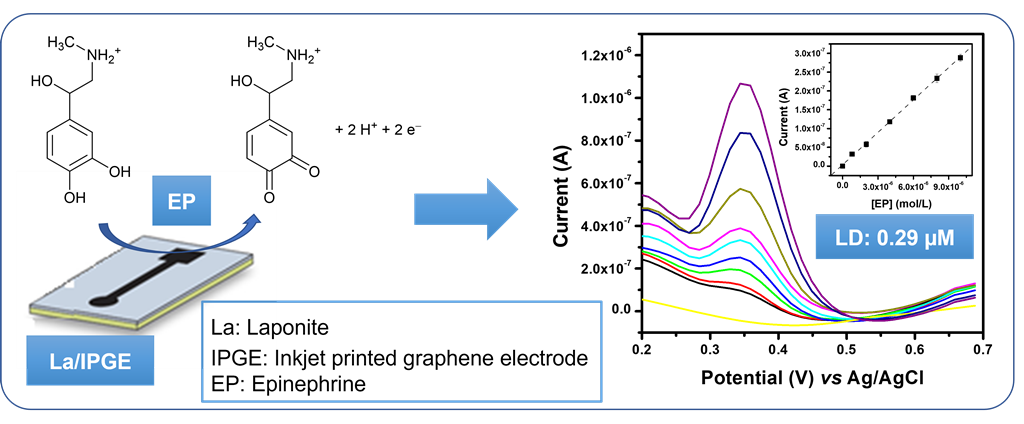
1. Introduction
Epinephrine (EP, also called adrenaline) is a molecule belonging to the catecholamine neurotransmitters’ family naturally synthesized in human system from L-phenylalanine and L-tyrosine. EP is generally founded in the central nervous system of mammals where it plays an important physiological role for muscle and tissue control, and also serves as a chemical mediator for transmitting nerve impulses to efferent organs [
1,
2]. Its clinical applications include the treatment of hypertension, the treatment of serious allergic reactions, bronchial asthma, heartbeat stimulation and emergency medical situations [
3]. EP is counted among molecules generally inducing neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer, Parkinson and Huntington diseases, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia that are problems causing significant impacts on human health around the world [
4]. These neurodegenerative diseases are caused by an imbalance of neurotransmitters in the brain and body due to the damage or destruction of the nerve cells that control cognitive functions [
5].
For the quantification of EP, several methods have been exploited that include chemiluminescence [
6], capillary electrophoresis [
7], liquid chromatography [
8] and fluorimetry [
9]. Although these methods are reliable and operate quite well, they meanwhile meet some drawbacks, mainly the requirement of long analysis times, the complexity of sample pretreatment or preparation, expensive equipment and manipulation by skilled operators. Electroanalytical methods that overcome most of these limitations are rapid, simple, easy to handle and low instrumentation and maintenance costs [
10,
11]. To date, several sensor devices have been proposed for the electrochemical determination of EP, as recently reviewed by Mattos et
al. [
12]. This demonstrates that the quantification of EP in physiological media as well as in pharmaceutical preparations remains attractive and of key importance in both analytical and biomedical sciences. Thus, there is a growing interest in electroanalytical chemistry of providing low cost, sensitive and selective sensors for the detection of EP. Some recent works in these lines include the detection of EP by using a glassy carbon electrode modified either by gold nanoparticles and cysteic acid film [
13] or by an ordered mesoporous carbon/nickel oxide composite [
14], and a screen-printed electrode modified with a nanocomposite film consisting of electrochemically reduced graphene oxide and NiO nanoparticles [
15].
Several previous studies have demonstrated the usefulness of clay minerals as electrodes’ modifiers. Yet, they can be used to increase the local concentration of various solid electrodes due to their ordered structure formed mainly by regular polyhedrals organized in a 3D stable network, to their flexible structure and to the intercalation ability that make them convenient for the entrapment of guest molecules [
16]. Laponite (La) is a synthetic clay with a structure and composition close to that of the natural clay mineral hectorite [
17]. Its disk-like shape has a thickness of 0.92 nm, an exchange capacity of 50-55 mmol/100 g and an average diameter of 25 nm with a surface area up of 370 m
2.g
-1. It bears a permanent negative surface charge on every single face and a positive charge distribution along the surface edges [
18,
19]. These properties make it an interesting electrode material, notably when the envisaged clay-modified electrode is designed for the electroanalysis of cationic species.
Taking into consideration the above mentioned La features, we interested in this work of proposing a simple and selective amperometric sensor for the electroanalysis and detection of EP in aqueous solution and in pharmaceutical formulation. This was achieved by depositing a thin film or La on an inkjet-printed graphene electrode (IPGE). The charge properties and the conductivity of the obtained La/IPGE were characterized by means of multisweep cyclic voltammetry (MCV) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), respectively. Afterwards, important parameters likely to influence the voltammetric response of EP were optimized using differential pulse voltammetry (DPV). Finally, the selectivity of the proposed sensor was investigated followed by its exploitation for the detection of EP in aqueous solution and in a real sample.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Electrochemical characterizations of simple and modified electrodes
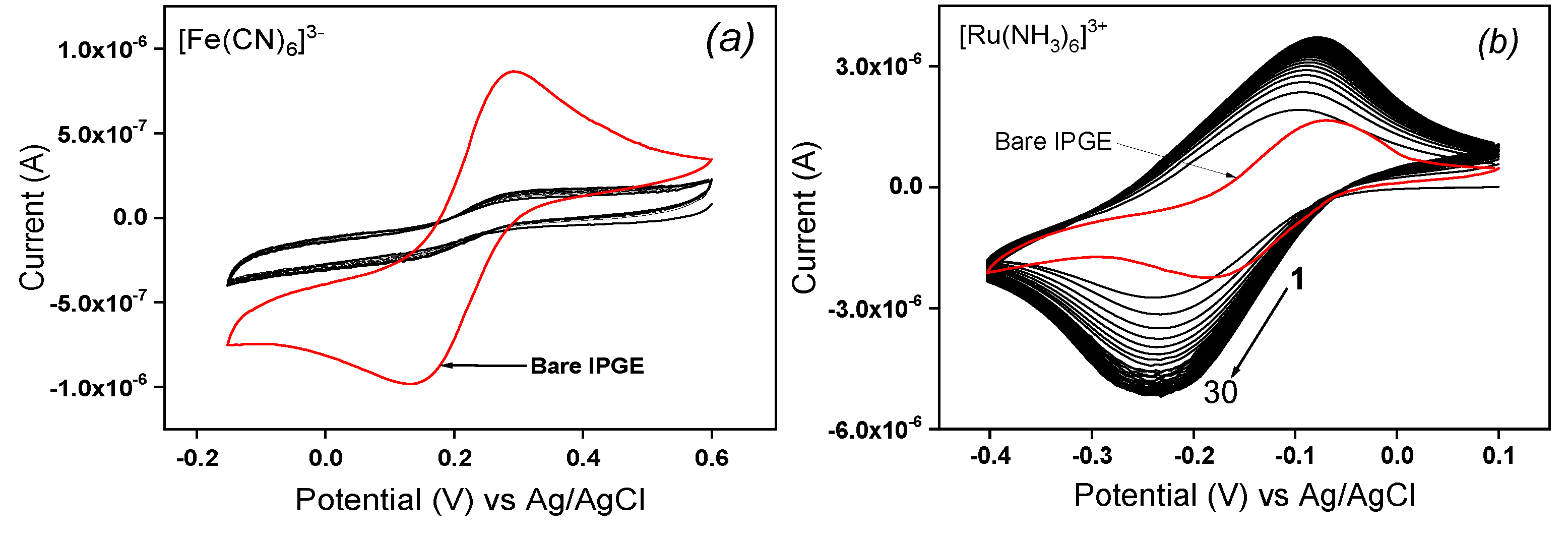
The electrochemical characterization of modified inkjet-printed electrode was done by MCV in neutral pH solution containing respectively two redox probes ([Fe(CN)
6]
3− and [Ru(NH
3)
6]
3+) generally considered for their ideal electrochemical behavior. The studied potential ranges were from -0.2 to 0.6 V and -0.4 to 0.2 V, for [Fe(CN)
6]
3− and [Ru(NH
3)
6]
3+, respectively. For the 30 cyclic scans realized with La/IPGE in 0.1 M KCl containing ([Fe(CN)
6]
3− (
Figure 1a), a poor accumulation of the probe traduced by flat voltammograms was observed, that was attributed to unfavorable electrostatic repulsion between the probe and La sheets both bearing a negative charge. By replacing the negatively charged redox probe by the cationic one ([Ru(NH
3)
6]
3+), a progressive accumulation of the analyte was noticed (
Figure 1b), which led to the saturation of the electrode from the 10
th cyclic scan. This result is due to the electrostatic attraction between La clay sheets negatively charged and [Ru(NH
3)
6]
3+ ions. The electrochemical response of the same cationic probe was also investigated on bare IPGE, and one can observe on
Figure 1b that the presence of La film on the IPGE sensitively increased the analyte signal as the current obtained upon saturation is more than 3-fold higher on La/IPGE compared to the response on unmodified electrode. One can partially concluded that La/IPGE could be favorably applied for the voltammetric analysis of cationic species.
2.2. EIS analysis of simple IPGE and La/IPGE
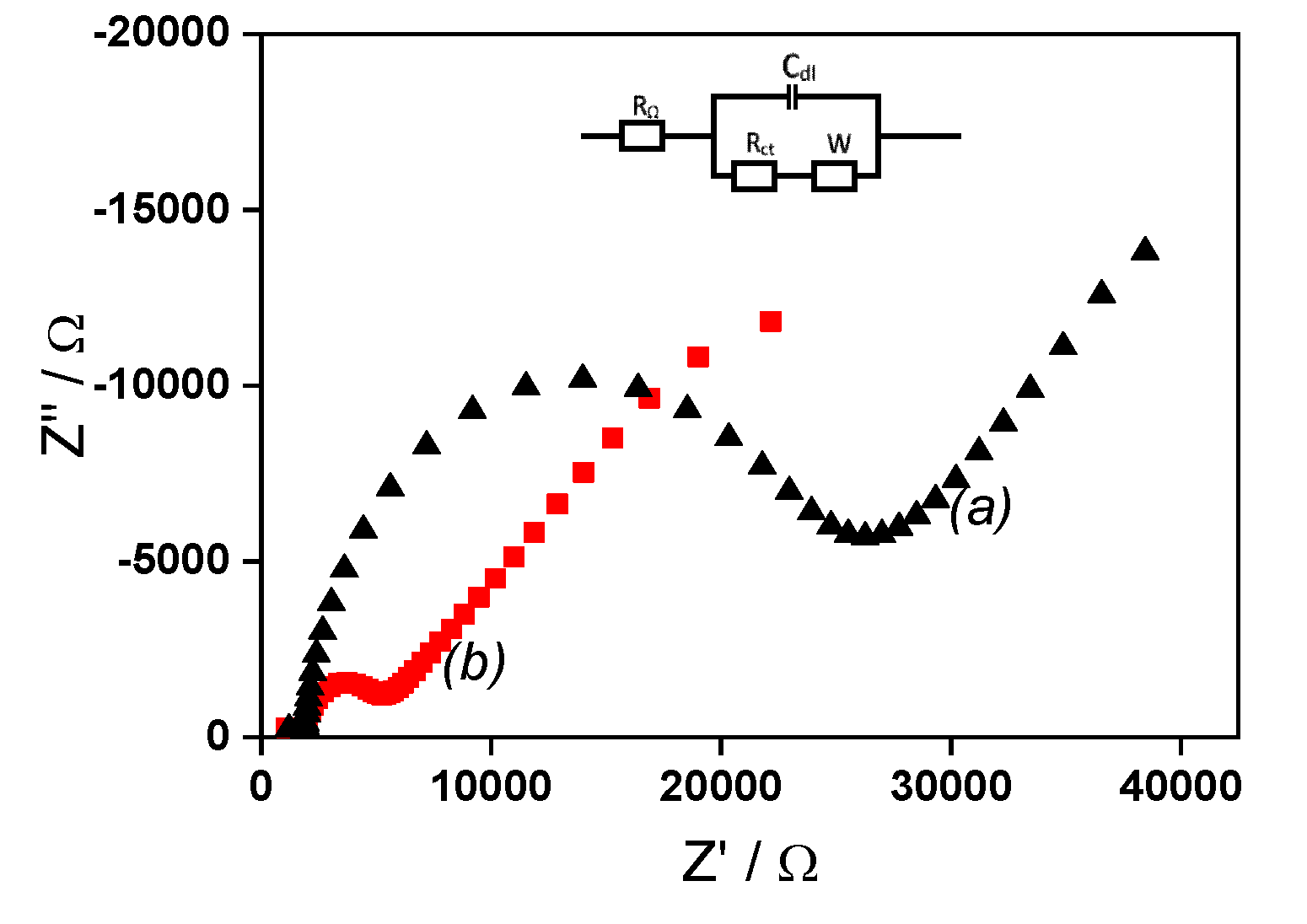
The charge transfer resistance (R
ct) of IPGE before and after it modification using the clay film was evaluated by EIS, in the frequency range of 0.01 Hz to 10000 Hz using [Fe(CN)
6]
3−/4− in 0.1 M KCl. The corresponding Nyquist plots are shown on
Figure 3. The unmodified IPGE presented the largest semicircle with a charge transfer resistance of 2299.6 Ω. Oppositely, the modified La/IPGE gave the lowest semicircle in the region of low frequency with a charge transfer resistance of 1510.9 Ω. These observations are typical of electrochemical processes characterized by electron transfer. As obtained in the previous section, the electron transfer is limited with bare IPGE, while favored on La/IPGE. Again, the behavior observed with La/IPGE can be explained by the best conductivity of the clay modified electrode, in accordance with the conclusion obtained in cyclic voltammetry.
2.3. Electrochemical detection of EP on the IPGE modified electrode
2.3.1. Electrochemical behavior of EP by cyclic voltammetry
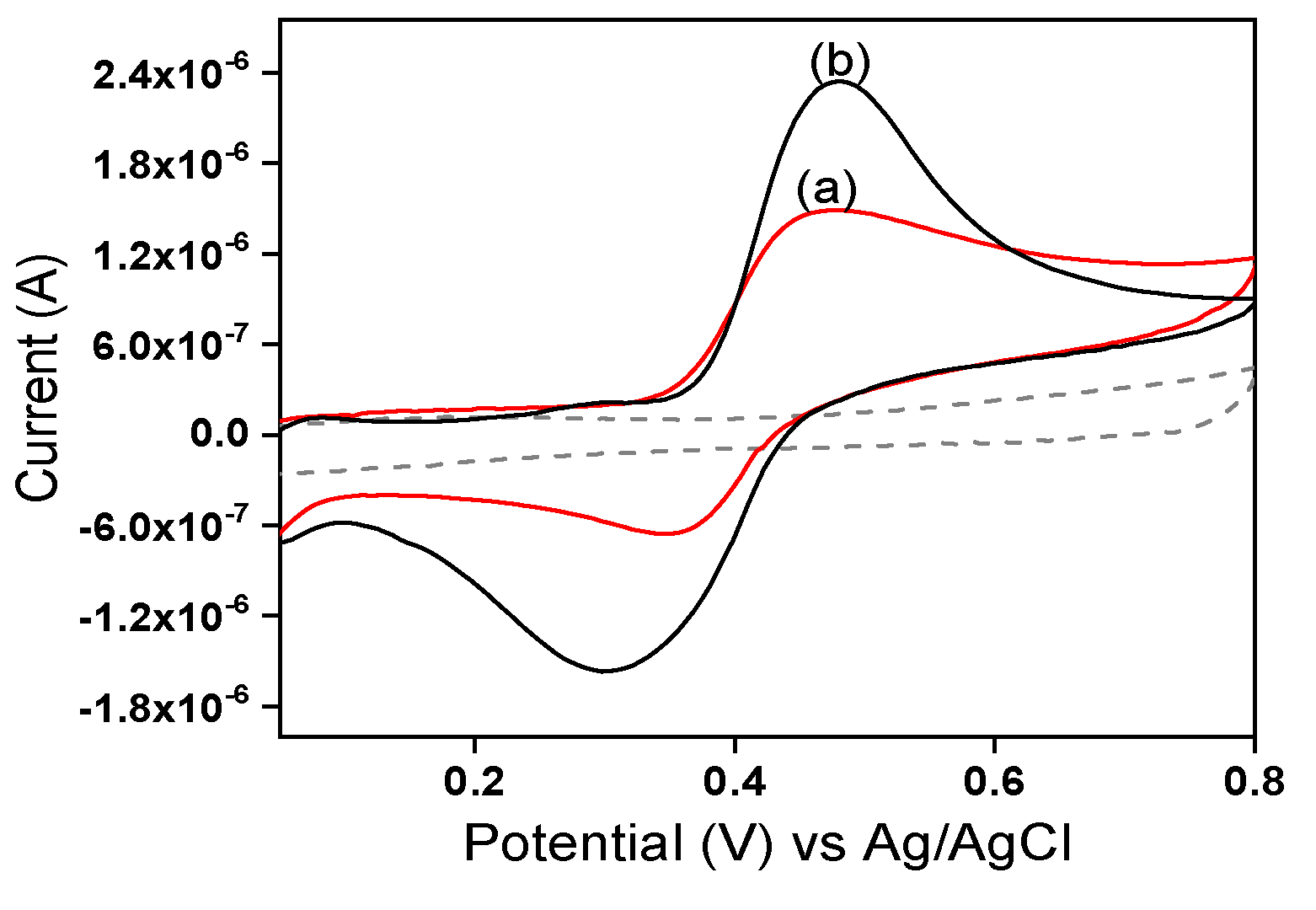
Preliminary investigations were undertaken by using cyclic voltammetry in 0.1 M of acetate buffer solution (pH 3.75) to both study the electrochemical behavior of EP and evaluate the contribution of the laponite clay used to modify IPGE. The electrochemical response of EP was shown to be a quasi-reversible system on both simple IPGE and laponite clay-modified La/IPGE. Peaks were obtained at +0.46 V with a current of 1.48 µA in anodic direction, and at +0.35 V with an intensity of -6.11 µA in cathodic branch for unmodified IPGE (
Figure 4a). Additionally, with laponite clay modified IPGE the signal occurs at +0.47 V with anodic peak current of 2.32 µA and at +0.31 V with reduction current peak of -1.56 µA (
Figure 4b).
Overall, it was noticed that the La/IPGE is more sensitive for EP compared to the bare IPGE. The presence of the clay mineral on IPGE has favored the retention of EP due to favorable interaction between the negatively charged clay platelets and the cationic form of EP.
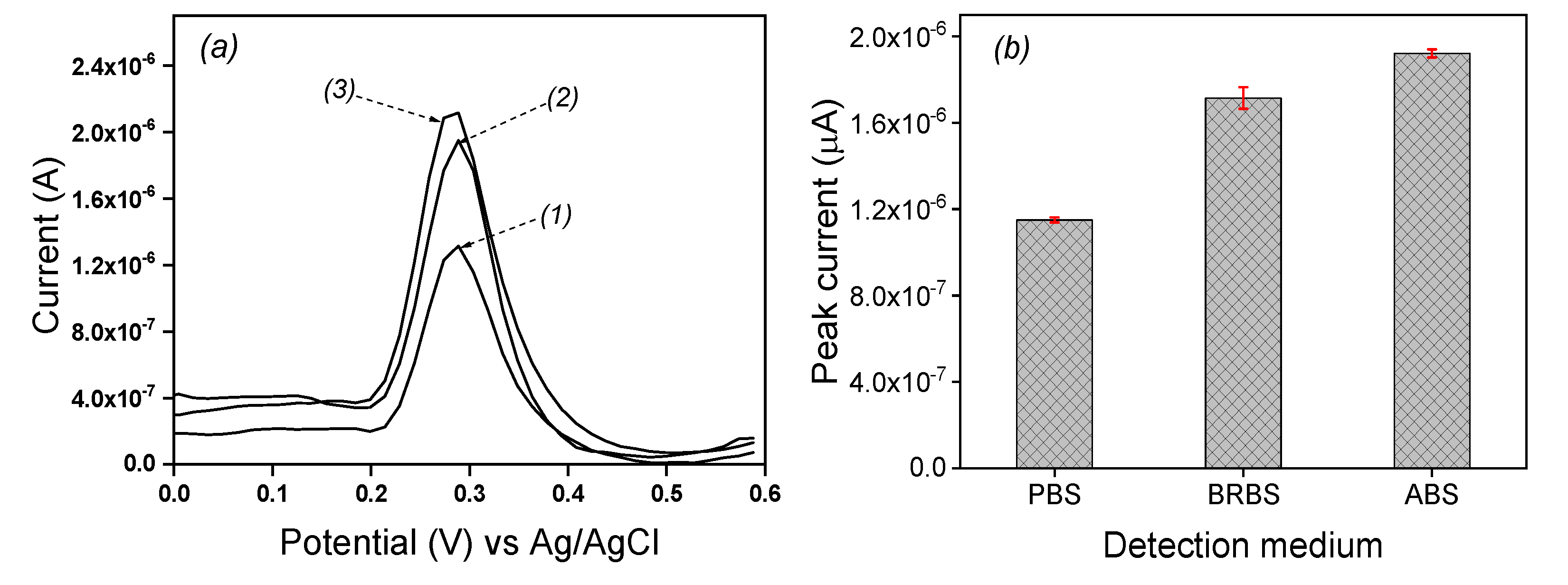
2.3.2. Influence of detection medium
Three media were tested to evaluate their individual influence on the electrochemical response of EP. Differential pulse voltammetry of 0.1 mM EP was recorded 0.1 M acetate buffer solution (ABS), Britton Robinson buffer solution (BRBS) and phosphate buffer solution (PBS) respectively at pH 5 on the laponite clay modified IPGE and the results are shown in
Figure 5a. The peak currents values of 1.23 µA, 1.721 µA and 1.949 µA were respectively obtained in PBS, BRBS and ABS as seen in
Figure 5b. The best current value was obtained in ABS and then, this solution was retained the further experiments.
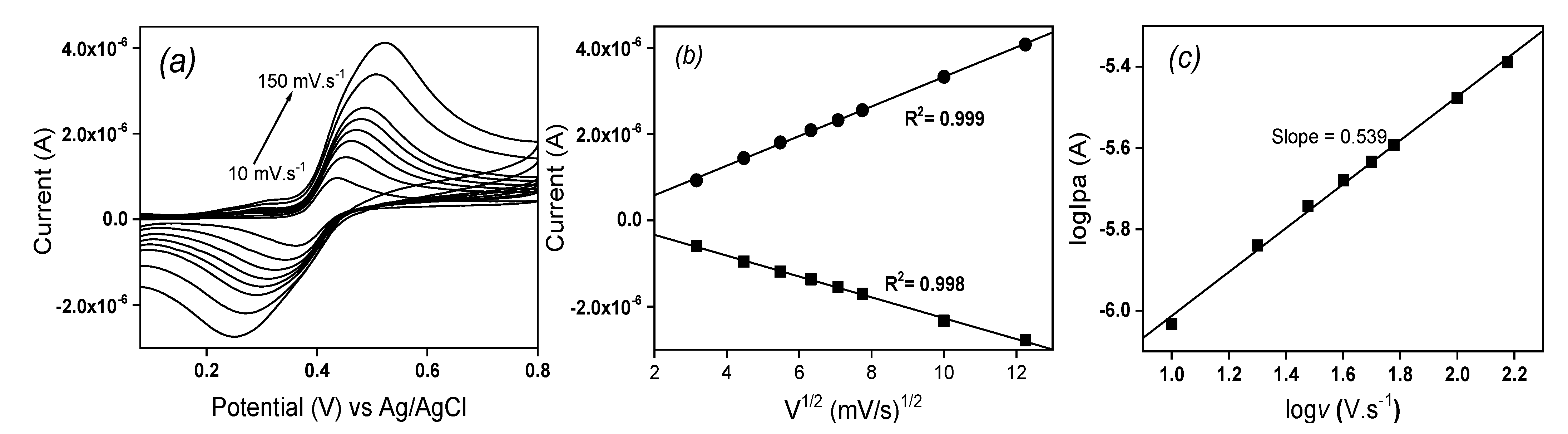
2.3.3. Influence of scan rate on the electrochemical response of EP on La/IPGE
The influence of the scan rate on the oxidation and reduction peaks of EP was studied using cyclic voltammetry in ABS (pH 3.75) on La/IPGE and the obtained results are shown on
Figure 6. It was observed that, increasing the scan rate from 10 to 150 mV s
-1 induced an increase in both anodic and cathodic peak currents of EP. Meanwhile, the anodic signal shifted towards more positive potential values and cathodic peaks to more negative potential values (
Figure 6a). By plotting both anodic and cathodic peaks current as a function of the square root of the scan rate in the studied range, a linear dependence was observed (
Figure 6b), indicating a diffusion-controlled process.
This fact was confirmed by also plotting the logarithmic of anodic peak current versus the logarithmic of the scan rate (
Figure 6c): a linear dependence was again obtained between both parameters, according to the following equation logIpa (µA) = -6.552 + 0.539 logv (V s
-1) (R
2 = 0.997). The slope value of 0.53 closed to the standard theoretical value of 0.5 confirmed the pure diffusion-controlled process [
20].
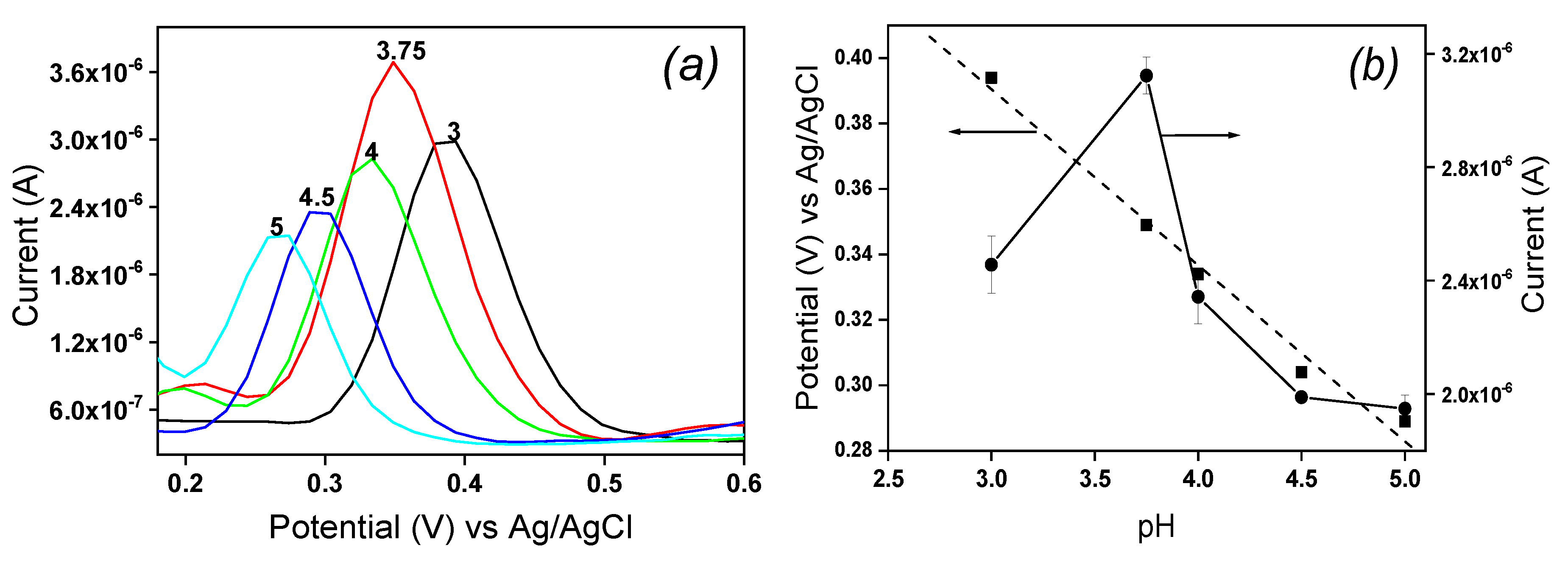
2.3.4. Influence of pH on the electrochemical response of EP
The redox behavior of EP implies protons, and the influence of pH on its electrochemical response was studied from 3 to 5 in 0.1 M ABS containing 10
-4 M EP by DPV. The results are shown in
Figure 7. It was observed that raising the pH of solution from 3 to 5 induced an increase in the peak current with a maximum reached at pH 3.75, then the peak current decreased for pH values between 3.75 and 5 (
Figure 7a). This behavior is due to the fact that, between pH 3 and 3.75, EP mainly exists in its cationic form noticed according to the distribution diagram established by Corona
et al. [
21]. Thus, the main affinity between the cationic form of EP and the negative charge on laponite sheets was electrostatic attraction.
From pH 4 to 5, the peak current gradually decreases due to the fact that EP existing in its molecular form at these pH values is no more attracted by the clay film on IPGE. In addition, the peak potential of EP shifted to more negative values and remained linearly on the pH values range studied as shown in
Figure 7b. The obtained anodic linear regression equation was E
pa (V) = -0.054 pH + 0.574 and the correlation coefficient was R
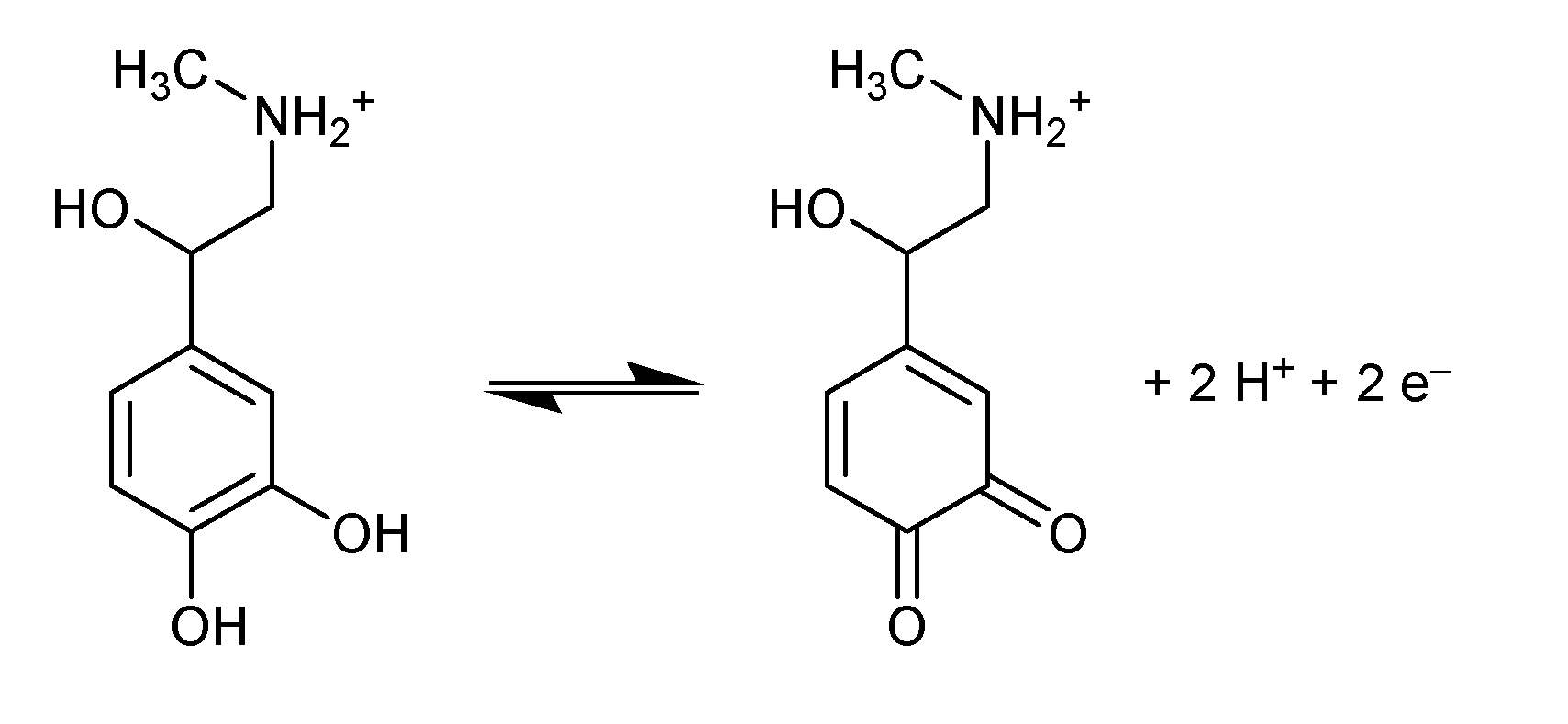
2 = 0.986. The slope value of -0.054 mV/pH near the Nernstian value of 0.059 suggested that an equal number of proton and electron is exchanged during electrochemical oxidation/oxidation of EP on La/IPGE sensor surface according to
Scheme 1, as previously observed by Hong
et al. [
22].
2.3.5. Influence of EP concentration and calibration curve
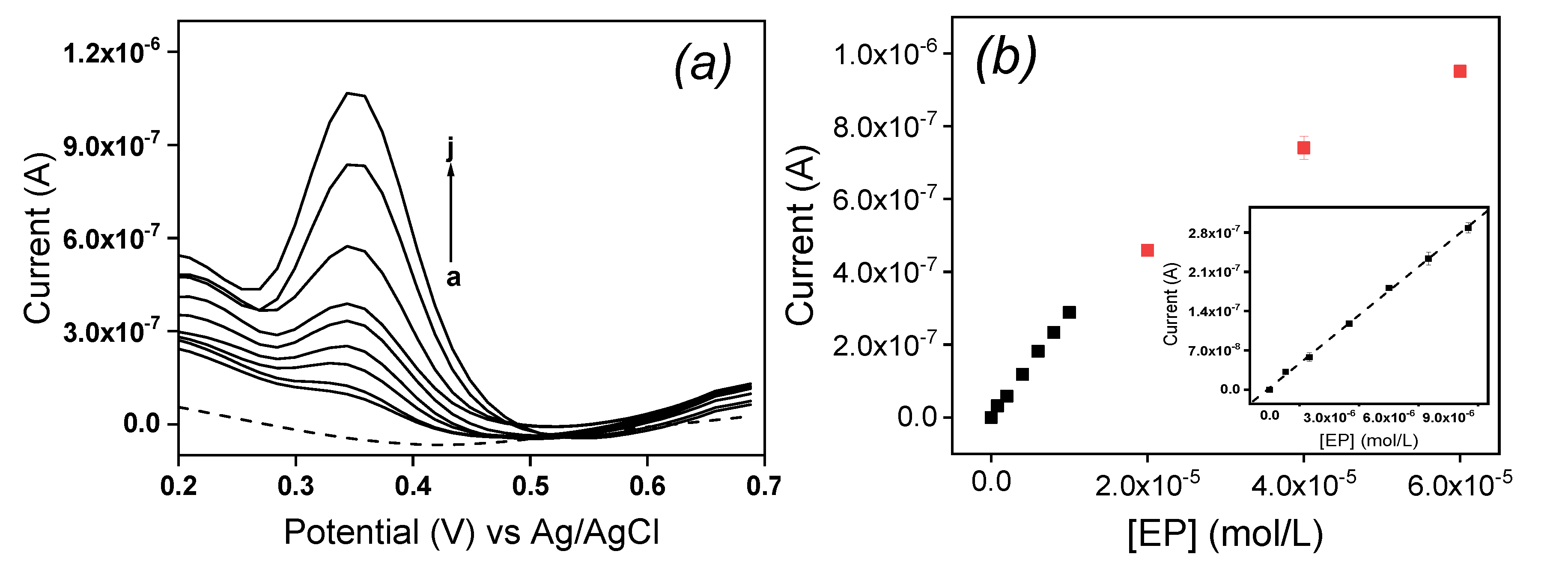
The influence of concentration of EP at La/IPGE in 0.1 M of ABS studied by DPV is shown on
Figure 8a: the peak current (Ip) increased with the increase of EP concentration in the range of 0.8 µM to 10 μM. The corresponding calibration curve is shown on
Figure 8b, which is described by the following equation (1):
The detection limit given by the relation 3S
b/m where S
b represents the standard deviation obtained from the blank and m the slope on the calibration plot [
22] was 0.26 µM. This result showed that La/IPGE can allow the detection of EP in the micromolar range in aqueous solution. The detection limit obtained in this work was compared with another data based on modified electrodes as gathered in
Table 1.
Globally, results obtained in this section indicated a good sensitivity of La/IPGE sensor towards the detection of EP, and that this sensor could serve as low-cost analytical device. However, before applying it for the quantification of EP in a real sample, the effect of potential compounds expected to interfere on the signal of EP was evaluated.
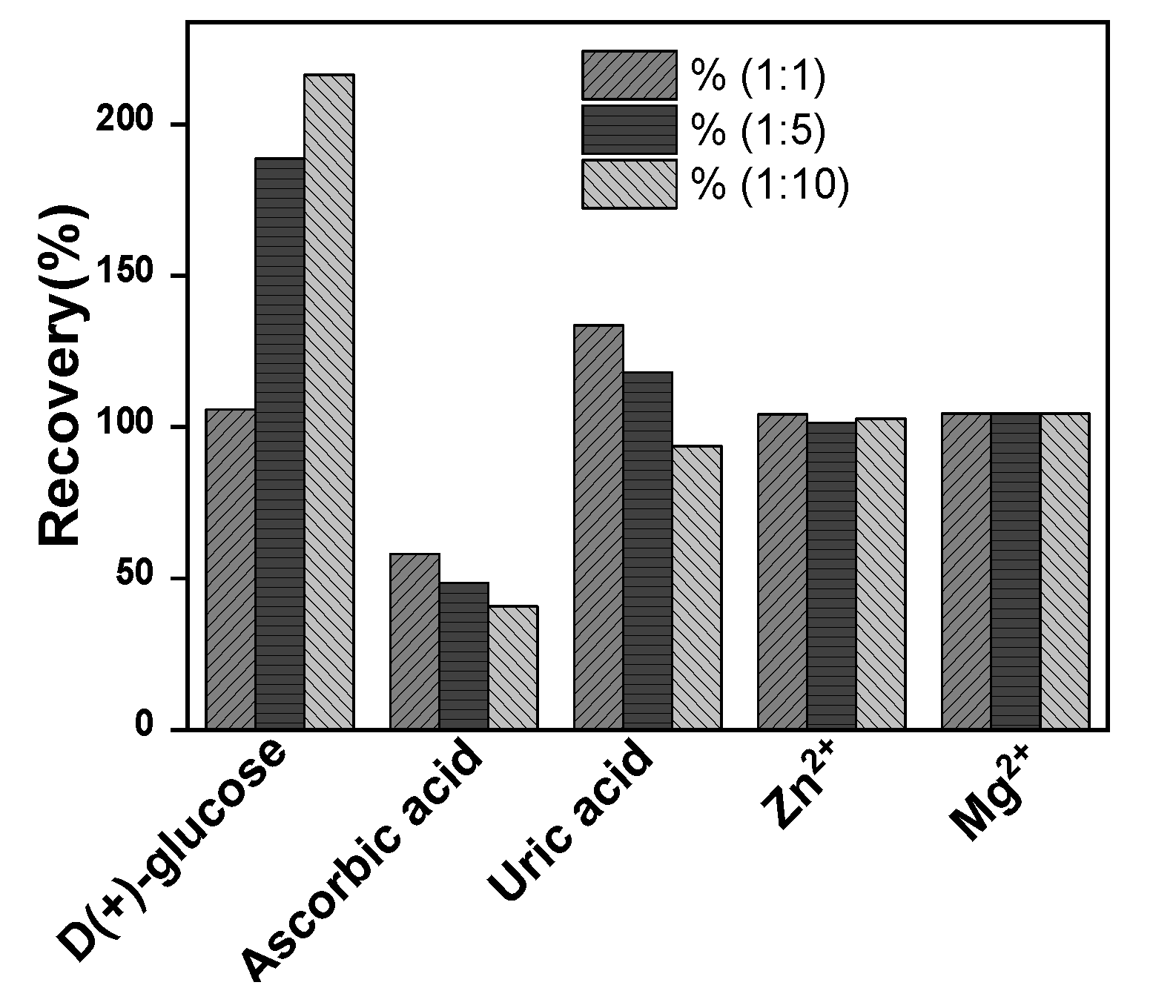
2.4. Interference study
The selectivity of La/IPGE sensor on the oxidation peak current of EP was evaluated by analyzing the effect of the presence in the same medium of EP, along with these compounds. They included as organic compounds ascorbic acid, uric acid, D-(+)-glucose; and two metals ions (Zn
2+ and Mg
2+) introduced in the supporting electrolyte at three different concentrations ratio as presented in
Figure 9. It was noticed that neither Zn
2+ nor Mg
2+ ions influence on the peak current of EP for the three investigated concentrations. However, ascorbic acid, uric acid and D-(+)-glucose significantly interfere on EP signal. This observation is due to the preferential occupation of both ascorbic and uric acid on the clay film on IPGE surface notably when the concentration of interfering species was increased. These observations somewhat limit the selectivity of La/IPGE sensor and indicated that it should be used in media not containing the studied organic compounds.
2.5. Analytical application
The analytical application of the La/IPGE elaborated sensor was done by using it to analyze adrenaline in commercial dose manufactured by Zhejg Tianfng pharmaceutical (China) purchased in a local market (Dschang city, West region, Cameroon). The sample was firstly diluted 100 and 400 times using the 0.1 M ABS supporting electrolyte, with the final pH adjusted at 3.7. An appropriate volume of the solution to be tested was added in the electrochemical cell containing the electrolyte solution and the peak current was measured. Using the calibration graph, the concentration in the solution was calculated. The data collected are shown in
Table 2.
Good recovery rates were obtained, revealing that the proposed sensor could serve for the electrochemical determination of EP in real sample.
3. Conclusions
This work was devoted for the preparation of an electrochemical sensor based on an inkjet-printed graphene electrode (IPGE), modified by a thin film of laponite (La) clay mineral. It was characterized by multisweep cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, and then applied for the sensitive analysis of EP in aqueous solution. Under optimal analysis conditions, the sensor gave a detection limit of 0.26 µM. The effect of some potential interfering species has shown that both zinc nor magnesium ions influence on the peak current of EP but ascorbic acid, uric acid and D-(+)-glucose significantly interfere on the electrochemical response of EP. Best recoveries were also obtained with the sensor after applying it for the determination of EP in a pharmaceutical preparation. The obtained results show that this sensor could serve as an alternative tool for the determination of EP not only in aqueous solution, but also in pharmaceutical preparation with a good sensitivity.
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Chemicals, reagents and materials
All chemicals were used without further purification. Epinephrine hydrochloride used as target analyte was purchased from Across Organics. The stock solution of EP was prepared at 10-2 M by dissolving 9 mg of epinephrine hydrochloride in 5 mL of PBS (pH 7), unless otherwise described. Working solutions of EP were prepared by dilution. Various buffer solutions were prepared using the following chemicals: Boric acid (>99%, Sigma-Aldrich), acetic acid (≥99.7%, Fluka) and phosphoric acid (85%, Sigma-Aldrich) for Britton Robinson buffer solution; Na2HPO4.2H2O (98%, Fluka) and KH2PO4 (99%, Normapur) for phosphate buffer solution and Sodium acetate (≥ 99.0%, Sigma-Aldrich) and acetic acid (≥99.7%, Fluka) for acetate buffer solution. The pH of buffer solutions used was adjusted by using decimolar solutions of HCl and NaOH (Merck). D-(+) glucose, ascorbic acid; uric acid were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich; potassium hexacyanoferrate (III and II) and KCl (99%, Prolabo), from Prolabo; Zn(NO3)3.6H2O (99%, BDH chemicals) Mg(NO3)3.6H2O (99%, Kermel).
Laponite clay with the chemical formula Na
0.7Si
8Mg
5.5Li
0.3O
20(OH)
4 [
27] used in this work was purchased from the Source Clay Repository Clay Mineral Society, Purdue University, USA. It was purified by collecting the fraction with particle size < 2 µm based on the Stokes law [
28].
4.2. Preparation of Inkjet-printed graphene electrode
The inkjet-printed graphene electrode was made according to a previous published work by our group [
29]. Briefly, two platforms were used: the first for deposition of layers of the graphene dispersion called the DMP-2850 inkjet printer followed by the X-Serie CeraPrinter from Ceradrop used to simultaneously print and photopolymerize with an integrated UV LED. For defining the electroactive surface area of any electrode, UV curable ink (EMD 6200 from Sun Chemical) and insulator was used. The modification of IPGE was done by drop-coating using laponite clay. For preparing the electrochemical sensor, 5 mg of laponite (< 2 µm particle size) clay were introduced in 1 mL of distilled water and dispersed by ultrasonication for 20 min. A volume of 0.5 µL of clay depending of it theoretically surface area (1 mm
2) was taken using appropriate micropipette, deposited on the active surface of IPGE and dried for 1 min at 110°C on a steam before its use for electrochemical investigations.
4.3. Apparatus
The electrochemical measurements were realized by using a µ-Autolab potentiostat (type III) running with GPES software and with standard three-electrode cell. Voltammetric responses were recorded in supporting electrolyte with an Ag/AgCl/3M KCl reference electrode, a steel rod counter electrode and bare IPGE or La/IPGE working electrode. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) of a known concentration of adrenaline were recorded in 0.1 M of phosphate buffer solution (PBS), Britton Robinson buffer solution (BRBS) and acetate buffer solution (ABS) at a known pH value in the potential range of 0 to 0.8 V. The pH values of solutions were measured and monitored with an Inolab pH-meter at room temperature. Additionally, both electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and cyclic voltammetric techniques were used for electrochemical characterization of unmodified and modified IPGE. For EIS measurements, 0.1 M KCl containing 1 mM [Fe(CN)6]3-/4- was used over the frequency range of 0.01 Hz to 10000 Hz. For MCV, 0.1 M KCl containing either 1 mM [Fe(CN)6]3- or [Ru(NH3)6]3+ was used for the charge investigation of La/IPGE.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: C.N.P., V.K.T., A.L., I.K.T. and K.Y.T.; Methodology: SL.Z.J., C.N.P., I.K.T., E.N.; Investigation, C.N.P., V.K.T.; Resources, E.N. and C.J.; Writing—original draft preparation: C.N.P., K.Y.T., I.K.T., E.N. and C.J.; Writing—review and editing: C.N.P., K.Y.T., I.K.T., E.N. and C.J.; Supervision, I.K.T., E.N. and C.J.; Project administration, I.K.T., E.N. and C.J.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support of the African Network of Electroanalytical Chemists (ANEC) and the International Science Programme (ISP, Sweden).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hussain, A.; Truelove, J.E. Prodrug approaches to enhancement of physicochemical properties of drugs IV: Novel epinephrine prodrug. J. Pharm. Sci. 1976, 65, 1510–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoukas, A.A.; Brunner, M.C. Epinephrine and the carotid sinus baroreceptor reflex. Influence on capacitive and resistive properties of the total systemic vascular bed of the dog. Circ. Res. 1980, 47, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, J.D.; Bonito, A.J.; Shugars, D.A. A systematic review of cardiovascular effects of epinephrine on hypertensive dental patients, Oral Surgery, Oral Med. , Oral Pathol., Oral Radiol. & Endodontol. 2002, 93, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hague, S.M.; Klaffke, S.; Bandmann, O. Neurodegenerative disorders: Parkinson's disease and Huntington's disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76, 1058–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borodovitsyna, O.; Flamini, M.; Chandler, D. Noradrenergic modulation of cognition in health and disease. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017, 6031478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Shen, L.; Lu, J. Flow injection chemiluminescence determination of epinephrine using epinephrine-imprinted polymer as recognition material. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 489, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britz-Mckibbin, P.; Wong, J.; Chen, D.D. Analysis of epinephrine from fifteen different dental anesthetic formulations by capillary electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. A 1999, 853, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fice, D.S.; Yeung, P.K. A simple high-performance liquid chromatography assay for simultaneous determination of plasma norepinephrine, epinephrine, dopamine and 3, 4-dihydroxyphenyl acetic acid. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1999, 21, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, S.; Jesny, S.; Sivasankaran, U.; Kumar, K.G. Fluorometric determination of epinephrine: A green approach. Anal. Sci. 2016, 32, 999–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonle, I.K.; Ngameni, E.; Tchieno, M.M.F.; Walcarius, A. Organoclay-modified electrodes: Preparation, characterization and recent electroanalytical applications. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2015, 19, 1949–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousty, C. Biosensing applications of clay-modified electrodes: A review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 396, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattos, G. J.; Mariano, R. S.; Sartori, E. R. Recent advances in electrochemical monitoring of epinephrine using carbon-based (bio) sensor devices for clinical applications. In Electrochemical Sensors Based on Carbon Composite Materials: Fabrication, properties and applications. 2022, 9-27, IOP Publishing, Editor Jamballi G Manjunatha.
- Karim-Nezhad, G.; Khorablou, Z. Selective analysis of epinephrine in the presence of uric acid by using an amplified electrochemical sensor employing a gold nanoparticle decorated cysteic acid film. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 6394–6402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhao, P.; Xie, Z.; Ni, M.; Wang, C.; Yang, P.; Xie, Y.; Fei, J. Selective determination of epinephrine using electrochemical sensor based on ordered mesoporous carbon / nickel oxide nanocomposite. Talanta 2021, 233, 122545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunes, O.; Sarilmaz, A.; Zeki Bas, S.; Ozmen, M.; Ozel, F.; Ersoz, M. Electrochemical detection of epinephrine based on a screen-printed electrode modified with nio−ergo nanocomposite film. Electroanalysis 2021, 33, 2460–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagaly, G.; Ogawa, M.; Dékany, I. Clay minerals organic interactions In: Bergaya F, Lagaly G. (eds.), 2nd edition, Handbook of clay science. Developments in Clay Science Elsevier, 2013, 5A, 435–505. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.-L.; Jiang, G.-C.; Xu, Y.; Deng, Z.-Q.; Wang, K. A new environmentally friendly water-based drilling fluids with laponite nanoparticles and polysaccharide/polypeptide derivatives. Petrol. Sci. 2022, 19, 2959–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perotti, G.F.; Barud, H.S.; Messaddeq, Y.; Ribeiro, S.J.L.; Constantino, V.R.L. Bacterial cellulose–laponite clay nanocomposites. Polymer, 2011, 52, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, G.A.; Freitas Moraes, I.C.; Gilles Hilliou, L.H.; Lourenço, R.V.; do Amaral Sobral, P.J. Nanocomposite-forming solutions based on cassava starch and laponite: Viscoelastic and rheological characterization. J. Food Eng. 2015, 166, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.; Zen, J.M.; Kumar, A.S.; Chen, P.Y. Flow injection analysis of zinc pyrithione in hair care products on a cobalt phthalocyanine modifed screen-printed carbon electrode. Talanta 2004, 62, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona-Avendaño, S.; Alarcón-Angeles, G.; Rojas-Hernández, A.; Romero-Romo, M.A.; Ramírez-Silva, M.T. Study on the stability of adrenaline and on the determination of its acidity constants. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2005, 61 (1-2), 305-311. [CrossRef]
- Ghoneim, M.M.; Hassanein, A.M.; Hammam, E.; Beltagi, A.M. Simultaneous determination of Cd, Pb, Cu, Sb, Bi, Se, Zn, Mn, Ni, Co and Fe in water by differential pulse stripping voltammetry at a hanging mercury drop electrode. Fres. J. Anal. Chem. 2000, 367, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkušić, E.; Redžić, S.; Kahrović, E.; Zahirović, E. Electrochemical determination of adrenaline at Ru(III) Schiff base complex modified carbon electrodes. Croat. Chem. Acta. 2017, 90, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Sun, Y.; Lin, X.; Tang, Y.; Liu, A.; Li, G.; Li, W.; Zhang, S. Selective determination of epinephrine in the presence of ascorbic acid and uric acid by electrocatalytic oxidation at poly(eriochrome black-t) film-modified glassy carbon electrode. Anal. Sci. 2007, 23, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babaei, A.; Mirzakhani, S.; Khalilzadeh, B. A sensitive simultaneous determination of epinephrine and tyrosine using an iron(III) doped zeolite-modified carbon paste electrode. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2009, 20, 1862–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Luo, H.Q.; Li, N.B. Simultaneous voltammetric measurement of ascorbic acid, epinephrine and uric acid at a glassy carbon electrode modified with caffeic acid. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 21, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajeu, K.Y.; Ebunang, D.V.T.; Tonleu, R.C.T.; Jiokeng, S.L.Z.; Ymele, E.; Tonle, I.K. Electroanalytical application of thiol-grafted laponite to the sensitive quantification of ciprofloxacin antibiotic. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2021, 51, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tcheumi, H.L.; Tonle, I.K.; Ngameni, E.; Walcarius, A. Electrochemical analysis of methylparathion pesticide by a gemini surfactant-intercalated clay-modified electrode. Talanta 2010, 81, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenang, S.L.; Dongmo, M.L.; Jiokeng, Z.L.S.; Kamdem, T.A.; Doungmo, G.; Tonle, I.K.; Bassetto, V.C.; Milica, J.; Lesch, A.; Girault, H. Montmorillonite clay-modified disposable ink-jet-printed grapheme electrode as a sensitive voltammetric sensor for the determination of cadmium(II) and lead(II). SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Multisweep cyclic voltammograms (30 scans) recorded on La/IPGE in 0.1 M KCl containing (a) 1 mM [Fe(CN)6]3- and (b) 1 mM [Ru(NH3)6]3+. The red curve represents the signal of the same probes on the bare IPGE. Potential scan rate: 30 mV/s.
Figure 1.
Multisweep cyclic voltammograms (30 scans) recorded on La/IPGE in 0.1 M KCl containing (a) 1 mM [Fe(CN)6]3- and (b) 1 mM [Ru(NH3)6]3+. The red curve represents the signal of the same probes on the bare IPGE. Potential scan rate: 30 mV/s.
Figure 3.
EIS recorded in 0.1 M KCl containing 1 mM [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− (a) on bare IPGE (black data points) and (b) on La/IPGE (red data points).
Figure 3.
EIS recorded in 0.1 M KCl containing 1 mM [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− (a) on bare IPGE (black data points) and (b) on La/IPGE (red data points).
Figure 4.
Cyclic voltammograms recorded in 0.1 M ABS (pH 3.75) containing 0.4 mM EP, (a) on bare IPGE (red curve) and (b) on La/IPGE. Potential scan rate: 50mV/s.
Figure 4.
Cyclic voltammograms recorded in 0.1 M ABS (pH 3.75) containing 0.4 mM EP, (a) on bare IPGE (red curve) and (b) on La/IPGE. Potential scan rate: 50mV/s.
Figure 5.
(a) DPV curves recorded on La/IPGE in (1) 0.1 M PBS, (2) 0.1 M BRBS and (3) 0.1 M ABS (all at pH 5) containing 10-4 M EP, (b) Corresponding peak currents.
Figure 5.
(a) DPV curves recorded on La/IPGE in (1) 0.1 M PBS, (2) 0.1 M BRBS and (3) 0.1 M ABS (all at pH 5) containing 10-4 M EP, (b) Corresponding peak currents.
Figure 6.
(a) CV curves recorded in 0.1 M ABS (pH 3.75) containing 0.1 mM EP on La/IPGE at different scan rates: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 100 and 150 mV.s-1, (b) Peak current of both anodic and cathodic vs square root of scan rate and (c) logIpa vs logv
Figure 6.
(a) CV curves recorded in 0.1 M ABS (pH 3.75) containing 0.1 mM EP on La/IPGE at different scan rates: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 100 and 150 mV.s-1, (b) Peak current of both anodic and cathodic vs square root of scan rate and (c) logIpa vs logv
Figure 7.
(a) DPV curves recorded on La/IPGE for 10-4 M EP in 0.1 M ABS at different pH values (3, 3.75, 4, 4.5 and 5); (b) EP anodic peak current and peak potential vs pH.
Figure 7.
(a) DPV curves recorded on La/IPGE for 10-4 M EP in 0.1 M ABS at different pH values (3, 3.75, 4, 4.5 and 5); (b) EP anodic peak current and peak potential vs pH.
Scheme 1.
Electrochemical oxidation mechanism of EP oxidation on La/IPGE [
22].
Scheme 1.
Electrochemical oxidation mechanism of EP oxidation on La/IPGE [
22].
Figure 8.
(a) DPV recorded at La/IPGE in 0.1 M ABS (pH 3.75) containing EP at varied concentrations: (a) 0 µM, (b) 0.8 µM, (c) 2 µM, (d) 4 µM, (e) 6 µM, (f) 8 µM, (g) 10 µM, (h) 20 µM, (i) 40 µM and (j) 60 µM. (b) plot of ip vs [EP] (inset: calibration curve of EP in selected linear range).
Figure 8.
(a) DPV recorded at La/IPGE in 0.1 M ABS (pH 3.75) containing EP at varied concentrations: (a) 0 µM, (b) 0.8 µM, (c) 2 µM, (d) 4 µM, (e) 6 µM, (f) 8 µM, (g) 10 µM, (h) 20 µM, (i) 40 µM and (j) 60 µM. (b) plot of ip vs [EP] (inset: calibration curve of EP in selected linear range).
Figure 9.
Influence of some potential interfering compounds on the DPV response of 0.1 mM EP with La/IPGE.
Figure 9.
Influence of some potential interfering compounds on the DPV response of 0.1 mM EP with La/IPGE.
Table 1.
Compared performance of some sensors towards the detection of EP.a).
Table 1.
Compared performance of some sensors towards the detection of EP.a).
| Modified electrodes |
Concentration range (µM) |
Detection limit (µM) |
Methods |
Ref. |
| GCE/Na[RuL2] |
3 - 136 |
3.49 |
FIA |
[23] |
| ECS/Na[RuL2]/cellulose acetate |
3 - 273 |
0.28 |
FIA |
[23] |
| Poly(EBT) modified GCE |
2.5 - 50 |
0.3 |
DPV |
[24] |
| Iron(III) doped zeolite-modified CPE |
0.9 - 216 |
0.44 |
DPV |
[25] |
| Caffeic acid modified GCE |
2 - 300 |
0.60 |
CV |
[26] |
| Laponite clay modified IPGE |
0.8 - 60 |
0.26 |
DPV |
This work |
Table 2.
Electrochemical quantification of EP in real sample.
Table 2.
Electrochemical quantification of EP in real sample.
| Sample |
Dilution rate |
[EP] added (µM) |
[EP] founded (µM) |
Recovery (%) |
| 1 |
100 |
54.58 |
51.45 |
94.26 |
| 2 |
400 |
18.19 |
20.34 |
111.18 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).