Submitted:
08 June 2023
Posted:
08 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
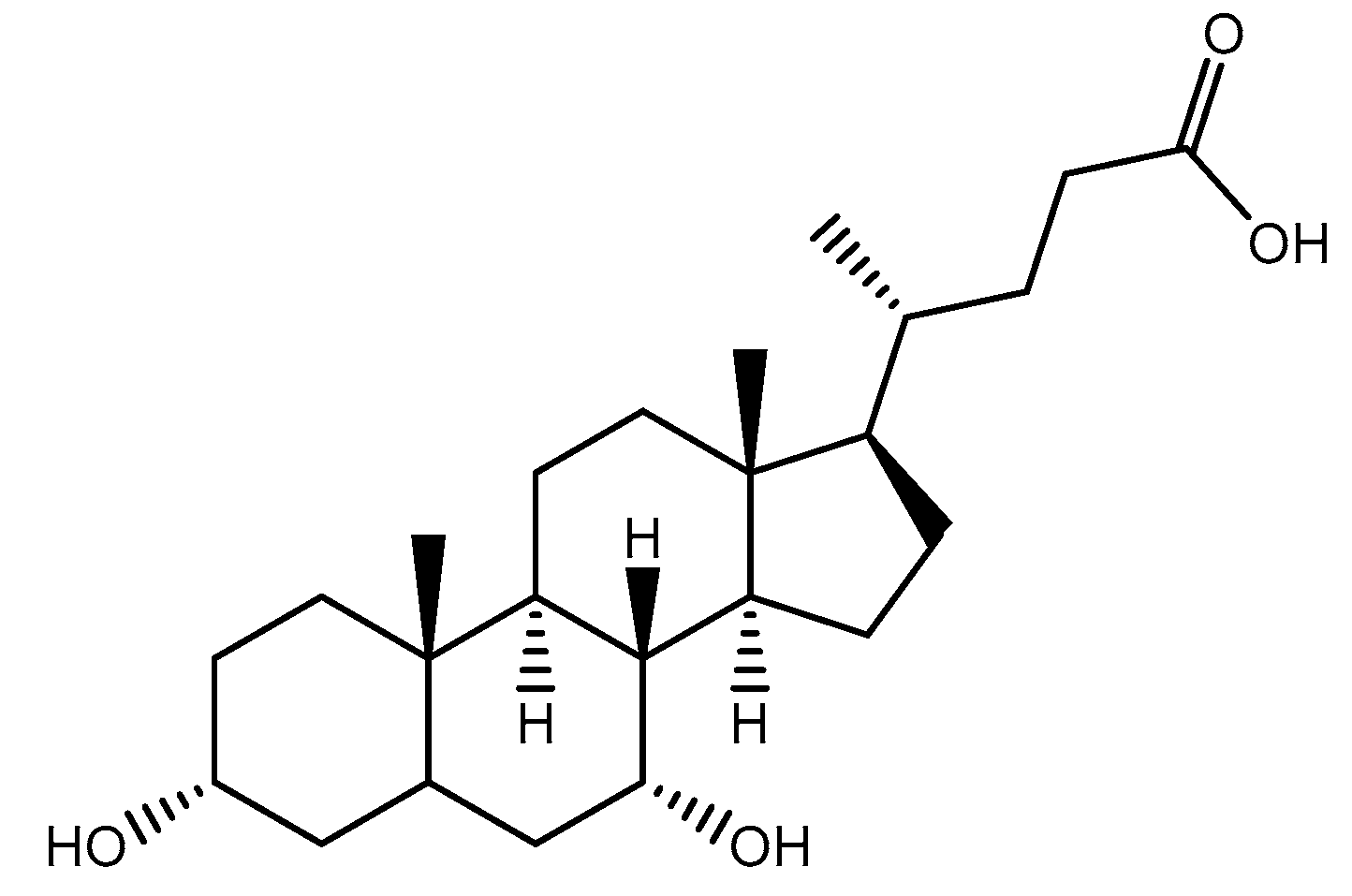
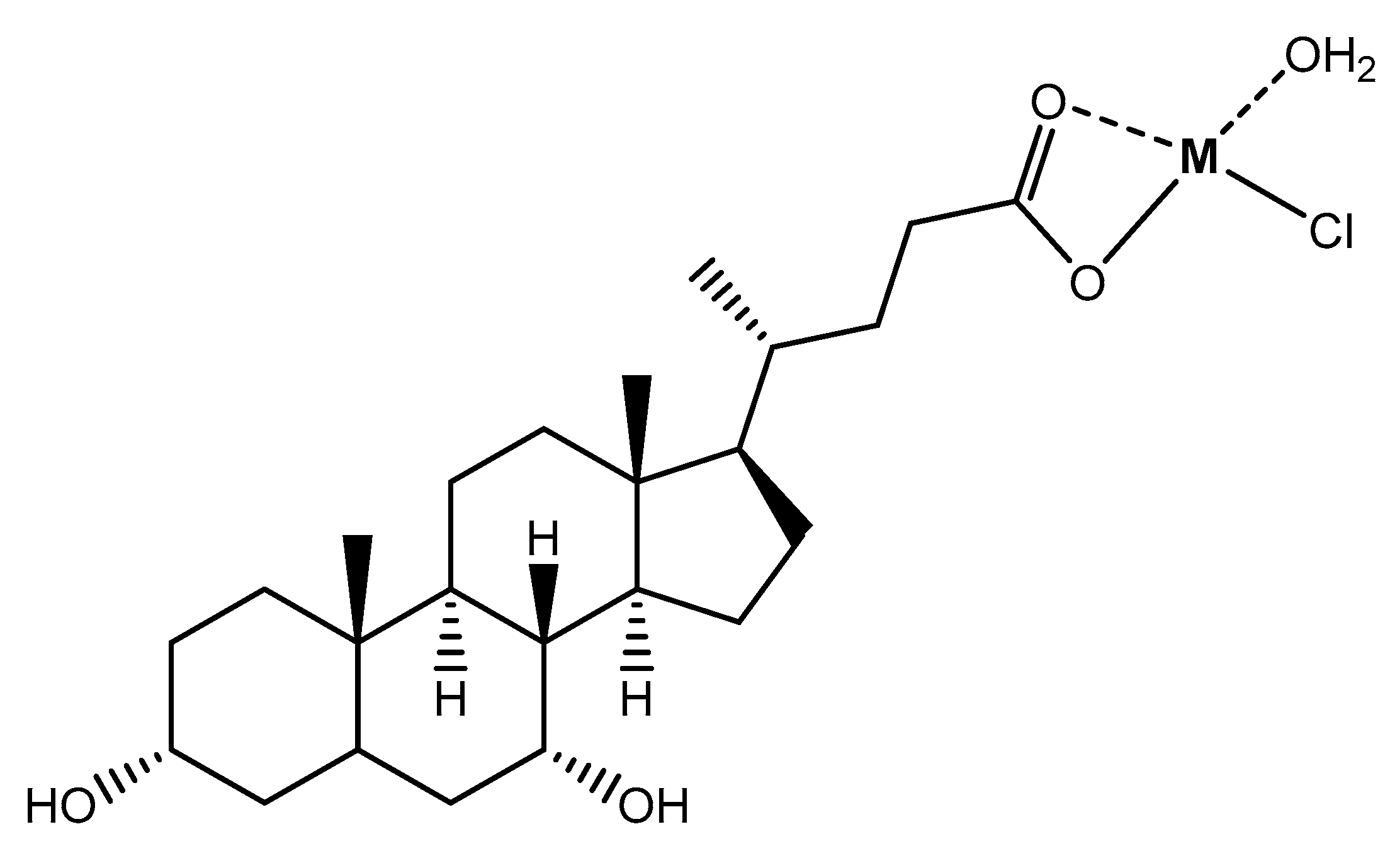
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation and characterization
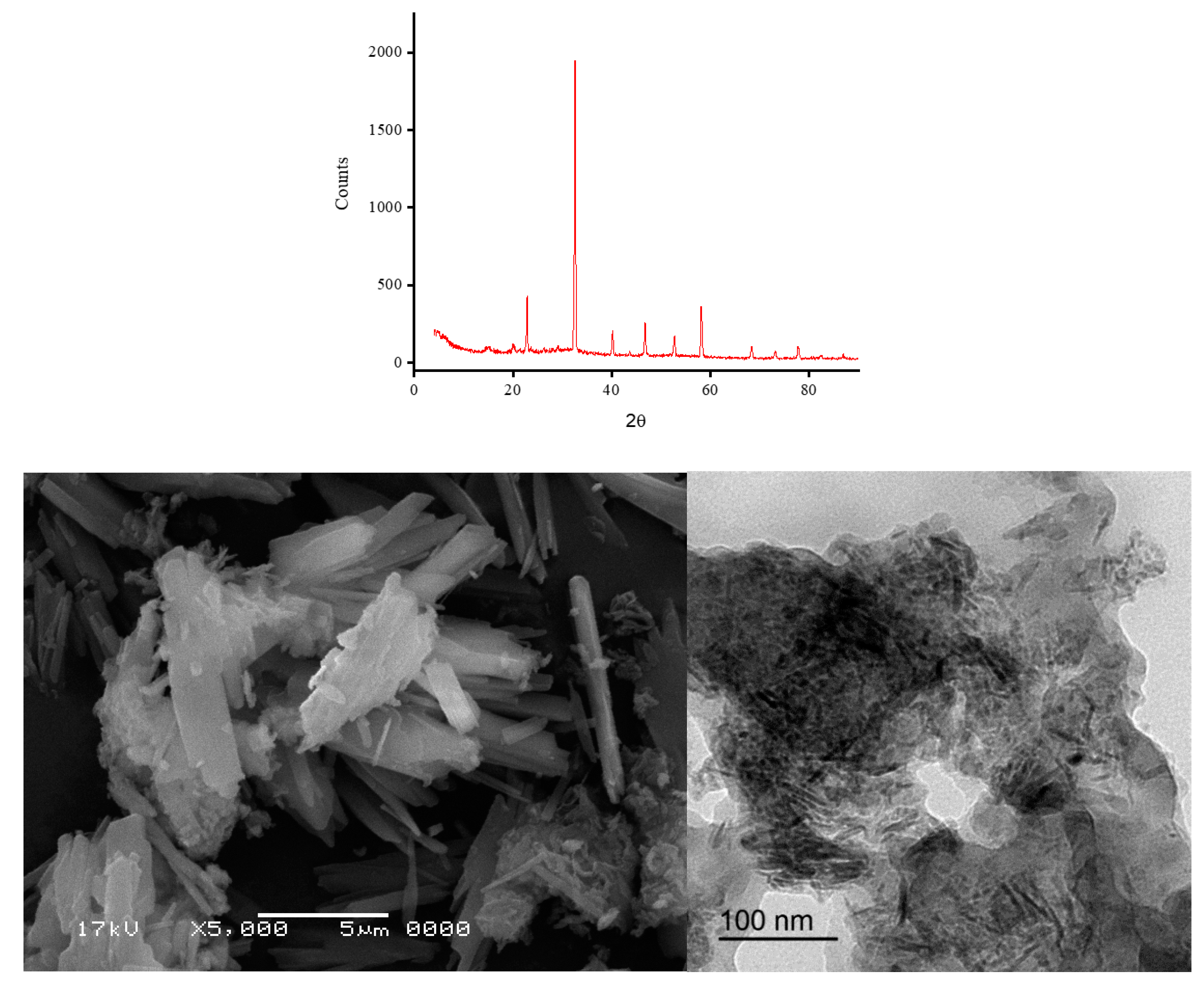
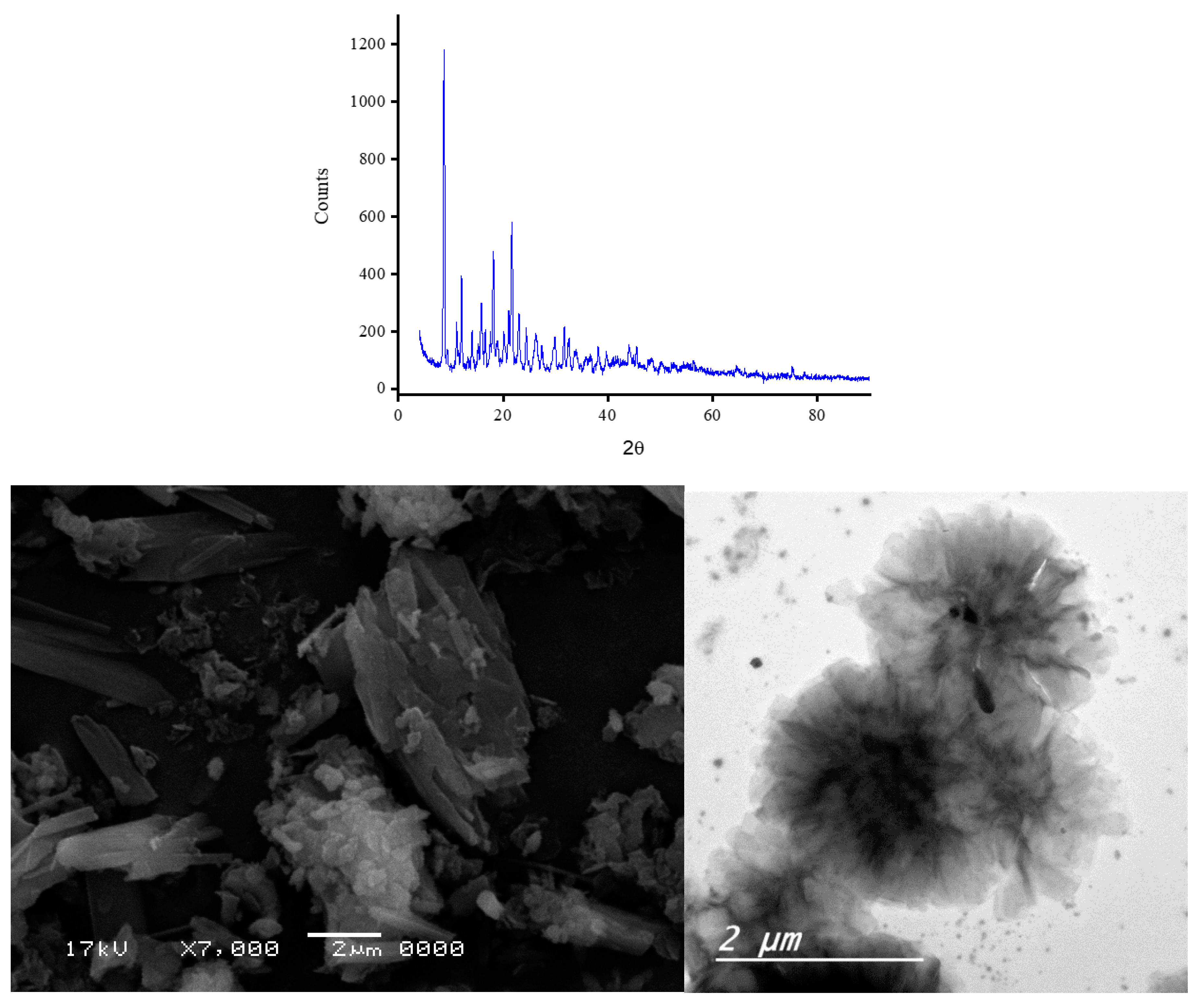
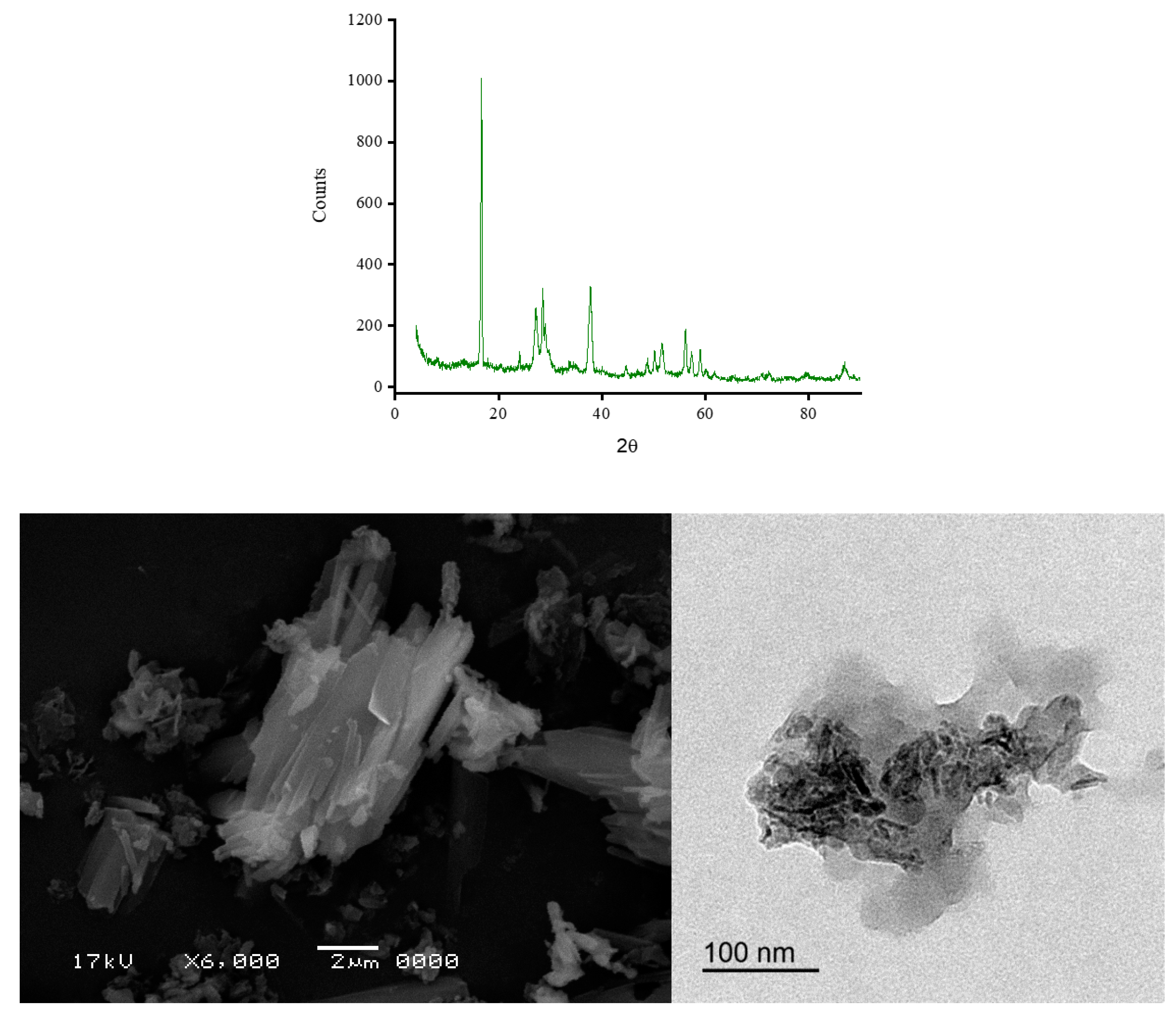
2.3. XRD spectra and microscopic images
2.4. In vitro antimicrobial experiments
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. Elemental compositions
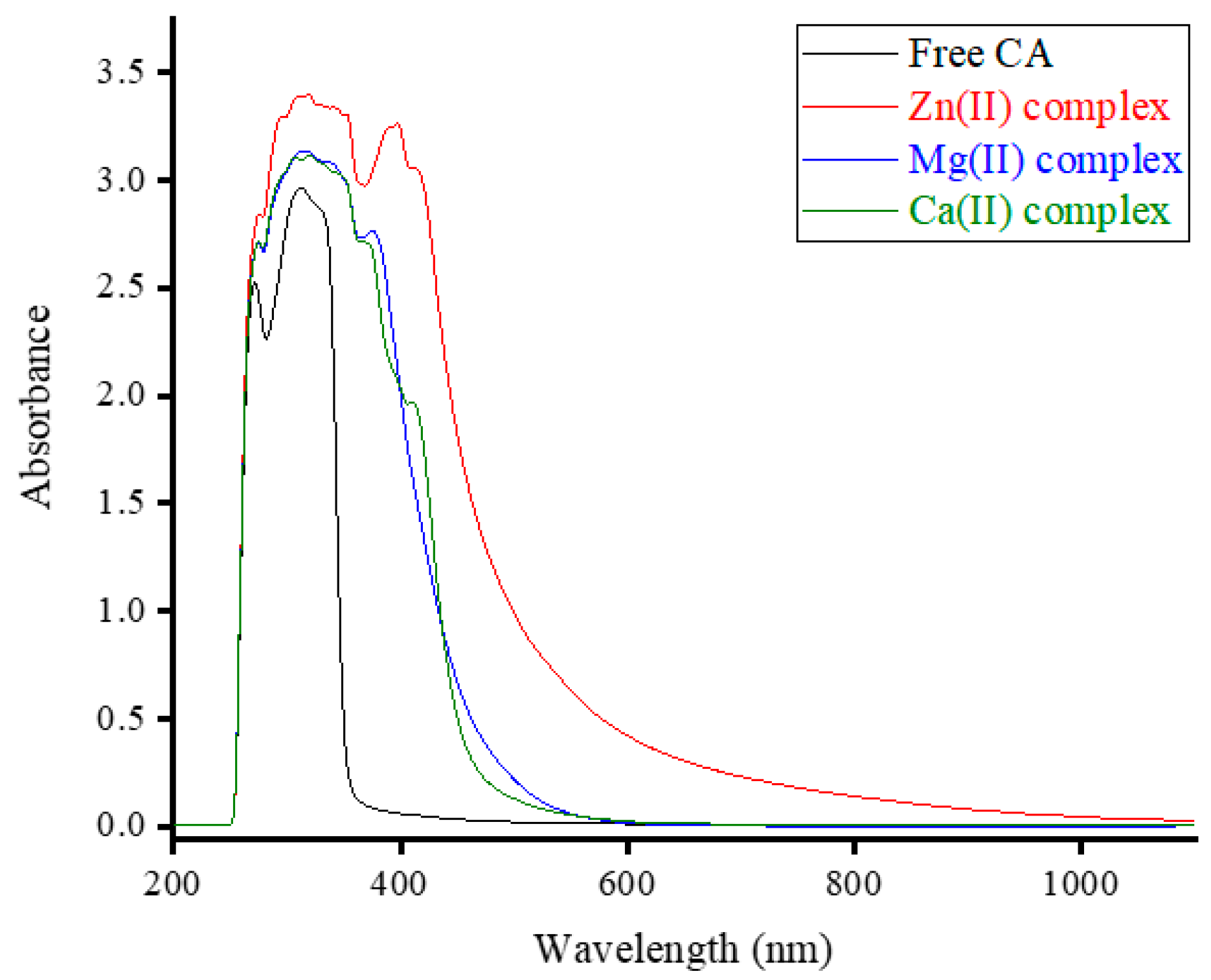
3.1.2. UV-visible spectra
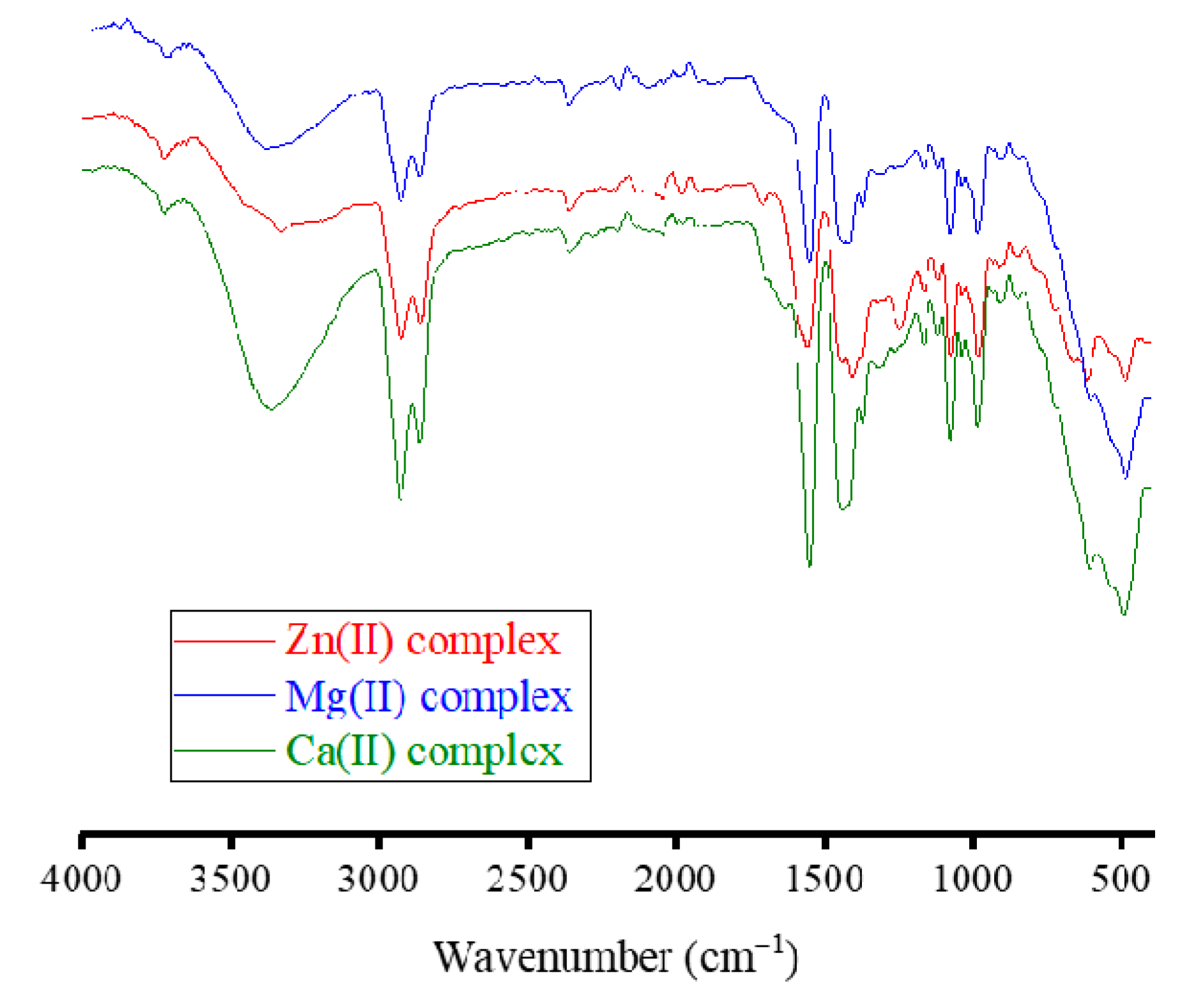
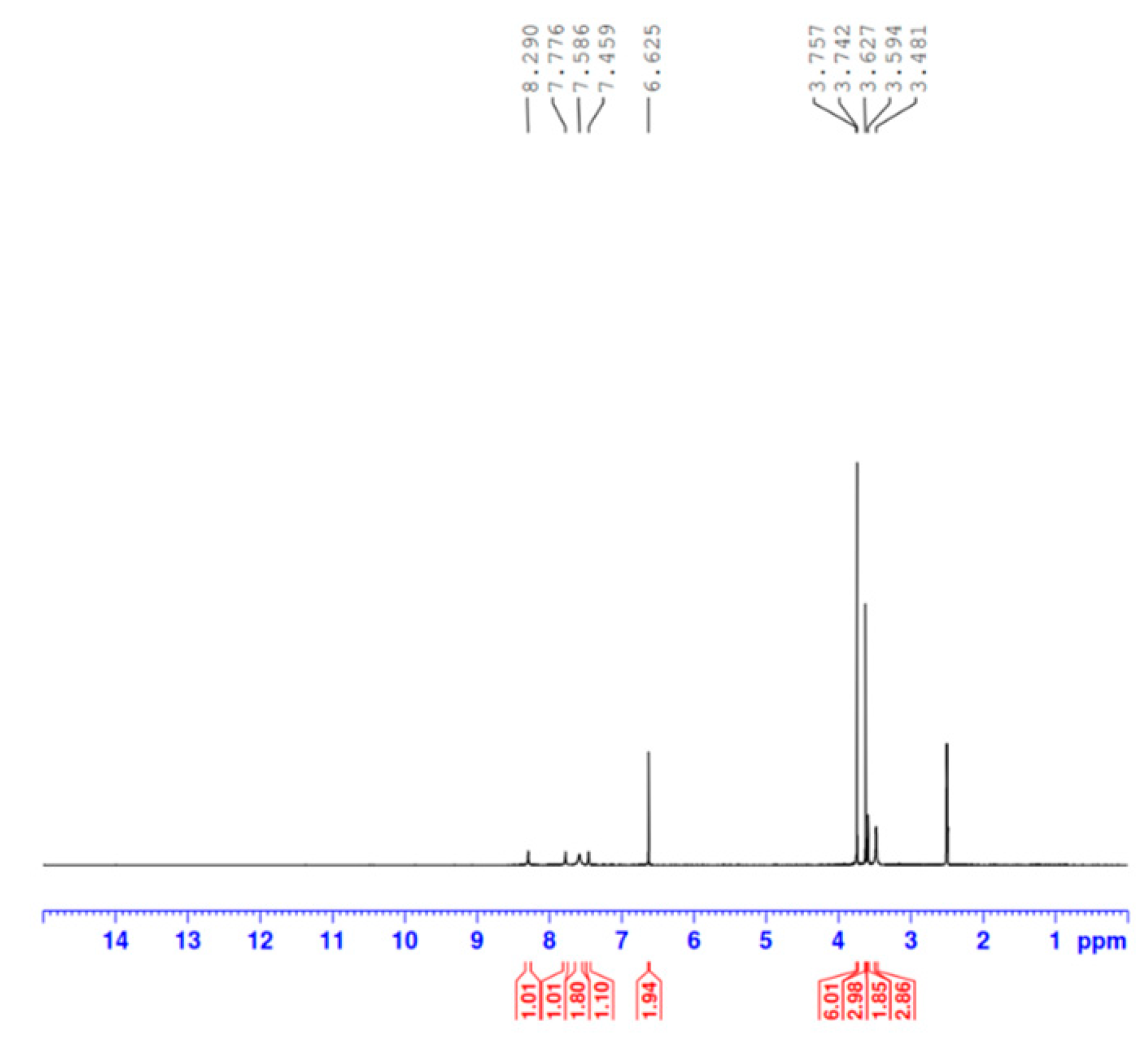
3.1.3. FT-IR and 1H NMR spectra
3.2. Morphology
3.3. Biological effects
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgements
References
- Lefebvre, P.; Cariou, B.; Lien, F.; Kuipers, F.; Staels, B. Role of Bile Acids and Bile Acid Receptors in Metabolic Regulation. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 147–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- S. Fiorucci, E. S. Fiorucci, E. Distrutti, Chenodeoxycholic Acid: An Update on Its Therapeutic Applications. In: Fiorucci, S., Distrutti, E. (eds) Bile Acids and Their Receptors. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology, vol 256. Springer, Cham, 2019, pp 265-282.
- Bateson, M.; Maclean, D.; Evans, J.; Bouchier, I. Chenodeoxycholic acid therapy for hypertriglyceridaemia in men. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1978, 5, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eloranta, J.J.; Kullak-Ublick, G.A. Coordinate transcriptional regulation of bile acid homeostasis and drug metabolism. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2005, 433, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A.C. Tella, J.A. A.C. Tella, J.A. Obaleye, M.D. Olawale, J.M.V. Ngororabanga, A.S. Ogunlaja, S.A. Bourned, C.R. Chimie 22 (1) (2019) 3-12.
- G.L. Eichhorn, L.G. G.L. Eichhorn, L.G. Marzilli, Advances in Inorganic Biochemistry Models in Inorganic Chemistry, PTR Prentice-Hall, Inc, New Jersey, 1994.
- M.N. Hughes, The Inorganic Chemistry of Biological Processes, 2nd ed., Wiley, Chichester [England], 1984.
- E. Alessio, Bioinorganic Medicinal Chemistry, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH and Co. KGaA, 2011.
- F. Trudu, F. F. Trudu, F. Amato, P. Vaňhara, T. Pivetta, E.M. Peña-Méndez. J. Havel, J. Appl. Biomed 2015, 13, 79. [Google Scholar]
- U. Singh, A.M. U. Singh, A.M. Malla, I.A. Bhat, A. Ahmad, M.N. Bukhari, S. Bhat, S. Anayutullah, A. A. Hashmi, Microb. Pathog. 93 (2016) 172.
- P.P. Netalkar, S.P. P.P. Netalkar, S.P. Netalkar, V.K. Revankar, Polyhedron 100 (2015) 215.
- M.A. Ragheb, M.A. M.A. Ragheb, M.A. Eldesouki, M.S. Mohamed, Spectrochim. Acta A 138 (2015) 585.
- Khan, T.-M.; Gul, N.S.; Lu, X.; Wei, J.-H.; Liu, Y.-C.; Sun, H.; Liang, H.; Orvig, C.; Chen, Z.-F. In vitro and in vivo anti-tumor activity of two gold(III) complexes with isoquinoline derivatives as ligands. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 163, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.; Li, Y.; Freisinger, E.; Qin, P.Z.; Sigel, R.K.O.; Mao, Z.-W. G-quadruplex DNA targeted metal complexes acting as potential anticancer drugs. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2017, 4, 10–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, T.T.; Azevedo, G.C.; Garcia, A.; Carpanez, A.G.; Lewer, P.M.; Paschoal, D.; Müller, B.L.; Dos Santos, H.F.; Matos, R.C.; Silva, H.; et al. Gold(I) complexes with aryl-thiosemicarbazones: Molecular modeling, synthesis, cytotoxicity and TrxR inhibition. Polyhedron 2017, 132, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- F. Trudu, F. F. Trudu, F. Amato, P. Vaňhara, T. Pivetta, E.M. Peña-Méndez, J. Havel, Coordination compounds in cancer: Past, present and perspectives, J. Appl. Biomed. 13 (2) (2015) 79-103.
- Qin, Q.-P.; Wang, S.-L.; Tan, M.-X.; Liu, Y.-C.; Meng, T.; Zou, B.-Q.; Liang, H. Synthesis of two platinum(II) complexes with 2-methyl-8-quinolinol derivatives as ligands and study of their antitumor activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 161, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, T.; Tang, S.-F.; Qin, Q.-P.; Liang, Y.-L.; Wu, C.-X.; Wang, C.-Y.; Yan, H.-T.; Dong, J.-X.; Liu, Y.-C. Evaluation of the effect of iodine substitution of 8-hydroxyquinoline on its platinum(ii) complex: cytotoxicity, cell apoptosis and telomerase inhibition. MedChemComm 2016, 7, 1802–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, Z.; Li, F.; Li, J.; Liang, F. Two hydrazone copper(ii) complexes: synthesis, crystal structure, cytotoxicity, and action mechanism. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 36077–36084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.W.; Kirby, W.M.M.; Sherris, J.C.; Turck, M. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing by a Standardized Single Disk Method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1966, 45, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biemer, J.J. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing by the Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion method. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 1973, 3, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- M.C. Serrano, M. M.C. Serrano, M. Ramírez, D. Morilla, A. Valverde, M. Chávez, A. Espinel-Ingroff, R. Claro, A. Fernández, C. Almeida, E. Martín-Mazuelos, A comparative study of the disc diffusion method with the broth microdilution and Etest methods for voriconazole susceptibility testing of Aspergillus spp., J. Antimicrob. Chemo-ther. 53 (2004) 739‒742.
- A Pfaller, M.; Burmeister, L.; Bartlett, M.S.; Rinaldi, M.G. Multicenter evaluation of four methods of yeast inoculum preparation. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1988, 26, 1437–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beecher, D.J.; Wong, A.C. Identification and analysis of the antigens detected by two commercial Bacillus cereus diarrheal enterotoxin immunoassay kits. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 4614–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Methods for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of Anaerobic Bacteria: Approved Standard M11-A3. NCCLS, Wayne, PA, USA (1993).
- Allan, J.R.; Baird, N.D.; Kassyk, A.L. Some first row transition metal complexes of nicotinamide and nicotinic acid. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 1979, 16, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztirk, F.; Şekerci, M.; Özdemir, E. Preparation of complexes of 1-amino-6,7-O-cyclohexylidene-4-azaheptane with transition metal acetates. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2006, 76, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathavan, S.; Chen-Tan, N.; Arfuso, F.; Al-Salami, H. The role of the bile acid chenodeoxycholic acid in the targeted oral delivery of the anti-diabetic drug gliclazide, and its applications in type 1 diabetes. Artif. Cells, Nanomedicine, Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 1508–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Fan, D.; Hua, X.; Zhang, T. Large-scale production of ursodeoxycholic acid from chenodeoxycholic acid by engineering 7α- and 7β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 42, 1537–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- K. Nakamoto, Infrared Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds, Wiley Interscience, John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY, USA, 2nd edition, 1970.
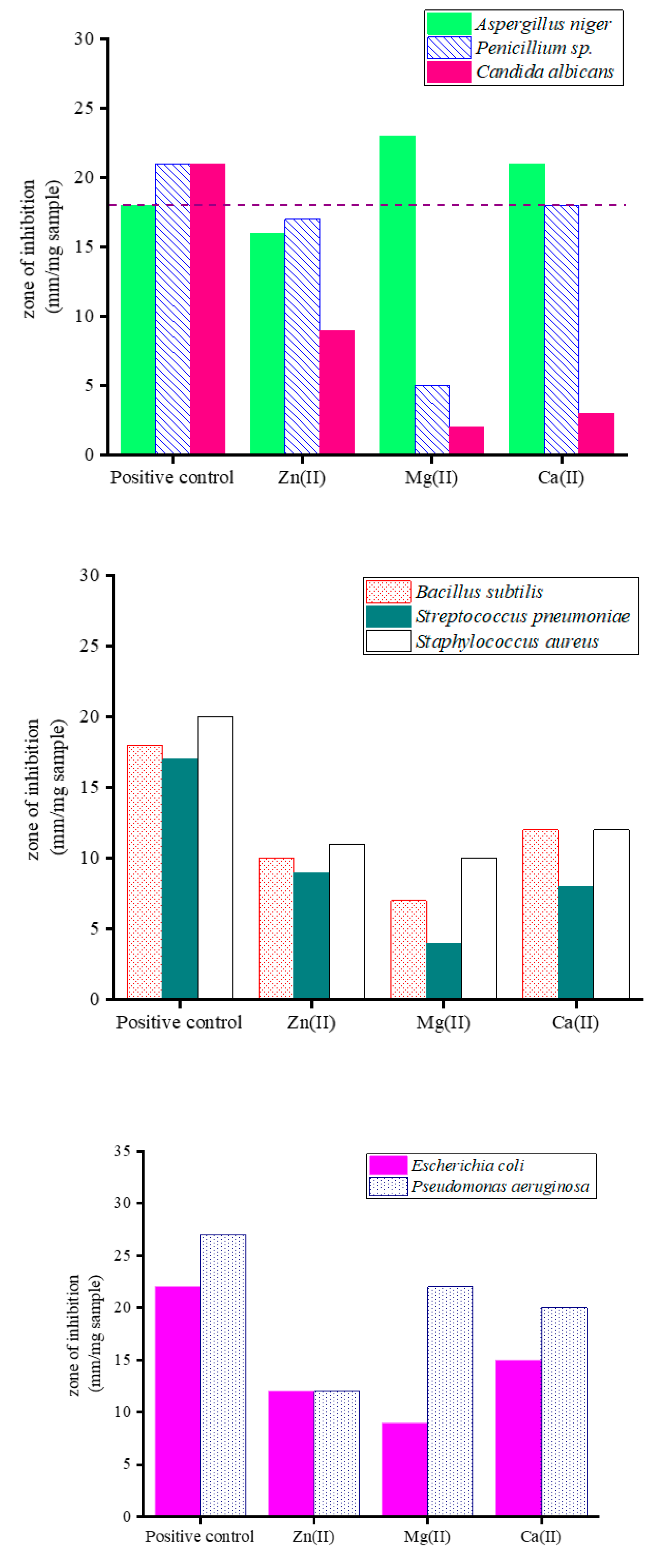
| Microbe | Positive controls | Complexes | |||
| Ketoconazole | Streptomycin | Zn(II) | Mg(II) | Ca(II) | |
| Fungi species: | |||||
| Aspergillus niger | 18.0 | - | 16.0 | 23.0 | 21.0 |
| Penicillium sp. | 21.0 | - | 17.0 | 5.0 | 18.0 |
| Candida albicans | 21.0 | - | 9.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 |
| Gram-positive species: | |||||
| Bacillus subtilis | - | 18.0 | 10.0 | 7.0 | 12.0 |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae | - | 17.0 | 9.0 | 4.0 | 8.0 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | - | 20.0 | 11.0 | 10.0 | 12.0 |
| Gram-negative species: | |||||
| Escherichia coli | - | 22.0 | 12.0 | 9.0 | 15.0 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | - | 27.0 | 12.0 | 22.0 | 20.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





