Submitted:
25 June 2023
Posted:
26 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Flow experiments of CO2 in complex pore structures
2.1. Traditional characterization of pore structures during CO2 microscopic flow
2.2. Effects of porosity and permeability characteristics on the microscopic flow mechanism of CO2
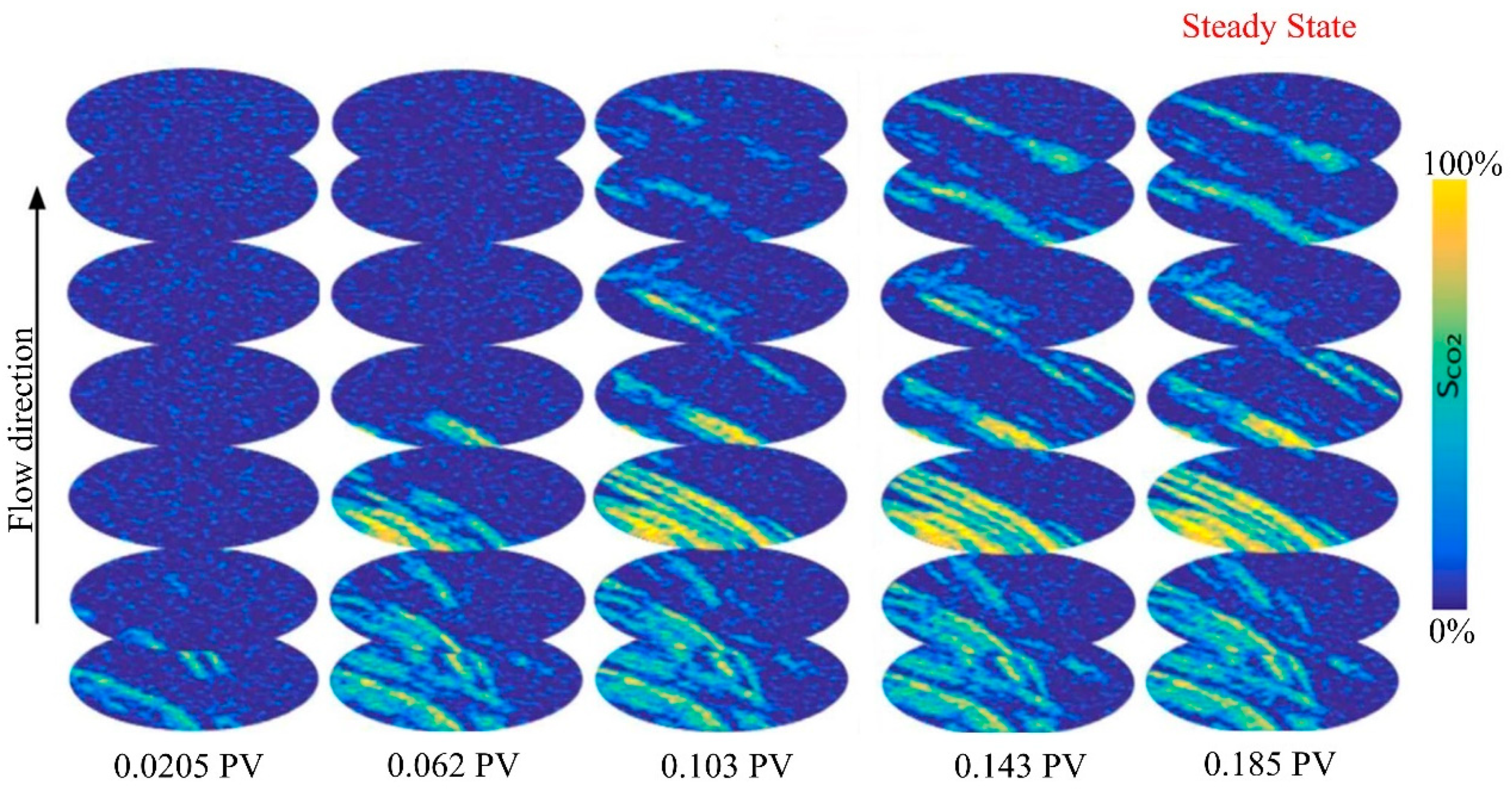
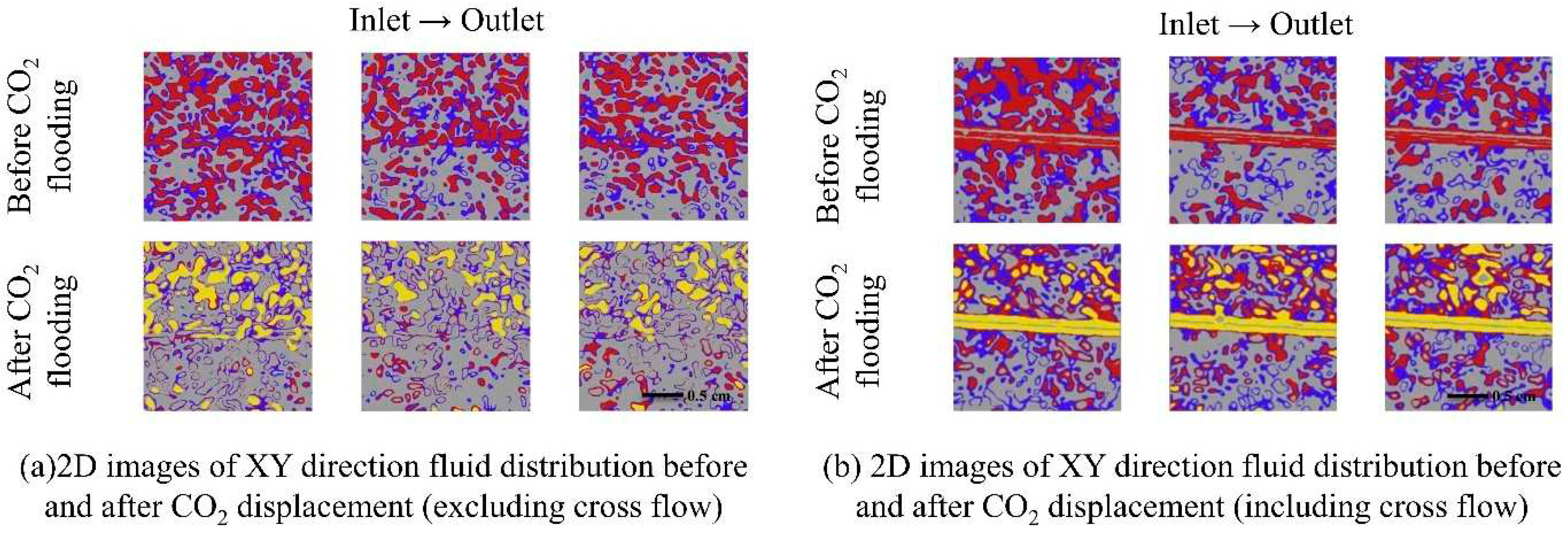
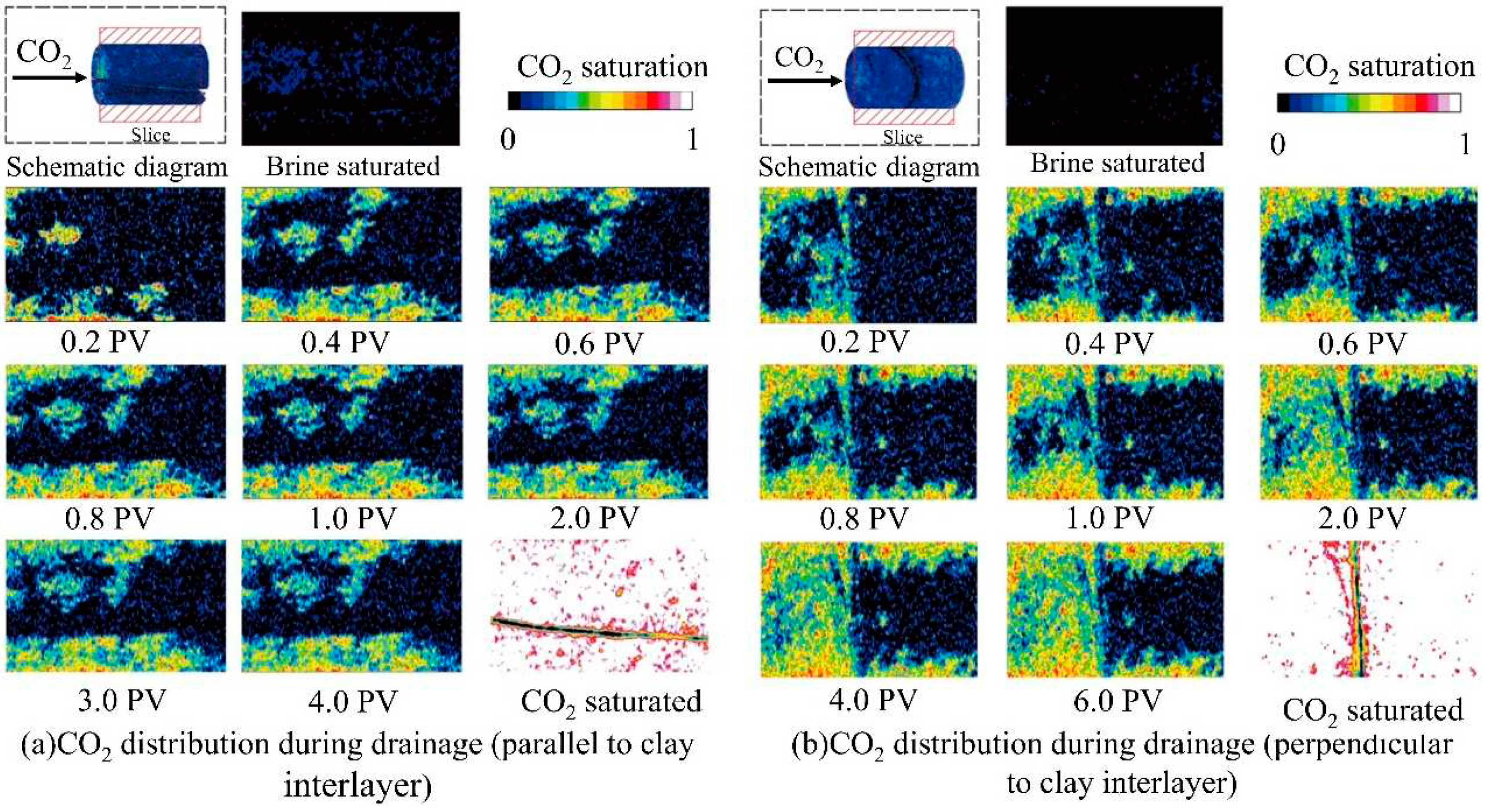
2.3. Two-phase flow law in CO2 microscopic flow

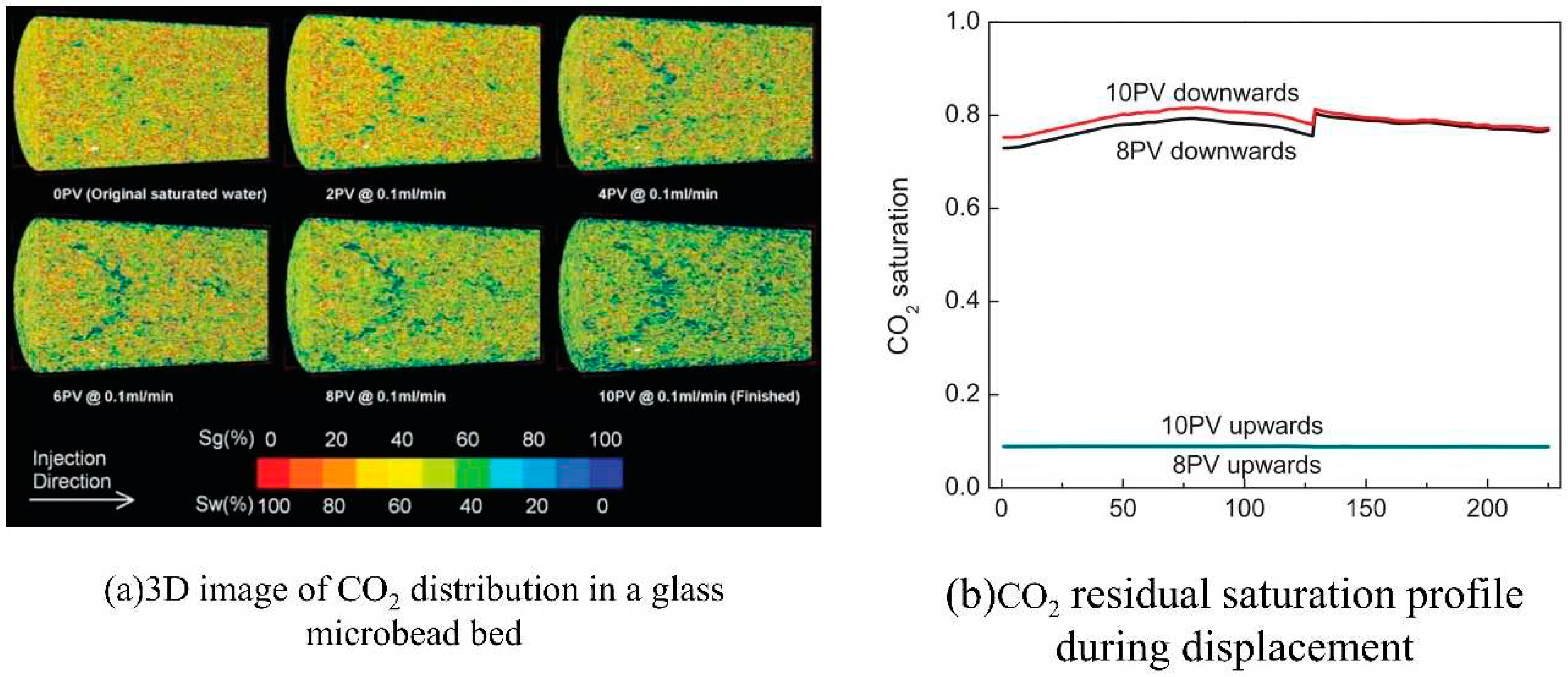
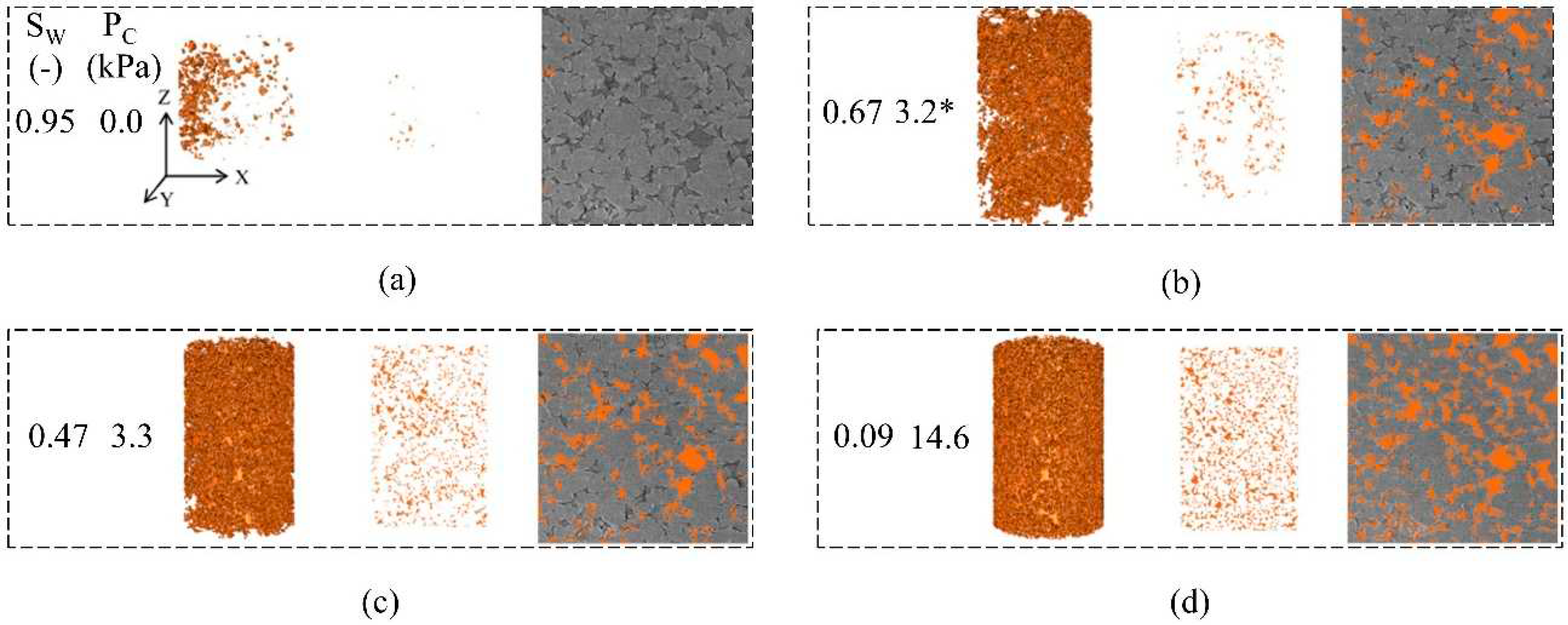
2.4. Microscopic flow of CO2 in different phase states
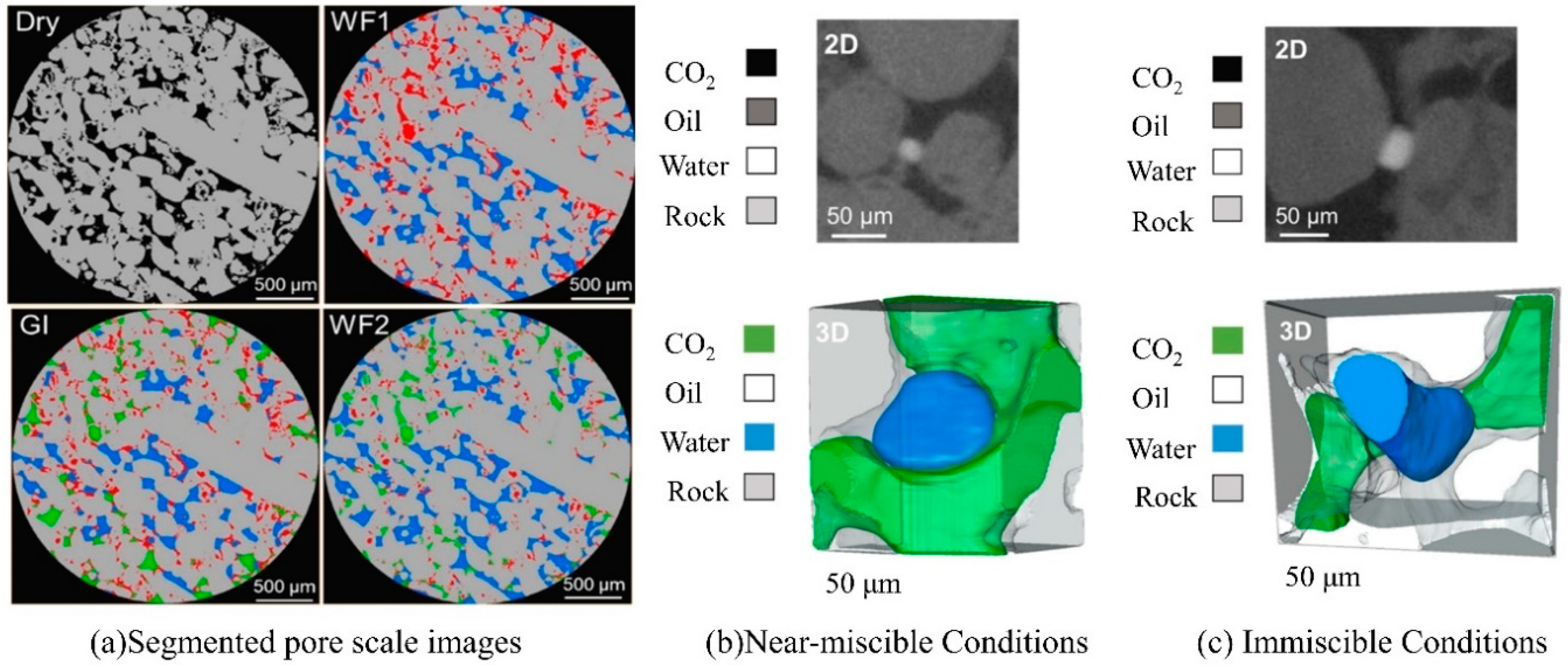
3. Theoretical model of CO2 flow in pore structures
4. Numerical simulation of CO2 flow in pore structures
4.1. Numerical simulation based on LBM
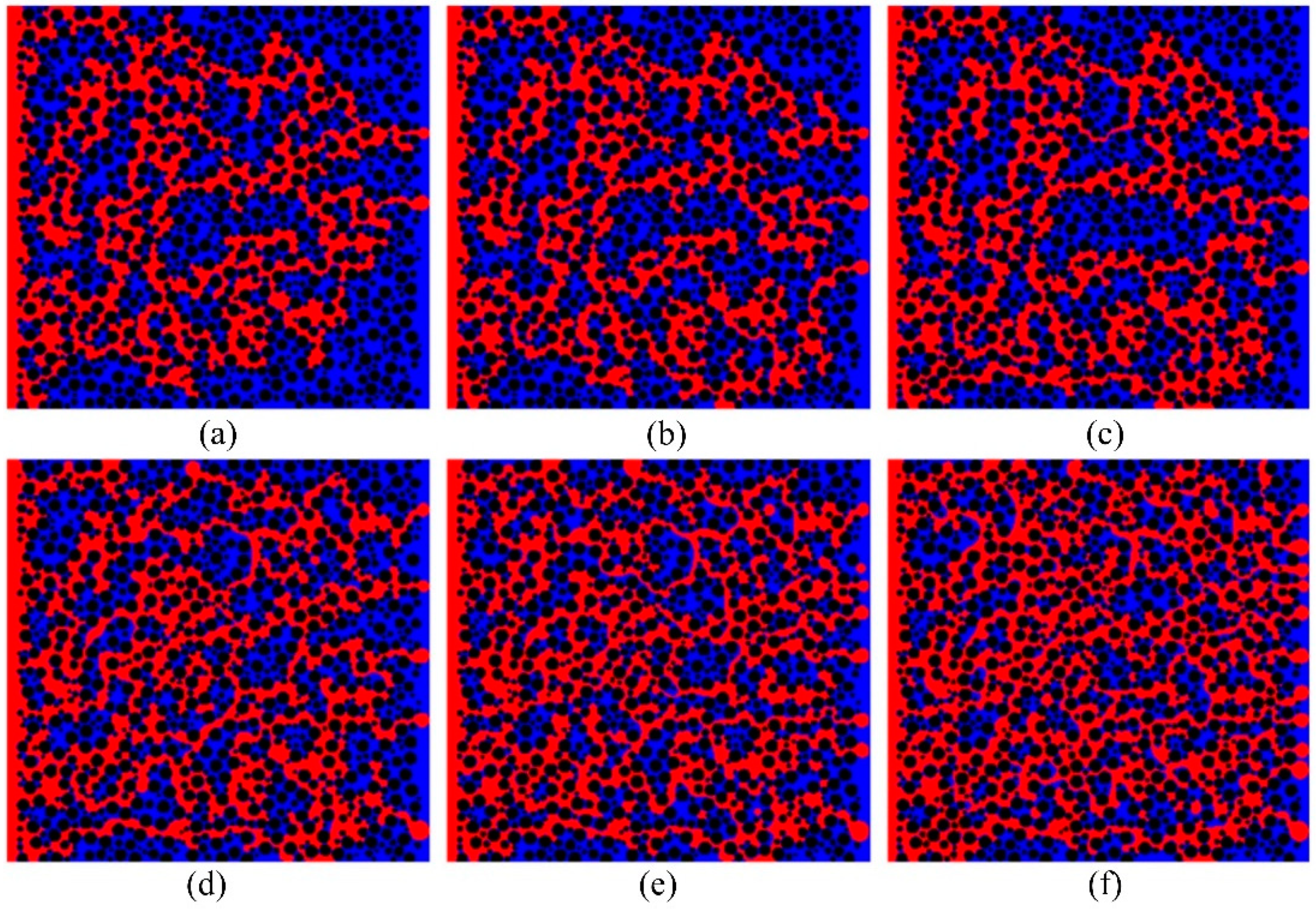
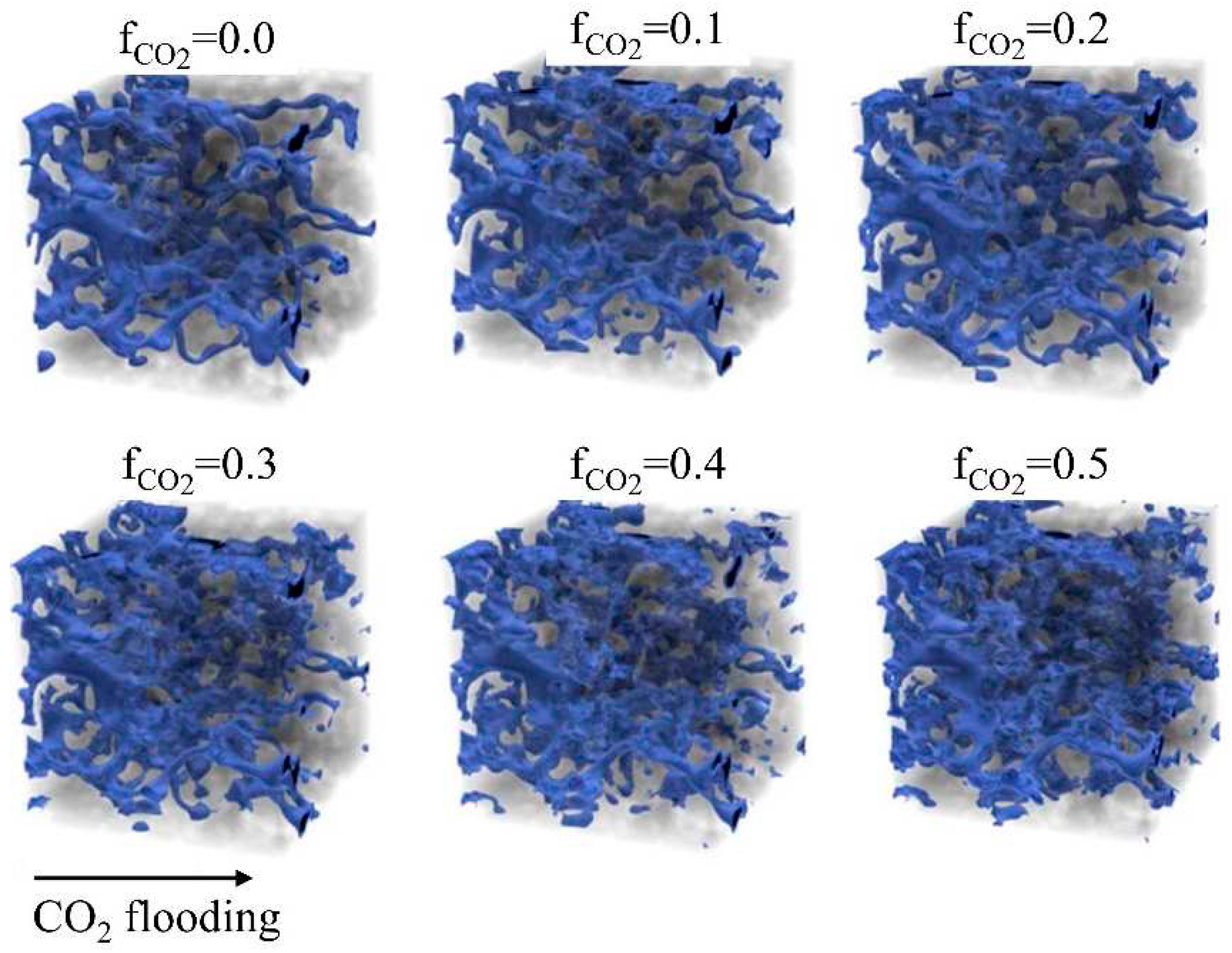
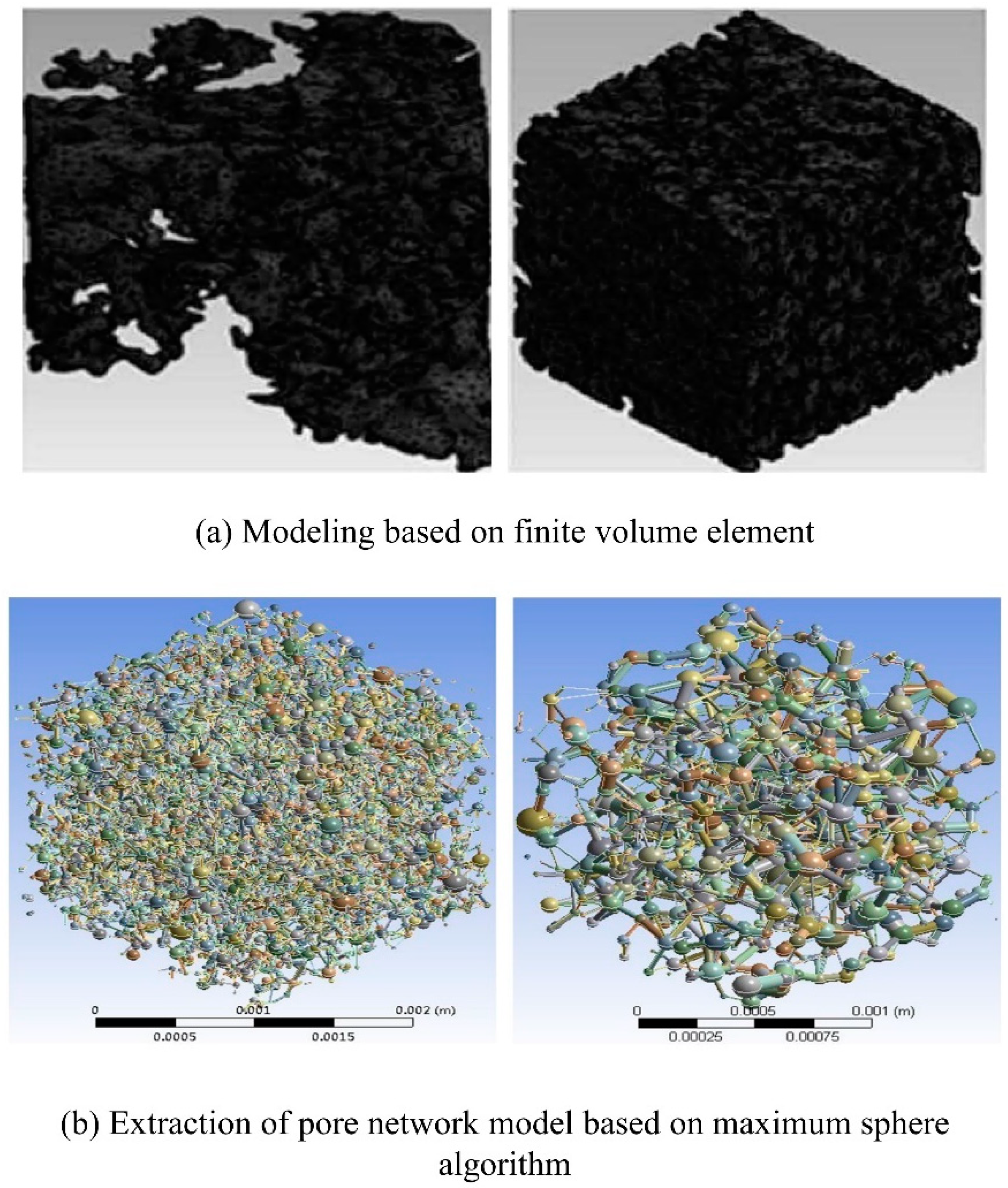
4.2. Numerical simulation based on PN
5. Conclusions and outlook
Data Availability
Acknowledgments
Declaration of Competing Interest
References
- Conversano, A.; Porcu, A.; Mureddu, M.; et al. Bench-scale experimental tests and data analysis on CO2 capture with potassium prolinate solutions for combined cycle decarbonization. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2020, 93, 102881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, A.M.; Karanikolos, G.N. CO2 capture adsorbents functionalized by amine – bearing polymers: A review. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2020, 96, 103005. [Google Scholar]
- Naghizadeh, A.; Larestani, A.; Nait Amar, M.; et al. Predicting viscosity of CO2–N2 gaseous mixtures using advanced intelligent schemes. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 2022, 208, 109359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaei-Farouji, M.; Vo Thanh, H.; Sheini Dashtgoli, D.; et al. Application of robust intelligent schemes for accurate modelling interfacial tension of CO2 brine systems: Implications for structural CO2 trapping. Fuel 2022, 319, 123821. [Google Scholar]
- Vitali, M.; Corvaro, F.; Marchetti, B.; et al. Thermodynamic challenges for CO2 pipelines design: A critical review on the effects of impurities, water content, and low temperature. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2022, 114, 103605. [Google Scholar]
- Soeder, D.J. Greenhouse gas sources and mitigation strategies from a geosciences perspective. Advances in Geo-Energy Research 2021, 5, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Cui, G. Influence of spectral characteristics of the Earth’s surface radiation on the greenhouse effect: Principles and mechanisms. Atmospheric Environment 2021, 244, 117908. [Google Scholar]
- Yoro, K.O.; Daramola, M.O. Chapter 1 - CO2 emission sources, greenhouse gases, and the global warming effect. Advances in Carbon Capture 2020, 3–28. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.H.; Yang, J.; Kim, D. Review of recent technologies for transforming carbon dioxide to carbon materials. Chemical engineering journal 2022, 427, 130980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, L.; Cai, Q.; et al. Potential impact assessment for China’s dry and wet areas under global warming targets. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth Parts A/B/C 2020, 116, 102838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, M.; Zhang, L.; Miao, X.; et al. Application of computed tomography (CT) in geologic CO2 utilization and storage research: A critical review. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering 2020, 83, 103591. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Foroozesh, J.; Edlmann, K.; et al. A comprehensive review of value-added CO2 sequestration in subsurface saline aquifers. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering 2020, 81, 103437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanzhong, W.; Nianmin, Z.; Xu, C.; et al. Geologic CO2 storage in arkosic sandstones with CaCl2-rich formation water. Chemical Geology 2020, 558, 119867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Hou, Z.; Li, Z.; et al. Numerical modeling for CO2 storage with impurities associated with enhanced gas recovery in depleted gas reservoirs. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering 2022, 102, 104554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanak, K.; Dixon, T. CO2 storage guidelines and the science of monitoring: Achieving project success under the California Low Carbon Fuel Standard CCS Protocol and other global regulations. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2022, 113, 103523. [Google Scholar]
- Medina-Martos, E.; Gálvez-Martos, J.-L.; Almarza, J.; et al. Environmental and economic performance of carbon capture with sodium hydroxide. Journal of CO2 Utilization 2022, 60, 101991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhosani, A.; Lin, Q.; Scanziani, A.; et al. Pore-scale characterization of carbon dioxide storage at immiscible and near-miscible conditions in altered-wettability reservoir rocks. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2021, 105, 103232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, M.; Adjiman, C.S.; Bardow, A.; et al. Carbon capture and storage (CCS): the way forward. Energy & Environmental Science 2018, 11, 1062–1176. [Google Scholar]
- Aminu, M.D.; Nabavi, S.A.; Rochelle, C.A.; et al. A review of developments in carbon dioxide storage. Applied Energy 2017, 208, 1389–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noy, D.J.; Holloway, S.; Chadwick, R.A.; et al. Modelling large-scale carbon dioxide injection into the Bunter Sandstone in the UK Southern North Sea. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2012, 9, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Liu, H.; Hou, Z.; et al. A Review of CO2 Storage in View of Safety and Cost-Effectiveness. Energies 2020, 13, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragui, K.; Bennacer, R.; Chen, L. Pore-scale modeling on supercritical CO2 invasion in 3D micromodel with randomly arranged spherical cross-sections. Energy Reports 2021, 7, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassen, R.N.; Plampin, M.R.; Sakaki, T.; et al. Effects of geologic heterogeneity on migration of gaseous CO2 using laboratory and modeling investigations. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2015, 43, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kogure, T.; Nishizawa, O.; et al. Different flow behavior between 1-to-1 displacement and co-injection of CO2 and brine in Berea sandstone: Insights from laboratory experiments with X-ray CT imaging. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2017, 66, 76–84. [Google Scholar]
- Saleem, U.; Dewar, M.; Chaudhary, T.N.; et al. Numerical modelling of CO2 migration in heterogeneous sediments and leakage scenario for STEMM-CCS field experiments. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2021, 109, 103339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steefel, C.I.; Molins, S.; Trebotich, D. Pore Scale Processes Associated with Subsurface CO2 Injection and Sequestration. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry 2013, 77, 259–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Mei, K.; Li, Z.; et al. Research on the Interface Structure during Unidirectional Corrosion for Oil-Well Cement in H2S Based on Computed Tomography Technology. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research 2016, 55, 10889–10895. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Ren, S.; Ren, B.; et al. Assessment of CO2 storage capacity in oil reservoirs associated with large lateral/underlying aquifers: Case studies from China. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2011, 5, 1016–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Li, Q.; Myers, M.; et al. Application of nuclear magnetic resonance technology to carbon capture, utilization and storage: A review. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering 2019, 11, 892–908. [Google Scholar]
- Kardjilov, N.; Manke, I.; Hilger, A.; et al. Neutron imaging in materials science. Materials Today 2011, 14, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Tsuji, T. Numerical investigations on the effect of initial state CO2 topology on capillary trapping efficiency. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2016, 49, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefny, M.; Qin, C.; Saar, M.O.; et al. Synchrotron-based pore-network modeling of two-phase flow in Nubian Sandstone and implications for capillary trapping of carbon dioxide. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2020, 103, 103164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, S.; Oedai, S.; Ott, H. Displacement and mass transfer between saturated and unsaturated CO2–brine systems in sandstone. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2013, 12, 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, L.E.; Klise, K.A.; Fuchs, S.; et al. Methods to measure contact angles in scCO2-brine-sandstone systems. Advances in Water Resources 2018, 122, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; Pei, G.; et al. A New Method for Artificial Core Reconstruction of a Fracture-Control Matrix Unit. Advances in Civil Engineering 2020, 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Song, R.; Liu, J.; et al. Mass transfer model of fracture-controlled matrix unit: Model derivation and experimental verification based on fractal theory and micro-CT scanning technology. Energy Reports 2020, 6, 3067–3079. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Liang, B.; Liu, J.; et al. Imbibition oil recovery of single fracture-controlled matrix unit: Model construction and numerical simulation. Capillarity 2022, 5, 32–40. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; Liang, B.; et al. The Influence of Pore Structure of the Core-Scale Fracture-Controlled Matrix Unit on Imbibition: Model Construction and Definition of the Fractal Coefficient. Lithosphere 2022, 2022, 6245345. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Song, R.; Liu, J.; et al. Pore-scale visualization and quantitative analysis of the spontaneous imbibition based on experiments and micro-CT technology in low-permeability mixed-wettability rock. Energy Science & Engineering 2020, 8, 1840–1856. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Liang, B.; et al. Complex wettability behavior triggering mechanism on imbibition: A model construction and comparative study based on analysis at multiple scales. Energy 2023, 275, 127434. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.-j.; Song, R.; Cui, M.-m. Improvement of predictions of petrophysical transport behavior using three-dimensional finite volume element model with micro-CT images. Journal of Hydrodynamics 2015, 27, 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Song, R.; Liu, J.; Cui, M. Single- and two-phase flow simulation based on equivalent pore network extracted from micro-CT images of sandstone core. Springerplus 2016, 5, 817. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krause, M.; Perrin, J.-C.; Kuo, C.-W.; et al. Characterization of CO2 storage properties using core analysis techniques and thin section data. Energy Procedia 2009, 1, 2969–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abell, A.B.; Willis, K.L.; Lange, D.A. Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry and Image Analysis of Cement-Based Materials. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 1999, 211, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; He, M.; Zhang, B.; et al. Pore structure characteristics and permeability of deep sedimentary rocks determined by mercury intrusion porosimetry. Journal of Earth Science 2016, 27, 670–676. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, X.Y.; Li, X.Q.; Zhang, J.Z.; et al. Characteristics of Pore Structure and Gas Content of the Lower Paleozoic Shale from the Upper Yangtze Plate, South China. Energies 2021, 14, 7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xu, J.; Chen, J. Applications of scanning electron microscopy in earth sciences. Science China Earth Sciences 2015, 58, 1768–1778. [Google Scholar]
- Xda, B.; Meng, W.; Cwa, B.; et al. Factors affecting shale microscopic pore structure variation during interaction with supercritical CO2. Journal of CO2 Utilization 2020, 38, 194–211. [Google Scholar]
- Loucks, R.G.; Reed, R.M.; Ruppel, S.C.; et al. Morphology, Genesis, and Distribution of Nanometer-Scale Pores in Siliceous Mudstones of the Mississippian Barnett Shale. Journal of Sedimentary Research 2009, 79, 848–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarkson, C.R.; Solano, N.; Bustin, R.M.; et al. Pore structure characterization of North American shale gas reservoirs using USANS/SANS, gas adsorption, and mercury intrusion. Fuel 2013, 103, 606–616. [Google Scholar]
- Ozotta, O.; Liu, K.; Gentzis, T.; et al. Pore Structure Alteration of Organic-Rich Shale with Sc-CO2 Exposure: the Bakken Formation. Energy & Fuels 2021, 35, 5074–5089. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Sang, S.; Pan, Z.; et al. Experimental study of supercritical CO2-H2O-coal interactions and the effect on coal permeability. Fuel 2019, 253, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khather, M.; Saeedi, A.; Rezaee, R.; et al. Experimental evaluation of carbonated brine-limestone interactions under reservoir conditions-emphasis on the effect of core scale heterogeneities. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2018, 68, 128–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.K.; Dawson, G.K.W.; Golab, A.; et al. A combined geochemical and μCT study on the CO2 reactivity of Surat Basin reservoir and cap-rock cores: Porosity changes, mineral dissolution and fines migration. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2019, 80, 10–24. [Google Scholar]
- Brattekås, B.; Haugen, M. Explicit tracking of CO2-flow at the core scale using micro-Positron Emission Tomography (μPET). Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering 2020, 77, 103268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, K.; Kogure, T.; Nishizawa, O.; et al. Experimental and Numerical Study of Residual CO2 Trapping in Porous Sandstone. Energy Procedia 2013, 37, 4093–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, P.G.; Senthilnathan, S.; Yoon, H.; et al. Comparison of Darcy’s law and invasion percolation simulations with buoyancy-driven CO2-brine multiphase flow in a heterogeneous sandstone core. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 2017, 155, 54–62. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, W.; Crandall, D.; Bruner, K.; et al. Core and Pore Scale Characterization of Liujiagou Outcrop Sandstone, Ordos basin, China for CO2 Aquifer Storage. Energy Procedia 2013, 37, 5055–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bayati, D.; Saeedi, A.; Myers, M.; et al. Insights into immiscible supercritical CO2 EOR: An XCT scanner assisted flow behaviour in layered sandstone porous media. Journal of CO2 Utilization 2019, 32, 187–195. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Li, Q.; Myers, M.; et al. Experimental and numerical investigation of supercritical CO2 migration in sandstone with multiple clay interlayers. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2021, 104, 103194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Myers, M.; Li, Q.; et al. Migration and storage characteristics of supercritical CO2 in anisotropic sandstones with clay interlayers based on X-CT experiments. Journal of Hydrology 2020, 580, 124239. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Li, X. Numerical simulation of displacement characteristics of CO2 injected in pore-scale porous media. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering 2016, 8, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Kogure, T.; Nishizawa, O.; Chiyonobu, S.; et al. Effect of Sub-core Scale Heterogeneity on Relative Permeability Curves of Porous Sandstone in a Water-supercritical CO2 System. Energy Procedia 2013, 37, 4491–4498. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Shen, Z.; et al. Estimation of CO2 Storage Capacity in Porous Media by using X-ray Micro-CT. Energy Procedia 2013, 37, 5201–5208. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, P.; Liu, Y.; Yang, W. Investigation on CO2 permeation in water-saturated porous media with disordered pore sizes. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science 2020, 119, 110207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lu, G.; et al. Experimental Evaluation of Injection Pressure and Flow Rate Effects on Geological CO2 Sequestration Using MRI. Energy Procedia 2017, 114, 4986–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Park, H.; Nishizawa, O.; et al. Fluid Distribution Effects on P-wave Velocity of CO2/brine Saturated Rocks: A Comparison Study and Implications for CO2 Storage Monitoring Using Seismic Method. Energy Procedia 2017, 114, 3786–3792. [Google Scholar]
- Herring, A.L.; Andersson, L.; Newell, D.L.; et al. Pore-scale observations of supercritical CO2 drainage in Bentheimer sandstone by synchrotron x-ray imaging. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2014, 25, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Teng, Y.; Lu, G.; et al. Experimental study on CO2 diffusion in bulk n-decane and n-decane saturated porous media using micro-CT. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2016, 417, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Yan, D.; Rossen, W.R. Steady-State Flow Behavior of CO2 Foam. SPE Journal 2013, 10, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Liu, N.; Lee, R. Effect of particle hydrophobicity on CO2 foam generation and foam flow behavior in porous media. Fuel 2014, 126, 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Fyen, T.; Bratteks, B.; Fern, M.A.; et al. Increased CO2 storage capacity using CO2-foam. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2020, 96, 103016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Nishio, S.; Hagiwara, N.; et al. Microbubble Carbon Dioxide Injection for Enhanced Dissolution in Geological Sequestration and Improved Oil Recovery. Energy Procedia 2014, 63, 7939–7946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patmonoaji, A.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, Z.; et al. Experimental and numerical simulation of supercritical CO2 microbubble injection into a brine-saturated porous medium. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2019, 91, 102830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, H.; Xue, Z.; Park, H.; et al. Migration characteristics of supercritical CO2 microbubble flow in the Berea sandstone revealed by voxel-based X-ray computed tomography imaging analysis. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering 2020, 77, 103233. [Google Scholar]
- Du, D.; Wang, D.; Jia, N.; et al. Experiments on CO2 foam seepage characteristics in porous media. Petroleum Exploration and Development 2016, 43, 499–505. [Google Scholar]
- McLendon, W.J.; Koronaios, P.; Enick, R.M.; et al. Assessment of CO2-soluble non-ionic surfactants for mobility reduction using mobility measurements and CT imaging. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 2014, 119, 196–209. [Google Scholar]
- Du, D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; et al. Experimental study on the inlet behavior of CO2 foam three phase displacement processes in porous media. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science 2019, 103, 247–261. [Google Scholar]
- Alhosani, A.; Lin, Q.; Scanziani, A.; et al. Pore-scale characterization of carbon dioxide storage at immiscible and near-miscible conditions in altered-wettability reservoir rocks. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2021, 105, 103232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Arshadi, M.; Piri, M. Near-miscible supercritical CO2 injection in oil-wet carbonate: A pore-scale experimental investigation of wettability state and three-phase flow behavior. Advances in Water Resources 2021, 158, 104057. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Y.; Li, Z.; Su, Y.; et al. Experimental investigation of CO2 storage and oil production of different CO2 injection methods at pore-scale and core-scale. Energy 2022, 254, 124349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HortonGeorge, W. Darcy’s Law. American Journal of Physics 1964, 32, 569. [Google Scholar]
- Mathias, S.A.; Gluyas, J.G.; Bryant, S.L.; et al. On the importance of relative permeability data for estimating CO2 injectivity in brine aquifers. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2013, 12, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, P.G.; Senthilnathan, S.; Yoon, H.; et al. Comparison of Darcy’s law and invasion percolation simulations with buoyancy-driven CO2-brine multiphase flow in a heterogeneous sandstone core. Journal of Petroleum Science & Engineering 2016, 155, 54–62. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, M.L.; Plampin, M.R.; Pawar, R.; et al. CO2 leakage in shallow aquifers: A benchmark modeling study of CO2 gas evolution in heterogeneous porous media. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2015, 39, 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, A.W.; Sharif, M.; Carlson, E.S. Numerical investigation of double diffusive natural convection of CO2 in a brine saturated geothermal reservoir. Geothermics 2013, 48, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathias, S.A.; Gluyas, J.G.; Bryant, S.L.; et al. On relative permeability data uncertainty and CO2 injectivity estimation for brine aquifers. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2013, 12, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guanhong, Feng, Tianfu, et al. Three-phase non-isothermal flow behavior of CO2-brine leakage from wellbores. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2017, 64, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhao, M.; Song, Y.; et al. Influence of Capillary Pressure and Injection Rate as well as Heterogeneous and Anisotropic Permeability on CO2 Transport and Displacement Efficiency in Water-Saturated Porous Media. Energy Procedia 2013, 37, 3945–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, E.M.; Yang, J.; Crawshaw, J.P.; et al. Pore Scale Models for Imbibition of CO2 Analogue Fluids in Etched Micro-model||junctions Using Micro-fluidic Experiments and Direct Flow Calculations. Energy Procedia 2013, 37, 3680–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovaysi, S.; Piri, M. Pore-scale dissolution of CO2+SO2 in deep saline aquifers. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2013, 15, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Valocchi, A.J.; Werth, C.; et al. Pore-scale simulation of liquid CO2 displacement of water using a two-phase lattice Boltzmann model. Advances in Water Resources 2014, 73, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswaran, S. Efficient Implementation of Turbulence Modeling for CFD. 363-367.
- Hang, S.C.; Park, H.C.; Huh, C.; et al. Numerical simulation of fluid flow and heat transfer of supercritical CO2 in micro-porous media. Energy Procedia 2011, 4, 3786–3793. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzoldi, A.; Colls, J.J.; Hill, T. Assessing the risk for CO2 transportation within CCS projects, CFD modeling. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2011, 5, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Godbole, A.; Lu, C.; et al. Investigation of the consequence of high-pressure CO2 pipeline failure through experimental and numerical studies. Applied Energy 2019, 250, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Hu, C. Numerical simulation of a rising CO2 droplet in the initial accelerating stage by a multiphase lattice Boltzmann method. Applied Ocean Research 2014, 45, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Chen, Shuyong, et al. Three-dimensional simulation of interfacial convection in CO2–ethanol system by hybrid lattice Boltzmann method with experimental validation. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering 2015, 23, 356–365. [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Zhan, H.; Lu, S.; et al. Pore Scale CO2 Displacement Simulation Based on Three Fluid Phase Lattice Boltzmann Method. Energy & Fuels 2019, 33, 10039–10055. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.; Kneafsey, T.J.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Scaling the impacts of pore-scale characteristics on unstable supercritical CO2-water drainage using a complete capillary number. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2019, 86, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhari, A.; Li, Y.; Bolster, D.; et al. A phase-field lattice Boltzmann model for simulating multiphase flows in porous media: Application and comparison to experiments of CO2 sequestration at pore scale. Advances in Water Resources 2018, 114, 119–134. [Google Scholar]
- Bakhshian, S.; Hosseini, S.A. Pore–scale analysis of supercritical CO2–brine immiscible displacement under fractional–wettability conditions. Advances in Water Resources 2019, 126, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Dalton, L.E.; Fan, M.; et al. The role of the spatial heterogeneity and correlation length of surface wettability on two-phase flow in a CO2-water-rock system. Advances in Water Resources 2020, 146, 103763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Dalton, L.; Crandall, D.; et al. Role of heterogeneous surface wettability on dynamic immiscible displacement, capillary pressure, and relative permeability in a CO2-water-rock system. Advances in Water Resources 2022, 165, 104226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atia, A.; Mohammedi, K. Pore-scale study based on lattice Boltzmann method of density driven natural convection during CO2 injection project. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering 2015, 23, 1593–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Su, Y.; Wang, W.; et al. CO2-oil diffusion, adsorption and miscible flow in nanoporous media from pore-scale perspectives. Chemical engineering journal 2022, 450, 137957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiotis, A.G.; Stubos, A.K.; Boudouvis, A.G.; et al. A 2-D pore-network model of the drying of single-component liquids in porous media. Advances in Water Resources 2001, 24, 439–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, H.J.; Tlke, J.; Schulz, V.P.; et al. Comparison of a Lattice-Boltzmann Model, a Full-Morphology Model, and a Pore Network Model for Determining Capillary Pressure–Saturation Relationships. Vadose Zone Journal 2005, 4, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benali, B.; Føyen, T.L.; Alcorn, Z.P.; et al. Pore-scale bubble population dynamics of CO2-foam at reservoir pressure. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2022, 114, 103607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Suzuki, A.; Ito, T. Estimating the seepage effect of SC-CO2 and water fracturing with a steady-state flow model considering capillary and viscous forces at the pore scale. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 2020, 184, 106483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.C.; Dai, S.; Jung, J. Supercritical CO2 and brine displacement in geological carbon sequestration: Micromodel and pore network simulation studies. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2016, 44, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Wan, J.; Kim, Y.; et al. Wettability effects on supercritical CO2–brine immiscible displacement during drainage: Pore-scale observation and 3D simulation. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 2017, 60, 129–139. [Google Scholar]
- Basirat, F.; Yang, Z.; Niemi, A. Pore-scale modeling of wettability effects on CO2–brine displacement during geological storage. Advances in Water Resources 2017, 109, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




