1. Introduction
The economic system is a structure formed by multi-agents interacting with each other and presenting their collective properties, such as self-organization and self-regulation [
1]. In this sense, we realize that one economic situation is associated with others and, in addition, is linked to social, environmental, scientific, and political variables, exercising a relationship of dependence or independence [
2]. Understanding these relationships and monitoring their dynamics enables diversifying investment, structuring, and planning [
3].
The interdependence between markets or the indices representing them is understood as a relationship, analysis of correlation, integration, or coupling between them [
4,
5,
6,
7,
8]. Where a change in behavior or interference in a system has the ability to disturb the dynamics of another system. In view of this, the contagion effect is understood as the transmission of the effects of a financial/economic disruption (crash or volatility) from one sector, region, or market to another [
8,
9,
10,
11]. The interdependence between markets is a well-regarded feature in times of stability but not so attractive in times of crisis, given the possibility of risk transmission (the contagion effect) and market failure [
3,
5,
6,
7,
9,
11].
Both globally and locally, society has constantly gone through various crises caused by the most diverse natures: energy and oil, 1980; Brazilian energy, 2001; the US housing market, 2008; the world economic recession, 2018; COVID-19, 2020; and the war between Russia and Ukraine, 2022. These instabilities generate numerous social and environmental problems, such as inflation, hunger, unemployment, food insecurity, shortages, deforestation, inadequate land exploitation, and desertification (irrational use of natural resources), problems that we can associate with the pillars of sustainability and their interconnections [
2,
8,
12]. Faced with the impact that the dynamics of interdependence or contagion have on understanding financial and economic markets and delineating investment strategies, investigations that contribute and extend research related to this theme are considered of great relevance.
Knowing what has already been produced by society is the first step towards continuity, development, adaptation, regulation, and application of scientific knowledge, especially when it comes to constantly changing phenomena subject to many interferences, such as economic relations. Faced with the questions raised, numerous methods can be combined to clarify a scientific investigation. Among them, we can mention bibliometrics. Bibliometric analysis represents one of the most consolidating and practical approaches to building the scientific memory of a given object of study.
In general terms, the bibliometric analysis represents an essential reference source for developing new research or even deepening scientific fields [
13,
14]. The Bibliometric techniques can be understood as a quantitative method to measure the interrelationships and impacts of publications within a given area of research using mathematical and statistical tools [
13,
15,
16,
17]. This approach brings, as a differential, the possibility of describing the evolution of scientific production in quali-quantitative terms. This review approach frequently addresses the evolution of scientific production by countries, authors, institutions or groups, and journals [
13,
14,
18,
19,
20,
21]. Although there are reviews in the literature that deal with themes associated with economic processes and their implications in general terms, productions that specifically deal with agricultural commodities in the light of interdependence or the effect of contagion are scarce in the literature. Some bibliometric studies associated with economics can be found, addressing: the most cited journals in economics [
22], field normalization and citation impact time in economics [
23], academic entrepreneurship [
18], agricultural production [
24], the interference of COVID-19 in publications in economics [
25], green economy focusing on economic and environmental factors [
26] and the accounting literature since the financial crisis of 2008–2009 [
27].
In this sense, we provide in this paper not only a brief bibliometric review of the current scientific production in the agricultural commodities market but also examine the literature that uses indexes of agricultural commodities to know what has been produced in the world literature on market interdependence in the context of agricultural commodities and to identify the commodities and methods used in the publications most cited over the decades.
To achieve the objective of this article, some questions were drawn that guided the construction of this research: What is the evolution of the number of publications on interdependence or contagion effect in the agricultural commodities market? Which countries have published the most studies on interdependence in the agricultural commodities market? What are the most cited publications on interdependence or the effect of contagion in the agricultural commodities market? Which authors published the most on interdependence or the effect of contagion in the agricultural commodities market? Which journals have published the most studies on interdependence or the effect of contagion in the agricultural commodities market? Which commodities are addressed in studies of interdependence or contagion in the agricultural market? What methods are applied in the studies to identify the interdependence or contagion effect in the agricultural commodities market?
2. Materials and Methods
This paper uses a bibliometric approach perspective to analyze the literary production of market interdependence. In addition, other topics, such as the contagion effect with agricultural indices associated with economic, social, environmental, and political perspectives at a given historical moment, were analyzed.
In our article, the Bibliometric method was used as an approach to examining the state of science through the production of scientific literature [
28] in order to offer possibilities for quantitative and qualitative analysis of the scientific production of countries, groups, institutions, authors, and journals [
13,
18,
29].
The development of this investigation can be identified from
Table 1, which contains the guiding questions, analysis, and data that led to this investigation.
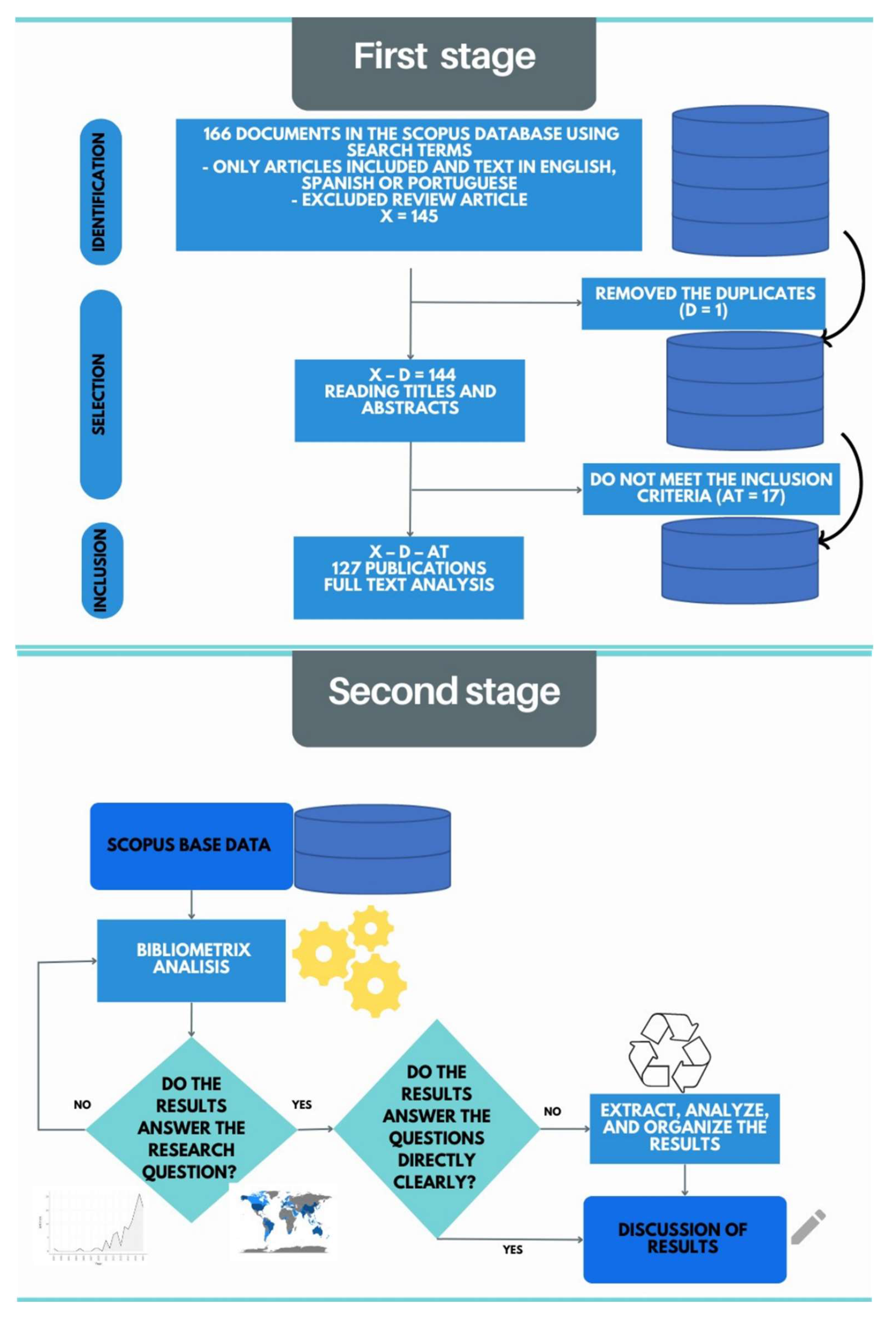
The methodological process to answer the research questions was developed in two stages. The first consists of building the database through identification, selection, and inclusion (
Figure 1). The SCOPUS database was used as a data source because it is comprehensive and multidisciplinary, with a more significant number of abstracts and citations [
30]. The second stage consists of processing and analyzing data for all articles or the subcategories indicated in
Table 1, and its dynamics can be understood in
Figure 1.
2.1. First Stage
The first stage began with a preliminary search in March 2022 in the SCOPUS database in order to identify the most commonly used terms and, thus, choose the keywords to compose the search terms, namely: (“agricultural commodities” OR “agriculture index” OR “livestock index” OR “agricultural index” OR “commodities agriculture” OR “commodities livestock”) AND (“Market Integration” OR “Market Interdependence” OR “Risk transmission” OR “contagion” OR “ Overflow” OR “Spillover” OR “Telecopling”). After defining the search terms, 145 articles were identified using the filters: only articles, texts in English, Spanish, or Portuguese, and review articles were excluded because they did not answer the guiding questions.
The selection of documents was developed as follows: search in the SCOPUS database based on the search terms, export to the Rayyan application (
https://www.rayyan.ai/) in which the screening of duplicates was carried out
, and reading the titles and abstracts. Subsequently, the search in the SCOPUS base was returned, excluding a duplicate,
, and the incompatible texts identified from reading the titles and abstracts
(
these documents were excluded because they did not fit the objective of this study or did not answer the research questions). A total of 127 documents were admitted (see
Table S1). In this stage, there was a concern about the accessibility of the complete texts, given the need to answer the questions “What commodities are addressed in studies of interdependence in the agricultural market?”, “What methods are applied in studies to identify interdependence in the agricultural commodities market?” and the associated sub-criteria are shown in
Table 1. By consensus among the researchers, 20% of the sample agreed to access the most cited articles by decade (see
Table 2,
Table 3,
Table 4 and
Table 5).
Figure 1 details the search and selection stage of the scientific articles included in this study, adapted from the Prisma-Scr Flowchart [
31].
The construction of the database followed the process shown in
Figure 1 with the identification of
documents, the exclusion of
duplicates, and
texts that do not fit this investigation after reading titles and abstracts. The number of documents included in
can be expressed by the equation
, the first stage's flowchart (
Figure 1), with the number of articles excluded and the reason for exclusion.
2.2. Second Stage
The primary analysis of the database was conducted through bibliometric analysis based on the questions raised in
Table 1. This entire step was initially developed with the support of Bibliometrix /R-project and Excel/Microsoft because it has descriptive analytical functions that support this research. Furthermore, concerning a bibliometric analysis, the Bibliometrix/R-project has been used by a growing number of publications [
18,
19,
20,
26] has an easy-to-use free version, allows you to import data directly from SCOPUS, among other statistical and visualization advantages [
20,
21].
With the Bibliometrix/R-project, tables and graphs were generated and analyzed to answer the research questions clearly and objectively. The development of this stage can be understood from
Figure 1.
Figure 1 illustrates the development of the second stage: database processing with Bibliometrix/R-project, analysis of possible answers to research questions, clarity of results, extraction and reorganization of information, and finally, discussion of results. Regarding the 20% of the most cited articles per decade that supported questions 3.6 and 3.7 of the next section, they were carried out independently and blindly by two researchers, and they agreed upon the divergences.
The following section presents the results, analysis, and discussion. The arguments and reflections presented in this article are related to the research questions, objectives, results found, authors' expertise, and literature.
The Materials and Methods should be described with sufficient details to allow others to replicate and build on the published results. Please note that the publication of your manuscript implies that you must make all materials, data, computer code, and protocols associated with the publication available to readers. Please disclose at the submission stage any restrictions on the availability of materials or information. New methods and protocols should be described in detail, while well-established methods can be briefly described and appropriately cited.
Research manuscripts reporting large datasets that are deposited in a publicly available database should specify where the data have been deposited and provide the relevant accession numbers. If the accession numbers have not yet been obtained at the time of submission, please state that they will be provided during review. They must be provided prior to publication.
Intervention studies involving animals or humans and other studies that require ethical approval must list the authority that provided approval and the corresponding ethical approval code.
3. Results
In this section, we seek to present and describe the results found according to the questions that guided this study. General information about data, keywords, authors, collaboration, and types of documents can be seen in the Supplementary material (
Table S2).
3.1. What is the Evolution of the Number of Publications on Interdependence or Contagion Effect in the Agricultural Commodities Market?
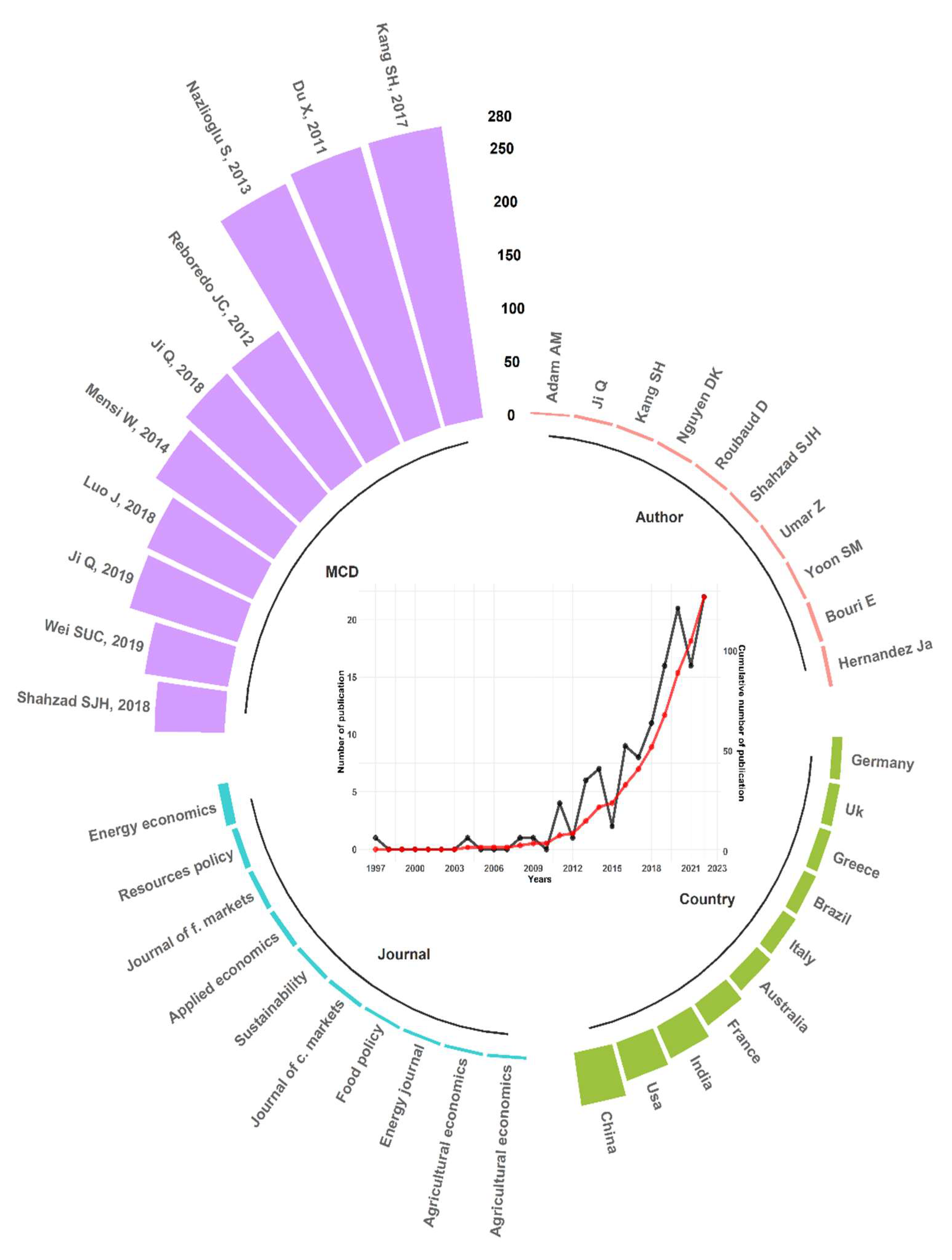
Figure 2 shows the growth of the annual scientific production from 1997 to 2022, corresponding to the 127 articles that comprise this study's database. In black, we have the number of articles published annually, and in red, the accumulated production of articles. The first article identified dates from 1997, with another production in the next ten years. The number of publications has increased sharply since 2015 and in the last decade (with a production of 94 articles).
The results show that scientific production was more significant in the last six years than in all previous years, which is evident in the slope of the cumulative production curve, which visibly shows itself as a function with exponential characteristics and properties. In this period, we can identify a slight reduction in scientific production from 2020 to 2021.
3.2. Which Countries Have Published the Most Studies on Interdependence or Effect of Contagion in the Agricultural Commodities Market?
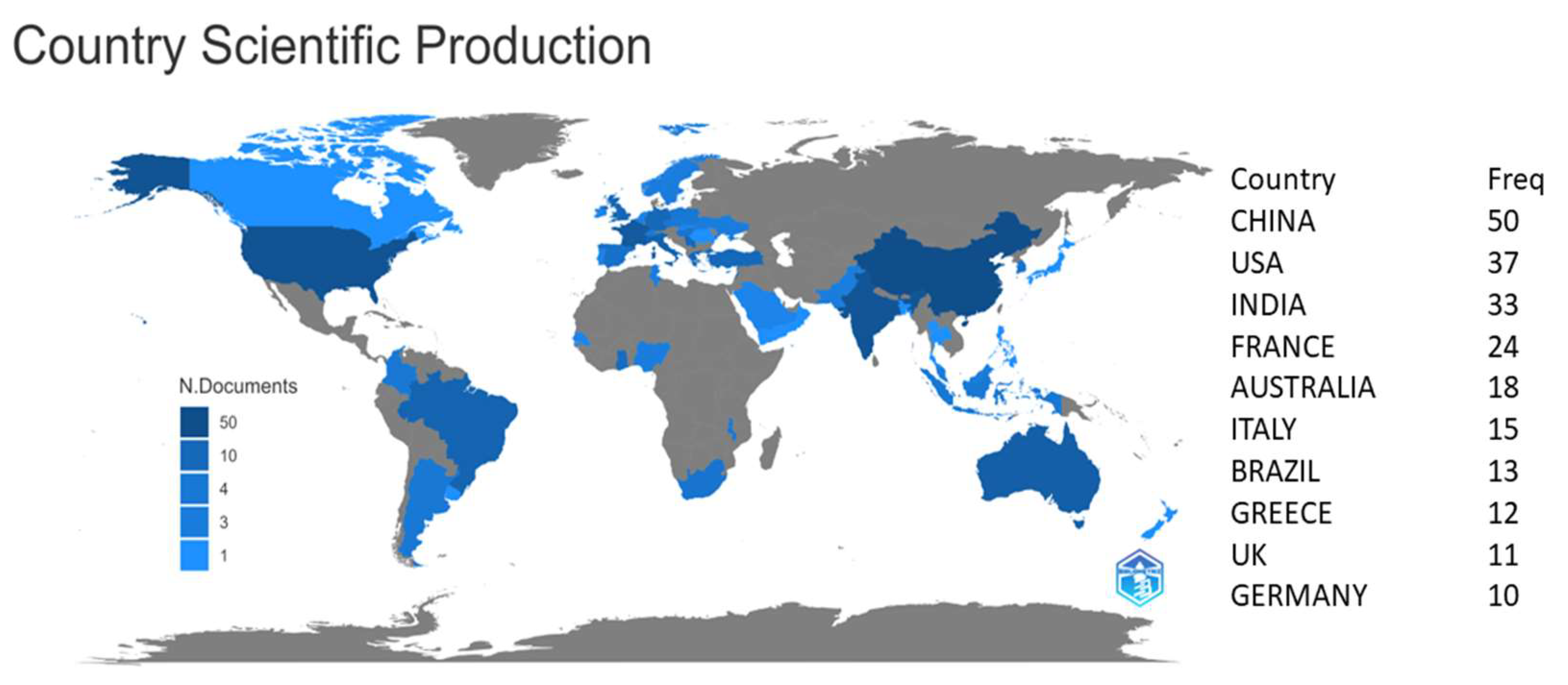
The thematic map (
Figure 3) shows the countries that published the most on the topic discussed in this study. The gradient of the blue color indicates the regions that published articles, so the stronger tones indicate a more outstanding scientific production, while the lighter tones are minor. Regions in shades of gray have negligible scientific production or have not been identified in this database. It is worth noting that
Figure 3 shows the countries linked to the publications and that the production accounting is assigned to all countries involved in production.
The map also shows how little some regions of the world discuss the topic, opening up space for scientific development in this area, especially in Russia because despite its economic influence and representativeness, it was not possible to identify linked scientific production.
3.3. What Are the Most Cited Publications on Interdependence or Contagion Effect in the Agricultural Commodities Market?
The most cited documents throughout the period studied, the top 10, are shown in
Figure 2, which shows us a set of documents between 2011 and 2019, on the left and right, the number of citations. In addition, it is possible to identify in the exact figure the primary author and the journal that published the text. There is significant diversity in the authorship of the top 10, except for the fifth and eighth articles, which belong to the same author. The ten most cited articles are well distributed over the years 2011 to 2019, that is, one article in 2011, one in 2012, one in 2013, one in 2014, one in 2017, three in 2018, and two in 2019. Throughout this period, there was an average of 163.4 citations with a sample standard deviation of ± 79.6.
3.4. Which Authors Have Published the Most on the Subject of Interdependence or Contagion Effect in the Agricultural Commodities Market?
Figure 2, on the upper and left, shows the authors who published the most on interdependence or the effect of contagion in the agricultural commodities market (in descending order of those who contributed the most to the literary area under analysis), with an average productivity of 3.1 publications per author. From the results obtained in
Figure 2, it can be seen that the authors Hernandez J.A. and Bouri E. are the most productive. The productions of Hernandez and Bouri represent the authorship of four articles each, followed by the same number of publications by authors Ji Q., Kang S.H., Nguyen D.K., Roubaud, D., Shahzad S.J.H. Umar Z. and Yoon S-M., who contributed three articles. Author Adam A.M., published two articles, as seen in the last line of
Figure 2.
3.5. Which Journals Have Published the Most Studies on Interdependence or the Effect of Contagion in the Agricultural Commodities Market?
The journals that most contributed to the publication of articles that analyze the phenomenon of interdependence or contagion in the agricultural commodities market are identified in
Figure 2, on the left and below.
In median terms, the ten journals shown in
Figure 2 have an average publication of 4.6 articles over the analyzed period. It is possible to notice that most magazines identified as more productive focus on themes associated with economy, commerce, business, or finance, accumulating a volume of more than 73.9% of the articles published.
3.6. Which Commodities Are Addressed in Studies of Interdependence or Contagion Effect in the Agricultural Market?
A sample with a minimum rate of 20% of the most cited articles per decade was defined among the authors, admitting 28 documents (see
Table 2). In
Table 3, the list of agricultural commodities with the most articles indexed by decade can be seen: 1997–2006 (the first decade), 2007–2016 (the second decade), and 2017–2022 (the third decade).
Table 4 presents with more clarity the frequency with which the commodity was studied in each period.
Table 2.
Describes the number of articles accepted in the sample. The first column presents the subdivision by decade, the second column the number of articles for each period, and the third column the admitted sample.
Table 2.
Describes the number of articles accepted in the sample. The first column presents the subdivision by decade, the second column the number of articles for each period, and the third column the admitted sample.
| |
Number of articles per decade |
Sample admitted |
| First decade |
2 |
2 |
| Second decade |
31 |
7 |
| Third decade |
94 |
19 |
The results obtained for the first decade can be seen in
Table 3. Rice and wheat were mentioned more frequently in the literature (two articles), followed by the study of cotton, corn, and soybeans (one article). In addition, it can be noted that in this decade, the article published in 2004 had a much higher number of citations than the article produced in 1997.
Table 3.
Agricultural commodities identified in the studies. The first column presents the subdivisions by decade, the second is the study’s identification, the third the number of citations, and in the fourth presents the commodities analyzed in that document.
Table 3.
Agricultural commodities identified in the studies. The first column presents the subdivisions by decade, the second is the study’s identification, the third the number of citations, and in the fourth presents the commodities analyzed in that document.
| |
Study7 |
Number of citations |
Commodity |
| First decade |
Tahir, Z., Riaz, K. (1997) |
3 |
Wheat, Cotton, Rice |
| Huang et al. (2004) |
55 |
Corn, Soybean, Rice, Wheat |
| Second decade |
Hernandez, M.A. (2014) |
57 |
Corn, Wheat, Soybean |
| Beckmann, J., Czudaj, R. (2014) |
57 |
Cotton, Wheat, Corn |
| Baquedano, F., Liefert, W. (2014) |
62 |
Wheat, Rice, Corn, Sorghum |
| Mensi, W. et al. (2014) |
124 |
Barley, Corn, Sorghum, Wheat |
| Reboredo, J. (2012) |
140 |
Corn, Soybean, Wheat |
| Nazlioglu, S. et al. (2013) |
255 |
Wheat, Corn, Soybean, Sugar |
| Du, X. et al. (2011) |
259 |
Corn, Wheat |
| Third decade |
Tiwari A.K. et al. (2022) |
24 |
Corn, Wheat, Soybean, Coffee, Cotton, Sugar |
| Umar, Z. et al. (2021) |
27 |
Soybean, Wheat, Cocoa, Coffee, Cotton, Feeder cattle, Lean hogs, Live cattle, Livestock Sugar |
| Arnade, C. et al. (2017) |
28 |
Beef, Corn, Cotton, Pork, Wheat, Soybean, Soybean Meal, Chicken, Rice |
| Hernandez, J. et al. (2019) |
28 |
Wheat, Corn, Rice |
| Umar, Z. et al. (2021) |
29 |
Wheat, Oats, Lumber, Rice, Rubber, Sugar, Cocoa, Coffee, Canola, Orange Juice, Cotton, Corn, Live Cattle, Feeder Cattle, Lean Hog |
| Saghaian, S. et al. (2018) |
30 |
Corn |
| Bonato, M. (2019) |
31 |
Corn, Soybeans, Wheat, Soybean oil, Coffee, Cotton, Sugar, Cocoa |
| Zafeiriou, E. et al. (2018) |
33 |
Soybean, corn |
| Barbaglia, L. et al. (2019) |
37 |
Corn, Wheat, Soybean, Sugar, Cotton, Coffee |
| Hung, N.T. |
40 |
Wheat, Oats, Corn, Soybeans, Sugar |
| Bouri, E. (2021) |
41 |
Cocoa, Coffee, Corn, Cotton, Orange juice, Soybean, Soybean meal, Sugar, Wheat |
| Yip, P. et al. (2020) |
46 |
Corn, Wheat, soybean |
| Dahl, R. et al. (2019) |
55 |
Corn, Wheat, Soybean, Soybean meal, Soybean oil, Canola, Cocoa, Sugar, Cotton, Coffee |
| Shahzad, S. (2018) |
69 |
Wheat, Corn, Soybean, Rice |
| Su, C. (2019) |
83 |
Corn, soybean, Tea, Cocoa |
| Ji, Q. et al. (2019) |
111 |
Live cattle, Cocoa, Coffee, Corn, Cotton, Lean hogs, Orange juice, Soybean, Wheat, Sugar |
| Luo, J. Ji, Q. (2018) |
115 |
Soybean, Corn, Cotton, Wheat, Palm |
| Ji, Q. et al. (2018) |
150 |
Corn, Rice, Soybean, Wheat |
| Kang, S. et al. (2017) |
275 |
Corn, Wheat, Rice |
In the second decade, the study of the present theme gained relevance in analyzing the commodities corn and wheat, which integrated the sample of seven articles. Soybean was analyzed in three articles and sorghum in two studies. Barley, cotton, rice, and sugar, on the other hand, were part of only one article.
We can see in the third decade all these commodities were present in at least one sample of the analyzed articles, standing out with their presence in 19 articles with the exception of barley and sorghum, which were not studied in any article in the third decade. With greater expressiveness, corn was analyzed in 18 articles, wheat in 16, soybean in 15, cotton in 10, sugar in 9, coffee in 8, cocoa in 7, and rice in 6.
Table 4 summarizes the frequency with which commodities were studied, emphasizing corn.
Overall, we analyzed 26 differentiated commodities in 28 articles. We can highlight the five commodities whose analysis in the context of the study of interdependence and the effect of contagion were more relevant, namely, corn (93%), wheat (89%), soybean (68%), cotton (43%) and sugar (36%). These five commodities were analyzed in articles during the three decades, and their analysis showed an increasing trend.
Table 4.
Number of times the commodity was studied in each decade and in the total period. In the first column, the commodity is presented; in the second, third, and fourth columns, the number of articles per decade that studied the commodity; and in the last column, the number of studies in which the commodity was studied throughout the period.
Table 4.
Number of times the commodity was studied in each decade and in the total period. In the first column, the commodity is presented; in the second, third, and fourth columns, the number of articles per decade that studied the commodity; and in the last column, the number of studies in which the commodity was studied throughout the period.
| Commodities |
Number articles |
Number articles |
Number articles |
All period |
| First decade 1997-2006 |
Second decade 2007-2016 |
Third decade 2017-2022 |
Barley
Beef
Canola |
|
1 |
|
1 |
| |
|
1 |
1 |
| |
|
2 |
2 |
| Chicken |
|
|
1 |
1 |
| Cocoa |
|
|
7 |
7 |
| Coffee |
|
|
8 |
8 |
| Corn |
1 |
7 |
18 |
26 |
| Cotton |
1 |
1 |
10 |
12 |
| Feeder cattle |
|
|
2 |
2 |
| Lumber |
|
|
1 |
1 |
| Lean hogs |
|
|
3 |
3 |
| Live cattle |
|
|
3 |
3 |
| Livestock |
|
|
1 |
1 |
| Oats |
|
|
2 |
2 |
| Orange juice |
|
|
3 |
3 |
| Palm |
|
|
1 |
1 |
| Pork |
|
|
1 |
1 |
| Rice |
2 |
1 |
6 |
9 |
| Rubber |
|
|
1 |
1 |
| Sorghum |
|
2 |
|
2 |
| Soybean |
1 |
3 |
15 |
19 |
| Soybean meal |
|
|
3 |
3 |
| Soybean oil |
|
|
2 |
2 |
| Sugar |
|
1 |
9 |
10 |
| Wheat |
2 |
7 |
16 |
25 |
| Tea |
|
|
1 |
1 |
3.7. What Methods Are Applied in the Studies to Identify Interdependence or Contagion Effect in the Agricultural Commodities Market?
Table 5 presents the methods used to identify interdependence and the effect of contagion in the most cited articles for decades. We emphasize that the methods to which this study refers consist of procedures declared in the selected articles and can be understood as the most concrete steps. In restricted terms of general explanation and less abstract, a concept that can revolve around the most abstract notions of methodology, model, or techniques was present [
32].
In the first decade, the article by Tahir, Z., and Riaz, K., applies Ravaillon methodology to study the integration between agricultural commodities selected for the sample. Later, in 2004, the article developed by Huang and others applied the Engle-Granger cointegration methodology to analyze the integration of Chinese markets.
In the second decade under analysis, in 2011, the author Du, X. et al. used a Bayesian methodology (SVMJ model) to study the contagion effect. In 2012, Reboredo, J.C, in his article, studied co-movements using various models of copulas. In the following year, Nazlioglu S. et al. examined the volatility transmission between the prices of selected agricultural commodities, applying the test of causality in the test of variance and impulse response functions to daily data (CIV-IRF). These are the most cited articles of the second decade.
Table 5.
Methods identified in the studies. The first column presents the subdivisions by decade, the second the identification of the study, the third the number of citations, and in the fourth the method presented by the authors of the document.
Table 5.
Methods identified in the studies. The first column presents the subdivisions by decade, the second the identification of the study, the third the number of citations, and in the fourth the method presented by the authors of the document.
| |
Study |
Number of citations |
Methods1
|
| First decade |
Tahir, Z., Riaz, K. (1997) |
3 |
Ravallion model |
| Huang et al. (2004) |
55 |
Cointegration Engle-Granger |
| Second decade |
Hernandez, M.A. (2014) |
57 |
VAR-BEKK-DCC-MGARCH |
| Beckmann, J., Czudaj, R. (2014) |
57 |
VAR-GARCH |
| Baquedano, F., Liefert, W. (2014) |
62 |
SEECM |
| Mensi, W. et al. (2014) |
124 |
VAR-BEKK-DCC-MGARCH |
| Reboredo, J. (2012) |
140 |
Copula models |
| Nazlioglu, S. et al. (2013) |
255 |
CIV - IRF |
| Du, X. et al. (2011) |
259 |
SVMJ |
| Third decade |
Tiwari A.K. et al. (2022) |
24 |
Quantile VAR |
| Umar, Z. et al. (2021) |
27 |
Granger causality tests and index of Diebold and Yilmaz |
| Arnade, C. et al. (2017) |
28 |
VAR-ECM |
| Hernandez, J. et al. (2019) |
28 |
CQ Approach |
| Umar, Z. et al. (2021) |
29 |
TVP-VAR |
| Saghaian, S. et al. (2018) |
30 |
BEKK-MGARCH |
| Bonato, M. (2019) |
31 |
Beta-GARCH |
| Zafeiriou, E. et al. (2018) |
33 |
ARDL |
| Barbaglia, L. et al. (2019) |
37 |
VAR |
| Hung, N.T. |
40 |
Wavelet Coherence with index of Diebold and Yilmaz |
| Bouri, E. (2021) |
41 |
TVP-VAR |
| Yip, P. et al. (2020) |
46 |
FIVAR |
| Dahl, R. et al. (2019) |
55 |
EGARCH |
| Shahzad, S. (2018) |
69 |
GARCH-Copulas |
| Su, C. (2019) |
83 |
Bivariant VAR model |
| Ji, Q. et al. (2019) |
111 |
Entropy Transfer |
| Luo, J. Ji, Q. (2018) |
115 |
HAR and DCC-GARCH |
| Ji, Q. et al. (2018) |
150 |
CoVaR-copulas |
| Kang, S. et al. (2017) |
275 |
DECO-GARCH |
In 2014, Beckmann, J., applied for the GARCH-in-mean VAR model. In the same year, Baquedano, F. and Liefert, W. applied an error correction model (SEECM) to identify cointegration. Finally, Mensi W. et al. and Hernandez M.A. used the VAR-BEKK-DCC-GARCH models to analyze possible market links.
In the third decade, in the year 2017, the authors Arnade, C. et al. used the VAR-ECM method to analyze the economic phenomenon of integration. In turn, Kang S. et al. applied the DECO-GARCH model to analyze the contagion effect.
In 2018, studies were developed by Hernandez, J. et al., who chose to use the CQ approach examining the effect of extreme quantiles of returns between commodities; by Saghaian, S. et al., who, like the authors Mensi, W. et al. (2014), used the BEKK-MGARCH method; by Shahzad, S. and by Ji, Q. et al. who used the same method, namely CoVAR, to study the contagion effect; by Luo, J., and Ji, Q. analyze the connectivity characteristics of variable volatility combined the multivariate heteroscedastic autoregressive model (HAR) with the DCC-GARCH model.
In 2019, Bonato, M., relied on a volatility model, the Beta GARCH model performed by Hansen et al. (2014). Barbaglia, L. et al., and Dahl, R. et al., in that same year, studied the contagion effect using the vector autoregressive model (VAR) and the EGARCH, respectively. J.I., Q. used a time-varying entropy-based approach to identify the direction of return spillovers. Su, C., chose to use a bivariate autoregressive vector to analyze dynamic causal relationships. Yip P. et al. 2020 employed the fractionally integrated VAR (FIVAR) model to capture the dynamic patterns of volatility spillover effects.
More recently, in 2021, the author Umar, Z., publishes two papers applying different techniques, Granger test methods with Diebold and Yilmaz index and TVP-VAR (Time varying parameter with Vector autoregressive). While in the same year he published an article with the objective of analyzing the overflow between agricultural commodities and oil using the Wavelet Coherence method with index of Diebold and Yilmaz. Later, in 2022, Tiwari A.K. applied the Quantile Vector autoregressive to develop his research.
4. Discussion
We discuss below the descriptive and analytical aspects visualized in the results achieved. According to an analysis of the publication’s development (see
Figure 2) 94 articles (or 74% of the total number of publications) were released between 2017 to 2022.
In the first decade, there was an average production of 0.2 articles. In the second decade, there was an average production of 3.1 articles per year, while in the third decade, the average production of articles was 15.7.
Even though there was a decline in scientific output from 2020 to 2021 (likely due to the global crisis brought on by COVID-19), it can be seen from the evolution of the number of publications, particularly in recent years, that there is a trend of growth of publications in relation to the theme by 2022. This is similar to the growth trends seen prior to the pandemic.
The distribution of scientific production is concentrated in a few countries, mainly: China, the USA, India, France, Australia, Italy, Brazil, Greece, the UK, and Germany (see
Figure 3). The first three are also the countries with the largest population in the world, and most have significant economic representation in the world. They are part of the G20, and China, the USA, France, and the UK participate in the permanent council of the UN (United Nations Organization). The correspondence between scientific production and development is evident in the representativeness of the countries that have published the most and their expression in the economic, political, and social world [
2,
5,
24].
In the articles that make up this database, the three most cited documents are in the journal Energy Economics (
https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/energy-economics), and 70% of the most cited articles are concentrated there. In addition, the three most cited articles have an average of 272 citations, with the first one dating from 2017, the second from 2011, and the third from 2013. While the ten most referenced articles have an average of 163 citations per document (see
Figure 2).
There is no clear trend toward older publications receiving more citations, as shown by the distribution of the most frequently cited articles by date.
Still, among the most cited documents, we have the authors who published the most (see
Figure 2), Ji Q., Kang S.H., and Shahzad S.J.H, with 3 articles each author.
Authors J.A. Hernandez and Bouri E., despite having the largest output (
Figure 2), have no documents that rank among the most frequently cited documents examined.
Figure 2 demonstrates that if we take into account the 3 articles published per year throughout 1997 to 2022, the average production per author is low. According to
Figure 2, the most productive authors are associated with the most diverse nations.
Figure 2 shows that Energy Economics has a greater number of publications on the subject of study, indicating a particular scientific relevance in studies that address agricultural commodities and energy. It is believed that the concentration of these studies in journals with an economic bias is somehow associated with the production of biofuels [
26,
33,
34,
35].
A sample of 20% of the articles that received the highest citations throughout the time period was gathered in order to identify the agricultural commodities and the research methodologies employed, as was described in the preceding section (see
Table 2).
Table 3 lists the commodities discussed in the most frequently cited studies for each period under analysis. As a result, we can see that the commodities needed to produce food for humans and animals are commonly used in the articles under study.
Furthermore, the association between energy and agricultural commodities in the most widely read and cited publications suggests the concern for both agricultural production and energy-related issues (biofuels). In particular, corn, wheat, and soybeans because they are globally popular foods and the source of biofuels.
Table 5 also includes a summary of the most frequently mentioned studies and research techniques for each time period.
In general, the non-co-occurrence of the analysis methods over the years shows that no universally accepted method contemplates the absolute universality of the phenomenon and that new methods, divergent or complementary, may arise with the development of research in this area.
The discussion of the results obtained in this study presents a direction for research involving agricultural commodities (food) and energy sources. In this sense, there is a global concern about more sustainable economic policies, efficiency, and rational use of environmental resources, that is, equitably balancing social, economic, and environmental needs, given that the planet is increasingly interconnected and the instability of one region is spread to others faster and faster [
1,
12].
5. Conclusions
This study assumes that the world is a complex system and has become increasingly globalized, reducing borders, and bringing cultures, economies, and policies closer together. In the same way, through the perspective of sustainability, we relate environmental, social, and economic issues. In this paper, we identify the main patterns of literature production associated with market interdependence, the effect of contagion using agricultural commodity indices, and the commodities and methods used in the most cited publications over the decades. Intending to carry out a bibliometric mapping, we outlined some questions (see
Table 1) that were answered in the previous sections.
We conclude from the results and discussions that the scientific production concerning the theme discussed in this article has grown faster and faster in recent years, mainly since the financial crisis of 2008, without concentration among the most cited and productive authors. However, there is a direction for discussion between agricultural commodities and energy. In addition, the most cited documents are published in magazines focused on economics, finance, or business.
Because of their large populations and high energy consumption, the world's two most significant powers, China, and the USA, are the greatest producers of knowledge on the subject. Supplies like corn, wheat, soy, cotton, and sugar, were the most studied products over the analyzed period (corn is highlighted as being present in 93% of the articles).
The many approaches taken to study the interdependence/effect contagion on the financial markets, particularly in the commodities markets, must also be emphasized. In this field, we also identify opportunities for the development of new or improved techniques.
When used to investigate financial phenomena like interdependence and the contagion effect, a variety of methods and approaches can arise and complement one another. As a result, it is impossible to identify a method or strategy that is generally accepted.
Among the main contributions, this article offers an overview of the evolution of the interdependence analysis or effect of contagion in the context of agricultural commodities, indicating directions and gaps. In addition, this study will allow for future thoughts associated with research questions, results, and considerations achieved with this methodological approach. These results still can be explored in dialogue with what has already been produced by humanity, bringing new scientific elements and other information that help understand these and eventually other phenomena.
However, subsequent research, like any temporal analysis, is expected to continue the issues raised here and use the information in this article. We also highlight that analyzing social networks, words, clusters, and other metrics point to new investigations concerning our object of study.
Supplementary Materials
Table S1: Database used in the research identifying the Study, Title and DOI. Arranged in descending order of publication date.; Table S2: General description about database. The description is divided into: Main information about data, Document contents, Authors, Authors collaboration and Document types.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.S., N.H., R.V., R.M.D., G.Z.; Methodology, T.S., R.V.; Data processing, T.S., R.V.; Writing—(original, draft, preparation), T.S., N.H., R.V., M.C., G.Z., R.M.D.; Supervision, R.V., G.Z., R.M.D.; Review and editing, T.S., N.H., R.V., R.M.D., G.Z., M.C.; Funding acquisition, R.M.D., R.V., M.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This paper is financed by Instituto Politécnico de Setúbal.
Data Availability Statement
The database of this research can be identified from the information contained in the methodology and quickly accessed in
Table S1.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for comments and suggestions from anonymous reviewers that helped improve the quality and presentation of the manuscript. We also thank Escola Superior de Ciências Empresariais from Instituto Politécnico de Setúbal for their collaboration. G. F. Zebende thanks CNPq (National Council for Scientific and Technological Development) (Process 310136/2020-2), a Brazilian agency.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mantegna, R.; Stanley, E. Introduction to Econophysics: Correlations and Complexity in Finance, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 1999; Vol. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Despard, M.; Chun, Y.; Grinstein-Weiss, M.; Roll, S. COVID-19 Job and Income Loss Leading to More Hunger and Financial Hardship.
- Dias, R.; Heliodoro, P.; Alexandre, P.; Santos, H.; Farinha, A. Les Ulis: EDP Sciences: Les Ulis 2021, p. 0 1029.
- Bertero, E.; Mayer, C. Structure and Performance: Global Interdependence of Stock Markets around the Crash of October 1987∗. Eur Econ Rev 1990, 34, 1155–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, E.F.; Ferreira, P.; Dionísio, A.; Zebende, G.F. An Econophysics Approach to Study the Effect of BREXIT Referendum on European Union Stock Markets. Physica A 2019, 523, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reboredo, J.C.; Rivera-Castro, M.A.; Zebende, G.F. Oil and US Dollar Exchange Rate Dependence: A Detrended Cross-Correlation Approach. Energy Econ 2014, 42, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.F. da; Pereira, É.J.D.A.L.; Filho, A.M.D.S.; Castro, A.P.N. de; Miranda, J.G.V.; Zebende, G.F. Quantifying Cross-Correlation between Ibovespa and Brazilian Blue-Chips: The DCCA Approach. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 2015, 424, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, T.P.; Horta, N.; Revez, C.; Dias, R.M.T.S.; Zebende, G.F. Effects of Interdependence and Contagion on Crude Oil and Precious Metals According to ΡDCCA: A COVID-19 Case Study. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, U.; Zebende, G.F.; Yu, Y.; Hussain, M.; Ali, A.; Abbas, G. Differential Market Reactions to Pre and Post Brexit Referendum. Physica A 2019, 515, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, K.; Rigobon, R. Measuring Contagion: Conceptual and Empirical Issues. In International Financial Contagion; Springer US: Boston, MA, 2001; pp. 43–66. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, M.F. da; Pereira, É.J.D.A.L.; Filho, A.M.D.S.; Castro, A.P.N. de; Miranda, J.G.V.; Zebende, G.F. Quantifying the Contagion Effect of the 2008 Financial Crisis between the G7 Countries (by GDP Nominal). Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 2016, 453, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra Paitan, C.; Verburg, P. Methods to Assess the Impacts and Indirect Land Use Change Caused by Telecoupled Agricultural Supply Chains: A Review. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, R.N.; Lima, A.T.C.; Lentini, C.A.D.; Miranda, G. v.; Mendonça, L.F.; Silva, M.A.; Cambuí, E.C.B.; Lopes, J.M.; Porsani, M.J. Oil Spill Detection and Mapping: A 50-Year Bibliometric Analysis. Remote Sens (Basel) 2020, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, M.M.M.; Mariano-Neto, E.; de Vasconcelos, R.N.; Dodonov, P.; Medeiros, J.M.M. Mapping the Research History, Collaborations and Trends of Remote Sensing in Fire Ecology. Scientometrics 2021, 126, 1359–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, J.; Wang, H. Real-Time Water Surface Object Detection Based on Improved Faster R-CNN. Sensors 2019, 19, 3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Thenkabail, P.S.; Wang, P. A Bibliometric Profile of the Remote Sensing Open Access Journal Published by MDPI between 2009 and 2018. Remote Sens (Basel) 2019, 11, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Su, S.-F.; Zhou, W. A Comprehensive Bibliometric Analysis of Uncertain Group Decision Making from 1980 to 2019. Inf Sci (N Y) 2021, 547, 328–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, A.M.; Bianchini, M.I.; Santos, L.A.C. Mapeamento Da Ciência Com o Pacote R Bibliometrix: Uma Aplicação No Estudo de Empreendedorismo Acadêmico.; 2018; Vol. 9, pp. 287–294.
- Harada, M.A.; Hirata, N.; Trein, C.A. Política Espacial e de Defesa: Science Mapping Da Produção Científica Internacional Utilizando o Pacote R-Bibliometrix; 2000.
- Lajeunesse, M.J. Facilitating Systematic Reviews, Data Extraction and Meta-Analysis with the Metagear Package for R. Methods Ecol Evol 2016, 7, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnenluecke, M.K.; Marrone, M.; Singh, A.K. Australian Journal of Management. May 3 2020, pp. 175–194.
- Beckmann, M.; Persson, O. The Thirteen Most Cited Journals in Economics. Scientometrics 1998, 42, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornmann, L.; Wohlrabe, K. Normalisation of Citation Impact in Economics. Scientometrics 2019, 120, 841–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irizaga, K.R.F.; Vanz, S.A.S. RELAÇÕES ENTRE A PRODUÇÃO CIENTÍFICA E A PRODUÇÃO AGROPECUÁRIA BRASILEIRA SOB O VIÉS DE UM ESTUDO BIBLIOMÉTRICO. Revista Brasileira de Pós-Graduação 2021, 17, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürgi, C.; Wohlrabe, K. The Influence of Covid-19 on Publications in Economics: Bibliometric Evidence from Five Working Paper Series. Scientometrics 2022, 127, 5175–5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusydiana, A.S.; Sukmana, R.; Laila, N.; Bahri, M.S. The Nexus Between a Green Economy and Islamic Finance: Insights from a Bibliometric Analysis. ICR Journal 2022, 13, 51–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, C.; Farinha, L.; Sebastião, J.R.; Régio, M. How the 2008–2009 Financial Crisis Shaped Fair Value Accounting Literature: A Bibliometric Approach. Adm Sci 2022, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Rueda, F.; López-Bassols, V. Implementing the OECD Frascati Manual: Proposed Reference Items for Business R&D Surveys. OECD Science, Technology and Industry Working Papers 2022.
- Mlambo-Thata, B. Evaluating Electronic Resource Programmes and Provision: Case Studies from Africa and Asia. Learned Publishing 2010, 23, 266–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsevier SCOPUS: Expertly Curated Abstract & Citation Database. Available online: https://www.elsevier.com/solutions/scopus (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Prisma-Scr Transparent Reporting of Systematic Reviews and Meta- Analyses Available online:. Available online: https://www.prisma-statement.org/ (accessed on 4 July 2022).
- Marconi, M. de A.; Lakatos, E.M. Fundamentos de Metodologia Científica, 6th ed.; Atlas: São Paulo, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pimentel, D.; Marklein, A.; Toth, M.A.; Karpoff, M.N.; Paul, G.S.; McCormack, R.; Kyriazis, J.; Krueger, T. Food Versus Biofuels: Environmental and Economic Costs. Hum Ecol 2009, 37, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales-Calderon, O.; Arantes, V. A Review on Commercial-Scale High-Value Products That Can Be Produced alongside Cellulosic Ethanol. Biotechnol Biofuels 2019, 12, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintino, D.D.; Cantarinha, A.; Ferreira, P.J.S. Relationship between US and Brazilian Ethanol Prices: New Evidence Based on Fractal Regressions. Biofuels, bioproducts and biorefining 2021, 15, 1215–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).