Submitted:
16 June 2023
Posted:
19 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
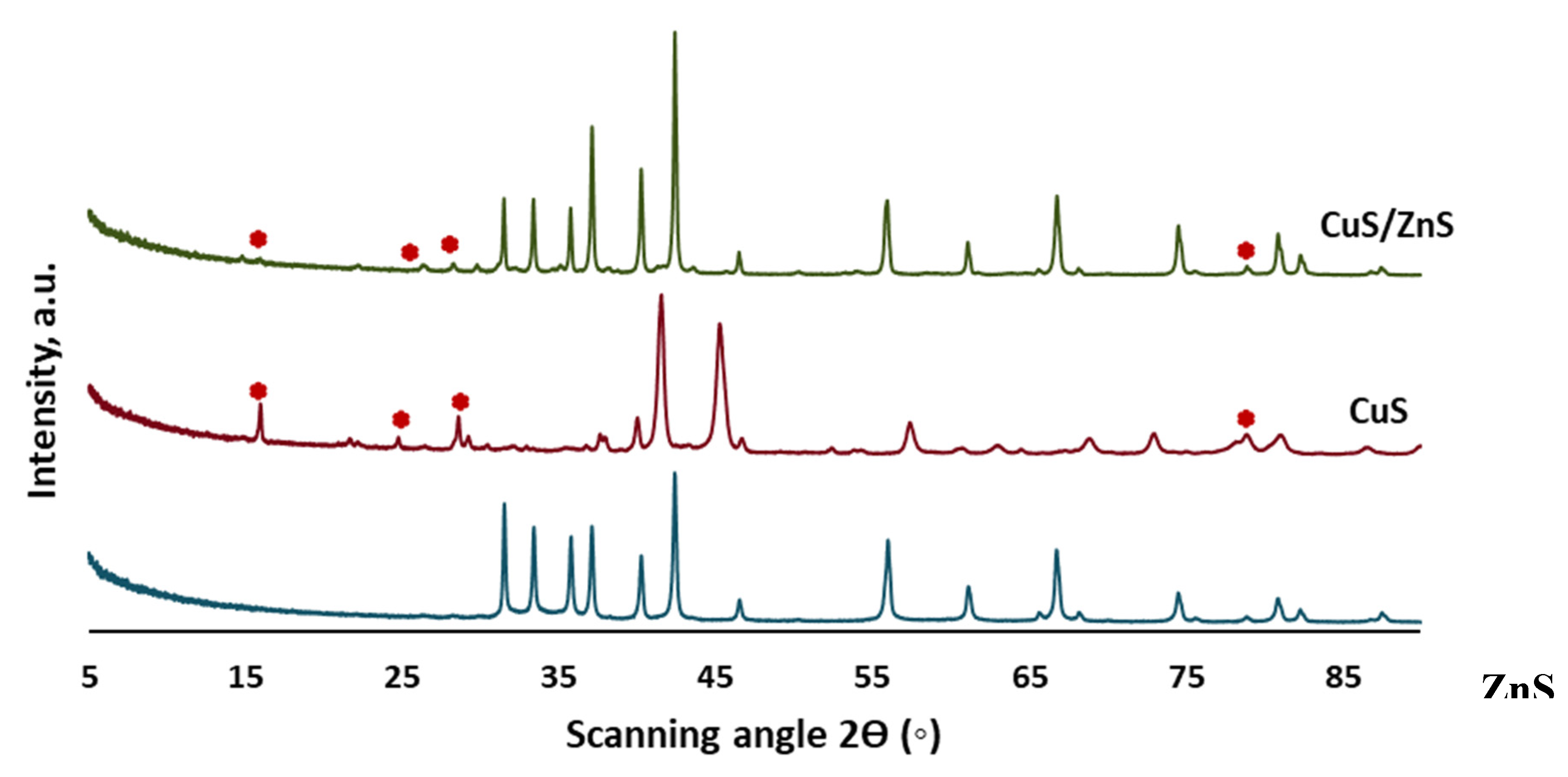
2.1. XRD Analysis
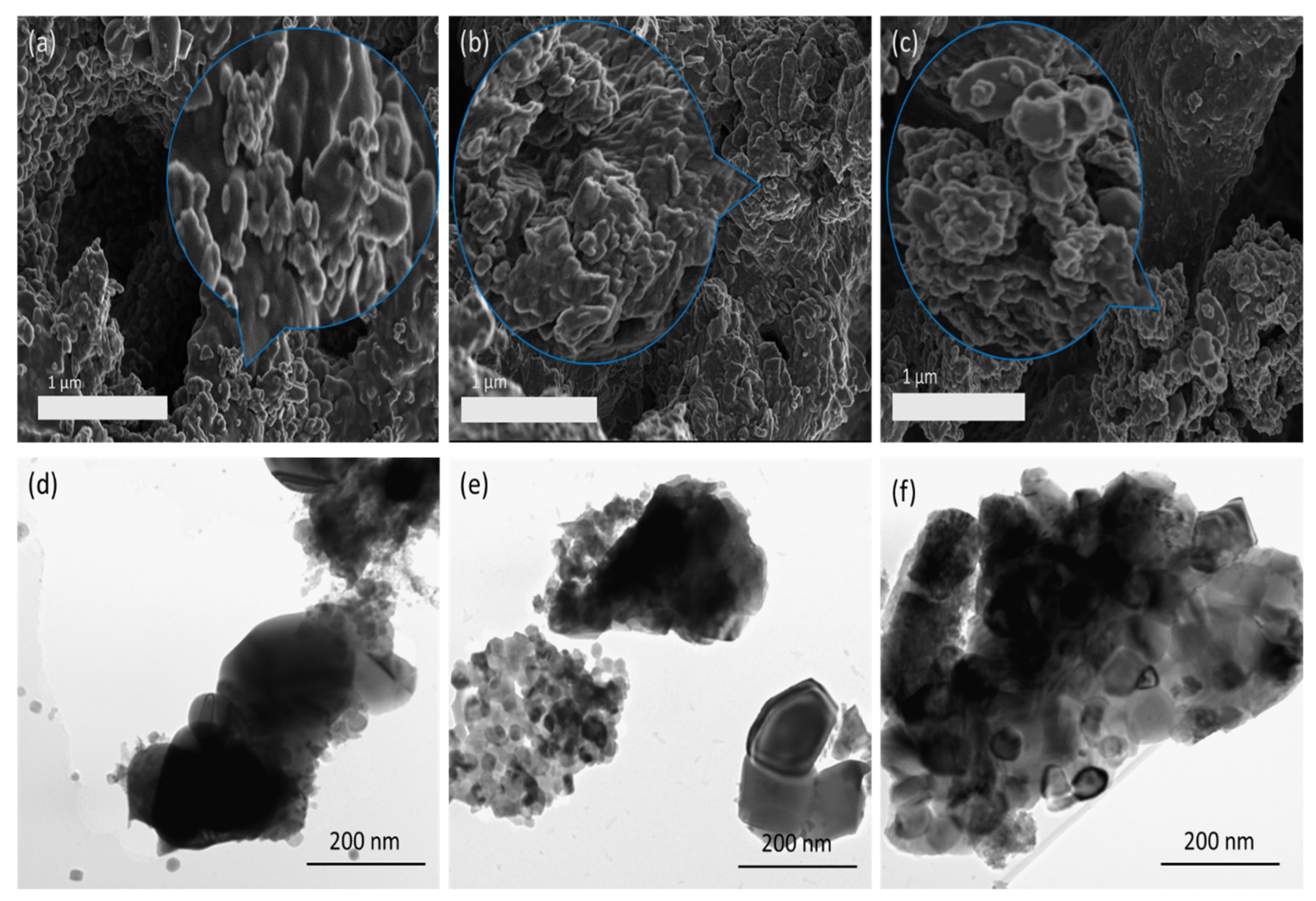
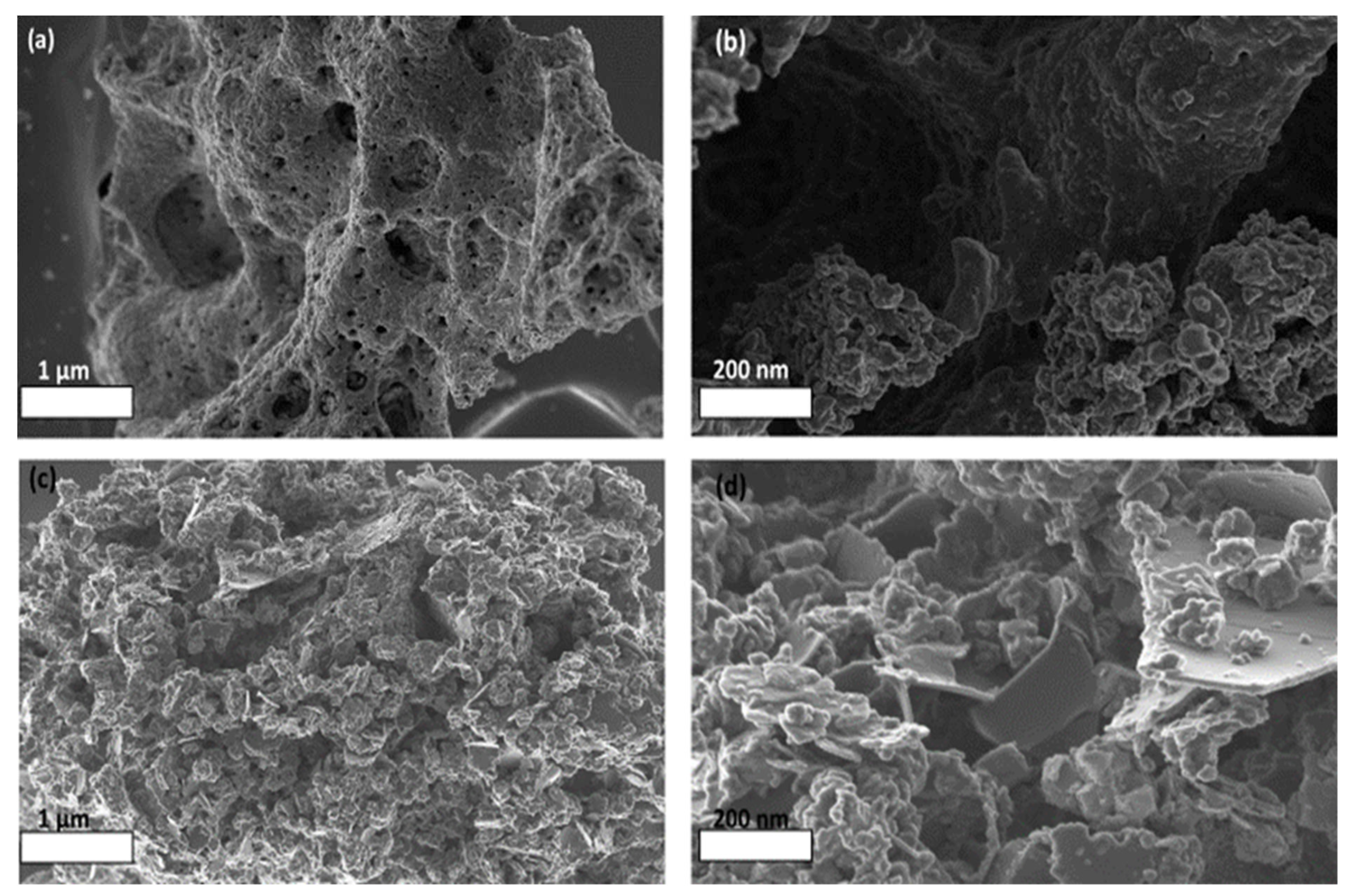
2.2. Catalyst Morphology
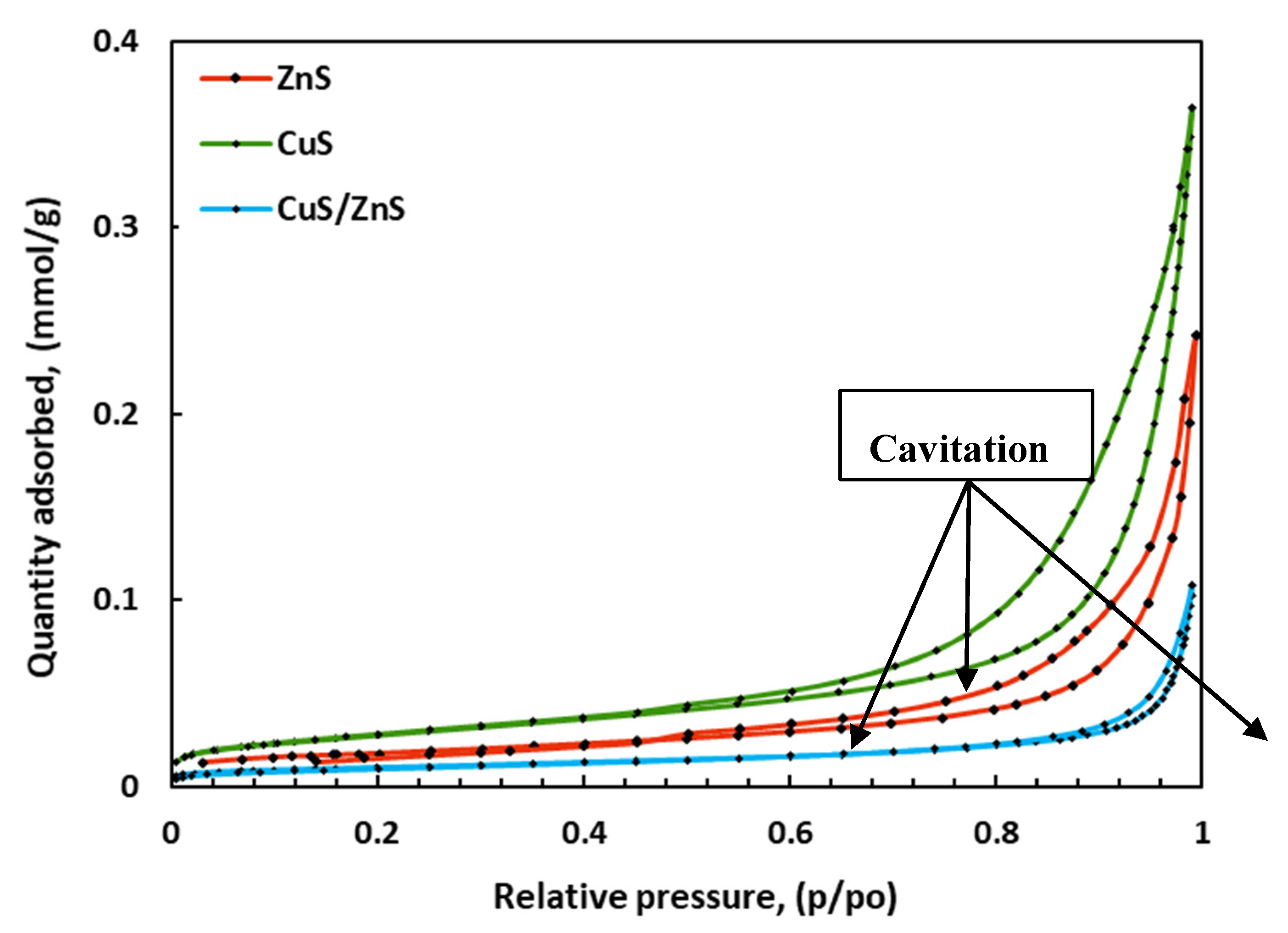
2.3. Surface Area and Pore Size Analysis
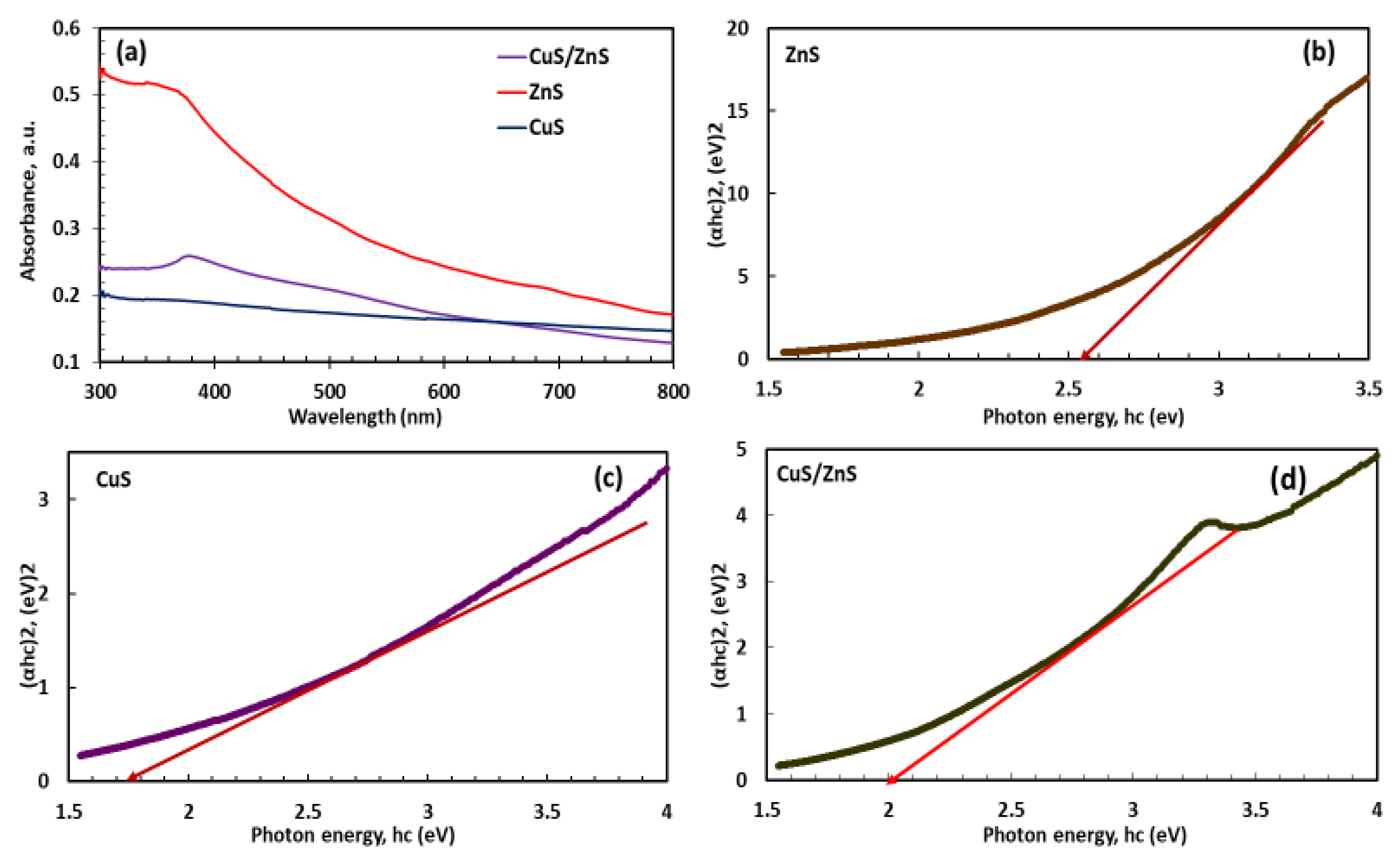
2.4. Photo-Absorption and Band Gap Analysis
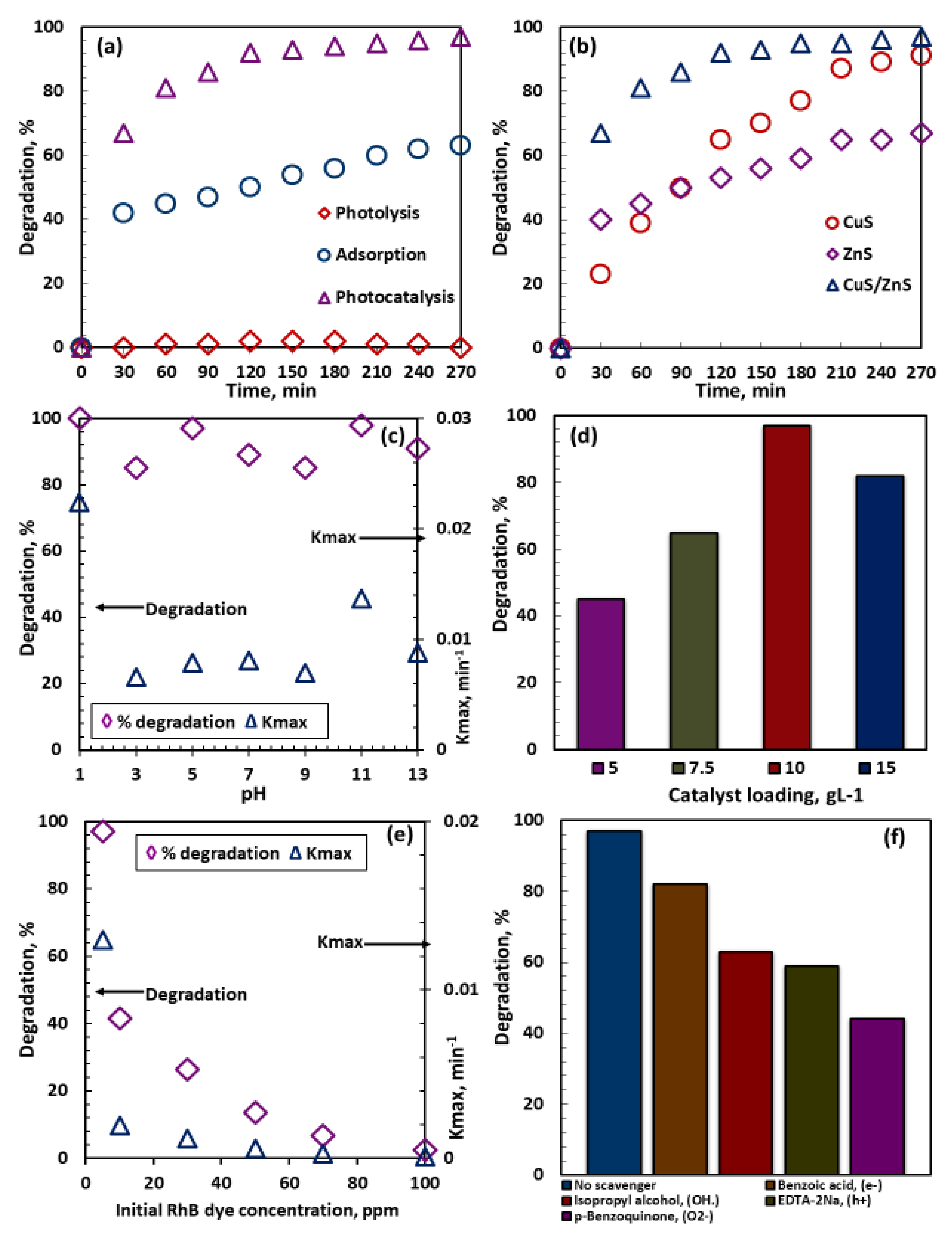
2.5. Photocatalytic Performance
2.5.1. Effect of Individual Catalyst Composites
2.5.2. Effect of Initial pH
2.5.3. Effect of Catalyst Loading
2.5.4. Effect of Initial Rhodamine B Dye Concentration
2.6. Radical Scavenging Test
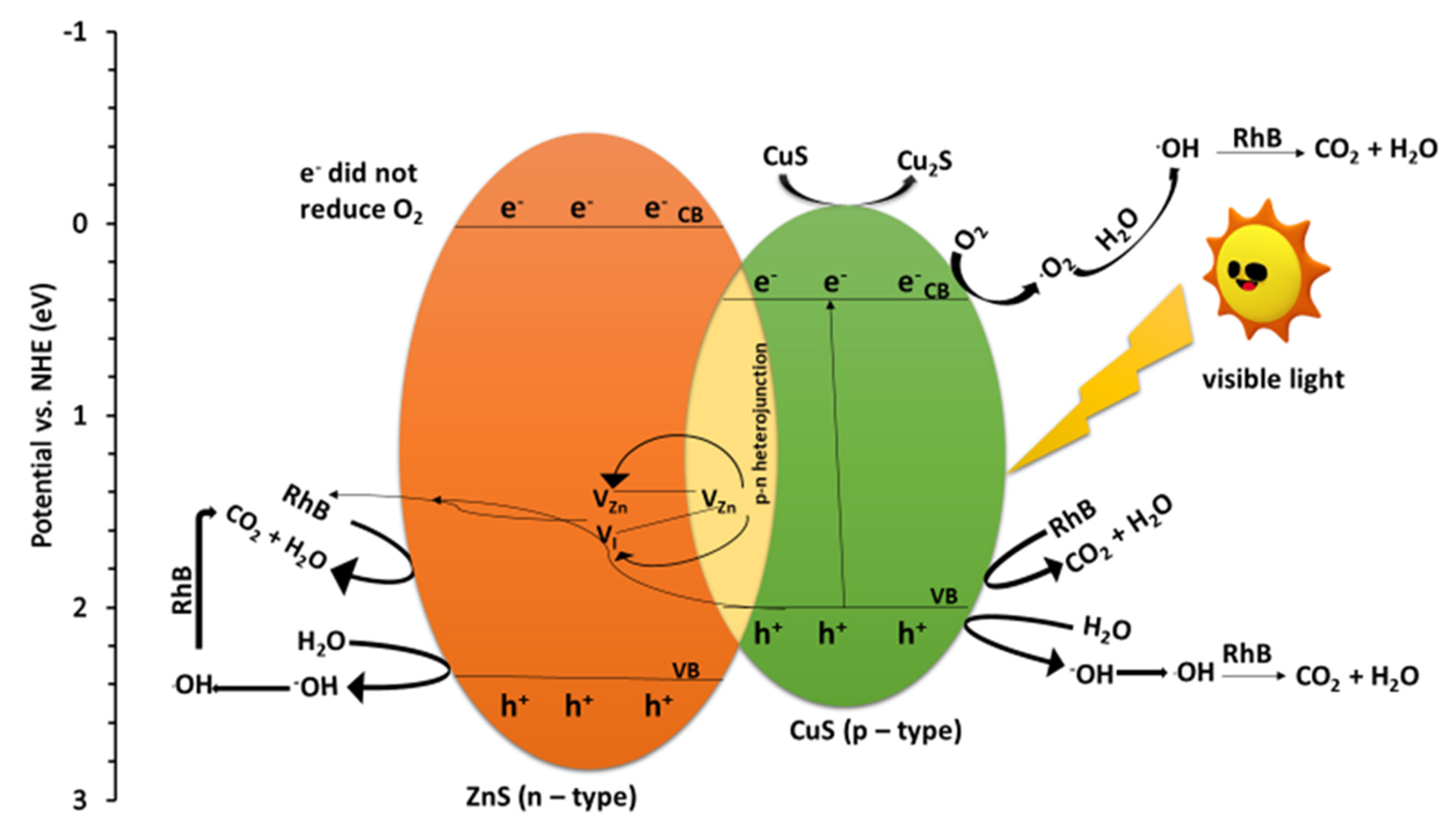
2.7. Mechanism
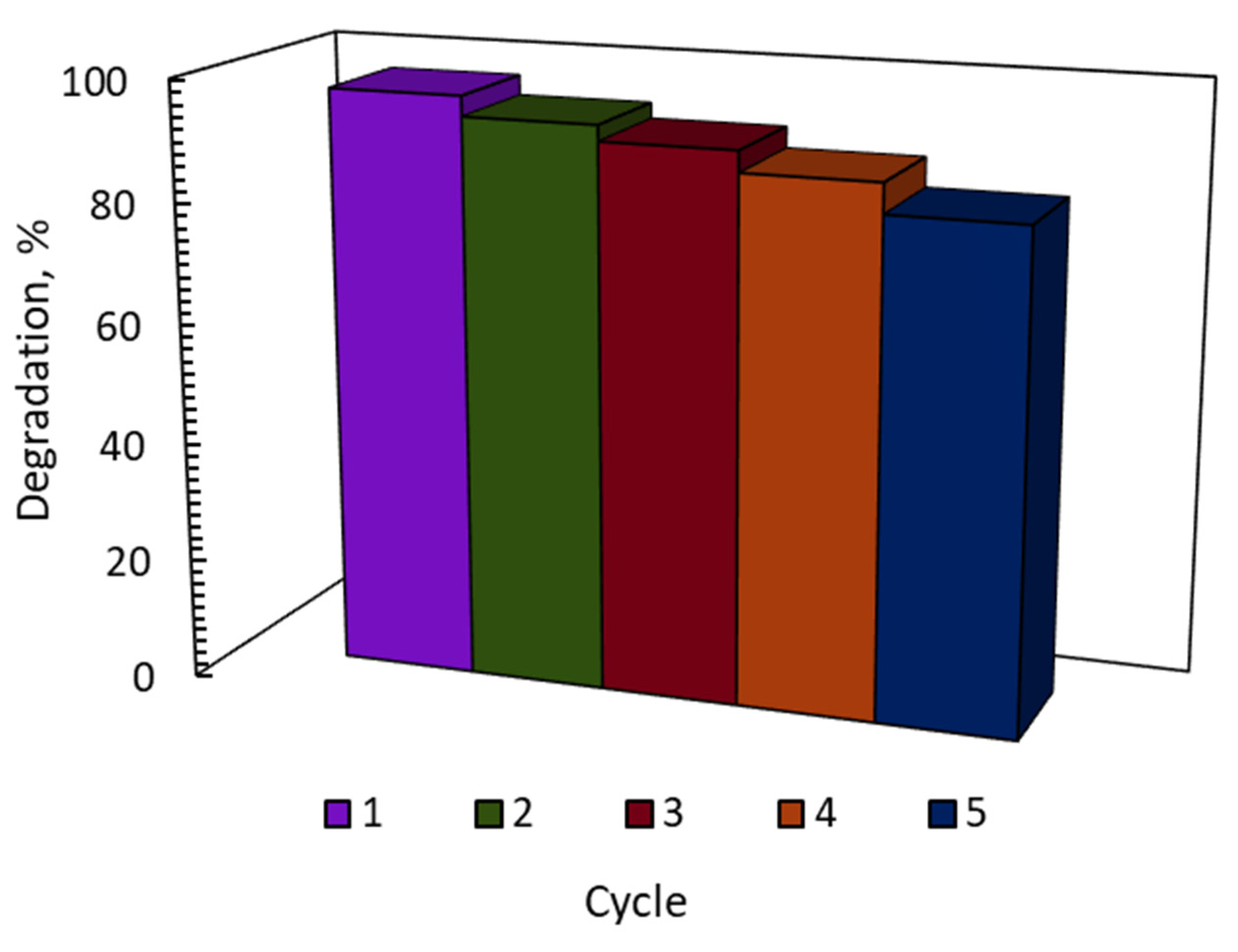
3. Catalyst Recyclability
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Catalyst Synthesis
4.3. Degradation Studies
4.4. Material Characterisation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, J.Y.; McCarty, S.; Glenn, E.; Neale, P.A.; Warne, M.S.J.; Escher, B.I. Mixture effects of organic micropollutants present in water: Towards the development of effect-based water quality trigger values for baseline toxicity. Water research 2013, 47, 3300–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Buriahi, A.K.; Al-Gheethi, A.A.; Kumar, P.S.; Mohamed, R.M.S.R.; Yusof, H.; Alshalif, A.F.; Khalifa, N.A. Elimination of rhodamine B from textile wastewater using nanoparticle photocatalysts: a review for sustainable approaches. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmen, Z.; Daniela, S. Textile organic dyes-characteristics, polluting effects and separation/elimination procedures from industrial effluents-a critical overview. IntechOpen Rijeka, 2012; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Hanafi, M.F.; Sapawe, N. A review on the water problem associate with organic pollutants derived from phenol, methyl orange, and remazol brilliant blue dyes. Materials Today: Proceedings 2020, 31, A141–A150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifzade, G.; Asghari, A.; Rajabi, M. Highly effective adsorption of xanthene dyes (rhodamine B and erythrosine B) from aqueous solutions onto lemon citrus peel active carbon: characterization, resolving analysis, optimization and mechanistic studies. RSC advances 2017, 7, 5362–5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajiboye, T.O.; Oyewo, O.A.; Onwudiwe, D.C. Adsorption and photocatalytic removal of Rhodamine B from wastewater using carbon-based materials. FlatChem 2021, 29, 100277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saigl, Z.M. Various adsorbents for removal of rhodamine b dye: A review. Indonesian Journal of Chemistry 2021, 21, 1039–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, M.S.; Savunthari, K.V.; Ethiraj, S. Synthesis of a copper (II) metal–organic framework for photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B dye in water. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2021, 28, 40835–40843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naciri, Y.; Ahsaine, H.A.; Chennah, A.; Amedlous, A.; Taoufyq, A.; Bakiz, B.; Ezahri, M.; Villain, S.; Benlhachemi, A. Facile synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic performance of Zn3 (PO4) 2 platelets toward photodegradation of Rhodamine B dye. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 2018, 6, 1840–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamuni, N.N.; Adewuyi, Y.G. Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) involving ultrasound for waste water treatment: a review with emphasis on cost estimation. Ultrasonics sonochemistry 2010, 17, 990–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cashman, M.A.; Kirschenbaum, L.; Holowachuk, J.; Boving, T.B. Identification of hydroxyl and sulfate free radicals involved in the reaction of 1, 4-dioxane with peroxone activated persulfate oxidant. Journal of hazardous materials 2019, 380, 120875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-F.; Liao, S.-C.; Hung, S.-W. The dc thermal plasma synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles for visible-light photocatalyst. Journal of photochemistry and photobiology A: Chemistry 2005, 174, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, B.; Fan, J.; Yu, J. S-scheme heterojunction photocatalyst. Chem 2020, 6, 1543–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Fang, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, X. Band-Gap engineering: a new tool for tailoring the activity of semiconducting oxide catalysts for CO oxidation. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters 2021, 12, 9188–9196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Shen, X.; Zhu, G.; Zhou, H.; Ji, Z.; Chen, K.; Yuan, A. Synthesis of ternary Ag/ZnO/ZnFe2O4 porous and hollow nanostructures with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 2016, 184, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Gao, Z.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, W.; Sun, C. A simple and effective method for fabricating novel p–n heterojunction photocatalyst g-C3N4/Bi4Ti3O12 and its photocatalytic performances. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 2016, 192, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, J.; Yu, J.; Jaroniec, M.; Wageh, S.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A. Heterojunction photocatalysts. Advanced materials 2017, 29, 1601694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Z.; Hu, J.; Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, X. Semiconductor heterojunction photocatalysts: design, construction, and photocatalytic performances. Chemical Society Reviews 2014, 43, 5234–5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harish, S.; Archana, J.; Navaneethan, M.; Ponnusamy, S.; Singh, A.; Gupta, V.; Aswal, D.; Ikeda, H.; Hayakawa, Y. Synergetic effect of CuS@ ZnS nanostructures on photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutant under visible light irradiation. RSC advances 2017, 7, 34366–34375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Wu, Z.; Lin, Z.; Yu, J. Enhanced visible light photocatalytic hydrogen production activity of CuS/ZnS nanoflower spheres. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 2015, 3, 13913–13919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, C.; Singh, A.; Sahoo, R.; Sasmal, A.K.; Negishi, Y.; Pal, T. Preformed ZnS nanoflower prompted evolution of CuS/ZnS p-n heterojunctions for exceptional visible-light driven photocatalytic activity. New Journal of Chemistry 2015, 39, 5628–5635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitinjak, E.M.; Masmur, I.; Marbun, N.V.M.D.; Hutajulu, P.E.; Gultom, G.; Sitanggang, Y. Direct Z-scheme of n-type CuS/p-type ZnS@ electrospun PVP nanofiber for the highly efficient catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol and mixed dyes. RSC advances 2022, 12, 16165–16173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moja, M.M.; Chirwa, E.; Tichapondwa, S.M. Visible light activated photocatalytic degradation of 2, 4-dichlorophenol using silver halide photocatalysts. 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Varghese, J. CuS–ZnS decorated graphene nanocomposites: Synthesis and photocatalytic properties. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids 2021, 156, 109911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rameshbabu, R.; Ravi, P.; Sathish, M. Cauliflower-like CuS/ZnS nanocomposites decorated g-C3N4 nanosheets as noble metal-free photocatalyst for superior photocatalytic water splitting. Chemical Engineering Journal 2019, 360, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mzimela, N.; Tichapondwa, S.; Chirwa, E. Visible-light-activated photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B using WO 3 nanoparticles. RSC advances 2022, 12, 34652–34659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichipi, E.O.; Tichapondwa, S.M.; Chirwa, E.M. Plasmonic effect and bandgap tailoring of Ag/Ag2S doped on ZnO nanocomposites for enhanced visible-light photocatalysis. Advanced Powder Technology 2022, 33, 103596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S. Ion-exchange synthesis and enhanced visible-light photoactivity of CuS/ZnS nanocomposite hollow spheres. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2010, 114, 13642–13649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Liu, J.; Zhu, W.; Hu, Z.-T.; Lim, T.-T.; Yan, X. Facile room-temperature synthesis of carboxylated graphene oxide-copper sulfide nanocomposite with high photodegradation and disinfection activities under solar light irradiation. Scientific reports 2015, 5, 16369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Hu, J.; Cong, S.; Zhao, Z.; Qiu, X. Hierarchical BiOCl microflowers with improved visible-light-driven photocatalytic activity by Fe (III) modification. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 2015, 174, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelifard, M.; Eshghi, H.; Mohagheghi, M.M.B. Synthesis and characterization of nanostructural CuS–ZnS binary compound thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Optics Communications 2012, 285, 4400–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshamsi, H.A.; Beshkar, F.; Amiri, O.; Salavati-Niasari, M. Porous hollow Ag/Ag2S/Ag3PO4 nanocomposites as highly efficient heterojunction photocatalysts for the removal of antibiotics under simulated sunlight irradiation. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanty, L.; Pattanayak, D.S.; Pradhan, D.; Dash, S.K. Synthesis of novel p-n heterojunction g-C3N4/Bi4Ti3O12 photocatalyst with improved solar-light-driven photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes. Environmental Quality Management 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Meng, X.; Song, X.; Feng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, G. Controllable synthesis of hierarchical CuS/ZnS hetero-nanowires as high-performance visible-light photocatalysts. RSC advances 2016, 6, 110266–110273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, J.; Liu, H.; Huang, J. Design, modification and application of semiconductor photocatalysts. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers 2018, 93, 590–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Materials | Surface area (m2g-1) |
Average poresize (nm) |
BJH Adsorption (4V/Å)* |
BJH Desorption (4V/Å)* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZnS | 4.06 | 12.03 | 73.47 | 75.61 |
| CuS | 8.73 | 11.22 | 60.68 | 82.43 |
| CuS/ZnS | 2.72 | 8.57 | 51.35 | 54.38 |
| Catalyst Loading (gL-1) |
Linear Regression (R2) | Kmax (min-1) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.097 | 0.0000 |
| 5 | 0.897 | 0.0034 |
| 7.5 | 0.947 | 0.0058 |
| 10 | 0.986 | 0.0186 |
| 15 | 0.905 | 0.0094 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





