1. Introduction
Considering the European Commission's environmental measures that have resulted in an increasing demand for lithium (Li) and other critical materials [
1], there is a current need for new geological exploration technologies to discover and evaluate possible European deposits. This need and possible ways to address it have been discussed in previous works [
1,
2,
3]. Studies focused on methodologies for locating and prospecting pegmatites are increasingly relevant, given their importance for the energy market in a scenario where new sources need to be identified.
Müller et al. [
3] delineated the goals of the ongoing Horizon 2020 GREENPEG project to develop exploration toolsets to identify buried pegmatites of both Li–Cs–Ta (LCT) and Nb–Y–F (NYF) chemical types. According to the authors, distinct exploration techniques are being tested at several scales, including i) remote sensing approaches, ii) helicopter-borne, drone-borne and ground-based geophysics (radiometry, magnetometry, electromagnetics, piezoelectric spectrometry, ground-penetrating radar, gravimetry, and resistivity), and iii) geochemical surveys (soil Ah and C-horizon mapping, stream sediment mapping, lithogeochemical mapping, and quartz element-trace mapping).
Steiner [
4] presented a review of exploration techniques for LCT pegmatites and a resulting workflow was proposed. The workflow starts with i) literature and desktop studies followed by ii) target selection under a Geographic Information System (GIS); in the selected targets, iii) follow-up field campaigns are conducted and if favorable evidence is found, iv) eventually drilling campaigns have to be employed [
4]. However, most of the exploration methods reviewed in this work for field campaigns are related to traditional geological mapping approaches or with geochemical surveys, namely rock geochemistry, and soil and stream sediment sampling campaigns.
The earlier work of Galeschuk and Vanstone [
5] already demonstrated the importance and success of geochemical exploration methods such as rock lithogeochemistry and selective leach soil geochemistry to identify buried LCT pegmatites in the Bird River Belt, Manitoba, Canada. Similar approaches have been conducted in recent years [
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11]. For example, geochemical analysis of stream sediment samples allowed the identification of anomalies and new prospects for LCT pegmatites in several areas in Ireland, Iran and Portugal, especially when employing multi-element statistical analysis and subsequently determined geochemical pathfinders [
6,
7,
8,
9]. Errandonea-Martin et al. [
10] presented a detailed lithogeochemical study that demonstrated that the LCT pegmatites from Fregeneda–Almendra (Iberian Peninsula) generated metasomatic haloes on their metasedimentary host rocks, with the magnitude of such haloes controlled by the degree of magmatic differentiation of pegmatitic melts. The authors demonstrated that Li and Cs display the greatest haloes which can serve as proxies for mineral exploration in fresh outcrops. Recently, Keyser et al. [
11] analyzed the concentrations of pegmatite-related trace elements in quartz for LCT pegmatites in Austria and Ireland, concluding that such trace element concentrations in quartz can serve as reliable proxies for Li mineralization, besides presenting crucial information to assess primary pegmatite chemical signatures.
Besides geochemical approaches, other exploration techniques have been evaluated. In 2010, Trueman [
12] conducted a study in which he considered the use of geophysical methods to the prospection of pegmatites. Having into account that the minerals contained in pegmatites are not responsive to these methods, he concluded that electromagnetic and gravimetric methods are favorable for outlining the structures and contacts between the pegmatites and host rock. However, the radiometric method was considered a poor alternative because the studied pegmatites had low uranium (U) and thorium (Th) concentrations. In 2016, Thomas et al. [
13] presented a study where the authors successfully employed radiometric data to define the pegmatitic zone. They used radiometric data from the Bird River belt, Manitoba, where numerous pegmatites outcrop, Tanco pegmatite being one of them.
In parallel, remote sensing (RS) approaches have been fine-tuned to detect both surface LCT and NYF pegmatites [
14,
15,
16]. The potential of RS data and image processing techniques and subsequent data integration in GIS for mineral exploration purposes was extensively reviewed by Rajesh [
17], while limitations and difficulties related to pegmatite exploration have also been identified [
18]. Rajesh [
17] highlighted the importance of imaging spectrometry, also known as hyperspectral RS, to delineate prospective areas of interest using distinct absorption features that occur in most minerals. One methodology to analyze absorption features and understand the composition of the rock is to use reflectance spectroscopy, which can be measured in the field or in the laboratory [
19,
20,
21]. This technique, associated with the pre-processing and processing and use of satellite images, can corroborate the presence of critical minerals enriched in Li, and related Li pegmatites. Several methodologies can be employed to identify the target minerals, such as comparing spectral data obtained
in situ with theoretical reference spectral curves. The United States Geological Survey (USGS) [
22], and ECOSTRESS [
23] spectral libraries provide some reference spectral curves, however, they are not focused on providing spectra for all Li minerals [
24].
Therefore, the joint use of RS, geophysical, and geochemical data/techniques, and GIS analysis contributes to improving the knowledge of potential areas, reducing possible local impacts and allowing the establishment of priorities with implications: (i) on investment to be carried out in the stages before the start of exploration; (ii) in the selection of the most eco-efficient technologies for blasting and ore treatment, preferably with no waste production; (iii) in the life-cycle of the mining operation; (iv) in the value chain of extracted raw materials, respecting the Cleaner Production (CP) principles; and (v) in the selection of methodologies to be used either in the monitoring of environmental impacts, or in their mitigation or remediation [
17,
25,
26].
The work presented in this study is within the scope of the project INOVMINERAL4.0, funded by Portugal2020, Compete2020, Lisbon2020 and the European Regional Development Fund, whose overall objective is the innovation and reorientation of the industrial models that sustain the Mineral Resources Sector, through the development of advanced technologies, new products and software that respond to the entire value chain: prospecting and mineral research, integrated valorization of mineral resources and gains in market share (
https://inovmineral.pt/).
Specifically, this study focuses on the Aldeia LCT pegmatite dykes, located in the Barroso-Alvão pegmatite field, one of the most economically important fields in Iberia and in Europe [
1,
27]. Considering the inherent costs of field campaigns to identify targets
in situ, this study presents alternatives to traditional geochemical exploration, focusing on a preliminary evaluation of the spectral signature of targets, subsequent RS approach and geophysical surveys at a specific site to serve as an added value for future exploration studies. The large amount of data generated under the INOVMINERAL4.0 project required the development of an open-source GIS framework to spatially present all the information collected in the project. In the last decades, webGIS applications have been widely developed to dynamically represent variables [
28]. In this work, the implementation of the webGIS was crucial for data storage, organization, and integration (
https://gis.fc.up.pt/INOVMineral/index.html).
Taking this into account, the following objectives were delineated: i) evaluate the potential of high spatial resolution elevation data for subsequent exploration works; ii) test geophysical exploration methods, namely radiometry, and evaluate the potential to discriminate LCT pegmatites; iii) present a methodology for obtaining reflectance spectral data on rock samples, culminating in the construction and availability of a spectral library that can be used as laboratory validation of field data, consequently stimulating the creation of other open access databases, in other locations; iv) compare the spectra obtained with a satellite data from Landsat 9, evaluating the potential of this new satellite for mineral exploration; and v) to present a webGIS implementation under the INOVMINERAL4.0 project, to spatially represent the data acquired in the project and disseminate them to the public.
Therefore, several research questions were delineated in this study: i) how can the acquisition of high spatial resolution elevation data be relevant to pegmatite exploration?; ii) can radiometry be a useful geophysical exploration tool for LCT pegmatites?; iii) can reflectance spectroscopy data be used as validation of RS approach?; and iv) can the new Landsat 9 data be suitable for the identification of surface LCT pegmatites?
1.1. Study Area
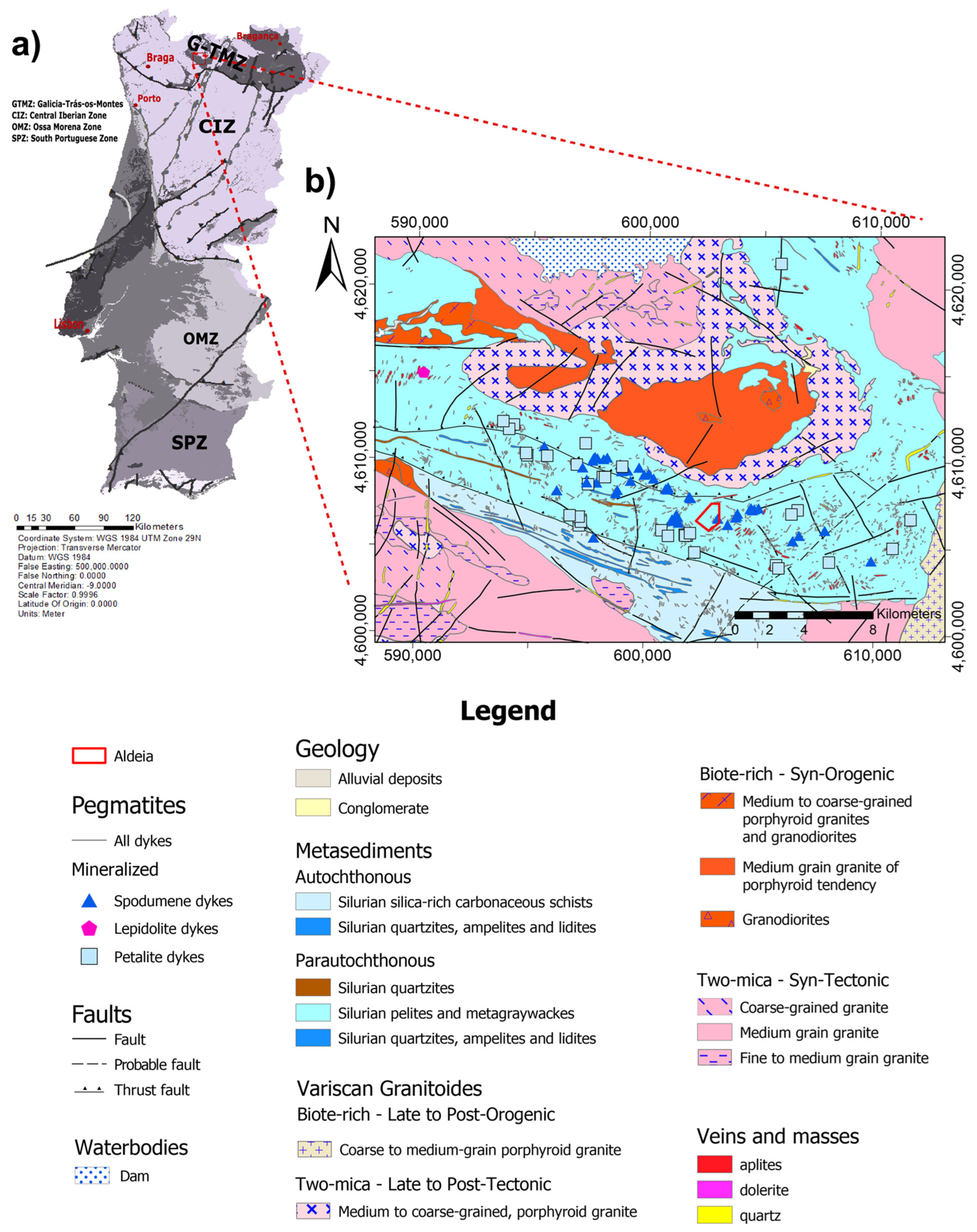
The research area is in the Ribeira de Pena region (Portugal), in an area known as Aldeia, where Li-bearing pegmatite resources are under study. The pegmatites are hosted by Silurian-age mica-schist in northern Portugal, more specifically within the Galicia-Trás-os-Montes zone (
Figure 1) [
29,
30,
31]. These deposits have an inferred and indicated resource of almost 45,000 tons of Li
2O [
32].
The aplite-pegmatite dykes of the Barroso-Alvão pegmatite field were classified by Martins [
33]and Dias [
34], using the concepts of Černý and Ercit [
35] classification as belonging to the LCT family, subdivided into the complex type, spodumene sub-type, and petalite sub-type. The first type, namely the spodumene complex type, is characterized by relatively high pressure (roughly 3 to 4 bar) crystallization, containing a significant amount of Li aluminosilicates, and representing the most common category of the pegmatite complex type. The LCT family comes from a fractionated melt fractionation enriched in Li, Rb, Cs, Be, Ta, Nb (Ta> Nb) and in large part in B, P, and F. There are three main sources for the LCT parental melt: (i) anatexis of metasedimentary and metavolcanic protoliths of the upper to the middle-underplated crust, (ii) a low percentage anatexis of meta-igneous rocks from the basement, or (iii) a mix of both [
35,
36].
A few thousand pegmatite bodies can be found at the Barroso-Alvão pegmatite field. Most of these bodies intrude on metasedimentary rocks, but barren ones can also be found intruding on the two mica granites and the biotite granites. The aplite-pegmatite bodies have different characteristics that allowed defining different groups [
33]): (i) intragranitic pegmatites (the only group found intruding granitic rocks); (ii) quartz-andalusite dykes, (iii) barren pegmatites, (iv) spodumene pegmatites, (v) petalite pegmatites, and (vi) lepidolite pegmatites, all intruding metasedimentary rocks.
In general, the dykes are vertical, flat, or with a variable dip. They can appear as lenticular or with elongated shapes, in some cases outcropping more than 500 meters along their strike. All aplite-pegmatite bodies are spatially associated with the two-mica peraluminous granites, and Lima [
30] considered the syn-to late-tectonic two-mica granites from the Cabeceiras de Basto complex as genetically related to the Li aplite-pegmatite bodies [
37].
The Li mineralization at the Barroso pegmatite field, which involves the Aldeia pegmatite (
Figure 1), among others, occurs predominantly in the form of spodumene-bearing pegmatites, which are hosted by metapelites and mica schists.
The Aldeia pegmatite dyke corresponds to a moderately west dipping tabular body defined over an area of 250 m N-S with a dip extent of 340 m [
32]. At depth, the body appears to bifurcate. The thickness variates from 10 m to 45 m, mineralized across the full width. The main pegmatite extends to the surface and is visible in an outcrop over a portion of the deposit. The pegmatite is also exposed in a quarry in the central portion of the mine where the geometry of the main pegmatite is visible, allowing the use of RS data and techniques to acquire its spectral signature.
Regarding the petrographic study conducted by Vasques [
31], it is generally possible to observe certain characteristics in the drill hole samples. Specifically, the white mica textures in the samples were lepidoblastic, suggesting a low-grade mylonite. Additionally, the andalusite had a poikilitic texture, indicating the possibility of rotation during growth, and apatites were located near the contacts with the pegmatite and had a detrital background.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample collection
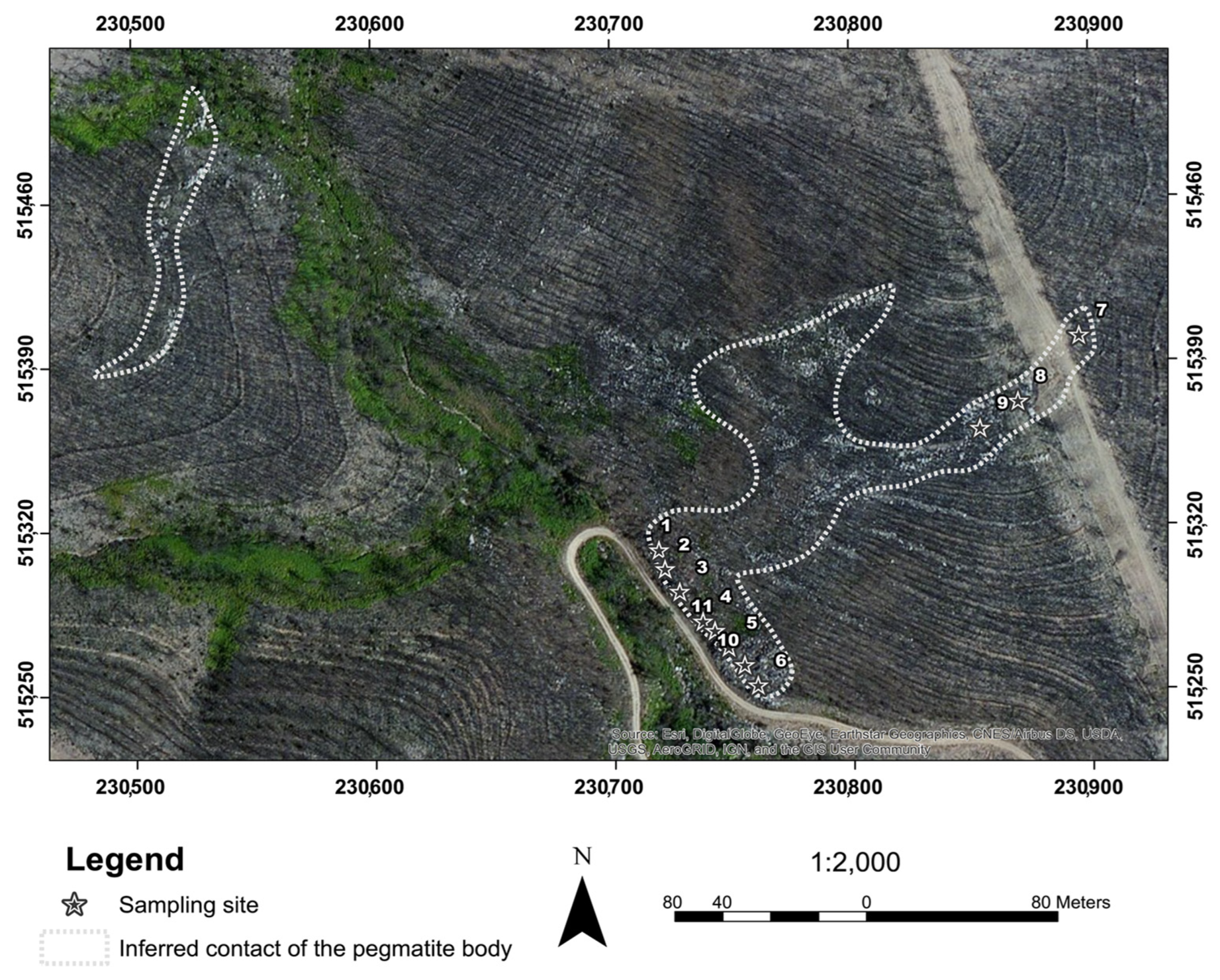
After careful selection, a total of 11 samples, which are representative of the pegmatite outcrops and metasedimentary host rocks, were collected on a field campaign between 19 and 20 of April 2021, performed on Canedo-Covas Mining Lease Application, integrated in Savannah Resources PLC Barroso Lithium Project. The focus was the validation of the LCT-pegmatite Aldeia petrographic studies [
31], specifically the spodumene mineralization on the target. The samples were collected where outcrops were accessible as shown in
Figure 2, with two sampling profiles: the first with a northwest-southeast trend, and the second more along a northeast-southwest path.
The samples were divided into seven classes, including both pegmatite and metasedimentary host-rocks, namely: (i) aplite-pegmatite; (ii) aplite-pegmatite with iron oxides; (iii) muscovite-schist; (iv) andalusite-schist; (v) metamorphic exudation quartz; (vi) aplite with iron oxides; and (vii) pegmatite with iron oxides. As aplite-pegmatite rocks of this region are very heterogeneous, sample types (i), (ii), (vi) and (vi) are representative of the pegmatite’s internal structure.
2.2. Data acquisition and data processing
2.2.1. Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) surveys
A DJI Matrice 300 RTK Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) with a DJI L1 Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) sensor on-board was used to acquire more detailed terrain information. LiDAR is an active remote sensing method that allows the acquisition of a point-cloud through a sensor that scans targets using a pulsed laser acting as a transmitter, and an optics system that collects the reflected light and focus it on a detector [
38]. The UAV has incorporated a GPS (Global Positional System)-RTK (Real Time Kinematic) sensor to estimate the position of the UAV/sensor system in real time. The system architecture consists of two or more satellite data receivers, one of them being a stationary GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) station and the other a rover GNSS station, both sharing data via a radio channel to perform real-time positioning corrections. The technique is based on carrier-phase differential GPS positioning [
39]. The Portuguese government, through a public institution called Direção-Geral do Território (DGT), created the ReNEP (Rede Nacional de Estações Permanentes GNSS), a public GPS/GNSS network of receivers installed across the country. In this study, the drone with the RTK was connected to the ReNEP Boticas GNSS station (closest ReNEP station), which uses a Leica GRX1200GG Pro receiver with a Leica AX1202GG antenna. To improve the positioning accuracy of the measurements the L1 LiDAR has an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) integrated with an update frequency of 200Hz.
2.2.2. Geophysical surveys
To conduct the geophysical investigation, an Exploranium GR-320 enviSPEC Gamma Ray Spectrometer with a GPX-21A detector (SIAC Exploranium, Mississauga, Ontario, Canada) was used to measure the following levels: (i) Total Counts (ToT), (ii) Potassium (K %), (iii) equivalent Uranium (eU ppm) and, (iv) equivalent Thorium (eTh ppm) emitted by the pegmatites and metasediments (mainly schists) in the study area. The system utilizes 256 or 516 channels and a high sensitivity 76x76 mm (3” x 3”) detector with a NaI (Tl) (Sodium Iodide [Thallium]) crystal and a resolution better than 9.0% FWHM (Full Width at Half Maximum) for Cesium-137. For each station, three measurements of 60 seconds were made, and the stations have a spacing of approximately five meters.
2.2.3. Spectral data acquisition and processing
To build the spectral library, the 11 samples collected were previously dried at 50°C in a muffle furnace for 24 hours. The spectral data were collected on different faces of each sample, considering the visible changes in its composition [
24].
The FieldSpec® 4 (ASD, Inc.) spectroradiometer was used for data acquisition, with a wavelength range of 300 to 2500 nm, and a data collection time of 0.2 seconds per spectrum through a 1.5 m optic fiber beam with a 25° bare field of view that results in a 10 mm spot size when employing a contact probe with an internal light source. The equipment model has a spectral resolution of 3 nm @ 700 nm and 10 nm @ 1400/2100 nm. Before the measurements start, the spectroradiometer was turned on for 30 minutes due to the different temperature-related sensitiveness of the detectors, and the contact probe lens was sanitized with alcohol. To calibrate the equipment, a white reflectance plate was measured both at the beginning of the measurements and during the process (whenever the ASD ViewSpec Pro™ software indicated this need).
In each analyzed sample point, an average of five measurements was performed with the ASD ViewSpec Pro™ software [
40] to increase the signal-to-noise ratio, totaling 47 final (raw) spectra in the end. Moreover, for each analysis point, a photographic record was made together with a description of its characteristics.
Finally, each spectrum was submitted to a quality check through visual inspection using the SpectraGryph software [
41] and was subsequently processed with a Python routine to remove the continuum and extract the absorption features [
24]. All results were inputted into the spectral library and the database was generated with the Microsoft Access (Microsoft Corporation) software.
2.3. Integration of spectral data through satellite image processing
To validate the importance and added value of the spectral library built in this study, for mineral exploration, satellite data, and image processing techniques were used to compare the spectra obtained in the laboratory and information obtained from RS data. By superimposing the satellite sensors' bands on key spectra, it is possible to identify the main absorption features and reflectance peaks in the visible and near-infrared (VNIR), and Shortwave Infrared Region (SWIR), cross-referencing laboratory data with the spectral range of each satellite band and thus determining the most suitable ones to be used in satellite image processing.
Landsat satellite imagery, one of the most common satellites used for mineral exploration, was processed to identify possible pegmatite outcrops in the Aldeia pegmatite vicinities. Landsat 8 Operational Land Imager (OLI) was launched on February 11, 2013, and has 11 spectral bands, including two thermal-infrared bands. The spatial resolution is 15 m and 30 m for the panchromatic and multispectral bands, respectively, while the spatial resolution of the thermal-infrared (TIR) bands is 100 m [
42]. Landsat 9 data also were selected to assess the potential of this space dataset for mineral exploration, in general, and for pegmatite exploration, in particular. Landsat 9 has collected images of the Earth’s surface since October 31, 2021. With a radiometric resolution of 14 bits, Landsat 9 can differentiate 16,384 shades of grey, allowing the sensors to detect more subtle differences on the Earth’s surface. This radiometric improvement can make Landsat 9 a powerful tool for lithological studies.
Table 1 exemplifies the radiometric difference between Landsat 7 Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus (ETM+), 8 (OLI) and 9 (OLI 2).
Landsat images are available for download through the USGS Earth Resources Observation (Earth Explorer portal) and Science (EROS) Center [
43].
Originally, this study intended to work only with the Landsat 8 image, however, the Landsat 8 image, acquired on August 21, 2018, was outdated compared to the mining exposition surface at the time of the fieldwork. Therefore, the Landsat 9 image, acquired on January 28, 2022, is more faithful to the current reality of the study area. As seen in
Table 2, Landsat 8 and 9 have the same spatial (30 m Ground Sample Distance, GSD) and spectral resolutions. The objective of image processing in this study was to demonstrate practically the applicability of spectral analysis in image processing.
Among the available images, the ones with less cloud cover (less than 10%) were chosen for download. The images were pre-processed using the Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin (SCP) plugin (version 7.10.6), available in the QGIS software (version 3.22.1). The atmospheric correction method used was the Dark Object Subtraction (DOS 1) algorithm [
44].
Regarding the methodological proceedings, first, the main absorptions and reflectance peaks were identified and analyzed based on the laboratory data, and the spectral mineralogy was identified by expert and literature-based knowledge [
45,
46]. After that, the main absorptions and reflectance features were compared with the spectral range of the satellite bands. Only the most significant spectrum of each sample was used in the analysis, totaling 10 spectra selected.
The processing method chosen to be applied in this study was the Principal Component Analysis (PCA), a multivariate statistical technique for dimensionality reduction, used to enhance and separate target spectral signatures from the background [
47,
48]. The number of components used to perform PCA depends on the objective criteria of the study or research. According to Johnson and Wichern [
49], several criteria may be suggested regarding the number of components to retain in PCA, but no criterion is satisfactory for all situations. As the selective PCA on two components achieved the best results in previous studies of mineral exploration [
50,
51], for this work PCA was tested with two-band subsets. The criteria chosen to select the most adequate bands was a combination of a band with higher pegmatite reflectance and a band with lower pegmatite reflectance. Thus, the bands used in this method were selected according to their spectral response compared to the rock samples from Aldeia pegmatite, namely: (i) PCA of bands 3 and 7; and (ii) PCA of bands 6 and 7. Taking into consideration that the host rock in the study area corresponds to schists, and that this rock has a high reflectance in band 4 and a strong absorption in band 7 due to the Al-OH absorption feature at 2.20 μm, a third PCA of bands 4 and 7 was computed specifically for schist [
52].
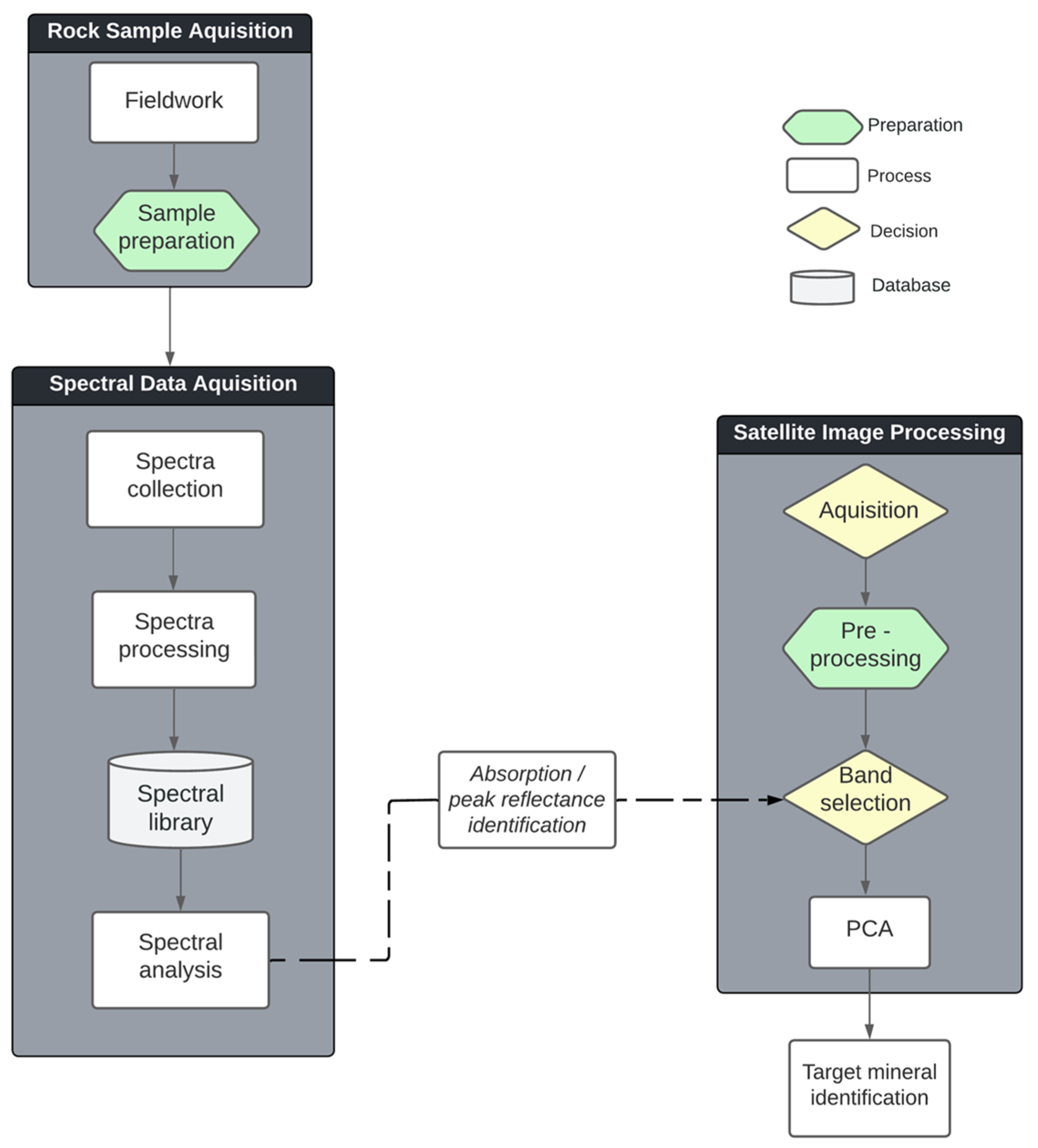
The step-by-step methodological processes and their integration for the identification of target minerals are explained in
Figure 3.
3. Data integration and visualization in a WebGIS
3.1. WebGIS
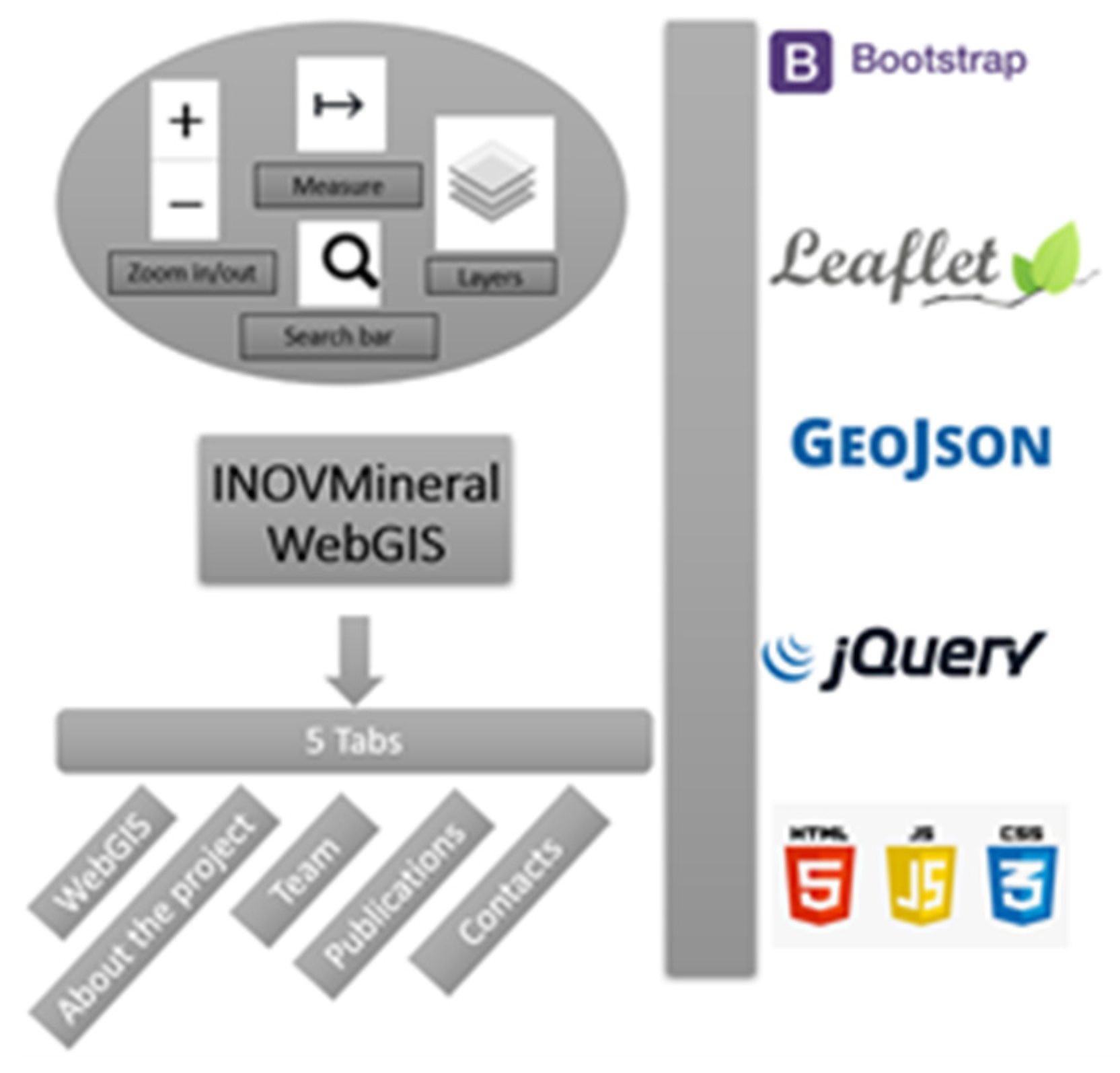
The webGIS platform was created using a web server (XAMPP), a popular PHP development environment (
https://www.apachefriends.org/) that includes MariaDB, PHP, and Perl. XAMPP is an easy-to-install and open-source package [
53]. To build interactive maps, Leaflet, an open-source JavaScript library designed for mobile-friendly maps was used (
https://leafletjs.com/). Also, several Leaflet plugins hosted in GitHub were used, such as leaflet.ajax, which enables the retrieval of JSON data (
https://github.com/calvinmetcalf/leaflet-ajax). These plugins allowed to insert geospatial information in the form of GeoJSON files, a format for encoding a variety of geographic data structures (
https://geojson.org/). Thus, in this study, the vector files were displayed as GeoJSON files. For JavaScript functionality, jQuery, a user-friendly library compatible with multiple browsers was employed (
https://jquery.com/). To ensure responsive and mobile-first design, we utilized Bootstrap, a widely-used framework for developing websites (
https://getbootstrap.com/).
The vector information in the platform was displayed as GeoJSON files in World Geodetic System 1984 (WGS84; EPSG: 4326) coordinate system. Raster layers were integrated into the platform through the leaflet-geoserver-request plugin (
https://github.com/iamtekson/leaflet-geoserver-request). The spectral library was represented as a points layer, where each point corresponds to a set of samples with valuable information. The point shapefile was converted to GeoJSON format using the L.geoJSON plugin from Leaflet. The properties of each point, including sample IDs, attributes, and photographs, are accessed and displayed through a popup tab created using HTML and JavaScript functions.
The webGIS is composed of five tabs: i) the “webGIS” tab where the geospatial information is presented under a base map, that can be chosen by the user; ii) the “About the project” tab which presents some information about the project; iii) the “Team” tab composed by information about the researchers of the project; iv) the “Publications” tab with a list of publications (and respective links) produced under the project and; v) the “Contacts” tab with a formulary to contact the researchers (
Figure 4). It is also composed of standard tools, installed from the third-party leaflet plugins database (
https://leafletjs.com/plugins.html), such as: zoom in and out; search bar; measure tool; and the layers tab, which allows to activate or deactivate the visualization of the layers under a base map (Open Street Map, Topo Map, Imagery or Watercolor;
Figure 4).
3.1.1. Digital Elevation Model (DEM)
The resulting LiDAR-derived ground points were used to create a Digital Elevation Model (DEM) with a 0.2 m spatial resolution. The RAW data generated by the sensor is in a DJI proprietary file format and was processed on the DJI Terra software to generate the LAS typical file format used in point clouds generated with laser scanning.
The raw point-cloud obtained was in LAS format and had 245.620.454 points. The first processing step was to compress the LAS file into a LAS compressed format file (LAZ) which turned the 7.77GB LAS point-cloud into a 2.09 GB LAZ file using the
las2las tool from LAStools software [
54]. The resulting compressed point-cloud was then processed with
lasground and
las2dem tools that are part of the software. The
lasground tool uses an algorithm proposed by Axelsson [
55] for ground classification and bare-Earth extraction. The
las2dem tool uses Delaunay triangulation to convert the LAZ file into a temporary Triangular Irregular Network (TIN) and rasterizes the ground-resulting points using linear interpolation [
56]. A hillshade model was generated from the DEM to better visualize the terrain. For public distribution and ease of visualization in the WebGIS, the original DEM was resampled to 10 m of spatial resolution.
3.1.2. Radiometry data
Based on the radiometric measurements obtained, it was possible to generate maps of K, eTh and eU, and the ratios eU/K, eTh/U and eTh/eU. To produce those maps, the data was inserted into the ArcGIS Pro (Esri, Redlands, CA, USA) software.In the Geostatistical Wizard, the Simple Kriging algorithm was used to interpolate the data. Then the Geostatistical Layer (GA Layer) for each element and ratios were exported to a contour layer and a 50 m buffer from each station was applied. To enhance visualization and to better integrate the data in the WebGIS a GeoTiff was created with a spatial resolution of 2.5 m.
3.1.3. Spectral data
The generated/processed products were organized in the spectral library, as described in
Table 3. Considering the generated products, it is possible to perform several analyses, both on the raw spectrum and continuum removed spectra to identify the main absorption features and reflectance peaks. The database was intended to be freely used by researchers and industry professionals alike, as well as by any other mining or exploration stakeholder and is distributed in the Zenodo platform [
57].
Because the data can be analyzed by different people with different backgrounds and potential uses, we prioritized data storage in a database, namely a .accdb Access format (Microsoft Office), which holds files with different extensions (jpeg, .pdf, .txt and .png, for example) as attachments all within a single file. The database can be later connected to a geographic information system.
The database's structure logic allows representing each measured spectrum to be equivalent to a line, which details the storage of data/inclusion of more than one file in each defined criterion and for the systematized/dynamized view of the characteristics of each sampled location. Therefore, all attributes related to each spectrum are represented as distinct database columns.
The spectral library was structured considering the analysis of two geologists who acted independently (to minimize subjectivity as much as possible) and by analytical results obtained from the spectroradiometer.
A first analytical approach was carried out based on the coloration of the sample, which allows for inferring possible mineralogical compositions. The results were compared to the spectroradiometer data and to reference spectral curves, which show the expected trend in the spectral response of certain minerals [
46]. Additionally, the knowledge about the geological formation of the study area was considered, to ratify the results obtained. This methodological systematization ensures that the available data resultant from this study is corroborated through different validation sources, minimizing the analytical subjectivity, and allowing the user to complement his studies with new analysis criteria, if necessary.
4. Results and discussion
4.1. UAV LiDAR
Processing the LAZ point cloud with lasground to classify ground points took 759.472 seconds on an AMD Ryzen 5 3600 6-Core Processor 3.60 GHz with 64Gb of RAM, and a Radeon RX 6700 XT MECH 2x 12G OC graphics card. The point cloud density was calculated using lasinfo (LAStools) and resulted in a 636.55 points/m2 density and an average distance between points of 0.04 m for the original point cloud file. The processed point cloud that was used to generate the DEM had a point density of 57.11 points/m2 and an average distance between points of 0.13 m.
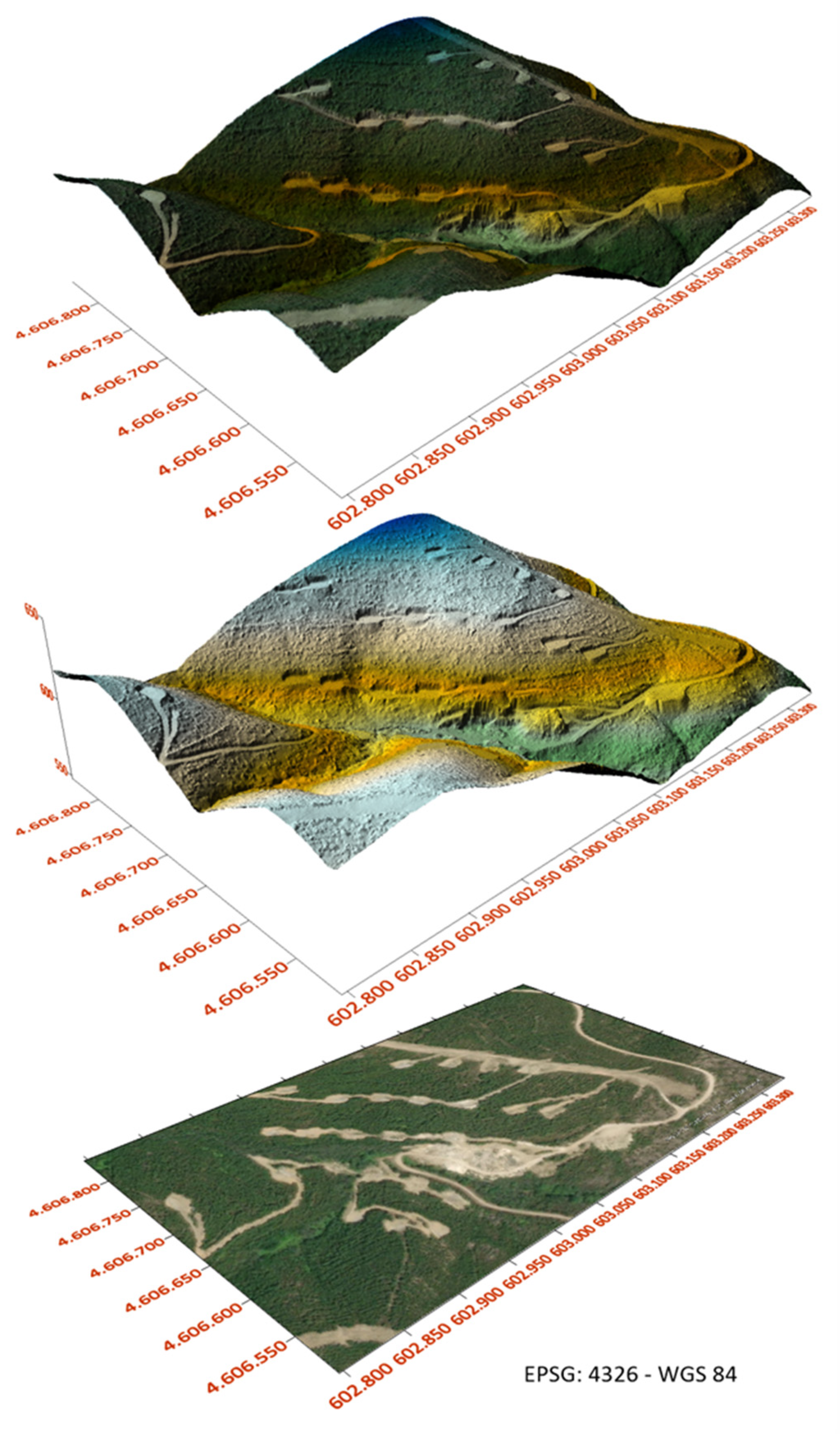
The resultant hillshade model is compared with the satellite imagery of the study area in
Figure 5. It is possible to observe the topographic depression caused by a stream crossing the study area in green color (
Figure 5). The access road and the small exploration at the base of the hill are also visible, highlighting the mine face wall, expanding to the hill, below the drill core platforms, and a small portion of pegmatite outcrop in positive relief in the area where the access road bifurcates in the base of the hill. The minimum and maximum altitude of the point cloud were 548.05m and 650.07m, respectively.
Although LiDAR sensors are a relatively new option for UAVs, this technology has been used since the 1960s [
58]. The possibility of attaching the LiDAR sensor to a UAV has brought a cost-effective way to do low-scale high-resolution laser altimetry in areas where airborne laser scanning would not be possible. In the case of this study, approximately 20 hectares of land were covered in under 15 minutes of flight, which highlights the advantages of using UAV-LiDAR.
4.2. Radiometry
After processing all radiometric data, it was possible to produce three maps.
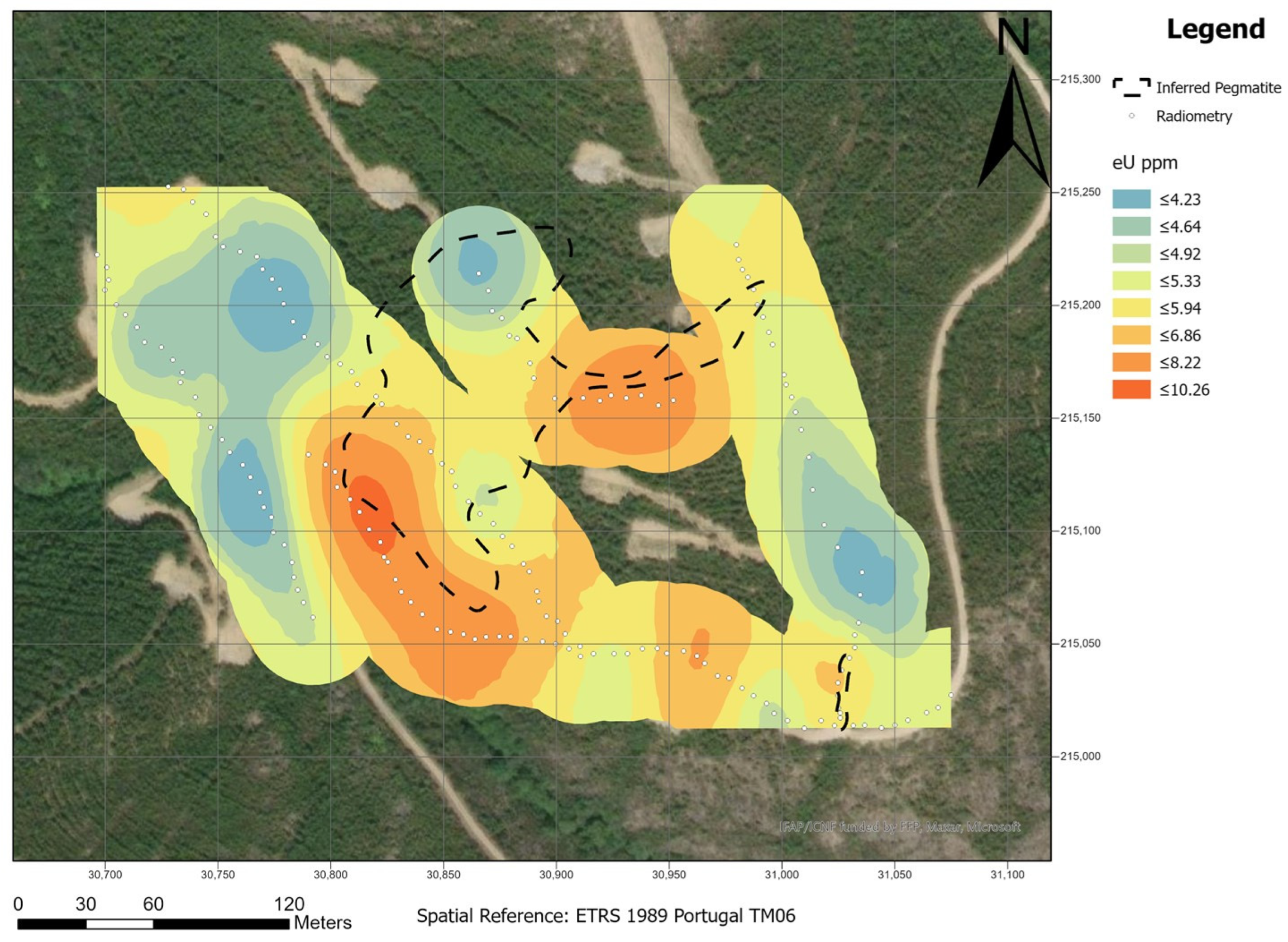
Figure 6 shows the eU map,
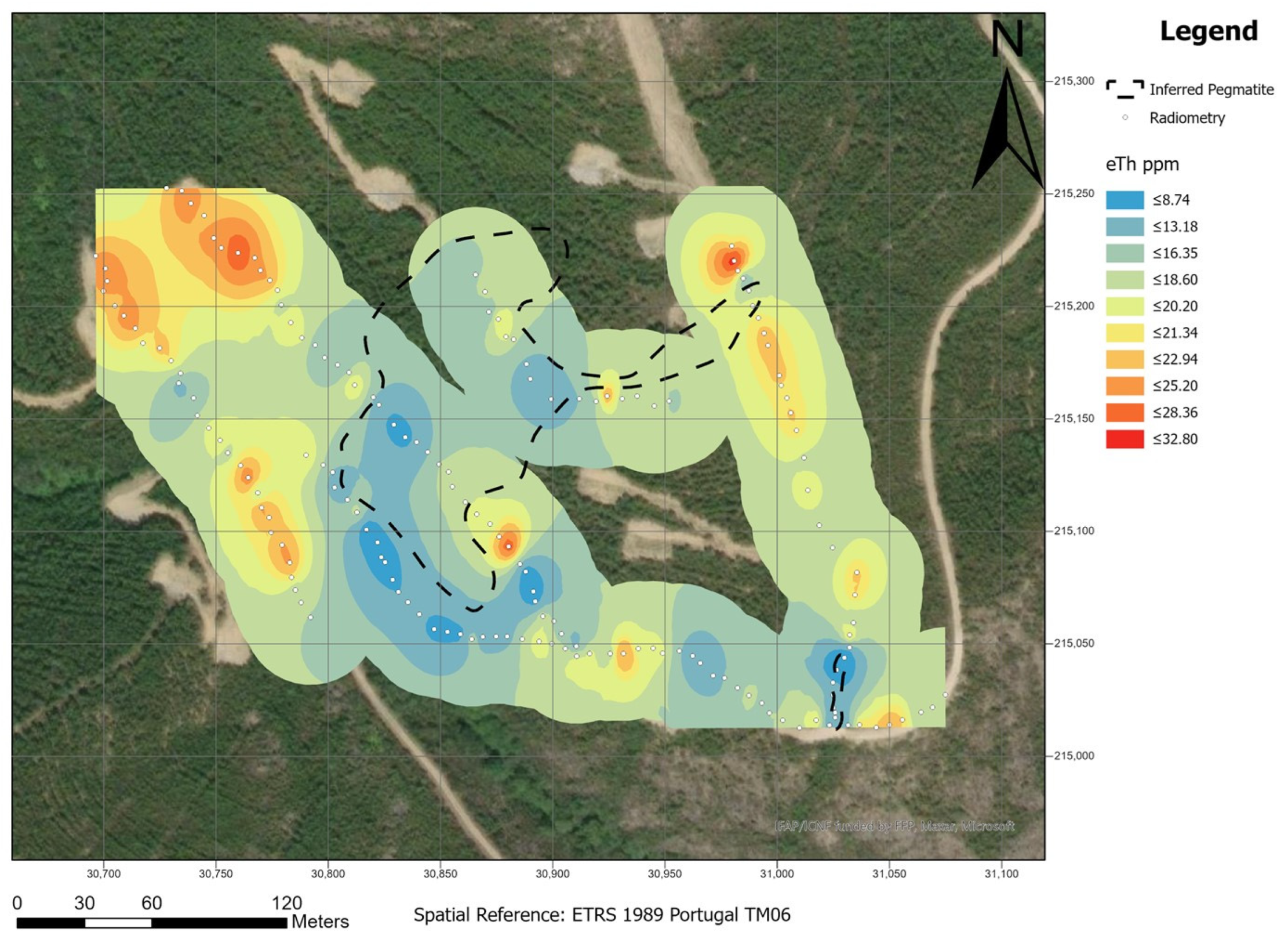
Figure 7 the eTh map and
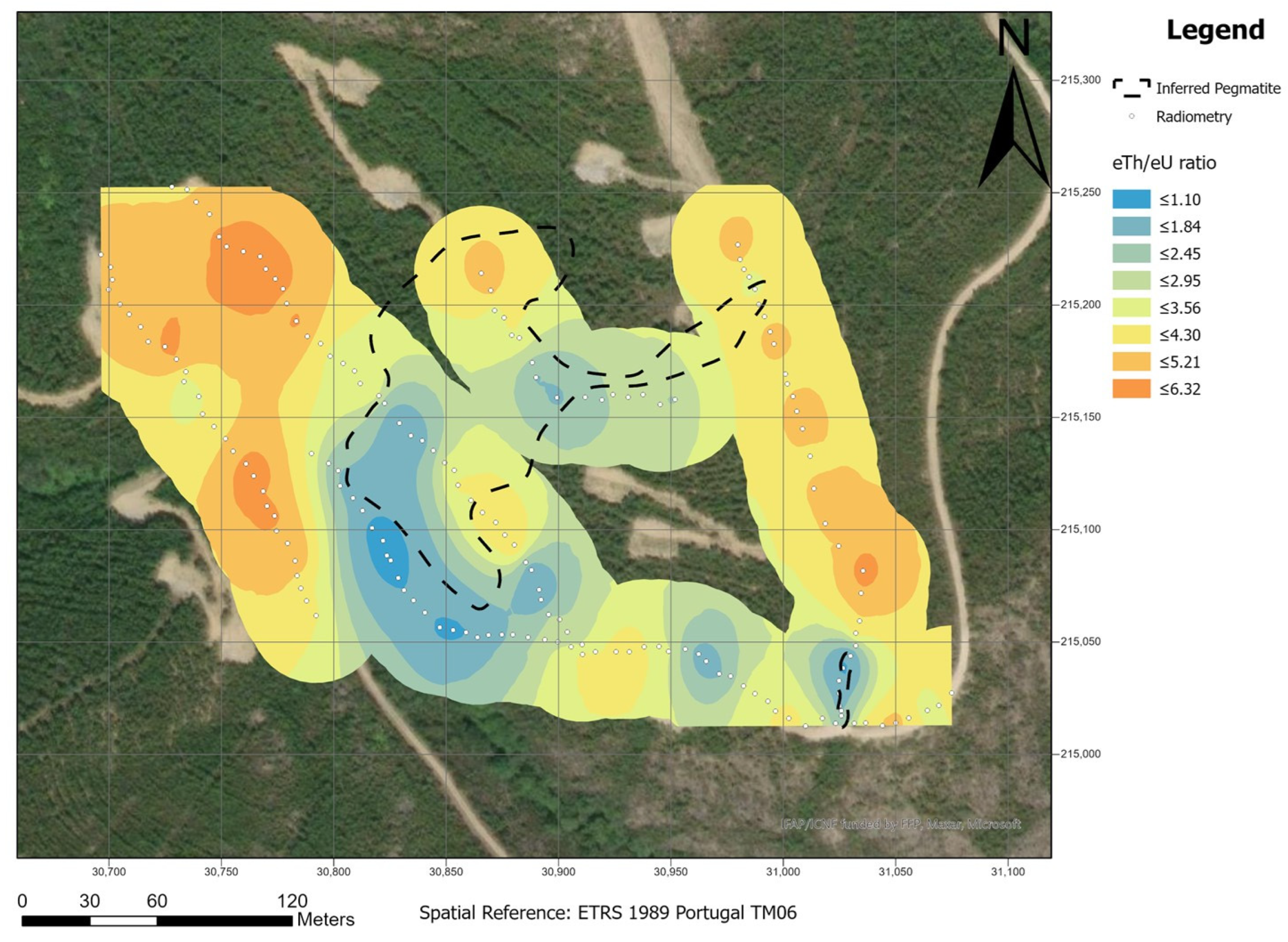
Figure 8 the ratio eTh/eU. The eU map shows higher concentration areas, which corresponds with the pegmatites at the surface. The lower concentration corresponds to the host rock. The eTh map shows the opposite behavior, where the higher concentration corresponds to the host rock and the lower concentration corresponds to the pegmatites. The eTh/eU ratio allows to better define the differences between the pegmatites (lower ratio) and the host rock (higher ratio).
In summary, the eTh map showed the worst correlation, while the eTh/eU ratio showed a good correlation with some of the outcropped pegmatites. The eU map presented the best results, where lower concentrations of eU are correlated with pegmatites.
Considering the results obtained in the Aldeia area, it is possible to say that radiometric data can be a good approach to complement other geological and geophysical studies. This is in agreement with previous findings in the Bird River belt, Manitoba [
13]. However, the ability to discriminate the pegmatites from their host rocks depends primarily on the different lithologies found in the study area. Thus, as advised by Trueman [
12], for this exploration method to be successful, a significant contrast between the U and Th contents must exist. In the Aldeia area, the best radiometric responses are from the Th and the Th/U ratio.
4.3. Spectral Library
In the library created it is possible to access several files in different formats, including: (i) a photograph of the location where the spectrum was collected within the sample (47 files in .jpeg format); (ii) the (raw) collected spectra consisting of the spectra for each sample, without any previous treatment (94 files with the same information, 47 of them in .txt format to import in any desired software and 47 in .pdf format for a quick preview of the resultant spectra, but in a vector format allowing the user to personalize the spectra plots); (iii) the processed spectra, consisting of the continuum removed files after computer processing (94 files with the same information, 47 in .txt and 47 in .pdf formats); (iv) the extracted spectra absorptions, corresponding only to the most prominent (deep) features, resulting in 173 files in .png format with the different absorption bands of the samples. All the information recorded in the spectral library as well as a brief description of each field can be found in
Table 3.
Figure 9 shows an example of the graphical products available in the spectral library for consultation and analysis.
First, the user can preview and import to the software the (raw) original reflectance spectrum (
Figure 9a). Then, the user can preview and import the already continuum-removed spectra represented in
Figure 9b. In the end, for each spectrum, all major absorption features (continuum removed reflectance below 0.93) were automatically identified and extracted (
Figure 9c,d) and provided in the database. In the case of
Figure 9, the spectrum was collected in an Aplite-Pegmatite sample, with the most prominent absorptions around ~1400 nm and ~2100 nm.
Considering the appearance of the sample, a first subjective analysis was performed to identify the minerals present in each sample, totaling seven classes as aforementioned (
Table 4). Of the 47 spectra, 28 (59.57%) correspond to Aplite-Pegmatite samples with muscovite, plagioclase, and quartz in their composition; nine spectra (19.15%) correspond to Aplite-Pegmatite samples with muscovite, plagioclase, quartz, and iron oxides identified; and five spectra (10.64%) were collected in Aplite samples with plagioclase, quartz, spodumene, and iron oxides. These three classes alone represent 42 (89.36%) of all spectra collected and the minerals identified are congruent with those expected in the region, considering the local geological setting (
Section 1.1).
4.3.1. Spectral Analysis
All 47 spectra were processed and analyzed to identify the most prominent absorption features and the corresponding spectral mineralogy. The spectral interpretation was achieved by analysis and comparison with the literature available information [
20,
21,
22,
45,
59]. In this study, the most representative spectra of each class were selected to exemplify the results. As can be observed in
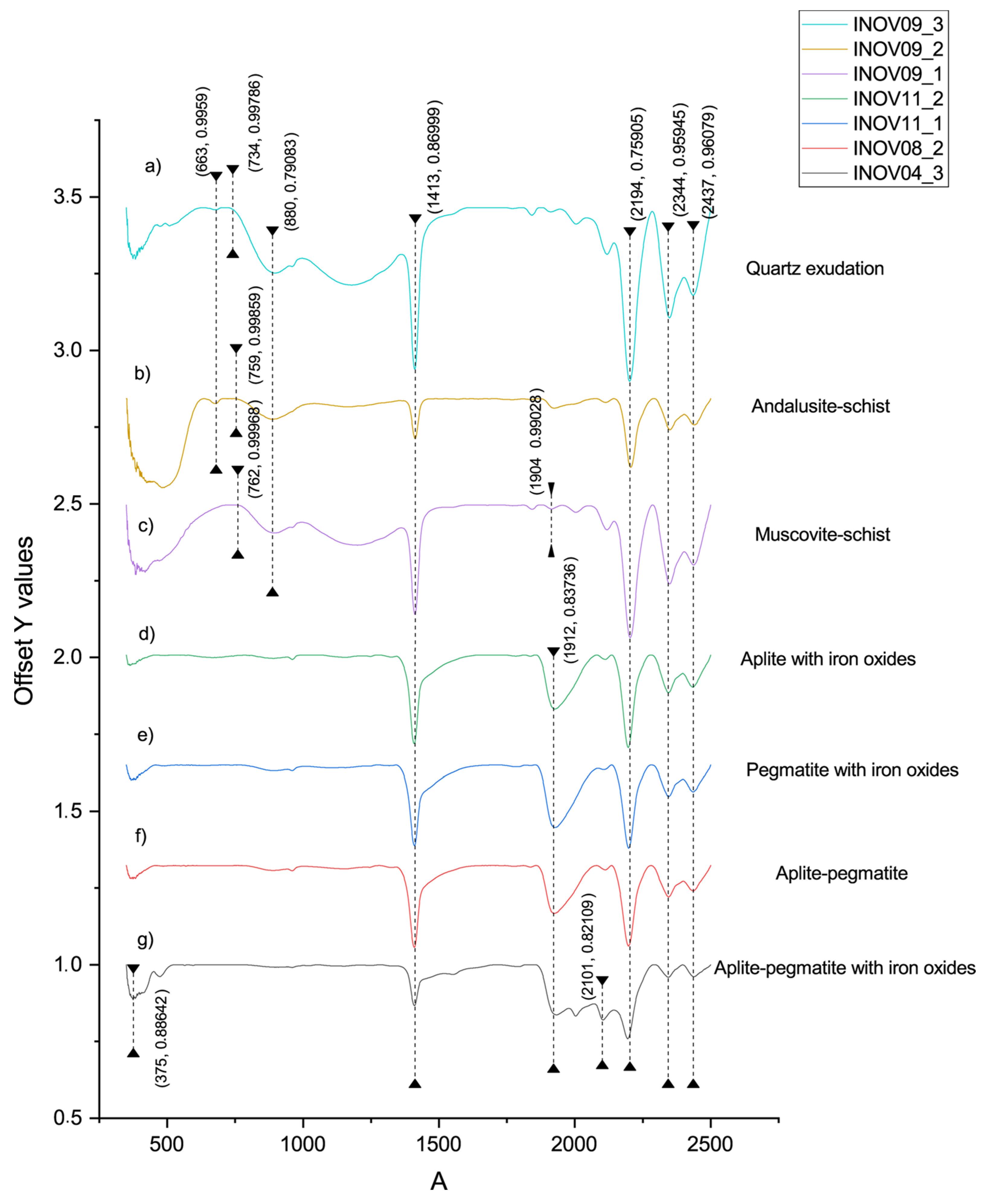
Figure 10, all spectra have one AlOH absorption feature around 2190 nm and two features around 2340 nm and 2440 nm. These features are present in the white mica group minerals, more specifically, in muscovite and illite. It is the presence of the AlOH secondary absorptions that, together with the symmetry and sharpness of the main AlOH absorption and absence of water feature, are decisive for the distinction of these minerals.
The spectrum INOV09_03 has two iron features (680 nm and 880 nm), in addition to a reflectance peak at ~730 nm, indicating the possible presence of hematite in this sample (
Figure 10a). Similar to the previous example, the spectrum INOV09_2 has the same absorptions and reflectance peak diagnostic of the presence of hematite (
Figure 10b). The spectrum INOV09_01 (
Figure 10c), also has diagnostic absorption features and reflectance peaks that indicate the presence of hematite (in the VNIR region). The weak to absent water absorption (~1904 nm) that together with the AlOH absorption (~2194) and the double AlOH secondary absorptions at ~2340 nm and ~2430 nm, can confirm the presence of muscovite in this sample (
Figure 10 a to c). This is expected in spectra b and c (
Figure 10b,c) since the schist hosting the pegmatites is expected to be more pelitic than psammitic, being muscovite an important rock-constituent mineral. When looking at the sample photograph corresponding to spectra INOV09_03, it is possible to understand that due to the large 10 mm spot size, muscovite layers affected the overall spectral signature.
The spectra INOV11_2 (
Figure 10d), INOV11_1 (
Figure 10e), INOV08_2 (
Figure 10f), and INOV04_3 (
Figure 10g) have a more pronounced, asymmetric water absorption shorter than the main AlOH absorption, that together with the double ALOH secondaries at ~2340 nm and ~2430 nm, indicate the presence of illite in these samples. However, the similarity of characteristic absorptions of minerals from the white mica group in these mixed spectra made distinguishing between illite and muscovite challenging. Within the white mica group, muscovite was identified from the absence of other characteristic absorptions that are diagnostic to identify illite, such as the absence or very weak water feature [
20,
21,
59]. On the other hand, illite shows a water absorption with a depth close to 1/3 of the depth of the main AlOH feature (
Figure 10d,f) [
20,
21,
59]. According to the analysis of the results, illite and muscovite can often appear mixed together (
Figure 10g); or mixed with clays such as montmorillonite (
Figure 10e) or kandite group minerals, due to the higher depth of the water feature when compared with the main AlOH absorption feature, or to the presence of an AlOH secondary triplet, respectively. In this spectrum, INOV04_3 (
Figure 10g), the occurrence of iron oxides is confirmed by the presence of iron features in the VNIR region (~375 nm and ~ 500 nm). Furthermore, the spectral curve is characteristic of the presence of orthoclase, with the two absorptions ~1410 nm and 1912 nm possibly indicative of the presence of aqueous fluid inclusions [
21].
The only Li-bearing mineral identified through its spectral features was cookeite, a Li-chlorite, due to the existence of two OH− absorptions located at ~1574 nm and ~1834 nm, and a broad, asymmetric Mg-OH feature at ~2355 nm [
20,
21,
59].
In general, the aplite-pegmatite samples can be well discriminated from the host rocks since the latter show very well-developed and pronounced iron features in the VNIR region diagnostic of hematite.
4.3.2. Comparison of the laboratory spectra and satellite imagery
A comparison was made between the built spectral library and the Landsat 8 and9 spectral resolution. This analysis was done in OriginPro software [
60] (version 2022).
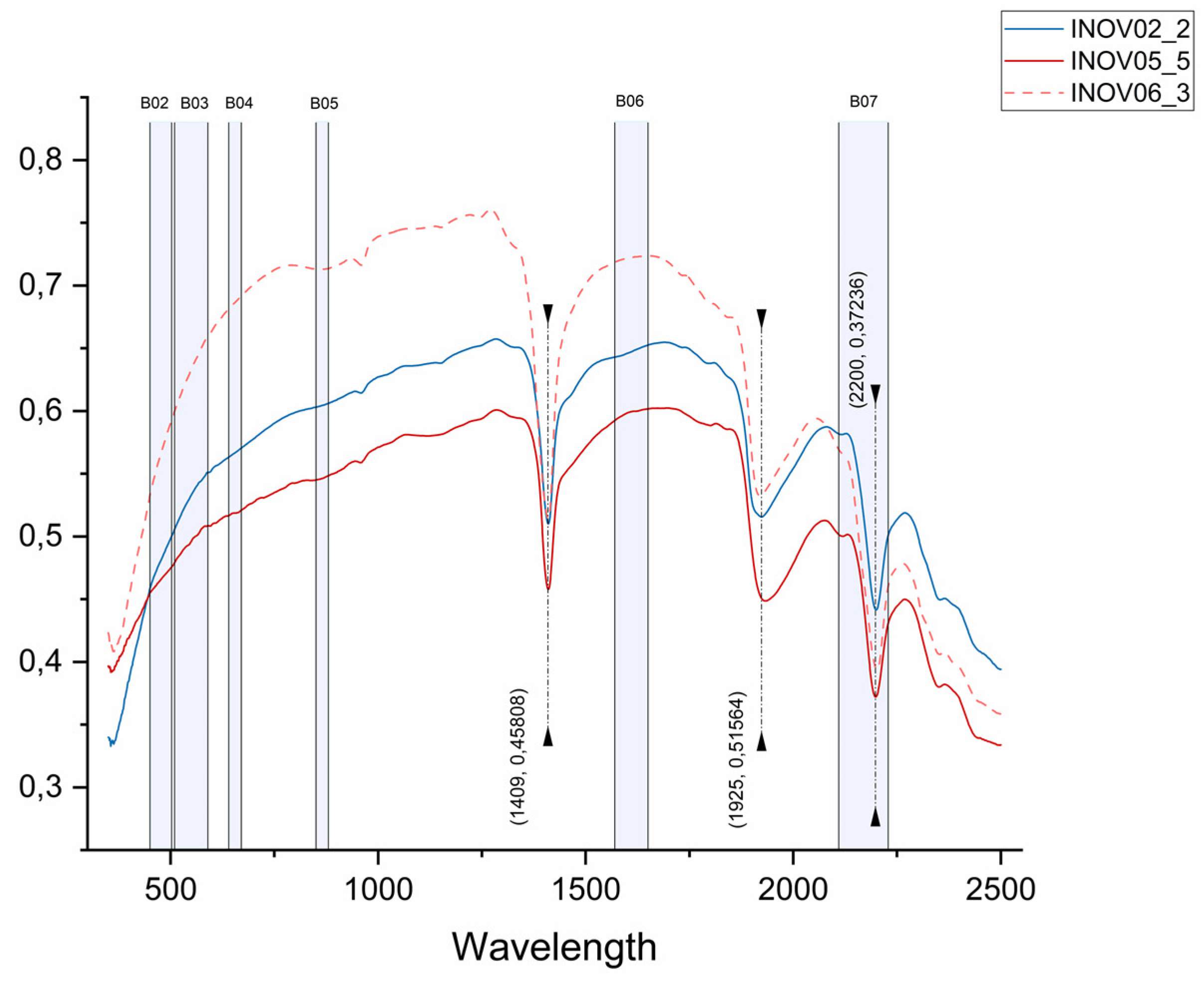
Figure 11 shows us an example using three Aplite-Pegmatite samples’ spectra. This class was chosen because it is the most representative of the samples studied. It was observed that the laboratory spectra have three main absorption features located around 1400 nm, 1925 nm, and 2200 nm. This last absorption feature around 2200 nm is the most prominent, as it is the only one covered by a Landsat band (band 7, SWIR 2). Regarding the reflectance peaks, the most relevant band is band 6 (SWIR 1), which covers a faint reflectance peak occurring around 1600 nm. However, band 3 (Green) and band 4 (Red), also match with the high reflectance of the target under study. After this analysis, bands 3, 4, 6, and 7 were selected and assigned in the method described in the following steps.
The available spectra (raw and with the continuum removed) allow the user to establish a relationship between the expected theoretical spectral curve and the empirical data obtained, which can favor more assertive prospecting processes through the selection of key satellite bands.
4.3.3. Principal Components Analysis (PCA)
To validate the spectral library built in the scope of INOVMINERAL4.0, information from the new Landsat 9 satellite was analyzed to evaluate its possible use for the delineation of LCT pegmatite prospective areas. The results confirm the high added value of such spectral database in the identification of outcropping pegmatites and the success of the combined approach presented in this work. Thus, the satellite data allowed for complementary analyses that can assist in the identification of LCT pegmatites, decreasing in situ campaigns, and optimizing human and financial resources and time. It is worth noting that there are limitations in the use of satellite data, especially concerning their spatial resolution (30 m GSD), which limits areas with low exposure to be captured in at least one sensor pixel, together with a high vegetation cover, and the fact that pegmatite bodies many times are smaller than the pixel size. However, the proposed method is extremely well-adapted and can be applied to other study areas. The results can be used for several exploration purposes such as the identification of new points of interest for exploration. Nonetheless, the mentioned limitations, especially when it comes to spatial resolution, can be complemented with more specific methodologies, such as the use of UAVs.
The tested PCA two-band subsets highlight the pixels of Aplite-Pegmatite with high values which are represented in bright white color. The other elements of the study area like vegetation and water are represented in shades of grey. In previous studies [
15,
61], PCA stood out for being able to identify the areas of interest with fewer false positives than other classical processing methods such as RGB combinations and Band Ratios.
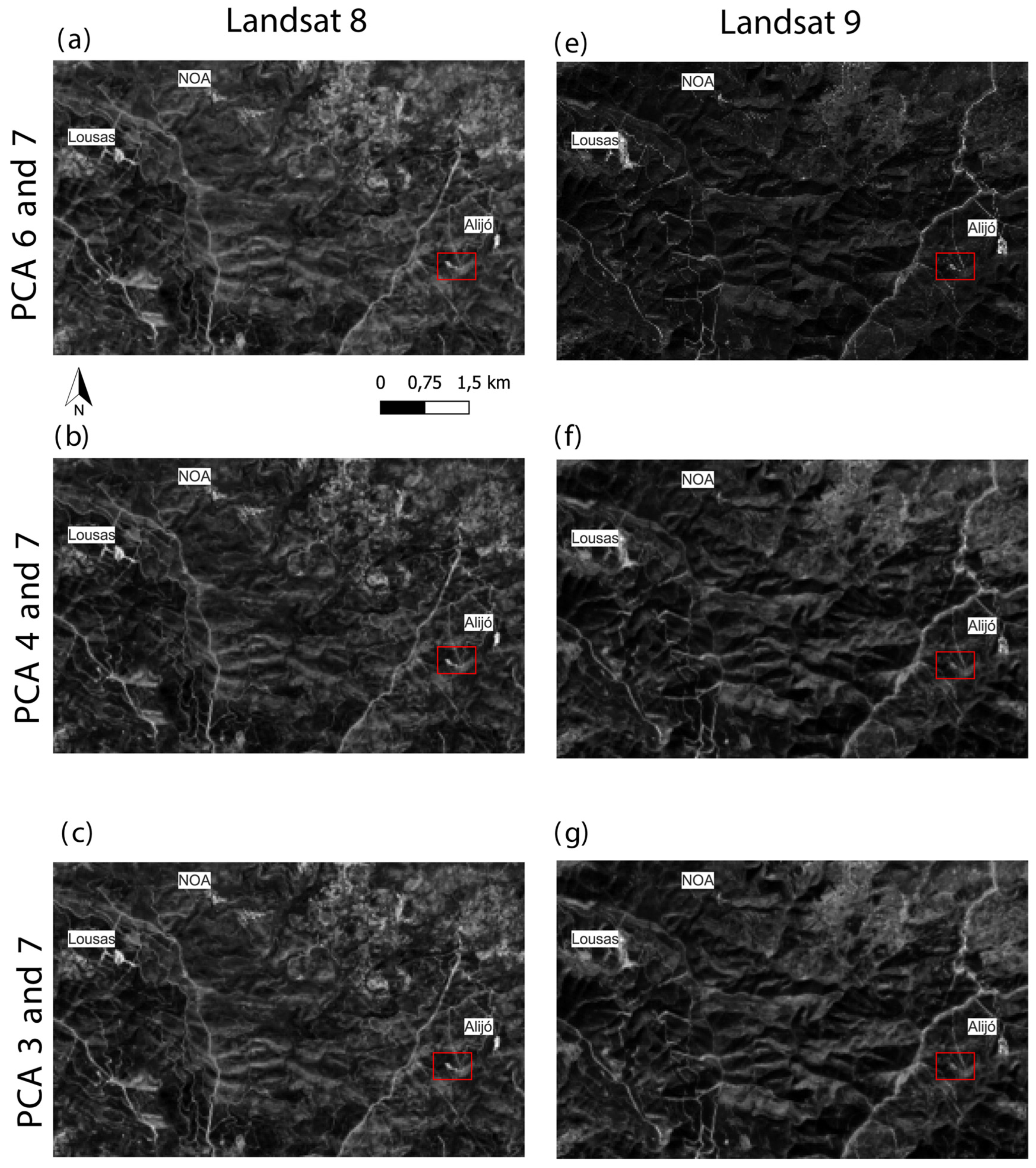
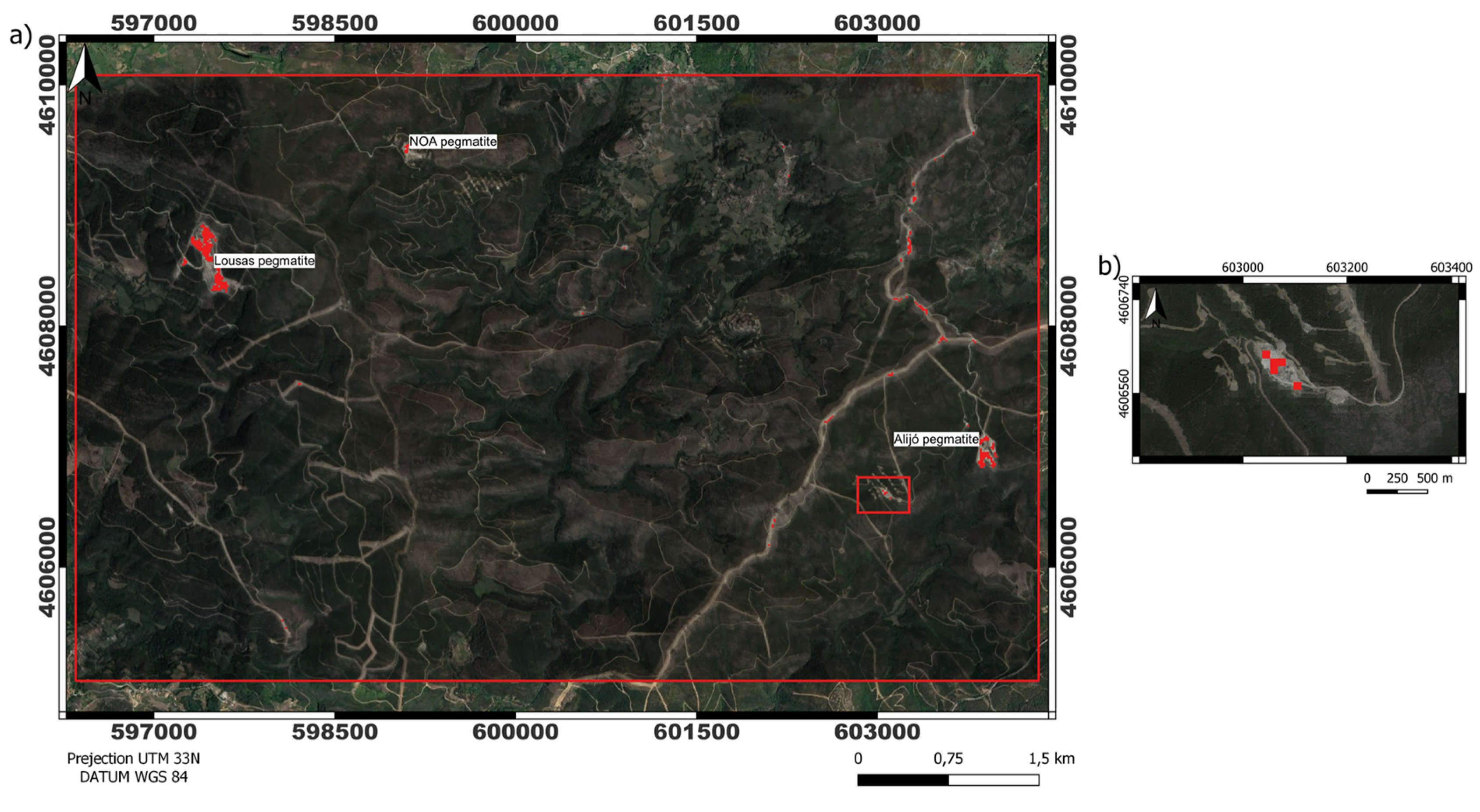
Taking this into account, PCA 6,7 was able to identify the other mining areas of the Barroso-Alvão pegmatite field, namely Lousas, NOA, and Alijó. Those are known LCT- pegmatite targets within a radius of 10 km of the Aldeia deposit. But the method was not successful in identifying the area of the Aldeia pegmatite. The PCA 3,7 and 4,7 obtained very similar results and were able to highlight the known pegmatites in the study area including the Aldeia pegmatite (
Figure 12). False positives occur on some roads and in urban areas for all PCA tested, but PCA 3,7 has fewer false positives.
The respective eigenvalues and eigenvectors are represented in
Table 5,
Table 6 and
Table 7. If the eigenvector values are positive in the highly reflective bands and negative in the absorption bands, the target is identified by bright pixels [
25,
62]. When the eigenvector values are inverted, i.e., when the band that should reflect is negatively valued in the matrix and the band that absorbs is positively valued, it is possible to multiplicate the image by (-1). This makes the targets appear in bright pixels instead of dark [
47,
63]. The PCA that needed to be multiplied by (-1) was the PC2 resultant from the PCA of bands 6 and 7 for both Landsat 8 and 9 satellites.
In all PCAs tested in this work, the first PC (PC1) is the one that explains the most variance percentage contained in the results. The highest variance, i.e., the highest percentage of information belongs to PC1 of Landsat 9 bands 6 and 7 (99.25 %). Similar to Landsat 9, the PCA with the highest variance result for Landsat 8 is PC1 from bands 6 and 7 (98.38%). When comparing the results of the two satellites, it is possible to see that Landsat 9 achieved higher variance values than Landsat 8.
Figure 12a,e represents the raster result of the PC1 generated from the PCAs. As we can see, the PCA of bands 6 and 7, besides obtaining the highest variance also managed to highlight points of known pegmatites in bright colors and with little false positives in relation to the background. It is notable that in all PCAs tested, in both satellites, the Aldeia pegmatite has very similar values to roads and urban areas. This generates false positives that can interfere negatively with the result analysis. To further highlight the pegmatites in the study area a categorization can be done, where red is assigned to the pixel value range of the known pegmatite areas (
Figure 13).
In the end, the adopted methodology served to evaluate the potential of the Landsat 8 and 9 satellite, with the PCA results, based on the subsets resultant from the comparison with the laboratory reference spectra, proving that this new satellite can be efficient for LCT pegmatite exploration. This potential use and the success of the combined approach are corroborated by the correct identification of known LCT pegmatite targets. However, considering the available spatial resolution of the satellite data (e.g., the Landsat 8/9 spatial resolution), the LCT pegmatites must present a good explosion, so that this approach is relevant for other users and mining stakeholders. Nevertheless, it is notable that despite the limitation in spatial resolution of the data, the method was able to identify the Aldeia pegmatite which does not have large dimensions when compared to the Landsat 8/9’s pixel size. Regarding the spatial limitation, it can be avoided using spectral unmixing-based methods [
64] or minimized considering the combination of complementary techniques, using a combined approach with other sensors with higher spatial resolution, such as UAV, and
in situ data collection, depending on the financial and human resources for its execution.
4.4. WebGIS
In this study, the results were presented in a new and intuitive webGIS, developed under the scope of the INOVMINERAL4.0 project (
https://gis.fc.up.pt/INOVMineral/index.html). The data can be disseminated to any user, with tools that can help to analyze the information provided. The webGIS provide free access to any user and can help with management decision-making.
The webGIS is composed of five tabs (
Figure 14): i) the “webGIS” tab where the geospatial information is presented under a base map; ii) the “About the project” tab which presents some information about the project; iii) the “Team” tab composed by information about the researchers of the project; iv) the “Publications” tab with a list of publications (and respective links) produced under the project and; v) the “Contacts” tab with a formulary to contact the researchers.
The development of a user-friendly webGIS allows users to dynamically visualize and analyze the data related to i) LiDAR-derived DEM of the area; ii) gamma-ray spectrometry maps; iii) reflectance spectroscopy data of the Aldeia pegmatite and host-rocks and iv) processed satellite images for LCT pegmatite exploration.
Figure 15 presents the content of the spectral library provided interactive through popups in the webGIS.
In the future, the webGIS will incorporate more tools to manipulate the data, as well as, to implement a better and more effective presentation of the spectral library.
5. Conclusions
The present research summarizes the contributions of the INOVMINERAL4.0 project for LCT pegmatite exploration by studying the spectral and geophysical properties of the Aldeia pegmatite in one of the most important pegmatite fields in Iberia and in Europe. After data interpretation and result integration in a GIS environment, with enhanced visualization through the implementation of a webGIS, it was possible to evaluate the potential of non-destructive exploration techniques such as geophysical radiometrics and remote sensing. Thus, the objectives of this study were accomplished, namely:
- i.
The obtention of high spatial resolution elevation data such as a LiDAR-derived DEM, can be very helpful in understanding pegmatite outcrop distribution and is a fundamental base layer to overlay other kinds of data.
- i.
ii. The acquisition of radiometric data through geophysical techniques can be a good approach to discriminate pegmatites and their host rocks, if their radiometric differences occur in a magnitude enough to be detected. Future studies must evaluate the penetration depth of this technique to detect buried pegmatites.
- i.
iii. A successful methodology was proposed to structure the reflectance spectroscopy data into a spectral library, with freely available public access data that can even serve as a source of validation in new scientific studies.
- i.
iv. The spectral library proposed in this study proved to be of high added value for space-based exploration. The superposition of the Landsat 9 bands over the selected reference spectra of distinct Aplite-Pegmatite samples allowed the selection of the best satellite bands for further testing.
- i.
v. The performance of Landsat 9 and Landsat 8 data were compared. At the same time, the potential use of the spectral library and the success of the combined approach (comparison with satellite data spectral resolution) were positively evaluated with the correct identification of known LCT pegmatite targets.
- i.
vi. The development of a user-friendly webGIS allowed data integration and visualization, as well as data sharing and dissemination to aid potential users in similar approaches.
It is intended that the data generated in this study, both those available in the spectral library and webGIS or the proposed multidisciplinary methodology, will stimulate scientific production elsewhere and contribute to meeting the available data needs regarding LCT pegmatite exploration. Nonetheless, it should be noted that in-depth and strategic knowledge of the methodology may be critical for expanding the study to other sites and detecting more LCT dikes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.C.-F., A.L., D.S., C.R.d.A. and A.C.T.; methodology, J.C.-F., D.S., C.R.d.A., R.R., A.A., L.D., R.M., A.L., and A.C.T.; software, J.C.-F., D.S., L.D.; validation, J.T.V., A.M., D.S., C.R.d.A. and J.C.-F.; formal analysis, J.C.-F., D.S., C.R.d.A., R.M., R.R., A.A., J.T.V., and A.M.; investigation, J.C.-F., D.S., C.R.d.A., R.R., A.A., J.T.V., and A.M.; resources, A.L., R.M., J.T.V, R.R., A.A. and A.C.T.; data curation, J.C.-F., C.R.d.A.; writing—original draft preparation, J.C.-F., D.S., C.R.d.A., R.R., A.A., J.T.V., A.M., and L.D.; writing—review and editing, J.C.-F., D.S., C.R.d.A., A.L. and A.C.T.; visualization, D.S., C.R.d.A., R.R., A.A., J.T.V., L.D. and J.C.-F.; supervision, R.M, A.L., A.C.T. and J.C.-F.; project administration, A.L., A.C.T; funding acquisition, A.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors acknowledge the support provided by Portuguese National Funds through the FCT – Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, I.P. (Portugal) projects UIDB/04683/2020 and UIDP/04683/2020 (Institute of Earth Sciences); through ANI and COMPETE 2020 as well as European funds through the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) with POCI-01-0247-FEDER-046083 INOVMINERAL project. Douglas Santos was financially supported by Portuguese national funds through FCT (Grant: UI/BD/154412/2023). Ricardo Ribeiro is financially supported within the compass of his Ph.D. thesis, ref. SFRH/BD/140266/2018. C.R.d.A. was financially supported by Portuguese national funds through FCT - Foundation for Science and Technology I.P. (Grant: PRT/BD/153518/2021). The spectroradiometer equipment was purchased under the European Commission’s Horizon 2020 innovation programme under grant agreement no. 869274, project GREENPEG New Exploration Tools for European Pegmatite Green-Tech Resources.
Data Availability Statement
The spectral library is publicly archived and published in the Zenodo platform
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7313964 under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The raw Landsat 9 images are available upon querying at the Earth Explorer portal, a USGS data portal to obtain earth imagery across existing geospatial data types available at
https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/. The processed Landsat 9 images presented in this research are available at request in the first stage, and then publically available at the end of the project in a WebGIS platform. The satellite image was processed using the QGIS open-access software, licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 license (CC BY-SA). Spectra continuum removal and absorption extraction were accomplished with a Python routine publically available at
https://www.mdpi.com/2306-5729/6/3/33/s1, © Copyright 2021 by Cardoso-Fernandes, J.; Silva, J.; Dias, F.; Lima, A.; Teodoro, A.C.; Barrès, O.; Cauzid, J.; Perrotta, M.; Roda-Robles, E.; Ribeiro, M.A., under a Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license, based on the PySptools open-source Python library, © Copyright 2013-2018, Christian Therien, licensed under an Apache License Version 2.0. and available on GitHub repository
https://github.com/ctherien/pysptools.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Savannah Resources PLC for access to the Aldeia pegmatite and for providing the samples used in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Gourcerol, B.; Gloaguen, E.; Melleton, J.; Tuduri, J.; Galiegue, X. Re-assessing the European lithium resource potential – A review of hard-rock resources and metallogeny. Ore Geology Reviews 2019, 109, 494–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blengini, G.A.; Latunussa, C.E.L.; Eynard, U.; Torres de Matos, C.; Wittmer, D.; Georgitzikis, K.; Pavel, C.; Carrara, S.; Mancini, L.; Unguru, M.; Blagoeva, D.; Mathieux, F.; Pennington, D. Study on the EU's list of Critical Raw Materials Final Report; European Commission: 2020.
- Müller, A.; Reimer, W.; Wall, F.; Williamson, B.; Menuge, J.; Brönner, M.; Haase, C.; Brauch, K.; Pohl, C.; Lima, A.; et al. GREENPEG - Exploration for pegmatite minerals to feed the energy transition: First steps towards the Green Stone Age. Geological Society, London, Special Publications 2022, 526, SP526-2021-189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, B.M. Tools and Workflows for Grassroots Li–Cs–Ta (LCT) Pegmatite Exploration. Minerals 2019, 9, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeschuk, C.R.; Vanstone, P.J. Exploration techniques for rare-element pegmatite in the Bird River greenstone belt, southeastern Manitoba. In Proceedings of the Exploration 07: Fifth Decennial International Conference on Mineral Exploration, Milkereit, B., Ed. 2007; pp. 823–839. [Google Scholar]
- Kaeter, D.; Menuge, J.F.; Harrop, J. Stream sediment geochemistry for regional prospectivity analysis: Tin, cesium, tantalum and tungsten anomalies in Leinster, southeast Ireland. In Proceedings of the 15th SGA Biennial Meeting, Glasgow, Scotland, 27-30 August 2019; 2019; pp. 1228–1231. [Google Scholar]
- Fyzollahhi, N.; Torshizian, H.; Afzal, P.; Jafari, M.R. Determination of lithium prospects using fractal modeling and staged factor analysis in Torud region, NE Iran. Journal of Geochemical Exploration 2018, 189, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadati, H.; Afzal, P.; Torshizian, H.; Solgi, A. Geochemical exploration for lithium in NE Iran using the geochemical mapping prospectivity index, staged factor analysis, and a fractal model. Geochemistry: Exploration, Environment, Analysis 2020, 20, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso-Fernandes, J.; Lima, J.; Lima, A.; Roda-Robles, E.; Köhler, M.; Schaefer, S.; Barth, A.; Knobloch, A.; Gonçalves, M.A.; Gonçalves, F.; Teodoro, A.C. Stream sediment analysis for Lithium (Li) exploration in the Douro region (Portugal): A comparative study of the spatial interpolation and catchment basin approaches. Journal of Geochemical Exploration 2022, 236, 106978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errandonea-Martin, J.; Garate-Olave, I.; Roda-Robles, E.; Cardoso-Fernandes, J.; Lima, A.; Ribeiro, M.d.A.; Teodoro, A.C. Metasomatic effect of Li-bearing aplite-pegmatites on psammitic and pelitic metasediments: Geochemical constraints on critical raw material exploration at the Fregeneda–Almendra Pegmatite Field (Spain and Portugal). Ore Geology Reviews 2022, 150, 105155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyser, W.; Müller, A.; Knoll, T.; Menuge, J.F.; Steiner, R.; Berndt, J.; Hart, E.; Fegan, T.; Harrop, J. Quartz chemistry of lithium pegmatites and its petrogenetic and economic implications: Examples from Wolfsberg (Austria) and Moylisha (Ireland). Chemical Geology 2023, 630, 121507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trueman, D.L. Exploring for a Tanco type pegmatite. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on the Geology of Rare Metals, Victoria, Canada, 9-10 November; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, M.D.; Ford, K.L.; Keating, P. Review paper: Exploration geophysics for intrusion-hosted rare metals. Geophysical Prospecting 2016, 64, 1275–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Bagas, L.; Li, K.; Jin, M.; Liu, Y.; Teng, J. Newly Discovered Triassic Lithium Deposits in the Dahongliutan Area, NorthWest China: A Case Study for the Detection of Lithium-Bearing Pegmatite Deposits in Rugged Terrains Using Remote-Sensing Data and Images. Frontiers in Earth Science 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.; Cardoso-Fernandes, J.; Lima, A.; Müller, A.; Brönner, M.; Teodoro, A.C. Spectral Analysis to Improve Inputs to Random Forest and other Boosted Ensemble Tree-Based Algorithms for Detecting NYF Pegmatites in Tysfjord, Norway. Remote Sensing 2022, 14, 3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemusse, U.; Lima, A.; Teodoro, A. Pegmatite spectral behavior considering ASTER and Landsat 8 OLI data in Naipa and Muiane mines (Alto Ligonha, Mozambique). In Proceedings of the SPIE, SPIE Remote Sensing, Berlin, Germany, 10–13 September 2018; Michel, U.; Schulz, K., Eds. SPIE: Bellingham, WA; 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rajesh, H.M. Application of remote sensing and GIS in mineral resource mapping - An overview. Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences 2004, 99, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso-Fernandes, J.; Teodoro, A.C.; Lima, A.; Perrotta, M.; Roda-Robles, E. Detecting Lithium (Li) Mineralizations from Space: Current Research and Future Perspectives. Applied Sciences 2020, 10, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.N.; Roush, T.L. Reflectance spectroscopy: Quantitative analysis techniques for remote sensing applications. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 1984, 89, 6329–6340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.N.; King, T.V.V.; Klejwa, M.; Swayze, G.A.; Vergo, N. High spectral resolution reflectance spectroscopy of minerals. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 1990, 95, 12653–12680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso-Fernandes, J.; Silva, J.; Perrotta, M.M.; Lima, A.; Teodoro, A.C.; Ribeiro, M.A.; Dias, F.; Barrès, O.; Cauzid, J.; Roda-Robles, E. Interpretation of the Reflectance Spectra of Lithium (Li) Minerals and Pegmatites: A Case Study for Mineralogical and Lithological Identification in the Fregeneda–Almendra Area. Remote Sensing 2021, 13, 3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokaly, R.F.; Clark, R.N.; Swayze, G.A.; Livo, K.E.; Hoefen, T.M.; Pearson, N.C.; Wise, R.A.; Benzel, W.M.; Lowers, H.A.; Driscoll, R.L.; Klein, A.J. USGS Spectral Library Version 7; 1035; Reston, VA, 2017; p 68.
- Meerdink, S.K.; Hook, S.J.; Roberts, D.A.; Abbott, E.A. The ECOSTRESS spectral library version 1.0. Remote Sensing of Environment 2019, 230, 111196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso-Fernandes, J.; Silva, J.; Dias, F.; Lima, A.; Teodoro, A.C.; Barrès, O.; Cauzid, J.; Perrotta, M.; Roda-Robles, E.; Ribeiro, M.A. Tools for Remote Exploration: A Lithium (Li) Dedicated Spectral Library of the Fregeneda–Almendra Aplite–Pegmatite Field. Data 2021, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiri, Z.; Lhissou, R.; El Harti, A.; Jellouli, A.; Chakouri, M. Recent advances in the use of public domain satellite imagery for mineral exploration: A review of Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 applications. Ore Geology Reviews 2020, 117, 103332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.A.; Thompson, K.F.; Johnston, P.; Santillo, D. An Overview of Seabed Mining Including the Current State of Development, Environmental Impacts, and Knowledge Gaps. Frontiers in Marine Science 2018, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, C.G.; Dias, F.L.; Lima, A.M.C. Largest spodumene lithium depositin western Europe. In Proceedings 15th biennial SGA meeting, Glasgow, Scotland, August 27-30; University of Glasgow: 2019; pp 1792–1795. 27 August.
- Duarte, L.; Teodoro, A.C.; Santos, P.; Rodrigues de Almeida, C.; Cardoso-Fernandes, J.; Flores, D. An Interactive WebGIS Integrating Environmental Susceptibility Mapping in a Self-Burning Waste Pile Using a Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis Approach. Geosciences 2022, 12, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julivert, M. Mapa tectónico de la Península Ibérica y Baleares Escala 1:1.000.000. Ministerio de Industria y Energía, Servicio de Publicaciones: Madrid, 1972; p 1 mapa.
- Lima, A. Estrutura, mineralogia e génese dos filões aplitopegmatíticos com espodumena da região do Barroso-Alvão. PhD thesis, Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal, 2000.
- Vasques, J.T. Lithogeochemistry and prospection of Lithium-bearing pegmatites and their host-rocks. Master thesis, Faculdade de Ciências da Universidade do Porto Porto, Portugal, 2021.
- Savannah Resources Plc. Annual Report and Financial Statements. Available online: https://www.savannahresources.com/media/1n0mjo35/sav-financial-statements-31-december-2019.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Martins, T. Multidisciplinary study of pegmatites and associated Li and Sn-Nb-Ta mineralisation from the Barroso-Alvão region. PhD thesis, Faculdade de Ciências da Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal, 2009.
- Dias, F. Lithium mineralizations of Barroso-Alvão aplite-pegmatite field. Master thesis, Faculdade de Ciências da Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal, 2016.
- Černý, P.; Ercit, T.S. Classification of granitic pegmatites revisited. Can. Mineral. 2005, 43, 2005–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, M.A.; Müller, A.; Simmons, W.B. A proposed new mineralogical classification system for granitic pegmatites. The Canadian Mineralogist 2022, 60, 229–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, T.n.; Lima, A.; Simmons, W.B.; Falster, A.U.; Noronha, F. GEOCHEMICAL FRACTIONATION OF Nb–Ta OXIDES IN Li-BEARING PEGMATITES FROM THE BARROSO–ALVÃO PEGMATITE FIELD, NORTHERN PORTUGAL. The Canadian Mineralogist 2011, 49, 777–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmand, T.G. Design for a Laser Rangefinder; 1965.
- Langley, R.B. RTK GPS. GPS World September 1998, 1998, Vol. 9,pp 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- ASD Inc. ViewSpec Pro™ User Manual. ASD Document 600555 Rev. A. Boulder, CO, USA, 2008.
- Menges, F. Spectragryph - optical spectroscopy software, Version 1.2.14. Available online: http://www.effemm2.de/spectragryph/ (accessed on 22 July 2020).
- U.S. Geological Survey Landsat—Earth Observation Satellites Fact Sheet 2015–3081, ver. 1.4. August 2022, 2022; p 4. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/fs/2015/3081/fs20153081.pdf.
- U.S. Geological Survey Landsat 9; 2019-3008; Reston, VA, 2019; pp 2-2.
- Chavez, P.S. Image-Based Atmospheric Corrections - Revisited and Improved. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing 1996, 62, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, G.R. Spectral signatures of particulate minerals in the visible and near infrared. Geophysics 1977, 42, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontual, S.; Merry, N.J.; Gamson, P. Spectral interpretation field manual. GMEX Spectral analysis guides for mineral exploration., 3rd ed.; AusSpec International Ltd.: Victoria, 2008; Vol. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Loughlin, W.P. Component Analysis for Alteration Mapping. Photogram. Eng. Rem. Sens. 1991, 57, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Harrison, A. Standardized principal components. International Journal of Remote Sensing 1985, 6, 883–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.A.; Wichern, D.W. Applied Multivariate Statistical Analysis. Pearson Prentice Hall: 2007; p 773-773.
- Santos, D.; Teodoro, A.; Lima, A.; Cardoso-Fernandes, J. Remote sensing techniques to detect areas with potential for lithium exploration in Minas Gerais, Brazil. In Proceedings of the SPIE, SPIE Remote Sensing, Strasbourg, France, 9–12 September 2019; Schulz, K.; Michel, U.; Nikolakopoulos, K. G., Eds. SPIE: Bellingham, WA; 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso-Fernandes, J.; Teodoro, A.C.; Lima, A. Remote sensing data in lithium (Li) exploration: A new approach for the detection of Li-bearing pegmatites. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation 2019, 76, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiri, Z.; Harti, A.E.; Jellouli, A.; Maacha, L.; Bachaoui, E.M. Lithological mapping using Landsat 8 OLI and Terra ASTER multispectral data in the Bas Drâa inlier, Moroccan Anti Atlas. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing 2016, 10, 016005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- XAMPP Apache. Available online: https://www.apachefriends.org (accessed on November 2022).
- Isenburg, M. LAStools-efficient Tools for LiDAR Processing. Available online: http://www.cs.unc.edu/~isenburg/lastools/ (accessed on 16 June 2023).
- Axelsson, P. DEM generation from laser scanner data using adaptive TIN models. International Archives of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing Amsterdam, Netherlands. 2000, 33, 110–117. [Google Scholar]
- Mielcarek, M.; Stereńczak, K.; Khosravipour, A. Testing and evaluating different LiDAR-derived canopy height model generation methods for tree height estimation. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation 2018, 71, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, C.R.; Santos, D.; Vasques, J.T.; Cardoso-Fernandes, J.; Lima, A.; Teodoro, A.C. A LCT Pegmatite Spectral Library of the Aldeia spodumene deposit: contributes to mineral exploration, Zenodo. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/7313964.
- McManamon, P.F. Lidar technologies and Systems. SPIE Press: Bellingham, Washington, USA, 2019; Vol. PM300, p 520.
- Hunt, G.R.; Salisbury, J.W. Visible and near-infrared spectra of minerals and rocks: I Silicate minerals. Modern Geology 1970, 1, 283–300. [Google Scholar]
-
Origin(Pro), Version Number 2022. OriginLab Corporation: Northampton, MA, USA.
- Teodoro, A.C.; Santos, D.; Cardoso-Fernandes, J.; Lima, A.; Brönner, M. Identification of pegmatite bodies, at a province scale, using machine learning algorithms: preliminary results. In Proc. SPIE 11863, Earth Resources and Environmental Remote Sensing/GIS Applications XII, SPIE Remote Sensing, 12 September 2021; SPIE: 2021. [CrossRef]
- Pour, A.B.; Hashim, M. Identification of hydrothermal alteration minerals for exploring of porphyry copper deposit using ASTER data, SE Iran. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences 2011, 42, 1309–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez Jr, P.S.; Kwarteng, A.Y. Extracting spectral contrast in Landsat Thematic Mapper image data using selective principal component analysis. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing 1989, 55, 339–348. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, D.; Cardoso-Fernandes, J.; Lima, A.; Teodoro, A.C. The potential of spectral unmixing method applied to PRISMA hyperspectral images in the identification of Li minerals: an evaluation for prospecting purposes. In SPIE Remote Sensing, Earth Resources and Environmental Remote Sensing/GIS Applications XIII, Berlin, Germany, SPIE: 2022. [CrossRef]
Figure 2.
The zoomed map of the sampling area within the Aldeia pegmatite, on the Mina do Barroso concession.
Figure 2.
The zoomed map of the sampling area within the Aldeia pegmatite, on the Mina do Barroso concession.
Figure 3.
Methodology workflow, with methodological processes and their integration for the identification of target minerals.
Figure 3.
Methodology workflow, with methodological processes and their integration for the identification of target minerals.
Figure 4.
Flowchart with all the programming languages and libraries used in the webGIS implementation.
Figure 4.
Flowchart with all the programming languages and libraries used in the webGIS implementation.
Figure 5.
Stacked images created with Surfer® (Golden Software, LLC): ArcGIS World Imagery Basemap (bottom); hillshade image of the area (middle); World Imagery Basemap draped over the hillshade model (top). The hillshade presents a slight coloration with the highest altitudes in blue color, lowest altitudes in green and intermediate areas in yellowish/orange color. .
Figure 5.
Stacked images created with Surfer® (Golden Software, LLC): ArcGIS World Imagery Basemap (bottom); hillshade image of the area (middle); World Imagery Basemap draped over the hillshade model (top). The hillshade presents a slight coloration with the highest altitudes in blue color, lowest altitudes in green and intermediate areas in yellowish/orange color. .
Figure 6.
Map of equivalent Uranium (eU) concentration in the Aldeia area. A 30 m buffer was applied to the Kriging interpolation.
Figure 6.
Map of equivalent Uranium (eU) concentration in the Aldeia area. A 30 m buffer was applied to the Kriging interpolation.
Figure 7.
Map of equivalent Thorium (eTh) concentration in the Aldeia area. A 30 m buffer was applied to the Kriging interpolation.
Figure 7.
Map of equivalent Thorium (eTh) concentration in the Aldeia area. A 30 m buffer was applied to the Kriging interpolation.
Figure 8.
Map of equivalent Thorium – equivalent Uranium (eTh/eU) ratio on the Aldeia area. A 30 m buffer was applied to the Kriging interpolation.
Figure 8.
Map of equivalent Thorium – equivalent Uranium (eTh/eU) ratio on the Aldeia area. A 30 m buffer was applied to the Kriging interpolation.
Figure 9.
Example of the graphical products of the spectra INOV5_2, available in the spectral library, for consultation and analysis: (a) Raw_spectra; (b) Processed_spectra (with removed continuum); (c) and (d) Spectra_absortions, with different wavelengths and depths, where crs is the continuum removed spectra; depth is the absorption depth and FWHM is the full width at half maximum.
Figure 9.
Example of the graphical products of the spectra INOV5_2, available in the spectral library, for consultation and analysis: (a) Raw_spectra; (b) Processed_spectra (with removed continuum); (c) and (d) Spectra_absortions, with different wavelengths and depths, where crs is the continuum removed spectra; depth is the absorption depth and FWHM is the full width at half maximum.
Figure 10.
Diagnostic absorptions of the spectra of each class: (a) Quartz exudation; (b) Andalusite-schist; (c) Muscovite-schist; (d) Aplite with iron oxides; (e) Pegmatite with iron oxides; (f) Aplite-pegmatite and (g) Aplite-pegmatite with iron oxides.
Figure 10.
Diagnostic absorptions of the spectra of each class: (a) Quartz exudation; (b) Andalusite-schist; (c) Muscovite-schist; (d) Aplite with iron oxides; (e) Pegmatite with iron oxides; (f) Aplite-pegmatite and (g) Aplite-pegmatite with iron oxides.
Figure 11.
Absorption features and reflectance peaks of reference spectra from the samples of the Aldeia pegmatite. Three Aplite-Pegmatite spectra were used as examples. The blue rectangles represent the spectral range of the Landsat 8 and9 bands superimposed on the raw spectra.
Figure 11.
Absorption features and reflectance peaks of reference spectra from the samples of the Aldeia pegmatite. Three Aplite-Pegmatite spectra were used as examples. The blue rectangles represent the spectral range of the Landsat 8 and9 bands superimposed on the raw spectra.
Figure 12.
PCA result for Landsat 8 and 9. The Aldeia pegmatite is highlighted by the red rectangle. (a) PCA of bands 6 and 7 for Landsat 8. (b) PCA of bands 4 and 7 for Landsat 8. (c) PCA of bands 3 and 7 for Landsat 8. (d) PCA of bands 6 and 7 for Landsat 9. (e) PCA of bands 4 and 7 for Landsat 9. (c) PCA of bands 3 and 7 for Landsat 9. Other pegmatite occurrences are highlighted in the figure.
Figure 12.
PCA result for Landsat 8 and 9. The Aldeia pegmatite is highlighted by the red rectangle. (a) PCA of bands 6 and 7 for Landsat 8. (b) PCA of bands 4 and 7 for Landsat 8. (c) PCA of bands 3 and 7 for Landsat 8. (d) PCA of bands 6 and 7 for Landsat 9. (e) PCA of bands 4 and 7 for Landsat 9. (c) PCA of bands 3 and 7 for Landsat 9. Other pegmatite occurrences are highlighted in the figure.
Figure 13.
Result for PCA on bands 3 and 7 for Landsat 9. (a) The Aldeia mining area is highlighted by the red rectangle. The pixels of Aplite-Pegmatite are highlighted in red, showing that the method was accurate in other known target locations apart from the training area (e.g., Lousas, NOA, and Alijó). (b) Aldeia mining area in focus. Pixels of Aplite-Pegmatite are highlighted in red.
Figure 13.
Result for PCA on bands 3 and 7 for Landsat 9. (a) The Aldeia mining area is highlighted by the red rectangle. The pixels of Aplite-Pegmatite are highlighted in red, showing that the method was accurate in other known target locations apart from the training area (e.g., Lousas, NOA, and Alijó). (b) Aldeia mining area in focus. Pixels of Aplite-Pegmatite are highlighted in red.
Figure 14.
Preview of the webGIS interface and respective tabs (top left corner). The map view shows the created DEM with an elevation ramp (low altitude in blue, high in light brown) and the sampling sites (blue dots) previously shown in
Figure 2. For each spot, the content of the spectral database can be previewed in an interactive way (
Figure 15). .
Figure 14.
Preview of the webGIS interface and respective tabs (top left corner). The map view shows the created DEM with an elevation ramp (low altitude in blue, high in light brown) and the sampling sites (blue dots) previously shown in
Figure 2. For each spot, the content of the spectral database can be previewed in an interactive way (
Figure 15). .
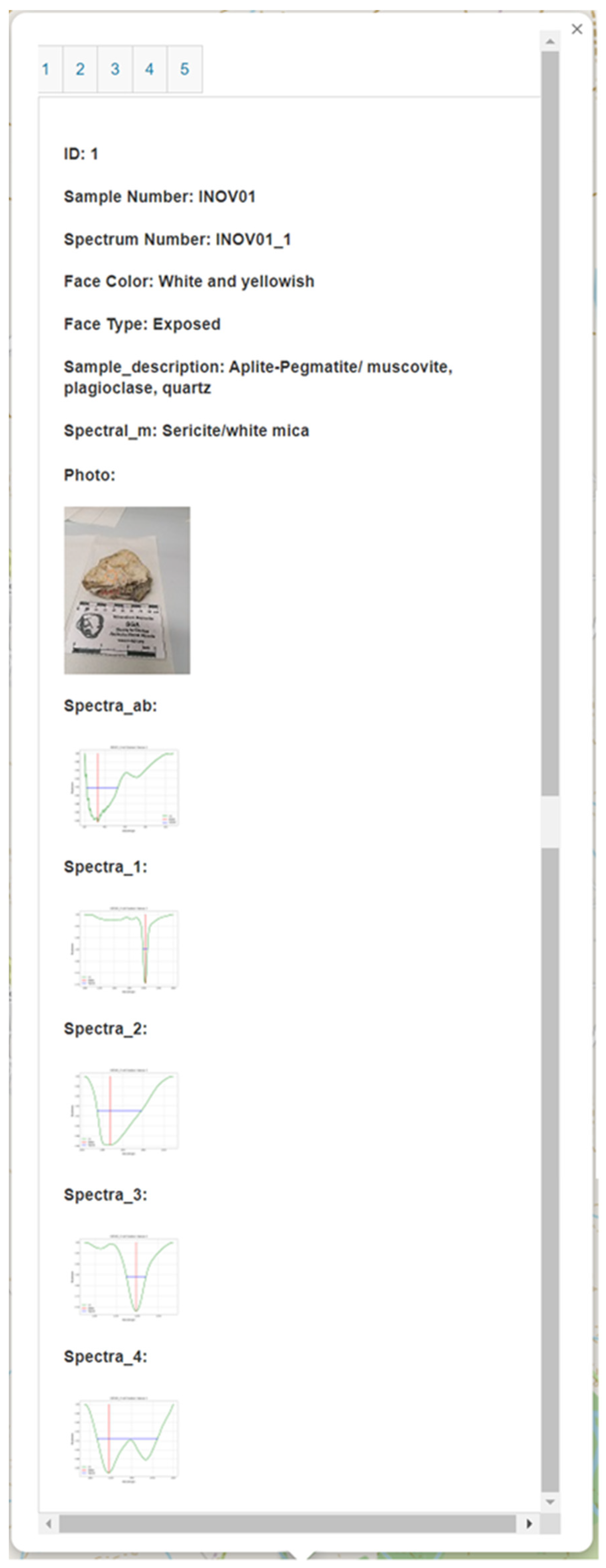
Figure 15.
Example of popup interface of the spectral library. This example corresponds to ID1 from sample number 1 (composed of 5 IDs, each ID respects a different spot analyzed within the sample).
Figure 15.
Example of popup interface of the spectral library. This example corresponds to ID1 from sample number 1 (composed of 5 IDs, each ID respects a different spot analyzed within the sample).
Table 1.
Comparison of Landsat 9 with previous satellites of the Landsat program [
26,
43].
Table 1.
Comparison of Landsat 9 with previous satellites of the Landsat program [
26,
43].
| Parameter |
Landsat 7 (ETM+) |
Landsat 8 (OLI) |
Landsat 9 (OLI 2) |
| Radiometric Resolution (bit) |
8
(256 shades) |
12
(4096 shades) |
14
(16,384 shades) |
| Temporal Resolution (day) |
16 |
16* |
16* |
| Spatial Resolution (m) |
30 (VNIR)
60 (TIR)
15 (Panchromatic -PAN) |
30 (VNIR)
100 (TIR)
15 (PAN) |
30 (VNIR)
100 (TIR)
15 (PAN) |
| Number of bands |
8 |
11 |
11 |
Table 2.
Information about the downloaded Landsat 8 and 9 image.
Table 2.
Information about the downloaded Landsat 8 and 9 image.
| |
Landsat 8 |
Landsat 9 |
| Date Acquired |
2018/08/21 |
2022/01/28 |
| Land Cloud Cover |
0.03% |
3.23% |
| Data Type |
OLI_TIRS_L1TP |
OLI_TIRS_L1TP |
| Product Map Projection |
UTM |
UTM |
| DATUM |
WGS84 Zone 29 N |
WGS84 Zone 29 N |
Table 3.
Description of the information contained in the spectral library [
57].
Table 3.
Description of the information contained in the spectral library [
57].
| Field name |
Description |
|
| ID |
Primary key generated from Access software. |
|
| Sample_nr |
Identification of the sample, represented by numbers from one to 11, for example: "INOV01", (...), "INOV11". |
|
| Spectrum_nr |
Spectrum identification. The number indicated after the "_" represents the spectrum measured in each sample, for example, in sample "INOV01" four spectra were obtained, represented by "INOV01_1", (...), and "INOV01_4". |
|
| Locality |
Place where the sample was obtained. |
|
| Sample_description |
Geological description of the sample, considering visual aspects. |
|
| WGS84_Zone |
UTM zone where the sample was extracted. |
|
| Latitude |
Coordinate WGS84, where the sample was extracted (Latitude). |
|
| Longitude |
Coordinate WGS84, where the sample was extracted (Longitude). |
|
| Preparation |
Indication of the sample preparation routine. |
|
| Analysis |
Equipment that was used in the spectrum collection. |
|
| Stored |
Localization of the laboratory where the collection was done and where the samples are kept. |
|
| Face_color |
Surface staining of the sample (visual observation). |
|
| Face_type |
Type of sample face (visual observation). Ex.: exposed and sawn. |
|
| Photo |
Photo indicating the area of the sample where the spectrum was collected (.jpg) |
|
| Raw_spectra |
Raw spectrum collected (.txt and .pdf). |
|
| Processed_spectra |
Processed spectrum, with removed continuum (.txt and .pdf). |
|
| Spectra_absorptions |
Main absorption features automatically extracted (.png) |
|
| Spectral_mineralogy |
Description of the sample considering the spectrally active minerals/compounds identified. |
|
Table 4.
Sample and analysis following the content of the spectral database.
Table 4.
Sample and analysis following the content of the spectral database.
| Sample description |
Number of spectra |
% of spectra |
| Aplite-Pegmatite with muscovite, plagioclase, quartz |
28 |
59.57 |
| Aplite-Pegmatite with muscovite, plagioclase, quartz, and iron oxides |
9 |
19.15 |
| Aplite with plagioclase, quartz, spodumene, iron oxides |
5 |
10.64 |
| Muscovite-schist |
2 |
4.26 |
| Andalusite-schist |
1 |
2.13 |
| Exudation quartz |
1 |
2.13 |
| Pegmatite with iron oxides |
1 |
2.13 |
Table 5.
Matrix of eigenvectors extracted after calculating the PCA on bands 6 and 7.
Table 5.
Matrix of eigenvectors extracted after calculating the PCA on bands 6 and 7.
| |
LC08 |
LC09 |
Variance (%) |
| PC |
Band 6 |
Band 7 |
Band 6 |
Band 7 |
LC08 |
LC09 |
| PC 1 |
-0.806750 |
0.590892 |
-0.835940 |
0.548820 |
98.38 |
99.25 |
| PC 2 |
-0.590892 |
-0.8067501 |
-0.548820 |
-0.835940 |
1.61 |
0.75 |
Table 6.
Matrix of eigenvectors extracted after calculating the PCA on bands 3 and 7.
Table 6.
Matrix of eigenvectors extracted after calculating the PCA on bands 3 and 7.
| |
LC08 |
LC09 |
Variance (%) |
| PC |
Band 3 |
Band 7 |
Band 3 |
Band 7 |
LC08 |
LC09 |
| PC 1 |
0.278870 |
-0.96032 |
0.278979 |
-0.960297 |
98.27 |
98.80 |
| PC 2 |
0.960328 |
0.278870 |
0.960297 |
0.278979 |
1.72 |
1.20 |
Table 7.
Matrix of eigenvectors extracted after calculating the PCA on bands 4 and 7.
Table 7.
Matrix of eigenvectors extracted after calculating the PCA on bands 4 and 7.
| |
LC08 |
LC09 |
Variance (%) |
| PC |
Band 4 |
Band 7 |
Band 4 |
Band 7 |
LC08 |
LC09 |
| PC 1 |
0.434049 |
-0.900889 |
0.398671 |
-0.917093 |
97.73 |
98.45 |
| PC 2 |
0.900889 |
0.434049 |
0.917093 |
0.3986717 |
2.27 |
1.55 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).