Submitted:
17 June 2023
Posted:
19 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
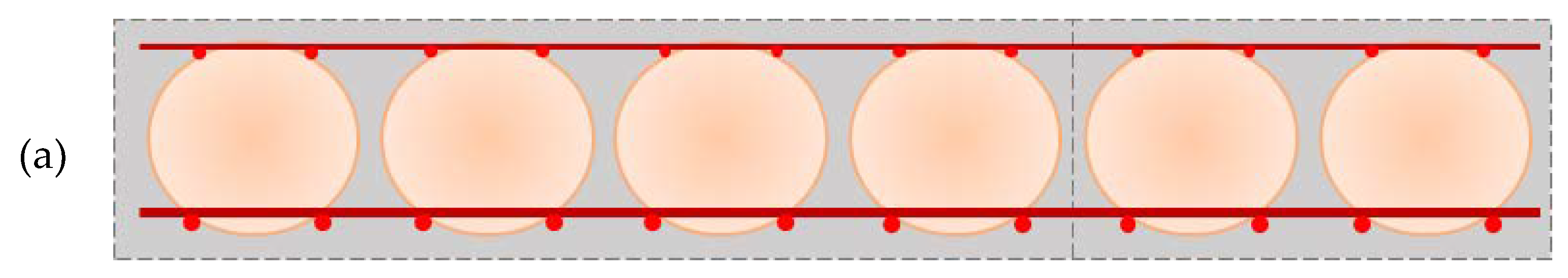
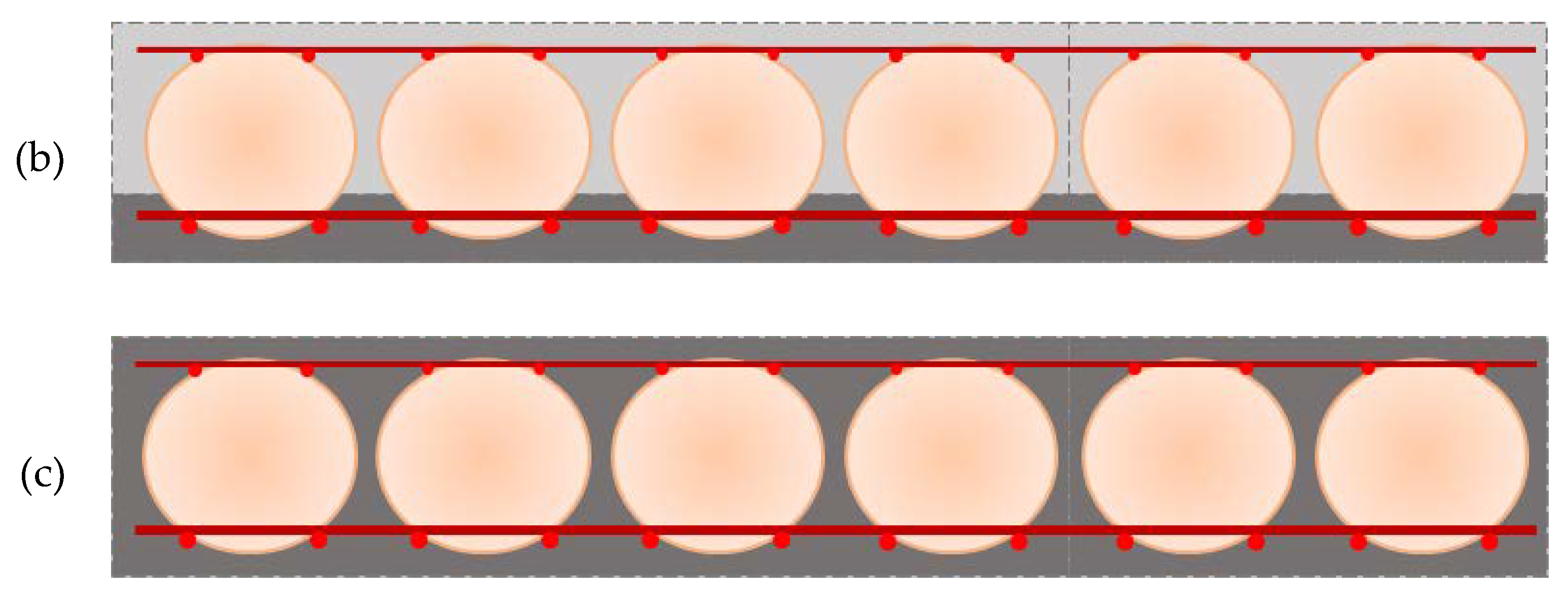
2.1. Lightweight Concrete Slabs
2.1.2. Serviceability Limit state of Bubble Deck Concrete Slabs
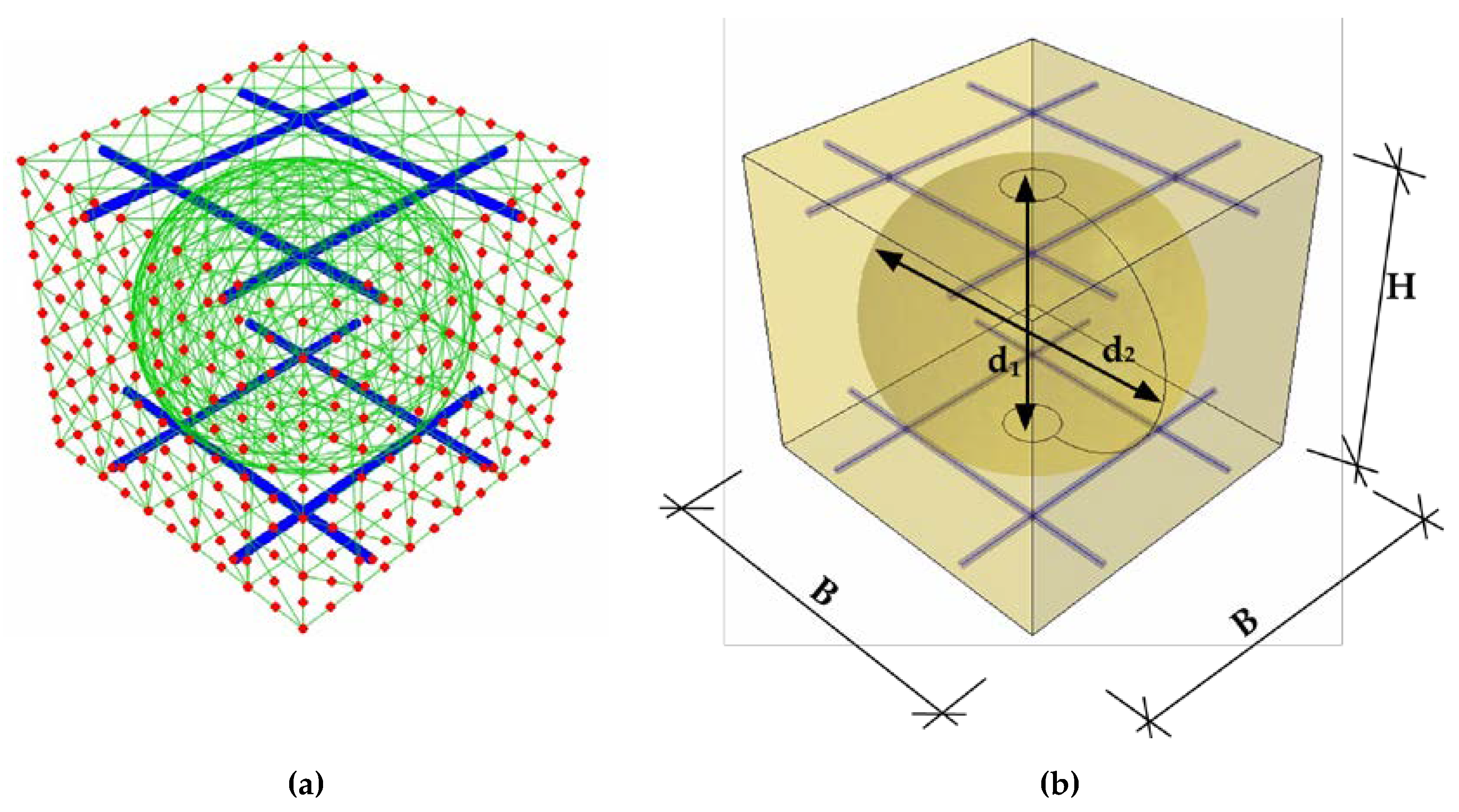
2.2. Numerical Homogenization of Slab
2.3. Study Framework and Optimization Problem Definition
2.4. Mathematical Optimization Procedure
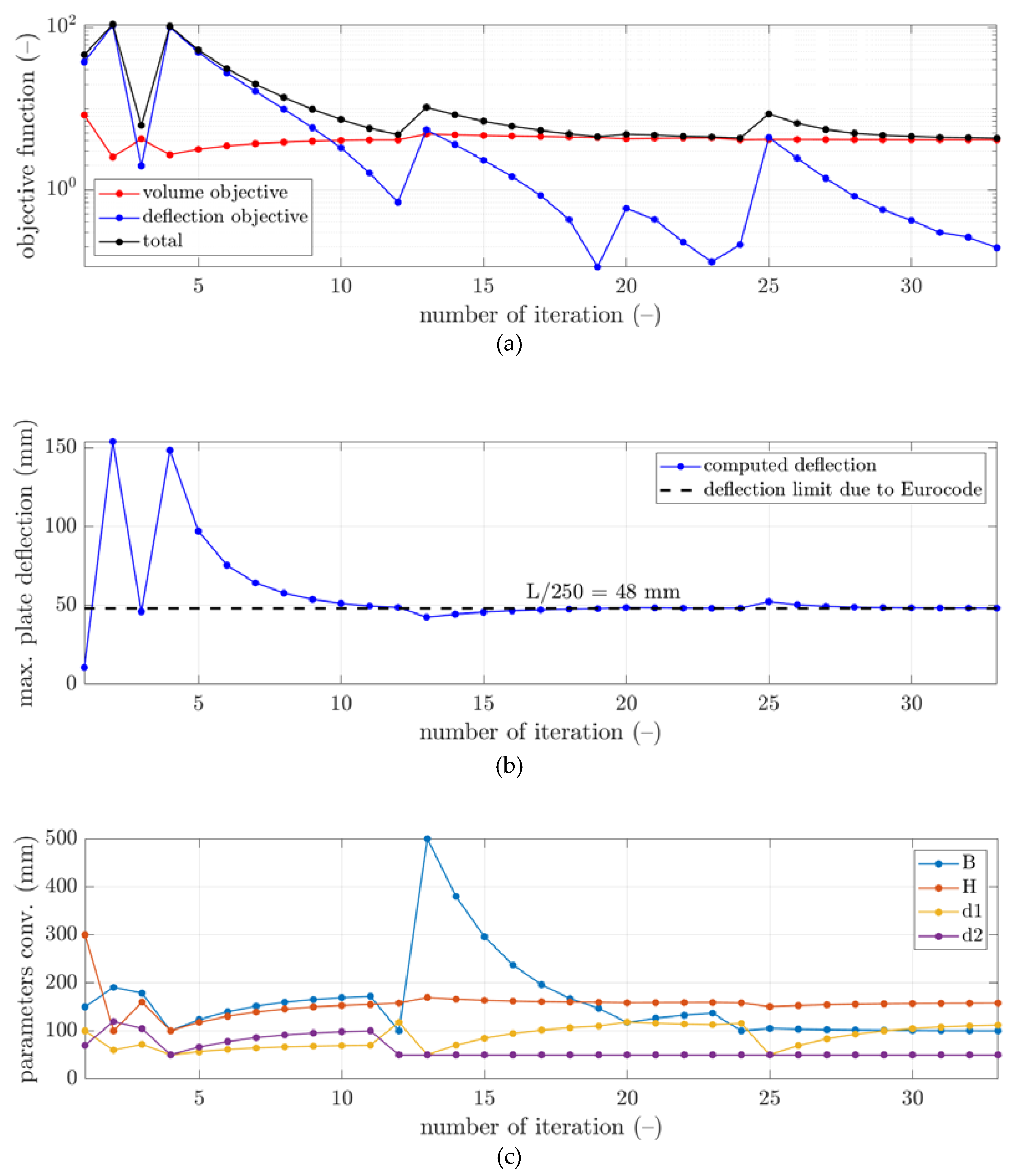
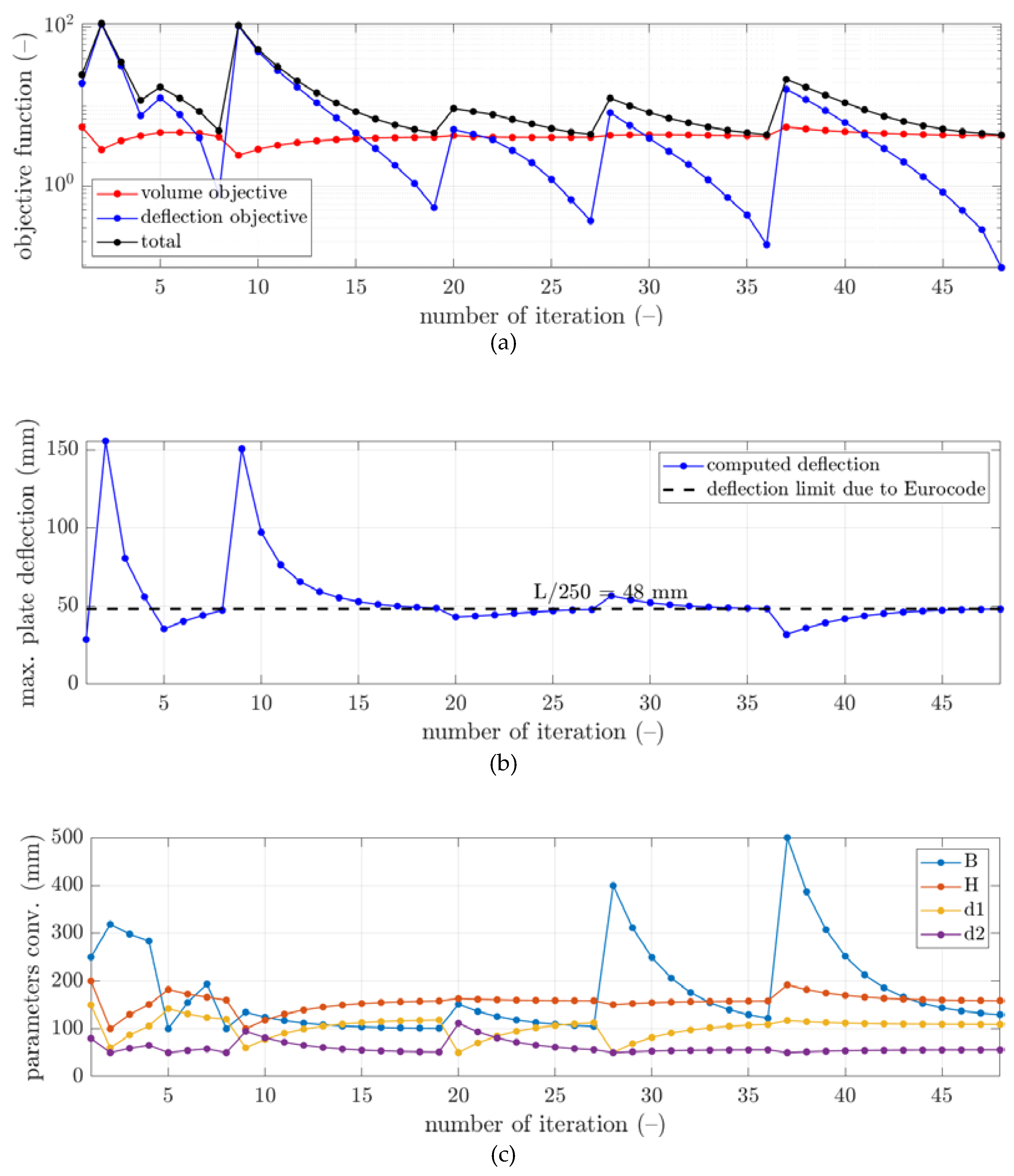
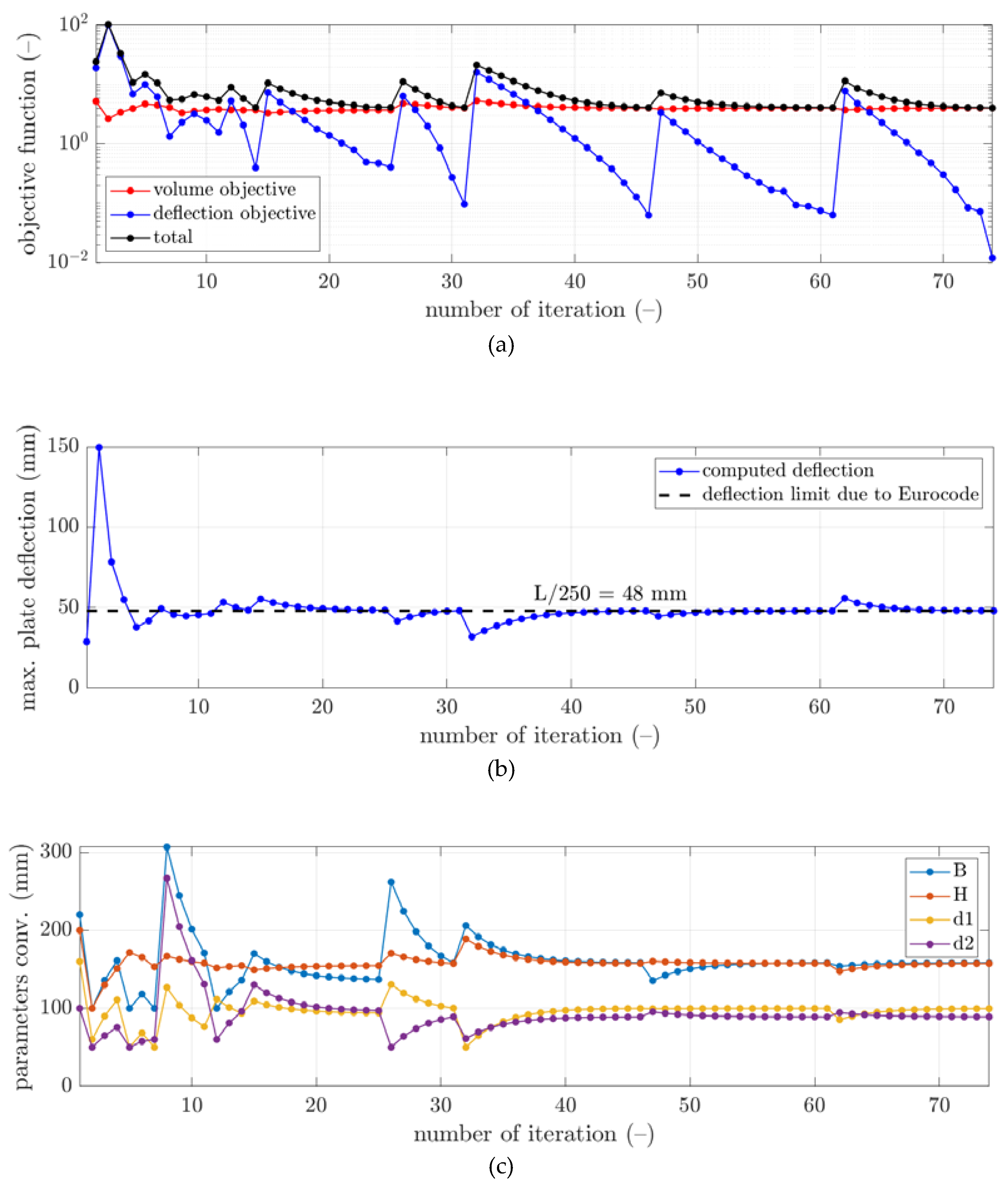
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, D.; Wu, G.; Lu, Y. Finite element modelling approach for precast reinforced concrete beam-to-column connections under cyclic loading. Eng. Struct. 2018, 174, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, E. Effects of cast-in-place concrete topping on flexural response of precast concrete hollow-core slabs. Eng. Struct. 2015, 98, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Torres, A.; Di Stefano, S.; Grillo, A.; Rodríguez-Ramos, R.; Merodio, J.; Penta, R. An asymptotic homogenization approach to the microstructural evolution of heterogeneous media. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 2018, 106, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymczak-Graczyk, A.; Ksit, B.; Laks, I. Operational Problems in Structural Nodes of Reinforced Concrete Constructions. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering 2019, 603, 032096. [CrossRef]
- Lichołai L Budownictwo ogólne. Tom 3. Elementy budynków podstawy projektowania, Arkady, Warszawa, 2008 (in polish).
- Ksit, B.; Szymczak-Graczyk, A. Rare weather phenomena and the work of large-format roof coverings. Civil and Environmental Engineering Reports 2019, 29, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirajkar, S.; Balapure, M.; Kshirsagar, T. Study of Bubble Deck Slab. International Journal of Research in Science & Engineering 2017, 7, 1–5.
- Quraisyah, A.D.S.; Kartini, K.; Hamidah, M.S.; Daiana K. Bubble Deck Slab as an Innovative Biaxial Hollow Slab – A Review. Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2020, 1711, 012003. [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Sneed, L.H.; Yang, Y.; He, R. Numerical Simulation of Prestressed Precast Concrete Bridge Deck Panels Using Damage Plasticity Model. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2015, 9, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzaros, K.A.; Mistakidis, E.S.; Perdikaris, P.C. A numerical model based on nonconvex–nonsmooth optimization for the simulation of bending tests on composite slabs with profiled steel sheeting. Eng. Struct. 2010, 32, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholamhoseini, A.; Gilbert, R.; Bradford, M.; Chang, Z. Longitudinal shear stress and bond–slip relationships in composite concrete slabs. Eng. Struct. 2014, 69, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, T.; Ramos, A.P.; Ruiz, M.F.; Muttoni, A. Design for punching of prestressed concrete slabs. Structural Concrete 2013, 14, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Greunen, J.; Scordelis, A.C. Nonlinear analysis of prestressed concrete slabs. Journal of Structural Engineering 1983, 109, 1742–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.R.; de Souza Rosa, J.P. Nonlinear numerical analysis of prestressed concrete beams and slabs. Engineering Structures 2020, 223, 111187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathurappan, G.; Rajogopalan, N.; Krishnamoorthy, C.S. Nonlinear finite element analysis of reinforced and prestressed concrete slabs with reinforcement (inclusive of prestressing steel) modelled as discrete integral components. Computers & Structures 1992, 44, 575–584. [CrossRef]
- Buannic, N.; Cartraud, P.; Quesnel, T. Homogenization of corrugated core sandwich panels. Compos. Struct. 2003, 59, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, K.; Kikuchi, N. Nonlinear homogenization method for practical applications. American Society of Mechanical Engineers, Applied Mechanics Division AMD 1995, 212, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, L.; Khizar, R.; Peng, B.; Wenbin, Y. Two-Step Homogenization of Textile Composites Using Mechanics of Structure Genome. Compos. Struct, 2017, 171, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbowski, T.; Marek, A. Homogenization of corrugated boards through inverse analysis. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Engineering and Applied Sciences Optimization, Kos Island, Greece, 4–6 June 2014; pp. 1751–1766. [Google Scholar]
- Hohe, J. A direct homogenization approach for determination of the stiffness matrix for microheterogeneous plates with application to sandwich panels. Compos. Part. B 2003, 34, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancolini, M.E. Evaluation of equivalent stiffness properties of corrugated board. Comp. Struct. 2005, 69, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbowski, T.; Gajewski, T. Determination of transverse shear stiffness of sandwich panels with a corrugated core by numerical homogenization. Materials 2021, 14, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiropoulos, S.; Kazakis, G.; Lagaros, N. D. Conceptual design of structural systems based on topology optimization and prefabricated components. Computers & Structures 2020, 226, 106136. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, Y.; Uzzaman, A.; Lim, J.B.; Abdelal, G.; Nash, D.; Young, B. Effect of web holes on web crippling strength of cold-formed steel channel sections under end-one-flange loading condition–Part I: Tests and finite element analysis. Thin-Walled Struct. 2016, 107, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parastesh, H.; Hajirasouliha, I.; Taji, H.; Sabbagh, A.B. Shape optimization of cold-formed steel beam-columns with practical and manufacturing constraints. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2019, 155, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojobi,A,O. ; Liew, K.M. Multi-objective optimization of high performance bio-inspired prefabricated composites for sustainable and resilient construction. Composite Structures 2022, 279, 114732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y. , Bhola, J. Design and optimization of prefabricated building system based on BIM technology. International Journal of System Assurance Engineering and Management 2022, 13, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Chen, Y.; Chang, R. Scheduling optimization of prefabricated construction projects by genetic algorithm. Applied Sciences 2021, 11, 5531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staszak, N.; Garbowski, T.; Ksit, B. Optimal Design of Bubble Deck Concrete Slabs: Sensitivity Analysis and Numerical Homogenization. Materials 2023, 16, 2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staszak, N.; Garbowski, T.; Szymczak-Graczyk, A. Solid Truss to Shell Numerical Homogenization of Prefabricated Composite Slabs. Materials 2021, 14, 4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, E.V.; Lima, M.; Strelets, K.I. Efficiency of Applying Sustainable Technology of Bubbledeck Technology in Concrete in Russia. Construction of Unique Buildings and Structures 2017, 11, 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Shetkar, A.; Hanche, N. An Experimental Study on Bubble Deck Slab System with Elliptical Balls. In Proceeding of NCRIET-2015 & Indian Journal of Scientific Research 2015, 21–27. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Hokrane, N.S.; Saha, S. Comparative Studies of Conventional Slab and Bubble Deck Slab Based on Stiffness and Economy. International Journal for Scientific Research & Development 2017, 5, 1396–1398. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs, A.C. BubbleDeck Floor System – An Innovative Sustainable Floor System. BubbleDeck Netherlands B.V., AD Leiden, the Netherlands, 2009.
- Jamal, J.; Jolly, J. A study on structural behaviour of bubble deck slab using spherical and elliptical balls. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology 2017, 4, 2090–20957. [Google Scholar]
- Konuri, S.; Varalakshmi, T.V.S. Review on Bubble Deck Slabs Technology and their Applications. International Journal of Scientific and Technology Research 2019, 8, 427–432. [Google Scholar]
- Kyng Consulting PTY Ltd, “BubbleDeck Design Guide for Compliance with BCA Using AS3600 and EC2,” BubbleDeck Australia and New Zealand, DG-V.1.2, 2008.
- PN-EN 1992-1-1:2008 - Eurocode 2: Design of concrete structures - Part 1-1: General rules, and rules for buildings, 2008.
- PN-EN 1990:2004 – Eurocode 0: Basics of structural design, 2004.
- Garbowski, T.; Knitter-Piątkowska, A.; Mrówczyński, D. Numerical Homogenization of Multi-Layered Corrugated Cardboard with Creasing or Perforation. Materials 2021, 14, 3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrówczyński, D.; Knitter-Piątkowska, A.; Garbowski, T. Non-Local Sensitivity Analysis and Numerical Homogenization in Optimal Design of Single-Wall Corrugated Board Packaging. Materials 2022, 15, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrówczyński, D.; Knitter-Piątkowska, A.; Garbowski, T. Numerical Homogenization of Single-Walled Corrugated Board with Imperfections. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staszak, N.; Szymczak-Graczyk, A.; Garbowski, T. Elastic Analysis of Three-Layer Concrete Slab Based on Numerical Homogenization with an Analytical Shear Correction Factor. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, J. N., Theory and analysis of elastic plates and shells, CRC Press, Taylor and Francis, 2007.
- Timoshenko, S.; Woinowsky-Krieger, S., Theory of plates and shells, McGraw-Hill New York, 1959.
- Software Version 2022a, Mathworks, Natick, Massachusetts, USA.
- Biggs, M.C. Constrained minimization using recursive quadratic programming. In Towards Global Optimization, North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1975.
- Han, S.P. A globally convergent method for nonlinear programming. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 1977, 22, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, M.J.D. The convergence of variable metric methods for nonlinearly constrained optimization calculations. In proceedings of the Special Interest Group on Mathematical Programming Symposium Conducted by the Computer Sciences Department at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, July 11–13, 1977. [CrossRef]
- Powell, M.J.D. A fast algorithm for nonlinearly constrained optimization calculations. Numer. Anal. 1978, 630, 144–157. [Google Scholar]
- Nocedal, J.; Wright, S.J. Numerical Optimization, 2nd ed.; Springer Series in Operations Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gajewski, T.; Staszak, N.; Garbowski, T. Parametric optimization of thin-walled 3D beams with perforation based on homogenization and soft computing. Materials 2022, 15, 2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| boundary | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 100 | 50 | 50 | |
| 500 | 500 | 500 | 500 |
| No. | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 150 | 300 | 100 | 70 | |
| 250 | 200 | 150 | 80 | |
| 220 | 200 | 160 | 100 | |
| 200 | 250 | 110 | 180 | |
| 170 | 150 | 90 | 90 |
| No. | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (–) | (–) | (–) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100.0 | 158.6 | 115.8 | 50.0 | 47.94 | 4.1314 | 0.0616 | 4.1930 | |
| 122.1 | 158.5 | 109.1 | 55.9 | 48.02 | 4.2193 | 0.0164 | 4.2357 | |
| 158.2 | 157.5 | 99.7 | 89.1 | 48.01 | 4.0593 | 0.0121 | 4.0714 | |
| 110.7 | 156.0 | 52.8 | 70.5 | 48.12 | 4.2505 | 0.1165 | 4.3669 | |
| 144.8 | 155.6 | 53.8 | 104.4 | 48.04 | 4.0600 | 0.0390 | 4.0990 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





