Submitted:
12 June 2023
Posted:
13 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Loose Belt Faults and Virtual Airflow Meters for Optimal Control
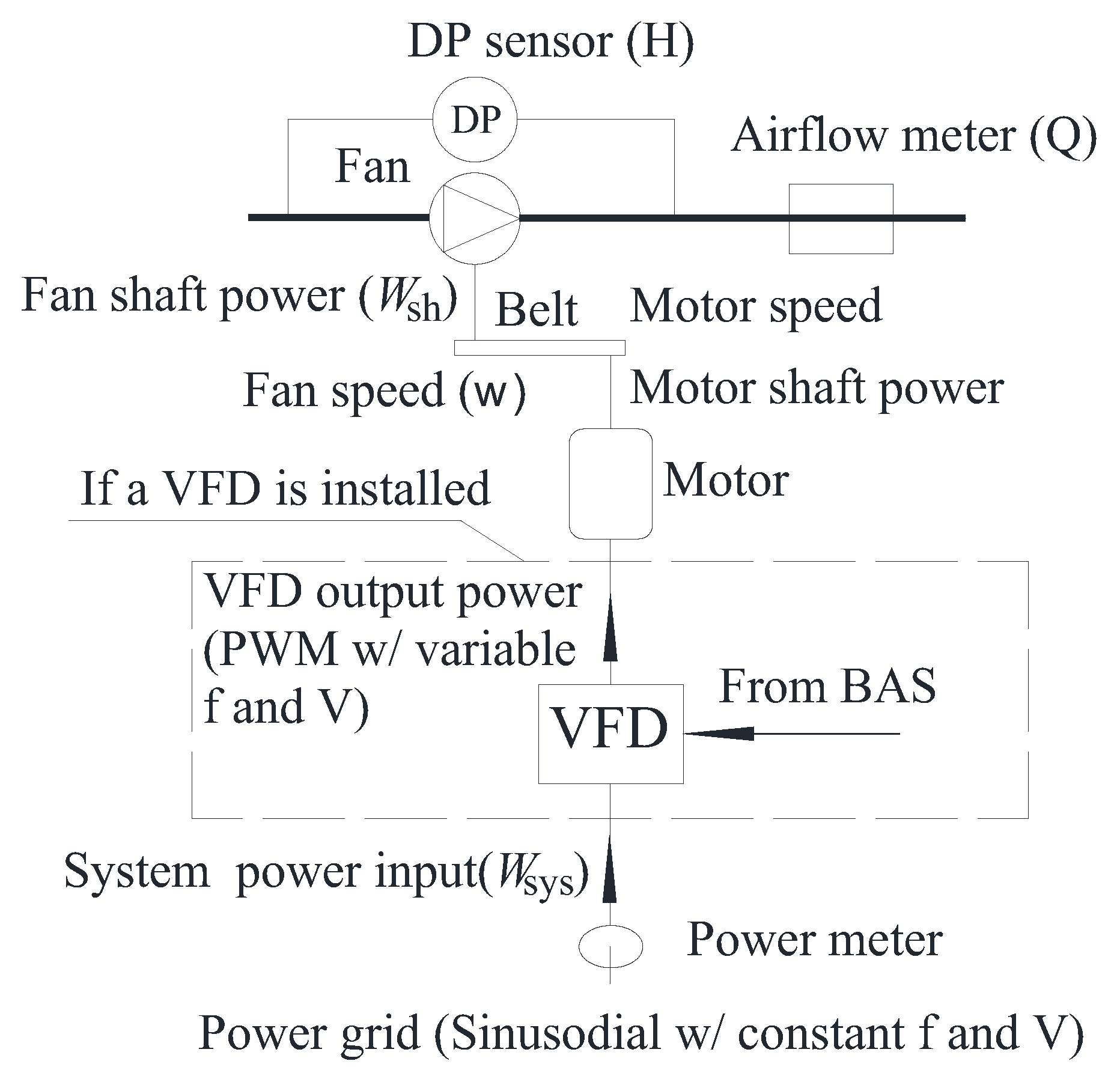
1.2. Configuration of Fan Systems
1.3. Energy Model of Fan Systems and Demand for Identification
1.4. Challenges to Identify the Energy Model
1.5. Objectives
2. Theory and Identification Approach
2.1. Fan Performance Curves at the Full Design Speed
2.2. Affinity Laws
2.3. Drive Efficiency and System Efficiency
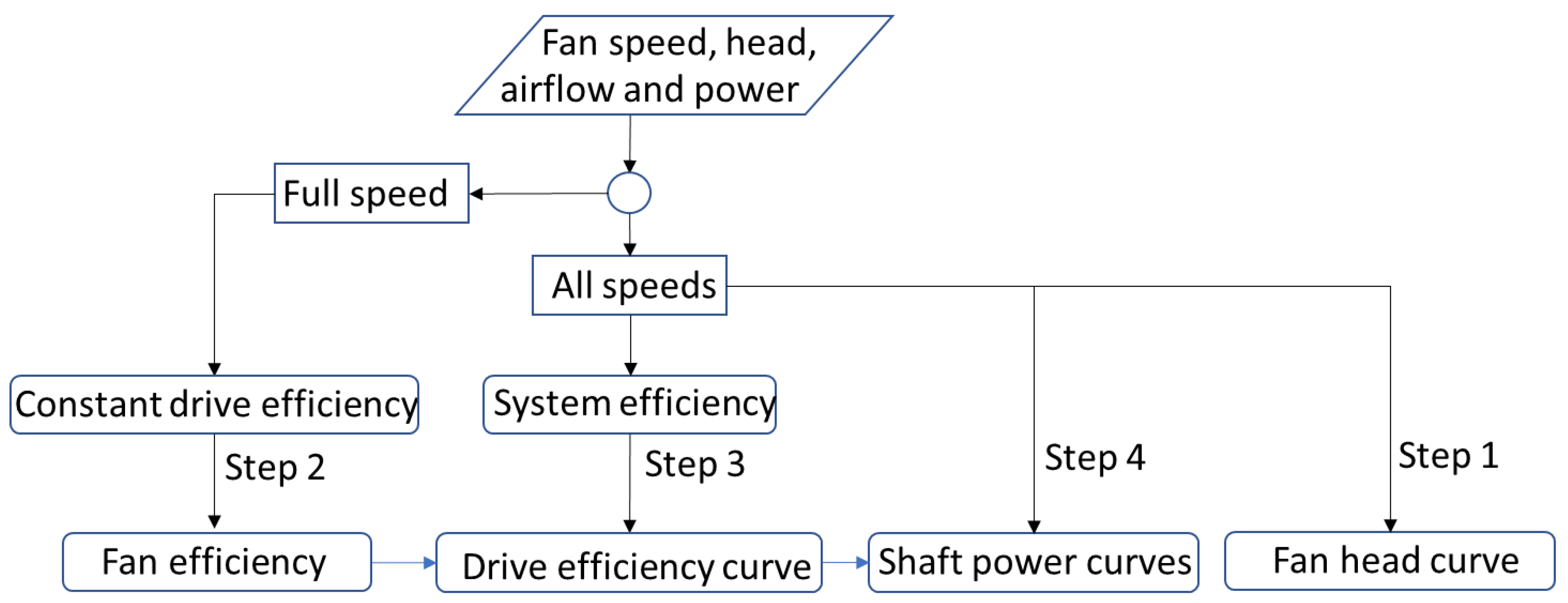
2.4. Identification Approach
- Using the available system efficiency
- Defining the equivalent fan efficiency and equivalent drive efficiency.
- Expressing them by two uncorrelated functions, the equivalent fan efficiency function of the ratio of fan head to airflow rate squared and the equivalent drive efficiency function of the fan speed, to separate the equivalent fan efficiency and equivalent drive efficiency from the system efficiency.
3. Model Identification Demonstration
3.1. Test System
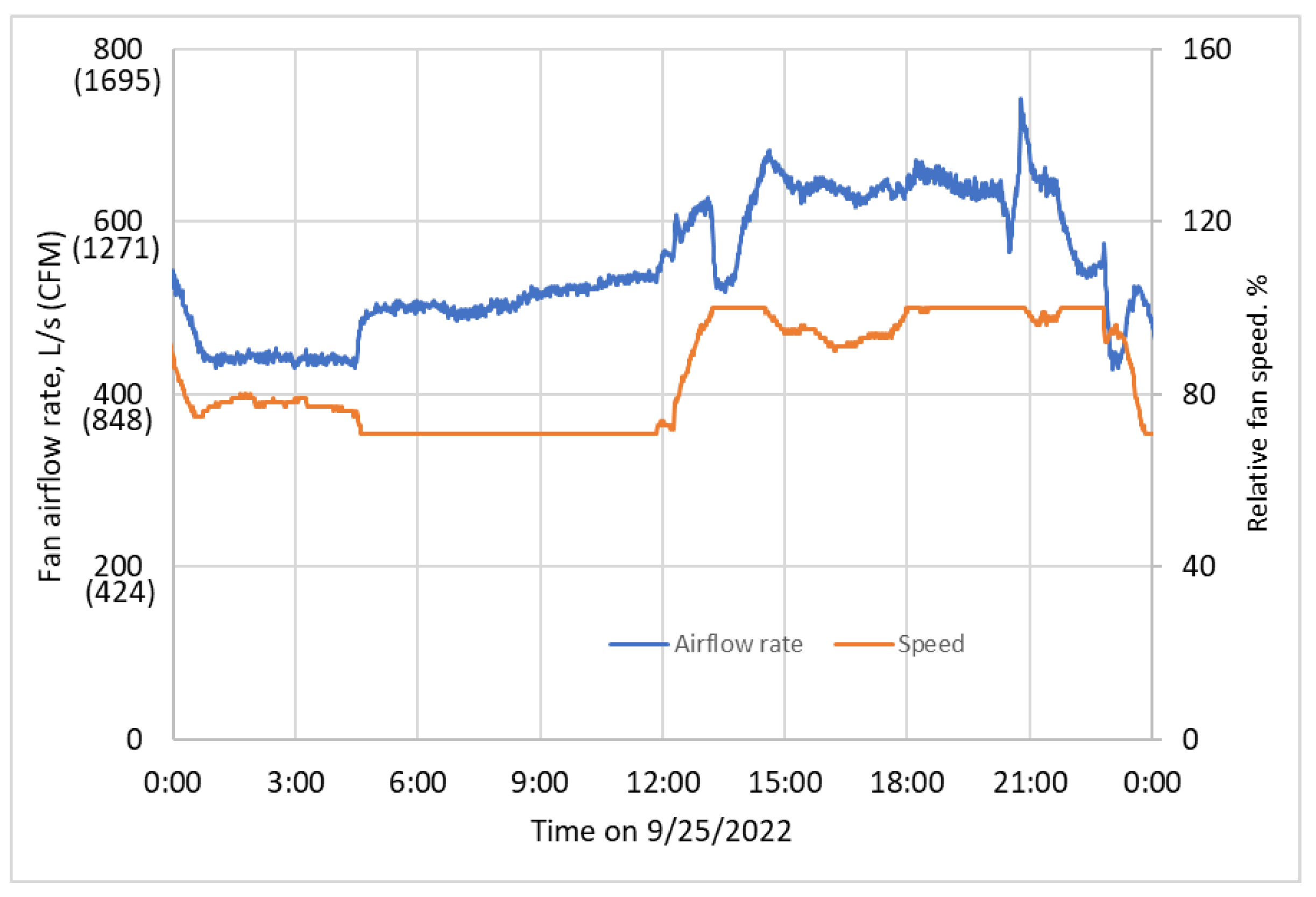
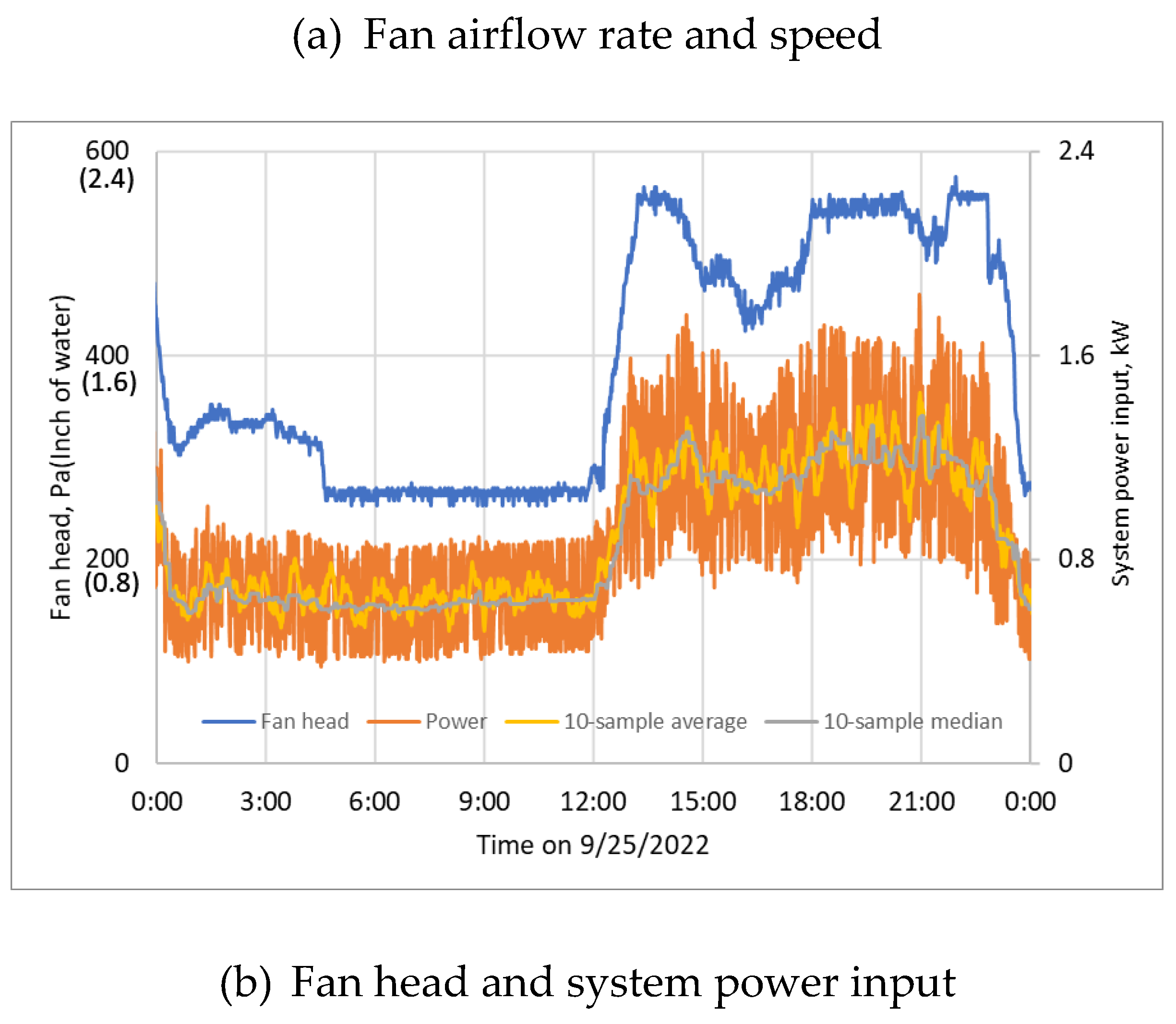
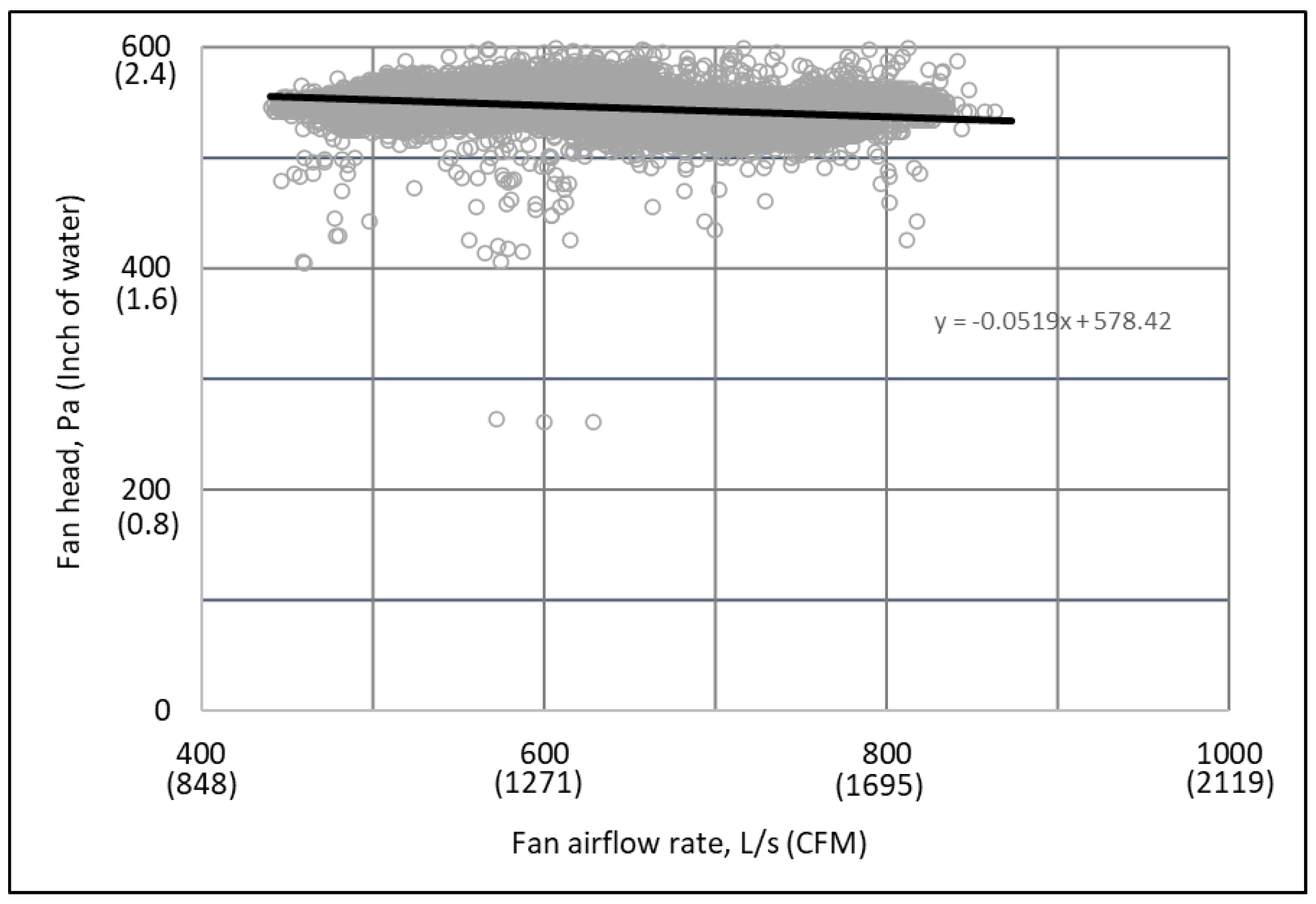
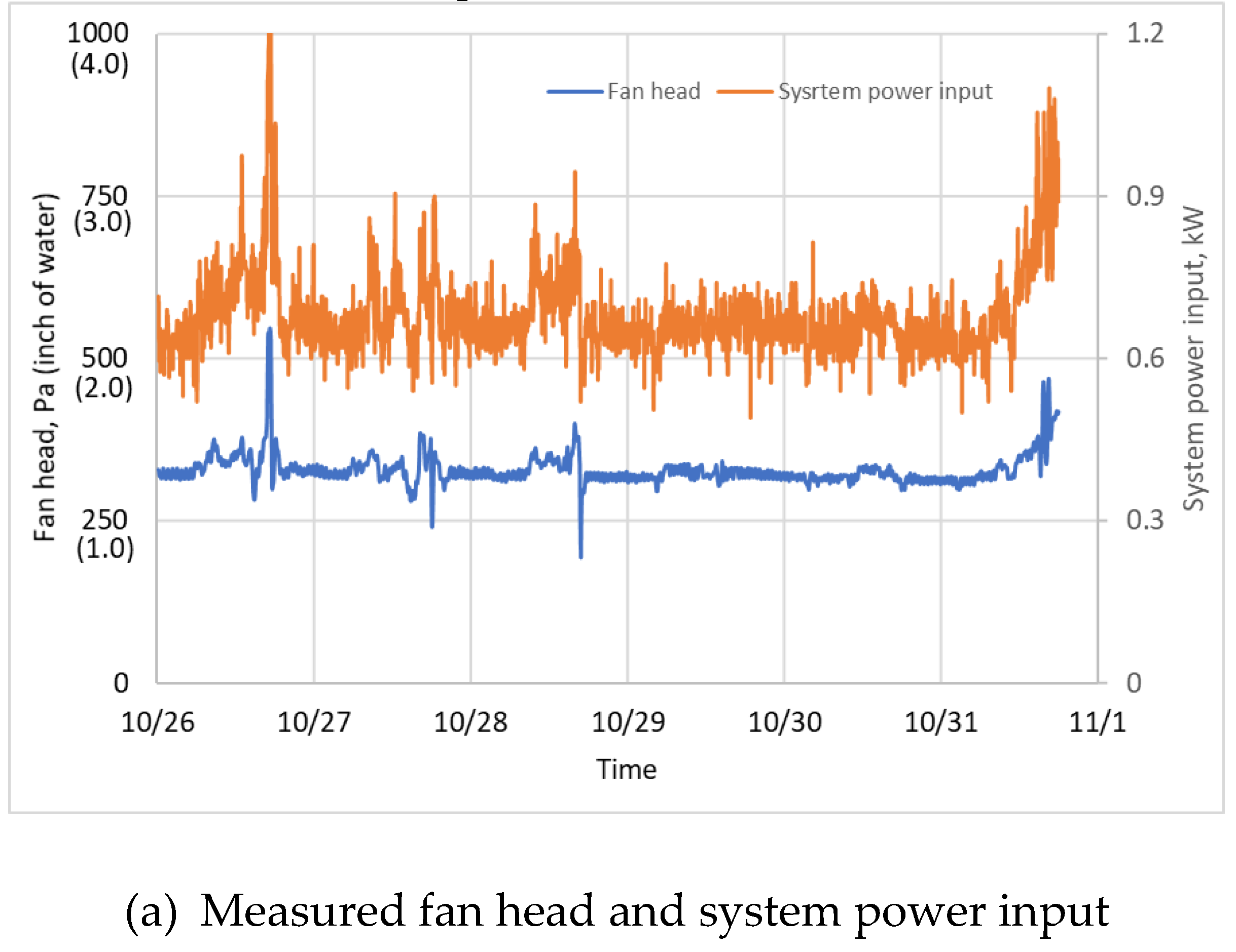
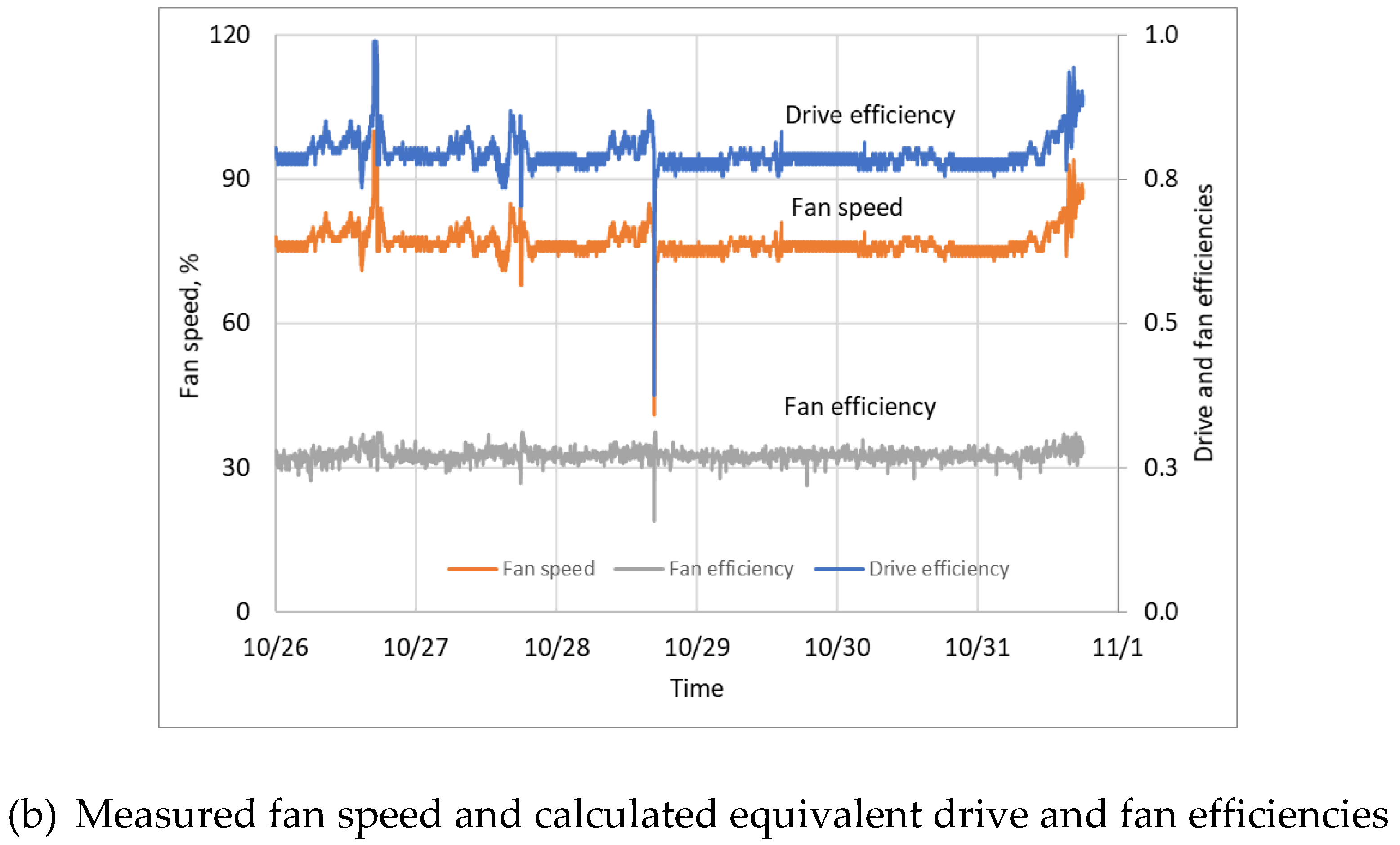
3.2. Measured Raw Performance Data
3.3. Manipulated Performance Data at the Full Design Speed
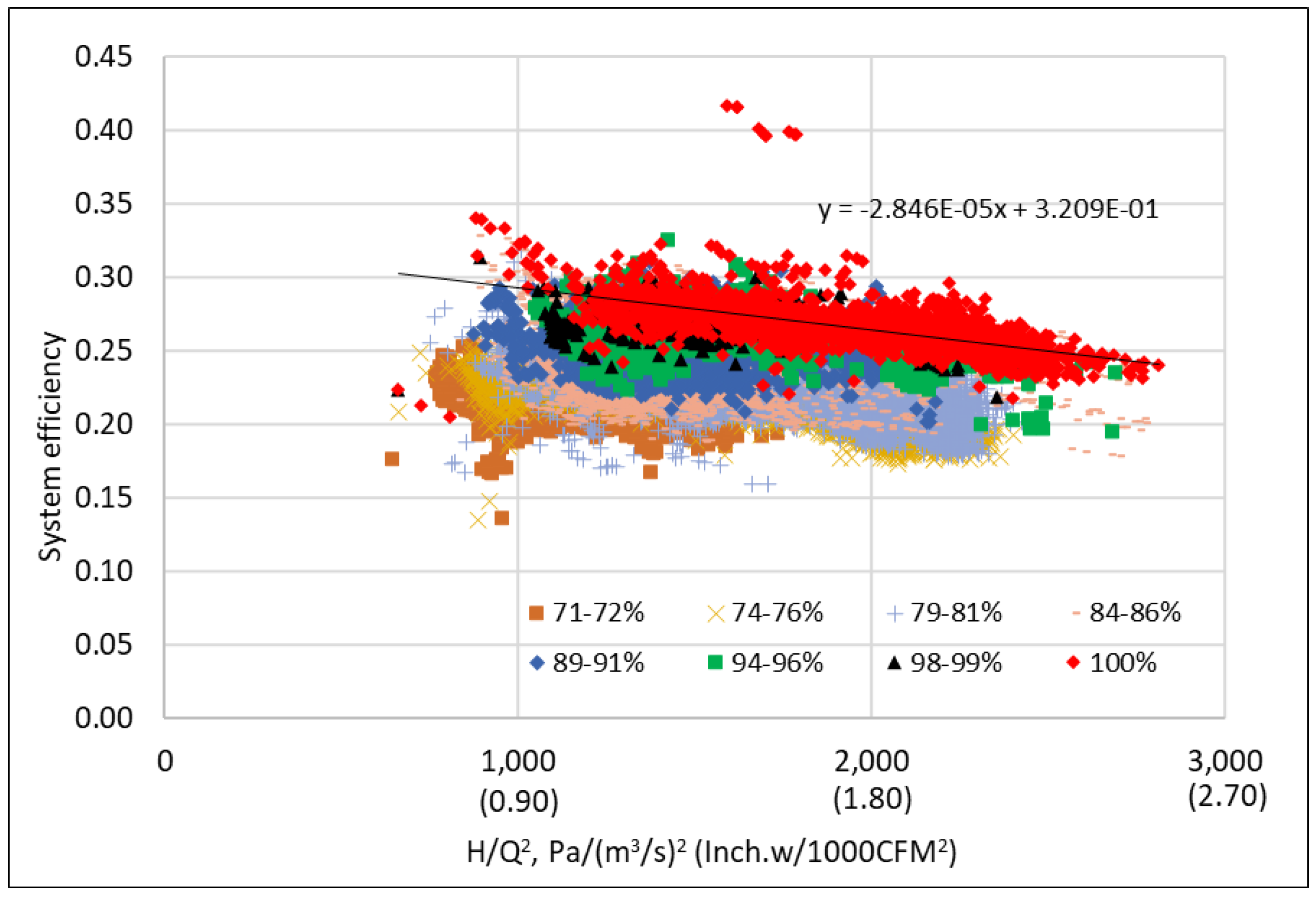
3.4. Speed-Independent Fan Efficiency Curve
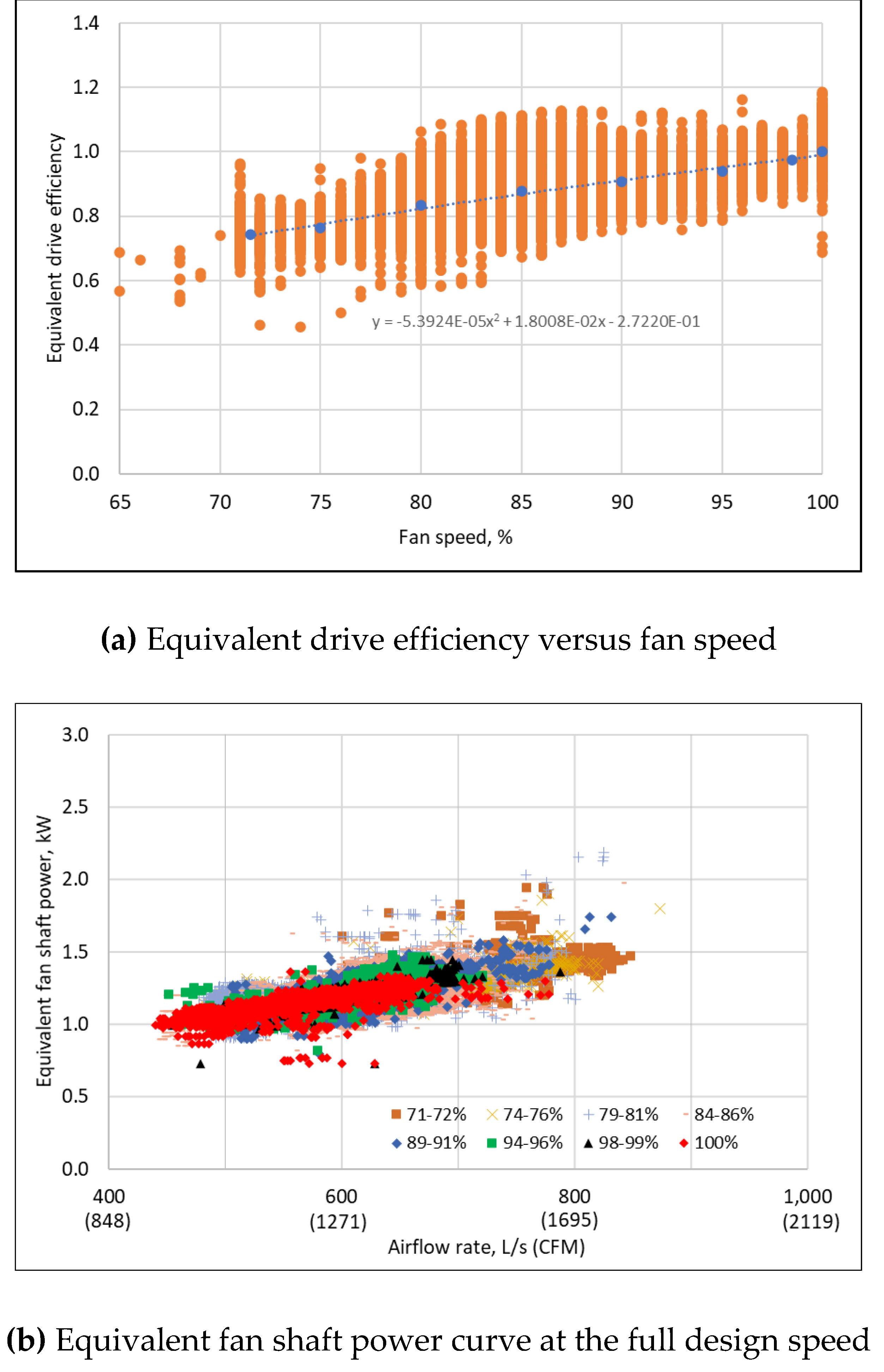
3.5. Drive Efficiency Curve
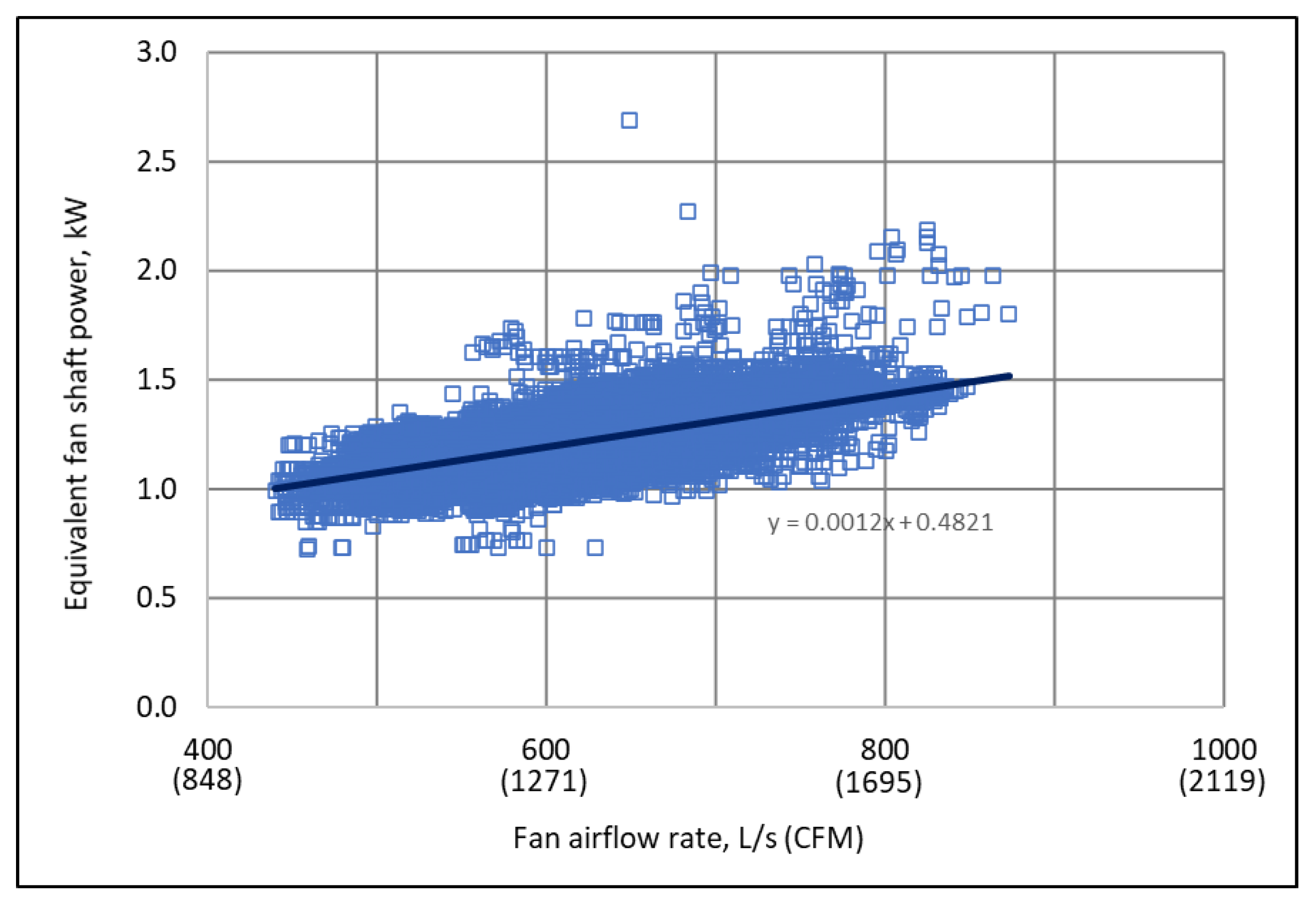
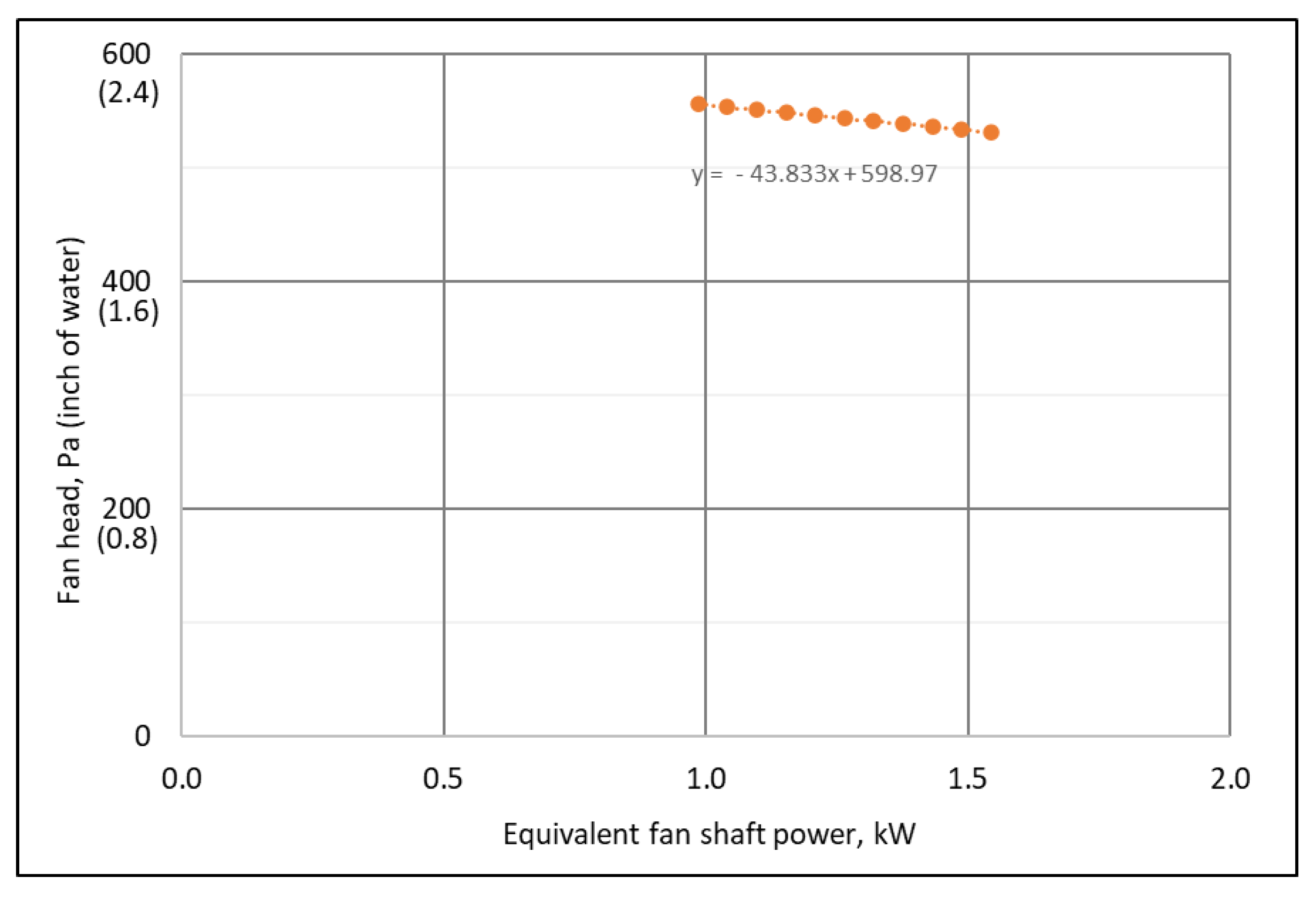
3.6. Fan Shaft Power Curve
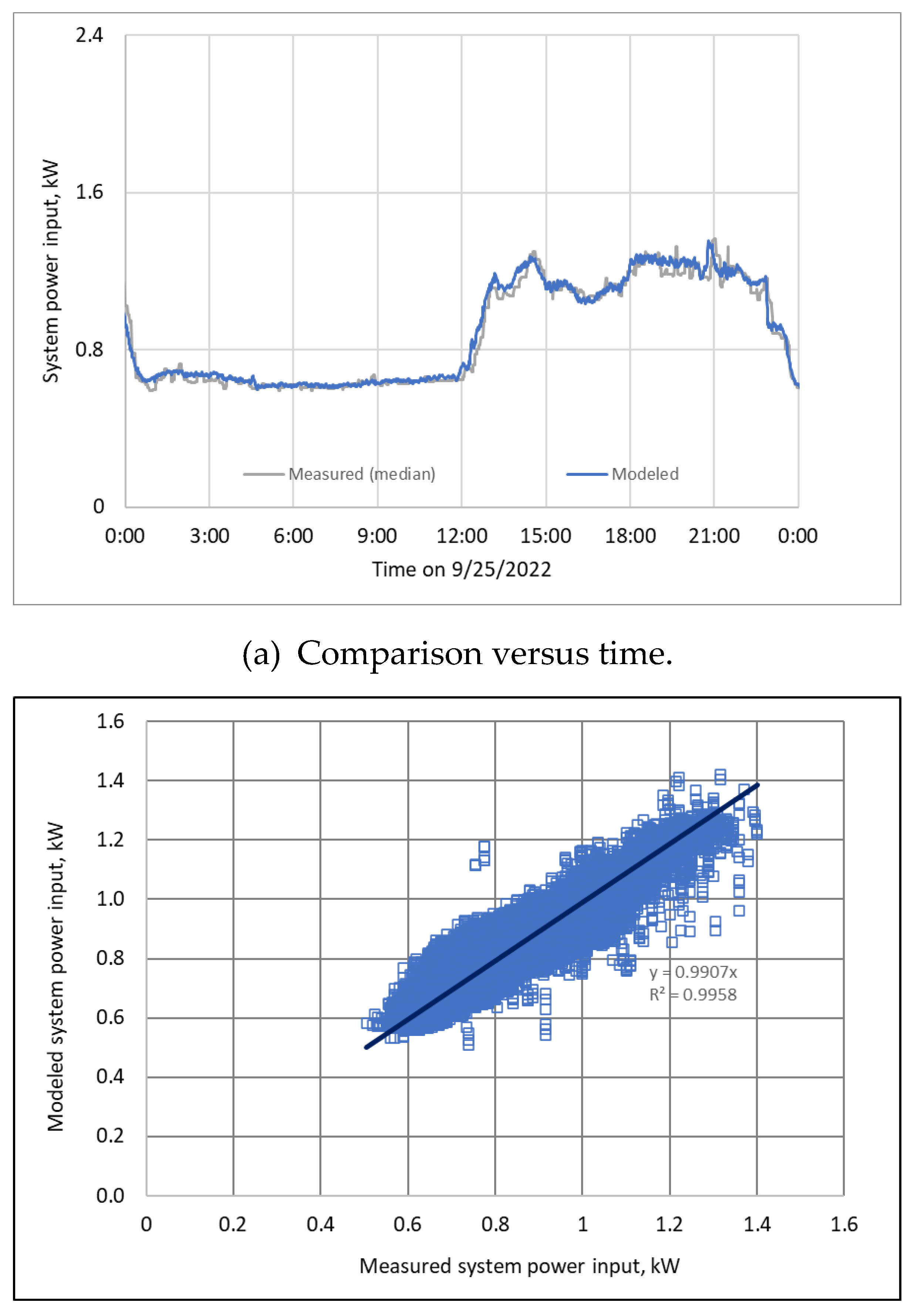
3.7. Energy Model and Overall Error Evaluation
4. Applications
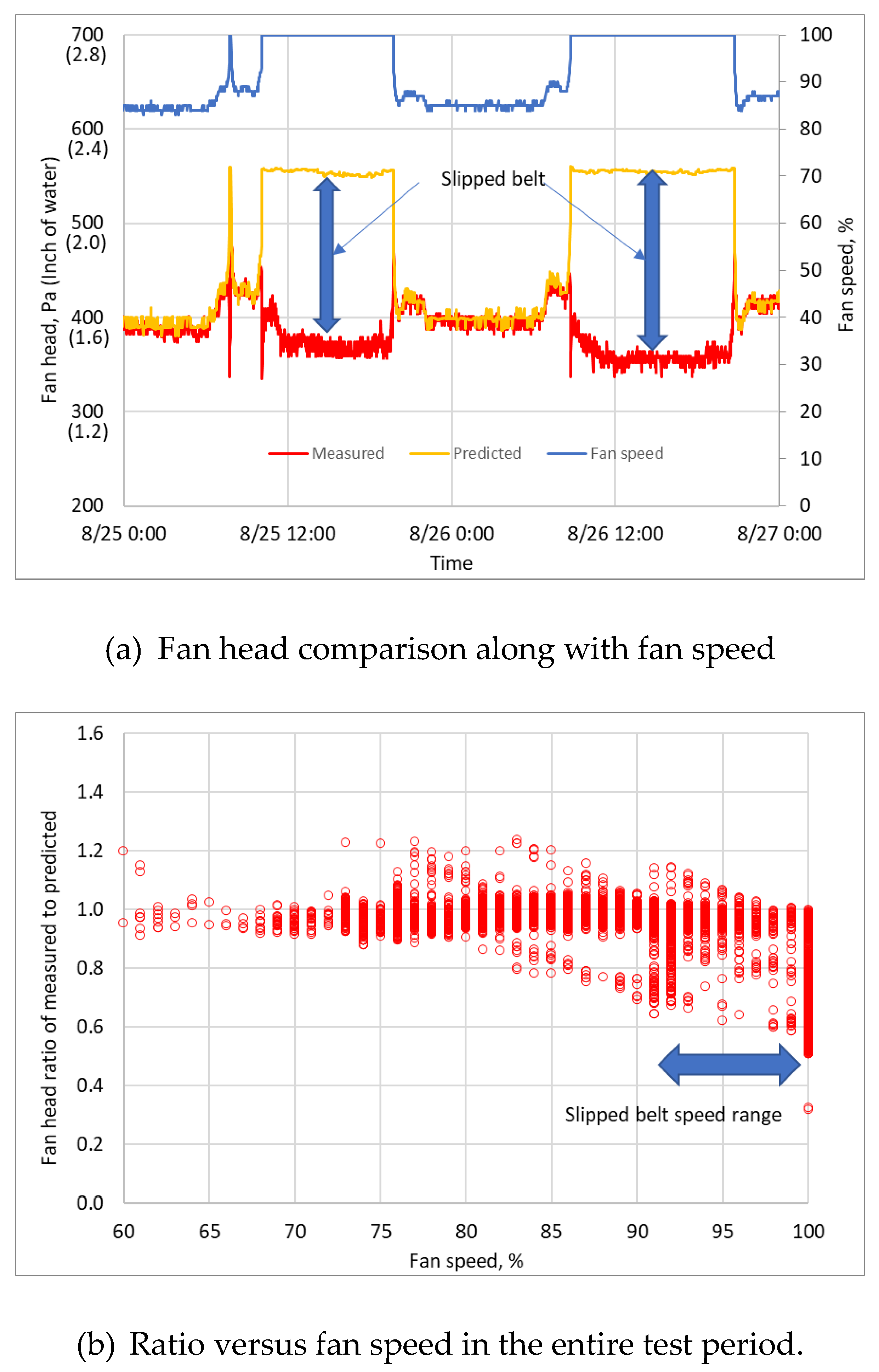
4.1. Fault Detection
4.2. Virtual Flow Meter Development
- The equivalent drive efficiency is determined by the available fan speed using Equation (20) and is applied to calculate the equivalent fan shaft power using Equation (17).
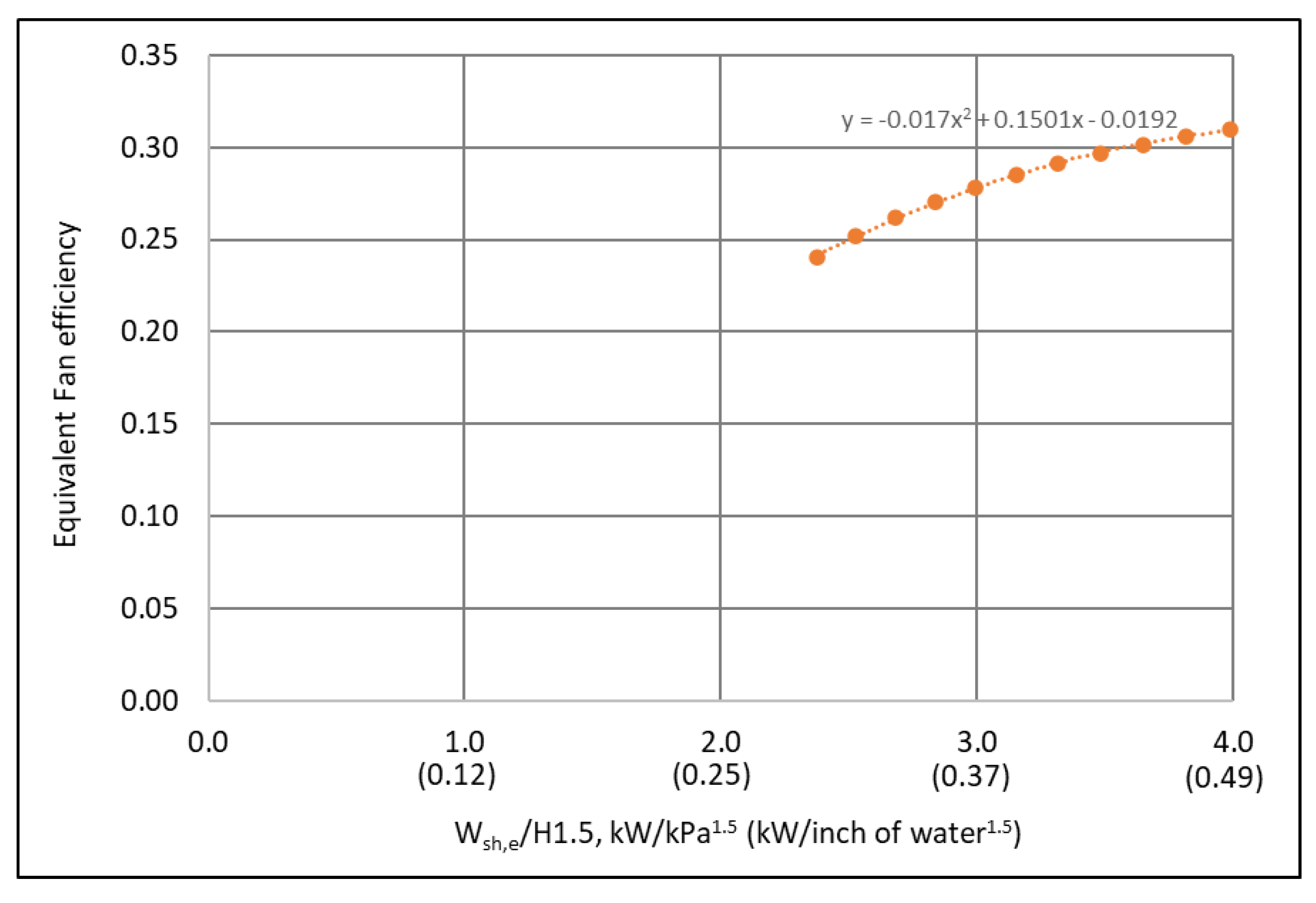
- According to the affinity laws, the equivalent fan efficiency can be represented as a function of the ratio of the equivalent shaft power to the fan head to the power of 1.5, as shown by Equation (9), independent with the fan airflow rate. Based on the identified fan head and equivalent shaft power curves shown in Figure 6 and Figure 9, the equivalent fan efficiency is presented in Figure 13 and is regressed as:where the equivalent fan shaft power is in kW and the fan head is in kPa.
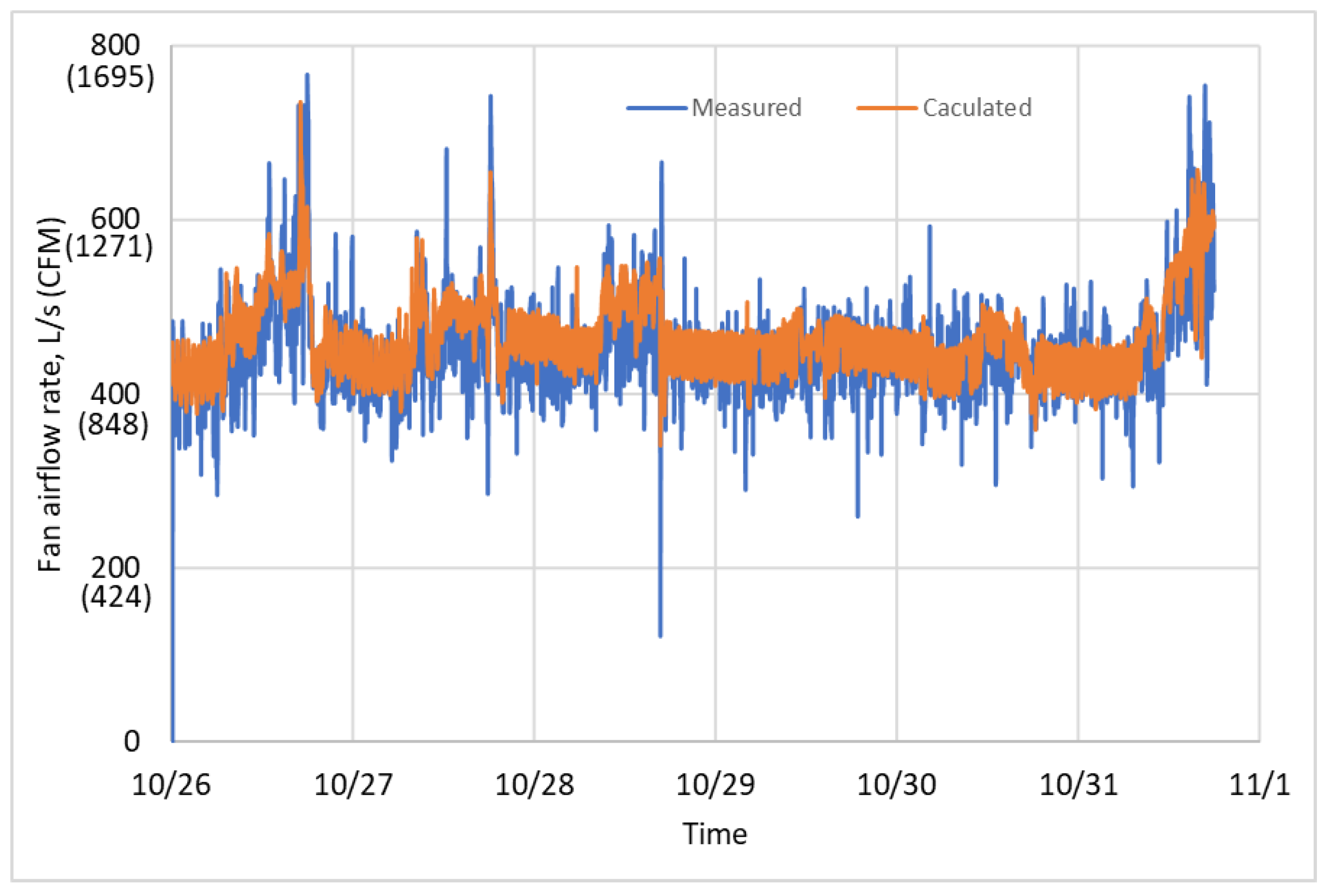
- The fan airflow rate can be virtually calculated from the measured fan head, speed, and system power input.
4.3. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Nomenclature
- f = general function or VFD output frequency
- H = fan head, Pa, kPa or inch of water
- Q = fan airflow rate, L/s, m3/s or CFM
- W = power, kW
- ω = fan speed, %
- η = efficiency
Subscripts:
- d = full design speed
- e = equivalent
- sh = shaft
- sys = drive system
References
- DOE, Energy Savings Potential and Opportunities for High-Efficiency Electric Motors in Residential and Commercial Equipment. 2013, The U.S. Department of Energy Building Technologies Office: Washington, DC.
- Friedman, H., et al., Building Commissioning: Innovation to Practice Technical Report. California Energy Commission, PIER Energy-Related Environmental Research Program. 2007, CEC-500-2008-074.
- Dong, J., et al., Development and calibration of an online energy model for AHU fan. 2019, Oak Ridge National Lab.(ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States).
- DOE, A sourcebook for industry: improving motor and drive system performance. 2008, Washington D.C.: The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy.
- Tukur, A. and K.P. Hallinan, Statistically informed static pressure control in multiple-zone VAV systems. Energy and Buildings, 2017. 135: p. 244-252. [CrossRef]
- Pang, X., M. Liu, and B. Zheng. Building pressure control in VAV system with relief air fan. in the Fifth International Conference for Enhanced Building Operations 2005. Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, October 11-13, 2005.
- Phalak, K. and G. Wang, Minimum outdoor air control and building pressurization with lack of airflow and pressure sensors in air-handling units. Journal of Architectural Engineering, 2016. 22(2): p. 04015017. [CrossRef]
- Hurt, R., et al., Preliminary Investigation of Active Demand Flexibility Control at Air-Handling Units Using Energy Feedback Control. ASHRAE Transactions, 2022. 128(1).
- Hughes, A., Electric Motors and Drives: Fundamentals, Types and Applications. 2nd ed. 2006, Burlington, MA: Newnes.
- McQuiston, F.C., J.D. Parker, and J.D. Spitler, Heating, ventilating, and air conditioning: analysis and design. 2004: John Wiley & Sons.
- IEEE, IEEE Std 112™-2017: IEEE Standard Test Procedure for Polyphase Induction Motors and Generators. 2017, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers: New York, NY, USA.
- Stein, J. and M.M. Hydeman, Development and Testing of the Characteristic Curve Fan Model. ASHRAE transactions, 2004. 110(1).
- Wildi, T., Electrical machines, drives and power systems, ed. t. Edition. 2002: Upper Saddle River: Pearson Education, Inc.
- Domijan, A., A. Abu-aisheh, and D. Czarkowski, Efficiency and separation of losses of an induction motor and its adjustable-speed drive at different loading/speed combinations. ASHRAE Transactions, 1997. 103(1): p. 228-234.
- Gao, X., S.A. McInerny, and S.P. Kavanaugh, Efficiencies of an 11.2 kW variable speed motor and drive. ASHRAE Transactions, 2001. 107.
- Burt, C.M., et al., Electric motor efficiency under variable frequencies and loads. Journal of irrigation and drainage engineering, 2008. 134(2): p. 129-136. [CrossRef]
- Wang, F., H. Yoshida, and M. Miyata, Total Energy Consumption Model of Fan Subsystem Suitable for Continuous Commissioning. ASHRAE Transactions, 2004. 110(1).
- Han, Z., L. Ding, and G. Wang, Experimental Investigation of Induction Motor Power Factor and Efficiency Impacted by Pulse Width Modulation Power and Voltage Controls of Variable-Frequency Drives. ASHRAE Transactions, 2021. 127: p. 817-828.
- DOE, Energy Tips: Motor Systems (Tip Sheet #11). 2012, The U.S. Department of Energy Advanced Manufacturing Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy: Washington, DC. .
- Krukowski, A. and C.P. Wray, Standardizing data for VFD. ASHRAE Journal, 2013. 55(12): p. 8-10.
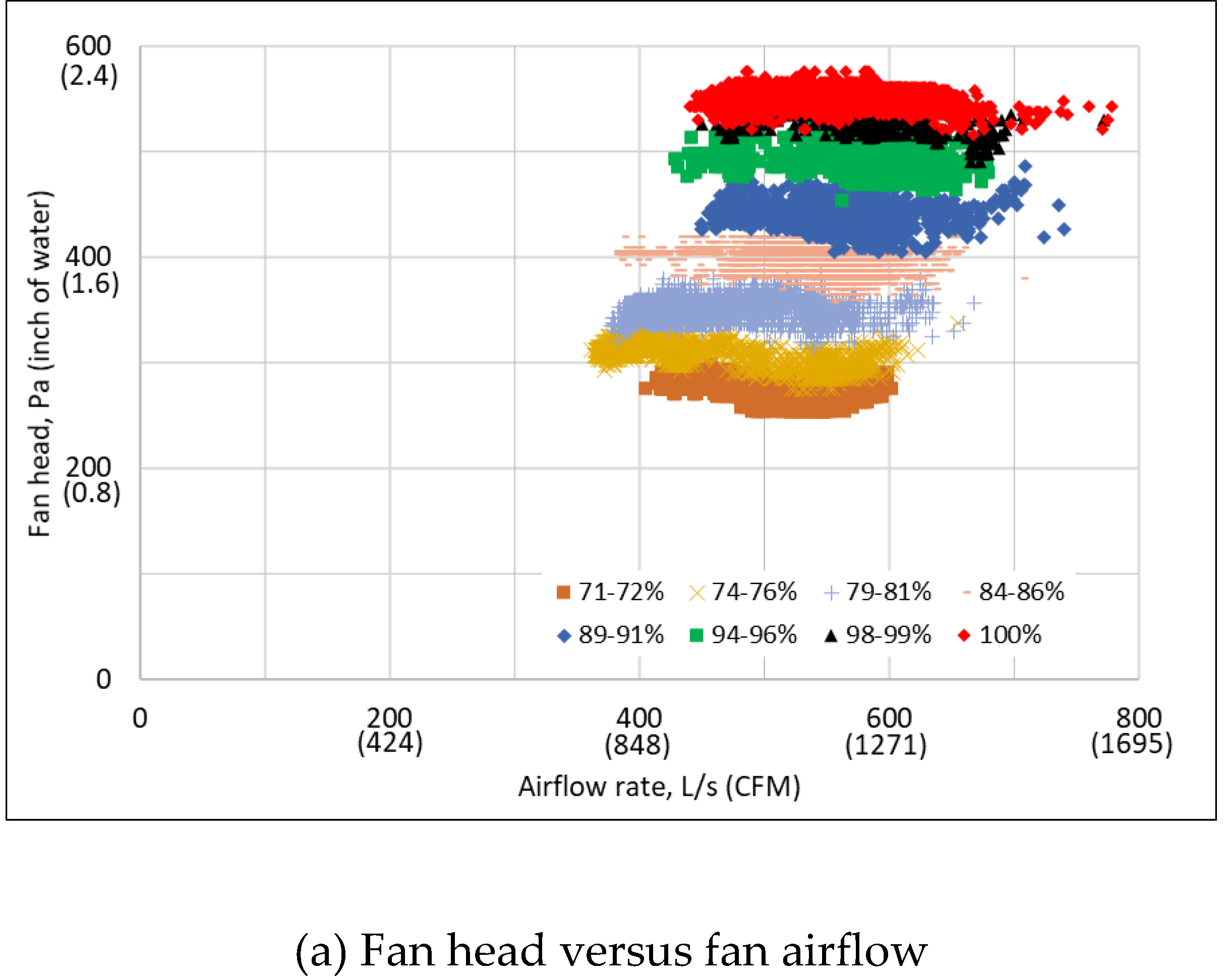
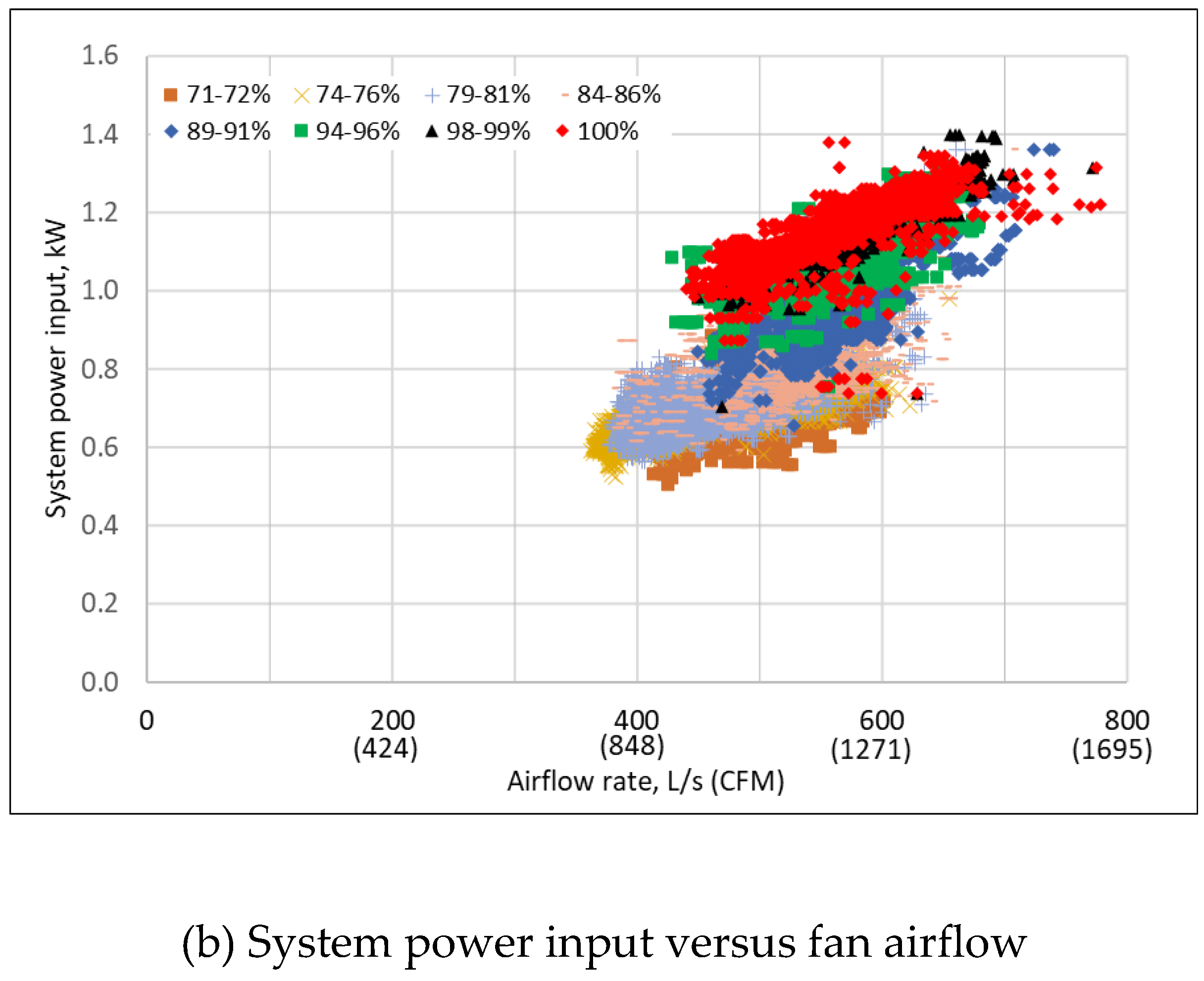
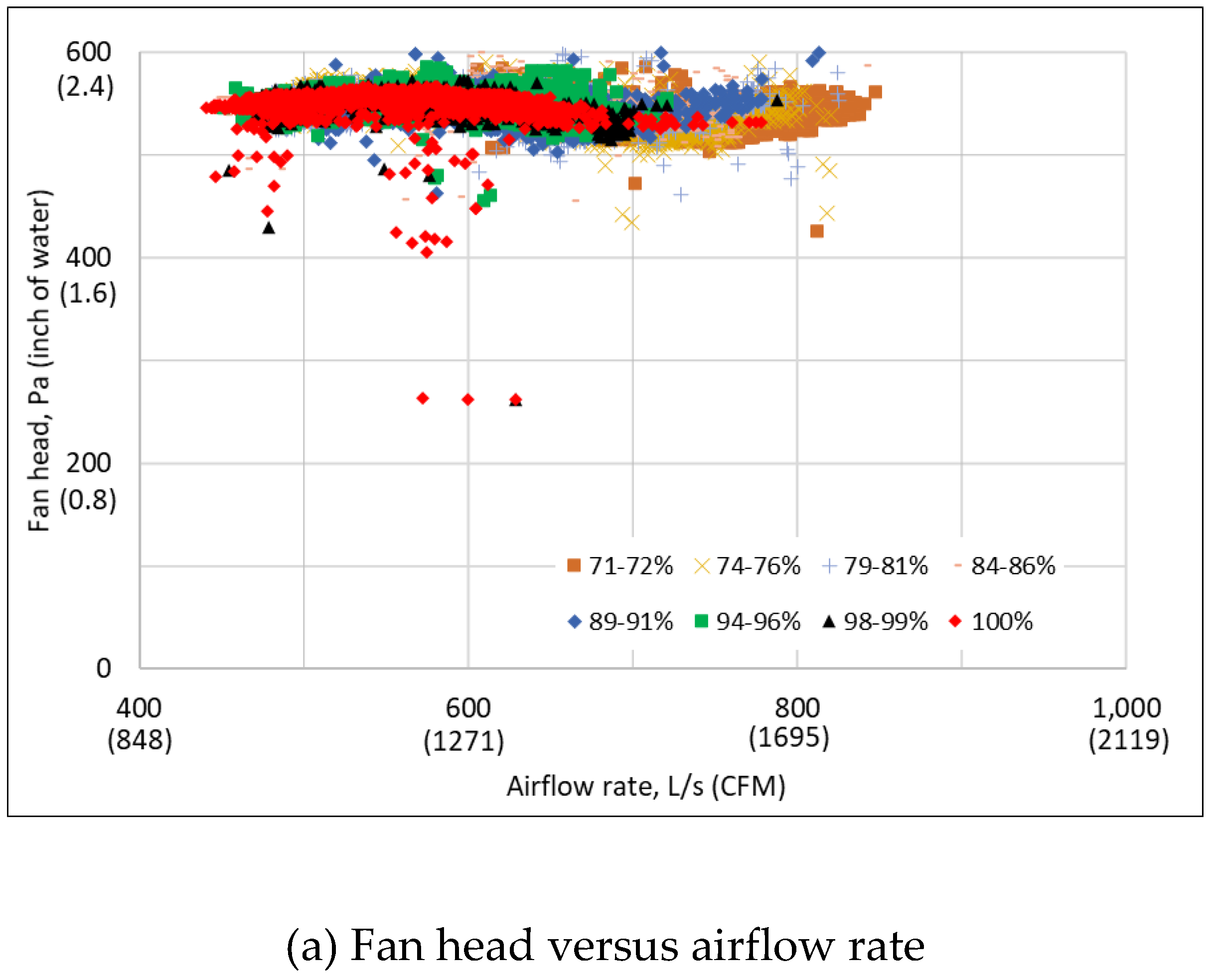
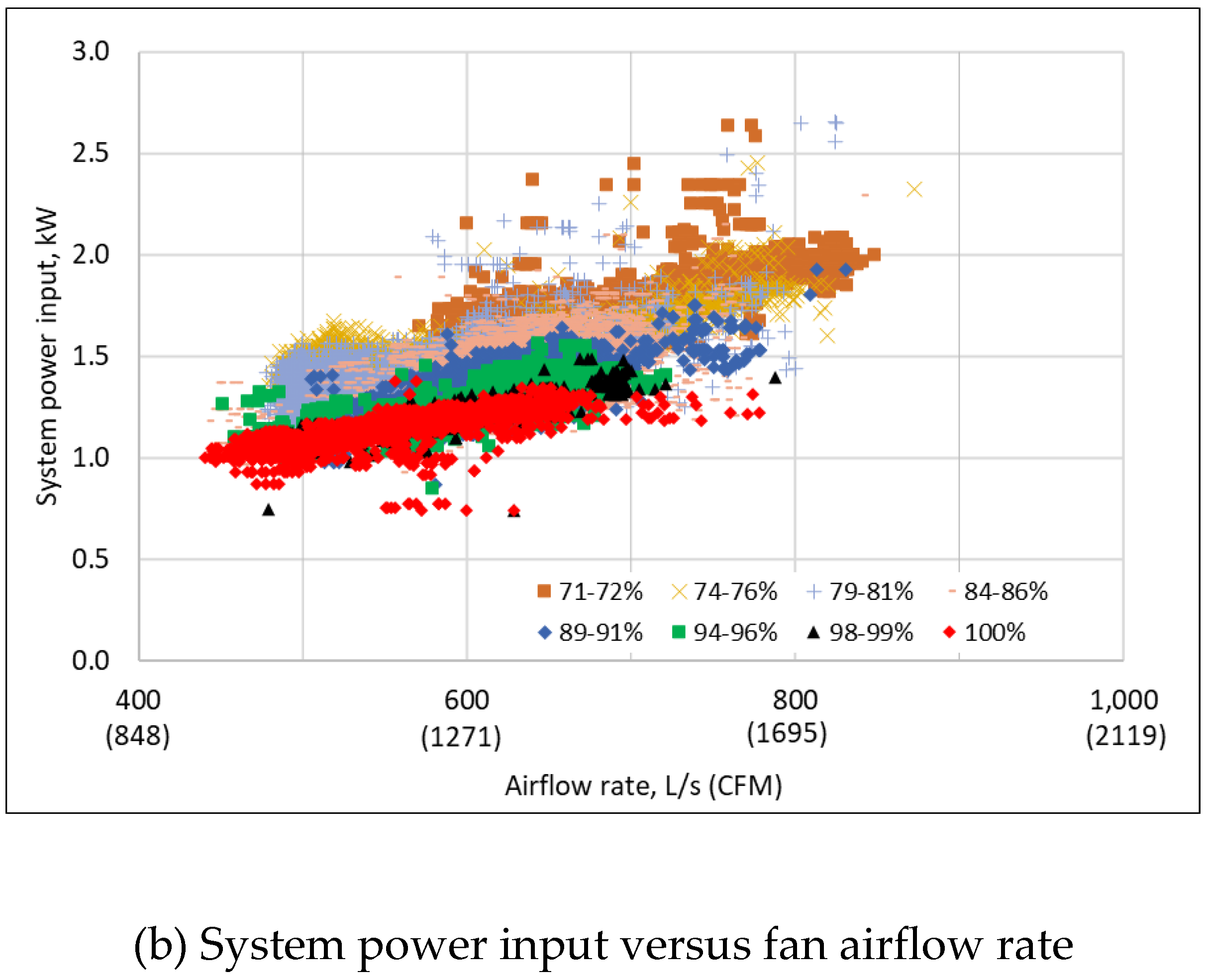
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




