Submitted:
21 June 2023
Posted:
22 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Random forest classification algorithm
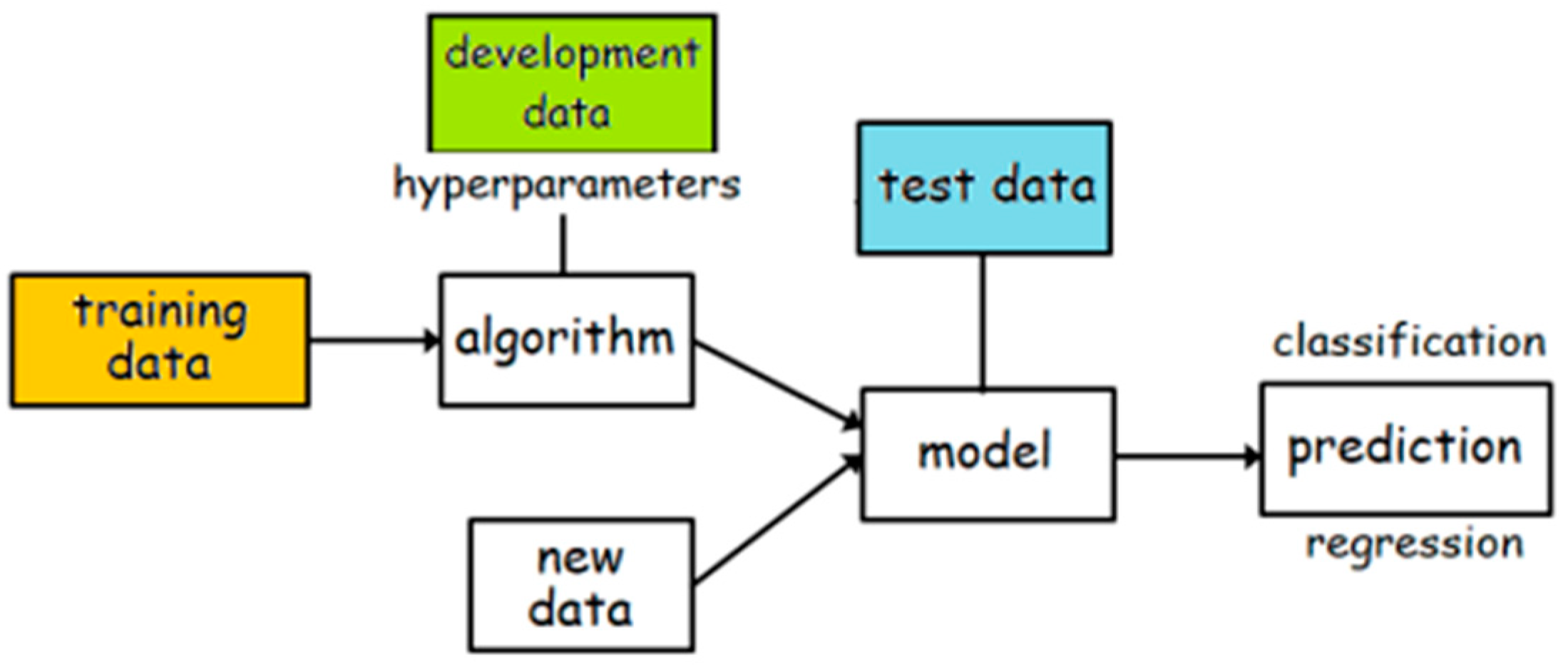
2.1. Methodology
2.2. Characteristics
3. Random forest classification algorithm
3.1. Data description
3.2. Data preprocessing
3.3. Data visualization
4. Experimental results
4.1. Implementation details
4.2. Training and development
4.3. Evaluation
| Method | Test accuracy | F1-score |
| Random forest | 85.62% | 85.48% |
4.4. Result
5. Conclusions
References
- Zhang, N.; Chen, Q. P2P loan default prediction model based on TF-IDF algorithm. Journal of Computer Applications 2018, 38, 3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.M.; Wang, Y.J.; Lai, M.Z. Credit risk prediction of supply chain financing enterprises based on IG-SVM model. Journal of Nanjing University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition) 2020, 44, 117–126. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.L.; Han, S.W.; Pang, J.H. Default risk prediction of enterprise loan based on machine learning method[J]. Modeling and Simulation 2021, 10, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.M.; Zhou, J.J. An empirical credit risk study of SEMs in small loan companies-based on logistic model and probit model[J]. Statistics and Applications 2014, 3, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, H.; Yan, X.; Liu, X. MapReduce-based adaptive random forest algorithm for multi-label classification. Neural Computing and Applications 2019, 31, 8239–8252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, G.; Meng, Q.; Finley, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Ye, Q.; Liu, T.Y. Lightgbm: A highly efficient gradient boosting decision tree. Advances in neural information processing systems 2017, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, G.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Bian, J.; Liu, T.Y. DeepGBM: A deep learning framework distilled by GBDT for online prediction tasks. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining; 2019; pp. 384–394. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, H.; Shi, X.; Rodrigue, A.K.; Feng, J.; Xia, Y.; Elhoseny, M.; Yuan, X.; Gu, L. Feature selection based on artificial bee colony and gradient boosting decision tree. Applied Soft Computing 2019, 74, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.; Jung, I.; Park, K.; Han, B. Tracking-by-segmentation with online gradient boosting decision tree. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision; 2015; pp. 3056–3064. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, R.; Wang, G.; Zhang, W.; Hsu, L.T.; Ochieng, W.Y. A gradient boosting decision tree based GPS signal reception classification algorithm. Applied Soft Computing 2020, 86, 105942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, S.; Zhao, M.; Chang, X.W.; Precup, D. Break the ceiling: Stronger multi-scale deep graph convolutional networks. Advances in neural information processing systems 2019, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Luan, S.; Hua, C.; Lu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, S.; Chang, X.; Precup, D. Revisiting heterophily for graph neural networks. Advances in neural information processing systems 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, S.; Zhao, M.; Hua, C.; Chang, X.W.; Precup, D. Complete the missing half: Augmenting aggregation filtering with diversification for graph convolutional networks. NeurIPS 2022 New Frontiers in Graph Learning Workshop (oral). 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Luan, S.; Zhao, M.; Hua, C.; Chang, X.W.; Precup, D. Complete the Missing Half: Augmenting Aggregation Filtering with Diversification for Graph Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.10822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, S.; Hua, C.; Lu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, S.; Chang, X.; Precup, D. Is Heterophily A Real Nightmare For Graph Neural Networks To Do Node Classification? arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.05641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, S.; Hua, C.; Lu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, S.; Chang, X.; Precup, D. Is Heterophily A Real Nightmare For Graph Neural Networks on Performing Node Classification? 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, C.; Luan, S.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, J. Graph Neural Networks Intersect Probabilistic Graphical Models: A Survey. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.06089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Liu, Z.; Luan, S.; Zhang, S.; Precup, D.; Bengio, Y. A consciousness-inspired planning agent for model-based reinforcement learning. Advances in neural information processing systems 2021, 34, 1569–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, S.; Zhao, M.; Chang, X.W.; Precup, D. Training matters: Unlocking potentials of deeper graph convolutional neural networks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.08838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, S.; Hua, C.; Lu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Chang, X.W.; Precup, D. When Do We Need GNN for Node Classification? arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.16979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, S.; Hua, C.; Xu, M.; Lu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Chang, X.W.; Fu, J.; Leskovec, J.; Precup, D. When Do Graph Neural Networks Help with Node Classification: Investigating the Homophily Principle on Node Distinguishability. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.14274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.; Luan, S.; Xu, M.; Ying, R.; Fu, J.; Ermon, S.; Precup, D. MUDiff: Unified Diffusion for Complete Molecule Generation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.14621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.; Luan, S.; Fu, J.; Precup, D. Multi-Dataset Multi-Task Framework for Learning Molecules and Protein-target Interactions Properties.
- Zhao, M.; Luan, S.; Porada, I.; Chang, X.W.; Precup, D. META-Learning State-based Eligibility Traces for More Sample-Efficient Policy Evaluation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.11439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, S.; Chang, X.W.; Precup, D. Revisit Policy Optimization in Matrix Form. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.09186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

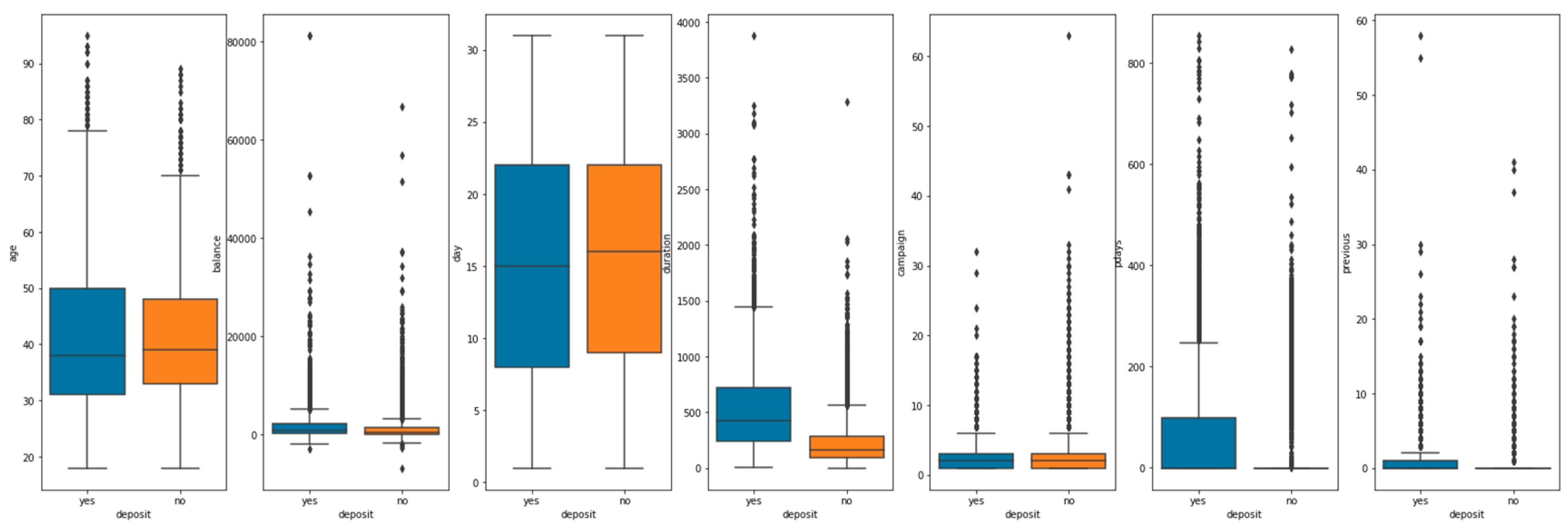
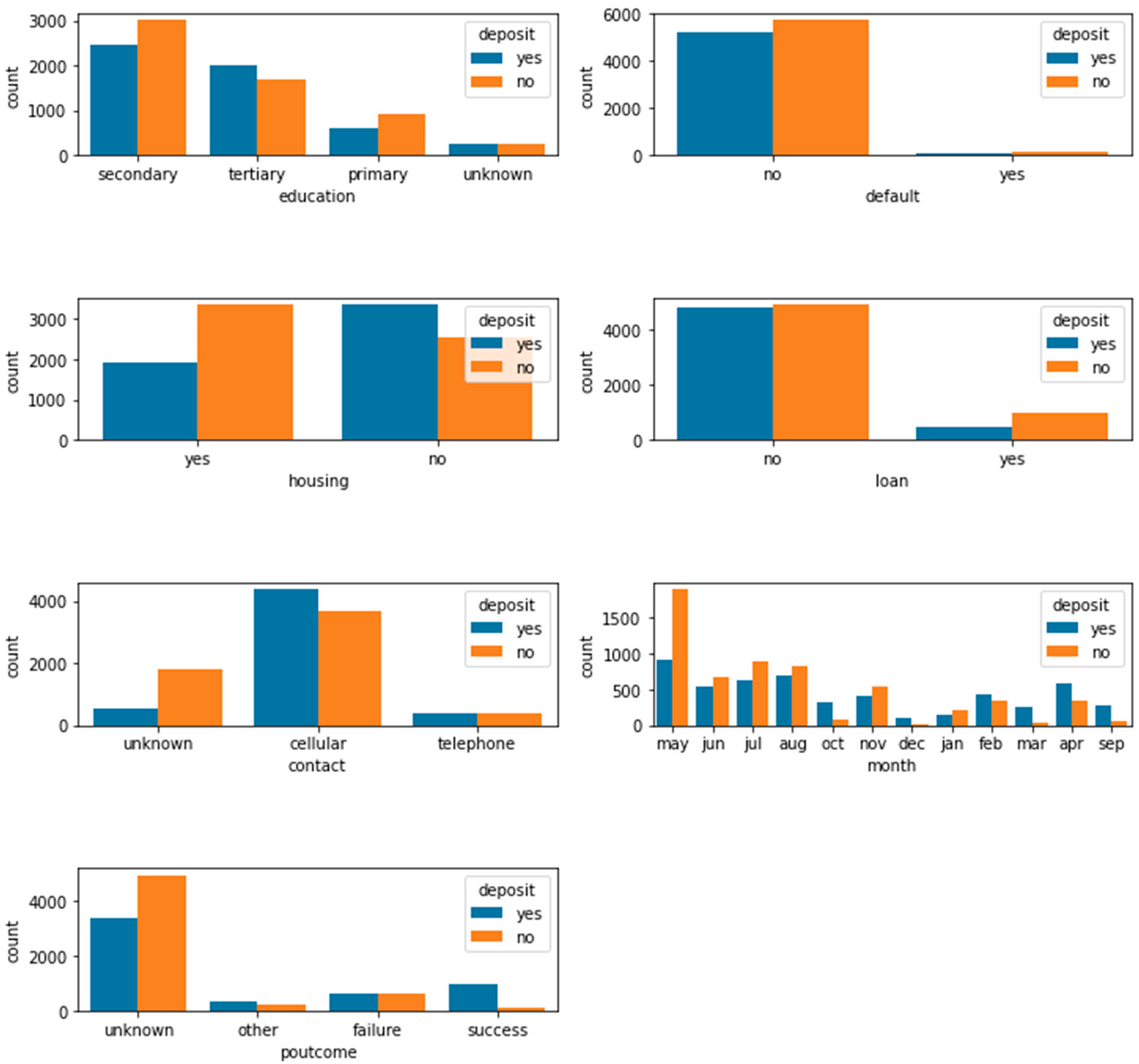
| Idx | Name of variables | Description of variables | type |
| 1 | Age | Age | int64 |
| 2 | Job | Types of occupation | object |
| 3 | Marital | Marital status | object |
| 4 | Education | Level of education | object |
| 5 | Default | Default record | object |
| 6 | Balance | The average account balance per year | int64 |
| 7 | Housing | Whether the individual has a home loan | object |
| 8 | Loan | Whether the individual has a loan record | object |
| 9 | Contact | The way to communicate with customers | object |
| 10 | Day | Day(date) of last contact | int64 |
| 11 | Month | Month(date) of last contact | object |
| 12 | Duration | The length of the last contact | int64 |
| 13 | Campaign | The number of times the customer was communicated in this activity | int65 |
| 14 | Pdays | How long has it been since the last time the client was contacted by the last campaign | int66 |
| 15 | Previous | The number of times you communicated with the customer prior to this event | int67 |
| 16 | Poutcome | The results of the last campaign | object |
| 17 | Deposit | Predict whether to lend to a borrower | object |
| Predicted True | 0 | 1 | All |
| 0 | 967 | 208 | 1175 |
| 1 | 113 | 945 | 1058 |
| All | 1080 | 1153 | 2233 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




