Submitted:
22 June 2023
Posted:
23 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
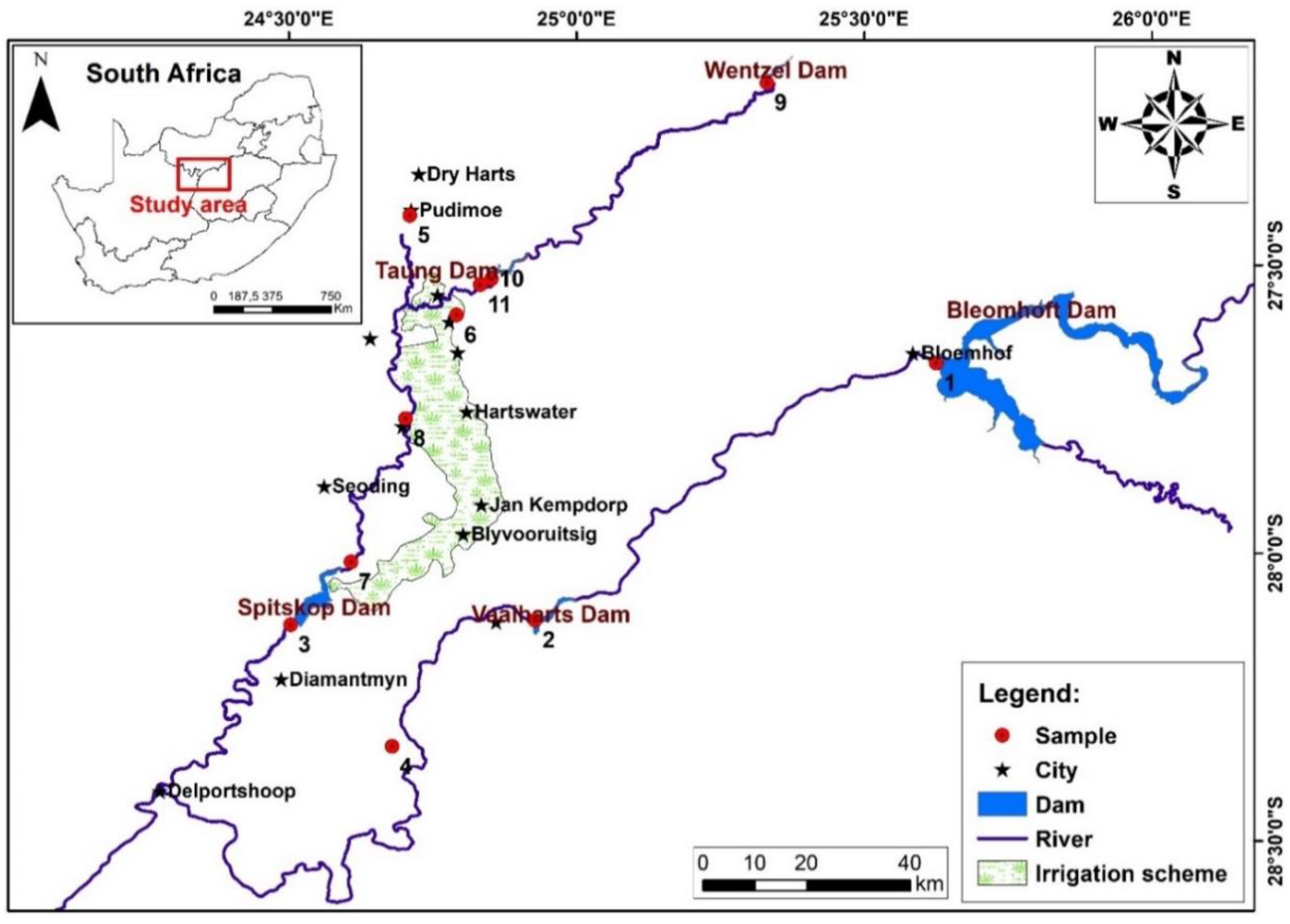
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Water Point and Analysis
2.3. Evaluation of Water Quality for Irrigation Purposes
- -
- -
- Na% = (Na++K+)/(Ca2++Mg2++Na++K+) *100
- -
- RSC= (HCO3-+CO32-)-(Ca2++Mg2+)
- -
- -
- MR= Mg2+/(Ca2++Mg2+)*100
- -
- KR=Na+/(Ca2++Mg2+)
- -
- PS= Cl- + 0.5*SO42-
2.4. Evaluation of Surface Water Quality for Drinking Purposes
2.4.1. Water Quality Index (WQI)
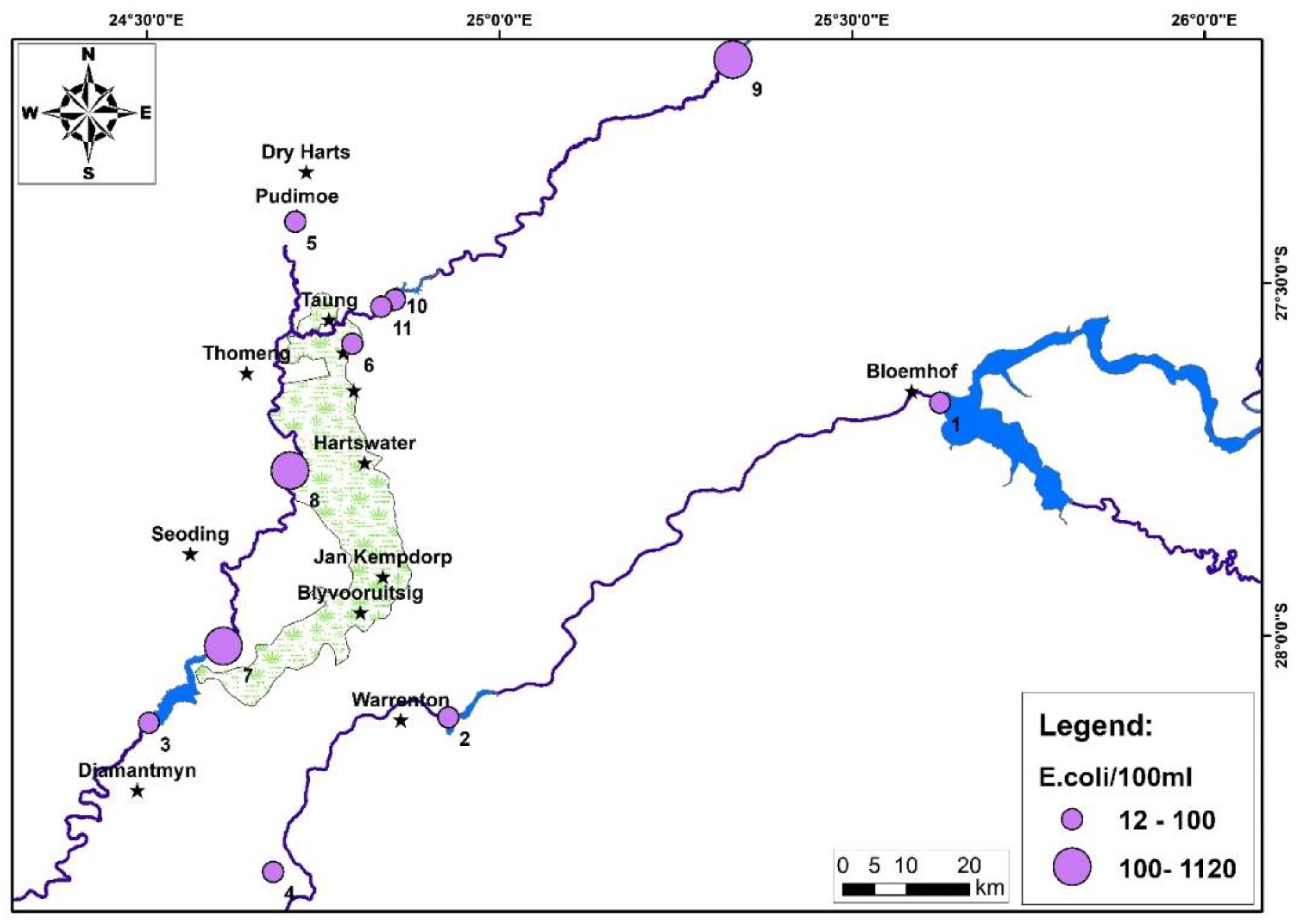
2.4.2. Escherichia coli (E. coli) in Drinking Water Sample
2.4.3. Heavy Metal Pollution Index (HMPI)
2.4.4. Heavy Metal Evaluation Index (HMEI)
3. Assessment of Human Health Risk
3.1. Average Daily Dose (ADD)
3.2. Hazard Quotient (HQ)
3.3. Cancer Risk (CR)
4. Results and Discussion:
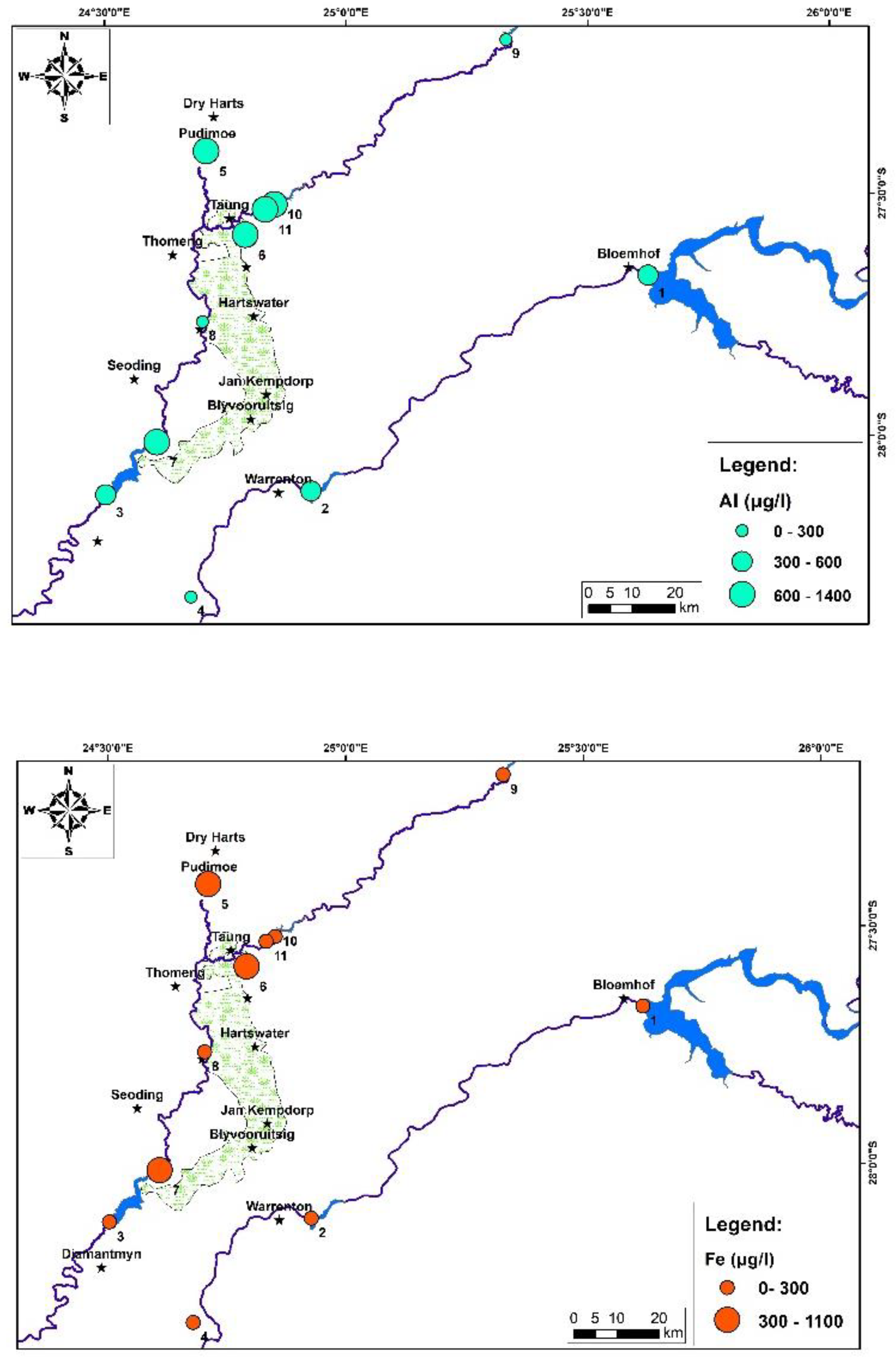
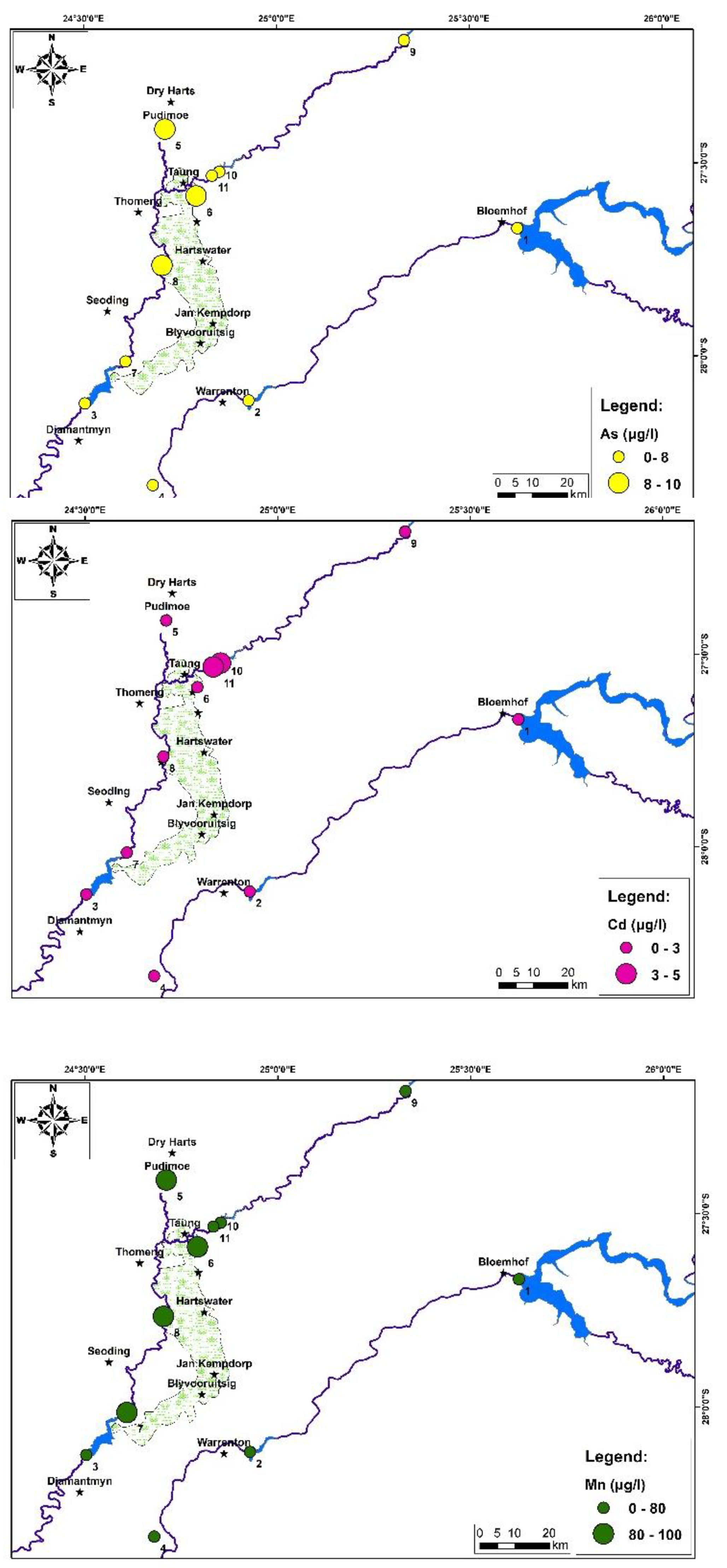
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferroukhi, R.; Nagpal, D.; Lopez-Peña, A.; Hodges, T.H; Mohtar, R.; Daher, B.; Mohtar, S.; Keulertz, M. Renewable Energy in the Water, Energy anf Food Nexus. www.irena.org/Publications 2015.
- UN-Water. Water and sanitation interlinkages across the 2030 Agenda for sustainable development. Geneva: UN-Water 2016.
- United Nations. Sustainable development goal 6 synthesis report 2018 on water and sanitation. New York: United Nations 2018.
- Charkhabi, A.H.; and Sakizadeh M. Assessment of spatial variation of water quality parameters in the most polluted branch of the Anzali wetland, northern Iran. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 2006, 15: 395-403.
- Mary-Lou, T.W.; Taillefert, M. Remote in situ voltammetric techniques to characterize the biogeochemical cycling of trace metals in aquatic systems. J. Environ. Monit 2008, 10: 30-54. [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, S.; Shah, M.T.; Khan, S. Health risk assessment of heavy metals and their source apportionment in drinking water of Kohistan region, northern Pakistan. Microchem J 2011, 98, 334–43. [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Maria, S.; Noor, J.; et al. Drinking water quality and human health risk in Charsadda district, Pakistan. J Clean Prod 2013, 60:93–101.
- Atafar, Z.; Mesdaghinia, A.; Nouri, J.; et al. Effect of fertilizer application on soil heavy metal concentration. Environ Monit Assess 2010,160(1–4):83–9. [CrossRef]
- Aggett, P.J. Iron. In: Erdman JWJ, Macdonald IA, Zeisel SH, eds. Present Knowledge in Nutrition. 10th ed. Ames: Wiley-Blackwell 2012,506-520.
- Anderson, G.J.; Darshan, D.; Wilkins, S.J.; Frazer, D.M. Regulation of systemic iron homeostasis. How the body responds to changes in iron demand. Biometals 2007, 20 (3-4):665-674. [CrossRef]
- Kwong, W.T.; Friello, P.; Semba, R.D. Interactions between iron deficiency and lead poisoning: idemiology and pathogenesis. Sci. Total Environ 2004. 330, 21–37. [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, V.S.D.; Santos, I.F.D.; Almeida, L.C.; Souza, C.T.D.; Júnior, J.B.D.S.; Souza, L. A.; Santos, L.O.D.; Ferreira, S.L.C. Spatio-temporal assessment, sources and health risks of water pollutants at trace levels in public supply river using multivariate statistical techniques. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 130942.
- Kazantzis, G. Cadmium, osteoporosis and calcium metabolism. Biometals 2004,17, 398–493. [CrossRef]
- El Sikaily, A.; El Nemr, A.; Khaled, A.; Abdelwehab, O. Removal of toxic chromium from wastewater using green algea Ulva lactuca and its activated carbon. J Hazard Mater 2007 148(1-2);216-228. [CrossRef]
- Yadav, K.K.; Kumar, V.; Gupta, N.; Kumar, S.; Rezania, S.; Singh, N. Human health risk assessment: study of a population exposed to fluoride through groundwater of Agra city, India. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol 2019. 106, 68–80. [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Patra, P.K. Contamination zoning and health risk assessment of trace elements in groundwater through geostatistical modelling. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf 2020. 189, 110038. [CrossRef]
- He. X.; Li, P. Surface water pollution in the middle Chinese Loess Plateau with special focus on hexavalent chromium (Cr6+): occurrence, sources and health risks. Expo Health 2020. [CrossRef]
- Bhutiani, R.; Kulkarni, D.B.; Khanna, D.R.; Gautam, A. Water quality, pollution source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in groundwater of an industrial area in North India. Expo. Health 2016, 8, 3–18. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Biswas, P.K.; Al Hasan, S.M.; Rahman, MM.; et al. The occurrences of heavy metals in farmland soils and their propagation into paddy plants. Environ. Monit. Assess 2018. 190, 201. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Yang, M.; Chen, X.; Liu, J. Health risk assessment and risk control: drinking groundwater in Yinchuan Plain, China. Expo. Health 2019 11 (1), 59–72. [CrossRef]
- Shams, M.; Tavakkoli Nezhad, N.; Dehghan, A.; Alidadi, H.; Paydar, M.; Mohammadi, A. A.; et al. Heavy metals exposure, carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic human health risks assessment of groundwater around mines in Joghatai, Iran. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem 2020. 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Mthembu, P.P.; Elumalai, V.; Brindha, K.; Li P. Hydrogeochemical processes and trace metal contamination in groundwater: impact on human health in the Maputaland coastal aquifer, South Africa. Expo Health 2020. [CrossRef]
- Mthembu, P.P.; Elumalai, V.; Li, P.; Uthandi, S.; Rajmohan, N.; Chidambaram, S. Integration of Heavy Metal Pollution Indices and Health Risk Assessment of Groundwater in Semi-arid Coastal Aquifers, South Africa. Exposure and Health 2022, 14:487–502. [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Li, J.; Gao, X.; Tian, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z. Human health ambient water quality criteria for 13 heavy metals and health risk assessment in Taihu Lake. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2022, 16, 41. [CrossRef]
- Le Chevallier, M.W.; Babcock, T. M.; Lee, R. G. Examination and characterization of distribution system biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 1987. 53:2714–2724. [CrossRef]
- Le Chevallier, M.W. Coliform regrowth in drinking water: a review. J. Am. Water Works Assoc 1990. 82:74–86. [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.L. Potential health risks associated with the persistence of Escherichia coli O157 in agricultural environments. Soil Use Manage. 1999, 15, 76–83. [CrossRef]
- Maisela, R.J. Realizing agricultural potential in land reform: the case of vaalharts irrigation scheme in the northern cape province (Magister Philosophiae in Land and Agrarian Studies, University of the Western Cape (UWC), South Africa 2007.
- Verwey, P.M.J.; Vermeulen, P.D. Influence of irrigation on the level, salinity and flow of groundwater at Vaalharts Irrigation scheme. Water SA 2011, 37(2), pp.155-164. Pretoria. [CrossRef]
- Kouras, A.; Katsoyiannis, I.; Voutsa, D. Distribution of arsenic in groundwater in the area of Chalkidiki, Northern Greece. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2007. [CrossRef]
- Scotcher, J.S.B. The green choice living farms Reference 2009/2010 version. World Wide Fund for Nature and Conservation International 2009.
- Goldblatt, A. Agriculture: Facts and Trends: South Africa. CEO WWF-SA 2010.
- Sharif, M.U.; Davis, R.K.; Steele, KF.; Kim, B.K.T.M.; Fazio, J.A. Inverse geochemical modelling of groundwater evolution with emphasis on arsenic in the Mississippi River Valley alluvial aquifer, Arkansas (USA). J Hydrol 2008 350:41–55. [CrossRef]
- Todd, D.K. Groundwater hydrology, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York 1980. 535p.
- Al-Salim, T.H. Groundwater quality of areas selected NE of Mousl city used for irrigation and drinking purposes, Al-Rafidain Eng 2009, 17(3).
- Aghazadeh, N.; Mogaddam, A. A. Assessment of groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agricultural uses in the Oshnavieh area, Northwest of Iran. J Environ Prot 2010, 1, 30. [CrossRef]
- Doneen, L.D. Notes on water quality in Agriculture Published as a Water Science and Engineering Paper 4001, Department of Water Science and Engineering, University of California 1964.
- Raghuanth, H, M. Groundwater, 2nd edn. New Age International Limited Publishers, New Delhi 1987.
- Szabolcs, I.; Darab, C. The influence of irrigation water of high sodium carbonate content of soils. In: Proceedings of 8th international congress of ISSS, transmission, vol 2, 1964. pp 803–812.
- Kelley, W,P.; Brown, S,M.; Liebig, G,F. Chemical effects of saline irrigation water on soils. Soil Sci 1940. 49: 95-107.
- Meireles, A.C.M.; Andrade, E.M.; Chaves, L.C.G.; Frischkorn, H.; Crisostomo, L.A. A new proposal of the classification of irrigation water. Revista Ciencia Agronomica 2010, 41(3), 349–357. [CrossRef]
- Ustaoglu, F.; Tepe, Y.; Tas, B. Assessment of stream quality and health risk in a subtropical Turkey river system: a combined approach using statistical analysis and water quality index. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 105815. [CrossRef]
- Sheykhi, V.; Moore, F. Geochemical characterization of Kor river water quality, Fars Province, Southwest Iran. Water Quality. Exposure and Health 2012, 4(1), 25–38. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Singh, A.; Jha, R.K.; Sahoo, B. B.; Sahoo, S. K.; Jha, V. Source characterization and human health risk assessment of nitrate in groundwater of middle Gangetic Plain India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2019 12(11), 339. [CrossRef]
- Li, L.L.; Jun, W.; Jian, L.; Kexin, Li.; Zhang, X.; Xiuyun, M.; Chunliang, G.; Juan, X. Water quality evaluation and ecological-health risk assessment on trace elements in surface water of the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 2022. [CrossRef]
- Duggal, V.; Rani, A.; Mehra, R.; Balaram, V. Risk assessment of metals from groundwater in northeast Rajasthan. J Geol Soc India 2017, 90, 77–84. [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, X.; Meng, X.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y. Appraising groundwater quality and health risks from contamination in a semiarid region of Northwest China. Expo. Health 2016, 8, 361–379. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, B. Human health risk assessment of groundwater nitrogen pollution in Jinghui canal irrigation area of the loess region, northwest China. Environment and Earth Science 2018, 77, 273. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wei, A.; Li, J.; Yan, L.; Li, J. Groundwater Quality Evaluation and Health Risk Assessment in the Yinchuan Region, northwest China. Exposure Health 2016 8, 443–456. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, P.; Chen, M.; Dong, Z.; Lu, C. Groundwater quality for potable and irrigation uses and associated health risks in southern part of Guan County, North China Plain. Environ Geochem Health 2010. [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Elumalai. V.; Subramani, T. Seasonal variation of drinking water quality and human health risk assessment in Hancheng City of Guanzhong Plain, China. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 469–485. [CrossRef]
- Schulze, R; Lynch, S; Maharaj M. Monthly rainfall and its inter-annual variability, Pretoria, South Africa 2006.
- Barnard, J.H.; Van rensburg, L.D.; Bennie, A.T.P.; Du preez, C.C. Simulating water uptake of irrigated field crops from non-saline water table soils: validation and application of the model SWAMP. Agric. Water Manage 2013, 126 19–32. [CrossRef]
- Seshoka, J.; de Lange ,W.; Faysse, N. The transformation of irrigation boards into water user associations in South Africa: Case Studies of the Lower Olifants, Great Letaba and Vaalharts Water User Associations. Working Paper 72. Colombo, Sri Lanka: International Water Management Institute 2004.
- Turton, T.; Meissner, R. A hydropolitical History of South Africa’s Major International River Basins. Pretoria, South Africa: AWIRU. Unpublished paper 2003.
- WRC (Water Research Commission). (2016): South African Mine Water Atlas. WRC Project 2016 No. K5/2234//3.
- Herold, C.E.; Bailey A.K. Long-Term Salt Balance of the Vaalharts Irrigation Scheme. Water Research Commission 1996.
- Ellington R.G. Quantification of the impact of irrigation on the aquifer underlying the vaalharts irrigation scheme, Master at the University of the Free State, South Africa, 2003.
- Streutker, A. The Dependence of Permanent Crop Production on Efficient Irrigation and Drainage at the Vaalharts Government Water Scheme. Water SA 1997, 3 (2).
- Gombar, O.; Erasmus C. Vaalharts Ontwaterings ,Projek, Pretoria 1976.
- Kent, L; De Grys, A. The Stratigraphy of South Africa. Handbook 8. Part 1: Lithostratigraphy of the Republic of South Africa, South West Africa/Namibia, and the Republics of Bophuthatswana, Transkei, and Venda. Pretoria: Geological Survey, Dept of Mineral and Energy Affairs, South Africa, 1980.
- Schutte, I.C. The Geology of the Christiana Area. Explanation of Sheet 2724 Scale 1:250 000. Council for Geoscience, Pretoria 1994.
- Ellington, R.; Usher, B.; Van Tonder, G. Quantification of the impact of irrigation on the groundwater resource in the Vaalharts Irrigation Scheme, Pretoria: WRC Report 1322/2/04, 2004.
- Xiao, J.; Wang, L.; Deng, L.; Jin, Z. Characteristics, sources, water quality and health risk assessment of trace elements in river water and well water in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ 2019. 650, 2004–2012. [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.I.C.E.; McClellan, N.I.; Deinniger R.A., et al. A water quality index crashing physiological barrier. Indicators of Environmental Quality 1972, 1, 173–182.
- Rostami, A.A.; Isazadeh, M.; Shahabi, M.; Nozari, H. Evaluation of geostatistical techniques and their hybrid in modelling of groundwater quality index in the Marand Plain in Iran. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2019. [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for drinking water quality, 4th edn. World Health Organization, 2011 Geneva.
- SANS. South Africa National Standard 2015. Drinking water; part 1: Microbiological, physical, aesthetic and chemical determinants; part 2: application of SANS 241-1. Available online: https:// www. mwa. co. th/ download/ prd01/ iDW standard/ South Africa and Water Standard SANS 241- 2015. pdf.
- Edet, A.E.; Offiong, O.E. Evaluation of water quality pollution indices for heavy metal contamination monitoring. A study case from Akpabuyo-Odukpani area, Lower Cross River Basin (southeastern Nigeria). Geo Journal 2002 57, 295–304. [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, M.V.; Praveena, S.M.; Chidambaram, S.; Nagarajan, R.; Elayaraja, A. Evaluation of water quality pollution indices for heavy metal contamination monitoring: a case study from Curtin Lake, Miri City, East Malaysia. Environ Earth Sci 2012 67, 1987–2001. [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.; Singh, A.K. Assessment of human health risk for trace metals in fish and shrimp collected from Subarnarekha river, India. Int J Environ Health Res 2014, 24:429–449. [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Little, J. C.; Chiu, N. Estimating exposure to chemical contaminants in drinking water. Environmental Science & Technology 2004, 38, 1799–1806. [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund. Vol I: Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part A). U.S. Environmental Protection Agency 1989.
- USEPA. Risk assessment guidance for superfund volume I: human health evaluation manual (part769E) United States Environmental Protection Agency 2004 .http://www.epa.gov/oswer/riskassessment/ragse/pdf/introduction.pdf.
- USEPA. Human Health Risk Assessment: Risk-Based Concentration Table. United States Environmental Protection Agency 2010. http://www.epa.gov/reg3hwmd/risk/human/rb-concentration_table/Generic_Tables/.
- Zeng, X.; Liu, Y.; You, S.; Zeng, G.; Tan, X.; Hu, X.; Hu, X.; Huang, L.; Li, F. Spatial distribution, health risk assessment and statistical source identification of the trace elements in surface water from the Xiangjiang River, China.Environ Sci Pollut Res 2015, 22:9400–9412. [CrossRef]
- Khelifi, F.; Mokadem, N.; Liu, G,; Yousaf, B.; Zhou, H.; Ncibi, K.; Hamed, Y. (2021): Occurrence, contamination evaluation and health risks of trace metals within soil, sediments and tailings in southern Tunisia, International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology 2021. [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Q. Risk assessment and seasonal variations of dissolved trace elements and heavy metals in the Upper Han River, China. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2010, 181(1), 1051–1058. [CrossRef]
- US-EPA (US Environmental Protection Agency). A risk assessment– multi way exposure spreadsheet calculation tool. Washington, DC: United States Environmental Protection Agency 1999.
- USEPA. Risk characterization handbook. EPA 100-B-00-002. Accessed November United States Environmental Protection Agency 2013.
- Wu, B.; Zhao, DY.; Jia, HY.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, XX.; Cheng, SP. Preliminary risk assessment of trace metal pollution in surface water from Yangtze River in Nanjing Section, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 2009 82, 405–409. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, GJ.; Liu, HQ.; Lam, PKS. Multivariate statistical evaluation of dissolved trace elements and a water quality assessment in the middle reaches of Huaihe river, Anhui, China. Sci Tot Environ 2017, 583:421–431. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.C.; Liao C.M. Health risk assessment on humans exposed to environmental polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons pollution sources. Science of the Total Environment, 2006 112 – 123. [CrossRef]
- Bekker, F. Quarterly water quality survey on the lower orange river. First quarterly survey for the 2021 period Feb/Mar 2021. Report reference 2021: Orange/C/2021.Clean Stream Environment Service. Stellenbosch (South Africa).
- Wade, T.J.; Xia, Y.; Mumford, J.; Wu, K.; Le, X.C.; Sams, E. ; et al. Cardiovascular disease and arsenic exposure in Inner Mongolia, China: a case-control study. Environ. Health 2015,14, 35. [CrossRef]
- Hanna, A.M.; LaChance, J.; Sadler, R.C.; Champney Schnepp, A. Elevated blood lead levels in children associated with the flint drinking water crisis: a spatial analysis of risk and public health response. Am. J. Public Health 2016, 106, 283–290. [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Liao, Q.; Chillrud, S.N.; Yang, Q.; Huang, L.; Bi, J.; et al. Environmental exposure to cadmium: health risk assessment and its associations with hypertension and impaired kidney function. Sci. Rep 2016. 6, 29989. [CrossRef]
- Adeyeye, O.; Xiao, C.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, X. State, source and triggering mechanism of iron and manganese pollution in groundwater of Changchun, Northeastern China. Environ. Monit. Assess 2020, 192, 619. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.F.; Mahmud, M.J.; Sadmani, A.H.M.A.; Chowdhury, A.I.; Anderson, W.B.; Bodruzzaman, A.B.M.; et al. Previously unrecognized potential threat to children from manganese in groundwater in Rohingya refugee camps in Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh. Chemosphere 2021, 266, 129128. [CrossRef]
- Michael, A.M. Irrigation theory and practices. Vikash Publishing House Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi 1992, pp 686–740.
- Besser, H.; Mokadem, N.; Redhouania, B.; Rhimi, N.; Khlifi, F.; Ayadi, Y.; Omar, Z.; Bouajila, A.; Hamed, Y. GIS-based evaluation of groundwater quality and estimation of soil salinization and land degradation risks in an arid Mediterranean site (SW Tunisia). Arab J Geosci 2017 10:350:. [CrossRef]
- Bauder T.A., Waskom R.M., Davis J.G. Irrigation water quality criteria. Colorado State University, US Department of Agriculture 2007.
- Costa, J.L.; Aparicio, V.C. Quality assessment of irrigation water under a combination of rain and irrigation. Agric Water Manag 2015, 159:299–306. [CrossRef]
- FAO. Water quality for agriculture; irrigation and drainage paper 29 Rev. 1. FAO 1985, Rome 174p.
- Vasanthavigar, M.; Srinivasamoorthy, K.; Vijayaragavan, K.; Rajiv Gandhi, R.; Chidambaram, S.; Anandhan, P.; Manivannan, R.; Vasudevan, S. Application of water quality index for groundwater quality assessment: Thirumanimuttar sub-basin, Tamilnadu, India 2010. Environ Monit Assess 2010, 171:595–609. [CrossRef]
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcot D.W. Water quality for agriculture. FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 1985, 29:1–144.
- Nagaraju, A.; Sunil Kumar, K.; Thejaswi, A. Assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation: a case study from Bandalamottu lead mining area, untur District, Andhra Pradesh, South India. Appl Water Sci 2014 4: 385–396. [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, K.; Elango L. Groundwater quality and its suitability for domestic and agricultural use in Tondiar river basin, Tamil Nadu, India. J. Environ Monit Assess 2012 184:3887–3899. [CrossRef]
- Singha S., Pasupuleti S., Singha S.S., Kumar S. Effectiveness of groundwater heavy metal pollution indices studies by deep-learning. J. Contam. Hydrol 2020. 235, 103718. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.A.; Bodrud-Doza, M.; et al. Spatio-temporal assessment of groundwater quality and human health risk: a case study in Gopalganj, Bangladesh. Expo Health 2017. [CrossRef]
- Sivapalan, M.; Blöschl, G. The growth of hydrological understanding: technologies, ideas, and societal needs shape the field. Water Resources Research, 2017 53 (10), 8137–8146. [CrossRef]

| Criteria | Class | Water Quality | No of samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Na% | < 20 | Excellent | 11 |
| 20-40 | Good | ||
| 40-60 | Permissible | ||
| 60-80 | Doudtful | ||
| > 80 | Unsuitable | ||
| SAR | < 10 | Excellent | 11 |
| 10--18 | Good | ||
| 18-26 | Doudtful | ||
| >26 | Unsuitable | ||
| RSC | < 1,25 | Good | 11 |
| 1,25 | Doudtful | ||
| > 2,5 | Unsuitable | ||
| MR | < 50 | Safe | 8 |
| > 50 | Unsafe | 3 | |
| PI | > 75 | Class I | |
| 25-75 | Class II | 8 | |
| < 25 | Class III | 3 | |
| KR | < 1 | Suitable | 11 |
| 1--2 | Marginal suitable | ||
| > 2 | Unsuitable | ||
| PS | < 3 | Good | |
| 3--15 | Medium | 1 | |
| > 15 | Not recommended | 10 | |
| EC | <250 | low | |
| (μS/cm) | 250-750 | Medium | 9 |
| 750-2250 | High | 2 | |
| >2250 | Very high |
| QWI | Water quality | Possible ranges of uses | No of Samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0-25 | Excellent | Drinking, irrigation and industrial | 1 |
| 25-50 | Good | Domestic, irrigation and industrial | 2 |
| 50-75 | Fair | Irrigation and industrial | 6 |
| 70-100 | Poor | Irrigation | 2 |
| 100-150 | Very poor | Restricted use for irrigation | 0 |
| >150 | Unfit for drinking | Proper treatment is required before use | 0 |
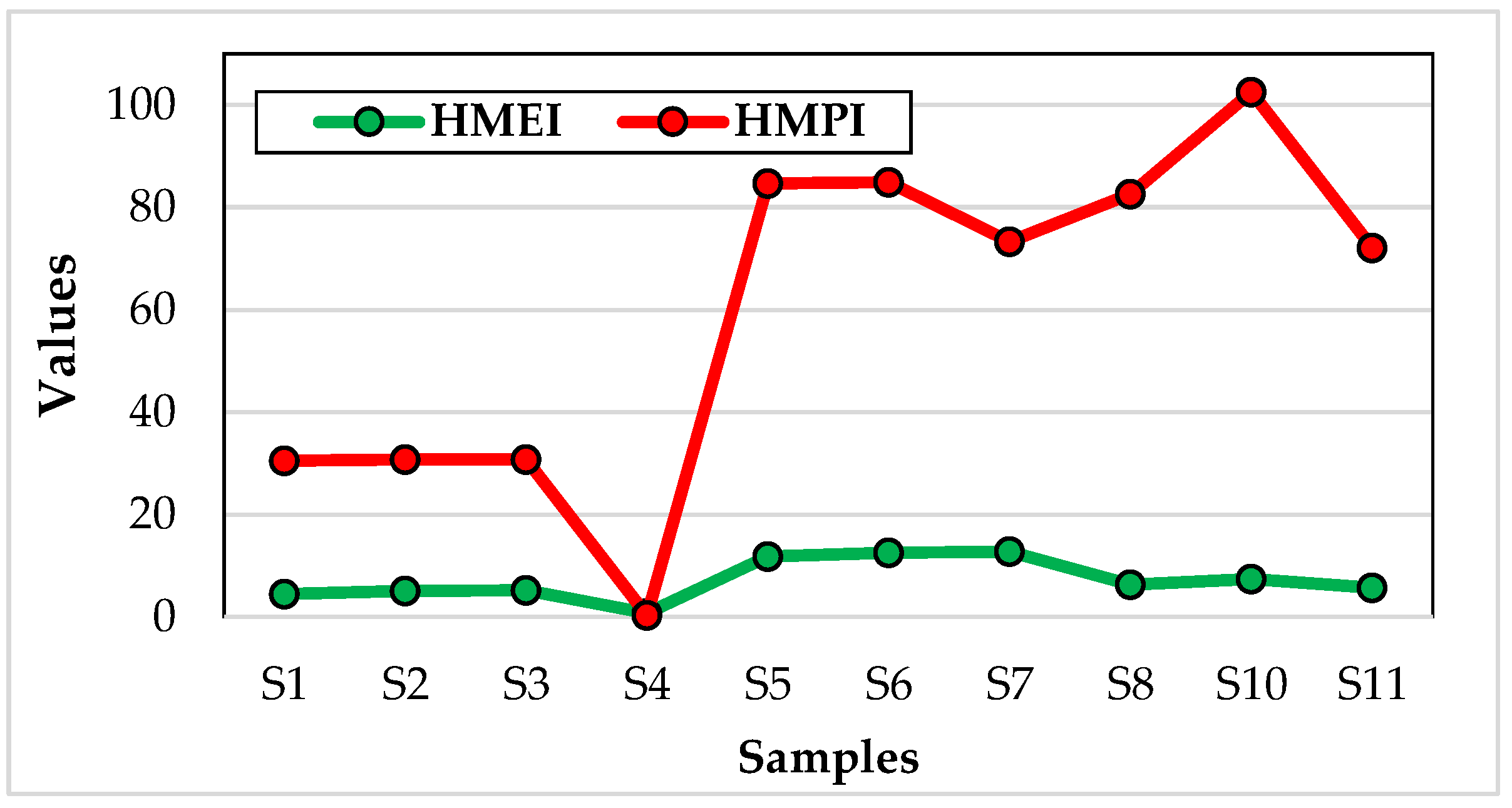
| Samples | HMEI | HMPI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4,45 | 30,5425 |
| 2 | 5,03333333 | 30,77498 |
| 3 | 5,2375 | 30,80668 |
| 4 | 0,716 | 0,264201 |
| 5 | 11,7671429 | 84,71713 |
| 6 | 12,5838095 | 84,94176 |
| 7 | 12,7338095 | 73,34104 |
| 8 | 6,3547619 | 82,63595 |
| 9 | 0 | 0 |
| 10 | 7,42072619 | 102,5304 |
| 11 | 5,70420238 | 72,07097 |
| Samples | Adult | Children | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ∑HQ ing | ∑HQ der | HI | ∑HQ ing | ∑HQ der | HI | |
| 1 | 1,069207 | 2,606938 | 3,676146 | 4,945441 | 76,90968 | 81,85512 |
| 2 | 1,074481 | 2,619452 | 3,693933 | 4,965578 | 77,27886 | 82,24444 |
| 3 | 1,074933 | 2,620525 | 3,695458 | 5,542647 | 77,3105 | 82,85315 |
| 4 | 0,034514 | 0,19821 | 0,232724 | 1,282466 | 5,84758 | 7,130046 |
| 5 | 1,598265 | 4,939994 | 6,538259 | 7,540822 | 145,7393 | 153,2801 |
| 6 | 1,585636 | 4,492906 | 6,078542 | 7,492603 | 132,5493 | 140,0419 |
| 7 | 0,603601 | 4,211413 | 4,815014 | 3,743014 | 124,2447 | 127,9878 |
| 8 | 1,524092 | 4,346879 | 5,870971 | 5,81926 | 128,2413 | 134,0605 |
| 9 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 10 | 0,885555 | 3,492052 | 4,377607 | 3,381211 | 103,0222 | 106,4034 |
| 11 | 0,68949 | 2,664164 | 3,353654 | 2,632597 | 78,59795 | 81,23055 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





