Submitted:
25 June 2023
Posted:
26 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
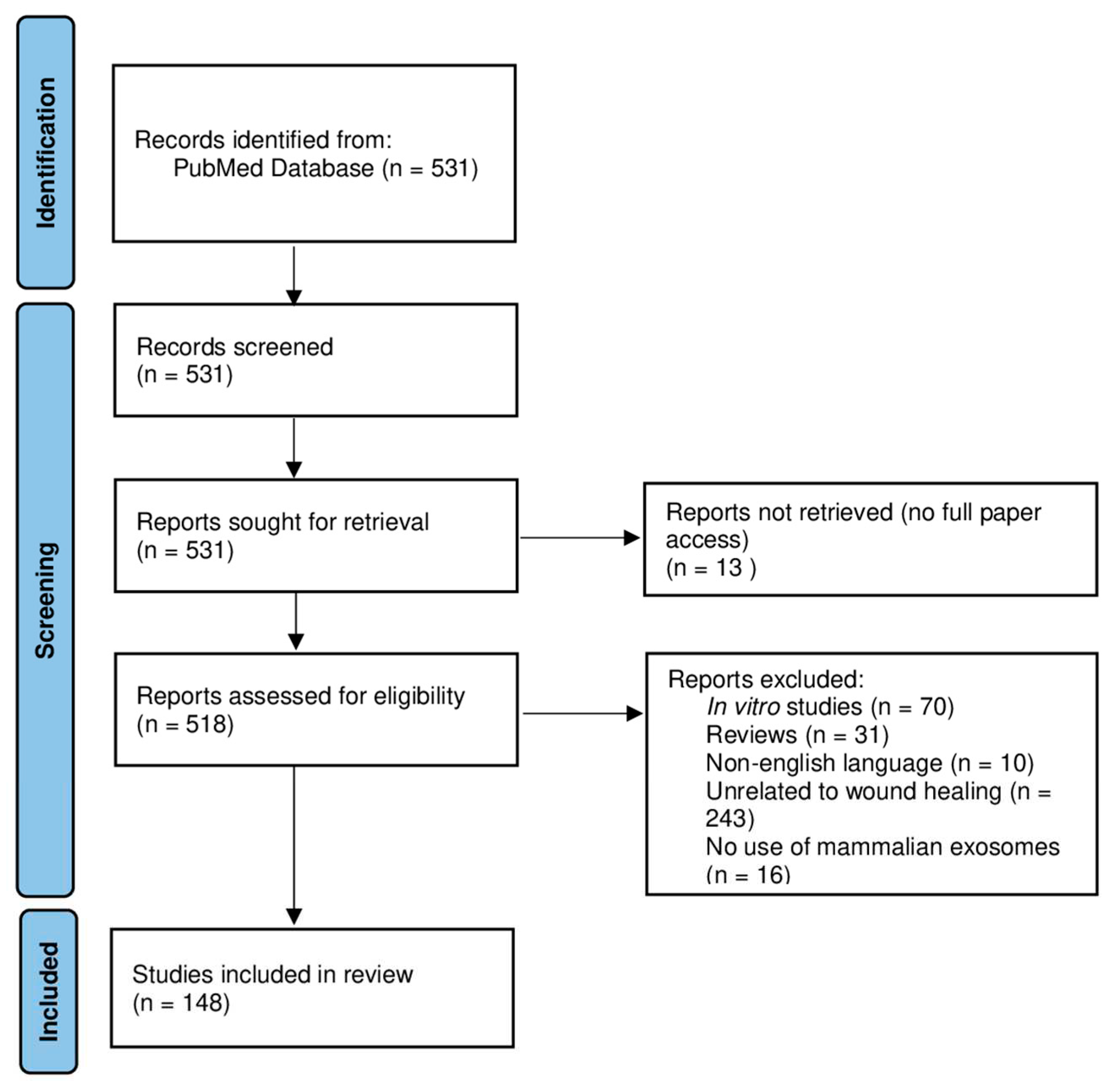
2. Data and Methods
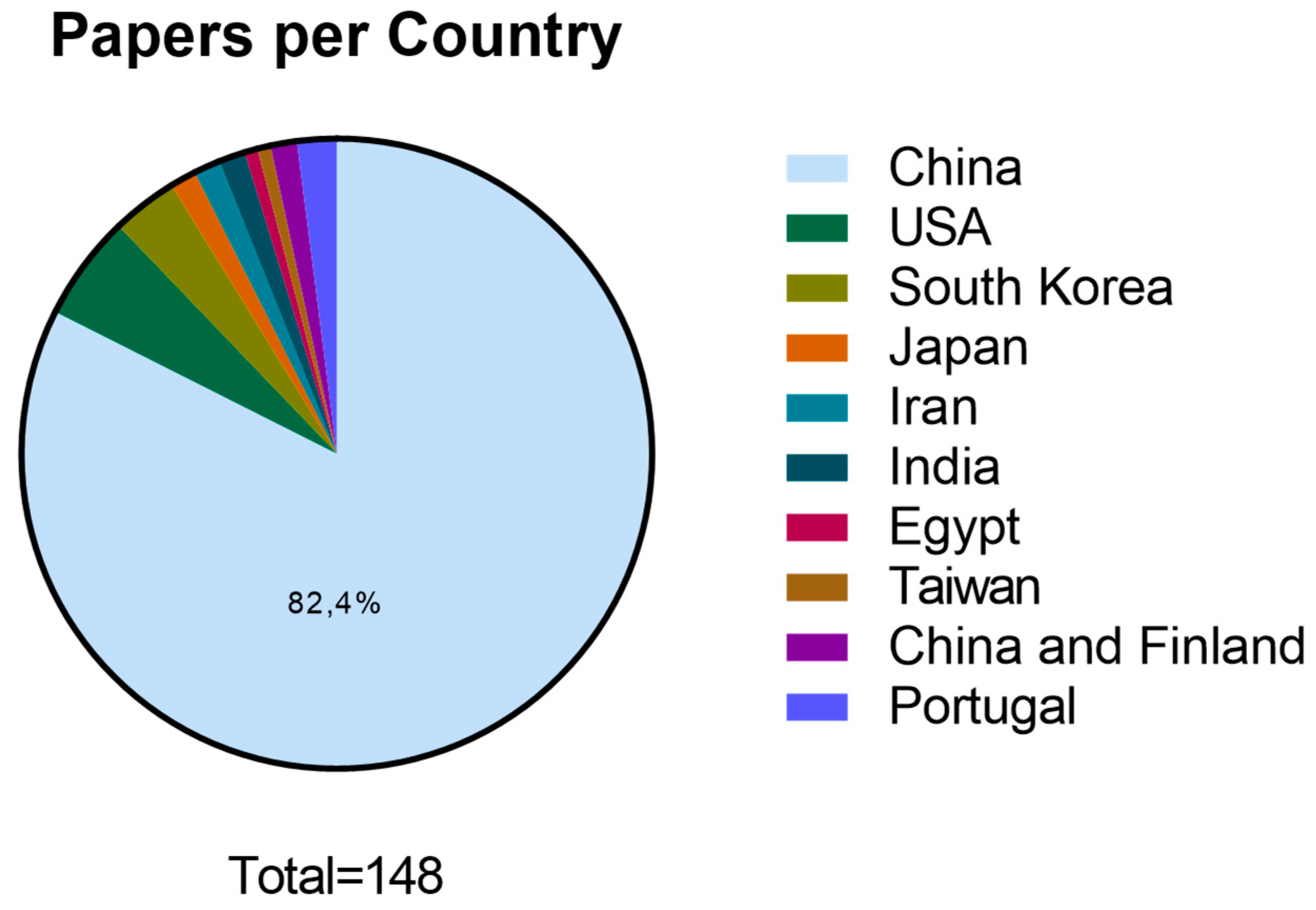
3. Results
3.1. Retrieved Data
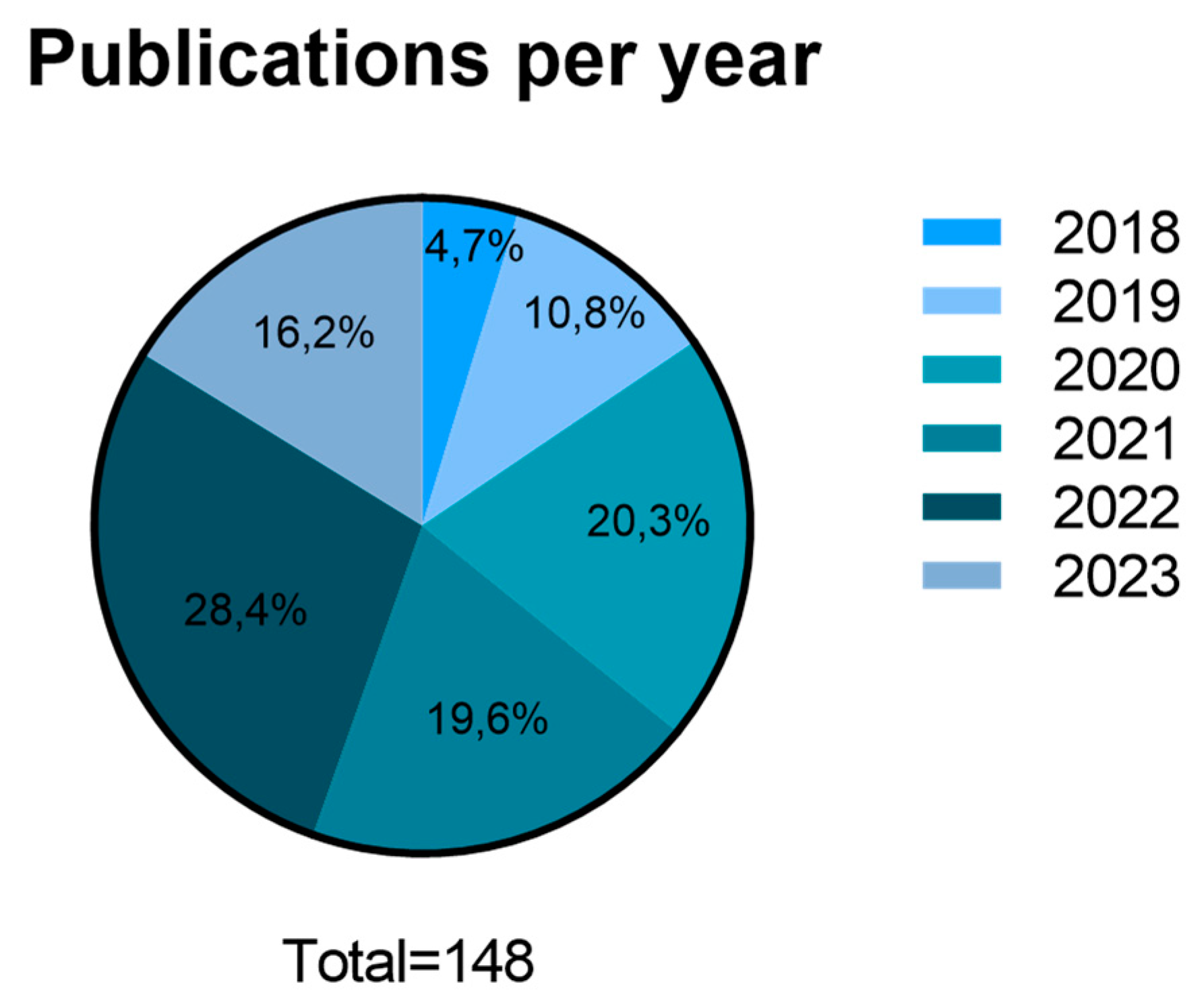
3.2. Scientific data production and publication distribution between 2018 and June 2023:
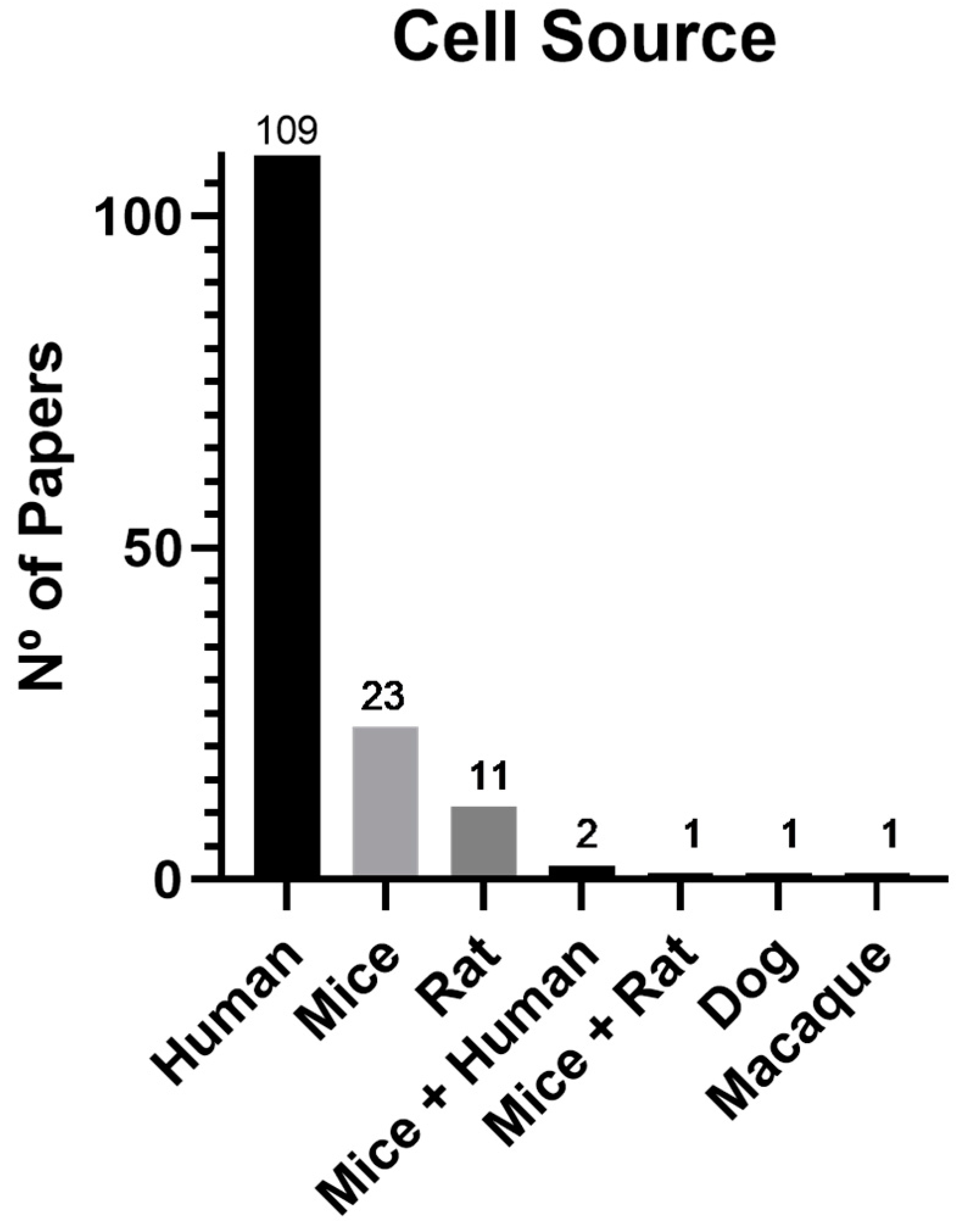
3.3. Cell source and type
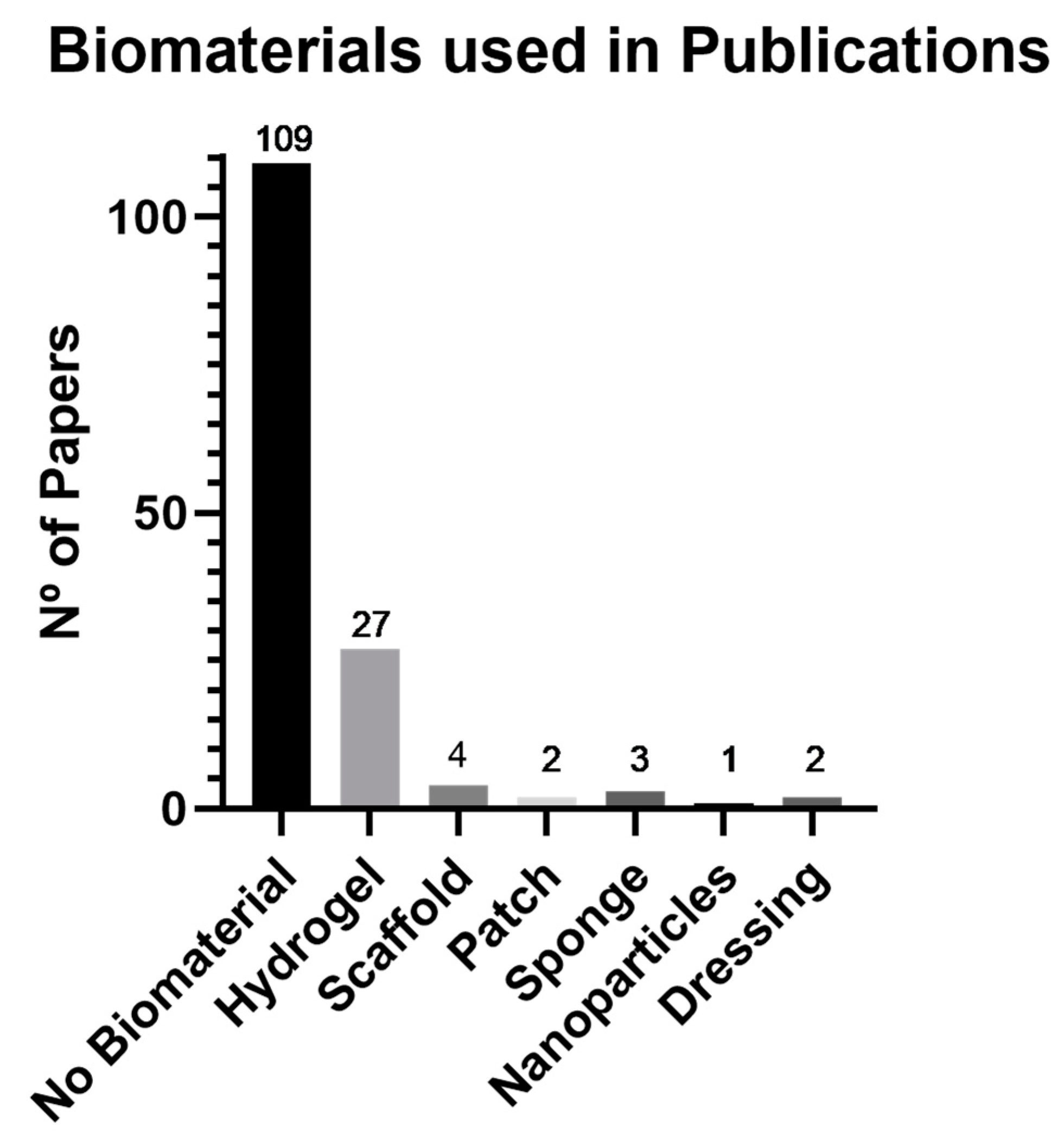
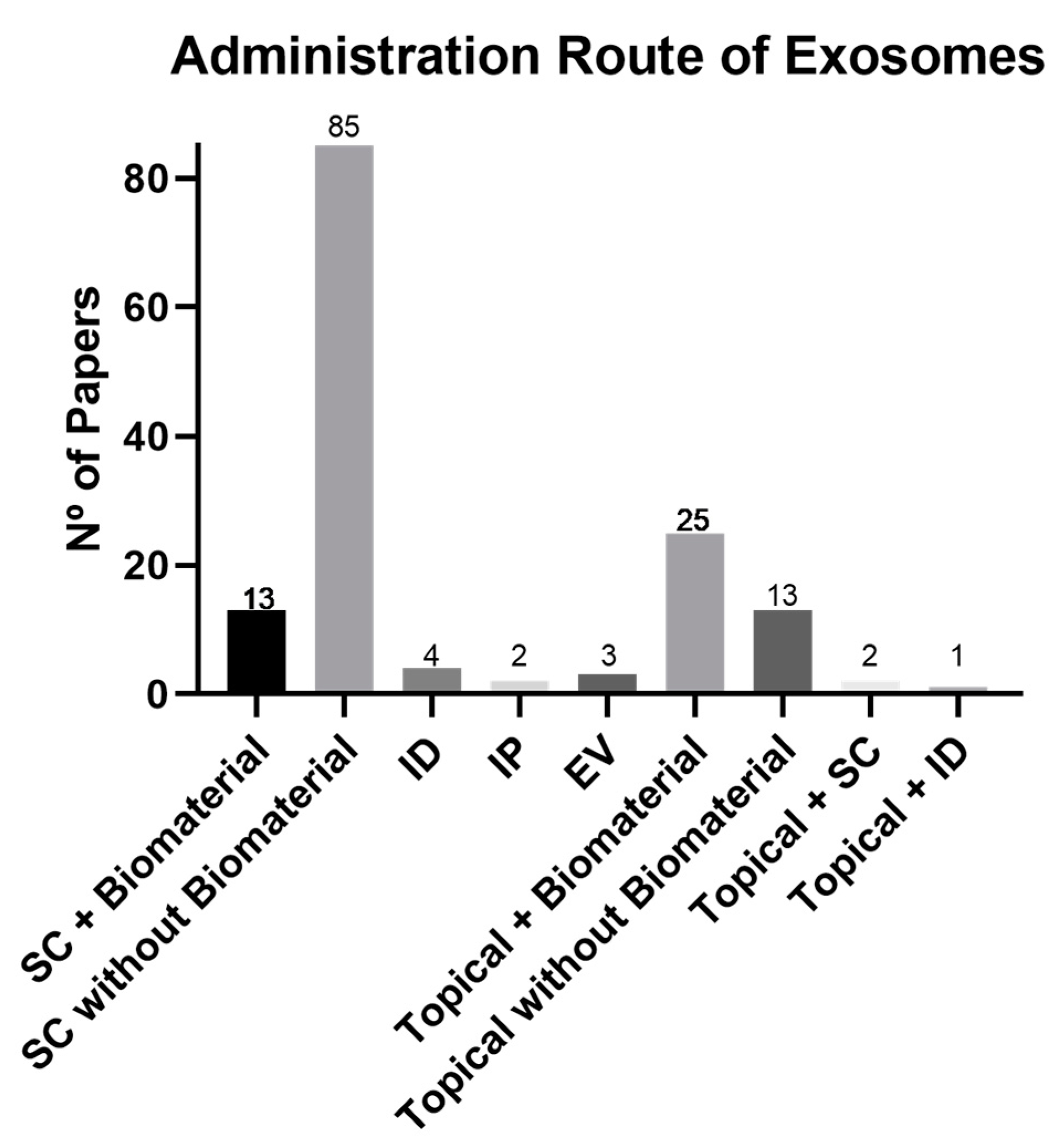
3.4. Biomaterials and Administration Route
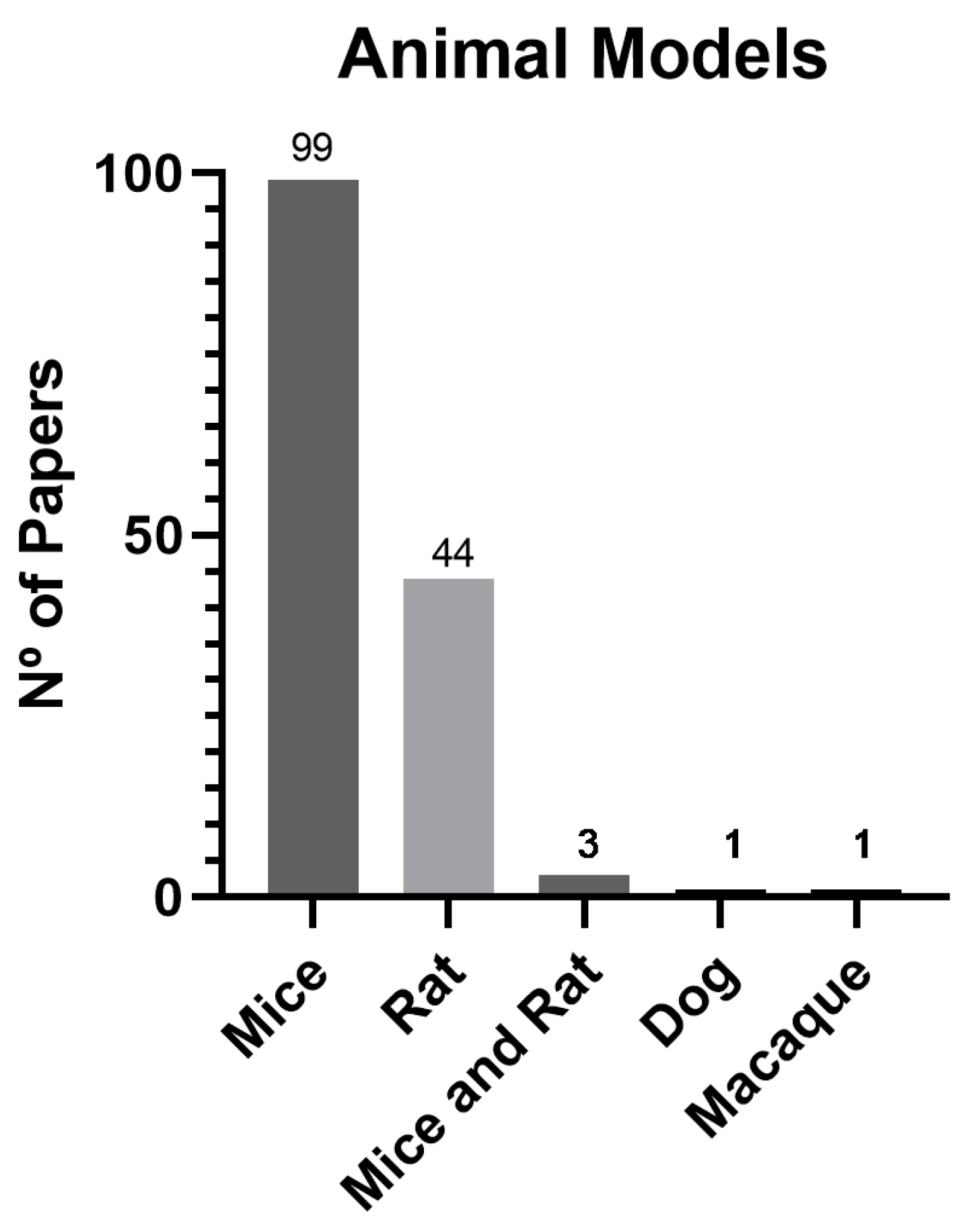
3.5. Animal Models
4. Discussion
4.1. Scientific data production and publication distribution between 2018 and June 2023:
4.2. Cell source and type
4.3. Biomaterials and Administration Route:
4.4. Animal Models
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Registration and protocol
Abbreviation
| ADSC | Adipose Tissue derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells |
| BMSC | Bone Marrow derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells |
| DPs | Dental Pulp derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells |
| EV | Endovenous |
| ID | Intradermal |
| IP | Intraperitoneal |
| iPSCs | Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells |
| MSCs | Mesenchymal Stem Cells |
| PMID | PubMed Identification |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| SC | Subcutaneous |
| UCMSC | Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells |
| UVEC | Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells |
References
- Carolina, M.; et al. Application of Cell-Based Therapies in Veterinary Dermatology, in Wound Healing—Recent Advances and Future Opportunities, M. Prof. Ana Colette, A. Dr. Rui Damásio, and G. Dr. Müzeyyen, Editors. 2023, IntechOpen: Rijeka. p. Ch. 1.
- Lopes, B.; et al. The Application of Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Wound Repair and Regeneration. Applied Sciences 2021, 11, 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Masawa, M.E.; et al. Efficacy and safety of small extracellular vesicle interventions in wound healing and skin regeneration: A systematic review and meta-analysis of animal studies. Theranostics 2022, 12, 6455–6508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; et al. Bioengineered MSC-derived exosomes in skin wound repair and regeneration. Front Cell Dev Biol 2023, 11, 1029671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: The dawn of diabetic wound healing. World J Diabetes 2022, 13, 1066–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, A.J.M.; et al. MSC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles to Heal Diabetic Wounds: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Preclinical Animal Studies. Stem Cell Rev Rep 2022, 18, 968–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikfarjam, S.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cell derived-exosomes: a modern approach in translational medicine. Journal of Translational Medicine 2020, 18, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells and application to skin wound healing. Cell Proliferation 2021, 54, e12993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasai, A.; et al. Role of Exosomes in Dermal Wound Healing: A Systematic Review. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2022, 142, 662–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.C.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: A novel and potential remedy for cutaneous wound healing and regeneration. World J Stem Cells 2022, 14, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; et al. Engineering Bioactive Self-Healing Antibacterial Exosomes Hydrogel for Promoting Chronic Diabetic Wound Healing and Complete Skin Regeneration. Theranostics 2019, 9, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; et al. Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Combined Pluronic F127 Hydrogel Promote Chronic Diabetic Wound Healing and Complete Skin Regeneration. Int J Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 5911–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; et al. Exosomes from human umbilical cord blood accelerate cutaneous wound healing through miR-21-3p-mediated promotion of angiogenesis and fibroblast function. Theranostics 2018, 8, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; et al. Melatonin-stimulated MSC-derived exosomes improve diabetic wound healing through regulating macrophage M1 and M2 polarization by targeting the PTEN/AKT pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther 2020, 11, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.; et al. GelMA/PEGDA microneedles patch loaded with HUVECs-derived exosomes and Tazarotene promote diabetic wound healing. Journal of Nanobiotechnology 2022, 20, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; et al. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes encapsulated in pluronic F127 hydrogel promote wound healing and regeneration. Stem Cell Res Ther 2022, 13, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; et al. Exosomes Derived from Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells with the Stimulation of Fe(3)O(4) Nanoparticles and Static Magnetic Field Enhance Wound Healing Through Upregulated miR-21-5p. Int J Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 7979–7993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; et al. Exosomes derived from pioglitazone-pretreated MSCs accelerate diabetic wound healing through enhancing angiogenesis. J Nanobiotechnology 2021, 19, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; et al. Hypoxia adipose stem cell-derived exosomes promote high-quality healing of diabetic wound involves activation of PI3K/Akt pathways. J Nanobiotechnology 2021, 19, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells overexpressing Nrf2 accelerate cutaneous wound healing by promoting vascularization in a diabetic foot ulcer rat model. Exp Mol Med 2018, 50, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; et al. All-in-One: Multifunctional Hydrogel Accelerates Oxidative Diabetic Wound Healing through Timed-Release of Exosome and Fibroblast Growth Factor. Small 2022, 18, e2104229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; et al. Exosomes Derived from Epidermal Stem Cells Improve Diabetic Wound Healing. J Invest Dermatol 2022, 142, 2508–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; et al. Exosome-Mediated Crosstalk between Keratinocytes and Macrophages in Cutaneous Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 12732–12748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; et al. Hypoxic ADSC-derived exosomes enhance wound healing in diabetic mice via delivery of circ-Snhg11 and induction of M2-like macrophage polarization. Biomed Pharmacother 2022, 153, 113463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; et al. Exosomes derived from atorvastatin-pretreated MSC accelerate diabetic wound repair by enhancing angiogenesis via AKT/eNOS pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther 2020, 11, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, X.; et al. A multifunctional antibacterial and self-healing hydrogel laden with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for accelerating diabetic wound healing. Biomater Adv 2022, 133, 112613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; et al. Circulating Exosomal miR-20b-5p Inhibition Restores Wnt9b Signaling and Reverses Diabetes-Associated Impaired Wound Healing. Small 2020, 16, e1904044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiekh, P.A.; Singh, A.; Kumar, A. Exosome laden oxygen releasing antioxidant and antibacterial cryogel wound dressing OxOBand alleviate diabetic and infectious wound healing. Biomaterials 2020, 249, 120020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; et al. SHED-derived exosomes promote LPS-induced wound healing with less itching by stimulating macrophage autophagy. J Nanobiotechnology 2022, 20, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; et al. Efficient Angiogenesis-Based Diabetic Wound Healing/Skin Reconstruction through Bioactive Antibacterial Adhesive Ultraviolet Shielding Nanodressing with Exosome Release. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 10279–10293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells stimulate regenerative wound healing via transforming growth factor-β receptor inhibition. Stem Cell Res Ther 2021, 12, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; et al. MSC-Derived Exosome Promotes M2 Polarization and Enhances Cutaneous Wound Healing. Stem Cells Int 2019 2019, 7132708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, G.; et al. Sustained Exosome-Guided Macrophage Polarization Using Hydrolytically Degradable PEG Hydrogels for Cutaneous Wound Healing: Identification of Key Proteins and MiRNAs, and Sustained Release Formulation. Small 2022, 18, e2200060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; et al. Exosomes derived from mmu_circ_0000250-modified adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote wound healing in diabetic mice by inducing miR-128-3p/SIRT1-mediated autophagy. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2020, 318, C848–c856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; et al. Exosomes released from educated mesenchymal stem cells accelerate cutaneous wound healing via promoting angiogenesis. Cell Prolif 2020, 53, e12830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, L.; et al. Adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes accelerate skin wound healing via the lncRNA H19/miR-19b/SOX9 axis. Lab Invest 2021, 101, 1254–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; et al. VH298-loaded extracellular vesicles released from gelatin methacryloyl hydrogel facilitate diabetic wound healing by HIF-1α-mediated enhancement of angiogenesis. Acta Biomater 2022, 147, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, J.S. , Selenium-Stimulated Exosomes Enhance Wound Healing by Modulating Inflammation and Angiogenesis. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; et al. Exosomes from Adipose Stem Cells Promote Diabetic Wound Healing through the eHSP90/LRP1/AKT Axis. Cells 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; et al. Exosome-Guided Phenotypic Switch of M1 to M2 Macrophages for Cutaneous Wound Healing. Adv Sci (Weinh) 2019, 6, 1900513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; et al. The MSC-Derived Exosomal lncRNA H19 Promotes Wound Healing in Diabetic Foot Ulcers by Upregulating PTEN via MicroRNA-152-3p. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2020, 19, 814–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; et al. Hypoxia-pretreated ADSC-derived exosome-embedded hydrogels promote angiogenesis and accelerate diabetic wound healing. Acta Biomater 2023, 157, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; et al. Human acellular amniotic membrane incorporating exosomes from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells promotes diabetic wound healing. Stem Cell Res Ther 2021, 12, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; et al. Serum exosomes accelerate diabetic wound healing by promoting angiogenesis and ECM formation. Cell Biol Int 2021, 45, 1976–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, W.; et al. Young fibroblast-derived exosomal microRNA-125b transfers beneficial effects on aged cutaneous wound healing. J Nanobiotechnology 2022, 20, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; et al. Cell-free therapy based on adipose tissue stem cell-derived exosomes promotes wound healing via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Exp Cell Res 2018, 370, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; et al. Microvesicles from human adipose stem cells promote wound healing by optimizing cellular functions via AKT and ERK signaling pathways. Stem Cell Res Ther 2019, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; et al. MiR146a-loaded engineered exosomes released from silk fibroin patch promote diabetic wound healing by targeting IRAK1. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2023, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; et al. Human embryonic stem cell-derived exosomes promote pressure ulcer healing in aged mice by rejuvenating senescent endothelial cells. Stem Cell Res Ther 2019, 10, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; et al. Comprehensive proteomic analysis of exosome mimetic vesicles and exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther 2022, 13, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.H.; et al. Exosomes from mmu_circ_0001052-modified adipose-derived stem cells promote angiogenesis of DFU via miR-106a-5p and FGF4/p38MAPK pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther 2022, 13, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; et al. Serum-derived exosomes accelerate scald wound healing in mice by optimizing cellular functions and promoting Akt phosphorylation. Biotechnol Lett 2021, 43, 1675–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; et al. Blockade of lncRNA-ASLNCS5088-enriched exosome generation in M2 macrophages by GW4869 dampens the effect of M2 macrophages on orchestrating fibroblast activation. Faseb j 2019, 33, 12200–12212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; et al. Exosomes Derived From Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Treat Cutaneous Nerve Damage and Promote Wound Healing. Front Cell Neurosci 2022, 16, 913009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; et al. Enhanced wound healing promotion by immune response-free monkey autologous iPSCs and exosomes vs. their allogeneic counterparts. EBioMedicine 2019, 42, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Quan, H. Adipose-derived stem cells-derived exosomes facilitate cutaneous wound healing by delivering XIST and restoring discoidin domain receptor 2. Cytokine 2022, 158, 155981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.; et al. Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Accelerate Diabetic Wound Healing via Ameliorating Oxidative Stress and Promoting Angiogenesis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2022, 10, 829868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; et al. Adipose mesenchymal stem cell exosomes promote wound healing through accelerated keratinocyte migration and proliferation by activating the AKT/HIF-1α axis. J Mol Histol 2020, 51, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, L.; et al. Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Accelerate Diabetic Wound Healing via Promoting M2 Macrophage Polarization, Angiogenesis, and Collagen Deposition. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; et al. MSC-derived exosomes attenuate cell death through suppressing AIF nucleus translocation and enhance cutaneous wound healing. Stem Cell Res Ther 2020, 11, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; et al. GelMA combined with sustained release of HUVECs derived exosomes for promoting cutaneous wound healing and facilitating skin regeneration. J Mol Histol 2020, 51, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; et al. Enhancing Cutaneous Wound Healing Based on Human Induced Neural Stem Cell-derived Exosomes. Int J Nanomedicine 2022, 17, 5991–6006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; et al. Engineered exosomes derived from miR-132-overexpresssing adipose stem cells promoted diabetic wound healing and skin reconstruction. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2023, 11, 1129538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, P.; et al. Exosomes derived from human amniotic epithelial cells accelerate diabetic wound healing via PI3K-AKT-mTOR-mediated promotion in angiogenesis and fibroblast function. Burns Trauma 2020, 8, tkaa020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, L.; et al. Exosomes derived from M2 macrophages induce angiogenesis to promote wound healing. Front Mol Biosci 2022, 9, 1008802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; et al. Combined topical and systemic administration with human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hADSC) and hADSC-derived exosomes markedly promoted cutaneous wound healing and regeneration. Stem Cell Res Ther 2021, 12, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; et al. Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Exosomes Delivered Using Silk Fibroin and Sericin Composite Hydrogel Promote Wound Healing. Front Cardiovasc Med 2021, 8, 713021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; et al. Macrophage-derived exosomes accelerate wound healing through their anti-inflammation effects in a diabetic rat model. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 2019, 47, 3793–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; et al. Bioinspired Adaptable Indwelling Microneedles for Treatment of Diabetic Ulcers. Adv Mater 2023, 35, e2210903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; et al. Preparation of exosomes encapsulated nanohydrogel for accelerating wound healing of diabetic rats by promoting angiogenesis. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 2021, 120, 111671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.F.; et al. PTH Derivative promotes wound healing via synergistic multicellular stimulating and exosomal activities. Cell Commun Signal 2020, 18, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; et al. Pharmaceutical Activation of Nrf2 Accelerates Diabetic Wound Healing by Exosomes from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int J Stem Cells 2022, 15, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; et al. Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Promote Wound Healing Through the WNT/β-catenin Signaling Pathway in Dermal Fibroblasts. Stem Cell Rev Rep 2022, 18, 2059–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote murine skin wound healing by neutrophil and macrophage modulations revealed by single-cell RNA sequencing. Front Immunol 2023, 14, 1142088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; et al. Application of adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes-loaded β-chitin nanofiber hydrogel for wound healing. Folia Histochem Cytobiol 2022, 60, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; et al. Exosomes Derived from Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Diabetic Chronic Wound Healing through SIRT3/SOD2. Cells 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöqvist, S.; et al. Exosomes derived from clinical-grade oral mucosal epithelial cell sheets promote wound healing. J Extracell Vesicles 2019, 8, 1565264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; et al. Exosomes derived from dental pulp stem cells accelerate cutaneous wound healing by enhancing angiogenesis via the Cdc42/p38 MAPK pathway. Int J Mol Med 2022, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; et al. Exosomes derived from autologous dermal fibroblasts promote diabetic cutaneous wound healing through the Akt/β-catenin pathway. Cell Cycle 2021, 20, 616–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camões, S.P.; et al. 3D-MSCs A151 ODN-loaded exosomes are immunomodulatory and reveal a proteomic cargo that sustains wound resolution. Journal of Advanced Research 2022, 41, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; et al. Placental stem cells-derived exosomes stimulate cutaneous wound regeneration via engrailed-1 inhibition. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2022, 10, 1044773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; et al. Exosome Mimetics-Loaded Hydrogel Accelerates Wound Repair by Transferring Functional Mitochondrial Proteins. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2022, 10, 866505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen Md, G.; et al. Effect of MicroRNA-146a Modified Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Exosomes on Rat Back Wound Healing. Int J Low Extrem Wounds 2021, 15347346211038092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; et al. MiR-221-3p targets HIPK2 to promote diabetic wound healing. Microvasc Res 2022, 140, 104306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; et al. Fetal Dermal Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Accelerate Cutaneous Wound Healing by Activating Notch Signaling. Stem Cells Int 2019, 2019, 2402916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; et al. miRNA-221-3p in Endothelial Progenitor Cell-Derived Exosomes Accelerates Skin Wound Healing in Diabetic Mice. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 2020, 13, 1259–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadpour, F.; et al. Effects of exosomes derived from fibroblast cells on skin wound healing in Wistar rats. Burns 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.H.; et al. Therapeutic Potential of Exosomes Derived from Diabetic Adipose Stem Cells in Cutaneous Wound Healing of db/db Mice. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvanian, S.; et al. Exosomal vimentin from adipocyte progenitors accelerates wound healing. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken) 2020, 77, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Born, L.J.; et al. HOTAIR-Loaded Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cell Extracellular Vesicles Enhance Angiogenesis and Wound Healing. Adv Healthc Mater 2022, 11, e2002070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; et al. Exosomes derived from TSG-6 modified mesenchymal stromal cells attenuate scar formation during wound healing. Biochimie 2020, 177, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; et al. Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Accelerate Cutaneous Wound Healing by Enhancing Angiogenesis through Delivering Angiopoietin-2. Stem Cell Reviews and Reports 2021, 17, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y., Y. Ju, and B. Fang, Exosomes from human adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal/stem cells accelerate angiogenesis in wound healing: implication of the EGR-1/lncRNA-SENCR/DKC1/VEGF-A axis. Hum Cell 2022, 35, 1375–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiekh, P.A., A. Singh, and A. Kumar, Data supporting exosome laden oxygen releasing antioxidant and antibacterial cryogel wound dressing OxOBand alleviate diabetic and infectious wound healing. Data Brief 2020, 31, 105671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; et al. The fabrication of a highly efficient self-healing hydrogel from natural biopolymers loaded with exosomes for the synergistic promotion of severe wound healing. Biomater Sci 2019, 8, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T., Z. Wang, and J. Sun, Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes stimulate cutaneous wound healing mediates through TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther 2020, 11, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakadia, B.M.; et al. Engineering homologous platelet-rich plasma, platelet-rich plasma-derived exosomes, and mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes-based dual-crosslinked hydrogels as bioactive diabetic wound dressings. Bioact Mater 2023, 28, 74–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvanian, S.; et al. Exosomal Vimentin from Adipocyte Progenitors Protects Fibroblasts against Osmotic Stress and Inhibits Apoptosis to Enhance Wound Healing. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.F.; et al. Hypoxic ucMSC-secreted exosomal miR-125b promotes endothelial cell survival and migration during wound healing by targeting TP53INP1. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2021, 26, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, M.; et al. Epidermal stem cell-derived exosomes promote skin regeneration by downregulating transforming growth factor-β1 in wound healing. Stem Cell Res Ther 2020, 11, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; et al. Engineered Human Adipose Stem-Cell-Derived Exosomes Loaded with miR-21-5p to Promote Diabetic Cutaneous Wound Healing. Mol Pharm 2020, 17, 1723–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; et al. Wound healing effects of a Curcuma zedoaria polysaccharide with platelet-rich plasma exosomes assembled on chitosan/silk hydrogel sponge in a diabetic rat model. Int J Biol Macromol 2018, 117, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; et al. Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Senescence Reduces the Wound Healing-Promoting Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Partially via miR-146a. Aging Dis 2021, 12, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalirfardouei, R.; et al. Promising effects of exosomes isolated from menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell on wound-healing process in diabetic mouse model. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 2019, 13, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, B.; et al. Saliva exosomes-derived UBE2O mRNA promotes angiogenesis in cutaneous wounds by targeting SMAD6. J Nanobiotechnology 2020, 18, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; et al. Exosome/metformin-loaded self-healing conductive hydrogel rescues microvascular dysfunction and promotes chronic diabetic wound healing by inhibiting mitochondrial fission. Bioact Mater 2023, 26, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K., T. Yu, and X. Wang, Inhibition of Circulating Exosomal miRNA-20b-5p Accelerates Diabetic Wound Repair. Int J Nanomedicine 2021, 16, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma-Derived Exosomal USP15 Promotes Cutaneous Wound Healing via Deubiquitinating EIF4A1. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021, 2021, 9674809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; et al. <Editors’ Choice> Effects of exosomes derived from the induced pluripotent stem cells on skin wound healing. Nagoya J Med Sci 2018, 80, 141–153. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelsaid, K.; et al. Exercise improves angiogenic function of circulating exosomes in type 2 diabetes: Role of exosomal SOD3. Faseb j 2022, 36, e22177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; et al. Endothelial progenitor cell derived exosomes mediated miR-182-5p delivery accelerate diabetic wound healing via down-regulating PPARG. Int J Med Sci 2023, 20, 468–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; et al. Exosomal miR-135a derived from human amnion mesenchymal stem cells promotes cutaneous wound healing in rats and fibroblast migration by directly inhibiting LATS2 expression. Stem Cell Res Ther 2020, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, W.; et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC01435 impedes diabetic wound healing by facilitating YY1-mediated HDAC8 expression. iScience 2022, 25, 104006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell-loaded β-chitin nanofiber hydrogel promote wound healing in rats. J Mater Sci Mater Med 2022, 33, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.H.; et al. Peroxiredoxin II with dermal mesenchymal stem cells accelerates wound healing. Aging (Albany NY) 2021, 13, 13926–13940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.J.; et al. Serpin-loaded extracellular vesicles promote tissue repair in a mouse model of impaired wound healing. J Nanobiotechnology 2022, 20, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; et al. Exosomes derived from Nr-CWS pretreated MSCs facilitate diabetic wound healing by promoting angiogenesis via the circIARS1/miR-4782-5p/VEGFA axis. Chin J Nat Med 2023, 21, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; et al. Exosomes Derived from Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Stimulated by Deferoxamine Accelerate Cutaneous Wound Healing by Promoting Angiogenesis. Biomed Res Int 2019, 2019, 9742765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; et al. Human Amniotic Fluid Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes as a Novel Cell-Free Therapy for Cutaneous Regeneration. Front Cell Dev Biol 2021, 9, 685873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, L.; et al. Exosomal microRNA-125a-3p from human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells promotes angiogenesis of wound healing through inhibiting PTEN. Mol Cell Biochem 2022, 477, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; et al. Exosomal MicroRNAs Derived from Human Amniotic Epithelial Cells Accelerate Wound Healing by Promoting the Proliferation and Migration of Fibroblasts. Stem Cells Int 2018, 2018, 5420463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; et al. Exosomes from linc00511-overexpressing ADSCs accelerates angiogenesis in diabetic foot ulcers healing by suppressing PAQR3-induced Twist1 degradation. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2021, 180, 109032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; et al. Inhibition of circulating exosomal microRNA-15a-3p accelerates diabetic wound repair. Aging (Albany NY) 2020, 12, 8968–8986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; et al. Adaptive Gelatin Microspheres Enhanced Stem Cell Delivery and Integration With Diabetic Wounds to Activate Skin Tissue Regeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2022, 10, 813805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; et al. Magnetic targeting enhances the cutaneous wound healing effects of human mesenchymal stem cell-derived iron oxide exosomes. J Nanobiotechnology 2020, 18, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; et al. Clinical-Scale Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Therapy for Wound Healing. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; et al. Local transplantation of GMSC-derived exosomes to promote vascularized diabetic wound healing by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin pathways. Nanoscale Adv 2023, 5, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; et al. Exosome loaded genipin crosslinked hydrogel facilitates full thickness cutaneous wound healing in rat animal model. Drug Deliv 2021, 28, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.F.; et al. Exosomal lncRNA KLF3-AS1 derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells stimulates angiogenesis to promote diabetic cutaneous wound healing. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2022, 183, 109126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, L.; et al. Human Keratinocyte-Derived Exosomal MALAT1 Promotes Diabetic Wound Healing by Upregulating MFGE8 via microRNA-1914-3p. Int J Nanomedicine 2023, 18, 949–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; et al. Exosomes derived from stem cells from apical papilla promote craniofacial soft tissue regeneration by enhancing Cdc42-mediated vascularization. Stem Cell Res Ther 2021, 12, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; et al. A moisturizing chitosan-silk fibroin dressing with silver nanoparticles-adsorbed exosomes for repairing infected wounds. J Mater Chem B 2020, 8, 7197–7212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, W.; et al. Exosomal miR-17-92 derived from human mesenchymal stem cells promotes wound healing by enhancing angiogenesis and inhibiting endothelial cell ferroptosis. Tissue Cell 2023, 83, 102124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; et al. Development of a novel RNAi therapy: Engineered miR-31 exosomes promoted the healing of diabetic wounds. Bioact Mater 2021, 6, 2841–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; et al. Dendritic epidermal T cells secreting exosomes promote the proliferation of epidermal stem cells to enhance wound re-epithelialization. Stem Cell Res Ther 2022, 13, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; et al. Genetic Background and Kinetics Define Wound Bed Extracellular Vesicles in a Mouse Model of Cutaneous Injury. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; et al. Analysis of miR-203a-3p/SOCS3-mediated induction of M2 macrophage polarization to promote diabetic wound healing based on epidermal stem cell-derived exosomes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2023, 197, 110573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; et al. Circulating Exosomal miR-181b-5p Promoted Cell Senescence and Inhibited Angiogenesis to Impair Diabetic Foot Ulcer via the Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2/Heme Oxygenase-1 Pathway. Front Cardiovasc Med 2022, 9, 844047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques-Antunes, H.; et al. The Kinetics of Small Extracellular Vesicle Delivery Impacts Skin Tissue Regeneration. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 8694–8707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; et al. M2 macrophage-derived exosome-encapsulated microneedles with mild photothermal therapy for accelerated diabetic wound healing. Mater Today Bio 2023, 20, 100649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, R.M.S.; et al. Development of an optimized and scalable method for isolation of umbilical cord blood-derived small extracellular vesicles for future clinical use. Stem Cells Transl Med 2021, 10, 910–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; et al. Optogenetic engineered umbilical cord MSC-derived exosomes for remodeling of the immune microenvironment in diabetic wounds and the promotion of tissue repair. J Nanobiotechnology 2023, 21, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; et al. Exosomes from microRNA-126 overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells promote angiogenesis by targeting the PIK3R2-mediated PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med 2021, 25, 2148–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, X.; et al. The Fas/Fap-1/Cav-1 complex regulates IL-1RA secretion in mesenchymal stem cells to accelerate wound healing. Sci Transl Med 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; et al. Lean adipose tissue macrophage derived exosome confers immunoregulation to improve wound healing in diabetes. J Nanobiotechnology 2023, 21, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate derived from PRP-Exos promotes angiogenesis in diabetic wound healing via the S1PR1/AKT/FN1 signalling pathway. Burns Trauma 2023, 11, tkad003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; et al. Hair follicle mesenchymal stem cell exosomal lncRNA H19 inhibited NLRP3 pyroptosis to promote diabetic mouse skin wound healing. Aging (Albany NY) 2023, 15, 791–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, G.; et al. Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Exosomal microRNA-19b Promotes the Healing of Skin Wounds Through Modulation of the CCL1/TGF-β Signaling Axis. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 2020, 13, 957–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; et al. Exosomal IRF1-loaded rat adipose-derived stem cell sheet contributes to wound healing in the diabetic foot ulcers. Mol Med 2023, 29, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; et al. Sprayable alginate hydrogel dressings with oxygen production and exosome loading for the treatment of diabetic wounds. Int J Biol Macromol 2023, 242 Pt 3, 125081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; et al. Inhibition of exosomal miR-24-3p in diabetes restores angiogenesis and facilitates wound repair via targeting PIK3R3. J Cell Mol Med 2020, 24, 13789–13803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.; et al. Biotin-Avidin System-Based Delivery Enhances the Therapeutic Performance of MSC-Derived Exosomes. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 8530–8550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, Y.U.; et al. Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived mmu-miR-291a-3p Inhibits Cellular Senescence in Human Dermal Fibroblasts Through the TGF-β Receptor 2 Pathway. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2019, 74, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; et al. Highly-expressed micoRNA-21 in adipose derived stem cell exosomes can enhance the migration and proliferation of the HaCaT cells by increasing the MMP-9 expression through the PI3K/AKT pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys 2020, 681, 108259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, M.C.; et al. Protecting human amnion and chorion matrices (HACM) during processing: Performance enhancement in a Diabetic Mouse Model and Human Co-culture System. Wound Repair Regen 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; et al. A therapeutic role of exosomal lncRNA H19 from adipose mesenchymal stem cells in cutaneous wound healing by triggering macrophage M2 polarization. Cytokine 2023, 165, 156175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahr, M.M.; et al. Proficiency of Carboxymethylcellulose as a Cryoprotectant. Clinical and Histological Evaluation of Cryopreserved Heterogenous Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Exosomal Hydrogel on Critical Size Skin Wounds in Dogs. Int J Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Res 2021, 15, 178–191. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; et al. Exosomes derived from human adipose mesenchymal stem cells attenuate hypertrophic scar fibrosis by miR-192-5p/IL-17RA/Smad axis. Stem Cell Res Ther 2021, 12, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huayllani, M.T.; et al. Adipose-derived stem cells in wound healing of full-thickness skin defects: a review of the literature. Journal of Plastic Surgery and Hand Surgery 2020, 54, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, C.; et al. An overview of the therapeutic potential of regenerative medicine in cutaneous wound healing. International Wound Journal 2017, 14, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaei, F., S. Rahmati, and M. Banitalebi Dehkordi, A review on different methods to increase the efficiency of mesenchymal stem cell-based wound therapy. Wound Repair and Regeneration 2019, 27, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golchin, A.; et al. Combination Therapy of Stem Cell-derived Exosomes and Biomaterials in the Wound Healing. Stem Cell Reviews and Reports 2022, 18, 1892–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustad, K.C.; et al. Enhancement of mesenchymal stem cell angiogenic capacity and stemness by a biomimetic hydrogel scaffold. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilforoushzadeh, M.A.; et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Spheroids Embedded in an Injectable Thermosensitive Hydrogel: An In Situ Drug Formation Platform for Accelerated Wound Healing. ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering 2020, 6, 5096–5109. [Google Scholar]
- Grada, A.; Mervis, J.; Falanga, V. Research Techniques Made Simple: Animal Models of Wound Healing. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2018, 138, 2095–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sami, D.G.; Heiba, H.H.; Abdellatif, A. Wound healing models: A systematic review of animal and non-animal models. Wound Medicine 2019, 24, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, S.; Martins-Green, M. Animal models for the study of acute cutaneous wound healing. Wound Repair and Regeneration 2023, 31, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peric, M.; et al. The rational use of animal models in the evaluation of novel bone regenerative therapies. Bone 2015, 70, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, R.B.M.; et al. The Usefulness of Systematic Reviews of Animal Experiments for the Design of Preclinical and Clinical Studies. ILAR Journal 2014, 55, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, S.E.; et al. Local delivery of allogeneic bone marrow and adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells for cutaneous wound healing in a porcine model. Journal of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine 2016, 10, E90–E100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochiai, H.; et al. Transplanted mesenchymal stem cells are effective for skin regeneration in acute cutaneous wounds of pigs. Regenerative Therapy 2017, 7, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinello, T.; et al. Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells improve the wound healing process of sheep skin. BMC Veterinary Research 2018, 14, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.; et al. Cell therapy with human MSCs isolated from the umbilical cord Wharton jelly associated to a PVA membrane in the treatment of chronic skin wounds. Int J Med Sci 2014, 11, 979–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enciso, N.; et al. Cutaneous wound healing: canine allogeneic ASC therapy. Stem Cell Research & Therapy 2020, 11, 261. [Google Scholar]
- Cibelli, J.; et al. Strategies for Improving Animal Models for Regenerative Medicine. Cell Stem Cell 2013, 12, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Ref | Year | Country | Cell Source | Cell Type | Biomaterial | Administration Route | Animal Models |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [11] | 2019 | China | Human | ADSC | Hydrogel | SC Injection | Mice |
| [12] | 2020 | China | Human | UCMSC | Hydrogel | SC Injection | Rat |
| [13] | 2018 | China | Human | UCMSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [14] | 2020 | China | Human | BMSC | x | SC Injection | Rat |
| [15] | 2022 | China | Human | UVEC | Patch | Patch | Mice |
| [16] | 2022 | China | Human | ADSC | Hydrogel | Topical | Mice |
| [17] | 2020 | China | Human | BMSC | x | SC Injection | Rat |
| [18] | 2021 | China | Rat | BMSC | x | SC Injection | Rat |
| [19] | 2021 | China | Human | ADSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [20] | 2018 | China | Human | ADSC | x | SC Injection | Rat |
| [21] | 2022 | China | Mice | BMSC | Hydrogel | SC Injection | Mice |
| [22] | 2022 | USA | Human | Epidermal | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [23] | 2020 | USA | Mice | Keratinocyte | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [24] | 2022 | China | Human | ADSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [25] | 2020 | China | Human | BMSC | x | SC Injection | Rat |
| [26] | 2022 | China | Rat | BMSC | Hydrogel | Topical | Rat |
| [27] | 2020 | China | Human | Peripheral Blood | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [28] | 2020 | India | Rat | ADSC | Scaffold | Scaffold | Rat |
| [29] | 2022 | China | Human | DPs | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [30] | 2019 | China | Human | ADSC | Scaffold | Scaffold | Mice |
| [31] | 2021 | China | Human | UCMSC | x | EV Injection | Rat |
| [32] | 2019 | China | Human | BMSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [33] | 2022 | Korea | Mice | BMSC | Hydrogel | SC Injection | Mice |
| [34] | 2020 | China | Human | ADSC | x | SC Injection | Rat |
| [35] | 2020 | China | Mice | BMSC | x | ID Injection | Mice |
| [36] | 2021 | China | Human | ADSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [37] | 2022 | China | Human | Epidermal | Hydrogel | SC Injection | Mice |
| [38] | 2022 | Korea | Human | ADSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [39] | 2022 | China | Human | ADSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [40] | 2019 | Korea | Mice | BMSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [41] | 2020 | China | Human | BMSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [42] | 2023 | China | Mice | ADSC | Hydrogel | SC Injection | Mice |
| [43] | 2021 | China | Human | ADSC | Scaffold | Scaffold | Mice |
| [44] | 2021 | China | Mice | Serum | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [45] | 2022 | China | Mice | Fibroblast | x | ID Injection | Mice |
| [46] | 2018 | China | Human | ADSC | x | SC and ID Injection | Mice |
| [47] | 2019 | China | Human | ADSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [48] | 2023 | China | Human | Placenta | Patch | Patch | Mice |
| [49] | 2019 | China | Human | Embryonic | x | Topical | Mice |
| [50] | 2022 | China | Human | UCMSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [51] | 2022 | China | Mice | ADSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [52] | 2021 | China | Rat and Mice | Serum | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [53] | 2019 | China | Human | Macrophage | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [54] | 2022 | China | Human | UCMSC | x | Topical | Mice |
| [55] | 2019 | China | Macaque | iPSCs | x | Topical | Macaque |
| [56] | 2022 | China | Mice | ADSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [57] | 2022 | China | Human | UCMSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [58] | 2020 | China | Human | ADSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [59] | 2022 | China | Human | UCMSC | x | SC Injection | Rat |
| [60] | 2020 | China | Human | UCMSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [61] | 2020 | China | Human | UVEC | Hydrogel | Topical | Rat |
| [62] | 2022 | China | Human | iPSCs | Hydrogel | Topical | Mice |
| [63] | 2023 | China | Mice | ADSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [64] | 2020 | China | Human | Amniotic Membrane | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [65] | 2022 | China | Human | UVEC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [66] | 2021 | China | Human | ADSC | x | Injection and Topical | Mice |
| [67] | 2021 | China | Human | UCMSC | Hydrogel | Topical | Mice |
| [68] | 2019 | China | Human | UVEC | x | SC Injection | Rat |
| [69] | 2023 | China | Human | UVEC | Hydrogel | Microneedle | Rat |
| [70] | 2021 | China | Human | UCMSC | Hydrogel | SC Injection | Rat |
| [71] | 2020 | China | Human | UVEC | Hydrogel | SC Injection | Rat |
| [72] | 2022 | China | Rat | BMSC | x | SC Injection | Rat |
| [73] | 2022 | China | Human | ADSC | x | SC Injection | Rat |
| [74] | 2023 | China | Human | UCMSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [75] | 2022 | China | Mice | ADSC | Hydrogel | Topical | Rat |
| [76] | 2022 | China | Human | ADSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [77] | 2019 | Japan | Human | Epithelial | x | Topical | Rat |
| [78] | 2022 | China | Human | DPs | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [79] | 2021 | China | Rat | Dermal | x | SC Injection | Rat |
| [80] | 2022 | Portugal | Human | UCMSC | x | SC Injection | Rat |
| [81] | 2022 | China | Rat | Placenta and ADSC | x | SC Injection | Rat |
| [82] | 2022 | China | Human | UCMSC | Hydrogel | SC Injection | Mice |
| [83] | 2021 | China | Human | ADSC | x | SC Injection | Rat |
| [84] | 2022 | China | Human | UVEC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [85] | 2019 | China | Human | Fetal dermal | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [86] | 2020 | China | Mice | BMSC | x | Topical | Mice |
| [87] | 2023 | Iran | Human | Fetal dermal | x | Topical | Rat |
| [88] | 2022 | Taiwan | Mice | ADSC and dermal | x | Topical | Mice |
| [89] | 2020 | China and Finland | Human | ADSC | x | IP Injection | Mice |
| [90] | 2022 | USA | Human | BMSC | x | SC Injection | Mice and Rat |
| [91] | 2020 | China | Human | BMSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [92] | 2021 | China | Human | UCMSC | x | SC Injection | Rat |
| [93] | 2022 | China | Human | ADSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [94] | 2020 | India | Rat | ADSC | Scaffold | Scaffold | Rat |
| [95] | 2019 | China | Human | Placenta | Hydrogel | SC Injection | Mice |
| [96] | 2020 | China | Human | BMSC | x | SC Injection | Rat |
| [97] | 2023 | China | Rat | BMSC and plasma | Hydrogel | Topical | Rat |
| [98] | 2021 | China and Finland | Human | ADSC | x | IP Injection | Mice |
| [99] | 2021 | China | Human | UCMSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [100] | 2020 | China | Human | Epidermal | x | SC Injection | Rat |
| [101] | 2020 | China | Human | ADSC | Hydrogel | Topical | Rat |
| [102] | 2018 | China | Human | Plasma | Sponge | Sponge | Rat |
| [103] | 2021 | China | Human | UCMSC and ADSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [104] | 2019 | Iran | Human | Menstrual Blood | x | ID Injection | Mice |
| [105] | 2020 | China | Human | Saliva | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [106] | 2023 | China | Human | ADSC | Hydrogel | SC Injection | Mice |
| [107] | 2021 | China | Human | Peripheral Blood | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [108] | 2021 | China | Mice | Plasma | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [109] | 2018 | Japan | Human | iPSCs | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [110] | 2022 | USA | Mice and Human | Plasma | x | Topical | Mice |
| [111] | 2023 | China | Human | UCMSC | x | Topical | Mice |
| [112] | 2020 | China | Human | Amnion | x | SC Injection | Rat |
| [113] | 2022 | China | Human | Keratinocyte | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [114] | 2022 | China | Mice | ADSC | Hydrogel | SC Injection | Rat |
| [115] | 2021 | China | Mice | Dermal | x | ID Injection | Mice |
| [116] | 2022 | USA | Mice | Skin | Sponge | Sponge | Mice |
| [117] | 2023 | China | Human | UCMSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [118] | 2019 | China | Human | BMSC | x | SC Injection | Rat |
| [119] | 2021 | China | Human | Amniotic Fluid | x | SC Injection | Rat |
| [120] | 2022 | China | Human | ADSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [121] | 2018 | China | Human | Amniotic Fluid | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [122] | 2021 | China | Human | ADSC | x | SC Injection | Rat |
| [123] | 2020 | China | Human | Peripheral Blood | x | Injection | Mice |
| [124] | 2022 | China | Rat | ADSC | Hydrogel | Topical | Rat |
| [125] | 2020 | China | Human | UCMSC | Nanoparticles | EV Injection | Rat |
| [126] | 2023 | Korea | Human | UCMSC | x | Injection and Topical | Mice and Rat |
| [127] | 2022 | China | Human | Gingival | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [128] | 2021 | China | Human | UCMSC | Hydrogel | Topical | Rat |
| [129] | 2022 | China | Human | BMSC | x | EV Injection | Mice |
| [130] | 2023 | China | Human | Keratinocyte | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [131] | 2021 | China | Human | DPs | x | Topical | Mice |
| [132] | 2020 | China | Human | UCMSC | Dressing | Topical | Mice |
| [133] | 2023 | China | Human | UCMSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [134] | 2021 | China | Human | Embryonic | x | SC Injection | Rat |
| [135] | 2022 | China | Mice | Dendritic epidermal T cells | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [136] | 2021 | USA | Mice | Skin | Sponge | Topical | Mice |
| [137] | 2023 | China | Human | Epidermal | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [138] | 2022 | China | Human | UVEC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [139] | 2019 | Portugal | Human | UCMSC | Hydrogel | Topical | Mice |
| [140] | 2023 | China | Mice | Macrophage | x | Topical | Rat |
| [141] | 2021 | Portugal | Human | UCMSC | Hydrogel | Topical | Mice |
| [142] | 2023 | China | Human | UCMSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [143] | 2021 | China | Human | BMSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [144] | 2018 | USA | Mice and Human | BMSCs, Skin and Gingiva | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [145] | 2023 | China | Mice | ADSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [146] | 2023 | China | Human | Plasma | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [147] | 2023 | China | Human | Hair follicle | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [148] | 2020 | China | Human | ADSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [149] | 2023 | China | Rat | ADSC | x | SC Injection | Rat |
| [150] | 2023 | China | Mice | BMSC | Dressing | Topical | Rat |
| [151] | 2020 | China | Human | Peripheral Blood | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [152] | 2023 | China | Rat | BMSC | Hydrogel | SC Injection | Mice and Rat |
| [153] | 2019 | Korea | Human | Fibroblast | x | Topical | Mice |
| [154] | 2020 | China | Human | ADSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [155] | 2023 | USA | Human | Placenta | x | Topical | Mice |
| [156] | 2023 | China | Human | ADSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| [157] | 2021 | Egypt | Dog | BMSC | Hydrogel | Topical | Dog |
| [158] | 2021 | China | Human | ADSC | x | SC Injection | Mice |
| Human (109 studies) | Mice (23 studies) | Rat (11 studies) | |
| BMSC | 11 (10,1%) | 6 (26,1%) | 4 (36,4%) |
| ADSC | 29 (26,6%) | 7 (30,4%) | 4 (36,4%) |
| UCMSC | 25 (22,9%) | X | X |
| UVECS | 8 (7,3%) | X | X |
| DP | 3 (2,8%) | X | X |
| Epidermal | 4 (3,7%) | X | X |
| Peripherical Blood | 4 (3,7%) | X | X |
| Placenta | 3 (2,8%) | X | X |
| Others | 22 (20,2%) | 10 (43,5%) | 3 (27,3%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





