Submitted:
19 June 2023
Posted:
20 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Biogenesis and functions of circRNAs
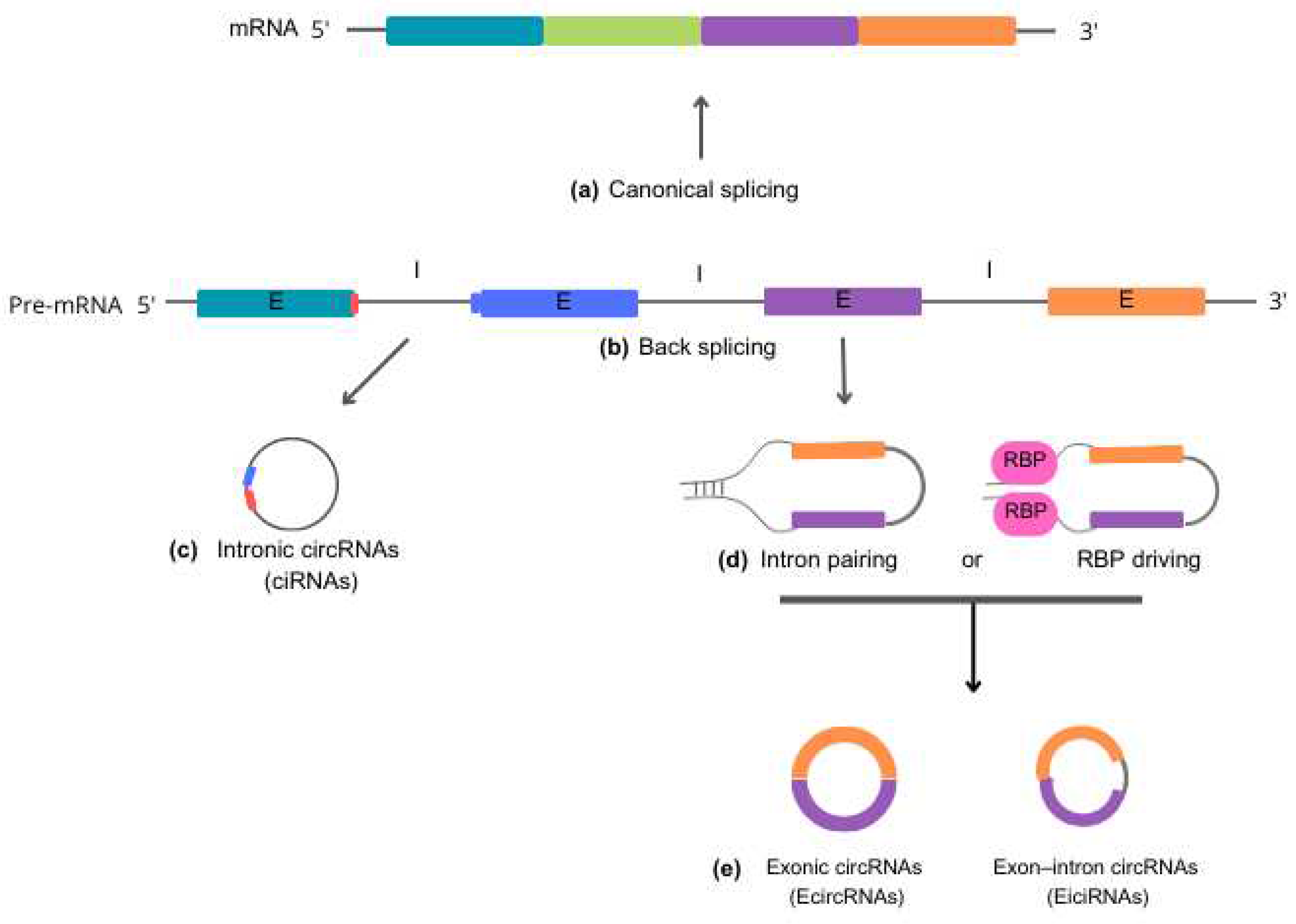
Function of circRNAs in the cellular metabolism
circRNAs regulating gene expression – interaction with DNA
- Direct regulation of gene expression:
- Regulation of DNA Methylation:
- Retrotransposon:
circRNAs regulating gene expression – interaction with RNA
- Regulation of gene expression:
- Sponges of miRNAs:
- Regulation of mRNA Stability:
circRNAs regulating cellular metabolism – interaction with protein
- Sponges and proteins:
- Protein translation:
circRNAs relationship between alpha-synuclein and microRNAs in the Parkinson’s Disease
circRNA in neuroinflammation
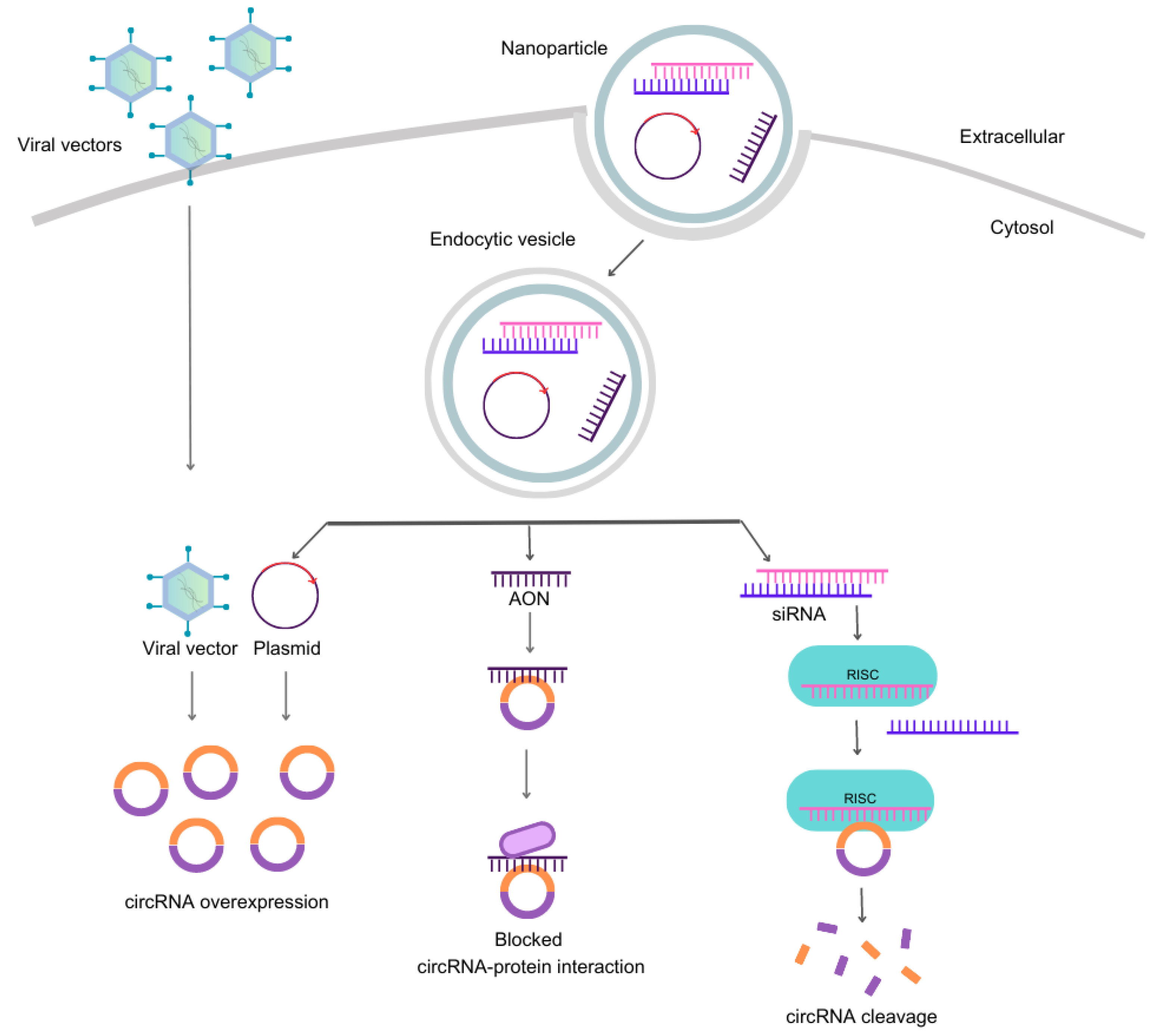
Scientific methodologies to target circRNAs
- 1.
- Strategies to downregulate circRNAs
- Synthetic small-interfering RNAs (siRNAs)
- Short-hairpin RNAi expressing vectors
- Antisense oligonucleotides (AONs)
- CRISPR/Cas systems for circRNA knockout or knockdown
- 2.
- Overexpression of circRNAs by nonviral– and viral-vectors
- 3.
- Investigating the role of circRNAs in models of neurodegenerative diseases: siRNAs and expression vectors in selected studies
- Paving the path for circRNA development: drawing on the success of siRNAs in reaching the market
- A critical inquiry: Are circRNAs gaining traction in the pharmaceutical market?
Conclusions
References
- Sanger, H.L.; Klotz, G.; Riesner, D.; Gross, H.J.; Kleinschmidt, A.K. Viroids are single-stranded covalently closed circular RNA molecules existing as highly base-paired rod-like structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1976, 73, 3852–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danan, M.; Schwartz, S.; Edelheit, S.; Sorek, R. Transcriptome-wide discovery of circular RNAs in Archaea. Nucleic Acids Res 2012, 40, 3131–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.; Cui, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, C.; Fan, D.; Gong, H.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, C.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, D.; et al. Transcriptome-wide investigation of circular RNAs in rice. RNA 2015, 21, 2076–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzman, J.; Gawad, C.; Wang, P.L.; Lacayo, N.; Brown, P.O. Circular RNAs are the predominant transcript isoform from hundreds of human genes in diverse cell types. PLoS One 2012, 7, e30733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memczak, S.; Jens, M.; Elefsinioti, A.; Torti, F.; Krueger, J.; Rybak, A.; Maier, L.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Gregersen, L.H.; Munschauer, M.; et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 2013, 495, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, L.S.; Andersen, M.S.; Stagsted, L.V.W.; Ebbesen, K.K.; Hansen, T.B.; Kjems, J. The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet 2019, 20, 675–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwal-Fluss, R.; Meyer, M.; Pamudurti, N.R.; Ivanov, A.; Bartok, O.; Hanan, M.; Evantal, N.; Memczak, S.; Rajewsky, N.; Kadener, S. circRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing. Mol Cell 2014, 56, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, C.; Bao, C.; Chen, L.; Lin, M.; Wang, X.; Zhong, G.; Yu, B.; Hu, W.; Dai, L.; et al. Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2015, 22, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sorrentino, J.A.; Wang, K.; Slevin, M.K.; Burd, C.E.; Liu, J.; Marzluff, W.F.; Sharpless, N.E. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA 2013, 19, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwanhausser, B.; Busse, D.; Li, N.; Dittmar, G.; Schuchhardt, J.; Wolf, J.; Chen, W.; Selbach, M. Global quantification of mammalian gene expression control. Nature 2011, 473, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak-Wolf, A.; Stottmeister, C.; Glazar, P.; Jens, M.; Pino, N.; Giusti, S.; Hanan, M.; Behm, M.; Bartok, O.; Ashwal-Fluss, R.; et al. Circular RNAs in the Mammalian Brain Are Highly Abundant, Conserved, and Dynamically Expressed. Mol Cell 2015, 58, 870–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, G.; Lorenzen, J.M. Biogenesis and Function of Circular RNAs in Health and in Disease. Front Pharmacol 2019, 10, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.Y.; Cai, Z.R.; Liu, J.; Wang, D.S.; Ju, H.Q.; Xu, R.H. Circular RNA: metabolism, functions and interactions with proteins. Mol Cancer 2020, 19, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, X.; Vlatkovic, I.; Babic, A.; Will, T.; Epstein, I.; Tushev, G.; Akbalik, G.; Wang, M.; Glock, C.; Quedenau, C.; et al. Neural circular RNAs are derived from synaptic genes and regulated by development and plasticity. Nat Neurosci 2015, 18, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, R.; Gao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, R.; Kadash-Edmondson, K.E.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Lin, L.; Xing, Y. isoCirc catalogs full-length circular RNA isoforms in human transcriptomes. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, C.; Cui, H.; Sun, J.; Zhou, P. Role of circRNAs in neurodevelopment and neurodegenerative diseases. J Mol Neurosci 2021, 71, 1743–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D'Ambra, E.; Capauto, D.; Morlando, M. Exploring the Regulatory Role of Circular RNAs in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Bian, Z. The Emerging Role of Circular RNAs in Alzheimer's Disease and Parkinson's Disease. Front Aging Neurosci 2021, 13, 691512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, C.; Chen, S.; Lu, S.; Yan, W.; Xiong, K.; Liu, F.; Yan, J. Current status and potential role of circular RNAs in neurological disorders. J Neurochem 2019, 150, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caba, L.; Florea, L.; Gug, C.; Dimitriu, D.C.; Gorduza, E.V. Circular RNA-Is the Circle Perfect? Biomolecules 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eger, N.; Schoppe, L.; Schuster, S.; Laufs, U.; Boeckel, J.N. Circular RNA Splicing. Adv Exp Med Biol 2018, 1087, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, F. CIRI: an efficient and unbiased algorithm for de novo circular RNA identification. Genome Biol 2015, 16, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conn, S.J.; Pillman, K.A.; Toubia, J.; Conn, V.M.; Salmanidis, M.; Phillips, C.A.; Roslan, S.; Schreiber, A.W.; Gregory, P.A.; Goodall, G.J. The RNA binding protein quaking regulates formation of circRNAs. Cell 2015, 160, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Du, L.; Bai, Y.; Han, B.; He, C.; Gong, L.; Huang, R.; Shen, L.; Chao, J.; Liu, P.; et al. CircDYM ameliorates depressive-like behavior by targeting miR-9 to regulate microglial activation via HSP90 ubiquitination. Mol Psychiatry 2020, 25, 1175–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.T.; Liu, J.; Li, F.; Yang, B.B. Targeting circular RNAs as a therapeutic approach: current strategies and challenges. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2021, 6, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.W.; Yang, W.; Liu, E.; Yang, Z.; Dhaliwal, P.; Yang, B.B. Foxo3 circular RNA retards cell cycle progression via forming ternary complexes with p21 and CDK2. Nucleic Acids Res 2016, 44, 2846–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patop, I.L.; Wust, S.; Kadener, S. Past, present, and future of circRNAs. EMBO J 2019, 38, e100836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes-Lopez, M.; Miura, P. Emerging Functions of Circular RNAs. Yale J Biol Med 2016, 89, 527–537. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.Y.; Zhai, M.; Huang, Y.; Xu, S.; An, T.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, R.C.; Liu, C.Y.; Dong, Y.H.; Wang, M.; et al. The circular RNA ACR attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing autophagy via modulation of the Pink1/ FAM65B pathway. Cell Death Differ 2019, 26, 1299–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Zhang, X.O.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, X.K.; Chen, L.L.; Yang, L. CircRNA-derived pseudogenes. Cell Res 2016, 26, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, T.; Panigrahi, C.; Das, D.; Chandra Panda, A. Circular RNA translation, a path to hidden proteome. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 2022, 13, e1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Han, Y.; Wang, S.; Wu, X.; Cao, J.; Sun, T. Circular RNAs: Biogenesis, Biological Functions, and Roles in Myocardial Infarction. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.B.; Jensen, T.I.; Clausen, B.H.; Bramsen, J.B.; Finsen, B.; Damgaard, C.K.; Kjems, J. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 2013, 495, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, W.L.; Marinov, G.K.; Liau, E.S.; Lam, Y.L.; Lim, Y.Y.; Ea, C.K. Inducible RasGEF1B circular RNA is a positive regulator of ICAM-1 in the TLR4/LPS pathway. RNA Biol 2016, 13, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garikipati, V.N.S.; Verma, S.K.; Cheng, Z.; Liang, D.; Truongcao, M.M.; Cimini, M.; Yue, Y.; Huang, G.; Wang, C.; Benedict, C.; et al. Circular RNA CircFndc3b modulates cardiac repair after myocardial infarction via FUS/VEGF-A axis. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulshofer, C.J.; Pfafenrot, C.; Bindereif, A.; Schneider, T. Methods to study circRNA-protein interactions. Methods 2021, 196, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aufiero, S.; Reckman, Y.J.; Pinto, Y.M.; Creemers, E.E. Circular RNAs open a new chapter in cardiovascular biology. Nat Rev Cardiol 2019, 16, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welden, J.R.; Stamm, S. Pre-mRNA structures forming circular RNAs. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech 2019, 1862, 194410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kos, A.; Dijkema, R.; Arnberg, A.C.; van der Meide, P.H.; Schellekens, H. The hepatitis delta (delta) virus possesses a circular RNA. Nature 1986, 323, 558–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdt, L.M.; Kohlmaier, A.; Teupser, D. Circular RNAs as Therapeutic Agents and Targets. Front Physiol 2018, 9, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meade, R.M.; Fairlie, D.P.; Mason, J.M. Alpha-synuclein structure and Parkinson's disease - lessons and emerging principles. Mol Neurodegener 2019, 14, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Schmidt, M.L.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M. Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 1997, 388, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titze-de-Almeida, R.; Titze-de-Almeida, S.S. miR-7 Replacement Therapy in Parkinson's Disease. Curr Gene Ther 2018, 18, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poewe, W.; Seppi, K.; Tanner, C.M.; Halliday, G.M.; Brundin, P.; Volkmann, J.; Schrag, A.E.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2017, 3, 17013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obeso, J.A.; Stamelou, M.; Goetz, C.G.; Poewe, W.; Lang, A.E.; Weintraub, D.; Burn, D.; Halliday, G.M.; Bezard, E.; Przedborski, S.; et al. Past, present, and future of Parkinson's disease: A special essay on the 200th Anniversary of the Shaking Palsy. Mov Disord 2017, 32, 1264–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Qi, L.; Sun, W.; Wang, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, H. CircSNCA downregulation by pramipexole treatment mediates cell apoptosis and autophagy in Parkinson's disease by targeting miR-7. Aging (Albany NY) 2018, 10, 1281–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleaveland, B.; Shi, C.Y.; Stefano, J.; Bartel, D.P. A Network of Noncoding Regulatory RNAs Acts in the Mammalian Brain. Cell 2018, 174, 350–362 e317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piwecka, M.; Glazar, P.; Hernandez-Miranda, L.R.; Memczak, S.; Wolf, S.A.; Rybak-Wolf, A.; Filipchyk, A.; Klironomos, F.; Cerda Jara, C.A.; Fenske, P.; et al. Loss of a mammalian circular RNA locus causes miRNA deregulation and affects brain function. Science 2017, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.; Chen, X.; Xu, M.; Liu, X.; Hu, X.; Xu, T.; Sun, H.; Pan, Y.; He, B.; Wang, S. CircHIPK3 promotes colorectal cancer growth and metastasis by sponging miR-7. Cell Death Dis 2018, 9, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Shamsuzzama; Jadiya, P.; Haque, R.; Shukla, S.; Nazir, A.. Functional Characterization of Novel Circular RNA Molecule, circzip-2 and Its Synthesizing Gene zip-2 in C. elegans Model of Parkinson's Disease. Mol Neurobiol 2018, 55, 6914–6926. [CrossRef]
- Hanan, M.; Simchovitz, A.; Yayon, N.; Vaknine, S.; Cohen-Fultheim, R.; Karmon, M.; Madrer, N.; Rohrlich, T.M.; Maman, M.; Bennett, E.R.; et al. A Parkinson's disease CircRNAs Resource reveals a link between circSLC8A1 and oxidative stress. EMBO Mol Med 2020, 12, e13551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, E.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Ouyang, T.; Pan, M.; Bai, Y.; Ge, Q. Transcriptomic Profiling of Circular RNA in Different Brain Regions of Parkinson's Disease in a Mouse Model. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry-Hyde, A.; Gray, L.G.; Chen, B.J.; Ueberham, U.; Arendt, T.; Janitz, M. Cell type-specific circular RNA expression in human glial cells. Genomics 2020, 112, 5265–5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Gao, J.; Liao, Q. Circular RNA circPTK2 regulates oxygen-glucose deprivation-activated microglia-induced hippocampal neuronal apoptosis via miR-29b-SOCS-1-JAK2/STAT3-IL-1beta signaling. Int J Biol Macromol 2019, 129, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Tang, Y.; Yu, M.; Wu, L.; Liu, F.; Ni, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Fei, J.; Wang, W.; et al. Downregulation of blood serum microRNA 29 family in patients with Parkinson's disease. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 5411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Cai, L.; Ma, X.; Shen, K. Autophagy-mediated circHIPK2 promotes lipopolysaccharide-induced astrocytic inflammation via SIGMAR1. Int Immunopharmacol 2023, 117, 109907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Han, B.; Bai, Y.; Zhou, R.; Gan, G.; Chao, J.; Hu, G.; Yao, H. Circular RNA HIPK2 regulates astrocyte activation via cooperation of autophagy and ER stress by targeting MIR124-2HG. Autophagy 2017, 13, 1722–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doxakis, E. Cell-free microRNAs in Parkinson's disease: potential biomarkers that provide new insights into disease pathogenesis. Ageing Res Rev 2020, 58, 101023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Zhu, W.K.; Qi, F.Y.; Che, F.Y. CircHIPK3 promotes neuroinflammation through regulation of the miR-124-3p/STAT3/NLRP3 signaling pathway in Parkinson's disease. Adv Clin Exp Med 2023, 32, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yao, Y.; Miao, N.; Wang, N.; Xu, X.; Yang, C. Neuroprotective effects of microRNA 124 in Parkinson's disease mice. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 2022, 99, 104588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Ye, Y.; Mao, H.; Lu, F.; He, X.; Lu, G.; Zhang, S. MicroRNA-124 regulates the expression of MEKK3 in the inflammatory pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. J Neuroinflammation 2018, 15, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fire, A.; Xu, S.; Montgomery, M.K.; Kostas, S.A.; Driver, S.E.; Mello, C.C. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1998, 391, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meister, G.; Tuschl, T. Mechanisms of gene silencing by double-stranded RNA. Nature 2004, 431, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carthew, R.W.; Sontheimer, E.J. Origins and Mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell 2009, 136, 642–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamore, P.D.; Tuschl, T.; Sharp, P.A.; Bartel, D.P. RNAi: double-stranded RNA directs the ATP-dependent cleavage of mRNA at 21 to 23 nucleotide intervals. Cell 2000, 101, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, K.A.; Langer, R.; Anderson, D.G. Knocking down barriers: advances in siRNA delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2009, 8, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titze-de-Almeida, R.; David, C.; Titze-de-Almeida, S.S. The Race of 10 Synthetic RNAi-Based Drugs to the Pharmaceutical Market. Pharm Res 2017, 34, 1339–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setten, R.L.; Rossi, J.J.; Han, S.P. The current state and future directions of RNAi-based therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2019, 18, 421–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.B.; Guthrie, E.H.; Huang, M.T.; Taxman, D.J. Short hairpin RNA (shRNA): design, delivery, and assessment of gene knockdown. Methods Mol Biol 2010, 629, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, J.J. Expression strategies for short hairpin RNA interference triggers. Hum Gene Ther 2008, 19, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, C.F.; Swayze, E.E. RNA targeting therapeutics: molecular mechanisms of antisense oligonucleotides as a therapeutic platform. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2010, 50, 259–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, C.; Wood, M.J.A. Antisense oligonucleotides: the next frontier for treatment of neurological disorders. Nat Rev Neurol 2018, 14, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.C.; Langer, R.; Wood, M.J.A. Advances in oligonucleotide drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2020, 19, 673–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhuri, K.; Bechtold, C.; Quijano, E.; Pham, H.; Gupta, A.; Vikram, A.; Bahal, R. Antisense Oligonucleotides: An Emerging Area in Drug Discovery and Development. J Clin Med 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovendorf, M.B.; Holm, A.; Petri, A.; Thrue, C.A.; Uchida, S.; Veno, M.T.; Kauppinen, S. Knockdown of Circular RNAs Using LNA-Modified Antisense Oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acid Ther 2023, 33, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveau, H.; Garneau, J.E.; Moineau, S. CRISPR/Cas system and its role in phage-bacteria interactions. Annu Rev Microbiol 2010, 64, 475–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banan, M. Recent advances in CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knock-ins in mammalian cells. J Biotechnol 2020, 308, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, F.A.; Hsu, P.D.; Wright, J.; Agarwala, V.; Scott, D.A.; Zhang, F. Genome engineering using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Nat Protoc 2013, 8, 2281–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidenreich, M.; Zhang, F. Applications of CRISPR-Cas systems in neuroscience. Nat Rev Neurosci 2016, 17, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavez, M.; Chen, X.; Finn, P.B.; Qi, L.S. Advances in CRISPR therapeutics. Nat Rev Nephrol 2023, 19, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L. The Biogenesis, Functions, and Challenges of Circular RNAs. Mol Cell 2018, 71, 428–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meganck, R.M.; Borchardt, E.K.; Castellanos Rivera, R.M.; Scalabrino, M.L.; Wilusz, J.E.; Marzluff, W.F.; Asokan, A. Tissue-Dependent Expression and Translation of Circular RNAs with Recombinant AAV Vectors In Vivo. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2018, 13, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meganck, R.M.; Liu, J.; Hale, A.E.; Simon, K.E.; Fanous, M.M.; Vincent, H.A.; Wilusz, J.E.; Moorman, N.J.; Marzluff, W.F.; Asokan, A. Engineering highly efficient backsplicing and translation of synthetic circRNAs. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2021, 23, 821–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecozzi, N.; Nenci, A.; Vera, O.; Bok, I.; Falzone, A.; DeNicola, G.M.; Karreth, F.A. Genetic tools for the stable overexpression of circular RNAs. RNA Biol 2022, 19, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Hong, Q. Circular RNA circDLGAP4 exerts neuroprotective effects via modulating miR-134-5p/CREB pathway in Parkinson's disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2020, 522, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Han, B.; Yang, L.; Chen, X.; Huang, R.; Wu, F.; Chao, J.; Liu, P.; Hu, G.; et al. Circular RNA DLGAP4 Ameliorates Ischemic Stroke Outcomes by Targeting miR-143 to Regulate Endothelial-Mesenchymal Transition Associated with Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity. J Neurosci 2018, 38, 32–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, Q.; Zhang, R.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xie, W.; Geng, D.; Wang, L. circ-Pank1 promotes dopaminergic neuron neurodegeneration through modulating miR-7a-5p/alpha-syn pathway in Parkinson's disease. Cell Death Dis 2022, 13, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Q.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Fang, J.; Ding, H.; Meng, J.; Zhang, J.; Fang, X.; Liu, H.; Ma, C.; et al. CircSV2b participates in oxidative stress regulation through miR-5107-5p-Foxk1-Akt1 axis in Parkinson's disease. Redox Biol 2022, 56, 102430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titze-de-Almeida, S.S.; Brandao, P.R.P.; Faber, I.; Titze-de-Almeida, R. Leading RNA Interference Therapeutics Part 1: Silencing Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis, with a Focus on Patisiran. Mol Diagn Ther 2020, 24, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paula Brandao, P.R.; Titze-de-Almeida, S.S.; Titze-de-Almeida, R. Leading RNA Interference Therapeutics Part 2: Silencing Delta-Aminolevulinic Acid Synthase 1, with a Focus on Givosiran. Mol Diagn Ther 2020, 24, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titze de Almeida, S.S.; Horst, C.H.; Soto-Sanchez, C.; Fernandez, E.; Titze de Almeida, R. Delivery of miRNA-Targeted Oligonucleotides in the Rat Striatum by Magnetofection with Neuromag((R)). Molecules 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marks, W.J., Jr.; Bartus, R.T.; Siffert, J.; Davis, C.S.; Lozano, A.; Boulis, N.; Vitek, J.; Stacy, M.; Turner, D.; Verhagen, L.; et al. Gene delivery of AAV2-neurturin for Parkinson's disease: a double-blind, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 2010, 9, 1164–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Y.; Bartus, R.T.; Manfredsson, F.P.; Olanow, C.W.; Kordower, J.H. Long-term post-mortem studies following neurturin gene therapy in patients with advanced Parkinson's disease. Brain 2020, 143, 960–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diener, C.; Keller, A.; Meese, E. Emerging concepts of miRNA therapeutics: from cells to clinic. Trends Genet 2022, 38, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, P.T.; Taban, Q.; Dar, M.A.; Mir, S.; Haq, Z.U.; Zargar, S.M.; Shah, R.A.; Ahmad, S.M. Deep Insights in Circular RNAs: from biogenesis to therapeutics. Biol Proced Online 2020, 22, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santer, L.; Bar, C.; Thum, T. Circular RNAs: A Novel Class of Functional RNA Molecules with a Therapeutic Perspective. Mol Ther 2019, 27, 1350–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merck and Orna Therapeutics Collaborate to Advance Orna’s Next Generation of RNA Technology. Available online: https://www.merck.com/news/merck-and-orna-therapeutics-collaborate-to-advance-ornas-next-generation-of-rna-technology/.
- Mehta, S.L.; Dempsey, R.J.; Vemuganti, R. Role of circular RNAs in brain development and CNS diseases. Prog Neurobiol 2020, 186, 101746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbo, S.; Maione, R.; Tripodi, M.; Battistelli, C. Next RNA Therapeutics: The Mine of Non-Coding. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




