1. Introduction
The identification of new ligands of specific receptors responsible for the regulation of immune responses and the uncovering of the mechanisms of action of these proteins are essential for understanding the functioning of the immune system.
We investigated the involvement of the Tag7 protein (PGLYRP1) in the regulation of immune mechanisms and discovered a number of new functions of this protein in the immune response. We have shown that Tag7 is a ligand of the TNFR1 proinflammatory receptor present on the surface of many cells, including immune and tumor cells. [
1] Via binding to TNFR1, Tag7 inhibits the death of tumor cells under the action of a specific ligand of this TNF receptor or DNA-hydrolyzing autoantibodies. [
2,
3] We also showed that Tag7 forms a stable, equimolar cytotoxic complex with the main heat shock protein Hsp70, which induces an apoptotic and necroptotic pathway of tumor cell death when interacting with TNFR1. [
2]
The study of the mechanisms of tumor cell death under the action of cytotoxic T-lymphocytes allowed us to establish that Tag7 exposed on the cell surface of CD4+-T lymphocytes can interact with Hsp70 on the surface of a tumor cell and ensure the binding of a lymphocyte to a target cell with subsequent induction of cell death due to the interaction of the FasL lymphocyte with the Fas receptor of a tumor cell. [
4]
One of the approaches to understanding the mechanisms of action of proteins in the regulation of the immune response, as well as to the use of these proteins in immunotherapy, is to identify biologically active epitopes of regulatory proteins interacting with receptors. Also, peptide fragments can simulate the functional activity of a full-sized protein. By binding to the receptor, they can both inhibit and activate its functions. Such functional peptides can be used as medications. [
5]
Recently, we have isolated peptide 17.1, located in the C-terminal region of the polypeptide chain of the Tag7 protein, which has the bifunctional activity inherent in a full-sized protein. Like Tag7, peptide 17.1 bound to TNFR1 and inhibited cell death processes induced by other ligands of this receptor. [
6] In combination with Hsp70, this peptide initiated apoptotic and necroptotic processes in the tumor cell. [
6] It has also been shown that the shortened fragment of this peptide, peptide 17.1A, also inhibits the activation of TNFR1 under the action of other ligands of this receptor. [
7] Both peptides showed a protective effect in the development of PATH-dependent autoimmune arthritis in a mouse model. [
6,
7]
The purpose of this study was to expand the understanding of the functional activity of peptide 17.1: (1) to divide the activity of bifunctional peptide 17.1, to identify its shortened fragments interacting with the TNFR1 receptor or with the Hsp70 protein; (2) to find out the possibility of binding of this peptide and its shortened fragments with the TNFR1 receptor on the surface of tumor cells and their effect on cytotoxic activity CD4+- T lymphocytes.
2. Results
2.1. Peptides 17.1A and 17.1B bind to TNFR1 on the cell surface.
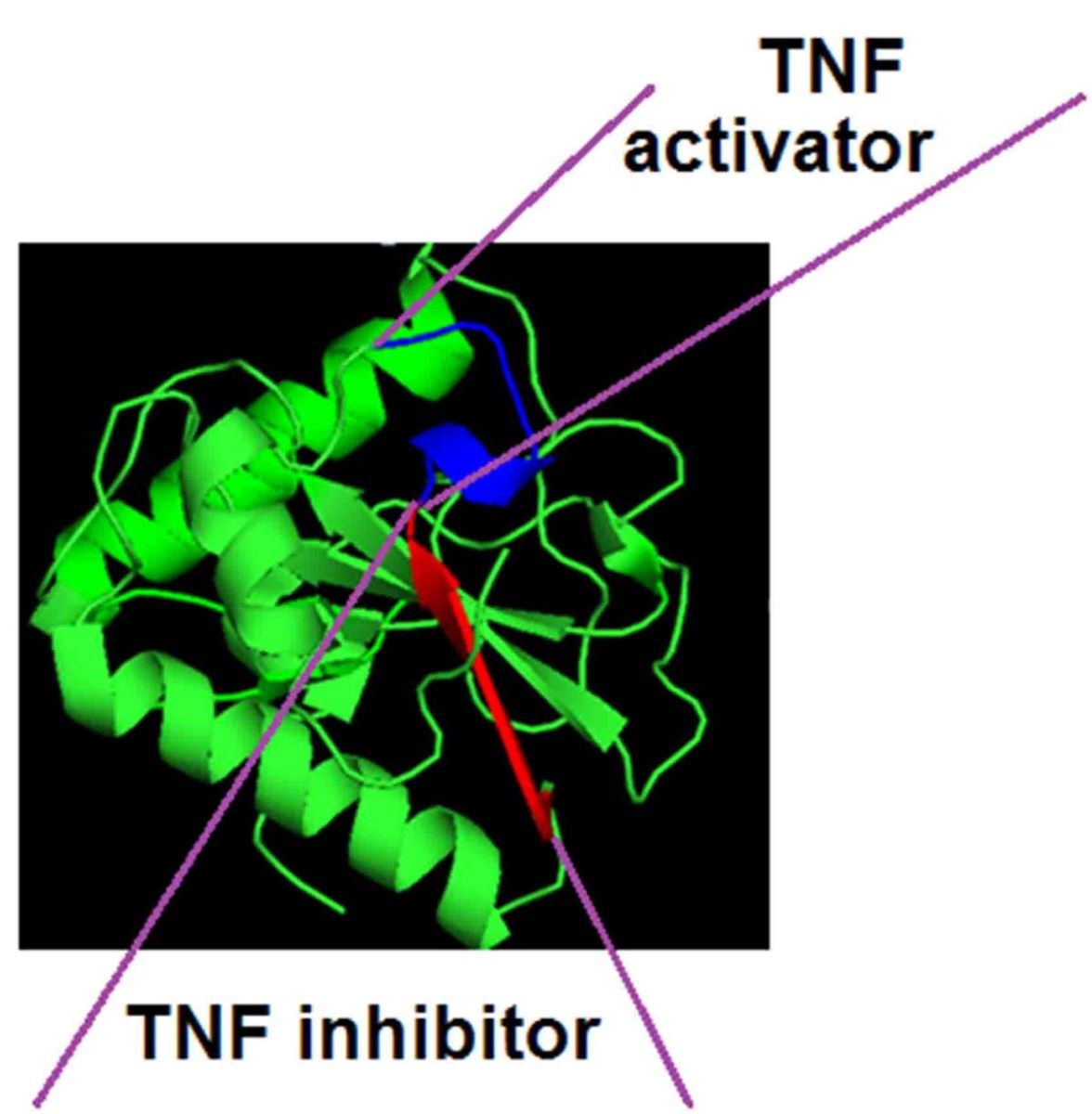
Previously, we found that peptide 17.1 (a.a. 141-157) is located in the C-terminal section of the polypeptide chain of the Tag 7 protein (PGLYRP1). [
6] The 3D structure of this protein is shown in Supplemental
Figure 1, the peptides used in this work are marked on it. It can be seen that the spatial structure of peptide 17.1 is heterogeneous. The n-terminal fragment of this peptide (a.a. 141-149) is not structured. The fragment corresponding to the section of the polypeptide chain (a.a. 150-156) represents the structure of the β-sheet. To separate the activities of bifunctional peptide 17.1, we synthesized peptides: 17.1B corresponding to the amino acid sequence of the N-terminal fragment (aa 141-149) and 17.1A corresponding to the amino acid sequence of the β-leaf (aa 150-156).
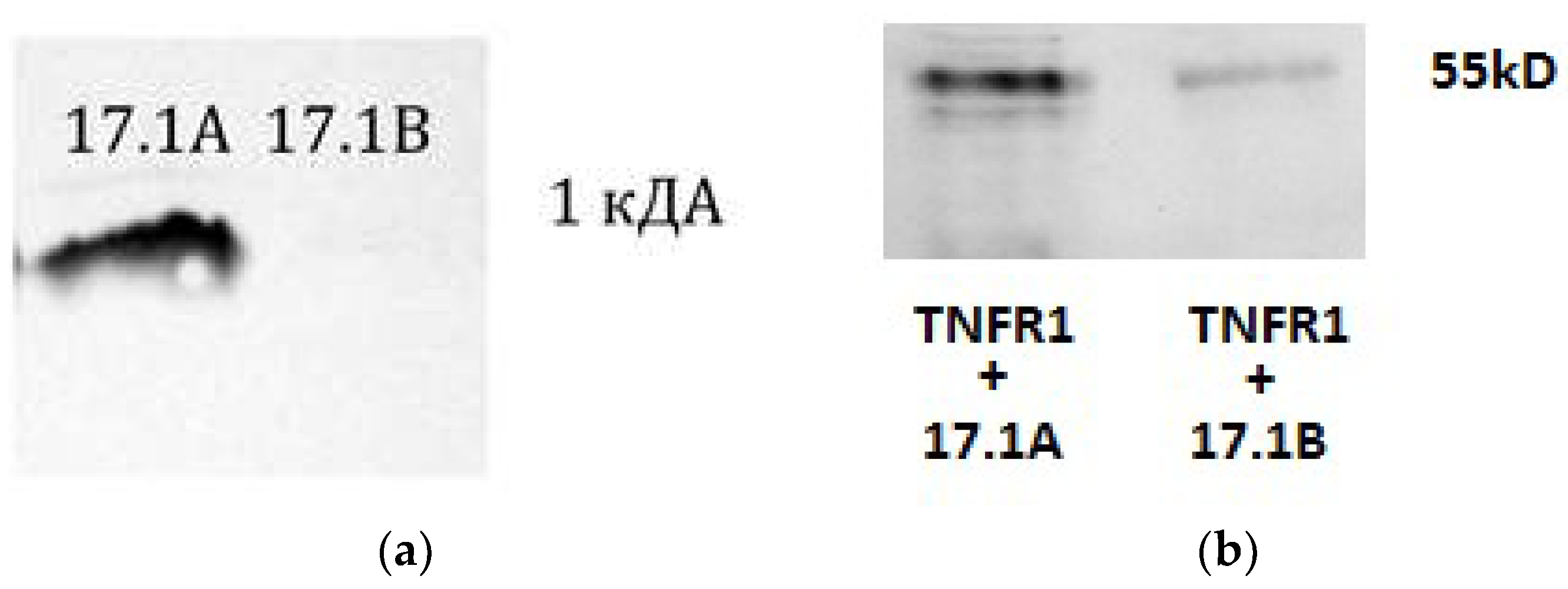
First, the ability of these peptides to bind to the TNFR1 receptor in solution was determined. For this purpose, affinity chromatography was performed using a column with a CN-Br-immobilized Sepharose soluble TNFR1 receptor domain (sTNFR1). (
Figure 1A). Earlier we showed [
7], and here we confirmed that the peptide 17.1A binds to sTNFR1. The interaction of peptide 17.1B with the soluble TNFR1 site could not be detected. It is possible that the 17.1B –TNFR1 complex dissociates rapidly due to the peptide’s weak affinity for this receptor.
However, as can be seen from the results in
Figure 1B, both peptides interact with the TNFR1 receptor exposed on the cell surface. After incubation of cells with biotinylated peptides in the presence of the BS
3 crosslinking reagent, the cell lysate was purified by magnetic separation with streptovidine. The bound material was separated and analyzed using SDS-PAAG and Western blot and detected using specific antibodies to TNFR1. As a result, two complexes of peptides 17.1A and 17.1B with TNFR1 with a molecular weight of 52 kDa can be seen (
Figure 1B). The 17.1B-TNFR1 complex was detected weaker, possibly due to the lower affinity of this peptide to the receptor.
2.2. Peptide 17.1A inhibits TNFR1-dependent cytotoxic activity.
TNFR1 is known to induce alternative cytotoxic processes that develop at different time intervals (apoptosis 3 hours after ligand addition, necroptosis 20 hours later). We have also shown that the cytotoxic Tag7-Hsp 70 complex and DNA hydrolyzing autoantibodies can be ligands of both TNFR1 and TNF. [
2,
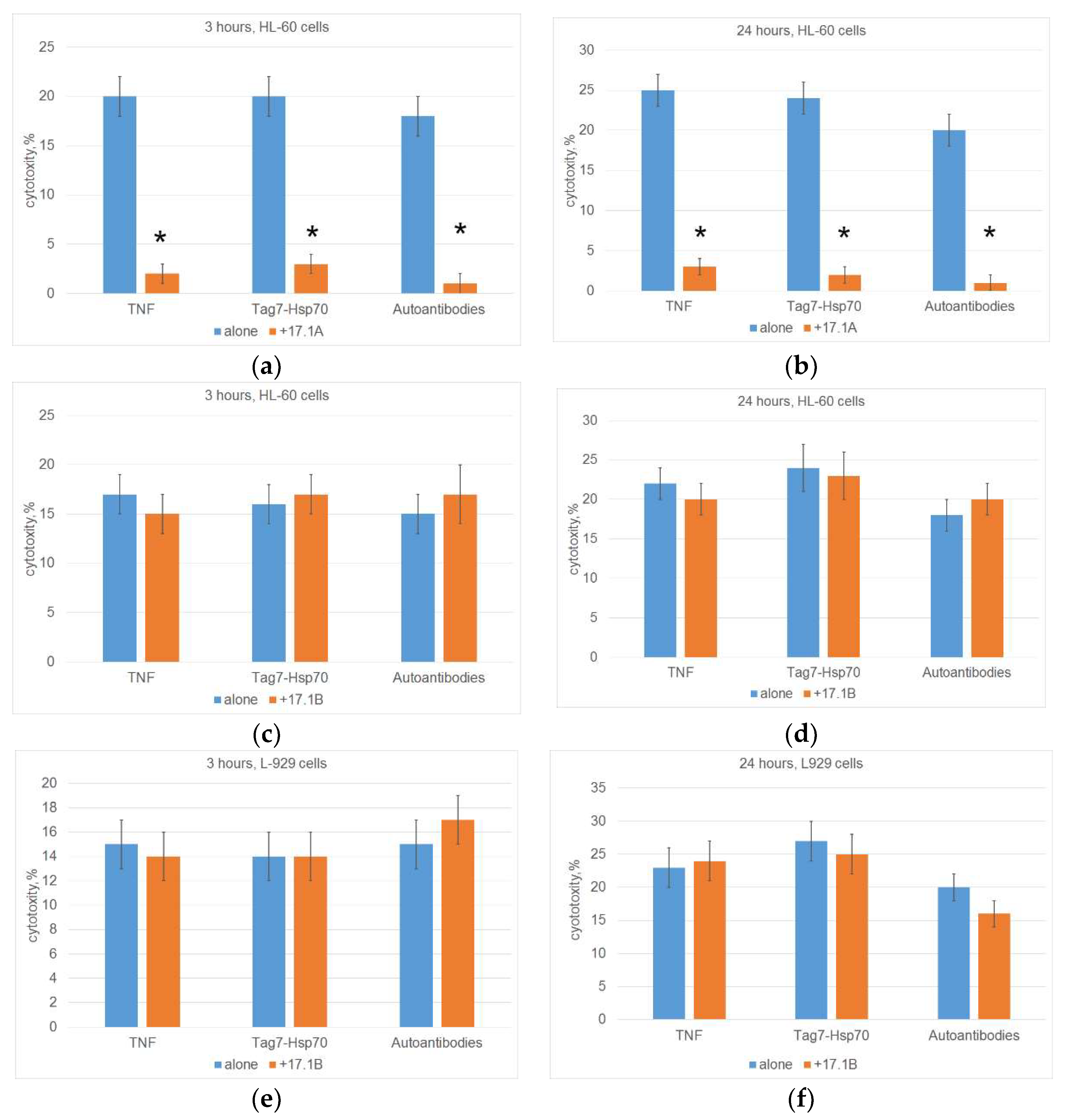
3] Next, we investigated the ability of synthesized peptides to compete with TNFR1 ligands and inhibit TNFR1-induced cytotoxicity. The results are shown in
Figure 2. Previously, we showed that peptide 17.1A inhibits the death of mouse cells of the L-929 line under the action of TNF, Tag7-Hsp 70 complex and DNA-hydrolyzing autoantibodies. Here we confirmed these results by showing that peptide 17.1A prevents the development of both apoptosis and necroptosis under the action of these ligands when human leukemia cells of the HL 60 line are used as target cells (
Figure 2A,B).
The results in Figures 2C, 2D, 2E, 2F indicate that, unlike peptide 17.1A, peptide 17.1B did not inhibit either apoptosis or necroptosis developing under the action of three TNFR1 ligands. Cytotoxic activity did not decrease when using both mouse fibroblasts and human leukemia cells as target cells.
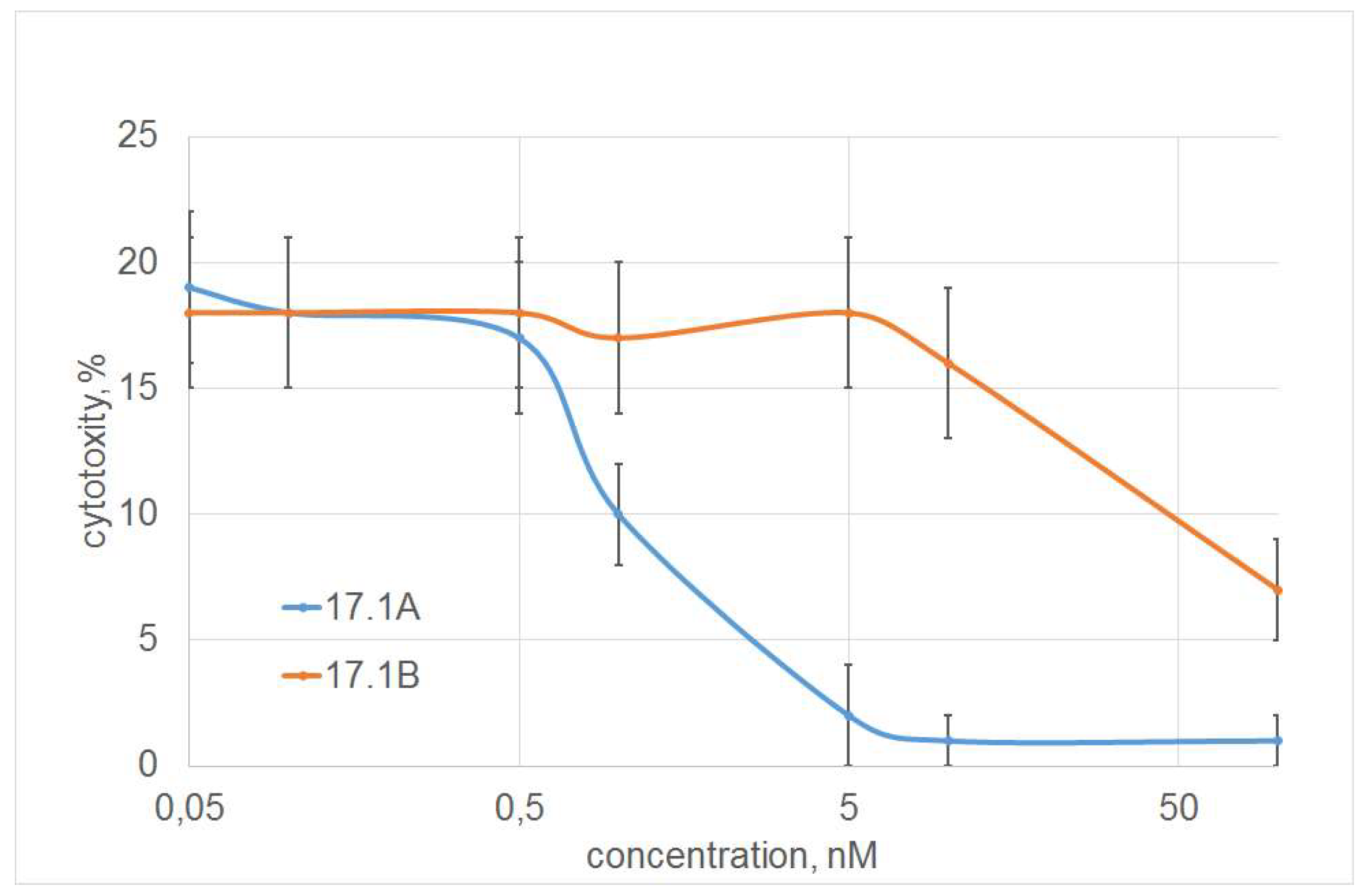
The dependence of inhibition on the concentration of peptide 17.1A was dose-dependent, half of the maximum inhibition (I
50) was 1 nM. Peptide 17.1B showed a weak inhibitory effect only at a concentration of 100 nM (
Figure 3).
Thus, peptide 17.1A fully reproduces the inhibitory activity of peptide 17.1 and the full-sized Tag7 protein. Peptide 17.1B appears to have a very low affinity for TNFR1 and is easily displaced by ligands of this receptor.
2.3. Peptide 17.1B induces cytotoxicity in combination with Hsp 70.
Next, we found out which fragments of peptide 17.1 are responsible for its other function—the ability to kill tumor cells in combination with Hsp70.
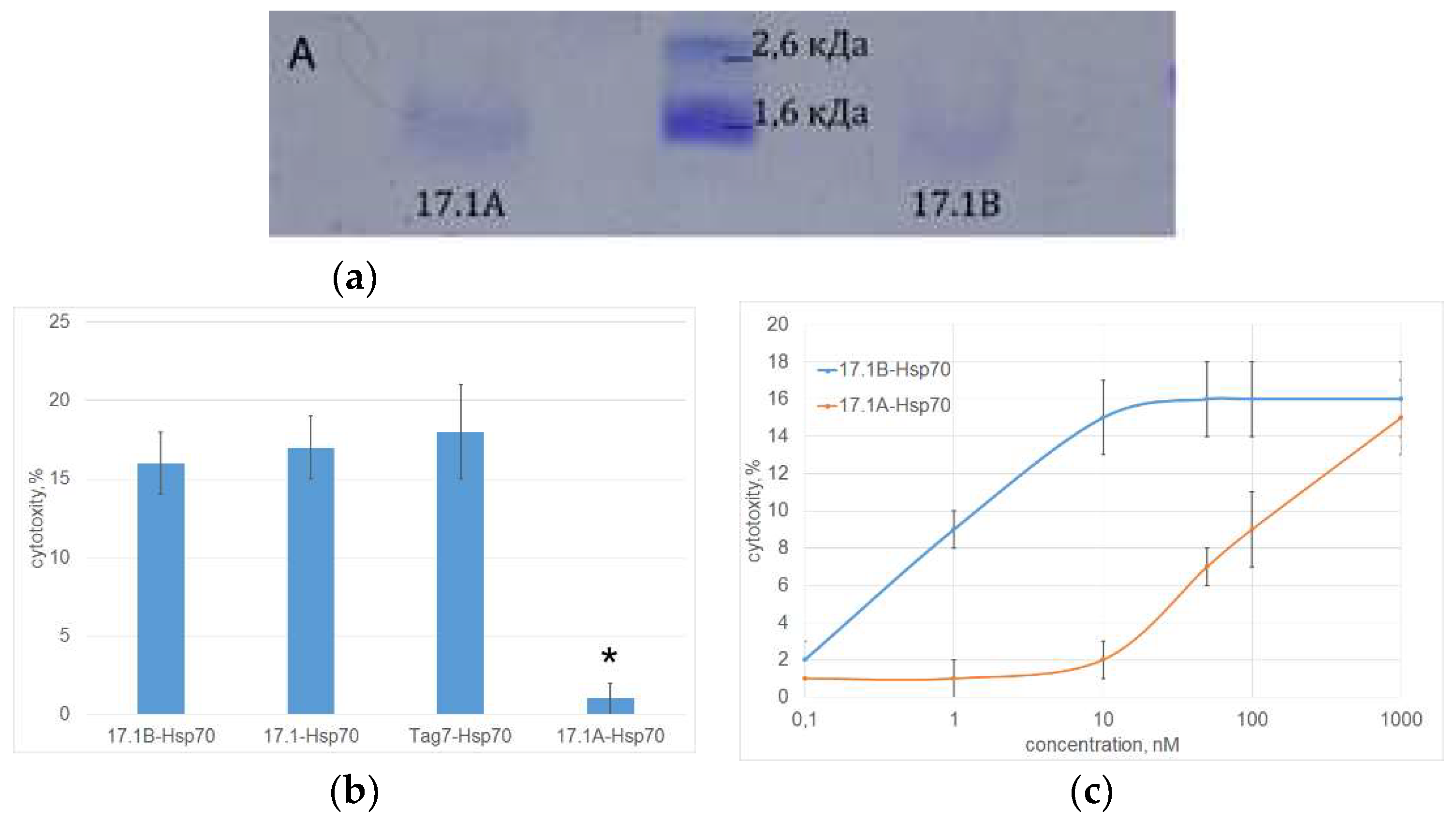
The interaction of both peptides with Hsp70 was also studied using affinity chromatography. Peptides bound to Hsp70 immobilized on Br-CN Sepharose were analyzed using Tricin SDS PAGE and detected by Coomassie staining (
Figure 4A). It can be seen that both peptide fragments have affinity for Hsp70. After staining, a clear band corresponding to the mobility of the peptide 17.1B and a weaker band corresponding to the mobility of the peptide 17.1A are detected.
The stability of Hsp70 complexes with the studied peptides and their ability to induce programmed cell death of tumor cells were investigated. As can be seen from the results in
Figure 4B, the cytotoxic activity of the 17.1B-Hsp70 complex is comparable to the cytotoxic activity of the 17.1-Hsp70 and Tag7-Hsp70 complexes. Cytotoxic activity of the 17.1A-Hsp70 complex was not detected. The dependence of cytotoxic activity on the concentration of the 17.1B-Hsp70 complex was dose-dependent, maximum cytotoxicity was achieved at a concentration of 10 nM (
Figure 4C). The 17.1A–Hsp70 complex also showed a weak cytotoxic effect at a concentration of 100 nM. These results suggest a lower affinity of peptide 17.1A to the Hsp70.
2.4. Peptide 17.1B inhibits the cytotoxic activity of CD4+-T lymphocytes.
As mentioned above, we have shown the participation of Tag7 exposed on the cell membrane of cytotoxic CD4+-T lymphocytes in the cytolysis of Hsp70-positive tumor cells by these lymphocytes. This protein ensured the binding of the lymphocyte to the target cell due to the formation of the intercellular Tag7-Hsp70 complex.
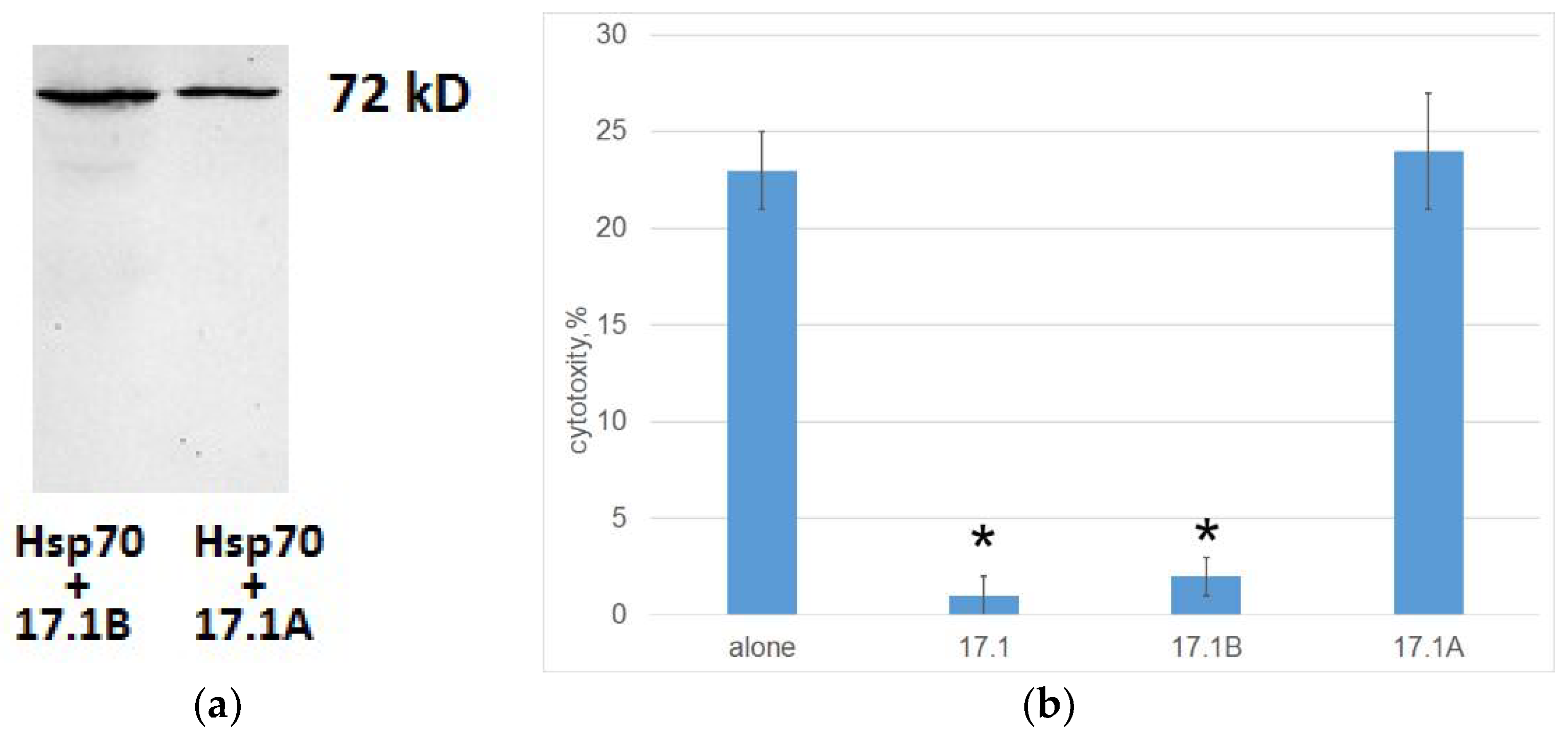
Here we found out whether peptides 17.1A and 17.1B bind to Hsp70 on the membrane of a tumor cell, and whether binding also prevents the interaction of a cytotoxic lymphocyte with this cell. Biotinylated peptides were incubated with cells in the presence of the BS3 crosslinking reagent.
Cell lysates were purified by magnetic separation with streptovidine. The bound material was analyzed using SDS-PAGE followed by a Western blot using specific antibodies to Hsp70. This made it possible to identify two complexes of biotinylated peptides 17.1A and 17.1B with Hsp70 with a mass of 70 kDa (
Figure 5A). Thus, both fragments of peptide 17.1 can bind to Hsp70.
Further, we investigated how this binding affects the induction of cell death by cytotoxic CD4+-T lymphocytes. Tumor cells of the K562 line were preincubated with peptides 17.1, 17.1A and 17.1B, then cytotoxic lymphocytes were added and cytotoxic activity was determined. It can be seen that peptides 17.1 and 17.1B completely block the cytotoxic effect of lymphocytes, whereas peptide 17.1A has no effect on cell death (
Figure 5B). Thus, although all three peptides can bind to Hsp70 on the cell surface, only peptide 17.1 and its fragment 17.1B have inhibitory activity. Apparently, peptide 17.1A has a low affinity for Hsp70 and forms an unstable complex with it.
2.5. Determination of the binding constants of peptides 17.1, 17.1A and 17.1B with TNFR1 and Hsp70.
Protein-protein interactions of sTNFR1 and Hsp70 with peptides 17.1, 17.1A and 17.1B and Tag7 protein were quantified using microscale thermophoresis (MST). This biophysical method is based on the movement of molecules in a temperature gradient, which strongly depends on the charge, the hydration shell and the size of the moving molecules. At least one of these qualities usually changes during the formation of the complex. Therefore, thermophoresis provides a sensitive and reliable method for analyzing and quantifying protein-protein interactions. [
8,
9,
10] The addition of peptides to labeled TNFR1 shows clear changes in thermophoresis, and the thermophoretic signals obtained with increasing concentrations follow a clear binding curve. (
Figure 6) From these binding curves, the apparent dissociation constants (Kd) presented in
Table 1 were obtained. The obtained constants indicate a highly specific interaction of Tag7, 17.1 and 17.1A with sTNFR1. Similarly, clear changes in the thermophoretic signal were observed when Tag7, 17.1 and 17.1B were added to the labeled Hsp70. The corresponding binding curves showed nanomolar values of apparent Kd. However, the addition of peptide 17.1B to labeled sTNFR1 showed a significantly lower apparent dissociation constant (Kd) equal to 6690(120) nM, which suggests a lower affinity of these molecules and well describes the inability of peptide 17.1B to compete with TNFR1 ligands for binding to this receptor. The same pattern was observed when peptide 17.1A was added to labeled Hsp70. The apparent dissociation constant (Kd) of 17.1A-Hsp70 was determined as 222(15) nM, which is also significantly lower than that in the 17.1B-Hsp70 complex. It is obvious that peptide 17.1A cannot form a strong complex with Hsp70, and this may explain its inability in combination with Hsp70 to cause TNFR1 receptor activation.
3. Discussion
Summarizing the above results, it should be emphasized that the paper expands the understanding of the mechanisms of regulatory action of the innate immunity protein Tag7 (PGLYRP1). For the first time, Tag7 epitopes responsible for the opposite functions of this protein were identified: inhibition of TNF-TNFR1 interaction and induction of programmed tumor cell death in combination with Hsp70 protein via TNFR1 receptor.
The TNF cytokine plays a key role in the development of the immune system and the pro-inflammatory immune response. [
11] It can also cause the death of tumor cells. [
12] TNF interacts with TNFR1 receptor, that is present on the surface of most cells, including tumor cells. [
13] The interaction of TNF with TNFR1 can induce intracellular signaling. Depending on the activity of enzymes associated with the intracellular domain of this receptor, this may be gene activation under the control of transcription factor NFkB or programmed cell death. [
14] NFkB-dependent activation regulates immune cell proliferation and pro-inflammatory immune response. [
15] However, excessive TNF activity leads to the emergence of many autoimmune diseases, and the regulation of the activity of this cytokine is an urgent task of modern immunology. [
16] It is known that antibodies to this cytokine and the soluble extracellular domain of its receptor (sTNFR1) are successfully used to suppress TNF activity. [
17]
We have previously shown that DNA-hydrolyzing autoantibodies and the innate immunity protein Tag7 can interact with TNFR1 and act as its ligands. [
2,
3]
Tag7 (PGLYPR1) is a multifunctional protein involved in the regulation of many immune processes. [
18] Its antibacterial activity is known. [
19] It has been shown that in synergy with the Toll receptor, it participates in antibacterial protection in insects. In mammals, it also prevents the development of bacterial infection. [
19] It has recently been established that PGLYPR1 is a ligand of the innate immunity receptor TREM1, whose main function is the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines. [
20] In this case, Tag7 acts as an inducer of inflammatory processes. It promotes the activation of pro-inflammatory cytokine genes, including TNF. [
21] The binding of Tag7 to TNFR1 prevents the interaction of this receptor with its TNF ligand, and here Tag7 can be considered as an anti-inflammatory cytokine. [
2]
The ability of Tag7 to form functional complexes with other proteins expands the range of its functions. The Tag7 complex with the Mts1 protein belonging to the S100 family of proteins induces lymphocyte chemotaxis. [
22] When Tag7 interacts with Hsp70, a cytotoxic complex is created. [
23] Tag7 in this complex retains the ability to interact with TNFR1, but its function is reversed. It does not inhibit the cytotoxic effect of TNF, but in contrary it acts like TNF cytokine, inducing programmed death of tumor cells.
A serious direction of modern biological science is the identification of peptide fragments of multifunctional proteins that perform one specific function. Such studies provide approaches to the detailed decoding of the mechanism of action of these proteins and the creation of new drugs. [
14] As mentioned above, we have localized the Tag7 site required to perform its two functions. [
6] Peptide 17.1 was synthesized with an amino acid sequence corresponding to this fragment, simulating both functional activities of a full-sized protein. When added to TNFR1 this peptide inhibited the cytotoxic effect of its ligands. [
6] In complex with Hsp70 peptide 17.1, induced the death of tumor cells. This peptide showed anti-inflammatory activity. With the development of autoimmune arthritis, it significantly reduced the destruction of cartilage and bone tissue and had an effect on the secretion of a wide range of cytokines and chemokines. [
6]
Here we managed to separate the functions of the bifunctional peptide 17.1. It was found that the N-terminal fragment of this peptide, the 8-membered peptide 17.1A, performs only one function. This peptide proved to be an effective inhibitor of the cytotoxic activity of TNF and autoantibodies, but unlike peptide 17.1, it did not induce cell death in complex with Hsp70 at physiological conditions. A quantitative assessment of the interaction of peptide 17.1A with both proteins indicates its high affinity for the TNFR1 receptor, almost the same as that of Tag7 and peptide 17.1, and significantly lower affinity for the Hsp70 protein.
The C-terminal fragment of the peptide 17.1–7-membered peptide 17.1B also performs only one function at physiological conditions. It had a low affinity for the TNFR1 receptor and did not inhibit the cytotoxicity of TNF and other ligands of this receptor. At the same time, it also, like Tag7 and peptide 17.1, bound to Hsp70 with higher affinity and formed a stable cytotoxic complex capable of killing tumor cells.
The high affinity of peptides 17.1 and 17.1B to Hsp70 allows them to form stable complexes (17.1-Hsp70 and 17.1B-Hsp70) on the surface of Hsp70+ tumor cells and prevent CD4+CD25+lymphocytes from interacting with these cells, blocking the cytotoxic activity of these lymphocytes. Peptide 17.1A, which has a low affinity for Hsp70, easily dissociates from the cell surface and does not inhibit the death of tumor cells under the action of these lymphocytes.
Thus, fragments of Tag7 responsible for the implementation of its anti-inflammatory and antitumor function have been identified. The results obtained can be used in autoimmune and antitumor therapy.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell cultivation and sorting
K562 and HL-60 cells were cultured in RPMI-1640 with 2 mm L-glutamine and 10% FCS (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, California). L929 cells were cultured in DMEM with 2 mm L-glutamine and 10% FCS (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, California) Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were isolated from the total pool of leukocytes of healthy donors, as described [
23], and cultured at a density of 4×10
6 cells/ml in the same medium with Tag7 (1nM) for 6 days.
4.2. Proteins and antibodies
Recombinant Tag7, sTNFR1 and Hsp70 were obtained as described [
2]. Tag7 peptides were added 30 minutes before the treatment of lymphocytes with activating agents.
4.3. Peptides
The peptides 17.1, 17.1A and 17.1B were synthesized as described in [
24]
4.4. Affinity chromatography, immunoadsorption and immunoblotting
A column with CNBr-activated sepharose 4B (GE Healthcare, USA) conjugated with sTNFR1 or Hsp70 was prepared as described in accordance with the manufacturer’s protocol. Peptides 17.1, 17.1A and 17.1B were biotinylated according to the protocol from [
25]. Biotinylated peptides were loaded into a column with sTNFR1 or Hsp70-sepharose. The excess peptide was washed out of the column using PBS containing 0.5 M NaCl and only PBS. The peptide was eluted with 0.25 M triethylamine (TEA), pH 12. The eluted material was resolved using Tricine-SDS-PAGE and applied to a nitrocellulose membrane [
26]. HRP-conjugated streptavidin (GE Healthcare, USA; 1:15,000; 1 h) was used for detection. The results were visualized using the ECL Plus kit (GE Healthcare, USA) in accordance with the manufacturer’s protocol. Chemiluminescence was recorded using iBright (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA). L929 or K562 cells (10
8 cells) were incubated with biotinylated peptides (1nM) in the presence of BS
3 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA), lysed in RIPA buffer (Sigma-Aldrich, USA) and purified using Dynabeads (M-280 sheep anti-rabbit IgG; Dynal Biotech ASA, Norway), conjugated with streptavidin in accordance with the manufacturer’s protocol. This material was resolved into 10% PAGE, followed by Western blotting using antibodies against TNFR1 or against Hsp70 (Abcam, Cambridge, UK).
4.5. Cytotoxicity assays
For cytotoxic tests, target cells were cultured in 96-well plates (6 × 104 cells per well) and mixed with lymphocytes in a ratio of 1:20. Cytotoxicity was measured after 24-hour incubation. The inhibition test was performed with peptides 17.1, 17.1A and 17.1B at a concentration of 1nM. Cytotoxic activity of lymphocytes was determined using the Cytotox 96 analysis kit (Promega, Madison, WI) in accordance with the manufacturer’s protocol.
4.6. Microscale Thermophoresis
The purified sTNFR1 and Hsp70 were fluorescently labeled using the Alexa Fluor 633 or Alexa Fluor 488 staining kit (Eugene, Oregon, USA) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. sTNFR1 and Hsp70 (200 nM) were incubated for 20 min with each compound in the dark at room temperature in 16 different concentrations obtained by sequential dilution, starting from the highest soluble concentration. Samples were loaded into glass capillaries (Monolith NT Capillaries) and analyzed by thermophoresis using Nano-Temperature Monolith NT apparatus 115. (IR laser power 10%). The signal quality was monitored by a NanoTemper Monolith device to detect possible autofluorescence of the ligand, deposition, aggregation, or ligand-induced changes in the photobleaching rate. The experiments were carried out in triplicate and processed using affinity analysis software (Nano-Temper).
4.7. Statistical analysis
The data were analyzed using the Statistica (StatSoft®) software. The results are presented as an average value ± SD. Statistically significant differences were determined using the t-test. The value of P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
5. Conclusions
We show that two peptides 17.1A and 17.1B have different affinities to the TNFR1 receptor and the Hsp70 protein, and each of them is able to perform only one function at physiological conditions: peptide 17.1A is only able to inhibit signal conduction through the TNFR1 receptor, and peptide 17.1B can only activate this receptor is in complex with Hsp70.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org., Figure S1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.P.S. and D.V.Y.; Methodology, D.M.Y. T.N.S. and L.P.S.; Software, D.V.Y. and D.M.Y.; Validation, L.P.S. and D.V.Y.; Formal Analysis, L.P.S. and D.V.Y.; Investigation, E.A.R., D.M.Y., T.N.S., L.P.S., and D.V.Y.; Resources, D.V.Y..; Data Curation, L.P.S. and D.V.Y.; Writing –Original Draft Preparation, L.P.S. and D.V.Y.; Writing—Review & Editing, L.P.S. and D.V.Y.; Supervision, L.P.S. and D.V.Y.; Project Administration, L.P.S. and D.V.Y.; Funding Acquisition, L.P.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by by Russian Science Foundation Grant 23-14-00076.
Informed Consent Statement
“Not applicable.”
Data Availability Statement
“Not applicable.”
Acknowledgments
This study was performed using the equipment of the Center for Precision Genome Editing and Genetic Technologies for Biomedicine of Institute of Gene Biology RAS.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Fischer, R.; Kontermann, R.E.; Pfizenmaier, K. Selective Targeting of TNF Receptors as a Novel Therapeutic Approach. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020, 8, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashin, D.V., Ivanova, O.K., Soshnikova, N.V., Sheludchenkov, A.A., Romanova, E.A., Dukhanina, E.A., Tonevitsky, A.G., Gnuchev, N.V., Gabibov, A.G., Georgiev, G.P., Sashchenko, L.P. Tag7 (PGLYRP1) in Complex with Hsp70 Induces Alternative Cytotoxic Processes in Tumor Cells via TNFR1 Receptor. J Biol Chem. 2015, 290, 21724-21731. [CrossRef]
- Sharapova, T.N., Romanova, E.A., Soshnikova, N.V., Belogurov, A.A. Jr, Lomakin, Y.A., Sashchenko, L.P., Yashin, D.V. Autoantibodies from SLE patients induce programmed cell death in murine fibroblast cells through interaction with TNFR1 receptor. Sci Rep. 2020 10, 11144. [CrossRef]
- Sashchenko, L.P., Dukhanina, E.A., Shatalov, Y.V., Yashin, D.V., Lukyanova, T.I., Kabanova, O.D., Romanova, E.A., Khaidukov, S.V., Galkin, A.V., Gnuchev, N.V., Georgiev, G.P. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes carrying a pattern recognition protein Tag7 can detect evasive, HLA-negative but Hsp70-exposing tumor cells, thereby ensuring FasL/Fas-mediated contact killing. Blood. 2007 110, 1997-2004. [CrossRef]
- Poznansky, S.A., Yu, M., Deng, K., Fu, Q., Markmann, J.F., LeGuern, C. Leveraging the tolerogenic potential of TNF-α and regulatory B cells in organ transplantation. Front Immunol. 2023 14, 1173672. [CrossRef]
- Romanova, E.A., Sharapova, T.N., Telegin, G.B., Minakov, A.N., Chernov, A.S., Ivanova, O.K., Bychkov, M.L., Sashchenko, L.P., Yashin, D.V. A 12-mer Peptide of Tag7 (PGLYRP1) Forms a Cytotoxic Complex with Hsp70 and Inhibits TNF-Alpha Induced Cell Death. Cells. 2020 9, 488. [CrossRef]
- Telegin, G.B., Chernov, A.S., Kazakov, V.A., Romanova, E.A., Sharapova, T.N., Yashin, D.V., Gabibov, A.G., Sashchenko, L.P. A 8-mer Peptide of PGLYRP1/Tag7 Innate Immunity Protein Binds to TNFR1 Receptor and Inhibits TNFα-Induced Cytotoxic Effect and Inflammation. Front Immunol. 2021 12, 622471. [CrossRef]
- Duhr, S.; Braun, D. Optothermal molecule trapping by opposing fluid flow with thermophoretic drift. Phys Rev Lett. 2006, 97, 038103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wienken, C.J., Baaske, P., Rothbauer, U., Braun, D., Duhr, S. Protein-binding assays in biological liquids using microscale thermophoresis. Nat Commun. 2010 1,100. [CrossRef]
- Jerabek-Willemsen, M., Wienken, C.J., Braun, D., Baaske, P., Duhr, S. Molecular interaction studies using microscale thermophoresis. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2011 9, 342-353. [CrossRef]
- Atretkhany, K.N., Gogoleva, V.S., Drutskaya, M.S., Nedospasov, S.A. Distinct modes of TNF signaling through its two receptors in health and disease. J Leukoc Biol. 2020 107, 893-905. [CrossRef]
- Freeman, A.J., Kearney, C.J., Silke, J., Oliaro, J. Unleashing TNF cytotoxicity to enhance cancer immunotherapy. Trends Immunol. 2021 42, 1128-1142. [CrossRef]
- Walczak, H. TNF and ubiquitin at the crossroads of gene activation, cell death, inflammation, and cancer. Immunol Rev. 2011, 244, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chédotal, H., Narayanan, D., Povlsen, K., Gotfredsen, C.H., Brambilla, R., Gajhede, M., Bach, A., Clausen, M.H. Small-molecule modulators of tumor necrosis factor signaling. Drug Discov Today. 2023 28, 103575. [CrossRef]
- Hop, H.T., Reyes, A.W.B., Huy, T.X.N., Arayan, L.T., Min, W., Lee, H.J., Rhee, M.H., Chang, H.H., Kim, S.. Activation of NF-kB-Mediated TNF-Induced Antimicrobial Immunity Is Required for the Efficient Brucella abortus Clearance in RAW 264.7 Cells. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 7, 437. [CrossRef]
- Lopetuso, L.R., Cuomo, C., Mignini, I., Gasbarrini, A., Papa, A. Focus on Anti-Tumour Necrosis Factor (TNF)-α-Related Autoimmune Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 24, 8187. [CrossRef]
- Eng, G.P., Bouchelouche, P., Bartels, E.M., Bliddal, H., Bendtzen, K., Stoltenberg, M. Anti-Drug Antibodies, Drug Levels, Interleukin-6 and Soluble TNF Receptors in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients during the First 6 Months of Treatment with Adalimumab or Infliximab: A Descriptive Cohort Study. PLoS One. 2016 11, 0162316. [CrossRef]
- Yashin, D.V., Sashchenko, L.P., Georgiev, G.P. Mechanisms of Action of the PGLYRP1/Tag7 Protein in Innate and Acquired Immunity. Acta Naturae. 2021 13: 91-101. [CrossRef]
- Dziarski, R., Gupta, D.. Mammalian PGRPs: novel antibacterial proteins. Cell Microbiol. 2006 8, 1059-1069. [CrossRef]
- Read, C.B., Kuijper, J.L., Hjorth, S.A., Heipel, M.D., Tang, X., Fleetwood, A.J., Dantzler, J.L., Grell, S.N., Kastrup, J., Wang, C., Brandt, C.S., Hansen, A.J., Wagtmann, N.R., Xu, W., Stennicke, V.W. Cutting Edge: identification of neutrophil PGLYRP1 as a ligand for TREM-1. J Immunol. 2015 194, 1417-1421. [CrossRef]
- Sharapova, T.N., Romanova, E.A., Ivanova, O.K., Sashchenko, L.P., Yashin, D.V. Cytokines TNFα, IFNγ and IL-2 Are Responsible for Signal Transmission from the Innate Immunity Protein Tag7 (PGLYRP1) to Cytotoxic Effector Lymphocytes. Cells. 2020 9, 2602. [CrossRef]
- Dukhanina, E.A., Kabanova, O.D., Lukyanova, T.I., Shatalov, Y.V., Yashin, D.V., Romanova, E.A., Gnuchev, N.V., Galkin, A.V., Georgiev, G.P., Sashchenko, L.P. Opposite roles of metastasin (S100A4) in two potentially tumoricidal mechanisms involving human lymphocyte protein Tag7 and Hsp70. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 106, 13963-13967. [CrossRef]
- Sashchenko, L.P., Dukhanina, E.A., Yashin, D.V., Shatalov, Y.V., Romanova, E.A., Korobko, E.V., Demin, A.V., Lukyanova, T.I., Kabanova, O.D., Khaidukov, S.V., Kiselev, S.L., Gabibov, A.G., Gnuchev, N.V., Georgiev, G.P. Peptidoglycan recognition protein tag7 forms a cytotoxic complex with heat shock protein 70 in solution and in lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 2004 279, 2117-2124. [CrossRef]
- Telegin, G.B., Chernov, A.S., Minakov, A.N., Balmasova, I.P., Romanova, E.A., Sharapova, T.N., Sashchenko, L.P., Yashin, D.V. Short Peptides of Innate Immunity Protein Tag7 Inhibit the Production of Cytokines in CFA-Induced Arthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 23, 12435. [CrossRef]
- Altin, J.G.; Pagler, E.B. A One-Step Procedure for Biotinylation and Chemical Cross-Linking of Lymphocyte Surface and Intracellular Membrane-Associated Molecules. Anal Biochem 1995, 224, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schägger, H. Tricine-SDS-PAGE. Nat Protoc 2006, 1, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
A. The peptides were biotinylated and applied to a column containing TNFR1 conjugated Sepharose. The bound material was eluted with triethylamine and resolved using Tricine SDS PAGE and visualized using streptovidine conjugated with peroxidase and ECL kit. B. The peptides were biotinylated and added to cells of the L929 line, followed by incubation for 1 hour. Next, the peptides were cross-linked with TNFR1 on the cell surface with BS3 reagent (Sigma). After stopping the reaction, the cells were lysed in RIP-A (Sigma) buffer in the presence of protease inhibitors. Lysate was purified by magnetic separation on M280 Streptavidin Beads. The obtained fractions containing 17.1 A-TNFR1 and 17.1 B-TNFR1 were analyzed using 12% SDS-PAGE electrophoresis and Western blot. Complexes were detected using primary polyclonal antibodies abTNFR1 and secondary antibodies anti-rabbit peroxidase-linked (ECL).
Figure 1.
A. The peptides were biotinylated and applied to a column containing TNFR1 conjugated Sepharose. The bound material was eluted with triethylamine and resolved using Tricine SDS PAGE and visualized using streptovidine conjugated with peroxidase and ECL kit. B. The peptides were biotinylated and added to cells of the L929 line, followed by incubation for 1 hour. Next, the peptides were cross-linked with TNFR1 on the cell surface with BS3 reagent (Sigma). After stopping the reaction, the cells were lysed in RIP-A (Sigma) buffer in the presence of protease inhibitors. Lysate was purified by magnetic separation on M280 Streptavidin Beads. The obtained fractions containing 17.1 A-TNFR1 and 17.1 B-TNFR1 were analyzed using 12% SDS-PAGE electrophoresis and Western blot. Complexes were detected using primary polyclonal antibodies abTNFR1 and secondary antibodies anti-rabbit peroxidase-linked (ECL).
Figure 2.
Cells (HL-60(A-D) or L-929 (E, F)) were pre-incubated with peptide 17.1A (A, B) or 17.1B (C-F) for 30 minutes, then a cytotoxic agent (TNF, Tag7-Hsp70 complex or Autoantibodies) was added and cytotoxic activity was then determined after 3 (A, C, E) or 24 hours (B, D, F) of cell incubation. n = 5 for each groups). (p-value: * < 0.05).
Figure 2.
Cells (HL-60(A-D) or L-929 (E, F)) were pre-incubated with peptide 17.1A (A, B) or 17.1B (C-F) for 30 minutes, then a cytotoxic agent (TNF, Tag7-Hsp70 complex or Autoantibodies) was added and cytotoxic activity was then determined after 3 (A, C, E) or 24 hours (B, D, F) of cell incubation. n = 5 for each groups). (p-value: * < 0.05).
Figure 3.
Dependence of inhibition of TNF cytotoxic activity on peptides 17.1 and 17.1B concentration. (L929 cells, 24 hour of incubation, peptides were added 30 min before incubation with TNF (1nM)) n = 5 for each point.
Figure 3.
Dependence of inhibition of TNF cytotoxic activity on peptides 17.1 and 17.1B concentration. (L929 cells, 24 hour of incubation, peptides were added 30 min before incubation with TNF (1nM)) n = 5 for each point.
Figure 4.
A. Peptides 17.1A and 17.1 B were incubated with Hsp70 in solution, coimmunoprecipitated with anti-Hsp70 Sepharose and the resulting material was resolved using Tricine SDS PAGE. B. Cytotoxic activity of Hsp70 protein complexes with full-size Tag7, peptides 17.1, 17.1A and 17.1B. (10nM) (p-value: * < 0.05). C. Concentration dependence of cytotoxic activity of 17.1-Hsp70 and 17.1B-Hsp70 complexes. (L929 cells, 24 hours of incubation) n=5 for each point.
Figure 4.
A. Peptides 17.1A and 17.1 B were incubated with Hsp70 in solution, coimmunoprecipitated with anti-Hsp70 Sepharose and the resulting material was resolved using Tricine SDS PAGE. B. Cytotoxic activity of Hsp70 protein complexes with full-size Tag7, peptides 17.1, 17.1A and 17.1B. (10nM) (p-value: * < 0.05). C. Concentration dependence of cytotoxic activity of 17.1-Hsp70 and 17.1B-Hsp70 complexes. (L929 cells, 24 hours of incubation) n=5 for each point.
Figure 5.
A. The peptides were biotinylated and added to cells of the K562 line, followed by incubation for 1 hour. Next, the peptides were cross-linked with Hsp70 on the cell surface with BS3 reagent (Sigma). After stopping the reaction, the cells were lysed in RIP-A (Sigma) buffer in the presence of protease inhibitors. Lysate was purified by magnetic separation on M280 Streptavidin Beads. The obtained fractions containing 17.1A-Hsp70 and 17.1B-Hsp70 were analyzed using 12% SDS-PAGE electrophoresis and Western blot. Complexes were detected using primary antibodies abHsp70 poly-AT and secondary antibodies anti-rabbit peroxidase-linked (ECL). B. Tumor cells of the K562 line were preincubated with peptides 17.1, 17.1A and 17.1B for 30 min., then cytotoxic lymphocytes were added and cytotoxic activity was determined. (24 hours incubation) n=5 for each point. (p-value: * < 0.05).
Figure 5.
A. The peptides were biotinylated and added to cells of the K562 line, followed by incubation for 1 hour. Next, the peptides were cross-linked with Hsp70 on the cell surface with BS3 reagent (Sigma). After stopping the reaction, the cells were lysed in RIP-A (Sigma) buffer in the presence of protease inhibitors. Lysate was purified by magnetic separation on M280 Streptavidin Beads. The obtained fractions containing 17.1A-Hsp70 and 17.1B-Hsp70 were analyzed using 12% SDS-PAGE electrophoresis and Western blot. Complexes were detected using primary antibodies abHsp70 poly-AT and secondary antibodies anti-rabbit peroxidase-linked (ECL). B. Tumor cells of the K562 line were preincubated with peptides 17.1, 17.1A and 17.1B for 30 min., then cytotoxic lymphocytes were added and cytotoxic activity was determined. (24 hours incubation) n=5 for each point. (p-value: * < 0.05).
Figure 6.
Microscale thermophoresis data for the interaction of Tag7 (A, E), peptides 17.1 (B, F), 17.1 (C, G) and 17.1 B (D, H) with proteins Hsp70 (A-D) and sTNFR1 (E-H). Each experiment was done in triplicate and the most common data is shown.
Figure 6.
Microscale thermophoresis data for the interaction of Tag7 (A, E), peptides 17.1 (B, F), 17.1 (C, G) and 17.1 B (D, H) with proteins Hsp70 (A-D) and sTNFR1 (E-H). Each experiment was done in triplicate and the most common data is shown.
Table 1.
Apparent dissociation constants obtained from microscale thermophoresis.
Table 1.
Apparent dissociation constants obtained from microscale thermophoresis.
| Ligands |
Kd, nM |
| Tag7-Hsp70 |
1,73±0,3 |
| 17.1-Hsp70 |
7,16±1 |
| 17.1A-Hsp70 |
222±15 |
| 17.1B-Hsp70 |
3,15±0,7 |
| Tag7-TNFR1 |
43,2±5 |
| 17.1-TNFR1 |
8,84±1 |
| 17.1A-TNFR1 |
5,44±1 |
| 17.1B-TNFR1 |
6690±120 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).