1. Introduction
Heat transfer is critical in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, electronics, and power generation. Heat pipes are widely used in these industries due to their efficient heat transfer capabilities [
1]. Heat pipes transfer heat from a heat source to a heat sink using a working fluid, typically a liquid or gas. The working fluid's thermal conductivity is a key parameter affecting the heat pipe's heat transfer effectiveness [
2].
Nanoparticles in heat pipes have been shown to improve their thermal conductivity significantly. Adding nanoparticles to the working fluid can enhance heat transfer by providing a large surface area for heat transfer and increasing the effective thermal conductivity of the fluid. The size of the nanoparticles can also significantly impact the heat transfer effectiveness of the heat pipe [
3].
Nanofluids have become an active research area due to their unique thermal and physical properties. Nanoparticles added to fluids can significantly enhance the heat transfer properties of the resulting nanofluid compared to conventional fluids [
4]. The increased heat transfer efficiency is attributed to the high surface area of nanoparticles, which allows for better interaction with the fluid molecules, resulting in improved thermal conductivity. Additionally, nanofluids offer several advantages over conventional fluids, such as improved stability, enhanced optical properties, and greater flexibility in composition and properties. These unique properties make nanofluids attractive for various applications, including heat transfer systems, lubrication, catalysis, and nanomedicine [
5].
The angle of the heat pipe is another important parameter that can influence the heat transfer characteristics of the heat pipe. The angle of the heat pipe affects the direction of the gravitational force acting on the working fluid, which can impact the flow pattern and heat transfer rate [
6]. Therefore, this study investigates the effect of different particle sizes and heat pipe angles on the thermal effectiveness of a cylindrical screen mesh heat pipe [
7]. The study aims to provide insights into the design and optimization of heat pipes for various applications by analyzing the heat transfer characteristics of the heat pipe with different particle sizes and heat pipe angles [
8].
While there have been previous studies investigating the effect of particle size and heat pipe angle on the thermal effectiveness of heat pipes, there still needs to be a research gap in understanding the combined effect of these parameters [
9]. Specifically, there needs to be more research on the thermal effectiveness of cylindrical screen mesh heat pipes using silver nanoparticles as the test substance with different particle sizes and heat pipe angles [
10]. This study addresses this research gap by investigating the heat transfer characteristics of the heat pipe with varying particle sizes and heat pipe angles [
11]. This study can provide insights into the design and optimization of heat pipes for various applications, where particle size and heat pipe angle can be optimized to achieve maximum heat transfer effectiveness. [
12]
The novelty of this study lies in the investigation of the combined effect of different particle sizes and heat pipe angles on the thermal effectiveness of a cylindrical screen mesh heat pipe [
13]. While previous studies have looked at the effect of particle size or heat pipe angle separately, this study provides insights into how these parameters interact and affect the heat transfer characteristics of the heat pipe [
14]. The use of silver nanoparticles as the test substance adds to the novelty of this study as it investigates the potential of these nanoparticles to improve the thermal conductivity and heat transfer effectiveness of the heat pipe [
15] [
16].
2. Preparation of Nanofluid and characterization
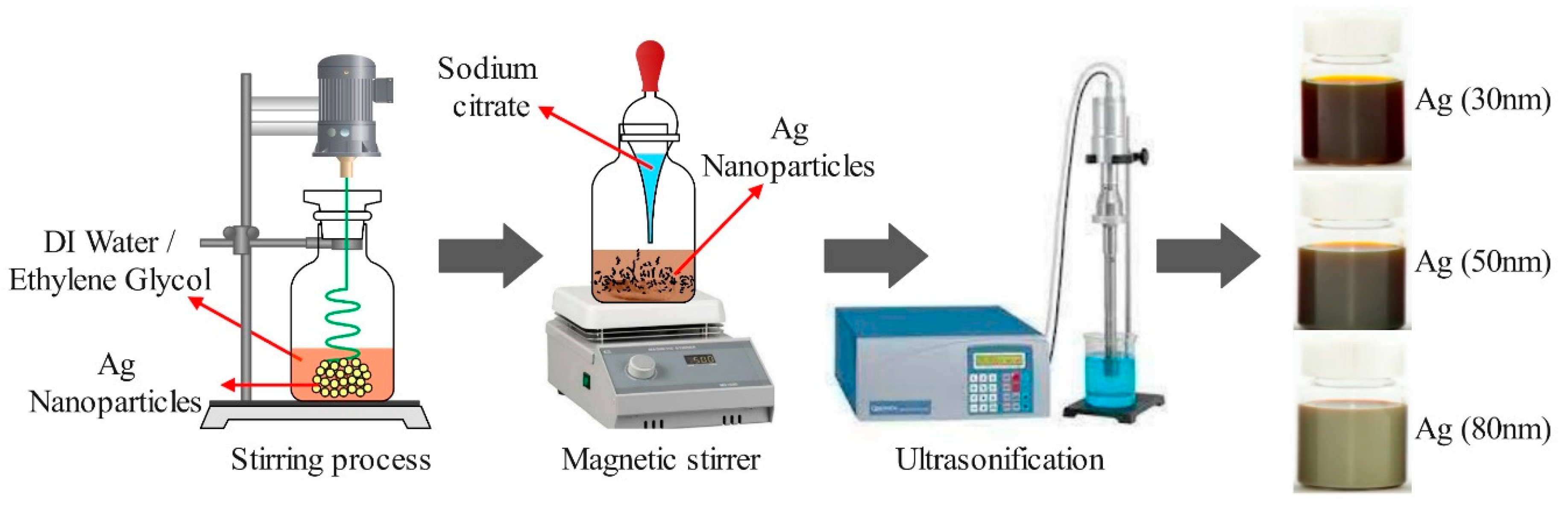
As depicted in
Figure 1, preparing a nanofluid containing silver nanoparticles of different sizes (20nm, 50nm, and 80nm) requires a series of steps. Firstly, the necessary quantity of silver nanoparticles is calculated and distributed into multiple containers. Subsequently, 100 mL of distilled water and 1 mL of sodium citrate are added to each container, followed by stirring to achieve complete nanoparticle dispersion. The containers are then placed on a magnetic stirrer and stirred for 30 minutes at room temperature. To ensure uniform dispersion of nanoparticles, each container is subjected to an ultrasonic bath for 30 minutes. Additionally, 10 mL of ethanol is added to each container and stirred for 10 minutes to prevent nanoparticle aggregation. This method produces a stable and uniform nanofluid containing silver nanoparticles of varying sizes, which can find applications in diverse fields such as heat transfer, antibacterial coatings, and biomedical imaging.
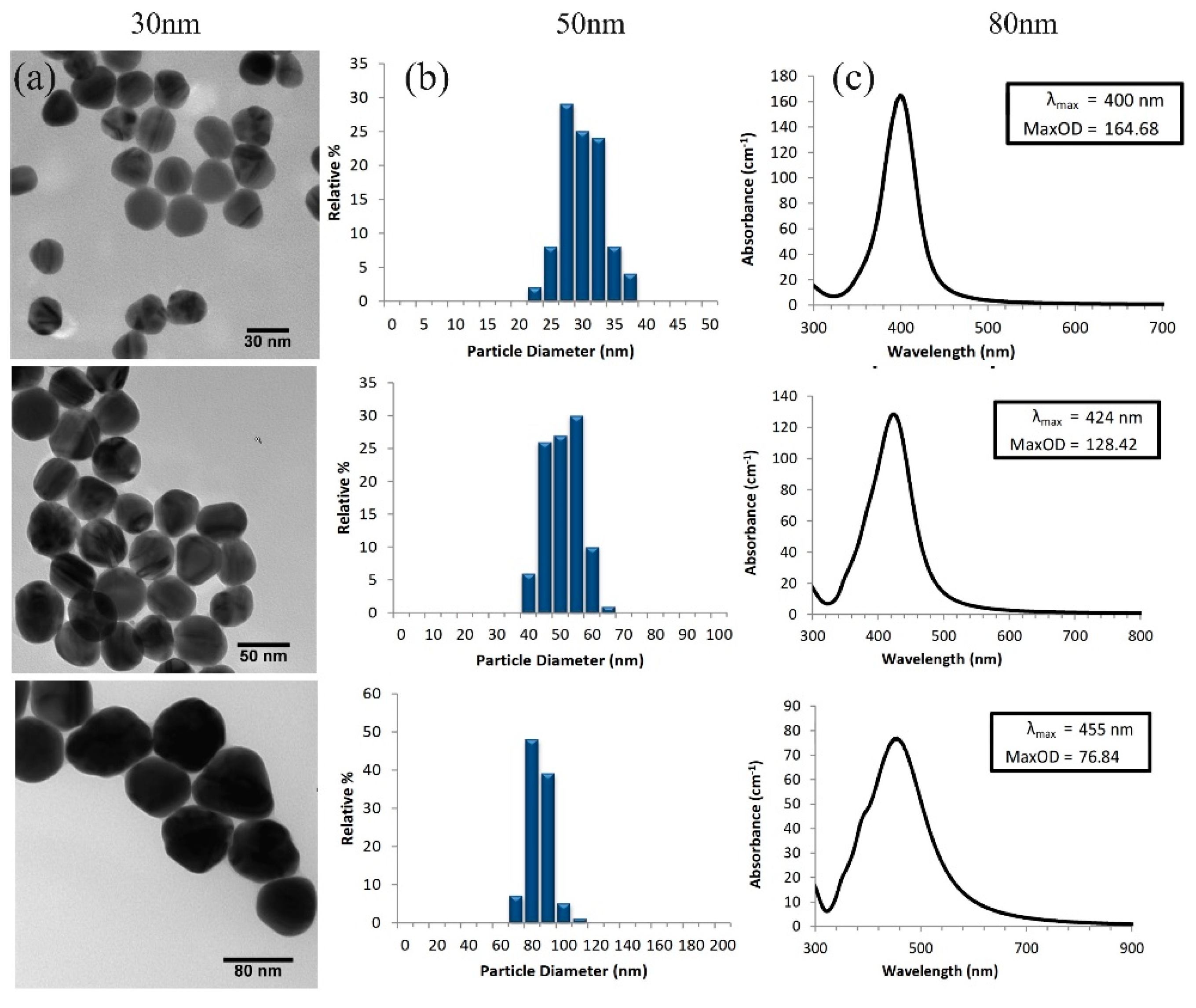
The size and morphology of the silver nanoparticles were confirmed using transmission electron microscopy (TEM) imaging. The images revealed uniformly dispersed spherical particles in the solution, with average sizes of 30 nm, 50 nm, and 80 nm for the different particle sizes. The size distribution was narrow, and aggregation was low, as depicted in
Figure 2(a). To further analyze the synthesized nanoparticles, UV-Vis spectrometry was utilized to measure the absorbance spectra of particles with sizes of 30 nm, 50 nm, and 80 nm. The analysis demonstrated that the absorbance peak shifted towards longer wavelengths as the particle size increased. The absorbance peaks were observed at 400 nm, 424 nm, and 455 nm for 30 nm, 50 nm, and 80 nm particles, respectively, as illustrated in
Figure 2(c). In summary, both TEM imaging and UV-Vis spectrometry confirmed the successful synthesis of silver nanoparticles with sizes of 20 nm, 50 nm, and 80 nm, and indicated that the absorbance spectra were influenced by the particle size, which matched the targeted particle size.
Based on the zeta potential analysis results, the 30nm particle size exhibited the highest zeta potential value of -33.5 mV, indicating excellent stability and a greater degree of repulsion between particles. The analysis further revealed that the 50nm particle size had a zeta potential value of -29.8 mV, while the 80nm particle size had a value of -25.2 mV. The findings indicate that the smaller particle size (20 nm) is more stable compared to the larger particle sizes (50 nm and 80 nm). Thus, the zeta potential analysis highlights the crucial role of particle size in nanofluid stability, with smaller particles showing better stability [
17].
3. Experimental Setup and Procedure
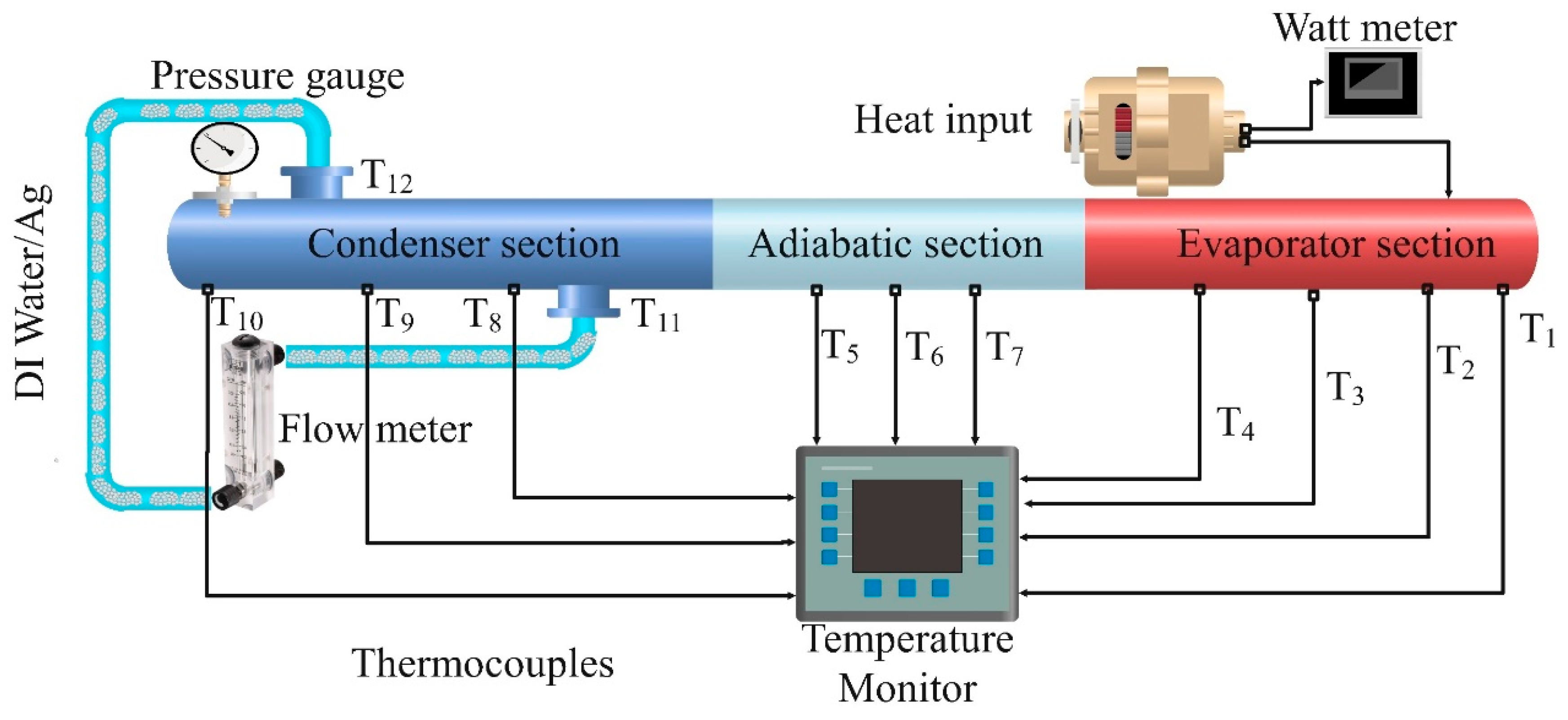
Figure 3 shows that cylindrical screen mesh heat pipes were constructed using standard copper tubes with an outer diameter of 19 mm, an inner diameter of 17 mm, and a length of 750 mm. The heat pipes comprised three sections: a 200 mm long evaporator section, a 250 mm long adiabatic section, and a 300 mm long condenser section. Distilled water was used as the base fluid, and silver nanoparticles of varying sizes, namely 30 nm, 50 nm, and 80 nm, were added to create different nanofluids. Nanoparticles were added in a volume concentration of 1% to obtain the desired particle size. To gauge the heat input into the heat pipe, a wattmeter with a reading of 120W was used. One end of the heat pipe was heated using a heating element, and the other was cooled using a water-cooled condenser.
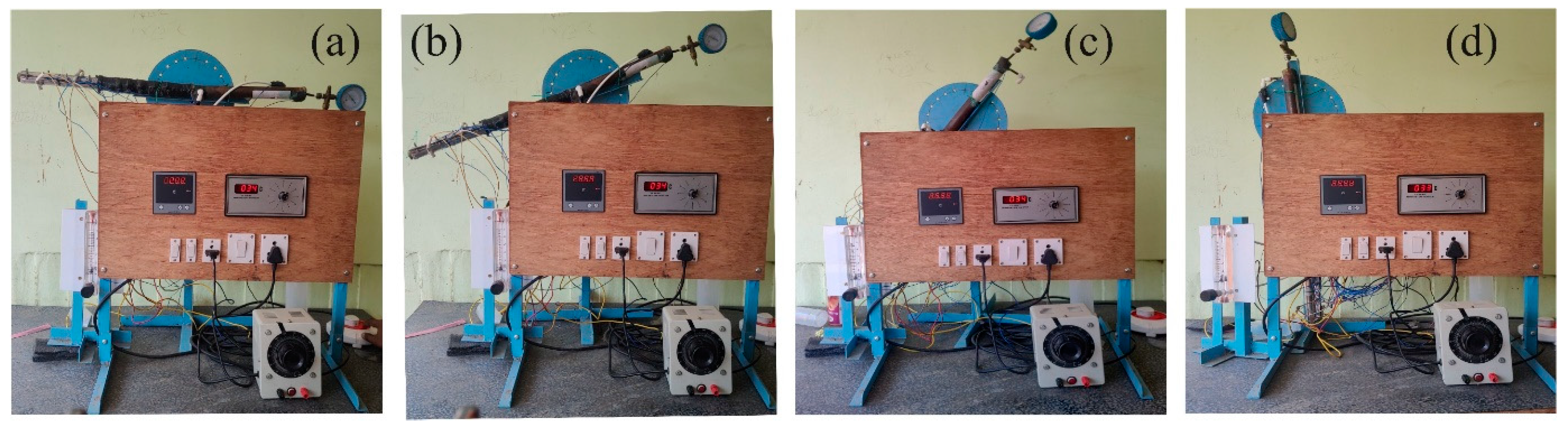
The heat pipe's temperature was monitored by a temperature monitor connected to 12 K-type thermocouples strategically positioned throughout the heat pipe. Precisely, four thermocouples were placed in the evaporator section, three in the adiabatic section, and three in the condenser section. Additionally, two thermocouples were utilized to measure the condenser's inlet and outlet temperatures, as shown in
Figure 4's photographic view. Furthermore, the flow rate of the nanofluid inside the heat pipe was measured using a flow meter, in addition to temperature and pressure readings. The mass flow rate of the nanofluid was calculated using a flow meter installed in the heat pipe's inlet line. The thermal performance of the cylindrical screen mesh heat pipe was compared for each nanofluid, and the experiment's data was analyzed to comprehend the impact of particle size variation on the heat pipe's thermal efficiency.
Table 1 displays the mesh sizes employed in designing and producing the cylindrical screen mesh heat pipe. The heat pipe measured 750 mm in length and had a diameter of 20 mm. Ag nanofluids with a 0.1 wt% concentration of Ag were used as the working fluids, while the wick structure was composed of 0.05 mm thick stainless steel screen mesh with 50-micron pores. K-type thermocouples were used to measure the heat source, sink, and pipe temperatures. The heat transfer rate was calculated using the mass flow rate, specific heat capacity, and temperature difference between the heat source and sink, employing the formula Q = mcT. The thermal resistance of the heat pipe was calculated using Rth = (T1-T2)/Q, where T1 and T2 represent the heat source and sink temperatures, respectively, and Q is the heat transfer rate. The overall efficiency of the heat pipe was computed using the equation = Q/(P Q), where P is the power input. The experiments were conducted in triplicate to ensure the accuracy of the results, and statistical analysis was employed to determine the significance of the findings. The study aimed to investigate and compare the impact of particle size variation on the thermal performance of an Ag nanofluid heat pipe.
It is crucial to closely monitor the cooling water's surface temperature and mass flow rate during the experiment, as they directly impact the results. An estimation of experimental values has been provided to assess the uncertainty surrounding the data.
4. Data processing
The volume concentration of nanoparticles can be calculated using Eq. 1, where ϕ represents the volume concentration of nanoparticles, mp is the mass of nanoparticles, and Vf is the total volume of the nanofluid [
18].
The heat transfer rate is evaluated as in Eq.2 where Q is the heat transfer rate, U is the overall heat transfer coefficient, A is the heat transfer area, and ΔT is the temperature difference between the hot and cold heat pipe [
19].
Thermal resistance is calculated as given in Eq. 3, where R is the thermal resistance.
As given in Eq. 4, overall efficiency is calculated, here η is the overall efficiency, Q is the heat transfer rate, and W is the power input [
20].
The Reynolds number is used to determine the fluid flow regime in the heat pipe. It is calculated using Eq. 5 where Re is the Reynolds number, ρ is the fluid density, V is the fluid velocity, D is the diameter of the heat pipe, and μ is the fluid's viscosity [
21].
To further address these uncertainties, future studies could explore the impact of the factors above on the thermal performance of cylindrical screen mesh heat pipes. The equipment used in the experiment could be improved to reduce measurement errors, and additional data could be collected to ensure the results' accuracy. Moreover, more research could be conducted on the effects of particle size and concentration on the thermal properties of nanofluids. Understanding these factors could help design more efficient heat pipes that can be used in various applications, including electronics cooling and solar thermal energy conversion. Overall, addressing and minimizing uncertainties in experimental results is essential obtain reliable data and draw meaningful conclusions [
22].
5. Results and Discussion:
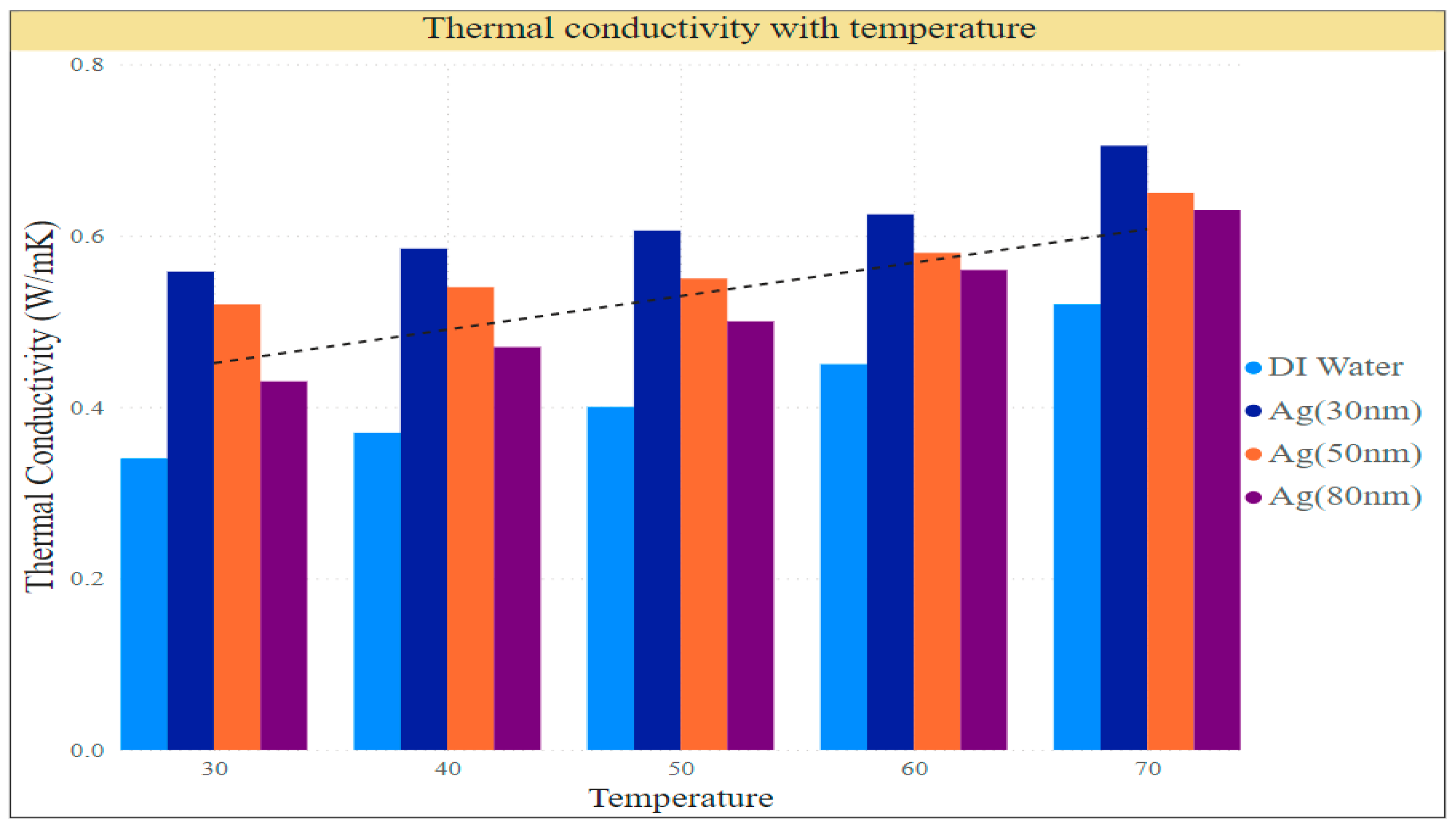
A comparative analysis was conducted in the current study to investigate the impact of particle size variation on the thermal efficiency of a cylindrical screen mesh heat pipe filled with silver nanoparticles, as shown in
Figure 5. Three different particle sizes, namely 30nm, 50nm, and 80nm, were used to assess the heat pipe's thermal performance over a range of temperatures from 30°C to 70°C.
The study found that the larger surface area-to-volume ratio of the silver nanoparticle fluid caused the thermal conductivity to increase as particle size decreased, improving the heat pipe's overall heat transmission performance. Furthermore, the thermal conductivity of the nanofluid increased at higher temperatures, further enhancing heat transfer performance. The study revealed that the best thermal performance was achieved using silver nanoparticles with a particle size of 30 nm, followed by 50 and 80 nm. These findings suggest that using smaller nanoparticles may improve the efficiency of cylindrical screen mesh heat pipes for heat transfer [
23]. The results of this study have significant implications for the design and enhancement of heat transfer systems, with the selection of nanoparticle size being a crucial factor in achieving the best performance.
The impact of silver nanoparticle diameter on the thermal performance of a cylindrical screen mesh heat pipe was investigated. Silver nanoparticles of three different sizes (30 nm, 50 nm, and 80 nm) were used at a concentration of 1% by volume. The results showed that using silver nanoparticles improved the heat transfer capabilities of the heat pipe, as indicated by a decrease in the temperature difference between the evaporator and condenser sections. Additionally, the size of the nanoparticles had a significant effect on the heat pipe's thermal performance. The study found smaller nanoparticles (30 nm) resulted in a minor temperature difference and better thermal performance, unlike larger nanoparticles (50 nm and 80 nm) with a lower heat transfer rate. These findings suggest that nanoparticle diameter is essential when designing and optimizing heat transfer systems [
24].
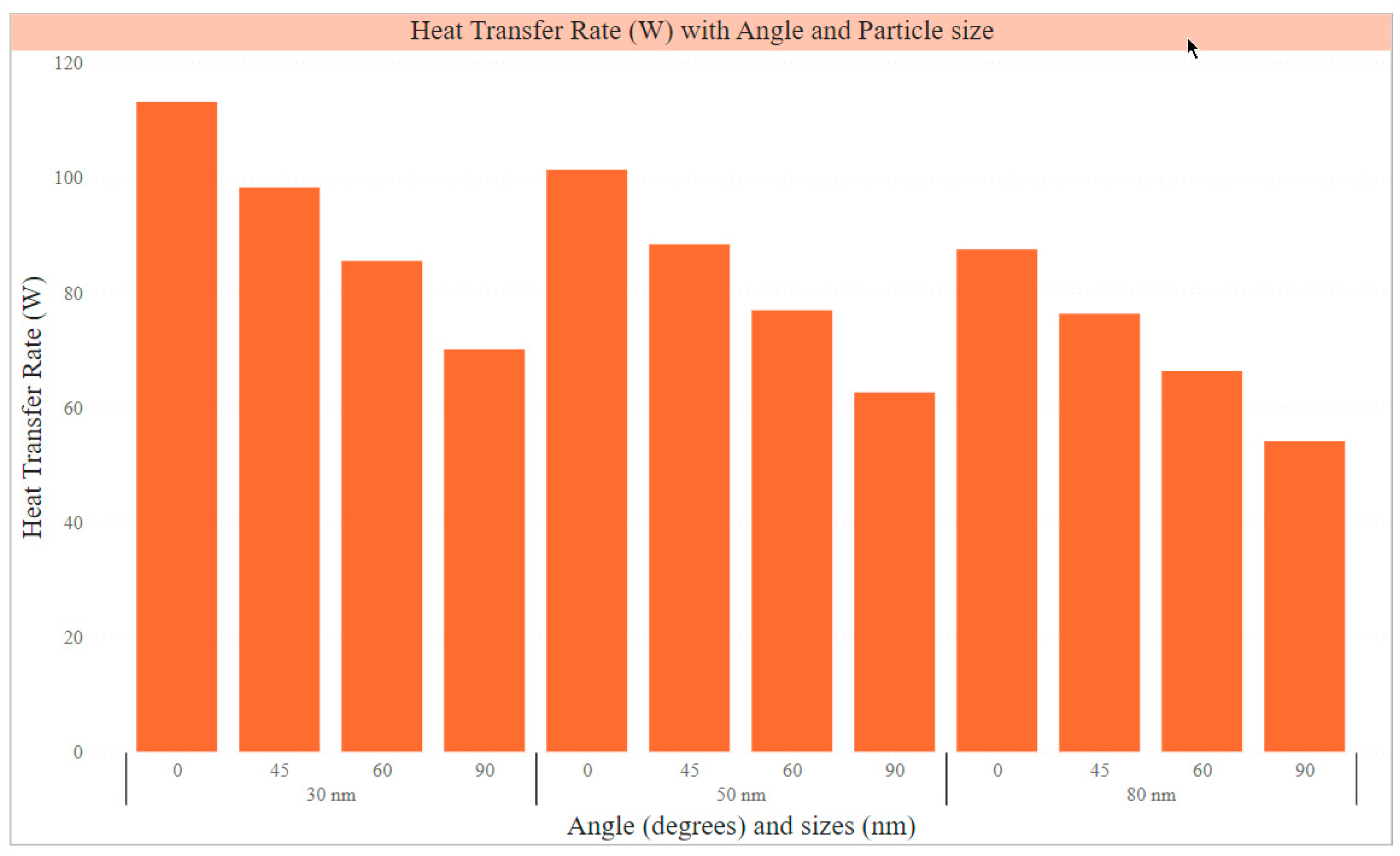
Figure 6 shows the heat transfer rates (in W) obtained from experiments conducted at different angles (in degrees) of a cylindrical screen mesh heat pipe using silver nanoparticles of various sizes. The silver nanoparticle sizes used were 30 nm, 50 nm, and 80 nm, all at a concentration of 1% by volume. For silver nanoparticles of size 30 nm, the heat transfer rates at angles 0°, 45°, 60°, and 90° were 113.2 W, 98.3 W, 85.5 W, and 70.1 W, respectively. Similarly, for silver nanoparticles of size 50 nm, the heat transfer rates at angles 0°, 45°, 60°, and 90° were 101.4 W, 88.4 W, 76.9 W, and 62.6 W, respectively. Finally, for silver nanoparticles of size 80 nm, the heat transfer rates at angles 0°, 45°, 60°, and 90° were 87.5 W, 76.3 W, 66.3 W, and 54.1 W, respectively. The figure suggests that the silver nanoparticles' size significantly influences the heat transfer rates in the cylindrical screen mesh heat pipe. Furthermore, the angle at which the heat pipe is oriented also affects the heat transfer rate [
25]. Using smaller silver nanoparticles (30 nm) resulted in higher heat transfer rates at all angles than larger ones (50 nm and 80 nm). The highest heat transfer rates were achieved at 0° angle for all nanoparticle sizes, with a decrease in the heat transfer rate observed as the angle was increased.
In addition, it was found that the heat pipe's angle also affected its thermal performance. Investigations were conducted at four different angles (0°, 45°, 60°, and 90°) to determine their impact on the heat transfer rate. The results showed that the heat pipe's thermal performance improved at a 45° angle, with the smallest temperature difference between the evaporator and condenser sections. The temperature difference was higher at 0° and 90° angles, indicating a lower heat transfer rate. Using silver nanoparticles of any size improved the temperature distribution along the heat pipe's axial length. A more even distribution of temperatures was achieved along the axial length of the heat pipe as the vapor temperature in the evaporator section dropped. In contrast, the temperature in the condenser section rose. The outcomes also revealed that the pressure drop across the heat pipe increased with silver nanoparticles, indicating increased flow resistance. The presence of nanoparticles in the working fluid, which can increase the fluid's viscosity, is blamed for the increase in flow resistance. The use of silver nanoparticles in cylindrical screen mesh heat pipes at a concentration of 1% by volume and a size of 30 nm produced the best thermal performance, with a notable improvement in the heat transfer rate and a more uniform temperature distribution along the axial length of the heat pipe, especially when the heat pipe is inclined at a 45° angle [
26]
.
The study examined the relationship between heat load and the cylindrical screen mesh heat pipe's thermal resistance, as shown in
Figure 7. In steps of 50 W, the heat load was changed from 50 W to 150 W, and the corresponding thermal resistance was measured. According to the results, the heat load increased, and the heat pipe's thermal resistance decreased. This suggests that as the heat load increased, the heat transfer rate did too. Because more heat is transferred from the evaporator section of the heat pipe to the condenser section, the thermal resistance decreases as the heat load , and the temperature differential between the two sections narrows [
27]. The experimental results indicated that the addition of silver nanoparticles to the working fluid at a volume concentration of 1% reduced the thermal resistance of the cylindrical screen mesh heat pipe. At a heat load of 50 W, the thermal resistance of the heat pipe decreased from 0.035 °C/W without nanoparticles to 0.031 °C/W with 30 nm nanoparticles, 0.033 °C/W with 50 nm nanoparticles, and 0.034 °C/W with 80 nm nanoparticles.
Similarly, at a heat load of 100 W, the thermal resistance decreased from 0.022 °C/W without nanoparticles to 0.018 °C/W with 30 nm nanoparticles, 0.019 °C/W with 50 nm nanoparticles, and 0.020 °C/W with 80 nm nanoparticles. At a heat load of 150 W, the thermal resistance decreased from 0.016 °C/W without nanoparticles to 0.012 °C/W with 30 nm nanoparticles, 0.013 °C/W with 50 nm nanoparticles, and 0.014 °C/W with 80 nm nanoparticles [
28] Furthermore, the experimental data demonstrated that using smaller nanoparticles (30 nm) resulted in a more significant reduction in thermal resistance than larger nanoparticles (50 nm and 80 nm) due to their higher surface area-to-volume ratio, which enhances heat transfer between the nanoparticles and the working fluid inside the heat pipe. Therefore, using silver nanoparticles, particularly of smaller sizes, at a volume concentration of 1% can effectively decrease the thermal resistance of the cylindrical screen mesh heat pipe.
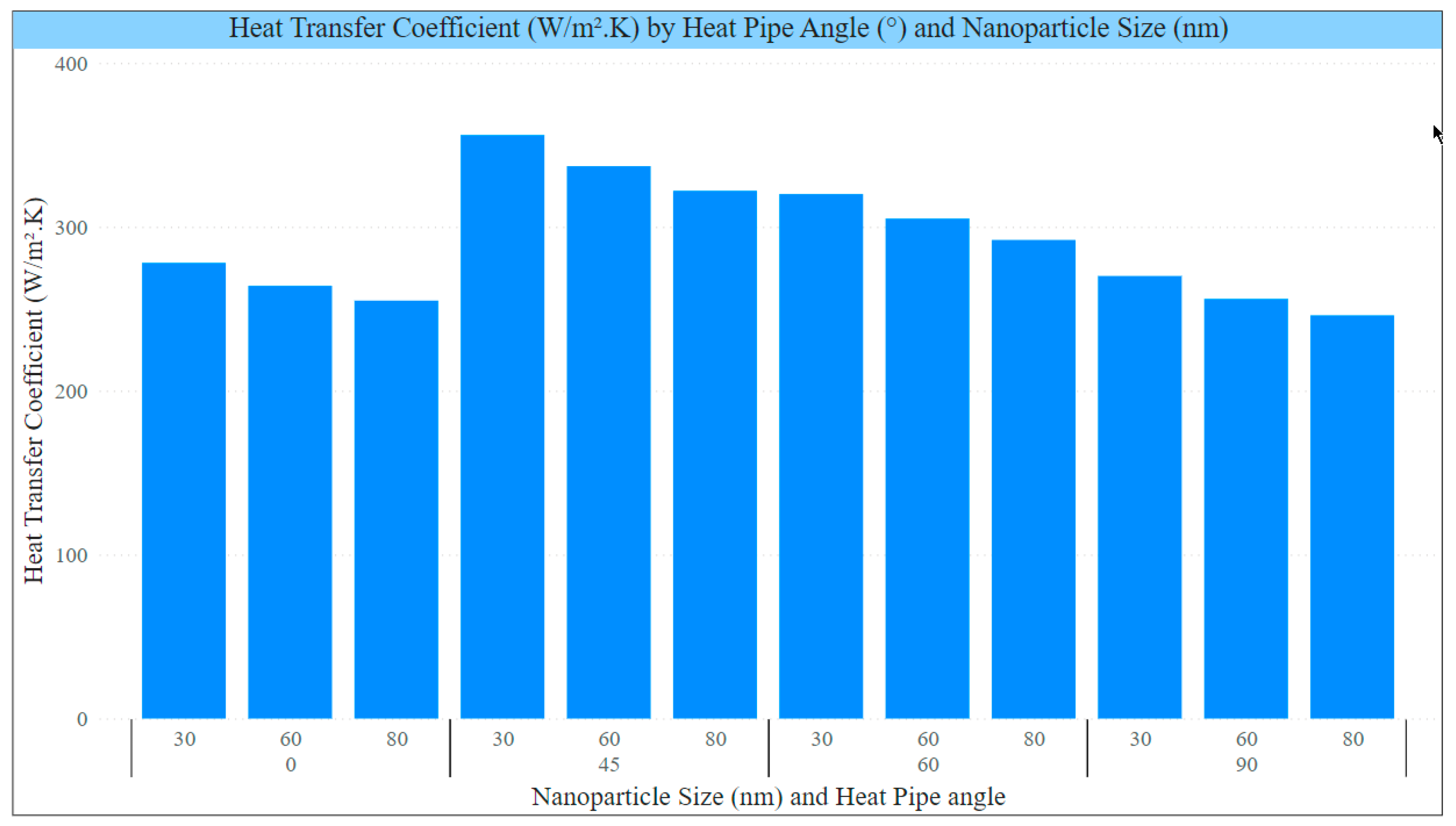
Figure 8 shows the heat transfer coefficient of a cylindrical screen mesh heat pipe with different angles and silver nanoparticles of different sizes and concentrations. The results indicate that using silver nanoparticles at a volume concentration of 1% improves the heat transfer coefficient compared to not using any nanoparticles. Additionally, the heat transfer coefficient is affected by the angle of the heat pipe. Using 30 nm silver nanoparticles at all angles results in the highest heat transfer coefficient, followed by 60 nm and 80 nm nanoparticles. This can be attributed to smaller nanoparticles' larger surface area-to-volume ratio, which improves heat transfer between the nanoparticles and the working fluid inside the heat pipe.
Regarding the heat pipe angle, the heat transfer coefficient was highest at a 45° angle for all nanoparticle sizes. At 0° and 90° angles, the heat transfer coefficient was lower than at 45°, indicating that the heat pipe's angle can impact its thermal performance. In conclusion, utilizing silver nanoparticles of smaller sizes and optimal volume concentration, along with optimizing the heat pipe's angle, can significantly improve the heat transfer coefficient of cylindrical screen mesh heat pipes.
6. Conclusions
The study investigated the impact of varying the size of silver nanoparticles on the thermal performance of cylindrical screen mesh heat pipes. The study found that smaller silver nanoparticles resulted in a larger surface area-to-volume ratio, which improved thermal conductivity and heat transfer performance. Additionally, using smaller nanoparticles resulted in a more uniform temperature distribution along the axial length of the heat pipe. The study also found that the angle at which the heat pipe is oriented affects the heat transfer rate. A 45° angle produces the smallest temperature difference between the evaporator and condenser sections. The study has significant implications for the design and optimization of heat transfer systems, as the size of nanoparticles is an essential factor to consider in achieving the best performance. Overall, using silver nanoparticles with a size of 30 nm at a concentration of 1% by volume produced the best thermal performance.
A comparison of three different silver nanoparticle sizes (30nm, 50nm, and 80nm) showed that using smaller nanoparticles (30nm) resulted in the best thermal performance for heat transfer in a cylindrical screen mesh heat pipe. At angles of 0°, 45°, 60°, and 90°, heat transfer rates for silver nanoparticles of size 30 nm were 113.2 W, 98.3 W, 85.5 W, and 70.1 W, respectively. For silver nanoparticles of size 50 nm, the heat transfer rates at the same angles were 101.4 W, 88.4 W, 76.9 W, and 62.6 W, respectively. Finally, for silver nanoparticles of size 80 nm, the heat transfer rates at the same angles were 87.5 W, 76.3 W, 66.3 W, and 54.1 W, respectively. The study observed an improvement in the thermal performance of the heat pipe at a 45° angle, where the temperature difference between the evaporator and condenser sections was the smallest. Additionally, the study showed that the thermal resistance of the cylindrical screen mesh heat pipe increased as the heat load increased, with a maximum thermal resistance of approximately 0.07 K/W observed at 150 W.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary materials, including additional figures, tables, or supporting data, are available upon request. Please contact the corresponding author, Ratchagaraja Dhairiyasamy, for access to the supplementary materials.
Author Contributions
Prabhu Alphonse contributed to the conception and design of the study, data collection, analysis, and interpretation. Muthukumarasamy Karthikeyan provided critical input and expertise during the study design, data analysis, and interpretation. Ratchagaraja Dhairiyasamy supervised the entire research process, including study design, data analysis, and interpretation. All authors were involved in the drafting and revision of the manuscript and have given final approval for its submission.
Funding
This research was conducted without any dedicated or specific funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data used in this research is available upon request. Please contact [ratchagaraja@gmail.com] for further details on accessing the data.
Acknowledgments
I express my profound gratitude to Aksum University for their exceptional support in facilitating this research.
Conflicts of Interest
“The authors declare no conflict of interest.”
List of Symbols and Abbreviations
| Symbol/Abbreviation |
Description |
Units |
| nm |
Nanometers |
nm |
| W |
Watts |
W |
| °C |
Degrees Celsius |
°C |
| % |
Percent by volume |
% |
| Figure |
Figure |
N/A |
| k |
Thermal conductivity |
W/mK |
| D |
Nanoparticle diameter |
nm |
| Q |
Heat transfer rate |
W |
| θ |
Angle of heat pipe |
° |
| R |
Thermal resistance |
K/W |
| T |
Temperature |
°C |
| ΔT |
Temperature difference |
°C |
| L |
Axial length of heat pipe |
m |
| V |
Volume of heat pipe |
m3
|
| A |
The surface area of the heat pipe |
m2
|
| φ |
Concentration of nanoparticles |
% |
| C |
Heat capacity |
J/kgK |
| ρ |
Density |
kg/m3
|
| ν |
Kinematic viscosity |
m2/s |
References
- Pedroso Silva Santos, B.; Rubio Arias, J.J.; Jorge, F.E.; Értola Pereira de Deus Santos, R.; et al. Nanocomposites of poly(vinylidene fluoride) with oxide nanoparticles for barrier layers of flexible pipes. Journal of Materials Research and Technology 2021, 15, 3547–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; He, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; et al. Investigation on the thermal performance of flat-plate heat pipes with various working fluids under different inclination angles. Energy Reports 2022, 8, 8017–8026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhan, A.L.S.; Solomon, A.B.; Sunder, S. Heat transport limitations and performance enhancement of anodized grooved heat pipes charged with ammonia under gravity and anti-gravity condition. Appl Therm Eng 2022, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Khalifa, N.T.; Saad, H.A.; Othman, H.A.; et al. Investigation of behavior of heat storage system including paraffin with involving MWCNT nanoparticles. J Energy Storage 2022, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riehl, R.R.; Martin, J.E.S.; Estella, J. Electronics thermal management applying heat pipes and pulsating heat pipes. Advances in Nanofluid Heat Transfer 2022, 403–446. [Google Scholar]
- Pathak, S.K.; Kumar, R.; Goel, V.; Pandey, A.K.; Tyagi, V. V. Recent advancements in thermal performance of nano-fluids charged heat pipes used for thermal management applications: A comprehensive review. Appl Therm Eng 2022, 216, 119023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahiraei, M.; Monavari, A. Irreversibility characteristics of a mini shell and tube heat exchanger operating with a nanofluid considering effects of fins and nanoparticle shape. Powder Technol 2022, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asirvatham, L.G.; Nimmagadda, R.; Wongwises, S. Heat transfer performance of screen mesh wick heat pipes using silver–water nanofluid. Int J Heat Mass Transf 2013, 60, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Tang, S.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; et al. Numerical simulation of a small high-temperature heat pipe cooled reactor with CFD methodology. Nuclear Engineering and Design 2020, 370, 110907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, A.T.; Saghir, M.Z. Heat Transfer Enhancement in Multiple Pipes Configuration using Different Fluid Mixtures: A Numerical Approach. International Journal of Thermofluids 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Kong, K.; Zhao, Y.; Chu, H. Tuning the luminescence properties of lanthanide coordination polymers with Ag@SiO2 nanoparticles. Dalton Transactions 2017, 46, 6447–6455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayel, V.; Slobodeniuk, M.; Bertossi, R.; Romestant, C.; Bertin, Y. Flat plate pulsating heat pipes: A review on the thermohydraulic principles, thermal performances and open issues. Appl Therm Eng 2021, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Genk, M.S.; Lianmin, H. An experimental investigation of the transient response of a water heat pipe. Int J Heat Mass Transf 1993, 36, 3823–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshteli, A.N.; Sheikholeslami, M. Solidification within a wavy triplex-tube heat storage unit utilizing numerical simulation considering Al2O3 nanoparticles. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 2020, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, R.; Ganesan, K.; Rajkumar, M.R.; Asirvatham, L.G.; Wongwises, S. Comparative study of the effect of hybrid nanoparticle on the thermal performance of cylindrical screen mesh heat pipe. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer 2016, 76, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, S.D.; Farahani, M.; Ghanbari, D. Heat transfer from R134a/oil boiling flow in pipe: Internal helical fin and hybrid nanoparticles. Chemical Engineering Research and Design 2021, 175, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadodun, O.G.; Kaood, A.; Hassan, M.A. Investigation of the entropy production rate of ferrosoferric oxide/water nanofluid in outward corrugated pipes using a two-phase mixture model. International Journal of Thermal Sciences 2022, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil, R.; Madurai Elavarasan, R.; Pugazhendhi, R.; Premkumar, M.; et al. A holistic review on the integration of heat pipes in solar thermal and photovoltaic systems. Solar Energy 2021, 227, 577–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xue, Y.; Qi, H.; Cai, W. An updated review on working fluids, operation mechanisms, and applications of pulsating heat pipes. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2021, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markal, B.; Candere, A.; Avci, M.; Aydin, O. Investigation of flat plate type pulsating heat pipes via flow visualization-assisted experiments: Effect of cross sectional ratio. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer 2021, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, S.; Liu, X.; He, S. A copper nanoparticle enhanced phase change material with high thermal conductivity and latent heat for battery thermal management. J Loss Prev Process Ind 2022, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, K.; Duan, R.; Xie, G.; Sundén, B. Enhanced thermal management by introducing nanoparticle composite phase change materials for cooling multiple heat sources systems. Energy 2021, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadiun, M.; Mohammadiun, H.; Alizadeh, R.; Mesgarpour, M.; et al. The effect of variable temperature and location on relative thermal conductivity (RTC) on the heat pipe in the presence of AL2O3 nanoparticles: Numerical and optimization approaches. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 2021, 124, 132–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wu, Y.T.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Ma, C.F. Flow and mixed convection heat transfer of Hitec salt in multi-sided heating pipes. Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments 2021, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohuri, B. Heat pipe design and technology: Modern applications for practical thermal management, second edition. Heat Pipe Design and Technology: Modern Applications for Practical Thermal Management, Second Edition 2016, 1–513. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Tang, Y.; Duan, L.; Tang, H.; et al. Thermal performance enhancement of micro-grooved aluminum flat plate heat pipes applied in solar collectors. Renew Energy 2020, 146, 2234–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Ma, X.; Wang, Y.; Yao, S.; Vafai, K. Amelioration of boiling heat transfer by 3D deposition structure of graphene-silver hybrid nanoparticle. Energy Conversion and Management: X 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, S.U.; Hasnain, S.; Ali, H.M.; Bano, S.; et al. Experimental investigation of aluminum fins on relative thermal performance of sintered copper wicked and grooved heat pipes. Progress in Nuclear Energy 2022, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).