the canonical PAX6 isoform. [
4] These isoforms have two DNA-binding domains, a paired domain (PD) and homeodomain (HD), followed by the proline-serine-threonine-rich domain (PSTD) [
5,
6]. PD is divided into the N-terminal subdomain (NTS) and the C-terminal subdomain (CTS). The subdomains bind to the DNA sequences of the target genes to regulate their transcriptional activity [
7].
Isolated foveal hypoplasia is a rare condition that lacks any other ocular manifestations. The autosomal dominant form of isolated foveal hypoplasia (FVH1, OMIM 136520) is known to be associated with hypomorphic mutations in the
PAX6 gene. Patients with FVH1 present with poor visual acuity and nystagmus. At present, approximately 680 different mutations in the
PAX6 gene are known to cause aniridia while only 12 different mutations of the
PAX6 gene are associated with isolated foveal hypoplasia (Human Gene Mutation Database, Professional version 2023.1,
https://portal.biobase-international.com/hgmd/pro/star/php). The
PAX6 mutations associated with isolated foveal hypoplasia have been found to be in the CTS region which suggests the critical role CTS plays in foveal development [
8,
9]. However, a few mutations were reported to be in other than the CTS, and their functional relevance remains unknown [
10].
We have recently reported two patients with
PAX6 mutations associated with FVH1 [
11]. Both were in other than the CTS, i.e., one was in the NTS and the other in the PSTD.
The purpose of this study was to determine the characteristics of 9 Japanese families with FVH1 and other PAX6-related phenotypes with foveal hypoplasia. The genotype-phenotype correlation of the PAX6 mutations was investigated using functional studies.
2. Materials and Methods
This was a multicenter retrospective case series study. The procedures used conformed to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki, and they were approved by the Ethics Committee of the University of Occupational and Environmental Health Japan (Project identification code 20-148; approved on Jan 18, 2021), Nagoya University (Project identification code 2010-1067; approved on Apr 1, 2010), The Jikei University School of Medicine (Project identification code 24-231 6997; approved on Dec 3, 2012) and National Hospital Organization Tokyo Medical Center (Project identification code R22-046; approved on Jul 28, 2022). A signed informed consent was obtained from all the patients or their parents.
2.1. Clinical Examination
We studied 17 patients from nine families (mean age 24 ± 21 years; range 1 to 68 years) diagnosed with six FVH1 families of which two were reported earlier [
11], two families with aniridia with corneal opacities, and one family with a peripheral corneal opacity and mild iris anomaly (
Table 1). The ocular examinations included measurements of the refractive error and visual acuity, and examinations by slit-lamp biomicroscopy, gonioscopy, and ophthalmoscopy. Optical coherence tomographic (OCT) images were recorded from all patients.
2.2. DNA Sequence Analysis
Genomic DNA was extracted from the peripheral blood using DNA extraction kits. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) followed by Sanger sequencing and/or whole exome sequencing was performed on the coding exons of the PAX6 gene. A detailed description of the sequencing procedures was presented elsewhere [
11,
12]. Reference sequences of PAX6 (NM_000280.4) were used with variations numbered based on its cDNA sequence with +1 corresponding to the first nucleotide of the initiation codon (ATG). The allelic frequency of the variants was searched by databases for the Japanese population (Human Genetic Variation Database, HGVD,
http://www.hgvd.genome.med.kyoto-u.ac.jp/; and the Tohoku Medical Megabank Organization database, Tommo3 (
https://www.megabank.tohoku.ac.jp/tommo/)) or other population databases of the 1000 genomes project (
http://www.internationalgenome.org/1000-genomes-browers) and the Genome Aggregation Database (gnomAD,
https://gnomad.broadinstitute.org/). A conservation of the amino acid residues among humans and other species, e.g., rhesus monkey, mice, elephant, chicken, zebrafish, and frog) was assessed by the UCSC Genome Browser (
https://genome.ucsc.edu/). The pathogenicity of the variants was predicted by six in-silico programs [
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18]. Finally, the pathogenicity of the variants was determined based on the recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) standard and guidelines [
19].
2.3. Functional Assay
2.3.1. Cell Lines and Culture
The human retinal pigment epithelium cell line, ARPE19/HPV16, and the human prostate cancer cell line, PC3, were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA). The immortalized human dopaminergic neuronal precursor cell line, LUHMES, was obtained from Applied Biological Materials Inc. (Richmond, BC, Canada). The LUHMES cells were cultured in DMEM/Ham's F-12 medium with N2 supplement (Gibco Invitrogen, Cat No. 17502048). The ARPE19/HPV16 and PC3 cells were cultured in DMEM/F12 (1:1 mixture of Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium and Ham's F12) and DMEM, respectively. All media were supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% (v/w) penicillin/streptomycin, and cells were maintained at 37° C with 5% CO2.
2.3.2. Antibodies
The anti-DYKDDDDK antibody (019-22394) conjugated with HRP was obtained from Fujifilm (Japan). The anti-beta-actin antibody (A3854) conjugated with HRP was obtained from Sigma (USA), and the anti-GAPDH antibody (sc-47724) conjugated with HRP and anti-Lamin A/C antibody (sc-7293) were obtained from Santa Cruz (USA).
2.3.3. Plasmid Preparation
The expression and reporter plasmids of pTA-5aCON-Luc and pCE-Flag-PAX6(5a) were kind gifts from Drs. Shimizu and Nishina, Department of Development and Regenerative Biology, Medical Research Institute, Tokyo Medical and Dental University, Tokyo [
20]. A DNA fragment containing 5aCON with a minimal promoter excised from pTA-5aCON-Luc and a poly A signal sequence were inserted upstream and downstream of nanoluciferase (Nluc) obtained from pNL1.1 (Promega, USA), respectively. The resulting DNA fragment was then placed in the lentiviral expression plasmid pCDH GFP-T2A-Puromycin (System Biosciences, USA). This resulted in the pCDH 5aCON-Nluc G2P plasmid. Similarly, a DNA fragment containing nine binding sites for GAL4 and adenovirus
major late promoter sequence excised from pGL4.35 luc2P 9xGAL4UAS_Hygro (Promega) and a poly A signal sequence were inserted upstream and downstream of nanoluciferase (Nluc), respectively. The resulting DNA fragment was then placed in the lentiviral expression plasmid pCDH RFP-T2A-Puromycin (System Biosciences), resulting in the pCDH 9xGAL4UAS-Nluc R2P plasmid. PAX6(5a) cDNA was excised from pCE-Flag-PAX6(5a) and inserted into the pcDNA3 RFP plasmid. Each missense mutant identified in this study (P20S, V78E, V83F, R128H, Q255L, V256E, N365K) and the other mutants found in a patient with aniridia (G65Rfs*5), were generated using the PrimeSTAR Mutagenesis Basal Kit (Takara Bio, Japan). To obtain pcDNA3 GAL4-DYK-PAX6-TA(WT) RFP and pcDNA3 GAL4-DYK-PAX6-TA(N379K) RFP, the PSTD region (269-422 aa) was amplified by PCR and added downstream of GAL4-Flag (PMID: 11282029). The resulting DNA fragment was then placed in the pcDNA3 RFP plasmid. Oligonucleotides were used to generate the mutants and the deletion constructs are shown in
Table 3.
2.3.4. Establishment of Lentivirus and Stable Expression Cells
Non-proliferative lentivirus was packaged using the lentivirus packaging system purchased from the System Biosciences. Briefly, the pCDH 5aCON-Nluc G2P or pCDH 9xGAL4UAS-Nluc R2P plasmids were mixed with a pPACKH1 plasmid mix consisting of pPACKH1-GAG, pPACKh1-REV, and pVSV-G (System Biosciences), and then transfected into COS1 cells using X-tremeGENE 9 DNA Transfection Reagent (Roche Molecular Biochemicals, Switzerland). After 36 hours, the culture medium was filtered through a 0.45 µm syringe filter and directly added to the PC3 cells. The infected cells were then cultured with 10 µg/mL puromycin (ant-pr; InvivoGen, CA, USA) for more than 2 weeks to establish the PC3-5aNluc and PC3-9Gal4Nluc cells.
2.3.5. RNA Preparation and Quantitative RT-PCR
Total RNA was purified using the miRNeasy Kit (217084; Qiagen, USA). qRT-PCR was performed as described [
21] using the following primer sets: Hs01088114_m1 for PAX6, and Hs01060665_g1 for β-actin (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, USA). The values were normalized to human β-actin expression. The comparative cycle time method was used to quantify the gene expression, and all samples were analyzed in duplicate.
2.3.6. Transfection of Expression Plasmid
A total of 1x105 PC3-5aNluc, PC3-9Gal4Nluc, and PC3 cells were seeded into a 35 mm dish. The following day, 5 µg of plasmid expressing each PAX6 protein was transfected into the cells using X-treme GENE 9. After 48 hours, the cells were washed twice with PBS and collected. Samples for the reporter assays and pull-down assays were immediately analyzed while the remaining samples were stored at -80°C for Western blot analysis.
2.3.7. Reporter Assay
After collecting the cells, 200 µL of Reporter Lysis Buffer (Promega) was added to the cell pellet and sonicated for 10 seconds. The cell lysate was then centrifuged at 10,000 g for 2 minutes, and 100 µL of the resulting supernatant was mixed with 100 µL of the reagent from the Nano-Glo Luciferase Assay System (Promega) in a 96-well white plate. The light intensity was measured using a luminometer (Luminescencer JNII RAB-2300; Atto, Japan).
2.3.8. Cell Fractionation and Pull-Down Assay
The cell pellets for the reporter assay were resuspended in 200 µL of hypotonic buffer A containing 10 mM Hepes–KOH (pH 7.9), 10 mM KCl, 0.1 mM EDTA–NaOH (pH 8.0), 0.1 mM EGTA, 1 mM dithiothreitol (DTT), and 0.5 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF). The suspension was incubated on ice for 15 minutes. Nonidet-P40 was added to a final concentration of 0.25% (5 µL of 10% stock solution), and the cells were gently resuspended and then centrifuged at 4,200 g for 5 minutes. The resulting supernatant was collected as the cytoplasmic fraction. For the nuclear pellet, two different methods were used for the analysis. To determine the nucleoplasmic to cytoplasmic ratio of PAX6 by Western blot, 205 µL of hypotonic buffer was added to the nuclear pellet to equalize the volumes of the nucleoplasmic and cytoplasmic fractions. Both fractionated samples were sonicated for 15 seconds and then centrifuged at 21,000 g for 10 minutes. Then, 40 µL of each resulting supernatant, the nucleoplasmic (Nuc) and cytoplasmic (Cyt) fractions, were used for Western blot analysis.
For the pull-down assays, three dishes were prepared for one condition. The nuclear pellet was resuspended in 150 µL of high salt buffer C containing 20 mM Hepes–KOH (pH 7.9), 0.4 M NaCl, 1 mM EDTA–NaOH, 1 mM EGTA, 1 mM DTT, and 0.5 mM PMSF, and incubated for 30 minutes on ice. The suspension was then centrifuged at 21,000 g for 10 minutes, and the resulting supernatant was used for the pull-down assay (50 µL) as well as input (20 µL). Single-stranded oligonucleotides (see
Table 3) were annealed, and biotinylated oligonucleotides were bound to M280 magnetic beads (Veritas) in buffer K which contained 100 mM KCl, 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), 0.05% NP-40, and 10% glycerol. The bound oligonucleotides were washed three times with buffer K using a magnetic stand and mixed with 50 µL of each Nuc fraction and 800 µL of buffer K. After binding for 30 minutes at room temperature using a rotating disk device, the samples were washed five times with buffer K using a magnetic stand. The resulting pellet was suspended in 40 µL of RIPA buffer and used for subsequent Western blotting.
2.3.9. Western Blot and Slot Blot
Next, 10 µL of 2x loading buffer and 3 µL of 1 M DTT were added to the sample prepared for the reporter assay, cell fractionation, and pull-down analysis. The mixture was boiled for 5 minutes and then subjected to SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). The separated proteins were transferred onto polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membranes, and respective primary antibodies, anti-Flag-HRP, anti-β-HRP, anti-GAPDH-HRP, and anti-Lamin A/C, were diluted as follows: anti-Flag and anti-β-actin antibodies were diluted 1/10,000, anti-GAPDH antibody was incubated at 1/1,000 dilution for 1 hour, and anti-Lamin A/C antibody was incubated at 1/1,000 dilution for 1 hour. Secondary anti-mouse IgG antibody conjugated HRP against anti-Lamin A/C antibody was diluted at 1/7,500 and incubated for 45 minutes. Bound antibodies conjugated with the target proteins were detected using a chemiluminescence kit (GE Healthcare Bio-Sciences, USA). The signal intensity was measured with the LAS 4000 Mini and Multi Gauge software version 3.0 (Fujifilm).
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Findings and Clinical Features
Sequence analysis of the PAX6 gene revealed seven heterozygous mutations, c.150_151insA (p.G65Rfs*5), c.233T>A (p.V78E), c.247G>T (p.V83F), c.383G>A (p.R128H), c.746A>T (p.Q255L), c.767T>A (p.V256E), and c.1032+5G>A. In addition, mutations c.58C>T (p.P20S) and c.1095T>G (p.N365K) were reported in our earlier study [
11] (
Table 2). All were novel mutations except for c.383G>A (p.R128H) that was reported in a family with mild aniridia [
22]. None of the mutations were found in population databases of HGVD, Tommo3, the 1000 genomes project, or gnomAD. All-corresponding codons were located at residues conserved among humans and other species, e.g., rhesus monkey, mouse, elephant, chicken, zebrafish, and frog, according to the UCSC Genome Browser. Pro20 and Gly65 were in the NTS; Val78, Val83, and Arg128 were in the CTS; Gln255 and Val256 were in the HD; and c.1032 (Gln344) and Asn365 were in the PSTD. The in-silico programs predicted varying degrees of scores for pathogenicity for all variants (
Table 2). Based on the ACMG criteria, all variants were considered to be pathogenic.
Table 2.
Pathogenicity assessment of the mutations in the PAX6 gene.
Table 2.
Pathogenicity assessment of the mutations in the PAX6 gene.
| Nucleotide Change |
Amino Acid Change |
Polyphen2 HumDIV [13] (Cutoff=0.85) |
GERP++ [14] (Cutoff=2) |
REVEL [15] (Cutoff=0.5)* |
M-CAP [16] (Cutoff=0.025) |
CADD Phred [17] (Cutoff=15)** |
SIFT [18] (Cutoff=0.05) |
Pathogenicity (Evidenced Criteria Points)*** |
| c.58C>T |
p.P20S |
0.980 |
4.48 |
0.927 |
0.939 |
23.900 |
0.010 |
Pathogenic
(PS=1, PM=2, PP=4) |
| c.150_151insA |
p.G65Rfs*5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pathogenic
(PVS=1, PS=1, PM=2, PP=1) |
| c.233T>A |
p.V78E |
1.000 |
5.35 |
0.979 |
0.957 |
28.600 |
0.000 |
Pathogenic
(PS=1, PM=3, PP=4) |
| c.247G>T |
p.V83F |
1.000 |
5.35 |
0.942 |
0.916 |
29.800 |
0.000 |
Pathogenic
(PS=1, PM=2, PP=4) |
| c.383G>A |
p.R128H |
0.997 |
3.83 |
0.933 |
0.786 |
28.100 |
0.000 |
Pathogenic
(PS=2, PM=3, PP=3) |
| c.764A>T |
p.Q255L |
0.999 |
5.47 |
0.984 |
0.822 |
34.000 |
0.000 |
Pathogenic
(PS=1, PM=2, PP=3) |
| c.767T>A |
p.V256E |
1.000 |
5.53 |
0.976 |
0.824 |
32.000 |
0.000 |
Pathogenic
(PS=2, PM=3, PP=3) |
| c.1032+5G>A |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pathogenic
(PVS=1, PM=2, PP=2) |
| c.1095T>G |
p.N365K |
0.736 |
NA |
0.499 |
0.145 |
8.266 |
0.020 |
Pathogenic
(PS=2, PM=2, PP=2) |
Table 3.
Oligonucleotides.
Table 3.
Oligonucleotides.
| PAX6 P20S FW |
GGGCGGTCACTGCCGGACTCCACCC |
| PAX6 P20S RV |
GCAGTGACCGCCCGTTGACAAAGAC |
| PAX6 V78E FW |
CGAGAGAAGCGACTCCAGAAGTTGT |
| PAX6 V78E RV |
GTCGCTTCTCTCGGTTTACTACCAC |
| PAX6 V83F FW |
CCAGAATTTGTAAGCAAAATAGCCC |
| PAX6 V83F RV |
TTACAAATTCTGGAGTCGCTACTCT |
| PAX6 R128H FW |
TTCTTCACAACCTGGCTAGCGAAAA |
| PAX6 R128H RV |
AGGTTGTGAAGAACTCTGTTTATTG |
| PAX6 Q255L FW |
GAATACTGGTATGGTTTTCTAATCG |
| PAX6 Q255L RV |
CATACCAGTATTCTTGCTTCAGGTA |
| PAX6 V256E FW |
TACAGGAATGGTTTTCTAATCGAAG |
| PAX6 V256E RV |
AACCATTCCTGTATTCTTGCTTCAG |
| PAX6 N365K FW |
GGTGAAGGGGCGGAGTTATGATACC |
| PAX6 N365K RV |
CCGCCCCTTCACCGAAGGGCTGGTG |
| 5aCON FW 5-biotin |
(Biothin)ATCTGAACATGCTCAGTGAATGTTCATTGACTCTC |
| 5aCON RV |
GAGAGTCAATGAACATTCACTGAGCATGTTCAGAT |
| TA FW |
(EcoRI) gaattcGAAAAACTGAGGAATCAGAGAAG |
The associated phenotypes were FVH1 for p.P20S, p.V78E, p.V83F, p.R128H, p.Q255L, and p.N365K (
Figure 1 and
Figure 2), aniridia with corneal opacity for p.G65Rfs*5 and p.V256E, and peripheral corneal opacity with mild iris anomaly for c.1032+5G>A (
Table 1). In a family with p.V256E (family 7), the proband who had bilateral aniridia with corneal opacity and cataract also had retinal detachments after cataract or glaucoma surgery on both eyes. The mother with the same mutation had no visual symptoms and was later found to have unilateral partial aniridia (
Figure 3). She had mild foveal hypoplasia with reduced foveal pits in both eyes. Regardless of the genotype, all examined patients had bilateral foveal hypoplasia detected in the OCT images. Three patients from family 1 (p.P20S), mother of family 7 (p.V256E), and Patient 17 had mild foveal hypoplasia of Grade 1b according to the classification by Thomas et al [
23,
24]. However, the other patients had severe Grade 3~4 foveal hypoplasia (
Table 1). Regardless of the genotype, goniodysgenesis was observed in 7 (88%) of the 8 patients who underwent gonioscopy. Of the 16 patients from nine families, the corrected visual acuity ranged from light perception to -0.2 logMAR units. Myopia ranging from -2.0 D to -12.5 D (median -4.3 D) was observed in 16 of the examined patients. Nystagmus was present in 5 (36%) of the 14 examined patients.
3.2. Functional Assays
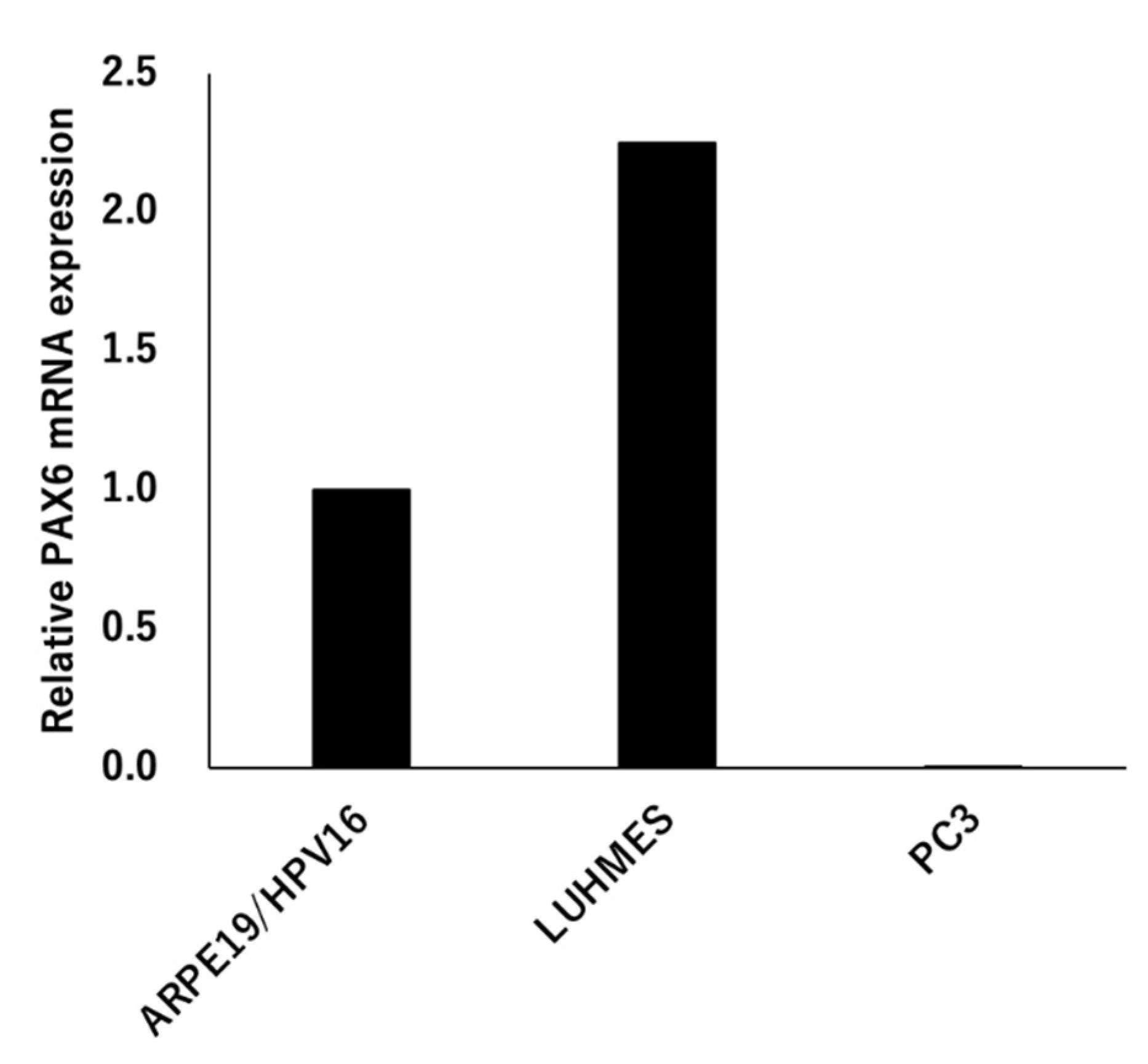
3.2.1. Expression Analysis of PAX6
The expression of PAX6 was analyzed using three types of cells, ARPE19/HPV16, LUHMES, and PC3. The expression of the mRNA of PAX6 increased LUHMES by 2.25 times when ARPE19/HPV16 was set to 1, but PC3 was not expressed (
Figure 4). The PC3 cells that were transfected with Flag-PAX6 and Flag-PAX6(5a) and immunoprecipitated with Flag were analyzed by Western blotting using two kinds of commercially available antibodies. These antibodies recognized Flag-PAX6, but the sensitivity and specificity of recognizing endogenous PAX6 was too low to assess (data not shown). These results suggested that ARPE19/HPV16 and LUHMES express PAX6, but it was not determined which isoform they expressed.
3.2.2. PAX6 Mutants and Transcriptional Activity via 5aCON
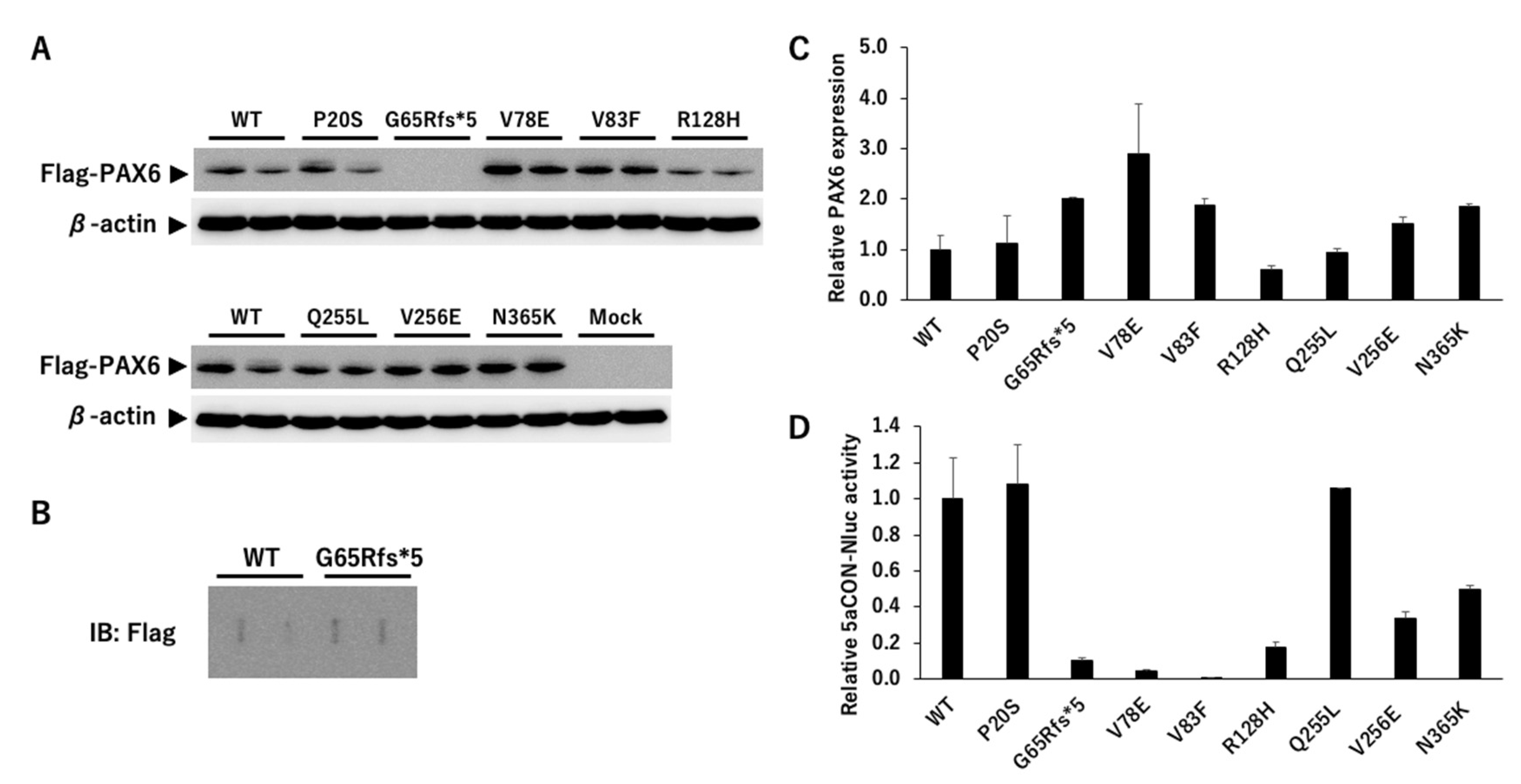
5aCON-Nluc (nanoluciferase) was stably transfected into PC3 cells not expressing PAX6 (PC3-5aNluc). 5aCON is a consensus site to which PAX6(5a) binds, and PAX6(5a) is known to increase the promoter activity with 5aCON. We generated different PAX6 mutants and transfected these mutants and wild-type into 5aCON-Nluc stably transfected PC3 cells. First, we examined whether there was any change in the expression level between the wild-type PAX6 and its mutants using a Flag antibody. Because the total number of amino acids in the PAX6 mutants, other than G65Rfs*5, is the same as that of the wild-type, the signals were observed at the same molecular weight positions (
Figure 5A). However, G65Rfs*5 was not observed (see
Figure 5A) because its molecular weight was less than 10 kDa even with a Flag tag due to a frameshift mutation. Because the molecular weights of PAX6 WT and G65Rfs*5 differed significantly and were expected to have different transcriptional capacities, the proteins were directly immobilized on a PVDF membrane using a slot blot apparatus. Although the signal was weak, it was possible to determine the expression ratio with the wild-type (
Figure 5B). Because the specificity of the anti-Flag antibody is high, we believe that the detected signal is derived from the Flag fusion protein. The results of normalizing the expression level of Flag with the expression level of β-actin are shown in
Figure 5C. The expression ratio of PAX6 mutants varied greatly and ranged from 0.6- to 2.9-fold.
Next, we measured the Nluc activity to evaluate the transcriptional activity of PAX6 dependent on 5aCON. Because the Nluc activity is affected by the expression level of PAX6, it was normalized using the expression ratio obtained from the data shown in
Figure 5C. While P20S and Q255L did not affect the transcriptional activity, all of the other mutants reduced the transcriptional activity (
Figure 5D). More specifically, the mutants of CTS, V78E, V83F, and R128H, significantly decreased the transcriptional activity as well as the truncation mutant of G65Rfs*5.
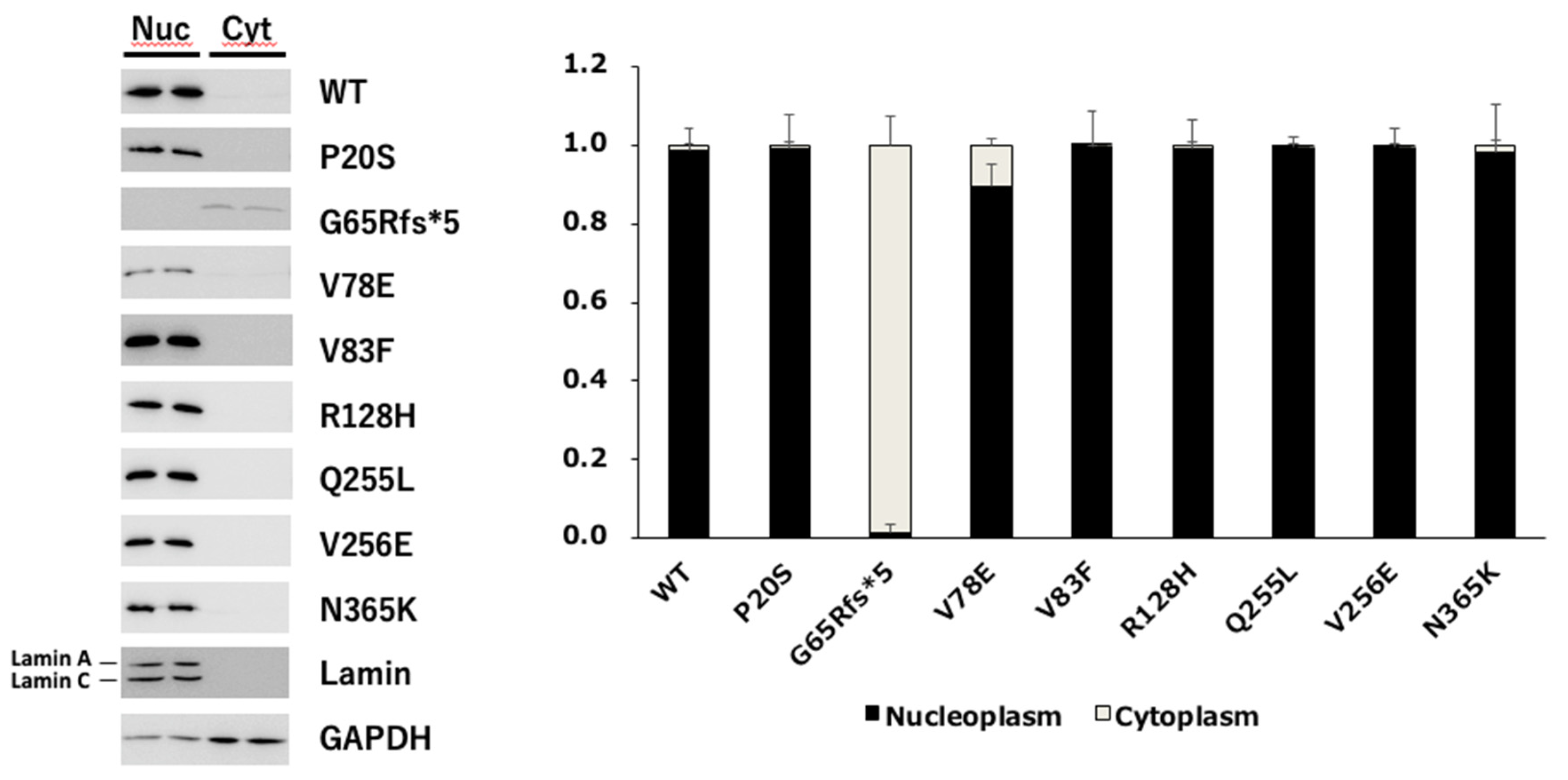
3.2.3. Nuclear Translocation Analysis of PAX6 Mutants
We first examined the nuclear location of each PAX6 mutant because some mutants were unable to activate the 5aCON-dependent transcriptional activity. PC3 cells expressing each mutant were fractionated into nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions, and the expression level of PAX6 in each fraction was determined by Western blotting (
Figure 6). To evaluate the accuracy of the PVDF , we also examined the expression levels of lamin A/C and GAPDH in the nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions. As expected, lamin A/C was almost detected in the nuclear fraction, while GAPDH was mainly detected in the cytoplasmic fraction. Based on these results, we examined whether the cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions could be effectively separated. Under these fractionation conditions, we examined the subcellular localization of PAX6. We found that most of the G65Rfs*5 mutants remained in the cytoplasm and did not translocate into the nucleus, while the other mutants translocated into the nucleus.
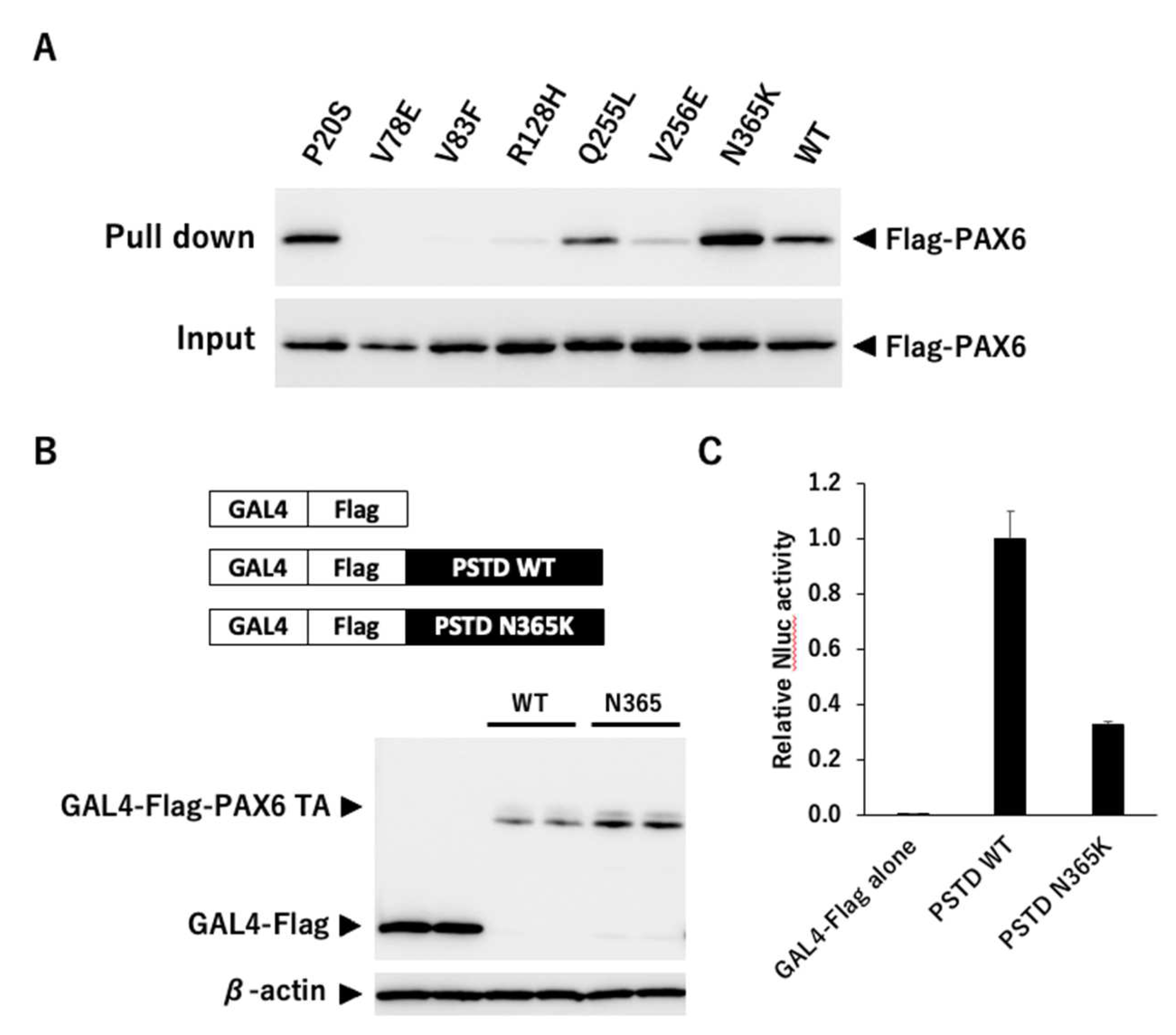
3.2.4. Binding Analysis of PAX6 Mutants and 5aCON
Because we found that mutants other than G65Rfs*5 could translocate into the nucleus, we next examined whether these mutants could bind to 5aCON. We mixed an oligonucleotide containing the sequence of 5aCON immobilized on magnetic beads with nuclear protein extracted from the nucleus of each cell, and analyzed the PAX6 protein bound to 5aCON by Western blotting. P20S and Q255L, which had normal transcriptional activity, bound to 5aCON as much as or even more than the wild-type PAX6 (
Figure 7A). In addition, V78E, V83F, R128H, and V256E, which have low 5aCON transcriptional activity, had low binding to 5aCON. On the other hand, N365K had a 50% reduction in the transcriptional activity of 5aCON, but bound more to 5aCON than the wild-type PAX6.
3.2.5. Transcription Activity Analysis using Gal4 System
Although N365K was able to bind to 5aCON, its 5aCON-mediated transcriptional activity was low. The GAL4 transcription system was used to determine the reason for this. The GAL4 protein is a transcription factor that binds to a specific DNA sequence known as the Upstream Activating Sequence (UAS) which is located upstream from the target gene. The binding of GAL4 to UAS recruits other transcription factors including the general transcription factors such as TATA-binding protein (TBP) and RNA polymerase II, to form a pre-initiation complex that initiates transcription of the target gene. As a feature of the GAL4 system, even if the DNA-binding ability of each transcription factor is originally different, it can be regarded as the same by fusing GAL4, and therefore it is necessary to remove the original DNA binding region. Only the PSTD region, a putative transactivation domain, was fused to GAL4. The protein expression levels from transfection were quantified (
Figure 7B), and the Nluc activity was normalized for protein abundance (
Figure 7C). As a result, the PSTD transcriptional activity of N365K was found to be 32% compared to its wild type.
4. Discussion
We analyzed patients with not only FVH1 but with foveal hypoplasia associated with varying degrees of corneal opacities and aniridia, viz., family 2 with p.G65Rfs*5, family 7 with p.V256E, and Family 8 with c.1032+5G>A. In these three families, the responsible mutations were in other than the CTS. Interestingly, family 7 showed remarkable phenotypic variations, i.e., a proband had typical aniridia with severe corneal opacity whereas the mother had unilateral partial aniridia and bilateral foveal hypoplasia with preserved BCVA. The functional assay showed that the truncation p.G65Rfs*5 mutation showed null transcriptional activity. The transcript of the truncation mutation possibly would be degraded by nonsense-mediated decay. This was supported by the phenotype of the patient that can be caused by haplo-insufficiency of the PAX6 gene. Nonetheless, when translated, the protein would not function because it did not translocate into the nucleus. The p.V256E had low 5aCON transcriptional activity. We did not analyze the c.1032+5G>A because the putative transcript of this splicing mutation was uncertain . However, the mutant can be transcribed as one of other minor transcripts, e.g., p.S346N for NM_001310159, and further studies are needed to determine the effects of the mutation on the formation of the fovea.
The rest of the families had a consistent FVH1 phenotype and all of which had missense mutations. However, the severity of foveal hypoplasia differed among the families. In families 3, 4, and 5, their responsible mutations, p.V78E, p.V83F and p.R128H, were in the CTS and consistently showed severe foveal hypoplasia of Grade 3 or 4. Earlier studies showed that most of the mutations causing FVH1 were found in the CTS [
8,
9]. From our study, for the mutations other than the CTS, the clinical severity was divided into mild foveal hypoplasia (p.P20S and p.N365K) [
11], and severe foveal hypoplasia (p.Q255L). Our results showed that the functional impairments associated with the mutations were diverse. The mutants P20S in the NTS and Q255L in the HD did not affect the transcriptional activity suggesting a different action from mutants in the CTS that induce hyperactivation on the NTS [
25]. Mutant N365K can bind more to the 5aCON than the wild-type
PAX6, however it had a decreased transcriptional activity. To determine the reason for this discrepancy, we used the GAL4 transcription system in the PSTD which is known to have transactivation actions [
26]. We found that transactivation of PSTD by N365K was reduced to 32%. The results support the idea that the transactivation by PAX6 was dependent on the location of mutation and type of the DNA-binding site [
27].
There are limitations in this study. An important limitation was that only mutations we found were evaluated and the number of patients with the mutations was small. However, isolated foveal hypoplasia is a rare condition, and only a few mutations have been analyzed functionally. Thus, there is limited information on the characteristics of foveal hypoplasia.
5. Conclusions
The results showed that mutations associated with foveal hypoplasia underlie a functional divergence between the DNA binding ability and the transcriptional activity. Mutations in the CTS consistently cause severe foveal hypoplasia. Widely distributed mutations in the PAX6 gene, not limited to the CST region, was responsible for isolated foveal hypoplasia. Our study expands the mutation spectrum of foveal hypoplasia that will be helpful for genetic counseling and provides a better understanding of the foveal development.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.M., H.I. and H.K.; methodology, I.M., H.I. and H.K.; investigation resources, all authors; data curation, H.I. and H.K.; writing—original draft preparation, I.M. and H.I..; writing—review and editing, all authors; supervision, H.I. and H.K.; funding acquisition, H.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research C (H.K., 20K09818) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of the University of Occupational and Environmental Health Japan (Project identification code 20-148; Jan 18, 2021 approved), Nagoya University (Project identification code 2010-1067; Apr 1, 2010 approved), The Jikei University School of Medicine (Project identification code 24-231 6997; Dec 3, 2012 approved) and National Hospital Organization Tokyo Medical Center (Project identification code R22-046; Jul 28, 2022 approved).
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects in-volved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available on request.
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs Shimizu and Nishina, Department of Development and Regenerative Biology, Medical Research Institute, Tokyo Medical and Dental University, Tokyo for the expression and reporter plasmids of pTA-5aCON-Luc and pCE-Flag-PAX6(5a). We thank We thank Duco Hamasaki, Professor Emeritus, Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, University of Miami, Miami, Florida, for his critical comments and valuable assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kondo, H., Foveal hypoplasia and optical coherence tomographic imaging. Taiwan J Ophthalmol 2018, 8, (4), 181-188. [CrossRef]
- Lima Cunha, D.; Arno, G.; Corton, M.; Moosajee, M., The Spectrum of PAX6 Mutations and Genotype-Phenotype Correlations in the Eye. Genes (Basel) 2019, 10, (12). [CrossRef]
- Cvekl, A.; Callaerts, P., PAX6: 25th anniversary and more to learn. Exp Eye Res 2017, 156, 10-21. [CrossRef]
- Azuma, N.; Tadokoro, K.; Asaka, A.; Yamada, M.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Handa, H.; Matsushima, S.; Watanabe, T.; Kohsaka, S.; Kida, Y.; Shiraishi, T.; Ogura, T.; Shimamura, K.; Nakafuku, M., The Pax6 isoform bearing an alternative spliced exon promotes the development of the neural retinal structure. Hum Mol Genet 2005, 14, (6), 735-45. [CrossRef]
- Jun, S.; Desplan, C., Cooperative interactions between paired domain and homeodomain. Development 1996, 122, (9), 2639-50. [CrossRef]
- Tang, H. K.; Singh, S.; Saunders, G. F., Dissection of the transactivation function of the transcription factor encoded by the eye developmental gene PAX6. J Biol Chem 1998, 273, (13), 7210-21. [CrossRef]
- Epstein, J. A.; Glaser, T.; Cai, J.; Jepeal, L.; Walton, D. S.; Maas, R. L., Two independent and interactive DNA-binding subdomains of the Pax6 paired domain are regulated by alternative splicing. Genes Dev 1994, 8, (17), 2022-34. [CrossRef]
- Azuma, N.; Nishina, S.; Yanagisawa, H.; Okuyama, T.; Yamada, M., PAX6 missense mutation in isolated foveal hypoplasia. Nat Genet 1996, 13, (2), 141-2. [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, H. W.; Orth, U.; Meyer-Konig, E.; Gal, A., [Hereditary foveal hypoplasia - clinical differentiation]. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd 2003, 220, (8), 559-62. [CrossRef]
- Hingorani, M.; Williamson, K. A.; Moore, A. T.; van Heyningen, V., Detailed ophthalmologic evaluation of 43 individuals with PAX6 mutations. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2009, 50, (6), 2581-90. [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, I.; Morita, H.; Kondo, H., Autosomal dominant foveal hypoplasia without visible macular abnormalities and PAX6 mutations. Jpn J Ophthalmol 2020, 64, (6), 635-641. [CrossRef]
- Suga, A.; Yoshitake, K.; Minematsu, N.; Tsunoda, K.; Fujinami, K.; Miyake, Y.; Kuniyoshi, K.; Hayashi, T.; Mizobuchi, K.; Ueno, S.; Terasaki, H.; Kominami, T.; Nao, I. N.; Mawatari, G.; Mizota, A.; Shinoda, K.; Kondo, M.; Kato, K.; Sekiryu, T.; Nakamura, M.; Kusuhara, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Yamamoto, S.; Mochizuki, K.; Kondo, H.; Matsushita, I.; Kameya, S.; Fukuchi, T.; Hatase, T.; Horiguchi, M.; Shimada, Y.; Tanikawa, A.; Yamamoto, S.; Miura, G.; Ito, N.; Murakami, A.; Fujimaki, T.; Hotta, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Iwata, T., Genetic characterization of 1210 Japanese pedigrees with inherited retinal diseases by whole-exome sequencing. Hum Mutat 2022, 43, (12), 2251-2264. [CrossRef]
- Adzhubei, I. A.; Schmidt, S.; Peshkin, L.; Ramensky, V. E.; Gerasimova, A.; Bork, P.; Kondrashov, A. S.; Sunyaev, S. R., A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat Methods 2010, 7, (4), 248-9. [CrossRef]
- Davydov, E. V.; Goode, D. L.; Sirota, M.; Cooper, G. M.; Sidow, A.; Batzoglou, S., Identifying a high fraction of the human genome to be under selective constraint using GERP++. PLoS Comput Biol 2010, 6, (12), e1001025. [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, N. M.; Rothstein, J. H.; Pejaver, V.; Middha, S.; McDonnell, S. K.; Baheti, S.; Musolf, A.; Li, Q.; Holzinger, E.; Karyadi, D.; Cannon-Albright, L. A.; Teerlink, C. C.; Stanford, J. L.; Isaacs, W. B.; Xu, J.; Cooney, K. A.; Lange, E. M.; Schleutker, J.; Carpten, J. D.; Powell, I. J.; Cussenot, O.; Cancel-Tassin, G.; Giles, G. G.; MacInnis, R. J.; Maier, C.; Hsieh, C. L.; Wiklund, F.; Catalona, W. J.; Foulkes, W. D.; Mandal, D.; Eeles, R. A.; Kote-Jarai, Z.; Bustamante, C. D.; Schaid, D. J.; Hastie, T.; Ostrander, E. A.; Bailey-Wilson, J. E.; Radivojac, P.; Thibodeau, S. N.; Whittemore, A. S.; Sieh, W., REVEL: An Ensemble Method for Predicting the Pathogenicity of Rare Missense Variants. Am J Hum Genet 2016, 99, (4), 877-885. [CrossRef]
- Jagadeesh, K. A.; Wenger, A. M.; Berger, M. J.; Guturu, H.; Stenson, P. D.; Cooper, D. N.; Bernstein, J. A.; Bejerano, G., M-CAP eliminates a majority of variants of uncertain significance in clinical exomes at high sensitivity. Nat Genet 2016, 48, (12), 1581-1586. [CrossRef]
- Kircher, M.; Witten, D. M.; Jain, P.; O'Roak, B. J.; Cooper, G. M.; Shendure, J., A general framework for estimating the relative pathogenicity of human genetic variants. Nat Genet 2014, 46, (3), 310-5. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Henikoff, S.; Ng, P. C., Predicting the effects of coding non-synonymous variants on protein function using the SIFT algorithm. Nat Protoc 2009, 4, (7), 1073-81. [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W. W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; Voelkerding, K.; Rehm, H. L., Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med 2015, 17, (5), 405-24. [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, N.; Watanabe, H.; Kubota, J.; Wu, J.; Saito, R.; Yokoi, T.; Era, T.; Iwatsubo, T.; Watanabe, T.; Nishina, S.; Azuma, N.; Katada, T.; Nishina, H., Pax6-5a promotes neuronal differentiation of murine embryonic stem cells. Biol Pharm Bull 2009, 32, (6), 999-1003. [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M.; Izumi, H.; Kurita, T.; Koi, C.; Morimoto, Y.; Yoshino, K., UBE2L6 is Involved in Cisplatin Resistance by Regulating the Transcription of ABCB6. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 2020, 20, (12), 1487-1496. [CrossRef]
- Yahalom, C.; Blumenfeld, A.; Hendler, K.; Wussuki-Lior, O.; Macarov, M.; Shohat, M.; Khateb, S., Mild aniridia phenotype: an under-recognized diagnosis of a severe inherited ocular disease. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2018, 256, (11), 2157-2164. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Thomas, M. G.; Andrews, C.; Chan, W. M.; Proudlock, F. A.; McLean, R. J.; Pradeep, A.; Engle, E. C.; Gottlob, I., Autosomal-dominant nystagmus, foveal hypoplasia and presenile cataract associated with a novel PAX6 mutation. Eur J Hum Genet 2014, 22, (3), 344-9. [CrossRef]
- Rufai, S. R.; Thomas, M. G.; Purohit, R.; Bunce, C.; Lee, H.; Proudlock, F. A.; Gottlob, I., Can Structural Grading of Foveal Hypoplasia Predict Future Vision in Infantile Nystagmus?: A Longitudinal Study. Ophthalmology 2020, 127, (4), 492-500. [CrossRef]
- Azuma, N.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Handa, H.; Hayakawa, M.; Kanai, A.; Yamada, M., Missense mutation in the alternative splice region of the PAX6 gene in eye anomalies. Am J Hum Genet 1999, 65, (3), 656-63. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.; Gorlov, I. P.; Chao, L. Y.; Singh, S.; Saunders, G. F., PAX6, paired domain influences sequence recognition by the homeodomain. J Biol Chem 2002, 277, (51), 49488-94. [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, B. K.; Yang, Y.; Cveklova, K.; Cvekl, A., Functional properties of natural human PAX6 and PAX6(5a) mutants. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2004, 45, (2), 385-92.Title of Site. Available online: URL (accessed on Day Month Year). [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
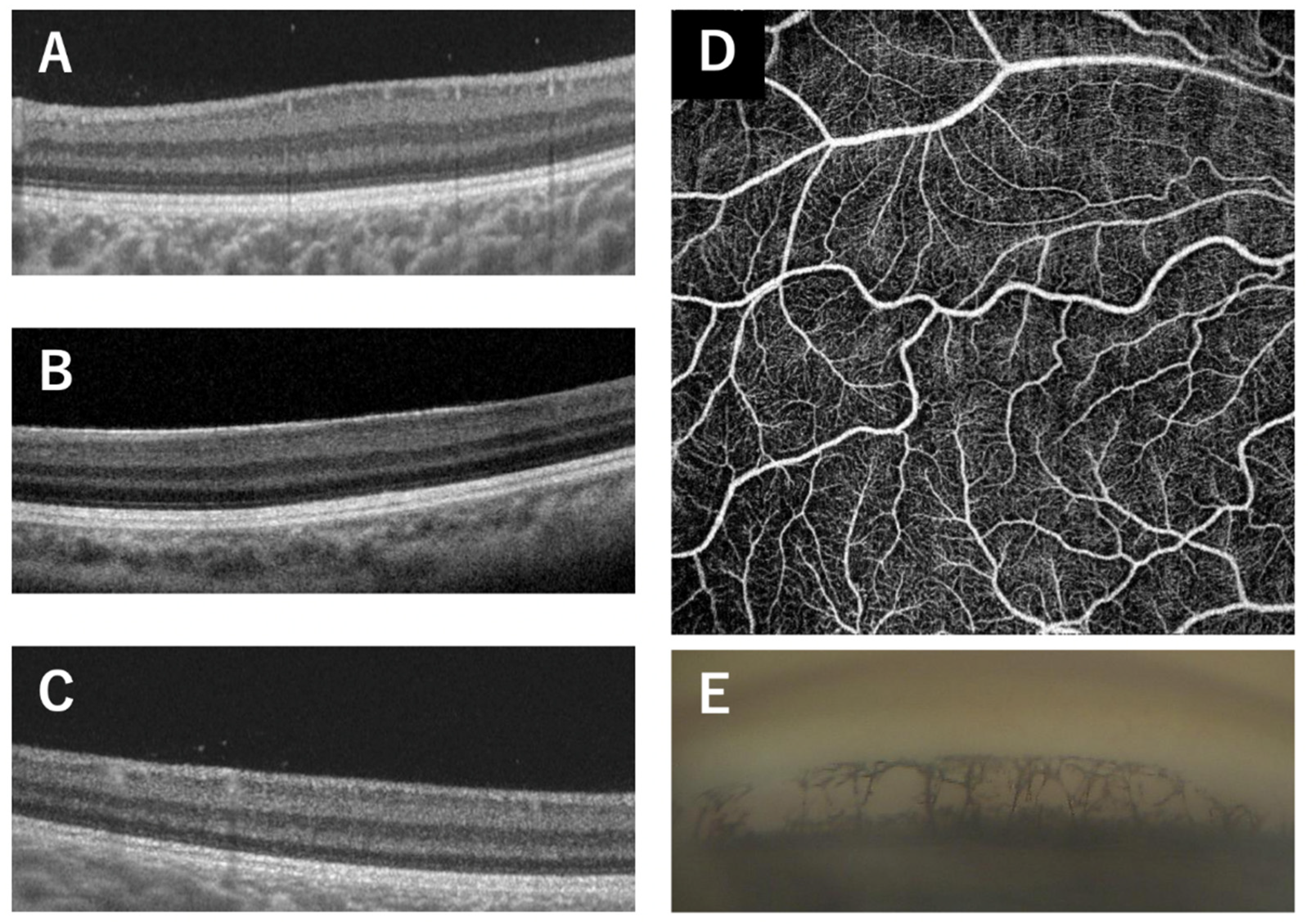
Clinical findings of Family 2 (Patient 5, 6, 7) carrying the p.V78E mutation in the PAX6 gene. OCT images of all patients show no foveal pit (A, Patient 5; B, Patient 6; C, Patient 7). The 1-year-old brother (Patient 7) underwent examinations under general anesthesia which showed an absence of the foveal avascular zone in the OCTA image (D) and goniodysgenesis (E).
Figure 1.
Clinical findings of Family 2 (Patient 5, 6, 7) carrying the p.V78E mutation in the PAX6 gene. OCT images of all patients show no foveal pit (A, Patient 5; B, Patient 6; C, Patient 7). The 1-year-old brother (Patient 7) underwent examinations under general anesthesia which showed an absence of the foveal avascular zone in the OCTA image (D) and goniodysgenesis (E).
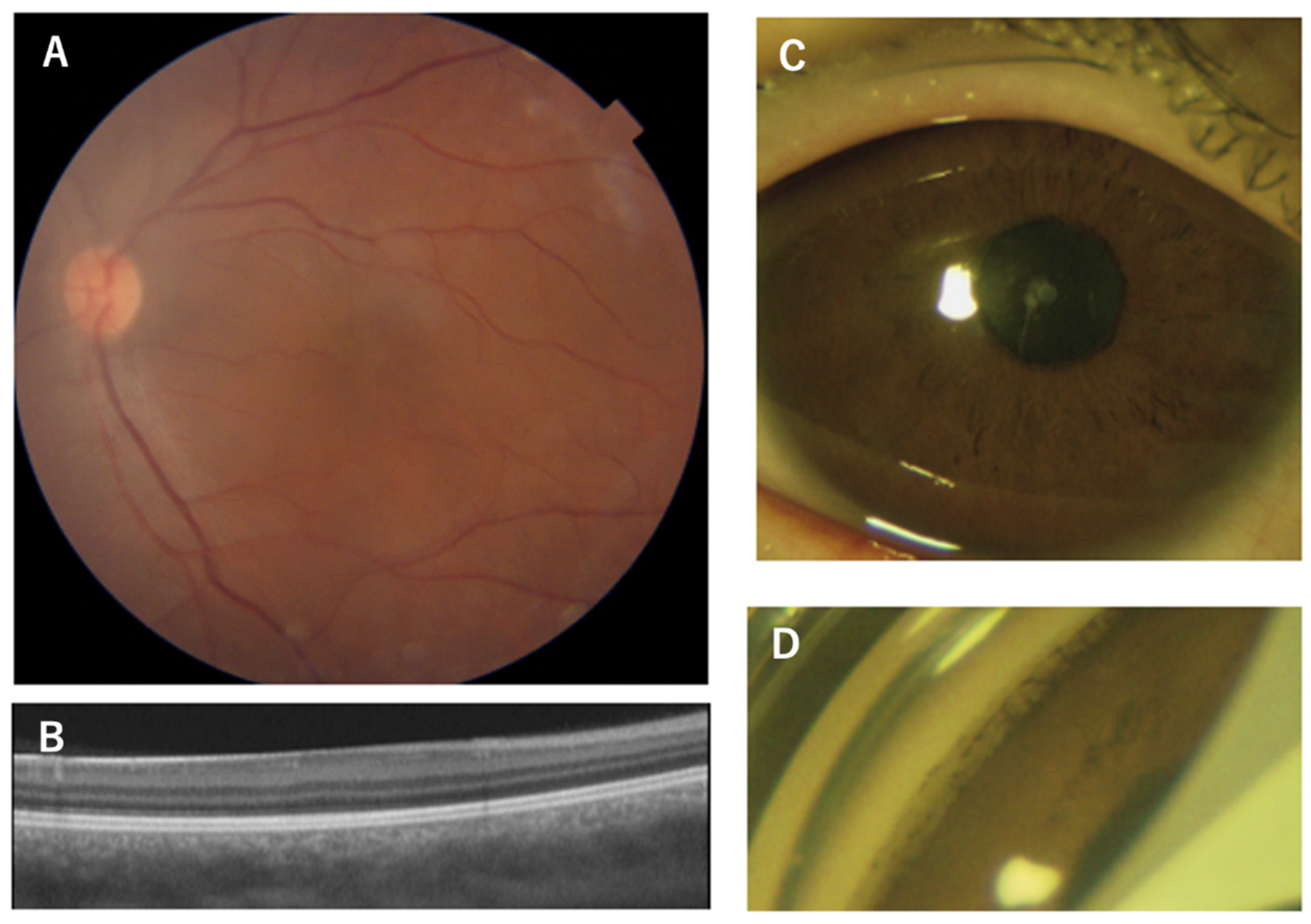
Figure 2.
Clinical findings of Patient 11, the 21-year-old male patient with the p.Q255L mutation in the PAX6 gene. Fundus photographs shows normal retinal appearance (A). OCT image shows no foveal pit (B). Slit-lamp photograph shows no obvious changes of the iris surface and slight cataract (C). Gonioscopic photograph shows goniodysgenesis (D).
Figure 2.
Clinical findings of Patient 11, the 21-year-old male patient with the p.Q255L mutation in the PAX6 gene. Fundus photographs shows normal retinal appearance (A). OCT image shows no foveal pit (B). Slit-lamp photograph shows no obvious changes of the iris surface and slight cataract (C). Gonioscopic photograph shows goniodysgenesis (D).
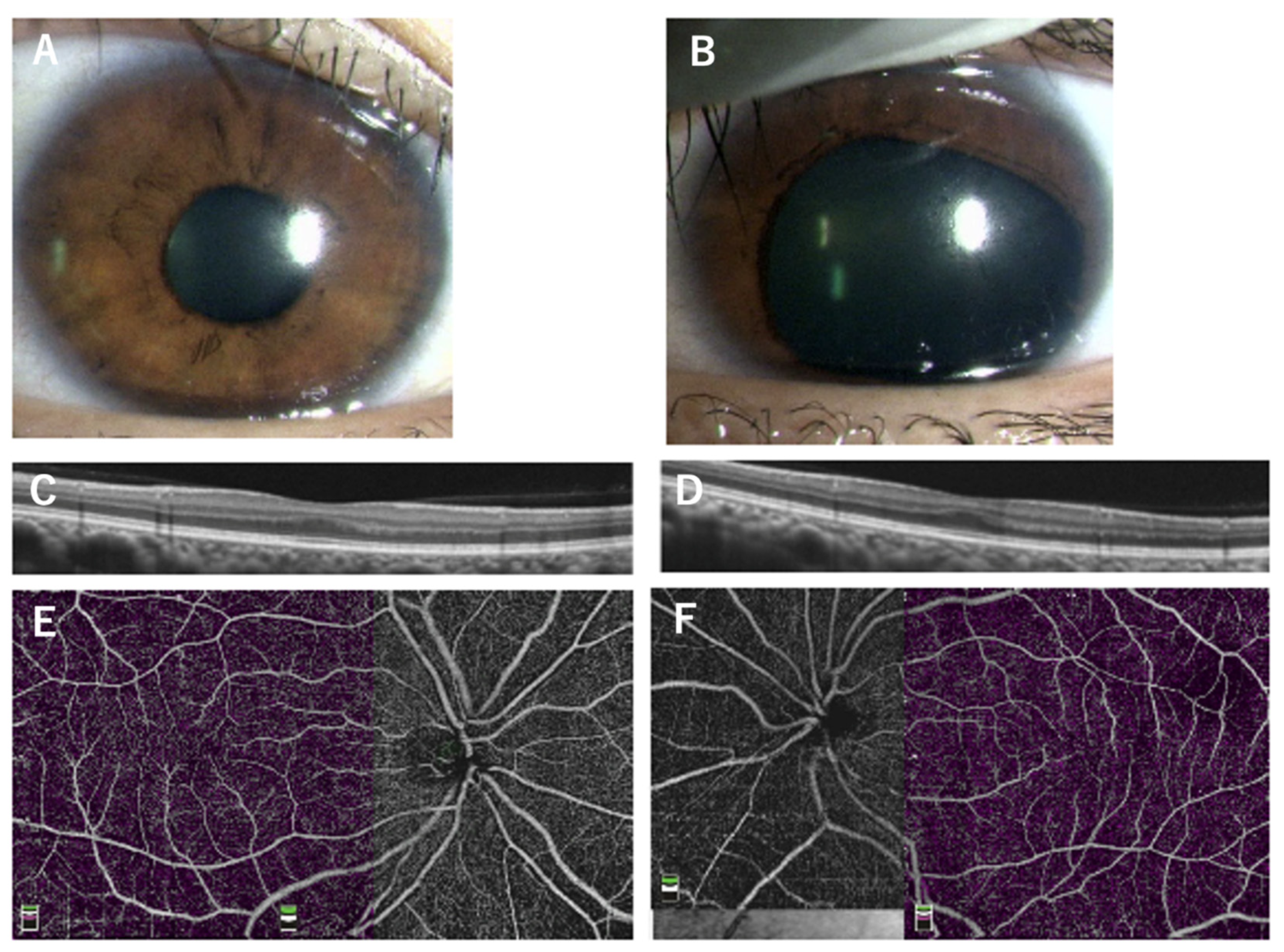
Figure 3.
Figure 3. Images of a 36-year-old mother of an aniridia patient with p.V256E mutation in the PAX6 gene. The images of the iris of the right eye is normal (A) but with partial aniridia in the lefte eye (B). OCT and OCTA images show reduced foveal pit (C, D) and no foveal avascular zone (E, F).
Figure 3.
Figure 3. Images of a 36-year-old mother of an aniridia patient with p.V256E mutation in the PAX6 gene. The images of the iris of the right eye is normal (A) but with partial aniridia in the lefte eye (B). OCT and OCTA images show reduced foveal pit (C, D) and no foveal avascular zone (E, F).
Figure 4.
PAX6 expression. Total RNA was extracted from ARPE19/HPV16, LUHMES, and PC3 cells, and the expression level of PAX6 mRNA was analyzed by qRT-PCR (ΔΔCT method). The expression level of ARPE19/HPV16 was set to 1 (n=1).
Figure 4.
PAX6 expression. Total RNA was extracted from ARPE19/HPV16, LUHMES, and PC3 cells, and the expression level of PAX6 mRNA was analyzed by qRT-PCR (ΔΔCT method). The expression level of ARPE19/HPV16 was set to 1 (n=1).
Figure 5.
Expression of exogenous PAX6. (A) Flag-tagged wild-type PAX6 and its mutants were transfected into PC3-5aNluc cells, and the cells were harvested 48 hours later. Cell lysates were examined by SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with anti-Flag antibody to detect the expression of the transfected PAX6 constructs. An anti-β-actin antibody was used as a loading control to normalize the protein expression levels (n=2). (B) Cell lysates expressing wild-type PAX6 and G65Rfs*5 were blotted onto membranes using slot blotting, and then blotted with anti-Flag antibody (n=2). (C) The results from A and B were normalized using the common signal which was the wild-type PAX6. The expression ratio of Flag to β-actin was calculated, and the value of wild-type was set to 1 (n=2). (D) 5aCON-Nluc activity induced by each PAX6 protein was measured, and normalized by β-actin expression levels in the cells (A and B).
Figure 5.
Expression of exogenous PAX6. (A) Flag-tagged wild-type PAX6 and its mutants were transfected into PC3-5aNluc cells, and the cells were harvested 48 hours later. Cell lysates were examined by SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with anti-Flag antibody to detect the expression of the transfected PAX6 constructs. An anti-β-actin antibody was used as a loading control to normalize the protein expression levels (n=2). (B) Cell lysates expressing wild-type PAX6 and G65Rfs*5 were blotted onto membranes using slot blotting, and then blotted with anti-Flag antibody (n=2). (C) The results from A and B were normalized using the common signal which was the wild-type PAX6. The expression ratio of Flag to β-actin was calculated, and the value of wild-type was set to 1 (n=2). (D) 5aCON-Nluc activity induced by each PAX6 protein was measured, and normalized by β-actin expression levels in the cells (A and B).
Figure 6.
Subcellular localization of wild-type PAX6 and its mutants. Plasmids expressing the wild-type PAX6 and its mutants were transfected into PC3 cells, and the cells were harvested. The harvested cells were fractionated into nucleoplasm and cytoplasm, and lysed in equal amounts. Equal volumes of the cell lysate were aliquoted, subjected to SDS-PAGE, and then transferred onto a membrane. The membrane was probed with anti-Flag antibody to detect the expression of the transfected PAX6 constructs. Lamin and GAPDH were also blotted as loading controls to confirm the accuracy of the fractionation procedure. The total of each expression level was set to 1, and the ratio of nucleoplasm to cytoplasm was determined (n = 2). Nuc and Cyt indicate nucleoplasm and cytoplasm, respectively.
Figure 6.
Subcellular localization of wild-type PAX6 and its mutants. Plasmids expressing the wild-type PAX6 and its mutants were transfected into PC3 cells, and the cells were harvested. The harvested cells were fractionated into nucleoplasm and cytoplasm, and lysed in equal amounts. Equal volumes of the cell lysate were aliquoted, subjected to SDS-PAGE, and then transferred onto a membrane. The membrane was probed with anti-Flag antibody to detect the expression of the transfected PAX6 constructs. Lamin and GAPDH were also blotted as loading controls to confirm the accuracy of the fractionation procedure. The total of each expression level was set to 1, and the ratio of nucleoplasm to cytoplasm was determined (n = 2). Nuc and Cyt indicate nucleoplasm and cytoplasm, respectively.
Figure 7.
5aCON binding activity and PSTD transcriptional activity. (A) The upper panel shows the results of pulling down indicated wild-type PAX6 and mutant PAX6 with immobilizing 5aCON on magnetic beads. The expression level of each Flag-PAX6 in the cell lysate used for pulldown is shown in the lower panel. (B) PC3-9Gal4Nluc cells were transfected with GAL4-Flag-tagged PTSD of wild-type or N365K, and harvested after 48 hours. Cell lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to a membrane for Western blotting using an anti-Flag antibody to detect expression of each construct. β-actin was used as a loading control to normalize protein expression levels. (n=2). (C) 9xGAL4UAS-Nluc activation by PSTD WT and N365K were measured, and normalized byβ-actin expression levels of in cells (B).
Figure 7.
5aCON binding activity and PSTD transcriptional activity. (A) The upper panel shows the results of pulling down indicated wild-type PAX6 and mutant PAX6 with immobilizing 5aCON on magnetic beads. The expression level of each Flag-PAX6 in the cell lysate used for pulldown is shown in the lower panel. (B) PC3-9Gal4Nluc cells were transfected with GAL4-Flag-tagged PTSD of wild-type or N365K, and harvested after 48 hours. Cell lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to a membrane for Western blotting using an anti-Flag antibody to detect expression of each construct. β-actin was used as a loading control to normalize protein expression levels. (n=2). (C) 9xGAL4UAS-Nluc activation by PSTD WT and N365K were measured, and normalized byβ-actin expression levels of in cells (B).
Table 1.
Mutations in the PAX6 gene and clinical features in patients with foveal hypoplasia.
Table 1.
Mutations in the PAX6 gene and clinical features in patients with foveal hypoplasia.
| Patient |
Age, sex |
Family No. |
Diagnosis |
Mutation (NM_000280.4) |
PAX6 domain |
logMAR visual acuity (R/L) |
Refraction (R/L) |
Nystagmus |
Gonio dysgenesis |
OCT grade* |
Reference |
| 1 |
13y, F |
1 (proband) |
FVH1 |
c.58C>T (p.P20S) |
PD (NTS) |
0.5/0.2 |
-3.75/-4.0 |
present |
present |
1b |
[11] |
| 2 |
34y, F |
1 (mother) |
FVH1 |
c.58C>T (p.P20S) |
|
0.1/0.1 |
-0.5/0 |
absent |
present |
1b |
[11] |
| 3 |
64y, M |
1 (grandfather) |
FVH1 |
c.58C>T (p.P20S) |
|
0.1/0 |
NA |
absent |
present |
1b |
[11] |
| 4 |
55, M |
2 (proband) |
aniridia, corneal opacity |
c.150_151insA (p.G65Rfs*5) |
PD (NTS) |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
This study |
| 5 |
3y, F |
3 (proband) |
FVH1 |
c.233T>A (p.V78E) |
PD (CTS) |
1.2/1.3 |
-2.0/-2.0 |
present |
NA |
4 |
This study |
| 6 |
33y, F |
3 (mother) |
FVH1 |
c.233T>A (p.V78E) |
|
1.0/1.0 |
-10.25/-12.0 |
present |
present |
4 |
This study |
| 7 |
1y, M |
3 (brother) |
FVH1 |
c.233T>A (p.V78E) |
|
1.2/1.4 |
+3.0/+3.75 |
present |
present |
4 |
This study |
| 8 |
6y, M |
4 (proband) |
FVH1 |
c.247G>T (p.V83F) |
PD (CTS) |
0.5/0.4 |
-7.125/-7.25 |
absent |
NA |
4 |
This study |
| 9 |
10y, M |
4 (brother) |
FVH1 |
c.247G>T (p.V83F) |
|
0/0.1 |
-4.5/-3.875 |
absent |
NA |
4 |
This study |
| 10 |
68y, M |
5 (proband) |
FVH1 |
c.383G>A (p.R128H) |
PD (CTS) |
0.2/0.3 |
NA |
NA |
NA |
3 |
This study |
| 11 |
21y, M |
6 (proband) |
FVH1 |
c.764A>T (p.Q255L) |
HD |
0.3/0.4 |
+0.75/-1.0 |
present |
present |
4 |
This study |
| 12 |
8y, F |
7 (proband) |
aniridia, corneal opacity, secondary retinal detachments |
c.767T>A (p.V256E) |
HD |
LP/1.7 |
NA/+16.5 |
NA |
NA |
NA |
This study |
| 13 |
36y, F |
7 (mother) |
unilateral partial aniridia |
c.767T>A (p.V256E) |
HD |
NA |
NA |
absent |
absent |
1b |
This study |
| 14 |
6y, M |
8 (proband) |
peripheral corneal opacity, mild iris anomaly, exotropia |
c.1032+5G>A |
PSTD |
0.1/0.1 |
+0.25/+0.5 |
absent |
NA |
3 |
This study |
| 15 |
41y, F |
8 (mother) |
peripheral corneal opacity, mild iris anomaly |
c.1032+5G>A |
PSTD |
0.2/0.1 |
+2.0/-1.25 |
absent |
NA |
3 |
This study |
| 16 |
37y, M |
8 (uncle) |
peripheral corneal opacity, mild iris anomaly |
c.1032+5G>A |
PSTD |
0.6/0.5 |
-2.0/-4.0 |
absent |
NA |
3 |
This study |
| 17 |
6y, F |
9 (proband) |
FVH1 |
c.1095T>G (p.N365K) |
PSTD |
-0.2/-0.1 |
-5.5/-5.75 |
absent |
present |
1b |
[11] |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).