1. Introduction
Because of its detrimental effects on the environment, public health, and the global economy, solid waste pollution is one of the most pressing issues in the world today. If various solid wastes are thus effectively utilised and recycled for the creation of building materials, etc. [
1,
2]. The primary binder for modern buildings is Portland cement. With more construction fields, it is anticipated that cement use will rise. According to the IEA, one of the strategies for lowering carbon emissions is to replace cement with other cementitious materials. [
3]. As a result, many studies substituted industrial waste and byproducts for cement in some cases [
4,
5,
6].
According to earlier studies, adding industrial wastes like slag, aluminium, and granite wastes to concrete reduces production costs and carbon emissions while also adding new qualities like improving the material's mechanical capabilities and durability. A lot of contemporary concrete mixtures are altered by the use of admixtures, which enhance the microstructure and lower the concentration of calcium hydroxide produce of cement hydration (CH) produce cement hydration by eating it in a pozzolanic reaction. The fine particle of pozzolanic materials in the concrete mixes creating a lot of nucleating sites for the hydration products to precipitate. As a result, concrete specimens are more homogeneous thanks to this technique. This is a result of the reaction between the pozzolanic material's amorphous silica (SiO2) and calcium hydroxide (CH), which is created during cement hydration process. In addition to, the fine grains' physical effects enable dense filling within the cement specimens and lessen the wall effect in the zone where paste meets fine and coarse aggregate [
7,
8,
9,
10,
11].
Fly ash (FA) and slag (GBFS) combined with recycled aggregate were researched and evaluated for use in the making of concrete in [
12,
13]. Compressive strength, rupture modulus, and shrinkage tests were carried out as part of an experimental programme that substituted recycled coarse aggregate with ratio 0%, 50%, and 100%, slag (GBFS) with ratio 0% and 50%, and fly ash (FA) with ratio 0% and 50% for the manufacturing of concrete. According to the findings, adding more recycled aggregate boosted the concrete's strength. The high quality of the recycled material or the mixing technique may be related to this performance. High-quality recycled concrete might be made by mixing recycled coarse aggregates, fly ash, and slag [
14,
15].
Several studies [
16,
17] examined the strength of normal concrete built with partial replacement of natural coarse particles from demolished waste concrete and manufacturing of sustainable concrete using various types of trash [
18,
19,
20]. The impact of using leftover ceramic aggregate in concrete, both coarse and fine, on the strength of the concrete was investigated. According to the findings, the concrete with waste ceramic aggregate enhanced the flexural strength, compressive strength, STS, and elastic modulus. [
21]. Equal amounts of recycled and conventional aggregates were employed. Marble dust was used in place of cement in increments of 2.5% from 0 to 10%. By replacing 5% of the cement with marble dust, compressive strength is increased by 8.3% while weight is reduced by 2%, according to results that were compared to those of ordinary concrete. Therefore, it is determined that the ideal dosage of marble dust in green concrete is 5% replacement. To increase the strength of concrete, granite waste will be used in place of cement and fine aggregate. 30% is shown to be the most advantageous percentage quantity of replacement. The use of granite powder will prevent disposal issues and related environmental challenges. By using granite waste, less river sand will be used, protecting natural resources [
22,
23].
A mixture of free metal and non-metal materials makes up aluminium dross (e.g., aluminium oxide (Al
2O
3) and salts). Along with metal oxides produced from the molten alloy, aluminium nitrides and carbides may also be present [
24]. The replacement levels of 5%, 10%, and 15% can be utilised to produce high-quality concrete. It has been shown that aluminium trash has pozzolanic qualities and slows down the setting times of concrete, making it potentially useful for hot-weather concreting. Due to its potential for usage in environmentally friendly concrete constructions, the prospective use of recycled aggregate made from construction and demolition debris has drawn increasing interest. Additionally, the scarcity of natural course and fine aggregates in some regions of the world necessitates the development of recycled course and fine aggregates as a substitute source of aggregates [
25].
The topic of recycling construction debris in the concrete industry was brought up by a number of academics [
26,
27,
28] since it can have a positive impact on the environment in terms of resource conservation, reduced demand for landfill space, energy savings and pollution reduction [
2,
29]. According to experiments [
30,
31] performed on concrete samples consist of by completely swapping out the original aggregates for recycled aggregates that contained a mineral admixture of flay ash (FA), slag (BFS) and silica fume (SF), concrete properties can be developed to meet requirements with the right mineral selection and proportioning. Creating nano-materials have superior physical and mechanical properties have drawn attention to nanotechnology in cement research in recent years [
32,
33,
34,
35]. Various types of nanoparticles have been effectively used in concrete to enhance its mechanical properties and great durability. Cement pastes have been effectively reinforced using silica nanoparticles, giving them good mechanical properties. The surrounding aggressive environment often leads to the deterioration of concrete structures. In a marine setting, the chloride ion (Cl-) entered the concrete through the water or sea winds that carried salt ions that eroded the concrete [
35,
36,
37,
38,
39,
40].
The impact of nano-silica fume, granite, slag, and aluminium waste on the physical and mechanical properties of concrete specimens produced by recycling aggregates is thoroughly examined in this research. The typical values utilised in practise were chosen for cement replacement levels in concrete mixes: 15% slag, 10% granite, 1, 5 % aluminium waste, and 1% nano-silica.
2. Materials and Methods
Portland Cement CEM1- 42.5 N, supplied by the Suez-cement business in Suez, Egypt. The Iron and Steel Factory in Helwan-Egypt, also produces granulated blast furnace slag (GBFS). The chemical parameters of raw materials used are shown in
Table 1, along with several other raw materials like Granite dust, Aluminium dross, and Nano-silica fume. The current study's aggregates were as a control coarse aggregate, crushed dolomite, D, as a coarse aggregate from the Attaka area of Suez-Egypt, has been used. After testing, old concrete cubes were crushed to create recycled concrete aggregate (RCA), W. According to (ESS 1109 and ASTM C637), coarse aggregates were divided into different fractions of size ranging from 5 to 20 mm by hand sieving. Local sand that had been cleaned on-site to get rid of harmful substances and chloride (Cl-) contamination served as the fine aggregate.
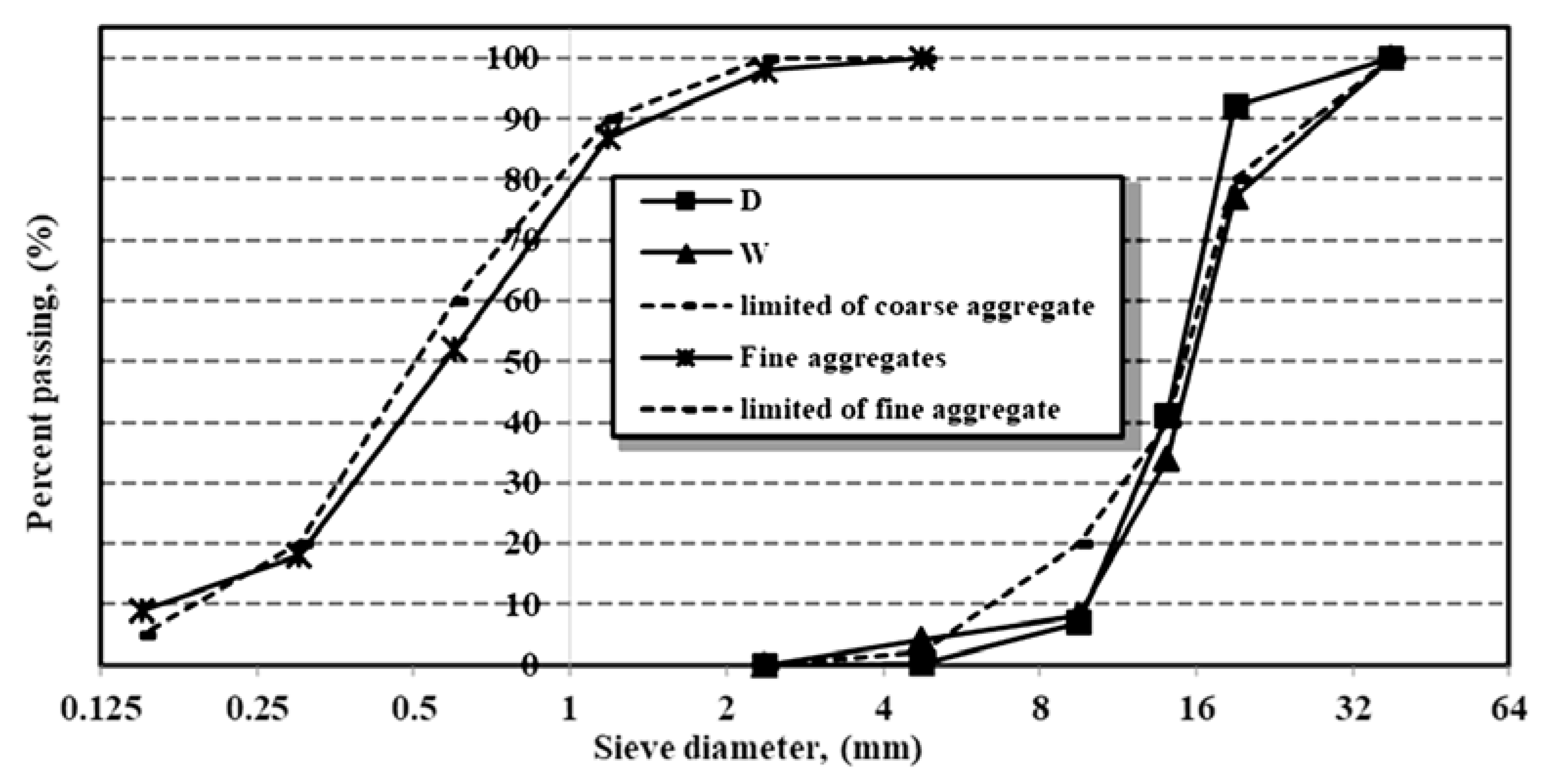
Figure 1 shows the grading curves for aggregates.
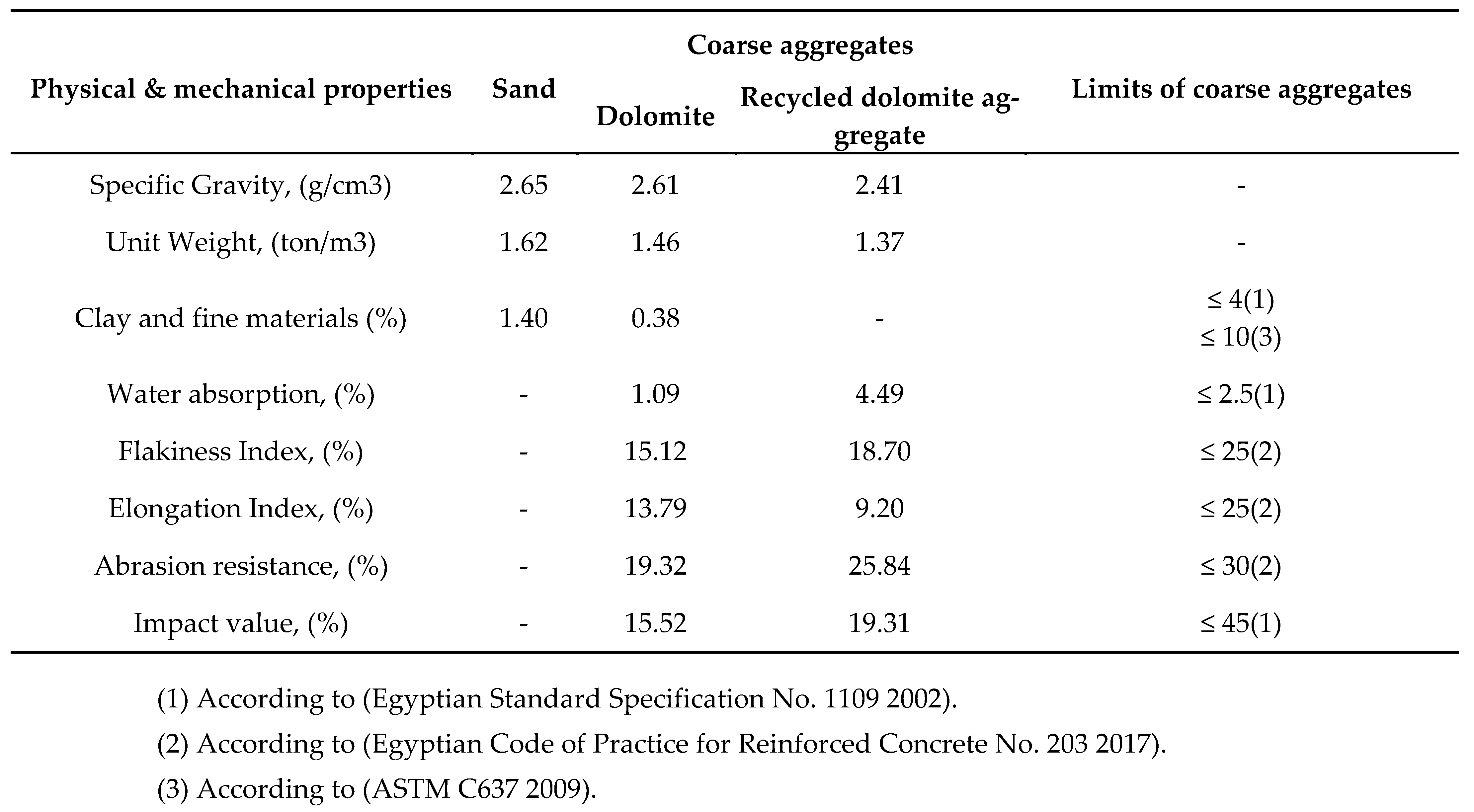
Table 2 lists the chemical compositions of aggregates. According to the limits outlined by the (ESS 1109 and ASTM C637), the physico-mechanical characteristics of coarse aggregates and its fine fraction were assessed. The results are displayed in
Table 3. Only when super plasticizer is used is it feasible to significantly reduce the amount of mixing water while maintaining a high level of workability. A Super plasticizer was employed to keep the droop at 10 ± 2 cm throughout.
Table 4 shows the concrete mix compositions.
Table 1.
Chemical composition of OPC, NS, granite and slag, (wt. %).
Table 1.
Chemical composition of OPC, NS, granite and slag, (wt. %).
| Oxide content, (%) |
OPC |
Nano silica |
Granite |
Slag |
Aluminum waste |
| SiO2
|
21.33 |
95.22 |
69.50 |
36.66 |
16.40 |
| AL2O3
|
3.99 |
0.32 |
14.50 |
10.32 |
75.90 |
| Fe2O3
|
3.15 |
0.85 |
3.01 |
0.52 |
1.97 |
| CaO |
62.04 |
0.26 |
3.0 |
38.88 |
1.64 |
| MgO |
2.52 |
0.55 |
0.64 |
1.70 |
1.01 |
| SO3
|
2.70 |
0.20 |
0.19 |
2.16 |
0.12 |
| L.O.I. |
3.75 |
1.50 |
0.65 |
0.13 |
0.10 |
| Na2O |
0.26 |
0.37 |
3.46 |
0.45 |
- |
| K20 |
0.22 |
0.51 |
4.29 |
1.02 |
- |
| cl- |
0.01 |
0.05 |
0.11 |
0.05 |
0.05 |
| TiO2
|
- |
- |
0.37 |
0.56 |
- |
| TOTAL |
99.95 |
99.98 |
99.99 |
99.97 |
99.61 |
| Ins. Res |
0.66 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| Na2OEq. |
0.41 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| L.S.F |
0.90 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| C3A |
5.22 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| C3S |
51.40 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| C2S |
22.47 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| C4AF |
9.59 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
Table 2.
Chemical analysis of starting materials, (wt. %).
Table 2.
Chemical analysis of starting materials, (wt. %).
| Oxides, (%) |
Dolomite |
Recycled dolomite aggregate |
Sand |
| SiO2 |
1.67 |
19.10 |
93.40 |
| Al2O3 |
0.07 |
2.45 |
2.03 |
| Fe2O3 |
0.01 |
1.50 |
0.98 |
| CaO |
35.54 |
37.61 |
0.71 |
| MgO |
17.51 |
8.87 |
0.25 |
| SO3-- |
0.13 |
1.51 |
0.30 |
| Cl- |
- |
0.13 |
0.08 |
| Na2O |
0.04 |
0.49 |
0.38 |
| K2O |
0.02 |
0.16 |
0.64 |
| TiO2 |
0.01 |
0.19 |
0.17 |
| BaO |
- |
- |
- |
| P2O5 |
0.01 |
- |
0.06 |
| MnO |
- |
- |
0.03 |
| (L.O.I) |
44.99 |
27.83 |
0.74 |
| Total |
99.97 |
99.97 |
99.92 |
Table 3.
Physical and mechanical properties of coarse aggregate and their fine portions.
Table 3.
Physical and mechanical properties of coarse aggregate and their fine portions.
Figure 1.
Sieve analysis of coarse and fine aggregates.
Figure 1.
Sieve analysis of coarse and fine aggregates.
Table 4.
Mix proportions for concrete per (1m3).
Table 4.
Mix proportions for concrete per (1m3).
| Composition |
Concrete ingredients, (kg/m3 ) |
| OPC |
Slag |
Granite |
Aluminum
waste |
Nano silica |
W |
Fine aggregates |
Coarse aggregates |
SP |
| Sand |
D |
W |
| D100 |
450 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
173 |
772 |
1544 |
- |
8.1 |
| D70W30 |
450 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
173 |
772 |
1081 |
463 |
9.7 |
| D70W30-IN |
450 |
- |
- |
- |
4.5 |
173 |
772 |
1081 |
463 |
9.5 |
| D70W30-1.5A-1N |
450 |
- |
- |
6.75 |
4.5 |
173 |
772 |
1081 |
463 |
9.6 |
| D70W30-10G-1N |
450 |
- |
45 |
- |
4.5 |
173 |
772 |
1081 |
463 |
9.4 |
| 70W30-15S-1N |
450 |
67.5 |
- |
- |
4.5 |
173 |
772 |
1081 |
463 |
9.1 |
A 180 kg pan mixer was used to make concrete. The method of mixing that was employed is as follows: The aggregates were combined for approximately (2 min.). Within the next fifteen seconds, the water was added in half its complete volume. Three minutes were spent combining the ingredients. Over the aggregate in the pan, the binder material (OPC+ admixtures) and super plasticizer were distributed equally, and mixing proceeded for 30 seconds. The mixer came to a standstill. The remaining water was added within the next 30 seconds after restarting the mixing process. After all the ingredients had been added, the mixing process went on for 3 minutes. To guarantee homogeneity, the concrete was repeatedly tipped over in the pan mixer after mixing was complete.
Fresh mixtures were slump tested for workability in accordance with (ASTM C143), and all samples were then cast into 100*100*100 mm cube molds by roughly layering and compact them on a vibrating table. Immediately after casting, concrete samples were wrapped in plastic and left in the lab for (24 hours) at (23 ±2 oC) and 100% relative humidity. Specimens were submerged in water after demolding until testing time. According to ASTM C511, curing was carried out. The cubes were exposed to strength measures, flexural and tensile splitting strength tests at ages of 28, and 90 days in accordance with EN 196-1:2016. The two ends has of each specimen were examined in compression after the flexural test. According to ASTM C1202, the proportion of water rapid chloride permeability (RCPT) testing was calculated in a one end of the specimen, a cylinder measuring 50 x 100 mm, was submerged in a 30% NaCl solution for the chloride penetration permeability test, and the other end was submerged in 0.3 M NaOH. Throughout the measuring period, a steady voltage was delivered across the specimen's ends (60 V). In 6 hours, the amount of electrical current that flowed (in Coulombs) through the sample was measured.
Samples from the chosen specimens were taken, processed, and tested under TGA/DTG and SEM after the compression test was completed at the age of 28 days. Axios (PW4400 WD-XRF) Sequential Spectrometer was used for the chemical analysis, and a five-ton German Brüf pressing machine with an ASTM-C109-compliant loading rate of 100 kg per minute was used for the compressive strength tests.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Workability
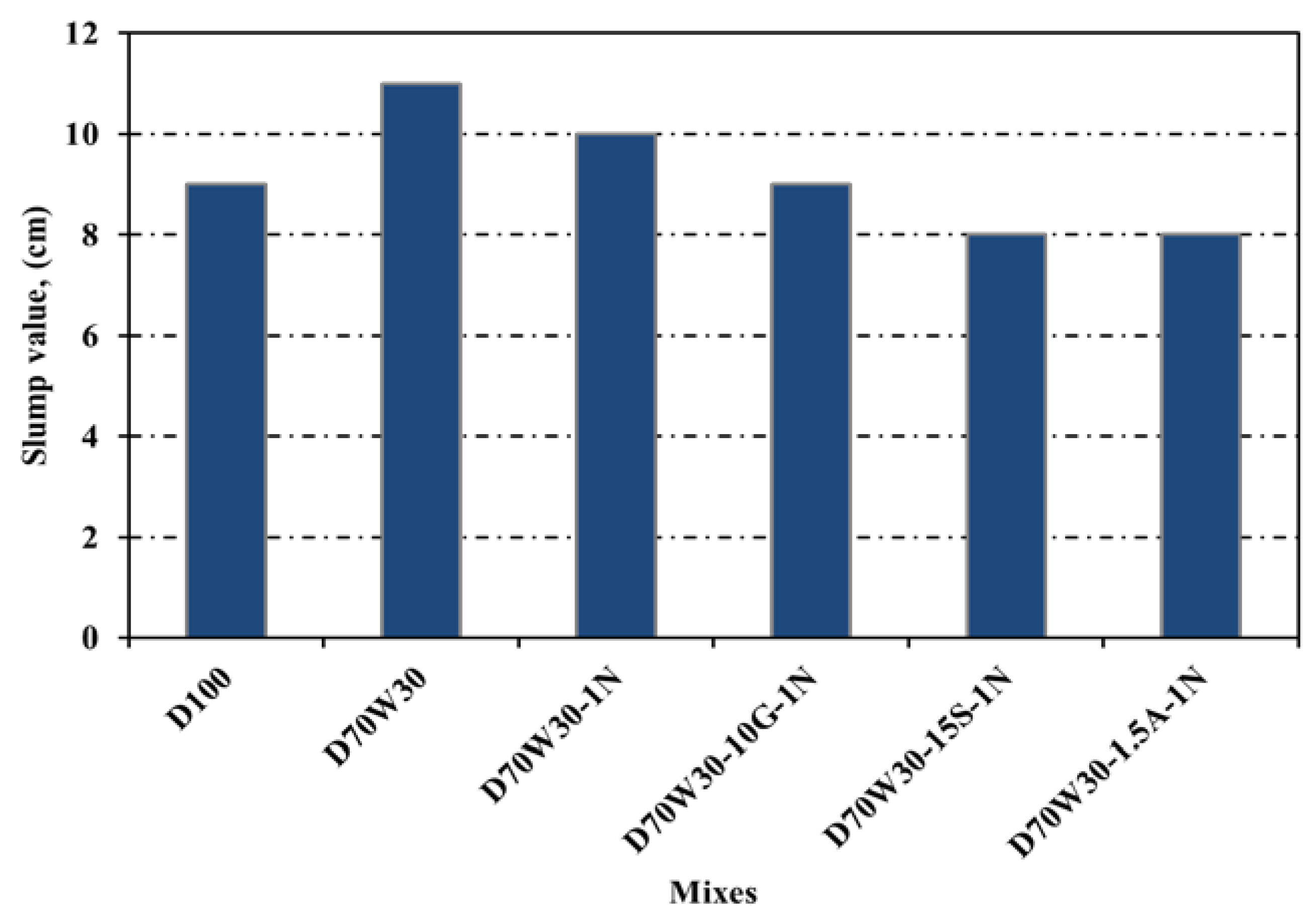
The slump test is the simplest to apply for determining workability. Almost all combinations had a droop between 10 - 12 cm as shown in
Figure 2. As a partial additive to Portland cement, the slump of fresh mixes containing dolomite aggregate D100, recycled concrete aggregate D70W30, and mixes containing recycled concrete aggregate mixed with 1% Nano-silica D70W30-1N, 1% Nano-silica and 10% granite D70W30-1N-10G, 1% Nano-silica fume and 15% blast furnace slag D70W30-1N-15S, and 1% Nano-silica and 1.5 aluminium waste D70W30-1N-1.5 (2). The findings indicate that concrete made with dolomite aggregate performs better than concrete including recycled aggregate in terms of workability. This is because recycled-aggregate is more porous and has a higher water absorption value
Table 3 than dolomite aggregate. In comparison to the control mix consisting of recycled aggregate, the slump value of concrete mixes including recycled aggregate is increase with an addition of 1% NS. The results also show that, in comparison to the control mix produced with recycled aggregate, the slump value of concrete mixes created with recycled aggregate increases with added binary cementing materials of 1% NS and 10% granite, 1% NS and 15% slag, and 1% NS and 1.5% aluminium trash. Due of its smoother forms and spherical structure, OPC requires less water when slag, granite, and Nano silica are added in part. Due to aluminium powder's higher water absorption value, the slump value of concrete mixtures decreases when aluminium waste is added (35, 40).
3.2. Compressive Strength
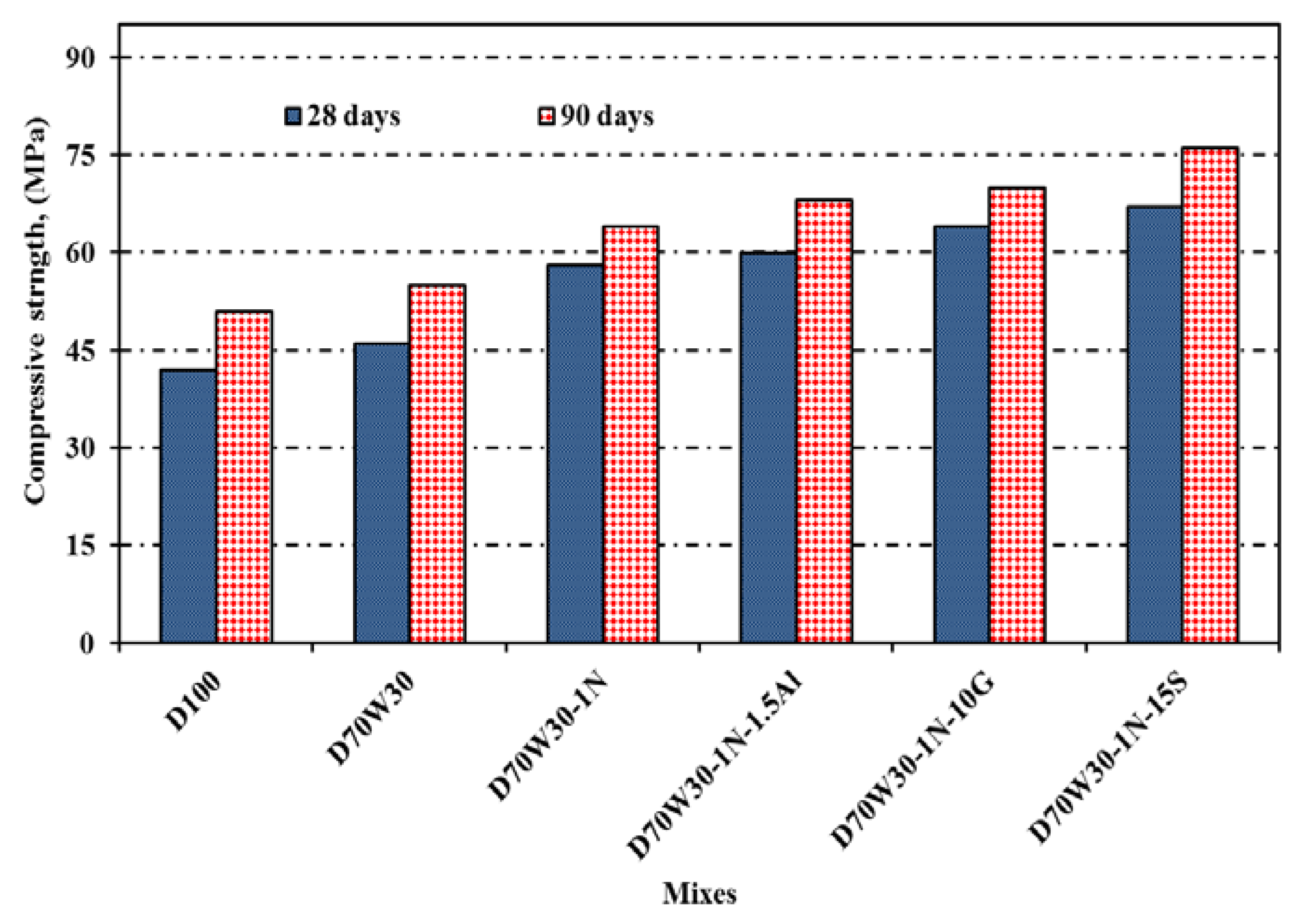
In
Figure 3 the compressive strengths of mixes made with recycled-concrete aggregate mixed with 1% Nano-silica D70W30-1N, 1% Nano-silica and 10% granite D70W30-1N-10G, 1% Nano-silica and 15% slag D70W30-1N-15S, and 1% Nano-silica and 1.5% aluminium waste D70W30-1N-1.5A as a partial additive to OPC are graphically represented. These mixes were all cured in tap water. The findings show that as the curing time is increased, the strength values of all concrete mixes increases. This results in a decrease in total porosity and an increase in the total content of binding centres in the specimens, which in turn results in an increase in compressive strength. as we used the same water content in all the concrete mixes despite the fact that the absorption of dolomite and recycled dolomite aggregates was different, but being not significant in the latter.
In this sense, the effective w/c is not lower in the concretes with recycled aggregates than in the concretes without them; because recycled aggregates was satisfied by water before used, for this reason, the compressive strength was higher in the concretes with recycled aggregates, in addition to the hydration process advances with curing time and increases the amount of cement hydration products that deposit in the open pore system of the hardened concrete. The findings show that concrete produced with recycled aggregate has better compressive strengths than concrete constructed of dolomite aggregate. This is because the physical and mechanical characteristics of recycled-aggregate improved the interlocking between their porous textures and cement paste.
In contrast, the results show that the compressive strength values increase with the addition of Nano-silica D70W30-1N and binary cementing materials D70W30-1N-10G, D70W30-1N-15S, and D70W30-1N-1.5A at age of 28 days, respectively, by 26.1%, 39.2%, 45.6%, and 30.9%. This is primarily caused by the amorphous silica concentration and fineness of Nano-silica, which together with granite, slag, and cementing materials has a filler effect and pozzolanic reaction that causes the refining of pores. As a result of the lime pozzolanic reaction, which precipitates in open pores to produce a more compact closed structure, lime that forms from the hydration of cement is converted into additional binding components.
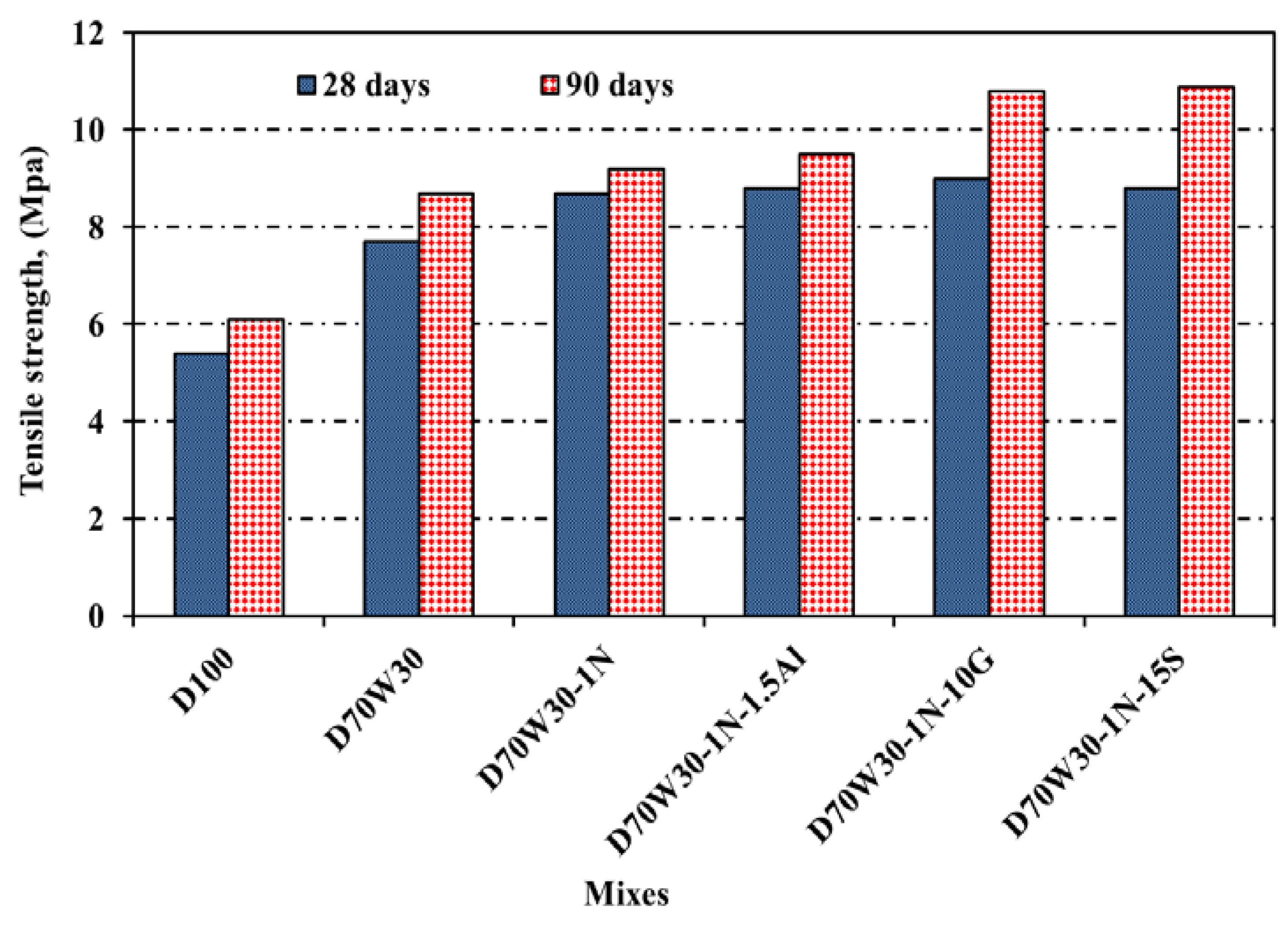
3.3. Tensile Splitting Strength
At days 28, and 90, the tensile strength values of the concrete mixes were assessed. The outcomes are shown in
Figure 4. The tensile splitting strength of the recycled-aggregate concrete and the recycled-aggregate concrete incorporating mineral admixtures of Nano-silica, granite, slag, and aluminium waste were higher than that of the equivalent control concrete mixes at all ages, as can be observed. The findings demonstrate that, at 28 days of age, the splitting tensile strength of the concrete mixes made with recycle aggregate D70W30 and recycle aggregate containing Nano-silica D70W30-1N as well as binary cementing materials of D70W30-1N-10G, D70W30-1N-15S, and D70W30-1N-1.5A increased by 42.6%, 61%, 66.6%, 70.3%, and 62.8%, respectively, compared to the concrete control D100. The maximum splitting tensile strength (more than the control concrete) and the highest strength improvements were found in the concrete mixtures made using recycled aggregate D70W30 and NS, slag, granite, and aluminium waste as mineral admixtures. This might be as a result of the mineral admixtures, which enhanced the microstructure of the interfacial-transition-zone (ITZ) and strengthened the binding between cement and aggregate in the concrete mixes.
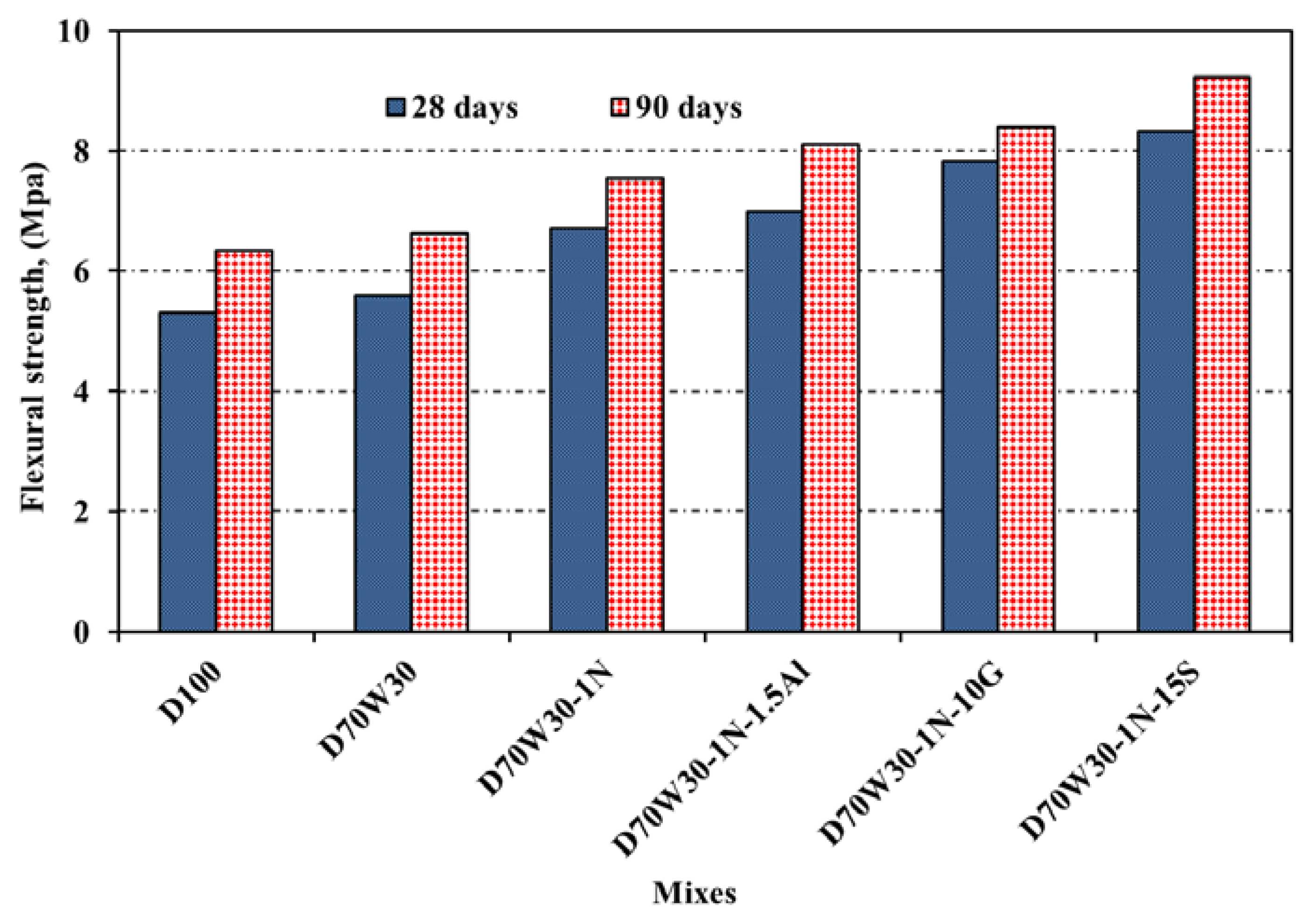
3.4. Flexural Strength
At days 28, and 90, the flexural strength values of the concrete mixes were assessed. The outcomes are shown in
Figure 5. In this case, the flexural strength also typically increases with curing times, just like the compressive strength does for all combinations. The flexural strength of the recycled-aggregate concrete and the recycled-aggregate concrete incorporating mineral admixtures of nano-silica, granite, slag, and aluminium waste were higher than that of the equivalent control concrete mixtures at all test ages, as can be observed. The findings indicate that, when compared to concrete control D100, the flexural strength of mixes made with recycle aggregate D70W30 and aggregate containing nano-silica D70W30-1N as well as binary cementing materials D70W30-1N-10G, D70W30-1N-15S, and D70W30-1N-1.5A increased by 5.3%, 26.3%, 47.2%, 56.7%, and 31.5%, respectively, at age of 28 days.
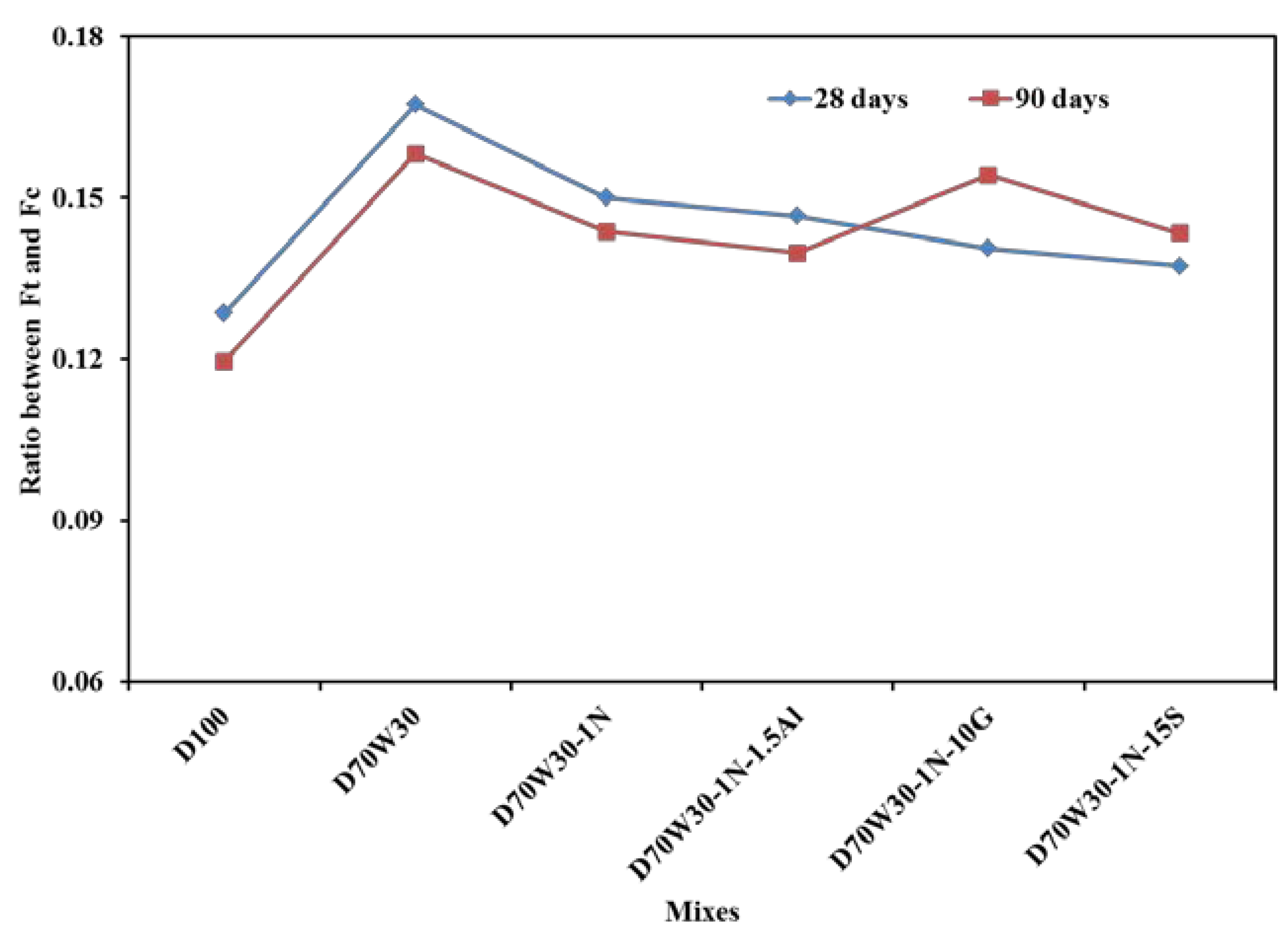
3.5. Strength Ratios
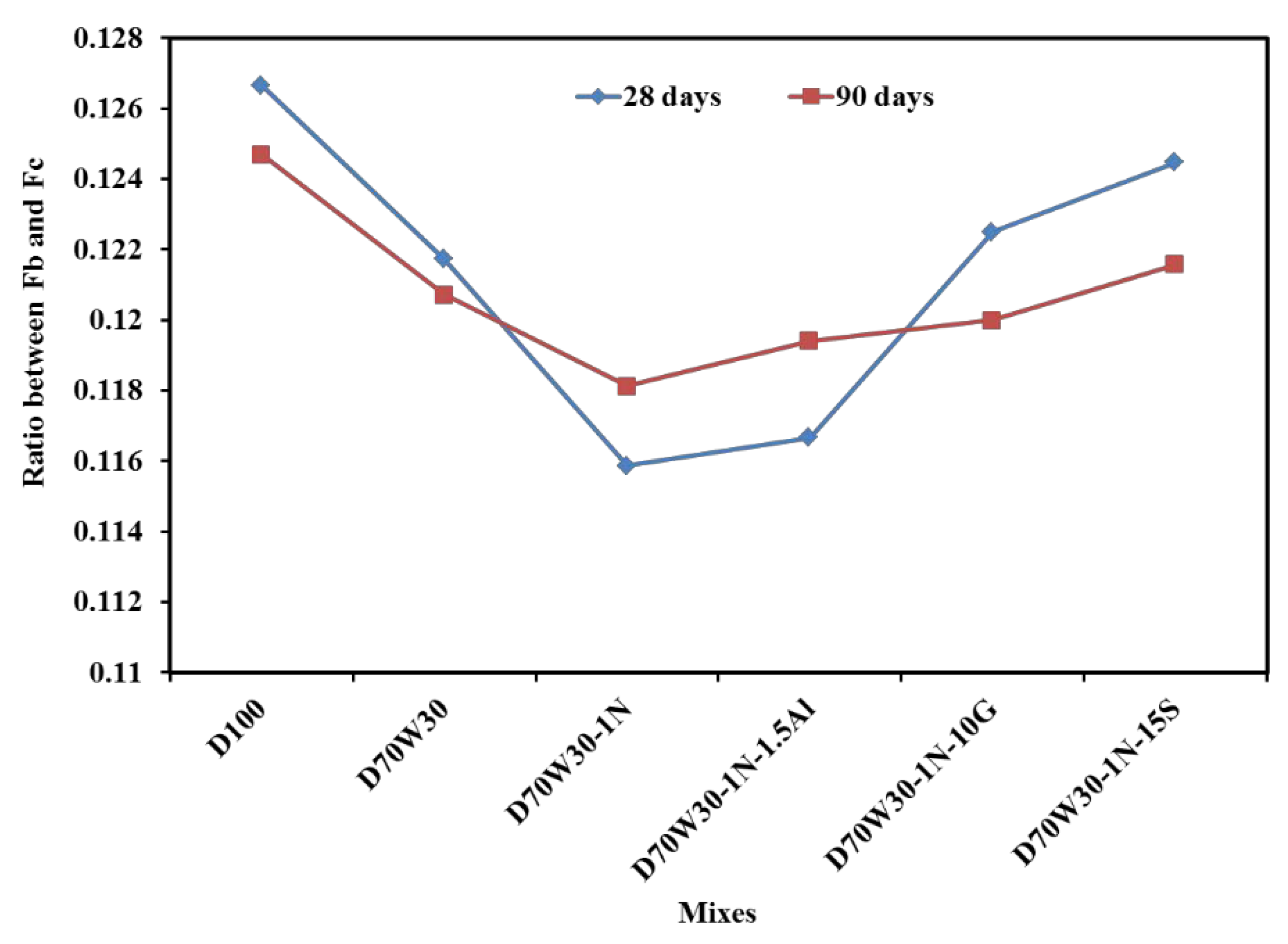
Figure 6 shows the calculated strength ratio between indirect tensile strength and compressive strength at 28 and 90 days for all mixes. The data in figure clearly indicated that the recycled aggretgate mix, D70W30, exahbits a higher strength ratio due to enhancement in indirect tensile strength at 28 and 90 days as compared to control mix, D100. The strength ratio showed slightly decreasing for othe mixes but still higher than that of control mix, D100. This finding was not found in case of flextural strength ratio as shown in
Figure 7. The control values, D100, are higher values. This may be attributed to change in enhancement rate of compressive , indirect tensile and flexural strength as result of used recycled aggregate and minerals admixtures
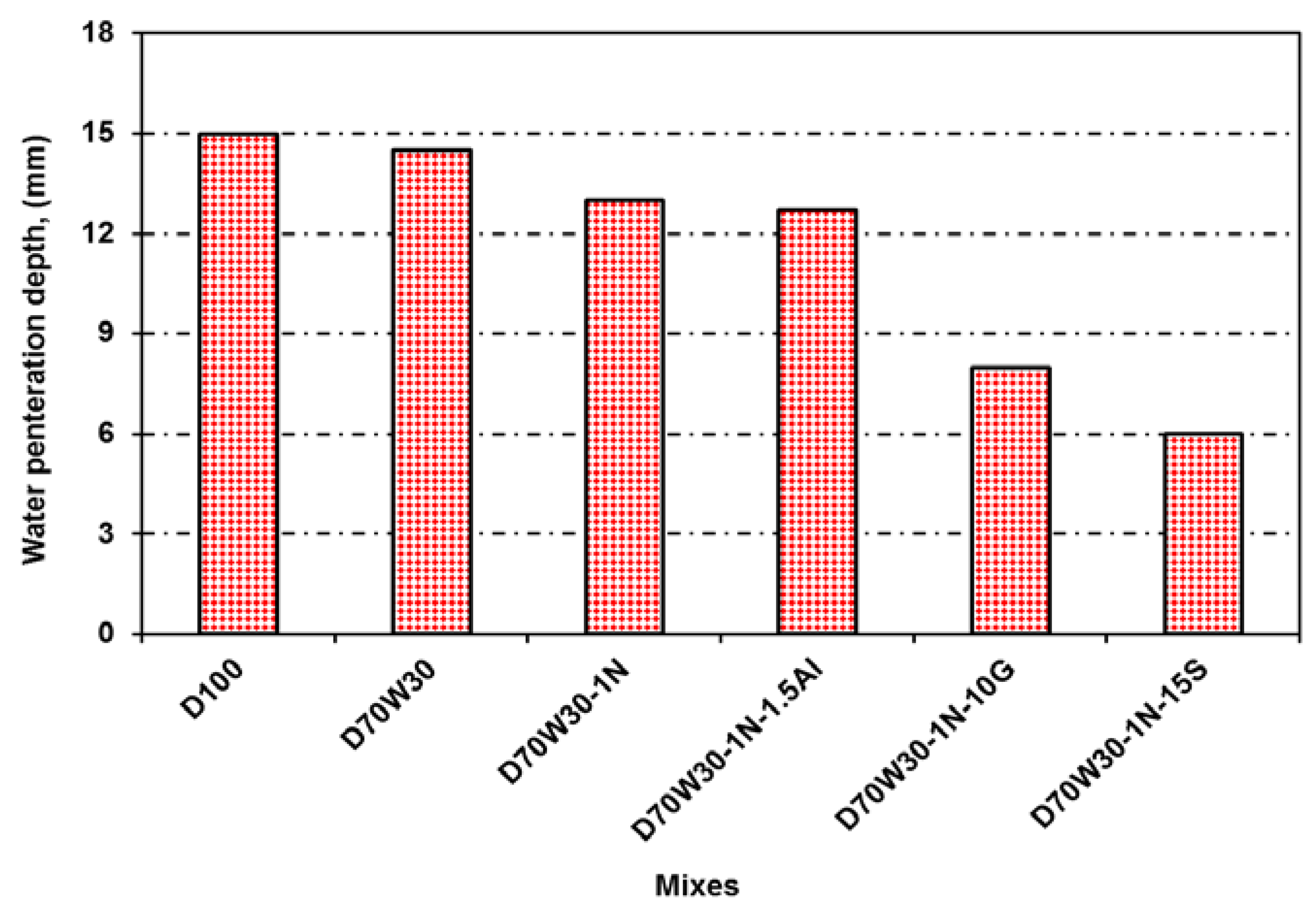
3.6. Water Permeability
By measuring the depth of water penetration under water pressure, the water permeability was indirectly determined. The impact of concrete type on concrete's ability to absorb water is seen in
Figure 8. It has been discovered that employing recycled aggregate concrete and recycled-aggregate concrete with mineral admixtures of Nano-silica, granite, slag, and aluminium waste reduces the water permeability of concrete when compared to control concrete mixtures. The findings indicate that, at a 28-day age, the water permeability of concrete mixes containing the recycle aggregates D70W30 and 70W30-1N, as well as binary cementing materials D70W30-1N-10G, D70W30-1N-15S, and D70W30-1N-1.5A, decreased by 3%, 13%, 46%, 60%, and 15%, respectively, compared to the concrete control D100.
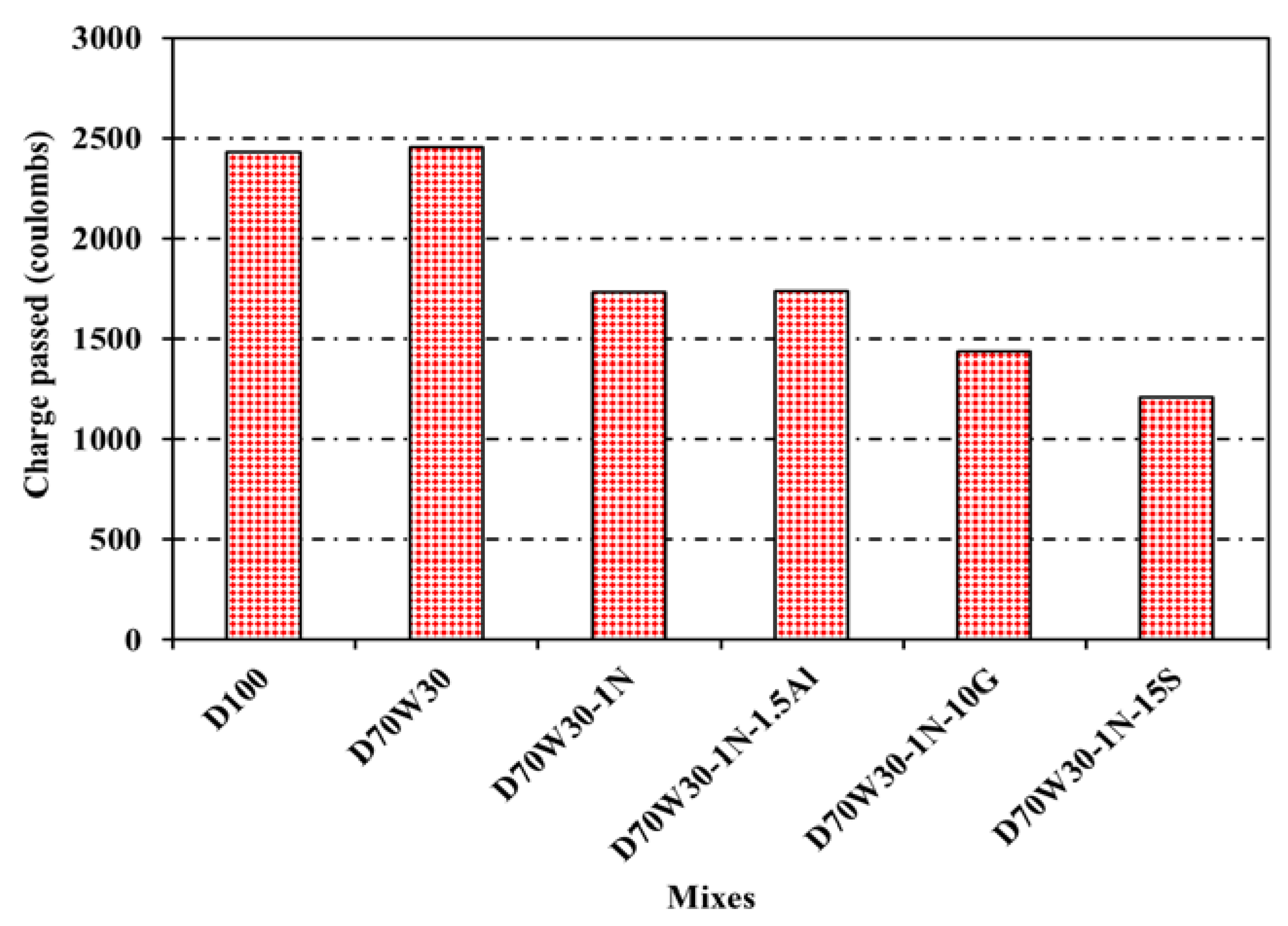
3.7. Rapid Chloride Permeability
As previously noted, the cylinder specimens underwent the RCPT in accordance with ASTM C1202-C97. At the conclusion of 6 hours of applying 60 volts, the total charge passed as represented by Coulombs was observed.
Figure 9 displays the measured values along with the standard deviations. At 28 days old, the concrete control D100 and the recycled aggregate version D70W30 display 2431 and 2454 Coulombs, respectively, which are categorised as having "moderate chloride permeability." With used concrete comprising recycle aggregate having Nano-silica D70W30-1N as well as binary cementing materials of D70W30-1N-1.5A, D70W30-1N-10G, and D70W30-1N-15S, respectively, this value was reduced to 1732, 1739, 1439, and 1210 Coulombs, which may be characterised as "low to moderate." With additional mineral admixtures, the overall trend of the findings reported in
Figure 7 supports a decrease in the total charge transmitted. This might be because the inclusion of mineral admixtures in the concrete enhanced the interfacial-transition-zone's (ITZ) microstructure and strengthened the link between the cement and the aggregate, resulting in a microstructure that was relatively dense and compact.
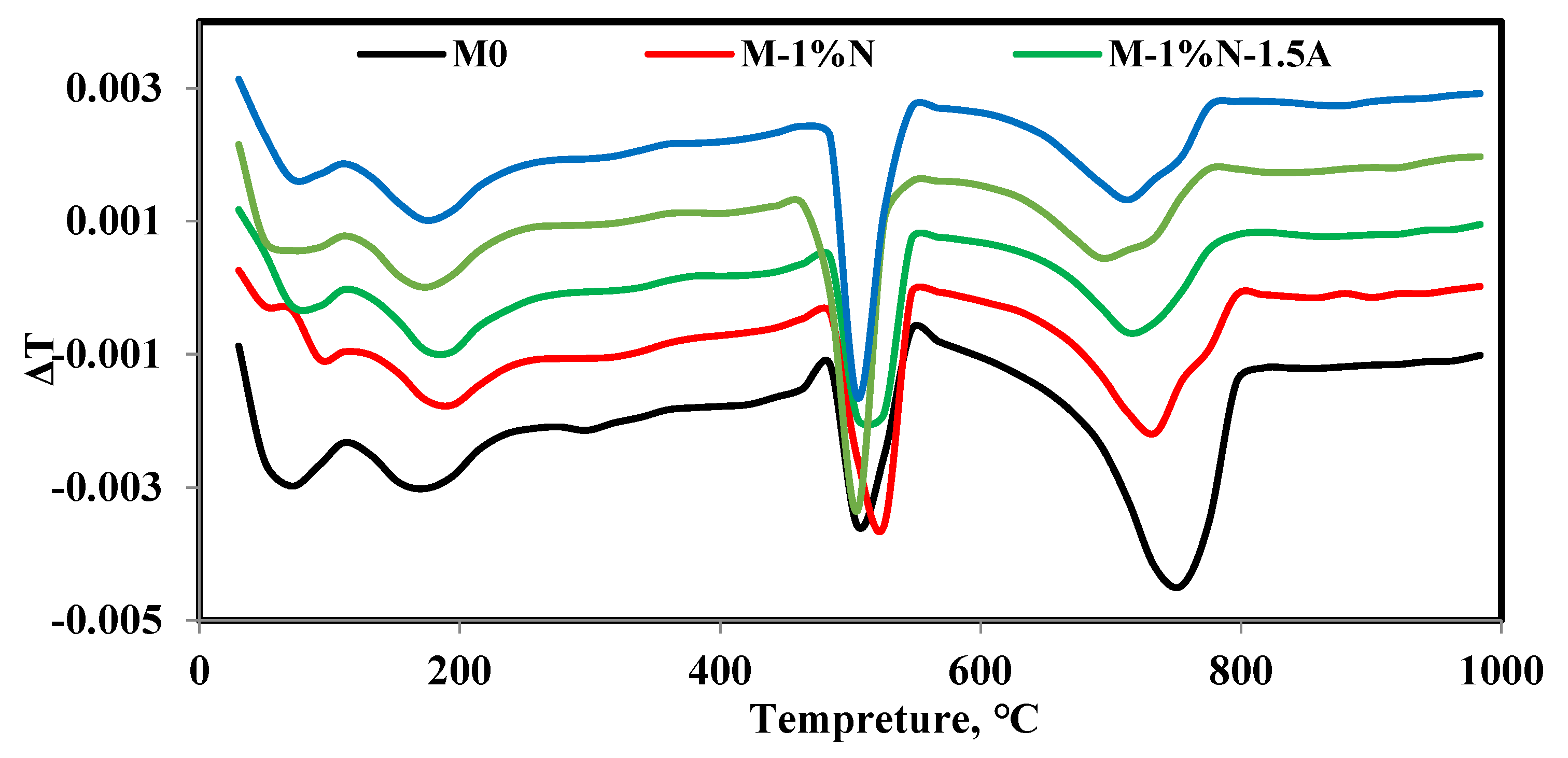
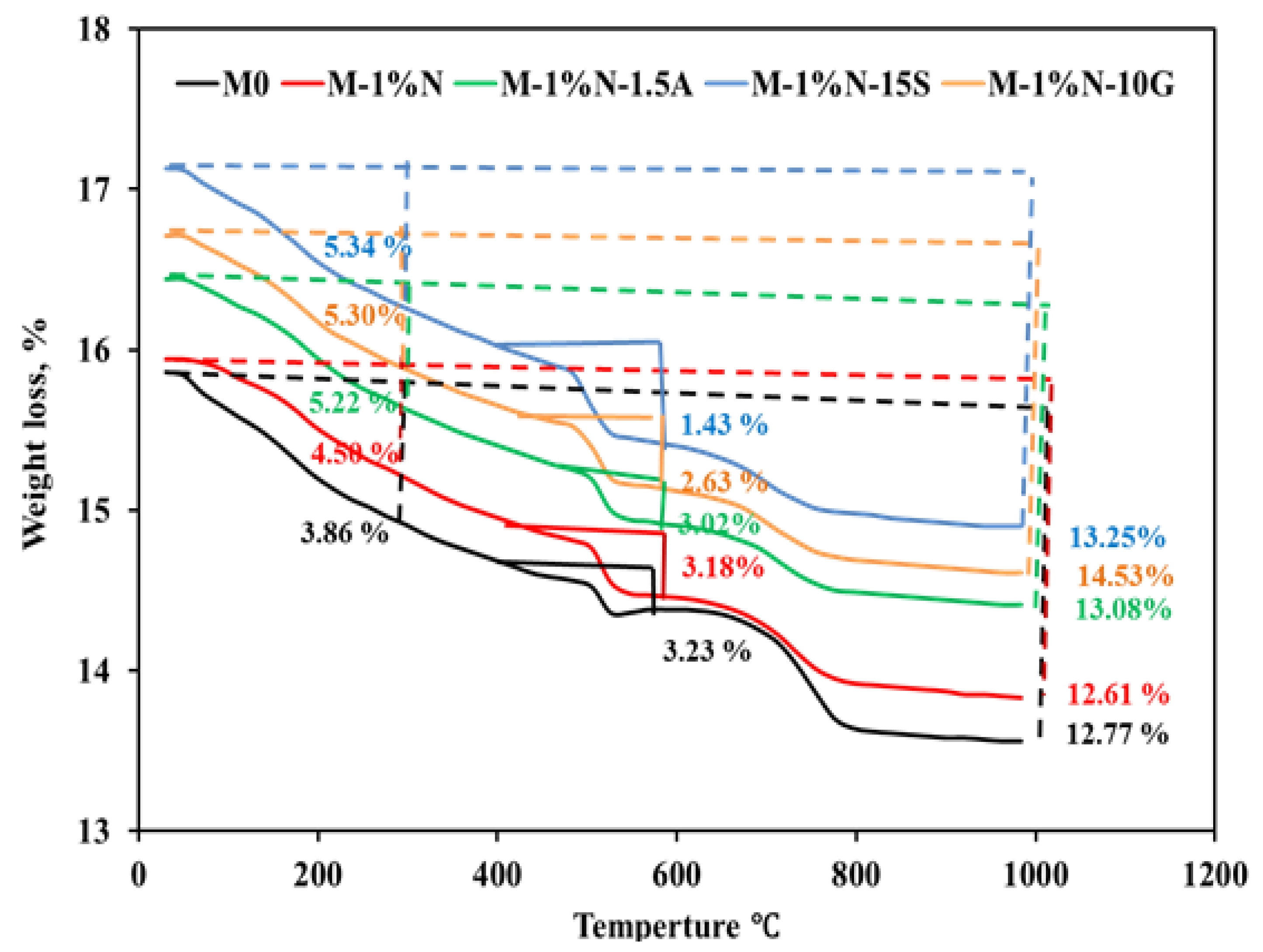
3.8. TGA/DTG analysis
At temperatures ranging from 25 oC to 1000
oC, all of the chosen samples were evaluated. After being hydrated for 28 days, the TGA/DTG curves of the OPC, OPC-1N, OPC-1N-1.5Al, OPC-1N-10G, and OPC-1N-15S samples are shown in
Figure 10 and
Figure 11. The majority of samples exhibit weight loss at temperatures below 300 oC, followed by losses at 500 oC and then at temperatures below 800
oC. According to some reports, the dehydration of free water and C-S-H gel is to blame for the weight loss below 300
oC (the major), which corresponds to the first main endothermic peak. For the samples OPC, OPC-1N, OPC-1N-1.5Al, OPC-1N-10G, and OPC-1N-15S, the major mass loss is roughly 3.86%, 4.50%, 5.22%, 5.30%, and 5.34%, respectively. According to the DTG curve, the addition of 1N, 1N-1.5Al, 1N-10G, and 1N-15S correspondingly causes an increase in peak intensity and weight loss. The breakdown of calcium hydroxide is responsible for the weight loss below 300
oC. The results show that the cement paste composed of OPC-1N-15S has the lowest peak intensity at 500
oC, while the weight loss for samples of OPC, OPC-1N, OPC-1N-1.5Al, OPC-1N-10G, and OPC-1N-15S is, respectively, 3.23%, 3.18%, 3.02%, 2.63%, and 1.43%. This reveals that OPC-1N-15S has a higher compressive strength than the other mixes and is consistent with the compressive strength data shown in
Figure 3 and implies a rise in C-S-H gel and a decrease in Ca (OH)2 generation. Weight loss occurs between 700 and 800
oC, which are related to the breakdown of poorly crystalline calcium carbonate.
3.9. Microstructure analysis
Figure 12 displays the scanning electron microscope (SEM) images for the concrete mixes prepared using D100, D70W30, D70W30-1N, and D70W30-15S-1N that was cured for up to 28 days in tap water. The micrographs of the concrete mixes D100, D70W30, D70W30-1N, and D70W30-15S-1N show a relatively compact microstructure (
Figure 12a, b, c, d). This is brought on by an increase in C-S-H phase and the rise of hydration products. In comparison to the other mixes, the concrete mix D70W30-15S-1N had a comparatively dense and compact microstructure. This is a result of the high pozzolanic activity of nano-silica and slag, which react with CH produced by cement hydration to form additional amounts of C-S-H gel that are then deposited in the pores throughout the concrete matrix, especially at the interfacial-transition-zone between the cement and aggregate particles.
4. Conclusions
From the above investigation we can conclude that: -
The slump values of the dolomite concrete decreases compared with recycle aggregate concrete.
The slump values of the concrete mixes improvement with addition 1 % NS and 15 % of slag to the Portland cement.
The incorporation of nano silica in the blends has a positive effect on the mechanical strength.
The concrete mix containing recycle aggregate have the highest compressive strength, tensile strength and flexural strength compared to concrete containing dolomite aggregate.
Using recycled aggregate and mineral admixtures causes changes in strength ratio of indirect tensile, flexural strength measured a ratio to compressive strength.
As far as the compressive strength is concerned, the addition 1 % NS and 15 % of slag improved the physico-mechanical properties of the recycled aggregate concretes compared to the other mixes after curing in tap water.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.A. and A. E.; methodology, A.F. and A.E.; validation, A.F. and A.E.; formal analysis, S.A.; A.F.; and A. E; writing—original draft preparation, A.F.; and A. E.; writing—review and editing, A.F.; and A. E.; supervision, S.A. and A. E.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gharieb M and Rashed A, M. An initial study of using sugar-beet waste as a cementitious material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek D M and El-Attar M M. Development of High-Performance Green Concrete using Demolition and Industrial Wastes for Sustainable Construction Dina. J. Am. Sci. 2012; 8 12–131. Available online: http://www.americanscience.org.
- Xu, J H, Fleiter T, and Fan Y, Eichhammer, CO 2 emissions reduction potential in China’s cement industry compared to IEA’s Cement Technology Roadmap up to 2050, j.apenergy. 2014. [CrossRef]
- Yadav A L, Sairam V, Muruganandam L, and Srinivasan K. An overview of the influences of mechanical and chemical pro V cessing on sugarcane bagasse ash characterisation as a supplementary cementitious material. J. Clean. Prod. 2020 245 118854. [CrossRef]
- Yousef M M, El-Sayed H A, Kandeel A M, Gharieb M, Aziz A A A. Chloride-binders and their effect on the physico-mechanical properties of sulfate-resisting cement (SRC) hardened pastes upon exposure to sea water attack, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022 29 20817–20828. [CrossRef]
- Khater H M, Ramadan W, and Gharieb M. Impact of alkali activated mortar incorporating different heavy metals on immobilization proficiency using gamma rays’ attenuation. Prog. Nucl. Energy. 2012 137 103729. [CrossRef]
- Guo X, Shi H and Wu K. Effects of steel slag powder on workability and durability of concrete. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Sci. Ed. 2014; 294. 29 733–739. [CrossRef]
- Page R J, and Fanourakis G C (2021) The Influence of Slag Fineness on the Workability of Cementitious Pastes, Concr. Bet. 2021; 120 6–12. Available online: www.concretesociety.co.za (accessed on 18 November 2021).
- Collins F and Sanjayan J G. Early Age Strength and Workability of Slag Pastes Activated by NaOH and Na2CO3. Cem. Concr. Res. 1998 28 (1998) 655–664. [CrossRef]
- Ann K Y, H.Y. Moon H Y, Kim Y B and Ryou J. Durability of recycled aggregate concrete using pozzolanic materials, Waste Manag. 2008; 28 993–999. [CrossRef]
- Correia J R, Brito J De and Pereira A S. Effects on concrete durability of using recycled ceramic aggregates. Mater. Struct. Constr. 2006 39 169–177. [CrossRef]
- Tam V W Y, Le K N, Evangelista A C J, Butera A, Tran C N N and Teara A. Effect of fly ash and slag on concrete: Properties and emission analyses. Front. Eng. Manag. 2019; 6 395–405. [CrossRef]
- Vesmawala G R, Patil Y D and Patil M V. A study on properties and effects of copper slag and marble dust in concrete, Int. J. Struct. Eng. 2018; 9 91. [CrossRef]
- Kurda, R., Silvestre, J. D., & de Brito, J. Life cycle assessment of concrete made with high volume of recycled concrete aggregates and fly ash. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2018; 139, 407-417. [CrossRef]
- Sandanayake M, Bouras, Y, Haigh, R, and Vrcelj, Z. Current sustainable trends of using waste materials in concrete—a decade review. Sustainability, 2020; 12(22), 9622. [CrossRef]
- Muhammad Usama Memon, Bashir Ahmed Memon, Mahboob Oad and Faraz Ahmed Chandio, Effect of Marble Dust on Compressive Strength of Recycled Aggregate Concrete, QUEST Res. J. 2020; 18 11–18. [CrossRef]
- Rashad A and Gharieb M M; An investigation on the effect of sea sand on the properties of fly ash geopolymer mortars, Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2021; 6 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Naji A J, Mousa M A and Malik S H. The Production of the Sustainable Concrete by using Different Types of plastic waste. Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences, 2019; 14,2SI,5557-5560. https.
- Fırat S, Kinuthia J, and Abu-Tair, A. (Eds.). Proceedings of 3rd International Sustainable Buildings Symposium; 2018 (ISBS 2017). Springer. [CrossRef]
- 20. Tavakoli D, Hashempour M, and Heidari A. Use of waste materials in concrete: A review. Pertanika J. Sci. Tech; 2018 nol, 26(2), 499-522. ISSN: 0128-7680© 2018 Universiti Putra Malaysia Press.
- Meena R V, Jain J K, Chouhan H S, and Beniwal A S. Use of waste ceramics to produce sustainable concrete: A review. Cleaner Materials, 2022 100085. [CrossRef]
- Priya S and Kumar S S S (2019). Strength and Characteristics of Modified Concrete by Means of Industrial By-Products, (2019) 4618–4622. [CrossRef]
- Rashad A M,. Khafaga S A and Gharieb M. Valorization of fly ash as an additive for electric arc furnace slag geopolymer cement, Constr. Build. Mater. 2012; 294 123570. [CrossRef]
- Manfredi O, Wuth W and Bohlinger I. Characterizing the physical and chemical properties of aluminum dross, Jom. 1997 49 48–51. [CrossRef]
- Elinwa A U and Mbadike E (2011). The use of Aluminum waste for concrete production, J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 2011; 10 217–220. [CrossRef]
- Seara-Paz S, B. González-Fonteboa B, Martínez-Abella F and González-Taboada I. Time-dependent behavior of structural concrete made with recycled coarse aggregates. Creep and shrinkage, Constr. Build. Mater. 2016 122 95–109. [CrossRef]
- González-Fonteboa B and Martínez -Abella F. Recycled aggregates concrete: Aggregate and mix properties, Mater. Constr. 2005 55 53–66. [CrossRef]
- Rashad A M and Gharieb M. Valorization of sugar beet waste as an additive for fly ash geopolymer cement cured at room temperature, J. Build. Eng. 2021; 44. [CrossRef]
- Kou S C, Poon C S and Agrela F. Comparisons of natural and recycled aggregate concretes prepared with the addition of different mineral admixtures, Cem. Concr. Compos; 2011. [CrossRef]
- Corinaldesi V and Moriconi G. Recycling of rubble from building demolition for low-shrinkage concretes, Waste Manag. 2010; 30 655–659. [CrossRef]
- Corinaldesi V, Letelier V and Moriconi G. Behaviour of beam-column joints made of recycled-aggregate concrete under cyclic loading, Constr. Build. Mater. 2011; 25 1877–1882. [CrossRef]
- Higgins D D. Increased sulphate resistance of ggbs concrete in the presence of carbonate. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2003; 25 913–919. [CrossRef]
- Han B, Zhang L, Jinping O, Han B, Zhang L, and Ou J (2017). Smart and Multifunctional Concrete Towards Sustainable Infrastructures. Springer; 2017; Singapore., 2017. [CrossRef]
- P. Jittabut P and Horpibulsuk S. Physical and microstructure properties of geopolymer nanocomposite reinforced with carbon nanotubes, Mater. Today Proc. 2019; 17 1682–1692. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.E. Seleem, Elshami, A., & Fawzy, A. Behaviour of sustainable concretes modified with mineral admixtures and Nano-silica against aggressive media attacks. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; 2022 (Vol. 1026, No. 1, p. 012052). IOP Publishing.
- Silva R V, De Brito J, Neves R, and Dhir. Prediction of chloride ion penetration of recycled aggregate concrete, Mater. Res. 2015; 18 427–440. [CrossRef]
- Kou S and Poon C S. Compressive strength, pore size distribution and chloride-ion penetration of recycled aggregate concrete incorporating class-F fly ash, J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2006; 21 130–136. [CrossRef]
- Kou S C, Poon C S and Chan D. Influence of Fly Ash as Cement Replacement on the Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete, J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2007 19 709–717. [CrossRef]
- Zhuang C and Chen Y (2019). (21919097 - Nanotechnology Reviews) The effect of nano-SiO2 on concrete properties_ a review.pdf, 562–572. [CrossRef]
- Muthu Kumar E and Ramamurthy K. Effect of fineness and dosage of aluminium powder on the properties of moist-cured aerated concrete, Constr. Build. Mater. J. 2015; 95 486–496. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).