1. Introduction
The United Nations (UN) Agenda 2030, inspired by the pledge leaving no one behind”, has put marginalized societies such as mountainous areas on the spotlight of global development discourse. Conventionally, people living in poor, lagging areas such as mountains are at high risk of being left behind (
Bennett 2020). Accordingly, achieving inclusive development requires localizing sustainable development goals (SDGs) to such areas (Wymann von Dach et al. 2018). Typically, compared to low lands, mountain areas are defined by higher poverty levels (Wester et al. 2019), more severe food insecurity (Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) 2020), higher and increasing vulnerability to disasters related to natural hazards and more severe climate change and variability effects (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) 2022). The lack of economic opportunities (Food and Agriculture Organization 2011) exacerbates the situation. Accordingly, mountainous communities opt for migration to address the effects of limited resources and opportunities.
Migration, recognised by the International Organisation of Migration (IOM) as an important cross-cutting element of the SDGs (Vidal and Laczko 2022), is hugely expected to significantly drive sustainable development in sending communities. Usually, remittances, mainly financial, and also social, are the most significant and direct channel connecting migration to livelihoods. However, mountainous areas such as Phuthadijthaba, South Africa, have geographical and economic specificities that hinder labour migration gains (Hunzai 2010). For instance, given the difficult terrains, the cost of labour migration is higher. These could include transport, money transfer fees, recruiting agency fees, and government fee and processing charges. Also, because of higher marginalisation, most migrants from marginalised areas are un/semi-skilled and therefore get low paying jobs (Andrea Membretti, Taylor, and Delves 2023). Thirdly, the rocky and mountainous terrain deters development of infrastructure and imposes cost premium on services (She et al. 2018). Ultimately, this disrupts easy of doing business and provides little return from invested remittances.
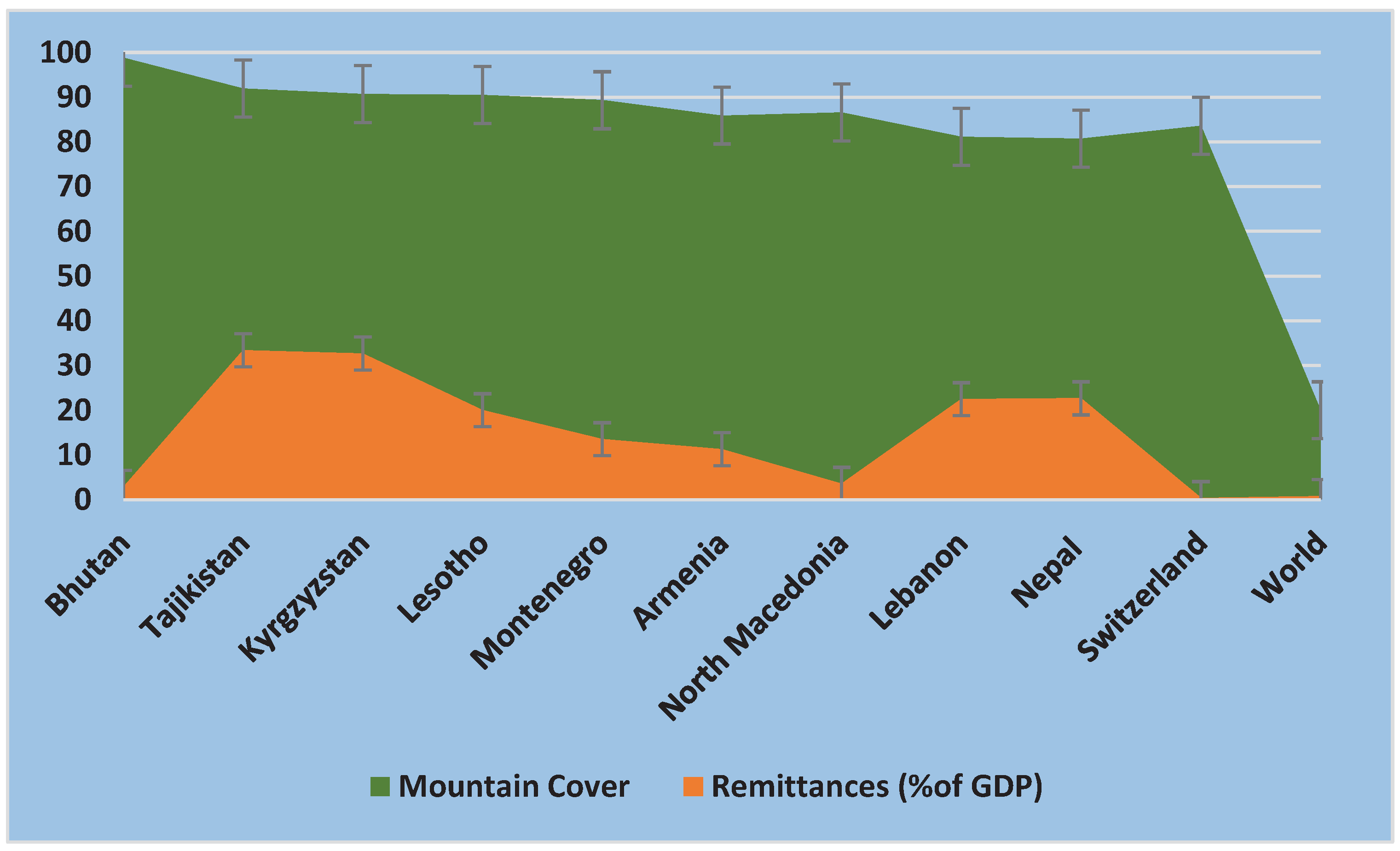
Nonetheless, the potential for remittances to impact livelihoods in mountain communities is very huge. Our analysis of data from World Bank (2023) show that the top 10 mountainous countries
1 in the world (See
Figure 1) have, on average, the highest share of remittances in gross domestic product (GDP) (20%) than any other country grouping. In these countries, mountains cover an average of 83.39% of the total area (World Population Review 2023). Globally, 20% of land is covered by mountains (World Population Review 2023) and remittances contribute only 0.78% of GDP in 2021 (World Bank 2023). In
Figure 1, we make this point very clear. Except for Bhutan, Switzerland, and Macedonia, the more mountainous a country is, the more remittances contribute to GDP. More importantly we observe that in most of these countries, higher mountain cover and higher remittances in GDP is on average, negatively correlated to GDP/capita. For instance, in Tajikistan, whose territory is 91.9% mountainous (the second largest), the share of remittances in GDP in 2021 stood at 33,4% (the highest), yet its GDP per capita is
$USD 897 (the lowest). From this brief analysis, we deduce that most mountainous countries are prone to high migration, and therefore higher remittances, yet they have lower GDP per capita than otherwise. This clearly shows the lack of income generating opportunities in mountainous areas.
The trend in mountainous areas, migration, remittances, and income levels, can easily be related to internal migration dynamics for large countries with different geographical landscapes like South Africa. The emerging city of Phuthadijthaba is a mountainous border city in South Africa, close to Lesotho (the most mountainous country in Africa by land cover). The city is in the Free State Province, with a contribution to national GDP of 5.14% in 2017 (Statistics South Africa 2019), the second last contributor after Northern Cape (2.19%). To add on, it’s a border town surrounded by better developed towns of Harrismith and Bethlehem, just 53 and 70kms away respectively. The city is home to over 400 000 people with high rates of unemployment-close to 50% in 2019- (Maluti-a-Phofung Municipality (MaP) 2019) and characterised by high levels of poverty (Mukwada and Mutana 2023). All these factors make the city prone to internal out-migration to better developed provinces and districts. Accordingly, a significant share of its population is more likely to be recipients of remittances-local to a larger extent, and international to a lesser extent. As we have shown above, high remittance receiving countries usually have lower GDP per capita. The GDP per capita for Phuthaditjhaba is estimated at USD 598 (just above 11 600 rands)/ year (ScalePay 2023) compared to national GDP per capita of the whole of South Africa of USD 7 055.00 (World Bank 2023). This clearly shows that Phuthaditjhaba has very low-income generating opportunities. The limited economic opportunities could be a push factor that drive individuals to migrate to other areas in a bid to fend for their families residing in the mountain city of Phuthaditjhaba.
We take this to raise a question on the role remittances play on livelihoods in mountainous communities. This major question has motivated the current study to carry out a systematic literature review on the interplay between migration, remittances, and livelihoods in mountainous area. We seek to answer the following sub-research questions: (1) what are the major sources of evidence?, (2) who are the main authors?, (3) which countries have received more research focus?, (4) what are the key thematic areas of research?, (5) what are the major trends and findings?, and more importantly, (6) what are the research gaps that studies on Phuthadijthaba could exploit?
In answering these questions, our study seeks to make an important contribution. While systematic literature reviews have been used to examine the role of remittances on various outcomes, we couldn’t find one focusing primarily on mountainous communities. This is notwithstanding that mountainous areas are distinct, have a complex and fragile ecosystems and economy. As such, the reasons for migration, the determination of remittances, how they are used, and their effectiveness in addressing social ills are different. In the literature, we find some SLRs on mountainous communities, targeting specific areas such as crop production (Babu et al. 2022; Gurung and Oh 2013; Santoro 2023). However, we could not find one which clearly zero-in on remittances in mountainous areas, despite the significant role it plays in recipient country GDPs. As we fill this gap, the evidence from this study becomes critical in providing key stakeholders with a hub of evidence that guides policy on enhancing sustainability of mountainous areas. Also, it opens more windows of research for future studies on the economics of remittances and lives in such areas.
The rest of the study proceeds as follows: Section details the methodology used,
Section 2 discusses the major findings,
Section 3 concludes by suggesting areas of further research.
2. Methodology
Instead of using the narrative literature review, our methodology benefits from a combination of two emerging approaches, the systematic literature review (SLR) and bibliometric analysis. While SLR has been developed two centuries ago for health science research (see Chalmers et al., 2002; Lame, 2019), it is only in recent years that its use in social science and business is gaining prominence (Li, Zhang, and Hsu 2023). A SLR is a literature review methodology used to gather, identify, and critically assess research sources (journals, articles, reports, books, etc) in an organized manner (Carrera-Rivera et al. 2022). Its advantages over traditional literature review are plenty. It uses unambiguous and systematic procedures (Lages et al. 2023) eliminates author bias (Mengist and Soromessa 2020), and therefore improves transparency (Lame 2019). In the end, it allows authors to deliver an explicit and comprehensive state of evidence on a chosen topic (Poklepović and Peričić 2019), making it easy to identify and fill research gaps in the literature.
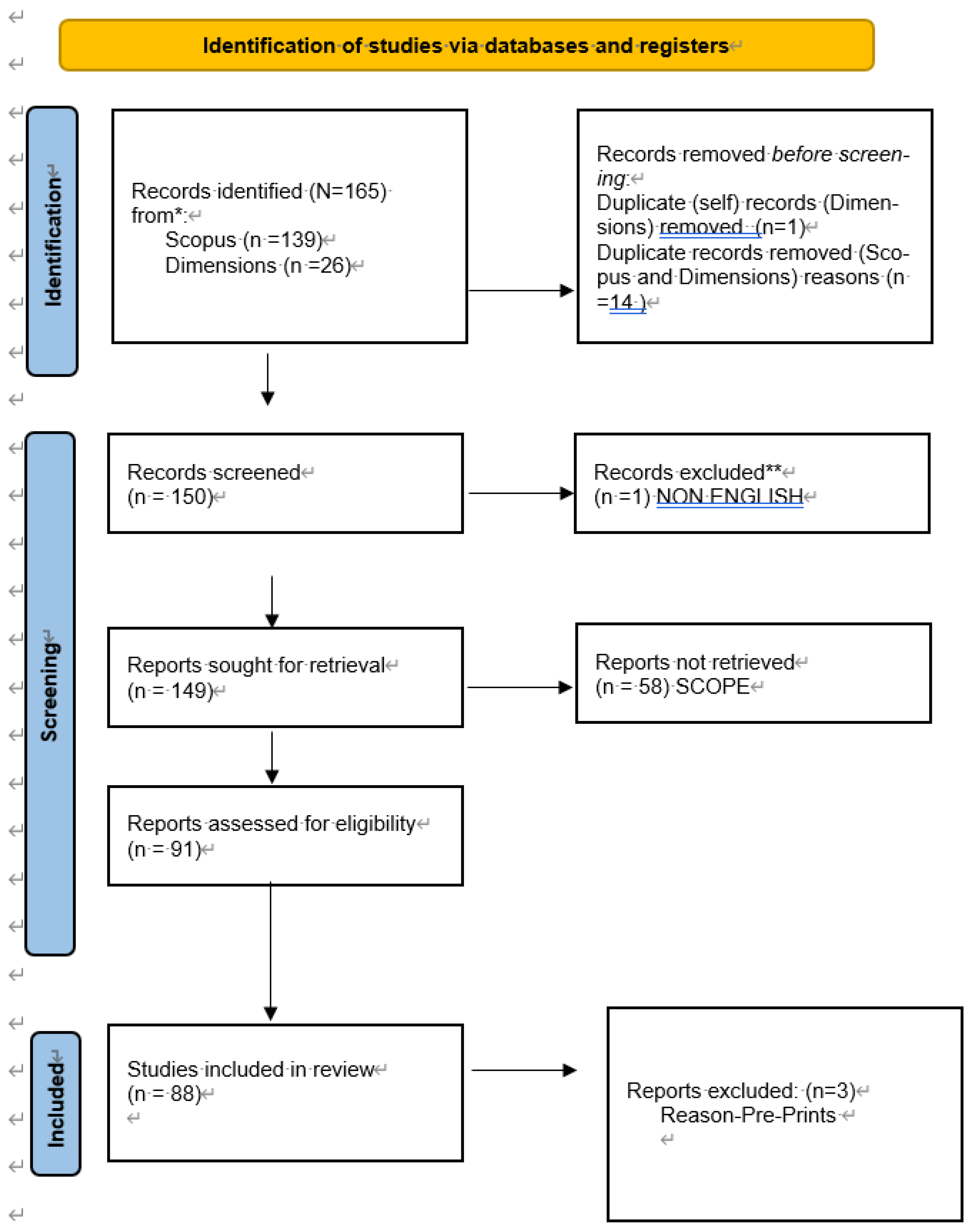
In carrying out the SLR, we follow the updated Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) 2020 Statement. As an upgrade to the 2009 Statement, the new version comprises of 27-to-do items, with a more robust checklist detailing reporting recommendations, an abstract checklist, and an improved flow diagram (
Figure 2) (Page et al. 2021). We use bibliometric analysis (BA) to complement findings from the PRISMA. While the SLR provides an important guideline on inclusion and exclusion of research themes, it does not provide a quantitative analysis of the same. That’s exactly what BA does. It encloses an array of a quantitative techniques (bibliometric analysis such as citation, co-occurrences) on bibliometric units (such as authors, journal, themes) (Donthu et al. 2021).
There are two main categories of BA, performance, and science mapping. The former involves performance indicators such as publication related metric, items such as citations, and number of documents, citation-related metrics, or a combination of both. Science mapping covers citation analysis, co-citation, bibliographic coupling, and co-authorship analysis (see Donthu et al., 2021 for detailed discussion). Researchers should choose the appropriate indicators depending on the specified research objective. Since one of our objectives is to examine the focal areas of research on remittances in mountainous areas, we used co-word analysis. Distinct from other science mapping techniques, which takes cited or citing documents the unit of analysis, co-word analysis assesses the exact content of the publication (Wang et al. 2022). To conduct the bibliometric co-word analysis, we used the latest VOSViewer 1.6.19 software by (Eck and Waltman 2023). This allowed us to generate the Network, Overlay, and Density Visualizations (See Figures 6–8).
2.1. Data sources
We obtained data on publications from two research data bases, Scopus and Dimensions. We chose Scopus because it is arguably the biggest source for bibliometric analysis. At the time of writing, it had 1.8+ billion cited references since 1970, 84+ million records, 17.6+ million, author profiles, 94.8+ thousand affiliation profiles, and 7+ thousand publishers (Elsevier, 2023). Many researchers rely on it for literature reviews due to its quality and trustworthiness (Baas, Schotten, and Plume 2020). We decided to exclude Web of Science in our searches due to close link between the two. In a comparative study by Kumar et al. (2021), it was documented that 99% of studies indexed in Web of Science are also indexed in Scopus. Hence including both would not significantly improve our search results. Instead, we complement the Scopus search with Dimension, a relatively new database (started in 2018). Dimensions uses different approaches for sourcing data (Kumar et al. 2021), hence giving us a different dimension. As at 01 April 2023, Dimensions had 134 million documents with 1.7Billion citations, 12 million datasets, 133 thousand policy documents, 151 million patents, among other scores (Dimensions 2023).
2.2. Search strategy
We used the new advanced search in Scopus using the syntax: TITLE-ABS-KEY (migration AND remittances) AND (mountain*). These are the three words we investigated. To broaden our results, we did not constrain the search to any filters at this stage. The search yielded 139 documents comprised of 111 articles, 12 book chapters, 10 reviews, two books, and one conference paper. The same search produced only 26 documents from Dimensions being 18 articles, five book chapters, and three pre-prints. We excluded and included according to PRISMA flow diagram in
Figure 2. Considering our research questions and objectives, we retrieved the following from each study: (1) title, abstract, and key words; (2) authors’ documents and citations; (3) sources’ documents and citations; (4) country documents and citations.
As can be seen from
Figure 2, we followed the three stages: (1) identification; (2) screening, and (3) finalization. In stage (1), we reported the documents identified from Scopus (139) and Dimensions (26). The source composition is given in
Figure 1. In stage (1) 15 duplicates, were removed. In stage (2), we conducted a language check. We removed one document with an English abstract, yet the paper is non-English. Also, we conducted a detailed assessment of the abstracts, and where we could not decide based on the abstract, we reviewed the paper to check its eligibility. Here we retained those papers with the three words migration”, remittances” and mountain”. The process eliminated 58 documents, representing the greatest share (35.15%) of the search results. Of these 1(1.72%) did not mention any of the three words, 5(8.62%) did not include the word remittances, 48(82.76%) excluded the word mountain”, 4(6.9%) excluded the words mountain and remittances”. In the last stage, we removed 3 more documents for the reasons given in
Figure 2. We did this for quality purposes, ensuring that only published and full documents are captured. Finally, 88 documents were considered for analysis.
3. Results and discussion
Our results are in two parts. We start by reporting results on the main journals, main authors, and focal country analysis. In the second phase, we present results from the bibliometric keyword co-occurrence analysis. At each unit of analysis, we highlight and discuss the key findings and where possible identify research gaps informing future studies on the interplay between migration, remittances, and livelihoods in Phuthadijthaba.
3.1. Main Journals
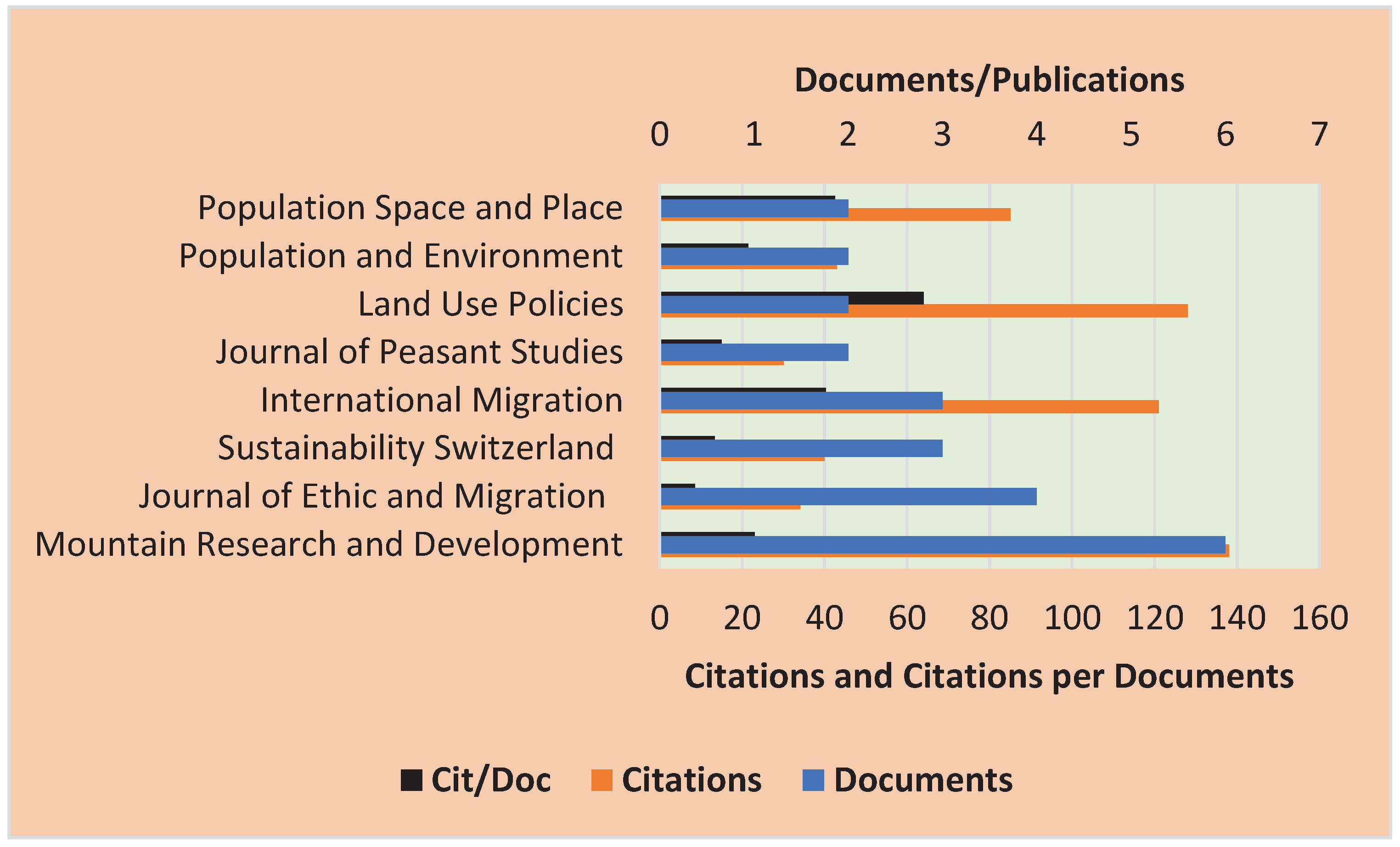
From Scopus database, the leading journals focusing on the interplay involving migration, remittances, and mountain issues are given in
Figure 3. In total, they provided 24(29.6%) of the final documents in Scopus. The leading journal is Mountain Research and Development with the most documents 6(7.4%) of the included documents. It also recorded the highest citation (128). This is followed by the Journal of Ethic and Migration 4(4.9%). These results can benefit future research interests on the interplay between migration, remittances, and sustainability issues in Phuthadijthaba, an emerging and marginalised mountainous City. Firstly, more information can be obtained from these top journals. The MRD is the most relevant source, because unlike other journals, is centered on mountain life. Its three peer-reviewed sections, MountainDevelopment, Mountain Research, and MountainAgenda, zero in on Transformation Knowledge”, Systems Knowledge,” and Target Knowledge” aspects (Scimago Research Group, 2023). As further results will show, it speaks more on migration, remittances, and outcomes of interest in mountainous areas.
3.2. Main authors
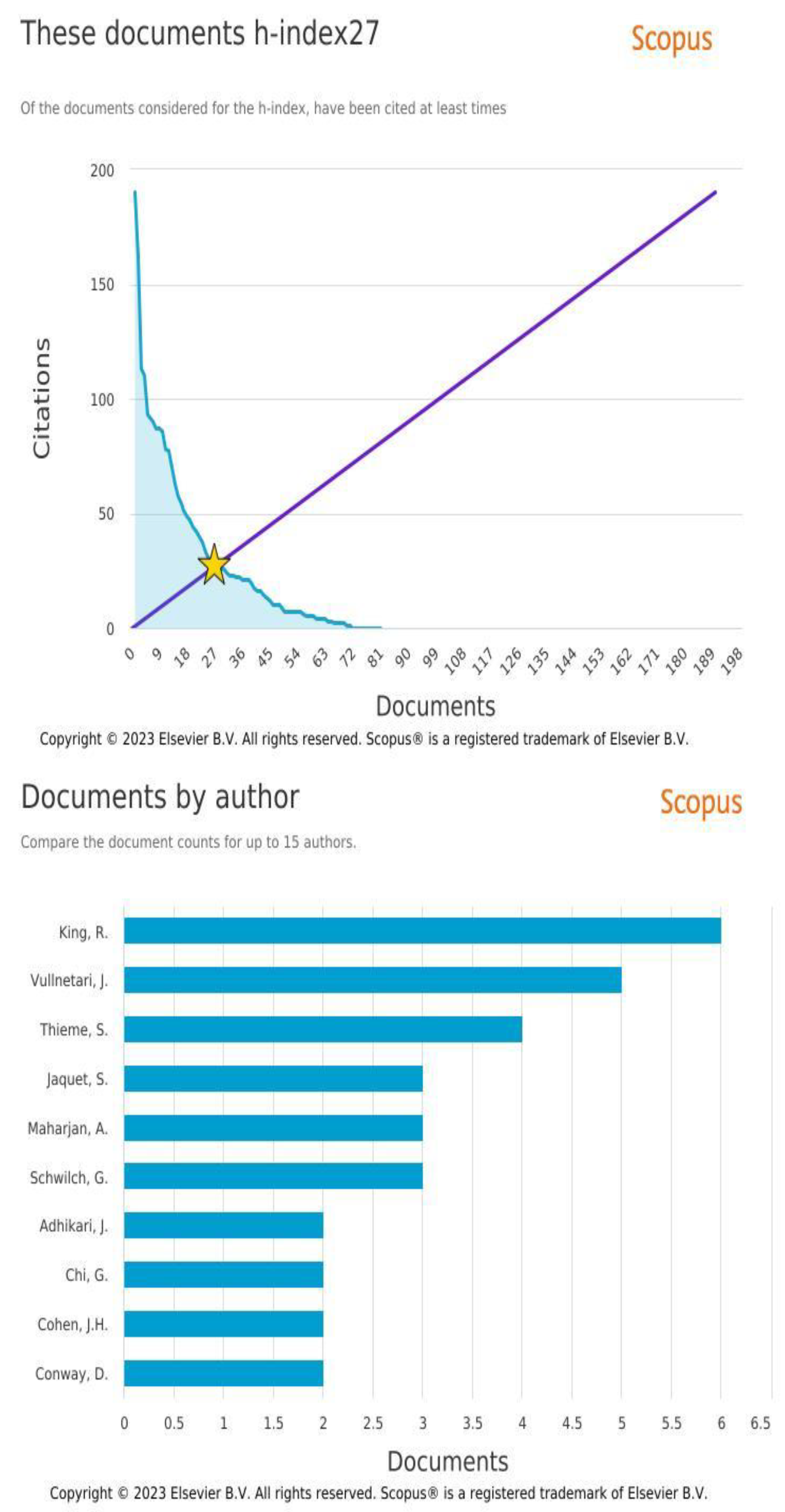
Results of author analysis are illustrated in
Figure 4(b). The main author is King, who collaborated in 6 publications (Russel King, Dalipaji, and Mai 2006; Russell King, Castaldo, and Vullnetari 2011; Russell King and Vullnetari 2006, 2009a, 2009b; Vullnetari and King 2008). All the documents take Albania as a migrant sending country and focuses on the gender and family aspects of remittances among the recipients, mainly women and the elderly. Out migration of people in mountain communities like Phuthaditjhaba can result in elderly, children and women remaining behind while other groups migrate to find better opportunities elsewhere. From the literature we deduce that the role of remittances is guided by gender and patriarchal issues. Also, in King et al. (2011), King & Vullnetari (2006), and Vullnetari & King (2008) the role of remittances in cushioning sending households from social isolation and loss of intimate-based trans-generational care and family relations is appreciated.
In King et al. (2011), the poverty alleviation role of remittances is confirmed. Only one, (Russell King and Vullnetari 2006) emphasized on internal migration as others focus on international migration. While King’s work is limited in terms of lack of heterogeneity (by focusing on Albania), and in time space, we draw important takeaways. Firstly, Albania becomes a potential candidate for comparable research from which Phuthadijthaba can benefit from. Secondly, we pick that the role of internal migration is sidelined even by top scholars in the field, irrespective of its dominance and potential. From this perspective, considering the economic impact of internal migration and remittances becomes an area of interest.
3.3. Country analysis
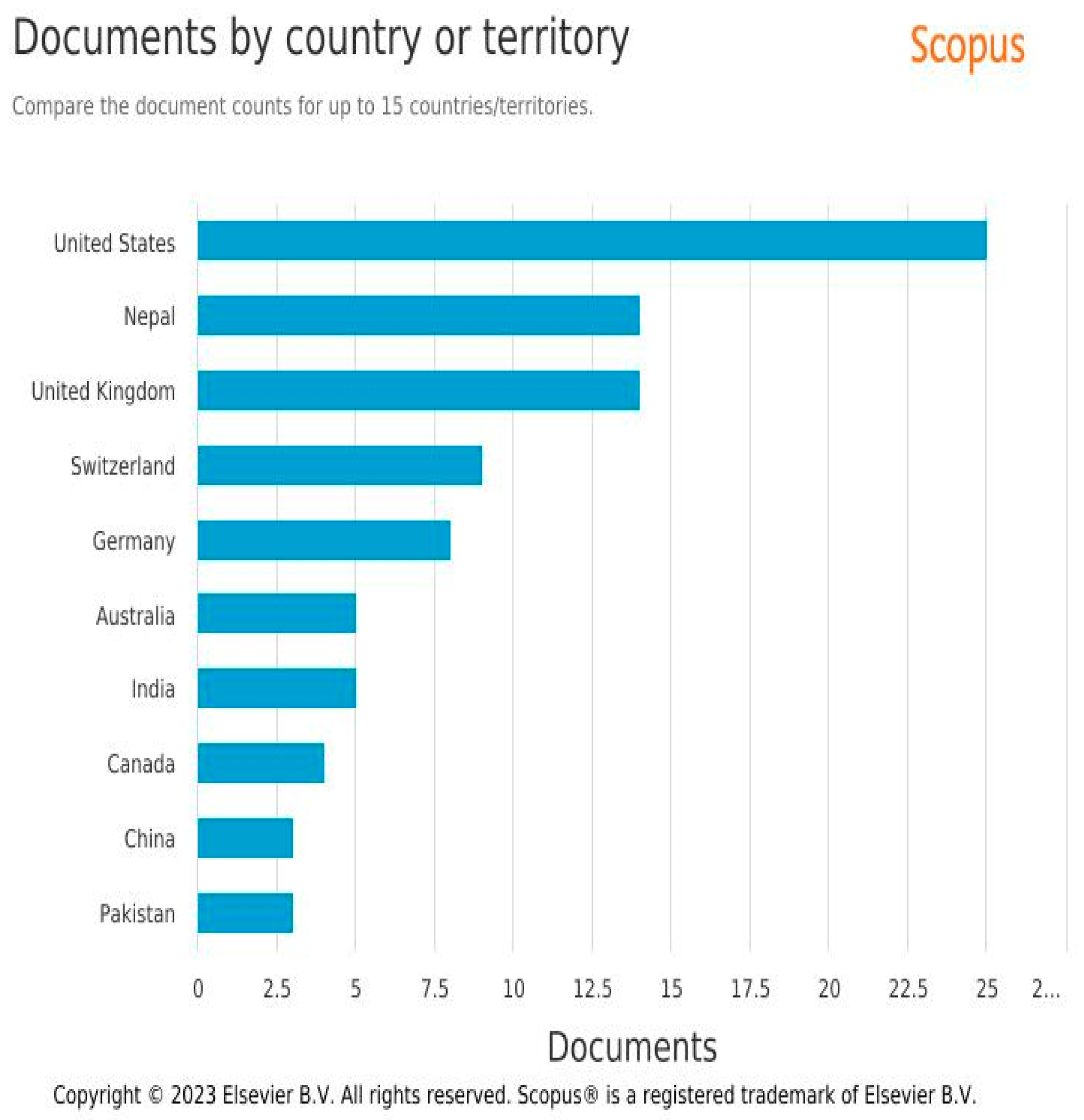
The main country associated with research on migration, remittances and mountain communities is the United States of America (USA) followed by Nepal receiving 25 and 14 document mentions respectively. We find USA’ s dominance not surprising, as has been the case in the past 40 decades, it remains the principal destination of migration. As shown in the IOM World Report on Migration, in 2020, the USA was home to 51 million migrants, with German a distant second with 16 million (McAuliffe and Triandafyllidou 2021). Given its proximity to Central American countries, most of which are mountainous, its logical that many studies have examined how such receiving countries are impacted. Since the impact of migration is mainly on sending countries, we find Nepal to be a more interesting case than USA.
The 14 documents on Nepal mainly focus the effects of migration and remittances on agriculture systems (Atreya 2022; Karki Nepal, Nepal, and Bluffstone 2022; A Maharjan and Knerr 2019), forestry systems (Bhandari et al. 2022; Shahi et al. 2022) or both (Sharma and Sharma 2017), and land management systems (Jaquet et al. 2016; Schwilch et al. 2017). Evidence by Atreya (2022) shows that overall, remittances positively impacts maize yield, and therefore food security. Nepal Karki et al. (2022) associate the positive impact of migration and remittances to its technology transfer effect. We also picked that another important role remittances play in mountainous communities is diversification of recipient household income. The findings by Shahi et al. (2022) and Maharjan et al. (2020) document that remittances lessens reliance on forest and agriculture income. These are the two major sources of income in mountainous areas, as well as worst affected by climate change. Phuthaditjhaba has pockets of agriculture activities, real estate and infrastructure development and other lively activities (Nawaz Hakro and Ahmad Fida 2009) (van Biljon 2023). Investigating the impact of migration and remittances on such activities can give an insight on the impact.
Accordingly, the role of remittances in climate adaptation strategies cannot be overlooked in mountainous communities such as Phuthadijthaba. While other mountainous areas are endowed with forestry resources they can count on, Phuthadijthaba mountains are virtually treeless grasslands. Accordingly, there is no opportunity for remittance recipients to invest in the timber industry. At the same time, the findings here suggest a potential area of investment that can go a long way in reducing poverty and climate change vulnerability. Phuthaditjhaba experiences harsh climatic conditions ranging from very cold temperatures, snow, hailstorm, flash floods and windy conditions (van Biljon 2023). It is importance to understand the role remittances play towards resilience against these harsh climatic conditions of Phuthaditjhaba.
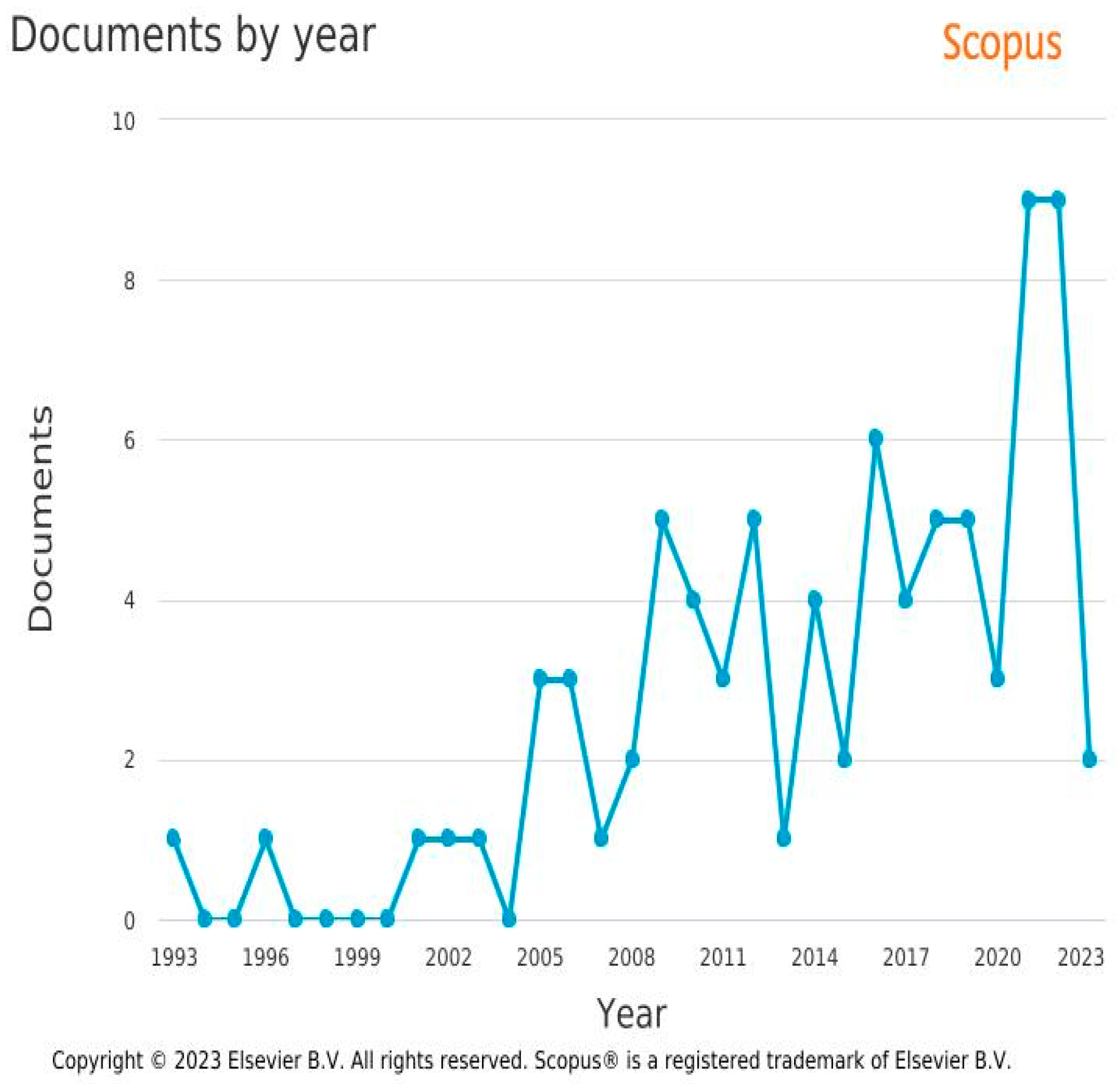
Figure 5.
(a) Documents by year (b). Documents by country.
Figure 5.
(a) Documents by year (b). Documents by country.
In addition, migration and remittances are found to have environmental sustainability effects. As Jaquet et al. (2023) show, remittances are mainly used for food and goods and less on agriculture. As a result, pressure on land is reduced. Also, internal movement to low lying lands and marketplaces often leads to land abandonment, which may comprehend environmental sustainability. This is complemented by Bhandari et al. (2022) who found out that remittances have led to increased forest regeneration in Nepal.
The takeaway point from these studies is that, in analyzing effects of remittances, emerging transmission mechanisms like technology transfer must be explored. Also, we acknowledge the growing role remittances are playing in climate adaptation strategies in mountainous areas. These findings are quite important in analyzing the interplay between migration, remittances, and sustainability in Phuthaditjhaba. However, we note that less attention has been given to issues on poverty eradication, and transition to green energies. While in the former, one argument can be the differences in the poverty levels (high in Phuthaditjhaba), the same cannot be said about the latter. As global environmental sustainability becomes the flagship policy focus, examining the role of remittances in renewable energy transition can help shape the same is mountainous areas.
Another finding we note from the country analysis is the dearth of such studies in Africa. Only three Ethiopia, Kenya, and Morocco countries are mentioned in two studies (Agoumy and Tamim 2009; Sugden et al. 2022). Ethiopia and Kenya feature in a comparative study with Nepal (Sugden et al. 2022). The study examined the interplay between cyclical labour migration and agrarian transition in the three countries. The major finding is that migration is mainly motivated by capital markets expansion with mediation from domestic cultural, political, and ecological dynamics.
Furthermore, as in most of the evidence already reviewed in this paper, remittances income is associated with increased agricultural productivity growth on one hand and increased land burden on the other. The lack of studies from Africa requires a shift of focus. Most studies from the findings have shown that remittances are connected to various forms of livelihoods, and climate related dynamics in mountainous areas. The case for Africa, and indeed Phuthadijthaba carries more weight considering higher levels of poverty and climate change vulnerabilities.
3.4. Key words
To generate deeper analysis of the main targeted aspects, we further carried out a bibliometric analysis of the key words from documents in Scopus. Results are shown in
Figure 6,
Figure 7 and
Figure 8.
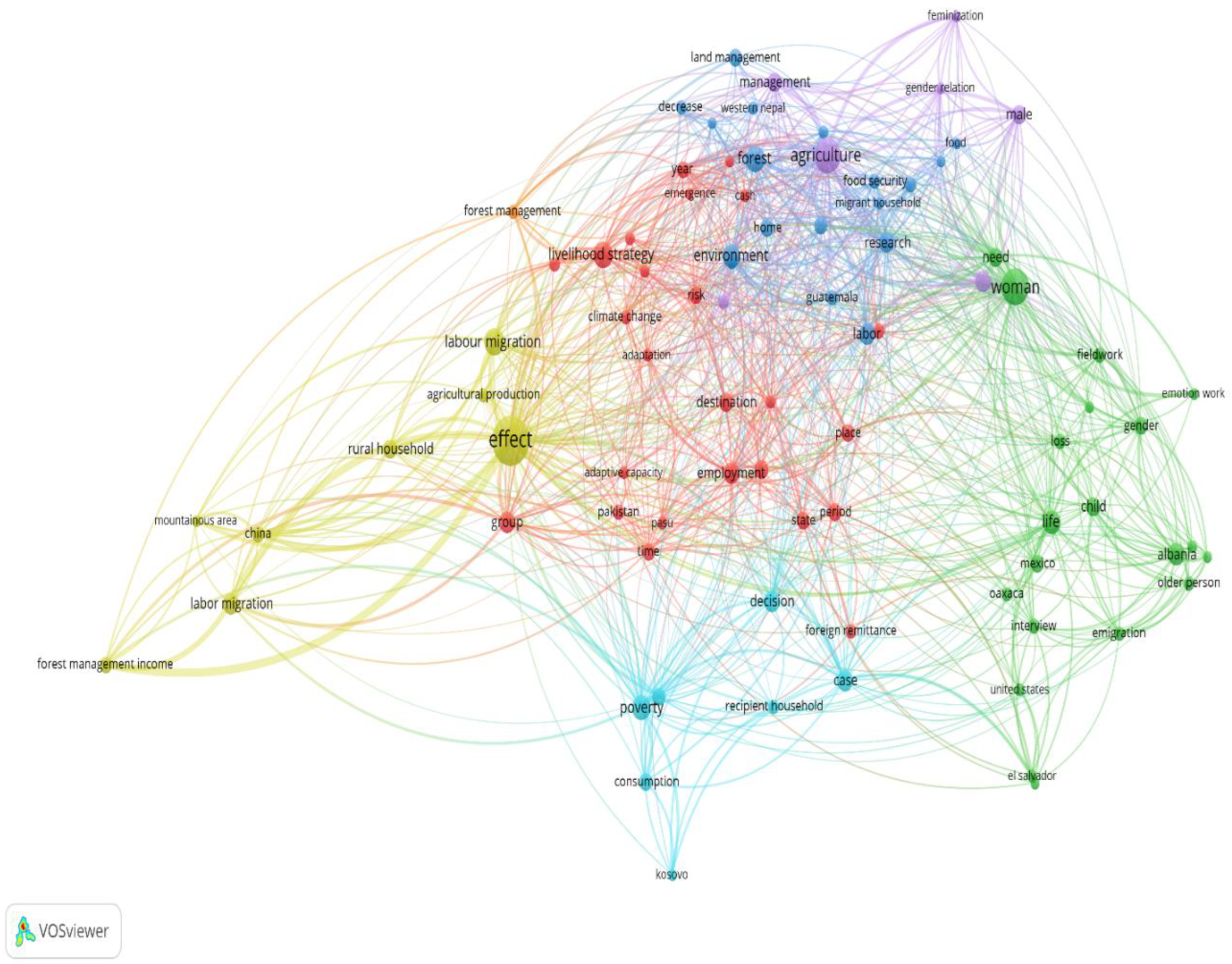
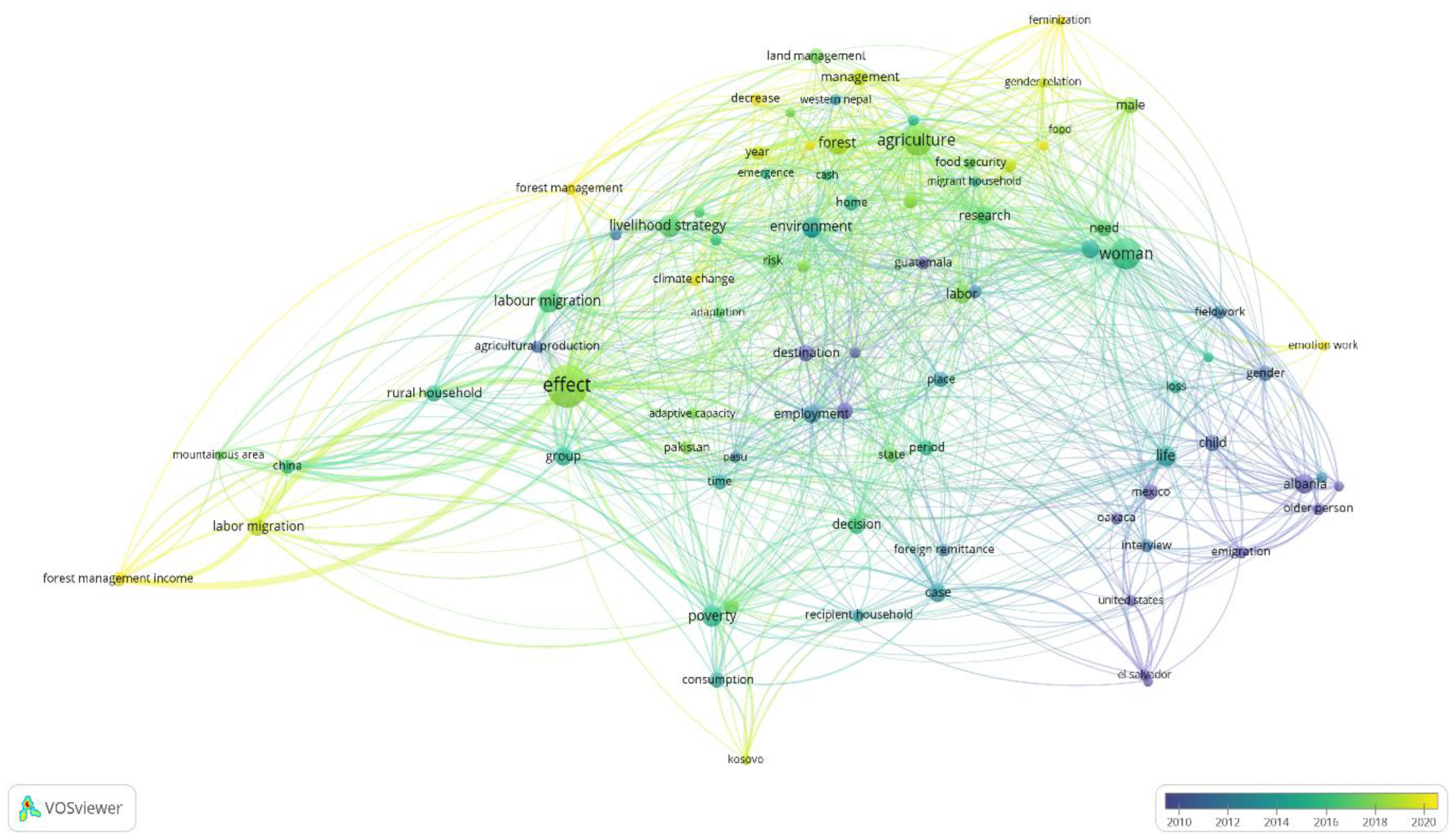
Figure 6 shows the Network Visualization showing the clusters, co-occurrences of words, number of links and strength of links. The network was generated from VOSViewer software (Eck and Waltman 2023). The Network Visualisation is showing the heatmap of the key words that were mentioned at least 5 times in all the studies under our literature review. Results of the bibliometric key word co-occurrence are explained by five elements of the visualization: the item, link, strength, network, and cluster.
An item is the unit of analysis, in our case key words. A link is a path connecting two terms (key words) with the connection measured by some positive value showing its strength (Eck and Waltman 2023). The link and strength in
Figure 6 therefore capture the number of documents/publications in which two key-words co-exist. A collection of items and links gives the network. Lastly, a cluster or community shows a group of strongly related items. The key words are shown in nodes, whose size and label shows their weight. Also, the distance between nodes show the relatedness of the key words (Eck and Waltman 2023).
Accordingly, it can be observed from
Figure 6 that the word effect has the biggest node, having been mentioned at least five times in 77 publications
2. The word has 69 links with a strength of 1036 (See
Table 1). In the vicinity of the effect node are the words agricultural production, rural household, labor migration, and adaptive capacity. The results suggest that most studies were examining the effect of migration and remittances on matters on various issues affecting mountain communities. Effect analysis was stronger on the nearby nodes. The second biggest node is on women”, with 41 co-occurrences and 50 links with a strength of 437. Its neighborhood is made up of the words gender, feminization, child, male, food security, male relations, and migrant household, among others.
The findings here shows that women are a focal group in the migration-remittances-mountain relationship. This area was mainly covered by (Russel King, Dalipaji, and Mai 2006; Russell King, Castaldo, and Vullnetari 2011; Russell King and Vullnetari 2009a) among others. The main findings from these studies were discussed under author analysis. Food security, child, and loss are close by to reflect the vulnerability of women to migration. It has been shown that women are less likely to migrate, and are left to take care of the children, are exposed more to loss of social intimacy and face food insecurity (Atreya 2022; Jaquet et al. 2016; Amina Maharjan et al. 2020; Satyal et al. 2017). It is critical to explore how migration and remittances impact women and their economic role in Phuthaditjhaba. Zooming the women” node (in VOSViewer) also shows that labour migration” is the furthest connection, signaling relatively low labor migration than males (Amina Maharjan et al. 2020). The rest of the research hotspots are shown in the co-occurrence’s statistics in
Table 1.
The results we presented in
Table 1 are of great importance to scholars, funders, and research institutions at large. If remittances are to propel the livelihoods of people in mountainous communities, then more effort should be put on the hotspots to maximize the return and minimize the costs of migration and remittances. Nonetheless, looking at
Table 1, we make an important observation. Emerging issues that stakeholders should focus on are not received deserving attention. In particular, transition to renewable energies has become an increasingly important feed into the global efforts to combat climate change. Mountainous communities are associated with energy poverty (Katsoulakos and Kaliampakos 2018). In its Renewables Readiness Assessment of the Kingdom of Bhutan, a mountainous country, the Renewable International Energy Agency (2019) revealed that despite the terrain, the potential for generation of renewable energy from solar and wind is huge. Key to the exploitation of the huge potential is financing.
It will be interesting therefore to analyze the role remittances can play in renewable energy transition in mountainous areas. In Phuthadijthaba, such an investigation is even more important for one major reason. The energy poverty is exacerbated by unavailability of alternative energy sources due absence of woodlands. In addition, the city experiences long hours of electricity load shedding. Also, there is very little uptake of solar energy, while there is no wind energy infrastructure. Accordingly, finding out how remittances can contribute to clean energy sustainability in Phuthadijthaba becomes imperative.
We also generated variants of the Network visualization in
Figure 7 and
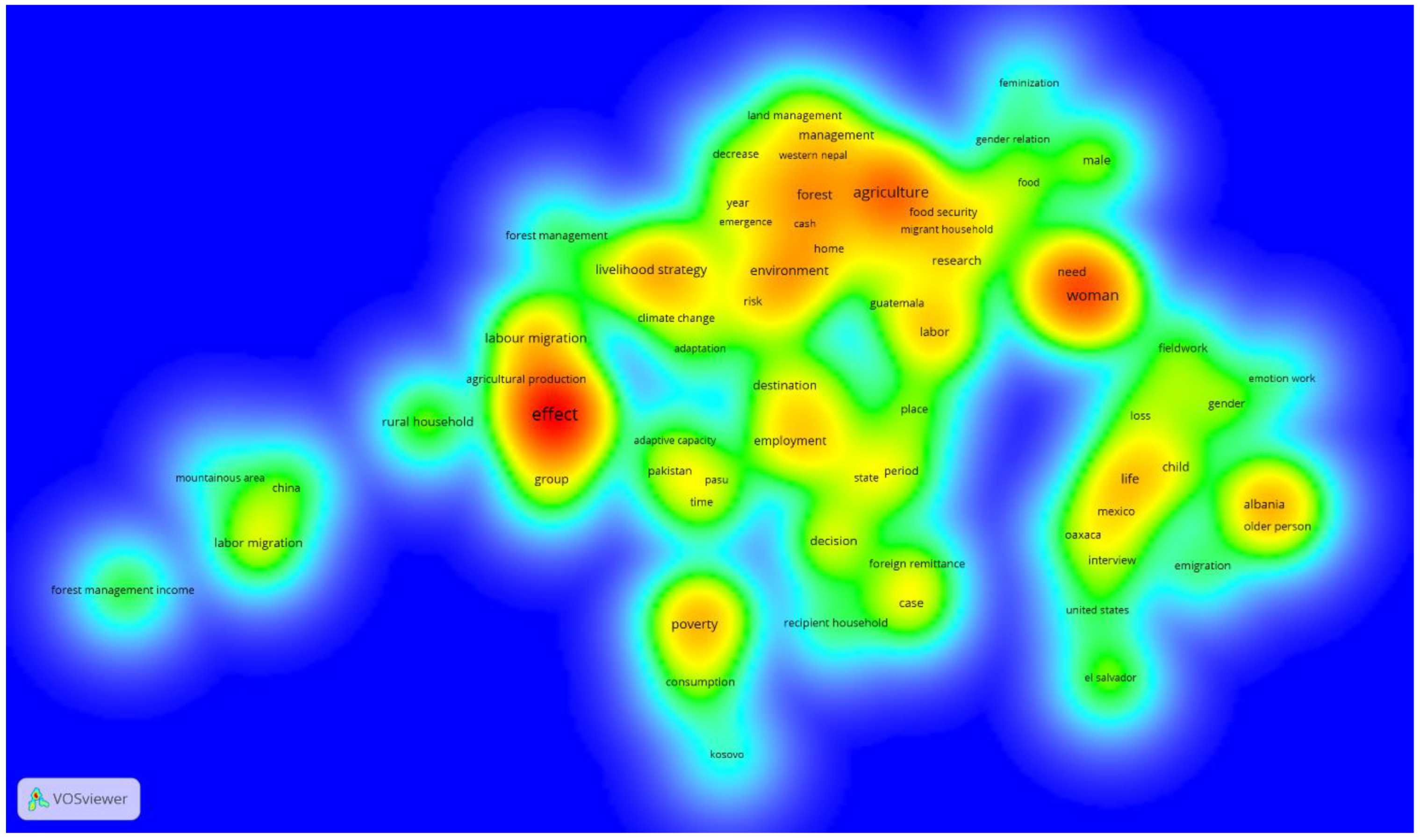
Figure 8. The former is a Density Visualisation and the latter is an Overlay visualisation. These provides another angle into our analysis. In
Figure 7, every point in the visualization has a colour that shows the density of key words at that point. The colours range from blue(lowest weight) to red(highest weight). It can be seen that the key words with the highest co-occurrence, links, link strength in
Table 1 are in the red zones. This identifies them as hotspots of research.
Similarly in
Figure 8, the Overlay visualisation reveals the scores for each key word, with the size proportional to the colour (blue lowest, yellow highest). We related the key word score to years, as shown in the key bar. From this, we are able to see the emerging trends in studies over time. For instance, focus has been moving from the determination of migration and foreign remittances to effects on land management, gendering issues, and food security, among others.
4. Conclusion and areas of further research
In light of these findings, we proffer important recommendations to researchers and policy makers with interests in migration, remittances and mountainous communities. We then suggest areas of research targeting Phuthadijthaba. Our findings on source documents reveals that Mountain Research and Development (MDR) journal is the most productive. As such researchers can rely on it for literature review and possible publication of their work. From author analysis, we find King Russel to be the main author. However, all his research were on Albania and the recent captured publication is over a decade old. Even so, drew important takeaways: (1) Albania becomes a potential candidate for comparable research from which Phuthadijthaba can benefit from (2) we pick that the role of internal migration is side-lined even by top scholars in the field, irrespective of its dominance and potential. From this perspective, considering the economic impact of internal migration and remittances becomes an area of interest.
Country analysis showed that Nepal is the most researched, and our studies on Phuthadijthaba can benefit from trans-local research. However, we note that less attention has been given to issues on poverty eradication, and transition to green energies. While in the former, one argument can be the differences in the poverty levels (high in Phuthaditjhaba), the same cannot be said about the former. As global environmental sustainability becomes the flagship policy focus, examining the role of remittances in renewable energy transition can help shape the same is mountainous areas.
Lastly, bibliometric co-word analysis pointed to gender, feminization, child, male, food security, male relations, and migrant household as the most studied areas. Researchers seeking to evaluate the impact of remittances can concentrate on these issues. Equally, organisations and governments can also focus funding, expenditure, and policy aspects one these hotspots. In a nutshell, our next studies on Phuthadijthaba will heavily get focus from these findings. Despite the contribution the study has made, other possible sources of literature such as Google scholar were not considered for data points. While we raise quality issues, including these may broaden the evidence.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Regret Sunge and Calvin Mudzingiri; Methodology, Regret Sunge; Software, Regret Sunge; Validation, Calvin Mudzingiri; Resources, Calvin Mudzingiri; Writing – original draft, Regret Sunge; Writing – review & editing, Calvin Mudzingiri.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
| 1 |
By area covered by mountains (World Population Review 2023) |
| 2 |
These values are obtained from zooming the data in VOSViewer, the files are attached in Appendix. One needs to install VOSViewer (downloadable for free at www.vosviewer.com). |
References
- Agoumy, Taoufik, and Mohamed Tamim. 2009. Migration, Networks and Territories in the Migration, Networks and Territories in the Ouneine Valley, High Atlas, Morocco. Journal of Ethnic and Migration Studies 35: 1679–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atreya, Kishor. 2022. Changing Gender Role Declines Maize Yield, but Remittances Offset: Findings from Migrant Households in the Central. Outlook on Agriculture 51: 247–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baas, Jeroen, Michiel Schotten, and Andrew Plume. 2020. Scopus as a Curated, High-Quality Bibliometric Data Source for Academic Research in Quantitative Science Studies. Quantitative Science Studies 1: 377–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, Roshan, and et al. 2022. Land Use Policy A Systematic Review and Gap Analysis of Drivers, Impacts, and Restoration Options for Abandoned Croplands in Nepal. Land Use Policy 120: 106237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, James G. 2020. Leave No One Behind: Guidelines for Project Planners and Practitioners.
- Bhandari, Ajay, and et al. 2022. Land Cover Change and Its Impact in Crop Yield: A Case Study from Western Nepal. e Scientific World Journal 2022: 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Biljon, Louw. 2023. Imagining the Future Phuthaditjhaba—Vision 2121. In Sustainable Futures in Southern Africa’s Mountains:Sustainable Development Goals Series. Edited by A. Membretti, S.J. Taylor and J.L. Delves. Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Carrera-Rivera, Angela, William Ochoa, Felix Larrinaga, and Ganix Lasa. 2022. MethodsX How-to Conduct a Systematic Literature Review: A Quick Guide for Computer Science Research✩. MethodsX 9: 101895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, Iain, Larry V Hedges, and Harris Cooper. 2002. A Brief Hoistory of Research Synthesis. Evaluation and the health proffessions 25: 12–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimensions. 2023. The World’s Largest Linked Research Database. Available online: https://www.dimensions.ai/ (accessed on 11 March 2022).
- Donthu, Naveen, and et al. 2021. How to Conduct a Bibliometric Analysis: An Overview and Guidelines. Journal of Business Research 133: 285–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, Nees Jan Van, and Ludo Waltman. 2023. Manual for VOSviewer Manual Version 1.6.19. (January). Available online: https://www.coursehero.com/file/192773571/Manual-VOSviewer-1619pdf/.
- Food and Agriculture Organization. 2011. Why Invest in Sustainable Mountain Development? Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization. https. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/i2370e/i2370e.pdf.
- Food and Agriculture Organization. 2020. Vulnerability of Mountain Peoples to Food Insecurity: Updated Data and Analysis of Drivers. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization. [Google Scholar]
- Gurung, Anup, and Sang Eun Oh. 2013. Conversion of Traditional Biomass into Modern Bioenergy Systems: A Review in Context to Improve the Energy Situation in Nepal. Renewable Energy 50: 206–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunzai, Kiran. 2010. Labour Migration and Remittances in the Mountains of Pakistan. Kathmandu, Nepal. [Google Scholar]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. 2022. Poverty, Livelihoods and Sustainable Development. In Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Edited by H.-O. Pörtner et al. Cambridge and New Yor: University Press, pp. 1171–274. [Google Scholar]
- Jaquet, Stephanie, Gitta Shrestha, Thomas Kohler, and Gudrum Schwilch. 2016. The Effects of Migration on Livelihoods, Land Management, and Vulnerability to Natural Disasters in the Harpan Watershed in Western Nepal. Mountain Research and Development 36: 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki Nepal, Aspara, Mani Nepal, and Randall Bluffstone. 2022. Labour Outmigration, Farmland Fallowing, Livelihood Diversification and Technology Adoption in Nepal. International Labour Review In Press. [Google Scholar]
- Katsoulakos, Nikolas M, and Dimitris C. Kaliampakos. 2018. The Energy Identity of Mountainous Areas: The Example of Greece. Journal of Mountain Science 15: 1429–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, Russel, Mirela Dalipaji, and Micola Mai. 2006. Gendering Migration and Remittances: Evidence from London and Northern Albania. Population, Space and Place 12: 409–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, Russell, Adriana Castaldo, and Julie Vullnetari. 2011. Gendered Relations and Filial Duties Along the Greek-Albanian Remittance Corridor. Economic Geography 87: 393–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, Russell, and Julie Vullnetari. 2006. Orphan Pensioners and Migrating Grandparents: The Impact of Mass Migration on Older People in Rural Albania. Ageing and Society 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, Russell, and Julie Vullnetari. 2009a. Remittances, Return, Diaspora: Framing the Debate in the Context of Albania and Kosova. Southeast European and Black Sea Studies ISSN 9: 385–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, Russell, and Julie Vullnetari. 2009b. The Intersections of Gender and Generation in Albanian Migration, Remittances and Transnational Care. Geografiska Annaler: Series B, Human Geography ISSN 91: 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, Vivek, Singh Prashasti, Singh Mousumi, and Karmakar Jacqueline. 2021. The Journal Coverage of Web of Science, Scopus and Dimensions: A Comparative Analysis. Scientometrics 126: 5113–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lages, Cristiana R, Rodrigo Perez-vega, Selma Kadic-Mglajlic, and Niloofar Borghei-Rzavi. 2023. A Systematic Review and Bibliometric Analysis of the Dark Side of Customer Behavior: An Integrative Customer Incivility Framework. Journal of Business Research 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lame, Guillaume The. 2019. Systematic Literature Reviews: An Introduction. Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Engineering Design (ICED19), Delft, 5–8 August 2019; Available online: https://www.cambridge.org/core/services/aop-cambridge-core/content/view/40D4CEA7A7CC3FB6ED6233E79A0A2A1F/S2220434219001690a.pdf/systematic_literature_reviews_an_introduction.pdf.
- Li, Hengyun, Lingyan Zhang, and Cathy H C Hsu. 2023. Research on User-Generated Photos in Tourism and Hospitality: A Systematic Review and Way Forward. Tourism Management 96: 104714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharjan, A, and B Knerr. 2019. Impact of Migration and Remittances on Agriculture: A Micro–Macro-Analysis. In Agricultural Transformation in Nepal. Edited by G. Thapa, A. Kumar and P. Joshi. Singapore: Springer Nature. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharjan, Amina, and et al. 2020. Migration and Household Adaptation in Climate-Sensitive Hotspots in South Asia. Current Climate Change Reports 1: 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maluti-a-Phofung Municipality (MaP). 2019. In Integrated Development Plan Maluti a Phofung 2018–2019. National Treasury, Republic of South Africa. Pretoria.
- McAuliffe, M, and A Triandafyllidou. 2021. International Organization of Migration (IOM). In World Migration Report 2022. Edited by M. McAuliffe and A. Triandafyllidou. Geneva, Switzerland: International Organization for Migration. Available online: https://publications.iom.int/books/world-migration-report-2022.
- Membretti, Andrea, Sue Jean Taylor, and Jess L. Delves. 2023. Sustainable Futures in Southern Africa’s Mountains. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland. [Google Scholar]
- Mengist, Wondimagegn, and Teshome Soromessa. 2020. MethodsX Method for Conducting Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis for Environmental Science Research. MethodsX 7: 100777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukwada, Geofrey, and Sarudzai Mutana. 2023. Surviving the Limits Imposed by a Changing Climate: The Case of Urban Drought and Water Supply Sustainability in Phuthaditjhaba. In Sustainable Futures in Southern Africa’s Mounatnous Cities: Multiole Perspectives of an Emerging City. Edited by Adrea Membretti, Sue Jean Taylor and Jess L. Delves. Springer Nature Switzerland. [Google Scholar]
- Nawaz Hakro, Ahmed, and Bashir Ahmad Fida. 2009. Trade and Income Convergence in Selected South Asian Countries and Their Trading Partners. the Lahore Journal of Economics 14: 49–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, Matthew J, and et al. 2021. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses. Research Methods and Reporting. [Google Scholar]
- Poklepović, Tanveer Tina, and Sarah Peričić. 2019. Why Systematic Reviews Matter? A Brief History, Overview and Practical Guide for Authors. Available online: https://www.elsevier.com/connect/authors-update/why-systematic-reviews-matter (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- Renewable International Energy Agency. 2019. Renewables Readiness Assessment: Kingdom of Bhutan. Abu Dhabi. Available online: https://www.irena.org/publications/2019/Dec/Renewables-Readiness-Assessment-Kingdom-of-Bhutan.
- Santoro, Antonio. 2023. Traditional Oases in Northern Africa as Multifunctional Agroforestry Systems: A Systematic Literature Review of the Provided Ecosystem Services and of the Main Vulnerabilities. Agroforestry Systems 97: 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyal, Poshendra, Krishna Shrestha, Hemant Ojha, and Bhaskar Vira. 2017. A New Himalayan Crisis ? Exploring Transformative Resilience Pathways. Environmental Development 23: 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ScalePay. 2023. Average Salary in Phuthaditjhaba, South Africa. Available online: https://www.payscale.com/research/ZA/Location=Phuthaditjhaba/Salary (accessed on 28 May 2023).
- Schwilch, Gudrun, and et al. 2017. Impacts of Outmigration on Land Management in a Nepali Mountain Area. In Identifying Emerging Issues in Disaster Risk Reduction, Migration, Climate Change and Sustainable Development. Edited by K. Sudmeier-Rieux et al. Spinger Nature. [Google Scholar]
- Shahi, Neha, Prabin Bhusal, Ganesh Paudel, and Jude Ndzifon. 2022. Trees, Forests and People Forest — People Nexus in Changing Livelihood Contexts: Evidence from Community Forests in Nepal. Trees, Forests and People 8: 100223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G, and E Sharma. 2017. Agroforestry Systems as Adaptation Measures for Sustainable Livelihoods and Socio-Economic Development in the Sikkim Himalaya. In Agroforestry. Edited by J. Dagar and V. Tewari. Springer Nature Singapore. [Google Scholar]
- She, Yujuan, and et al. 2018. Constraints to Achieve Infrastructure Sustainability for Mountainous Townships in China. Habitat International 73: 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics South Africa. 2019. Four Facts about Our Provincial Economies. Data Stories (March). Available online: https://www.statssa.gov.za/?p=12056 (accessed on 5 March 2023).
- Sugden, Fraser, Likimyelesh Nigussie, Liza Debevec, and Ravic Nijbroek. 2022. Migration, Environmental Change and Agrarian Transition in Upland Regions: Learning From. The Journal of Peasant Studies ISSN 49. [Google Scholar]
- Vidal, Mosler E, and F Laczko. 2022. Migration and the SDGs: Measuring Progress. Geneva, Switzerland: Available online: https://publications.iom.int/system/files/pdf/SDG-an-edited-volume.pdf.
- Vullnetari, Julie, and Russell King. 2008. ‘Does Your Granny Eat Grass?’ On Mass Migration, Care Drain and the Fate of Older People in Rural Albania. Global Networks 8: 139–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Xinxin, Zeshui Xu, Yong Qin, and Marinko Skare. 2022. Foreign Direct Investment and Economic Growth: A Dynamic Study of Measurement Approaches and Results. Economic Research-Ekonomska Istraživanja 35: 1011–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wester, Philippus, Arabinda Mishra, Aditi Mukherji, and Arun Bhakta Shrestha. 2019. The Hindu Kush Himalaya Assessment:Mountains, Climate Change, Sustainability and People. eds. Philippus Wester, Arabinda Mishra, Aditi Mukherji, and Arun Bhakta Shrestha. Cham: Springer Nature Singapore. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. 2023. World Bank Development Indicators. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.MKTP.CD (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- World Population Review. 2023. Most Mountainous Countries in the World. Most Mountainous Countries in the World Author. Available online: https://worldpopulationreview.com/country-rankings/most-mountainous-countries%0AAbout (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Wymann von Dach, Susanne, and et al. 2018. Localizing the SDGs for Resilience of Mountain People and Ecosystems: Leaving No One in Mountains Behind. Available online: https://www.fao.org/fileadmin/user_upload/mountain_partnership/docs/Issue_Brief_Leaving_No_One_in_Mountains_Behind.pdf.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).