Submitted:
14 June 2023
Posted:
14 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Project Overview
2.1.1. Preliminary Construction Scheme Comparison
2.1.2. Mining Method Tunnel Scheme
2.2. Numerical Calculation Model and Method
3. Results
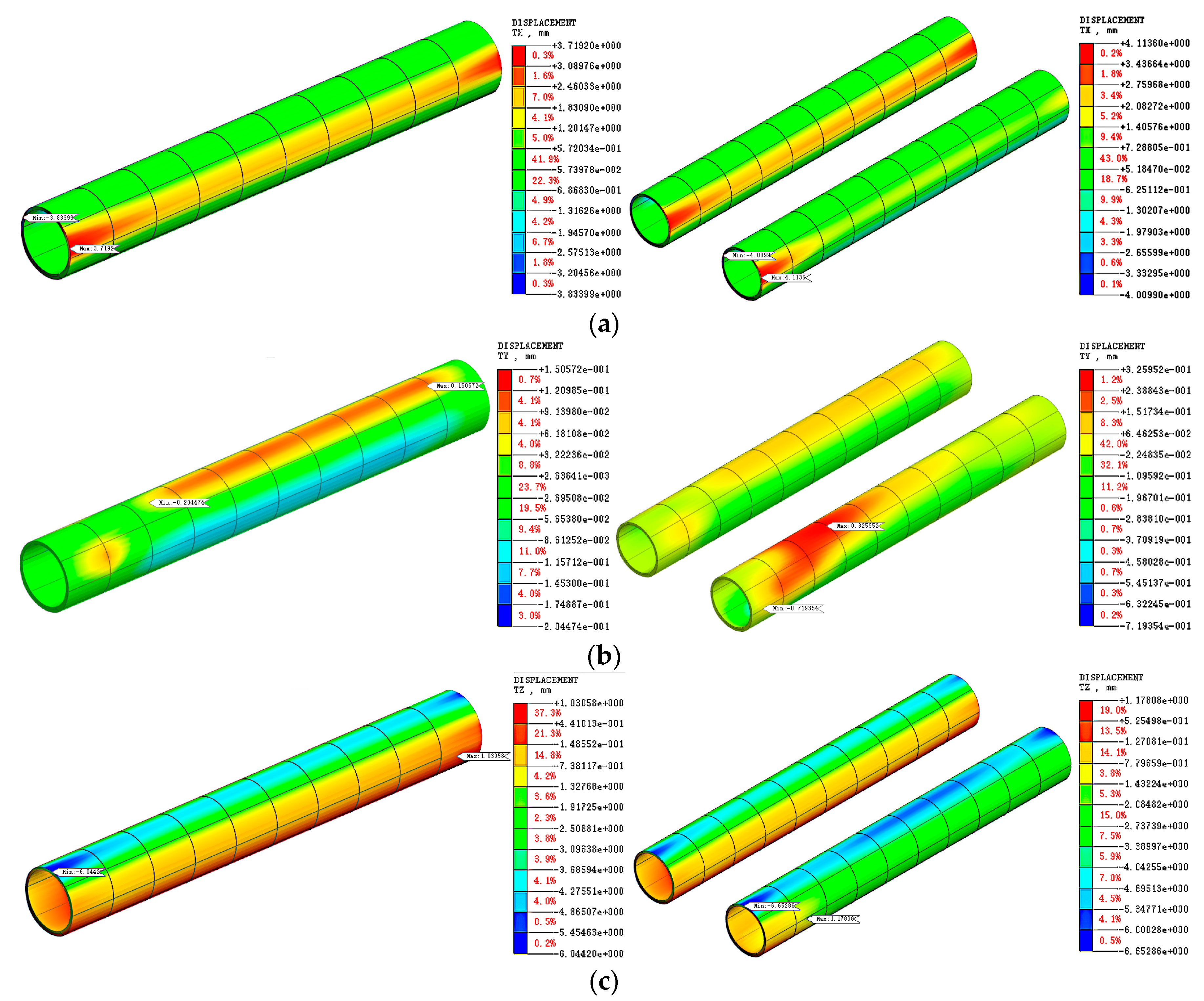
3.1. Three-Dimensional Model Mesh Simulation Results
3.1.1. Single Tunnel Single Ring Construction Process Numerical Simulation Results
3.1.2. Single and Twin Tunnel Completed Numerical Simulation Results
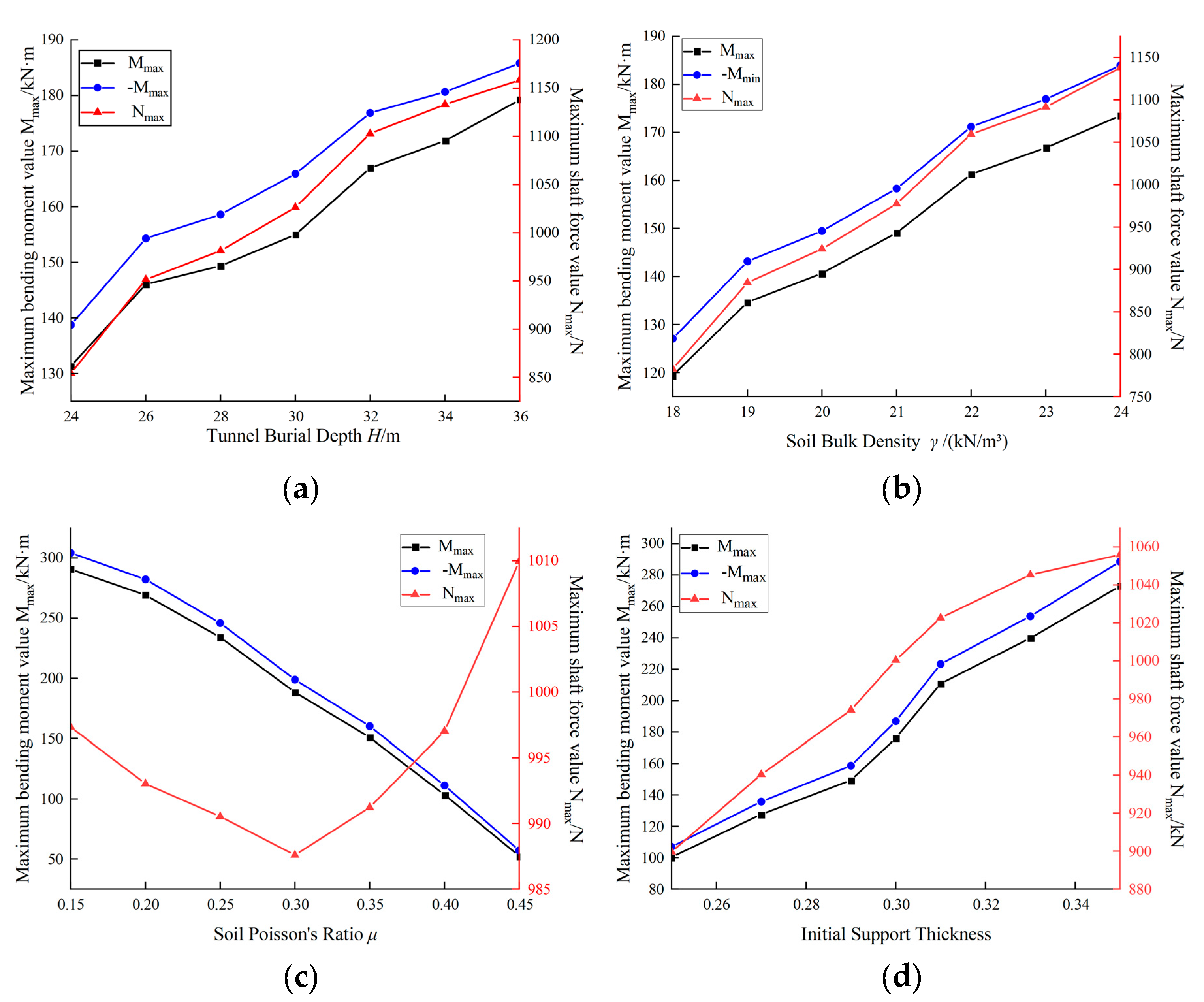
3.2. Force Characteristics Results of Initial Support
3.2.1. Impact of Tunnel Burial Depth on the Force Exerted on Initial Support
3.2.2. Impact of Soil Bulk Density on the Force Exerted on Initial Support
3.2.3. Influence of Soil Poisson's Ratio on Forces Experienced by Initial Support
3.2.4. Influence of Initial Support Thickness on Forces Experienced by Initial Support
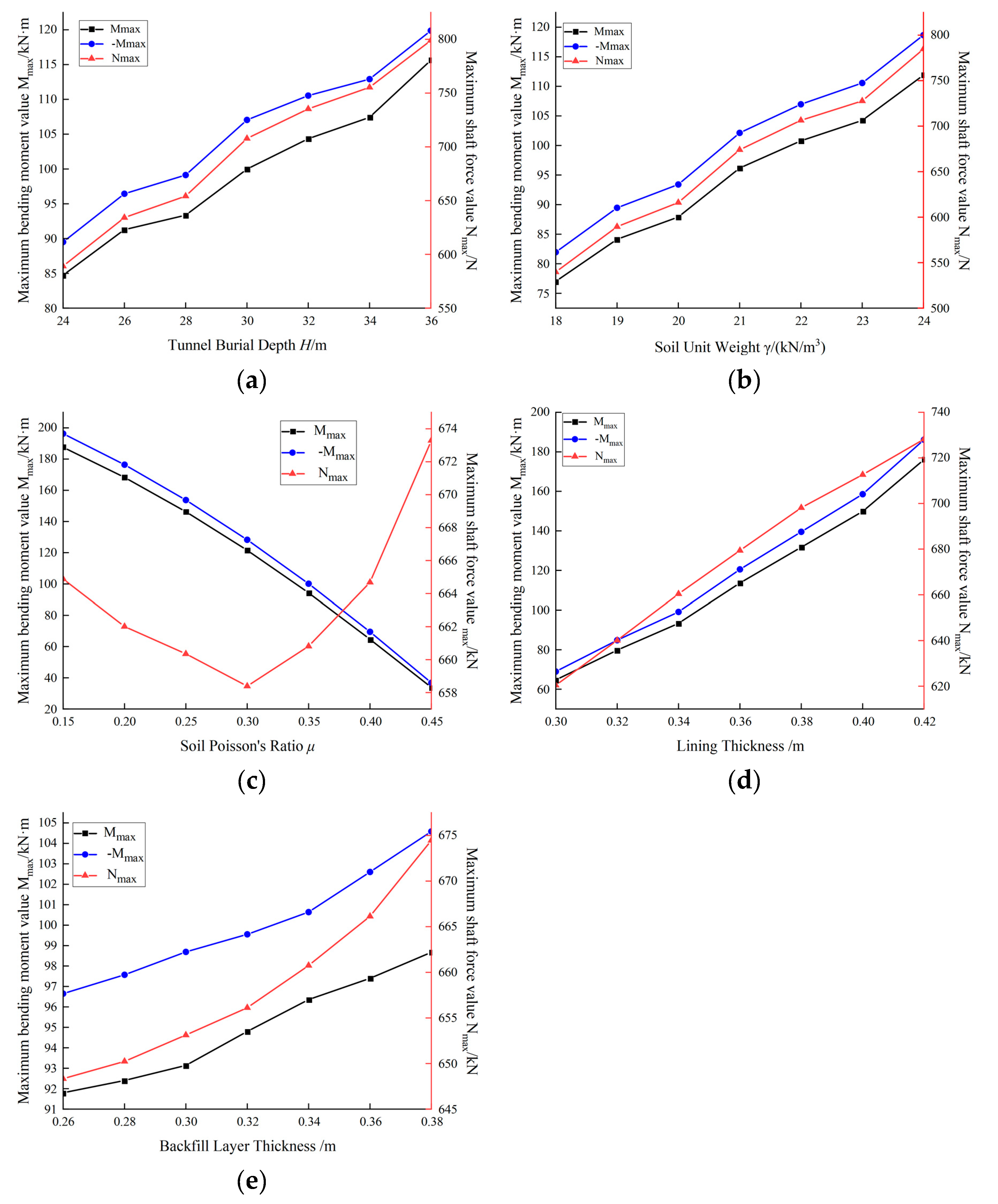
3.3. Force Characteristics Results of Segment
3.3.1. Influence of Tunnel Burial Depth on Segment Forces
3.3.2. Influence of Soil Unit Weight on Segment Forces
3.3.3. Influence of Soil Poisson's Ratio on Segment Forces
3.3.4. Influence of Lining Thickness on Segment Forces
3.3.5. Influence of Backfill Layer Thickness on Segment Forces
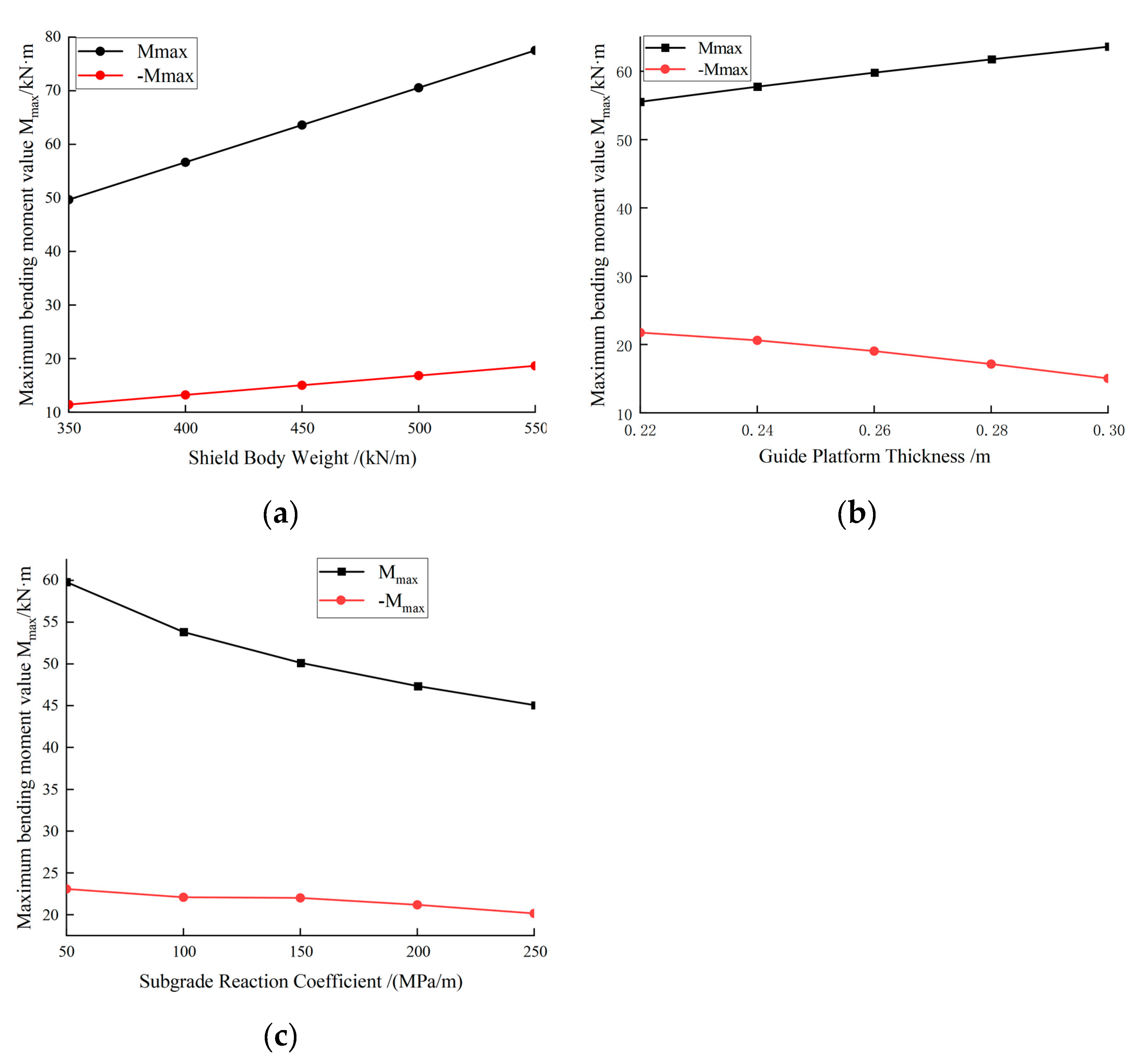
3.4. Stress Behaviour of Guide Platform
3.4.1. Influence of Shield Body Weight on Guide Platform Stress
3.4.2. Influence of Guide Platform Thickness on Guide Platform Stress
3.4.3. Influence of Subgrade Reaction Coefficient on Guide Platform Stress
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
5.1. Recommendations for Initial Support Design Criteria
5.2. Recommendations for Segments Design Criteria
5.3. Recommendations for Guiding Platform Design Criteria
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bi Jingdong, Zhao Dejie. Research on construction technology of large-diameter shield tunneling empty pushing through mining method[J]. Urban Rapid Rail Transit Research 2021, 24, 90–94. [Google Scholar]
- Erharter, G.H. , Goliasch, R. & Marcher, T. On the Effect of Shield Friction in Hard Rock TBM Excavation[J]. Rock Mech Rock Eng 2023, 56, 3077–3092. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, WY. , Lee, SW. Experimental Study on Waterproofing Performance of Segments Based on Sealant Installation Methods[J]. KSCE J Civ Eng 2023, 27, 857–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li Jianming. New technology for shield tunneling empty pushing through mining method[J]. Railway Standard Design 2011, 11, 93–96. [Google Scholar]
- Hong Kairong, Li Zhijun, Chen Kui, et al. Development of translational-pneumatic integrated device for hydraulic shield / TBM mainframe [J]. Chinese Journal of Railway Engineering 2021, 38, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- B. T. Le, T.T.T. Nguyen, S. Divall, et al. A study on large volume losses induced by EBPM tunnelling in sandy soils[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 2023, 132, 104847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie Li, Yi Gong, Shu-peng Zhao, et al. Material and processing optimization on disc cutter of tunnel boring machine for failure prevention[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis 2022, 138, 106363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenge Qiu, Xufeng Ai, Yuchao Zheng, First application of mechanized method using earth pressure balance TBM with large horseshoe-shaped cross section to loess mountain tunnel: A case study of Baicheng tunnel[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 2022, 126, 104547. [CrossRef]
- J. N. Shirlaw, T.O. Henderson, I.S. Haryono, et al.The effect of altering the slurry circulation system on TBM tunnelling in weathered Kowloon granite[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 2022, 124, 104474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao Yanwei, Weng Zicai, Zhang Zhaohuang. Application analysis of shield technology in tunnel construction [J]. Journal of China Academy of Water Resources and Hydropower Research 2020, 18, 502–507. [Google Scholar]
- M. D. Goel, Shivani Verma, Jagriti Mandal, et al.Effect of blast inside tunnel on surrounding soil mass, tunnel lining, and superstructure for varying shapes of tunnels[J]. Underground Space 2021, 6, 619–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md Shariful Islam, Magued Iskander,Three-dimensional numerical investigation of ground settlement caused by piggyback twin tunnels[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 2023, 134, 104970. [CrossRef]
- Xinghua Fang, Junsheng Yang, Xuemin Zhang, et al. Numerical modeling of open TBM tunneling in stratified rock masses using a coupled FDM-DEM method[J]. Computers and Geotechnics 2023, 156, 05251. [Google Scholar]
- Deming Xu, Yusheng Wang, Jingqi Huang, et al. Prediction of geology condition for slurry pressure balanced shield tunnel with super-large diameter by machine learning algorithms[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 2023, 131, 104852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussaine, S.M. , Mu L. Intelligent Prediction of Maximum Ground Settlement Induced by EPB Shield Tunneling Using Automated Machine Learning Techniques[J]. Mathematics 2022, 10, 4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang Chen, Kimihiro Hashiba, Zhitao Liu, et al. Spatial-temporal fusion network for maximum ground surface settlement prediction during tunnel excavation[J]. Automation in Construction 2023, 147, 104732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang Rui, Qi Taiyue, Feng Jian, et al. Analysis and application of positive inversion of tunnel construction parameters based on genetic algorithm with BP neural network[J]. Journal of Railways 2016, 38, 98–104. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan Hengfeng, Liang Rongzhu, Kang Cheng, et al. Three-dimensional refined numerical simulation study on deformation mechanism of subway shield tunnel under surface sudden loading [J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering 2023, 30, 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Lv Xilin, Zhao Yucheng, Cai Jiantao. Numerical simulation of subsidence deformation induced by shield tunnel construction disturbance in water-rich sand layer [J]. Modern Tunnel Technology 2020, 57, 104–109. [Google Scholar]
- Martin Ziegler, Arash Alimardani Lavasan, Simon Loew,Stress evolution around a TBM tunnel in swelling clay shale over four years after excavation[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 2022, 128, 104649. [CrossRef]
- Xiao-Wei Ye, Xiao-Long Zhang, Hong-Qian Zhang, et al. Prediction of lining upward movement during shield tunneling using machine learning algorithms and field monitoring data[J]. Transportation Geotechnics 2023, 41, 101002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongwei Huang, Jiaqi Chang, Dongming Zhang, et al. Machine learning-based automatic control of tunneling posture of shield machine[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering 2022, 14, 1153–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuyan Tan, Weizhong Chen, Tao Zou, et al. Real-time prediction of mechanical behaviors of underwater shield tunnel structure using machine learning method based on structural health monitoring data[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering 2023, 15, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid Elbaz, Shui-Long Shen, Annan Zhou, et al. Prediction of Disc Cutter Life During Shield Tunneling with AI via the Incorporation of a Genetic Algorithm into a GMDH-Type Neural Network[J]. Engineering 2021, 7, 238–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiangzhen Zhou, Chuang Zhao, Xuecheng Bian. Prediction of maximum ground surface settlement induced by shield tunneling using XGBoost algorithm with golden-sine seagull optimization[J]. Computers and Geotechnics 2023, 154, 105156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou Weijia, Ma Jia, An Jianyong, et al. On the application of large-area anchor cable group extraction construction technology in deep sand narrow fertilizer trough [J]. Building construction 2022, 44, 2191–2193. [Google Scholar]
- Kangjian Zhang, Xing Zhao, Zhiqiang Zhang, Influences of tunnelling parameters in tunnel boring machine on stress and displacement characteristics of surrounding rocks[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 2023, 137, 105129. [CrossRef]
- Cai Yuelong, Du Wei. Numerical simulation of tunnel excavation by CRD method [J]. Engineering and construction 2018, 32, 114–115. [Google Scholar]
- Su Xiaokun. Study on the value range of surrounding rock boundary in numerical simulation of tunnel excavation [ J ]. Railway Engineering 2012, 3, 64–68. [Google Scholar]
- Yan Zhuang, Xiaoyan Cui, Shunlei Hu. Numerical simulation and simplified analytical method to evaluate the displacement of adjacent tunnels caused by excavation[J]. Tunnelling and Underground SpaceTechnology 2023, 132, 104879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang Yunlong, Liu Xuezeng, Zhang Qiang. Analysis and application of stiffness analysis of tube sheet annular joint in metro shield tunnel based on bolt-convex tenon connection[J]. Tunnel Construction 2020, 40, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Technical specification for structural safety protection of urban rail transit (with explanatory notes on provisions):CJJ/T 202-2013[S]. 2013.
- Duan Junmeng. Research on the mechanical response of pipe sheet for shield tunnel liaison channel construction[D]. Beijing Jiaotong University, 2019.
- Cui Huan. Finite element analysis of force characteristics of shield pipe sheet [D]. Shenyang University of Technology, 2021.
- Jiang Yuyu. Structural analysis and health monitoring of shield tunnel pipe sections [D]. Dalian University of Technology, 2020.
- Jutao Qiu, Xiaojun Zhou, Yusheng Shen, et al. Failure mechanism of the deep-buried metro tunnel in mixed strata: Physical model test and numerical investigation[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 2023, 139, 105224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yueyue Zhu, Cheng Liu, Xiaotian Yin, et al. Analysis of the Internal Force and Deformation Characteristics of Double-Layer Lining Structure of Water Conveyance Tunnel[J]. Geofluids 2022, 9159632.
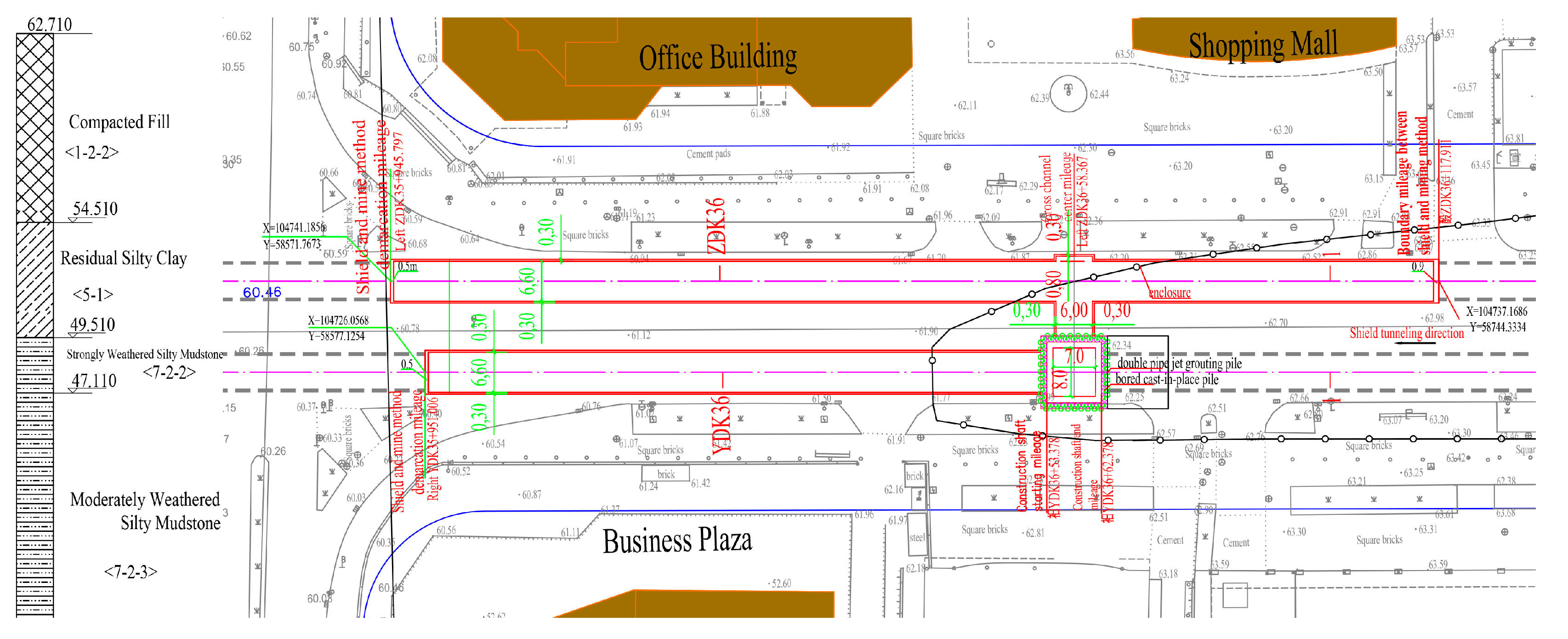
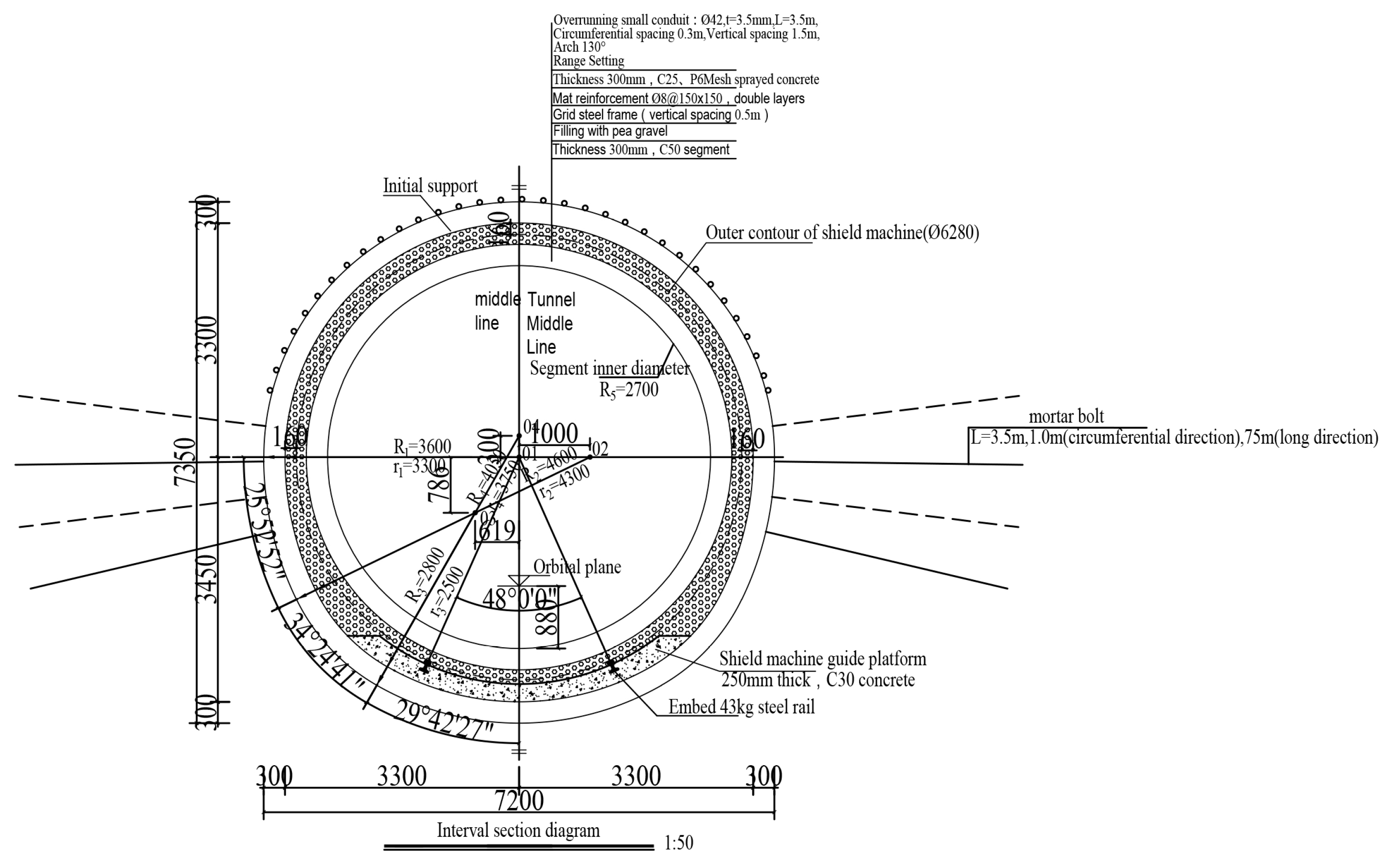
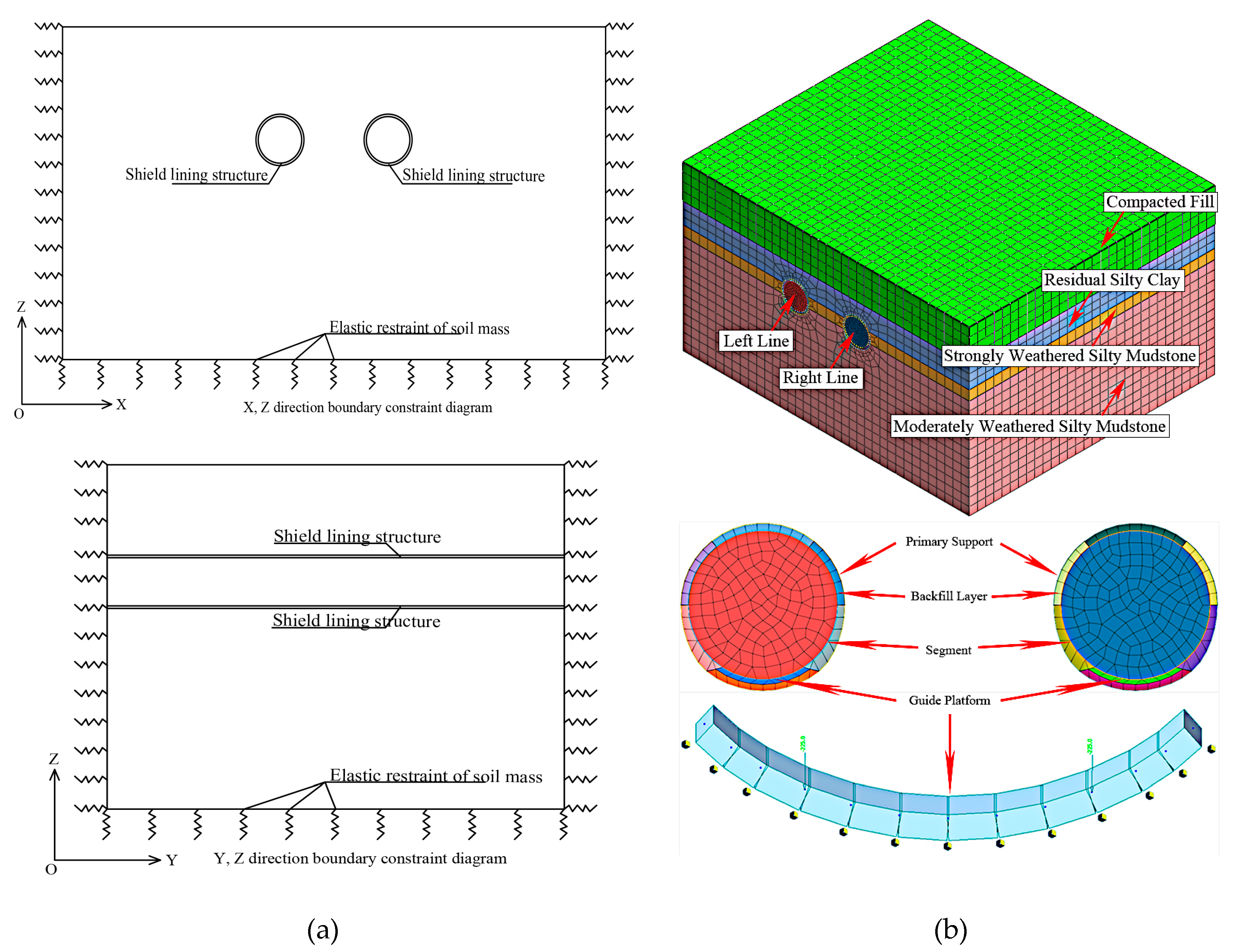
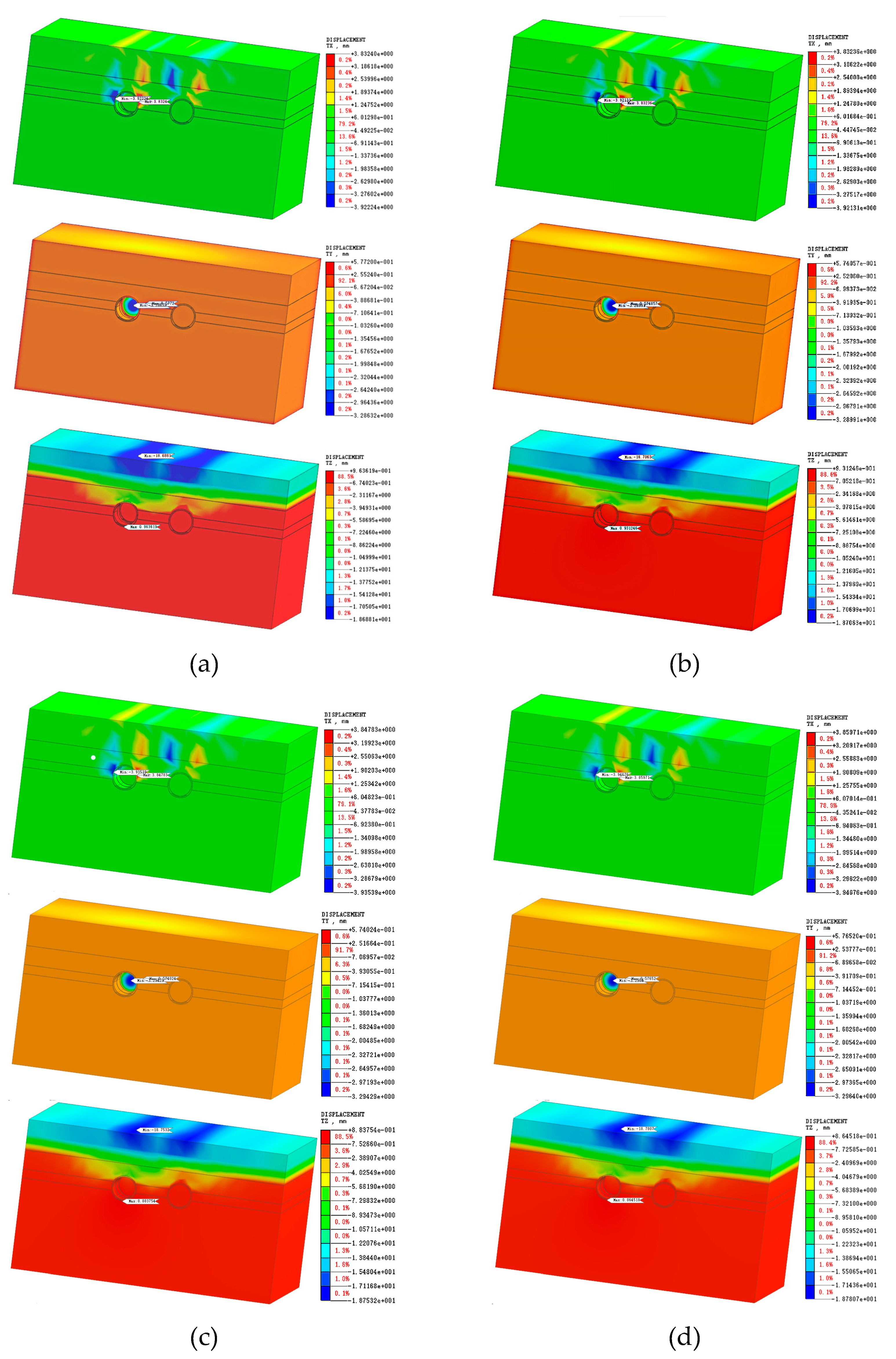
| Soil and Rock Name | Natural Density ρ/(g/cm2) | Cohesion c/kPa | Internal Friction Angle Φ/(°) | Compression Coefficient/MPa-1 | Deformation Modulus /MPa | Poisson's Ratio μ | Subgrade Reaction Coefficient | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical Kv/(MPa/m) | Horizontal Kh/(MPa/m) | |||||||
| Compacted Fill | 1.97 | 12.0 | 15.6 | 0.35 | / | / | 14 | 18 |
| Residual Silty Clay | 2.00 | 30.0 | 15.0 | 0.30 | 25 | 0.30 | 45 | 35 |
| Strongly Weathered Silty Mudstone | 2.29 | 45.0 | 28.0 | 0.20 | 120 | 0.25 | 150 | 140 |
| Moderately Weathered Silty Mudstone | 2.31 | 150.0 | 32.0 | / | 2500* | 0.22 | 240 | 220 |
| Safety Control Indicators | Early Warning Value | Control Value |
|---|---|---|
| Tunnel Horizontal Displacement | < 10 mm | < 20 mm |
| Tunnel Vertical Displacement | < 10 mm | < 20 mm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




