1. Introduction
Neurotrophins are a well-studied class of neurotrophic proteins that play important roles in both neurological and non-neurological functions. The initial discovery of nerve growth factor (NGF) [
1] paved the way for the identification of homologue proteins including brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) [
2], neurotrophin (NT)-3 [
3] and NT-4 [
4]. The first tropomyosin receptor kinase (Trk) was originally discovered as a receptor tyrosine kinase with transforming growth activity [
5]. It was later on demonstrated that neurotrophins bind to the cognate Trk family of receptors where NGF preferentially binds to TrkA [
6], BDNF and NT-4 binds to TrkB [
7] and NT-3 binds to TrkC [
8].
The p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR) binds the pro-neurotrophins with higher affinity than the neurotrophins [
9]. Additionally, the findings of the formation of TrkA/P75NTR heterodimers [
10], the binding of NT-3 to TrkA [
11] and differential signaling [
12] are likely to contribute to the complex signaling of Trk-receptors.
Subsequently, the roles of both NGF and BDNF and their receptors in AD were clarified [
13,
14,
15]. In the past 10 years, the role of BDNF-Val66Met (BDNF-Met) polymorphism in the progression of cognitive decline in both sporadic and familial AD has been well described [
16,
17,
18]. Additionally, those who carry both the BDNF-Met and the ApoE4 alleles have significantly higher amyloid-beta load than non-carriers [
19,
20]. Studies with ApoE4 and BDNF-Met allele carriers have demonstrated a correlation between genotype and memory impairment in older non-symptomatic ApoE4 carriers [
21,
22], in patients with mild cognitive impairment [
23] and in preclinical AD [
22]. Also, the BDNF-Met allele is associated with increased levels of biomarkers such as tau and phospho-tau as well as to poorer cognitive performance in non-symptomatic as well as in symptomatic dominantly inherited Alzheimer’s disease [
24].
Apart from its role in AD, BDNF have also been shown to be decreased in neuropsychiatric disorders such as depression [
25] and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) [
26]. A role for BDNF in Rett syndrome has also been described suggesting that dysregulation of the BDNF gene may affect the severity of this pathology [
27,
28,
29].
The results from later stage clinical trial with the two approved anti-amyloid monoclonal antibodies aducanumab and lecanemab [
30] as well as the more recently described and not yet approved donanemab [
31], have only demonstrated a 35% reduction in deterioration of the integrated Alzheimer’s disease rating scale (iARDS) over time. This is in combination with the established role of BDNF-Met in cognitive impairment in AD clearly shows that there is a need for new treatments for AD that improve memory using a different mechanism of action than the anti-amyloid antibodies. One such approach could be to target the BDNF pathway. Considering that most AD patients or their care partners ranked improved memory of higher importance than clearance of amyloid pathology [
32], and in light of the high societal costs associated with anti-amyloid monoclonal antibodies, it is crucial to develop cost-effective therapies with cognitive enhancing effects. Indeed, several attempts have been made to identify small molecule activators of neurotrophin signaling [
33,
34] or inducers of neurotrophin levels [
35]. Additionally, E2511, a selective positive modulator of TrkA was reported to specifically enhance trophic signaling and to reverse cholinergic neuronal loss in a model of AD [
36]. Importantly, these effects were observed without the induction of hyperalgesia, suggesting that it is possible to differentiate NGF-induced trophic signaling from induction of hyperalgesia. We recently described the identification of triazinetrione derivatives, including ACD856, a pan-Trk positive allosteric modulator with significant pro-cognitive effect [
37]. Additionally, ACD856 increased the levels of certain neurotransmitters and demonstrated antidepressant-like function [
38]. ACD856 has completed both a single and multiple ascending dose study in healthy volunteers. The compound demonstrated excellent pharmacokinetic properties and was well tolerated [
39].
We describe herein the preclinical characterization of ACD856 and demonstrate that the compound has significant neuroprotective effects, increase the levels of BDNF, potentiate neurite outgrowth and evidence of neuroplastic adaption leading to improved cognitive function and long-lasting antidepressant-like effects.
3. Discussion
Patients with AD exhibit a large degeneration of cholinergic neurons in specific areas of the brain, such as the basal forebrain [
53]. The role of cholinergic dysfunction in AD and aged related cognitive dysfunction was early on proposed [
54]. This hypothesis has been supported by the demonstration that NGF prevents degeneration of cholinergic neurons in the basal forebrain in non-human primates [
55]. Several attempts have been made to centrally deliver NGF [
56,
57], and there are indeed results demonstrating a positive effect of NGF [
58,
59]. Also, acetylcholine esterase inhibitors have been shown to have a long-term effect on both mortality and cognitive decline [
60]. More recently, it was demonstrated that reduction of NGF levels leads to astrocytic conversion and induction of a neurotoxic response [
61], suggesting that improved NGF levels or TrkA-signaling in astrocytes can have a neuroprotective effect. Taken together, these data demonstrate the important role of NGF in the maintenance of cholinergic function. Hence, therapies aiming at enhancing the NGF/TrkA cascade could potentially improve or restore cholinergic function.
BDNF is well known to play a role in synaptic plasticity [
62,
63], cognition, regeneration of neurons [
64] and protective effects against several toxins, including Ab-induced synaptotoxicity [
65] or tau-induced neurodegeneration [
66]. Therefore, there is a great potential for therapeutics that will enhance BDNF/TrkB signaling in a wide range of different diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease [
67].
The in vitro experiments presented herein indicate that ACD856 functioned as a positive allosteric modulator with partial agonism. Furthermore, the molecule possessed a neurotrophic efficacy, as judged by its positive effects on neurite outgrowth and SNAP25 levels in PC12 cells. Additionally, the effects observed after glucose and pyruvate withdrawal in primary neurons suggest a neuroprotective role forACD856, which causes neurons to rapidly adapt to maintain high metabolic activity and an increased pool of ATP. Consistent with this, our results also indicate that ACD856 may help neurons switch to a glutamine-fueled mitochondrial metabolism which may reduce excitotoxic stress but also providing them with considerable amount of energy that is especially important for brain regions affected by hypoglycemia. Even more interestingly, the neuroprotective effect of ACD856 was not limited to hypoglycemic situations since also a protective effect was observed of ACD856 in Ab1-42-induced synaptotoxicity. This demonstrates that the compound could have a broad range of neuroprotective effects, mimicking some of the previously reported effects of BDNF.
BDNF was early on demonstrated to be involved in learning processes by the use heterozygous BDNF-knockout mice [
68,
69]. Furthermore, it was shown that BDNF levels were reduced in aged animals, which correlated with reduced hippocampal volume and memory performance. BDNF expression was reported to be selectively reduced in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) in aged mice [
70], demonstrating that aging indeed can influence BDNF levels. The role of the BDNF Val66Met polymorphism has also been demonstrated in older adults where carriers demonstrate reduced executive function [
71] and episodic memory [
72]. The finding that ACD856 increased the levels of BDNF in both cortical neurons and in the brain of aged animals (
Figure 5 and
Figure 7), could be a likely explanation for the cognitive enhancement and antidepressant-like effects for ACD856 observed
in vivo. The increased levels of BDNF after treatment with ACD856 demonstrate that the compound provides neurotrophic support in preclinical models also by increasing the levels of BDNF.
Thus, the neurotropic support, and the neuroprotective and neurorestorative effects described in this paper, along with the lack of major adverse events in the clinical studies including pain or allodynia [
39], suggest that ACD856 is well suited as a therapy to enhance, protect and possibly restore cognitive domains in the brain. The fact that ACD856 can increase the activity of TrkA, TrkB and TrkC receptors, thus enhancing the signaling of all the neurotrophins, combined with its high exposure in the CNS, makes it likely that ACD856 will have both restorative and protective effects as well as a cognitive enhancing effect in diseases characterized by cognitive dysfunction. The lowering of the effective dose and the sustained antidepressant-like effects seen in vivo after repeated dosing of ACD856 suggest a mechanism involving neuronal adaption.
Estimations of human efficacious plasma concentration and pharmacologically active dose (PAD) were based on the estimated unbound C
max and the observed pharmacological effect in the mouse cognition passive avoidance model after single dose administration. The minimum and maximal pharmacologically active dose (PAD) in mice after single administrations were identified as 0.3 mg/kg (s.c.) and 1.0 mg/kg (s.c.), respectively. Since the in vitro TrkA EC
50 value was demonstrated to be similar between human and rat, and the homology of TrkA between rat and mouse is high (96% identity) [
37], it is believed that the PAD for ACD856 corresponds to a human dose generating an unbound C
max in the range of 50 to 70 ng/mL. Interestingly, a single dose of 30 mg ACD856 generated a plasma concentration of unbound ACD856 of 32 ng/mL in man [
39], which is well in line with the values of unbound ACD856 in mice plasma at 1.0 mg/kg reported herein (25-52 ng/mL).
The introduction of new treatments for AD including the anti-amyloid monoclonal antibodies aducanumab, lecanemab (aka Leqembi) and donanemab opens up new possibilities for adjuvant therapies. The preclinical data presented in this article suggests that ACD856 may fulfill many of the criteria for an adjuvant therapy to anti-amyloid treatment or as a stand-alone treatment, if the preclinical results are reproduced in patients.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and chemicals
Recombinant human NGF (450-01) and BDNF (450-02) were purchased from PeproTech (London, UK). GlutaMAX™ Supplement (35050061), StemPro™ Accutase™ Cell Dissociation Reagent (11599686), heat inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS) (10500064) or horse serum (26050070), G418 sulfate (10131027), penicillin-streptomycin (15140148), protease inhibitor (Pierce™ A32955) and phosphatase inhibitor (A32957), modified Dulbecco’s PBS Tween™ buffer (Pierce™ 28346), MEM (31095029), Neurobasal SFM (21103049), Neurobasal™-A medium, no D-glucose, no sodium pyruvate (A2477501), RPMI Medium 1640 (11875101), Leibovitz’s L-15 medium (11415049), B-27™ supplement (17504-044), EBSS (14155063) were purchased from Thermo Fisher Scienific. Resazurin (Ready-to-use solution) was acquired from TCI Europe (Zwijndrecht, Belgium). The mitochondrial ToxGlo™ assay kit (G8001) was purchased from Promega Corporation (Madison, WI). The PathHunter Detection Kit (93-0001) was obtained from Eurofins DiscoverX.
The following antibodies were used in this study: mouse anti-beta tubulin (G-8) (sc-55529, Santa Cruz), rabbit anti-phospho-p44/42 MAPK (ERK1/2) (Thr202/Tyr204) (D13.14.4E) (4370, Cell Signaling), rabbit anti-SNAP25 (PA1-740, Invitrogen), rabbit phospho-TrkA (Tyr674/675)/TrkB (Tyr706/707) (C50F3) (4621, Cell Signaling), mouse anti-beta actin (C4) (sc-47778, Santa Cruz).
4.2. Cell lines and cell culture conditions
The human osteosarcoma cell lines U2OS-TrkA/p75-SHC1 and U2OS-TrkB/p75-SHC1 were acquired from Eurofins DiscoverX Corporation (Fremont, CA, US). Cells were maintained sub-confluent in MEM medium supplemented with 10% FBS, 1% penicillin/streptomycin, and hygromycin/geneticin/puromycin. Immortalized SH-SY5Y cell line expressing TrkB was purchased from Kerafast (Boston, MA, USA) and maintained in complete growth medium, consisting of RPMI1640, GlutaMAX, 10% FBS, 1% penicillin/streptomycin, and 0.3 mg/mL geneticin. The PC12 cell line was purchased from ATCC (LGC Standards GmbH, Wesel, Germany), and maintained in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS, 1% penicillin/streptomycin. All cell cultures were maintained at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2.
4.3. Animals
All animal experiments were conducted in C57BL/6J male mice from Charles River, Germany. All animals were permitted to acclimate to the animal facilities and had unrestricted access to food and water. Animals were handled by the same researcher for at least three days before the start of the studies. All protocols were approved by the Stockholm County court’s regional ethics committee in compliance with the Swedish Animal Welfare Act 2018:1192 and directive 2010/63/EU (NIH publication No. 85-23). The experiments were carried out under the ethical permit ID1640 (in vivo studies) and 2181-2021 (primary neuronal cell cultures). Every effort was made to reduce animal suffering and the number of animals used in the experiments.
4.4. Isolation and culture of mouse primary neurons
Mouse cortical neuronal cultures were prepared from day 16—17 of embryonic development. For precise identification, embryonic brain cortex was dissected in 5-mL EBBS (Ca2+/Mg2+ free) on a 60-mm Petri dish using a Leica stereo microscope. The tissue was transferred to a 15 mL tube and digested for 15 min at 37°C in EBSS with trypsin-EDTA (0.25%). Once the tissue had sunk to the bottom, the solution was discarded. Thereafter, cells were mechanically disaggregated in EBSS containing DNAse I using a glass Pasteur pipette. The supernatant was transferred to a fresh 15 mL tube and the remaining non-dissociated tissue was discarded. Trituration was performed twice, and the pooled supernatant was centrifuged at 500 rpm for 5 minutes. Cell pellets were then resuspended in 10 mL of fresh Neurobasal medium containing 2% B-27 and 0.5 mM L-glutamine and 100 units/mL penicillin and streptomycin. Ten microliters of the diluted cells were placed in a hemocytometer for counting. Dissociated primary cortical neurons were cultured in poly-D-lysine coated 96-Well plates at a cell density as described in assay sections below. Half of the medium was changed every 5 days. All cell cultures were maintained at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2.
4.5. TrkA and TrkB PathHunter® Cell-Based Assays
The TrkA or TrkB cell-based PathHunter® assays were used to characterize the potency and efficacy of ACD856. The assays use enzyme fragment complementation (EFC) to analyze protein–protein interactions. TrkA or TrkB receptors are phosphorylated upon ligand activation (NFG and BDNF respectively), leading to an interaction with SHC-1. Trk-receptors are fused to an enzyme donor tag, and SHC-1 is fused to a larger part of β-gal called an enzyme acceptor. The interaction leads to an active β-gal enzyme that will hydrolyze a substrate generating a luminescence signal. The assays were performed as previously described (#Cell paper). Briefly, 10,000 cells per well in 20 mL of MEM medium supplemented with 0.5% horse serum were seeded in 384-well white plates (CulturePlate, PerkinElmer) and incubated overnight at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2. Thereafter, in vitro effect of ACD856 was tested using eight different concentrations ranging from 0,01 to 30 µM using 10 ng/mL of NGF or BDNF. The test compound plate was diluted with 10 mL of Leibovitz’s L15 medium containing 10 ng/mL of NGF or BDNF and pipetted into the cell plate using a Biomek NX automated workstation. Plates also included min-control and max-control wells (containing assay media or 30 ng/mL of ligand, respectively). After a three-hour incubation at room temperature, 7 mL of substrate was added to each well followed by a 60-minute incubation. The chemiluminescence was then measured using a SpectraMax iD5 plate reader from Molecular devices. Raw values were used to calculate EC50 values (µM) and the efficacy (%) of ACD856 by setting the maximal response (DMSO control + ligand 30 ng/mL) to 100% and the negative control (DMSO control without ligand) to 0%.
4.6. Resazurin assay
Resazurin assay was used to measure the metabolic capacity of PCN cells treated with increasing doses of BDNF, NGF, and ACD856 using a model of energy deprivation-induced neurotoxicity. Cells were seeded at 10 x 105 cells/well in 96-well plates and treated at DIV4-5 in Neurobasal-A media with 2% B27 and 2 mM glutamine (no glucose or pyruvate was present). Two hours after treatment, a 10% volume of resazurin ready-to-use solution was added to the cell culture media and the plates were returned to the incubator for a further four hours. Resazurin reduction is directly proportional to metabolic function and was evaluated fluorometrically at 540 nm excitation and 580 nm emission wavelengths using a SpectraMax iD5 plate reader. Results were presented as a percentage change compared to control group.
4.7. Measurement of cell membrane integrity and ATP levels
Mitochondrial ToxGlo assay was used to evaluate the cell membrane integrity and the ATP levels of PCN cells. At DIV4-5, cells seeded at 10 x 105 cells/well in 96-well plates were treated for six and three hours with increasing doses of neurotrophins and ACD856 respectively, in Neurobasal-A media containing 2% B27 and 2 mM glutamine. No glucose or pyruvate was present in the cell media to prevent non-mitochondrial ATP production from glycolysis. Then, bis-AAF-R110, a fluorogenic substrate that is exclusively cleaved by proteases released from membrane-compromised cells was added and plate was incubated at 37°C for 30 minutes. Fluorescence was measured at 485 nm (Ex) /530 nm (Em) using a SpectraMax iD5 plate reader. Next, the ATP detection reagent was added, and luminescence was measured after 5 min incubation to assess ATP levels in lysed cells. The results were displayed as a percentage change relative to the control group.
4.8. Measurement of human phospho-TrkB by ELISA
A DuoSet ELISA human phospho-TrkB was used to measure tyrosine-phosphorylated human TrkB in cell lysates. SH-SY5Y-TrkB cells (10 x 104 cells) were seeded in 96-well plates overnight. The day after, cells were exposed for 10 min to 30 ng/mL of BDNF +/- ACD856 at a concentration of 0.3-3 mM and immediately lysed on ice for 15 minutes followed by centrifugation at 500 x g for 5 minutes. The ELISA procedure was performed following the manufacturer’s specifications. Briefly, cell supernatant was transferred to an ELISA plate previously coated with the capture antibody and blocked at RT for 2 hours (samples were run in duplicate). Then, the plate was incubated for 2 h with the diluted HRP-labelled anti-phosphotyrosine antibody, followed by 20 min of incubation with substrate Solution. The reaction was stopped with 2 M H2SO4 and immediately measured, using a microplate reader set to 450 nm, and with wavelength correction set to 540 nm. Intermediate washing steps were performed before and after each incubation step with a wash buffer.
4.9. Quantification of BDNF by ELISA
Detection of endogenous BDNF was performed with a Human/Mouse BDNF DuoSet ELISA (DY248) in PCN (10 x 104 cells/well) between days in vitro (DIV) 10-14. The cells were microscopically examined before and after treatments and wells with abnormal neuron morphology or disrupted cell layer were excluded. The determination was carried out according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Briefly, 96-well Maxisorp plates (NUNC) were coated with 100 mL/well of capture antibody and incubated overnight. Non-specific binding was blocked for 90 min using 5% BSA in tris-buffered saline with 0.3% Triton X-100 (TBS-T) followed by repeated rinsing with TBS-T. After 6 h of treatment, 10x lysis buffer containing protease inhibitor and EDTA-free was added to the cell plates and incubated for 20 minutes followed by centrifugation at 1000 rpm for 2 min. Then, 100 mL of samples or standard samples were added to the coated plate and was kept overnight at 4oC. ELISA plates were washed four times followed by an incubation of 2h with 100 mL/well of detection antibody. After repeated washing steps, 100 mL/well of Streptavidin-HRP was added and incubated for 20 min. After washing, 100 mL/well of substrate solution was added and incubated for 25 min. The reaction was stopped by adding 50 mL of stop solution and the absorbance was immediately measured at 450 nm using a SpectraMax iD5 plate reader from Molecular Devices. Unless otherwise mentioned, all incubations were conducted in a shaker at 300 rpm and room temperature. All samples were run in duplicates. The standard curve ranged from 11 to 1500 pg/mL BDNF. Concentrations of BDNF were calculated using the regression line of the BDNF standard curve. According to the manufacturer, the BDNF ELISA kit has no cross-reactivity with other neurotrophic factors, such as NGF, NT-3, and NT-4, at 50 ng/mL
4.10. Immunocytochemistry analysis of neurite outgrowth, SNAP-25 and ERK1/2 staining
PC12 cells (2000 cells/well) were cultured in 384-well black poly-D-lysine plates coated with clear bottom (PerkinElmer ViewPlate), coated with 0.1 mg/mL Collagen IV and 0.025 mg/mL vitronectin, and treated with 0 or 3 ng/mL NGF, for 5 days in humidified atmosphere at 5% CO2. Mouse primary cortical neurons (25 x 103 cells per well) were cultured in 96-well plates coated with poly-D-lysine and incubated with DMSO or ACD856. Incubations were terminated by the addition of 16% paraformaldehyde to yield a final concentration of 4%. Thereafter, plates were placed +4oC for at least 60 minutes. Fixed cells were washed twice with TBS-T and blocked for 1 hour in TBS-T containing 2.5% BSA. Thereafter, sequential incubations with primary and secondary antibodies in blocking buffer were performed at 4°C overnight. PC12 cells were stained with anti-β-tubulin mouse antibody (Santa Cruz sc-55529) (dilution 1:200) and Alexa fluor 488-goat anti-mouse antibody (dilution 1:750). Anti-SNAP25 antibody (dilution 1:200) and Alexa Fluor 647-goat anti-rabbit antibody (dilution 1:750) were used for staining of SNAP25. Mouse primary cortical neurons were stained with anti-phospho-p44/42 MAPK (ERK1/2) rabbit monoclonal antibody (Cell Signaling CS-4370) (dilution 1:200) and Alexa Fluor 647 goat anti-rabbit antibody (dilution 1:750). Nuclei were stained with Hoechst fluorescent DNA dye. High-content imaging/analysis was performed on a Thermo Scientific Cellomics Array Scan VTI HCS Reader using Cellomics Scan Software.
4.11. Western Blot Analysis
Phosphorylated ERK 1/2 (pERK1/2) levels were evaluated in mouse primary neurons between DIV10-15. Cells were seeded at (60 x 104 cells) in 6-well plates coated with poly-D-Lysine. The activation of the Trk signaling pathway was induced with 10 ng/mL ligand for 20 min. Cells were thereafter immediately lysed on ice, sonicated, and denatured at 95oC for 10 min on a heating block. Proteins were separated on a Novex Bis-Tris 4-12% gel and transferred to a PVDF membrane using an iBlot instrument (Invitrogen). The membrane was blocked using 5% BSA in TBS-T followed by incubation with anti-phospho-p44/42 MAPK (ERK1/2) rabbit monoclonal antibody (Cell Signaling CS-4370) (dilution 1:1000) in TBS-T with 0.1% BSA for at least 60 minutes. Membranes were thereafter washed three times and thereafter incubated with horseradish peroxidase-coupled secondary goat anti-rabbit antibodies for 60 minutes. After washing, western blot detection reagent (Forte, Millipore) was added and immunoreactive proteins were detected by luminescence using C-DiGit Blot Scanner and quantified with Image Studio™ Software. (LI-COR Biosciences, Bad Homburg, Germany).
4.12. Passive avoidance test
The passive avoidance (PA) task is an associate learning paradigm that is based on Pavlovian fear-conditioning and instrumental conditioning and conducted as previously described [
37] in male C57BL/6J mice (n = 7–8/group) from Charles River Laboratories, Sulzfeld, Germany. Briefly, vehicle or ACD856 (0.1, 0.3, or 1 mg/kg) were administered either as a single dose on the training day (Day 4) or once daily for 4 days (Day 1-4). The last injection was given 60 min prior to training. Moreover, on the training day (Day 4), scopolamine (Sigma Aldrich, Stockholm, Sweden) at 0.3 mg/kg or vehicle was administered once s.c. 30 min prior to training. No compound was administered on the test day, conducted 24 h after training (Day 5) where retention latencies and time spent in the bright compartment were determined.
4.13. Forced swim test
The FST is one of the most frequently used behavioral tests for measuring depressive-like behavior in rodents. Animals placed in cylinders containing water rapidly become immobile, demonstrated by floating passively or making only movements necessary to remain afloat. Based on an immobility response induced by inescapable exposure to stress, the FST also has strong predictive validity because short-term administration of antidepressant compounds from a variety of pharmacological classes reduces immobility time in the FST. These drugs include tricyclic antidepressants, MAO inhibitors, atypical antidepressants, and SSRIs [
73].
Depression-like behavior was assessed in male C57BL/6J mice using a modified version of the FST, as described previously [
74]. This included a two-day protocol test, with pre-exposure to water 24 h prior to the test (day one of FST), which seems to be a more accurate and sensitive technique in detecting depression-like behavior in mice than the standard method of a single exposure (one day test) [
75,
76]. Animals were individually placed in a vertical glass cylinder (50 cm high, 20 cm in diameter, CMA) filled with tap water up to 35 cm (25±0.5°C). Two swimming sessions were conducted: a 10 min pre-test (day one) followed 24 h later (day two) by a 6 min test session. The total duration of immobility as well as latency to the first immobility were recorded during the 6 min test. After each swimming session, the mice were gently removed and placed in home cage together with dry napkins. Immobility was defined as floating passively in an upright position in water, with only small movements necessary to keep the head above the water surface. The floating time was considered as an index of depression-like behavior. The glass cylinder was cleaned thoroughly between each animal.
4.14. Plasma protein binding
The fraction unbound drug (fu) in plasma from mice was determined by equilibrium dialysis at 37°C for 4 hours using RED devices. The drug molecule at a concentration of 10 µM was added to plasma from CD-1 or C57/Bl6 mice and dialyzed against phosphate buffer saline (pH 7.4). After dialysis, the drug concentration in the buffer and plasma was quantified by LC-MS/MS analysis as described below.
4.15. Pharmacokinetic studies and LC-MS/MS analysis of ACD856
Male C57BL/6J mice were administered with a single subcutaneous dose of 1 mg/kg ACD856 and blood was collected at 7 time-points, i.e., at 15 min, 30 min, 1 h, 2 h, 4 h, 8 h and 24 h post-dosing. Plasma was separated within 30 minutes by centrifugation at 3000xg (+4°C) for 10 minutes. Pharmacokinetic parameters were evaluated by non-compartmental analysis based on plasma compound concentrations determined by LC-MS/MS analysis.
Standards for a calibration curve, ranging from 10-10,000 nM, and quality control (QC) samples were prepared in blank mouse plasma by spiking plasma with ACD856 from a 10 mM DMSO stock. Calibration standards and QC samples were prepared just before the analysis. Plasma samples were precipitated by 100% methanol containing 50 nM Warfarin as internal standard. After centrifugation, the supernatant was transferred to an autosampler glass vial and the concentration of ACD856 was determined by LC-MS/MS. An Acquity UPLC system (Waters) coupled to a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer (Xevo TQ-S micro, Waters) operating in multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode was used for detection of compound. Samples were separated on a BEH C18 column (2.1 x 50 mm, 1.7 µm, Waters) kept at 60˚C using a gradient consisting of a mixture of A) 0.1% formic acid in water and B) 0.1% formic acid in acetonitrile, as follows; 0-0.4 min, 5% B; 1.4-1.6 min, 100% B; 1.65-2.00 min, 5% B. Flow rate was 0.5 mL/min and the sample were kept at 10˚C in an autosampler. For ionization of compounds, electrospray in negative mode (ESI-) was used with the following conditions: capillary voltage, 1.9 kV; desolvation gas temperature, 500˚C and gas flow, 1000 L/hr. The optimized transitions for ACD856 were; precursor ion 385.968 m/z, product ions 160.994 and 267.087 m/z, and cone and collision energies were 30 V and 8 V, respectively. TargetLynx software was used for integration of compound peak area and a calibration curve were made by fitting the analyte concentrations versus the peak area ratios of the analyte to internal standard using the most suitable regression model and weighting method.
4.16. Statistical analysis
All statistical computations were carried out using GraphPad Prism Software, version 9.3.1. Half maximal effective concentrations (EC50 values) were calculated using non-linear regression analysis. Unpaired t-tests were used to compare two groups. For experiments with more than two groups, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed followed by Dunnett’s post hoc tests for groupwise comparisons. Data values are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM), unless otherwise stated in the legend of each figure. The significance level was accepted at p < 0.05 for a 95% confidence interval.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.P-F., J.S., G.N., and P.F.; methodology, C.P-F., S.J., M.B., M.D., N.M., A.R., V.L., and P.F.; project administration, C.P-F., and P.F.; writing original draft, C.P-F., and P.F.; review and editing, C.P-F., J.S., M.B., M.D., V-L, G.N. and P.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Figure 1.
Increased activation of NGF-TrkA signaling through interaction of SHC-1 and TrkA. Dose-response effect of ACD856 was investigated in the absence or presence of five different concentrations of NGF. U2OS-TrkA/SHC-1/p75NTR cells were treated with DMSO or ACD856 and NGF for 3 hours. The response was measured with luminescence as described in Materials and Methods. The same data were used to visualize the results either as a consequence of a change in the concentrations of NGF (a) or as a change in the concentrations of ACD856 (b). Dose-response curves of NGF in the presence of increasing concentrations of NGF (a). Red circle and line depict activity in the absence of NGF. The following concentrations of ACD856 were used, 3 nM (solid squares), 100 nm (open diamonds), 300 nM (solid triangles), 1 mM (solid diamonds), 3 mM (open circle), 10 mM (open squares), 30 mM (open triangles.) Dose-response curves of ACD856 in the absence or presence of increasing concentrations of NGF (b). Red circle and line depict activity in the absence of NGF. The following concentrations of NGF were used, 0.3 ng/mL (solid squares), 1 ng/mL (solid triangles), 3 ng/mL (solid diamonds), 10 ng/mL (open squares), 30 ng/mL (open circle). Dashed line in both figures indicate the activity of 30 ng NGF/mL in the presence of DMSO to which all other values were normalized to. Data shown are the mean +/- SEM (n=12) from three independent experiments where each experiment was performed in quadruplicates.
Figure 1.
Increased activation of NGF-TrkA signaling through interaction of SHC-1 and TrkA. Dose-response effect of ACD856 was investigated in the absence or presence of five different concentrations of NGF. U2OS-TrkA/SHC-1/p75NTR cells were treated with DMSO or ACD856 and NGF for 3 hours. The response was measured with luminescence as described in Materials and Methods. The same data were used to visualize the results either as a consequence of a change in the concentrations of NGF (a) or as a change in the concentrations of ACD856 (b). Dose-response curves of NGF in the presence of increasing concentrations of NGF (a). Red circle and line depict activity in the absence of NGF. The following concentrations of ACD856 were used, 3 nM (solid squares), 100 nm (open diamonds), 300 nM (solid triangles), 1 mM (solid diamonds), 3 mM (open circle), 10 mM (open squares), 30 mM (open triangles.) Dose-response curves of ACD856 in the absence or presence of increasing concentrations of NGF (b). Red circle and line depict activity in the absence of NGF. The following concentrations of NGF were used, 0.3 ng/mL (solid squares), 1 ng/mL (solid triangles), 3 ng/mL (solid diamonds), 10 ng/mL (open squares), 30 ng/mL (open circle). Dashed line in both figures indicate the activity of 30 ng NGF/mL in the presence of DMSO to which all other values were normalized to. Data shown are the mean +/- SEM (n=12) from three independent experiments where each experiment was performed in quadruplicates.
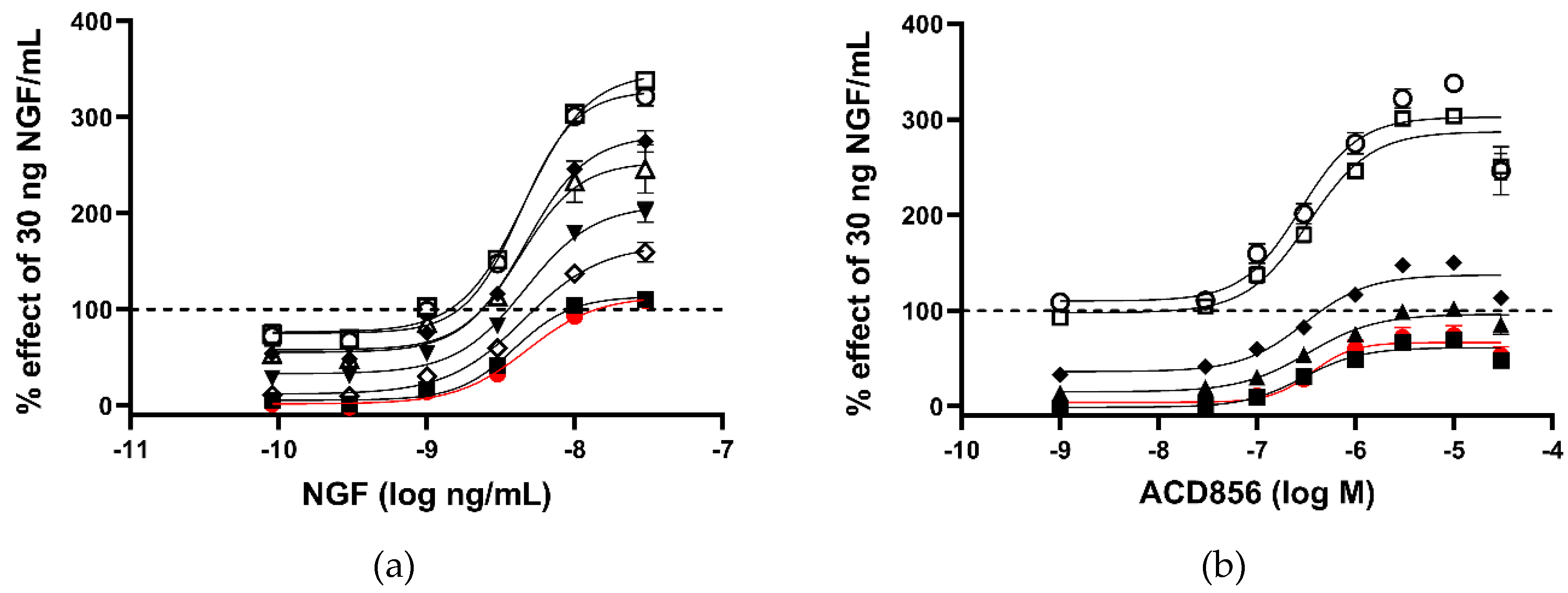
Figure 2.
Increased activation of TrkB and downstream signaling through ERKK1/2 MAPK phosphorylation by BDNF and ACD856. Levels of phosphorylated TrkB receptors were determined by ELISA in SH-SY5Y cells overexpressing the human TrkB receptor (a). Effect of 0 (open bars), 10 (light grey bars) or 30 ng BDNF/mL (dark grey bars) and time course on BDNF-induced TrkB tyrosine phosphorylation are depicted as the mean of one experiment performed in quadruplicates +/- SEM *p < 0.05. SH-SY5Y-TrkB cells were incubated with 30 ng BDNF/mL for 10 minutes in the absence (DMSO) or presence of increasing concentrations of ACD856 (b). A significant increase of human pTrkB was observed with 300 nM ACD856. Data shown are the mean value +/- SEM from three independent experiments where each experiment was performed using at least 5 technical repeats. The effect of different neurotrophic factors on the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and Trk-receptors were investigated (c). Cortical neurons were stimulated with 10 ng/mL of the indicated factors and the levels of pERK1/2 (upper panel), phospho-Trk (tyrosine 674/675) (mid panel) and beta-actin as a loading control (lower panel) were analyzed by Western blot. Primary cortical neurons were incubated with 300 nM ACD856 for the indicated time periods in the absence of exogenous BDNF (d). The levels of phosphorylated ERK1/2 were determined by immunocytochemistry. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 compared to control group at one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. Data shown are the mean value of all replicates +/- SEM from three different experiments.
Figure 2.
Increased activation of TrkB and downstream signaling through ERKK1/2 MAPK phosphorylation by BDNF and ACD856. Levels of phosphorylated TrkB receptors were determined by ELISA in SH-SY5Y cells overexpressing the human TrkB receptor (a). Effect of 0 (open bars), 10 (light grey bars) or 30 ng BDNF/mL (dark grey bars) and time course on BDNF-induced TrkB tyrosine phosphorylation are depicted as the mean of one experiment performed in quadruplicates +/- SEM *p < 0.05. SH-SY5Y-TrkB cells were incubated with 30 ng BDNF/mL for 10 minutes in the absence (DMSO) or presence of increasing concentrations of ACD856 (b). A significant increase of human pTrkB was observed with 300 nM ACD856. Data shown are the mean value +/- SEM from three independent experiments where each experiment was performed using at least 5 technical repeats. The effect of different neurotrophic factors on the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and Trk-receptors were investigated (c). Cortical neurons were stimulated with 10 ng/mL of the indicated factors and the levels of pERK1/2 (upper panel), phospho-Trk (tyrosine 674/675) (mid panel) and beta-actin as a loading control (lower panel) were analyzed by Western blot. Primary cortical neurons were incubated with 300 nM ACD856 for the indicated time periods in the absence of exogenous BDNF (d). The levels of phosphorylated ERK1/2 were determined by immunocytochemistry. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 compared to control group at one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. Data shown are the mean value of all replicates +/- SEM from three different experiments.
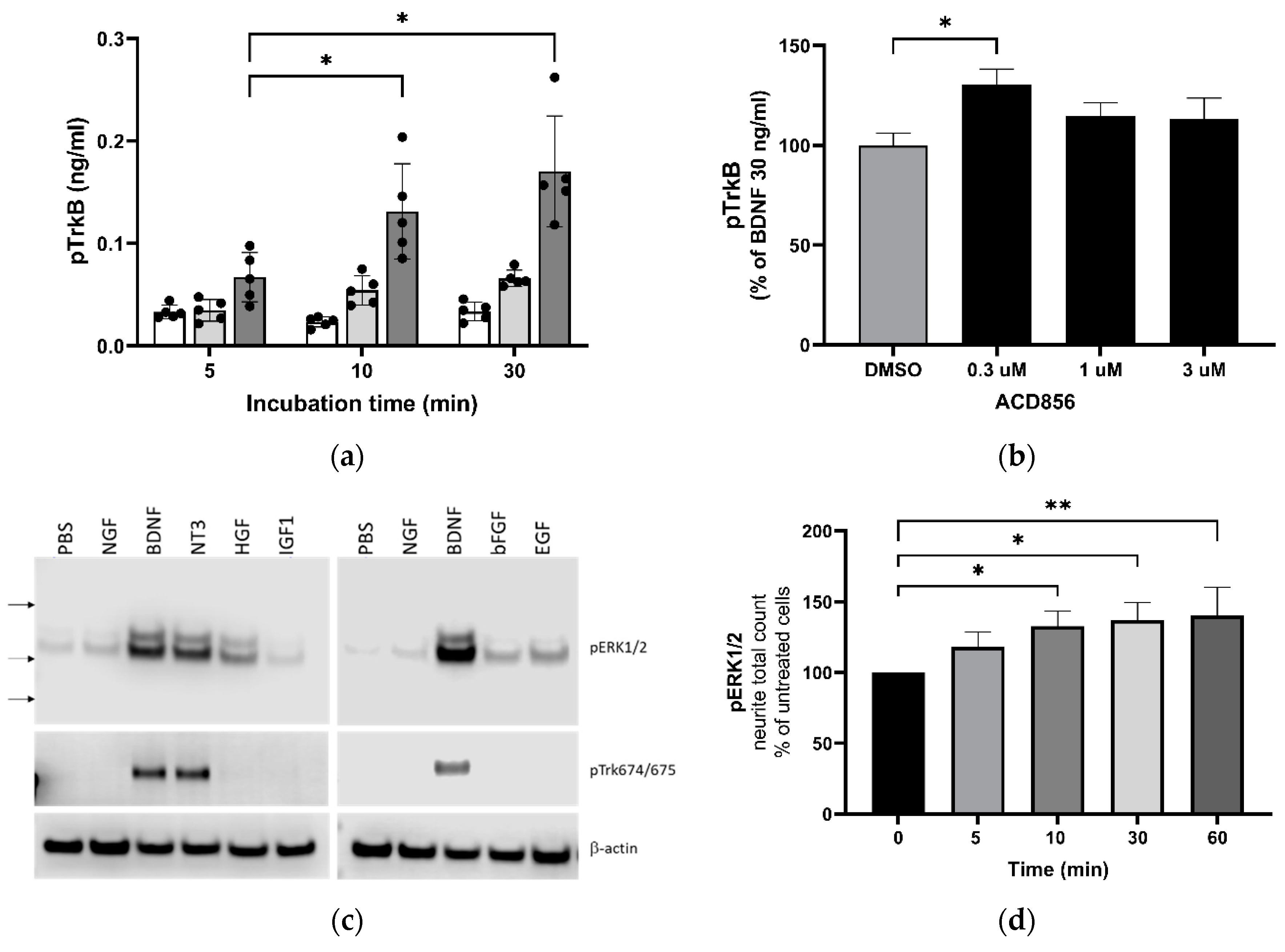
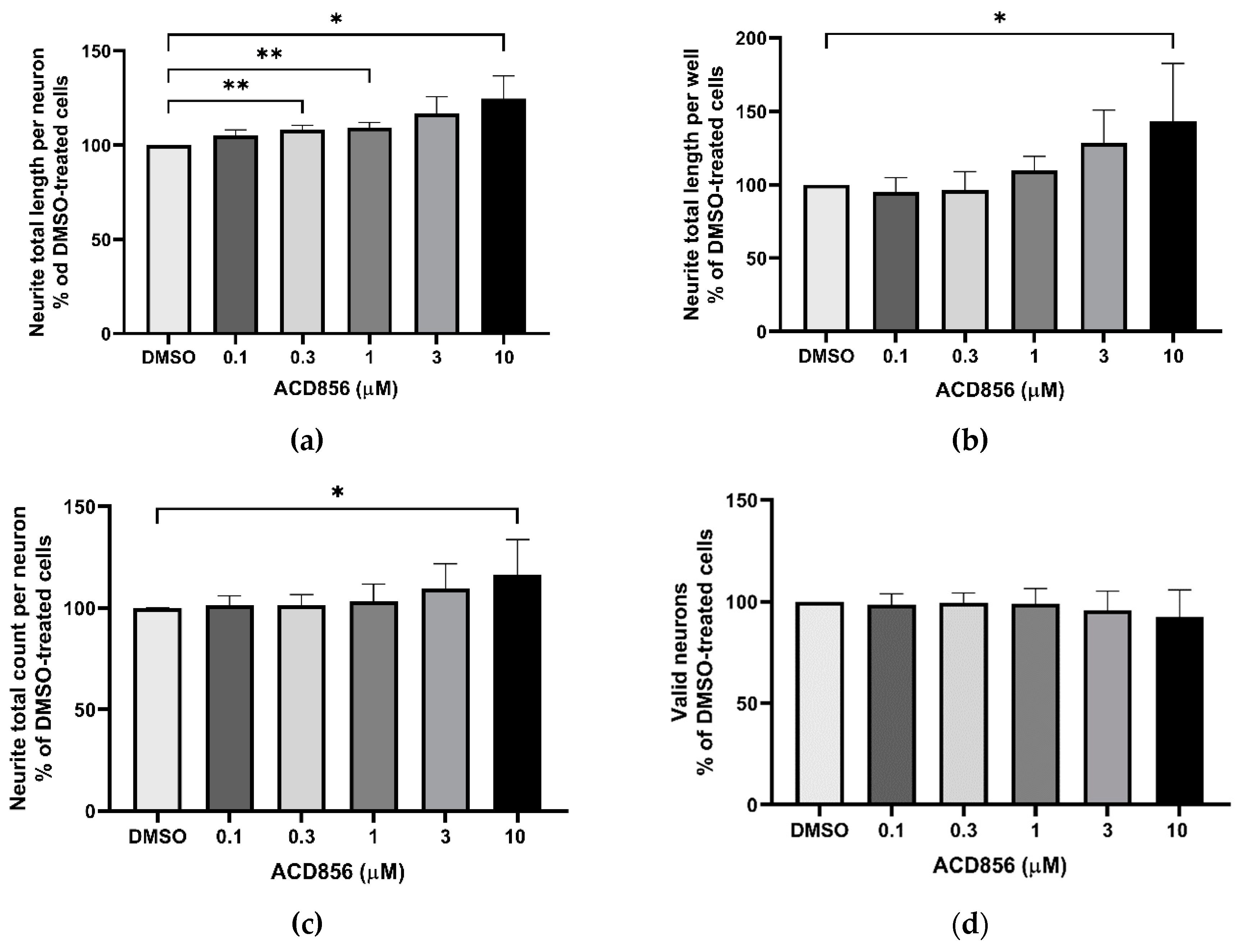
Figure 3.
Potentiation of NGF-induced neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells by ACD856. PC12 cells were treated with 3 ng NGF/mL for 5 days in the absence or presence of increasing concentrations of ACD856. Cells were fixed with PFA and anti-tubulin antibodies were used to visualize neurite processes. A dose-response effect of ACD856 was observed for neurite total length per neuron (a), neurite total length per well (b) and neurite total count per neuron (c). There was no significant effect on the number of neurons (d). *p-value < 0.05, **p-value < 0.01 compared to control group at one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. Data shown are the mean of average values from each experiment +/- S.D. (n=5 independent experiments).
Figure 3.
Potentiation of NGF-induced neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells by ACD856. PC12 cells were treated with 3 ng NGF/mL for 5 days in the absence or presence of increasing concentrations of ACD856. Cells were fixed with PFA and anti-tubulin antibodies were used to visualize neurite processes. A dose-response effect of ACD856 was observed for neurite total length per neuron (a), neurite total length per well (b) and neurite total count per neuron (c). There was no significant effect on the number of neurons (d). *p-value < 0.05, **p-value < 0.01 compared to control group at one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. Data shown are the mean of average values from each experiment +/- S.D. (n=5 independent experiments).
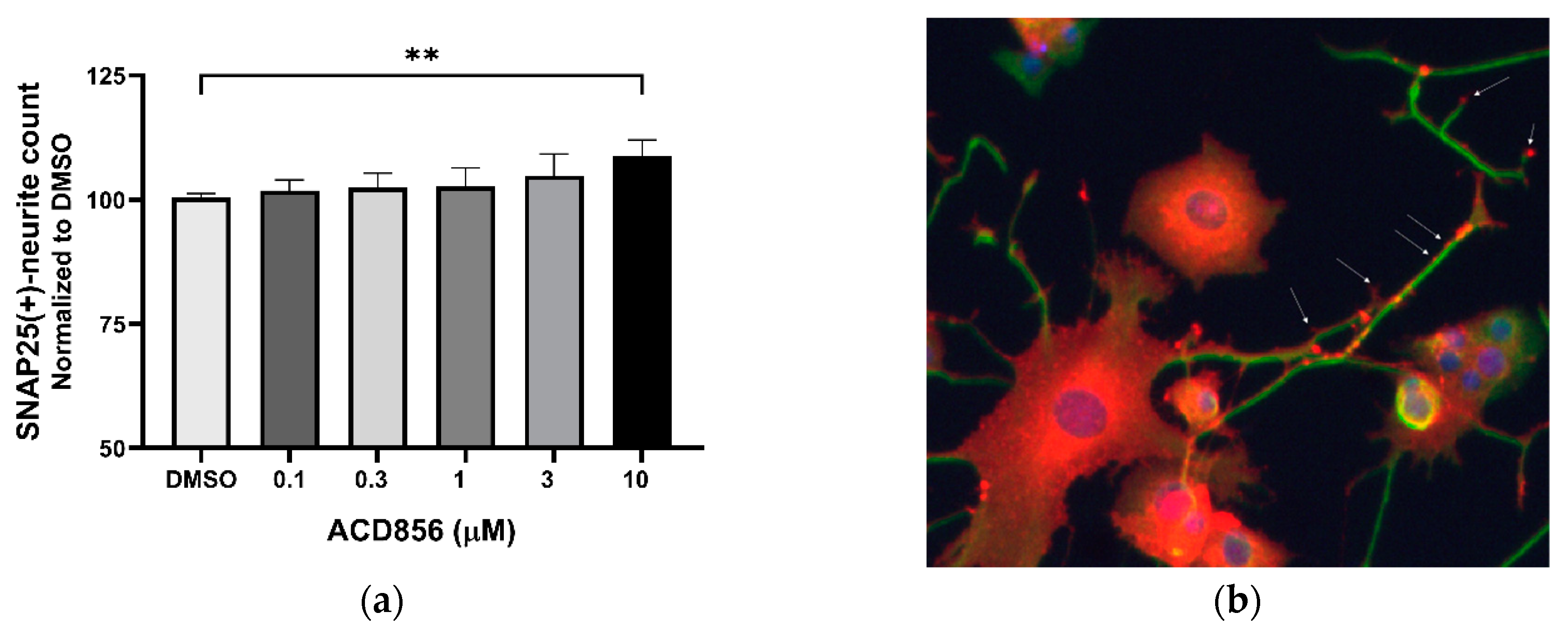
Figure 4.
Increase of SNAP25-containing neurites in PC12 cells by ACD856. PC12 cells were treated with 3 ng NGF/mL for 5 days in the absence or presence of increasing concentrations of ACD856. Cells were fixed with PFA and anti-SNAP25 (red) or anti-beta tubulin (green) antibodies were used to visualize cells and neurites. A dose-response effect of ACD856 was observed for SNAP25-positive neurite total count per neuron (a). The SNAP25-protein was mainly localized to the cell body, neurites and especially in buddings of neurites or at nerve endings (indicated with arrows) (b). **p-value < 0.01, compared to control group at one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. Data shown are the mean of average values from individual experiments +/- SD. (n=3).
Figure 4.
Increase of SNAP25-containing neurites in PC12 cells by ACD856. PC12 cells were treated with 3 ng NGF/mL for 5 days in the absence or presence of increasing concentrations of ACD856. Cells were fixed with PFA and anti-SNAP25 (red) or anti-beta tubulin (green) antibodies were used to visualize cells and neurites. A dose-response effect of ACD856 was observed for SNAP25-positive neurite total count per neuron (a). The SNAP25-protein was mainly localized to the cell body, neurites and especially in buddings of neurites or at nerve endings (indicated with arrows) (b). **p-value < 0.01, compared to control group at one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. Data shown are the mean of average values from individual experiments +/- SD. (n=3).
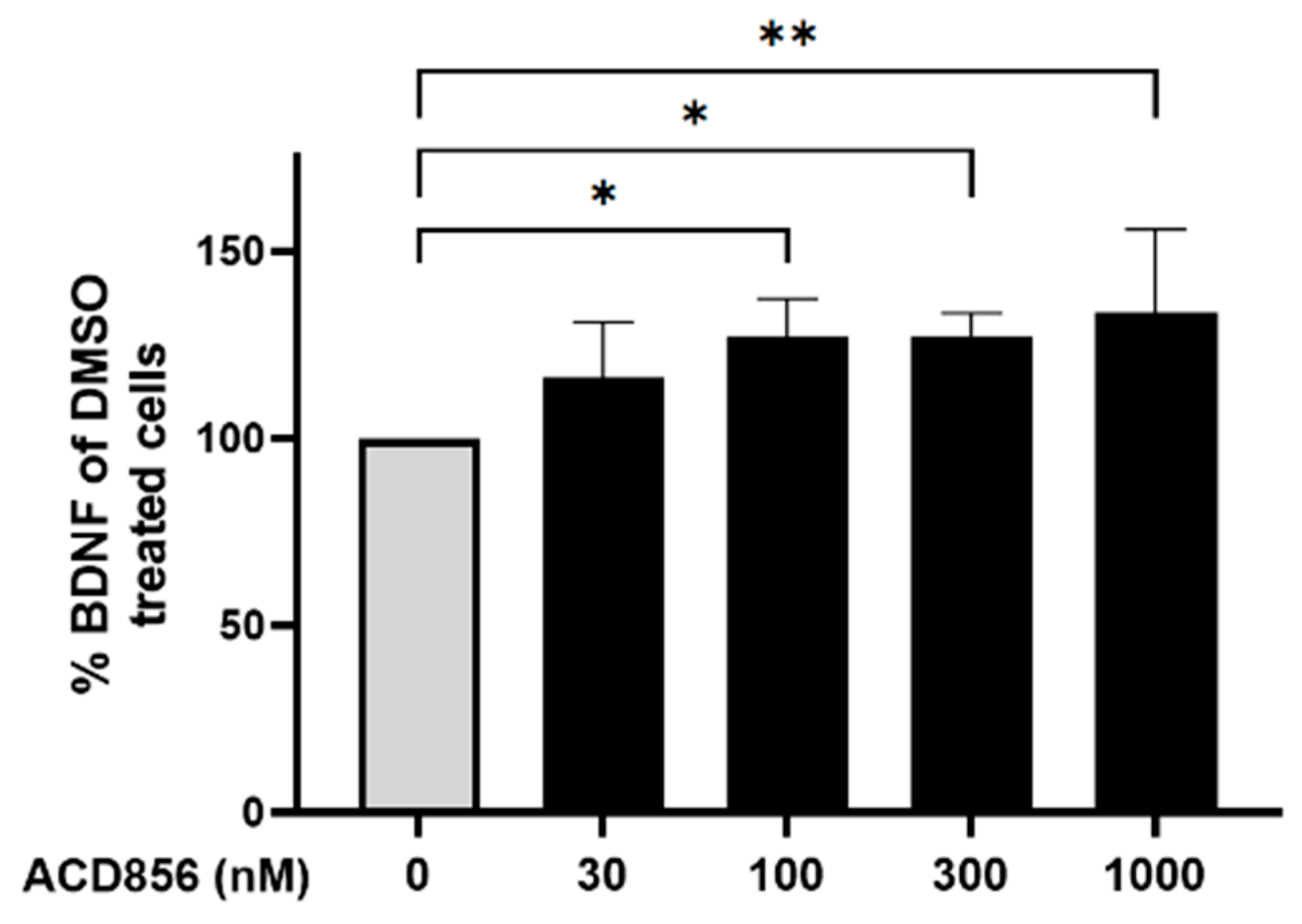
Figure 5.
Cortical neurons were incubated with ACD856 in NB-media for 6 hours and the BDNF levels were determined by ELISA. Data shown are the mean +/- SD from four independent experiments where each experiment was performed using six technical replicates. Each sample was analyzed in duplicates in the ELISA assay. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs DMSO-control values. The absolute level of BDNF in DMSO-treated samples was 7.9 +/- 1.7 ng/mL (mean +/- S.D., n=5).
Figure 5.
Cortical neurons were incubated with ACD856 in NB-media for 6 hours and the BDNF levels were determined by ELISA. Data shown are the mean +/- SD from four independent experiments where each experiment was performed using six technical replicates. Each sample was analyzed in duplicates in the ELISA assay. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs DMSO-control values. The absolute level of BDNF in DMSO-treated samples was 7.9 +/- 1.7 ng/mL (mean +/- S.D., n=5).
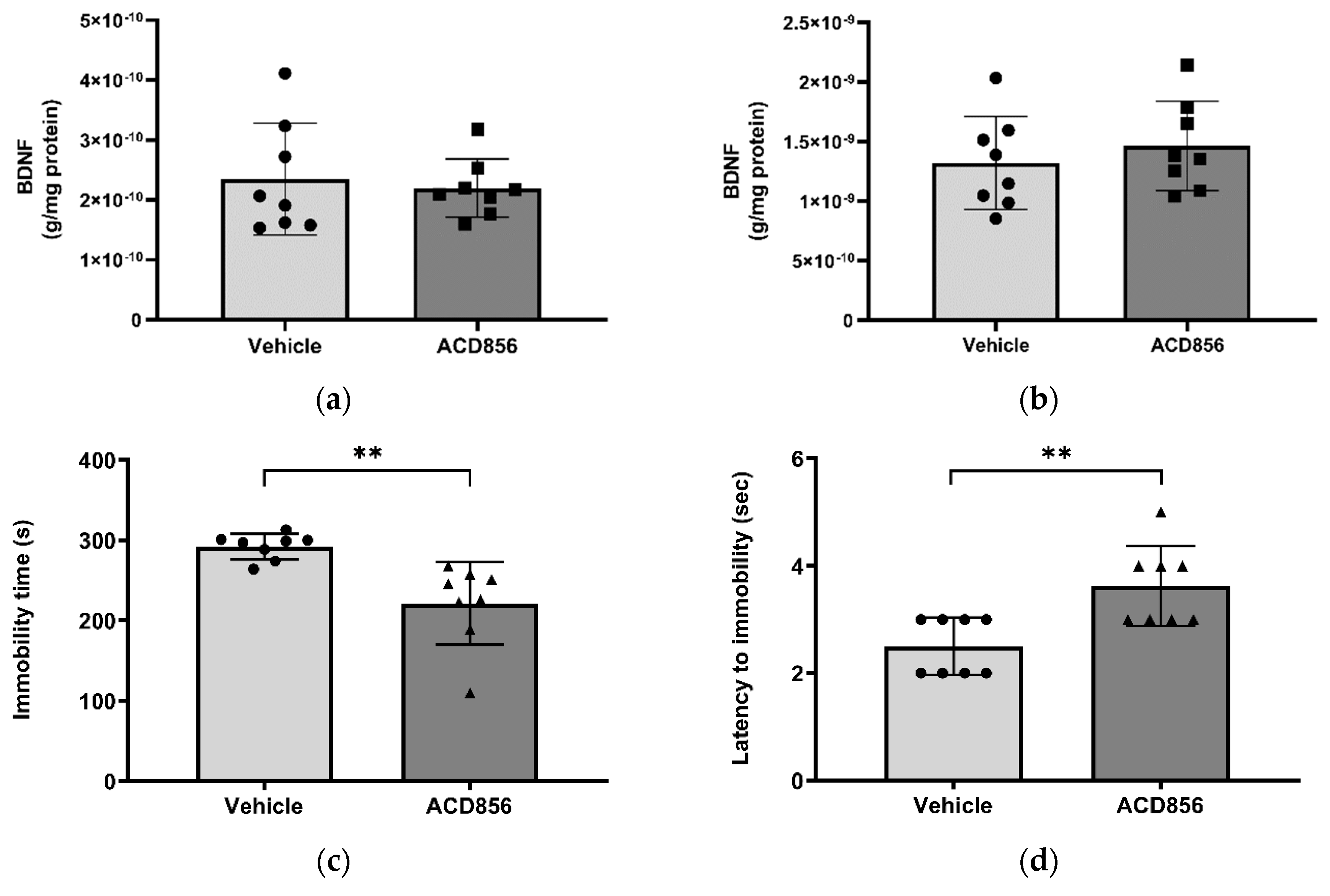
Figure 6.
Effects of ACD856 on BDNF levels and depression-like behavior in mice. Animals were dosed with 3mg/kg ACD856 by oral administration once daily for 5 days. Cortex (a) and hippocampus (b) were dissected and the BDNF levels were determined by ELISA after completion of the forced swim test (c and d). The immobility time (c) and the latency to first immobility (d) were recorded manually. Data shown are the mean +/- SD, n=8. **p < 0.01 vs vehicle treated animals.
Figure 6.
Effects of ACD856 on BDNF levels and depression-like behavior in mice. Animals were dosed with 3mg/kg ACD856 by oral administration once daily for 5 days. Cortex (a) and hippocampus (b) were dissected and the BDNF levels were determined by ELISA after completion of the forced swim test (c and d). The immobility time (c) and the latency to first immobility (d) were recorded manually. Data shown are the mean +/- SD, n=8. **p < 0.01 vs vehicle treated animals.
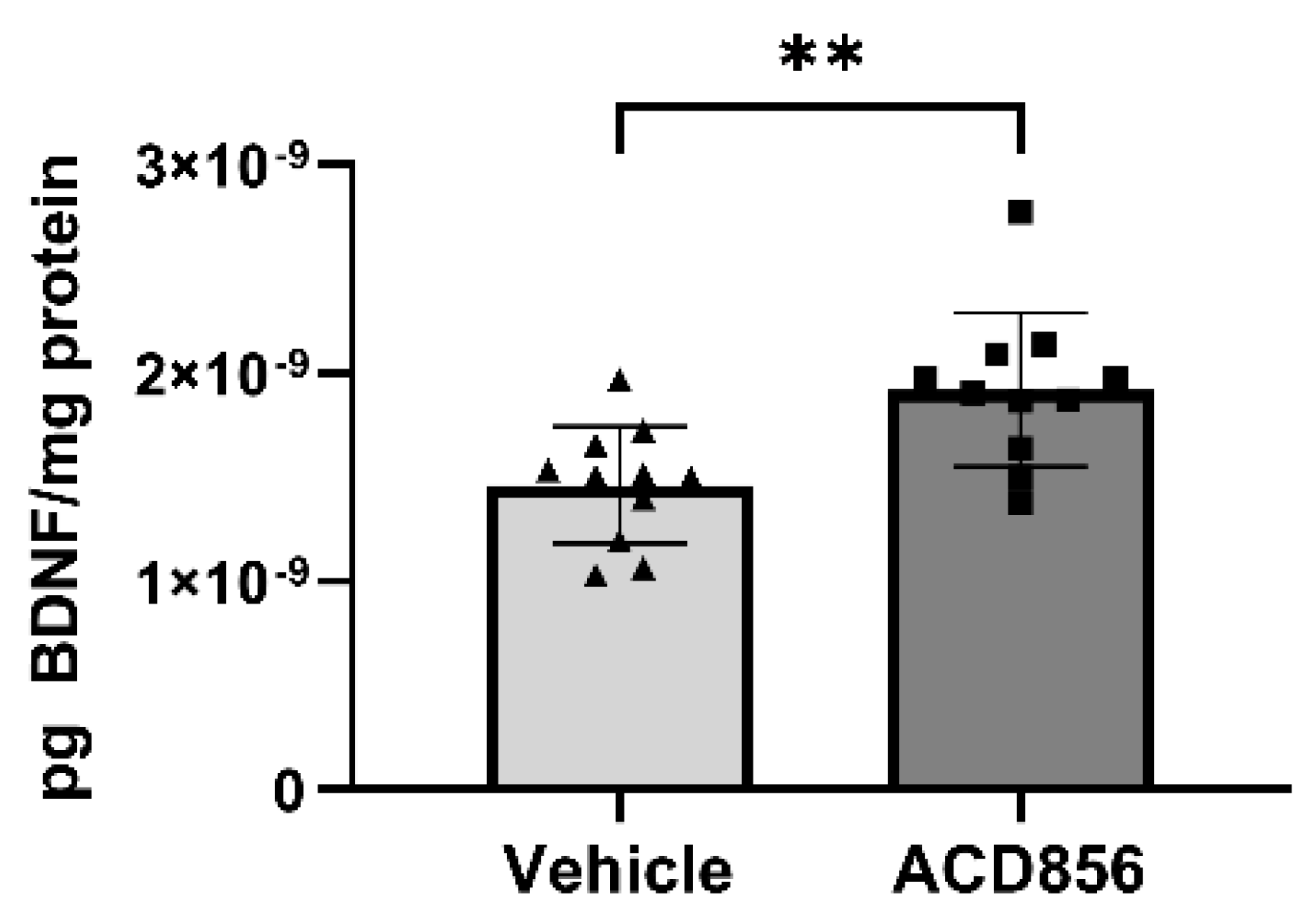
Figure 7.
ACD856 increases the levels of BDNF in the brain of aged animals. 21 months old mice were dosed with 5mg/kg ACD856 once daily for 4 weeks by s.c. injection. The left hemisphere of each brain was homogenized and the BDNF levels were determined by ELISA. Data shown are the mean +/- SD, n=11-12 animals. All samples were analyzed in duplicates in the ELISA assay and BDNF levels were normalized to protein content in each sample. Individual data for each animal is the mean of the duplicate determinations. **p < 0.01 vs vehicle treated animals using Students t-test. .
Figure 7.
ACD856 increases the levels of BDNF in the brain of aged animals. 21 months old mice were dosed with 5mg/kg ACD856 once daily for 4 weeks by s.c. injection. The left hemisphere of each brain was homogenized and the BDNF levels were determined by ELISA. Data shown are the mean +/- SD, n=11-12 animals. All samples were analyzed in duplicates in the ELISA assay and BDNF levels were normalized to protein content in each sample. Individual data for each animal is the mean of the duplicate determinations. **p < 0.01 vs vehicle treated animals using Students t-test. .
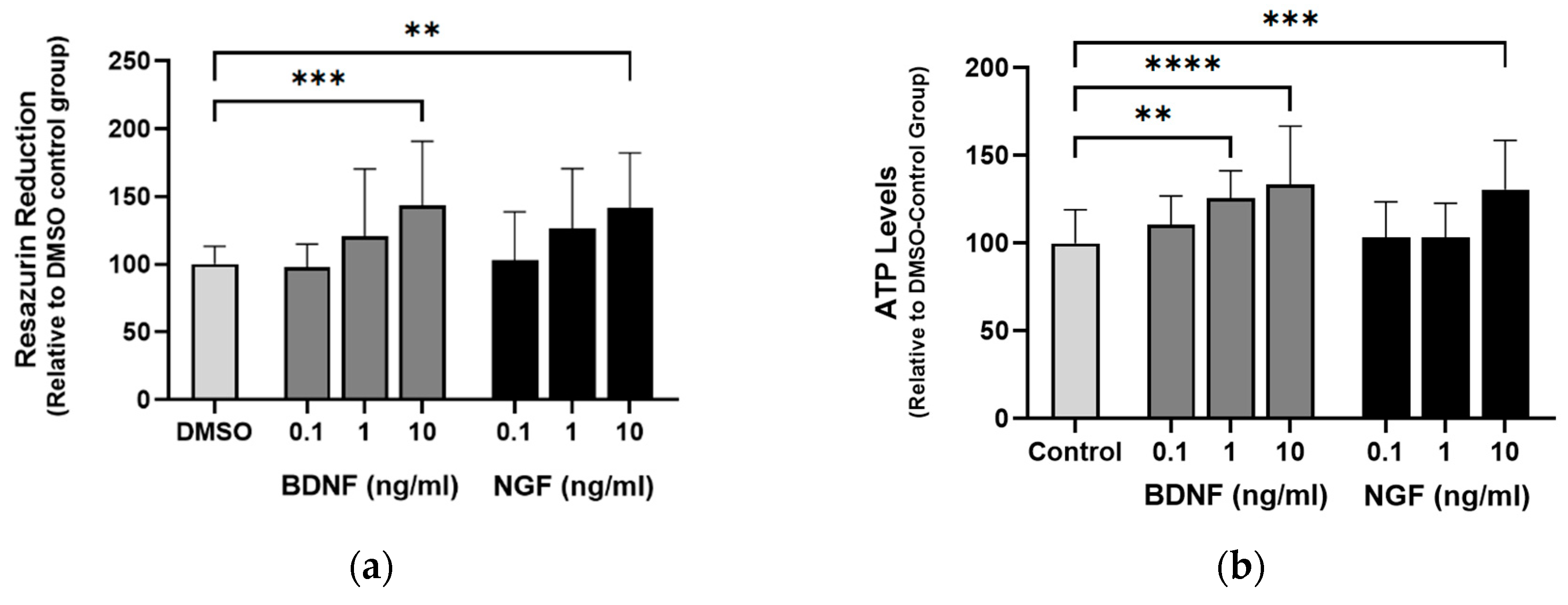
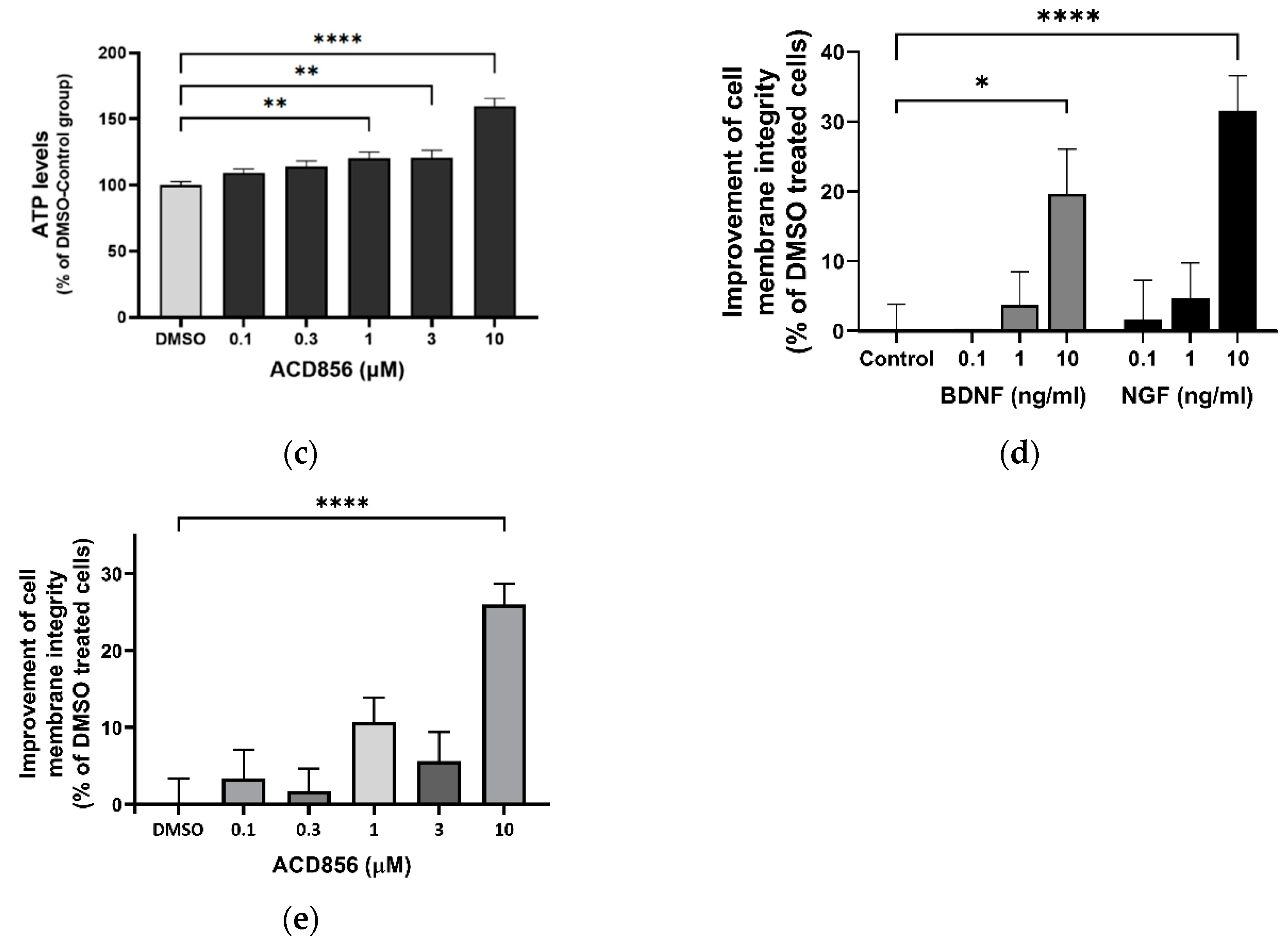
Figure 8.
ACD856, BDNF and NGF prevent energy-deprivation-induced stress in cortical neurons. Primary neurons were treated at DIV 4-5 with increasing doses of BDNF, NGF and ACD856 in Neurobasal-A medium without glucose and sodium pyruvate. Metabolic activity was determined by measuring reduction of resazurin (a). Levels of ATP increased in the presence of BDNF and NGF (b) and ACD856 (c). Cell membrane integrity was significantly increased by BDNF and NGF (d) or ACD856 (e) in response to glucose and pyruvate withdrawal. Data shown are the mean of all replicates +/- SEM from at least three different primary cultures. *p-value < 0.05, **p-value < 0.01, ***p-value < 0.001, ****p-value < 0.0001 compared to control group at one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test.
Figure 8.
ACD856, BDNF and NGF prevent energy-deprivation-induced stress in cortical neurons. Primary neurons were treated at DIV 4-5 with increasing doses of BDNF, NGF and ACD856 in Neurobasal-A medium without glucose and sodium pyruvate. Metabolic activity was determined by measuring reduction of resazurin (a). Levels of ATP increased in the presence of BDNF and NGF (b) and ACD856 (c). Cell membrane integrity was significantly increased by BDNF and NGF (d) or ACD856 (e) in response to glucose and pyruvate withdrawal. Data shown are the mean of all replicates +/- SEM from at least three different primary cultures. *p-value < 0.05, **p-value < 0.01, ***p-value < 0.001, ****p-value < 0.0001 compared to control group at one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test.
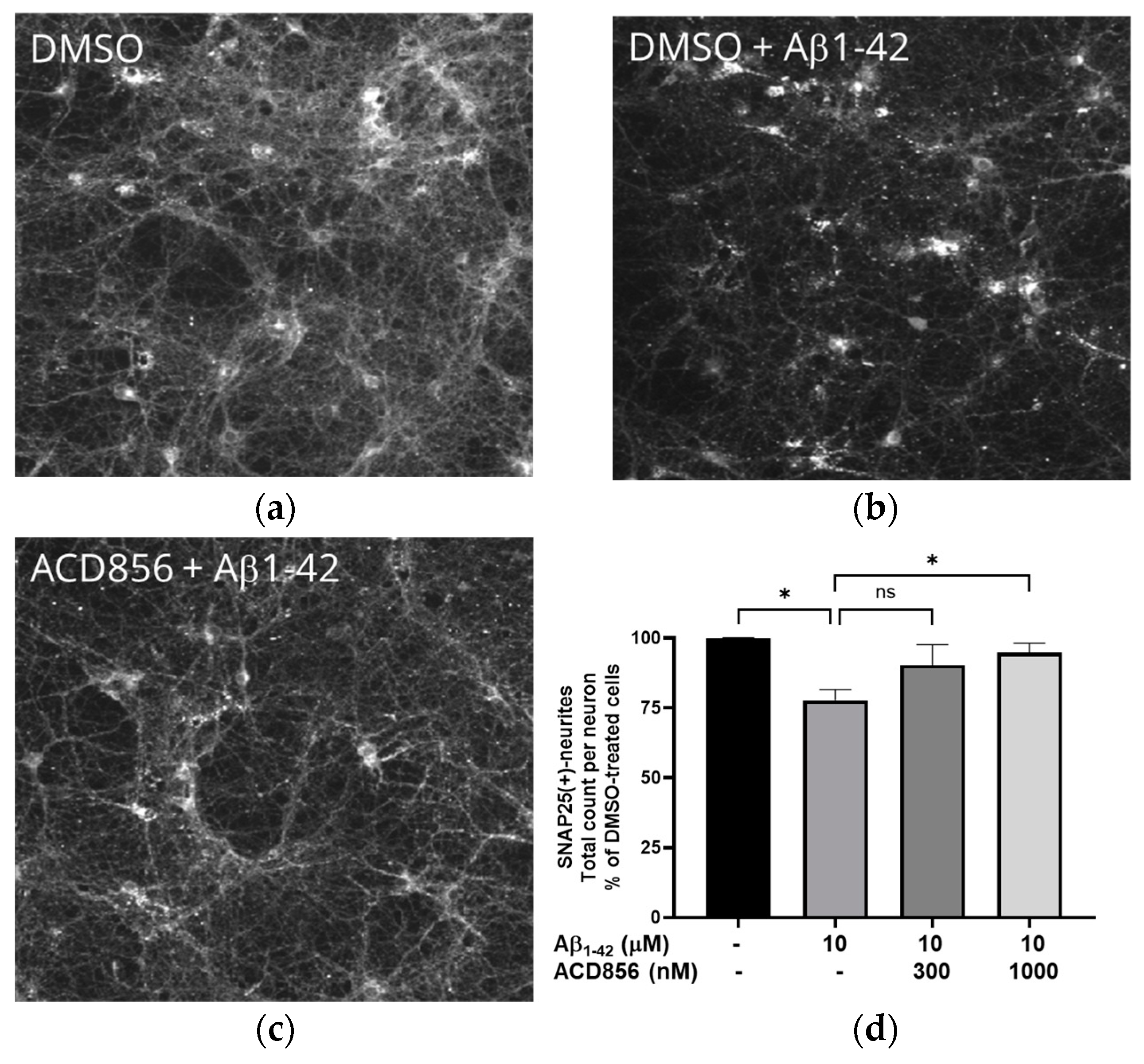
Figure 9.
ACD856 prevented Abeta-induced decrease of SNAP25 positive neurites in cortical neurons. Primary neurons were treated at DIV 13 with vehicle (DMSO) (a), 10 mM Ab1-42 (b) or ACD856+10 mM Ab1-42 (c) for 96 hours in NB-medium supplemented with B27. The levels of SNAP25 were visualized and quantified by immunocytochemistry (d). *p-value < 0.05 using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. Data shown are the mean +/- S.D. of the average results from four independent experiments where each individual condition was performed using six different wells. The data are from four different preparations of cortical neurons.
Figure 9.
ACD856 prevented Abeta-induced decrease of SNAP25 positive neurites in cortical neurons. Primary neurons were treated at DIV 13 with vehicle (DMSO) (a), 10 mM Ab1-42 (b) or ACD856+10 mM Ab1-42 (c) for 96 hours in NB-medium supplemented with B27. The levels of SNAP25 were visualized and quantified by immunocytochemistry (d). *p-value < 0.05 using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. Data shown are the mean +/- S.D. of the average results from four independent experiments where each individual condition was performed using six different wells. The data are from four different preparations of cortical neurons.
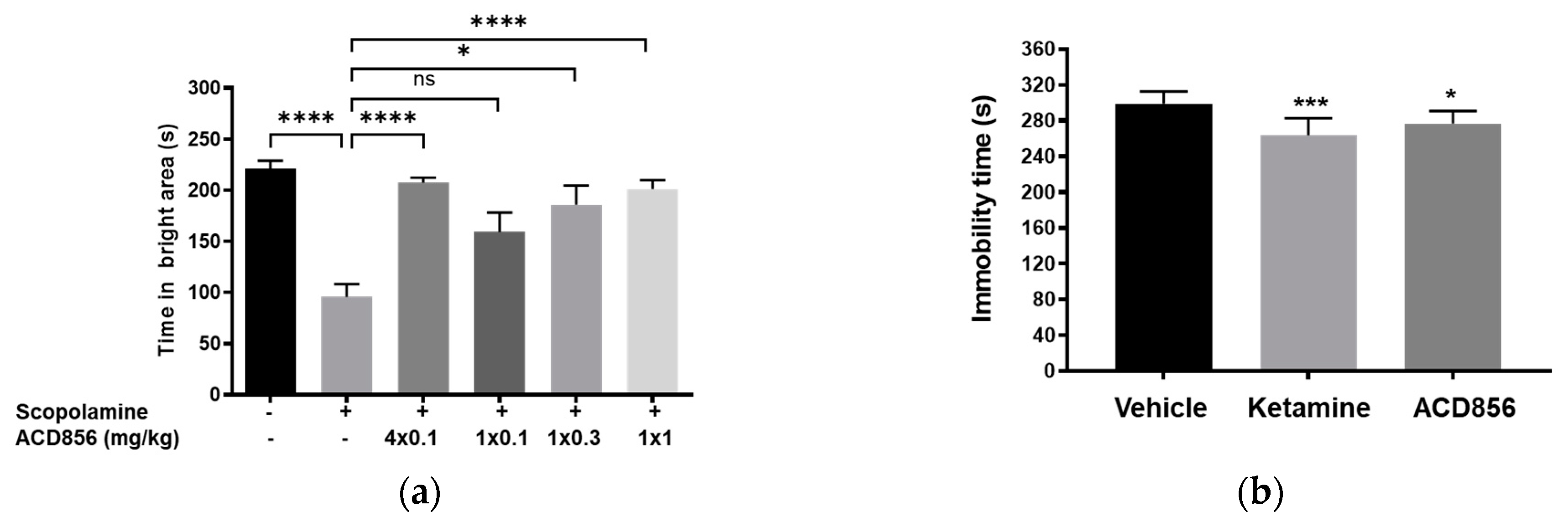
Figure 10.
Effects of repeated administration of ACD856 on cognition and antidepressant-like behavior. ACD856 was administered s.c. for 4 consecutive days at 0.1 mg/kg or as a single s.c. dose at 0.1, 0.3 or 1 mg/kg 60 min prior to the experiment, in combination with scopolamine (0.3 mg/kg, s.c.) ACD856 reversed scopolamine-induced memory impairment at the indicated doses (a). *p < 0.05 or **** p < 0.0001 for scopolamine treated animals vs the control group or ACD856-treated animals. Mice were injected for five days with a single dose of ACD856 (1 mg/kg, s.c.) per day or with a single dose of 10 mg/kg ketamine seven days prior to swimming session (b). Both ACD856 and Ketamine displayed prolonged antidepressive-like effects (p < 0.05; p <0.001) significantly reducing the immobility time in the forced swim test compared with vehicle treated mice. The bars represent the immobility time (seconds), mean ± SD (n = 6-8 mice per group). The statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test. *p<0.05; ***p<0.001 vs vehicle treated group.
Figure 10.
Effects of repeated administration of ACD856 on cognition and antidepressant-like behavior. ACD856 was administered s.c. for 4 consecutive days at 0.1 mg/kg or as a single s.c. dose at 0.1, 0.3 or 1 mg/kg 60 min prior to the experiment, in combination with scopolamine (0.3 mg/kg, s.c.) ACD856 reversed scopolamine-induced memory impairment at the indicated doses (a). *p < 0.05 or **** p < 0.0001 for scopolamine treated animals vs the control group or ACD856-treated animals. Mice were injected for five days with a single dose of ACD856 (1 mg/kg, s.c.) per day or with a single dose of 10 mg/kg ketamine seven days prior to swimming session (b). Both ACD856 and Ketamine displayed prolonged antidepressive-like effects (p < 0.05; p <0.001) significantly reducing the immobility time in the forced swim test compared with vehicle treated mice. The bars represent the immobility time (seconds), mean ± SD (n = 6-8 mice per group). The statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test. *p<0.05; ***p<0.001 vs vehicle treated group.