Submitted:
19 June 2023
Posted:
19 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
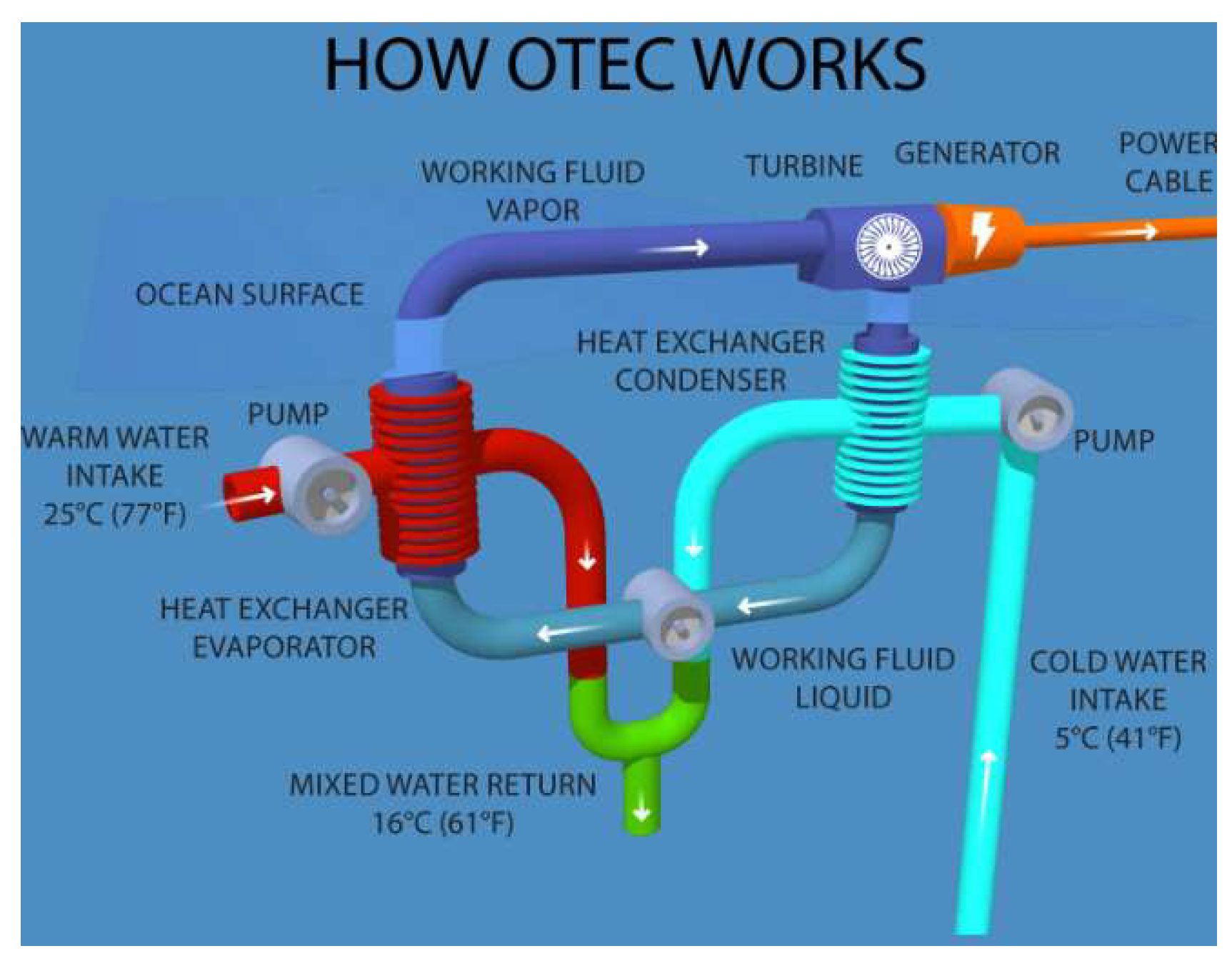
1. Introduction
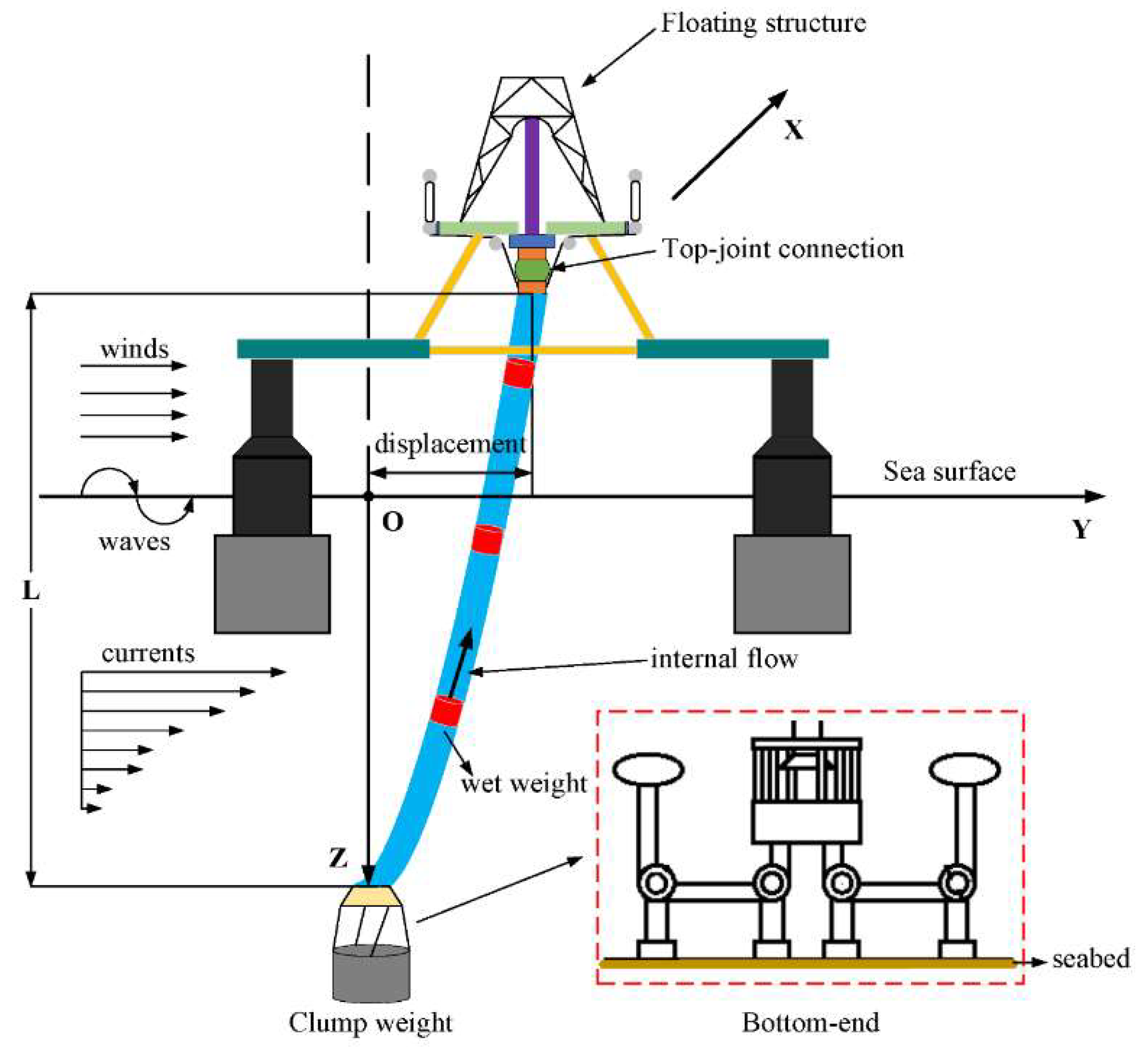
2. Analytical Simulation
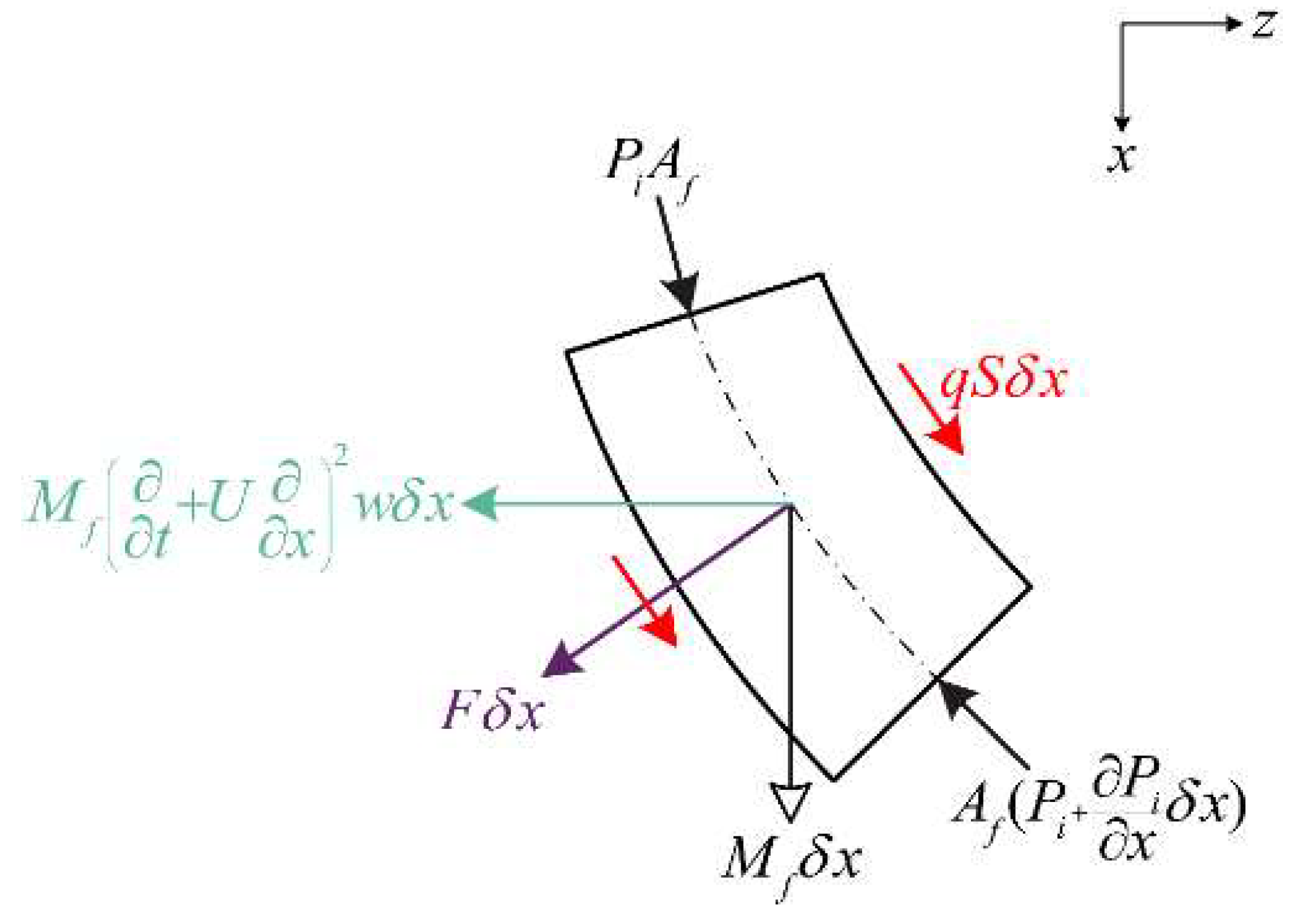
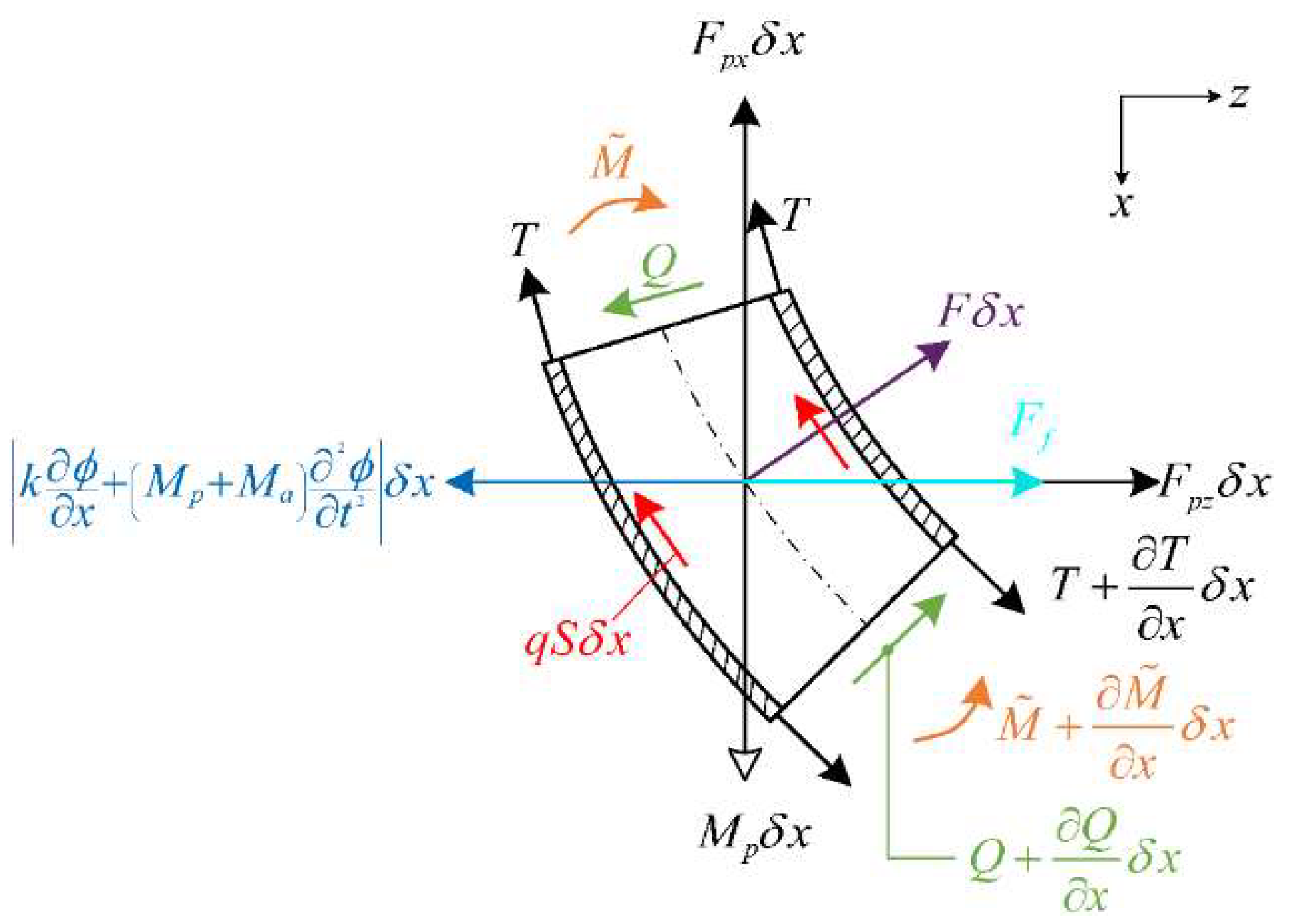
2.1. Governing General Equation
2.2. Boundary Condition and General Solutions
2.3. Convergence and Accuracy
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Parameter Sensitivity Analysis
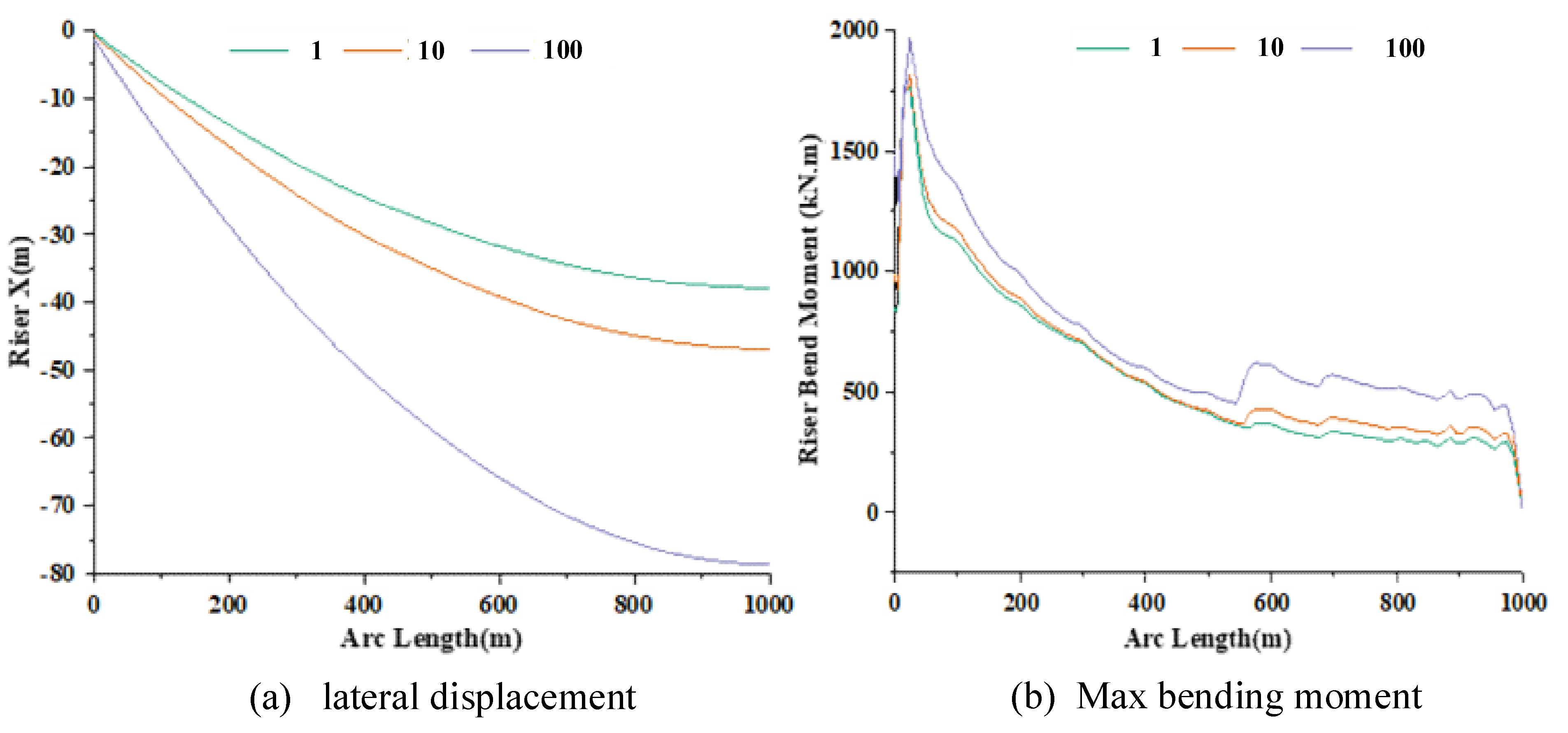
3.1.1. Effects of Waves
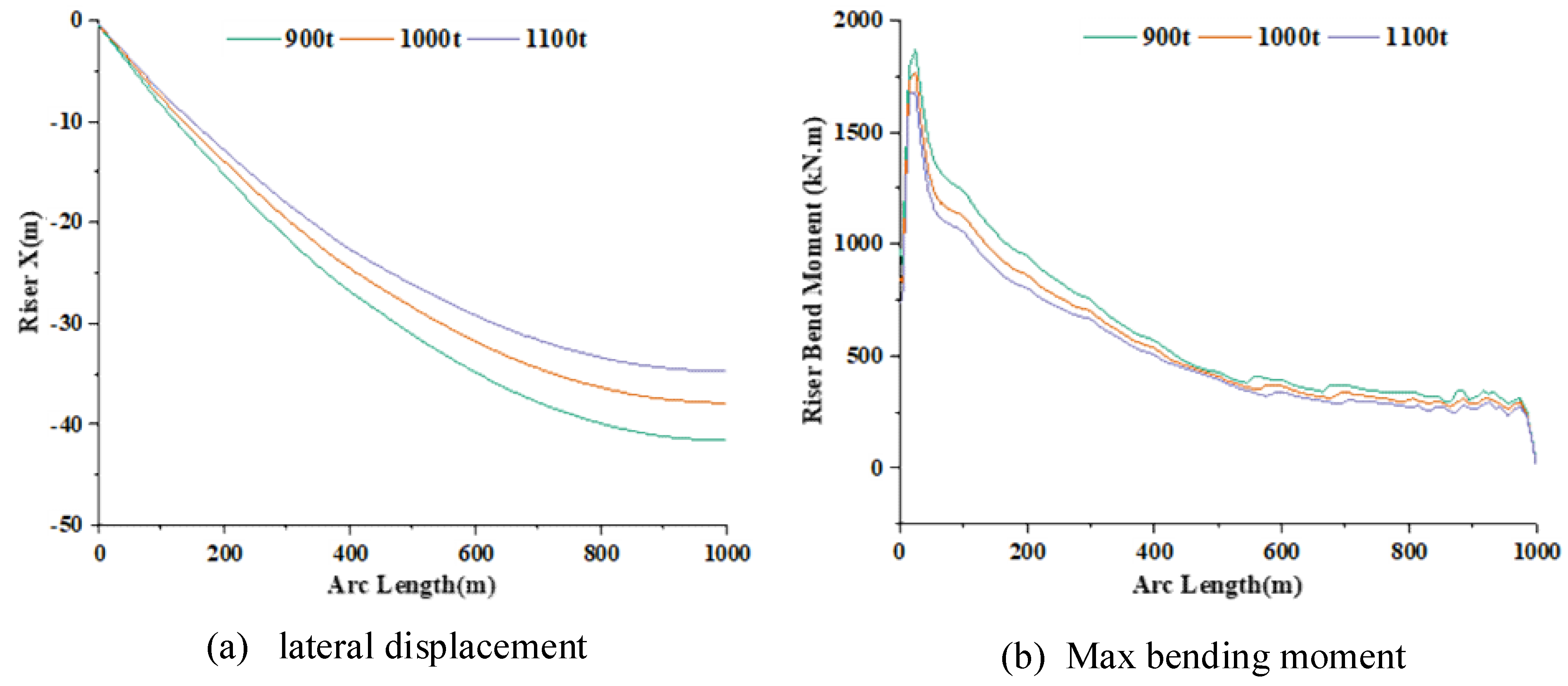
3.1.2. Effects of the Clump Weight
3.1.3. Effects of Internal Flow Velocity
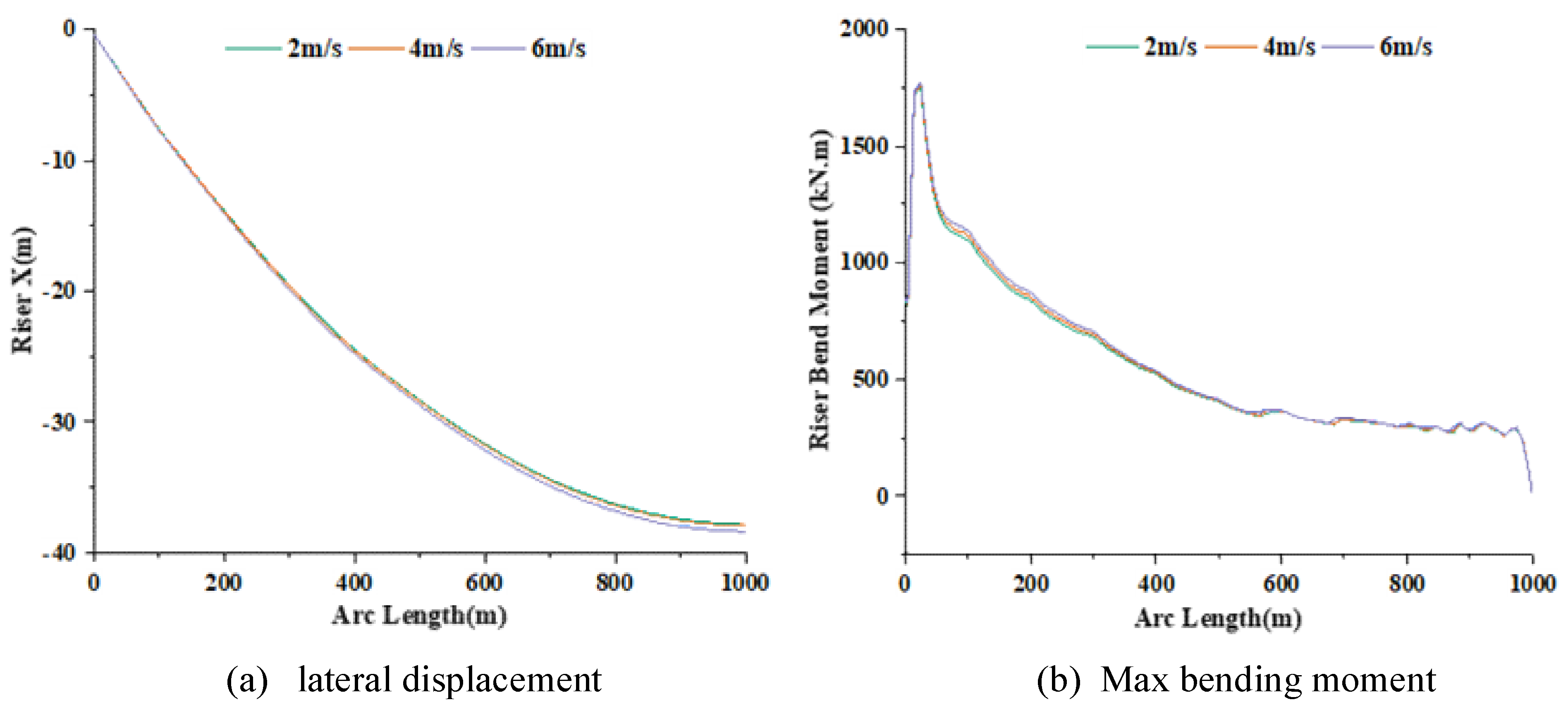
3.1.4. Effects of Current Velocity
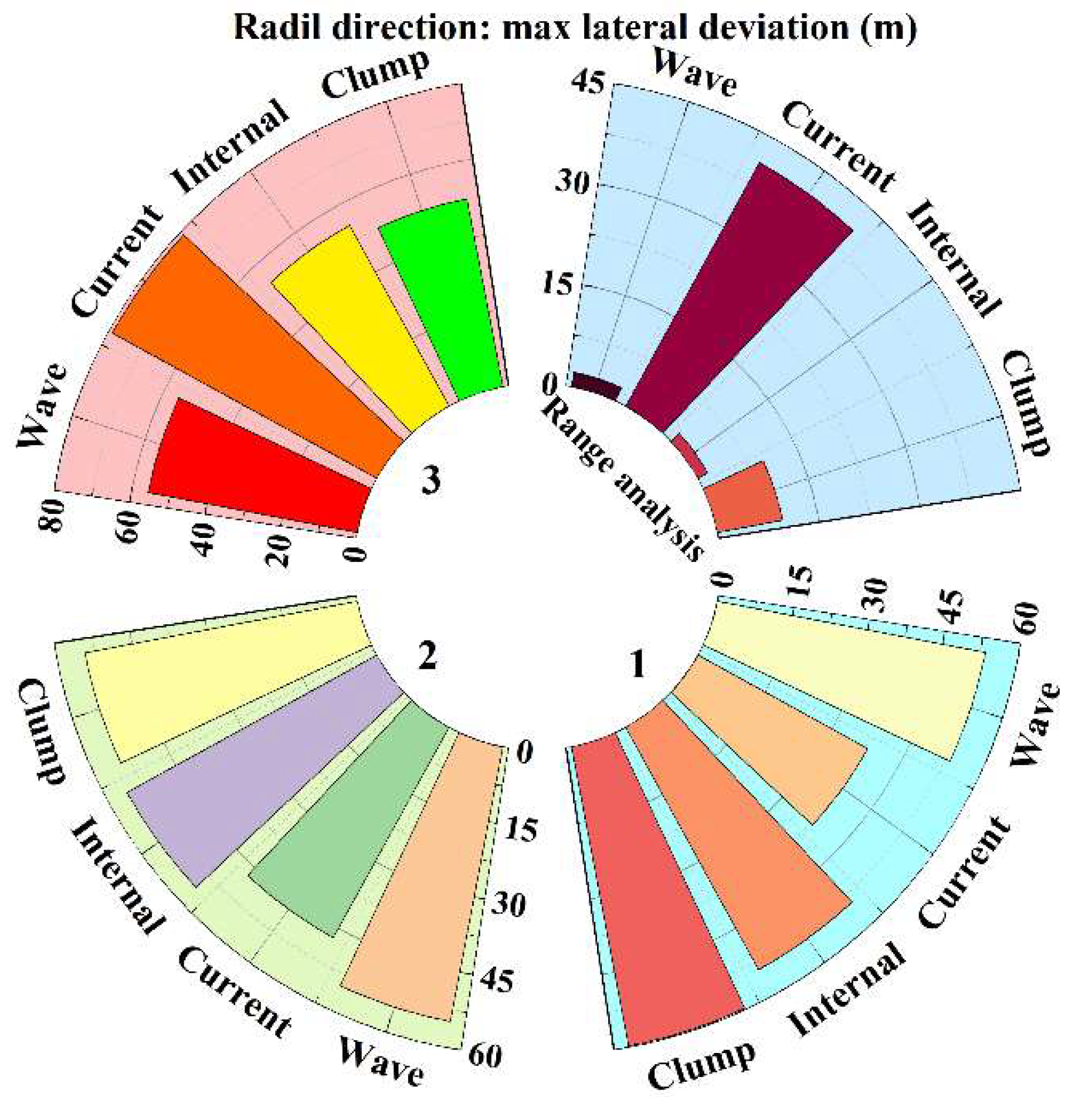
3.2. Orthogonal Analysis of Key Parameters
3.2.1. Analysis of Orthogonal Experiments
3.2.2. Simulation Date Analysis
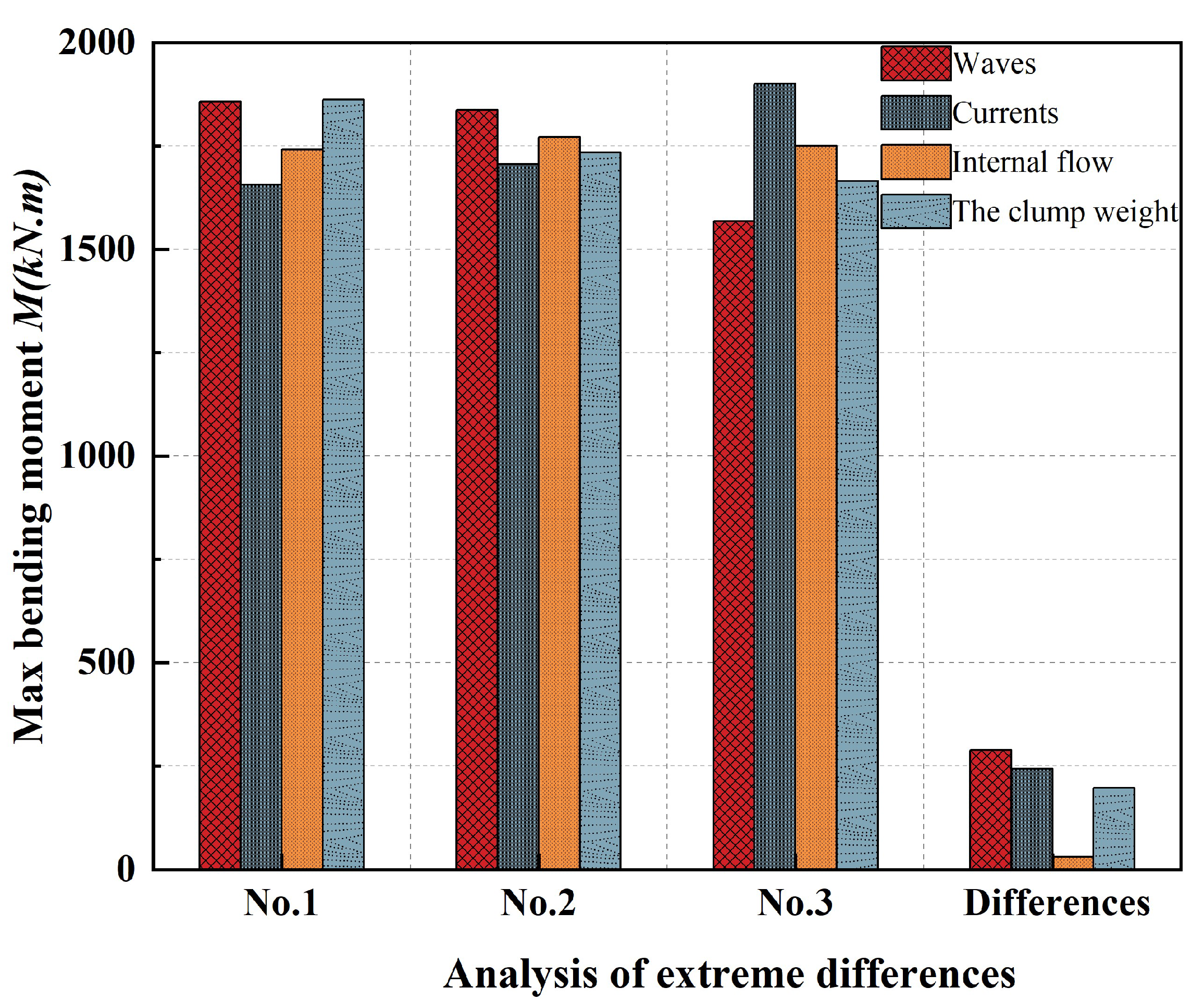
3.2.3. Extremum Difference Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Makai ocean engineering. ocean thermal energy conversion [EB / OL]. Available online: https:∥www. makai. com/ ocean-thermal-energy conversion.
- Herrera, J.; Sierra, S.; Ibeas, A. Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion and Other Uses of Deep Sea Water: A Review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiputra, R.; Utsunomiya, T. Stability based approach to design cold-water pipe (CWP) for ocean thermal energy conversion (OTEC). Appl. Ocean Res. 2019, 92, 101921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiputra, R.; Utsunomiya, T. Linear vs non-linear analysis on self-induced vibration of OTEC cold water pipe due to internal flow. Appl. Ocean Res. 2021, 110, 102610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Cao, P.; Erwin, R.; Kibbee, S. OTEC Cold Water Pipe Global Dynamic Design for Ship-Shaped Vessels. Ocean. Renew. Energy 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuiper, G.; Metrikine, A. Dynamic stability of a submerged, free-hanging riser conveying fluid. J. Sound Vib. 2005, 280, 1051–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halkyard, J.; Sheikh, R.; Marinho, T.; Shi, S.; Ascari, M. Current Developments in the Validation of Numerical Methods for Predicting the Responses of an Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) System Cold Water Pipe. Volume 7: Ocean Space Utilization; Professor Emeritus J. Randolph Paulling Honoring Symposium on Ocean Technology 2014. [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Halkyard, J.; Kurup, N.; Jiang, L. Coupled Analysis Approach in OTEC System Design. Volume 4: Offshore Geotechnics; Ronald W. Yeung Honoring Symposium on Offshore and Ship Hydrodynamics. 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lockheed Martin. 2011. NAVFAC Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) Project. Port Hueneme, CA: Naval Facilities Engineering Command. Port Hueneme, CA.
- Xiang, S.; Cao, P.; Erwin, R.; Kibbee, S. OTEC Cold Water Pipe Global Dynamic Design for Ship-Shaped Vessels. Ocean. Renew. Energy 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitken, J. XIV. An account of some experiments on rigidity produced by centrifugal force. London, Edinburgh, Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1878, 5, 81–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourriéres, F. (1939). Sur un phénomène d'oscillation auto-entretenue en mécanique des fluides réels.
- Housner, G.W. Bending Vibrations of a Pipe Line Containing Flowing Fluid. J. Appl. Mech. 1952, 19, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R. W. GREGORY and M. P. PAIDOUSSIS 1966a Proceedings of the Royal Society (London) A, 293, 512-527. Unstable oscillation of tubular cantilevers conveying fluid. I. Theory.
- R. W. GREGORY and M. P. PAIDOUSSIS 1966b Proceedings of the Royal Society (London) A, 293, 528-542. Unstable oscillation of tubular cantilevers conveying fluid. II. Experiments.
- T. BROOKE BENJAMIN 1961a Proceedings of the Royal Socicty (London) A, 261,457-486. Dynamics of a system of articulated pipes conveying fluid. I. Theory.
- Wu, M.C.; Lou, J.Y.K. Effects of rigidity and internal flow on marine riser dynamics. Appl. Ocean. Res. 1991, 13, 235–244. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.Y.; Wang, S.Q.; Wu, J.N.; et al. Dynamic Characteristics of Marine Risers Conveying Fluid[J]. China Ocean Engineering. 2000, 14, 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.M.; Guo, H.Y.; Meng, F.S. Effect of internal flow on the dynamic behavior of top tensioned riser[J]. Journal of Ship Mechanics 2010, 14, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, D.; Chung, J. In-plane and out-of-plane motions of an extensible semi-circular pipe conveying fluid[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration 2008, 311, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghayesh, M.H.; Païdoussis, M.P.; Modarres-Sadeghi, Y. Three-dimensional dynamics of a fluid-conveying cantilevered pipe fitted with an additional spring support and an end-mass[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration 2011, 330, 2869–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uczko, J.; Czerwiński, A. Parametric vibrations of flexible hoses excited by a pulsating fluid flow, Part I: modelling, solution method and simulation[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2015; 55, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uczko, J.; Czerwiński, A. Nonlinear three-dimensional dynamics of flexible pipes conveying fluids[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2017; 55, 235–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, A.; Païdoussis, M.; Van, K. On the dynamics of curved pipes transporting fluid. Part I: Inextensible theory. J. Fluids Struct. 1988, 2, 221–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, A.; Païdoussis, M.; Van, K. On the dynamics of curved pipes transporting fluid Part II: Extensible theory. J. Fluids Struct. 1988, 2, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.H.; Seyed, F.B. Review of flexible riser modelling and analysis techniques[J]. Engineering Structures 1995, 17, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, K.; Datta, T.K. Vibrations of lazy "S" risers due to vortex shedding under lock-in[C]. Offshore Technology Conference, Texas, USA, 1988; pp. 451–458. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, A.K. Review of flexible risers and articulated storage systems[J]. Ocean Engineering 1994, 21, 733–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatjigeorgiou, I.K. A finite differences formulation for the linear and nonlinear dynamics of 2D catenary risers[J]. Ocean Engineering 2008, 35, 616–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zeng, G.; Wei, F. A new matrix method for solving vibration and stability of curved pipes conveying fluid[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration 2002, 251, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.J.; Wen, J.H.; Yu, D.L.; et al. The vibration properties of a periodic composite pipe in 3D space[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration 2009, 328, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Zha, X.; Jiang, X.; Wang, L.; Leng, J.; Cao, Z. Semi-analytical solution for dynamic behavior of a fluid-conveying pipe with different boundary conditions. Ocean Eng. 2018, 163, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.; Su, J. Dynamic Behavior of Pipes Conveying Gas–Liquid Two-Phase Flow. Nuclear Engineering and Design 2015, 292, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.; Su, J. Vibration behavior of marine risers conveying gas-liquid two-phase flow. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering, American Society of Mechanical Engineers, Newfoundland, Canada; 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; An, C.; Liang, W.; Duan, M.; Estefen, S.F. Semi-analytical solution for soil-constrained vibration of subsea free-spanning pipelines. Ships Offshore Struct. 2018, 13, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; An, C.; Duan, M.; Su, J. Combined damping model for dynamics and stability of a pipe conveying two-phase flow. Ocean Eng. 2019, 195, 106683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, N.; Lin, W.; Qin, Q. Bifurcations and chaotic motions of a curved pipe conveying fluid with nonlinear constraints. Comput. Struct. 2006, 84, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paidoussis, M.P. Fluid-Structure interactions: Slender structures and axial flow; Academic Press: London, 1998; Volume l. [Google Scholar]
- Chibueze, N.O.; Ossia, C.V.; Okoli, J.U. On the Fatigue of Steel Catenary Risers. Strojniški Vestnik-Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2016; 62, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paidoussis, M.P.; Luu, T.P. Dynamics of a Pipe Aspirating Fluid Such as Might be Used in Ocean Mining. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 1985, 107, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paidoussis, M.P. Dynamics of Tubular Cantilevers Conveying Fluid. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 1970, 12, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Nomenclature | Description |
|---|---|
| EI | Bending stiffness (N/m2) |
| L | Pipe length (m) |
| Mp | Mass of the internal flow per unit length (kg/m) |
| Mf | Mass of the pipe per unit length (kg/m) |
| T | Axial equivalent tension (N) |
| U | Velocity of the internal flow (m/s) |
| Transverse displacement of the pipe (m) | |
| Af | Internal cross-sectional areas (m2) |
| A0 | External cross-sectional areas (m2) |
| Density of the seawater (kg/m3) | |
| Ca | Added mass coefficient |
| Internal pressure of the pipe | |
| External pressure of the pipe | |
| Cd | Adapted drag coefficient |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Bending stiffness (Gpa) | 30 |
| Inner diameter (m) Outer diameter (m) |
1.5 1.6 |
| Density of the seawater (kg/m3) The density of the pipe (kg/m3) |
1025 1760 |
| Pipe length (m) | 1000 |
| Axial equivalent tension | 0 |
| External flow velocity (m/s) | 1.09 |
| Velocity of the internal flow (m/s) | 5.0 |
| Top fluid pressure (Pa) | |
| Poisson's ratio | 0.3 |
| Adapted drag coefficient Additional mass coefficient |
1.0 1.0 |
| Pipe Section Location | Numerical Simulation Method (m) | DQM METHOD (m) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0.8536 | 0.8934 |
| 0.3 | 0.4952 | 0.4879 |
| 0.5 | 0.3016 | 0.2991 |
| 0.7 | 0.1954 | 0.2047 |
| 0.9 | 0.1187 | 0.1152 |
| Periodicity (year) | 1 | 10 | 100 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wave | Significant wave height (m) | 4.8 | 5.8 | 6.5 |
| Max wave height (m) | 8.3 | 10.0 | 11.3 | |
| Period (s) | 7.8 | 9.0 | 9.8 | |
| Horizontal | Factors | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wave (m) | Current (m/s) | Internal Flow Velocity (m/s) | The Clump Weight (t) | |
| 1 | 4.8 | 0.99 | 2 | 900 |
| 2 | 5.8 | 1.09 | 4 | 1000 |
| 3 | 6.5 | 1.42 | 6 | 1100 |
| Number | Wave (m) | Current (m/s) | Internal Flow Velocity (m/s) | The Clump Weight (t) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.8 | 0.99 | 2 | 900 |
| 2 | 4.8 | 1.09 | 4 | 1000 |
| 3 | 4.8 | 1.42 | 6 | 1100 |
| 4 | 5.8 | 0.99 | 4 | 1100 |
| 5 | 5.8 | 1.09 | 6 | 900 |
| 6 | 5.8 | 1.42 | 2 | 1000 |
| 7 | 6.5 | 0.99 | 6 | 1000 |
| 8 | 6.5 | 1.09 | 2 | 1100 |
| 9 | 6.5 | 1.42 | 4 | 900 |
| Numbers | Max Lateral Displacement (m) | Max Bending Moment (kN.m) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 41.46 | 1854.8 |
| 2 | 46.8 | 1806.88 |
| 3 | 72.33 | 1910.79 |
| 4 | 34.73 | 1668.64 |
| 5 | 51.57 | 1892.18 |
| 6 | 78.35 | 1950.59 |
| 7 | 37.96 | 1446.81 |
| 8 | 42.88 | 1417.94 |
| 9 | 86.16 | 1840.65 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





