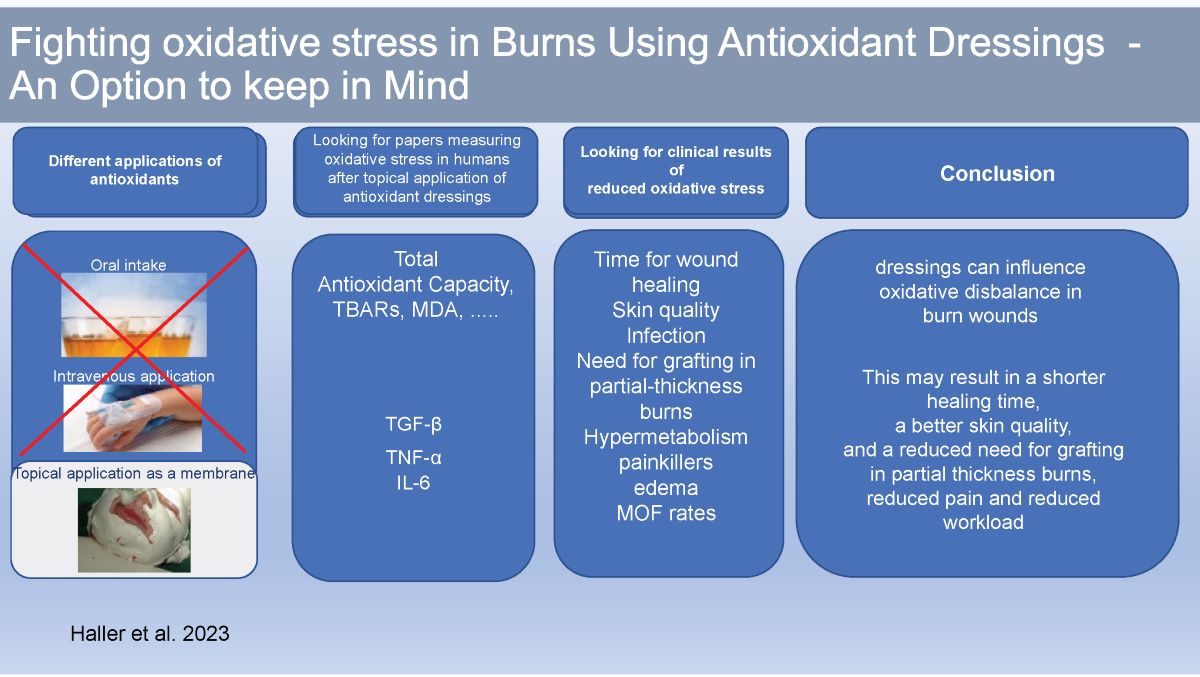
1. Introduction
Chemically, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly reactive free radical molecules with an unpaired outer orbital electron. ROS is a collective term for many oxygen-containing reactive species, including superoxide as the most critical, hydrogen peroxide, nitric oxide, hydrogen radicals, singlet oxygen, peroxyl radicals, alkoxyl radicals, peroxynitrite, and others [
1]. Ongoing research on the effects of free radicals began in 1900 [
2] and has continued over the years, with nine researchers receiving Nobel prizes for related research between 1900 and 2020 [
3].
ROS contributes to normal cell metabolism. They are integral to energy provision and function as signaling molecules. They can cause cell damage and death unless balanced with antioxidants. ROS and reactive nitrogen species can be derived from the mitochondrial respiratory chain in mitochondrial membranes via oxidoreductases, and by the Fenton reaction in peroxisomes, the endoplasmic reticulum, xenobiotic mechanisms in lipophilic substrates, unsaturated fatty acid production, protein folding, and arachidonic acid production in the plasma membrane. In addition, the lysosomes also produce ROS. Mitochondrial nitric oxide synthase (MitNOS) may be involved in reversing the inhibition of cellular respiration to pathological inhibition by ONOO
- [
4].
In corporal burns that exceed approximately 20% of the total burn surface area (TBSA), the local inflammatory reaction becomes systemic, and the body produces an acute phase response [
5] and produces ROS to eliminate dead tissue for subsequent replacement.
Excess ROS production leads to the synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α or interleukins (ILs), such as IL1-b, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10. Moreover, excessive ROS levels can negatively affect cell physiology and wound healing, reducing oxidative stress essential in burn treatment. Oxidative radicals can change capillary permeability and lead to edema generation with disturbance in organ perfusion resulting in ileus [
6], compartment syndromes, wound healing disturbances [
7,
8], burn shock, and imbalance between intra- and extravascular fluid, which leads to organ failures such as acute kidney injury (AKI) or a deterioration of the heart function with an accompanying cytokine storm. Additionally, muscle cell degeneration, hypermetabolism, long-term neurodegeneration, and liver dysfunction are normal body reactions following oxidative imbalance. Mitochondria, the ATP providers, inflammasomes, and peroxisomes are essential sources of ROS in this situation.
Diverse methods have been used to reduce the harmful effects of oxidative stress and its complications. Current treatment standards in burns intend to resolve the burn-immanent oxidative imbalance and the burn shock caused by direct tissue injury, hypovolemia, and multiple mediators due to an imbalance in oxygen needs and availability by fluid therapy, pain management, and energy loss reduction. Early necrosectomy, metabolic balancing, vitamin and trace element supplementation, and systemic and topical treatment strategies have been proven successful and are standard care practice in many burn units. Although the systemic use of antioxidants has been explored in a broad range of studies, little research has been conducted on the influence of specific dressings on oxidative stress in burn wounds. Dressings, however, have imminent impact on systemic and local burn wound metabolism and healing.
Dressings reduce temperature, energy, and fluid loss, prevent infection, influence metabolism positively, and reduce healing time; however, there are limited reports on burn wound treatment with antioxidative dressings and their effect on clinical parameters. Additionally, reports on measurable oxidative stress parameters demonstrating the effects of antioxidative dressings and their results in more extensive studies are lacking.
In this review, we examine the impact of occlusive and non-occlusive dressings and the impact of different dressing types on oxidative stress used during burn therapy. We focus on clinical parameters such as skin quality, healing time, reduction in areas requiring grafting with split-skin in partial-thickness burns, and the necessity of dressing changes. Additionally, laboratory parameters such as total oxidant capacity (TOC), total antioxidant capacity (TAC), GLDH, TBARS, and cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-6, and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, were used to test the hypothesis that antioxidative dressings has positive effects on wound healing.
This review promotes knowledge about burn treatment based on reducing local and systemic oxidative stress by topical membrane application, using positive side effects, such as reducing pain and water loss, providing a bacteria-proof barrier, and reducing workload. In addition, a shorter healing time, reduced local and systematic inflammation, and improved skin quality suggest that treatment with antioxidative dressings is a feasible and powerful strategy.
2. Literature Search
We searched PubMed and ScienceDirect and used Google Scholar and Google to identify appropriate studies using the keywords: “dressings,” “products,” “inflammation,” and “oxidative stress in burns.” Specific brands and generic names were also used. Critical terms included inflamm*, oxid*, antioxid*, MDA, catalase, and lipid peroxi*. Twelve clinical studies were selected from 71 retrieved studies, where only two clinical trials were unrelated to sunburn, UV irradiation, or NO2 pain treatment. We also used reference lists of retrieved papers in our analysis.
As demonstrated in
Figure 1, we performed a structured search of articles using PubMed, Google Scholar, ScienceDirect, and Google, focusing on four main topics: 1) dressings and synonyms, 2) a search for products used as medical dressings, 3) inflammation and keywords for oxidative stress, and 4) Medical Subject Headings (MESH) burns.
Next, we performed another series of searches using the brand and generic names of relevant products, where the search terms “agar,” “alginate,” “carrageenan,” “pectin,” “gelatin,” “hydrogel,” “Poly Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid (PLGA),” “Polyurethane (PU),” “Polycaprolactone (PCL),” “Kerecis,” OR “fish skin” were used. The synonyms we searched for are shown in
Figure 1.
Finally, the set was completed using the references cited in the retrieved papers. We retrieved 71 studies directly related to oxidative stress in burns.
3. Effects of Oxidative Stress on Burn Injuries
ROS are integral components of multiple cellular pathways, and excessive ROS damages cells. Additionally, oxidative stress, trace elements, and vitamin deficiency correlate with burn injury severity, prognosis, and length of hospital stay [
9,
10,
11,
12,
13], significantly impacting wound healing, organ function, and patient outcomes. Therefore, a short overview of the effects of oxidative stress in burns is given below.
Shedding the endothelial glycocalyx, which usually protects the vascular endothelium, ROS, and proinflammatory cytokines, can cause capillary leakage and lead to edema development by activating heparinase and matrix metalloprotease [
9,
10]. The shedding of the endothelial glycocalyx decreases endothelial NO synthase activity, producing NO through a process regulated by mechanotransduction [
11]. Reduced endothelial NO synthase activity releases ROS, creating a positive feedback loop and an inflammatory cascade. As a result, levels of the intravascular fluid necessary to maintain organ perfusion are reduced. Capillary leakage [
12] may represent the foundation of organ failure, as it reduces blood circulation and often leads to compensatory hyperresuscitation, resulting in "fluid creep" [
13].
Additionally, accumulated interstitial fluid can cause pulmonary edema, bowel wall edema [
6], paralytic ileus, malabsorption, anastomotic leakage, and disturbed wound healing [
7,
8], which may lead to possible ocular, extremity, and abdominal compartment syndromes and AKI. Furthermore, upper respiratory tract edema can cause airway obstruction and bronchospasms, and chemical substances can damage the lower respiratory tract, which is aggravated by inhaling irritants such as smoke, resulting in ROS release and inflammation [
14]. The effect of ROS on inflammation was verified in IL-6 knockout and anti-IL-6-treated mice, in which reduced pulmonary inflammation was observed [
15]. In contrast, myeloperoxidase levels in the lung increased after burn injury, and oxandrolone could not attenuate it [
16].
The heart function immediately after the burn deteriorates in an “ebb phase.” The patient becomes tachycardic and hyperinflammatory after 48 h [
17]. Therefore, it has been hypothesized that burn-induced cardiac depression is related to the inability of β-adrenergic receptors to react to the added stimuli. Calcium metabolism may play a role, and superoxide influences this [
18]. Prolonged depletion of Ca
2+ stores via the leakage of the sarcoplasmic reticulum leads to reduced myocyte contractility. Mitochondrial Ca
2+ overload precedes ventricular contractile dysfunction, suggesting that Ca
2+ disturbances induce this dysfunction [
19].
AKI from burns occurs mainly during the shock phase [
20] and leads to the accumulation of toxic nitrogen byproducts and a reduction or cessation of urine excretion. Hypovolemia, mechanical tissue destruction, and cardiac dysfunction combined with the elevation of inflammatory mediator levels are components of early AKI [
21]. Oxidative stress may be a mechanism for later AKI after burn injury, predominantly in sepsis [
22]. Burn injuries may also cause compartment syndrome-releasing myoglobin by rhabdomyolysis and precipitation in the renal tubules generating free oxygen radicals [
23]. Utilizing immune cells and mediators, radicals can cause AKI [
24]. Additionally, ROS can depolarize the glucosamine chains of proteoglycans, which may increase the permeability of glomerular glycocalyx, causing proteinuria [
25].
Hypermetabolism and hypercatabolism are side effects of mitochondrial oxidative stress injury that cause oxidative stress and affect bone and muscle. Mitochondrial oxidative stress injury depresses muscle cells and muscle mass as a long-term persistent response to burn injuries. Based on observations after burning in murine white adipose tissue, the existence of thermogenically functioning mitochondria and proton leakage, with uncoupling and apoptosis as regulatory mechanisms of oxidative stress, has been proposed [
26]. Furthermore, researchers have reported that muscles local to the burn wound exhibit diminished coupling of the respiratory chain to ATP production and increased apoptosis under ROS influence, compared to that in distant muscles [
26]. Therefore, ROS forms a part of the hypermetabolic response by muscle mass loss and reduced biosynthesis of muscular proteins.
Furthermore, oxidative stress aggravated by hypermetabolism may exceed the protein folding capacity of mitochondrial degraded, misfolded, and damaged proteins [
27] and activate mitophagy or apoptosis [
28,
29,
30]. In addition, intensive care-mediated sedation contributes to muscle loss by inactivation [
31,
32]
Therefore, the attenuation of hypermetabolism may rely on a decrease in oxidative stress, potentially by improving mitochondrial function [
27].
Oxidative stress in burn injuries is attributed to long-term neurodegeneration, as mitochondrial dysfunction affects oligodendrocytes, which manage axon myelination.
After acute burn injury, liver dysfunction can increase the mortality risk, as demonstrated by Gong et al. in young adults with excessive burns [
33]. Malondialdehyde levels, which indicate oxidative stress in the liver, increase after burn injury, and oxandrolone treatment can reduce these levels [
16]. Furthermore, liver weight increases significantly after burn injury due to hepatic edema formation [
34]. In association with hypermetabolism and elevated catecholamine levels, stimulated lipolysis and white adipose tissue browning after burn injury are accompanied by uncoupling protein accumulation in white adipocytes [
35] and hepatic steatosis.
3.1. Burn Wound Progression
Burn wound progression, or the deepening of a burn wound from superficial to deep, is linked to oxidative stress and is considered multicausal. Most studies have investigated apoptosis in the early period after injury when no therapeutic actions can be taken [
36]. Shupp et al. claimed that oxidative stress-induced endothelial damage contributes to tissue damage [
36]. Lanier et al. [
37] found that necrosis, not apoptosis, is the most prominent cause of cell death during burn injury progression; furthermore, showed significant advancement of necrosis at 1–4 h post-burn and concluded that interventions should be performed within 4 h after injury to reduce progression. Apoptosis was not identified as a part of early burn wound progression but was observed at necrotic and viable tissue borders. Gravante et al. [
38] reported reduced autophagy levels and increased apoptosis and inflammation levels during early wound progression, with elevated myeloperoxidase activity in the superficial layers. However, elevated levels of autophagy were detected in the deep layers and interpreted as a protective mechanism.
Reducing oxidative stress via curcumin therapy improved wound healing in the “mid anaphase" [
39,
40]. Moreover, the application of lactate polymers [
41], which degrade into lactate and lactic acid [
42], may promote healing, as lactate inhibits Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) channels [
43] and has antioxidative properties [
44,
45]. However, the beneficial effects of dressings on burn wound progression depend on moving the balance from the activation to the inactivation of free radicals [
46,
47]. In addition, changes in perfusion, temperature, edema formation, and toxic serum species can influence the degree of necrosis.
3.2. Keloids and Hypertrophic Scarring
Keloids and hypertrophic scarring result from disturbed wound healing. Ogawa suggests viewing both fibroblastic disorders as the consequences of endothelial dysfunction and inflammation of the dermis of different degrees [
48]. Predisposing components delay wound healing, wound depth, the tension of the scars, hypertension, sex hormones, and cause a disbalance of oxidant and antioxidant mediators in the dermis.
3.3. ROS Levels Are Essential Components of Wound Healing and Hypertrophic Scar Development
The proliferation of dermal fibroblasts and the ECM is attributed to different pathways, such as the TGF-/Smad, PI3k/AKT, or p38/MAPK pathways [
49] to matrix metalloproteinases, tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases, and decorin [
50]. Higher levels of ROS in hypertrophic scar fibroblasts were confirmed having a reduced expression of nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and a downregulation of ROS-scavenging genes [
50,
51]. Endogenous ROS scavenger administration is postulated as prophylaxis or as a treatment option to balance ROS and antioxidants and attenuate the symptoms of scars [
52]
Adipose-derived stem cells suppress hypertrophic scar fibrosis via the p38/MAPK pathway [
49] or promote apoptosis by inhibiting Nrf2 and decorin expressions in hypertrophic scar fibroblasts [
53]. In addition, the inhibition of collagen production by the TGF-β/SMAD pathway-mediated CRIF1 inhibition might be an additional way to negatively influence hypertrophic scar formation [
54].
The effects of adipose-derived stem cells on hypertrophic scar fibrosis were tested successfully
in vitro and
in vivo [
54]. However, no applications in humans have been documented to date.
3.4. Oxidative Stress and Post-Burn Metabolic Changes
TNF-α and NLRP3-positive inflammasomes are activated by an increase in unsaturated fatty acids, ROS, and mitochondrial dysfunction and can mediate the secretion of IL-1β and IL-18 and play a critical role in post-burn inflammation-induced protein breakdown and hypermetabolism under oxidative stress [
27]. Di Gioia et al. demonstrated that the endogenous oxidization of lipids promotes hyperinflammation by the hyperproduction of IL-1β in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages [
55]. Metabolic disorders closely related to oxidative stress [
56,
57] in burns linked to IL-1-β and IL-6 [
58] include insulin resistance, muscle loss, mitochondrial dysfunction, and hyperlactatemia. Additionally, cytokines downregulate the expression of insulin receptor substrate 1, potentially contributing to hyperglycemia and elevated metabolic responses upon thermal injury [
59].
Catalase is primarily found in peroxisomes and erythrocyte cytosol. It is highly concentrated in mitochondria in the liver and is a crucial antioxidant that mediates the conversion of cellular H
2O
2 to water and oxygen. It is a central redox molecule in several biological processes [
60]. Depending on its concentration, the cellular context, and kinetics, catalase can either activate highly toxic hydroxyl radicals with redox-active metal ions and physiological levels of H
2O
2 or function as a signaling molecule [
61,
62,
63,
64]. Catalase deficiency results in insulin resistance, and oxidative damage to β-islets mediates it [
64]. Conversely, catalase overexpression improves mitochondrial function in insulin-resistant muscle cells. Insulin resistance reduces glucose uptake in muscular cells, and catecholamines, corticosteroids, and inflammatory mediators induce hypermetabolism. Muscular catabolism triggers a loss of muscle mass as overall protein synthesis is reduced [
65]. Because of the influence of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma [
66], the risk of metabolic syndrome [
67], hypermetabolism, and white adipose tissue browning by oxidative uncoupling has been hypothesized. Other suspected activating factors for white adipose tissue browning include catecholamines [
68], glucocorticoids [
69], cytokines [
70], glucagon [
71], and mitochondrial damage [
72].
4. Oxidative Stress: Definitions and Critical Players
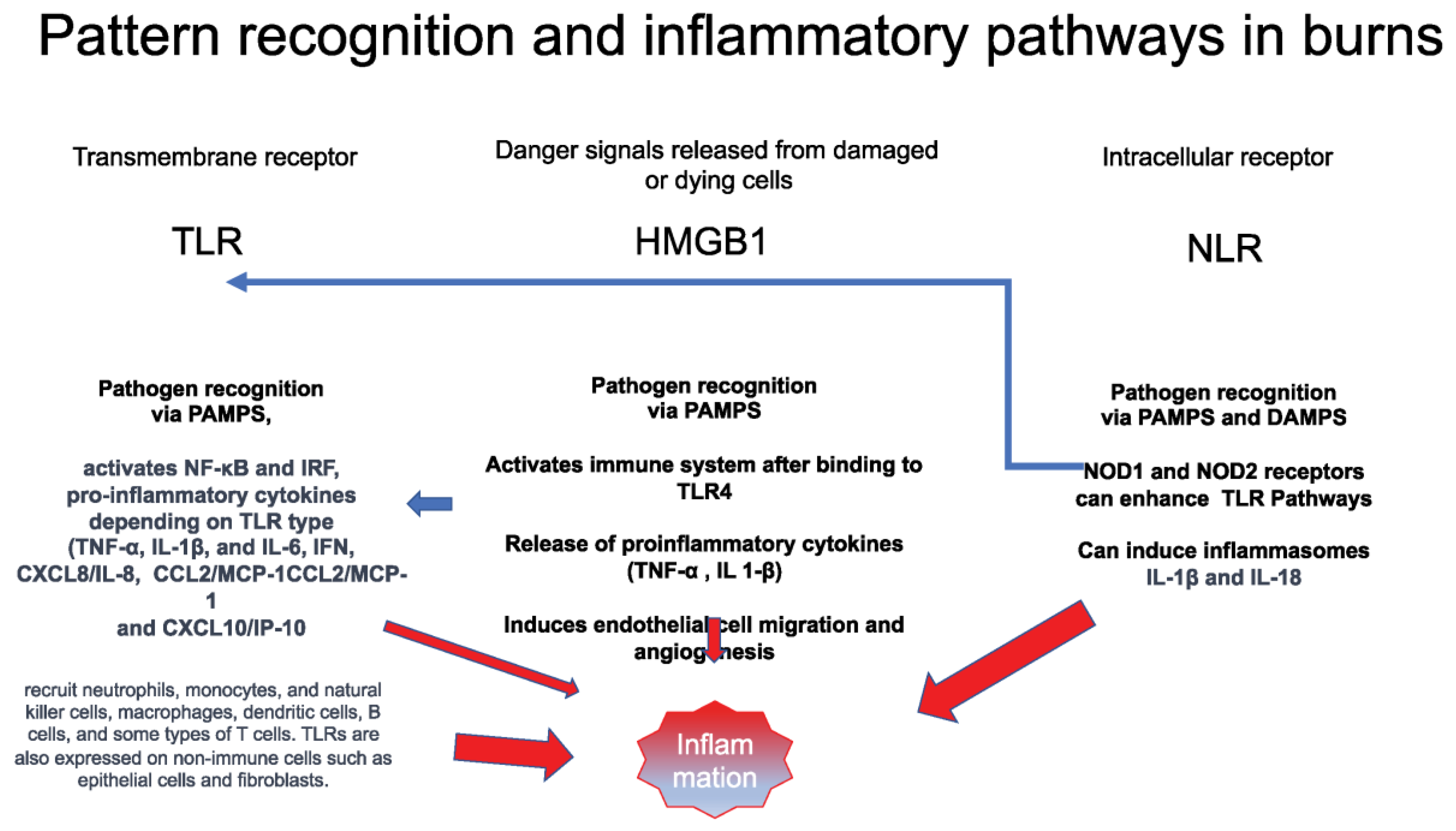
Tissue damage by thermal injury releases damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) that activate High Mobility Group Box 1 (HMBG1), transmembrane receptors (TLRs), and intracellular receptors (NLRs), enhancing the inflammatory response, as demonstrated in
Figure 2.
HMGB1 is an endogenous mediator that increases the affinity of transcription factors and amplifies the inflammatory response [
73]. Dependent on the redox state of the molecule, HMGB1 is a critical factor in triggering chemoattraction and cytokine responses during inflammation [
74].
Pattern recognition Toll-like receptors (TLRs) react with fragmented-extracellular and Nod-like receptors (NLRs) in response to the extracellular presence of intracellular particles [
75]. TLRs and NLRs are expressed by polymorphonuclear leukocytes and epithelia and activated simultaneously by alarmins with common precursors of monocytes/macrophages [
76,
77,
78].
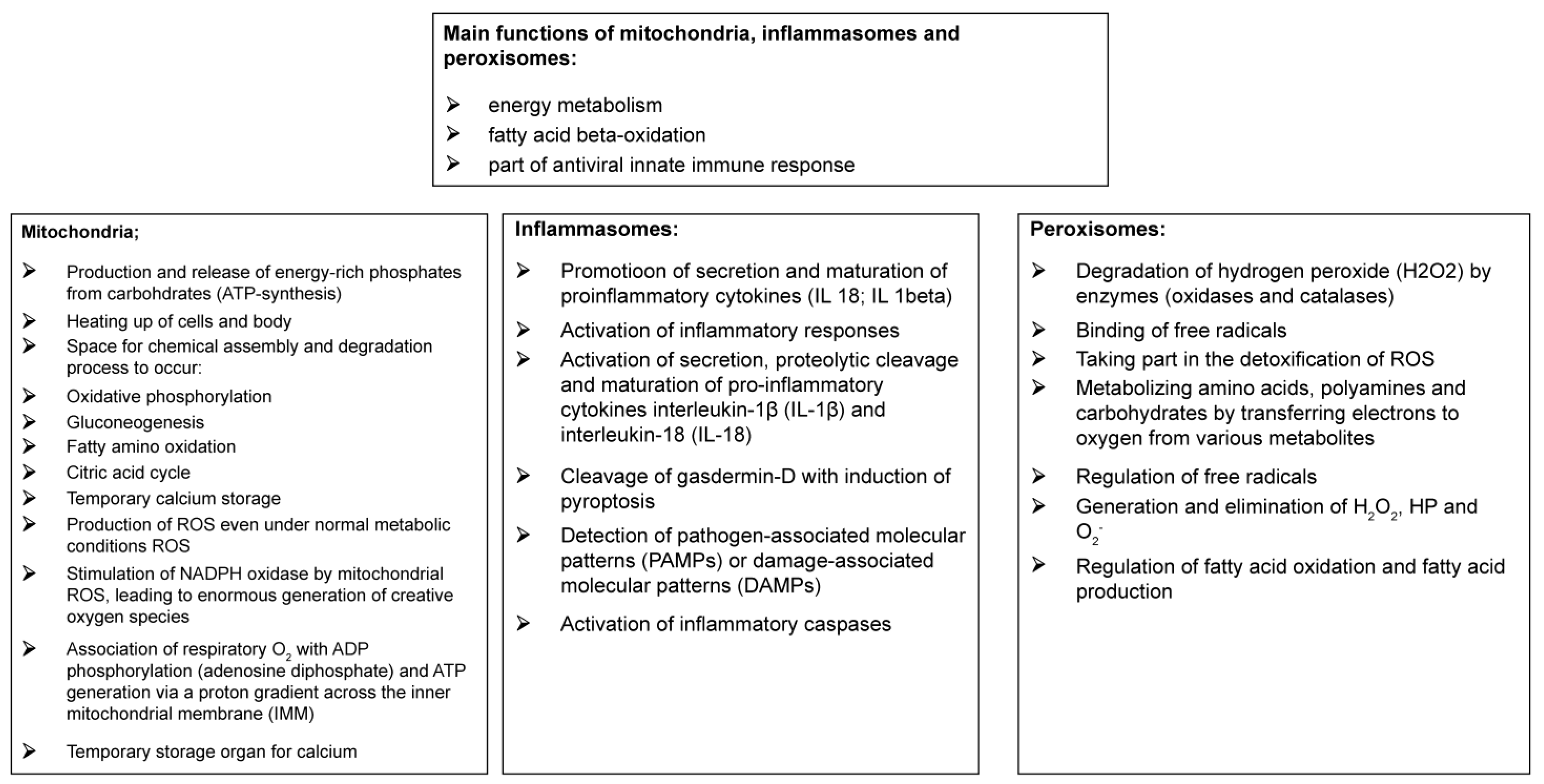
Figure 3 describes the main functions of mitochondria, inflammasomes, and peroxisomes.
4.1. Mitochondria
Mitochondria, considered the ATP providers and cellular heat sources [
80], produce energy-rich phosphates from carbohydrates and appropriately release and divide ROS. Mitochondria, inflammasomes, and peroxisomes are critical sources of ROS.
4.2. Inflammasomes
Inflammasomes are multiprotein complexes comprising NLRs and an adapter protein, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD (ASC), which contribute to the formation of the effector molecule, pro-caspase 1 [
80].
4.3. Peroxisomes
Peroxisomes, which are single membrane-enclosed cell organelles, and inflammasomes produce ROS even under normal metabolic conditions [
81]. In addition, mitochondrial ROS and protein kinases within the electron transport chain stimulate NADPH oxidase, which is an extensive trigger for the generation of ROS [
82].
Antioxidants, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, glutathione peroxidase, and peroxiredoxins [
83], build a complex intracellular defense system [
82,
84]. Uncoupling mitochondria from ATP generation for heat production is a metabolic strategy used under oxidative stress to reduce the efficiency of cellular ATP production and produce heat instead of ATP, which can be interpreted as a protective mechanism against oxidative stress in muscles and organs [
84]. In addition, uncoupling proteins attenuates excessive ROS production by promoting heat production and uncoupling ATP synthesis in cellular respiration via proton leaks [
84].
However, burn-induced mitochondrial-increased ROS formation causes an unfolded protein response in the mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum [
85] with potentially harmful side effects [
86]. Responses to uncoupling may include cell death, autophagy, inhibition of mitochondrial ATP production, thermogenesis, and a decrease in membrane potential that will modify ROS production [
87].
Mitochondrial uncoupling increases the metabolic rate in burn victims [
88]. Inflammasomes are critical to wound healing after burning by linking pathogen identification and immune response [
89]. NLR multiprotein complexes form inflammasomes, activating caspase-1 activation and inducing pyroptotic cell death.
Activated inflammasomes promote the secretion and maturation of proinflammatory cytokines, such as IL-18 and IL-1β [
90], via the proteolytic effect of caspase 1 and the cleavage of gasdermin. Additionally, gasdermin D forms pores on cell membranes, leading to a type of inflammatory cell death called pyroptosis [
91]. Gasdermin also regulates the IL-1 release from macrophages, thereby permitting IL-1 passage across intact lipid bilayers.
Peroxisomes, previously known as microbodies, are ubiquitous cellular organelles with a single membrane. They are formed from the endoplasmic reticulum and play a role in detoxifying reactive anion species. Additionally, they metabolize amino acids, polyamines, and carbohydrates [
92] by transferring electrons to oxygen from various metabolites [
93]. Peroxisomes are not linked to oxidative phosphorylation, but regulate free radicals by quickly adapting to a changing environment to generate or eliminate H
2O
2 and O
2 [93, 94]. Additionally, they play a central role in ROS metabolism and mitochondria [
95]. Moreover, they have been identified as central regulators of immune function and inflammation [
95] and are considered an essential source of signaling molecules [
94].
5. Antioxidative Treatment with Dressings
Antioxidant therapy may promote wound healing beyond re-epithelialization. Various topical antioxidant carrier materials have been studied for their anti-inflammatory and cytotoxic effects in animals and cell cultures. [
96,
97,
98]. A few studies have investigated the impact of dressings on systemic oxidative stress in humans after burn injuries, limited studies have measured the reduction in oxidative stress induced by wound dressings.
Table 1 and the following sections present various dressings and their effects on oxidative stress and burn wound healing.
5.1. Inorganic Materials
5.1.1. Metal Chelators as Lotions or Solution
Metals are catalysts for lipid peroxides to generate lipid radicals and ROS [
120]. Metal chelators, such as disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetate and methyl sulfonyl methane, bind metal ions and have been evaluated as lotions for brass-mediated contact burns in pigs, namely with repeated application starting at 15 min after the injury and continuing up to 72 h without a secondary dressing [
121]. EDTA disodium, as a metal chelating agent, and methyl sulfonyl methane, as a permeability enhancer, have effectively decreased horizontal and vertical burn wound progression. In repeated applications, the lotion markedly reduced burn-induced aldehyde dehydrogenase levels, burn-induced elevations of IL-6, TNF-α, TNF-α converting enzyme, and lipid aldehyde production (protein-HNE) [
122].
Metal chelators may exert their antioxidative effects in burns by binding to metal ions during the early stages of oxidative stress activation [
123]. They have been tested in animals but not humans, as significant side effects are expected [
124].
Cerium is not known to form chelates with other metal ions or to act as a metal chelator to sequester or remove metal ions from the body. Therefore, cerium nitrate is generally not classified as a metal chelator. However, treatment with a single application of cerium nitrate solution in a randomized controlled study using a burn comb model in rats has shown that re-epithelialization was considerably higher in the treated group than in the control group [
125]. This effect has been attributed to the binding of cerium nitrate to a lipid–protein complex that would otherwise activate the inflammatory response by inducing oxidative stress [
126]. Furthermore, cerium nitrate, in combination with silver sulfadiazine (SSD), was effective in delaying the need for excision and grafting in burn patients [
127]. However, although cerium nitrate was found to prevent post-burn immunosuppression, human studies investigating the effects of this treatment on antioxidants or oxidative stress parameters have not been conducted. Additionally, Flammacerium® may be helpful for patients who cannot receive oral or intravenous antibiotics, such as those with allergies, intolerance, or contraindications to systemic antibiotics. In such cases, topical antimicrobial therapy with Flammacerium® may be the only feasible option for preventing and treating infections in burn wounds.
5.1.2. Silver Nanoparticles
Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) have been used in wound healing applications [
128]. Their internalization in cells occurs via endosomes and lysosomes, as well as in mitochondria and the nucleus, depending on their size and surface modifications [
129,
130].
AgNPs have been shown to induce oxidative stress, degrade the endoplasmic reticulum stress sensor activating transcription factor-6, which activates NLRP-3 inflammasomes, and can also result in genotoxicity and apoptosis [
129]. Although
in vitro results were the only results identified, it is worth noting that capping silver nanoparticles with poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) and ascorbic acid can enhance their antioxidant properties and reduce their oxidant properties [
131]. Furthermore, AgNPs can be incorporated into membranes, thus, practical applications are to be expected [
132].
The wound healing potential of multifunctional chitosan/gelatin@tannic acid cryogels decorated with in situ reduced AgNPs was evaluated in rats. The results demonstrated an effective elimination of bacteria from the wound exudate compared to chitosan gel or chitosan gel with tannic acid [
133]. Additionally, the composite material was found to reduce the levels of TNF-α and ROS, suggesting potential anti-inflammatory benefits. Based on these findings, the authors propose this composite material as a promising treatment method for infected wounds.
AgNPs produced via green synthesis using
Cestrum nocturnum extract have demonstrated their ability to scavenge free radicals and reduce oxidative stress in cells, indicating their antioxidant activity. It is important to note that although AgNPs can cause oxidative stress, coating, and green synthesis can reduce this effect, they do not act as antioxidants. Uncoated AgNP solutions did not significantly affect the healing time of second-degree burns in rats compared to saline solutions [
134]. Additionally, AgNPs have been shown to effectively inhibit the growth of several bacterial strains, demonstrating their antibacterial activity. Therefore, the green synthesis of AgNPs using
Cestrum nocturnum extract holds promise as it can provide dual benefits of both antioxidant and antibacterial activities, making it a potential candidate for various biomedical applications. Several other green nanoparticles have also demonstrated antioxidant effects, which are believed to be due to the preferential sorption of extract components on the surfaces of nanoparticles. Some nanoparticles have even shown antitumor effects, suggesting their potential use in cancer treatment. Further research could help identify additional green nanoparticles with promising antioxidative and therapeutic properties.[
135].
However, it is essential to note that further research is needed to fully understand the efficacy and safety of these nanoparticles in different contexts [
136]. Even though the use of AgNO
3 nanoparticles may have some potential benefits, concerns exist over potential issues, such as bacterial resistance, toxicity, and the generation of free radicals [
137]. Unfortunately, no data from animal studies or human applications on this topic is available, highlighting the need for additional research to thoroughly understand the potential risks and benefits of nanoparticles.
5.2. Biological Materials
5.2.1. Potatoes
Boiled potato peels have been suggested as a treatment for minor burns [
99]. However, compared to honey, this treatment showed a longer healing time (16 days versus 10.4 days) [
138]. Additionally, ferulic acid (FA) was identified as a radical-scavenging compound in the peel [
139]. Although the preparation of boiled potato peels can be laborious, it is accessible in rural settings, making it a recommended treatment for low-resource areas [
140].
5.2.2. Silk
The antioxidant capacity of silk fibroin and silk sericin, proteins from
Bombyx mori, was evaluated
in vitro and compared to ascorbic acid, vitamin E, butylated hydroxytoluene, and linoleic acid. Sericin has a higher antioxidant capacity than vitamins C, E, and BHT [
141]. Various assays confirmed the antioxidant properties of silk fibroin and silk sericin, including the 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) assay, which measures radical-scavenging activity. Furthermore, silk fibroin and silk sericin have been demonstrated to prevent cell death in L929 cells and H
2O
2-mediated cell death, as evidenced by a trypan blue and lactate dehydrogenase assay. A catalase assay has also validated the antioxidant activity of these silk proteins [
142].
Sericin from different sources exhibited varying antioxidant capacities, possibly due to flavonoids and polyphenols. In addition, treatment with enriched silk extracts has been found to reduce the number of apoptotic cells in a drug-induced phototoxicity cell model, compared to chlorpromazine, and significantly attenuated the release of IL-1α [
143].
It should be noted that although silk fibroin hydrogels induced a mild immune reaction [
104], silk sericin was found to activate the immune response [
104]. Moreover, silk sericin has been shown to induce pro-oxidative stress and trigger apoptosis in human cancer cells [
144]. However, treatment with enriched silk extracts has been found to reduce the number of apoptotic cells, compared to chlorpromazine, in a drug-induced phototoxicity cell model and significantly attenuated IL-1α release [
143].
5.2.3. Porcine Xenograft
In assessing the inflammatory response to various dressing methods, the impact of porcine xenografts on systemic inflammatory reaction (SIRS) was compared with that of betadine ointment gauzes on burn wounds of varying sizes. CRP (C-reactive protein) levels in the serum were measured at 1, 4, 7, and 14 days following the burn. The pigskin-grafted group exhibited significantly lower CRP levels than the betadine gauze treatment control group [
145]. In addition, the findings of Mühl et al. suggest a correlation between oxidative stress and CRP levels in burns, indicating that CRP may indirectly reflect oxidative stress levels [
146]. Therefore, herein, the use of porcine xenografts may have helped reduce oxidative stress based on the modulated immune response, promoting tissue regeneration and reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. However, no other studies on this topic could be identified.
5.2.4. Amniotic Membrane
Amniotic membranes possess antioxidative properties. In particular, human amniotic epithelial cells reduce the release of reactive oxygen species, superoxide anion, and hydrogen peroxide (also known as the oxidative burst) in co-cultured neutrophils [
147]. Furthermore, human mesenchymal amniotic stem cell-conditioned medium modulated oxidative stress and its pathological consequences in mice [
148]. Amnion was sliced into strips and incubated with H
2O
2 solutions of varying concentrations, and the uptake of reactive oxygen species (ROS) was measured within the first hour. It was observed that the amnion strips could remove ROS at all tested concentrations. However, the percent removal rate of ROS was negatively correlated with the concentration of the H
2O
2 solution. [
149]. The antioxidant properties of amniotic membranes were proven by Alipour et al.
in vitro but have not been confirmed in human studies [
107].
Following decellularization, the amniotic membrane comprises collagen and an extracellular matrix and does not contain cells or DNA [
150]. Decellularized amniotic membranes protect retinal pigment epithelia from oxidative stress in cell cultures and reduce oxidative stress in ocular injuries caused by exposure to mustard gas [
106]. These effects may be attributed to the preserved extracellular matrix that contains components such as hyaluronic acid [
151,
152].
These studies suggest that cellular and decellularized amniotic membranes reduce oxidative stress in burn wounds and be helpful as a dressing. A human study reported a reduced need for dressing changes with amniotic membranes, but no significant differences were observed in healing time or scarring compared with traditional ointments [
107].
5.2.5. Acellular Dermal Matrices
Allo Derm® is a decellularized dermal dressing made from cadaver skin, but there are no human studies on its antioxidant properties. Lab tests on peritoneal macrophages from Swiss mice showed that Alloderm® did not activate oxidative stress. Based on the rat model used in the study, it was observed that AlloDerm had higher levels of cell growth and COX-2 levels compared to decellularized rat muscle. However, the decellularized muscle matrix was more effective in reducing inflammation and fibrosis than AlloDerm. These results suggest that the decellularized muscle matrix may be more suitable for promoting tissue regeneration and reducing inflammation and fibrosis in a rat model. However, it is essential to note that these findings may not necessarily apply to other animal models or humans, and further research is needed to confirm the effectiveness of decellularized muscle matrix for tissue regeneration in different contexts. A possible antioxidant effect of Alloderm® in the lab was determined by peritoneal macrophages from Swiss mice exposed to acellular dermal matrices and compared to Zymosan-Sigma and LPS-Sigma activated macrophages. The release of NO and H
2O
2 as positive control showed statistically significantly higher values in the LPS group than in the ADM group. In the study mentioned, it was observed that serum did not show any significant difference compared with the ADM group, indicating that it did not have a therapeutic effect in the study context [
109].
Regarding the use of ECM scaffolds as carriers for therapeutic agents, a review article by Da discussed the potential benefits of using an acellular dermal matrix (ADM) loaded with various agents, such as cerium dioxide nanoparticles (CeO2 NP), carbon-chitosan nanoparticles (Cn-Cs ADM), and curcumin, which has antioxidant properties.
Oxidative DNA damage may cause the potential genotoxicity of the engineered Cerium nanoparticles, Nanoceria (cerium dioxide nanoparticles). Additionally, a change in ROS generation under changing pH conditions might determine the pro- or antioxidative activities of nanoceria [
153]. For example, catalase and SOD mimetic activity reduce oxidative stress depending on their size at a neutral pH, whereas oxidase and peroxidase, activated at an acidic pH, may cause toxic effects and limit their usability [
154,
155].
Oxidative DNA damage may cause the potential genotoxicity of the engineered Cerium nanoparticles, Nanoceria (cerium dioxide nanoparticles).
5.2.6. Other Products Used as Artificial Dermis Are Matriderm®, Integra®, and Apligraf®
Collagen species from human, bovine, or porcine sources may have similar antioxidant effects as some collagen extracts from the skin, and gills of various fish species have shown such effects [
156]. Apligraf®, which merges a dermal layer of human fibroblasts, bovine type 1 collagen, and allogeneic keratinocytes, and Matriderm®, a bovine collagen-elastin matrix, are examples of collagen-based products. Integra® also contains cross-linked collagen from bovine collagen tendons, glycosaminoglycans, and a synthetic polysiloxane layer. Apligraf® has been evaluated in deep dermal wounds in humans, where completely excised wounds were treated with Apligraf®, Mepitel®, or a control group with split-skin. Apligraf® was found to function only as a temporary biological dressing with higher macrophages, and T-cell counts under the Apligraf® [
157]. It has been suggested that matrix metallopeptidase (MMP)-9 may be a marker of oxidative stress in sleep apnea [
158]. However, when tested in reconstructive surgery using Integra®, changes in MMP-2 and MMP-9 levels were insignificant compared to baseline levels [
108].
No reports on the effects of these products on oxidative stress could be found.
6. Encapsulation of Medications in Carriers
In a rat model, insulin was enclosed in microspheres made of polylactide (D, L-lactic-co-glycolic acid) and embedded in an alginate sponge dressing. This formulation showed a moderate decrease in wound area compared to a placebo, but it improved the healing of burn wounds [
111]. In the treatment group, earlier recruitment of neutrophils was observed compared with the placebo group, along with sustained lower lipid peroxidation levels after day 3, indicating enhanced leukocyte clearing function. Angiogenesis was found to be three times higher than that in the placebo group. Blood glucose levels in both groups followed the natural daily cycle, and no hypoglycemia (<60 mg/dl) was observed, although insulin application decreased blood glucose levels 4–6 h after application. Second Harmonic Generation (SHG) microscopy revealed that collagen fibers were dismantled in the insulin group, whereas the collagen fibers in the placebo group appeared thicker. SOD activity decreased within the first 3 days of insulin treatment, whereas catalase and glutathione levels increased simultaneously, reducing H
2O
2 levels. MDA levels, an indicator of lipid peroxidation, decreased from day 3 to 8 but returned to placebo levels on day 9. Additionally, polylactide surface coatings may support their effect on antioxidative activity [
159].
6.1. Hydrogels as Carriers
Hydrogels can serve as carriers for bioactive molecules and antioxidants. Polysaccharide-based hydrogels can be cross-linked with essential oils to generate radical-scavenging and achieve antioxidant effects [
114,
160,
161]. In conclusion, curcumin, N-acetyl cysteine, quercetin, and chitosan have been identified as potential antioxidants for local applications, and early results suggest that they could be incorporated into carriers with promising results [
162].
Dopamine is known for its antioxidant properties and can be polymerized into cross-linked hydrogels made from dextran. Additionally, cross-linked hydrogels from dextran and polydopamine dose-dependently exhibited antioxidant properties [
163]. Polyethylene imine was found not to affect the antioxidant activity. Curcumin was applied as an antioxidant in a rat model via fully degradable thermosensitive polymeric micelles made of a polyethylene glycol-polycaprolactone polymer [
39]. In the ex-vivo model, curcumin was used as an antioxidant in fully degradable thermosensitive polymeric micelles made of a polyethylene glycol-polycaprolactone polymer. This preparation formed a gel at body temperature, decreasing SOD levels and increasing catalase levels, resulting in improved wound healing compared to dextran. These findings suggest that using curcumin-loaded polymeric micelles promotes wound healing by modulating antioxidative activity in the wound bed. Chitosan hydrogels have been proposed as vehicles for nanocomposites combined with curcumin [
164,
165]. However, further research is needed to determine the effectiveness of this approach in clinical settings.
Puerarin and FA were incorporated into polydopamine nanoparticles, which were then embedded into polyethylene glycol diacrylate [
114]. The hydrogel preparation containing puerarin and FA incorporated in polydopamine nanoparticles and embedded in polyethylene glycol diacrylate promoted faster wound healing in rats compared to other hydrogels. In addition, oxidative stress, as measured by DPPH* and *OH scavenging ability, was significantly reduced after treatment with the hydrogel.
Hybrid hydrogels are hydrogels where the forces of crosslinking between polymeric chains are chemical and physical [
166]. Hybrid hydrogels incorporating polydopamine/puerarin nanoparticles in rats [
167] improved the survival of stem cells under oxidative stress due to their antioxidant properties in a model with periodontal ligament stem cells. In addition, wound healing, assessed in a rat model, was accelerated with polyethylene polydopamine puerarin hydrogel compared to phosphate-buffered saline, indicating the therapeutic potential of the tested material.
No reports on topical applications of hydrogels inducing a reduction in oxidative in human wounds were found. The blending induced antioxidant properties with antioxidant components, where polyphenols were suggested as a better choice compared to antioxidant enzymes [
161,
168].
6.2. Fish Skin Gelatin Hydrolysate
The
in vitro antioxidant capacity of gelatin derived from Nile tilapia was tested by determining the reduction of DPPH (2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl), hydroxyl and superoxide radicals, viability determination in cell culture, and the determination of intracellular ROS, and the determination of radical-mediated DNA damage. Evaluation of the free radicals scavenging abilities of the gelatin showed the highest scavenging ability for hydroxyl radicals, more than for DPPH and superoxide radicals in RAW 264.7 cells. No cytotoxicity in RAW 264.7 was found, as determined by cytotoxicity assays. The sequence of an active protein could be identified, and it was hypothesized that the radical-scavenging ability might be due to non-aromatic amino acids [
169]. Based on their structure, peptides from different sources may have antioxidant capacities [
170].
6.3. Fish Skin and Nanofibers
When testing the industrial relevance of residuals from the fishing industry
in vitro by oxygen absorbance capacity, DPPH scavenging activity, hydroxyl radical-scavenging activity, and 2,2′-azino-di-3-ethylbenzthiazolin-6-sulfonic acid, the skin of Atlantic cod showed antioxidative properties, weaker than those of Atlantic salmon [
171]. The high lipid content in salmon can lead to the production of peroxides via autooxidation, which may have influenced the results by increasing the values of the peroxides neutralized. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, available in fish skin, are suggested to improve wound healing, although no randomized studies on wounds and poly unsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) in humans could be identified. In animals, topically applied cross-linked electrospun tilapia collagen nanofibers exhibited faster wound healing in a rat model by inducing keratinocyte differentiation and proliferation by upregulating the involucrin, filaggrin, and type 1 transglutaminase gene expression [
172]. In another animal study, a mixture of soybean, olive, and fish oil rich in PUFA was systemically administered and compared to a placebo group. The results showed significantly different wound sizes on days 3, 5, 10, and 14, with smaller wound sizes in the PUFA group. Furthermore, the levels of TNF-α initially decreased in the placebo group but increased again after 72 h and were significantly higher than in the PUFA group [
173].
Fish skin has been used in different ways in burns treatment.
In a pediatric case involving superficial partial-thickness burns covering 18% of the body surface area, a non-processed allograft sterilized by glycerolizing and irradiation was tested. The allograft resulted in complete healing within 10 days. It is important to note that this allograft was not processed with chemicals [
174].
In a pilot study involving 30 children with superficial partial-thickness burns, tilapia fish skin was compared to silver sulfadiazine as a treatment option. The results showed no statistically significant difference in the days until complete re-epithelialization [
175]. After removing the dressing, the Clinical Global Impression Scale-Improvement (CGI-I) results showed no significant difference between the tilapia fish skin and silver sulfadiazine groups. The Faces Pain Scale-Revised was used to evaluate pain, and the area under the curve (AUC) did not show any statistically significant difference between the groups [
176].
In a phase 2 randomized controlled trial, treatment with unprocessed fish skin that had undergone sterilization was compared to treatment with silver sulfadiazine in cases of partial-thickness burns [
175]. The trial included three groups with different types and severity of second-degree burns: one group with less than 10% burned surface area receiving outpatient care, one with 10–20% burned surface area receiving inpatient care, and one with deep second-degree burns covering 5–15% of the body surface area receiving inpatient care. Each group was randomized into a test group receiving treatment with tilapia fish skin and a control group receiving treatment with silver sulfadiazine. The results showed that the healing time with tilapia skin was significantly shorter than with silver sulfadiazine in each group. Pain intensity, as measured by a Visual Analog Scale, and analgesic requirements were also lower in the inpatient group. In addition, fish skin treatment patients required significantly fewer dressing changes. The study did not explain the difference in results between the previous pilot study and this phase 2 trial.
Acellular fish skin (AFS, marketed as Kerecis®) is prepared by a gentle processing method that results in sheets of intact fish skin with all cells and antigenic materials removed, leaving only the extracellular matrix. AFS has been tested in different types of wounds, such as foot ulcers [
177,
178] and donor areas for burns [
178], but rarely in burns.
Yoon et al. compared the healing time of wounds treated with AFS from Kerecis®, bovine collagen (ProHeal®) after 2 days of treatment, and a non-treatment group. The results showed a significantly shorter healing time in the AFS group. The authors also noted delays in covering donor areas due to excessive discharge from acute wounds. Water absorption was significantly higher in the collagen group, and the AFS group exhibited faster degradation when tested by immersion in a collagenase solution. In an
in vitro cell culture, higher cell proliferation was observed under AFS, and the morphology of the proliferating cells (keratinocytes and HUVECs) on AFS was well stretched after 3 days and even aggregated on day 7, whereas the cells on the other template were spindle-shaped [
178].
Kirsner et al. compared the healing properties of AFS to dehydrated amnion–chorion membranes. Fish skin treatment exhibited improved wound healing compared to that under amniotic membrane treatment in a randomized study with 4 mm punch biopsies from the skin of healthy volunteers [
179]. Stone et al. [
180] compared the re-epithelialization and contraction rates, hydration, and trans-epidermal water loss of AFS to fetal bovine dermis [
180], where they reapplied fetal splitskin graft (FSG) after 7 days, and the wounds healed by secondary intention. They found faster epithelialization, a smaller wound size on day 7, and increased granulation tissue with a higher blood flow than normal tissue; no differences in the transepidemal water loss (TEWL) could be found. Initially, observed seroma formation could be avoided by fully expanding the meshed template and securing it with additional staples. Significant contracture rates were found on day 14, 1 week after reapplication of FSG but resolved later and equal in the later course during secondary healing, regardless of the treatment.
A nonrandomized retrospective single-case study was conducted in humans to compare AFS to polylactide (PLM; Suprathel®) in partial-thickness burns after enzymatic debridement. Superficial partial-thickness burns were treated using PLM, whereas deep partial-thickness wounds were treated using autologous split-thickness skin grafts or AFS [
181]. According to the nonrandomized retrospective single-case study, the results were superior in patients who received AFS treatment compared to those who received PLM regarding the Patent Observer Scar Assessment Scale, pliability, vascularity, pigmentation, pain relief, and itchiness. However, the study did not evaluate the dressing procedure and removal criteria, and further evaluation is needed in a prospective randomized study.
Even though fish skin has shown potential for reducing oxidative stress in burns, oxidative stress parameters have not been evaluated in human studies. Therefore, further research is needed to fully understand the effects of fish skin on oxidative stress in burns.
Seafood allergies may limit the usage of fish skin dressings. A nationwide survey found that 5.9% of US households reported allergic reactions to fish or shellfish. Specifically, 2% of individuals were allergic to shellfish, 0.4% to fish, and 0.2% to both. Therefore, it is essential to consider potential seafood allergies when using fish skin dressings in clinical practice. Additionally, reactions may include anaphylaxis, particularly in children [
182,
183].
Fully synthetic materials such as PLM and polyurethane (PUM) membranes are also used in wound dressings. PLMs, including Suprathel® and SupraSDRM (Suprathel dermal replacement matrix), are fully resorbable dermal and epidermal templates comprising a copolymer of polylactide, trimethylene carbonate, and ε-caprolactone. These membranes have varying porosities, thicknesses, and pore sizes. For example, Suprathel® has interconnected pores of approximately 5–50 µm in size and is approximately 1 mm thick, whereas SupraSDRM® is structured with bimodal pores of 80–300 µm in size and has a thickness of approximately 2 mm. In an intravital mouse model, the smaller pores of Suprathel® allow for endothelial generation [
184], and the bigger pores correlate with new tissue formation [
185]. Furthermore, they might be linked to a higher lactate release.
PLMs are biodegradable materials that degrade in a humid environment into monolactides and lactate. They trigger neoangiogenesis and strengthen the vessel structure by converting procollagen to collagen. Furthermore, combined with ascorbic acid, they can initiate the creation of new vessels and promote collagen and ECM deposition, possibly via the induction and formation of ROS [
186].
Higher lactate levels have been linked to multiple effects, including stabilization of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α, induction of VEGF and TGF-β, and increased metalloproteinase activity [
187]. Lactate release gradually decreases as partial-thickness wounds heal, and the moist environment decreases. This could explain the decrease in TGF-β levels after day 10 of treatment [
119]. Reducing TGF-β levels may decrease myofibroblast production, resulting in a lower rate of wound contraction and lower formation of hypertrophic scars [
188].
Lactate has also been shown to inhibit TRPV1 channels, which are relevant for pain sensation and the development of the burn cytokine cascade [
43].
In addition, topical application of PLMs reduces oxidative stress locally and systemically in burns [
41,
118,
119]. Moreover, the membranes are resorbed within 4–8 weeks without triggering a foreign body reaction [
189,
190].
Lactate is an essential component of polylactides and exhibits radical-scavenging properties [
45,
191,
192]. The lactate-dependent and oxidative stress-reducing functions in burns were confirmed in clinical trials. As a result, significant pain relief of up to 60% [
191,
192,
193], a low rate of infections [
194], fast wound healing [
186,
191,
195,
196], good cosmetic and functional outcomes in superficial and deep burns [
197,
198,
199], weak inflammatory reaction [
184], and a reduced transplantation rate in partial -thickness burns [
144,
200]were described. Furthermore, PLM triggers tissue neogenesis, promotes TGF-β accumulation, and reduces TNF-α and IL-6 levels in blood and tissue compared to HF [
201]. Additionally, partial-thickness burns treated with PLMs exhibited higher quality and number of telomeres in healed burn wounds [
41] and a shorter healing time in partial-thickness burns than HF [
118]. Hence, recent research demonstrated that Supra SDRM® is a potent starter of neovascularization and neoangiogenesis. It promotes the generation of ECM and collagen and resorbs quickly, leaving a newly created tissue with regular vascularization in the wound [
193]
6.4. Polyurethane Foam
Novosorb
TM is a biodegradable, fully synthetic polyurethane foam membrane designed for biological applications. The visible pores on the membrane measure 188 ± 84 µm and feature a non-degradable polyurethane seal for temporary use. Novosorb
TM acts as a dermal template that promotes faster CD31
+ cell growth compared to Integra [
194]. Vascularization was consistent in the wound bed and margins, and the degree of vascularization correlated with dermal fibroblast ingrowth. Preliminary studies comparing Novosorb
TM biodegradable temporizing matrix (BTM) and Integra® in athymic mice showed that Novosorb
TM resulted in more extensive vascularization and caused a higher level of inflammation, as described by Cheshire [
195]. After 2 weeks, the levels of most inflammatory markers, including chemokine motive ligands and colony-stimulating factors, IL-1, IL-4, IL-12, and IL-13, did not differ significantly between Integra and BTM. However, both products exhibited a higher IL-10 to IL-6 ratio than proinflammatory macrophages, which promotes the transition of M1 to M2 macrophages, the pro-wound healing phenotype [
194].
Moreover, flexible polyurethane foams (PUFs) have been found to possess antioxidant properties, which can be further enhanced by isosorbide. This suggests that using isosorbide-treated PUFs may help to improve wound healing by reducing oxidative stress in the wound area [
196].
The vascularized template can be grafted with skin later [
197,
198], showing residual polyurethane even after 18 months. The vitality of adult fibroblasts and keratinocytes was assessed after 2 weeks
in vitro. The BTM group revealed a significantly higher survival of the human epidermis and keratinocytes [
194]. In a clinical retrospective evaluation, 20 patients with different indications, including seven with burns, were treated with BTM [
199]. Wounds were cleaned, and BTM was applied in a dual-step procedure, fixed with staples or sutures, and covered with autologous split-skin after 23.5 (13–49) days. BTM was integrated in 15 of 20 patients and evaluated by vascularization and recapillarization. In a prospective study on severe burns in 30 patients with a TBSA of a median of 44%, the mean split-skin uptake 7 days after BTM application was 81.9%, and the mean split-skin uptake relative to the area applied was 95.2%. The mean time for sealing membrane removal was 31.9 days. The contraction was approximately 5% and did not increase significantly over 12 months. BTM was fully integrated despite local infections [
200].
The successful application of sprayed keratinocytes on BTM usually needs a split-skin mesh as a supporting structure [
197]. However, a human study did not evaluate oxidative stress parameters, and currently, Novosorb® BTM cannot provide long-term results.
7. Impact of Dressings on Oxidative Stress in Human Burn Injuries
Occlusive dressings with multilayer gauze were shown to adapt heat production in burn patients for plus 10.5% when they felt comfortable, and 49% above the predicted normal levels without dressings when they felt cold [
201]. In addition, plasma catecholamine levels in patients with bandaged burns differed from those with undressed burns. However, no significance could be calculated due to small numbers and high standard deviations. Catecholamines might shift the hypothalamic thermoregulatory point upwards, but they were not found to be the primary mediators of hypermetabolism.
When comparing non-occluded to semi-occlusive dressings with surgical tape in a randomized rat incision model, semi-occluded wounds exhibited significantly reduced epidermal thickness and mitotic activity on days 3, 7, and 10 compared to non-occluded dressings. However, in non-occluded wounds, dermal cellularity was increased, which was interpreted as an effect of ongoing inflammation. In addition, IL-1α and TNF-α levels were significantly reduced in semi-occlusive wounds, approaching those seen in occluded wounds on day 10. However, no difference in wound healing time between occluded and air-exposed wounds was found [
202].
Besides their occlusive specifications, different burn dressings were assessed in PLM or hydrofiber Ag (HFAg) in children with deep, 20%–50% TBSA partial-thickness burns or healthy control [
118]. Furthermore, determining the TOC, TAC, MDA, and glutathione (GSH) levels, PLM treatment led to higher total antioxidant capacity and glutathione levels than in the HFAg group. These findings confirmed that different dressings exhibit differential healing properties beyond wound closing. TBSA partial-thickness burns or healthy control [
118]. The study demonstrated a significant reduction of oxidative stress and healing time in the PLM group compared to HFAg. These findings confirmed that different dressings exhibit differential healing properties beyond wound closing, and wound occlusion by itself did not reduce oxidative stress.
In a non-randomized study in deep burns, early skin grafting within 7–15 d after injury (n = 107) compared to patients treated with the granulation method and later skin grafting in humans (n = 249). Early grafting increased the glutathione levels with other positive effects on the patient, such as the stabilization of the acid-base mismatch [
203]. However, this study had a potential selection bias; early excision, split-skin grafting, and antioxidative dressings might have influenced the healing qualities of burn wounds. In addition, no publications on the influence of early grafting on oxidative stress in burn wounds could be identified.
Branski et al. compared the effects of early grafting with laminated Integra® to cadaver skin on post-burn metabolism in extensive burns after early excision [
204]. When measuring acute phase proteins, the Integra group showed highly significant C-3 and haptoglobin values compared with cadaver skin on admission and discharge. In addition, the constitutive proteins, prealbumin and transferrin, were also significantly elevated at these time points. These findings were interpreted as an improved liver function. In addition, Apolipoprotein B, another marker of liver function, was higher in the Integra group, where triglyceride levels were not significantly different in the treatment groups.
The improved liver function after Integra application might be interpreted as a symptom of reducing oxidative stress [
47], whereas the elevated acute phase proteins contradict this.
8. Laboratory and Clinical Effects of Antioxidant Dressings
8.1. Quality of Skin after Antioxidative Dressing
Antioxidative dressings have proven effects on wound healing and resulting skin quality, telomere length, and cell count in the healed skin after burns compared to other dressings.
In partial-thickness pediatric burns, the effects of PLM, HFAG, and SSD dressings, and a control group on telomere length in nucleated blood cells and telomerase expression in the skin were compared [
41]. PLM treatment resulted in the highest telomerase expression in the skin, resulting in the highest squamous cell counts in the basal layer of the epidermis.
The effects of PLM and HFAg on serum oxidative stress parameters and healing time in partial-thickness burns were investigated in 40 children. TAC, TOC, GSH, MDH, and epithelialization times were evaluated in blood samples [
118]. The results showed higher oxidative stress (TAC minus TOC levels) in the HFAg group. The serum oxidant level (TOC) in the HFAg group increased significantly on days 3 and 12 compared with PLM and non-burn control. The TAC levels of PLM were significantly higher in controls from day 3 to day 21. The effects of PLM and HFAg on serum oxidative stress parameters and healing time in partial-thickness burns were investigated in 40 children. TAC, TOC, GSH, MDH, and epithelialization times were evaluated clinically and in blood samples [
118]. The results showed higher oxidative stress (TAC minus TOC levels) in the HFAg group. The serum oxidant level (TOC) in the HFAg group increased significantly on days 3 and 12 compared with PLM and non-burn control. The TAC levels of PLM were significantly higher in controls from day 3 to day 21.
Because of reduced oxidative stress, the PLM group had a shorter healing time of 13.5 days compared to 21 days in the HFAg group.
Synoptical, antioxidant dressings showed a differentiated effect on serum oxidative stress parameters with clinical consequences, such as a shortening of healing time in a single study.
Cytokine levels of IL-6, TNF-α, and TGF-β in tissue and serum were evaluated under different dressings in 43 partial-thickness burns. Twenty-two children who underwent standard surgical procedures were included as controls [
119].
PLM application reduced the inflammatory reaction in blood and tissue and elevated TGF-β levels in both burned and normal skin compared with HFAg treatment. Additionally, reduced oxidative stress in the PLM group resulted from increased total antioxidant capacity and glutathione levels, with decreased total oxidant capacity and malondialdehyde levels compared with the HFAg group.
IL-1 levels in the PLM group were reduced compared with those in the HFAg group after day 3 and were comparable to control levels after day 14. IL-6 levels were comparable to control levels after 2–3 weeks, and TGF-β levels in the PLM group reached three times those in the HFAg group after 2 weeks.
The authors concluded that PLM quickly regulated local and systemic inflammation in wound tissues. Additionally, an increased level of TGF-β3 was seen in the PLM group for 14 days before normalizing. The reduced TGF-β reduces myofibroblast generation's stimulus and reduces hypertrophic scar development.
8.2. Cytokine Reaction in Cells
Cells from the stratum basale to the stratum corneum were stained for TNF-α, IL-6, and TGF-β antibodies, and a ratio of staining in 100 cells was calculated.
TNF-α and IL-6 expression in cells was significantly higher from day 7 to day 21 in the HFAg group compared to PLM, and the TGF-β expression was significantly higher from day 7 to day 21 compared to the other groups.
In conclusion, the authors stated that inflammation in partial-thickness burns could be reduced by mitigating the proinflammatory effect of TNF-α and IL-6 during burn injury by an antioxidant dressing (PLM) treatment.
Reduced oxidative stress may explain better healing conditions under antioxidative dressings than other dressings comparable to split-skin grafting in deep, partial-thickness burns [
205]. The authors observed a longer healing time in PLM-treated patients. Although after 15 days, 44% of the copolymer-treated patients without grafting and 88.9% in the split-thickness skin grafted wounds were healed, full epithelialization was found after 30 days in both groups, demonstrating non-inferiority of the PLM to those treated with split-thickness skin grafts. After 1 year, patients evaluated the cosmetic results of PLM as superior. They supported the eligibility of PLM for treating deep partial-thickness burns.
Galati et al. [
206] evaluated the use of split-thickness skin grafts versus temporary antioxidative dressings with PLM in deep dermal hand burns, focusing on scar elasticity and perfusion. In their retrospective follow-up of 80 patients with a minimum post-treatment period of 1 year, they found no statistically significant differences in scores on the Patient and Observer Scar Assessment Scale, Observer Scar Assessment Scale, Patient Scar Assessment Scale, or Vancouver Scar Scale. The effects were classified as beneficial, particularly in the elderly, chronically ill, multimorbid, or severely burned patients lacking donor sites.
8.3. Reducing Oxidative Stress may Reduce the Rate of Partial-thickness Burns needing Grafting
Blome-Eberwein et al. [
207] demonstrated a reduced need for grafting after PLM treatment compared to traditional treatment in their study on superficial and deep partial-thickness burns in adults and children. All 229 burn patients treated with PLM healed conservatively without grafting. They reported a rate of burn wound progression to full-thickness of 5.2% and an infection rate of 3.8%. In addition, the healing time was faster than that with Biobrane®, Mepitel®, and Transcyte® [
208], and the rate of hypertrophic scarring was minimal.
This reasoning may also explain the shift in the therapeutic management of partial-thickness burns over 14 years described by Schriek et al., where 1184 of 2084 children were treated with caprolactone dressings or an alternative material [
152]. This study demonstrated a reduction in the frequency of grafting procedures from 23.95% to 8.26% under PLM treatment, with the number of procedures requiring general anesthesia dropping from 3.22 per patient to 1.75, with overall reduced treatment costs.
9. Limitations
No prospective randomized clinical studies with large number of patients were found on this topic, and many commercial products do not have studies on their effects on oxidative stress or inflammatory response. The scarcity of publications hinders the general evaluation of the possible local and systemic effects of topical antioxidative dressings in humans.
10. Conclusions
ROS and oxidative stress represent parts of the cleaning and healing mechanism in response to burn wounds, yielding potentially severe side effects on organs and tissues. Although several wound dressings may reduce oxidative stress, their antioxidative effects have not been verified in humans, and only a few studies have examined their effects in detail.
In this review, we examined studies verifying the influence of dressings on oxidative stress and presented clinical observations of reduced oxidative stress after wound treatment. The topic of antioxidant treatment in wounds recently became the focus of interest owing to an increased understanding of the influence of free oxygen radicals on wound healing, with many in vitro studies; however, there are no reports on human trials. Evaluating the effect of antioxidant dressings with fewer dressing changes and other positive side effects may contribute to further progress.
We found that the antioxidative effect was confirmed in polylactide-containing dressings, which have been shown to attenuate oxidative stress and hypermetabolism in prospective and randomized studies. Studies on curcumin, N-acetyl cystein, quercetin, and chitosan have recently been published, showing initial evidence of efficacy in accelerating wound healing [
209]. Furthermore, nanofibers as an appropriate system for delivery [
47] and polydopamine nanoparticles with incorporated oxidized dextran/chitosan hybrid hydrogels [
96] were demonstrated. The effects of these dressings appear to extend beyond those of occlusive wound healing and early surgery as sources of reduced oxidative stress and antioxidative effects.
Positive indicators for the effect of antioxidant dressings may be the promotion of wound healing, a reduced grafting rate in partial-thickness burns, and reduced hypertrophic scarring [
207,
210]. Additionally, antioxidant membranes may even reduce dermal inflammation after wound closure, preceding hypertrophic scarring.
Findings, such as shorter healing time, improved telomere length, and a reduced need for split-skin grafting in partial-thickness burns in clinical randomized and cohort studies, supported enhanced skin quality but still need confirmation in prospective studies with a higher number of patients. Nevertheless, these clinical effects might motivate us to proceed, enhance this kind of treatment, and open new research and development in a hitherto largely neglected aspect. Despite this, the positive outcomes observed in these studies should motivate further research and development in this area, as it may lead to improved patient treatments. There are still many challenges to be addressed, such as the lack of prospective and randomized clinical studies with a sufficient number of participants to evaluate the effects of wound dressings on oxidative stress, edema reduction, clinical stabilization, ventilation time, or the need for analgesics, as well as their application in radiation burns. However, case reports and observational studies suggest promise and should encourage and motivate further research in this area.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methods, and review: H.L.H., M.D., L.P.K., M.R., F.S., and B.H. Writing, original draft preparation, review, and editing: H.L.H., F.S., S.P.N., H.L, D.B., M.R., S.R., and M.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are publicly available, as cited in the references.
Acknowledgments
Editing costs were paid by Polymedics Innovations GmbH, Denkendorf. The company had no role in the study’s design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, manuscript writing, or the decision to publish the results.
Conflicts of Interest
Herbert Haller was and Matthias Rapp is a consultant for Polymedics Innovations GmbH for training and teaching and for other companies not dealing with the paper's topic. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
- Li, Y.R.; Trush, M. Defining ROS in Biology and Medicine. React. Oxyg. Species 2016, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomberg, M. On the Preparation of Triphenylchlormethane. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1900, 22, 752–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Meo, S.; Venditti, P. Evolution of the Knowledge of Free Radicals and Other Oxidants. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 9829176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Meo, S.; Reed, T.T.; Venditti, P.; Victor, V.M. Role of ROS and RNS Sources in Physiological and Path Ological Conditions. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim Korkmaz, H.; Ulrich, M.M.W.W.; van Wieringen, W.N.; Vlig, M.; Emmens, R.W.; Meyer, K.W.; Sinnige, P.; Krijnen, P.A.J.J.; Van Zuijlen, P.P.M.M.; Niessen, H.W.M.M.; et al. The Local and Systemic Inflammatory Response in a Pig Burn Wound Model With a Pivotal Role for Complement. J. Burn Care Res. 2017, 38, e796–e806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Y.; Chen, H. New Insights in Intestinal Oxidative Stress Damage and the Health Intervention Effects of Nutrients: A Review. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 75, 104248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, M.M.; Revelly, J.P.; Carron, P.N.; Bernath, M.A. Surréanimation Uquidienne Pré et Intrahospitalière Des Patients Brûlés: Fréquente et Néfaste. Rev. Med. Suisse 2010, 6, 2410–2415. [Google Scholar]
- Jedlicka, J.; Becker, B.F.; Chappell, D. Endothelial Glycocalyx. Crit. Care Clin. 2020, 36, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchimido, R.; Schmidt, E.P.; Shapiro, N.I. The Glycocalyx: A Novel Diagnostic and Therapeutic Target in Sepsis. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manon-Jensen, T.; Multhaupt, H.A.B.; Couchman, J.R. Mapping of Matrix Metalloproteinase Cleavage Sites on Syndecan-1 and Syndecan-4 Ectodomains. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 2320–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potje, S.R.; Paula, T.D.-C.; Paulo, M.; Bendhack, L.M. The Role of Glycocalyx and Caveolae in Vascular Homeostasis and Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2021, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillenwater, J.; Garner, W. Acute Fluid Management of Large Burns. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2017, 44, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruitt, B. Protection from Excessive Resuscitation: Pushing the Pendulum Back. J. Trauma - Inj. Infect. Crit. Care 2000, 49, 567–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daryani, R.; LaLonde, C.; Zhu, D.; Weidner, M.; Knox, J.; Demling, R.H. Effect of Endotoxin and a Burn Injury on Lung and Liver Lipid Peroxidation and Catalase Activity. J. Trauma 1990, 30, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.M.; Bird, M.D.; Zahs, A.; Deburghgraeve, C.; Posnik, B.; Davis, C.S.; Kovacs, E.J. Pulmonary Inflammation after Ethanol Exposure and Burn Injury Is Attenuated in the Absence of IL-6. Alcohol 2013, 47, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Herndon, D.N.; Szabo, C. Oxandrolone Protects against the Development of Multiorgan Failure, Modulates the Systemic Inflammatory Response and Promotes Wound Healing during Burn Injury. Burns 2019, 45, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillory, A.N.; Clayton, R.P.; Herndon, D.N.; Finnerty, C.C. Cardiovascular Dysfunction Following Burn Injury: What We Have Learned from Rat and Mouse Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magder, S. Volume and Its Relationship to Cardiac Output and Venous Return. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballard-Croft, C.; Carlson, D.; Maass, D.L.; Horton, J.W. Burn Trauma Alters Calcium Transporter Protein Expression in the Heart. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 97, 1470–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielson, C.B.; Duethman, N.C.; Howard, J.M.; Moncure, M.; Wood, J.G. Burns: Pathophysiology of Systemic Complications and Current Management. J. Burn Care Res. 2017, 38, e469–e481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.; Neyra, J.A.; Madni, T.; Imran, J.; Phelan, H.; Arnoldo, B.; Wolf, S.E. Acute Kidney Injury after Burn. Burns 2017, 43, 898–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.A.; Park, C.W. Catalytic Antioxidants in the Kidney. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desforges, J.F.; Better, O.S.; Stein, J.H. Early Management of Shock and Prophylaxis of Acute Renal Failure in Traumatic Rhabdomyolysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 322, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlakou, P.; Liakopoulos, V.; Eleftheriadis, T.; Mitsis, M.; Dounousi, E. Oxidative Stress and Acute Kidney Injury in Critical Illness: Pathophysiologic Mechanisms - Biomarkers - Interventions, and Future Perspectives. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Ramnath, R.D.; Foster, R.R.; Wylie, E.C.; Fridén, V.; Dasgupta, I.; Haraldsson, B.; Welsh, G.I.; Mathieson, P.W.; Satchell, S.C. Reactive Oxygen Species Modulate the Barrier Function of the Human Glomerular Endothelial Glycocalyx. PLoS One 2013, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, C.; Herndon, D.N.; Bhattarai, N.; Ogunbileje, J.O.; Szczesny, B.; Szabo, C.; Toliver-Kinsky, T.; Sidossis, L.S. Differential Acute and Chronic Effects of Burn Trauma on Murine Skeletal Muscle Bioenergetics. Burns 2016, 42, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunbileje, J.O.; Herndon, D.N.; Murton, A.J.; Porter, C. The Role of Mitochondrial Stress in Muscle Wasting Following Severe Burn Trauma. J. Burn Care Res. 2018, 39, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, G.L. The Role of Bone Secreted Factors in Burn-Induced Muscle Cachexia. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2018, 16, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.M.; Youle, R.J. The Accumulation of Misfolded Proteins in the Mitochondrial Matrix Is Sensed by PINK1 to Induce PARK2/Parkin-Mediated Mitophagy of Polarized Mitochondria. Autophagy 2013, 9, 1750–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeschke, M.G. Postburn Hypermetabolism: Past, Present, and Future. J. Burn Care Res. 2016, 37, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehat, A.; Huebinger, R.M.; Carlson, D.L.; Zang, Q.S.; Wolf, S.E.; Song, J. Burn Serum Stimulates Myoblast Cell Death Associated with IL-6-Induced Mitochondrial Fragmentation. Shock 2017, 48, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazzini, B.; Märkl, T.; Costas, C.; Blobner, M.; Schaller, S.J.; Prowle, J. The Rate and Assessment of Muscle Wasting during Critical Illness : A Systematic Review and Meta - Analysis. Crit. Care 2023, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Long, X.; Xu, H.; Yang, X.; Guo, Q. The Changes and Prognostic Value of Liver Function in Young Adults with Severe Burn: A Retrospective Observational Study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018, 97, e13721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeschke, M.G.; Micak, R.P.; Finnerty, C.C.; Herndon, D.N. CHANGES IN LIVER FUNCTION AND SIZE AFTER A SEVERE THERMAL INJURY. Shock 2007, 28, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullahi, A.; Samadi, O.; Auger, C.; Kanagalingam, T.; Boehning, D.; Bi, S.; Jeschke, M.G. Browning of White Adipose Tissue after a Burn Injury Promotes Hepatic Steatosis and Dysfunction. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shupp, J.W.; Nasabzadeh, T.J.; Rosenthal, D.S.; Jordan, M.H.; Fidler, P.; Jeng, J.C. A Review of the Local Pathophysiologic Bases of Burn Wound Progression. J. Burn Care Res. 2010, 31, 849–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanier, S.T.; McClain, S.A.; Lin, F.; Singer, A.J.; Clark, R.A.F. Spatiotemporal Progression of Cell Death in the Zone of Ischemia Surrounding Burns. Wound Repair Regen. 2011, 19, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravante, G.; Palmieri, M.B.; Esposito, G.; Delogu, D.; Santeusanio, G.; Filingeri, V.; Montone, A. Apoptotic Death in Deep Partial Thickness Burns vs. Normal Skin of Burned Patients. J. Surg. Res. 2007, 141, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, C.Y.; Wu, Q.J.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, D.D.; Luo, F.; Zhao, X. .. .; Wei, Y.Q.; Qian, Z.Y. A Biodegradable Hydrogel System Containing Curcumin Encapsulated in Micelles for Cutaneous Wound Healing. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 6377–6387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Wu, H.; Guo, B.; Dong, R.; Qiu, Y.; Ma, P.X. Antibacterial Anti-Oxidant Electroactive Injectable Hydrogel as Self-Healing Wound Dressing with Hemostasis and Adhesiveness for Cutaneous Wound Healing. Biomaterials 2017, 122, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gürünlüoğlu, K.; Demircan, M.; Koç, A.; Koçbıyık, A.; Taşçı, A.; Durmuş, K.; Gürünlüoğlu, S.; Gözükara Bağ, H. The Effects of Different Burn Dressings on Length of Telomere and Expression of Telomerase in Children With Thermal Burns. J. Burn Care Res. 2019, 40, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaaba, N.F.; Jaafar, M. A Review on Degradation Mechanisms of Polylactic Acid: Hydrolytic, Photodegradative, Microbial, and Enzymatic Degradation. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2020, 60, 2061–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Roche, J.; Walther, I.; Leonow, W.; Hage, A.; Eberhardt, M.; Fischer, M.; Reeh, P.W.; Sauer, S.; Leffler, A. Lactate Is a Potent Inhibitor of the Capsaicin Receptor TRPV1. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annesley, T.M.; Till, G.O.; Ward, P.A. Cutaneous Thermal Burn and Oxidant-Mediated Acute Lung Injury: Appearance in Serum of Lung-Related LDH Isoenzyme. J. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1985, 1, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groussard, C.; Morel, I.; Chevanne, M.; Monnier, M.; Cillard, J.; Delamarche, A. Free Radical Scavenging and Antioxidant Effects of Lactate Ion: An in Vitro Study. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 89, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Meo, S.; Reed, T.T.; Venditti, P.; Victor, V.M. Role of ROS and RNS Sources in Physiological and Pathological Conditions. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parihar, A.; Parihar, M.S.; Milner, S.; Bhat, S. Oxidative Stress and Anti-Oxidative Mobilization in Burn Injury. Burns 2008, 34, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, R. Keloid and Hypertrophic Scars Are the Result of Chronic Inflammation in the Reticular Dermis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Gao, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; He, T.; Guan, H.; Zheng, Z.; et al. Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells Suppress Hypertrophic Scar Fibrosis via the P38/MAPK Signaling Pathway. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2016, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, J.; Sun, J.; Chen, M. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Hypertrophic Scar by Inhibiting Bioactivity and Inducing Apoptosis in Hypertrophic Scar Fibroblasts. Cells 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Felice, B.; Garbi, C.; Santoriello, M.; Santillo, A.; Wilson, R.R. Differential Apoptosis Markers in Human Keloids and Hypertrophic Scars Fibroblasts. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2009, 327, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carney, B.C.; Chen, J.H.; Kent, R.A.; Rummani, M.; Alkhalil, A.; Moffatt, L.T.; Rosenthal, D.S.; Shupp, J.W. Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging Potential Contributes to Hypertrophic Scar Formation. J. Surg. Res. 2019, 244, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirakami, E.; Yamakawa, S.; Hayashida, K. Strategies to Prevent Hypertrophic Scar Formation: A Review of Therapeutic Interventions Based on Molecular Evidence. Burn. Trauma 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laloze, J.; Fiévet, L.; Desmoulière, A. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Regenerative Medicine: State of Play, Current Clinical Trials, and Future Prospects. Adv. wound care 2021, 10, 24–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Gioia, M.; Spreafico, R.; Springstead, J.R.; Mendelson, M.M.; Joehanes, R.; Levy, D.; Zanoni, I. Endogenous Oxidized Phospholipids Reprogram Cellular Metabolism and Boost Hyperinflammation. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, H.; Ikeda, K.; Shinozaki, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Ikegami, Y.; Fu, M.; Nakamura, T.; Yasuhara, S.; Yu, Y.-M.; Martyn, J.A.J.; et al. Burn-Induced Muscle Metabolic Derangements and Mitochondrial Dysfunction Are Associated with Activation of HIF-1α and MTORC1: Role of Protein Farnesylation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlanga-Acosta, J.; Iglesias-Marichal, I.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, N.; Mendoza-Marí, Y.; García-Ojalvo, A.; Fernández-Mayola, M.; Playford, R.J. Review: Insulin Resistance and Mitochondrial Dysfunction Following Severe Burn Injury. Peptides 2020, 126, 170269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auger, C.; Knuth, C.M.; Abdullahi, A.; Samadi, O.; Parousis, A.; Jeschke, M.G. Metformin Prevents the Pathological Browning of Subcutaneous White Adipose Tissue. Mol. Metab. 2019, 29, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auger, C.; Samadi, O.; Jeschke, M.G. The Biochemical Alterations Underlying Post-Burn Hypermetabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta - Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 2633–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lismont; Revenco; Fransen Peroxisomal Hydrogen Peroxide Metabolism and Signaling in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3673. [CrossRef]
- Philp, A.; Macdonald, A.L.; Watt, P.W. Lactate--a Signal Coordinating Cell and Systemic Function. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 4561–4575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, G.A. The Science and Translation of Lactate Shuttle Theory. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 757–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, G.A.; Arevalo, J.A.; Osmond, A.D.; Leija, R.G.; Curl, C.C.; Tovar, A.P. Lactate in Contemporary Biology: A Phoenix Risen. J. Physiol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, A.; Yan, L.J.; Jana, C.K.; Das, N. Role of Catalase in Oxidative Stress- And Age-Associated Degenerative Diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, F.N.; Herndon, D.N.; Jeschke, M.G. The Hypermetabolic Response to Burn Injury and Interventions to Modify This Response. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2009, 36, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinaik, R.; Barayan, D.; Abdullahi, A.; Jeschke, M.G. NLRP3 Inflammasome Mediates White Adipose Tissue Browning after Burn. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2019, 317, E751–E759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatami, M.; Saidijam, M.; Yadegarzari, R.; Borzuei, S.; Soltanian, A.; Arian, M.S.; Goodarzi, M.T. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-ΓGene Expression and Its Association with Oxidative Stress in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome. Chonnam Med. J. 2016, 52, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; He, Y.; Wu, S.; Li, X.; Lin, X.; Gan, M.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Niu, L.; Zhang, S.; et al. Factors Associated with White Fat Browning: New Regulators of Lipid Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramage, L.E.; Akyol, M.; Fletcher, A.M.; Forsythe, J.; Nixon, M.; Carter, R.N.; van Beek, E.J.R.; Morton, N.M.; Walker, B.R.; Stimson, R.H. Glucocorticoids Acutely Increase Brown Adipose Tissue Activity in Humans, Revealing Species-Specific Differences in UCP-1 Regulation. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omran, F.; Christian, M. Inflammatory Signaling and Brown Fat Activity. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). 2020, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-García, I.; Milbank, E.; Diéguez, C.; López, M.; Contreras, C. Glucagon, GLP-1 and Thermogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Park, A.; Oh, K.J.; Lee, S.C.; Kim, W.K.; Bae, K.H. The Role of Adipose Tissue Mitochondria: Regulation of Mitochondrial Function for the Treatment of Metabolic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzer, J.C.J.; Tiffner, K.; Kainz, S.; Reisenegger, P.; Bernardelli de Mattos, I.; Funk, M.; Lemarchand, T.; Laaff, H.; Bal, A.; Birngruber, T.; et al. A Novel Human Ex-Vivo Burn Model and the Local Cooling Effect of a Bacterial Nanocellulose-Based Wound Dressing. Burns 2020, 46, 1924–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venereau, E.; Schiraldi, M.; Uguccioni, M.; Bianchi, M.E. HMGB1 and Leukocyte Migration during Trauma and Sterile Inflammation. Mol. Immunol. 2013, 55, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, T.; Kawai, T. Toll-Like Receptor Signaling Pathways. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierawska, O.; Małkowska, P.; Taskin, C.; Hrynkiewicz, R.; Mertowska, P.; Grywalska, E.; Korzeniowski, T.; Torres, K.; Surowiecka, A.; Niedźwiedzka-Rystwej, P.; et al. Innate Immune System Response to Burn Damage—Focus on Cytokine Alteration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeksema, M.A.; de Winther, M.P.J. Epigenetic Regulation of Monocyte and Macrophage Function. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2016, 25, 758–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzyszczyk, P.; Schloss, R.; Palmer, A.; Berthiaume, F. The Role of Macrophages in Acute and Chronic Wound Healing and Interventions to Promote Pro-Wound Healing Phenotypes. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.; Dean, J.M.; Lodhi, I.J. Peroxisomes as Cellular Adaptors to Metabolic and Environmental Stress. Trends Cell Biol. 2021, 31, 656–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platnich, J.M.; Muruve, D.A. NOD-like Receptors and Inflammasomes: A Review of Their Canonical and Non-Canonical Signaling Pathways. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 670, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, T.; Shakuo, T.; Kahiwagi, A.; Yasuda, N.; Amor, W. Ben; Morinaga, H.; Khan, M.A.; Shinozaki, S.; Kaneki, M.; Martyn, J.; et al. 44 Defects in Mitophagy Response in Burns Involved in Poor Regeneration Capacity. J. Burn Care Res. 2020, 41, S29–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobjeva, N. V; Chernyak, B. V NETosis: Molecular Mechanisms, Role in Physiology and Pathology. Biochem. 2020, 85, 1178–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Simoni, S.; Linard, D.; Hermans, E.; Knoops, B.; Goemaere, J. Mitochondrial Peroxiredoxin-5 as Potential Modulator of Mitochondria-ER Crosstalk in MPP+-Induced Cell Death. J. Neurochem. 2013, 125, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadenas, S. Mitochondrial Uncoupling, ROS Generation and Cardioprotection. Biochim. Biophys. Acta - Bioenerg. 2018, 1859, 940–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuth, C.M.; Auger, C.; Jeschke, M.G. Burn-Induced Hypermetabolism and Skeletal Muscle Dysfunction. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2021, 321, C58–C71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, P.; He, X.; Ren, H.; Wang, F. Role of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Autophagy Axis in Severe Burn-Induced Intestinal Tight Junction Barrier Dysfunction in Mice. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demine, S.; Renard, P.; Arnould, T. Mitochondrial Uncoupling: A Key Controller of Biological Processes in Physiology and Diseases. Cells 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busiello, R.A.; Savarese, S.; Lombardi, A. Mitochondrial Uncoupling Proteins and Energy Metabolism. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul-Sater, A.A.; Saïd-Sadier, N.; Ojcius, D.M.; Yilmaz, Ö.; Kelly, K.A. Inflammasomes Bridge Signaling between Pathogen Identification and the Immune Response. Drugs of Today 2009, 45, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Latz, E.; Xiao, T.S.; Stutz, A. Activation and Regulation of the Inflammasomes. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazon-Riquelme, P.; Lopez-Castejon, G. The Inflammasomes, Immune Guardians at Defence Barriers. Immunology 2018, 155, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cara, F. Peroxisomes in Host Defense. PLOS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fransen, M.; Lismont, C.; Walton, P. The Peroxisome-Mitochondria Connection: How and Why? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandalio, L.M.; Rodríguez-Serrano, M.; Romero-Puertas, M.C.; del Río Luis, A. Role of Peroxisomes as a Source of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Signaling Molecules. Subcell. Biochem. 2013, 69, 231–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cara, F.; Andreoletti, P.; Trompier, D.; Vejux, A.; Bülow, M.H.; Sellin, J.; Lizard, G.; Cherkaoui-Malki, M.; Savary, S. Peroxisomes in Immune Response and Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Bao, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Wu, H.; Gu, Z. Reduced Polydopamine Nanoparticles Incorporated Oxidized Dextran/Chitosan Hybrid Hydrogels with Enhanced Antioxidative and Antibacterial Properties for Accelerated Wound Healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 257, 117598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrell, J.G.; McLaughlin, S.W.; Tie, L.; Laurencin, C.T.; Chen, A.F.; Nair, L.S. Curcumin-Loaded Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Nanofibres: Diabetic Wound Dressing with Anti-Oxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2009, 36, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otang-Mbeng, W.; Sagbo, I.J. Cytotoxic, Cellular Antioxidant, and Antiglucuronidase Properties of the Ethanol Leaf Extract from Bulbine Asphodeloides. Sci. World J. 2021, 2021, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulcin, İ.; Alwasel, S.H. Metal Ions, Metal Chelators and Metal Chelating Assay as Antioxidant Method. Processes 2022, 10, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal, S.; Perramón, M.; Casals, G.; Oró, D.; Ribera, J.; Morales-Ruiz, M.; Casals, E.; Casado, P.; Melgar-Lesmes, P.; Fernández-Varo, G.; et al. Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles Protect against Oxidant Injury and Interfere with Oxidative Mediated Kinase Signaling in Human-Derived Hepatocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, S.; Jain, J.; Rajwade, J.M.; Paknikar, K.M. Cellular Responses Induced by Silver Nanoparticles: In Vitro Studies. Toxicol. Lett. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.; Li, Y.; Tjong, S.C. Bactericidal and Cytotoxic Properties of Silver Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Beltran, N.P.; Chaidez-Quiroz, C.; Lopez-Cuevas, O.; Ruiz-Cruz, S.; Lopez-Mata, M.A.; Del-Toro-Sanchez, C.L.; Marquez-Rios, E.; Ornelas-Paz, J.D.J. Phenolic Compounds of Potato Peel Extracts: Their Antioxidant Activity and Protection against Human Enteric Viruses. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, N.; He, L.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Lu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Niu, H. Silk Sericin Activates Mild Immune Response and Increases Antibody Production. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2021, 17, 2433–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, T.; Vaughn, A.E.; Seal, S.; Liechty, K.W.; Zgheib, C. Silk Fibroin-Based Therapeutics for Impaired Wound Healing. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, A.; Giuliano, E.A.; Sinha, N.R.; Mohan, R.R. Ocular Toxicity of Mustard Gas: A Concise Review. Toxicol. Lett. 2021, 343, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branski, L.K.; Herndon, D.N.; Celis, M.M.; Norbury, W.B.; Masters, O.E.; Jeschke, M.G. Amnion in the Treatment of Pediatric Partial-Thickness Facial Burns. Burns 2008, 34, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nessler, M.B.; Puchała, J.; Chrapusta, A.; Nessler, K.; Drukała, J. Levels of Plasma Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMP-2 and MMP-9) in Response to INTEGRA® Dermal Regeneration Template Implantation. Med. Sci. Monit. 2014, 20, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendramini, A.P.; Melo, R.F.; Marcantonio, R.A.C.; Carlos, I.Z. Biocompatibility of Acellular Dermal Matrix Graft Evaluated in Culture of Murine Macrophages. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2006, 14, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shildrick, T. Lessons from Grenfell: Poverty Propaganda, Stigma and Class Power. Sociol. Rev. 2018, 66, 783–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhall, S.; Silva, J.P.; Liu, Y.; Hrynyk, M.; Garcia, M.; Chan, A.; Lyubovitsky, J.; Neufeld, R.J.; Martins-Green, M. Release of Insulin from PLGA–Alginate Dressing Stimulates Regenerative Healing of Burn Wounds in Rats. Clin. Sci. 2015, 129, 1115–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilchez, A.; Acevedo, F.; Cea, M.; Seeger, M.; Navia, R. Applications of Electrospun Nanofibers with Antioxidant Properties: A Review. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellali, M.; Iurciuc, C.E.; Savin, C.L.; Spahis, N.; Djennad, M.; Popa, M. Hydrogel Films Based on Chitosan and Oxidized Carboxymethylcellulose Optimized for the Controlled Release of Curcumin with Applications in Treating Dermatological Conditions. Molecules 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Q.; Zhang, S.; Fu, C.; Yu, L.; Xin, P.; Gu, Z.; Cao, Z.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y. More Natural More Better: Triple Natural Anti-Oxidant Puerarin/Ferulic Acid/Polydopamine Incorporated Hydrogel for Wound Healing. J. Nanobiotechnology 2021, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Wang, W.; Xu, X.; Nie, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gould, O.E.C.; Ma, N.; Lendlein, A. Biofunction of Polydopamine Coating in Stem Cell Culture. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 10748–10759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiakos, G.; Kuang, Z.; Lo, E. Improved Skin Regeneration with Acellular Fish Skin Grafts. Eng. Regen. 2020, 1, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.; Bannenberg, G.; Rice, H.B.; Schutt, E.; Mackay, D. Oxidation in EPA- and DHA-Rich Oils: An Overview. Lipid Technol. 2016, 28, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürünlüoğlu, K.; Demircan, M.; Taşçı, A.; Üremiş, M.M.; Türköz, Y.; Bağ, H.G.; Akıncı, A.; Bayrakçı, E.; Gürünlüoglu, K.; Demircan, M.; et al. The Effects of Two Different Burn Dressings on Serum Oxidative Stress Indicators in Children with Partial Burn. J. Burn Care Res. 2019, 40, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demircan, M. Impaction of the Polylactic Membrane or Hydrofiber with Silver Dressings on the Interleukin-6, Tumor Necrosis Factor-α, Transforming Growth Factor-3 Levels in the Blood and Tissues of Pediatric Patients with Burns. Turkish J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2020, 27, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, C.; Decker, E. Metal Chelators as Antioxidants. Available online: https://lipidlibrary.aocs.org/chemistry/physics/lipid-oxidation-and-antioxidants/metal-chelators-as-antioxidants (accessed on 31 January 2023).
- Ayadi, A. El; Wang, C.Z.; Zhang, M.; Wetzel, M.; Prasai, A.; Finnerty, C.C.; Enkhbaatar, P.; Herndon, D.N.; Ansari, N.H. Metal Chelation Reduces Skin Epithelial Inflammation and Rescues Epithelial Cells from Toxicity Due to Thermal Injury in a Rat Model. Burn. trauma 2020, 8. [Google Scholar]
- El Ayadi, A.; Salsbury, J.R.; Enkhbaatar, P.; Herndon, D.N.; Ansari, N.H. Metal Chelation Attenuates Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Vertical Burn Progression in a Porcine Brass Comb Burn Model. Redox Biol. 2021, 45, 102034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresgen, N.; Eckl, P. Oxidative Stress and the Homeodynamics of Iron Metabolism. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 808–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, A. Chelation Therapy Side Effects Available online: https://www.news-medical.net/health/Chelation-Therapy-Side-Effects.aspx.
- Eski, M.; Ozer, F.; Firat, C.; Alhan, D.; Arslan, N.; Senturk, T.; Işik, S. Cerium Nitrate Treatment Prevents Progressive Tissue Necrosis in the Zone of Stasis Following Burn. Burns 2012, 38, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauck, A.K.; Bernlohr, D.A. Thematic Review Series: Lipotoxicity: Many Roads to Cell Dysfunction and Cell Death: Oxidative Stress and Lipotoxicity. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 1976–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholten-Jaegers, S.M.H.J.; Nieuwenhuis, M.K.; van Baar, M.E.; Niemeijer, A.S.; Hiddingh, J.; Beerthuizen, G.I.J.M. Epidemiology and Outcome of Patients With Burns Treated With Cerium Nitrate Silversulfadiazine. J. Burn Care Res. 2017, 38, e432–e442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, P.D.; Banas, D.; Durai, R.D.; Kabanov, D.; Hosnedlova, B.; Kepinska, M.; Fernandez, C.; Ruttkay-Nedecky, B.; Nguyen, H.V.; Farid, A.; et al. Silver Nanomaterials for Wound Dressing Applications. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, L.; Chen, Q.; Chen, C. Cytotoxic Potential of Silver Nanoparticles. Yonsei Med. J. 2014, 55, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AshaRani, P. V.; Low Kah Mun, G.; Hande, M.P.; Valiyaveettil, S. Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity of Silver Nanoparticles in Human Cells. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevanović, M.; Bračko, I.; Milenković, M.; Filipović, N.; Nunić, J.; Filipič, M.; Uskoković, D.P. Multifunctional PLGA Particles Containing Poly(l-Glutamic Acid)-Capped Silver Nanoparticles and Ascorbic Acid with Simultaneous Antioxidative and Prolonged Antimicrobial Activity. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, M.G.M.; Batista, J.P.; de Faria, E.H.; Ciuffi, K.J.; Rocha, L.A.; Nassar, E.J.; da Silva, J.V.L.; Oliveira, M.F.; Maia, I.A. Silver Nanoparticle Incorporation into Flexible Polyamide 12 Membranes. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2022, 102, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Yuan, Y.; Ding, L.; Li, J.; Jia, J.; Li, Z.; He, D.; Yu, Y. Multifunctional Chitosan/Gelatin@tannic Acid Cryogels Decorated with in Situ Reduced Silver Nanoparticles for Wound Healing. Burn. Trauma 2022, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, D.A.N.; Saladini, M.S.; Viroel, F.J.M.; Dini, M.M.J.; Pickler, T.B.; Amaral Filho, J.; Santos, C.A. Dos; Hanai-Yoshida, V.M.; Grotto, D.; Gerenutti, M.; et al. Are Silver Nanoparticles Useful for Treating Second-Degree Burns? An Experimental Study in Rats. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 11, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flieger, J.; Franus, W.; Panek, R.; Szymańska-Chargot, M.; Flieger, W.; Flieger, M.; Kołodziej, P. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Natural Extracts with Proven Antioxidant Activity. Molecules 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshari, A.K.; Srivastava, R.; Singh, P.; Yadav, V.B.; Nath, G. Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Cestrum Nocturnum. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2020, 11, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, J.L.; Tajkarimi, M.; Cunningham, Q.; Campbell, A.; Nonga, H.; Harrison, S.H.; Barrick, J.E. Rapid Evolution of Silver Nanoparticle Resistance in Escherichia Coli. Front. Genet. 2015, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subrahmanyam, M. Honey Dressing versus Boiled Potato Peel in the Treatment of Burns: A Prospective Randomized Study. Burns 1996, 22, 491–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nara, K.; Miyoshi, T.; Honma, T.; Koga, H. Antioxidative Activity of Bound-Form Phenolics in Potato Peel. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 1489–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitter, C.C.; Erickson, T.B. Management of Burn Injuries in the Wilderness: Lessons from Low-Resource Settings. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2016, 27, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manosroi, A.; Boonpisuttinant, K.; Winitchai, S.; Manosroi, W.; Manosroi, J. Free Radical Scavenging and Tyrosinase Inhibition Activity of Oils and Sericin Extracted from Thai Native Silkworms ( Bombyx Mori ). Pharm. Biol. 2010, 48, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.P.; Mandal, B.B. Antioxidant Potential of Mulberry and Non-Mulberry Silk Sericin and Its Implications in Biomedicine. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 108, 803–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosena, A.; Koobkokkruad, T.; Eaknai, W.; Bunwatcharaphansakun, P.; Maniratanachote, R.; Aueviriyavit, S. Protective Effect of Thai Silk Extracts on Drug-Induced Phototoxicity in Human Epidermal A431 Cells and a Reconstructed Human Epidermis Model. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 188, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.P.; Mandal, B.B. Silk Sericin Induced Pro-Oxidative Stress Leads to Apoptosis in Human Cancer Cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 123, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Shen, R.; Tan, J.; Chen, X.; Pan, Y.; Ruan, S.; Zhang, F.; Lin, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. The Study of Inhibiting Systematic Inflammatory Response Syndrome by Applying Xenogenic (Porcine) Acellular Dermal Matrix on Second-Degree Burns. Burns 2007, 33, 477–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühl, D.; Woth, G.; Drenkovics, L.; Varga, A.; Ghosh, S.; Csontos, C.; Bogár, L.; Wéber, G.; Lantos, J. Comparison of Oxidative Stress & Leukocyte Activation in Patients with Severe Sepsis & Burn Injury. Indian J. Med. Res. 2011, 134, 69–78. [Google Scholar]
- Alipour, R.; Motedayyen, H.; Sereshki, N.; Rafiee, M.; Alsahebfosul, F.; Pourazar, A. Human Amniotic Epithelial Cells Affect the Functions of Neutrophils. Int. J. Stem Cells 2020, 13, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalouchi, F.; Falak, R.; Bakhshesh, M.; Sharifiaghdam, Z.; Azizi, Y.; Aboutaleb, N. Human Amniotic Membrane Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Conditioned Medium Reduces Inflammatory Factors and Fibrosis in Ovalbumin-Induced Asthma in Mice. Exp. Physiol. 2021, 106, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockington, D.; Agarwal, P.; Young, D.; Caslake, M.; Ramaesh, K. Antioxidant Properties of Amniotic Membrane: Novel Observations from a Pilot Study. Can. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 49, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazão, L.P.; Vieira de Castro, J.; Nogueira-Silva, C.; Neves, N.M. Decellularized Human Chorion Membrane as a Novel Biomaterial for Tissue Regeneration. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, M.; Mendes, C.; Bittencourt, J.V.S. ;... Effects of the Application of Decellularized Amniotic Membrane Solubilized with Hyaluronic Acid on Wound Healing. Ann. Biomed. …, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schriek, K.; Ott, H.; Sinnig, M. Paradigm Shift in Treatment Strategies for Second-Degree Burns Using a Caprolactone Dressing (Suprathel®)? A 15-Year Pediatric Burn Center Experience in 2084 Patients. Eur. Burn J. 2021, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, T.A.J.; Rocha, T.L.; Franchi, L.P. Detection of DNA Damage Induced by Cerium Dioxide Nanoparticles: From Models to Molecular Mechanism Activated. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1048, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifi, M.A.; Seal, S.; Godugu, C. Nanoceria, the Versatile Nanoparticles: Promising Biomedical Applications. J. Control. Release 2021, 338, 164–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, P.; Ong, C.; Bay, B.H.; Baeg, G.H. Nanotoxicity: An Interplay of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Cell Death. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 1163–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Medrano, J.R.; Quiñones-Muñoz, T.A.; Arce-Ortíz, A.; Torruco-Uco, J.G.; Hernández-Martínez, R.; Lizardi-Jiménez, M.A.; Varela-Santos, E. Antioxidant Activity of Collagen Extracts Obtained from the Skin and Gills of Oreochromis Sp. J. Med. Food 2019, 22, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, M.; Ojeh, N.; Livingstone, R.; Price, R.; Navsaria, H. Survival of Apligraf in Acute Human Wounds. Tissue Eng. 2004, 10, 1180–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniaci, A.; Iannella, G.; Cocuzza, S.; Vicini, C.; Magliulo, G.; Ferlito, S.; Cammaroto, G.; Meccariello, G.; De Vito, A.; Nicolai, A.; et al. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Biomarker Expression in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, M.S.; Berret, J.F.; Singh, S.; Vinu, A.; Karakoti, A.S. Redox Active Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles: Current Status and Burning Issues. Small 2021, 17, 2102342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luís, Â.; Duarte, A.; Gominho, J.; Domingues, F.; Duarte, A.P. Chemical Composition, Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Anti-Quorum Sensing Activities of Eucalyptus Globulus and Eucalyptus Radiata Essential Oils. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 79, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Han, S.; Gu, Z.; Wu, J. Advances and Impact of Antioxidant Hydrogel in Chronic Wound Healing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 9, 1901502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comino-Sanz, I.M.; López-Franco, M.D.; Castro, B. ;... The Role of Antioxidants on Wound Healing: A Review of the Current Evidence. J. Clin. …, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- O’Connor, N.A.; Syed, A.; Wong, M.; Hicks, J.; Nunez, G.; Jitianu, A.; Siler, Z.; Peterson, M. Polydopamine Antioxidant Hydrogels for Wound Healing Applications. Gels 2020, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, R.; Erawati, T.; Fauziah, F.; Yuniarti, W.M. Formulation, Physical Characterization and Wound Healing Activity Evaluation of Carboxymethyl Chitosan-Curcumin Carbomer-Based Hydrogel. Int. J. Drug Deliv. Technol. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahimirad, S.; Abtahi, H.; Satei, P.; Ghaznavi-Rad, E.; Moslehi, M.; Ganji, A. Wound Healing Performance of PCL/Chitosan Based Electrospun Nanofiber Electrosprayed with Curcumin Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, S.; Hina, M.; Iqbal, J.; Rajpar, A.H.; Mujtaba, M.A.; Alghamdi, N.A.; Wageh, S.; Ramesh, K.; Ramesh, S. Fundamental Concepts of Hydrogels: Synthesis, Properties, and Their Applications. Polymers (Basel). 2020, 12, 2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ou, Q.; Xin, P.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J. Polydopamine/Puerarin Nanoparticle-Incorporated Hybrid Hydrogels for Enhanced Wound Healing. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 4230–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ternullo, S.; Schulte Werning, L.V.; Holsæter, A.M.; Škalko-Basnet, N. Curcumin-In-Deformable Liposomes-In-Chitosan-Hydrogel as a Novel Wound Dressing. Pharmaceutics 2019, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendis, E.; Rajapakse, N.; Byun, H.G.; Kim, S.K. Investigation of Jumbo Squid (Dosidicus Gigas) Skin Gelatin Peptides for Their in Vitro Antioxidant Effects. Life Sci. 2005, 77, 2166–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.-B.; He, T.-P.; Li, H.-B.; Tang, H.-W.; Xia, E.-Q. The Structure-Activity Relationship of the Antioxidant Peptides from Natural Proteins. Molecules 2016, 21, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pampanin, D.M.; Haarr, M.B.; Sydnes, M.O. Natural Peptides with Antioxidant Activity from Atlantic Cod and Atlantic Salmon Residual Material. Int. J. Appl. Res. Nat. Prod. 2016, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, N.; Xue, Y.; Ding, T.; Liu, X.; Mo, X.; Sun, J. Electrospun Tilapia Collagen Nanofibers Accelerating Wound Healing via Inducing Keratinocytes Proliferation and Differentiation. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2016, 143, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.C.; Yang, F.L.; Subeq, Y.M.; Tien, C.C.; Chao, Y.F.C.; Lee, R.P. Lipid Emulsion Enriched in Omega-3 PUFA Accelerates Wound Healing: A Placebo-Controlled Animal Study. World J. Surg. 2018, 42, 1714–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, B.A.; Lima Júnior, E.M.; De Moraes Filho, M.O.; Fechine, F.V.; De Moraes, M.E.A.; Silva Júnior, F.R.; Do Nascimento Soares, M.F.A.; Rocha, M.B.S. Use of Tilapia Skin as a Xenograft for Pediatric Burn Treatment: A Case Report. J. Burn Care Res. 2019, 40, 714–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima Júnior, E.M.; Moraes Filho, M.O. De; Forte, A.J.; Costa, B.A.; Fechine, F.V.; Alves, A.P.N.N.; Moraes, M.E.A. De; Rocha, M.B.S.; Silva Júnior, F.R.; Soares, M.F.A.D.N.; et al. Pediatric Burn Treatment Using Tilapia Skin as a Xenograft for Superficial Partial-Thickness Wounds: A Pilot Study. J. Burn Care Res. 2020, 41, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masand, P.; O’Gorman, C.; Mandel, F.S. Clinical Global Impression of Improvement (CGI-I). Schizophr. Res. 2010, 1, 125–126. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.K.; Polanco, T.O.; Lantis, J.C. A Prospective, Postmarket, Compassionate Clinical Evaluation of a Novel Acellular Fish-Skin Graft Which Contains Omega-3 Fatty Acids for the Closure of Hard-to-Heal Lower Extremity Chronic Ulcers. Wounds 2016, 28, 112–118. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, J.; Yoon, D.; Lee, H.; Lee, J.; Jo, S.; Kym, D.; Yim, H.; Hur, J.; Chun, W.; Kim, G.; et al. Wound Healing Ability of Acellular Fish Skin and Bovine Collagen Grafts for Split-Thickness Donor Sites in Burn Patients: Characterization of Acellular Grafts and Clinical Application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 205, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsner, R.S.; Margolis, D.J.; Baldursson, B.T.; Petursdottir, K.; Davidsson, O.B.; Weir, D.; Lantis, J.C. Fish Skin Grafts Compared to Human Amnion/Chorion Membrane Allografts: A Double-Blind, Prospective, Randomized Clinical Trial of Acute Wound Healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2020, 28, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, R.; Saathoff, E.C.; Larson, D.A.; Wall, J.T.; Wienandt, N.A.; Magnusson, S.; Kjartansson, H.; Natesan, S.; Christy, R.J. Accelerated Wound Closure of Deep Partial Thickness Burns with Acellular Fish Skin Graft. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallner, C.; Holtermann, J.; Drysch, M.; Schmidt, S.; Reinkemeier, F.; Wagner, J.M.; Dadras, M.; Sogorski, A.; Houschyar, K.S.; Becerikli, M.; et al. The Use of Intact Fish Skin as a Novel Treatment Method for Deep Dermal Burns Following Enzymatic Debridement: A Retrospective Case-Control Study. Eur. Burn J. 2022, 3, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Kuriyama, T.; Nakagawara, R.; Aihara, M.; Hamada-Sato, N. Allergy to Fish Collagen: Thermostability of Collagen and IgE Reactivity of Patients’ Sera with Extracts of 11 Species of Bony and Cartilaginous Fish. Allergol. Int. 2016, 65, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicherer, S.H.; Muñoz-Furlong, A.; Sampson, H.A. Prevalence of Seafood Allergy in the United States Determined by a Random Telephone Survey. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 114, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ring, A.; Goertz, O.; Steinau, H.; Steinstraesser, L.; Langer, S. Angiogenic Response to Degradable Lacto-Capromer Terpolymer Dermis Substitutes. Available online: https://www.egms.de/static/en/meetings/dgch2009/09dgch161.shtmlshtml (accessed on 14 August 2021).
- Ring, A.; Langer, S.; Homann, H.H.; Kuhnen, C.; Schmitz, I.; Steinau, H.U.; Drücke, D. Analysis of Neovascularization of PEGT/PBT-Copolymer Dermis Substitutes in Balb/c-Mice. Burns 2006, 32, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, T.K.; Aslam, R.S.; Beckert, S.; Wagner, S.; Ghani, Q.P.; Hussain, M.Z.; Roy, S.; Sen, C.K. Aerobically Derived Lactate Stimulates Revascularization and Tissue Repair via Redox Mechanisms. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2007, 9, 1115–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nareika, A.; He, L.; Game, B.A.; Slate, E.H.; Sanders, J.J.; London, S.D.; Lopes-Virella, M.F.; Huang, Y. Sodium Lactate Increases LPS-Stimulated MMP and Cytokine Expression in U937 Histiocytes by Enhancing AP-1 and NF-ΚB Transcriptional Activities. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2005, 289, E534–E542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottmann, R.M.; Trawick, E.; Judge, J.L.; Wahl, L.A.; Epa, A.P.; Owens, K.M.; Thatcher, T.H.; Phipps, R.P.; Sime, P.J. Pharmacologic Inhibition of Lactate Production Prevents Myofibroblast Differentiation. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2015, 309, L1305–L1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlig, C.; Rapp, M.; Hartmann, B.; Hierlemann, H.; Planck, H.; Dittel, K.-K.K. Suprathel®-An Innovative, Resorbable Skin Substitute for the Treatment of Burn Victims. Burns 2007, 33, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, M.; Schappacher, R.; Ulrich, P.; For, C.L. First Application Results of a New Type of Synthetic Polylactide Matrix (SupraSDRM ®) for Deep Dermal to Full Thickness Burns as a Dermal Skin Substitute with Two-Step Split-Skin Covering. In Proceedings of the Abstract Book 19th European Burns Association Congress; 2022; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Machefer, G.; Groussard, C.; Vincent, S.; Zouhal, H.; Faure, H.; Cillard, J.; Radák, Z.; Gratas-Delamarche, A. Multivitamin-Mineral Supplementation Prevents Lipid Peroxidation during “the Marathon Des Sables”. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2007, 26, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herz, H.; Blake, D.R.; Grootveld, M. Multicomponent Investigations of the Hydrogen Peroxide- and Hydroxyl Radical-Scavenging Antioxidant Capacities of Biofluids: The Roles of Endogenous Pyruvate and Lactate. Free Radic. Res. 1997, 26, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 193. Rapp, M; Haller, H. SDRM, a Fully Resorbable Dermal Template as a Starter of Collagen Neogenesis and Angiogenesis for Treating Tissue Defects in Full-Thickness Burns. under Publ. 2023.
- Banakh, I.; Cheshire, P.; Rahman, M.; Carmichael, I.; Jagadeesan, P.; Cameron, N.R.; Cleland, H.; Akbarzadeh, S. A Comparative Study of Engineered Dermal Templates for Skin Wound Repair in a Mouse Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheshire, P.A.; Herson, M.R.; Cleland, H.; Akbarzadeh, S. Artificial Dermal Templates: A Comparative Study of NovoSorbTM Biodegradable Temporising Matrix (BTM) and Integra ® Dermal Regeneration Template (DRT). Burns 2016, 42, 1088–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.R.; Liang, J.Y.; Ryu, H.; Song, G.S.; Lee, D.S. Effects of Isosorbide Incorporation into Flexible Polyurethane Foams: Reversible Urethane Linkages and Antioxidant Activity. Molecules 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, K.W.; Austin, C.L.; Thompson, S.J. Treatment of a Full-Thickness Burn Injury With NovoSorb Biodegradable Temporizing Matrix and RECELL Autologous Skin Cell Suspension: A Case Series. J. Burn Care Res. 2020, 41, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J. E. Greenwood, MD, M. J. Wagstaff, M.; Greenwood, J. Changing Practice in the Surgical Management of Major Burns - Delayed Definitive Closure. In Proceedings of the ABA 2018 Posters; 2018.
- Schlottmann, F.; Obed, D.; Bingöl, A.S.; März, V.; Vogt, P.M.; Krezdorn, N. Treatment of Complex Wounds with NovoSorb® Biodegradable Temporising Matrix (BTM)-A Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Outcomes. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.H.; Brown, J.N.; Dantzer, E.J.G.; Maitz, P.K.M.; Vandervord, J.G.; Wagstaff, M.J.D.; Barker, T.M.; Cleland, H. Wound Healing and Dermal Regeneration in Severe Burn Patients Treated with NovoSorb® Biodegradable Temporising Matrix: A Prospective Clinical Study. Burns 2022, 48, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, F.T.J.; Bowser, B.H.; Crabtree, J.H. The Effect of Occlusive Dressings on the Energy Metabolism of Severely Burned Children. Ann. Surg. 1981, 193, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.C.; Mertz, P.M.; Eaglstein, W.H. Second-Degree Burn Healing: The Effect of Occlusive Dressings and a Cream. J. Surg. Res. 1990, 48, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabaev, B.; Shakirov, B.; Fayazov, A. Influence of Skin Grafts on Oxidation-Reduction Processes in Elderly and Old People with Deep Burns. Indian J. Burn. 2013, 21, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branski, L.K.; Herndon, D.N.; Pereira, C.; Mlcak, R.P.; Celis, M.M.; Lee, J.O.; Sanford, A.P.; Norbury, W.B.; Zhang, X.J.; Jeschke, M.G. Longitudinal Assessment of Integra in Primary Burn Management: A Randomized Pediatric Clinical Trial. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 35, 2615–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, M.; Selig, H.F.; Lumenta, D.B.; Kamolz, L.P.; Mittlböck, M.; Frey, M. The Use of Suprathel(®) in Deep Dermal Burns: First Results of a Prospective Study. Burns 2012, 38, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galati, V.; Vonthein, R.; Stang, F.; Mailaender, P.; Kisch, T. Split Thickness Skin Graft versus Application of the Temporary Skin Substitute Suprathel in the Treatment of Deep Dermal Hand Burns: A Retrospective Cohort Study of Scar Elasticity and Perfusion. Int. J. Burns Trauma 2021, 11, 312–320. [Google Scholar]
- Blome-Eberwein, S.A.; Amani, H.; Lozano, D.D.; Gogal, C.; Boorse, D.; Pagella, P. A Bio-Degradable Synthetic Membrane to Treat Superficial and Deep Second Degree Burn Wounds in Adults and Children – 4 Year Experience. Burns 2021, 47, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blome-Eberwein, S.A.A.; Amani, H.; Lozano, D.D.; Boorse, D.; Pagella, P.; S. A., B.-E.; H., A.; D.D., L.; D., B.; P., P.; et al. First Results from Application of an Absorbable Synthetic Membrane to Superficial and Deep Second Degree Wounds. J. Burn Care Res. 2014, 35, S156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comino-Sanz, I.M.; López-Franco, M.D.; Castro, B.; Pancorbo-Hidalgo, P.L. The Role of Antioxidants on Wound Healing: A Review of the Current Evidence. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashaan, Z.M.; Krijnen, P.; Allema, J.H.; Vloemans, A.F.; Schipper, I.B.; Breederveld, R.S. Usability and Effectiveness of Suprathel® in Partial Thickness Burns in Children. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2017, 43, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).