1. Introduction
S-Allyl-L-cysteine (SC) is a major constituent containing maximum bioactive organosulfur compound obtained from garlic and has various biological applications by different mechanisms [
1]. SC is an amino acid (contains sulfur) obtained from bulbs of garlic and onion contains antioxidant activity [
2,
3], anti-cancer properties [
4,
5], anti-hepatopathic activity [
6] and neurotrophic activity [
7,
8]. A famous metabolite of allyl esters and allyl aldehydes is S-Allyl-L-cysteine (SC) [
9]. Nowadays, SC is the only marker compound that is used in clinical studies participating the garlic eating [
10]. S-Allyl-L-cysteine has also the most important for antimicrobial effects on gram-positive a)
Bacillus cereus; b)
Staphylococcus aureus; and Gram Negative: a)
Escherichia coli; b)
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, c)
Salmonella typhimurium; d)
Proteus mirabilis [
11,
12,
13]. Therefore, the oral bioavailability of SC is very important for the biological response of free- S-Allyl-L-cysteine [
14,
15].
Patient compliance is a very important criterion for oral delivery showing poor bioavailability is a problem still not solved [
16]. Drugs have a problem with oral delivery to maintain their enrichment of therapeutic concentration by application of dose increment or the use of novel drug delivery which will increase the pharmacokinetic parameters. If we enhanced the dose or multiple dosing which is drug wastage, not economical, enhancement of induction of adverse effects, and most important of costly drugs. Nanoformulation scientists are working nowadays on the same situation and their solutions with nano drug delivery [
17].
Nanoformulation is a great solution for the enhancement of a drug’s bioavailability from its modification in dosage forms for water-soluble drugs [
18]. Both copolymers polyglycolic acid (PGA) and polylactic acid (PLA) are copolymers responsible for the Poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) which is already got the approval from US-FDA for clinical application [
19]. PLGA showed great biocompatibility with degradability in physiological environments previously giving lactic acid and glycolic acid as biodegradation products which are natural metabolites. Based on these helpful applications, people are using PLGA as a carrier for the delivery of drugs and food. A macromolecule i.e. Radix Ophiopogonis polysaccharide which showed very less water solubility encapsulated via PLGA followed by PEGylation of PLGA to enhance its solubility and
in vivo bioavailability [
20]. Tanshinone IIA was encapsulated by the combination of glycyrrhetinic acid and PLGA biodegradable micelles which were used to target hepatocellular carcinoma [
21].
Our proposed current research showed the enhancement of S-Allyl-L-cysteine (SC) bioavailability via loaded PLGA NPs. SC loaded PLGA NPs were developed by emulsion solvent evaporation techniques containing the lowest PDI with the help of high-pressure homogenization. The current drug showed maximum dissoluble in basic pH of water than in distilled water. Therefore, ammonia solution was chosen as the inner aqueous phase solvent in this way we enhanced the solubility, encapsulation, and drug loading in PLGA NPs of SC. All the characterization-related parameters were performed like in vitro release, physicochemical characteristics, particle size, PDI, Zeta Potential, etc. All the effects related to nanoformulation parameters for SC PLGA-NPs were performed and examined.
On the basis of previous literature, they have published their reports on various methods for garlic extracts sample analysis or method based on simultaneous analysis with more compounds [
22,
23,
24]. There are two plasma analysis methods available for S-Allyl-L-Cysteine but in which one of them has developed in μg per mL (0.10 to 100) and another one has a drawback run time of up to 12 minutes [
1,
25]. On the other side, we found that there was no method available up to nanogram level analysis in plasma SC-alone with sensitivity up to picogram level with very less time run time i.e. 2.0 minutes for the examination of our drug. We have developed a novel LC-MS bioanalytical method for S-Allyl-L-Cysteine and validated it successfully for pharmacokinetic parameters examination of S-Allyl-L-Cysteine PLGA NPs. Our method showed various advantages like high sensitivity, maximum efficiency, lower retention, and run time for the examination of PK parameters in the plasma.
This is a first-time report to prepare SC PLGA Nanoparticles used in the increment of bioavailability of S-Allyl-L-Cysteine. The S-Allyl-L-Cysteine oral bioavailability was improved via PLGA NPs and to maintain the drug therapeutic level after oral delivery. SC PLGA NPs showed great effective-controlled and sustained release. A comparative PK-study was performed for the SC-S and SC PLGA NPs with the help of PK-examination (AUC0–t, Cmax, Kel, t1/2, etc.) and also comparative bioavailability based on the successfully developed and validated LC-MS/MS method. Finally, we have also performed the most important antimicrobial study for SC-S and optimized-SC PLGA NPs against gram-positive (Bacillus cereus, Staphylococcus aureus) and gram-negative bacteria (Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Salmonella typhi) for the antibacterial activity with 100µl of SC-S and SC PLGA NPs samples and another one is a dose-dependent antibacterial activity with 30 µl; 50 µl and 100 µl of SC-S and SC PLGA NPs samples.
2. Materials and Methods
S-Allyl-L-Cysteine was purchased from Sigma. Poly (vinyl alcohol, MW 25,000) and PLGA were bought from Polysciences Inc, 400 Valley Road. We used LC-MS grade solvents like Acetonitrile, Methanol, ammonium acetate, formic acid, and ammonium formate were bought from Sigma-Aldrich Corporation (St. Louis, MO, USA). Milli–Q–Water i.e. Ultra-pure-water was used in the entire study. Other chemicals were used analytical grade from various marketable sources. For antimicrobial activity, Mueller-Hinton agar medium and for bacterial culture, Mueller-Hinton broth were purchased from Oxoid, UK.
Nanoparticles Preparations for S-Allyl-L-cysteine
We have used the emulsion solvent evaporation method for the development of S-Allyl-L-cysteine PLGA NPs [
26]. We dissolved PLGA (55mg) in the 6.0 ml dichloromethane and on the other side, 30 mg S-Allyl-L-cysteine was dissolved in 1.5 ml ethanol. We performed the experiment on the ice with the help of sonication for up to 2 min for the emulsification. Now 10 ml 0.3% PVA has been added drop by drop by walls of tubes in the mixture of PLGA solution. After that more emulsification was performed at 0ºC with the help of sonicator extra two minutes. Now this solution stirrer the whole night for the evaporation of DCM at room temperature. The next day, we centrifuged the whole solution for forty minutes up to eighteen thousand rpm. After that collected the supernatant and then discarded it. Now ppt was again dissolved into Milli-Q-water and got it in the suspended form. These pellets were freeze-dried to get the SC loaded PLGA NPs.
Morphology of S-Allyl-L-cysteine
Determination of particle size is very important to study the NPs. The size of particles is going to be smaller which means enhancing the surface area of drug absorption [
27]. We have used the Zetasizer for the examination of particles-size, PDI, and ZP. We diluted our preparation prior to determining the size of the particle, PDI, and ZP. We performed this experiment at 25.0°C and also scattering angle was fixed at 90° [
26].
TEM Study for SC PLGA NPs
The transmission electron microscope was used to determine the size, shape, and structure of the SC PLGA NPs. Dispersed nanosuspension was added into the TEM grids containing the carbon support film having holes. The specimen inside the TEM grids were dried by air followed inserting it for TEM imaging. We have taken the TEM images [
27].
Other Characterization of SC PLGA NPs
We examined the %EE and %LC of the optimized nanoparticles with the help of the ultracentrifugation technique for thirty minutes at four °C at 15,000.0 rpm. We have taken the supernatant-free amount of S-allyl cysteine to determine the actual amount from our in-house developed method LC-MS. We measured three times and after that used the below equation to the %EE & %LC calculation of SC PLGA NPs [
26]:
%Process Yield was calculated based on the below-mentioned formula:
The release amount of in vitro for S-Allyl Cysteine
We performed the release of SC
in vitro via a before-treated dialysis membrane containing the pore size positive 2.4nm, ∼12.0–14.0 kD cut-off molecular weight [
26]. We prepared the NaCl (0.2% w/v) in HCl (0.7% v/v) and maintained the pH: 1.20 as a medium for the simulated gastric fluid and another one pH:6.80 as simulated intestinal fluid not containing enzymes. We maintained the 37.0±1.0°C temperature continuously stirring for up to six hours at 100rpm. We checked for any leakage in the dialysis bag after that kept SC PLGA NPs in the dialysis bags in which SC:0.5mg. We chose 30, 60, 120, 240, 360, 480, 720, and 1440 minutes for sampling time points to evaluate the release of S-allyl cysteine from SC-S and SC PLGA NPs. We withdraw the 1.0 mL sample for each sampling point. We filtered the withdrawn samples from a 0.22 μm syringe filter for the determination of S-allyl cysteine from our developed LC-MS/MS method.
Animal Examination
We have taken ethical approval from the Animal ethical approval Committee, Imam Abdulrahman Bin Faisal University (IAU) for PK/PD studies. We have withdrawn all rats from IAU Animal House containing 190 to 220 grams weight as separated as grouped i.e. 5-6 in each cage, followed by maintaining the natural light & dark cycle with free reachable to food and water. We have also maintained the temperature at 20-30°C with 50-550% humidity. We followed the IAU laboratory-prescribed conditions.
Standard and quality control samples preparation
We prepared the stock in the water (1mg/mL) with the help of a vortexer for five minutes. We performed further dilution for the preparation of calibration curves with the help of 5% spiking (950µL plasma + 50µL aqueous) in blank plasma spiking obtained the final standard plasma samples i.e. 5.0, 10.0, 49.5, 214.4, 424.4, 640.0, 850.0, 1000.0 ng/mL for the calibration curve. We have also prepared the QCs dilutions (5.01, 14.90, 445.00, and 840.00ng/mL) in the spiking of plasma for the determination of inter- and intra-day precision and accuracy. All prepared aliquots were stored to freeze at –40.0ºC before the analysis.
A Sample Preparation in Plasma
We kept all plasma samples inside into the deep freezer before going to bioanalysis at –80 ºC. We have withdrawn all plasma samples based on requirements and kept them to thaw at room temperature for equilibration followed by vortexing. 550 µL sample was transferred into the fresh test tube on the ice bath and the 5.0% Formic Acid was added to the breaking of plasma protein with help of vortexing. Now add the Methanol (4mL) and kept on the shaker for shaking for up to fifteen minutes. The centrifugation was done for all samples for ten minutes four thousand rpm at 4.0 ºC. We dried under N2 Steam water bath 2.5 mL supernatants which were taken into fresh test tubes. The mobile phase (750 µL) was transferred into dried test tubes and then vortexed for four minutes to reconstitute. We have transferred reconstituted samples into the vials. Samples were injected (10µL) into LC-MS for analysis.
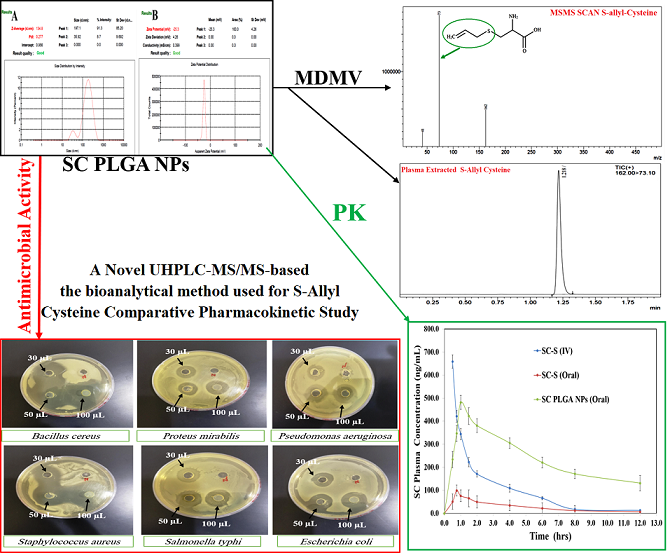
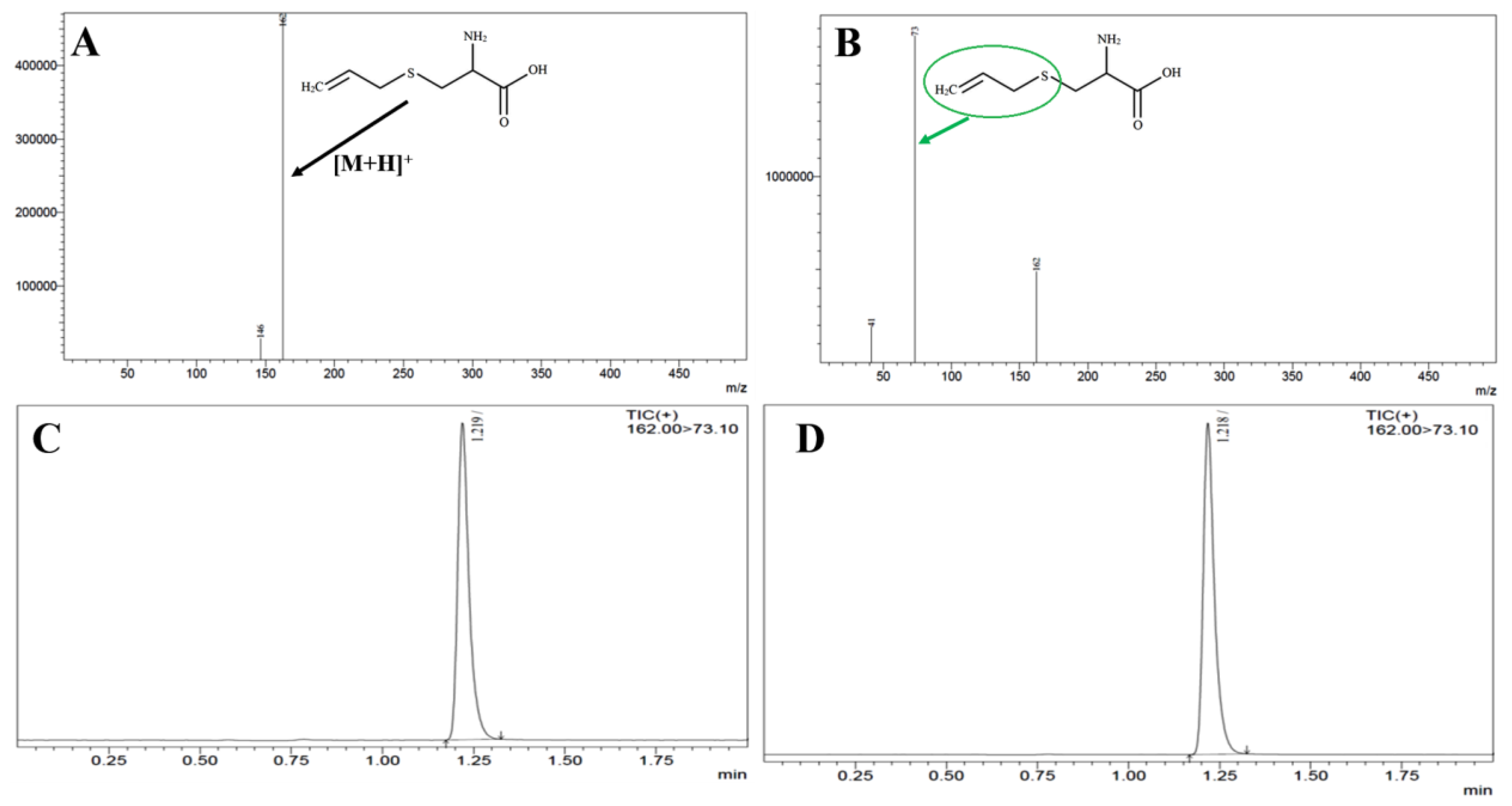
LC-MS bioanalytical development and their validation for S-Allyl-L-Cysteine
Shimadzu LCMS-8050 contains ESI with triple quadrupole with the help of Waters ACQUITY Column C-18 (100.0 mm; 1.70 μm) developed a novel method with highly sensitive & great resolution of chromatogram used for bioanalysis and pharmacokinetic elution and separation by binary-solvent-manager Shimadzu UHPLC. We optimized our method with mobile phase (methanol: formic-acid (0.10%) :: 92:08), flow rate:0.30ml/min, injection-volume (10µl), and 2.0 min of total run time. Argon gas was used as collision gas, scan time (one-min.), inter scan (0.02 seconds) having 30,000 μ/s & 0.10μ scan step. The +ve ion mode and collision energy (–13.0eV) was used for the quantification of SC and their mass spectra are shown in
Figure 4. SC quantity in plasma was determined by Lab Solution Software Version 5.93 (Kyoto, Japan). All the samples (CC & QC) were freshly prepared and plasma unknown samples were quantified with them (
Figure 4). US-FDA guidelines were followed at the time of method validation that was given the excellent results into their fit relationship of concentration-detector response and a regression equation (1/x
2) was used [
26,
27].
Pharmacokinetic Evaluation
We have withdrawn rats (18, 200–240 g) from the animal house and divided them into three groups for oral [SC-S or SC PLGA NPs] and iv (SC-S) with 15 mg/kg dose administration. Heparinized tubes were used for the collection of rat plasma samples at various time intervals (0.0-, 0.5, 0.75, 1.0-, 1.5-, 2.0, 4.0, 6, 8, and 12-hrs). We centrifuged all collected blood samples at 4000 rpm for 7 min to separate the plasma. We stored our plasma samples at –80 ºC [
28]. All the parameters related to the PK study were analyzed which are half-life time (t
1/2), elimination rate constant (Ke), Highest-plasma quantity of SC (C
max), and the time of highest plasma quantity (T
max), etc.
A comparative study of SC PLGA NPs for antimicrobial activity by Agar well diffusion method
Strains of Bacteria
We have collected all Gram +ve and Gram –ve bacteria clinical isolates from Clinical Laboratory Sciences Department, Applied Medical Sciences College, King Saud University, Riyadh.
Agar well diffusion method
We have used the Agar well diffusion method to examine the antimicrobial activity of SC-S and SC PLGA NPs. We have prepared all Petri plates with help of Mueller-Hinton agar for six various microbial strains. We poured sterile Mueller-Hinton agar (18-20ml) into all separated Petri plates. After solidification of media, sterile cotton buds were used to inoculate bacterial cultures (50 μl) prepared in Mueller-Hinton broth, and 6 mm wells were made in the plates with the help of a sterile cork borer according to Boyanova et al and Feroze et al with some modifications [
29,
30]. The activity was evaluated against two Gram-positive (
Staphylococcus aureus and
Bacillus cereus) and four Gram-negative (
Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhi, Proteus mirabilis, and
Pseudomonas aeruginosa) bacterial species. Two separate studies were performed:
1. Antibacterial activity with 120µl of SC-S and SC PLGA NPs samples;
2. Dose-dependent antibacterial activity with 30 µl; 50 µl and 100 µl of SC-S and SC PLGA NPs samples. We incubated all the plates at 37ºC for 18-24 hours to measure the zone of inhibition in mm. We have performed the all tests in triplicate.
Statistical analysis
The student’s t-test was used to apply for statistics followed by one-way ANOVA and showed all the data in mean±SD in which all values were statistically significant (**p<0.01).
3. Results
NPs Preparation and their characterization
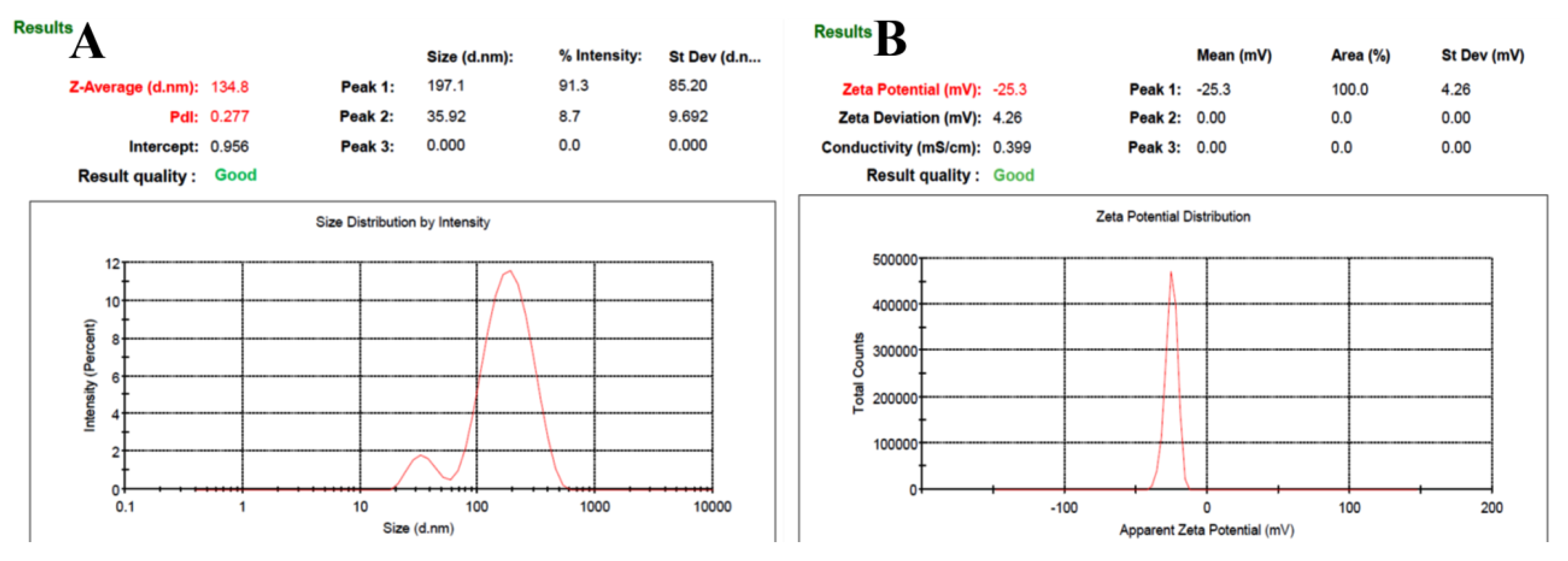
We used solvent evaporation techniques for the preparation of SC PLGA NPs.
Figure 1 showed the PS, ZP, & PDI for the optimized-NPs characterization. We found the particle size i.e. 134.8 ± 4.61 nm, dispersion (PDI: 0.277 ± 0.004), and zeta potential (−25.3 ± 1.03). %EE and % DL were determined i.e. 82.36 ± 4.01 % and 5.13 ± 0.10, respectively [
32].
Nanoparticles Analysis by TEM
We analyzed our developed NPs showed spherical-shaped as mentioned with <200 nm as shown in
Figure 2.
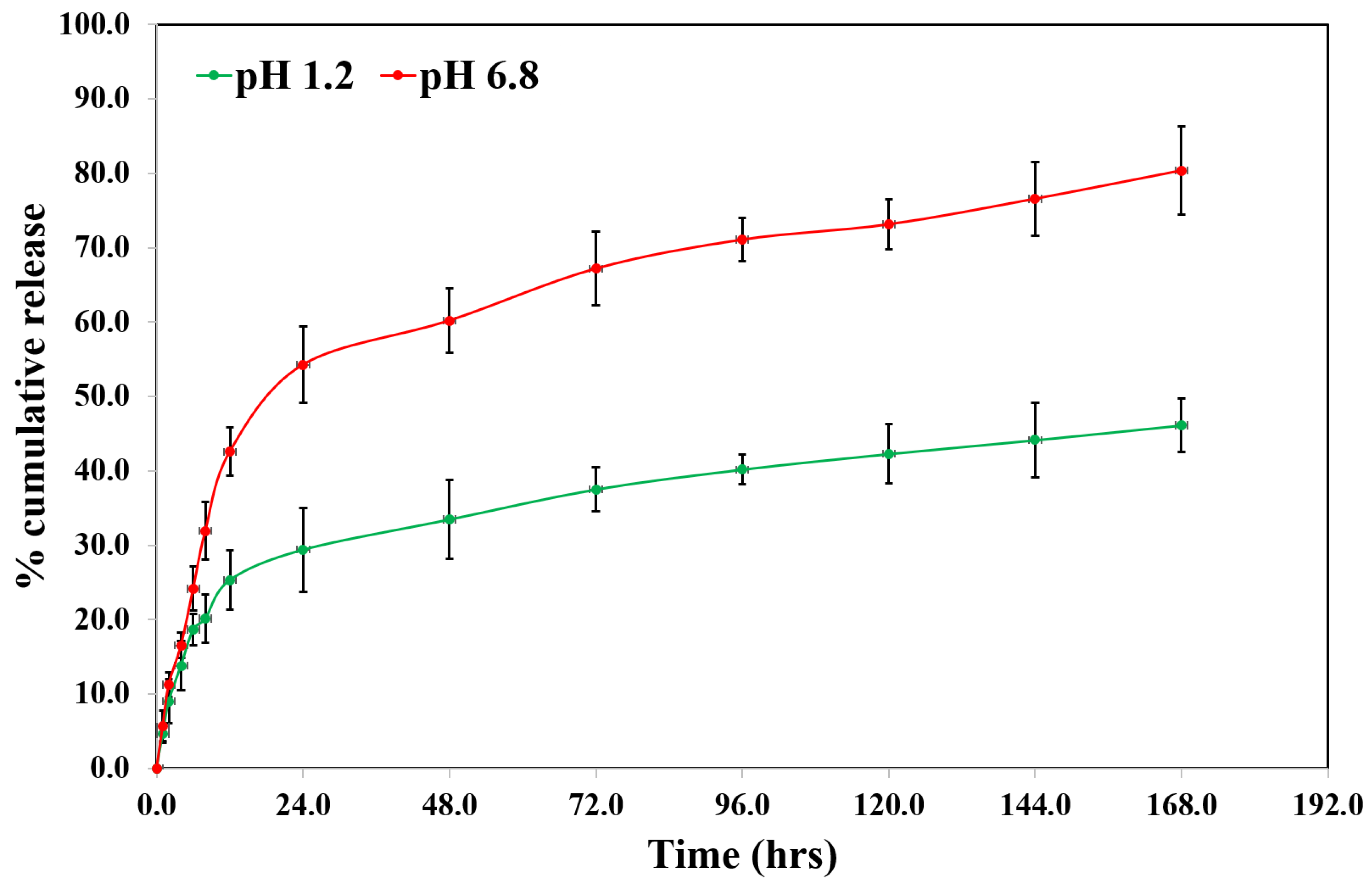
Release kinetics (in vitro)
S-Ally-L-Cysteine was released from SC-PLGA-NPs in different environmental conditions like two different juices (gastric & intestinal). SC showed a fast release up to the first twelve hours in simulated gastric and intestinal fluids (
Figure 3). It can be because the SC bonded loosely upon or near of the NPs surface [
32]. After that it showed a very slow release up to 46.14 ± 4.93% in the artificial gastric fluids and sustained & delayed release up to 80.39 ±3.64% in the artificial intestinal fluids.
Bioanalytical method development and validation
We have optimized one method and validated represented in Figures 4A & 4B (MS & MS/MS scans of SC) and their chromatograms (Figures 4C & 4D). We have observed the >77.09±5.07% recovery for SC (n=6) from extracted plasma. We have also examined the linearity of the developed method i.e. r
2>0.993 (1–1000 ng mL
-1). Intra-batch was 1.88–3.82% and inter-batch was 2.61–4.23%precision for all levels of QCs for SC. Accuracy (%) was 93.02 to 99.40% for intra-batch and 2.61 to 4.23% for all levels of QCs for SC with % Recovery for all QCs 77.09±5.07% to 81.28±3.96 (
Table 1). We have also determined all types of stability validation for our developed method which showed under the acceptance limit of US FDA guidelines. Furthermore, the results regarding
Ex vivo stability data for S-Allyl Cysteine (SC) experiments are represented in
Table 2 [
33,
34].
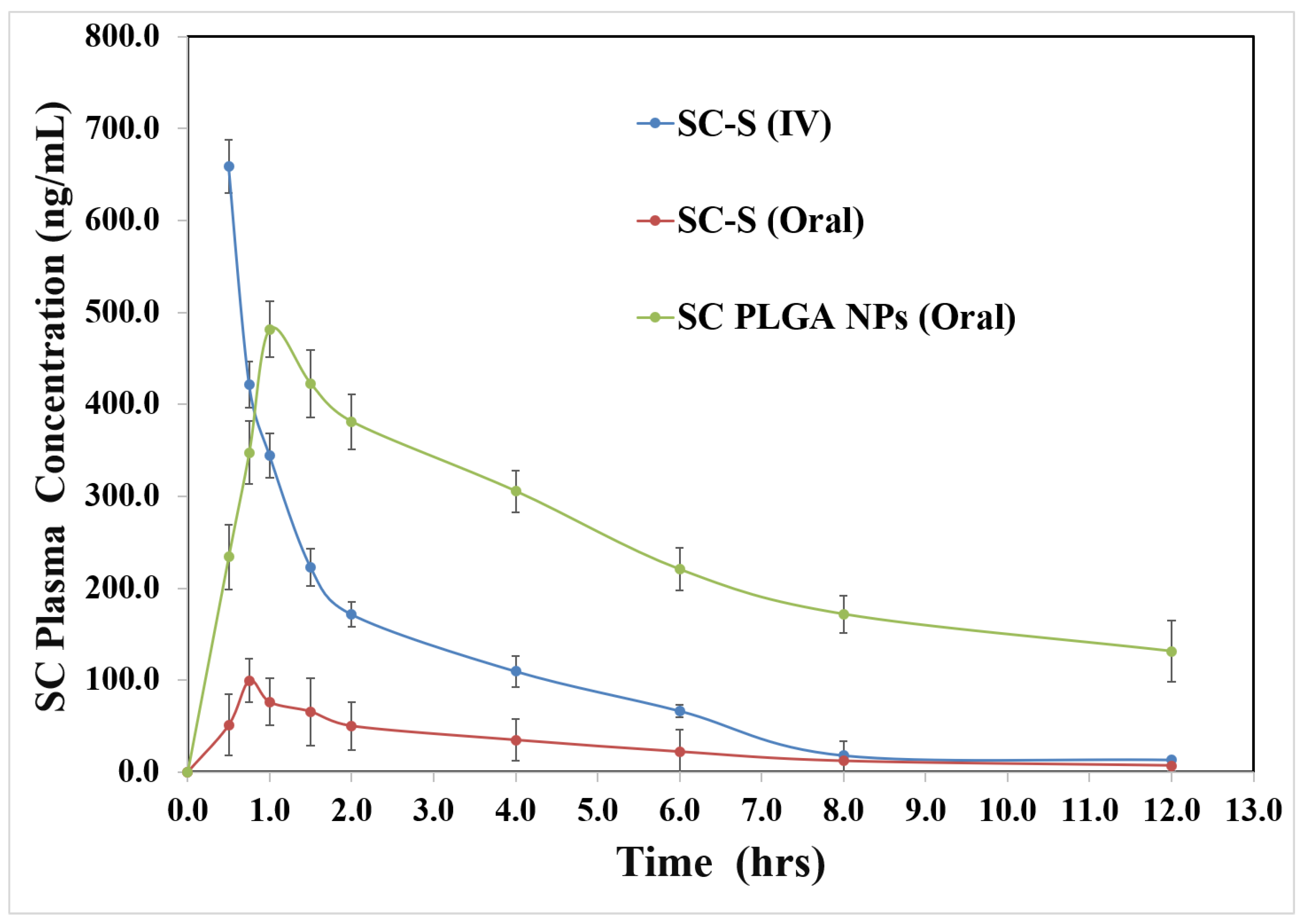
In vivo Bioavailability and Pharmacokinetics
S-Allyl-L-Cysteine shows the maximum plasma concentration-time (for iv & oral administration of SC-S and SC PLGA NPs), which is exhibited in
Figure 5; pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated and summarized in
Table 3. The peak plasma concentrations of SC from SC loaded NPs was found to be highest as compared to free SC-S. We were also found to be the value of t
1/2 and t
max i.e. 7.38±0.316 & 1.00 hours respectively, which was greater than SC-S for oral and iv administration. We have found that SC PLGA NPs showed greater plasma concentration, smaller amount of clearance, and higher half-life as compared with free SC-S in rats. SC-S showed smaller C
max may be due to the lower amount of permeation, self-aggregation, and delayed metabolism facilitated through P-glycoprotein (P-gp) efflux pump. On the other side, enhancement of C
max and AUC
0-t shown for SC PLGA NPs may be due to the reduction in first-pass metabolism of SC PLGA NPs reaches to the systemic circulation via gut-related lymphatic tissue [
28].
Figure 4.
MS Scan [A], MSMS Scan [B], chromatograms of extracted plasma [C] and [D] of S-Allyl Cysteine.
Figure 4.
MS Scan [A], MSMS Scan [B], chromatograms of extracted plasma [C] and [D] of S-Allyl Cysteine.
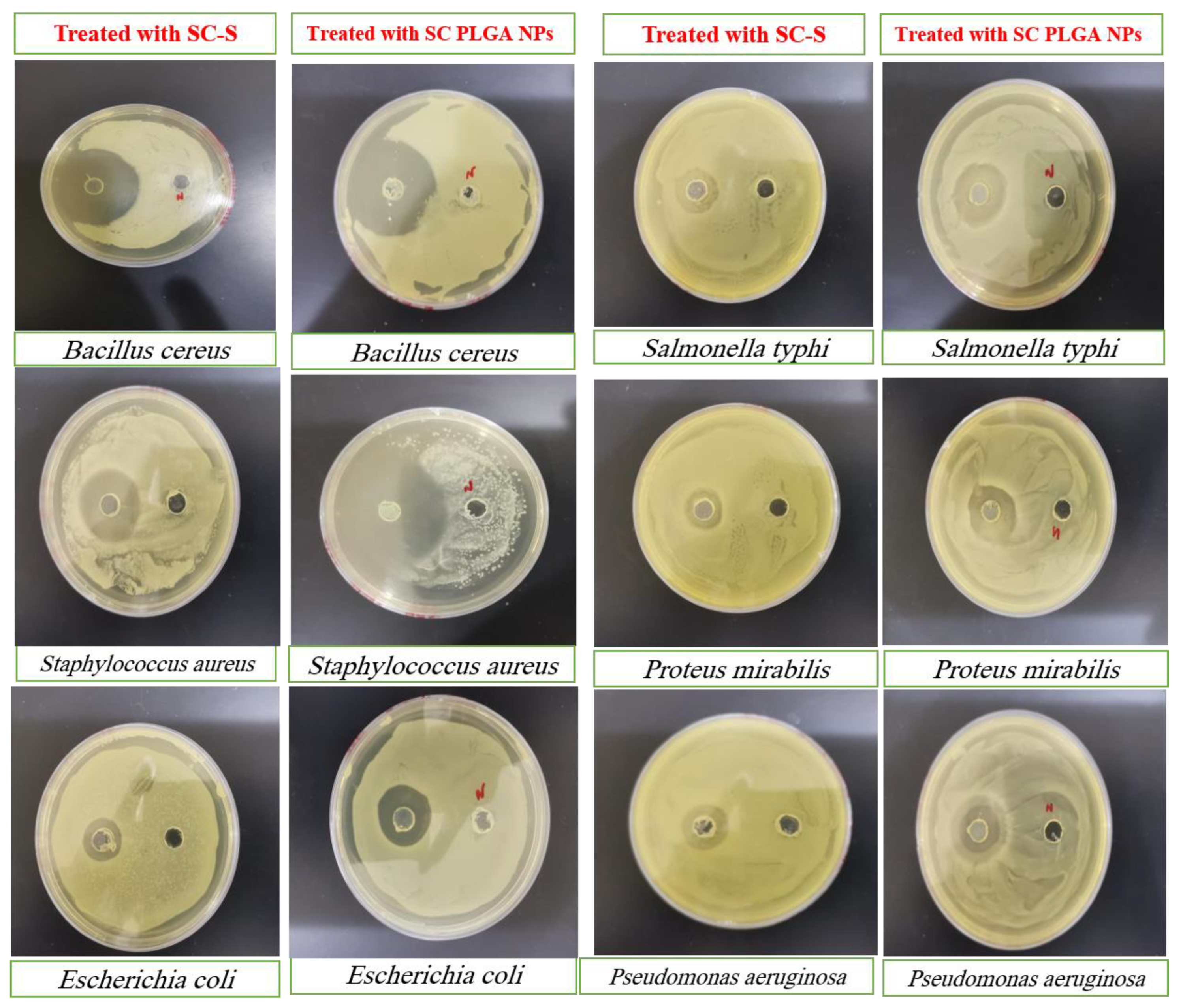
Antibacterial activity
The antimicrobial potential (inhibition zone) of pure SC-S and SC PLGA NPs against different strains of Gram Positive (
Staphylococcus aureus and
Bacillus cereus) and Gram-negative (
Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhi, Proteus mirabilis, and
Pseudomonas aeruginosa) bacterial species shown in
Table 4. All the antimicrobial potential effects of SC PLGA NPs are statistically significant (p<0.01) against various strains of gram +ve and Gram –ve bacterial species as compared to those treated with pure SC-S (
Table 4,
Figure 6). Our optimized polymeric nanoparticles of S-Allyl-L-cysteine (SC PLGA NPs) have maximum effects against these pathogenic microbial strains [
35].
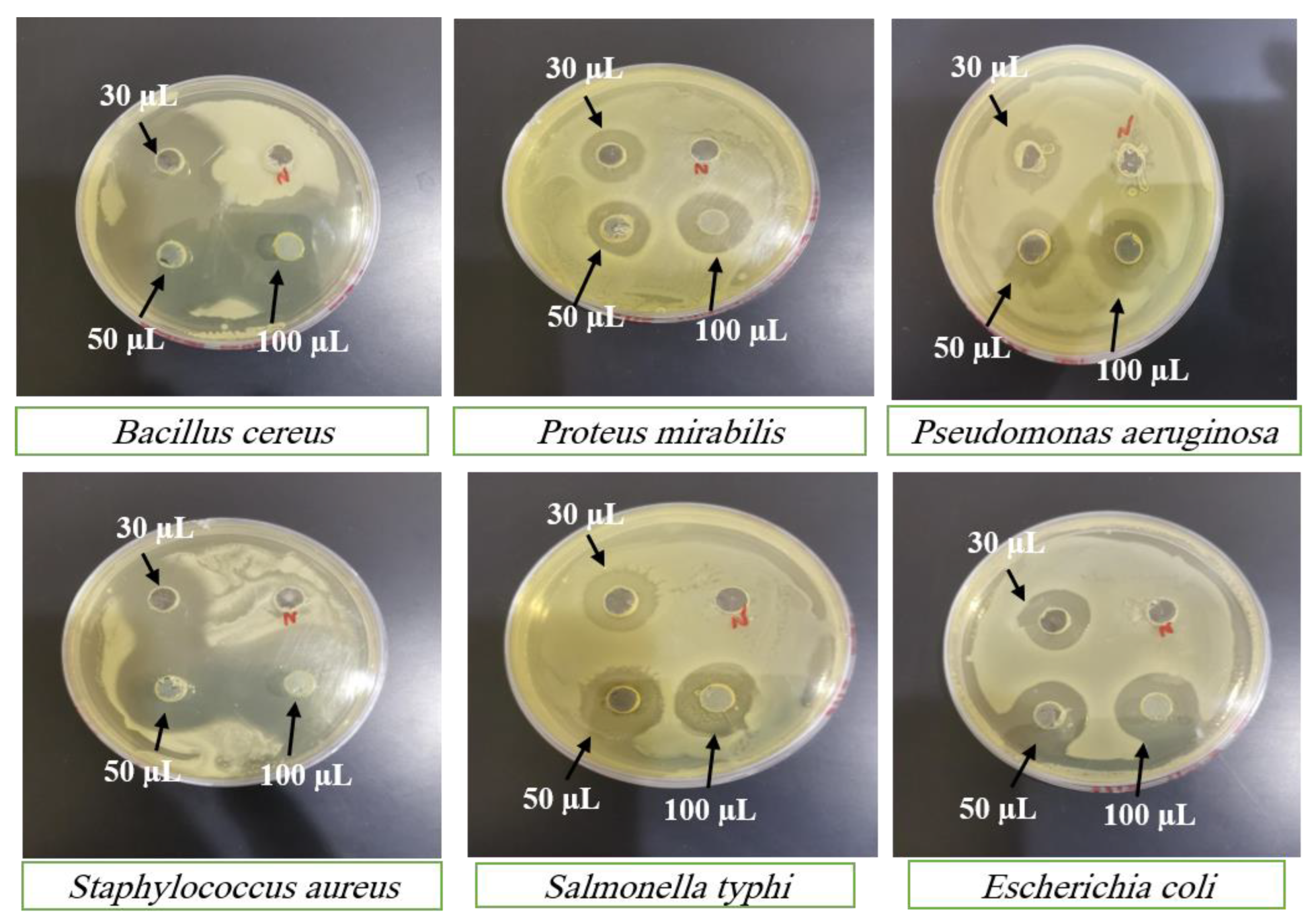
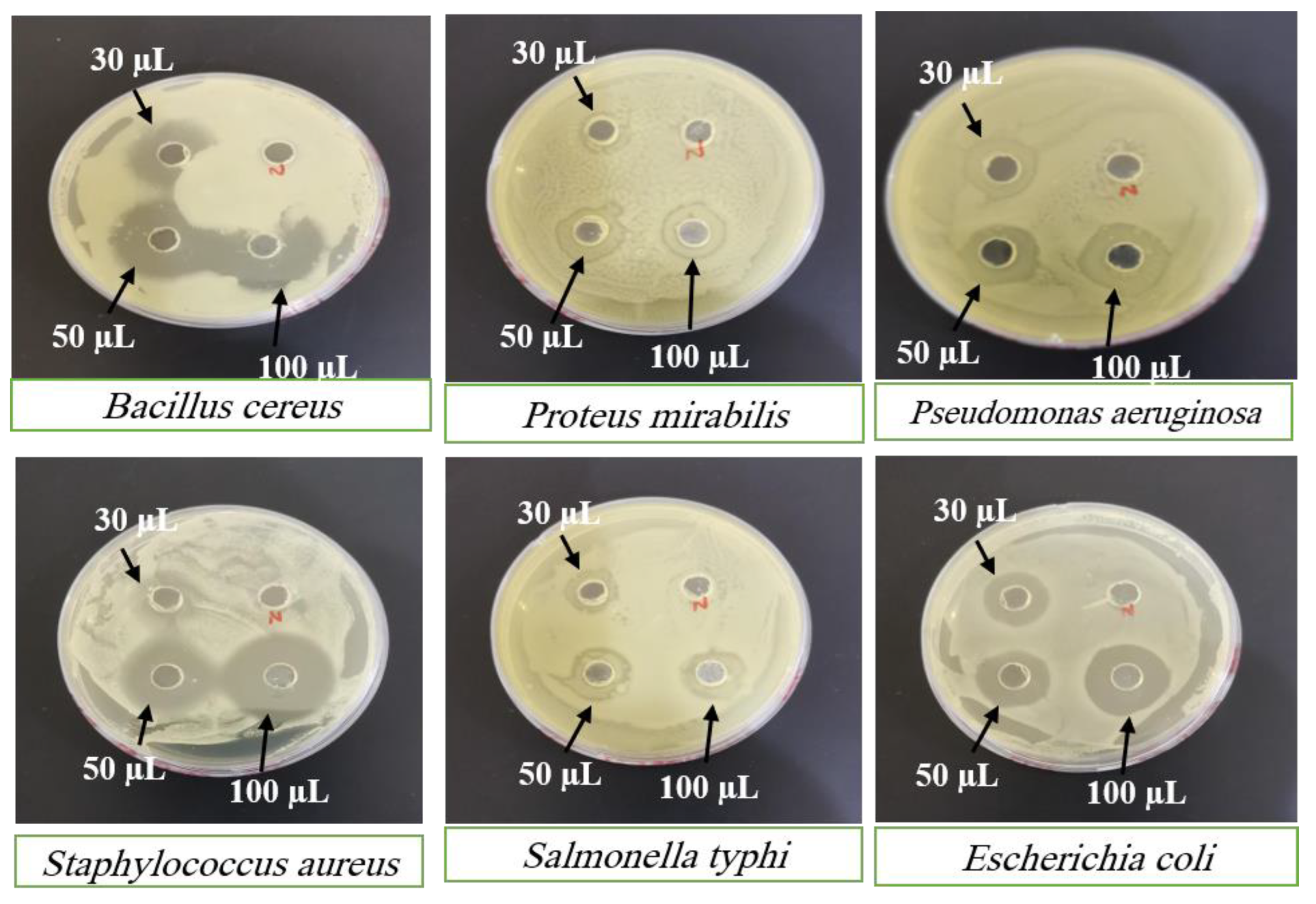
SC PLGA NPs showed wonderful antibacterial activity against many species of bacterial strains. SC PLGA NPs for antibacterial activity were evaluated for many species and different concentrations of SC against gram +ve and gram –ve strains.
Figure 7 showed antibacterial activity for many concentrations (30 µl; 50 µl and 100 µl) of SC PLGA NPs and SC-S. The zone of inhibition increases parallel to the enhancement of concentration i.e. 30 to 50 to 100 mL. Sterile distilled water was used as the negative control shown no inhibition on both strains (
Figure 7 and
Figure 8). The SC PLGA NPs exhibited better antibacterial activity as compared to free SC-S only, because SC encapsulated inside the PLGA NPs increased the stability and decreased the agglomeration (
Figure 7 and
Figure 8;
Table 5 and
Table 6). Thus, the uniform distribution of NPs i.e. PDI showed very small value (0.277) which is also responsible for the enhancement of the antibacterial activity of SC loaded PLGA NPs. A significant result was found for SC PLGA NPs based on dose as compared to SC-S and also showed the dose-dependent effect for both preparations SC PLGA NPs and SC-S in which higher dose (100 µl) showed the maximum Inhibition Zone as compared to 50µl and 30 µl for both preparations [
36]. Based on the concentration-dependent effect of SC loaded PLGA NPs was found to be increased zone of inhibition as compared to their free SC-S zone of inhibition (
Figure 7 and
Figure 8;
Table 5 and
Table 6). Based on this data observation, the antibacterial effect of SC loaded PLGA NPs was enhanced. It was also published before that the antibacterial activity of SC loaded PLGA NPs against gram +ve and gram –ve strains of bacteria [
37]. This is a point we can say that the antibacterial effect of SC PLGA NPs is size and dose dependent and also supported by previously published reports [
38,
39], which have shown that SC loaded PLGA NPs have more potential against gram –ve bacteria than gram +ve bacteria (
Figure 7 &
Table 5). We have also concluded that the enhancement of the size of NPs is parallel to the reduction of their antibacterial effects [
41]. SC PLGA NPs showed great potential for antioxidant and antibacterial effects. We have also found that the antibacterial activity of SC PLGA NPs related to the S-Allyl-L-Cysteine concentration and the quantity of SC PLGA NPs in the medium [
36,
41].
4. Discussions
One of the most common uses of drug administration i.e. oral route has a great advantage of great patient compliance with a very small cost of dosage forms when compared to subcutaneous, intramuscular, and iv injection. The oral route of drug administration showed their degradation and is very difficult to reach the minimum effective concentration (MEC) showing their therapeutic effect. Here nanoformulation (NPs) is used for oral drug delivery to enhance their solubility and protect them from digestive enzymes by changing their pH environment which is very important for PLGA polymer given to the oral route. It’s very important to the degradation of PLGA with biocompatible in the presence of physiological environments, the safety of products biodegradation, and different grades of availability commercially. S-Ally-L-Cysteine found in garlic, is an organosulfur compound that is water-soluble extracted from garlic contributing to various beneficial properties in aging and so many disease models. Scavenging properties of reactive oxygen species (ROS) of S-Ally-L-Cysteine has given great protection with antidiabetic properties, etc. [
32].
Therefore, we used solvent evaporation techniques for the preparation of SC PLGA NPs. We optimized the particle size i.e. 134.8 ± 4.61 nm, dispersion (PDI: 0.277 ± 0.004), and zeta potential (−25.3 ± 1.03). %EE and % DL were determined i.e. 82.36 ± 4.01 % and 5.13 ± 0.10, respectively [
32]. For
in vitro release study, PLGA showed protonation from their carboxyl groups in the presence of an acidic environment responsible for the NPs aggregation that converts the shapes into a stable structure up to a limit of SC release from NPs. In case increasing the pH of artificial intestinal juice, stimulating the release of SC from the SC-PLGA-NPs because of this time enhancement of absorption of water which stimulates the water penetration in the core of NPs. Based on the above observation, we finalized that a very small quantity of SC could be released from the PLGA NPs in the stomach when it was administered orally. On the other side, the residues showed a sustained release & effective treatment. The most important part i.e. SC was released first exponentially which is related to the surface of NPs with a sustained and controlled release of SC indicating the entrapped SC inside the core of NPs.
We optimized a highly sensitive bioanalytical method in the 1–1000 ng mL-1 linearity range which was used for the Pharmacokinetic study. Optimized nanoformulation was successfully used for antimicrobial activity against gram +ve and gram –ve strains.
5. Conclusion
The researchers have prepared and optimized the S-Ally-Cysteine PLGA NPs with the help of the emulsion solvent evaporation technique. SC PLGA NPs showed <134.8±4.61 nm containing the spherical and homogeneous shape of NPs which was confirmed by TEM examination with 5.13±0.10% loading capacity of SC. We have found a sustained release profile for SC PLGA NPs as reproducing same digestion conditions in gastric fluid (pH 1.2) and intestinal juice (pH 6.8) over 168.0 hours. The highly sensitive LC-MS-based bioanalytical method containing a run time of 2.0 minutes was successfully developed and validated. We have used this method effectively for the evaluation of plasma pharmacokinetic parameters of developed SC PLGA NPs. We have found higher oral bioavailability as compared to conventional bioavailability. The oral bioavailability of SC PLGA NPs was significantly (p<0.01) increased 4.83 times more as compared to orally given SC-S in rats. Moreover, the results also indicated that encapsulating S-Allyl-L-Cysteine in PLGA NPs enhanced the antibacterial effects of SC against all tested species of bacteria that are represented in the broad-spectrum antimicrobial effect of both Gram +ve and Gram –ve bacteria. Therefore, SC loaded PLGA may be an excellent drug-active compound as an antibacterial agent. In the future, this method will be a great beneficial method for antimicrobial activity in the routine practice of life. Therefore, a need for more time evaluation research on the industrial scale of antimicrobial effects is required for the optimized nanoformulation (SC PLGA NPs).
Funding
Prince Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University, Alkharj, Saudi Arabia have supported financially to conduct this study (PSAU/2023/R/1444).
Acknowledgments
All researchers are very thankful to IRMC-Animal-House, Imam Abdulrahman Bin Faisal University, Saudi Arabia.
Competing Interests
The authors didn’t show any type of competing interest.
References
- Lee S, Chang N I, Yoo M, Choi J H, Shin D. Development and Validation of S-Allyl-L-Cysteine in Rat Plasma Using a Mixed-Mode Reversed-Phase and Cation-Exchange LC–ESI–MS/MS Method: Application to Pharmacokinetic Studies. Journal of Chromatographic Science 2015; 53:54–59. https://doi.org/10.1093/chromsci/bmu013. [CrossRef]
- Numagami, Y., Ohnishi, S.T.; S-Allylcysteine inhibits free radical production, lipid peroxidation and neuronal damage in rat brain ischemia; Journal of Nutrition, (2001); 131(3s): 1100S–1105S. [CrossRef]
- Ide, N., Lau, B.H.S.; S-Allylcysteine attenuates oxidative stress in endothelial cells; Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy, (1999); 25(5): 619–624. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z., Li, M., Chen, K., Yang, J., Chen, R., Wang, T., et al.; S-Allylcysteine induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in androgenindependent human prostate cancer cells; Molecular Medicine Reports, (2012); 5(2): 439–443. [CrossRef]
- Pai, M.H., Kuo, Y.H., Chiang, E.P., Tang, F.Y.; S-Allylcysteine inhibits tumour progression and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in a mouse xenograft model of oral cancer; British Journal of Nutrition, (2012); 108(1): 28–38. [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, S., Kasuga, S., Matsuura, H.; Prevention of liver damage by aged garlic extract and its components in mice; Phytotherapy Research, (1989); 3(2): 50–53.
- Nishiyama, N., Moriguchi, T., Morihara, N., Saito, H.; Ameliorative effect of S-allylcysteine, a major thioallyl constituent in aged garlic extract, on learning deficits in senescence accelerated mice; Journal of Nutrition, (2001); 131(3S): 1093S–1095S. [CrossRef]
- Javed, H., Khan, M.M., Khan, A., Vaibhav, K., Ahmad, A., Khuwaja, G., et al.; S-Allyl cysteine attenuates oxidative stress associated cognitive impairment and neurodegeneration in mouse model of streptozotocininduced experimental dementia of Alzheimer’s type; Brain Research, (2011); 1389: 133–142. [CrossRef]
- Nagae, S., Ushijima, M., Hatono, S., Imai, J., Kasuga, S., Matsuura, H., et al.; Pharmacokinetics of the garlic compound S-allylcysteine; Planta Medica, (1994); 60(3): 214–217. [CrossRef]
- Rosen, R., Hiserodt, R., Fukuda, E., Ruiz, R., Zhou, Z., Lech, J., et al.; The determination of metabolites of garlic preparations in breath and human plasma; Biofactors, (2000); 13(1–4): 241–249. [CrossRef]
- Kyung KH. Antimicrobial properties of allium species. Current Opinion in Biotechnology. 2012: 23 (2): 142-147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2011.08.004. [CrossRef]
- Yoshida H, Katsuzaki H, Ohta R, Ishikawa K, Fukuda H, Fujino T, Suzuki A. Antimicrobial Activity of the Thiosulfinates Isolated from Oil-Macerated Garlic Extract. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry. 1999; 63 (3): 591–594, https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.63.591. [CrossRef]
- Mi-Kyung C, Kyung-Yeon C, Joo-Young L, Kyu-Hang K. Antimicrobial Activity of Chemical Substances Derived from S-Alk(en)yl-L-Cysteine Sulfoxide (Alliin) in Garlic, Allium sativum L. Food Science and Biotechnology. 2007; 16 (1):1-7. 1226-7708(pISSN)/2092-456(eISSN).
- Amagase, H., Petesch, B.L., Matsuura, H., Kasuga, S., Itakura, Y.; Intake of garlic and its bioactive components; Journal of Nutrition, (2001); 131(3s): 955S–962S. [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.E., Cho, S.Y.,Won, Y.D., Lee, S.H., Park, H.J.; A comparative study of the different analytical methods for analysis of S-allyl cysteine in black garlic by HPLC; Food Science and Technology, (2012); 46(2): 532–535. [CrossRef]
- Pathak K, Raghuvanshi S. (2015). Oral bioavailability: issues and solutions via nanoformulations. Clin Pharmacokinet 54:325–57. [CrossRef]
- Cherniakov I, Domb AJ, Hoffman A. (2015). Self-nano-emulsifying drug delivery systems: an update of the biopharmaceutical aspects. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 12:1121–33. [CrossRef]
- Ozeki T, Tagami T. (2013). Functionally engineered nanosized particles in pharmaceutics: improved oral delivery of poorly water-soluble drugs. Curr Pharm Des 19:6259–69. [CrossRef]
- Zhao W, Li J, Jin K, et al. (2016). Fabrication of functional PLGA-based electrospun scaffolds and their applications in biomedical engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 59:1181–94. [CrossRef]
- Shi X, Lin X, Zheng X, et al. (2014). Injectable long-acting systems for Radix Ophiopogonis polysaccharide based on mono-PEGylation and in situ formation of a PLGA depot. Int J Nanomed 9: 5555–5563. [CrossRef]
- Chen F, Zhang J, He Y, et al. (2016). Glycyrrhetinic acid-decorated and reduction-sensitive micelles to enhance the bioavailability and antihepatocellular carcinoma efficacy of tanshinone IIA. Biomater Sci 4: 167–82. [CrossRef]
- Matsutomo T, Stark T D., Hofmann T. Targeted screening and quantitative analyses of antioxidant compounds in aged-garlic extract. European Food Research and Technology. 2018; 244:1803–1814. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-018-3092-6. [CrossRef]
- Kim S, Park S-L, Lee S, Lee S-Y, Ko S, Yoo M. UPLC/ESI-MS/MS analysis of compositional changes for organosulfur compounds in garlic (Allium sativum L.) during fermentation. Food Chemistry 211 (2016) 555–559. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.05.102. [CrossRef]
- Zhu Q, Kakino K, Nogami C, Ohnuki K, Shimizu K. An LC-MS/MS-SRM Method for Simultaneous Quantification of Four Representative Organosulfur Compounds in Garlic Products. Food Anal. Methods (2016) 9:3378–3384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-016-0535-1. [CrossRef]
- Park T, Oh J-H, Lee JH, Park S C, Jang Y P, Lee Y-J. Oral Administration of (S)-Allyl-L-Cysteine and Aged Garlic Extract to Rats: Determination of Metabolites and Their Pharmacokinetics. Planta Med 2017; 83(17): 1351-1360. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0043-111895. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad N, Al-Ghamdi MJA, Alnajjad HSM, Al Omar BBA, Khan MF, Almalki ZS, Albassam AA, Ullah Z, Khalid MS, Ashraf K. A comparative Brain Toxico-Pharmacokinetics study of a developed Tannic Acid nanoparticles in the treatment of epilepsy. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology. 2022a. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2022.103772. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad N, Khalid MS, Al Ramadhan AM, Alaradi MZ, Al Hammad MR, Ansari K, Alqurashi YD, Khan MF, Albassam AA, Ansari MJ, Akhtar S. Dilshad M. Preparation of melatonin novel-mucoadhesive nanoemulsion used in the treatment of depression. Polym Bull. 2022b. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-022-04436-3. [CrossRef]
- Liu Y, Wu X, Mi Y, Zhang B, Gu S, Liu G, Li X. PLGA nanoparticles for the oral delivery of nuciferine: preparation, physicochemical characterization and in vitro/in vivo studies. Drug Deliv. 2017; 24(1): 443–451. https://doi.org/10.1080/10717544.2016.1261381. [CrossRef]
- Boyanova, L., Gergova, G., Nikolov, R., Derejian, S., Lazarova, E., Katsarov, N., Mitov I., Krastev, Z. (2005). Activity of Bulgarian propolis against 94 Helicobacter pylori strains in vitro by agar-well diffusion, agar dilution and disc diffusion methods. Journal of Medical Microbiology, 54(5), 481–483. https://doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.45880-0. [CrossRef]
- Feroze N, Arshad B, Younas M, Afridi M I, Saqib S, Ayaz A. Fungal mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and evaluation of antibacterial activity. Microsc Res Tech. 2020; 83(1):72-80. https://doi.org/10.1002/jemt.23390. [CrossRef]
- Colín-González AL, Santamaría A. Chapter 20 - Garlic, Gastrointestinal Protection and Oxidative Stress. Gastrointestinal Tissue. Oxidative Stress and Dietary Antioxidants. 2017, Pages 275-288. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-805377-5.00020-5. [CrossRef]
- Sun SB, Liu P, Shao FM, et al. (2015). Formulation and evaluation of PLGA nanoparticles loaded capecitabine for prostate cancer. Int J Clin Exp Med 8:19670–81.
- US FDA. Guidance for Industry Bioanalytical Method Validation; 2001. Available from:http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformation/Guidances/UCM070107.pdf. [Lastaccessed on 2018 May 24].
- Ahmad N. Rasagiline-encapsulated chitosan-coated PLGA nanoparticles targeted to the brain in the treatment of parkinson's disease. Journal of Liquid Chromatography & Related Technologies. 2017; 40 (13): 677-690. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826076.2017.1343735. [CrossRef]
- Arokiyaraj, S., Vincent, S., Saravanan, M., Lee, Y., Oh, Y. K., & Kim, K. H. (2017). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Rheum palmatum root extract and their antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Artificial Cells, Nanomedicine, and Biotechnology, 45(2), 372–379. https://doi.org/10.3109/21691401.2016.1160403. [CrossRef]
- Shehzad A, Qureshi M, Jabeen S, Ahmad R, Alabdalall A H, Aljafary M A, Al-Suhaimi E. Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles using Rhazya stricta. PeerJ. 2018; 6:e6086. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.6086. [CrossRef]
- Singh M, Singh S, Prasad S, Gambhir IS. 2008. Nanotechnology in medicine and antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles. Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures 3(3):115–122.
- Arasoglu T, Derman S, Mansuroglu B. Comparative evaluation of antibacterial activity of caffeic acid phenethyl ester and PLGA nanoparticle formulation by different methods. Nanotechnology. 2016; 27(2):025103. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/27/2/025103. [CrossRef]
- Sana SS, Dogiparthi LK. 2018. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Givotia moluccana leaf extract and evaluation of their antimicrobial activity. Materials Letters 226:47–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2018.05.009. [CrossRef]
- Kaviya S, Santhanalakshmi J, Viswanathan B. 2011. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Polyalthia longifolia leaf extract along with D-sorbitol: Study of antibacterial activity. Journal of Nanotechnology 2011(4):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/152970. [CrossRef]
- Rauf A, Khan A, Dawood Z, Uddin G, Farooq U, Maalikb A. 2016. Synthesis, characterization and bioactivities of silver nanoparticles using ethanolic and aqueous extracts of Rhazya strictica. In: NanosmatAt: The University of Texas at Arlington, Texas, USA, 1–704.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).