Submitted:
14 June 2023
Posted:
15 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
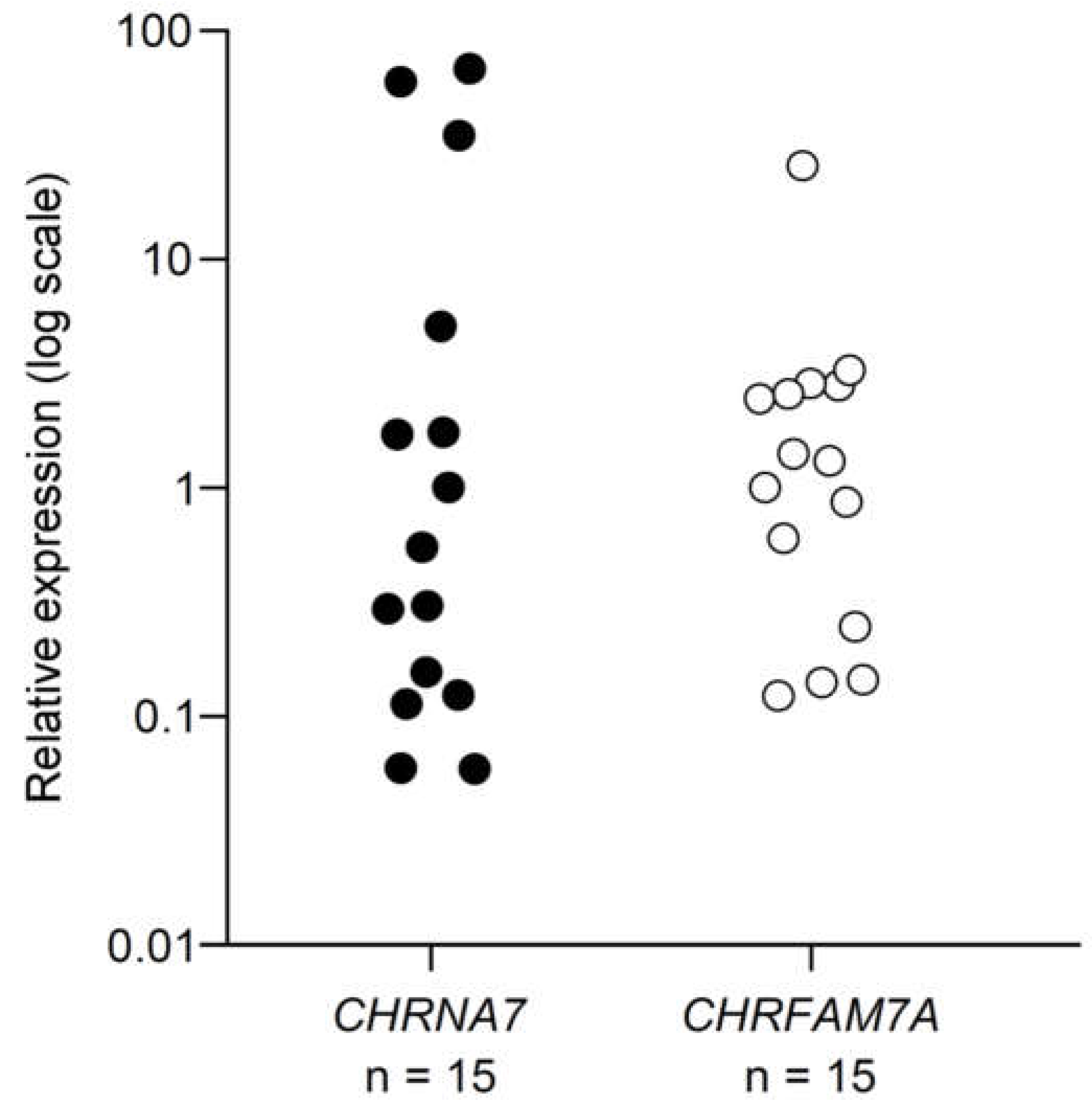
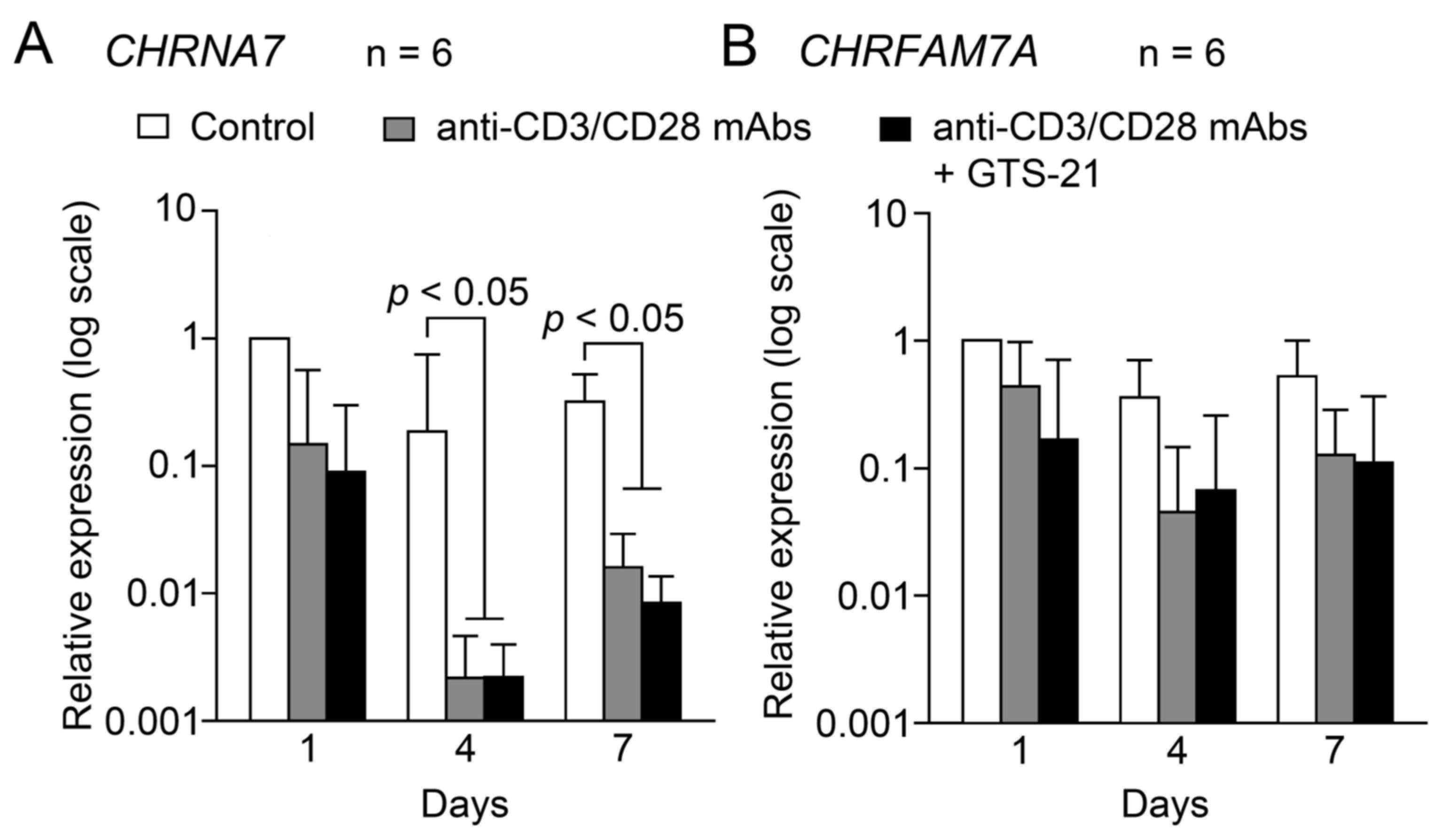
2.1. mRNA expression of α7 and dupα7 subunits
2.1.1. Under the resting conditions
2.1.2. Changes during TCR-activation
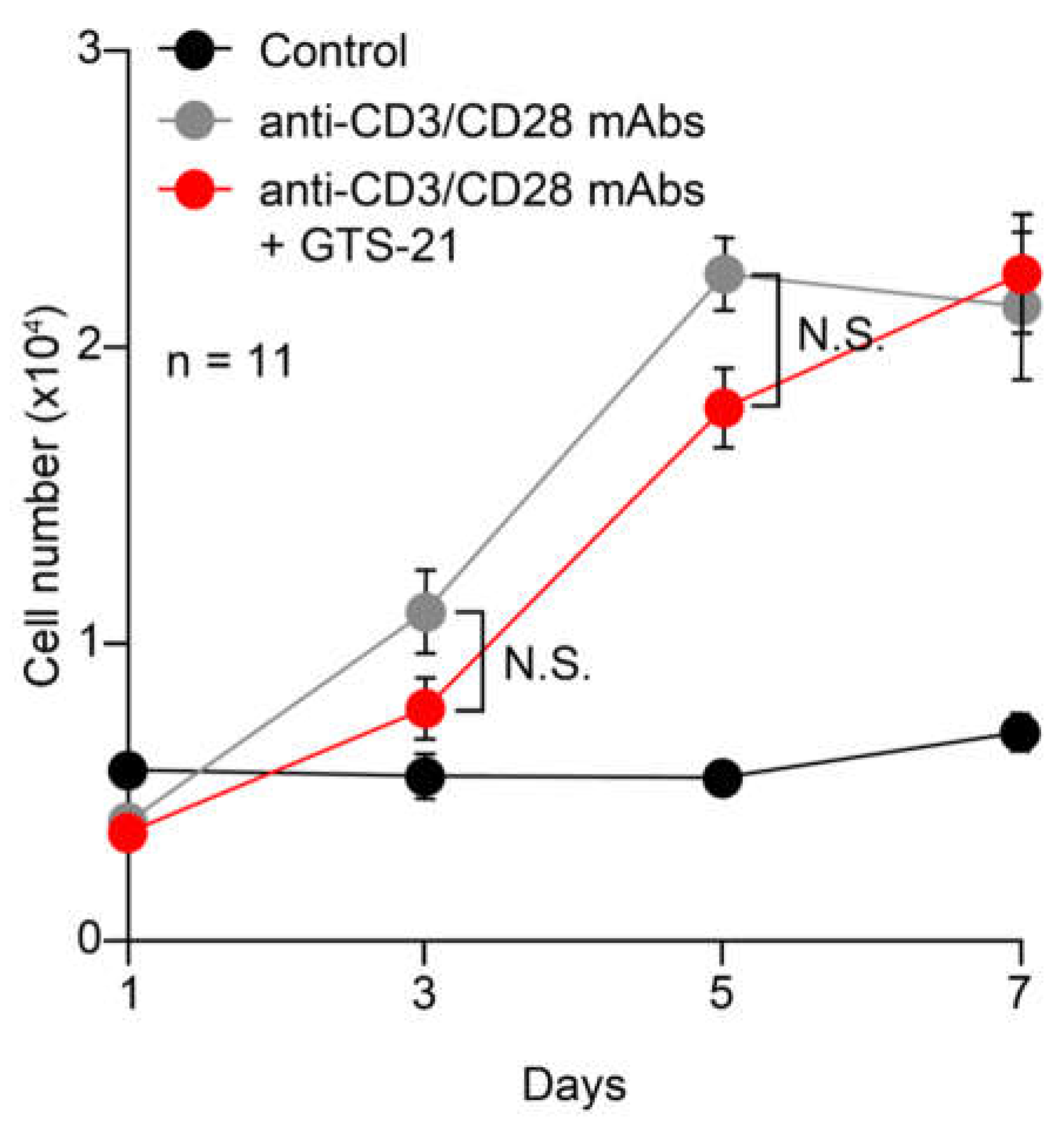
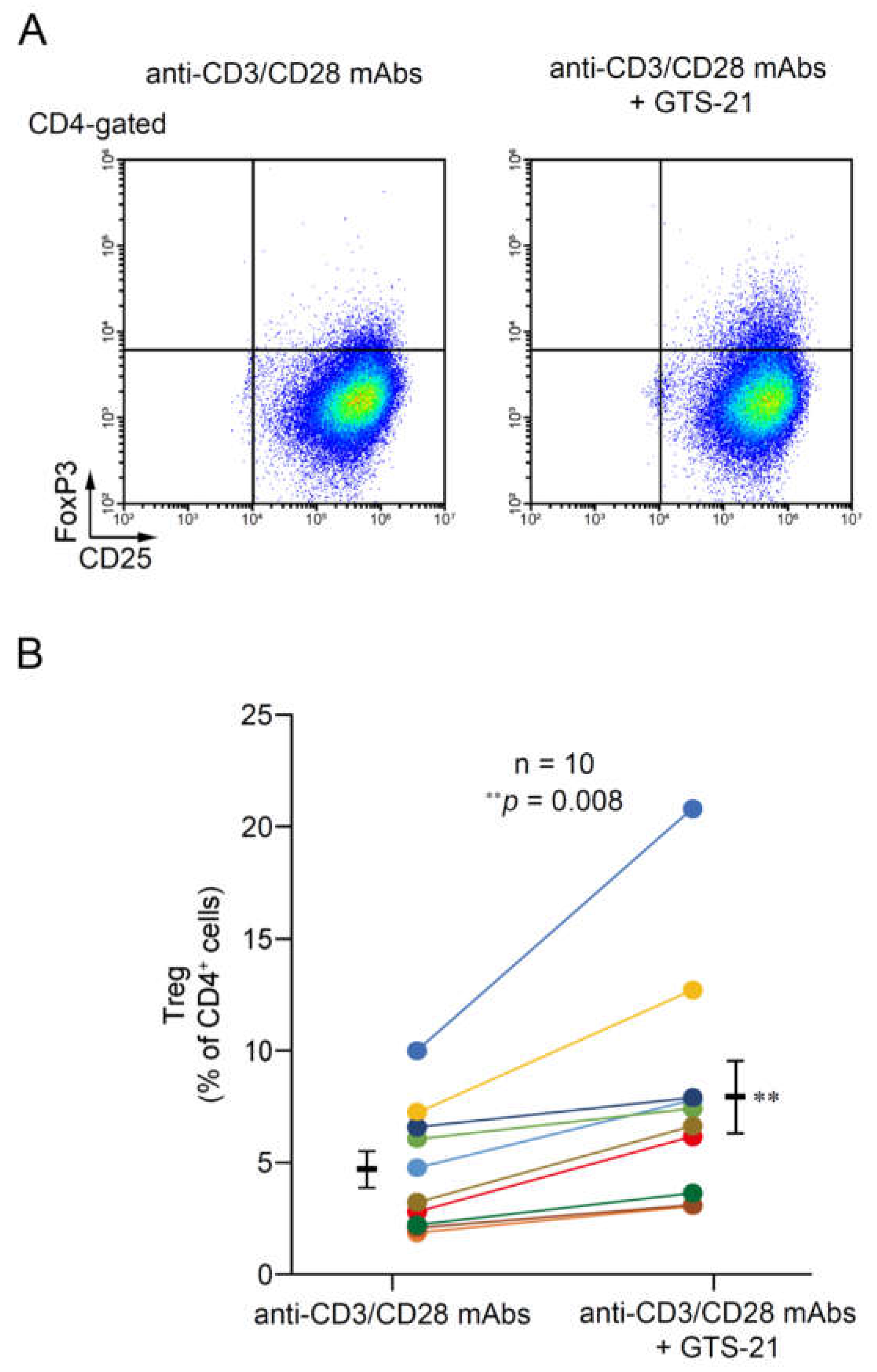
2.2. Effects of GTS-21 on CD4+ T cell proliferation and Treg development
2.2.1. Proliferation
2.2.2. Treg development
3. Discussion
3.1. Expression of mRNAs for α7 and dupα7 subunits in resting human CD4+ T cells
3.2. Expression of α7 and dupα7 subunit mRNAs during TCR activation
3.3. Effects of GTS-21 on proliferation
3.4. The effect of GTS-21 on Treg development in TCR-activated CD4+ T cells
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell culture
4.1.1. CHRNA7 and CHRFAM7A expression under the resting conditions
4.1.2. CHRNA7 and CHRFAM7A expression during T cell activation
4.1.3. Effects of GTS-21 on TCR-activated T cell proliferation
4.1.4. Effects of GTS-21 on Treg development in TCR-activated T cells
4.2. Real-time PCR
4.3. Flow cytometry for Treg development
4.4. Statistical analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sato, K.Z.; Fujii, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Yamada, S.; Ando, T.; Kazuko, F.; Kawashima, K. Diversity of mRNA expression for muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes and neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunits in human mononuclear leukocytes and leukemic cell lines. Neurosci Lett 1999, 266, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, K.; Fujii, T. Extraneuronal cholinergic system in lymphocytes. Pharmacol Ther 2000, 86, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawashima, K.; Fujii, T. The lymphocytic cholinergic system and its biological function. Life Sci 2003, 72, 2101–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawashima, K.; Fujii, T. Expression of non-neuronal acetylcholine in lymphocytes and its contribution to the regulation of immune function. Front Biosci 2004, 9, 2063–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, K.; Yoshikawa, K.; Fujii, Y.X.; Moriwaki, Y.; Misawa, H. Expression and function of genes encoding cholinergic components in murine immune cells. Life Sci 2007, 80, 2314–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Tajima, S.; Yamada, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Sato, K.Z.; Matsui, M.; Misawa, H.; Kasahara, T.; Kawashima, K. Constitutive expression of mRNA for the same choline acetyltransferase as that in the nervous system, an acetylcholine-synthesizing enzyme, in human leukemic T-cell lines. Neurosci Lett 1999, 259, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Yamada, S.; Misawa, H.; Tajima, S.; Fujimoto, K.; Suzuki, T.; Kawashima, K. Expression of choline acetyltransferase mRNA and protein in t-lymphocytes. Proc Japan Acad. 1995, 71B, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Yamada, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Misawa, H.; Tajima, S.; Fujimoto, K.; Kasahara, T.; Kawashima, K. Induction of choline acetyltransferase mRNA in human mononuclear leukocytes stimulated by phytohemagglutinin, a T-cell activator. J Neuroimmunol 1998, 82, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Kawashima, K. An independent non-neuronal cholinergic system in lymphocytes. Jpn J Pharmacol 2001, 85, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinner, I.; Kawashima, K.; Schauenstein, K. Rat lymphocytes produce and secrete acetylcholine in dependence of differentiation and activation. J Neuroimmunol 1998, 81, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnawski, L.; Shavva, V.S.; Kort, E.J.; Zhuge, Z.; Nilsson, I.; Gallina, A.L.; Martinez-Enguita, D.; Heller Sahlgren, B.; Weiland, M.; Caravaca, A.S.; et al. Cholinergic regulation of vascular endothelial function by human ChAT(+) T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2023, 120, e2212476120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, T.; Takada-Takatori, Y.; Kawashima, K. Regulatory mechanisms of acetylcholine synthesis and release by T cells. Life Sci 2012, 91, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Yu, M.; Ochani, M.; Amella, C.A.; Tanovic, M.; Susarla, S.; Li, J.H.; Wang, H.; Yang, H.; Ulloa, L.; et al. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha7 subunit is an essential regulator of inflammation. Nature 2003, 421, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, Y.X.; Fujigaya, H.; Moriwaki, Y.; Misawa, H.; Kasahara, T.; Grando, S.A.; Kawashima, K. Enhanced serum antigen-specific IgG1 and proinflammatory cytokine production in nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha7 subunit gene knockout mice. J Neuroimmunol 2007, 189, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosas-Ballina, M.; Olofsson, P.S.; Ochani, M.; Valdes-Ferrer, S.I.; Levine, Y.A.; Reardon, C.; Tusche, M.W.; Pavlov, V.A.; Andersson, U.; Chavan, S.; et al. Acetylcholine-synthesizing T cells relay neural signals in a vagus nerve circuit. Science 2011, 334, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoover, D.B.; Poston, M.D.; Brown, S.; Lawson, S.E.; Bond, C.E.; Downs, A.M.; Williams, D.L.; Ozment, T.R. Cholinergic leukocytes in sepsis and at the neuroimmune junction in the spleen. Int Immunopharmacol 2020, 81, 106359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Mashimo, M.; Moriwaki, Y.; Misawa, H.; Ono, S.; Horiguchi, K.; Kawashima, K. Expression and Function of the Cholinergic System in Immune Cells. Front Immunol 2017, 8, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Mashimo, M.; Moriwaki, Y.; Misawa, H.; Ono, S.; Horiguchi, K.; Kawashima, K. Physiological functions of the cholinergic system in immune cells. J Pharmacol Sci 2017, 134, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, K.; Fujii, T.; Moriwaki, Y.; Misawa, H.; Horiguchi, K. Non-neuronal cholinergic system in regulation of immune function with a focus on alpha7 nAChRs. Int Immunopharmacol 2015, 29, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galitovskiy, V.; Qian, J.; Chernyavsky, A.I.; Marchenko, S.; Gindi, V.; Edwards, R.A.; Grando, S.A. Cytokine-induced alterations of alpha7 nicotinic receptor in colonic CD4 T cells mediate dichotomous response to nicotine in murine models of Th1/Th17- versus Th2-mediated colitis. J Immunol 2011, 187, 2677–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defiebre, C.M.; Meyer, E.M.; Henry, J.C.; Muraskin, S.I.; Kem, W.R.; Papke, R.L. Characterization of a Series of Anabaseine-Derived Compounds Reveals That the 3-(4)-Dimethylaminocinnamylidine Derivative Is a Selective Agonist at Neuronal Nicotinic Alpha-7/I-125-Alpha-Bungarotoxin Receptor Subtypes. Molecular Pharmacology 1995, 47, 164–171. [Google Scholar]
- Mashimo, M.; Komori, M.; Matsui, Y.Y.; Murase, M.X.; Fujii, T.; Takeshima, S.; Okuyama, H.; Ono, S.; Moriwaki, Y.; Misawa, H.; et al. Distinct roles of alpha7 nAChRs in antigen-presenting cells and CD4(+) T cells in the regulation of T cell differentiation. Front Immunol 2019, 10, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashimo, M.; Fujii, T.; Ono, S.; Moriwaki, Y.; Misawa, H.; Kawashima, K. Minireview: Divergent roles of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed on antigen-presenting cells and CD4(+) T cells in the regulation of T cell differentiation. Int Immunopharmacol 2020, 82, 106306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gault, J.; Robinson, M.; Berger, R.; Drebing, C.; Logel, J.; Hopkins, J.; Moore, T.; Jacobs, S.; Meriwether, J.; Choi, M.J.; et al. Genomic organization and partial duplication of the human alpha7 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene (CHRNA7). Genomics 1998, 52, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, B.; Williamson, M.; Collier, D.; Wilkie, H.; Makoff, A. A 3-Mb map of a large Segmental duplication overlapping the alpha7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene (CHRNA7) at human 15q13-q14. Genomics 2002, 79, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lucas-Cerrillo, A.M.; Maldifassi, M.C.; Arnalich, F.; Renart, J.; Atienza, G.; Serantes, R.; Cruces, J.; Sanchez-Pacheco, A.; Andres-Mateos, E.; Montiel, C. Function of partially duplicated human alpha7 nicotinic receptor subunit CHRFAM7A gene: potential implications for the cholinergic anti-inflammatory response. J Biol Chem 2011, 286, 594–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araud, T.; Graw, S.; Berger, R.; Lee, M.; Neveu, E.; Bertrand, D.; Leonard, S. The chimeric gene CHRFAM7A, a partial duplication of the CHRNA7 gene, is a dominant negative regulator of alpha7*nAChR function. Biochem Pharmacol 2011, 82, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasala, M.; Corradi, J.; Bruzzone, A.; Esandi, M.D.; Bouzat, C. A human-specific, truncated 7 nicotinic receptor subunit assembles with full-length 7 and forms functional receptors with different stoichiometries. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2018, 293, 10707–10717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinkus, M.L.; Graw, S.; Freedman, R.; Ross, R.G.; Lester, H.A.; Leonard, S. The human CHRNA7 and CHRFAM7A genes: A review of the genetics, regulation, and function. Neuropharmacology 2015, 96, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xiao, C.; Indersmitten, T.; Freedman, R.; Leonard, S.; Lester, H.A. The Duplicated alpha 7 Subunits Assemble and Form Functional Nicotinic Receptors with the Full-length alpha 7. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2014, 289, 26451–26463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, T.W.; Dang, X.; Yurchyshyna, M.V.; Coimbra, R.; Eliceiri, B.P.; Baird, A. A Human-Specific alpha7-Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Gene in Human Leukocytes: Identification, Regulation and the Consequences of CHRFAM7A Expression. Mol Med 2015, 21, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertrand, D.; Lee, C.H.; Flood, D.; Marger, F.; Donnelly-Roberts, D. Therapeutic Potential of alpha7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Pharmacol Rev 2015, 67, 1025–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertrand, D.; Terry, A.V., Jr. The wonderland of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Biochem Pharmacol 2018, 151, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, H.; Takenouchi, T.; Azuma, R.; Wesnes, K.A.; Kramer, W.G.; Clody, D.E.; Burnett, A.L. Safety, pharmacokinetics, and effects on cognitive function of multiple doses of GTS-21 in healthy, male volunteers. Neuropsychopharmacology 2003, 28, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabbani, N.; Nordman, J.C.; Corgiat, B.A.; Veltri, D.P.; Shehu, A.; Seymour, V.A.; Adams, D.J. Are nicotinic acetylcholine receptors coupled to G proteins? Bioessays 2013, 35, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.R.; Kabbani, N. Alpha 7 nicotinic receptor coupling to heterotrimeric G proteins modulates RhoA activation, cytoskeletal motility, and structural growth. J Neurochem 2016, 138, 532–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.R.; Nordman, J.C.; Bridges, S.P.; Lin, M.K.; Kabbani, N. Identification and characterization of a G protein-binding cluster in alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J Biol Chem 2015, 290, 20060–20070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordman, J.C.; Kabbani, N. An interaction between alpha7 nicotinic receptors and a G-protein pathway complex regulates neurite growth in neural cells. J Cell Sci 2012, 125, 5502–5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jonge, W.J.; Ulloa, L. The alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor as a pharmacological target for inflammation. Br J Pharmacol 2007, 151, 915–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashimo, M.; Takeshima, S.; Okuyama, H.; Matsurida, A.; Murase, M.; Ono, S.; Kawashima, K.; Fujii, T. alpha7 nAChRs expressed on antigen presenting cells are insensitive to the conventional antagonists alpha-bungarotoxin and methyllycaconitine. Int Immunopharmacol 2020, 81, 106276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razani-Boroujerdi, S.; Boyd, R.T.; Davila-Garcia, M.I.; Nandi, J.S.; Mishra, N.C.; Singh, S.P.; Pena-Philippides, J.C.; Langley, R.; Sopori, M.L. T cells express alpha7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunits that require a functional TCR and leukocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase for nicotine-induced Ca2+ response. J Immunol 2007, 179, 2889–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benfante, R.; Antonini, R.A.; De Pizzol, M.; Gotti, C.; Clementi, F.; Locati, M.; Fornasari, D. Expression of the alpha7 nAChR subunit duplicate form (CHRFAM7A) is down-regulated in the monocytic cell line THP-1 on treatment with LPS. J Neuroimmunol 2011, 230, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villiger, Y.; Szanto, I.; Jaconi, S.; Blanchet, C.; Buisson, B.; Krause, K.H.; Bertrand, D.; Romand, J.A. Expression of an alpha7 duplicate nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-related protein in human leukocytes. J Neuroimmunol 2002, 126, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, T.; Tsuchiya, T.; Yamada, S.; Fujimoto, K.; Suzuki, T.; Kasahara, T.; Kawashima, K. Localization and synthesis of acetylcholine in human leukemic T cell lines. J Neurosci Res 1996, 44, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Fujimoto, K.; Kawashima, K. Expression of acetylcholine in lymphocytes and modulation of an independent lymphocytic cholinergic activity by immunological stimulation. Biog Amine 2003, 17, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Inoue, T.; Kawashima, K. Upregulation of mRNA encoding the M5 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor in human T- and B-lymphocytes during immunological responses. Neurochem Res 2003, 28, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashimo, M.; Iwasaki, Y.; Inoue, S.; Saito, S.; Kawashima, K.; Fujii, T. Acetylcholine released from T cells regulates intracellular Ca(2+), IL-2 secretion and T cell proliferation through nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Life Sci 2017, 172, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Galitovskiy, V.; Chernyavsky, A.I.; Marchenko, S.; Grando, S.A. Plasticity of the murine spleen T-cell cholinergic receptors and their role in in vitro differentiation of naive CD4 T cells toward the Th1, Th2 and Th17 lineages. Genes Immun 2011, 12, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, X.; Eliceiri, B.P.; Baird, A.; Costantini, T.W. CHRFAM7A: a human-specific alpha7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene shows differential responsiveness of human intestinal epithelial cells to LPS. FASEB J 2015, 29, 2292–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.R.; Ullah, A.; Bak, E.; Jafri, M.S.; Kabbani, N. Ionotropic and metabotropic mechanisms of allosteric modulation of alpha7 nicotinic receptor intracellular calcium. Mol Pharmacol 2018, 93, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jonge, W.J.; van der Zanden, E.P.; The, F.O.; Bijlsma, M.F.; van Westerloo, D.J.; Bennink, R.J.; Berthoud, H.R.; Uematsu, S.; Akira, S.; van den Wijngaard, R.M.; et al. Stimulation of the vagus nerve attenuates macrophage activation by activating the Jak2-STAT3 signaling pathway. Nat Immunol 2005, 6, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grau, V.; Richter, K.; Hone, A.J.; McIntosh, J.M. Conopeptides [V11L;V16D]ArIB and RgIA4: powerful tools for the identification of novel nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in monocytes. Front Pharmacol 2018, 9, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabbani, N.; Nichols, R.A. Beyond the channel: metabotropic signaling by nicotinic receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2018, 39, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treinin, M.; Papke, R.L.; Nizri, E.; Ben-David, Y.; Mizrachi, T.; Brenner, T. Role of the alpha7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor and RIC-3 in the Cholinergic Anti-inflammatory Pathway. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem 2017, 17, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, H.; Ruan, Y.; Malik, K.U. Localization and characterization of the subtypes(s) of muscarinic receptor involved in prostacyclin synthesis in rabbit heart. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1996, 276, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nizri, E.; Irony-Tur-Sinai, M.; Lory, O.; Orr-Urtreger, A.; Lavi, E.; Brenner, T. Activation of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory system by nicotine attenuates neuroinflammation via suppression of Th1 and Th17 responses. J Immunol 2009, 183, 6681–6688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, B.K.; Loring, R.H. GTS-21 has cell-specific anti-inflammatory effects independent of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. PLoS One 2019, 14, e0214942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papke, R.L.; Lindstrom, J.M. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: Conventional and unconventional ligands and signaling. Neuropharmacology 2020, 168, 108021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Báez-Pagán, C.A.; Delgado-Vélez, M.; Lasalde-Dominicci, J.A. Activation of the Macrophage alpha7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor and Control of Inflammation. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 2015, 10, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradi, J.; Bouzat, C. Understanding the bases of function and modulation of alpha7 nicotinic receptors: implications for drug discovery. Mol Pharmacol 2016, 90, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, T.; Kawahara, A.; Fujii, H.; Nakagawa, Y.; Minami, Y.; Liu, Z.J.; Oishi, I.; Silvennoinen, O.; Witthuhn, B.A.; Ihle, J.N.; et al. Functional activation of Jak1 and Jak3 by selective association with IL-2 receptor subunits. Science 1994, 266, 1045–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eto, D.; Lao, C.; DiToro, D.; Barnett, B.; Escobar, T.C.; Kageyama, R.; Yusuf, I.; Crotty, S. IL-21 and IL-6 are critical for different aspects of B cell immunity and redundantly induce optimal follicular helper CD4 T cell (Tfh) differentiation. PLoS One 2011, 6, e17739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, J.W.; Lu, P.; Majumder, P.; Ahmed, R.; Boss, J.M. STAT3, STAT4, NFATc1, and CTCF regulate PD-1 through multiple novel regulatory regions in murine T cells. J Immunol 2014, 192, 4876–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Shea, J.J.; Murray, P.J. Cytokine signaling modules in inflammatory responses. Immunity 2008, 28, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stritesky, G.L.; Muthukrishnan, R.; Sehra, S.; Goswami, R.; Pham, D.; Travers, J.; Nguyen, E.T.; Levy, D.E.; Kaplan, M.H. The transcription factor STAT3 is required for T helper 2 cell development. Immunity 2011, 34, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.O.; Panopoulos, A.D.; Nurieva, R.; Chang, S.H.; Wang, D.; Watowich, S.S.; Dong, C. STAT3 regulates cytokine-mediated generation of inflammatory helper T cells. J Biol Chem 2007, 282, 9358–9363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossarizza, A.; Chang, H.D.; Radbruch, A.; Acs, A.; Adam, D.; Adam-Klages, S.; Agace, W.W.; Aghaeepour, N.; Akdis, M.; Allez, M.; et al. Guidelines for the use of flow cytometry and cell sorting in immunological studies (second edition). Eur J Immunol 2019, 49, 1457–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




