1. Introduction
The growing demand for effective and secure systems has led to the development of operational maintenance processes to improve system availability and operational safety while achieving cost-effectiveness. Predictive maintenance is one such process that utilizes data analytics and machine learning algorithms to predict potential failures before they occur [
1,
2]. This approach has widespread adoption in the manufacturing, energy, and transportation industries. Predictive maintenance can identify patterns and anomalies indicative of impending issues by analyzing real-time data obtained from sensors and other sources. This enables maintenance teams to take proactive measures, such as replacing faulty components or adjusting operating conditions, thereby preventing failures [
3,
4].
Unexpected and untimely failures remain a significant challenge for maintenance practices today. Depending on the severity of the failure, it can disrupt the proper functioning of a manufacturing line or, in more severe cases, lead to a complete shutdown, resulting in substantial expenses ranging from the procurement of spare components to equipment replacement. Hence, it becomes crucial to comprehend the behavior of equipment [
5]. Such understanding forms a solid foundation for determining optimal maintenance policies tailored to each piece of equipment and its components. This leads to significant cost savings by optimizing inspection frequencies, reducing component replacements and stocking, improving pre-maintenance work, and minimizing repair times.
To predict the future behavior of equipment and components, it is valuable to employ a tool that fits theoretical models to the dataset to identify potential failures accurately and rapidly. Analysis and estimation processes are supported by statistical techniques, methods, and procedures that facilitate modeling the system by adjusting predefined distributions or calculating customized distribution functions [
6,
7]. These statistical techniques offer valuable tools for data-driven decision-making, enabling the identification of underlying patterns and trends in complex systems.
Statistical techniques prove beneficial in predicting future trends and outcomes. Analyzing historical data allows statisticians to develop models and predictions that aid in strategic decision-making. Leveraging statistical techniques, it becomes possible to forecast when equipment will require repair or replacement and allocate resources, accordingly, thus saving time, money and preventing unplanned downtime. Furthermore, statistical analysis can optimize maintenance schedules and identify opportunities for improving maintenance processes [
8,
9].
In some cases, estimating statistical distribution parameters can be challenging to solve [
10,
11,
12]. This article presents a procedure for resolving such difficulties, employing the Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithm. The proposed procedure offers a structured and practical approach to estimating Weibull distribution parameters, even in challenging scenarios where conventional methods may fail. By leveraging the EM algorithm, the estimation process becomes more precise and reliable, enhancing decision-making capabilities. This method helps estimate distribution parameters in realistic situations.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Chapter 2 highlights the main practical problems that are generally associated with the analysis of data from the historical record of mechanical equipment failures, namely the existence of censored data.
Chapter 3 provides an overview of the concepts and theoretical foundations underlying the method for determining Weibull distribution parameters. Since maximum likelihood equations often lack analytical solutions due to their complexity, the Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithm is presented as a resolution technique. The EM algorithm analysis is performed in the presence of censored data, aligning with its application in the case study.
Chapter 4 showcases the real-world application of the proposed methodology. The study focuses on a system comprising five centrifugal pumps in the petrochemical industry. Weibull distribution parameters are estimated using the maximum likelihood method through the EM algorithm. The confidence interval of the estimated parameters, obtained via the bootstrap method, is presented.
Chapter 5 concludes the paper by summarizing the essential findings and highlighting the significance of the proposed methodology in improving maintenance practices and system reliability.
2. Reliability analysis with censored data
The Weibull distribution is widely utilized in reliability studies, survival analysis, and various other fields due to its versatility. It is commonly employed for modeling the failure rates of components and systems and estimating their lifetimes. The Weibull distribution can effectively fit data from diverse sources, including laboratory tests, field data, and warranty claims. Estimating its parameters can be accomplished through methods such as maximum likelihood estimation, enabling the development of models that facilitate predictions of future failures and comparisons of reliability among different products or designs.
Maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) is fundamental for estimating unknown parameters in statistical models [
13,
14]. This approach involves determining the parameter values that maximize the likelihood function, constructed based on the observed data and the parameters. The resulting estimates are frequently employed for making predictions and inferences about the underlying population from which the data was sampled.
The likelihood function is established by considering the joint probability distribution of the observed data. In simpler terms, it quantifies the probability of obtaining the observed data for various parameter values [
15]. The Maximum Likelihood Estimation method seeks to identify the parameter values that maximize this likelihood function, thereby providing the most plausible parameter estimates (Equation (1)).
Where, xi = x1, x2, …, xn is a sample of n independent observations of the random variable X from a distribution with probability density function f(x, θ), and θi = θ1, θ2, …, θn is the vector of unknown parameters.
In practical applications, it is often more convenient to maximize the log-likelihood function instead of the likelihood directly [
16,
17]. The log-likelihood function offers several advantages, as it is a monotonically increasing function of the likelihood and simplifies mathematical calculations. Consequently, the Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE) problem can be transformed into a maximization problem of the log-likelihood.
Assuming that each failure time (
ti=
t1,
t2, ...,
tn) represents an independent data point from the same representative population following the Weibull distribution with scale parameter η and shape parameter β, the log-likelihood function for the Weibull distribution with complete data is expressed as follows (Equation (2)):
Once the log-likelihood function is defined, a variety of optimization techniques, including numerical optimization algorithms, can be employed to identify the maximum of the function. The parameter values that correspond to this maximum are considered as the Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE) estimates. These estimates represent the most likely values for the parameters given in the observed data. By maximizing the log-likelihood function, we obtain parameter estimates that provide the best fit to the data, in accordance with the Weibull distribution model.
2.1. Historical failure data type
Historical failure data, documenting past failures, holds significant importance in reliability analysis, guiding decision-making related to maintenance strategies, equipment replacement or refurbishment, spare part stocking, and warranty policies. Through data analysis, optimal maintenance intervals can be determined, critical components that frequently fail can be identified, and the cost-effectiveness of different maintenance approaches can be assessed.
When considering historical fault data, it can be categorized into two types based on the availability of information: complete data and censored data [
10,
18].
Complete data refers to records where the exact failure time or event occurrence time is known without any uncertainty. In other words, there is no censoring present in the data, and the failure times are fully observed. Complete data provides precise information about when the failure event occurred, enabling accurate analysis of reliability metrics and statistical modeling.
On the other hand, censored data refers to observations in which the exact failure time or event occurrence time is either unknown or partially known. Censoring occurs in different forms:
Left censoring occurs when the event of interest (failure) has occurred before the study started, and only the time since the event is known. In such cases, the data provides a lower bound for the failure time, but the exact time remains unknown.
Right censoring occurs when the event of interest (failure) has not occurred by the end of the observation period or study duration. The data indicates that the failure event will occur at some point in the future, but the exact time is unknown. Right censoring often occurs in reliability tests, where a specified number of units are tested until the end of the study period, and the unfailed units are right-censored.
Interval censoring arises when the exact failure time is unknown, but it is known that the failure occurred within a certain time interval. This form of censoring provides information about a range of possible failure times.
Understanding the type of censoring present in the data is crucial for appropriate data analysis and modeling, as different techniques are employed to handle each type. By properly accounting for censored data, a more accurate and comprehensive reliability analysis can be performed, facilitating informed decision-making in maintenance and operational strategies. Censoring data is denoted by
δi variable to indicate that the event is censored, that is [
19] (Equation (3)),
Censored data poses a challenge in statistical analysis as it contains incomplete information and introduces uncertainty in the failure times. Specialized statistical methods are necessary to appropriately handle censored data, accounting for the missing information and capturing the uncertainty. By employing these methods, more accurate predictions and informed decisions can be made based on the available data.
Censored data is frequently encountered in reliability studies when analyzing the historical failure data of equipment. Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of censored data and its impact on reliability analysis is crucial to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the results. Handling censored data correctly is of utmost importance to avoid biased results and maintain the validity of the conclusions drawn from the analysis. By applying appropriate statistical techniques for censored data, researchers can obtain more robust and trustworthy findings, enabling effective decision-making in reliability and maintenance practices.
3. Expectation-Maximization algorithm
The estimation of Weibull distribution parameters in the presence of censored data often poses challenges, as closed-form analytical solutions for the maximum likelihood equations are typically unavailable. Explicit formulas to directly solve for parameter estimates are not feasible in this case.
When dealing with censored data, the likelihood function becomes more intricate, incorporating both observed failure times and censored observations. The likelihood function includes terms representing the probabilities of observed failure times and the probabilities of failure times being censored.
Due to the complexity of the problem, analytical solutions for the maximum likelihood equations are not viable. Instead, numerical methods and iterative algorithms are commonly employed to estimate the parameters that maximize the likelihood function [
20]. These methods iteratively update the parameter estimates until convergence is achieved, searching for the values that optimize the likelihood function.
In this work, the Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithm was chosen among other numerical methods due to its demonstrated effectiveness in producing reliable results [
21,
22]. The EM algorithm, introduced by Dempster, Laird, and Rubin in 1977, is an iterative optimization algorithm [
23]. It is widely used in reliability and survival analysis, as well as in other fields such as machine learning, data mining, and bioinformatics [
24,
25,
26]. The EM algorithm is a powerful statistical tool for estimating parameters in complex models, particularly in situations involving incomplete or censored data, where analytical solutions are challenging [
27,
28]. The algorithm alternates between two steps: the E-step (Expectation step) and the M-step (Maximization step). In the E-step, the algorithm calculates the expected value of the log-likelihood function based on the current parameter estimates. In the M-step, it maximizes the expected value of the log-likelihood function with respect to the parameters [
23,
29].
The log-likelihood function for the complete data set X is denoted as lc (x, θ). When incomplete data is present, certain events are unknown, and the observed data set is represented as Y, while Z represents the unknown data. Consequently, X can be expressed as a function of (y, z).
The EM algorithm with the presence of incomplete data can be summarized as follows:
Initialization: The algorithm begins by initializing the model's parameters, denoted as
θ(0). This initialization can be done randomly or with reasonable initial values. It is crucial to pay attention to the choice of initial values as poor selection can result in slow convergence of the algorithm. Additionally, since the maximum likelihood equation can have multiple solutions corresponding to local maxima, the choice of initial values becomes significant. A comparative study on different strategies for choosing initial values was conducted by [
30], highlighting the dependency of the strategy on the selection of initial solutions.
-
E-step (Expectation step): In the E-step, the algorithm calculates the expected values of the missing or unobserved data, given the current parameter estimates. This step involves computing the posterior probability distribution of the missing data, which represents the uncertainty about their values. The expectation is taken with respect to the conditional distribution of the missing data, conditioned on the observed data and the current parameter estimates.
To perform the E-step, the algorithm typically utilizes the complete-data likelihood function, which incorporates both the observed and missing data. However, since the missing data is not available, the algorithm computes the expectation of the complete-data log-likelihood instead. This expectation is often referred to as the “Q-function” (Equation (4)).
- 3.
-
M-step (Maximization step): In the M-step, the algorithm updates the parameter estimates to maximize the expected log-likelihood computed in the E-step. It treats the expected values of the missing data as if they were observed and finds the parameter values that maximize the log-likelihood of the complete data.
To maximize the expected log-likelihood, the algorithm employs standard optimization techniques such as gradient descent or closed-form solutions tailored to specific models. The M-step involves solving for the optimal values of the parameters by maximizing the Q-function with respect to the parameters. This can be achieved through numerical optimization methods that iteratively update the parameter estimates until convergence is reached. Gradient-based methods estimate the gradient of the log-likelihood with respect to the parameters and adjust the parameter values in the direction of steepest ascent. Closed-form solutions, on the other hand, exploit the specific structure of the model to derive explicit expressions for the optimal parameter estimates (Equation (5)).
The choice of optimization technique depends on the complexity of the model and the computational efficiency required. Gradient-based methods are widely used due to their versatility and ability to handle a broad range of models. However, for simpler models, closed-form solutions may offer faster and more efficient estimation. The M-step plays a crucial role in refining the parameter estimates by iteratively improving their values based on the available data. By maximizing the log-likelihood of the complete data, the algorithm finds parameter values that optimize the fit between the model and the observed and expected data. This step is essential for obtaining accurate and reliable parameter estimates in the presence of incomplete data.
- 4.
Iteration: After completing the E-step and M-step, the algorithm checks for convergence. If the change in the log-likelihood or the parameter estimates falls below a certain threshold, the algorithm terminates. Otherwise, it continues to iterate by returning to the E-step and repeating the process until convergence is achieved.
The convergence guarantees of the EM algorithm ensure that the likelihood of the model increases or remains constant with each iteration. However, it is important to note that the algorithm may converge to a local maximum of the likelihood function rather than the global maximum. This behavior arises due to the inherent non-convex nature of the likelihood function. Consequently, running the algorithm multiple times with different initializations is often recommended [
30]. This strategy helps mitigate the risk of getting trapped in suboptimal solutions and increases the chances of finding the global maximum.
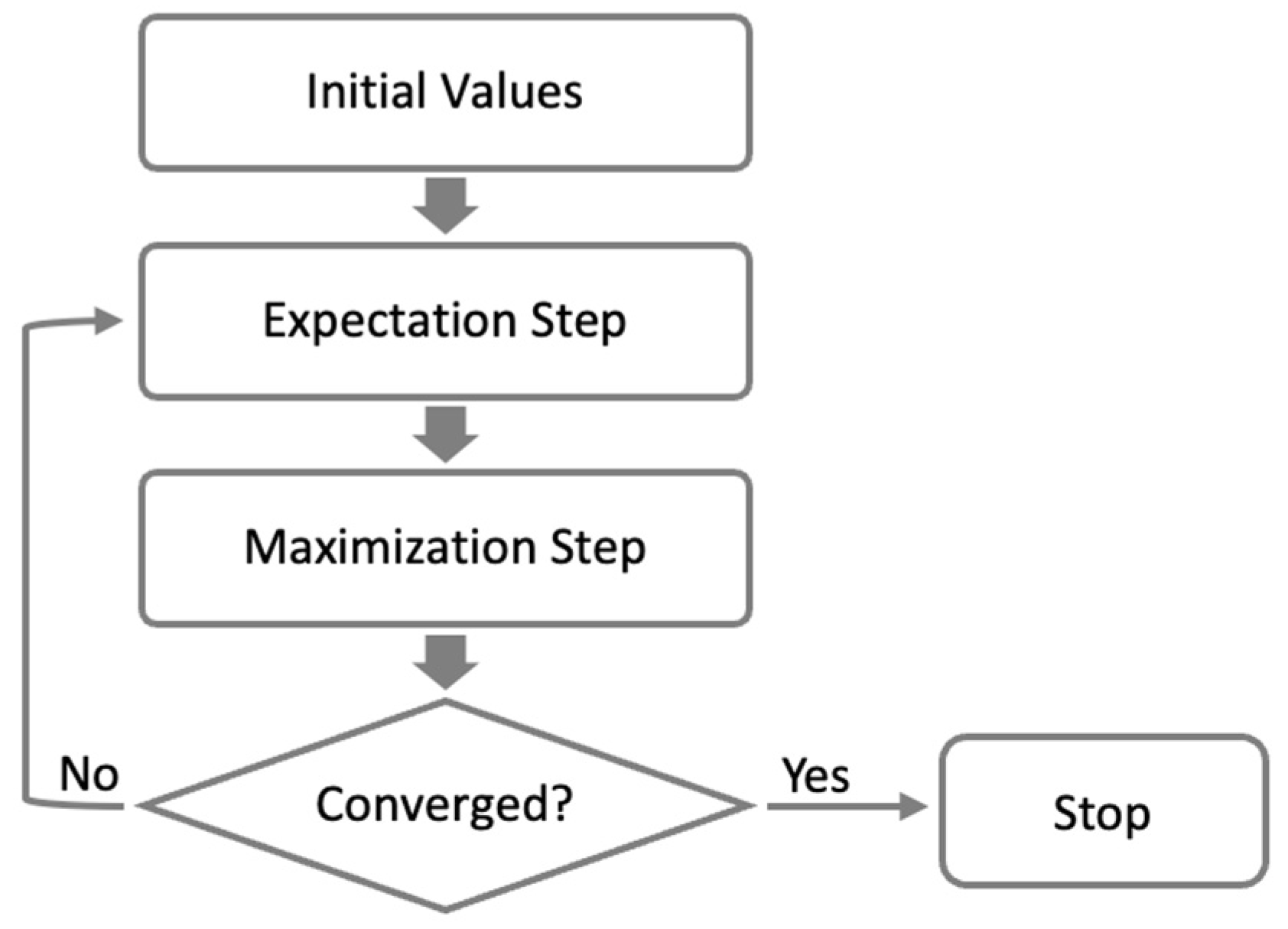
Figure 1 illustrates the interactive process of the EM algorithm, demonstrating how the algorithm iteratively updates the parameter estimates and improves the likelihood of the model. The stepwise nature of the algorithm is evident, with the E-step estimating the missing data and the M-step refining the parameter estimates based on the completed data. The iteration continues until convergence, resulting in optimized parameter estimates that maximize the likelihood of the complete data.
The iterative nature of the EM algorithm allows it to handle complex models and accommodate incomplete or censored data effectively. By leveraging the E-step and M-step iteratively, the algorithm refines the parameter estimates, improving the overall fit between the model and the observed data. Convergence serves as a criterion for determining when the algorithm has reached a stable solution, ensuring the reliability and accuracy of the estimated parameters.
Reliability studies often involve analyzing data in which the failure times of equipment or systems are subject to right-censoring. Right-censoring occurs when the observed failure times are limited by the study's duration, and failures beyond that duration are not observed. To address the challenge of right-censored data in reliability analysis, the EM algorithm proves to be an effective approach.
The EM algorithm offers a powerful framework for estimating the parameters of a chosen reliability model when working with censored data. In the case of right-censored data, the algorithm employs an iterative process. It imputes the unobserved failure times based on the current parameter estimates and updates the parameter estimates using the imputed failure times. This iterative process enables the incorporation of censored data and enhances the accuracy of parameter estimation.
During the E-step of the EM algorithm for right-censored data in reliability studies, the survival probabilities are computed for each observation using the current parameter estimates. These survival probabilities represent the probability of survival beyond the censoring time for each observation. Subsequently, the survival probabilities are utilized to impute the failure times for the censored observations.
The Q equation, which characterizes the E-step in the EM algorithm for right-censored data, can be expressed as follows, as presented in [
31] (Equation (6)):
This equation captures the estimation of the missing failure times based on the available survival probabilities. By imputing the failure times for the censored observations, the algorithm iteratively refines the parameter estimates, progressively improving the fit between the reliability model and the right-censored data.
As seen above, the step M is design to find the solution θk+1 which maximizes Q(θ, θk+1). Once the failure times are imputed, the M-step of the EM algorithm proceeds to update the parameter estimates. In this step, the algorithm maximizes the expected complete-data log-likelihood, which incorporates both the observed failure times and the imputed failure times. By incorporating the imputed failure times, the algorithm effectively accounts for the censoring information and provides more accurate parameter estimates.
The EM algorithm, when applied to right-censored data, offers a robust approach for estimating reliability parameters in the presence of censored observations. It overcomes the limitations imposed by censoring, such as incomplete failure time information, and ensures that the analysis incorporates all available data to make reliable inferences about the reliability characteristics of the system or equipment under study.
It is important to note that the specific implementation of the EM algorithm for censored data in reliability studies relies on the chosen reliability model, such as the Weibull distribution, and the assumptions made about the underlying distribution.
The utilization of appropriate statistical techniques can significantly enhance the analysis and estimation process. These procedures enable the modeling of the system based on the fit of a predefined distribution. In the following section, a case study will be presented to demonstrate the effectiveness of this approach in a real-world scenario.
4. Case study
One of the objectives of this case study is to apply the EM algorithm to find the solution of the function obtained by the maximum likelihood method in the parameter estimation of the Weibull distribution using right-censored data. The case study analyzes the failure history of five centrifugal pumps used by a petrochemical company for pumping similar-density oil, specifically emphasizing bearing failures. Over seven years, these pumps experienced recurrent failures, resulting in significant downtime and a decrease in the overall reliability of the pumping system.
Centrifugal pumps play a critical role in various industries by transporting fluids. Their design allows them to handle various fluid viscosities and temperatures, making them versatile for different applications.
Reliability is essential for ensuring the efficient and uninterrupted operation of these pumps. The bearing system within centrifugal pumps is particularly crucial as its performance directly impacts the overall reliability of the pump.
The collected data revealed that bearing failures accounted for significant failures, representing approximately 38% of the total. This highlights the importance of investigating and addressing bearing failures to improve the reliability and performance of the pumping system.
Bearing failures can have severe consequences, including costly downtime, repairs, safety hazards, and environmental risks. Estimating the parameters of the Weibull distribution based on limited and censored data enables plant operators to proactively monitor and maintain critical components such as bearings to ensure continuous and safe operations. The failure data collected were analyzed to determine the frequency of each failure mode over the seven years. This analysis provides insights into the relative importance of each failure mode in contributing to the overall failure rate.
Failures between regular inspections conducted by the maintenance staff, which happen at least every 8 hours, were considered complete data. Hence, it was assumed that the exact moment of failure was well-known, as the time between inspections was relatively short compared to the total observed time.
The last recorded data point for each pump represents the end of the study rather than an actual failure. This type of situation, as mentioned earlier, is known as right-censored data, where the observed data is incomplete due to the study ending without observing all potential failures.
Treating the last recorded time for each pump as right-censored data is a good approach since it indicates that the failure times for those pumps are unknown, as they were still operating when the study concluded.
The Expectation-Maximization algorithm was employed to estimate the parameters of the Weibull distribution using the maximum likelihood method with right-censored data. The iterative process was implemented using the R statistical program.
The least squares method was utilized to determine the initial solution
θ(0). The iterative method terminated when the difference between iteration
k+1 and
k was smaller than 0.1.
Table 1 presents the expected values for
β and
η for the bearings of the five analyzed centrifugal pumps obtained through the EM algorithm. Confidence intervals for each parameter are also provided.
Given the small size of the data sample, the bootstrap-t method was employed to determine the confidence intervals with a confidence level of 95% [
32].
For all bearings, the shape parameter
β was found to be greater than 1. The scale parameter
η exhibited values ranging between 509.95 and 656.96 operation days. In the bootstrap method, 1000 resampling iterations were performed to obtain reliable estimates.
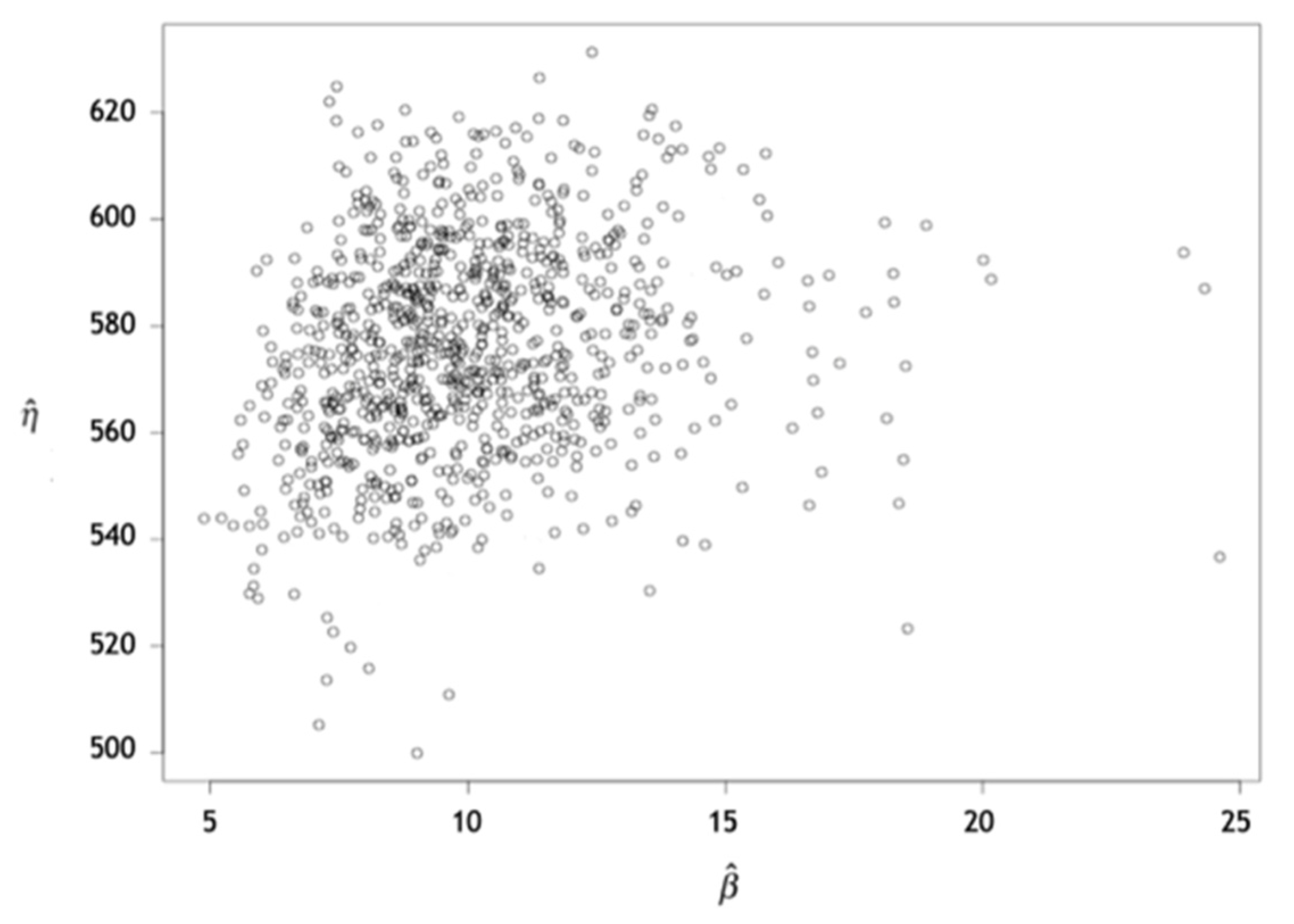
Figure 2 visually presents the confidence interval of the estimated parameters of the Weibull distribution specifically for bearing 1. These intervals were derived from the information obtained through the bootstrap method.
Various tests are available to assess the quality of fit between the data and the theoretical distribution. In this study, the Kolmogorov-Smirnov (K-S) test was chosen due to its simplicity and reliable results, especially for datasets with a limited amount of data.
The K-S test involves three steps:
-
Formulation of hypotheses:
The null hypothesis (H0) states that the population from which the data is derived follows the Weibull distribution. The alternative hypothesis (H1) suggests that the population does not follow the Weibull distribution.
-
Determination of the D value:
The D value is calculated as the maximum absolute difference between the sample distribution function F(ti) and the population distribution function F(t). This value is compared to the critical value, which depends on the sample size (n) and the chosen significance level (α). Additionally, the critical value is adjusted based on the shape parameter value (β):
K = 0.70 (β > 3.0)
K = 0.75 (1.5 < β < 3)
K = 0.8 (β < 1.5)
-
Comparison:
If the test statistic D is greater than or equal to the corrected critical value (D ≥ k x critical value), the null hypothesis is rejected (Reject H0). The p-value also provides insight into the quality of the fit. The p-value represents the probability of observing results as extreme as those obtained if the null hypothesis is true. A large p-value supports H0, while a small p-value indicates evidence against H0. If the p-value is greater than 0.05, there is no evidence against H0. For bearing 1, with a sample size of n = 6 and a significance level of α = 5%, the following results were obtained:
D = 0.218 < 0.363 (0.70 x 0.519)
p-value = 0.5294 > 0.05
Based on these results, the null hypothesis is not rejected, indicating that the population from which the data is derived follows the Weibull distribution. Similar results were obtained for the other bearings.
Estimating Weibull parameters provides valuable insights for optimization efforts and informed decision-making. By understanding failure patterns through parameter estimation, system designs can be optimized, appropriate materials can be selected, and maintenance intervals can be determined. Reliability estimates derived from Weibull analysis serve as a quantitative basis for decision-making, facilitating efficient resource allocation, reducing downtime, and improving system performance.
Furthermore, Weibull analysis enables comparative analysis of failure data from different systems, components, or designs. By comparing the estimated parameters, the relative reliability of various products or configurations can be assessed.
5. Conclusions
The analysis of historical failure data for industrial equipment, such as centrifugal pumps in an oil refinery, is a complex task due to censored data and missing information. However, analyzing historical failure data to monitor systems and perform maintenance tasks effectively is essential.
In cases where censored data is present, the equation from the maximum-likelihood method needs an analytical solution due to its complexity. Therefore, in this work, the EM algorithm was proposed as a solution to estimate the parameters. The EM algorithm has demonstrated its effectiveness in reliability estimation for such cases, leading to significant cost savings and improved safety. With the increasing complexity and criticality of modern systems, accurate reliability estimation has become more crucial than ever, and the use of advanced statistical methods, such as the EM algorithm, is essential to achieve this goal. For instance, in an oil refinery, a failure in a pump bearing can result in costly shutdowns and even hazardous accidents. Plant operators can proactively monitor and maintain critical components like bearings, ensuring continuous and safe operations by employing the EM algorithm to estimate the Weibull distribution parameters based on limited and censored data.
Furthermore, these methods can be applied to the oil industry and other sectors, such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare, where limited and censored failure data are expected. However, it is essential to note that the predictions of the EM algorithm will be more accurate with more significant amounts of data and higher data quality.
Additionally, using the EM algorithm enables the utilization of maintenance action data, further enhancing its usefulness. In conclusion, applying the EM algorithm for reliability estimation in scenarios with limited and censored data shows excellent promise and merits further research and exploration.
Author Contributions
J.S. conceptualized the study, developed the methodology, and wrote the paper. P.V. provided validation and reviewed the manuscript. P.M. provided validation and reviewed the manuscript. L.F. supervised the study and reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript for publication.
Funding
This work is funded by National Funds through the FCT – Foundation for Science and Technology, I.P., within the scope of the project Ref. UIDB/05583/2020. Furthermore, we would like to thank the Research Centre in Digital Services (CISeD) and the Instituto Politécnico de Viseu for their support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Binding, A.; Dykeman, B.; Pang, S. Machine Learning Predictive Maintenance on Data in the Wild. IEEE 5th World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT), Limerick, Ireland, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kao, H.; Yang, S. Service Innovation and Smart Analytics for Industry 4.0 and Big Data Environment. Procedia CIRP, 2014, 16, 3-8. [CrossRef]
- Chuang, S.Y.; Sahoo, N.; Lin, H.W.; Chang, Y.H. Predictive Maintenance with Sensor Data Analytics on a Raspberry Pi-Based Experimental Platform. Sensors, 2019, 19, 3884. [CrossRef]
- Uppal, M.; Gupta, D.; Goyal, N.; Imoize, A.L.; Kumar, A.; Ojo, S.; Pani, S.K.; Kim, Y.; Choi, J. A Real-Time Data Monitoring Framework for Predictive Maintenance Based on the Internet of Things. Complexity, 2023, 2023, 1-14. [CrossRef]
- Anunciação, P.; Dinis, V.; Peñalver, A.; Esteves, F. Functional Safety as a critical success factor to industry 4.0. Procedia Computer Science, 2022, 204, 45-53. [CrossRef]
- Held, L.; Bové, D. Applied Statistical Inference, Likelihood and Bayes, Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Tobias, P.A.; Trindade, D.C. Applied Reliability, Chapman & Hall/ CRC Press: Florida, USA, 2011.
- Abernethy, R.B. The New Weibull Handbook, Robert B. Abernethy: Florida, USA, 2006.
- Kang, Z.; Catal, C.; Tekinerdogan, B. Remaining Useful Life (RUL) Prediction of Equipment in Production Lines Using Artificial Neural Networks. Sensors, 2021, 21, 932. [CrossRef]
- Gijbels, I. Censored data. Wires Computational Statistics, 2010, 2, 178–188. [CrossRef]
- Anghel, C.G.; Ilinca, C. Parameter Estimation for Some Probability Distributions Used in Hydrology. Appl. Sci., 2022, 12, 12588. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gao, Z.; Du, C.; Bi, S.; Fang, Y.; Yun, F.; Fang, S.; Yu, Z.; Cui, Y.; Shen, X. Parameter Estimation of Three-Parameter Weibull Probability Model Based on Outlier Detection. RSC Advances, 2022, 12 (53), 34154-34164. [CrossRef]
- Chambers, R.L.; Steel, D.G; Wang, S; Welsh, A.H. Maximum Likelihood Estimation for Sample Surveys, Chapman & Hall/ CRC Press: Florida, USA, 2012.
- Balakrishnan, N.; Kundu, D.; Ng, H.K.T. Point and Interval Estimation for a Simple Step-Stress Model with Type-II Censoring. Journal of Quality Technology, 2007, 39, 35-47. [CrossRef]
- Aghamohammadi, R.; Laval, J.A. Parameter Estimation of the Macroscopic Fundamental Diagram: A Maximum Likelihood Approach. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2022, 140, 103678. [CrossRef]
- Akram, M.; Hayat A. Comparison of Estimators of the Weibull Distribution. Journal of Statistical Theory and Practice, 2014, 8(2), 238-259. [CrossRef]
- Teimouri, M.; Hoseini, S.M.; Nadarajah, S. Comparison of Estimation Methods for the Weibull Distribution. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Statistics, 2013, 47(1), 93-109. [CrossRef]
- Lawless, J.F. Statistical Models and Methods for Lifetime Data, John Wiley & Sons: New Jersey, USA, 2003. [CrossRef]
- Al-Omari, A. I.; Aidi, K.; AlSultan, R. Power Darna Distribution with Right Censoring: Estimation, Testing, and Applications. Appl. Sci., 2022, 12, 8272. [CrossRef]
- Willis, B.H.; Baragilly, M.; Coomar, D. Maximum Likelihood Estimation Based on Newton-Raphson Iteration for the Bivariate Random Effects Model in Test Accuracy Meta-Analysis. Stat Methods Med Res, 2020, 29(4), 1197-1211. [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, N.; Mitra, D. Left Truncated and Right Censored Weibull Data and Likelihood Inference with an Illustration. Computational Statistics and Data Analysis, 2012, 56, 4011-4025. [CrossRef]
- McLachlan, G.J.; Krishnan, T. The EM Algorithm and Extensions. John Wiley & Sons: New Jersey, USA, 2008. [CrossRef]
- Dempster, A.P.; Laird, N.M.; Rubin, D.B. Maximum Likelihood from Incomplete Data Via the EM Algorithm. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, 1977, 39(1), 1-38.
- Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, X. EM Algorithm for Estimating Reliability of Multi-Release Open Source Software Based on General Masked Data. IEEE Access, 2021, 9, 18890-18903. [CrossRef]
- Mikolajczyk, K.; Schmid, C. A Performance Evaluation of Local Descriptors. IEEE IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2005, 27, 1615-1630. [CrossRef]
- Davies, K.; Pal, S.; Siddiqua, J.A. Stochastic EM Algorithm for Generalized Exponential Cure Rate Model and an Empirical Study. Journal of Applied Statistics, 2021, 48 (12), 2112–2135. [CrossRef]
- Wall, M.M.; Amemiya, Y. Nonlinear Structural Equation Modeling as a Statistical Method. Handbook of Latent Variable and Related Models, 2007, 321–343. [CrossRef]
- Kayid, M.; Al-Maflehi, N.S. EM Algorithm for Estimating the Parameters of Quasi-Lindley Model with Application. Journal of Mathematics, 2022, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Nagaraju, V.; Fiondella, L.; Zeephongsekul, P.; Wandji, T. An Adaptive EM Algorithm for the Maximum Likelihood Estimation of Non-Homogeneous Poisson Process Software Reliability Growth Models. International Journal of Reliability, Quality and Safety Engineering, 2017, 24(4), 35-41. [CrossRef]
- Karlis, D., Xekalaki, E. Choosing Initial Values for the EM Algorithm for Finite Mixtures. Computational Statistics and Data Analysis, 2003, 41, 577-590.
- Ferreira, L.A.; Silva, J. Parameter Estimation for Weibull Distribution with Right Censored Data Using EM Algorithm. eksploatacja i Niezawodnosc – Maintenance and Reliability, 2017; 19 (2), 310–315. [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.Y.; Arasan, J.; Midi, H.; Bakar, M.R.A. Jackknife and Bootstrap Inferential Procedures for Censored Survival Data. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2015, 1682, 1-6. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).