1. Introduction
To a great extent, the fate of neuronal cells is controlled by the effects of growth factors, such as neurotrophins. The neurotrophin family consists of the secreted growth factors BDNF, NGF and NT3/4 whose main functions are to induce neuronal survival and regeneration, thus allowing neurons to survive, differentiate and grow [
1,
2]. All of these biological effects are specifically mediated through binding of neurotrophins to the high affinity Trk receptors and the low affinity p75 pan-neurotrophin receptor. These receptors can function independently or interact naturally and functionally with each other, in ways that can change the signaling characteristics of each receptor [
3].
The pan-neurotrophin receptor p75NTR, is a member of the TNF death receptors superfamily. Its wide expression in many cell types and its controversial signaling pathways, have increased the scientific interest on this receptor. While the most distinguished effects of p75NTR are related to programmed cell death, recent studies have revealed its role in regulating cellular responses, such as cellular proliferation and survival [
4,
5,
6] particularly when acting as a co-receptor of Trk receptors for mature neurotrophins [
3,
7]. The p75NTR signaling properties are predominantly mediated by the death domain of the receptor, through the recruitment or release of specific intracellular interactors in its surface [
8,
9].
Neutrophic effects in brain function and repair have highlighted these growth factors and their receptors as promising therapeutic candidates for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. However, despite their proven beneficial effects on the survival and protection of neurons, their therapeutic usefulness is limited due to their polypeptide nature and limited BBB permeability. Attempts to bypass these limitations, such as ICV infusion [
10,
11] or intranasal delivery of BDNF and NGF [
12,
13] have shown limited therapeutic effects in clinical trials and only a small amount of the applied drug finally reaches the CNS with intranasal delivery.
Previous research efforts of our lab have revealed the ability of the endogenous neurosteroid dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) to block neuronal apoptosis by binding and activating the NGF receptors, namely TrkA and p75NTR [
14,
15,
16]. However, DHEA is metabolized
in vivo to androgens and estrogens, and thus can increase the risk for hormone-dependent cancer development. To overcome these problems, small molecules – chemical analogs of DHEA - that sustain the neurotrophin effects but lack the undesired endocrine effects could be pharmacologically useful. BNN27, a C-17-spiro derivative of DHEA, was one of the first chemical compounds to be tested and it has been shown that it acts through the selective activation of both p75NTR and TrkA receptor [
17,
18]. More recently, a library of novel small molecules based on the aforementioned ones have been synthesized, with improved pharmacological properties and lacking the endocrine side effects of the parental molecule.
In the present study, we focus on the biological evaluation of the compound ENTA-044, a chemical entity derived from DHEA, with a C17 structural modification. We investigated its interaction with the neurotrophin receptors, especially p75NTR and TrkB. ENT-A044 stood out, for its effects on p75NTR, among several others DHEA synthetic analogs that were screened for their ability to activate neurotrophin receptors. We now report its role in activating death signaling pathways in p75NTR-transfected HEK293T cells challenged with serum deprivation, as well as survival pathways in P7 mouse hippocampal neural stem cells expressing TrkB receptor. Additionally, we identify the activated signaling pathways mediated by p75 receptor’s interactor protein RIP2. Noticeably, we report for the first time the expression of p75NTR in human induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs)-derived Neural Precursor Cells (NPCs) and the subsequent death signaling pathways mediated by treatment with ENT-A044. Our results propose that ENT-A044 not only can be used as a lead molecule for the development of non-selective agonists acting on p75NTR and leading on cell death, but also could be exploited as a research tool for deciphering the pleiotropic signaling pathways mediated by p75NTR in a cell-specific manner.
2. Results
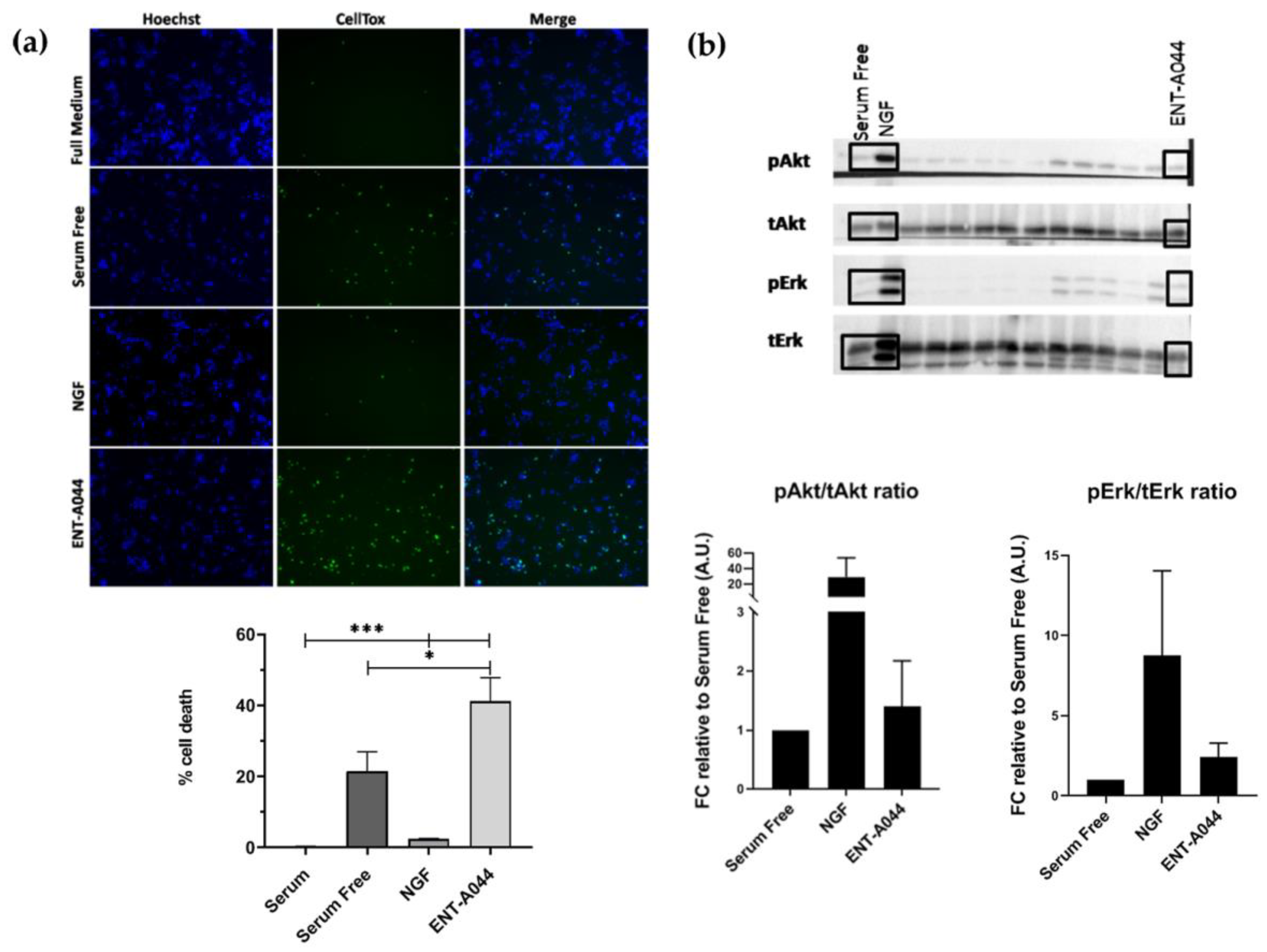
2.1. ENT-A044 induce cell death of PC12 cells
PC12 cells, a cell line that express TrkA and p75NTR[
19], is commonly used for studying neurotrophin-dependent effects, mainly by evaluating their neuroprotective actions. We tested ENT-A044 in PC12 cells under serum starvation conditions in order to induce cell death. Cells were treated for 24h with NGF or the compound, in the absence of serum, and the CellTox cytotoxicity assay was performed to identify apoptotic cells. ENT-A044 did not protect PC12 cells from cell death caused by serum deprovation, and surprisingly, it significantly augmented cell death (
Figure 1a). Given the fact that our compound promotes cell death of PC12 cells expressing TrkA receptor and p75NTR, we assumed that the observed cell death is probably mediated by the actions of the pro-apoptotic p75 death receptor. To investigate the underlying mechanism, we firstly explored the possibility that ENT-A044 interacts with the TrkA neurotrophin receptor and its downstream signaling kinases Akt and Erk1/2. Thus, PC12 cells were starved of serum for 4h and then treated with NGF (100 ng/ml) or ENT-A044 (500 nM) for 20 minutes. In parallel, other analogs of the same chemical library were also tested. Western blot analysis revealed that ENT-A044 cannot induce the phosphorylation of kinases Akt and Erk1/2 that are known to be activated upon TrkA activation and have been associated with NGF promotion of cell survival (
Figure 1b), while other compounds of similar structure were able to activate these kinases [
20]. Thus, considering the inability of ENT-A044 to activate the TrkA receptor, the observed cell death in PC12 is probably mediated by p75NTR.
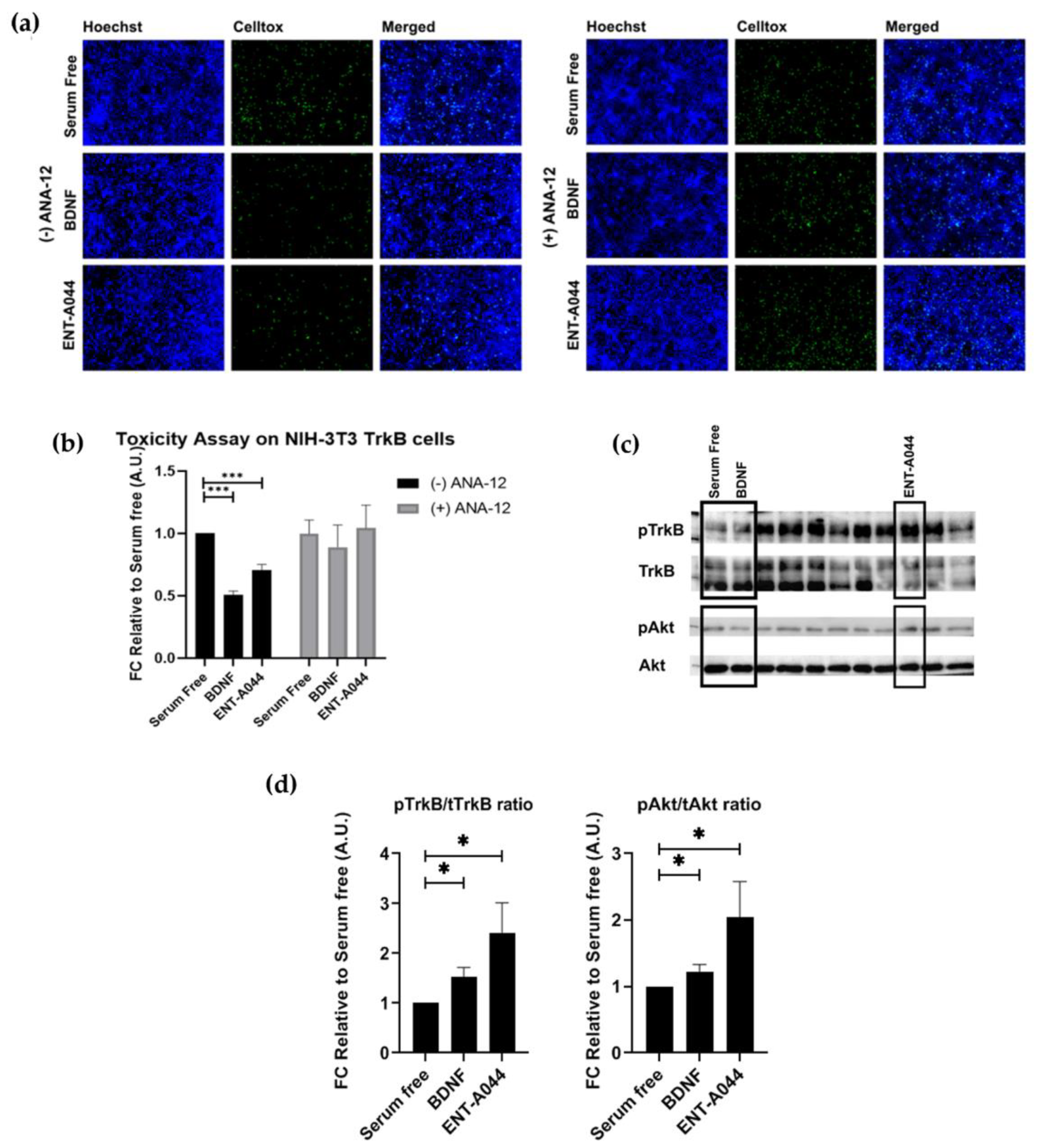
2.2. ENT-A044 activates TrkB receptor and its downstream signaling kinase Akt and protects NIH-3T3/TrkB cells from serum deprivation-induced cell death
Next, we investigated the capacity of ENT-A044 to activate the TrkB receptor before emphasizing on the effects of ENT-A044 on p75NTR. For this purpose, we used NIH-3T3 cells stably transfected with the TrkB receptor, NIH-3T3-TrkB, treated for 24h with BDNF or ENT-A044 in the absence of serum. Cells were then stained with CellTox reagent and Hoechst to identify apoptotic cells. ENT-A044 seems to protect NIH-3T3-TrkB cells from induced cell death. In order to confirm the involvement of TrkB in the protective effect of ETN-A044, we treated cells with BDNF or the compound in the presence of a selective TrkB inhibitor, ANA-12. As it is depicted on the right panels of
Figure 2a,b, the inhibition of TrkB receptor totally abolishes the neuroprotective effect of ENT-A044 and BDNF, clearly indicating TrkB receptor as the exclusive mediator of cell protection. To further evaluate this hypothesis, we tested whether ENT-A044 activates the TrkB downstream signaling kinase Akt. For that reason, we used primary astrocytes isolated from the cortex of postnatal day 2 (p2) mouse pups which endogenously express TrkB. Cells where starved of serum for 4h and then treatments with BDNF (500 ng/ml) or ENT-A044 (500 nM) for 20 minutes, were followed. Western blot analysis revealed that ENT-A044 induces the phosphorylation of TrkB receptor as well as the phosphorylation of kinase Akt (
Figure 2c,d), suggesting that ENT-A044 can activate TrkB receptor and its downstream signaling.
2.3. ENT-A044 promotes cell death by activating p75NTR in transiently transfected HEK293T cells
Following the observed cell death on PC12 cells and TrkB activation by ENT-A044, we then proceeded to study our compound’s implementation in p75NTR activation, as well. HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with the plasmid for the expression of human p75NTR. Treatment of these cells with ENT-A044 revealed an increase in observed death following serum deprivation induced cell death
(Figure 3a,b). HEK293T cells that were not transfected with p75NTR plasmid (wild type HEK293T cells) were also treated with ENT-A044, having no differences from serum free condition (data no shown). Phosphorylation of JNK protein was also measured in order to define the exact signaling pathways that are involved in induction of cell death. JNK, a kinase of the mitogen activated protein kinases, is activated upon p75NTR activation, phosphorylates cJun and triggers apoptotic signaling pathways by the up-regulation of proapoptotic genes [
21,
22]. After 30 minutes treatments with NGF or our compound, phosphorylation of JNK was increased (
Figure 3c). Thus, ENT-A044 can activate JNK mediated death signaling pathways via p75NTR.
To better characterize the p75NTR signaling pathways that are activated by ENT-A044 we performed immunoprecipitation assay. p75NTR lacks intracellular enzymatic activity and its signaling is dependent on interacting proteins -like TRAF6 and RIP2- with receptor’s death domain. Performing co-immunoprecipitation experiments for p75NTR and its interactors TRAF6 and RIP2, we observed that there was no significant recruitment of TRAF6 upon p75 receptor activation using our compound (
Figure 3d), while the RIP2 protein exhibits a significant interaction with the p75NTR in treated samples with ENT-A044 (
Figure 3e). Thus, we clearly show that ENT-A044 can induce multiple, but not all, signaling cascades of the p75NTR, offering a valuable experimental tool for deciphering signaling properties of the receptor.
As HEK293T cells are expressing only p75NTR, it seems that ENT-A044 can induce cell death when only p75NTR is being expressed, while it has opponent effects when TrkB receptor is also co-expressed as in the case of astrocytes. Due to those results, we examined the effects of ENT-A044 in a system where both TrkB and p75NTR are being expressed. As a first step, we used co-transfected HEK293T cells with both TrkB and p75NTR plasmids. Cell tox assay, showed survival or death of cells according to which receptor is present. More specifically, when both receptors are present, ENT-A044 predominantly leads to survival (
Figure S1). This is a clear indication that ENT-A044-dependent signaling on TrkB receptor can overcome the death signaling pathway that is triggered by p75NTR in a cell-specific manner.
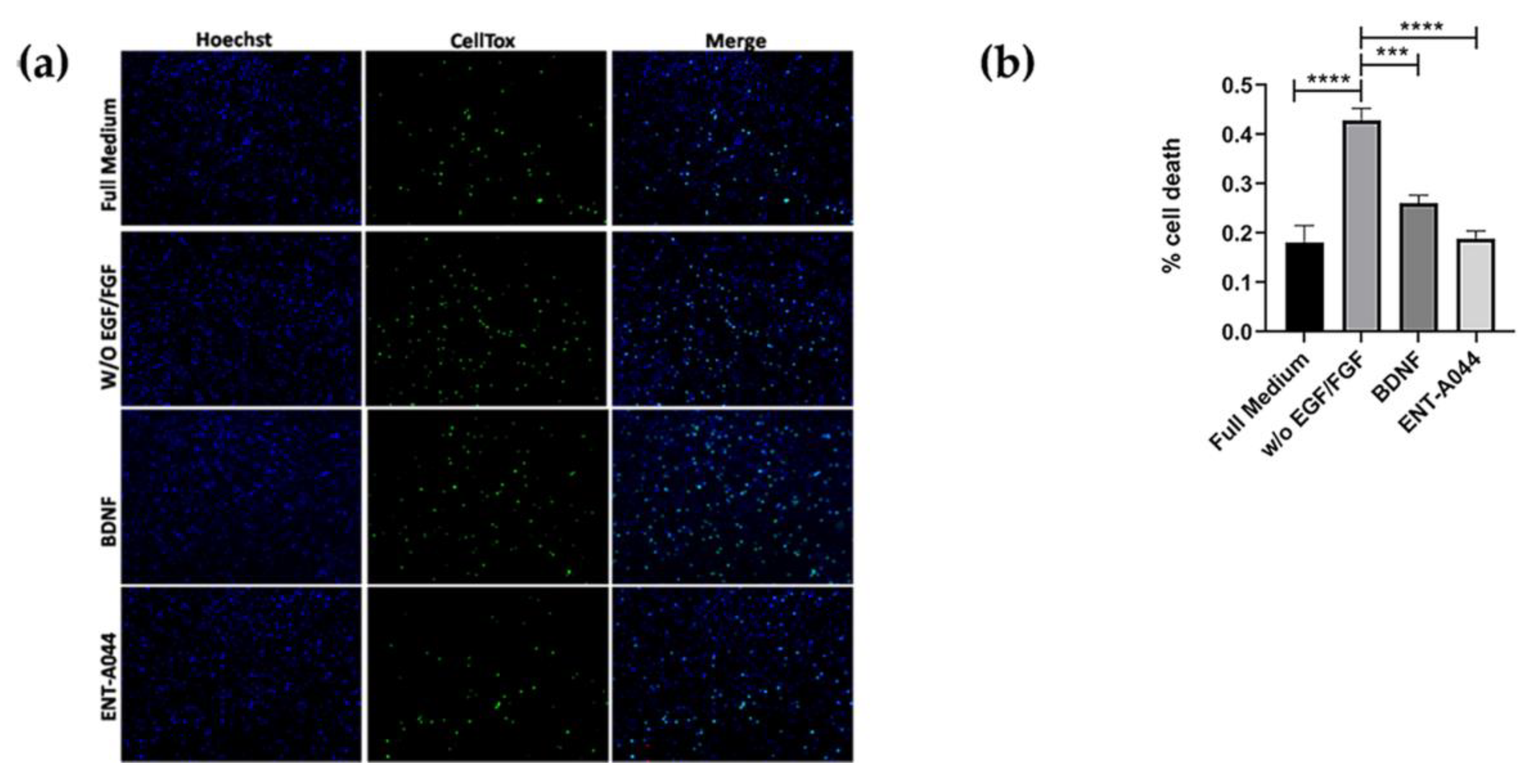
2.4. ENT-A044 promotes cell death in p7 mouse hippocampal NSCs
Furthermore, we also used primary cultures from P7 mouse hippocampal NSCs, that express both TrkB and p75NTR (
Figure S2), showing that, when both of the receptors are present, ENT-A044 treatment for 48h can lead to survival signaling, in agreement with previous results on HEK293T cells (
Figure 4). P7 hippocampal NSCs were also tested upon compound treatment for 24hrs, having no significant results (although there is a trend of protection), probably due to the fact that significant cell death is not observed before 48hrs (
Figure S2).
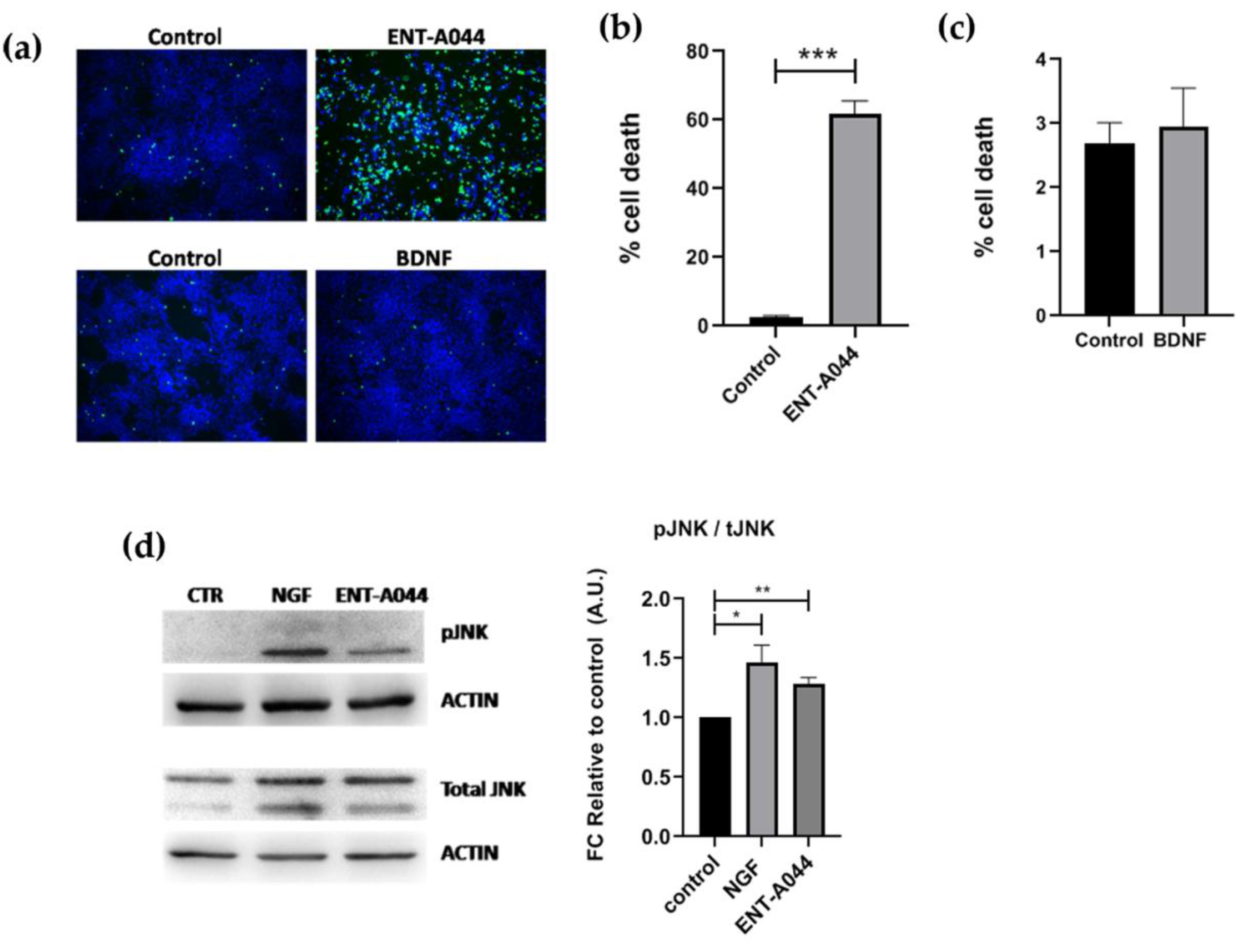
2.5. ENT-A044 shows a strong pro-apoptotic effect on human NPCs
Lastly, we moved on to human cells of neural origin and tested the effect of ENT-A044 on human neural progenitor cells (NPCs). NPCS were generated by human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) and express both TrkB and p75NTR receptors (
Figure S3). NPCs treatment with ENT-A044 for 48hrs has a detrimental effect on cell survival, as revealed by Celltox cytotoxicity assay (
Figure 5a,b). The apoptotic effect of ENT-A044 is in line with the increased levels of pJNK found in NPCs upon treatment with the compound for 24hrs. Increased pJNK was also observed upon cell treatment with NGF, suggesting the activation of an apoptotic signaling pathway totally mediated by p75NTR in these cells (
Figure 5d). On the other hand, we observe that treatment with BDNF for 24hrs cannot induce cell death mediated by p75NTR, independently of its expression in human NPCs (
Figure 5c). Thus, ENT-A044 is leading to cell death mediated by p75NTR in human NPCs, although these cells express both p75NTR and TrkB receptor, indicating significant differences between human and mouse neuronal cell functions that are mediated by neurotrophin receptors.
3. Discussion
Our research group has shown that endogenous neurosteroid dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), which consist a lipophilic small molecule, can act on TrkA and p75NTR, preventing neuronal apoptosis [
14,
16]. However, DHEA is metabolized
in vivo to estrogens and androgens, affecting the endocrine system and therefore, the long-term use of DHEA as a potential treatment of neurodegeneration is problematic, particularly in patients with genetic predisposition to hormone-dependent tumors (breast, endometrium, ovaries, prostate) [
23,
24]. To overcome these limitations of DHEA and to take advantage of the beneficiary effects of this small molecule, Calogeropoulou et al. developed a chemical library of synthetic C17-derivatives of DHEA [
24] with anti-apoptotic properties, lacking androgenic/estrogenic actions. These novel molecules are BBB-permeable and most importantly they act as neurotrophin mimetics to address the neuroprotective and neurogenic effects of endogenous neurotrophins. BNN27, a C17-spiroepoxy steroid derivative, was shown to specifically interact with and activate the TrkA receptor inducing phosphorylation of TrkA tyrosine residues and down-stream neuronal survival-related kinase signaling [
18]. It can also interact with p75NTR as well, inducing the recruitment of effector proteins RIP2 and TRAF6 to the receptor and the release of RhoGDI in primary granular cells of the cerebellum, inducing also neuroprotective effects [
17]. Recently, Rogdakis et al., showed that ENT-A013, a chemically stable and more potent compound compared to BNN27, selectively activates TrkA receptor and exerts neuroprotective, anti-amyloid actions [
20].
The present study provides evidence for one of these synthetic compounds that although activates both TrkB and p75NTR neurotrophin receptors, it exerts differential signaling and cellular effects in a cell specific manner, depending on which receptor is expressed and surprisingly, on the species origin -mouse or human- of the neuronal cell. It is of special notice that ENT-A044 is a compound structurally similar to ENT-A013, a well characterized TrkA activator, deriving from the same synthetic procedures [
20]. However, ENT-A044 cannot activate TrkA as it is obvious from the total absence of phosphorylation of Akt and Erk kinases, that are the most significant downstream signals of the TrkA receptor. On the other hand, we observed TrkB phosphorylation and Akt phosphorylation in TrkB expressing cells, showing that signaling pathways mediated by TrkB are activated upon ENT-A044 treatment. Exploring in depth our initial observation that ENT-A044 induces cell death on PC12 cells, which are expressing both TrkA and p75NTR, and even after serum-deprivation induced apoptosis, we investigated if this effect is mediated by p75NTR. In agreement with this hypothesis, in transiently transfected HEK293T cells which are expressing only p75NTR, our compound increased the levels of cell death, while in naive HEK293T cells, ENT-A044 had no effect on cell death. Thus, cell death resulting from treatment with ENT-A044 is clearly driven by p75NTR activation. More specifically, this death signal is primarily executed through the activation of JNK protein, which is well known to be implicated in cell death signaling pathways originated from p75NTR [
9].
p75NTR, as a member of TNFR superfamily, includes a Death Domain at its intracellular part, which affords the most of its signaling functions [
9]. Depending on the ligand which activates the receptor and the cell type, its actions ranging from cell survival to cell death, while the co-expression of Trk receptors or other co-receptors like sortilin or Nogo can also differentiate the final cellular outcome [
5,
25]. Enhancing of neuronal survival by p75NTR has been associated to the activation of the transcription factor NFkB [
26], after RIP2 recruitment. More specifically, activation of the transcription factor NFkappaB upon the recruitment of RIP2 protein to p75NTR, leads to survival signals on specific neuronal populations [
27,
28]. ENT-A044 efficiently induced the association and interaction of p75NTR with its effector protein RIP2, in transiently transfected HEK293T-p75 cells and had no significant effects on interaction with TRAF6 protein, inducing cell apoptosis. Since, when ENT-A044 activates both TrkB and p75NTR, resulting in cell survival, an important question has immerged whether there is a triangle interaction between RIP2, p75NTR and TrkB receptor which is combinatorically leading towards survival signaling pathways. In transiently transfected HEK293T-TrkB/p75 cells and primary cultures of mouse p7 hippocampal NSCs, ENT-A044 can trigger the survival signaling pathway activated by TrkB receptor and overcome the cell death which is activated by p75NTR in the absence of TrkB. In the last case, p75NTR-dependent induction of cell death overcomes the protective RIP2 signaling, most probably due to significant induction of the pro-apoptotic JNK signal.
Finally, we showed for the first time to our knowledge that p75NTR is being expressed in NPCs generated by hiPSCs. These neural precursors are expressing TrkB receptor as well. In contrast with our previous results in mouse cell or cell lines, where both receptors are being co-expressed, ENT-044 has a totally different effect in human neural stem cells leading to significant induction of cell death. Given the fact that treatment with NGF also increased the levels of pJNK, this apoptotic role is exclusively mediated by p75NTR since TrkA receptor is not expressed. These different cellular responses between mouse and human neural cells could reflect differences between endogenous neurotrophins and ENT-A044 in their affinity with the responsive receptors, as well as different signaling capabilities due to diverse intracellular protein cargo. In addition, based on previous studies, it could be possible that ENT-A044 is modulating receptor’s structure, as well as the interaction between p75NTR and its co-receptors like Trks or sortilin [
29]. In support of this hypothesis, we have shown that the our initially tested compound, BNN27, has different binding sites in TrkA and p75NTR compared to NGF [
18].
Last but not least, taking advantage of ENT-A044 mediating cell death through p75NTR, we could therapeutically exploit this compound against diseases like cancer, targeting the elimination of cancer cells. p75NTR role in cancer is controversial. On the one hand, it has been shown to act as a tumor suppressor as well as a prognostic factor in cancers while on the other hand it participates in tumor aggressiveness [
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35] Goh et al., showed that NSC49652, a small molecule targeting the p75NTR transmembranes domain, can induce apoptosis of melanoma cells acting through p75NTR, taking advantage of the fact that several cancers such as neural crest-derived melanoma, express high levels of p75NTR [
36].
All the aforementioned observations highlight the controversial nature of p75NTR, and further analysis on the signaling pathways and mechanisms that are being activated from this receptor are necessary. Molecules like ENT-A044 can offer a valuable experimental tool in order to dissect these pleiotropic functions of the receptor, not only between different cell types but even between different species. Additionally, small-sized compounds with desirable pharmacological properties like ENT-A044, could offer novel therapeutic approaches against neurodegenerative diseases or tumors growth and cancers.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines
HEK293T cells were obtained from LGC Promochem GmbH (Teddington, UK) and cultured under DMEM medium (11965084, Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA) containing 10% Fetal Bovine Serum (10270106, Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA) and 100 units/mL Penicillin and 0.1 mg/mL Streptomycin (15140122, Gibco, Grand Island, NY,USA) at 5% CO
2 and 37ºC. They were transiently transfected with human p75NTR and TrkB plasmids, as well as with TRAF6 and RIP2 plasmids, using Turbofect Transfection Reagent (R0531, Thermo Fisher Scientific), according to manufacturers’ instructions. Plasmids expressing p75NTR and TrkB were previously described [
14,
17,
18]. Transfected cells were typically used on the second day after transfection. NIH3T3 cells were grown in the same medium, stably transfected with human TrkB plasmid. PC12 cells were cultured under the same medium as well, containing 10% Horse Serum and 5% Fetal Bovine Serum. All cells were used between passages 5–20.
4.2. Primary Cell Cultures
Primary hippocampal NSCs were isolated from postnatal day 7 (p7) mouse pups (C57BL/6J, The Jackson Laboratory, Bar Harbor, ME, USA). These cells were grown in DMEM/F12 medium containing, B27 supplement without vitamin A, D-glucose, Primocin (0,1mgr/ml), FGF (0,02μgr/ml), EGF (0,02μgr/ml) and Heparin (0,1mgr/ml), at 5% CO2 and 37ºC. They were checked every day for neurospheres formation and their morphology - primary neurospheres observed after 5-7 days - when relatively large but bright in the center neurospheres have formed, a passage of the cells was necessary using accutase. Glial cultures were isolated from the cortex of postnatal day 2 (p2) mouse pups (C57BL/6J, The Jackson Laboratory, Bar Harbor, ME, USA). Cells were grown in high glucose DMEM medium containing, 200U/ml penicillin, 200μgr/ml streptomycin and 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS). At day 7, anti-mitotic agent Ara-C was added in the medium at a final concentration of 10μM for 3 to 4 days to target the highly proliferative microglial cells. When Ara-C is being removed, primary astrocytes have reached a purity of 97% percentage and cultured at 5% CO2 and 37ºC. For all the experiments cells were plated on PDL/laminin and the assays were performed after 24hrs.
4.3. Generation and Culture of human Neural Progenitor Cells (NPCs)
NPCs were generated from human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) as previously described [
37] Briefly, iPSCs colonies were sectioned and enzymatically detached from mouse embryonic fibroblasts. The pieces of iPSCs colonies were collected and cultured as embryoid bodies, in suspension, in a medium consisting of knockout DMEM (Invitrogen) , 20% (vol/vol) Knockout Serum Replacement (Invitrogen), 1 mM β-mercaptoethanol (Invitrogen), 1% nonessential amino acids (NEAA; Invitrogen), 1% penicillin/streptomycin/glutamine (PAA) supplemented with 10 µM SB-431542 (Ascent Scientific), 1 µM dorsomorphin (Tocris), 3 µM CHIR99021 (CHIR; Axon Medchem), and 0.5 µM purmorphamine (Alexis). After two days, the medium was changed to N2B27 medium containing ½ DMEM-F12 (Invitrogen) and ½ Neurobasal (Invitrogen) supplemented with N2 supplement (Invitrogen), B27 supplement lacking vitamin A (Invitrogen), 1% penicillin/streptomycin/glutamine supplemented with the aforementioned small-molecules. On day 4, SB-431542 and dorsomorphin were replaced with 150 µM ascorbic acid (AA; Sigma). On day 6, the spheres were cut into smaller pieces and plated on Matrigel-coated plates (BD Biosciences) in the N2B27 medium supplemented with 3 µM CHIR, 0.5 µM SAG (Cayman Chemical), and 150 µM AA. When confluent, cells were split by treatment with accutase (Sigma). The identity of the cells was verified with immunocytochemistry for NESTIN and SOX1.
4.4. Treatments with compound ENTA-044
Cells were starved from serum for four hours, in order to be synchronized prior to treatment and then stimulated with 100 ng/mL NGF or/and BDNF 500ng/mL and the examined compound ENT-A044(500nM). For the activation of the receptors tested, and for the Immunoprecipitation assay treatments lasted for 20 minutes. For the phosphorylation of JNK protein, treatments lasted for 30 minutes or 24hours, as indicated [
9]. NPCs were treated with 1μM of the ENT-A044for 48h for the celltox assay and 24h for the western blot analysis.
4.5. ImmunoPrecipitation and Immunoblotting
Cells were suspended in Pierce™ IP Lysis Buffer (87788, Thermo Fischer Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) supplemented with protease inhibitors (539138, Calbiochem, Darmstadt, Germany) and phosphatase inhibitors (524629, Calbiochem, Darmstadt, Germany). Lysates, pre-cleared for one hour with protein G-plus Agarose beads (sc-2002, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Dallas, TX, USA) and immunoprecipitated with p75NTR antibody (1:100, ab6172, Abcam plc., Cambridge, UK), overnight at 4oC. Protein G-plus agarose beads were incubated with the lysates for 4hrs at 4oC with gentle shaking. Beads were collected by centrifugation and re-suspended in 2x SDS loading buffer and subjected to Western blot against Traf6 antibody (1:2000, ab33915, Abcam, plc.,Cambridge, UK) and RIP2 (1:1000, ADI- AAP-460, Enzo Life Sciences Farmingdale). For immunoblot (IB) analysis, the beads were suspended in sodium dodecyl sulfate- loading buffer and separated by SDS-PAGE. Proteins were transferred to nitrocellulose membranes and blotted with the corresponding antibodies. Whole cell lysates were subjected to Western blot against TrkA (1:1000, 06-574, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), phosphorylated TrkB (1:1000, ABN1381, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), TrkB (1:1000, 07-225-I, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), p75NTR (1:1000, 839701, Biolegend, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA), Traf6 (1:2000, ab33915, Abcam, plc., Cambridge, UK) phosphorylated Akt (1:1000, 9721S, Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA), phosphorylated Erk1/2 (1:1000, 9101S, Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA), total Akt (1:1000, 4691S Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA) and total Erk1/2 (1:1000, 4695S, Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA).
4.6. Cell Tox Assay
After 24hours of treatments, we use the CellTox™ Green Cytotoxicity Assay kit (G8742, Promega Corporation, Maddison, WI, USA) to assess survival of NIH-3T3, PC12, HEK293T, p7 hippocampal NSCs under serum or EGF/FGF deprivation conditions, respectively. NPCs were studied 48hrs later. Cells were plated in 96-well plates, starved for 4 h and then treated with NGF (100 ng/mL) and/or BDNF (500ng/mL) and compound ENT-A044(500 nM) in the presence or absence of p75NTR inhibitor MC-192 (2,5ng/ml, ab6172, Abcam, plc., Cambridge, UK) for 24 h and TrkB inhibitor ANA-12 100μM (SML0209, Sigma-Aldrich, Burlington, MA, US). CellTox assay reagents and Hoescht (1:10,000, H3570, Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) were added to each well for 30 minutes and cells were imaged with a fluorescent microscope (Zeiss AXIO Vert A1, Zeiss, Jena, Germany). Positive cells for cell tox reagent were normalized to total number of cells for each image. We also refreshed the examined compound, as well as BDNF or/and NGF and HEK293T cells and p7 hippocampal NSCs, were imaged again after 48 hours as well.
4.7. Statistical Analysis
All values are expressed as the mean ± s.e.m. Student’s t-test was used for the comparison of two groups and one-way ANOVA was used for multiple group comparisons. A p < 0.05 was considered to mark statistical significance. Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism 7 (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA).
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at:
Preprints.org,
Figure S1: ENT-A044 promotes cell survival in transfected HEK293Tcells, expressing only TrkB receptor or p75NTR and TrkB, as well.
Figure S2: p75NTR and TrkB receptor expression by p7 mouse hippocampal NSCs and human iPSCs – derived NPCs.
Figure S3: ENT-A044 has no significant effects on p7 hippocampal NSCs after 24h treatments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.C.; methodology, M.A.P., T.R., D.C., M.P., K.N.,K.C.; validation, M.A.P., T.R., D.C., M.P., K.N.,K.C.; formal analysis, investigation, resources, I.C.; data curation, writing—original draft preparation, M.A.P.; writing—review and editing, M.A.P., I.C.; visualization, supervision, I.C.; project administration, I.C.; funding acquisition, A.G., I.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme “Euroneurotrophin” under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement No. 765704. It was also co-financed by Greece and the European Union (European Social Fund-ESF) through the Operational Programme «Human Resources Development, Education and Lifelong Learning» in the context of the Act “Enhancing Human Resources Research Potential by undertaking a Doctoral Research” Sub-action 2: IKY Scholarship Programme for PhD candidates in the Greek Universities». The study was also supported from the national Flagship Action “Hellenic Precision Medicine Network in Neurodegenerative Diseases”, funded by the Ministry of Development and Investment and the General Secretariat for Research and Innovation (GSRI), and lastly supported by the Hellenic Foundation for Research and Innovation (H.F.R.I) under the ‘’1st Call for H.F.R.I. Research Projects to support Faculty members and Researchers and the procurement of high-cost research equipment’’ (Project Number: 2301, KA10490).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of FORTH (protocol code 262272 and date of approval 29 October 2018, FORTH Institute animal license: EL91-BIObr-01 and EL91-BIOexp-02).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All materials are available upon request. Synthetic compounds are available under a Material Transfer Agreement with the University of Crete, FORTH and National Hellenic Research Foundation.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Ioanna Kanteli, for her help on methodology and data implementation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- E. J. Huang and L. F. Reichardt, “Neurotrophins: roles in neuronal development and function.,” Annu Rev Neurosci, vol. 24, pp. 677–736, 2001. [CrossRef]
- S. J. Allen and D. Dawbarn, “Clinical relevance of the neurotrophins and their receptors.,” Clin Sci (Lond), vol. 110, no. 2, pp. 175–91, Feb. 2006. [CrossRef]
- M. V. Chao, “Neurotrophins and their receptors: A convergence point for many signalling pathways,” Nat Rev Neurosci, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 299–309, Apr. 2003. [CrossRef]
- B. R. Kraemer, S. O. Yoon, and B. D. Carter, “The Biological Functions and Signaling Mechanisms of the p75 Neurotrophin Receptor,” 2014, pp. 121–164. [CrossRef]
- R. Meeker and K. Williams, “The p75 neurotrophin receptor: at the crossroad of neural repair and death,” Neural Regen Res, vol. 10, no. 5, p. 721, 2015. [CrossRef]
- J. J. Gentry, P. A. Barker, and B. D. Carter, “The p75 neurotrophin receptor: multiple interactors and numerous functions,” 2004, pp. 25–39. [CrossRef]
- M. F. Defreitas, P. S. Mcquillen, and C. J. Shatz, “A Novel p75NTR Signaling Pathway Promotes Survival, Not Death, of Immunopurified Neocortical Subplate Neurons,” 2001.
- M. Vilar et al., “Activation of the p75 Neurotrophin Receptor through Conformational Rearrangement of Disulphide-Linked Receptor Dimers,” Neuron, vol. 62, no. 1, pp. 72–83, Apr. 2009. [CrossRef]
- I. Charalampopoulos, A. Vicario, I. Pediaditakis, A. Gravanis, A. Simi, and C. F. Ibáñez, “Genetic Dissection of Neurotrophin Signaling through the p75 Neurotrophin Receptor,” Cell Rep, vol. 2, no. 6, pp. 1563–1570, Dec. 2012. [CrossRef]
- T. Zigova, V. Pencea, S. J. Wiegand, and M. B. Luskin, “Intraventricular Administration of BDNF Increases the Number of Newly Generated Neurons in the Adult Olfactory Bulb,” Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience, vol. 11, no. 4, pp. 234–245, Jul. 1998. [CrossRef]
- H. Frielingsdorf, D. R. Simpson, L. J. Thal, and D. P. Pizzo, “Nerve growth factor promotes survival of new neurons in the adult hippocampus,” Neurobiol Dis, vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 47–55, Apr. 2007. [CrossRef]
- S. Capsoni et al., “Intranasal ‘painless’ Human Nerve Growth Factors Slows Amyloid Neurodegeneration and Prevents Memory Deficits in App X PS1 Mice,” PLoS One, vol. 7, no. 5, p. e37555, May 2012. [CrossRef]
- S. Capsoni and A. Cattaneo, “Getting Into the Brain: The Intranasal Approach to Enhance the Delivery of Nerve Growth Factor and Its Painless Derivative in Alzheimer’s Disease and Down Syndrome,” Front Neurosci, vol. 16, Mar. 2022. [CrossRef]
- I. Lazaridis et al., “Neurosteroid Dehydroepiandrosterone Interacts with Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) Receptors, Preventing Neuronal Apoptosis,” PLoS Biol, vol. 9, no. 4, p. e1001051, Apr. 2011. [CrossRef]
- I. Charalampopoulos, E. Remboutsika, A. N. Margioris, and A. Gravanis, “Neurosteroids as modulators of neurogenesis and neuronal survival,” Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism, vol. 19, no. 8, pp. 300–307, Oct. 2008. [CrossRef]
- I. Charalampopoulos et al., “Dehydroepiandrosterone and allopregnanolone protect sympathoadrenal medulla cells against apoptosis via antiapoptotic Bcl-2 proteins,” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 101, no. 21, pp. 8209–8214, 04. 20 May. [CrossRef]
- I. Pediaditakis et al., “BNN27, a 17-Spiroepoxy Steroid Derivative, Interacts With and Activates p75 Neurotrophin Receptor, Rescuing Cerebellar Granule Neurons from Apoptosis,” Front Pharmacol, vol. 7, Dec. 2016. [CrossRef]
- I. Pediaditakis et al., “Selective and differential interactions of BNN27, a novel C17-spiroepoxy steroid derivative, with TrkA receptors, regulating neuronal survival and differentiation.,” Neuropharmacology, vol. 111, pp. 266–282, 2016. [CrossRef]
- P. A. Barker and E. M. Shooter, “Disruption of NGF binding to the low affinity neurotrophin receptor p75LNTR reduces NGF binding to TrkA on PC12 cells,” Neuron, vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 203–215, Jul. 1994. [CrossRef]
- T. Rogdakis et al., “Development and Biological Characterization of a Novel Selective TrkA Agonist with Neuroprotective Properties against Amyloid Toxicity,” Biomedicines, vol. 10, no. 3, Mar. 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. Estus, W. J. Zaks, R. S. Freeman, M. Gruda, R. Bravo, and E. M. Johnson, “Altered gene expression in neurons during programmed cell death: identification of c-jun as necessary for neuronal apoptosis.,” Journal of Cell Biology, vol. 127, no. 6, pp. 1717–1727, Dec. 1994. [CrossRef]
- M. Palmada et al., “c-jun is essential for sympathetic neuronal death induced by NGF withdrawal but not by p75 activation,” Journal of Cell Biology, vol. 158, no. 3, pp. 453–461, Aug. 2002. [CrossRef]
- N. A. Compagnone and S. H. Mellon, “Neurosteroids: biosynthesis and function of these novel neuromodulators.,” Front Neuroendocrinol, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 1–56, Jan. 2000. [CrossRef]
- T. Calogeropoulou et al., “Novel Dehydroepiandrosterone Derivatives with Antiapoptotic, Neuroprotective Activity,” J Med Chem, vol. 52, no. 21, pp. 6569–6587, Nov. 2009. [CrossRef]
- B. Lu, P. T. Pang, and N. H. Woo, “The yin and yang of neurotrophin action,” Nat Rev Neurosci, vol. 6, no. 8, pp. 603–614, Aug. 2005. [CrossRef]
- M. Hamanoue, G. Middleton, S. Wyatt, E. Jaffray, R. T. Hay, and A. M. Davies, “p75-Mediated NF-κB Activation Enhances the Survival Response of Developing Sensory Neurons to Nerve Growth Factor,” Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience, vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 28–40, Jul. 1999. [CrossRef]
- B. D. Carter et al., “Selective Activation of NF-κB by Nerve Growth Factor Through the Neurotrophin Receptor p75,” Science (1979), vol. 272, no. 5261, pp. 542–545, Apr. 1996. [CrossRef]
- A. Vicario, L. Kisiswa, J. Y. Tann, C. E. Kelly, and C. F. Ibáñez, “Neuron-type-specific signaling by the p75NTR death receptor regulated by differential proteolytic cleavage,” J Cell Sci, Jan. 2015. [CrossRef]
- A. Nykjaer, T. E. Willnow, and C. M. Petersen, “p75NTR – live or let die,” Curr Opin Neurobiol, vol. 15, no. 1, pp. 49–57, Feb. 2005. [CrossRef]
- T. Okumura, Y. Shimada, M. Imamura, and S. Yasumoto, “Neurotrophin receptor p75NTR characterizes human esophageal keratinocyte stem cells in vitro,” Oncogene, vol. 22, no. 26, pp. 4017–4026, Jun. 2003. [CrossRef]
- T. Okumura et al., “The Biological Role of the Low-Affinity p75 Neurotrophin Receptor in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma,” Clinical Cancer Research, vol. 12, no. 17, pp. 5096–5103, Sep. 2006. [CrossRef]
- H. Jin et al., “p75 Neurotrophin Receptor Suppresses the Proliferation of Human Gastric Cancer Cells,” Neoplasia, vol. 9, no. 6, pp. 471–478, Jun. 2007. [CrossRef]
- H. Yuanlong et al., “The inhibitory effect of p75 neurotrophin receptor on growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells,” Cancer Lett, vol. 268, no. 1, pp. 110–119, Sep. 2008. [CrossRef]
- S.-D. Huang et al., “Self-renewal and chemotherapy resistance of p75NTR positive cells in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas,” BMC Cancer, vol. 9, no. 1, p. 9, Dec. 2009. [CrossRef]
- S. Blondy et al., “Neurotrophins and their involvement in digestive cancers,” Cell Death Dis, vol. 10, no. 2, p. 123, Feb. 2019. [CrossRef]
- E. T. H. Goh et al., “A Small Molecule Targeting the Transmembrane Domain of Death Receptor p75NTR Induces Melanoma Cell Death and Reduces Tumor Growth,” Cell Chem Biol, vol. 25, no. 12, pp. 1485-1494.e5, Dec. 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. Ehrlich et al., “Rapid and efficient generation of oligodendrocytes from human induced pluripotent stem cells using transcription factors,” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 114, no. 11, Mar. 2017. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
(a) Cell tox assay on PC12 cells after 24 hrs and treatments with the tested compound ENT-A044 (500nM). Quantification of cell tox+ cells (green)/Hoechst+ cells (blue), one way ANOVA, * p < 0,05, *** p < 0,001 mean±SEM of triplicate measurements. (b) Representative blots from western blot analysis on lysates from PC12 cells after 20 minutes of treatments with NGF (100ng/ml), synthetic analogs and the compound ENT-A044 (500nM). Quantification analysis of pAkt and pErk expression (one-way ANOVA against control serum free, mean±SEM of triplicate measurements).
Figure 1.
(a) Cell tox assay on PC12 cells after 24 hrs and treatments with the tested compound ENT-A044 (500nM). Quantification of cell tox+ cells (green)/Hoechst+ cells (blue), one way ANOVA, * p < 0,05, *** p < 0,001 mean±SEM of triplicate measurements. (b) Representative blots from western blot analysis on lysates from PC12 cells after 20 minutes of treatments with NGF (100ng/ml), synthetic analogs and the compound ENT-A044 (500nM). Quantification analysis of pAkt and pErk expression (one-way ANOVA against control serum free, mean±SEM of triplicate measurements).
Figure 2.
(a) Cell tox assay on stable transfected NIH-3T3-TrkB cells after 24 hrs and treatments with the tested compound ENT-A044 (500nM). ANA12, the TrkB inhibitor, was also used. (b) Quantification of cell tox+ cells (green)/Hoechst+ cells (blue), t-test against control serum free, *** p < 0,001, mean±SEM of triplicate measurements (c) Representative blots from Western blot analysis on lysates from primary mouse cultures of astrocytes after 20 minutes treatments with BDNF (500ng/ml) and the tested compound ENT-A044 (500nM) (d) Quantification analysis of pTrkB and pAkt expression (t-test against control serum free, * p < 0,05, mean±SEM of five measurements).
Figure 2.
(a) Cell tox assay on stable transfected NIH-3T3-TrkB cells after 24 hrs and treatments with the tested compound ENT-A044 (500nM). ANA12, the TrkB inhibitor, was also used. (b) Quantification of cell tox+ cells (green)/Hoechst+ cells (blue), t-test against control serum free, *** p < 0,001, mean±SEM of triplicate measurements (c) Representative blots from Western blot analysis on lysates from primary mouse cultures of astrocytes after 20 minutes treatments with BDNF (500ng/ml) and the tested compound ENT-A044 (500nM) (d) Quantification analysis of pTrkB and pAkt expression (t-test against control serum free, * p < 0,05, mean±SEM of five measurements).
Figure 3.
HEK293T cells were transiently co-transfected with the plasmid cDNAs of p75NTR and/or TRAF6 and/or RIP2. (a) Cell tox assay on transfected HEK293T cells after 48 hrs and treatments with the tested compound ENT-A044 (500nM). (b) Quantification of cell tox+ cells (green)/Hoechst+ cells (blue), one-way ANOVA, * p < 0,05, ** p < 0,01, mean±SEM of triplicate measurements. (c) Western blot analysis on transfected HEK293T cells after 30minutes treatments with the tested compound (500nM) and quantification of pJNK expression (unpaired t-test against control serum free, * p < 0,05, mean±SEM of triplicate measurements). (d) Transfectants were exposed for 20 min to BDNF (500 ng/ml) & the tested compound and lysates were immunoprecipitated with p75NTR-specific antibody and then immunoblotted with antibodies against TRAF6. Total lysates were analyzed for p75NTR or actin expression by immunoblotting (unpaired t-test against control serum free, ns no significant, mean±SEM of triplicate measurements). (e) Transfectants were exposed for 20 min to BDNF (500 ng/ml) & the tested compound and lysates were immunoprecipitated with p75NTR-specific antibody and then immunoblotted with antibodies against RIP2. Total lysates were analysed for p75NTR or actin expression by immunoblotting (unpaired t-test against control serum free, *** p < 0,005, mean±SEM of triplicate measurements).
Figure 3.
HEK293T cells were transiently co-transfected with the plasmid cDNAs of p75NTR and/or TRAF6 and/or RIP2. (a) Cell tox assay on transfected HEK293T cells after 48 hrs and treatments with the tested compound ENT-A044 (500nM). (b) Quantification of cell tox+ cells (green)/Hoechst+ cells (blue), one-way ANOVA, * p < 0,05, ** p < 0,01, mean±SEM of triplicate measurements. (c) Western blot analysis on transfected HEK293T cells after 30minutes treatments with the tested compound (500nM) and quantification of pJNK expression (unpaired t-test against control serum free, * p < 0,05, mean±SEM of triplicate measurements). (d) Transfectants were exposed for 20 min to BDNF (500 ng/ml) & the tested compound and lysates were immunoprecipitated with p75NTR-specific antibody and then immunoblotted with antibodies against TRAF6. Total lysates were analyzed for p75NTR or actin expression by immunoblotting (unpaired t-test against control serum free, ns no significant, mean±SEM of triplicate measurements). (e) Transfectants were exposed for 20 min to BDNF (500 ng/ml) & the tested compound and lysates were immunoprecipitated with p75NTR-specific antibody and then immunoblotted with antibodies against RIP2. Total lysates were analysed for p75NTR or actin expression by immunoblotting (unpaired t-test against control serum free, *** p < 0,005, mean±SEM of triplicate measurements).
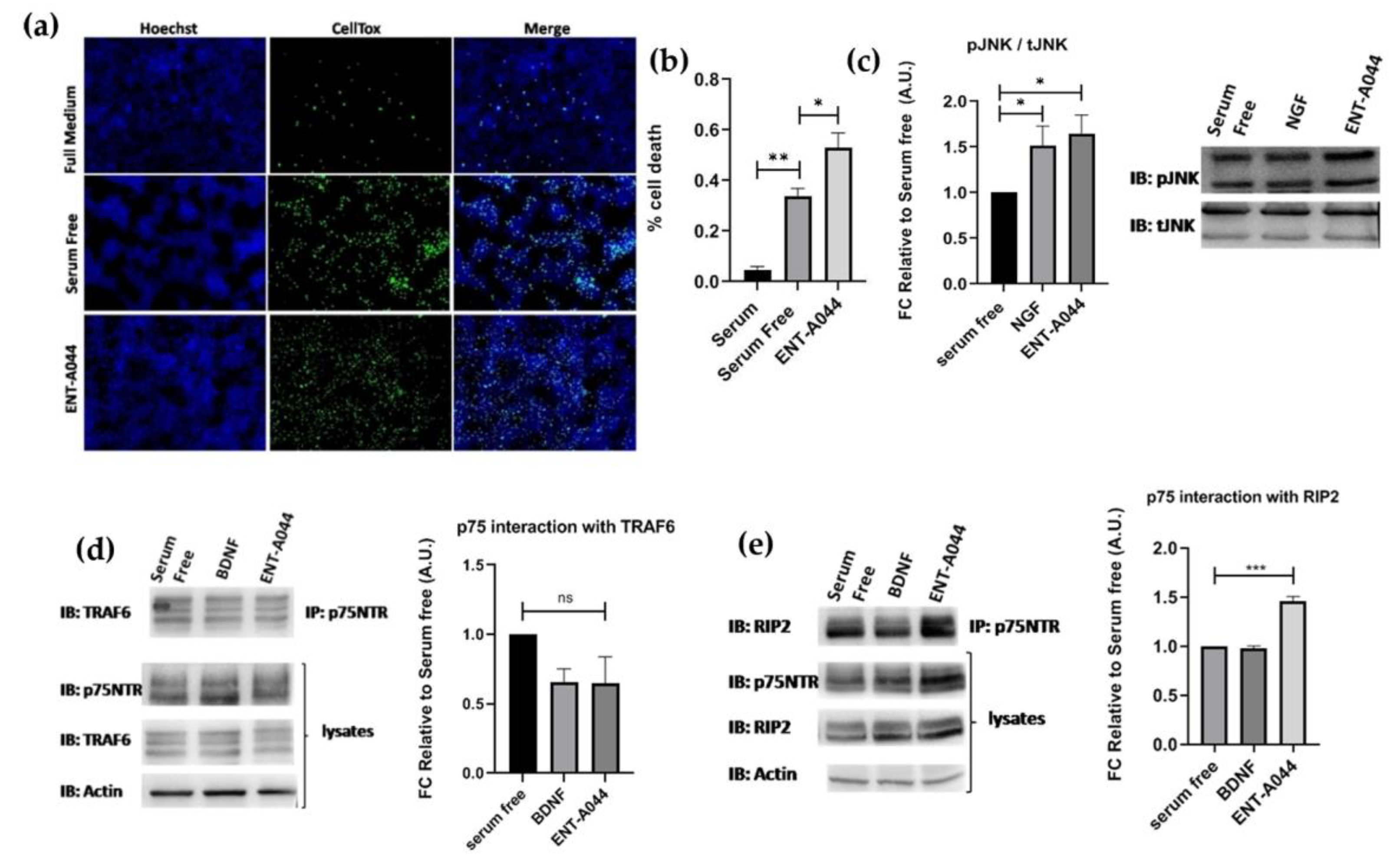
Figure 4.
(a) Cell tox assay on P7 mouse hippocampal NSCs after 48 hrs treatments with the tested compound ENT-A044 (500nM). (b) Quantification of cell tox+ cells (green)/Hoechst+ cells (blue), one-way ANOVA, *** p < 0,005, **** p < 0,0001, mean±SEM of triplicate measurements.
Figure 4.
(a) Cell tox assay on P7 mouse hippocampal NSCs after 48 hrs treatments with the tested compound ENT-A044 (500nM). (b) Quantification of cell tox+ cells (green)/Hoechst+ cells (blue), one-way ANOVA, *** p < 0,005, **** p < 0,0001, mean±SEM of triplicate measurements.
Figure 5.
(a) Representative images of Cell tox assay on human NPCs after 48 hrs treatment with ENT-A044 (1μM) and BDNF (500ng/ml). (b), (c) Quantification of dead cells (green)/Hoechst + cells (blue), t-test, ns no significant, **** p < 0,001, mean±SEM of triplicate measurements (d) Images and quantification of Western blot analysis for p-JNK and total JNK on NPCs treated with ENT-A044 (1μM) or NGF (100ng/ml) for 24hrs (unpaired t-test against control, * p < 0,05, ** p < 0,005, mean±SEM of triplicate measurements).
Figure 5.
(a) Representative images of Cell tox assay on human NPCs after 48 hrs treatment with ENT-A044 (1μM) and BDNF (500ng/ml). (b), (c) Quantification of dead cells (green)/Hoechst + cells (blue), t-test, ns no significant, **** p < 0,001, mean±SEM of triplicate measurements (d) Images and quantification of Western blot analysis for p-JNK and total JNK on NPCs treated with ENT-A044 (1μM) or NGF (100ng/ml) for 24hrs (unpaired t-test against control, * p < 0,05, ** p < 0,005, mean±SEM of triplicate measurements).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).