Submitted:
20 June 2023
Posted:
21 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
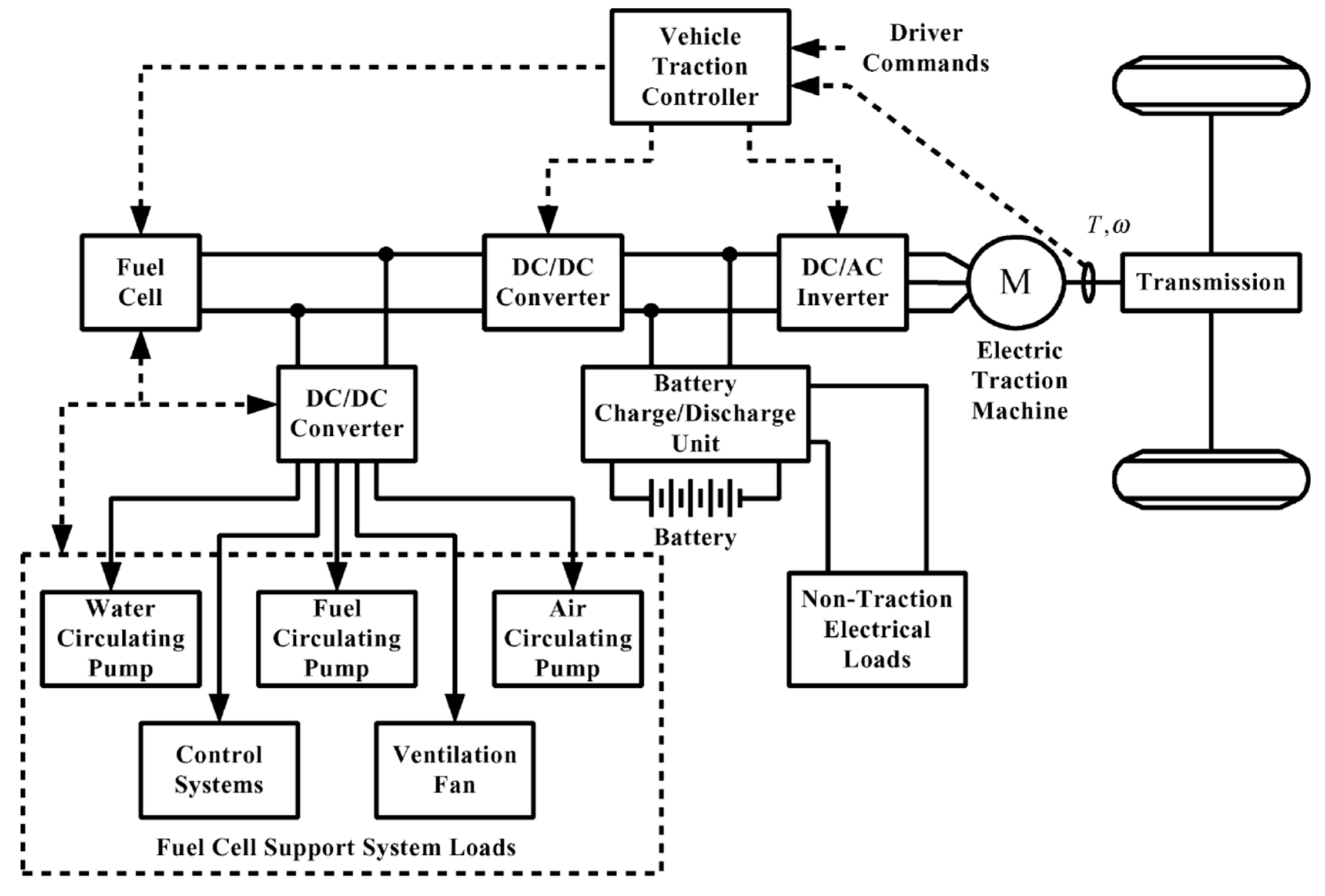
Fuel cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV)
Supercapacitor
Performance Simulation
Technical Data
Energy Evaluation
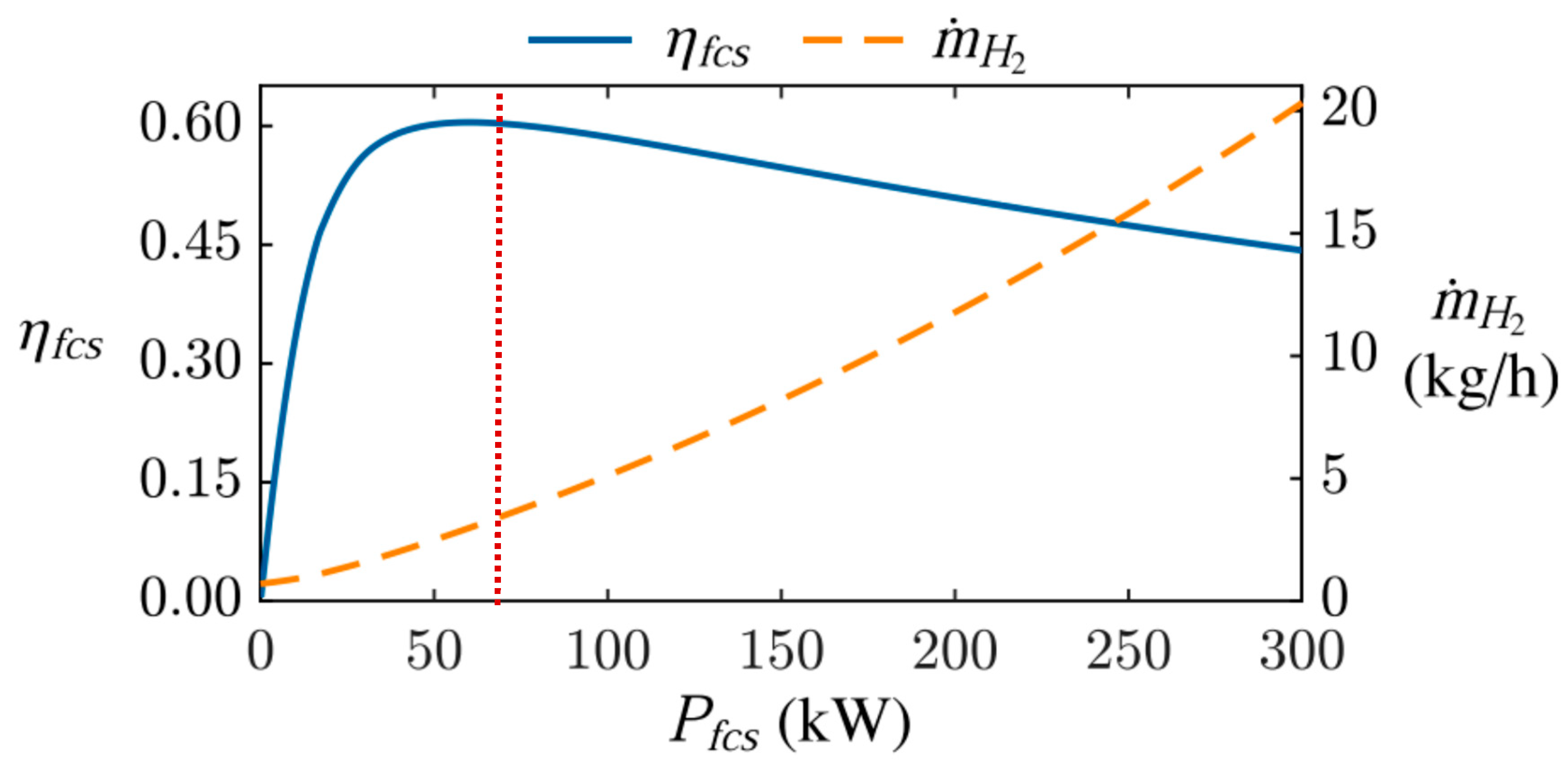
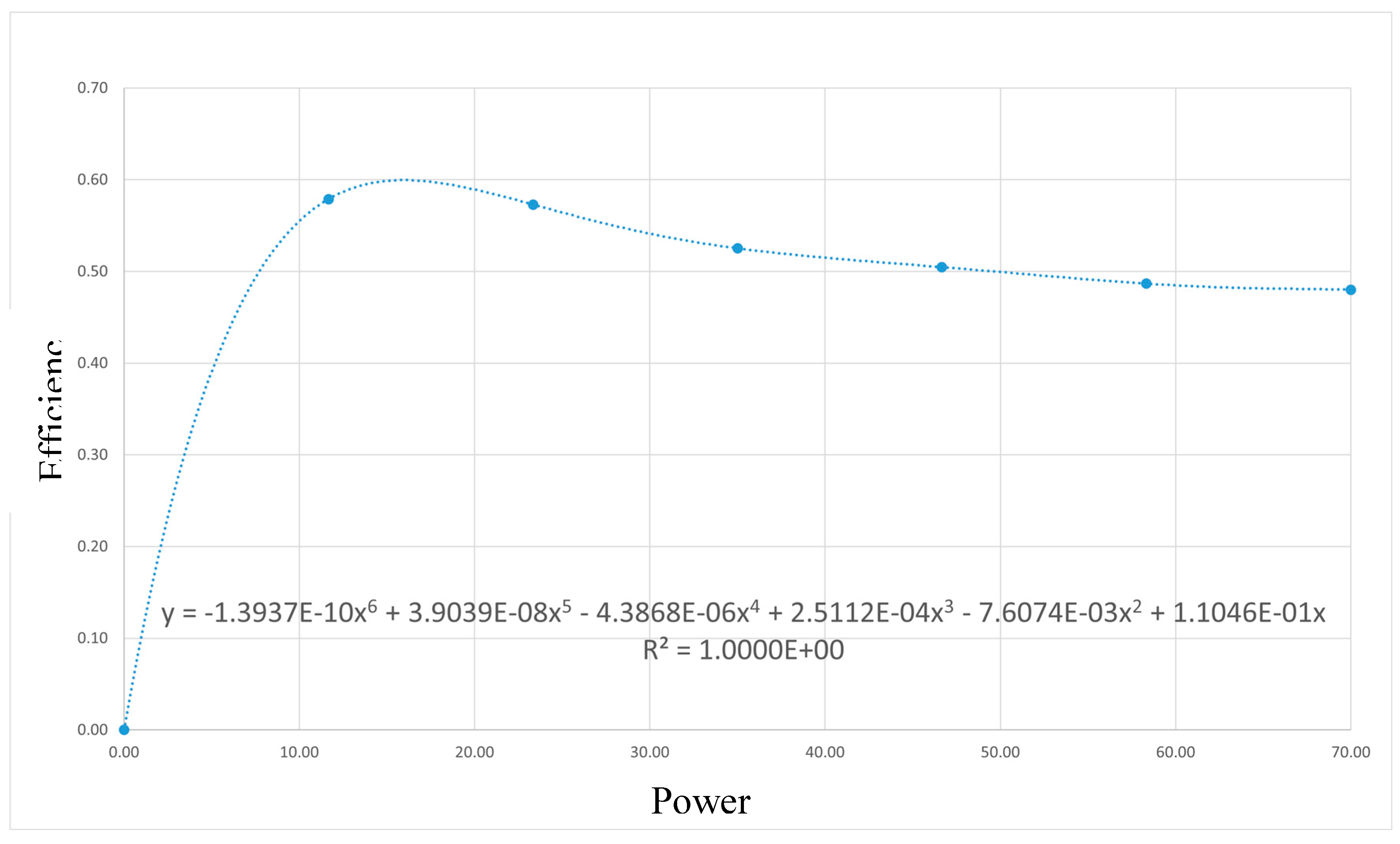
Simulation Results
| Driving mode | Energy demanding level | |||
| Magnitude | Low | Medium | High | |
| ECO | Charge consumption rate (Ah/km) | 0.468 | 0.470 | 0.472 |
| Energy consumption rate (Wh/km) | 187.316 | 188.090 | 188.760 | |
| Charge consumption rate (Ah/100 km) | 46.829 | 47.023 | 47.190 | |
| Energy consumption rate (Wh/100 km) | 18.732 | 18.809 | 18.876 | |
| Capacity (Ah) | 187.316 | 188.090 | 188.760 | |
| Energy (kWh) | 74.926 | 75.236 | 75.504 | |
| Battery mass (kg) | 549.594 | 551.315 | 552.802 | |
| NORMAL | Charge consumption rate (Ah/km) | 0.569 | 0.571 | 0.573 |
| Energy consumption rate (Wh/km) | 227.483 | 228.360 | 229.109 | |
| Charge consumption rate (Ah/100 km) | 56.871 | 57.090 | 57.277 | |
| Energy consumption rate (Wh/100 km) | 22.748 | 22.836 | 22.911 | |
| Capacity (Ah) | 227.483 | 228.360 | 229.109 | |
| Energy (kWh) | 90.993 | 91.344 | 91.644 | |
| Battery mass (kg) | 638.848 | 640.796 | 642.461 | |
| SPORT | Charge consumption rate (Ah/km) | 0.587 | 0.589 | 0.591 |
| Energy consumption rate (Wh/km) | 234.892 | 235.709 | 236.392 | |
| Charge consumption rate (Ah/100 km) | 58.723 | 58.927 | 59.098 | |
| Energy consumption rate (Wh/100 km) | 23.489 | 23.571 | 23.639 | |
| Capacity (Ah) | 234.892 | 235.709 | 236.392 | |
| Energy (kWh) | 93.597 | 94.284 | 94.557 | |
| Battery mass (kg) | 655.314 | 657.131 | 658.648 | |
| NORMAL/ECO | SPORT/NORMAL | SPORT/ECO |
| 1.214 | 1.032 | 1.254 |
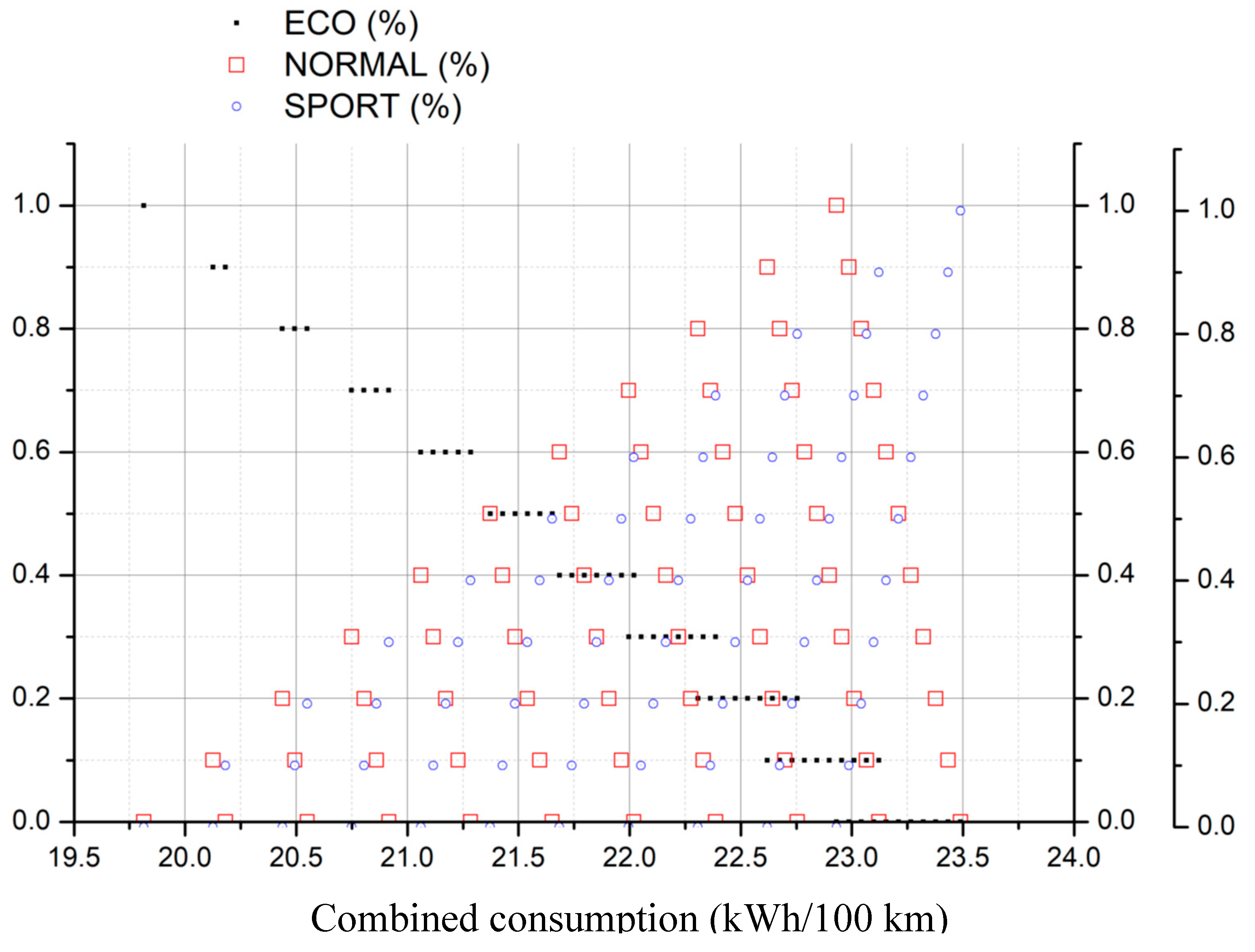
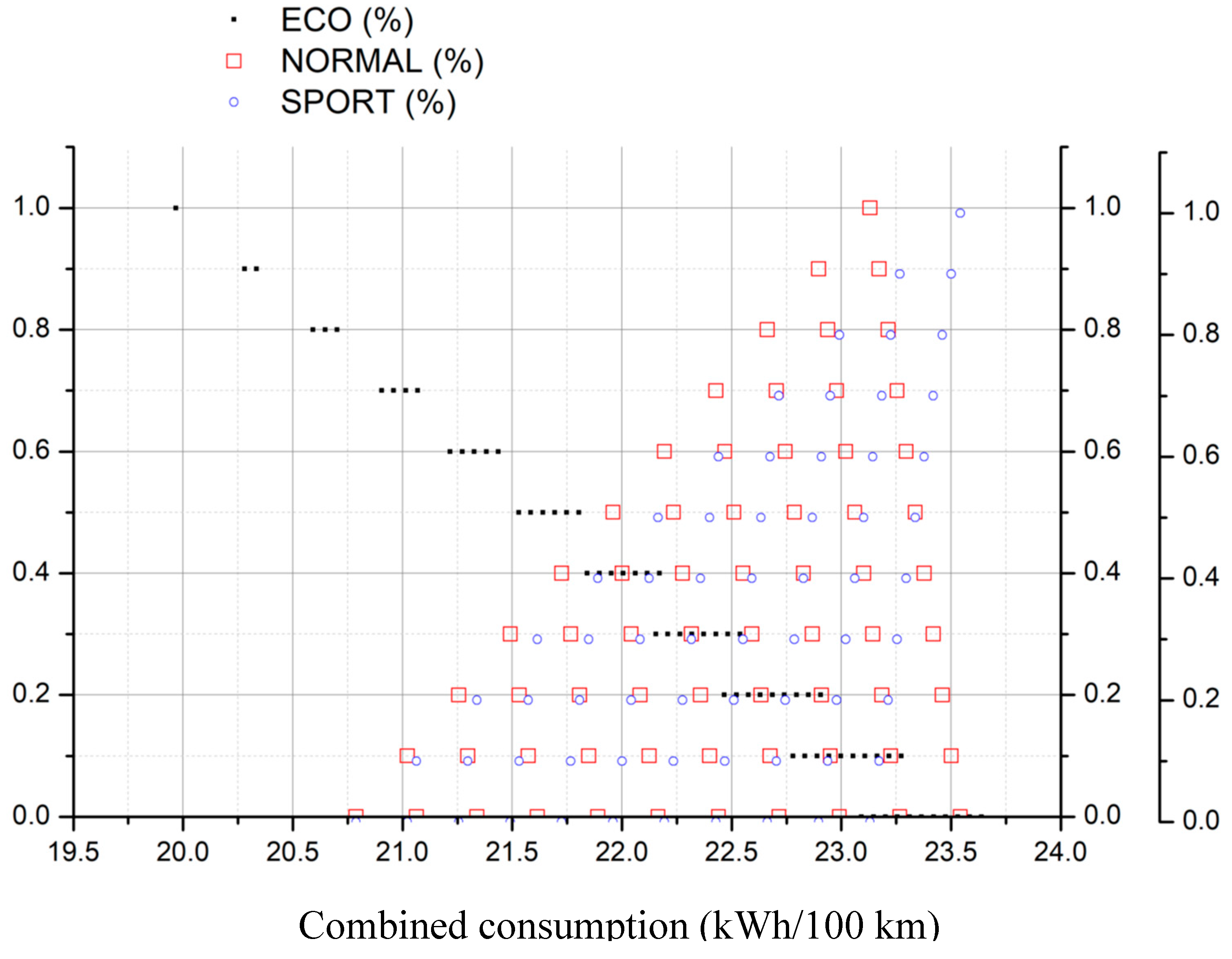
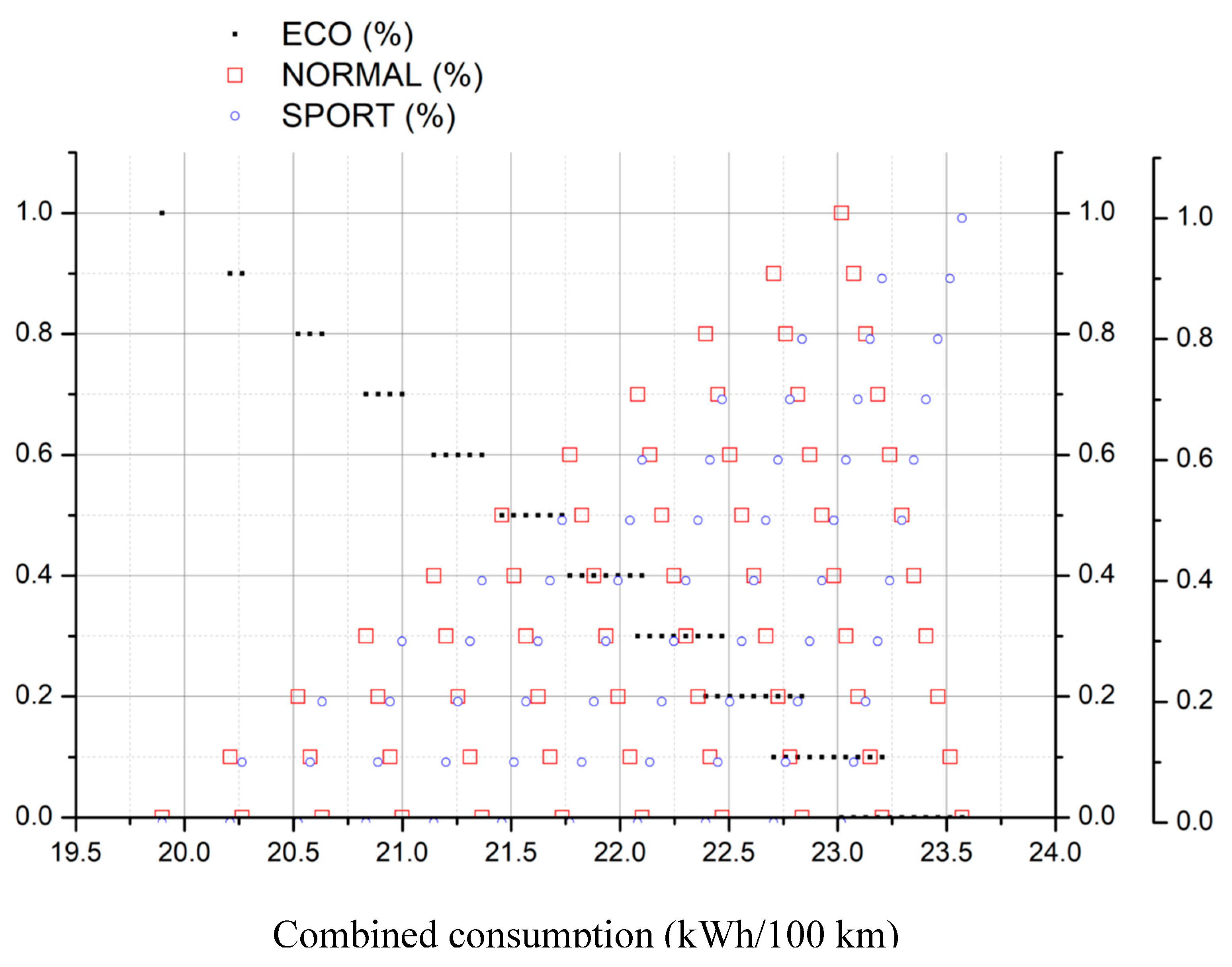
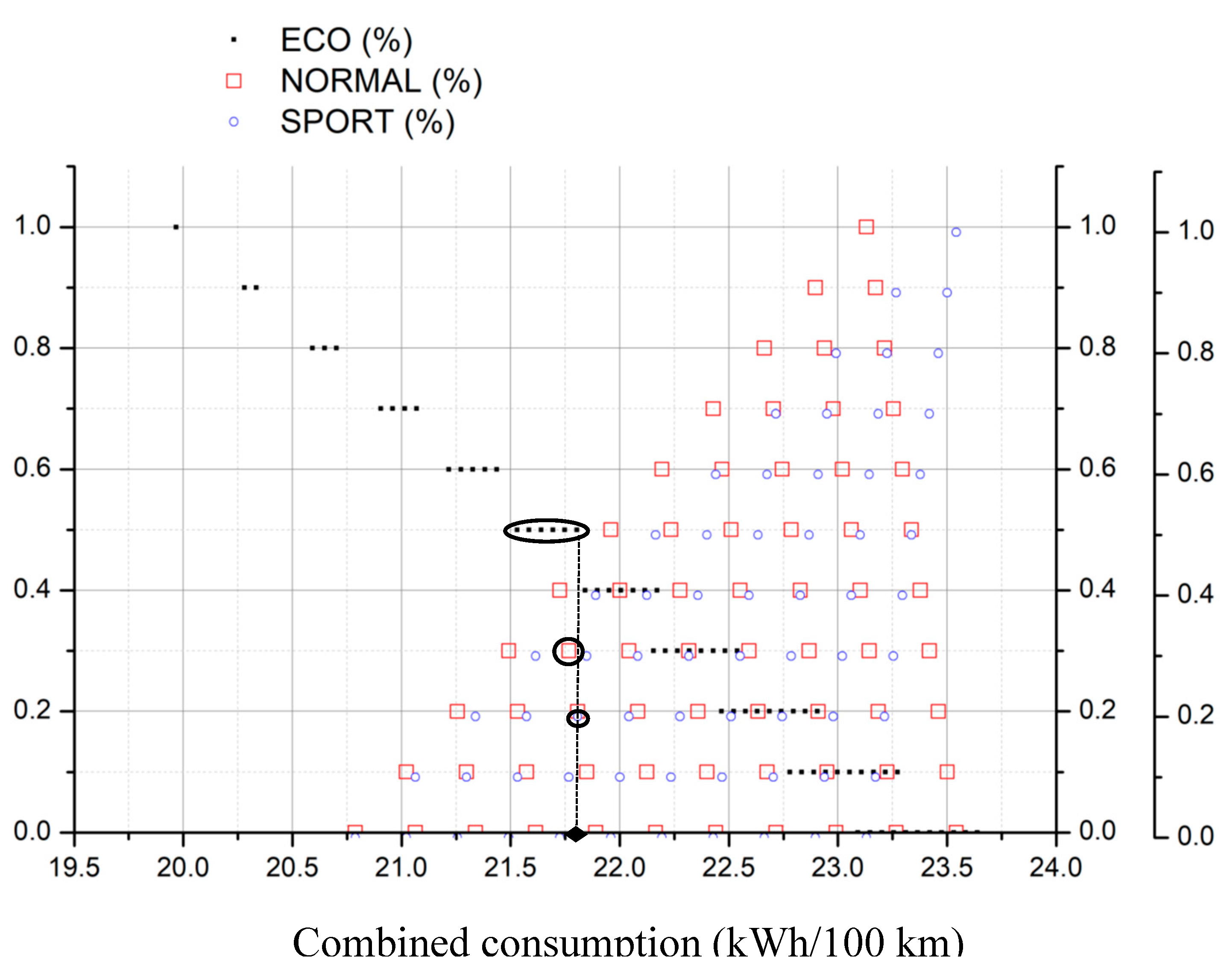
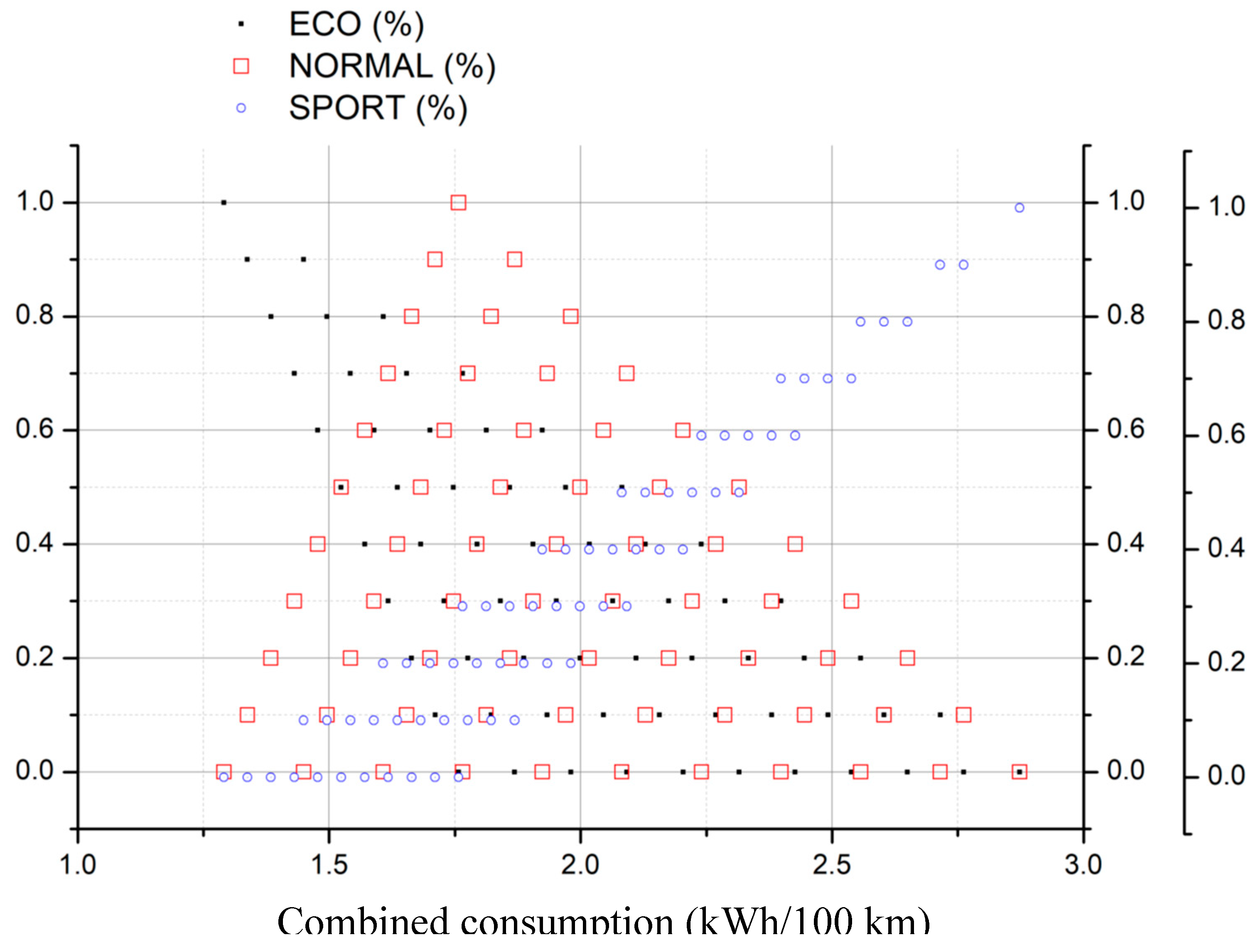
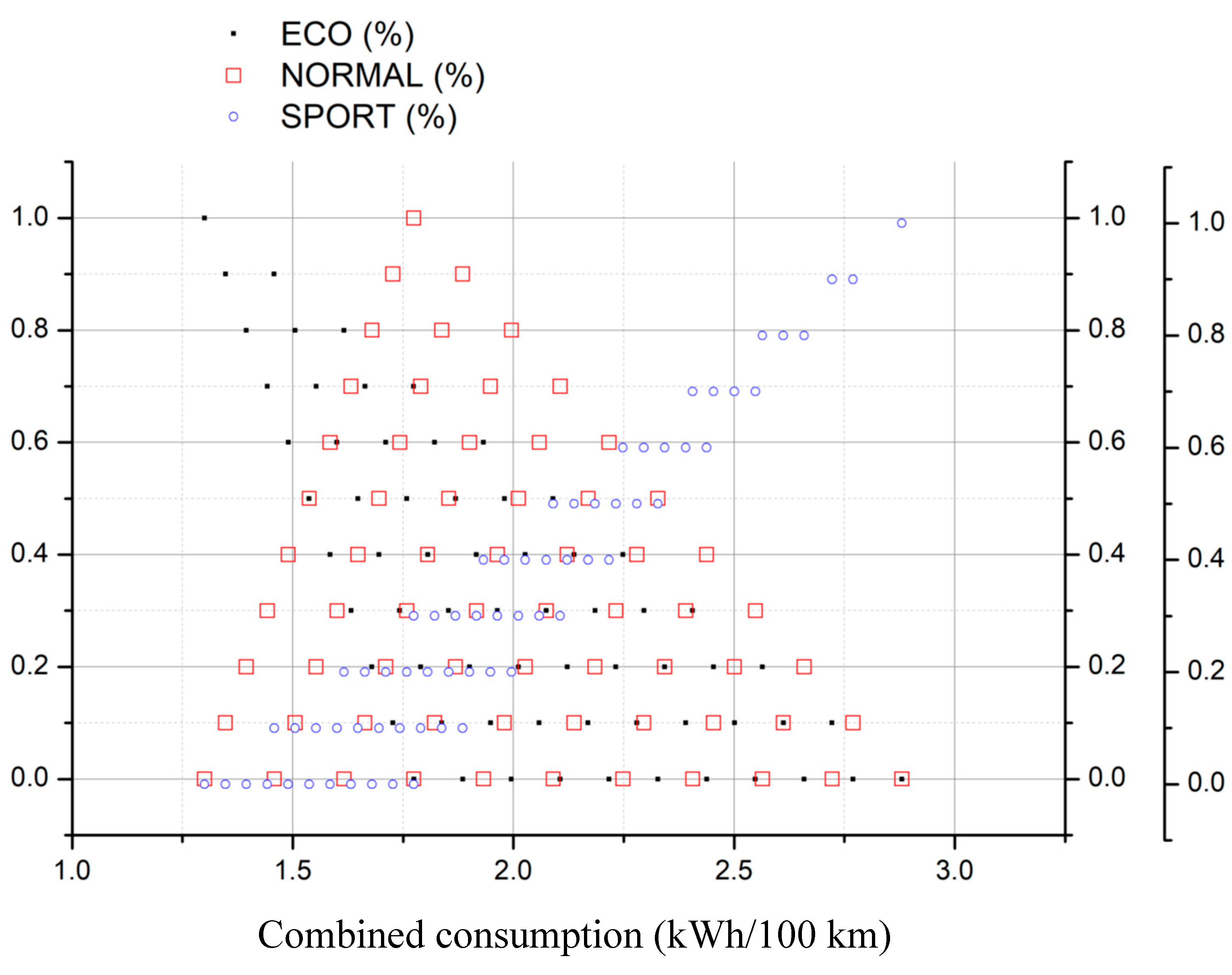
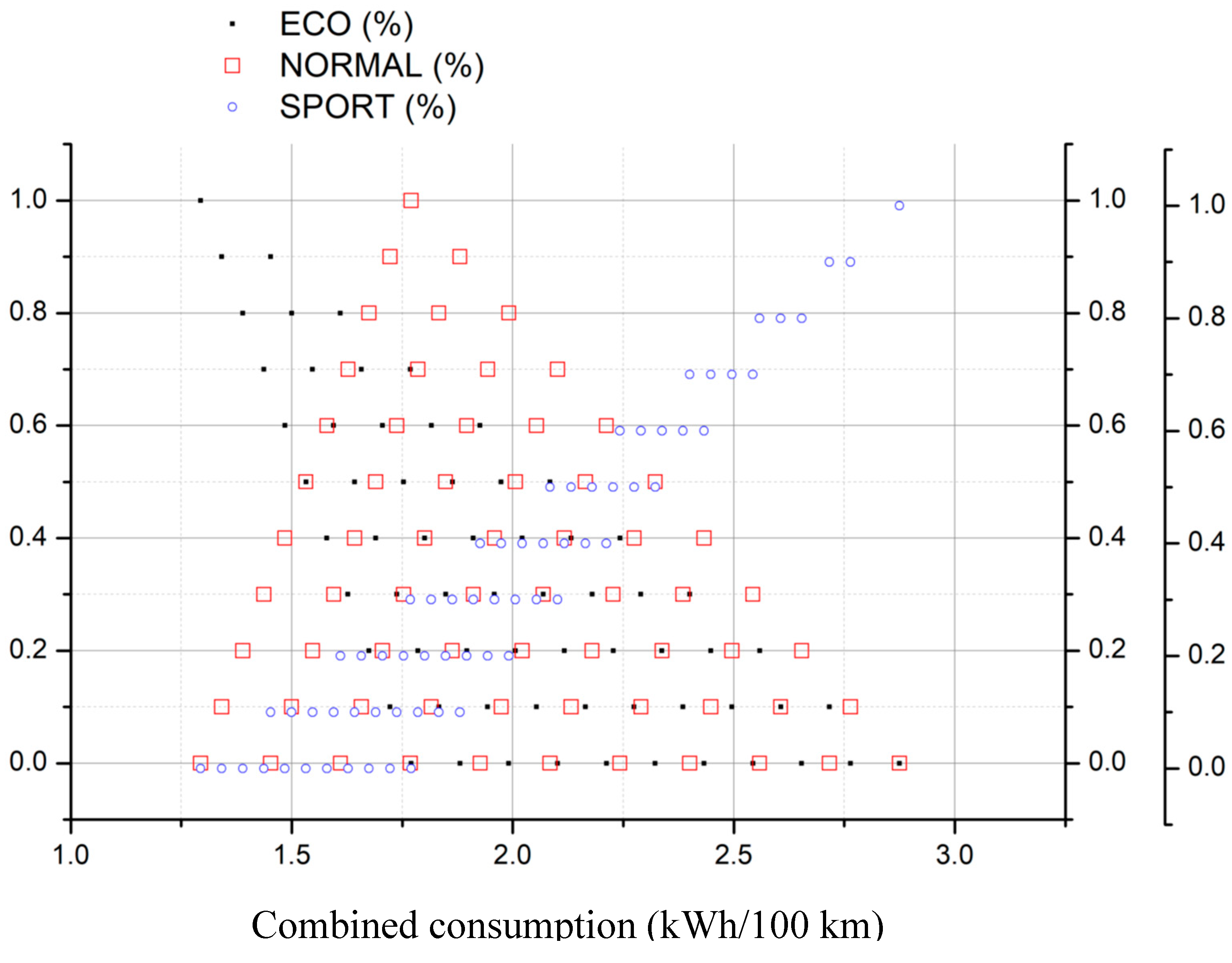
- Chose the type of demanding energy rate and select the corresponding figure
- Select the fraction of conservative (ECO), moderate (NORMAL) and aggressive (SPORT) driving mode for the acceleration
- Search for the selected values in the figure
- Draw a vertical line downwards, joining all points of selected values until reaching the X-axis
- The crossing point corresponds to the searched value
| Driving mode | Energy demanding level | |||
| Magnitude | Low | Medium | High | |
| ECO | Energy consumption rate (Wh/km) | 123.84 | 124.28 | 124.66 |
| Energy consumption rate (Wh/100 km) | 12.38 | 12.43 | 12.47 | |
| Hydrogen consumption (kg/100 km) | 1.29 | 1.29 | 1.30 | |
| Energy (kWh) | 49.53 | 49.71 | 49.86 | |
| Vehicle mass (kg) | 1178 | 1178 | 1178 | |
| NORMAL | Energy consumption rate (Wh/km) | 136.55 | 137.00 | 137.38 |
| Energy consumption rate (Wh/100 km) | 13.66 | 13.70 | 13.79 | |
| Hydrogen consumption (kg/100 km) | 1.76 | 1.77 | 1.77 | |
| Energy (kWh) | 54.62 | 54.80 | 54.95 | |
| Vehicle mass (kg) | 1178 | 1178 | 1178 | |
| SPORT | Energy consumption rate (Wh/km) | 148.11 | 148.56 | 148.95 |
| Energy consumption rate (Wh/100 km) | 14.81 | 14.86 | 14.90 | |
| Hydrogen consumption (kg/100 km) | 2.87 | 2.87 | 2.88 | |
| Energy (kWh) | 59.24 | 59.42 | 59.58 | |
| Vehicle mass (kg) | 1178 | 1178 | 1178 | |
| NORMAL/ECO | SPORT/NORMAL | SPORT/ECO |
| 1.103 | 1.084 | 1.196 |
| 1.214* | 1.032* | 1.254* |
| ↓Magnitude | Driving mode → | ECO | NORMAL | SPORT |
| Energy (kWh)/Energy consumption rate (kWh/100 km) | 34% | 40% | 37% | |
Conclusions
References
- Narins, T. P. (2017). The battery business: Lithium availability and the growth of the global electric car industry. The Extractive Industries and Society, 4(2), 321-328.
- Sonoc, A., & Jeswiet, J. (2014). A review of lithium supply and demand and a preliminary investigation of a room temperature method to recycle lithium ion batteries to recover lithium and other materials. Procedia Cirp, 15, 289-293.
- Egbue, O., & Long, S. (2012). Critical issues in the supply chain of lithium for electric vehicle batteries. Engineering Management Journal, 24(3), 52-62.
- Wanger, T. C. (2011). The Lithium future—resources, recycling, and the environment. Conservation Letters, 4(3), 202-206.
- Ljunggren Söderman, M., Kushnir, D., & Sandén, B. A. (2013). Will metal scarcity limit the use of electric vehicles?.
- Narins, T. P. (2017). The battery business: Lithium availability and the growth of the global electric car industry. The Extractive Industries and Society, 4(2), 321-328.
- Liu, B., Zhang, Q., Liu, J., Hao, Y., Tang, Y., & Li, Y. (2022). The impacts of critical metal shortage on China's electric vehicle industry development and countermeasure policies. Energy, 248, 123646.
- Thomas, C. E. (2009). Fuel cell and battery electric vehicles compared. international journal of hydrogen energy, 34(15), 6005-6020.
- Contestabile, M., Offer, G. J., Slade, R., Jaeger, F., & Thoennes, M. (2011). Battery electric vehicles, hydrogen fuel cells and biofuels. Which will be the winner?. Energy & Environmental Science, 4(10), 3754-3772.
- Wanitschke, A., & Hoffmann, S. (2020). Are battery electric vehicles the future? An uncertainty comparison with hydrogen and combustion engines. Environmental Innovation and Societal Transitions, 35, 509-523.
- Bartolozzi, I., Rizzi, F., & Frey, M. (2013). Comparison between hydrogen and electric vehicles by life cycle assessment: A case study in Tuscany, Italy. Applied energy, 101, 103-111.
- Wong, E. Y. C., Ho, D. C. K., So, S., Tsang, C. W., & Chan, E. M. H. (2021). Life cycle assessment of electric vehicles and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles using the greet model—A comparative study. Sustainability, 13(9), 4872.
- Muthukumar, M., Rengarajan, N., Velliyangiri, B., Omprakas, M. A., Rohit, C. B., & Raja, U. K. (2021). The development of fuel cell electric vehicles–A review. Materials Today: Proceedings, 45, 1181-1187.
- Yuan, Y., & Yuan, X. (2023). Does the development of fuel cell electric vehicles be reviving or recessional? Based on the patent analysis. Energy, 272, 127104.
- Dixon, J. (2010, March). Energy storage for electric vehicles. In 2010 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (pp. 20-26). IEEE.
- Chau, K. T., Wong, Y. S., & Chan, C. C. (1999). An overview of energy sources for electric vehicles. Energy Conversion and Management, 40(10), 1021-1039.
- Khaligh, A., & Li, Z. (2010). Battery, ultracapacitor, fuel cell, and hybrid energy storage systems for electric, hybrid electric, fuel cell, and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles: State of the art. IEEE transactions on Vehicular Technology, 59(6), 2806-2814.
- Muthukumar, M., Rengarajan, N., Velliyangiri, B., Omprakas, M. A., Rohit, C. B., & Raja, U. K. (2021). The development of fuel cell electric vehicles–A review. Materials Today: Proceedings, 45, 1181-1187.
- C. Armenta-Déu, J.P. Carriquiry and S. Guzmán (2019) Capacity correction factor for Li-ion Batteries: Influence of the Discharge Rate, Journal of Energy Storage, Volume 25, October 2019, 100839, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2019.100839.
- C. Armenta-Déu, J.P. Carriquiry (2020) aplication of Statistical Method to Determine Lithium Battery Capacity for Electric Vehicles, Journal of Automobile Engineering and Applications, Volume 7, Issue 2, pp. 25-35. [CrossRef]
- C. Armenta-Déu (2021) Reduction of Electric Vehicle Driving Range due to Battery Capacity Fading, Journal of Automobile Engineering and Applications, Volume 8, Issue 2. [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y., Zhao, W., Li, Z., Liu, B., & Wang, K. (2021). SOC estimation of lithium-ion battery considering the influence of discharge rate. Energy Reports, 7, 1436-1446.
- Pay, S., & Baghzouz, Y. (2003, June). Effectiveness of battery-supercapacitor combination in electric vehicles. In 2003 IEEE Bologna Power Tech Conference Proceedings, (Vol. 3, pp. 6-pp). IEEE.
- Oukkacha, I., Sarr, C. T., Camara, M. B., Dakyo, B., & Parédé, J. Y. (2021). Energetic Performances Booster for Electric Vehicle Applications Using Transient Power Control and Supercapacitors-Batteries/Fuel Cell. Energies, 14(8), 2251.
- Kouchachvili, L., Yaïci, W., & Entchev, E. (2018). Hybrid battery/supercapacitor energy storage system for the electric vehicles. Journal of Power Sources, 374, 237-248.
- Benmouiza, K., & Cheknane, A. (2018). Analysis of proton exchange membrane fuel cells voltage drops for different operating parameters. International journal of hydrogen energy, 43(6), 3512-3519.
- Xu, Z., Qi, Z., He, C., & Kaufman, A. (2006). Combined activation methods for proton-exchange membrane fuel cells. Journal of power sources, 156(2), 315-320.
- Van Der Linden, F., Pahon, E., Morando, S., & Bouquain, D. (2023). A review on the Proton-Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell break-in physical principles, activation procedures, and characterization methods. Journal of Power Sources, 575, 233168.
- Qi, Z., & Kaufman, A. (2003). Quick and effective activation of proton-exchange membrane fuel cells. Journal of power sources, 114(1), 21-31.
- Dey, T., Singdeo, D., Bose, M., Basu, R. N., & Ghosh, P. C. (2013). Study of contact resistance at the electrode–interconnect interfaces in planar type Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. Journal of Power Sources, 233, 290-298.
- Chae, K. J., Choi, M., Ajayi, F. F., Park, W., Chang, I. S., & Kim, I. S. (2008). Mass transport through a proton exchange membrane (Nafion) in microbial fuel cells. Energy & Fuels, 22(1), 169-176.
- Barbir, F. (2012). PEM fuel cells: theory and practice. Academic press.
- Halper, M. S., & Ellenbogen, J. C. (2006). Supercapacitors: A brief overview. The MITRE Corporation, McLean, Virginia, USA, 1.
- Sharma, P., & Kumar, V. (2020). Current technology of supercapacitors: A review. Journal of Electronic Materials, 49(6), 3520-3532.
- Jalal, N. I., Ibrahim, R. I., & Oudah, M. K. (2021, August). A review on Supercapacitors: Types and components. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series (Vol. 1973, No. 1, p. 012015). IOP Publishing.
- Banerjee, S., Sinha, P., Verma, K. D., Pal, T., De, B., Cherusseri, J., ... & Kar, K. K. (2020). Capacitor to supercapacitor. Handbook of Nanocomposite Supercapacitor Materials I: Characteristics, 53-89.
- Kadir, M. F. Z. (2021). Non-faradaic-based supercapacitor fabricated with fish skin gelatin biopolymer electrolyte. Ionics, 27, 2219-2229.
- Arbizzani, C., Yu, Y., Li, J., Xiao, J., Xia, Y. Y., Yang, Y., ... & Passerini, S. (2020). Good practice guide for papers on supercapacitors and related hybrid capacitors for the Journal of Power Sources. J. Power Sources, 450(227636.10), 1016.
- Conway, B. E., Birss, V., & Wojtowicz, J. (1997). The role and utilization of pseudocapacitance for energy storage by supercapacitors. Journal of power sources, 66(1-2), 1-14.
- Barpanda, P., Fanchini, G., & Amatucci, G. G. (2008). Faradaic and Non-Faradaic Reaction Mechanisms in Carbon-iodine Nanocomposites Electrodes for Asymmetric Hybrid Supercapacitors. ECS transactions, 13(17), 13.
- Sinha, P., & Kar, K. K. (2020). Introduction to supercapacitors. In Handbook of Nanocomposite Supercapacitor Materials II: Performance (pp. 1-28). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
- Mei Sam. Multiwalled carbon nanotubes based nanocomposites for supercapacitors. 325,2006.
- Himadry Shekhar Das, Chee Wei Tan, and A. H.M. Yatim. Fuel cell hybrid electric vehicles: A review on power conditioning units and topologies. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 76(February):268–291, 2017.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Supercapacitor (accessed online: 17/06/2023).
- A. S. Samosir and A. H.M. Yatim. A novel control strategy of bidirectional dc-dc converter for interfacing ultracapacitor to fuel cell electric vehicles system based on dynamic evolution control. International Review of Electrical Engineering, 5(1):64–69, 2010.
- Julius Partridge and Dina Ibrahim Abouelamaimen. The role of supercapacitors in regenerative braking systems. Energies, 12(14), 2019.
- Hyundai NEXO breaks world distance record twice, https://www.hyundai.news/eu/articles/press-releases/hyundai-nexo-breaks-worlddistance-record-twice.html, accesso:03/01/2023, 2018.
- Ferrara, Alessandro, Jakubek, Stefan, Hametner, Christoph (2021). Energy management of heavy-duty fuel cell vehicles in real-world driving scenarios: Robust design of strategies to maximize the hydrogen economy and system lifetime. Energy Conversion and Management, 232:113795.
- Boretti, A. (2013) Analysis of the regenerative braking efficiency of a latest electric vehicle.SAE Technical Papers, 12.
- Kunz, M. R., Dufek, E. J., Yi, Z., Gering, K. L., Shirk, M. G., Smith, K., ... & Tanim, T. R. (2021). Early battery performance prediction for mixed use charging profiles using hierarchal machine learning. Batteries & Supercaps, 4(7), 1186-1196.
- Ragone, M., Yurkiv, V., Ramasubramanian, A., Kashir, B., & Mashayek, F. (2021). Data driven estimation of electric vehicle battery state-of-charge informed by automotive simulations and multi-physics modeling. Journal of Power Sources, 483, 229108.
- Toyota. Outline of the Mirai. Technical Report November, 2014. https://www.smartcirculair.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/Toyota-Mirai-FCV_Posters_LR.pdf.
- Z. Cerovsky and Pavel Mindl. Regenerative braking by electric hybrid vehicles using super capacitor and power splitting generator. In 2005 European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications, volume 2005, pages 10 pp.–P.10. IEEE, 2005.
- Hydrogen Type 4 Cylinder 700 bar 51L, https://hyfindr.com/marketplace/components/hydrogentanks/ hydrogen-type-4-cylinder-700-bar-51l/, (accessed online: 15/11/2022).
- Hydrogen Type 4 Cylinder 700 bar 185L, https://hyfindr.com/marketplace/components/hydrogentanks/ hydrogen-type-4-cylinder-700-bar-185l/, (accessed online: 16/11/2022).
- EATON Electronics Division. XLM Supercapacitor 62 V and 69 V, 130 F Module, 2021.
- Armenta-Déu, C. and Cortés, H. (2022) Advance Method to Calculate Real Driving Range for Electric Vehicles, Journal of Automobile Engineering and Automation, Volume 9, Issue 3, pp.1-19, http://engineeringjournals.stmjournals.in/index.php/JoAEA/index.
- Armenta-Déu, C. and Cattin, E. (2023) A new method to determine electric vehicle range I real driving conditions, International Journal of Vehicle Performance, Volume 9, Issue 1, pp.91-107. [CrossRef]
- Armenta-Déu, C. and Cortés, H. (2023) Hybrid Method to Calculate Real Driving Range for Electric Vehicles in Urban Routes, Vehicles 5(2), 492-498. [CrossRef]
- L. García-Arranz and C. Armenta-Déu (2021) Performance Tests to Determine Driving Range in Electric Vehicles, Journal of Mechatronics and Automation, Volume 8, Issue 2, pages 10-20.
- M. Hanako Olmedilla-Ishishi and C. Armenta-Déu (2020) Seasonal Variation of Electric Vehicles Autonomy: Application to AC/DC Dual Voltage Operation, Journal of Mechatronics and Automation,b Volume 7, Issue 3 p.1-16. [CrossRef]
- M. Martínez-Arriaga and C. Armenta-Déu (2020) Simulation of the Performance of Electric Vehicle Batteries Under Variable Driving Conditions, Journal of Automobile Engineering and Applications, Volume 7, Issue 3, pp.1-15. [CrossRef]
- Zhifeng Que, Shixue Wang, and Weiyi Li. Potential of Energy Saving and Emission Reduction of Battery Electric Vehicles with Two Type of Drivetrains in China. Energy Procedia, 75:2892–2897, aug 2015.
- Sulaiman, N., Hannan, M. A., Mohamed, A., Majlan, E. H., & Daud, W. W. (2015). A review on energy management system for fuel cell hybrid electric vehicle: Issues and challenges. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 52, 802-814.
- Wu, Y., & Gao, H. (2006). Optimization of fuel cell and supercapacitor for fuel-cell electric vehicles. IEEE transactions on Vehicular Technology, 55(6), 1748-1755.
| Slope (º) | Initial speed (km/h) | Final speed (km/h) | Number of segments | Driving condition |
|
-1 |
0 60 60 70 70 60 |
60 60 70 70 60 0 |
4 1 3 1 3 7 |
Acceleration Constant speed Acceleration Constant speed Deceleration Braking |
|
0 |
0 50 50 90 90 50 |
50 50 90 90 50 0 |
5 10 4 2 4 9 |
Acceleration Constant speed Acceleration Constant speed Deceleration Braking |
|
1 |
0 50 50 80 80 50 |
50 50 80 80 50 0 |
5 3 4 5 4 9 |
Acceleration Constant speed Acceleration Constant speed Deceleration Braking |
| Slope (º) | Initial speed (km/h) | Final speed (km/h) | Number of segments | Driving condition |
|
-3 |
0 60 60 70 70 60 |
60 60 70 70 60 0 |
4 1 3 1 3 7 |
Acceleration Constant speed Acceleration Constant speed Deceleration Braking |
|
0 |
0 50 50 90 90 50 |
50 50 90 90 50 0 |
5 10 4 2 4 9 |
Acceleration Constant speed Acceleration Constant speed Deceleration Braking |
|
3 |
0 50 50 80 80 50 |
50 50 80 80 50 0 |
5 3 4 5 4 9 |
Acceleration Constant speed Acceleration Constant speed Deceleration Braking |
| Slope (º) | Initial speed (km/h) | Final speed (km/h) | Number of segments | Driving condition |
|
-5 |
0 60 60 70 70 60 |
60 60 70 70 60 0 |
4 1 3 1 3 7 |
Acceleration Constant speed Acceleration Constant speed Deceleration Braking |
|
0 |
0 50 50 90 90 50 |
50 50 90 90 50 0 |
5 10 4 2 4 9 |
Acceleration Constant speed Acceleration Constant speed Deceleration Braking |
|
5 |
0 50 50 80 80 50 |
50 50 80 80 50 0 |
5 3 4 5 4 9 |
Acceleration Constant speed Acceleration Constant speed Deceleration Braking |
| Parameter | Value |
| Front area (A) | 2.5 |
| Aerodynamic coefficient (Cx) | 0.3 |
| Rolling coefficient (μ) | 0.03 |
| Air density (ρ) | 1.225 |
| Discharge efficiency (ηD ) | 0.85 |
| Regenerative process energy efficiency (ηr ) | 0.70 |
| Vehicle mass (kg) | 1000 |
| Battery voltage (V) | 400 |
| Maximum power (kW) | 150 |
| Parameter | Value |
| Front area (A) | 2.5 |
| Aerodynamic coefficient (Cx) | 0.3 |
| Rolling coefficient (μ) | 0.03 |
| Air density (ρ) | 1.225 |
| Fuel Cell average efficiency (ηD ) | 0.55 |
| Discharge efficiency (%) | 0.80 |
| Regenerative process energy efficiency (ηr ) | 0.90 |
| Vehicle mass (kg) | 1000 |
| Operating voltage (V) | 69 |
| Supercapacitor maximum power (kW) | 16 |
| Fuel Cell maximum power (kW) | 70.15 |
| Hydrogen storage tank mass (kg) | 85.71 |
| Fuel Cell mass (kg) | 56 |
| Fuel Cell consumption rate (kg/100 km) | 0.95 |
| Supercapacitor capacitance (F) | 130 |
| Supercapacitor mass (kg) | 14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





