1. Introduction
During development of the central nervous system, neuronal cells undergo continuous and dynamic morphogenesis [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6]. Morphogenesis involves neurite outgrowth and elongation, neuronal process navigation, and synapse formation to form neuronal networks [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6]. Neurite outgrowth and elongation are the initial steps in establishing neuronal networks; however, the whole molecular mechanism underlying a variety of neuronal cell morphological differentiation steps, including outgrowth and elongation of neuronal processes, is not yet fully understood [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6]. In neurological diseases, neuronal cell morphogenesis can be affected at the initial steps as well as at the various other stages [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6]
Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) are neurodegenerative diseases that overlap in clinical, genetic, and pathological presentation [
7,
8]. Therefore, FTD and ALS are now considered a single spectrum disorder. It is thought that one of the common molecular and cellular FTD/ALS pathological mechanisms is impaired proteostasis, especially for abnormal and/or inhibitory trafficking coupling endosome to lysosome [
7,
8]. One of the protein components that constitutes these proteostasis pathways is believed to be charged multivesicular body protein 2B (CHMP2B) [
7,
8,
9,
10]. CHMP2B is a core component of the endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT) machinery, and it coordinates the scission of intracellular membranes [
7,
8,
9,
10]. The ESCRT machinery recognizes ubiquitinated proteins at the membrane surface of endosomes or multivesicular bodies (MVBs) to couple endosomes and MVBs to lysosomes [
7,
8,
9,
10]. As expected, dysfunction of CHMP2B (e.g., due to various amino acid mutations) can result in moderate to severe neurological diseases, including the FTD/ALS spectrum [
7,
8,
9,
10].
FTD/ALS type 7 is an autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disorder characterized by onset of FTD and/or ALS primarily in adulthood, and it is caused by various positions of mutations in CHMP2B [
7,
8,
11]. Patients with amino acid mutations including the Thr104Asn (T104N) mutation of CHMP2B have predominantly ALS phenotypes whereas other patients with other mutations have predominantly FTD phenotypes [
7,
8,
11]. A few patients with further other mutations have both phenotypes [
7,
8,
11]; however, the reason why phenotypes differ depending on the position of the mutation is unknown. Despite the relationship between mutations in CHMP2B and diseases, it is unclear whether and how a mutation in CHMP2B affects neuronal cells. In the present study, we describe, for the first time, that CHMP2B with the T104N mutation [
12] greatly inhibits process elongation in the N1E-115 cell line, a widely used model of neuronal differentiation [
13,
14]. Cells expressing the T104N mutant protein caused Golgi stress, whereas a decrease in Golgi stress recovered the ability of cells to elongate processes, providing evidence of a potential pathological molecular and cellular mechanism underlying FTD/ALS7.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Antibodies and siRNA sequences
Key antibodies used and plasmids generated in this study are listed in
Table 1. Sequences of 19-mer siRNAs with dTdT (Fasmac, Kanagawa, Japan) and DNA primers (Fasmac) are described in Figure S2.
2.2. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)
The cDNAs were prepared from total RNA extracted using Isogen (Nippon Gene, Tokyo, Japan) with the PrimeScript RT Master Mix kit (Takara Bio, Kyoto, Japan) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. PCR amplification from reverse transcription products was performed using Gflex DNA polymerase (Takara Bio) with 30 to 36 cycles, each consisting of a denaturation reaction at 98°C (0.2 min), an annealing reaction at 56 to 65°C (0.25 min) depending on the annealing temperature, and an extension reaction at 68°C (0.5 min). The resultant PCR products were loaded onto 1% to 2% agarose gels (Nacalai Tesque, Kyoto, Japan).
2.3. Cell line culture and differentiation
Mouse neuronal N1E-115 and green monkey kidney epithelial COS-7 cells (JCRB Cell Bank/Japan Health Sciences Foundation, Osaka, Japan) were cultured on 6- or 10-cm cell culture dishes (Nunc/ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) in high-glucose Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium (DMEM; Nacalai Tesque) containing 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS) (ThermoFisher Scientific) and penicillin-streptomycin (ThermoFisher Scientific) in 5% CO
2 at 37°C. COS-7 and N1E-115 cells are known to have high transfection efficiency and neuronal differentiation ability, respectively. Cell lines stably expressing the wild-type (indicated as WT in the figure)
chmp2b gene or the gene with the T104N mutation were selected in the presence of G418 (Nacalai Tesque) as described previously [
15] and isolated as a single clone. To induce differentiation, N1E-115 cells were cultured in DMEM and 1% FBS containing penicillin-streptomycin in 5% CO
2 at 37°C for 48 hours. Cells with processes more than one cell body in length were considered to be process-bearing cells (i.e., differentiated cells) [
16]. Under these conditions, attached cells incorporating trypan blue (Nacalai Tesque) were estimated to be less than 5% in each experiment.
2.4. siRNA transfection
Mouse neuronal N1E-115 cells were transfected with the respective synthesized 21-mer small interfering (si)RNAs with dTdT using the ScreenFect siRNA transfection kit (Fujifilm, Tokyo, Japan) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. The medium was replaced 4 hours after transfection and was generally used for 48 hours after transfection for cell biological and biochemical experiments. Under these conditions, attached cells incorporating trypan blue were estimated to be less than 5% in each experiment.
2.5. Denatured polyacrylamide electrophoresis and immunoblotting
Cells were lysed in lysis buffer (50 mM HEPES-NaOH, pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 3 mM MgCl
2, 1 mM dithiothreitol, 1 mM phenylmethane sulfonylfluoride, 1 μg/mL leupeptin, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM Na
3VO
4, 10 mM NaF, and 0.5% NP-40). For normal denatured conditions, cell lysates were denatured in sample buffers (Fujifilm), and samples were separated on a sodium dodecylsulfate polyacrylamide gel (Nacalai Tesque). The electrophoretically separated proteins were transferred to a polyvinylidene fluoride membrane (Fujifilm), blocked with Blocking One (Nacalai Tesque), and immunoblotted using primary antibodies, followed by peroxidase enzyme-conjugated secondary antibodies. Peroxidase-reactive bands were captured using an image scanner (Canon, Tokyo, Japan) and scanned using CanoScan software (Canon). The blots shown in the figures are representative of 3 blots. We performed some sets of experiments in immunoblotting studies and quantified other immunoreactive bands with one control’s immunoreactive band as 100% using Image J software (
https://imagej.nih.gov/).
2.6. Fluorescence images
Cells on coverslips were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (Nacalai Tesque) or 100% cold methanol (Nacalai Tesque) and blocked with Blocking One. Slides were incubated with primary antibodies and then with Alexa Fluor fluorescent-conjugated secondary antibodies. The coverslips were mounted using the Vectashield kit (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA, USA). The fluorescent images were collected and merged with microscope systems FV1200 or FV3000 equipped with a laser-scanning Fluoview apparatus and software (both from Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). The images in the figures are the representative of 3 images and were analyzed using Image J software.
2.7. Statistical analyses
Values are shown as means ± standard deviation (SD) of separate experiments. Intergroup comparisons were made using unpaired Student’s t-test in Excel (Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA). A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was followed by a Tukey’s multiple comparison test using Graph Pad Prism (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). Differences were considered statistically significant when p<0.05.
2.8. Ethics statement
Techniques using genetically modified cells and related techniques were performed in accordance with a protocol approved by the Tokyo University of Pharmacy and Life Sciences Gene and Animal Care Committee (Approval Nos. LS28-20 and LSR3-011).
4. Discussion
FTD and ALS are neurodegenerative diseases with overlapping symptoms and causes; as such, they are commonly considered a single spectrum disorder. Abnormalities in the homeostasis of biomaterials involving dysfunctional protein clearance, impaired RNA metabolism, and aberrant formation of complexes of proteins with RNA are emerging as key events underlying FTD/ALS pathogenesis. It is likely that these processes, including protein and nucleotide clearance, interact with each other at the molecular level, converging on a common molecular pathogenic pathway [
25,
26,
27,
28]. Studies on FTD/ALS7-associated CHMP2B reveal that CHMP2B preferentially participates in protein clearance [
11,
12]. Recent findings show that CHMP2B regulates casein kinase 1 (CK1) phosphorylation of TAR DNA-binding protein of 43kDa (TDP-43), which binds to RNAs as well as some DNAs [
29]. TDP-43 is also involved in FTD/ALS [
30]. Detailed analyses of the pathogenic mutations of CHMP2B will allow us to identify the relationship between CHMP2B and RNA metabolism through TDP-43. In the present study, WT CHMP2B typically displayed MVB-like structures in cells; in contrast, the T104N mutant protein exhibited aggregate-like structures; however, it is unknown whether these structures exist in the Golgi body as an aggregate-like complex containing RNA. Additionally, it is unclear whether the structure directly exhibits toxic gain-of-function in cells.
It is more likely that a common pathological molecular mechanism of FTD/ALS spectrum is impaired proteostasis, especially for abnormal trafficking coupling endosome to lysosome. Among protein components that constitute these proteostasis pathways, CHMP2B is a core component of the ESCRT machinery and coordinates scission of intracellular membranes such as endosome membranes. The ESCRT is composed of sequential subcomplexes, ESCRT-0 to ESCRT-III, and facilitates endosome to lysosome transport in almost all cell types, including neuronal cells [
9,
10]. Before and during the formation of endosomes involving MVB, ESCRT plays a key role in intracellular membrane transport and remodeling, primarily at endosomes [
9,
10]. The ESCRT-III subcomplex involving CHMP2B shapes their membranes, cooperates with vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein (VPS) 4 as the ATPase, and undergoes fission of the membrane neck from inside the endosome. The ESCRT-0 to -II subcomplexes mainly contribute to the formation of the ESCRT-III subcomplex [
9,
10]. Therefore, mutations in CHMP2B of the ESCRT-III subcomplex give rise to several neurodegenerative diseases because all ESCRT protein components are required for appropriate morphogenesis and function of neuronal cells [
9,
10,
11,
12]. Because CHMP2B protein with the T104N mutation exhibits aggregate-like structures but not MVB-like structures, this mutant protein seems unlikely to be functional within the ESCRT system. If this hypothesis is true, it is conceivable that loss of function of CHMP2B underlies the cellular basis of FTD/ALS pathogenesis.
The Golgi stress pathway is thought to mitigate the effects of specific stresses within cells or to arrest the cell cycle, as seen in the unfolded protein response (UPR) established in the ER. Increasing evidence indicates that Golgi stress is mediated by four major pathways through (1) HSP47, (2) TFE3 and possible downstream targets such as the structural proteins composing the Golgi body, (3) CREB3 and Arf4, and (4) caspase-2 [
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24]. First, HSP47 is an ER chaperone and it is likely that HSP47 is also localized in the Golgi body. HSP47 is thought to protect the Golgi body from various stresses [
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24], and expression levels of HSP47 were comparable in cells expressing WT and mutant CHMP2B. Second, TFE3 is an essential transcription factor controlling the genes that encode Golgi body structural proteins such as GM130, the intracellular vesicle transporting molecules, and Golgi-resident enzymes mediating glycosylation [
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24]. Because GM130 is upregulated in cells expressing mutated CHMP2B, it is thought that its pathway through TFE3 is responsible for Golgi stress induced by mutated CHMP2B proteins. Third, the specific targeting pathway of the transcription factor CREB3 is the small GTPase Arf4 [
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24]. Arf4 is upregulated in cells expressing mutated CHMP2B. The pathway through Arf4 may be responsible for Golgi stress induced by mutated CHMP2B proteins. Fourth, active caspase-2 mainly plays a non-apoptotic role, lacking the ability to activate effector caspases such as caspase-3. Procaspase-2 is also present in the cytoplasmic surface of the Golgi body. The prodomain of procaspase-2 is cleaved to generate active caspase-2, probably suppressing the functions of the Golgi body by cleaving proteins such as golgin-160 [
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24]; however, cleaved active caspase-2 results in a decrease in cells expressing mutated CHMP2B, indicating that the pathway through caspase-2 is not involved in Golgi stress in cells expressing mutated CHMP2B. Thus, we focused only on the pathway through CREB3 and Arf4, because the pathway through TFE3 and molecules such as GM130 significantly contribute homeostasis of the Golgi body [
31]. As expected, knockdown of Arf4, possibly acting through decreasing Golgi stress, recovered morphological differentiation with process elongation in cells expressing mutated CHMP2B.
Arf4 is a small GTPase and is thought to participate in intracellular vesicle trafficking with other Arf-family small GTPases. The Arf family of small GTPases are composed of class I (Arf1 and Arf2 and/or Arf3), class II (Arf4 and Arf5), and class III (Arf6). Class I GTPases such as Arf1 regulate the vesicle transporting system around the Golgi body, and the class III GTPase Atf6 primarily controls vesicle transporting around the intracellular surface of the plasma membrane. In contrast, the precise role of the class II GTPase Arf4 remains unclear [
32,
33]. For example, Ezratty et al. reported that Arf4 regulates polarized exocytosis to act through the complex between the basal body and the ciliary body. It is thus likely that Arf4 regulates Notch signaling in epidermal morphological differentiation [
34]. Wang et al. reported that Arf4 and the guanine-nucleotide exchange factor GBF1 synergize with the sensory receptor cargo to regulate trafficking of the ciliary membrane [
35]. It is thought that the activities of Arf4 are precisely associated with the formation of the ciliary membrane [
36,
37]. It will be important to determine which organelles in the cognate intracellular membrane transporting are mediated by Arf4 and how this is achieved. In addition, it remains unclear how signaling around Arf4 is related to the response to Golgi stress.
The question of why and how CHMP2B is involved in promoting process elongation remains to be answered. In the initial steps of neuronal morphological differentiation, cells undergo dynamic morphogenesis such as neurite outgrowth and elongation. Dynamic morphogenesis requires synthesis of many membrane lipids and proteins to achieve neurite outgrowth and elongation. Therefore, during cell development, a quality control step of protein is required; that is, proteostasis. It is possible that CHMP2B, as the ESCRT-III subcomplex component, and other ESCRT components directly or indirectly monitor fine-tuned neurite outgrowth and elongation. Here we show that FTD/ALS7-associated mutation of CHMP2B inhibits neuronal morphological differentiation. Mutated CHMP2B is specifically localized in the Golgi body to trigger Golgi stress. In contrast, knockdown of Arf4, a Golgi stress mediator, recovers the ability of cells to differentiate. Further studies on the relationship of mutated CHMP2B with Golgi stress are needed to increase our understanding of the detailed mechanisms by which the FTD/ALS7-associated mutation of CHMP2B inhibits neuronal morphological differentiation using cells and genetically modified mice, as well as of a possible causal relationship between inhibitory differentiation and the early stages of neurodegeneration in FTD/ALS7. Additional studies will allow us to elucidate the role of Golgi stress as a potential molecular and cellular pathological mechanism underlying FTD/ALS7 and might lead to the development of therapeutic target–specific drug candidates for FTD/ALS7 and other types of FTD/ALS.
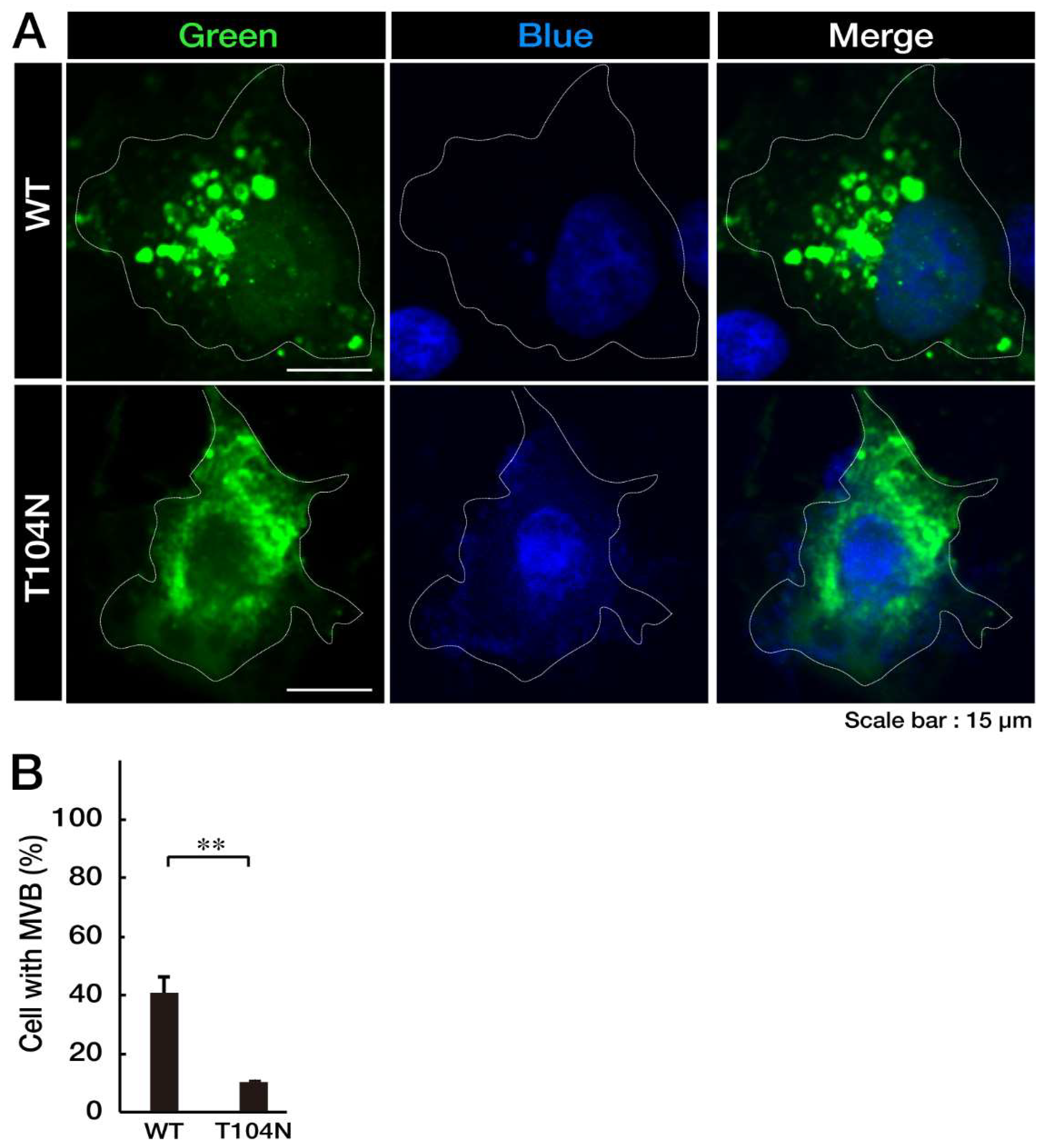
Figure 1.
Wild-type CHMP2B is present in circular MVB-like structures in cells, whereas CHMP2B with the T104N mutation forms aggregate-like structures. (A, B) COS-7 cells (indicated by white dotted lines) were transfected with the plasmid encoding wild-type (WT) CHMP2B tagged with EGFP at its N-terminus or EGFP-tagged CHMP2B with the T104N mutation. Transfected cells (green) were stained with DAPI to detect nuclear positions (blue). Cells with circular MVB-like structures are statistically depicted in the graph (** p<0.01; n = 10 fields). MVB, multivesicular bodies; WT, wild-type; EGFP, enhanced green fluorescent protein; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.
Figure 1.
Wild-type CHMP2B is present in circular MVB-like structures in cells, whereas CHMP2B with the T104N mutation forms aggregate-like structures. (A, B) COS-7 cells (indicated by white dotted lines) were transfected with the plasmid encoding wild-type (WT) CHMP2B tagged with EGFP at its N-terminus or EGFP-tagged CHMP2B with the T104N mutation. Transfected cells (green) were stained with DAPI to detect nuclear positions (blue). Cells with circular MVB-like structures are statistically depicted in the graph (** p<0.01; n = 10 fields). MVB, multivesicular bodies; WT, wild-type; EGFP, enhanced green fluorescent protein; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.
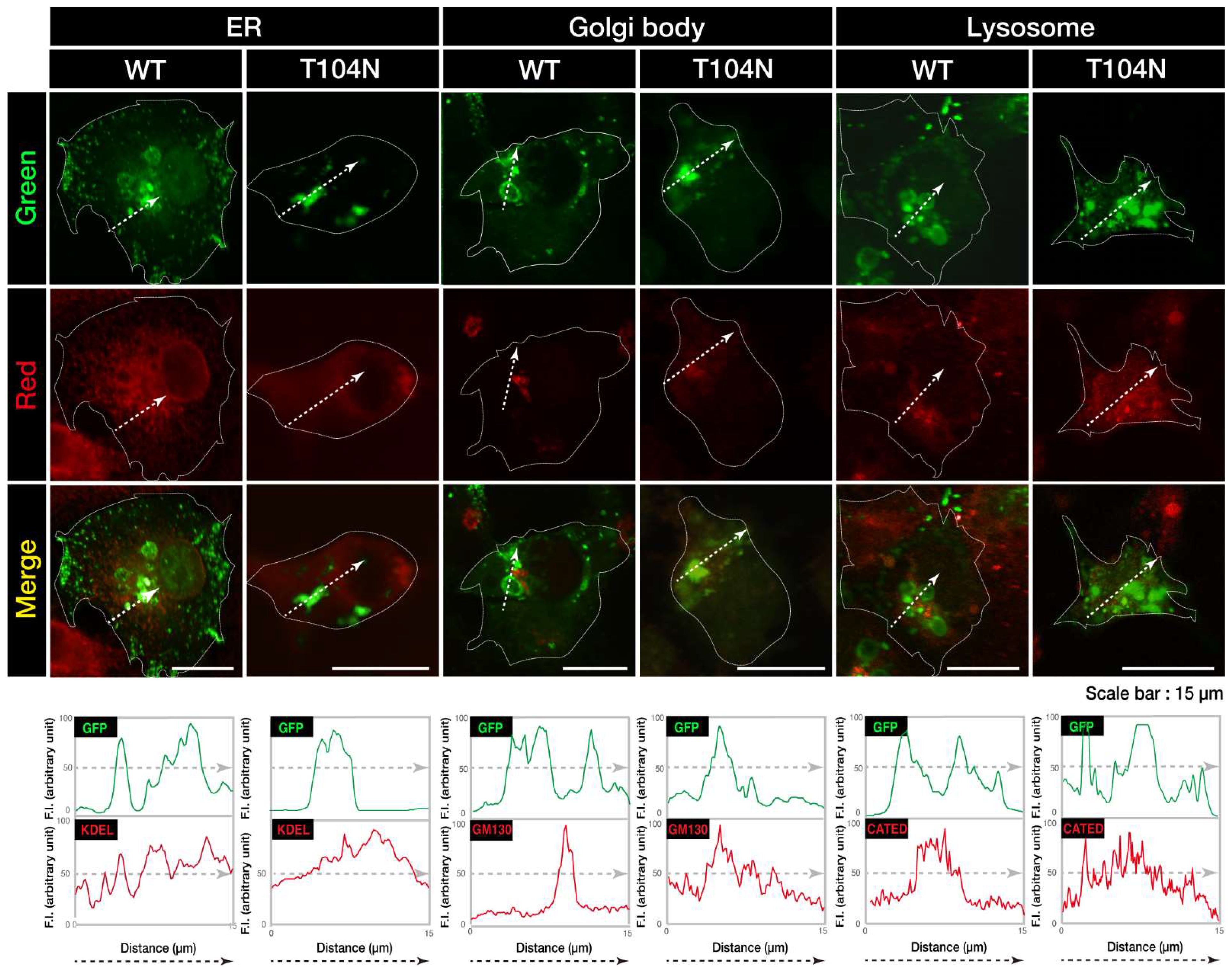
Figure 2.
CHMP2B with the T104N mutation forms aggregate-like structures in the Golgi body. (A, B) COS-7 cells were transfected with the plasmid encoding the GFP-tagged wild-type (WT) or mutated CHMP2B (T104N). Transfected cells (green) were stained with an antibody against the ER-specific antigen KDEL (red), the Golgi body-specific antigen GM130 (red), or the lysosome-specific antigen cathepsin D (CATED, red). The approximate outlines of the cells are shown by white dotted lines. Scan plots were performed along the white lines in the direction of the arrows in the green and red images. Graphs showing fluorescence intensity (F.I.; arbitrary units) along the lines in the direction of the arrows are depicted in the bottom panels. GFP, green fluorescent protein; WT, wild-type; ER, endoplasmic reticulum.
Figure 2.
CHMP2B with the T104N mutation forms aggregate-like structures in the Golgi body. (A, B) COS-7 cells were transfected with the plasmid encoding the GFP-tagged wild-type (WT) or mutated CHMP2B (T104N). Transfected cells (green) were stained with an antibody against the ER-specific antigen KDEL (red), the Golgi body-specific antigen GM130 (red), or the lysosome-specific antigen cathepsin D (CATED, red). The approximate outlines of the cells are shown by white dotted lines. Scan plots were performed along the white lines in the direction of the arrows in the green and red images. Graphs showing fluorescence intensity (F.I.; arbitrary units) along the lines in the direction of the arrows are depicted in the bottom panels. GFP, green fluorescent protein; WT, wild-type; ER, endoplasmic reticulum.
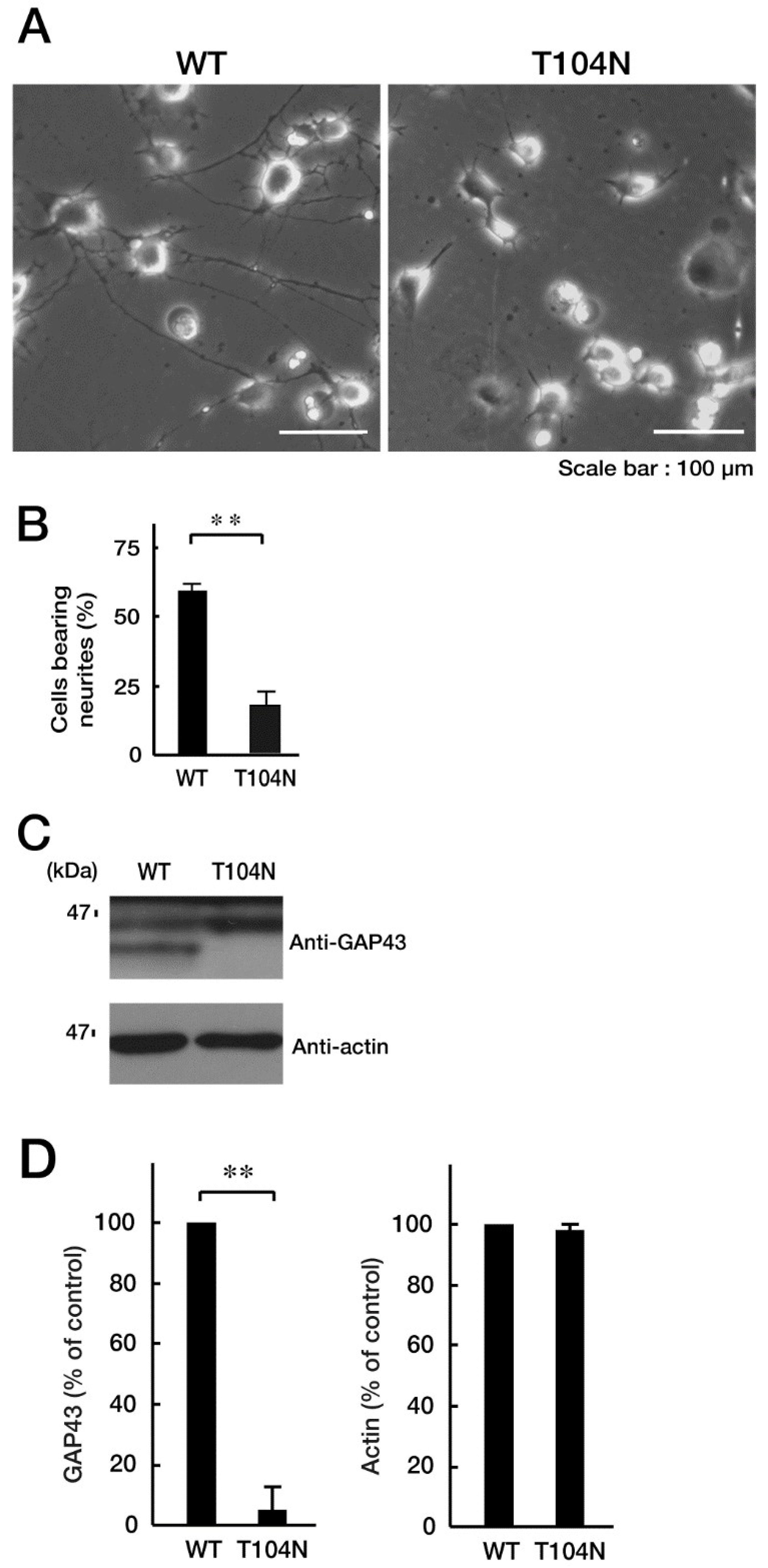
Figure 3.
CHMP2B with the T104N mutation inhibits neuron-like process extension. N1E-115 cells with WT or mutated CHMP2B (T104N) were allowed to differentiate for 48 hours. Typical cell images after 48 hours are shown in (A). (B) Cells with processes with a body length more than one cell were counted as cells with neurites and statistically shown in the graph (** p<0.01; n = 10 fields). (C, D) The lysates of cells following the induction of differentiation (48 hours) were immunoblotted with an antibody against neuron-specific marker GAP43 and actin as the internal marker protein, and their immunoreactive band intensities are statistically depicted (D) (** p<0.01; n = 3 blots). WT, wild-type.
Figure 3.
CHMP2B with the T104N mutation inhibits neuron-like process extension. N1E-115 cells with WT or mutated CHMP2B (T104N) were allowed to differentiate for 48 hours. Typical cell images after 48 hours are shown in (A). (B) Cells with processes with a body length more than one cell were counted as cells with neurites and statistically shown in the graph (** p<0.01; n = 10 fields). (C, D) The lysates of cells following the induction of differentiation (48 hours) were immunoblotted with an antibody against neuron-specific marker GAP43 and actin as the internal marker protein, and their immunoreactive band intensities are statistically depicted (D) (** p<0.01; n = 3 blots). WT, wild-type.
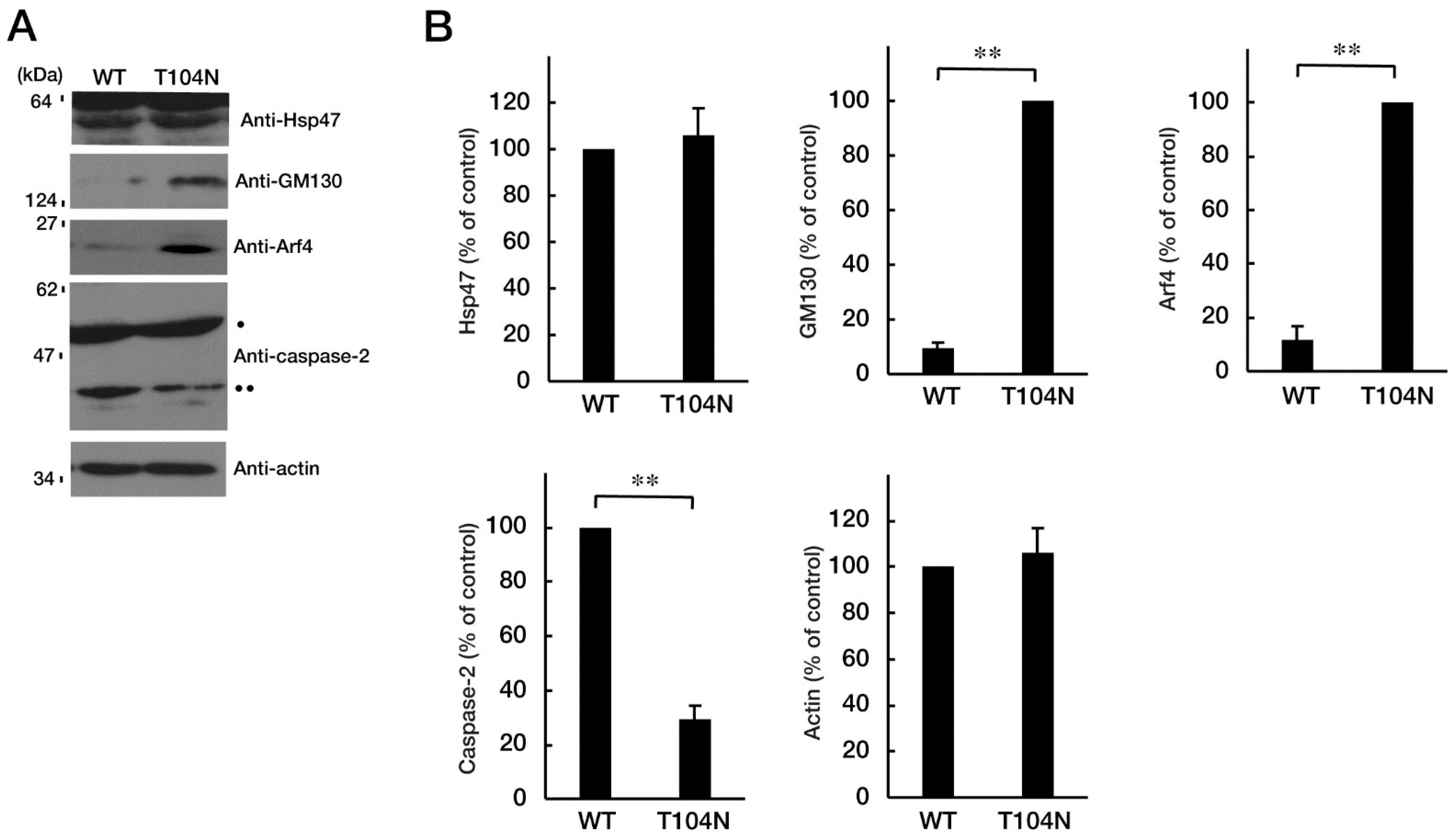
Figure 4.
CHMP2B with the T104N mutation upregulates Golgi stress signal. (A, B) N1E-115 cells with WT or mutated CHMP2B (T104N) were allowed to differentiate for 48 hours and lysed. The lysates were immunoblotted with an antibody against Golgi stress marker Hsp47, GM130, Arf4, cleaved caspase-2 (indicated with **; pro-caspase-2 indicated with *), or control actin, and their immunoreactive band intensities are statistically depicted in the graph (** p<0.01; n = 3 blots). WT, wild-type.
Figure 4.
CHMP2B with the T104N mutation upregulates Golgi stress signal. (A, B) N1E-115 cells with WT or mutated CHMP2B (T104N) were allowed to differentiate for 48 hours and lysed. The lysates were immunoblotted with an antibody against Golgi stress marker Hsp47, GM130, Arf4, cleaved caspase-2 (indicated with **; pro-caspase-2 indicated with *), or control actin, and their immunoreactive band intensities are statistically depicted in the graph (** p<0.01; n = 3 blots). WT, wild-type.
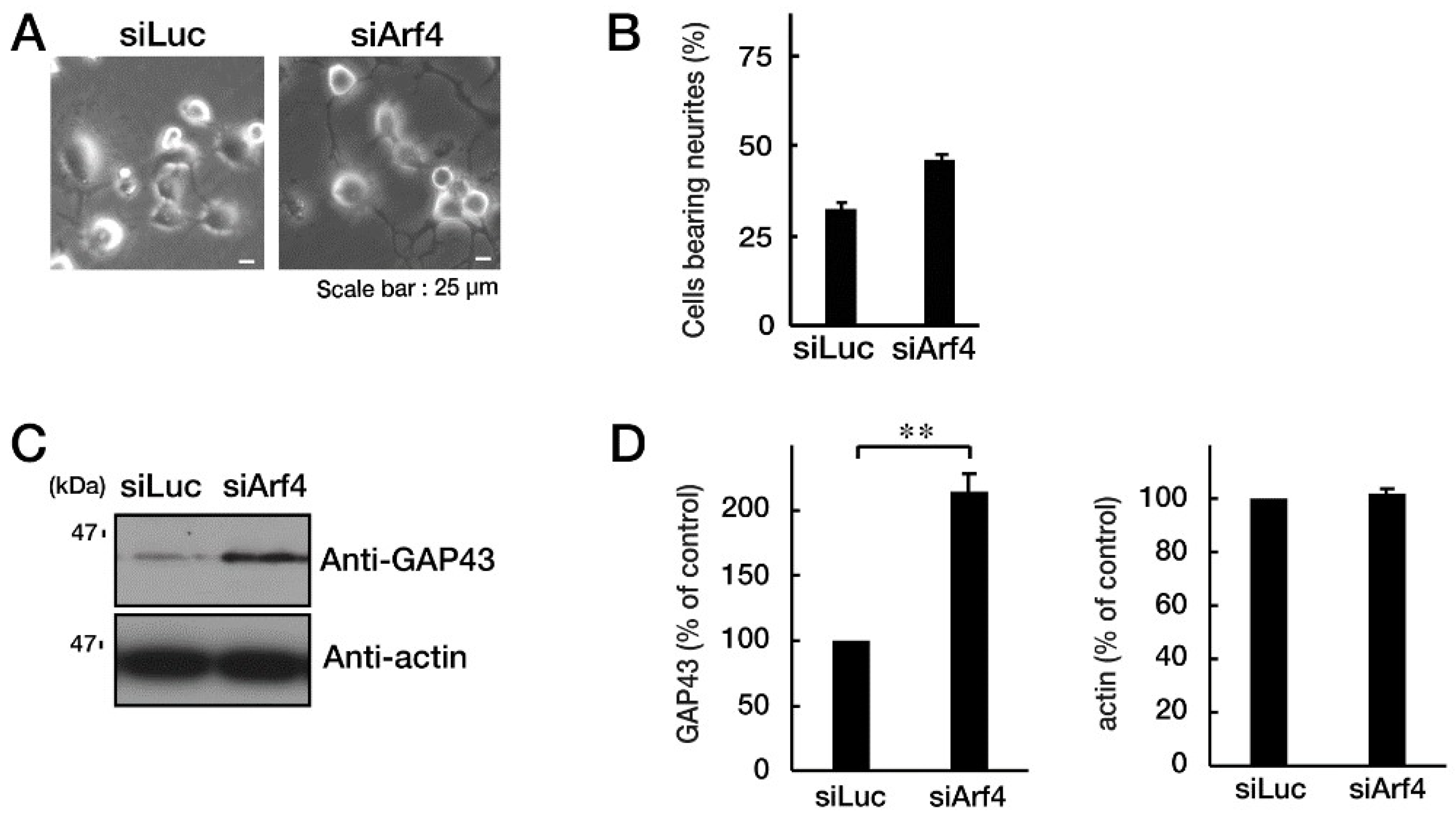
Figure 5.
Knockdown of Arf4 recovers phenotypes of cells with CHMP2B with the T104N mutation. N1E-115 cells with mutated CHMP2B were transfected with control luciferase (Luc) or Arf4 siRNA and allowed to differentiate for 48 hours. Typical cell images after 48 hours are shown in (A). (B) Cells with processes of more than one cell body length were counted as cells with neurites and are statistically depicted in the graph (* p<0.05; n = 10 fields). (C, D) The lysates were immunoblotted with an antibody against GAP43 or control actin, and their immunoreactive band intensities are statistically depicted in the graph (** p<0.01; n = 3 blots).
Figure 5.
Knockdown of Arf4 recovers phenotypes of cells with CHMP2B with the T104N mutation. N1E-115 cells with mutated CHMP2B were transfected with control luciferase (Luc) or Arf4 siRNA and allowed to differentiate for 48 hours. Typical cell images after 48 hours are shown in (A). (B) Cells with processes of more than one cell body length were counted as cells with neurites and are statistically depicted in the graph (* p<0.05; n = 10 fields). (C, D) The lysates were immunoblotted with an antibody against GAP43 or control actin, and their immunoreactive band intensities are statistically depicted in the graph (** p<0.01; n = 3 blots).
Table 1.
Key antibodies and plasmids used in this study.
Table 1.
Key antibodies and plasmids used in this study.
| Reagent or material |
Company or source |
Cat. No. |
Lot. No. |
Concentration used |
| Antibody |
|
|
|
|
| Anti-heat shock protein (HSP) 47 |
Santa Cruz Biotechnology |
sc-5293 |
I2118 |
Immunoblotting (IB), 1/200 |
| Anti-Arf4 |
Proteintech |
11673-1-AP |
00048284 |
IB, 1/1,000 |
| Anti-caspase-2 |
Abcam |
ab179520 |
GR209449-2 |
IB, 1/1,000 |
| Anti-actin |
MBL |
M177-3 |
007 |
IB, 1/5,000 |
| Ant-growth-associated protein 43 (GAP43) |
Santa Cruz Biotechnology |
sc-17790 |
J0920 |
IB, 1/5,000 |
| Anti-Lys-Asp-Glu-Leu (KDEL) |
MBL |
M181-3 |
004 |
IF, 1/200 |
| Anti-130 kDa Golgi membrane protein (GM130) |
BD Biosciences |
610823 |
8352796 |
IB, 1/500 and IF, 1/200 |
| Anti-cathepsin D |
Abcam |
ab75852 |
GR260148-33 |
IF, 1/200 |
| Anti-IgG (H+L chain) (Rabbit) pAb-HRP |
MBL |
458 |
353 |
IB, 1/5,000 |
| Anti-IgG (H+L chain) (Mouse) pAb-HRP |
MBL |
330 |
365 |
IB, 1/5,000 |
| Goat pAb to Ms IgG (Alexa Fluor 488 conjugate) |
abcam |
ab150113 |
GR173498-1 |
IF, 1/500 |
| Alexa Fluor TM 594 goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) |
invitrogen |
A11005 |
226-8383 |
IF, 1/500 |
| Alexa Fluor TM 488 goat anti-rabbit IgG (H+L) |
invitrogen |
A11008 |
075-1094 |
IF, 1/500 |
| Alexa Fluor TM 594 goat anti-rabbit IgG (H+L) |
invitrogen |
A11012 |
201-8240 |
IF, 1/500 |
| Recombinant DNA |
|
|
|
|
| pEGFP-C1-human CHMP2B |
Generated in this study |
Not applicable |
|
1.25 µg of DNA per 6 cm dish |
| pEGFP-C1-human CHMP2B with the T104N mutation |
Generated in this study |
Not applicable |
|
1.25 µg of DNA per 6 cm dish |