1. Introduction
The construction of road infrastructure is fundamental to the growth of any country, as it not only increases the employment rate but also improves national and international trade and the connectivity and mobility of people [
1]. Chile has an approximate length of 880,150 km, with 25% of the network being paved, 21% roads with essential solutions, and 54% unpaved roads [
2]. According to the 2017 Road Map prepared by the Chilean Roads Authority, roads (highways and paths) are constructed according to their flexibility from asphalt, concrete, gravel, and earth materials [
3]. A significant amount of materials, energy, and human resources are required to carry out this type of construction, not only in design and construction but also in the conservation and rehabilitation of existing roads [
4].
The transport industry plays a fundamental role in the country, accounting for 5.1% of its gross domestic product (GDP) [
5]. In addition, this industry also plays a role in transporting food to supply people in the event of disasters and pandemics, as MERCOSUR indicates [
6].
However, the sector will achieve this sustainability improvement if a balance between economic, social, and environmental aspects is maintained [
7]. To achieve such sustainability, the transport and construction sectors must be able to use more clean energy and fewer natural resources without compromising performance and efficiency [
8]. Studies and research are needed to help develop regulations, protocols, and methodologies capable of making construction sustainable and using road technologies to make this happen [
9,
10].
The AASHTO methodology is used in pavement design in Chile and has demonstrated reasonably accurate pavement performance predictions [
11]. In particular, this methodology focuses on rationalising the stress state at any point under the pavement and estimating the fatigue consumption for each stress state [
12]. This requires data associated with material properties (modulus of elasticity of bonded layers (E), resilient modulus of unbound and subgrade layers (MR), and Poisson’s ratio), layer thickness, loads (magnitude, geometry, number of repetitions, pressure), coordinates, and climate. However, this method does not consider moisture damage caused by a lack of adhesion between the aggregate–binder system, which is relevant when studying specific pavement failure pathologies [
13].
Currently, due to the use of the AASHTO standard in Chile, susceptibility to moisture damage is not considered in pavement design, which impacts the occurrence of severe water damage to roads [
14].
Meanwhile, according to the Global Footprint Network (GFN), Chile is the first Latin American country to enter “ecological overshoot” [
15]. This implies that the country’s ecological footprint has exceeded the average global biocapacity, understood as the biological sufficiency of ecosystems to regenerate resources in a renewable way and absorb the different wastes generated by people [
16]. The data indicate that Chile’s biocapacity corresponds to 3.5 global hectares (gha) per person, and its ecological footprint is 4.3 gha per person, so there is a deficit of 0.8 gha [
17]. According to World Bank estimates, around 1.3 billion tonnes of waste were generated in 2020, which could reach 2.2 billion tonnes by 2025, and only 10% of this is recycled [
18]. The country has indeed made an enormous effort to apply norms and protocols that can regularise this situation, such as the Law for the Promotion of Recycling, which obliges manufacturers to manage the waste derived from their products. Still, unfortunately, the figures indicate that more is needed [
19]. In particular, the plastic used to make bottles is one of the materials that could be 100% recycled [
20]. However, every year more than 55,000 tonnes of this virgin material enter the country, and less than 15% is reused, and even companies that use recycled PET (rPET) as raw material are forced to import more than 10,000 tonnes to supply their factories [
21].
This research is based on the study of the behaviour of asphalt mixtures modified with plastic from recycled polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles, using water sensitivity and indirect tensile strength tests to analyse the parameters associated with the adhesion and cohesion of these asphalt mixtures and their durability over time.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Aggregates
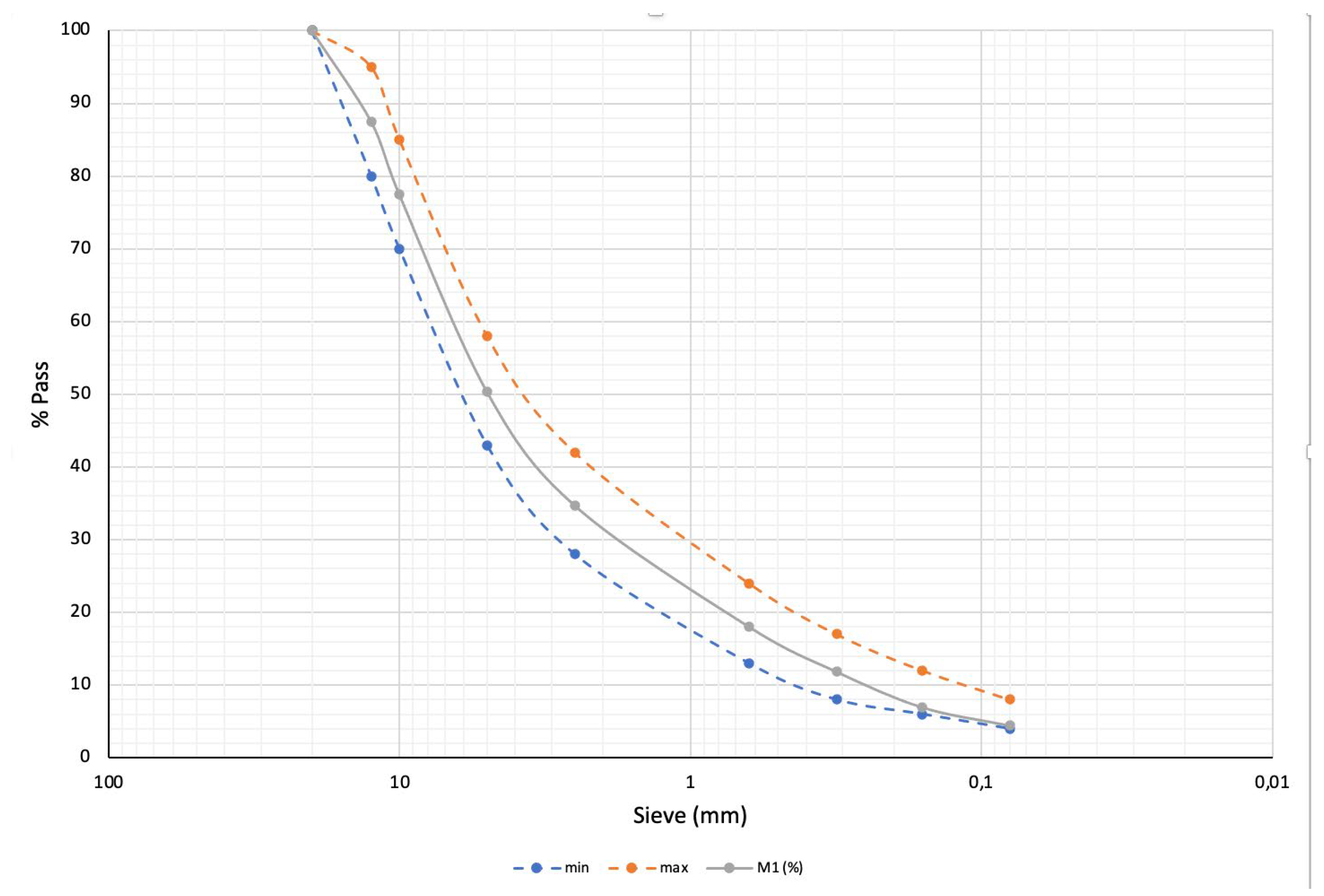
The aggregates used in the investigation came from a natural gravel quarry. The dosage conforms to a grain size band of type IV-A-12 [
11]. In addition, as the material is not washed, an adjustment is made to the centre of the size band used (
Figure 1).
Table 1 shows the main characteristics of the aggregates.
2.2. Bitumen
The bitumen used is a CA-24 asphalt cement [
12]. The essential specifications of the material are shown in
Table 2.
2.3. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
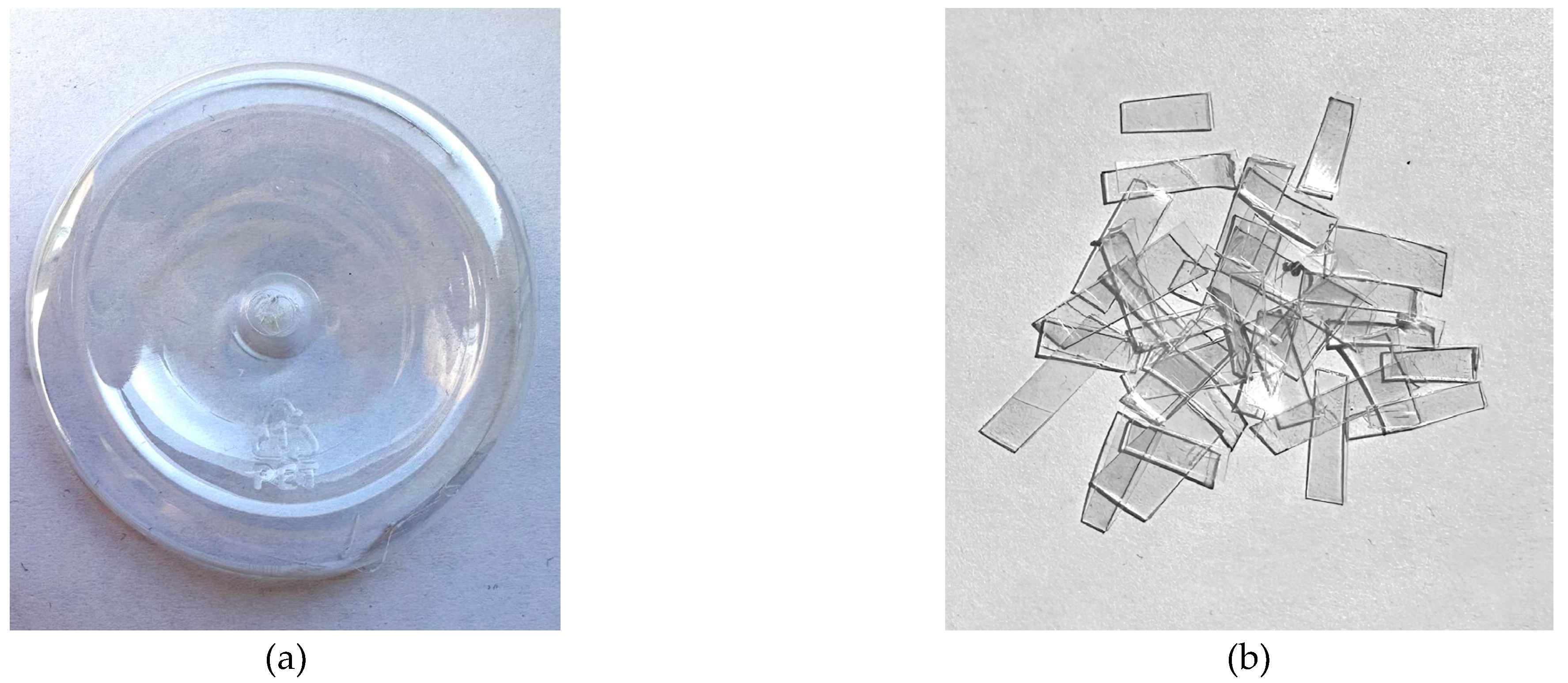
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a transparent polymer with good mechanical properties and dimensional stability under variable load that can improve the mechanical properties of the asphalt mix. Based on the physical properties of the polymer, it reaches a glass transition temperature of 70 °C, i.e. it changes its internal composition, modifying its texture, and providing good stiffness and permanent deformation characteristics.
In this research, PET made of recycled beverage bottles with a density of 0.90 g/cm
3 and 10-mm-long fibres is considered (
Figure 2).
2.4. Dosage, production and air void content
For the research, a total of 72 samples were manufactured using the UNE-EN 12697-12 standard, where the first eight samples are called reference mixtures, and the remaining 40 correspond to samples manufactured with different percentages of PET (6%, 10%, 14%, 18%, and 22%).
In addition, a total of 24 samples were manufactured according to the ASTM D4867 and AASHTO T-283 standards, with a total of six samples for each test for the reference mixtures and another six samples with 6% PET, as the results obtained with this additive content exceeded the minimum TSR values established by the UNE standards.
Table 3 summarises the number of samples manufactured according to the different percentages of PET and the procedures used (according to UNE, ASTM, and AASHTO) to manufacture each sample.
The manufacturing process was carried out in accordance with UNE standards. The aggregates were previously heated in a laboratory oven at 180 °C and the bitumen at 155 °C. Once the materials were heated, the aggregate was homogeneously mixed with the PET particles (according to the quantity per series) for two minutes to distribute the polymer without melting it. The bitumen and mineral filler were added and mixed until a homogeneous mixture was achieved. It should be noted that the incorporation of the polymer corresponds to a dry process, where it was mixed with the aggregate before adding the binder. This procedure was chosen because the melting temperature of PET is higher than the manufacturing temperature of the Marshall test samples (150–170 °C) [
16]. For the compaction process, 50 blows per face were applied by an automatic Marshall hammer, which was necessary to increase the percentage of voids in the sample intentionally. Once compacted, the sample was unmoulded at 20 ± 5 °C.
It is important to note that the American standard indicates a different procedure than the European standard. After mixing, the sample must be left to stand in an oven at 60 °C for 16 hours before compaction, which is considered “short-term ageing”. Subsequently, the temperature is increased ad hoc to place it in the moulds and proceed with the compaction. Another important consideration is that no specific number of blows per face is required. However, ranges of void percentages are considered, i.e. for the ASTM standard, air void values between 6% and 8%, and for the AASHTO standard, between 6.5% and 7.5%, are indicated.
2.6. Indirect tensile strength on moisture damage
The objective of the indirect tensile moisture damage test is to analyse whether the aggregate–binder system that makes up the bituminous mix is susceptible to the effect of water. Research has shown that the temperature must be concentrated between 10 and 25 °C for the resistance value to vary linearly. When working with temperatures above 30 °C, the values show dispersion, and the function becomes parabolic (viscous component).
Table 4 shows the parameters to be considered in the indirect tensile water sensitivity test for each procedure according to the UNE, ASTM, and AASHTO standards.
Finally, the maximum stress is determined, calculated as a function of the compressive load applied along the diametrical axes of the sample up to the cracking point, obtaining the indirect tensile strength.
The conserved resistance value (ITS) is calculated for each sample using the following expression (a):
where
corresponds to indirect tensile strength (kPa),
is the maximum breaking load (N),
is the diameter of the sample (mm), and
is the height of the sample (mm).
This result will be the mean value of the dry and wet samples subset, obtaining the indirect tensile strength ratio (TSR) according to expression (b):
where
corresponds to the ratio of indirect tensile strengths (%),
is the average indirect tensile strength of the wet lot (kPa), and
is the average indirect tensile strength of the dry lot (kPa).
3. Results
3.1. Air voids in asphalt mixtures
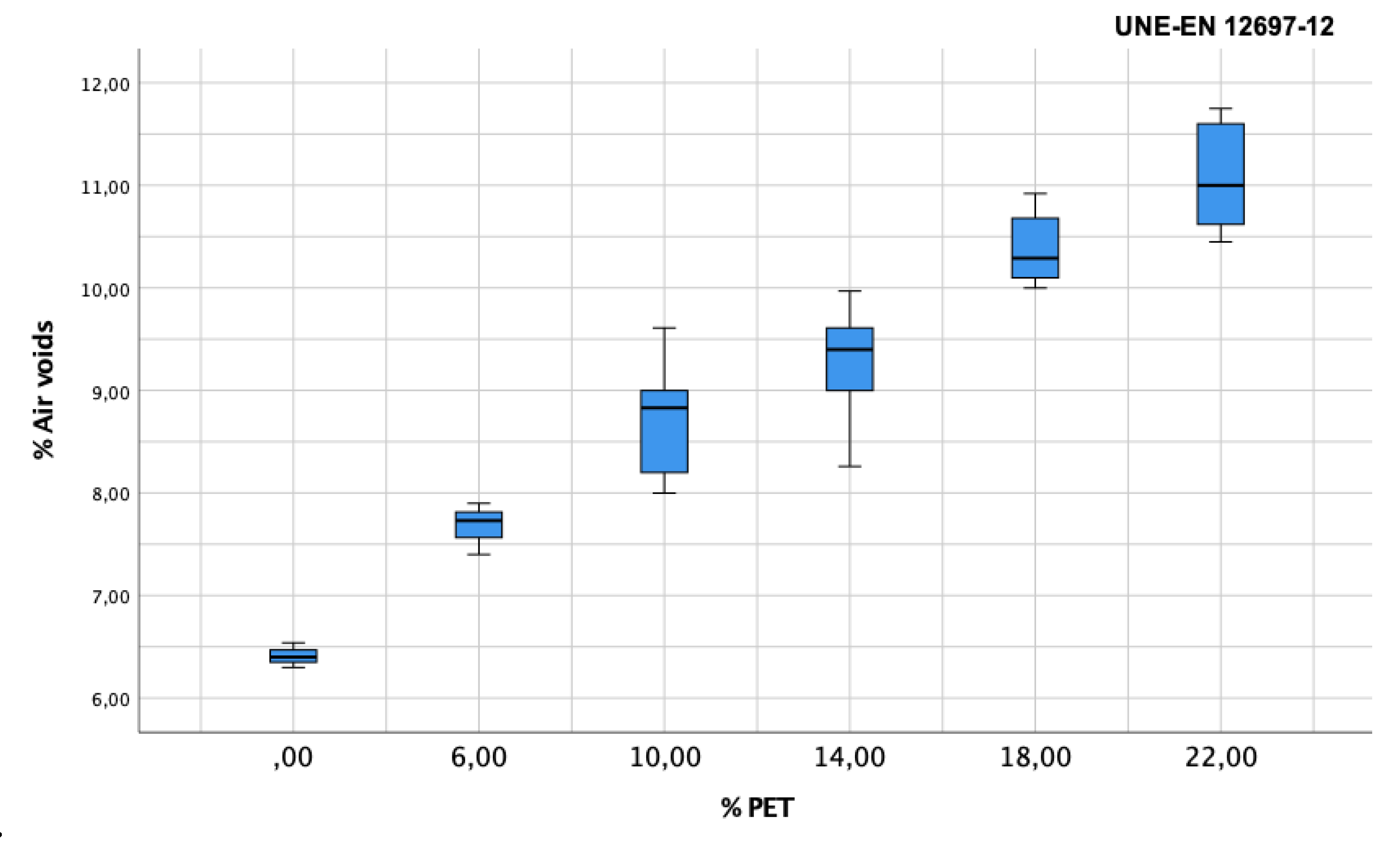
Different percentages of PET (0%, 6%, 10%, 14%, 18%, and 22%) by weight of bitumen were incorporated in a total of 48 test samples compacted at 50 blows per face (according to the UNE standard).
Figure 3 shows that in all the test samples, the percentage of voids reaches the established values of 6% and 12%, depending on the PET content. Given that the mixture with 6% PET is the one with the lowest void content (7–8%), it is the one that most closely resembles the reference mixture, so it was decided to use this dosage for the subsequent study with the American standards before the results were obtained for sensitivity to water by indirect traction.
Subsequently, 12 test samples were manufactured, of which six were reference samples and the other six were modified with 6% PET (by weight of bitumen). As indicated above, the American standard classifies the test samples according to the percentage of air voids present in each.
Figure 4 shows the results obtained, applying a compaction of 50 blows per side for both standards. ASTM D48-64 indicates that the percentage of voids should be between 6% and 8%, and the values obtained comply with the established limits. In the case of the AASHTO standard, a range is established between 6.5% and 7.5% voids in the mix, and as can be seen in
Figure 4, all the values comply with the established limits.
3.2. Indirect tensile strength on moisture damage samples
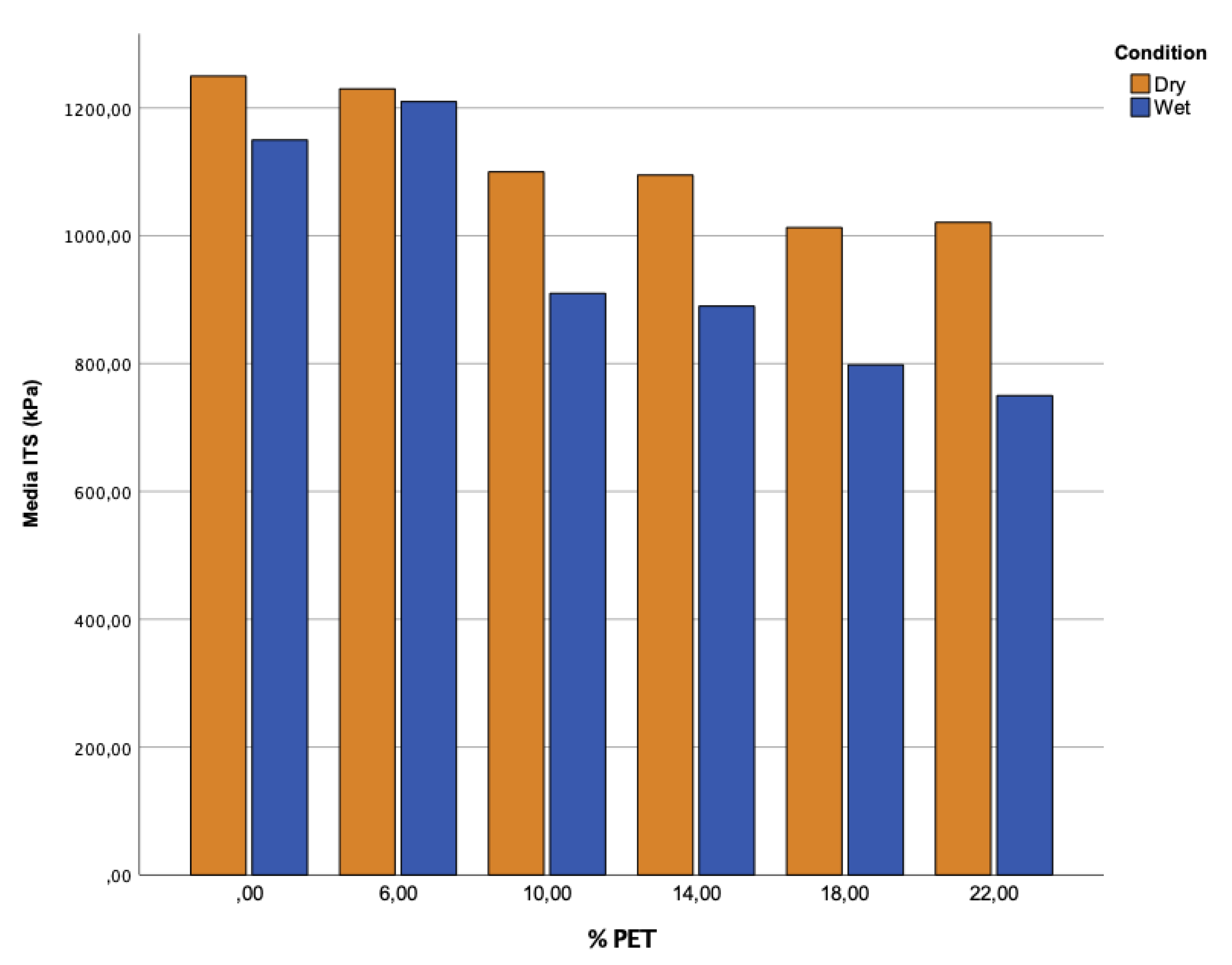
Figure 5 shows the results obtained from the indirect tensile moisture damage test. It is observed that as the amount of PET in the mixtures increases, there is a decrease in the indirect tensile strength between the dry- and wet-conditioned subgroups. There is a slight increase in the samples manufactured with 10% PET (M3), which could be relevant when calculating the optimal amount of the additive to improve the mechanical properties of the asphalt mix. However, as there is a considerable difference between the mean ITSs of the series, the mix is expected to have a higher susceptibility to water.
The ITS values shown in
Figure 5 indicate that the wet samples with 0% and 6% PET had lower tensile strength than the other samples with 10%, 14%, 18%, and 22% PET.
In the reference samples (0% PET), there is a significant difference in strength between the dry and wet samples. Due to this, the samples show a higher susceptibility to water, which helps to look for new additives (such as PET) to help minimise possible damage.
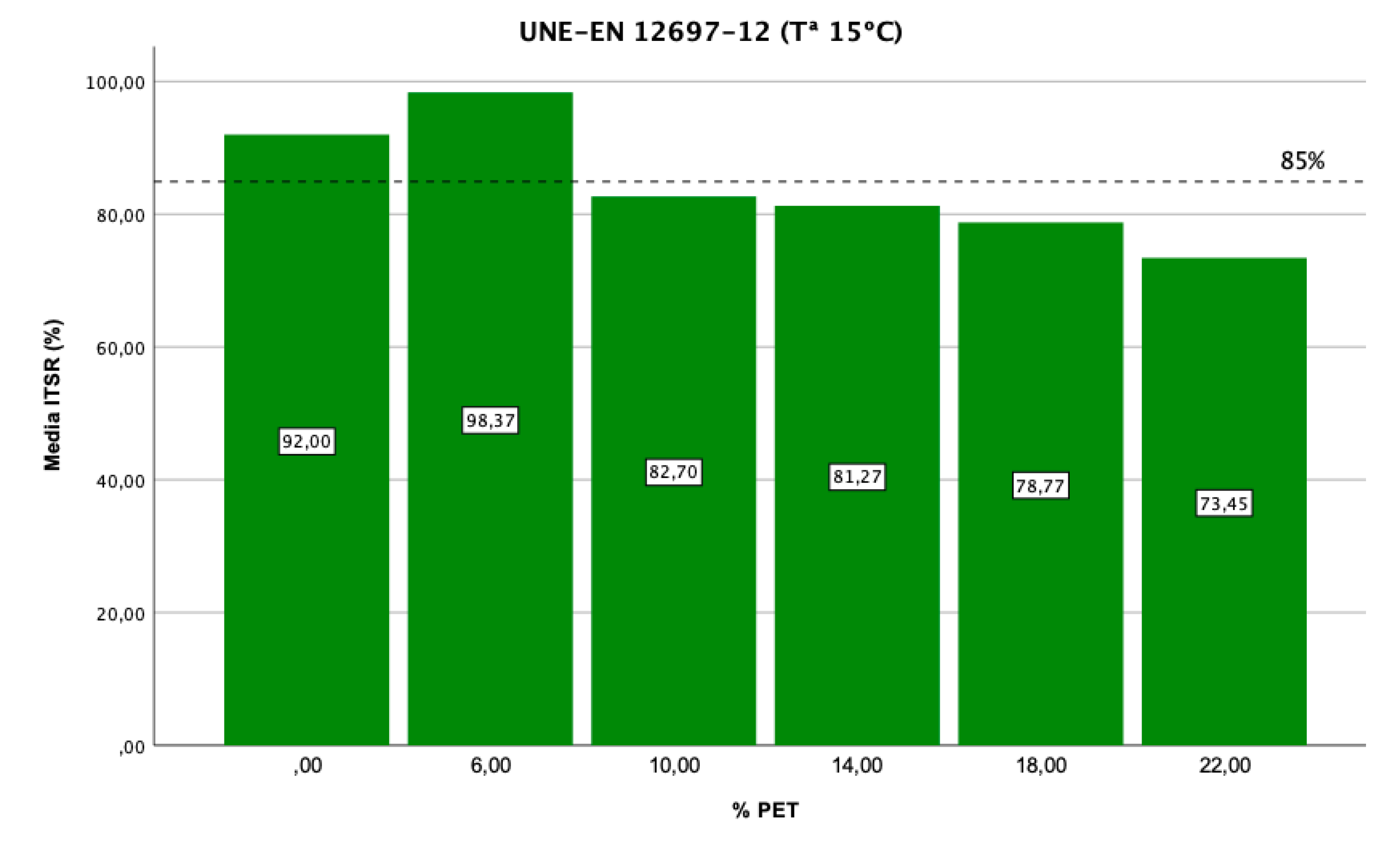
Figure 6 shows the ratio of indirect traction for each series (TSR) and the minimum limit established by the UNE standard to comply with its application in the wearing course. The reference mix (0%) complies with the requirement, although adding 6% PET improves its resistance, reaching 98% TSR. The samples manufactured with 10%, 14%, 18%, and 22% PET do not meet the strength requirements established in the standard and are therefore discarded from further analysis.
Regarding the results obtained from the indirect tensile strength test for the ASTM and AASHTO standards,
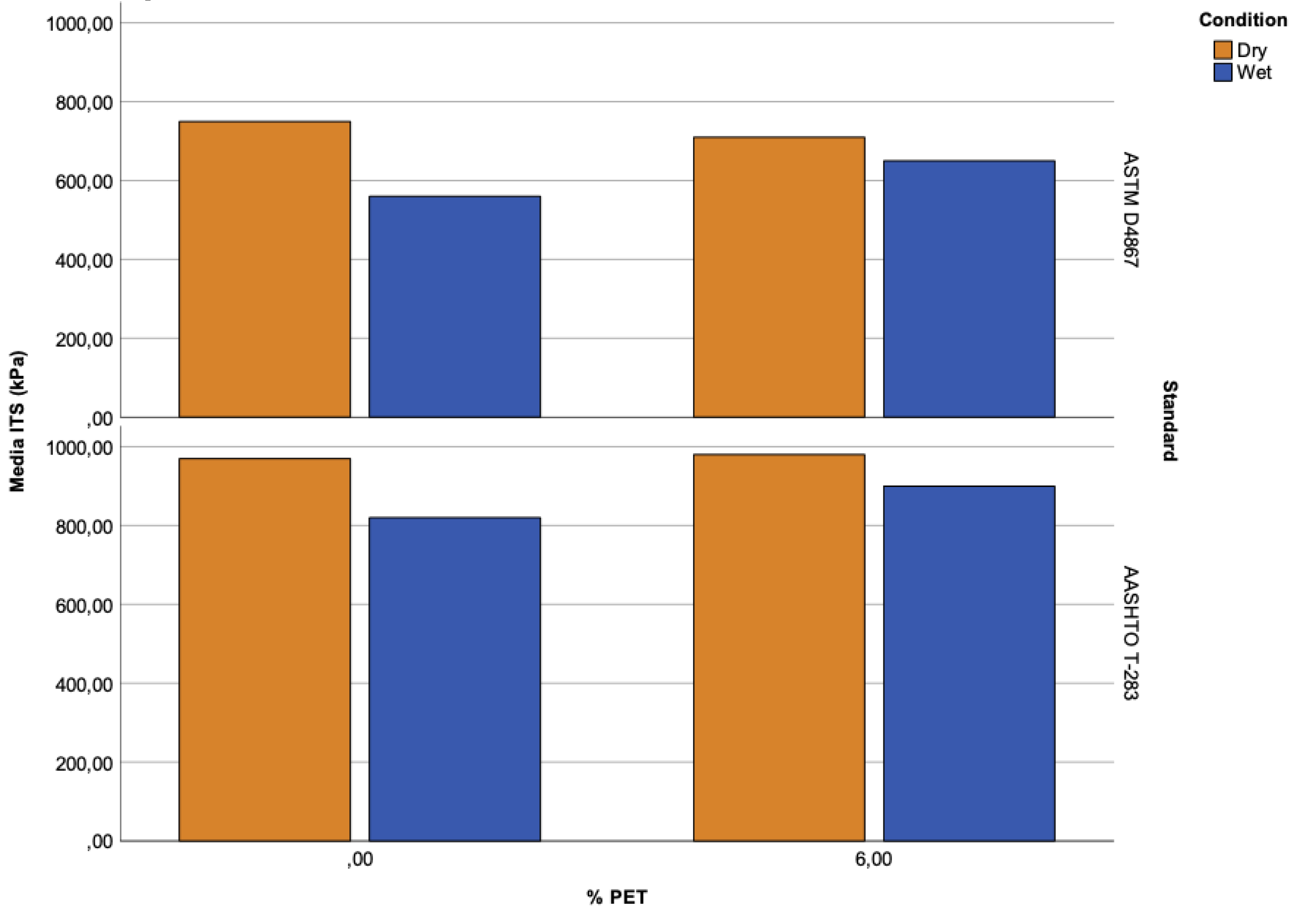
Figure 7 shows that the wet samples have a lower tensile strength, reducing the total strength of the asphalt mixtures. However, for the dry mixtures, a similar strength is observed for both standards, although regarding the percentage of air voids, the ASTM samples are the ones with the lower strength.
Figure 8 shows the TSR values for the mixtures manufactured according to the procedures established in the ASTM and AASHTO standards. The results obtained for the ASTM standard indicate that the reference mixtures have a high susceptibility to water, as they do not reach the established limit of 75%. However, the mixtures with 6% PET substantially improve their resistance, reaching 91% TSR, which indicates that the mix could be used in a wearing course.
Concerning the strength results obtained according to the AASHTO standard, the reference mixtures and those modified with 6% PET comply with the established limit of 80% TSR. However, the reference mix is most susceptible to moisture damage, as it does not comply with the established limit (75%).
It should be noted that these strength values are below those established by the UNE standard, which could be due to the test temperature, as there is a 10 °C difference between the ASTM and UNE standards (from 25 to 15 °C). It is important to note that the lower the temperature, the higher the stiffness of the asphalt mixtures. In addition, there is a high conditioning temperature to which the test samples are subjected (60 °C).
3.3. Discussion of results
The results obtained for the three study standards and the additive percentage, considering the indirect tensile strength and the ratio of the values for each sub-assembly, are presented below.
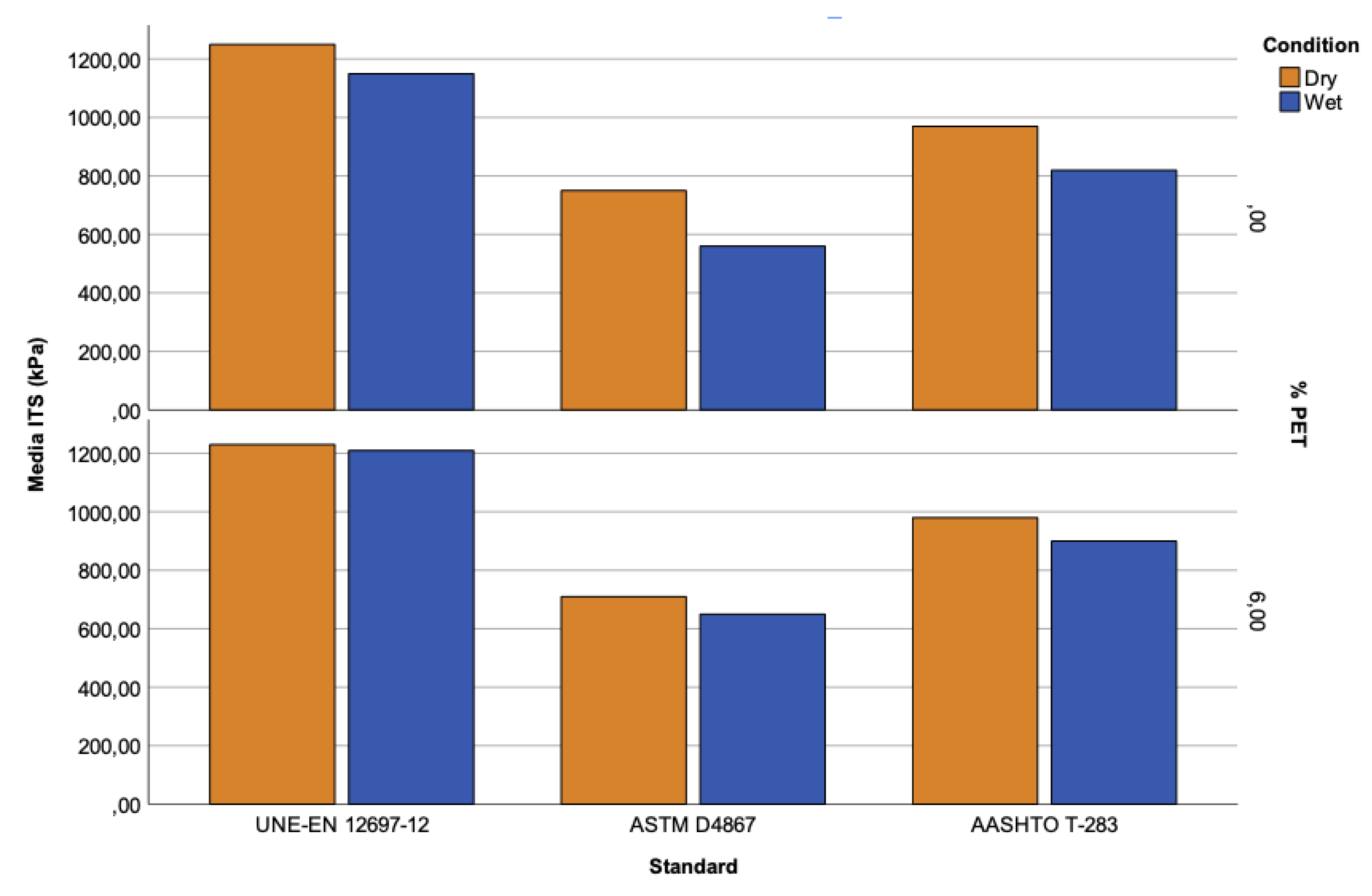
Figure 9 shows that (in general) the results obtained according to UNE-EN 12697-12 are higher than those of the rest of the standards, indicating that these samples have a higher resistance to the load applied by indirect tension. This is due to the difference in the samples’ conditioning temperature (25 °C) for the ASTM and AASHTO standards, since the samples tend to lose strength when the temperature increases. On the other hand, the results obtained for the reference samples manufactured according to the UNE standard indicate that they are more sensitive to water’s effect than the AASHTO standard. This fact may seem strange, since it would be expected that the samples subjected to freeze-thaw cycles (AASHTO) would present more significant damage due to the effect of water.
For samples made with 6% PET (in general), there is not much difference between the dry and wet samples for each standard, although the wet samples show a lower indirect tensile strength.
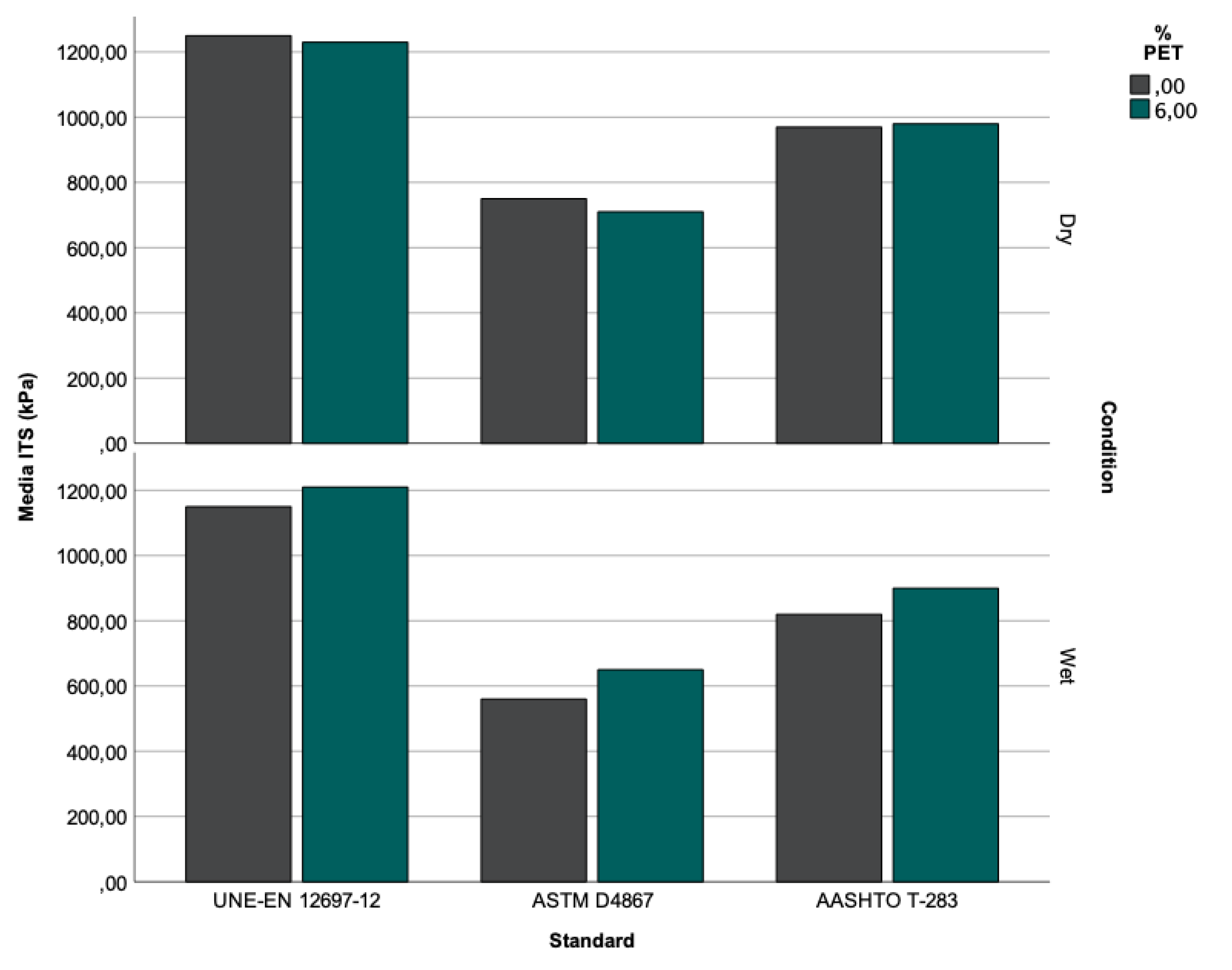
Figure 10 shows the samples’ reactions to the change in conditions to which they were exposed during the TSR test. The samples modified with 6% PET show higher strength under all three standard procedures, indicating that this additive is recommended to reduce possible moisture damage.
4. Conclusions
Water susceptibility is a phenomenon that can cause severe deterioration of asphalt pavements if left unchecked. In this research, the main damage mechanisms associated with the effect of water are analysed based on the tensile water susceptibility test (TSR) according to three different standard procedures (UNE, ASTM, and AASHTO) on referential asphalt mixtures modified with a polymeric additive (PET).
The use of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) as an additive in asphalt mixtures causes a decrease in the mass-to-volume ratio (density) relative to the reference samples and an increase in the void ratio of the asphalt mixtures.
The reference samples (0%) tested according to the UNE standard complied with the limits established for application in wearing courses. However, adding 6% PET considerably improved their resistance, reaching 98% TSR. The samples made with 10%, 14%, 18%, and 22% PET did not meet the strength requirements established in the standard and were therefore discarded from further analysis.
The samples tested according to ASTM D4867 showed higher water susceptibility indices for the reference mixtures (0%), behaving as unstable mixtures under the study conditions. However, with the addition of 6% PET, the mixtures’ stability increased, and their susceptibility to water decreased, obtaining results that were within the limits established by the standards.
The samples tested according to the AASHTO T-283 standard showed a lower susceptibility to water than those following the previous standard. This is due to the ageing of the samples prior to compaction, where the aggregate achieves a better adhesion with the binder, which in turn improves the indirect tensile strength behaviour of the sample.
Finally, this research demonstrates that the effect of water can be a severe problem for pavements and should therefore always be considered at the design stage. The choice of asphalt mix types can considerably reduce water damage to the pavement structure and increase the pavement's service life.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.M.Q. and A.C.R.; methodology, D.M.Q. and A.C.R.; software, E.G. and M.A.F.A.; validation, D.M.Q. and A.C.R.; formal analysis, D.M.Q. and A.C.R.; investigation, E.G. and M.A.F.A.; resources, D.M.Q.; data curation, D.M.Q. and A.C.R.; writing—original draft preparation, E.G.; writing—review and editing, D.M.Q. and A.C.R.; visualization, D.M.Q. and A.C.R.; supervision, D.M.Q. and A.C.R.; project administration, D.M.Q.; funding acquisition, D.M.Q. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the institutional support provided by the Vice-Rectory for Research, Development and Artistic Creation (VIDCA UACh).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Molenaar, A.A.A. Durable and Sustainable Road Constructions for Developing Countries. Procedia Eng. 2013, 54, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerio de Obras Públicas. Dirección de Vialidad. Red Vial Nacional. Dimensionamiento y Carcaterísticas.; Santiago de Chile, 2022.
- Vialidad, D. de Cuadernillo de La Carta Caminera de Chile; Santiago de Chile, 2017.
- Kraemer, C.; Pardillo, J.M.; Rocci, S.; Romana, M.; Sánchez, V. Y Del Val, MA, Ingeniería de Carreteras. Vol. II. Editor. McGraw Hill 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Rojas, J.J.B.; Villa, D.A.C.; Castrillón, M.A.T. Comparativo de Las Condiciones de Transporte Terrestre de Carga Entre Los Países Miembro de La Alianza Del Pacífico. Rev. En-contexto 2016, 155–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baca, V.G.; San Martin, M.S. Geopolítica Del Proyecto de Integración de La Infraestructura Regional Sudamericana. Iberoam. Bus. J. 2022, 5, 36–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xie, J.; Wu, S.; Li, J.; Barbieri, D.M.; Zhang, L. Life Cycle Energy Consumption by Roads and Associated Interpretative Analysis of Sustainable Policies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 141, 110823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Carmen Rubio, M.; Moreno, F.; Martínez-Echevarría, M.J.; Martínez, G.; Vázquez, J.M. Comparative Analysis of Emissions from the Manufacture and Use of Hot and Half-Warm Mix Asphalt. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 41, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, V.Y.; Le, K.N. Sustainable Construction Technologies: Life-Cycle Assessment; Butterworth-Heinemann: 2019; ISBN 0128117508.
- Huang, Y.; Ng, E.C.Y.; Zhou, J.L.; Surawski, N.C.; Chan, E.F.C.; Hong, G. Eco-Driving Technology for Sustainable Road Transport: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 93, 596–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Officials, T. AASHTO Guide for Design of Pavement Structures, 1993; Aashto, 1993; Vol. 1; ISBN 1560510552.
- Thenoux Zeballos, G.A. Evaluación Técnica Del Pavimento y Comparación de Métodos de Diseño de Capas de Refuerzo Asfáltico. 1995.
- Thenoux Zeballos, G.A. Análisis Mecanicista de Estructuras de Pavimentos Utilizadas En Chile, Diseñadas Por El Método AASHTO-93. 1999.
- Caro-Spinel, S.; Alvarez-Lugo, A.E. Evaluación de La Susceptibilidad Al Da Ño Por Humedad de Mezclas Asfálticas Empleando Propiedades Termodinámicas. Rev. Fac. Ing. Univ. Antioquia 2011, 95–104. [Google Scholar]
- Movilla-Quesada, D.; Raposeiras, A.C.; Lagos-Varas, M.; Munoz-Caceres, O.; Andres-Valeri, V.-C.; Troncoso, L. Study of the Optimal Dosage of Celullose Ash as a Contribution Filler in Asphalt Mixtures Based on Its Adhesiveness under Moisture Conditions. SUSTAINABILITY 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgenson, A.K.; Clark, B. Ecologically Unequal Exchange in Comparative Perspective: A Brief Introduction. Int. J. Comp. Sociol. 2009, 50, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almond, R.E.A.; Grooten, M.; Juffe Bignoli, D.; Petersen, T. Living Planet Report 2022–Building a Nature-Positive Society. World Wildl. Fund 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Raihan, A. Toward Sustainable and Green Development in Chile: Dynamic Influences of Carbon Emission Reduction Variables. Innov. Green Dev. 2023, 2, 100038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León Wielandt, P.; Vatter Rodríguez, M. Análisis de La Ley N° 20.920 Que Establece Marco Para La Gestión de Residuos, La Responsabilidad Extendida Del Productor y Fomento Al Reciclaje: Deficiencias Regulatorias y Desafíos En Su Implementación. 2020.
- Elías, R. Mar Del Plástico: Una Revisión Del Plástico En El Mar. 2015.
- Martínez, C.A.C. Reducción de Los Desechos Plásticos En Chile: Elementos Para Profundizar Nuestra Regulación. Rev. Derecho Ambient. 2020, 97–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).