1. Introduction
For dam-break flows over mobile beds, spatial variations of densities of sediment-laden flow is considerable and may impose significant impacts on flow fields (Cao et al. 2004). Since flow densities are not constants but spatial functions, dam-break flows over mobile beds are often modeled by the variable density shallow water equations (VDSWEs) (Cao et al. 2004; Wu & Wang 2007; Rosatti et al. 2008; Leighton et al. 2010; Begnudelli & Rosatti 2011; Wu et al. 2011; Li et al. 2013; Guan et al. 2014). As the name implies, the VDSWEs is an extension of the shallow water equations (SWEs) and is also based on the shallow water assumption (Vreugdenhil 1994). Besides, the following simplifications are employed in the derivation of the VDSWEs (Fraccarollo & Capart 2002; Cao et al. 2004): (1) the flow is dominated by suspended sediment load; (2) there are no obvious lags between sediment particles and water.
To account for its hyperbolic nature, the VDSWEs is often solved by the Godunov-type finite volume method (LeVeque 2002; Toro 2009). A thorough review about the application of the method to the numerical solution of the SWEs is given by Toro and Garcia-Navarro (2007). Being different from the SWEs, density of sediment-laden flow in the VDSWEs is an independent variable. To simplify the solution of the VDSWEs, Brufau et al. (2000) and Cao et al. (2004) reformulated the VDSWEs by moving the density-related terms to the right-hand side of the equations. After the reformulation, the left-hand side of the equations has the same form as the SWEs, while the right-hand side has two additional terms than the SWEs. Cao et al. (2004) pointed out that one additional term represents the effect of spatial variation of flow densities and the other one described the momentum exchange between flow and bed. Since the reformulated VDSWEs has the same left-hand side as the SWEs, it is a common practice to apply the previously well-developed Godunov-type SWEs solvers to solve the VDSWEs and to discretize the additional terms by a central difference scheme (Cao et al. 2004; Wu et al. 2011; Li et al. 2013; Guan et al. 2014).
However, one of the two additional terms on the right-hand side involves the gradient of density/concentration. Mathematically, the term represents a product of the Heaviside function by the Dirac function. Across discontinuous fronts of a density field, its mathematical meaning is not well-defined (Pares 2006; Castro et al. 2007). Numerically, this term originates from the advection term of the VDSWEs and it should to be discretized by an upwind scheme. Cozzolino et al. (2013) argued that it is difficult to maintain the conservative property (C-property) (Bermudez & Vazquez 1994) of numerical models based on the reformulated VDSWEs. Cozzolino et al. (2013) also suggested that the better way to create a well-balanced model is to solve the original formulation of the VDSWEs.
The objective of this paper is to present a novel well-balanced numerical model for the simulation of dam-break flows over mobile bed. The model is based on the original formulation of the VDSWEs. In the model, the Godunov-type finite volume method is applied to solve the system of equations simultaneously. As far as we know, the model is the first two-dimensional model that solves the VDSWEs using a well-balanced numerical scheme.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows: in
Section 2, the governing equations, i.e. the two-dimensional variable density shallow water equations, and its two formulations are presented. In
Section 3, the well-balanced numerical scheme is developed for the VDSWEs. In
Section 4, the proposed model is tested against three test cases and the results are discussed and compared with observations. Finally, the main conclusions are drawn in Section 5.
2. Governing Equations
In this study, the dam-break flows over mobile beds are described by the variable density shallow water equations (VDSWEs). In the VDSWEs, the mixture of water and sediment is treated as a continuum, and both phases are moving together at the same velocity. The system of governing equations consists of volume, mass and momentum conservation equations for flow and sediment. For a sediment-laden flow, the bulk volume conservation equation is written as:
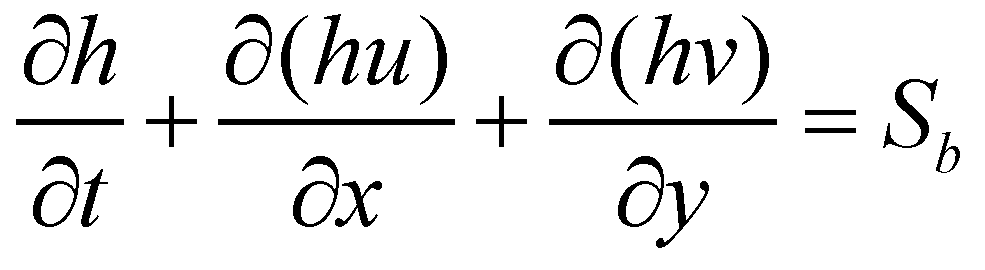
(1)
where
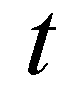
is time;
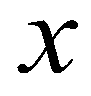
and
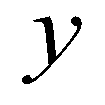
are the spatial coordinates;
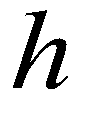
is the flow depth;

and
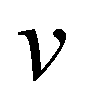
are the depth-averaged flow velocities in
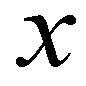
and
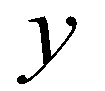
directions, respectively;
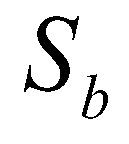
is the sediment exchange rate between flow and bed. Since the density of a sediment-laden flow is a spatial function, the mass conservation equation of is expressed as:
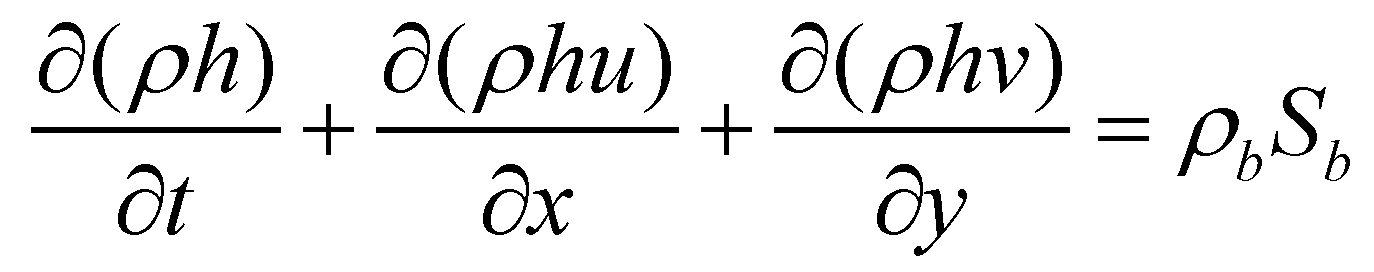
(2)
where
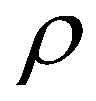
is the density of the sediment-laden flow;
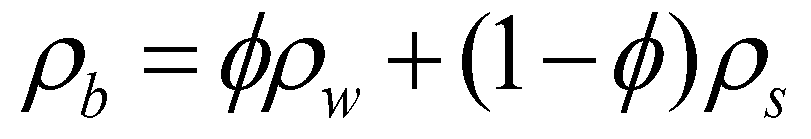
is the density of the saturated mobile bed;
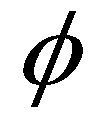
is the porosity of the mobile bed;
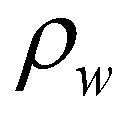
is the density of the water;
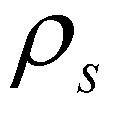
is the density of the bed material. The concentration of sediment-laden flow can be calculated by
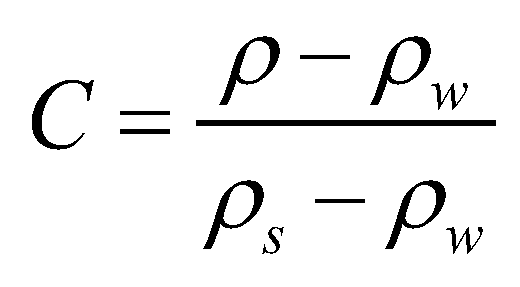
. The depth-averaged momentum conservation equations in
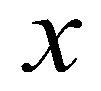
and
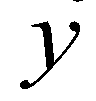
directions are given as:
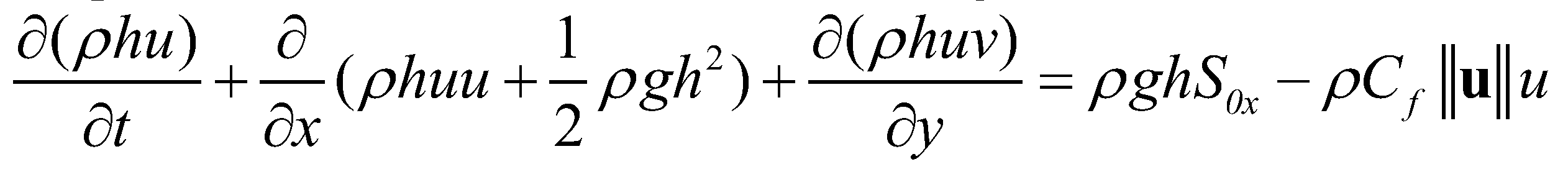
(3)
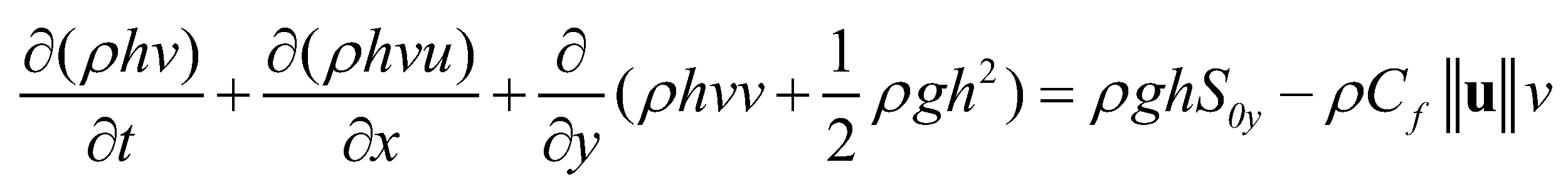
(4)
where
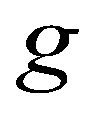
is the gravitational acceleration;
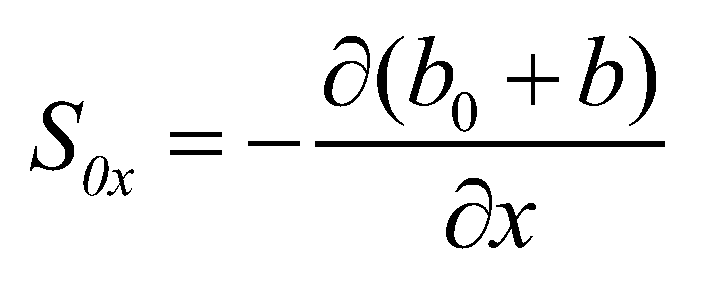
and
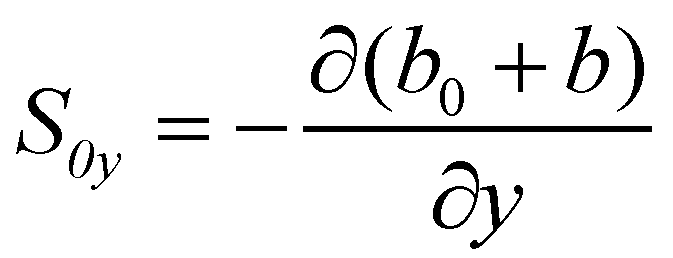
are the
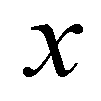
and
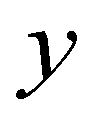
components of bed slope;
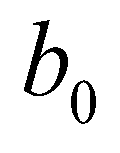
is the elevation of the immobile bed;
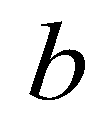
is the depth of the mobile bed;
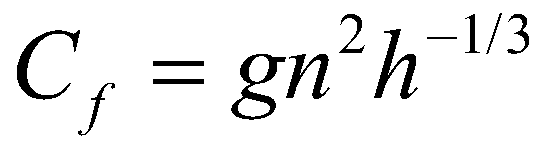
is the drag coefficient;
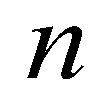
is Manning’s roughness coefficient;
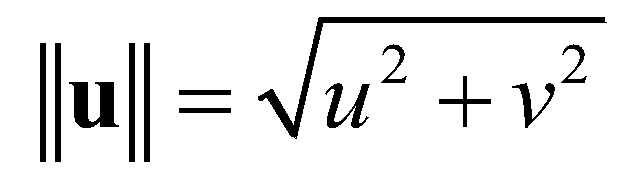
is the magnitude of the flow velocity;

is the velocity vector.
The system of governing equations can also be written in a vectorial form as:
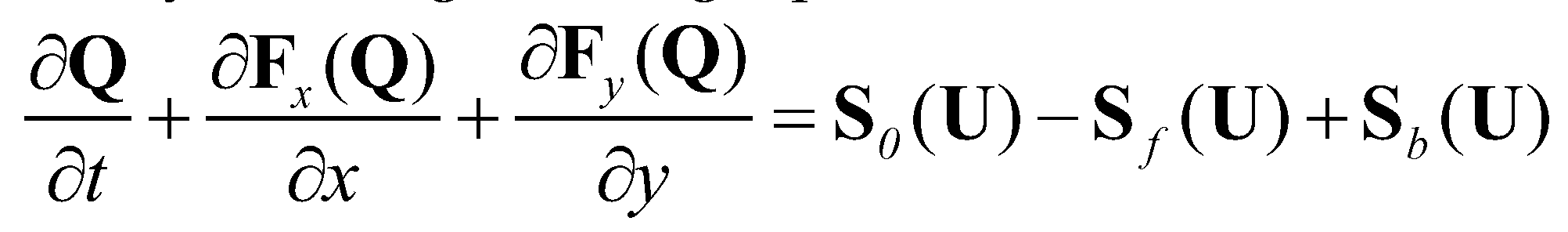
(5)
where
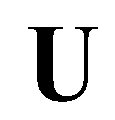
and
are the vectors of primitive variables and conservative variables:
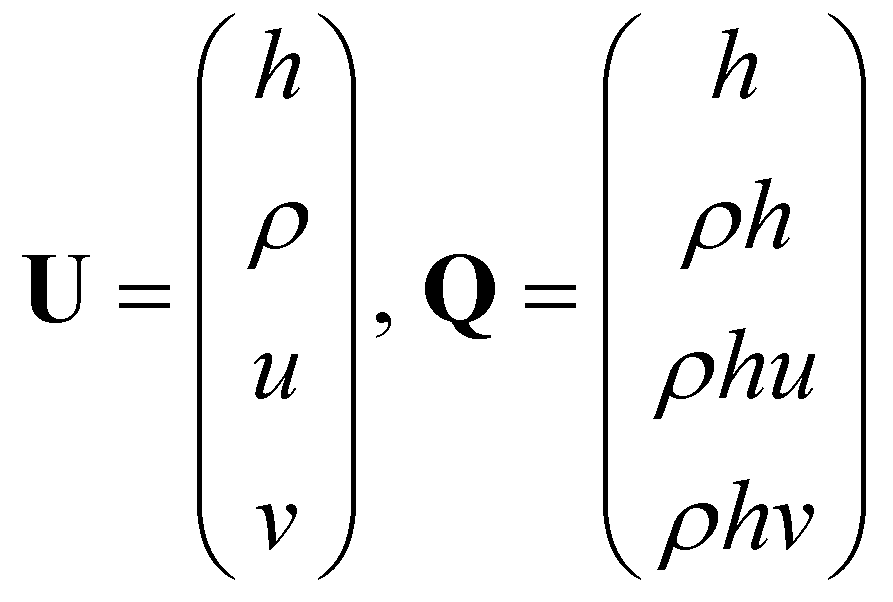
(6)
,
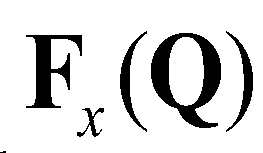
and
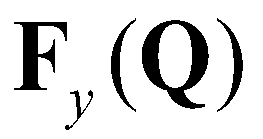
are the vectors of advective fluxes:
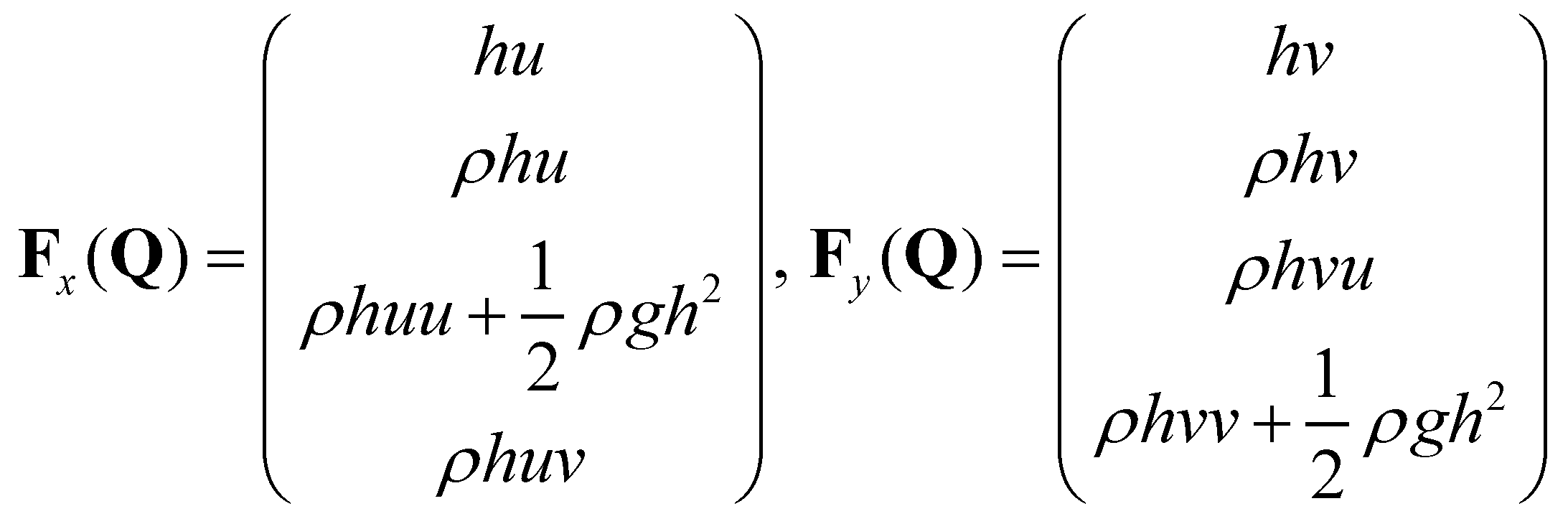
(7)
, and
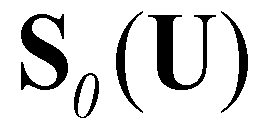
,
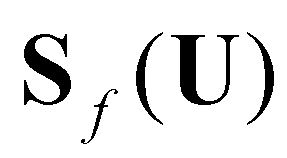
and
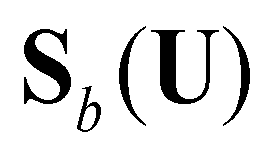
are the bed slope, bed friction, and bed material source terms:
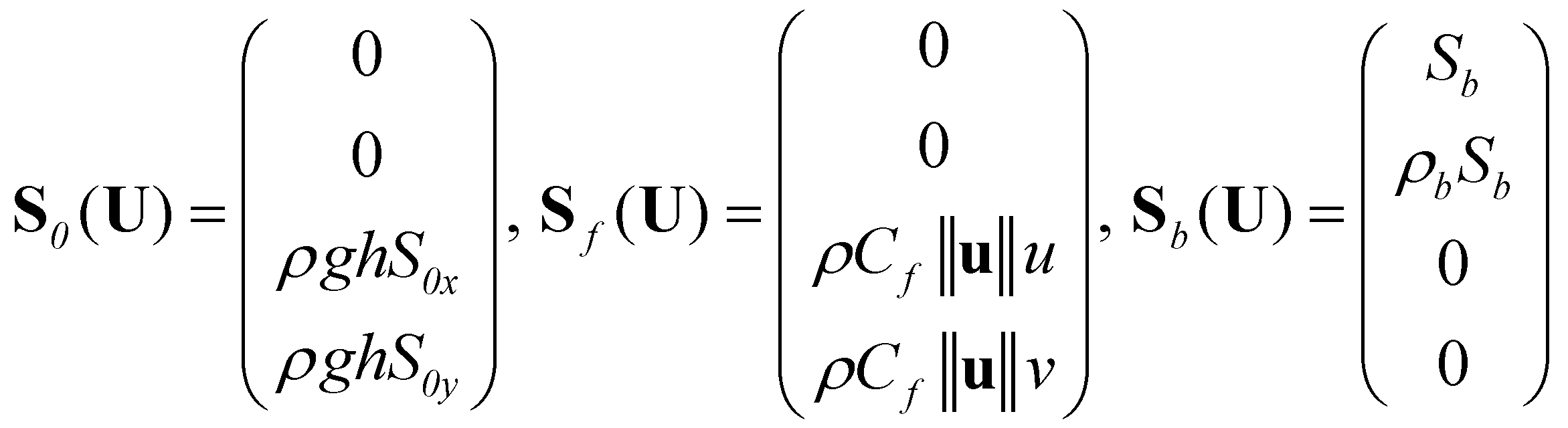
(8)
Equation (5) represents a system of time dependent, nonlinear hyperbolic partial differential equations. This system may result in sharp and discontinuous solutions even if starting from continuous initial conditions.
2.1. Nonequilibrium Sediment Transport Model
The evolution of mobile bed is described by the following conservation equation of bed material:
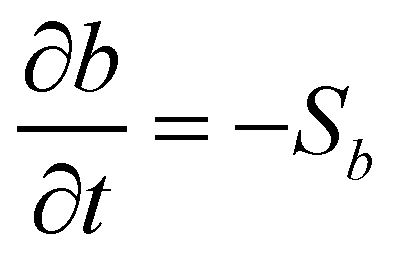
(9)
The mass exchange between sediment-laden flow and mobile bed is evaluated by the nonequilibrium sediment transport equation (Armanini & Di Silvio 1988; Wu & Wang 2007). It reads:
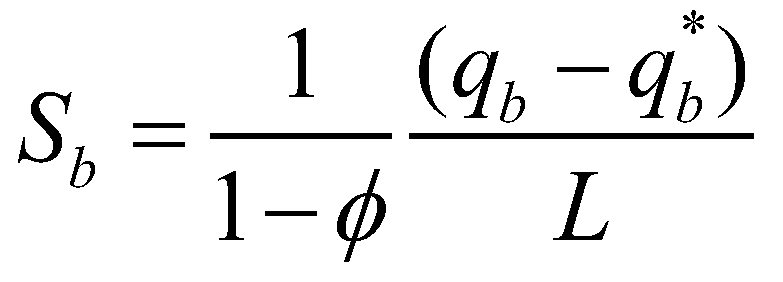
(10)
where
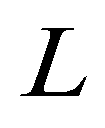
is the nonequilibrium adaption length of sediment transport;
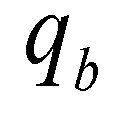
is the actual flux of sediment transport; and
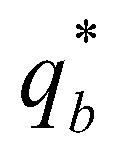
is the sediment transport capacity or the equilibrium sediment transport rate. On account of the recommendations of El Kadi Abdeerezzak and Paquier (2010) and Van Emelen
et al. (2014), the sediment transport capacity is calculated by the modified Meyer-Peter-Müller (MPM) formula:
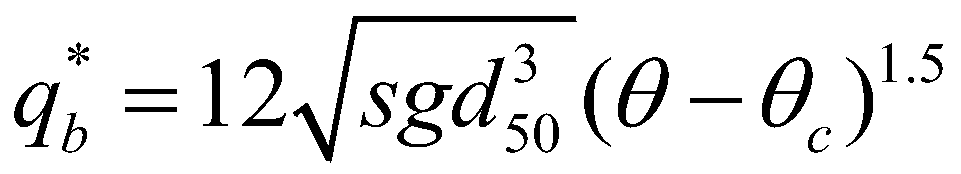
(11)
where
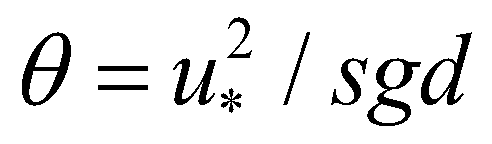
is the Shields number;
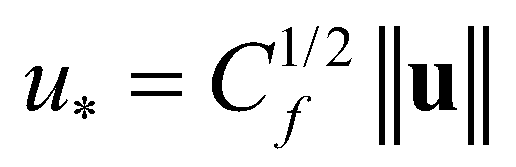
is the friction velocity;
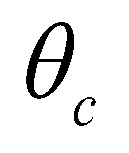
is the critical Shields number.
The nonequilibrium adaption length denotes the spatial lag between actual sediment transport rate and its saturation/equilibrium rate. It is calculated by Wu (2004):
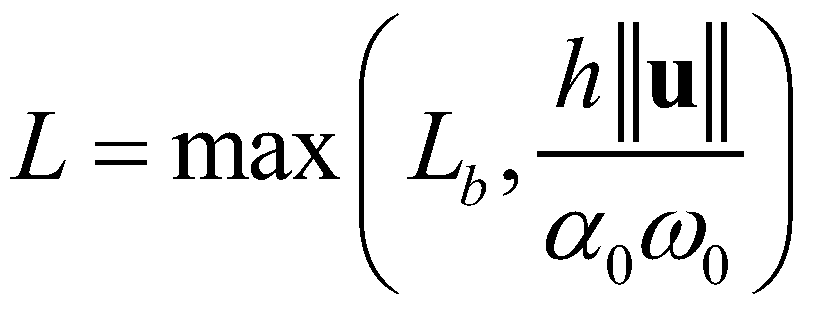
(12)
where
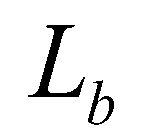
is the adaption length of bed-load;
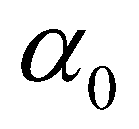
is the adaption coefficient of suspended-load;
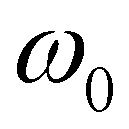
is the settling velocity of a single sediment particle. Since there have been no consensus on
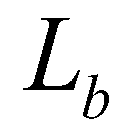
and
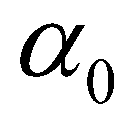
, both parameters are treated as calibration parameters in the proposed model. The settling velocity of sediment particle is calculated by Cao (1999):
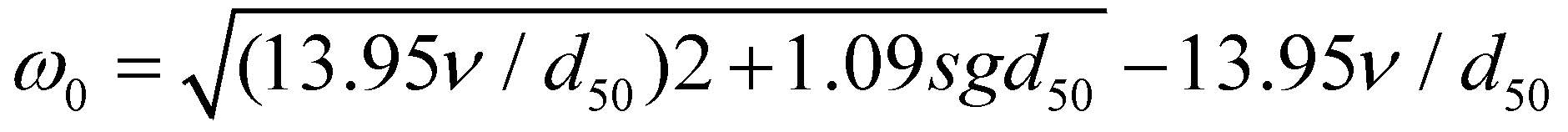
(13)
where
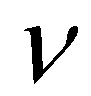
is the kinematic viscosity of water;
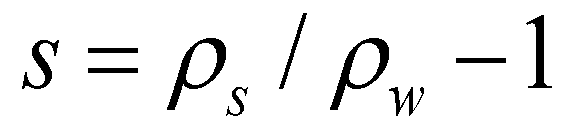
is the specific gravity of submerged sediment particle;
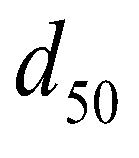
is the median diameter of sediment particle.
2.2. Numerical Methods
2.2.1. Godunov-type Finite Volume Method
The integral form of the VDSWEs over a computational cell can be written as:
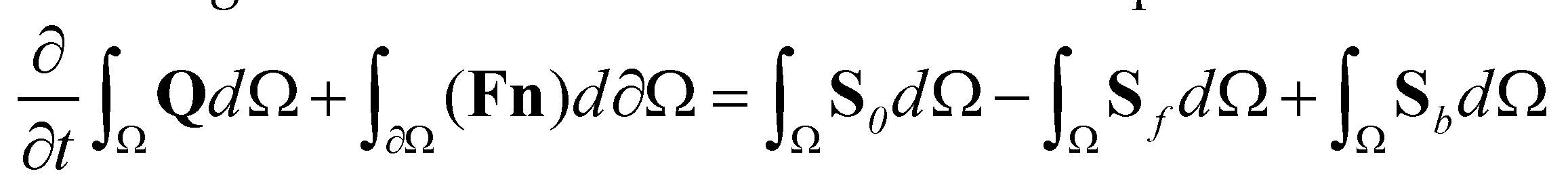
(14)
where
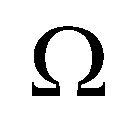
represents a computational cell;
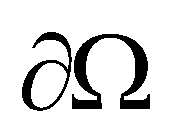
is the boundary of the cell;
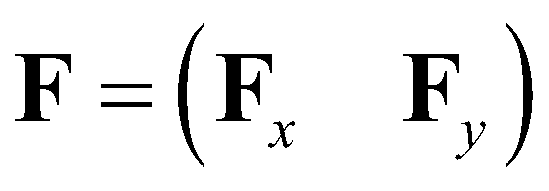
is the matrix of fluxes;
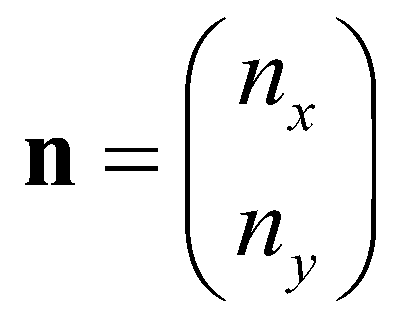
is the outward unit normal vector;
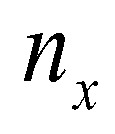
and
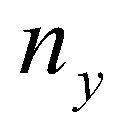
are the components of the normal vector in
and
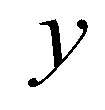
directions, respectively; and
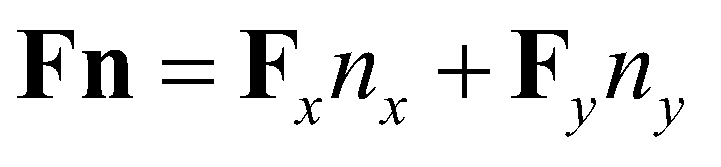
is the fluxes normal to the cell boundary designated by

. In this study, the fully coupled system of governing equations is solved by the first-order Godunov-type finite volume method over a regular Cartesian mesh. For a rectangular cell, the fluxes across the cell boundaries are calculated by
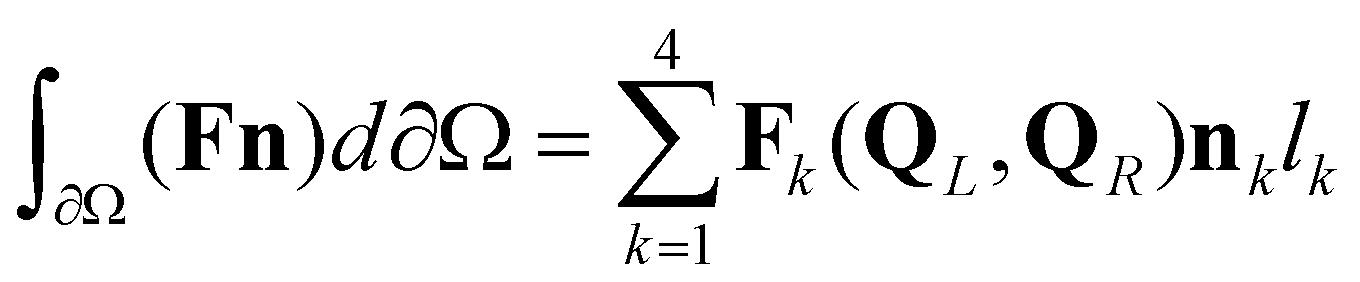
(15)
where subscript
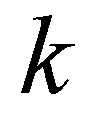
is the edge index; subscript
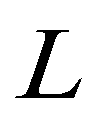
and
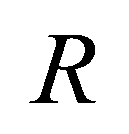
denote the left and right edges of a cell boundary, respectively;
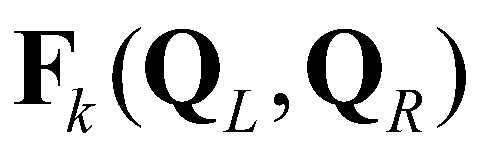
is the Riemann fluxes at the edge
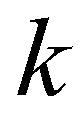
;
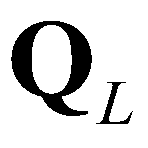
and
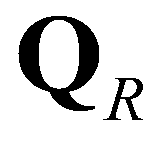
are the vectors of conservative variables reconstructed at the left and right edges, respectively;
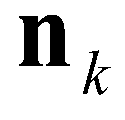
is the unit normal vector for the
kth edge;
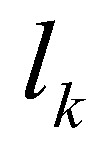
is the length of the
kth edge.
A first-order, two-step fractional scheme is employed in the numerical model to update the solution at each time step:
Step one:
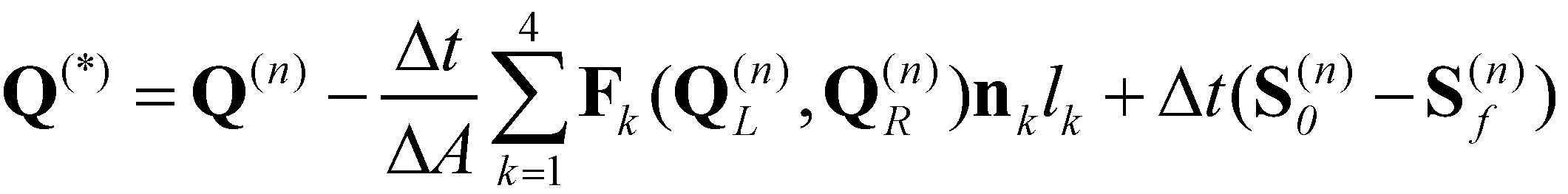
(16)
Step two:
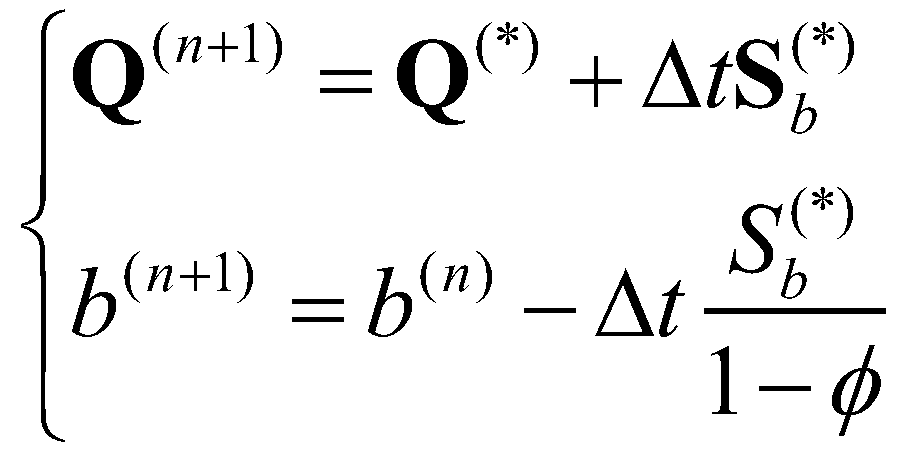
(17)
where superscript
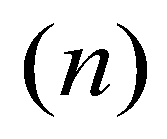
denotes the solution at time step
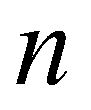
; superscript
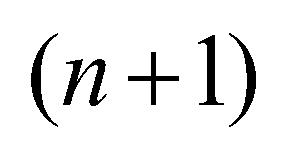
denotes the time step
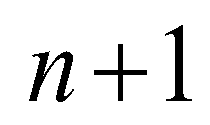
; superscript

denotes the intermediate solution between time step
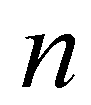
and
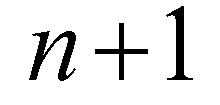
.
Time steps are limited by two stability conditions. The first is the Courant-Friedrichs-Lewy (CFL) condition that requires the maximum CFL number should not be greater than 0.5 (LeVeque 2002) at each time step. The second is the bed change condition that limits the change of mobile bed at each time step up to 10% of the local bed depth (Wu et al. 2011).
2.2.2. HLLC Approximated Riemann Solver
The HLLC (Harten-Lax-van Leer-Contact) approximate Riemann solver (Toro 2009) is extended to calculate numerical fluxes across cell boundaries. The wave structure of a typical HLLC solution is demonstrated in Cozzolino
et al. (2013). The solution is separated by three waves: the slowest wave (
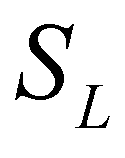
), the middle wave (
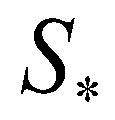
), and the fastest wave (
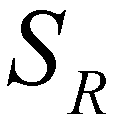
). There are four constant states in the solution: the left state (
), the right state (
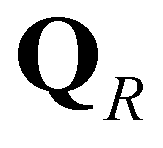
), the left star state (
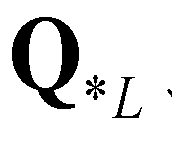
), and the right star state (
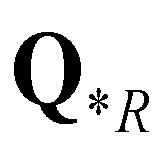
). The corresponding HLLC numerical flux
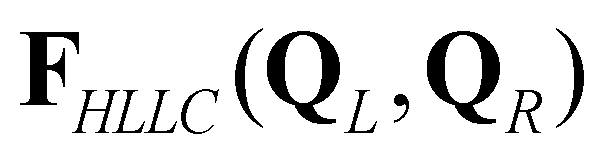
is defined as:
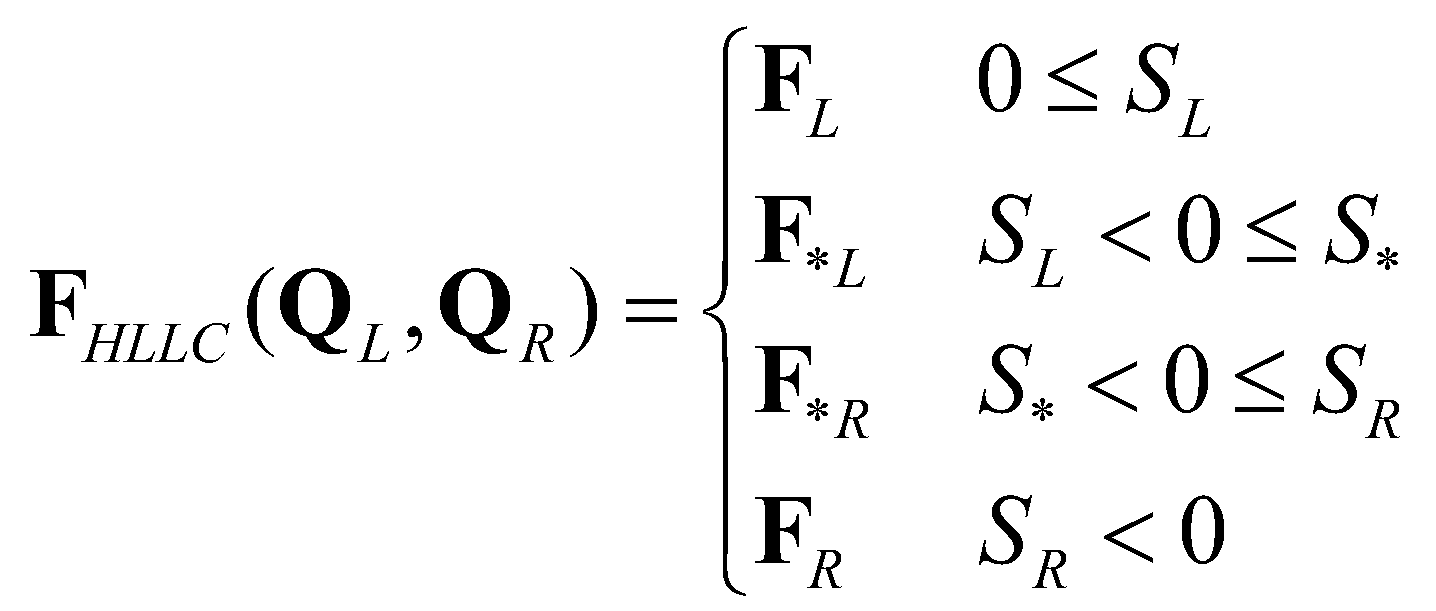
(18)
where
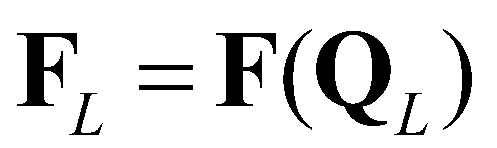
represents the supercritical flow from the left to the right;
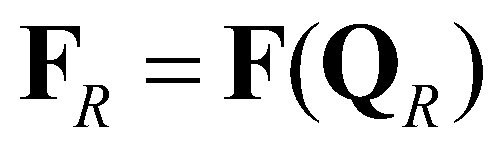
represents the supercritical flow from the right to the left;
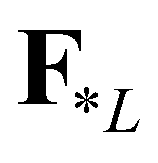
and
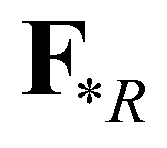
are the fluxes at the star regions. By applying the Rankine-Hugoniot conditions across the waves,
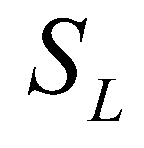
and
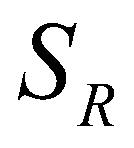
, the numerical fluxes at the star regions can be calculated by:
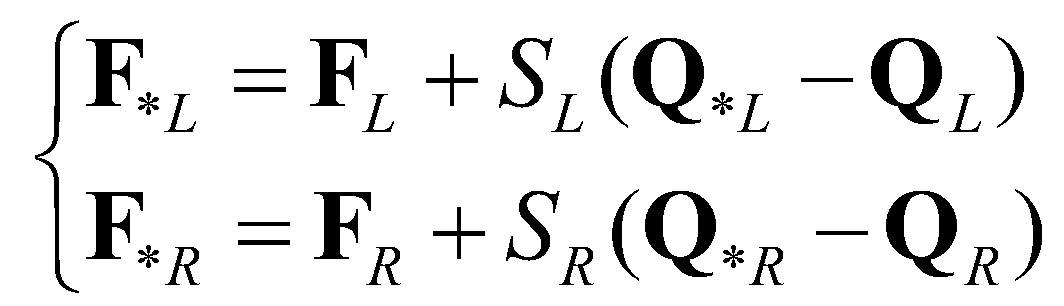
(19)
The middle wave speed is estimated by Cozzolino et al. (2013):
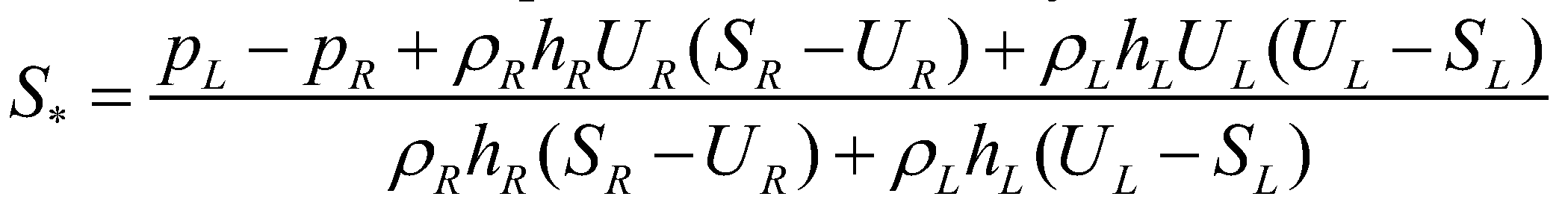
(20)
where
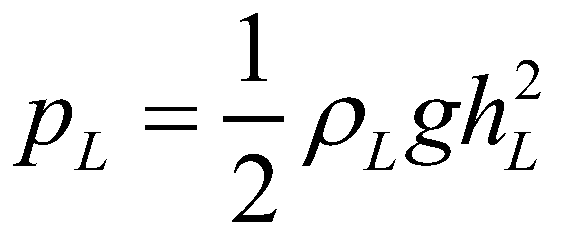
and
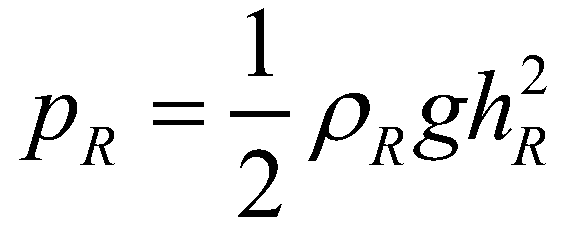
are the hydrostatic pressures at the left and right edges, respectively;
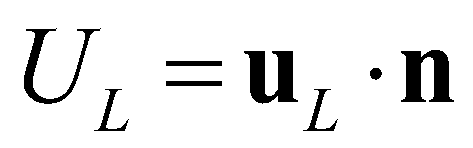
and
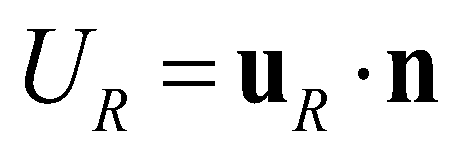
are the normal velocities at the left and right edges, respectively. The left and right states at the star regions can be determined by:
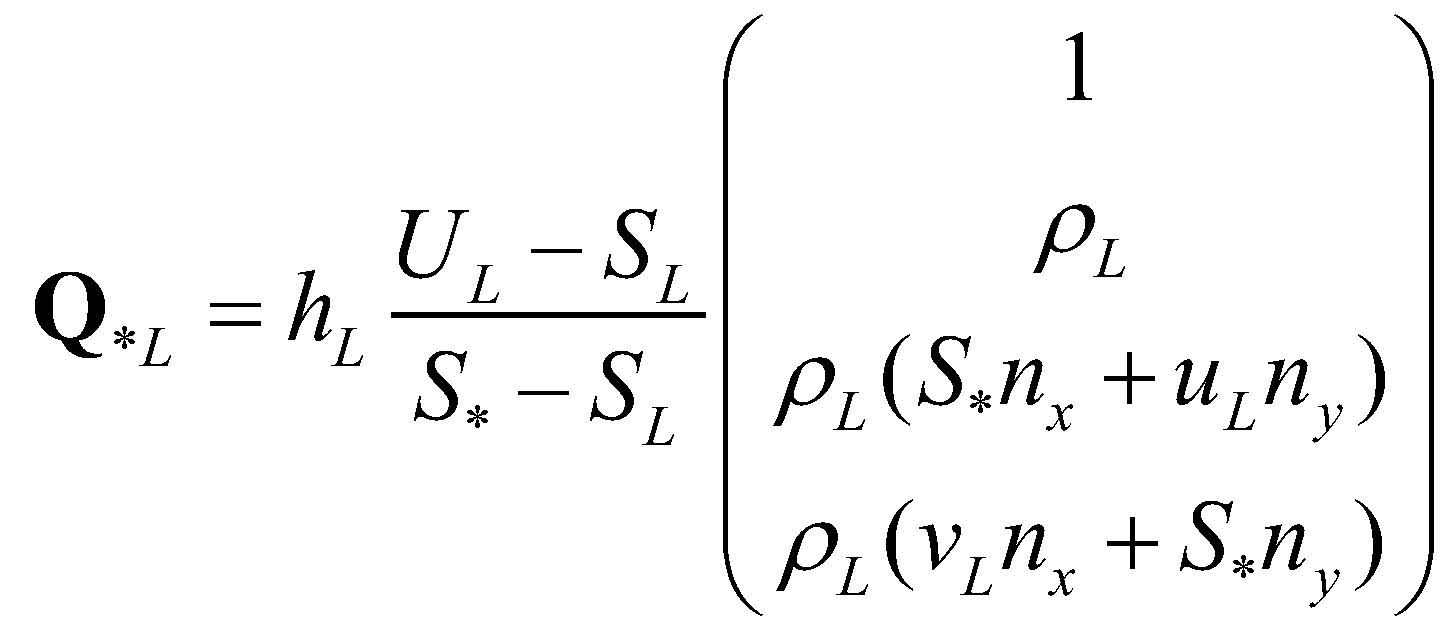
(21)
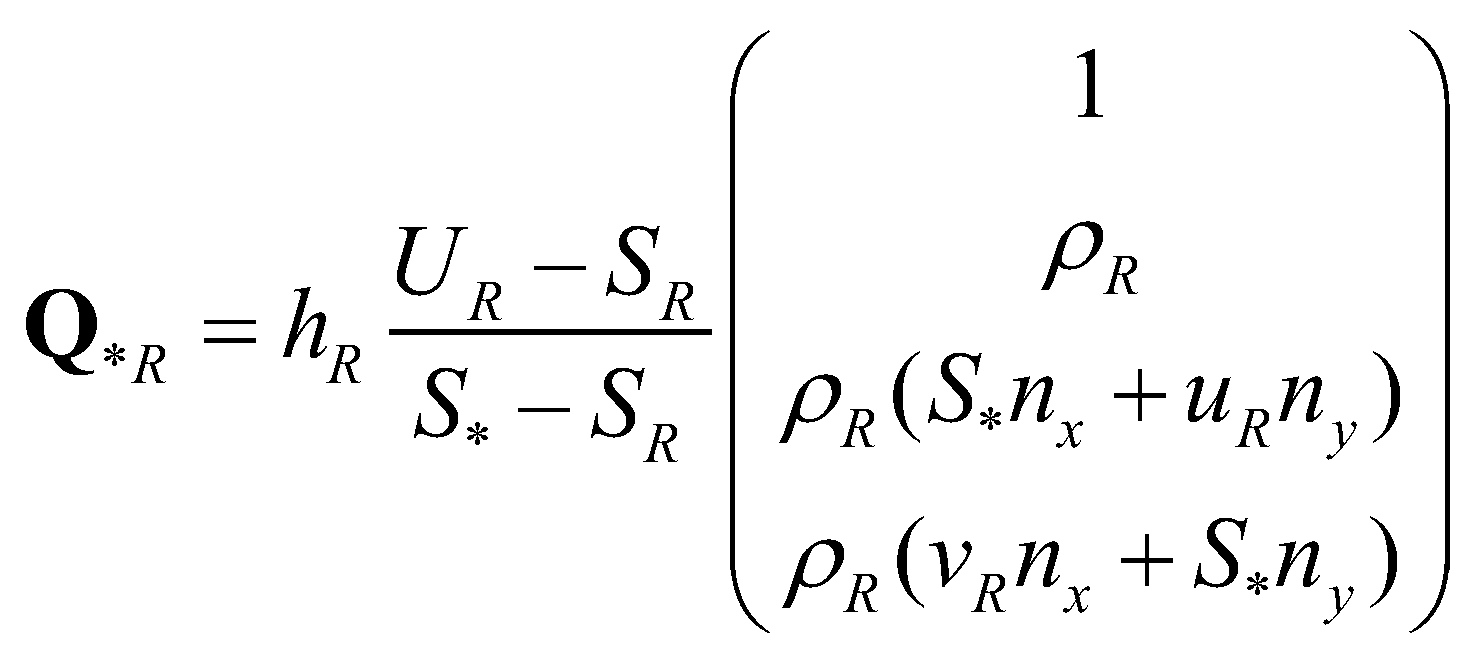
(22)
The left and right wave speeds are estimated by:
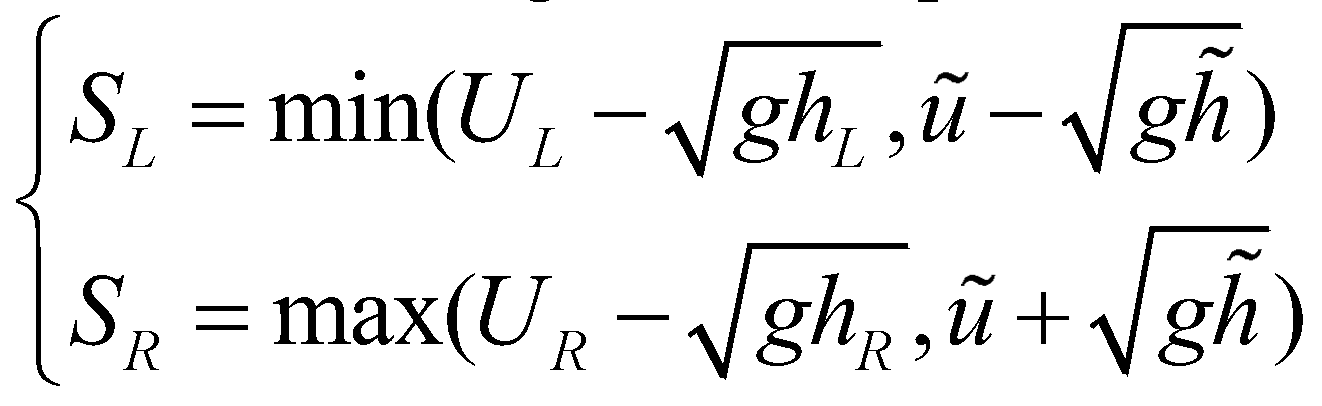
(23)
where
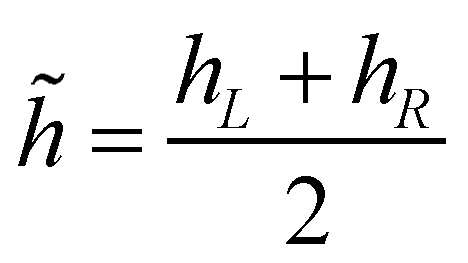
and
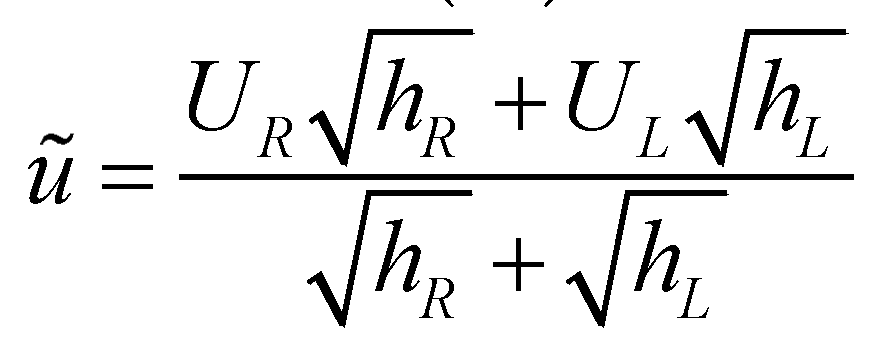
are the Roe averaged flow depth and velocity.
2.2.3. Well-balanced Scheme for the VDSWEs
Without any loss of generality, only one-dimensional equations are considered in this section. For a stationary flow (
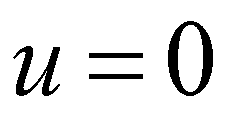
), the momentum equation of SWEs becomes:
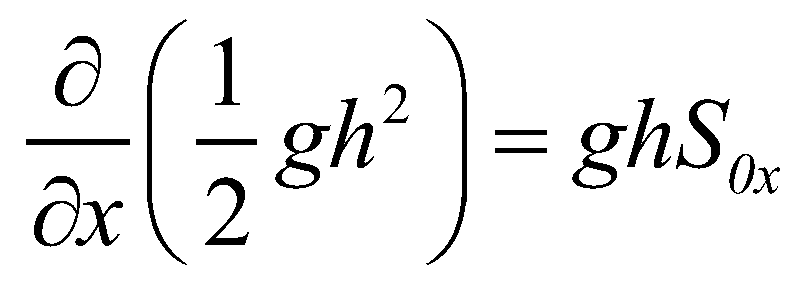
(24)
If a numerical scheme can maintain this stationary state, the scheme is called a well-balanced scheme (Greenberg & Leroux 1996), and also it is said to satisfy the conservation property (or C-property) (Bermudez & Vazquez 1994).
As to the VDSWEs, the momentum equation changes into:
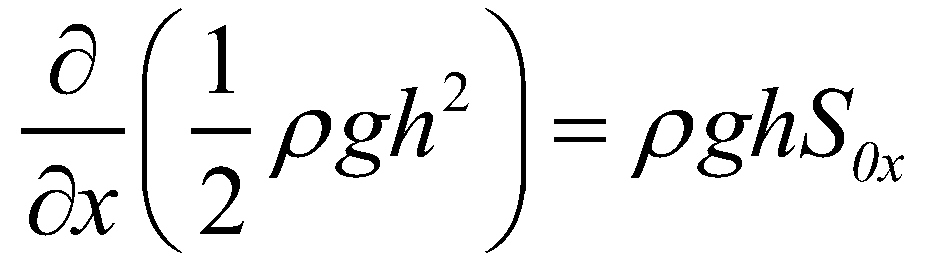
(25)
It is obvious that the definition of a well-balanced scheme or the conservative property can be extended to the VDSWEs, if a numerical scheme can maintain Equation (25). Rearranging Equation (25) into a similar form as Equation (24):
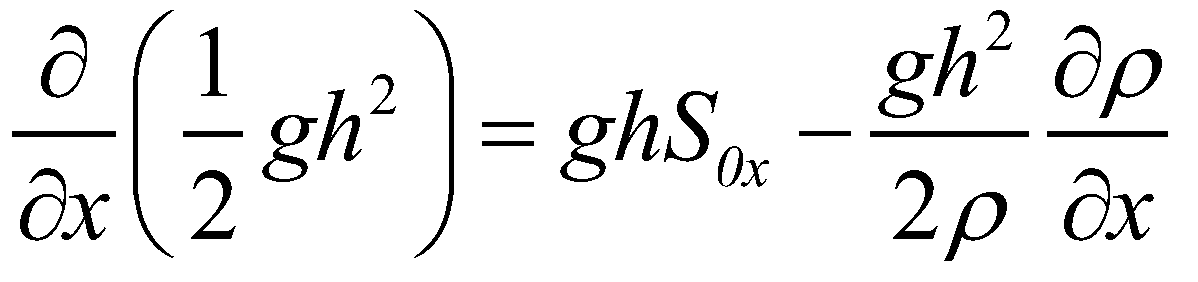
(26)
Since the density gradient term on the right hand side comes from the advection term of Equation (25), the term bears an upwind characteristics. It is difficult to maintain the conservative property of a numerical scheme if this term is discretized by a central difference method.
To create a well-balanced scheme, the hydrostatic reconstruction approach (Audusse
et al. 2004) for the SWEs is incorporated into the proposed model. According to the approach, the bed elevation at the cell interface (
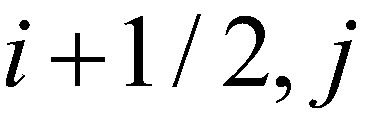
) between the cell (
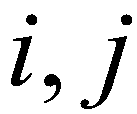
) and the cell (
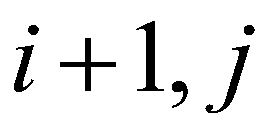
) is evaluated by
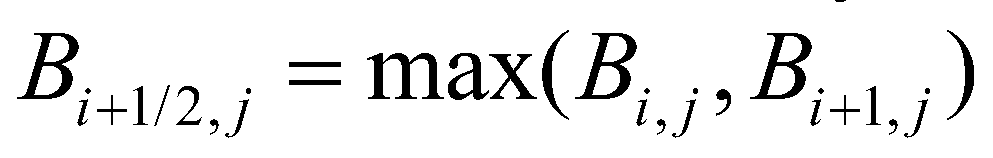
(27)
where
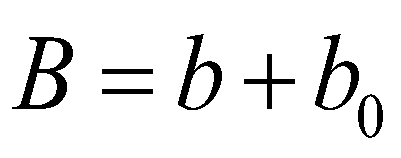
is the bed elevation; subscript
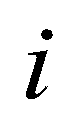
and
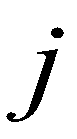
are the cell indices in
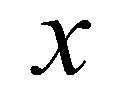
and
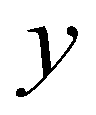
directions; subscript
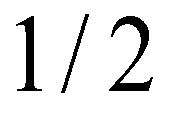
represents the cell boundary. Then, flow depths at the left and right sides of a cell boundary are reconstructed as:
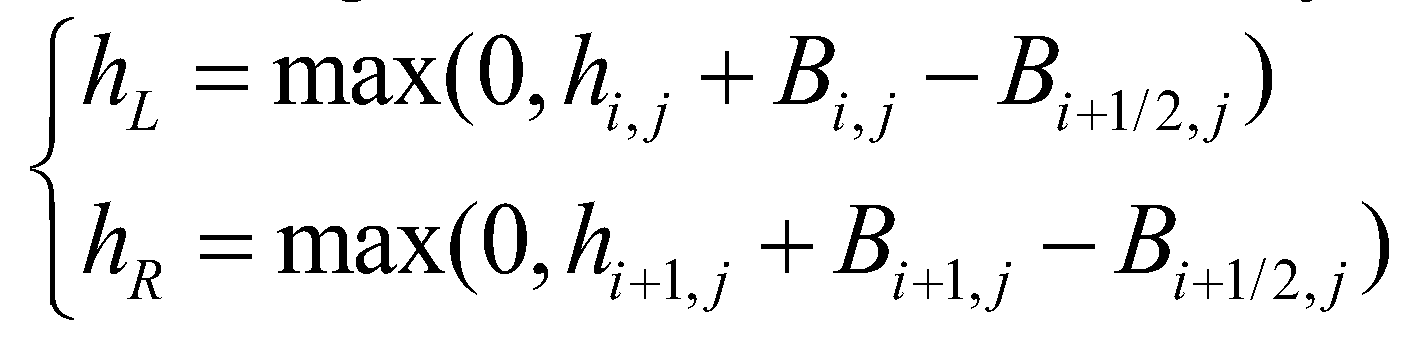
(28)
The reconstructed conservative variables at the cell boundary equal to:
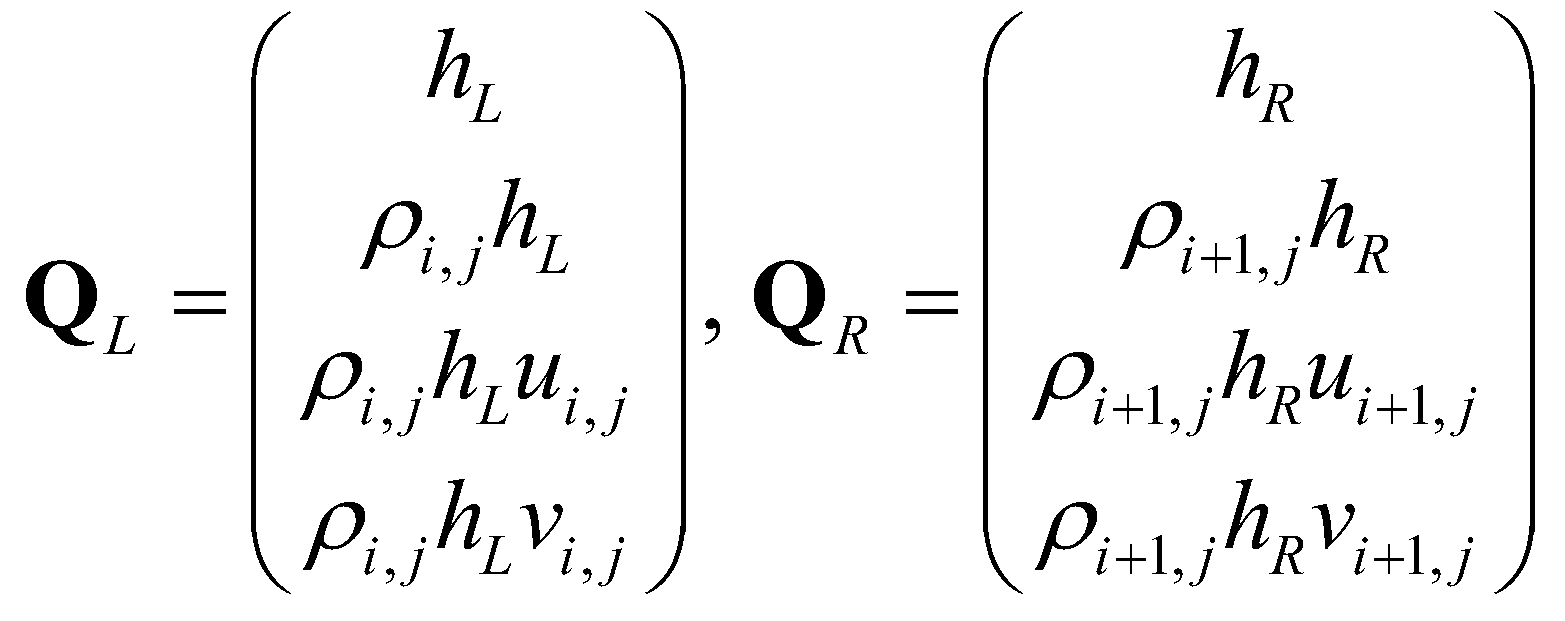
(29)
Accordingly, the bed slope term at the cell center is discretized as:
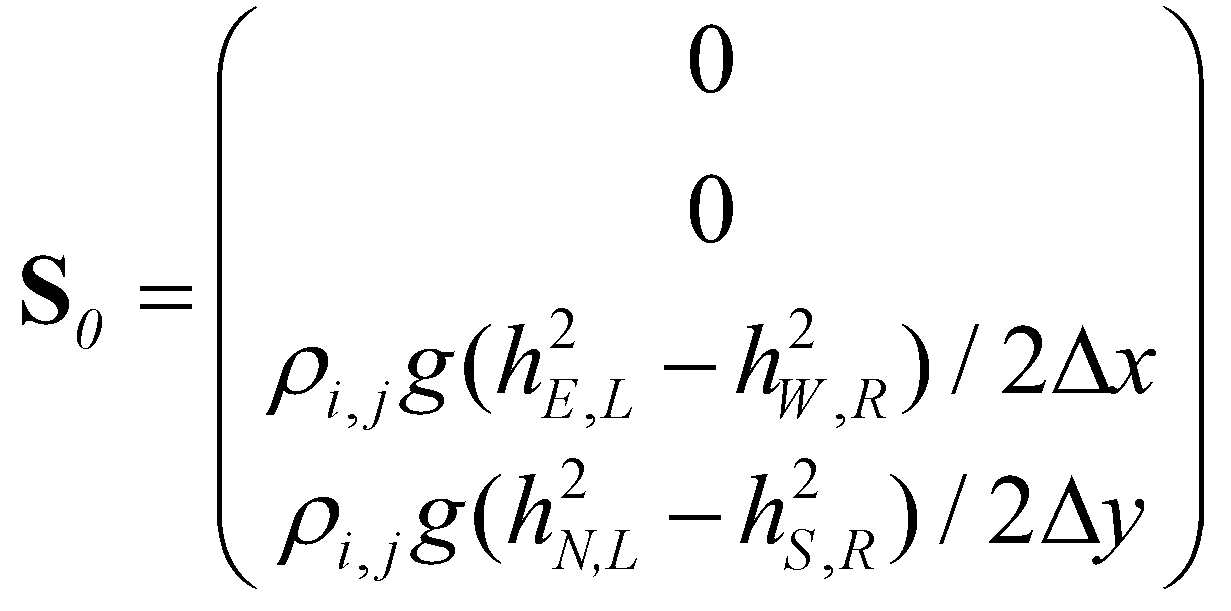
(30)
where subscript E, W, N, and S represent the east, west, north, and south sides of a cell.
To prove the well-balanced property of the scheme, the numerical discretization to a stationary flow is presented. For a flow in hydrostatic equilibrium state, the wave speeds are:
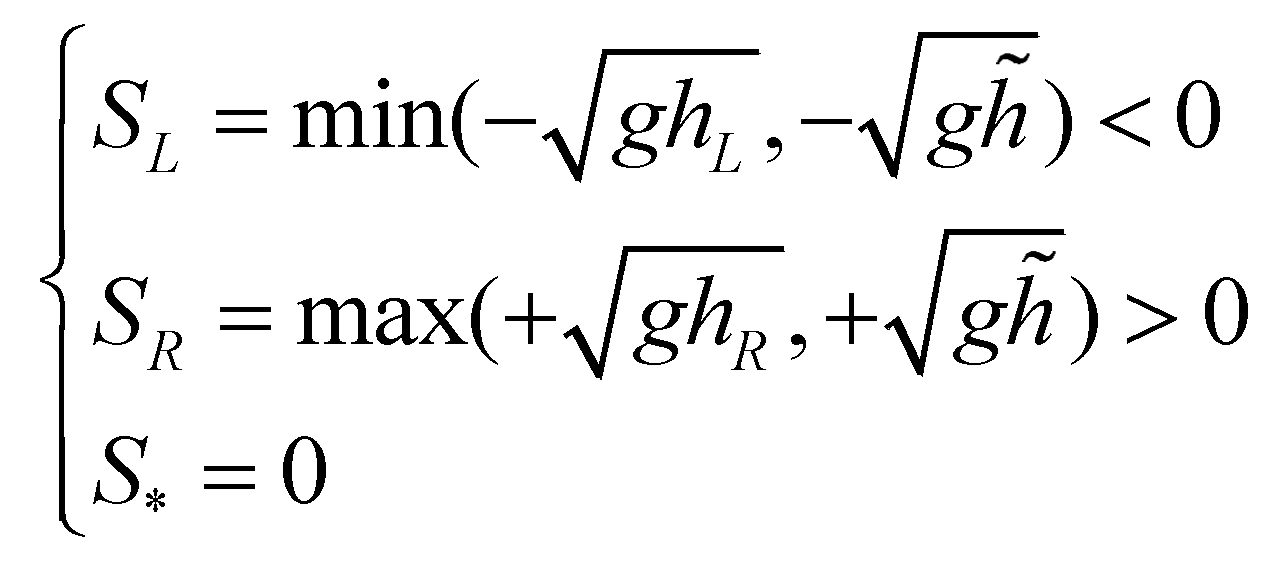
(31)
For the cell i, the left-hand side (LHS) of Equation (25) is discretized as:
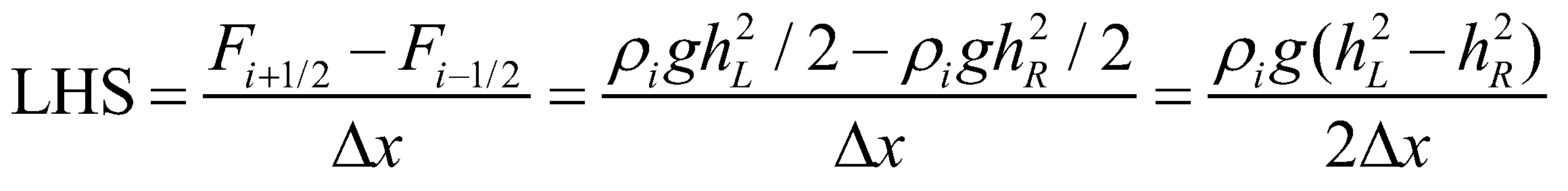
(32)
while the right-hand side (RHS) of Equation (25) equals:
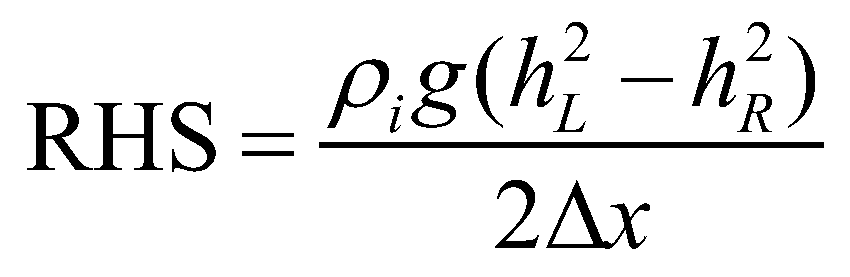
(33)
Since the left hand side is exactly equal to the right hand side, the proposed numerical scheme is a well-balanced scheme.
3. Results
The numerical method was tested by using two cases: one is a synthetic case of standing contact discontinuity, and the other is dam break flow with sediment concentration gradient.
3.1. Standing Contact-Discontinuity
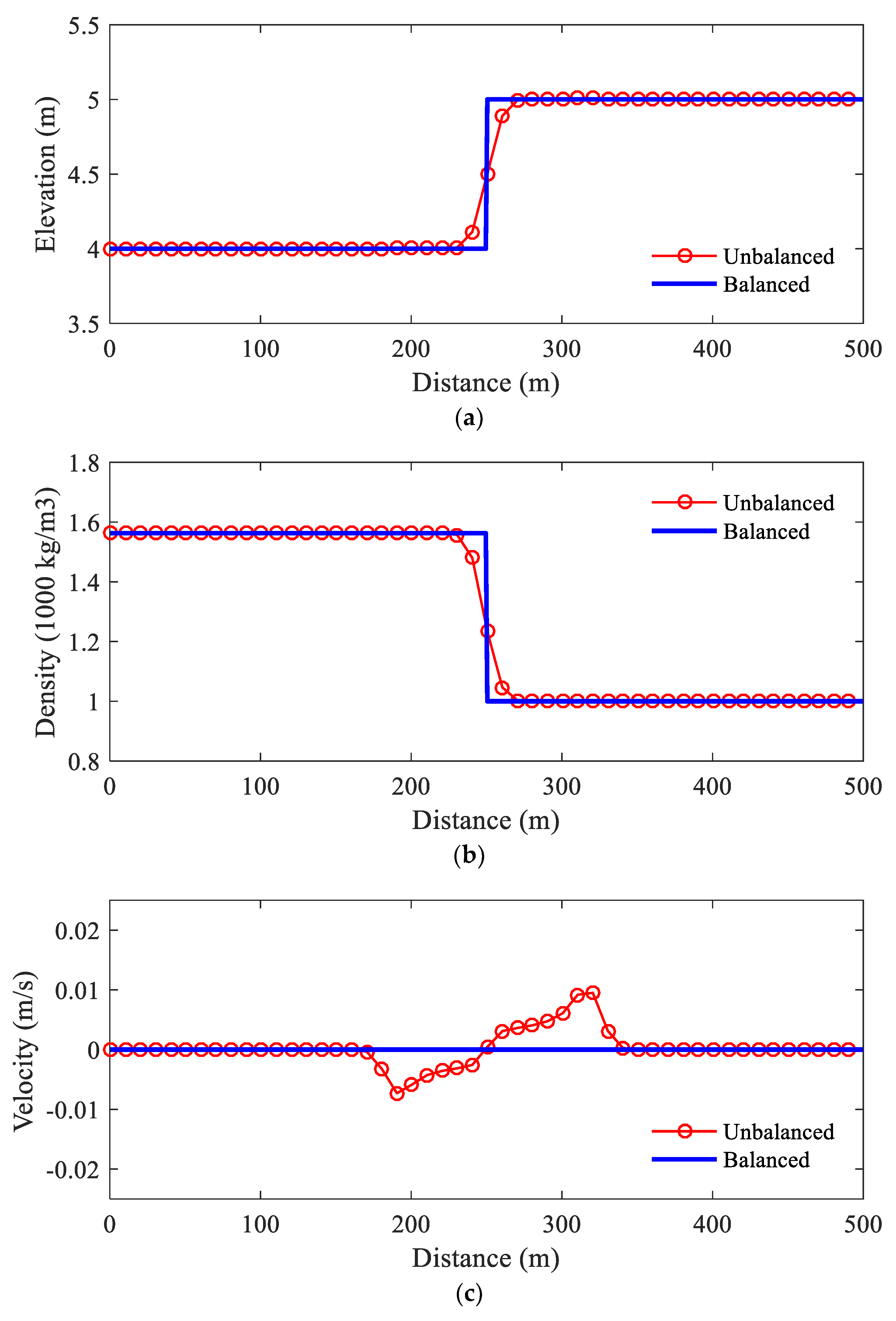
The aim of this synthetic case is to demonstrate the well-balanced property of the model. The case is proposed by Cozzolino et al. (2013): assuming a stationary fluid in a flume (L = 500 m) with a flat bed and both sides of the flume are solid walls, the initial conditions is given as:
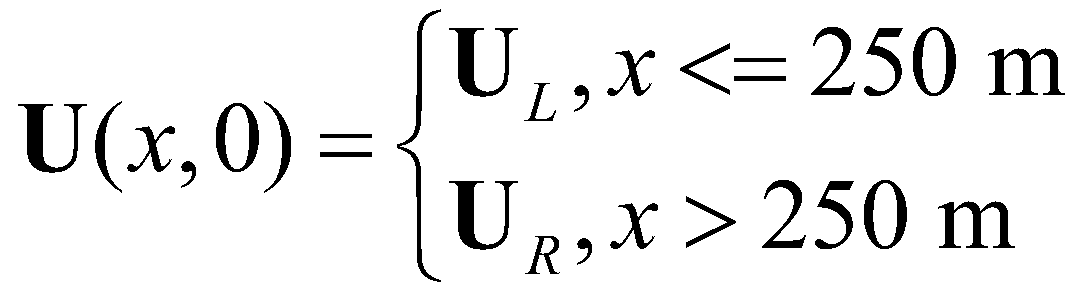
(34)
with:
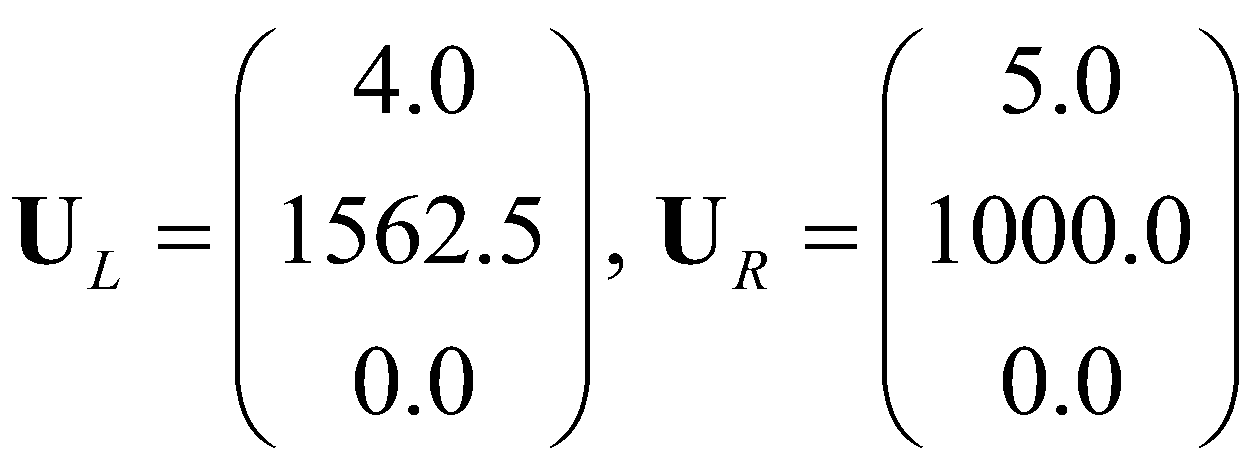
(35)
For the given initial condition, the hydrostatic pressure is constant through the flume. The discontinuity at x0 = 250 m is a standing contact-discontinuity and the corresponding solution is of fluid at stationary state.
The numerical simulation is carried out over a Cartesian mesh with Δx =1 m. For the simulation, the time step is Δt = 0.02 s and the simulation time is t
max =10 s. The simulation results, including surface profile, density profile, and velocity profile, are shown in
Figure 1. The profiles of the results are identical to the stationary solution of this test. Therefore, the well-balance property of the numerical model is confirmed by this test case.
Besides, the results of an unbalanced scheme (Cao
et al. 2004) are also plotted in
Figure 1. It is apparent that there are two oscillations propagate toward the upstream and downstream ends of the flume and the unbalanced scheme cannot keep the stationary state solution. These comparisons demonstrate the advantage of a well-balanced scheme over an unbalanced scheme: a well-balanced scheme can maintain the exact equilibrium between the hydrostatic pressure term and the bed slope term and there are no oscillations in the solution of a well-balanced scheme.
3.2. Case 1: One-dimensional Dam-break Flow over Mobile Bed
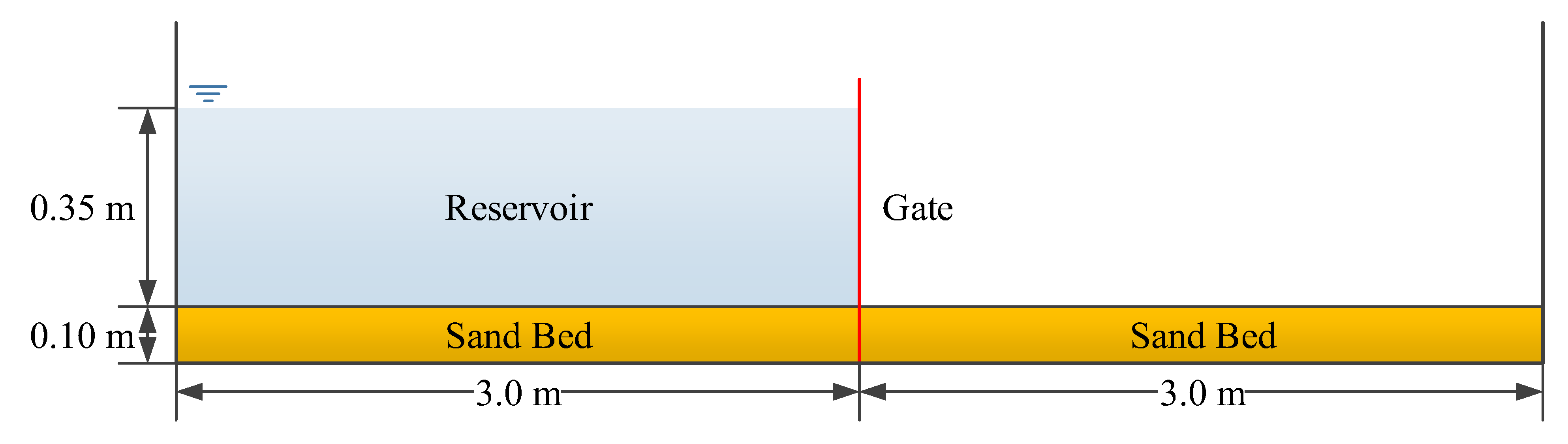
In this test case, the model is applied to a one-dimensional laboratory experiment (Spinewine & Zech 2007). The objective of this experiment is to investigate the erosional behavior of dam-break flow over mobile bed. The setup of the experiment is shown in
Figure 2. The flume is 6 m long, 0.25 m wide, and 0.7 m high. The flume is equipped with a fast downward-moving gate, which is used to simulate idealized dam-break events. The experiment uses a flat, loose granular sediment bed with following parameters: the density of sediment particle, p
s = 2683 kg/m
3; the median diameter of sand, d
50 = 1.82 mm; the settling velocity,
0 = 0.16 m/s; and the porosity, = 0.47. The Manning’s roughness coefficient was estimated to be n = 0.0165 s/m
1/3.
Initially, the reservoir at the upstream is filled with water to a depth, h = 0.35 m. The downstream of the flume is dry bed. The mobile bed layer consists of fully saturated sands with an initial thickness, b = 0.1 m. As to the boundary conditions, the upstream boundary condition is wall boundary, and the transmissive boundary condition is applied to the downstream boundary. At time t = 0 s, the gate was suddenly removed to create a dam-break flow. During the experiment, the dam-break flow is recorded by several high speed digital cameras. The total experimental time, tmax = 1.5 s.
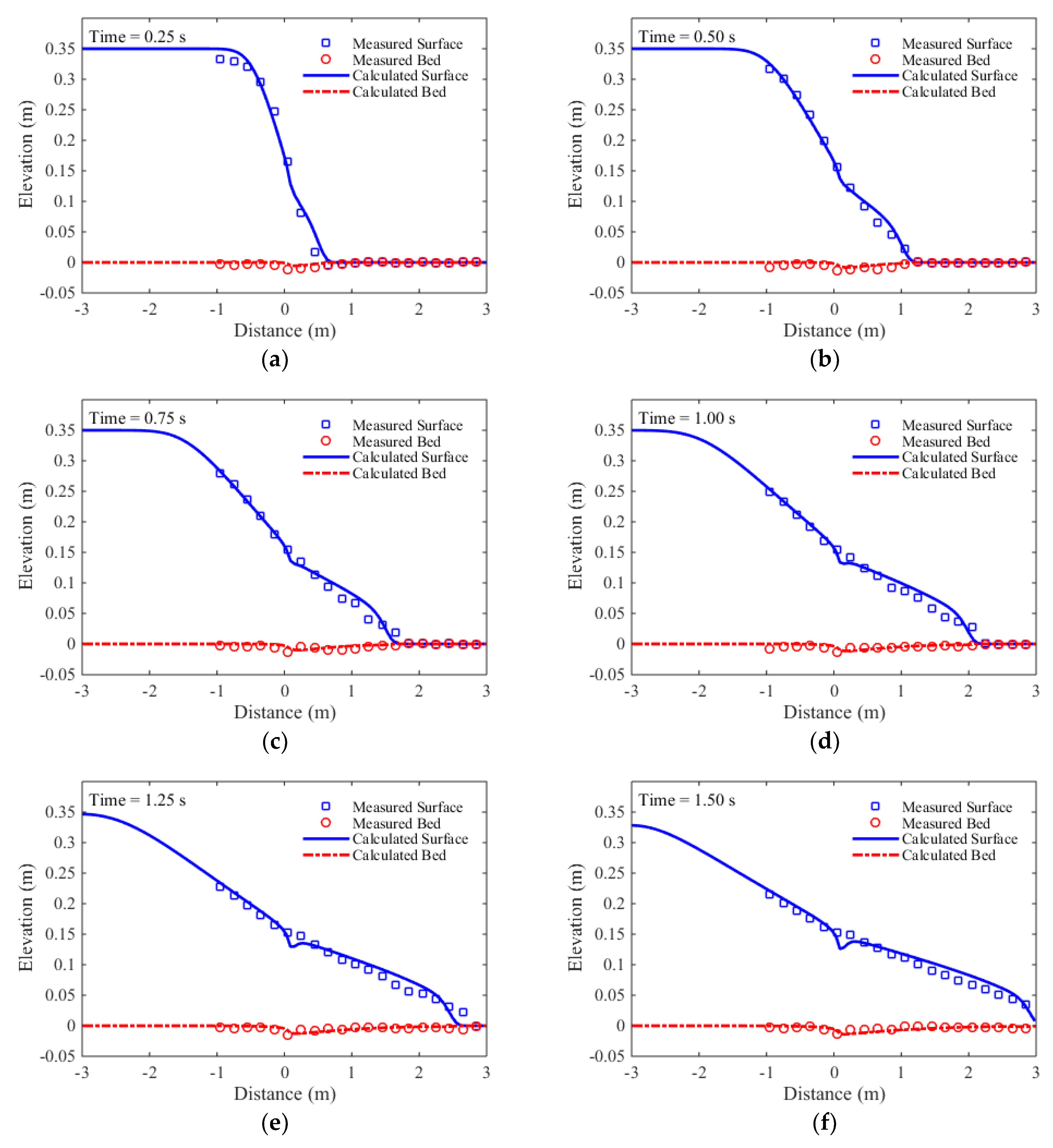
The numerical simulation is carried out with the following parameters: Δx = 0.06 m and Δt = 0.001 s. In
Figure 3, the calculation results are compared with the measured data at T= 0.25 s, 0.50 s, 0.75s, 1.00 s, 1.25 s, and 1.50 s. An overall comparison shows reasonably well agreements between the calculated results and the measurements. Not only the propagation of the shock-front is accurately predicted, but also the temporal evolution of free surface agrees well with the interface tracking results of the digital cameras. Although the bed changes are not significant in the experiment, the magnitudes of the simulated bed changes are consistent with the measurements.
To quantitatively evaluate the accuracy of the developed model, the RMSEs and NRMSEs of the simulated results are calculated and shown in
Table 1. As shown in
Table 1, the RMSEs of the simulated surface profiles are around 0.01 m, while the RMSEs of the simulated bed profiles are less than 0.05 m. However, the NRMSEs of the simulated bed profiles are much greater than the simulated surface profiles. This reveals that the simulated surface profiles are more accurate than the simulated bed profiles.
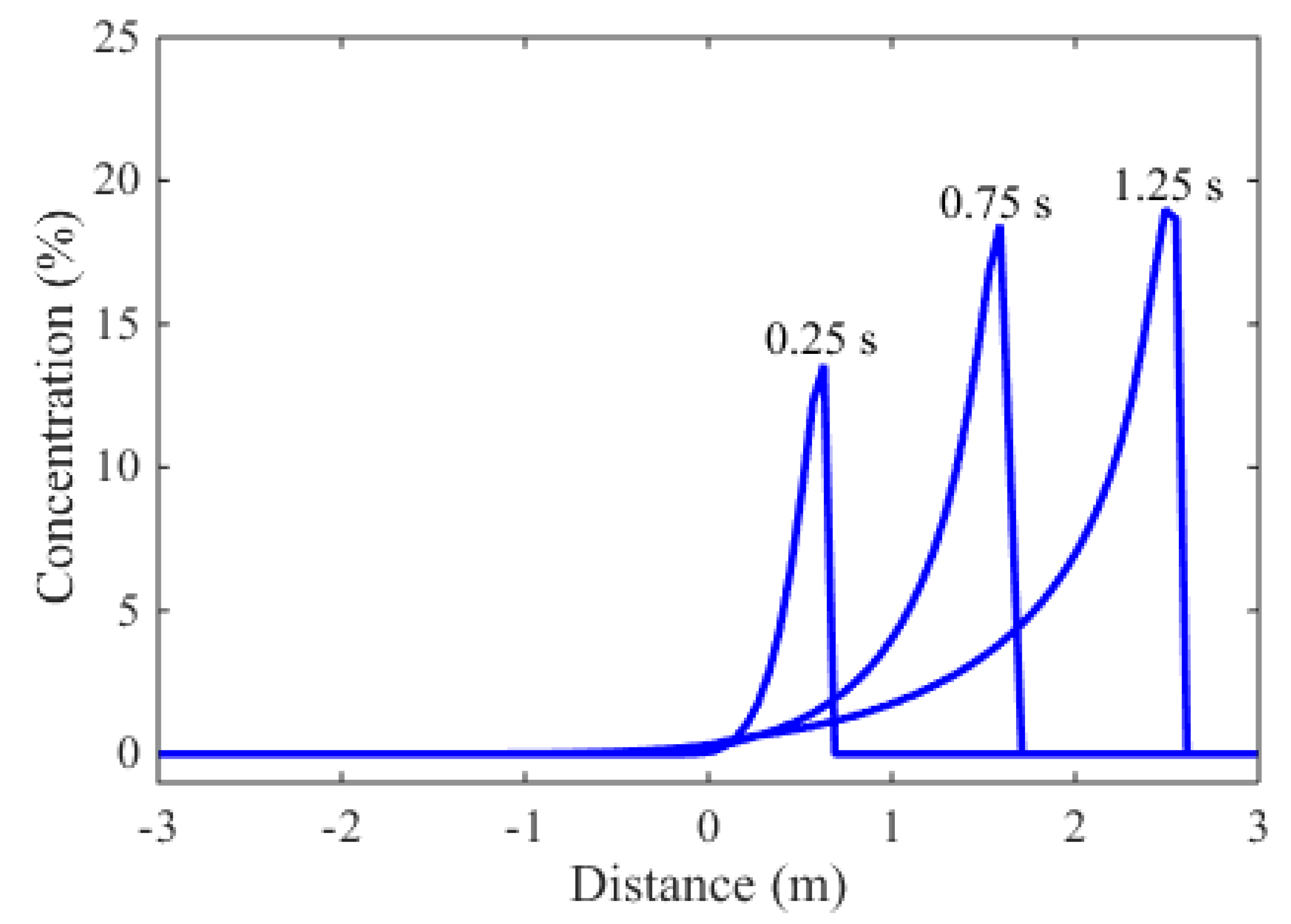
The simulated concentration profiles at different time instants are plotted in
Figure 4. The existence of high concentration at the shock front (about 20%) justifies the significance of the variable density effect. This is also a challenge to the numerical modeling of sediment transport because the concentration profile is discontinuous at the shock wave front.
Figure 4 demonstrated that the proposed model is able to capture this concentration discontinuity without introducing spurious oscillations.
3.3. Case 2: Two-dimensional dam-break flow over mobile bed
This laboratory experiment was conducted at the Hydraulics Unit of the Mechanical and Civil Engineering Laboratory, Universite catholique de Louvain, Belgium (Soares-Frazao
et al. 2012). The experiment aims to provide a benchmark test case to validate numerical models for the simulation of dam-break flow over mobile bed (Wu
et al. 2011; Canelas et al. 2013; Li
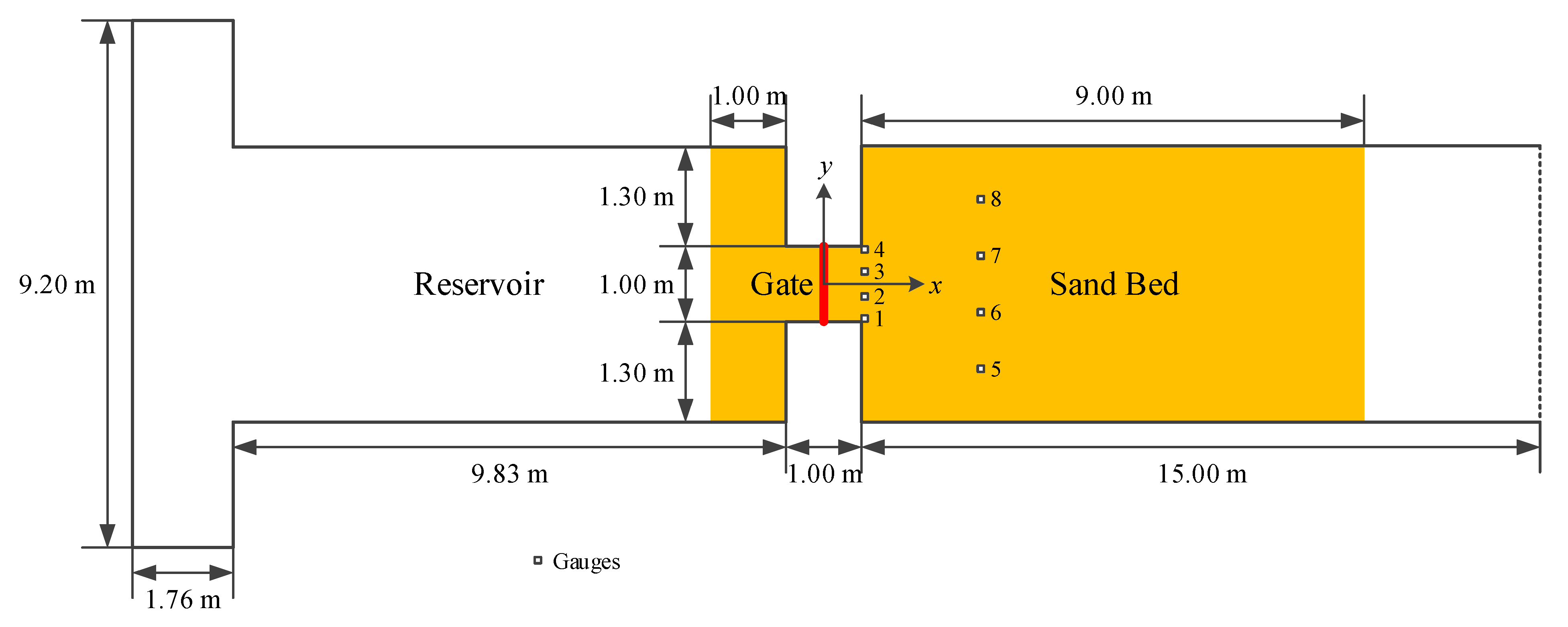
et al. 2013). The experiment is a dam-break flow from an upstream reservoir flowing into a flume over a mobile bed made of uniform coarse particles. A schematic view of the flume is shown in
Figure 5. The length of the flume is 36 m; the width of the flume is 3.6 m. The breached dam is located in a narrow reach (1 m long and 1 m wide) between two impervious blocks. The upstream of the flume was a reservoir, whereas the downstream is a flooded channel. The origin of the coordinates is situated at the center of the dam. The Manning’s coefficient for the sandy bed is given as .
The bottom of the flume was covered with a layer of saturated sand, which expanded from 1 m upstream of the dam to 9 m downstream. The thickness of mobile sand layer is 8.5 cm. The related properties of the sand layer are: the mean diameter of the particles, d50 = 1.61 mm; the porosity of bed material, ε = 0.42; the density, ps = 2630 kg/m3; and the critical Shields parameter, = 0.047 . The Manning’s roughness coefficient for this sandy channel is measured as n = 0.0165 s/m1/3.
The dam-break flow was triggered by rapidly lifting the gate separating the reservoir and the channel. The initial water level in the reservoir is 0.47 m, while the downstream channel is initially dry (h=0 m). The wall boundary condition is applied to the upstream end of the reservoir, and similarly, the transmissive boundary condition is imposed at the downstream outlet of the flume. The experiment lasted for 20 s. During the experiment, eight sonic water level gauges were used to record water levels. The bed profiles were measured after the experiment along three longitudinal lines: y = 0.2 m, y = 0.7 m, and y = 1.45 m.
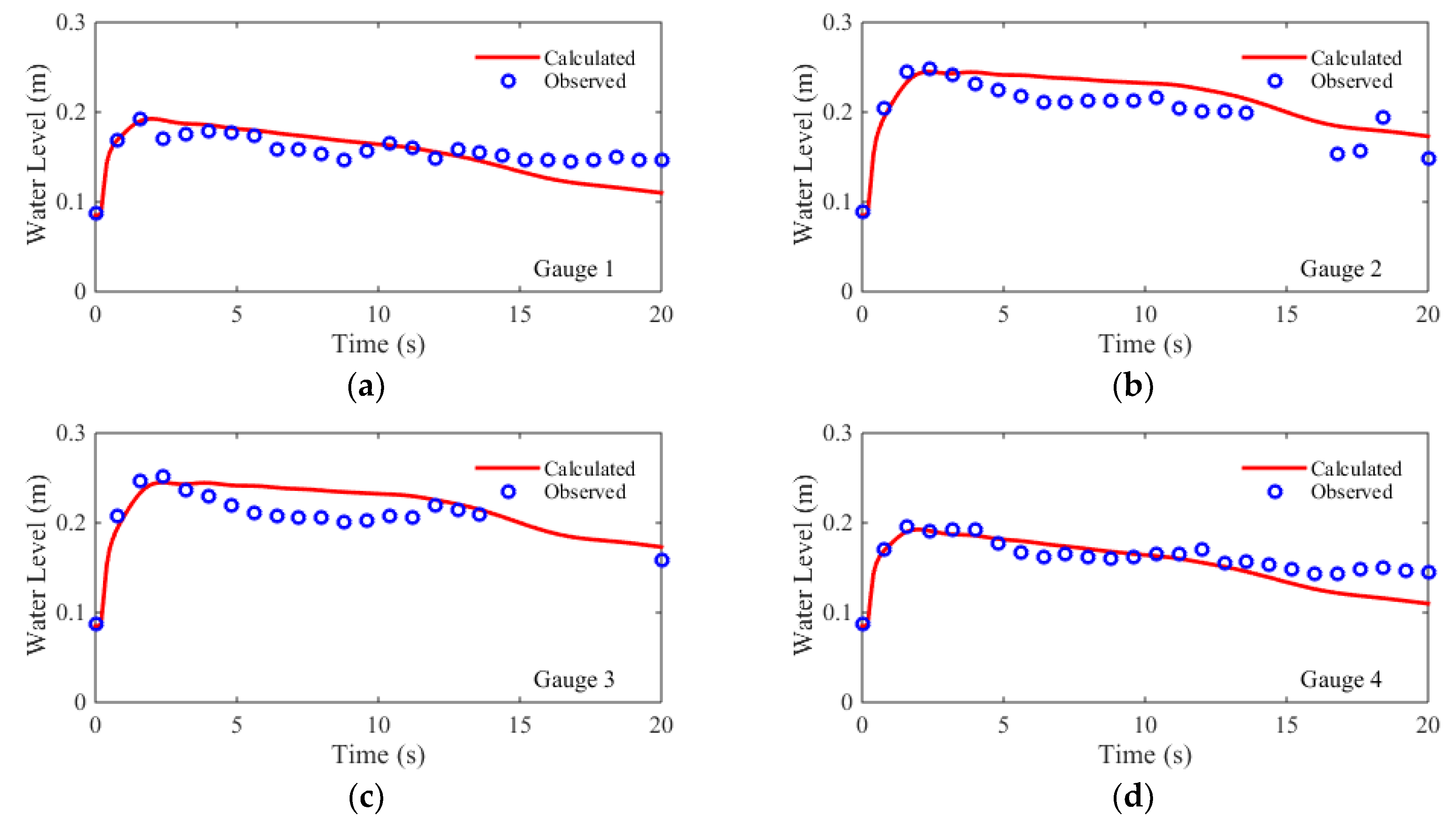
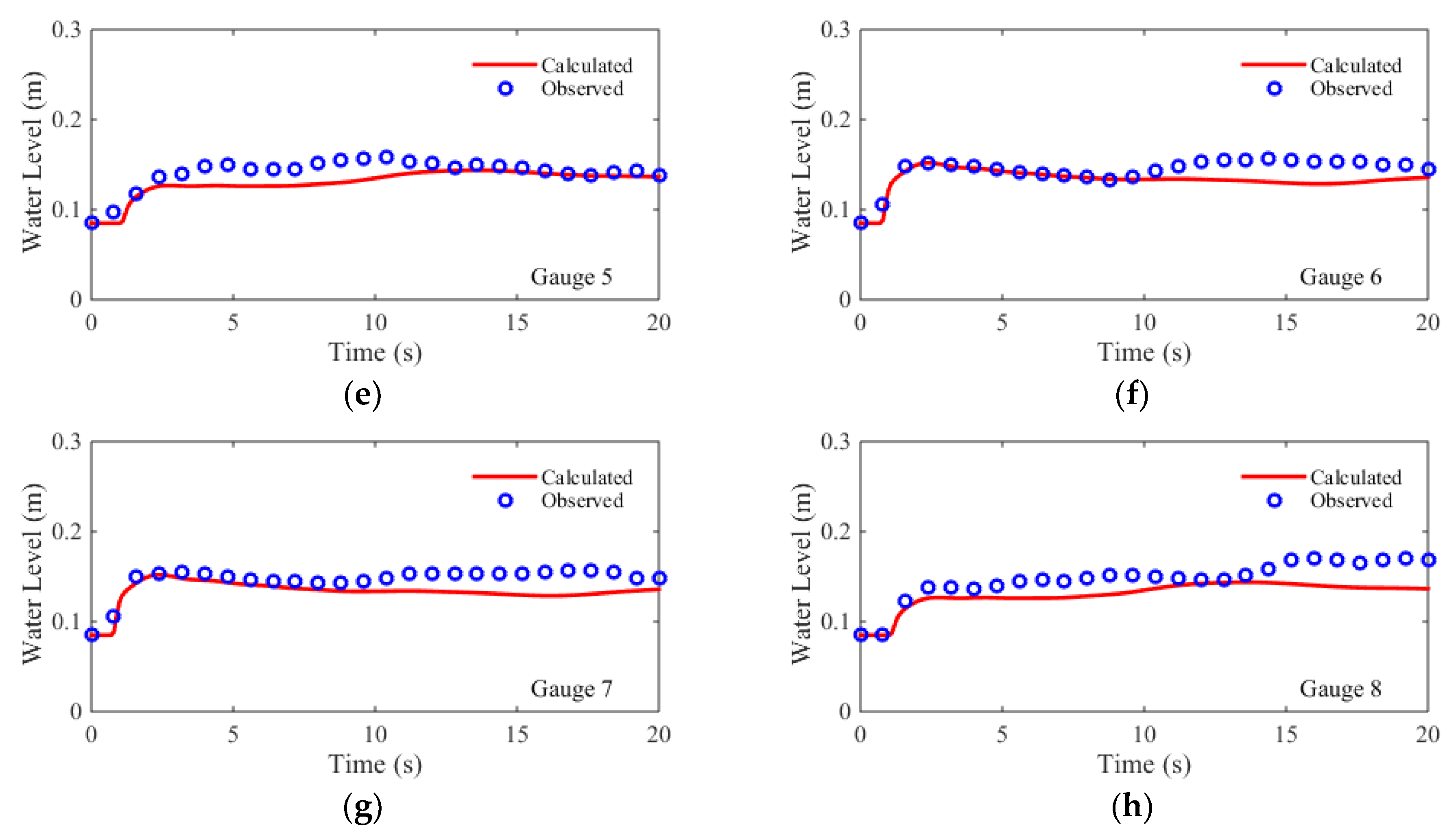
For the numerical simulation, the flume is discretized using a Cartesian mesh (Δx = Δy = 0.1 m), with a total of 10,602 rectangular cells. The time step is set to be Δt= 0.01 s. The comparisons of simulated and measured water level hydrographs at eight gauges are shown in
Figure 6. The quantitative evaluation indices, i.e., the RMSEs and the NRMSEs, are shown in
Table 2. The comparisons showed that, at all eight gauges, both the arrival times of the dam-break waves and the peak water levels are accurately predicted. At the early stage of experiment, the water levels at the gauges, G2 and G3, are overpredicted, while the water levels are underpredicted at the gauges, G5 and G8. At the late stage, the water levels are underpredicted at G1, G4, G6, G7, and G8. For the symmetric gauge pairs (G1/G4, G2/G3, G5/G8, and G6/G7), the simulated hydrographs are nearly symmetrical except for the results at G5 and G8 at the late stage. The RMSEs of the predicted water level hydrographs are between 0.015 m and 0.02 m, while the NRMSEs are between 12% and 22%. The NRMSE results of the upstream gauges (G1, G2, G3, and G4) are better than the downstream gauges (G5, G6, G7, and G8). A possible explanation is that, as the dam-break flow propagating from upstream to downstream, three dimensional flow effects becomes more dominant.
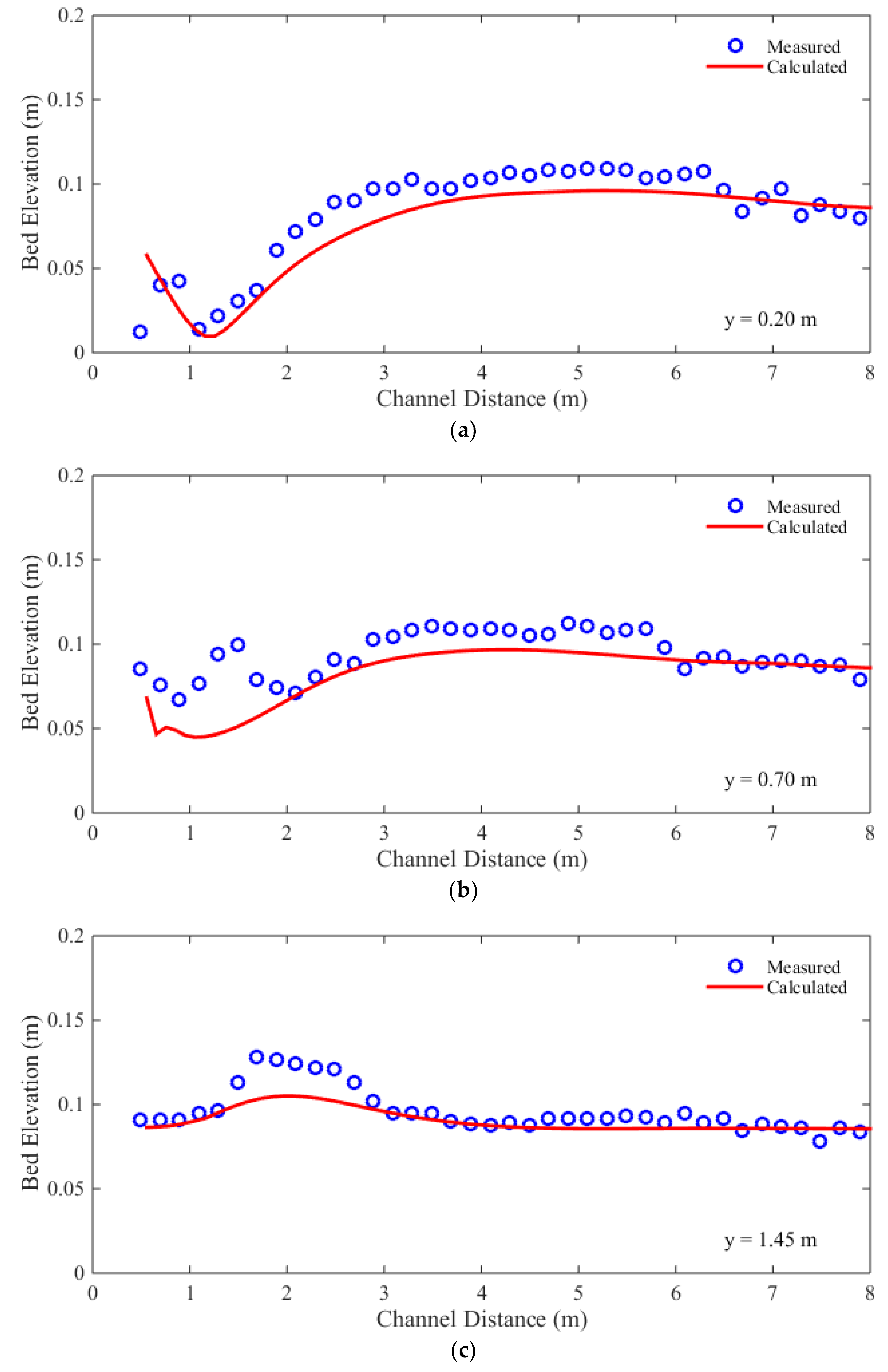
The comparisons between the calculated and measured bed profiles along the longitudinal lines at the end of the experiment are shown in
Figure 7. The RMSEs and the NRMSEs are shown in
Table 3. The magnitudes of RMSEs are between 0.009 m and 0.017 m, while the NRMSEs’ are between 14% and 33%. The simulated mean bed profiles matched the measurements at all three measured longitudinal lines. Although the calculated and the measured bed profiles have the same trends, the calculated bed profiles are smoother than the measured bed profiles. This implies that the developed model cannot capture the local perturbations generated by 3D flow effects (Canelas
et al. 2013). These perturbations are caused by the flow in the vertical direction, and cannot be captured by a 2D depth-averaged model. On the other hand, the energy dissipations caused by these perturbations can be calculated by turbulence modeling method (Yu & Duan 2012). It thus follows that further researches are necessary for incorporating turbulence model into the proposed model.
3.4. Case 3: 1996 Lake Ha! Ha! catastrophic flood event
In this case, the performance of the proposed model is tested against a field event: the 1996 Lake Ha! Ha! catastrophic flood event, in the Saguenay region of Quebec, Canada (
Figure 8). A detailed description of this flood event and extensively documented data are provided by Capart
et al. (2007). Brooks and Lawrence (1999) gave a detailed geomorphic description about the event. Ferreira
et al. (2009) and El Kadi Abderrezzak and Paquier (2009) carried out a one-dimensional numerical simulation of this event.
From July 18 to 21, 1996, an extreme precipitation event affected the Saguenay region of Quebec, Canada. At the Ha! Ha! Lake, an earthfill dyke was being overtopped by up to 0.26 m of water, and a new outlet channel formed. Overall, of water was estimated to have drained from the lake. The failure of the dyke resulted in a peak discharge of 8 times the 100-year flood. The Ha! Ha! River was severely damaged by the resulting flood flow (Brooks & Lawrence 1999).
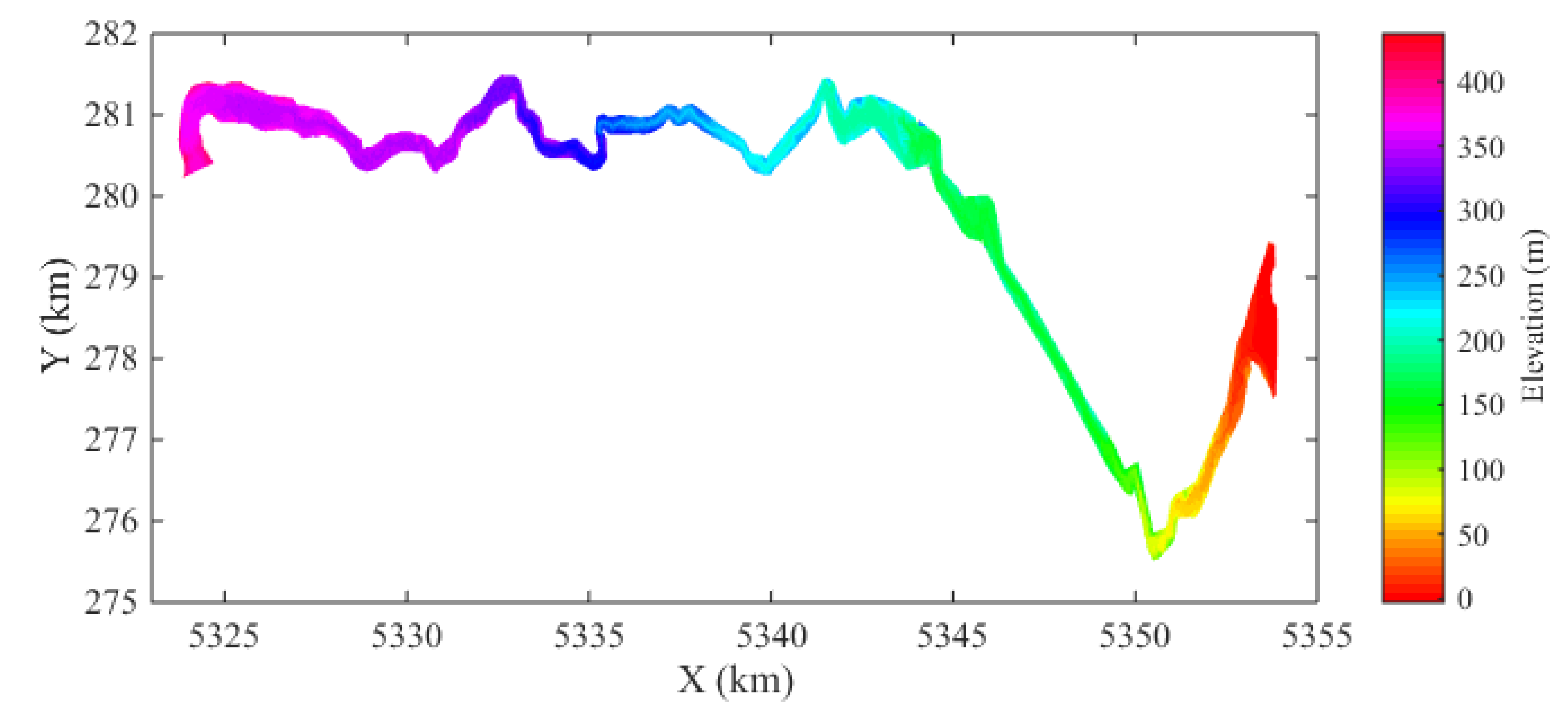
The numerical simulation started with the digital elevation model (DEM) of the Ha! Ha! River, which was surveyed in May 1994 (Capart et al. 2007). The spatial data is based on the Modified Transverse Mercator (MTM) projection, zone 7 coordinates (NAD83). The spatial ranges of the DEM data are: 275,000 m x 282,000 m on the east-west direction, and 5318000 mN y 5354000 mN. In addition to the DEM data, the geometry data of evenly spaced cross sections are also provided. These 363 cross sections spaced at 100 m interval, and are oriented approximately normal to the central line of the Ha! Ha! River. Each cross section is identified by its streamwise distance measured from the failed dyke. In spite of abundant data, it has to be pointed out that the average error of the preflood riverbed elevations is estimated to be about 2 m (El Kadi Abderrezzak & Paquier 2009).
Based on the field observation and photo interpretation, superficial materials exposed along the channel and floodplains are classified as noncohesive sediment (sand and gravel), cohesive sediment (glaciomarine or glaciodiamicton), or bedrock (Capart et al. 2007). Due to the lack of sufficient field data, the influence of cohesion on sediment transport was not considered in the numerical model. According to El Kadi Abderrezzak and Paquier (2009), the median diameter of bed material for the whole Ha! Ha! River is equal to 0.5 mm, the density of bed material is ps = 2650 kg/m and the porosity equals to 0.4. Besides, the influence of bedrock on the channel profile was studied in Capart et al. (2007), the bedrock constraint was also imposed in this simulation for which the outcrops of bedrocks or coarse glacial deposits are assumed to act as rigid, non-erodible beds.
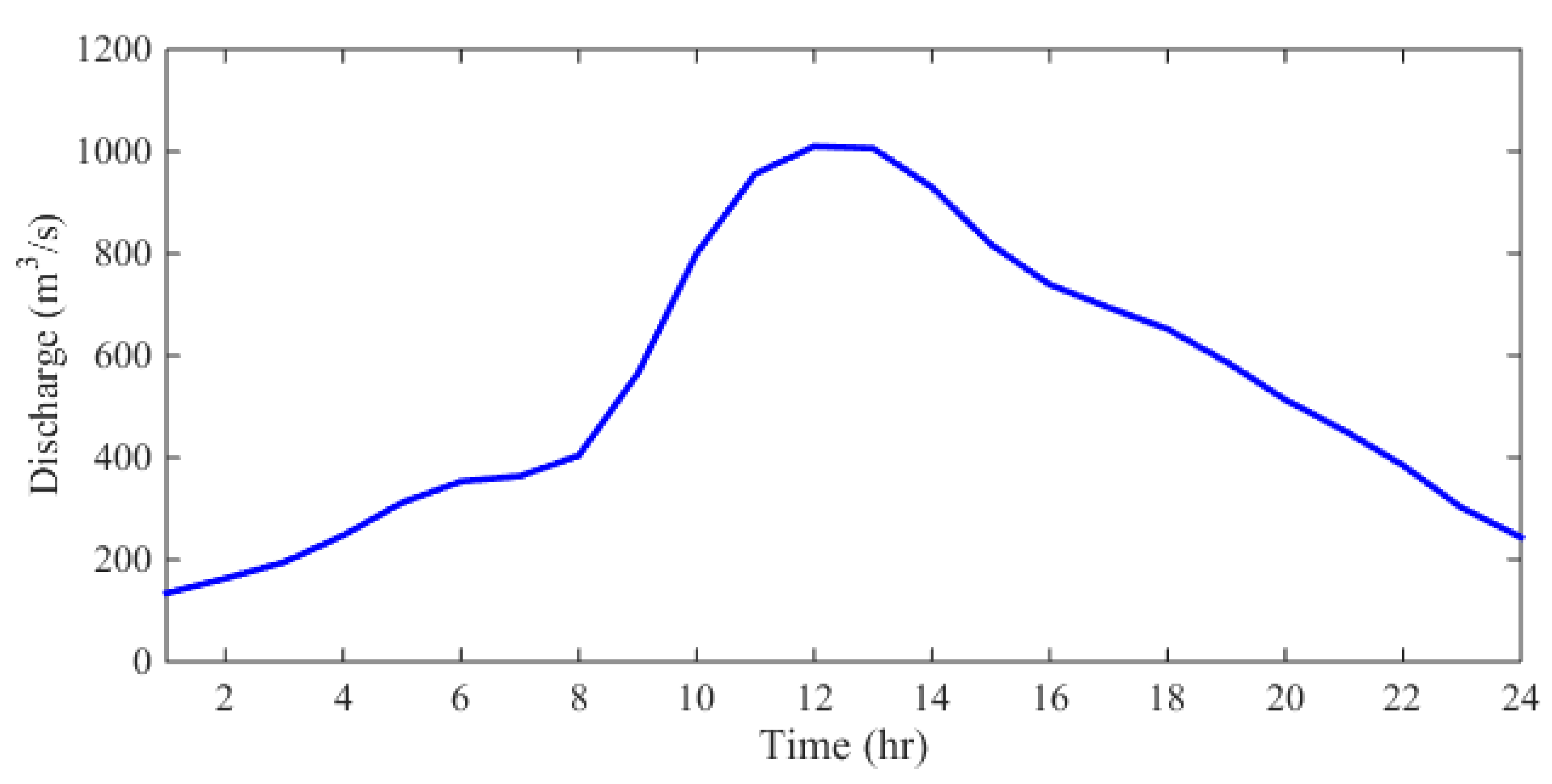
Initially, the Ha! Ha! River is assumed to be dry everywhere. The discharge hydrograph shown in
Figure 9 is used as the upstream inflow boundary condition, and the inflow is assumed to be clear water (El Kadi Abderrezzak & Paquier 2009). The downstream boundary at the Ha! Ha! Bay is set to satisfy the transmissive boundary condition. The overtopping occurred at 14:00 on July 19, 1996. The lake is estimated to be emptied in 18 hours. During the event, the water level of the lake dropped from 381 m to 370 m. The total simulation time is set to be 24 hours. For the numerical simulation, the river is discretized by a Cartesian mesh with Δx = Δy = 20m. The time step size is Δt = 0.5 s.
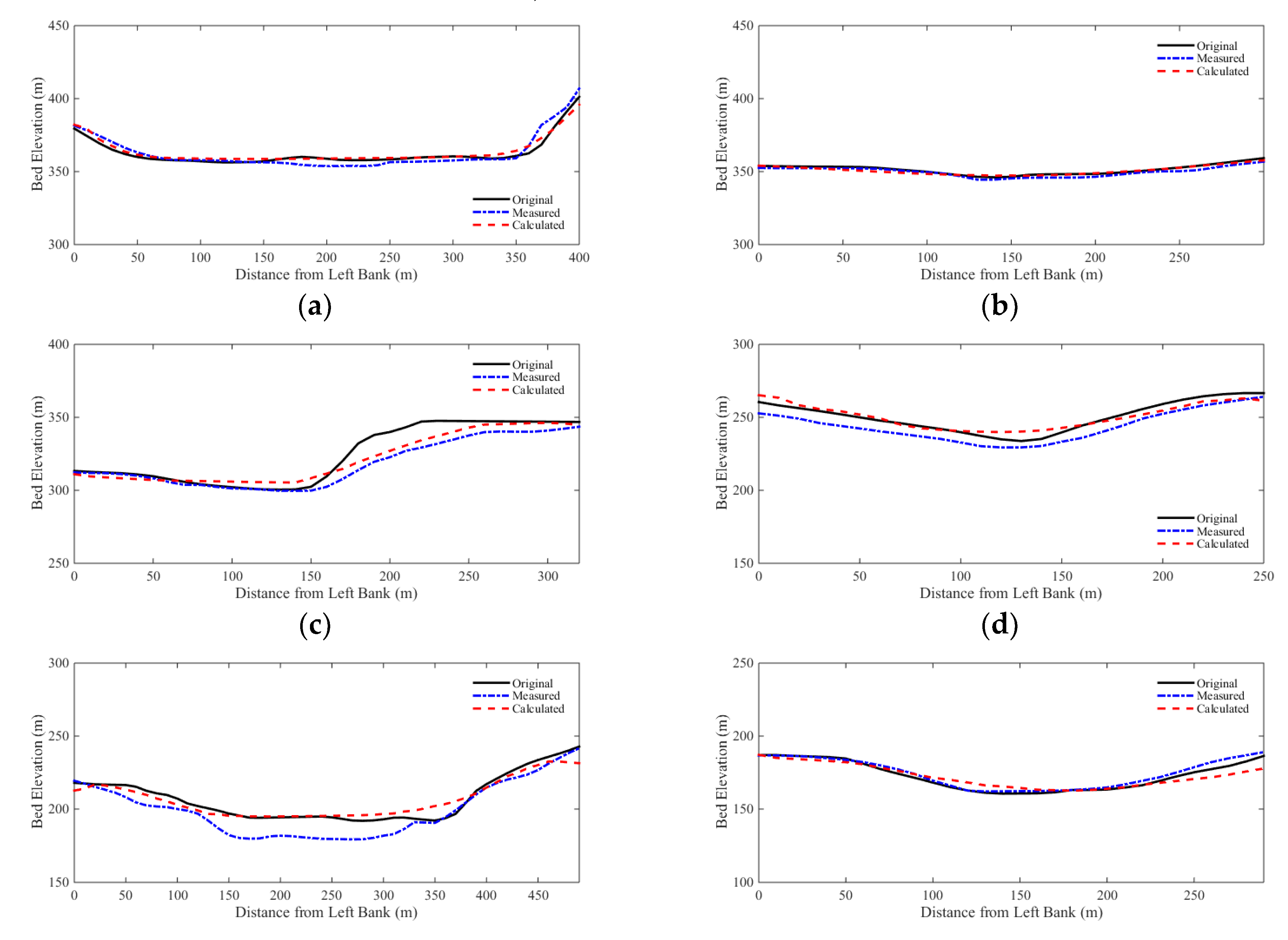
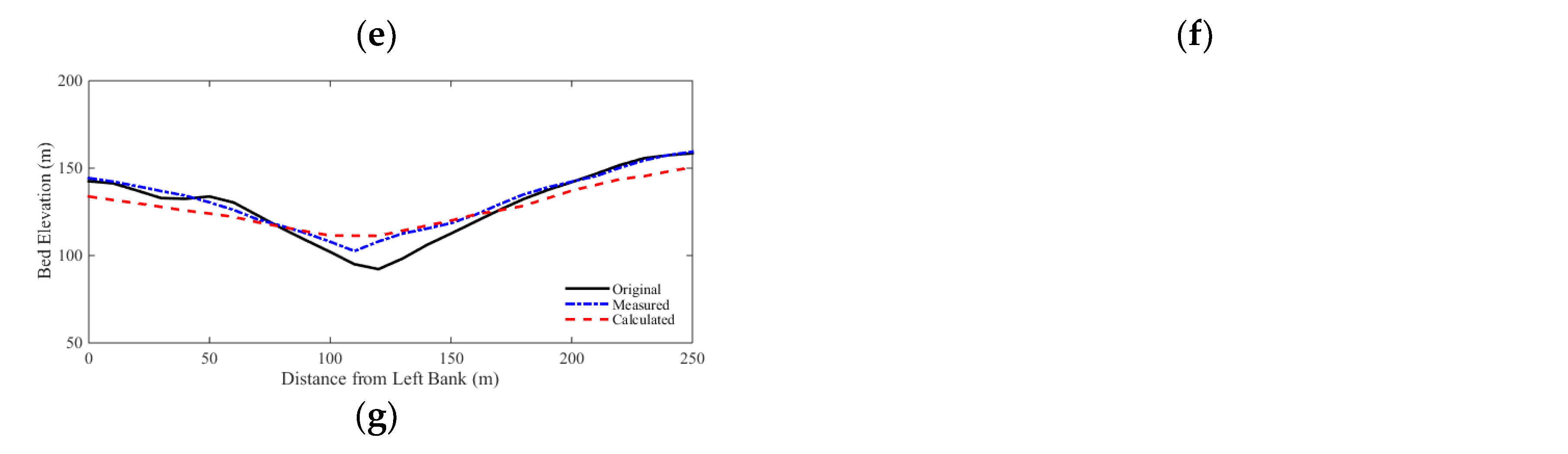
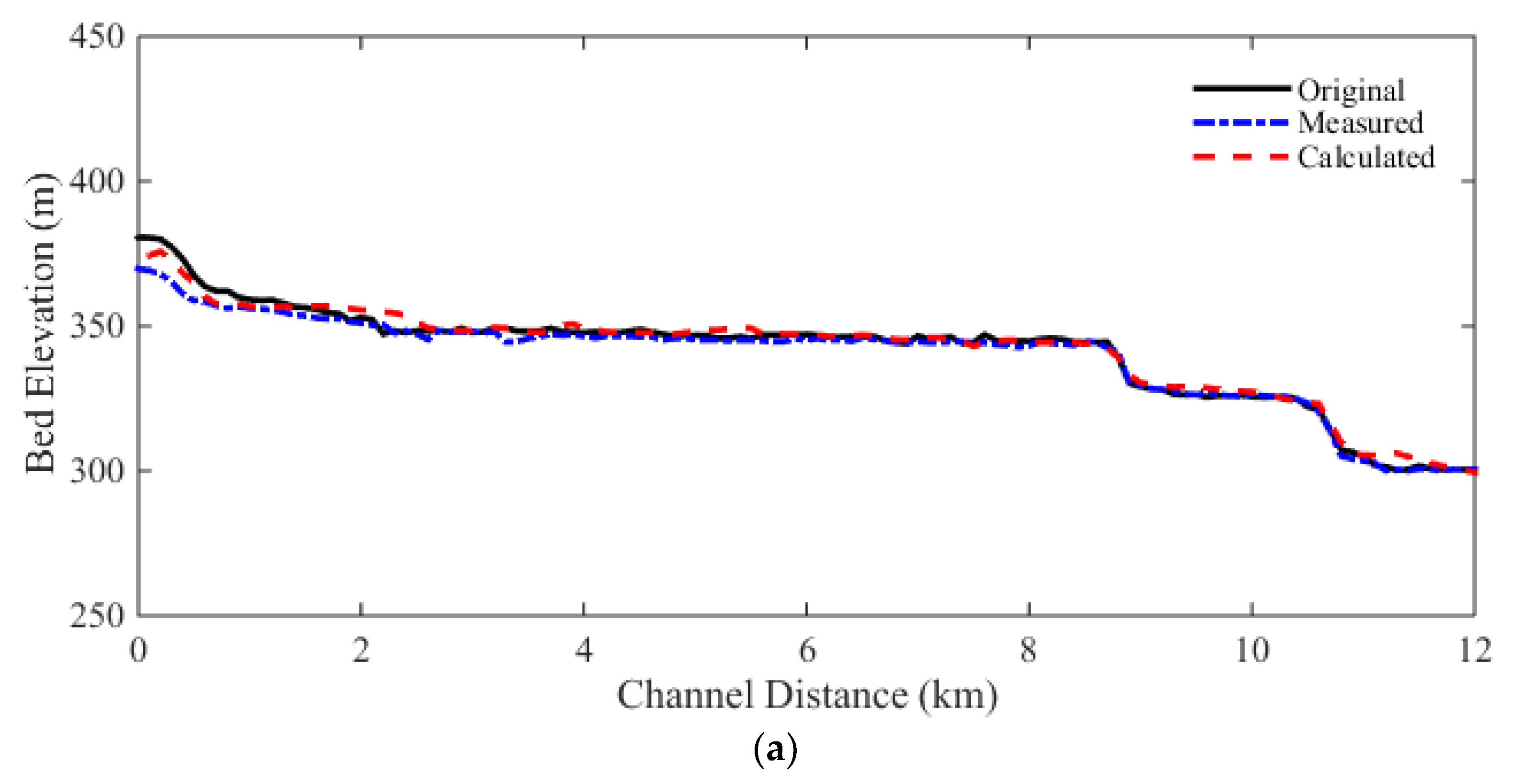
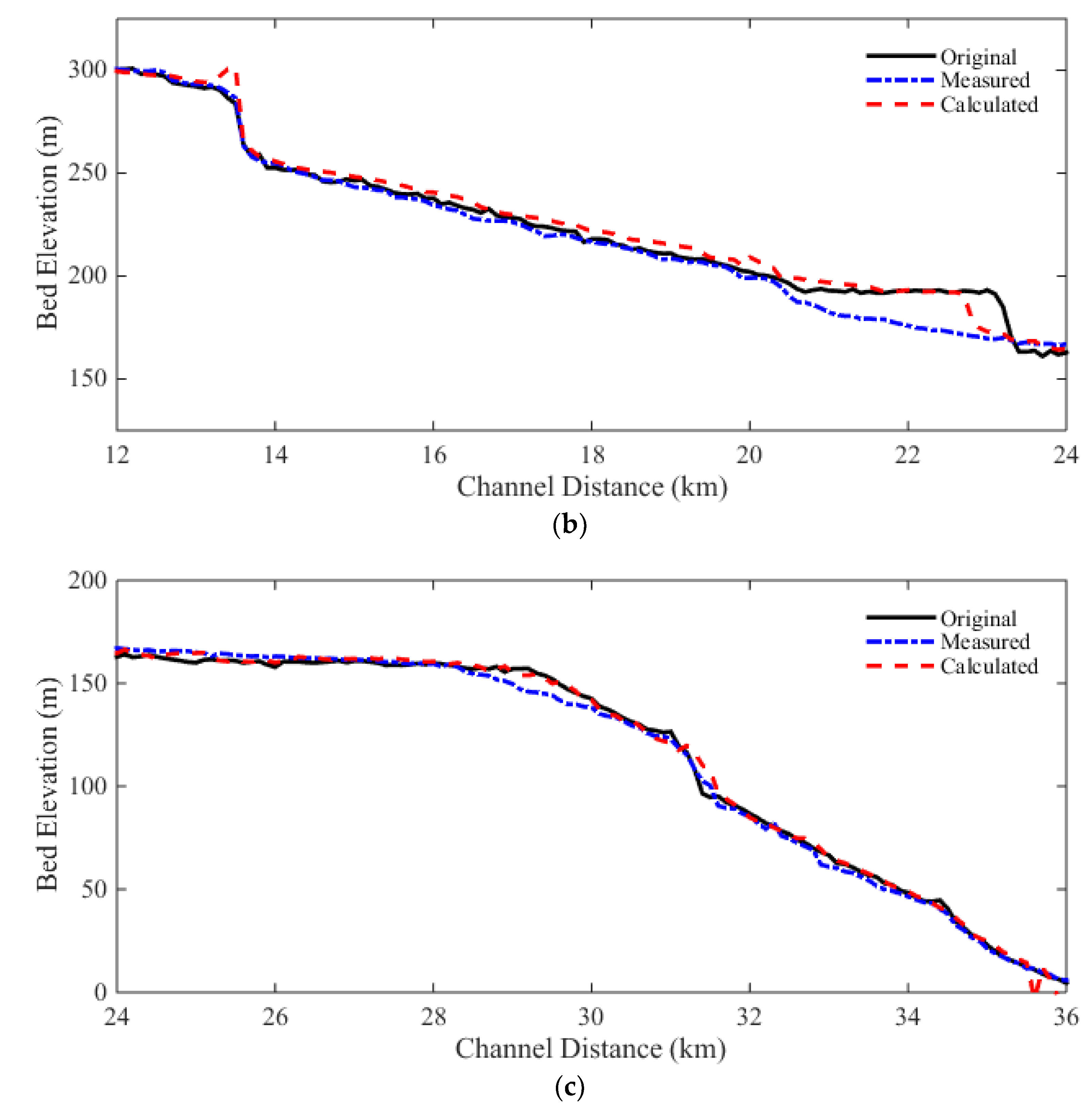
Comparisons of the selected cross sections along the river are shown in
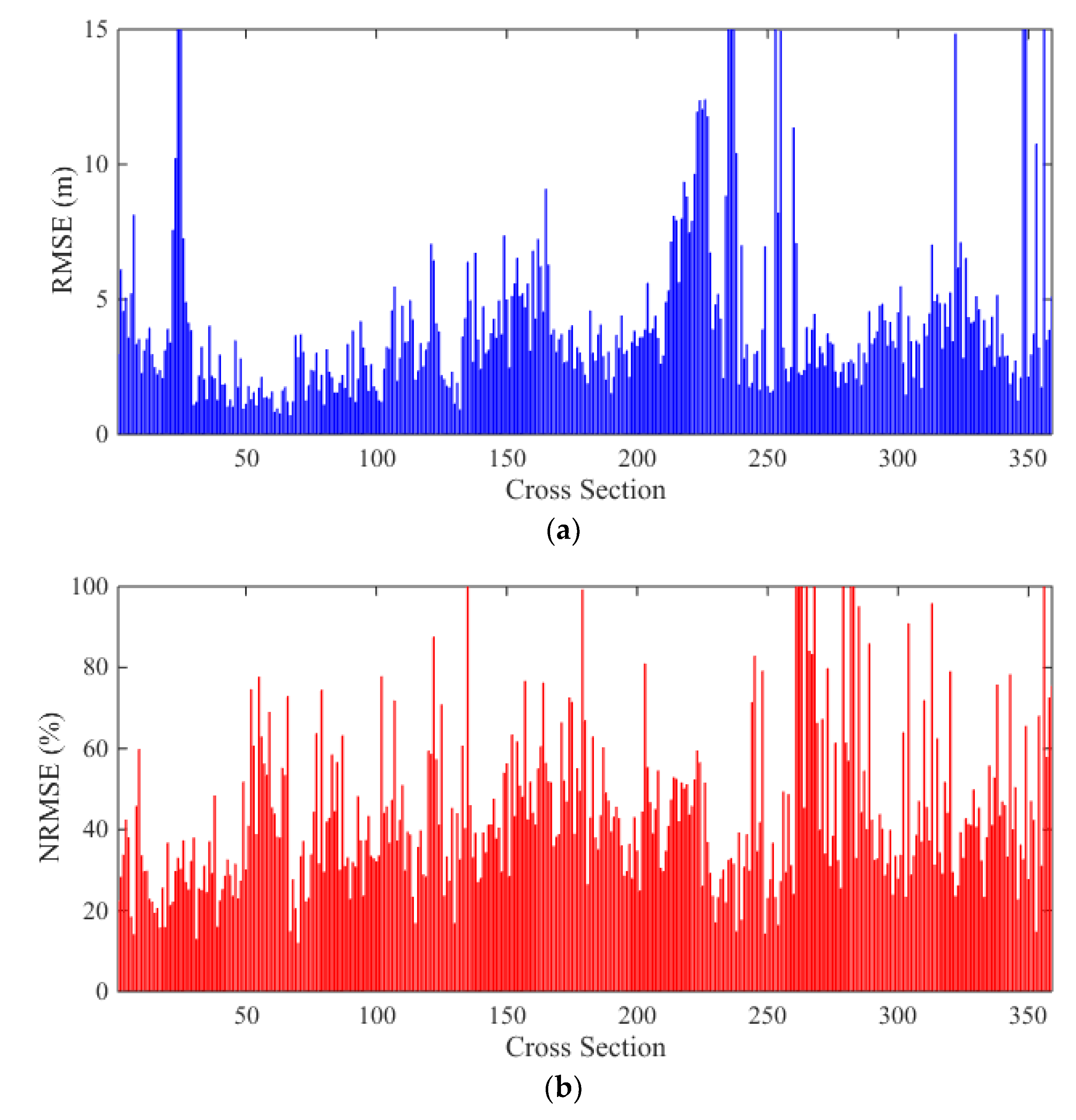
Figure 10. The cross sectional changes are reasonably well predicted by the model. The RMSEs and NRMSEs of bed elevation changes are calculated for all cross sections, and are shown in
Figure 11. The average of RMSEs is 4.4 m, and the average of NRMSEs is 49.53%. As shown in
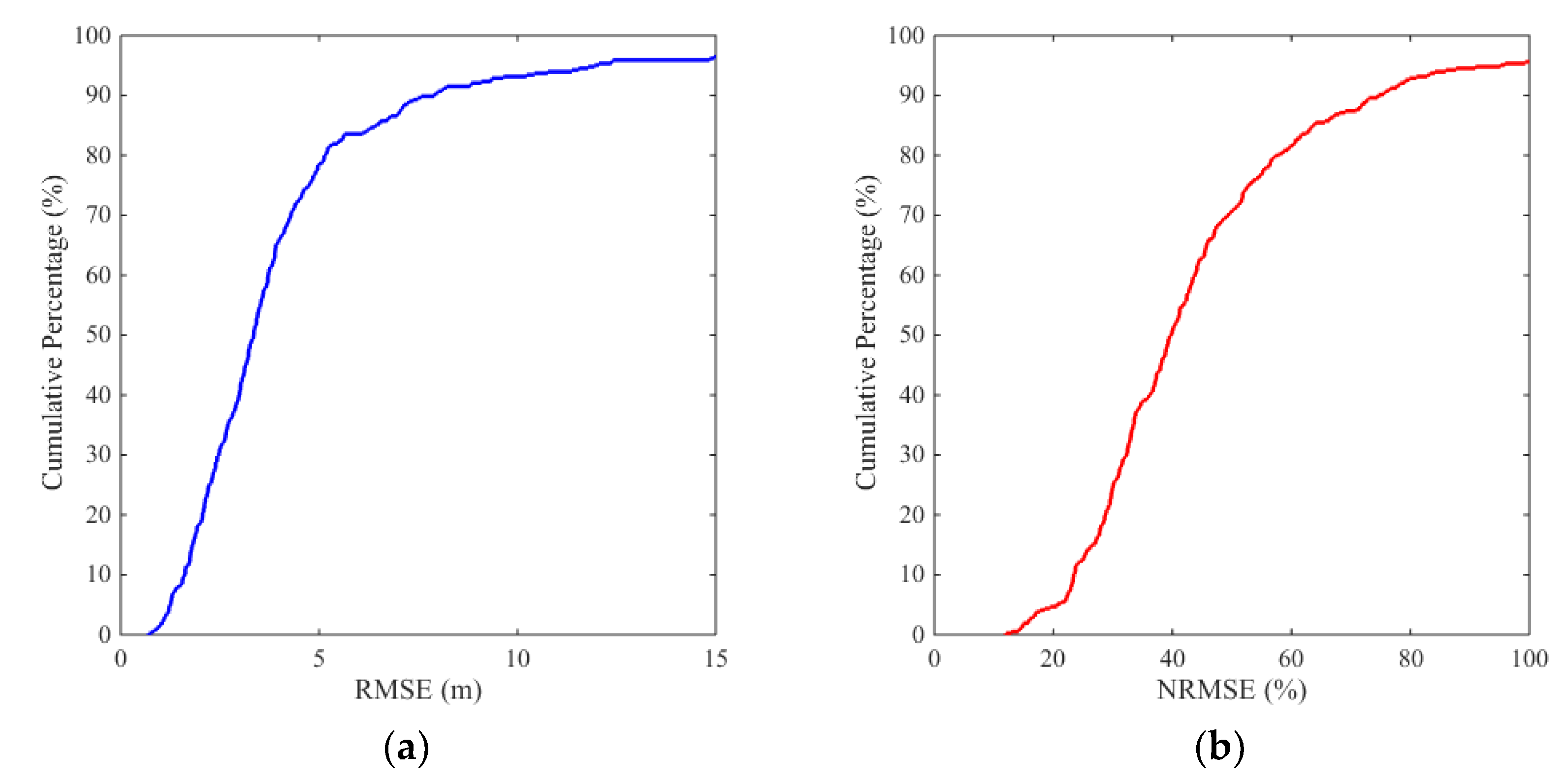
Figure 12, among all the data, 50% of the RMSEs are less than 3.3 m, and 90% of the RMSEs are less than 7.9 m. As to the NRMSEs, about 50% cross sections have NRMSE values less than 40%, and 90% of the NRMSEs are less than 70%.
In the longitudinal direction, the measured and calculated thalwegs are plotted in
Figure 13. The RMSE of thalweg change is 5.3 m, and the NRMSE is 20.18%. It is obvious that the model performed better in the longitudinal direction than in the cross sectional direction. Also, the simulated thalweg profile at the middle reach is overestimated, especially at the 23 km from the channel mouth. According to El Kadi Abderrezzak and Paquier (2009), this part of the channel is controlled by outcrops of bedrocks. During the 1996 flood event, a new reach formed at the right floodplain and the bed was eroded up to 20 m there. The proposed model failed to predict this geomorphic change.
For this real-world flood event, although the RMSEs of bed elevation (in meter scale) are two orders of magnitude greater than the laboratory cases (in centimeter scale), the NRMSEs of bed elevation (49.53% in horizontal direction and 20.18% in longitudinal direction) are at the same order of magnitude as the laboratory cases (24.68% for 1D dam-break flow case, 20.96% for 2D dam-break flow case). Since there is no consensus on which sediment transport equation is most suitable for a specific river reach, an appropriate calibration procedure by using different bed load transport equation and varying Manning’s roughness coefficient is needed to reach better matches of modeling results with observations. The focus of this paper is the new well-balanced numerical scheme for solving the VDSWEs, this calibration procedure was not performed for each testing case. Nevertheless, the simulating results of bed elevation changes satisfactorily match both the laboratory and field observations. Therefore, the developed well-balanced numerical scheme for solving VDSWEs is proved to be a robust and accurate method for simulating dam-break flows over mobile beds.
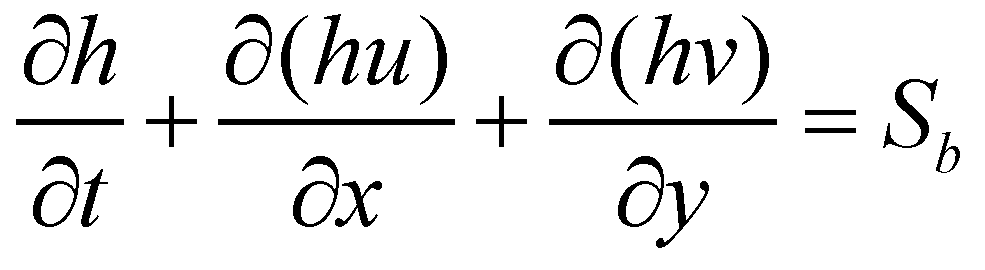 (1)
(1)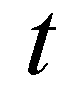 is time;
is time; 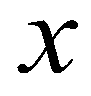 and
and 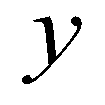 are the spatial coordinates;
are the spatial coordinates; 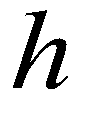 is the flow depth;
is the flow depth;  and
and 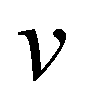 are the depth-averaged flow velocities in
are the depth-averaged flow velocities in 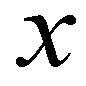 and
and 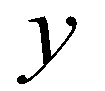 directions, respectively;
directions, respectively; 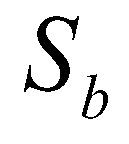 is the sediment exchange rate between flow and bed. Since the density of a sediment-laden flow is a spatial function, the mass conservation equation of is expressed as:
is the sediment exchange rate between flow and bed. Since the density of a sediment-laden flow is a spatial function, the mass conservation equation of is expressed as: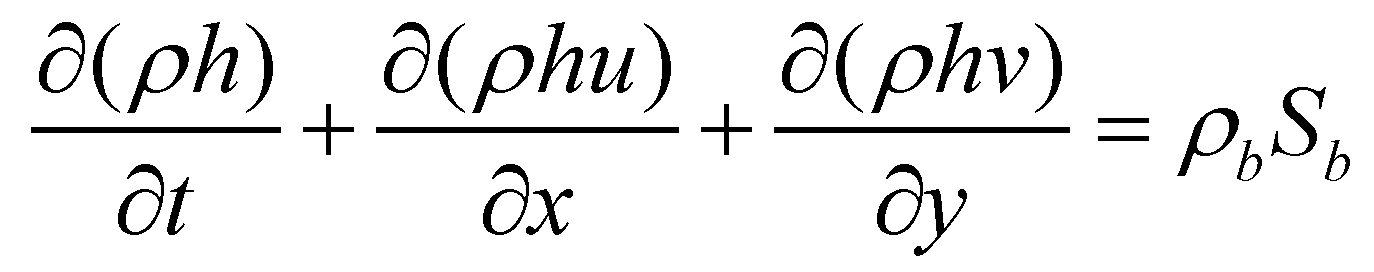 (2)
(2)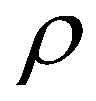 is the density of the sediment-laden flow;
is the density of the sediment-laden flow; 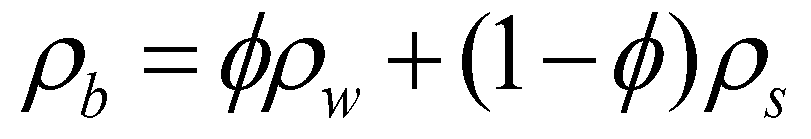 is the density of the saturated mobile bed;
is the density of the saturated mobile bed; 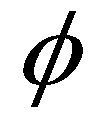 is the porosity of the mobile bed;
is the porosity of the mobile bed; 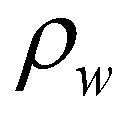 is the density of the water;
is the density of the water; 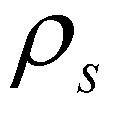 is the density of the bed material. The concentration of sediment-laden flow can be calculated by
is the density of the bed material. The concentration of sediment-laden flow can be calculated by 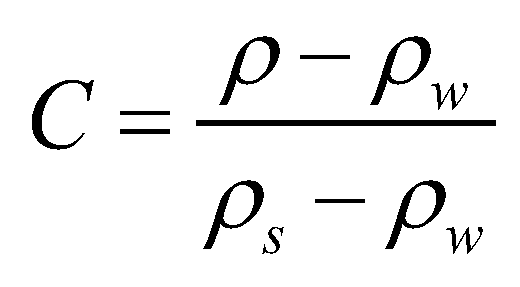 . The depth-averaged momentum conservation equations in
. The depth-averaged momentum conservation equations in 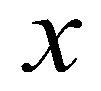 and
and 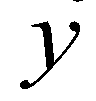 directions are given as:
directions are given as: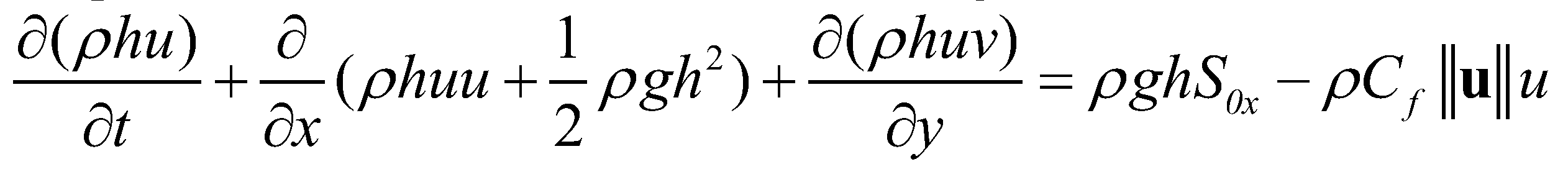 (3)
(3)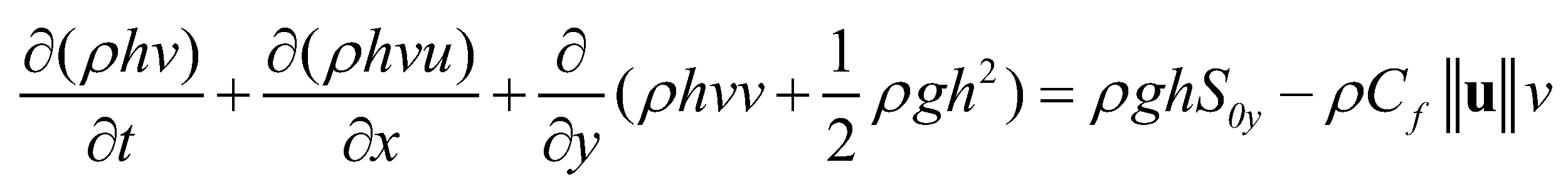 (4)
(4)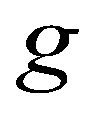 is the gravitational acceleration;
is the gravitational acceleration; 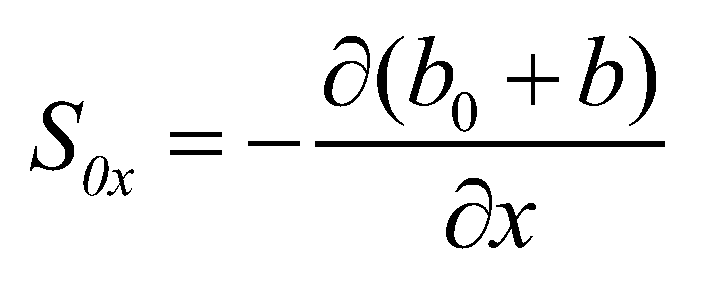 and
and 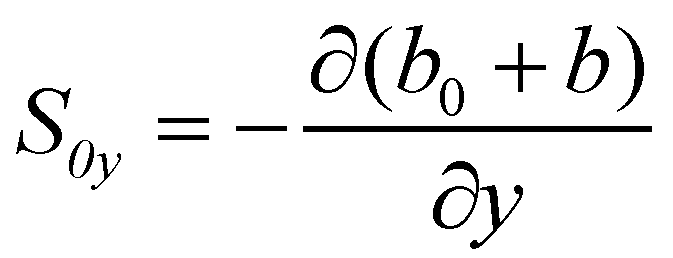 are the
are the 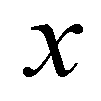 and
and 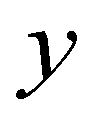 components of bed slope;
components of bed slope; 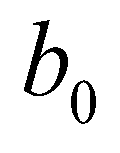 is the elevation of the immobile bed;
is the elevation of the immobile bed; 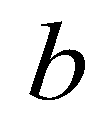 is the depth of the mobile bed;
is the depth of the mobile bed; 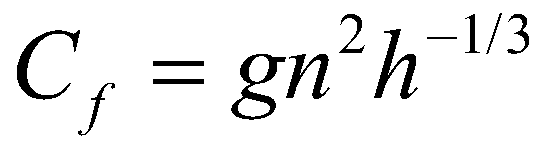 is the drag coefficient;
is the drag coefficient; 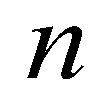 is Manning’s roughness coefficient;
is Manning’s roughness coefficient; 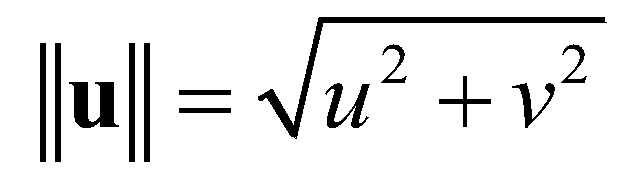 is the magnitude of the flow velocity;
is the magnitude of the flow velocity;  is the velocity vector.
is the velocity vector. (5)
(5)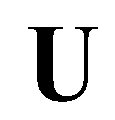 and
and 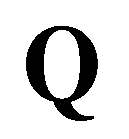 are the vectors of primitive variables and conservative variables:
are the vectors of primitive variables and conservative variables: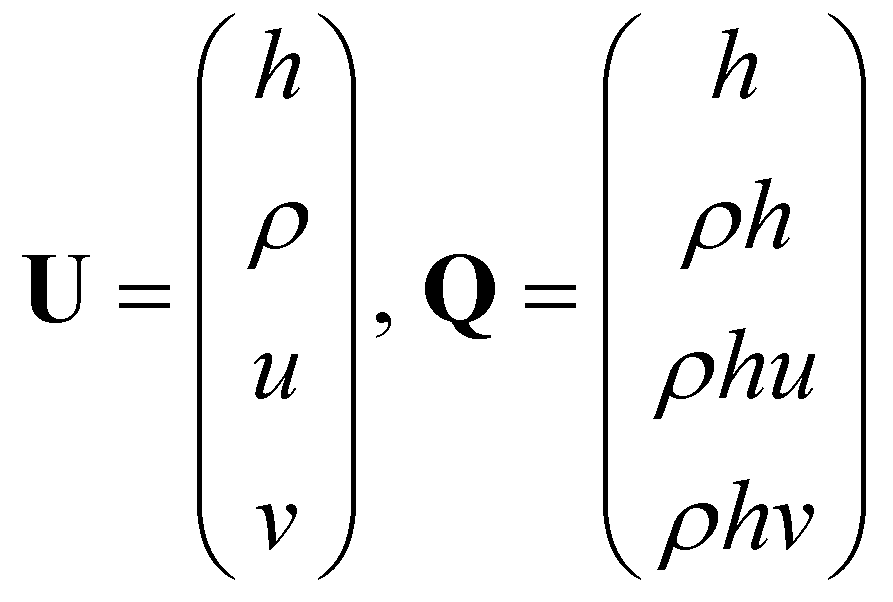 (6)
(6)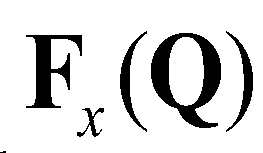 and
and 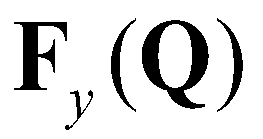 are the vectors of advective fluxes:
are the vectors of advective fluxes: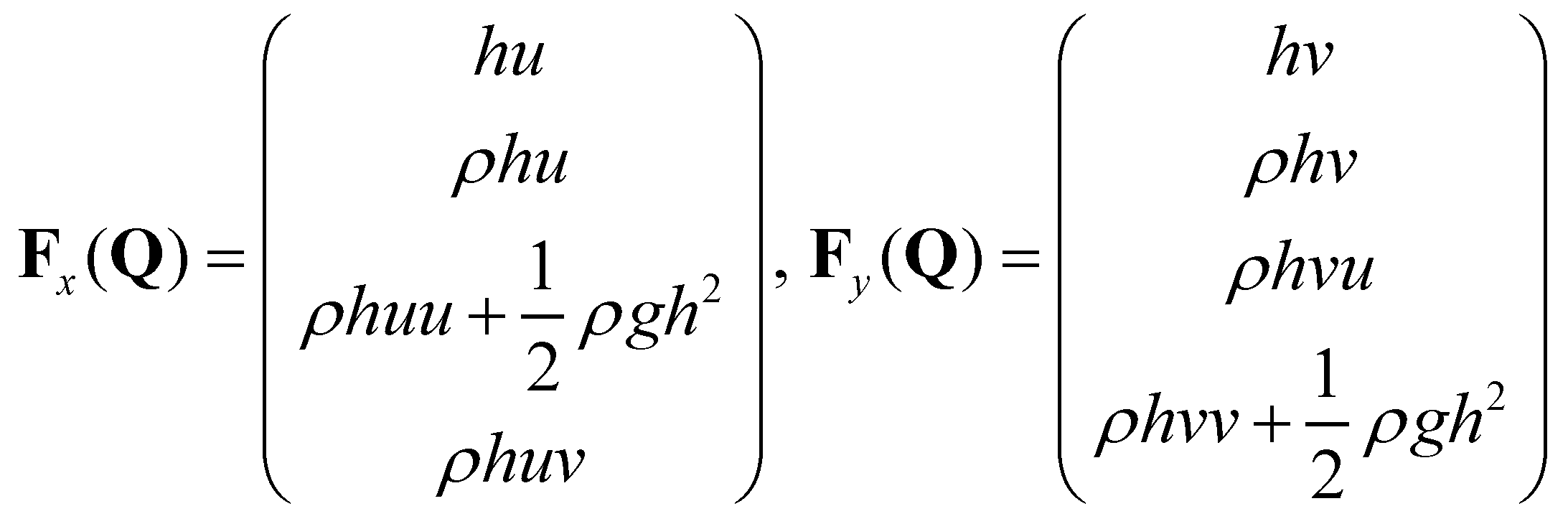 (7)
(7)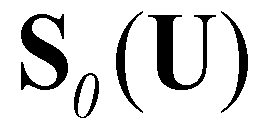 ,
, 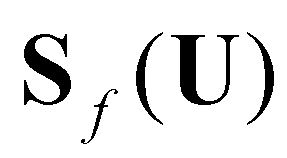 and
and 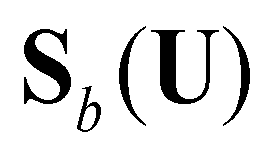 are the bed slope, bed friction, and bed material source terms:
are the bed slope, bed friction, and bed material source terms: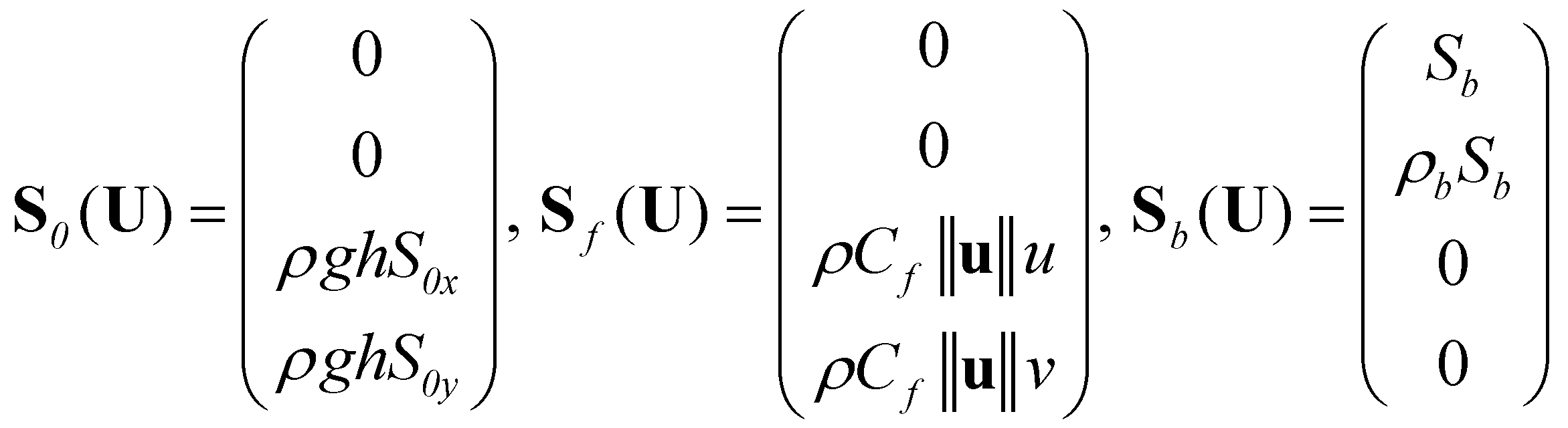 (8)
(8)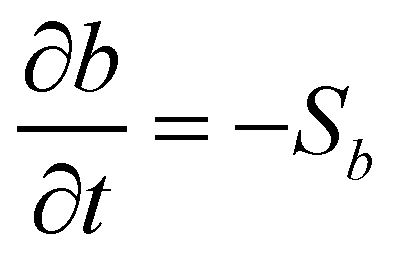 (9)
(9)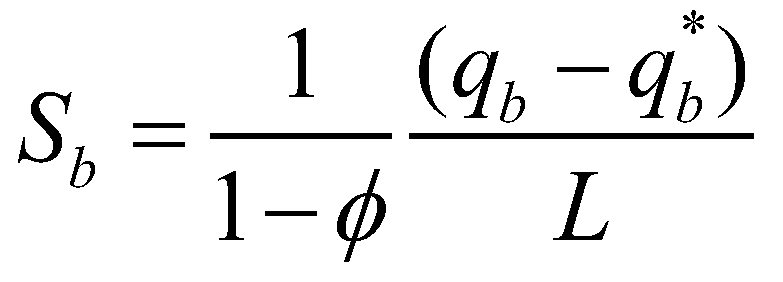 (10)
(10)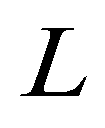 is the nonequilibrium adaption length of sediment transport;
is the nonequilibrium adaption length of sediment transport; 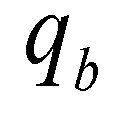 is the actual flux of sediment transport; and
is the actual flux of sediment transport; and 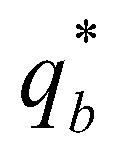 is the sediment transport capacity or the equilibrium sediment transport rate. On account of the recommendations of El Kadi Abdeerezzak and Paquier (2010) and Van Emelen et al. (2014), the sediment transport capacity is calculated by the modified Meyer-Peter-Müller (MPM) formula:
is the sediment transport capacity or the equilibrium sediment transport rate. On account of the recommendations of El Kadi Abdeerezzak and Paquier (2010) and Van Emelen et al. (2014), the sediment transport capacity is calculated by the modified Meyer-Peter-Müller (MPM) formula: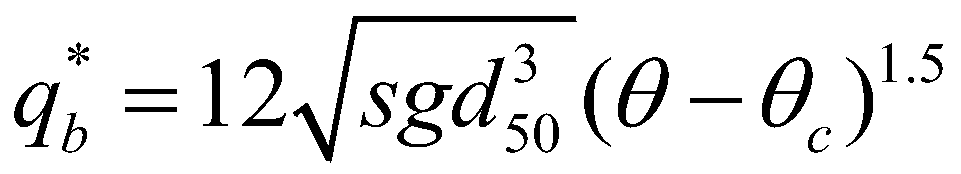 (11)
(11)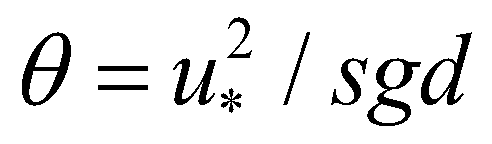 is the Shields number;
is the Shields number; 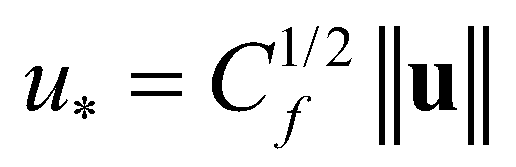 is the friction velocity;
is the friction velocity; 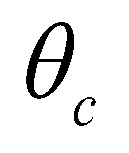 is the critical Shields number.
is the critical Shields number.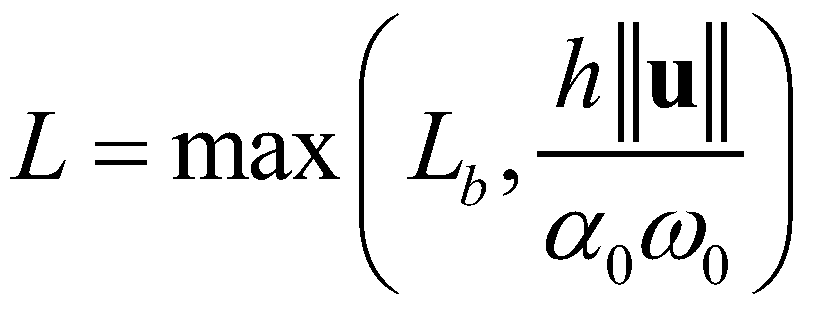 (12)
(12)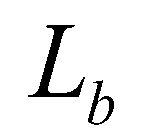 is the adaption length of bed-load;
is the adaption length of bed-load; 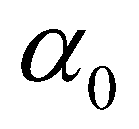 is the adaption coefficient of suspended-load;
is the adaption coefficient of suspended-load; 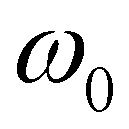 is the settling velocity of a single sediment particle. Since there have been no consensus on
is the settling velocity of a single sediment particle. Since there have been no consensus on 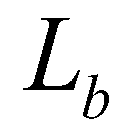 and
and 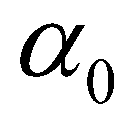 , both parameters are treated as calibration parameters in the proposed model. The settling velocity of sediment particle is calculated by Cao (1999):
, both parameters are treated as calibration parameters in the proposed model. The settling velocity of sediment particle is calculated by Cao (1999):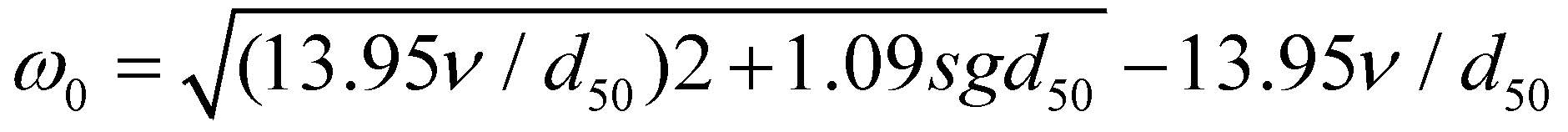 (13)
(13)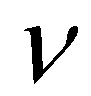 is the kinematic viscosity of water;
is the kinematic viscosity of water; 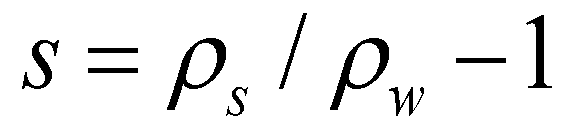 is the specific gravity of submerged sediment particle;
is the specific gravity of submerged sediment particle; 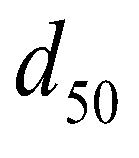 is the median diameter of sediment particle.
is the median diameter of sediment particle.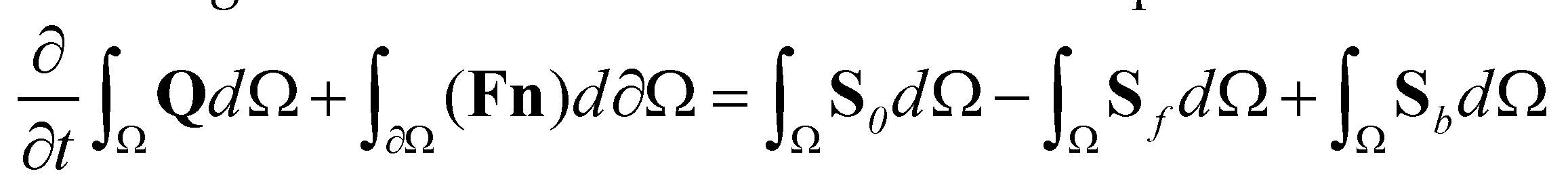 (14)
(14)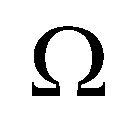 represents a computational cell;
represents a computational cell; 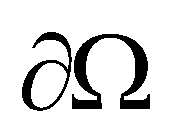 is the boundary of the cell;
is the boundary of the cell; 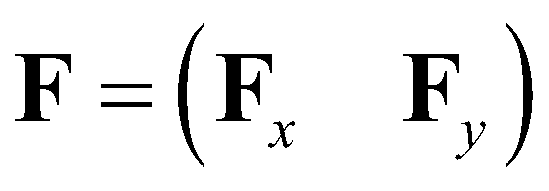 is the matrix of fluxes;
is the matrix of fluxes; 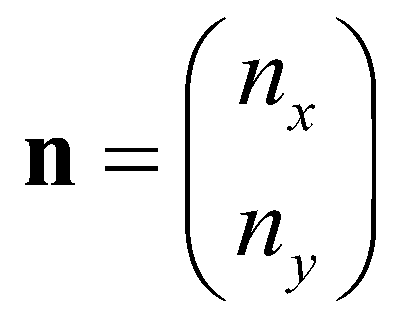 is the outward unit normal vector;
is the outward unit normal vector; 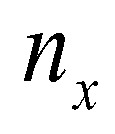 and
and 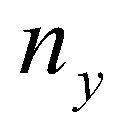 are the components of the normal vector in
are the components of the normal vector in  and
and 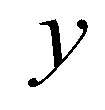 directions, respectively; and
directions, respectively; and 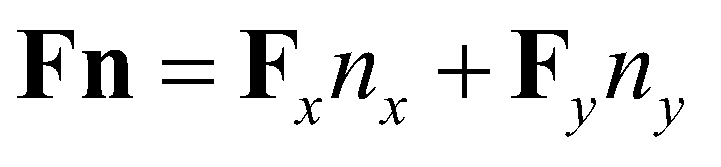 is the fluxes normal to the cell boundary designated by
is the fluxes normal to the cell boundary designated by  . In this study, the fully coupled system of governing equations is solved by the first-order Godunov-type finite volume method over a regular Cartesian mesh. For a rectangular cell, the fluxes across the cell boundaries are calculated by
. In this study, the fully coupled system of governing equations is solved by the first-order Godunov-type finite volume method over a regular Cartesian mesh. For a rectangular cell, the fluxes across the cell boundaries are calculated by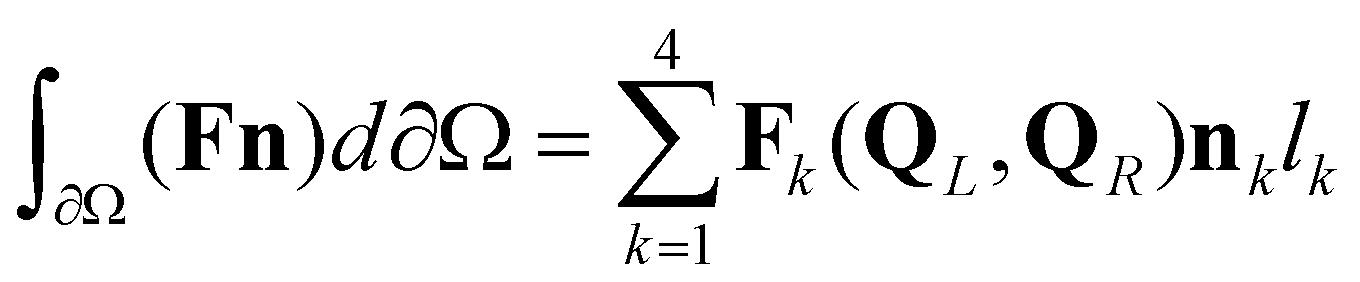 (15)
(15)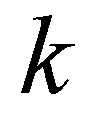 is the edge index; subscript
is the edge index; subscript  and
and  denote the left and right edges of a cell boundary, respectively;
denote the left and right edges of a cell boundary, respectively; 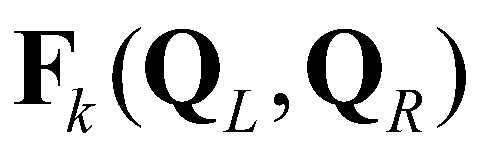 is the Riemann fluxes at the edge
is the Riemann fluxes at the edge  ;
; 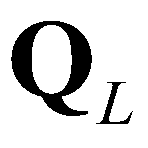 and
and 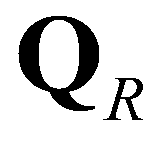 are the vectors of conservative variables reconstructed at the left and right edges, respectively;
are the vectors of conservative variables reconstructed at the left and right edges, respectively; 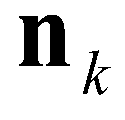 is the unit normal vector for the kth edge;
is the unit normal vector for the kth edge; 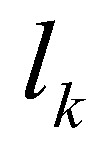 is the length of the kth edge.
is the length of the kth edge.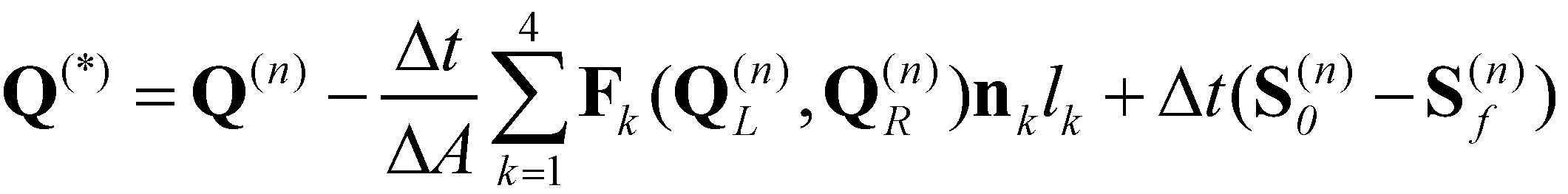 (16)
(16)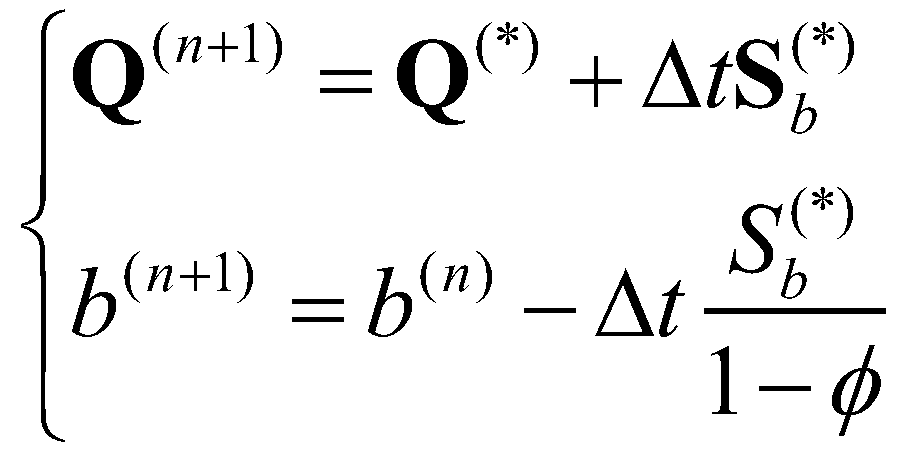 (17)
(17) denotes the solution at time step
denotes the solution at time step  ; superscript
; superscript 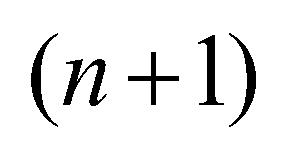 denotes the time step
denotes the time step 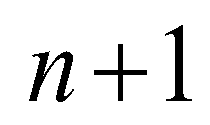 ; superscript
; superscript  denotes the intermediate solution between time step
denotes the intermediate solution between time step 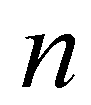 and
and 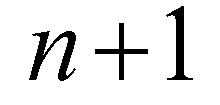 .
.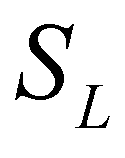 ), the middle wave (
), the middle wave (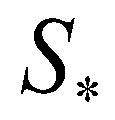 ), and the fastest wave (
), and the fastest wave (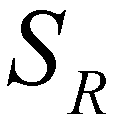 ). There are four constant states in the solution: the left state (
). There are four constant states in the solution: the left state (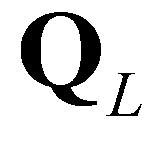 ), the right state (
), the right state (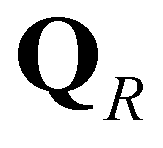 ), the left star state (
), the left star state (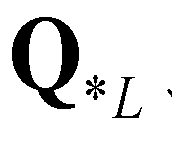 ), and the right star state (
), and the right star state (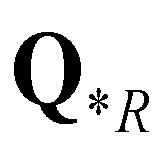 ). The corresponding HLLC numerical flux
). The corresponding HLLC numerical flux 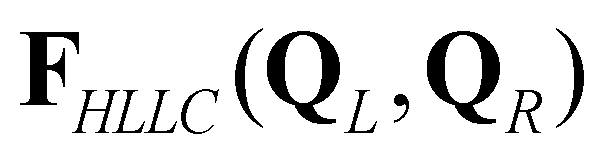 is defined as:
is defined as: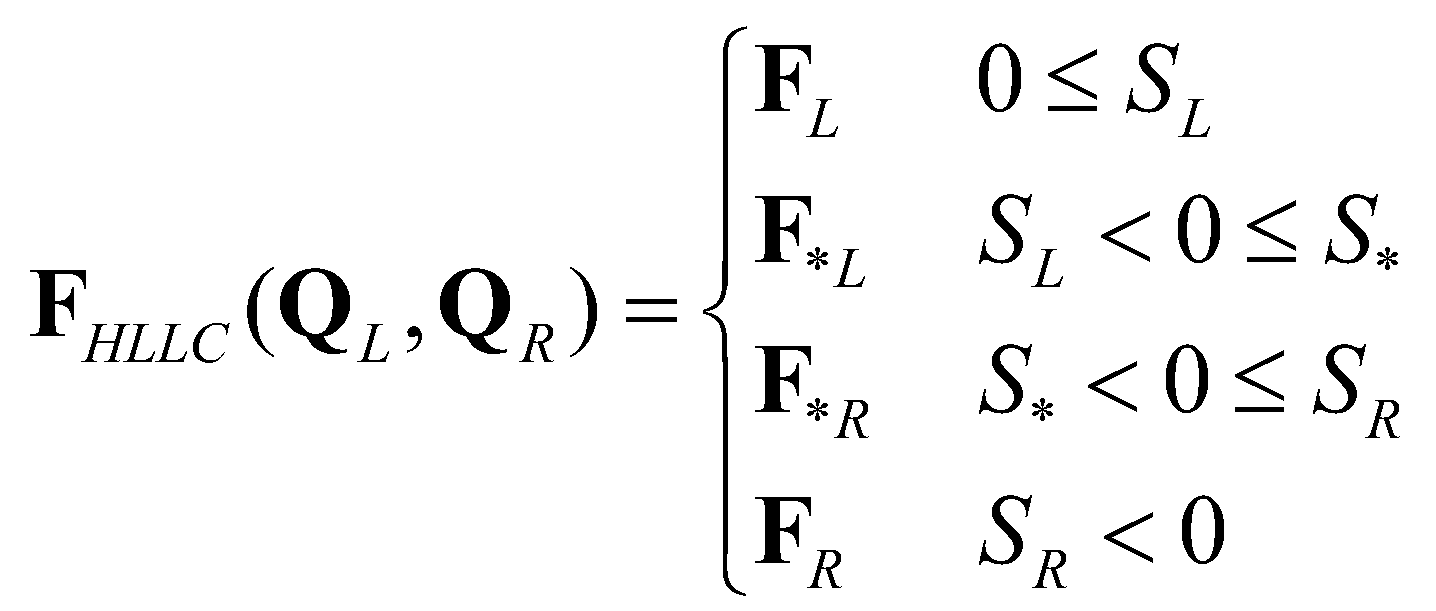 (18)
(18)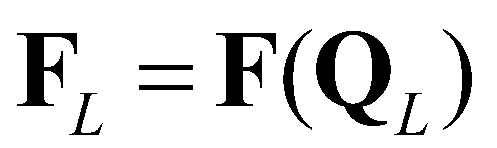 represents the supercritical flow from the left to the right;
represents the supercritical flow from the left to the right; 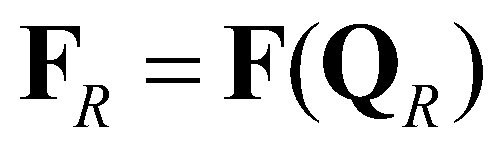 represents the supercritical flow from the right to the left;
represents the supercritical flow from the right to the left; 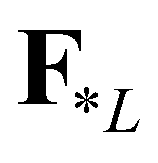 and
and 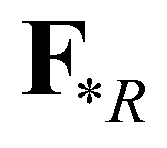 are the fluxes at the star regions. By applying the Rankine-Hugoniot conditions across the waves,
are the fluxes at the star regions. By applying the Rankine-Hugoniot conditions across the waves, 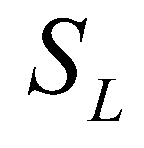 and
and 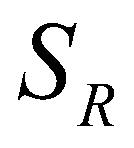 , the numerical fluxes at the star regions can be calculated by:
, the numerical fluxes at the star regions can be calculated by: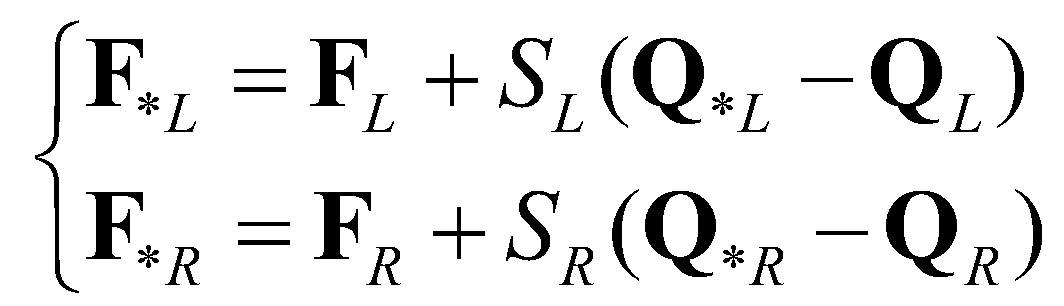 (19)
(19)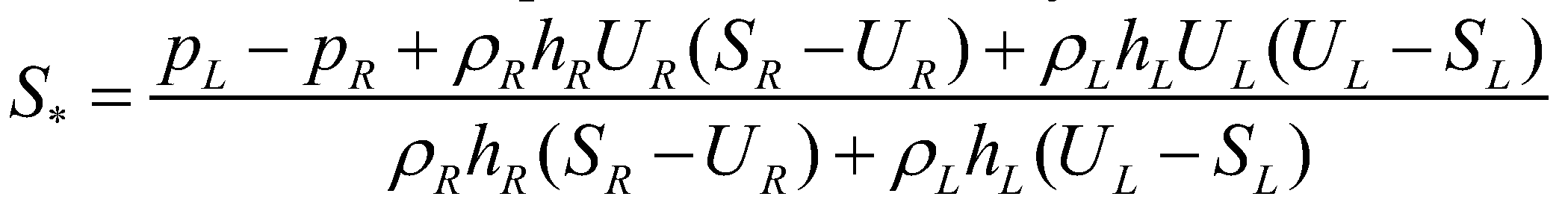 (20)
(20)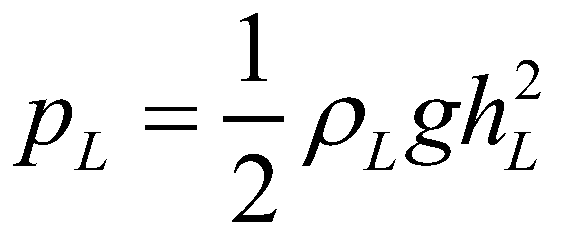 and
and 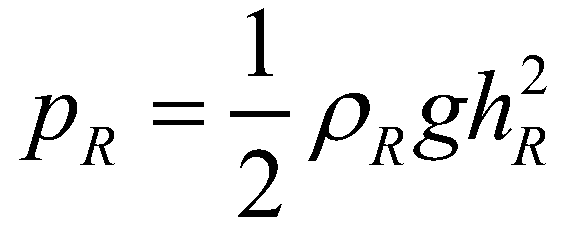 are the hydrostatic pressures at the left and right edges, respectively;
are the hydrostatic pressures at the left and right edges, respectively; 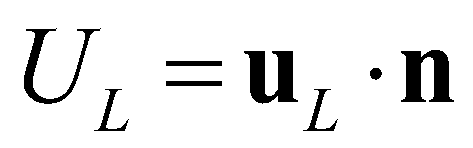 and
and 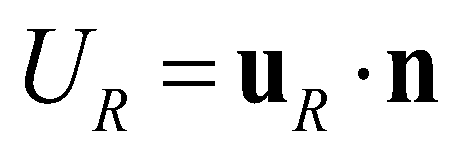 are the normal velocities at the left and right edges, respectively. The left and right states at the star regions can be determined by:
are the normal velocities at the left and right edges, respectively. The left and right states at the star regions can be determined by: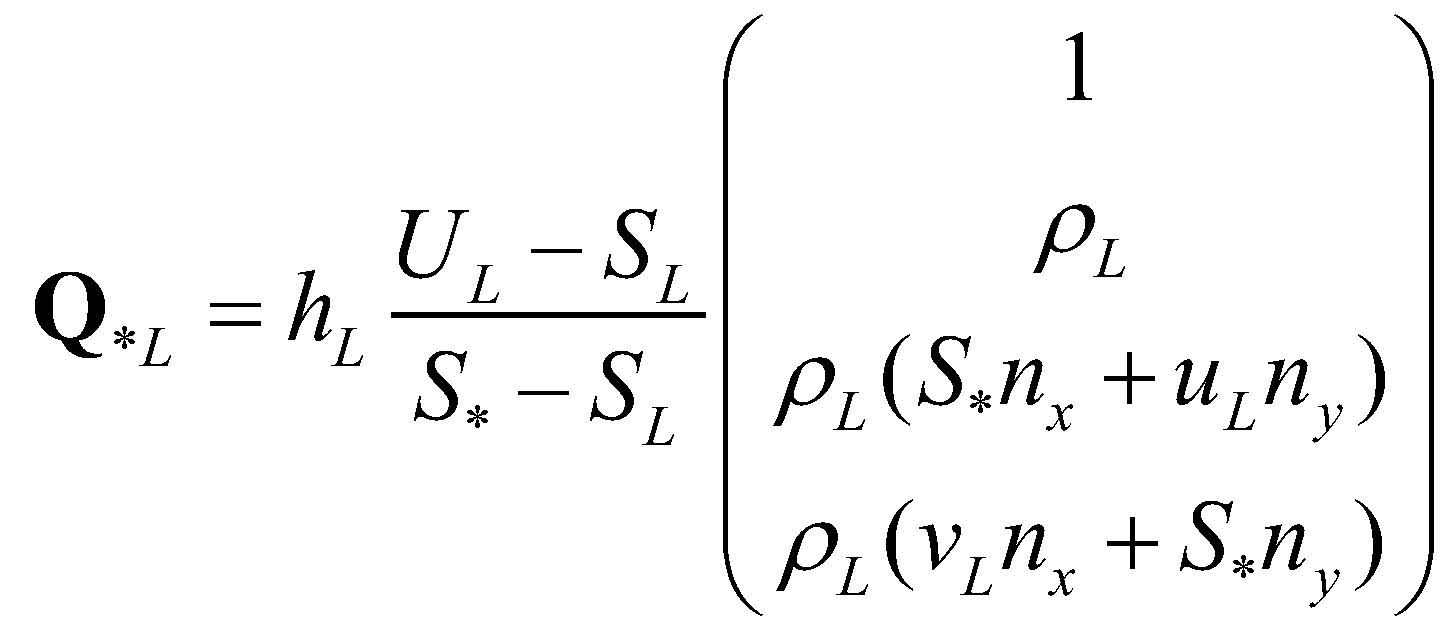 (21)
(21)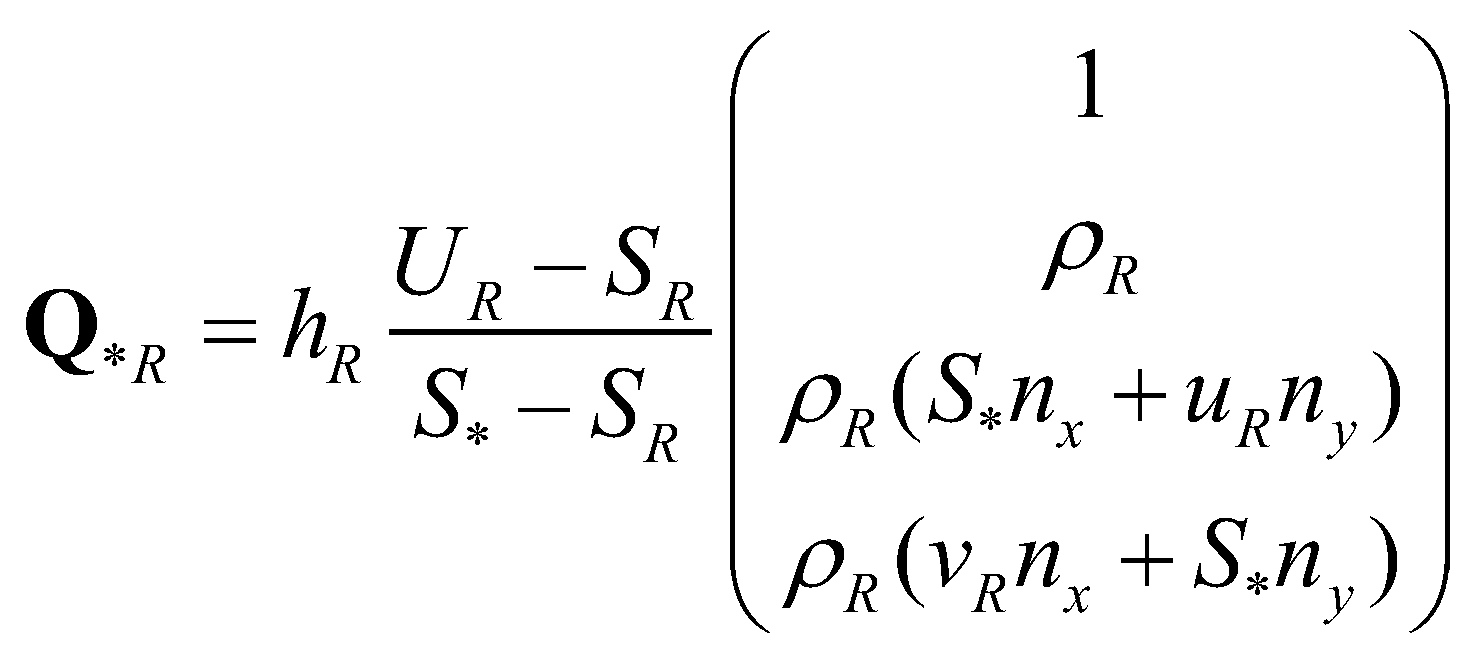 (22)
(22)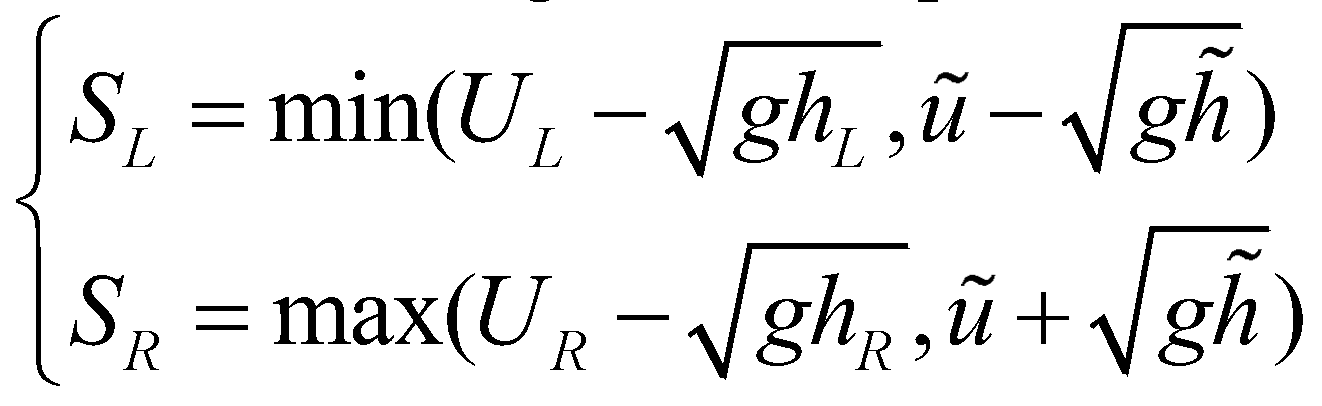 (23)
(23)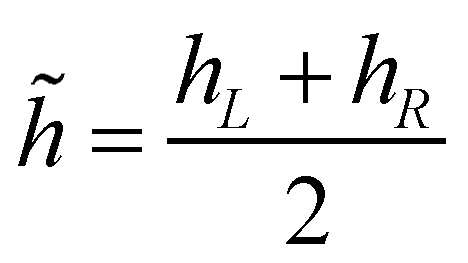 and
and 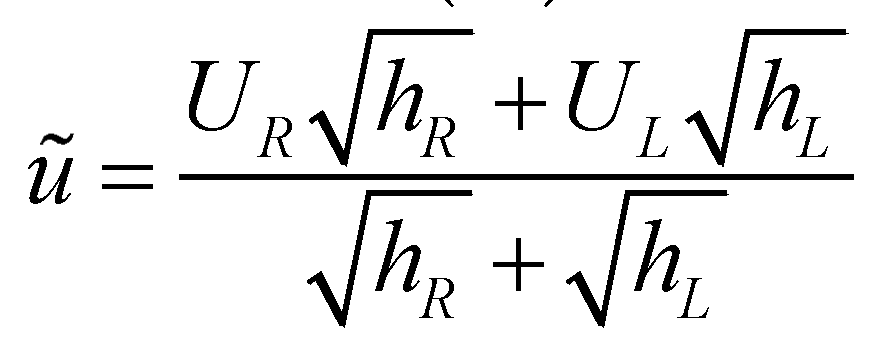 are the Roe averaged flow depth and velocity.
are the Roe averaged flow depth and velocity.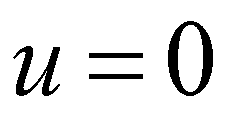 ), the momentum equation of SWEs becomes:
), the momentum equation of SWEs becomes: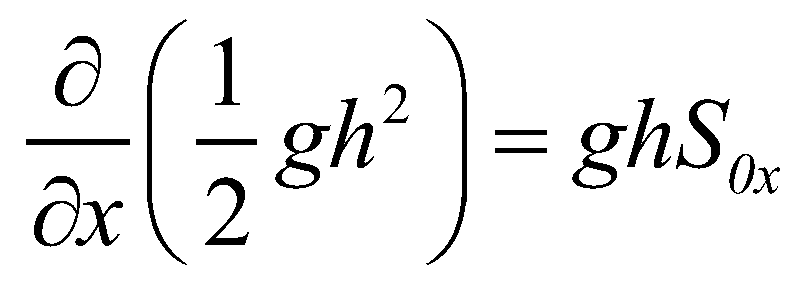 (24)
(24)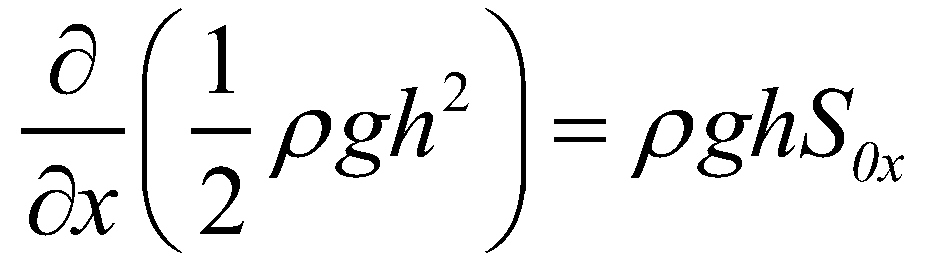 (25)
(25)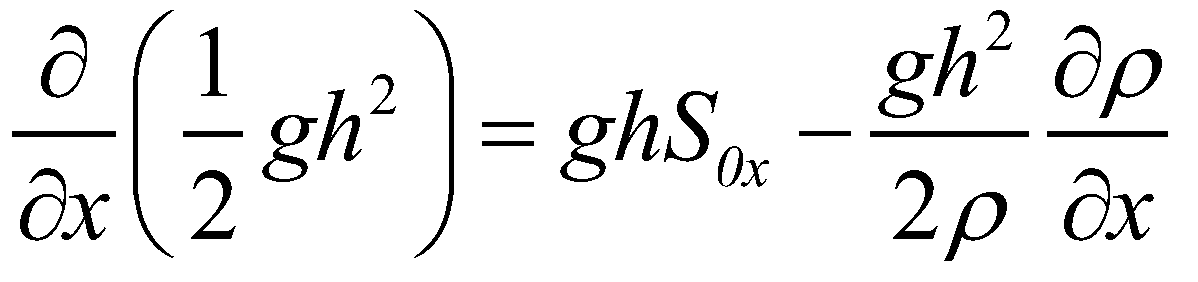 (26)
(26)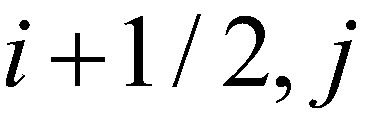 ) between the cell (
) between the cell (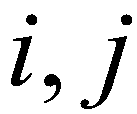 ) and the cell (
) and the cell (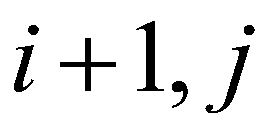 ) is evaluated by
) is evaluated by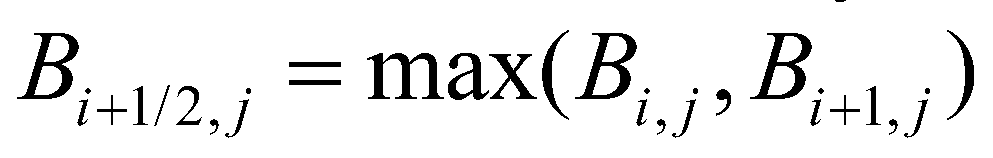 (27)
(27)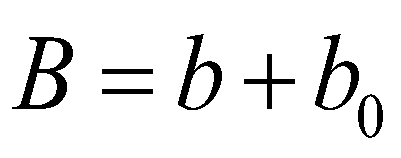 is the bed elevation; subscript
is the bed elevation; subscript 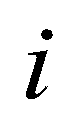 and
and 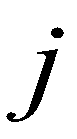 are the cell indices in
are the cell indices in 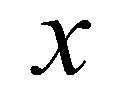 and
and 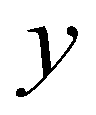 directions; subscript
directions; subscript 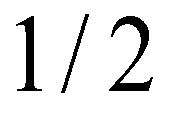 represents the cell boundary. Then, flow depths at the left and right sides of a cell boundary are reconstructed as:
represents the cell boundary. Then, flow depths at the left and right sides of a cell boundary are reconstructed as: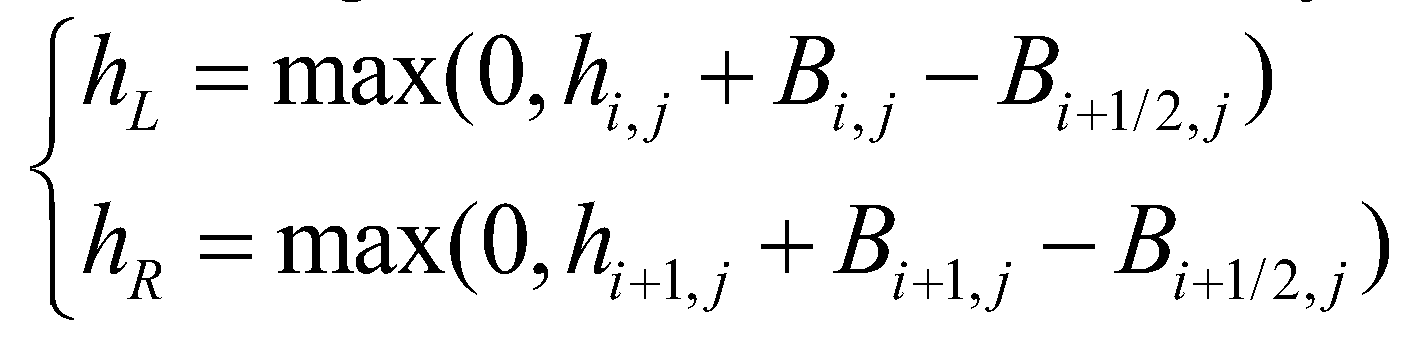 (28)
(28)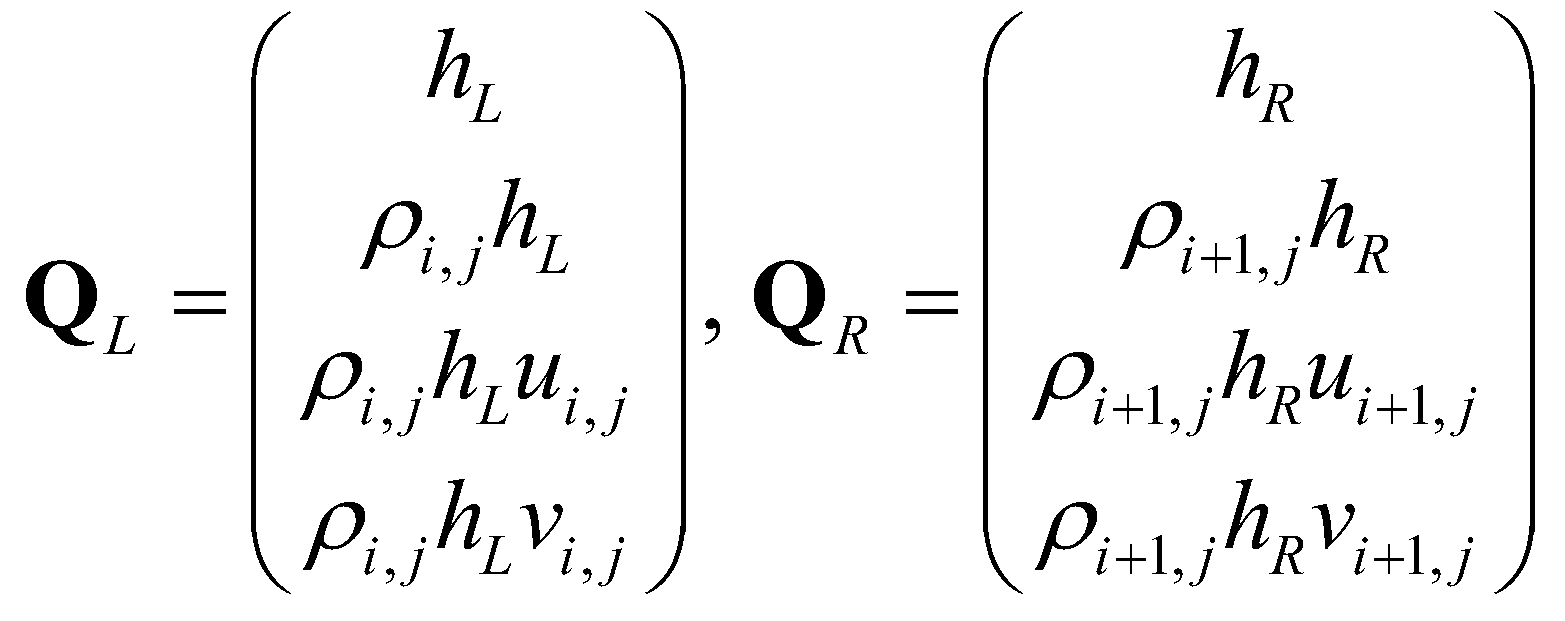 (29)
(29)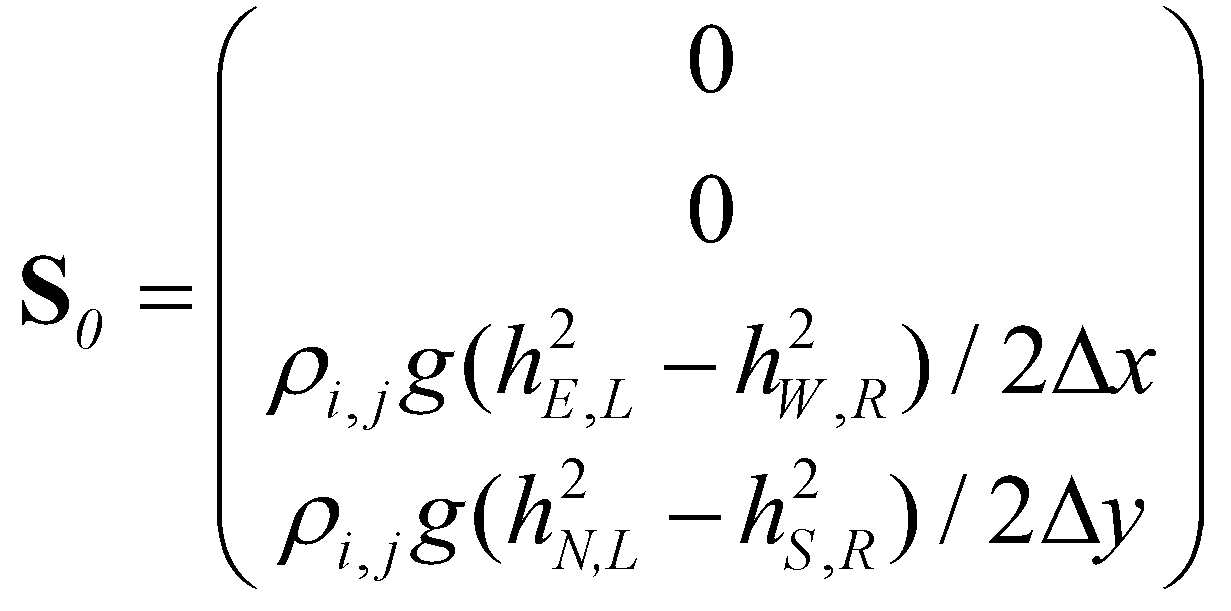 (30)
(30)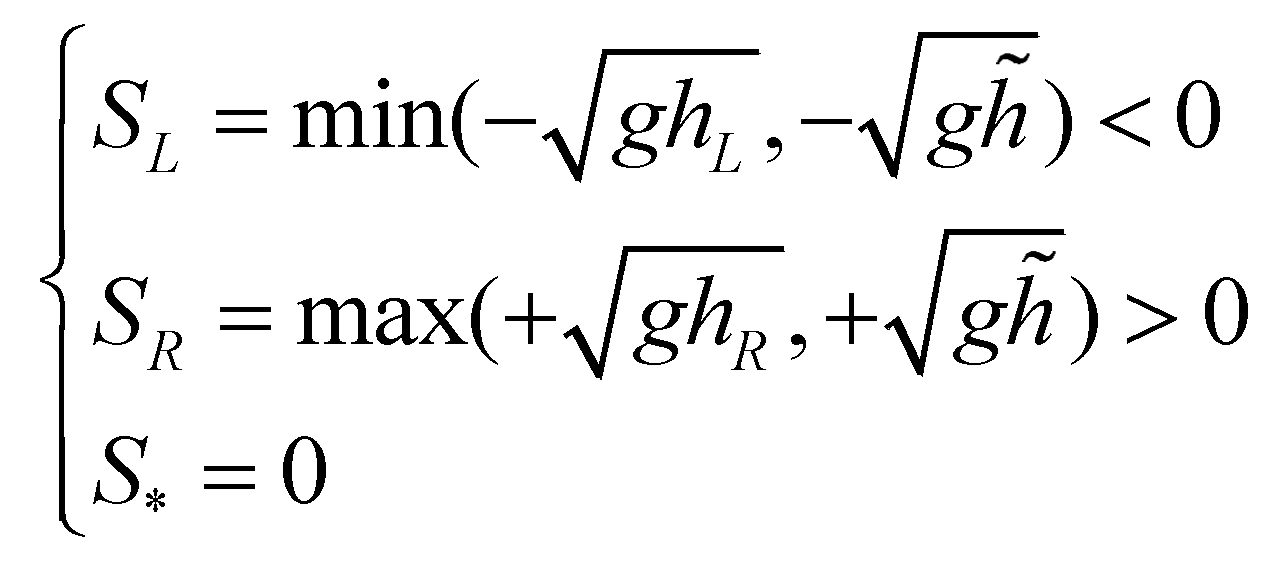 (31)
(31)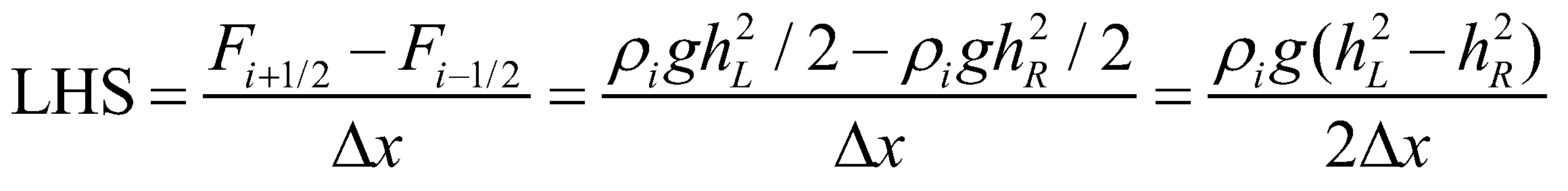 (32)
(32)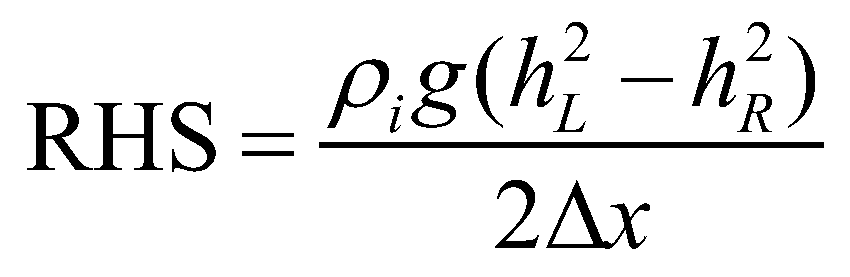 (33)
(33)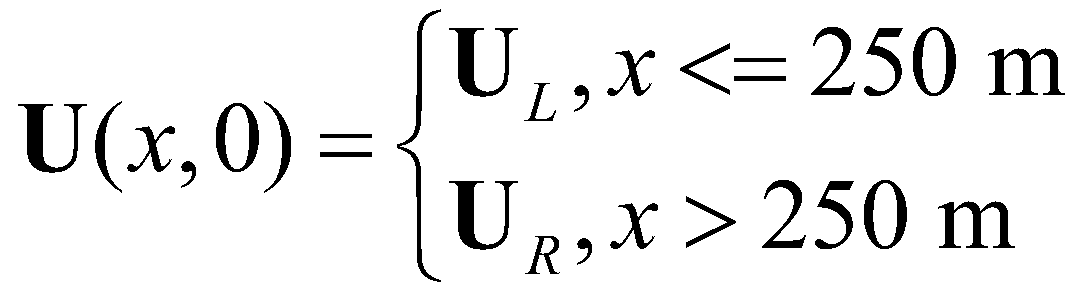 (34)
(34)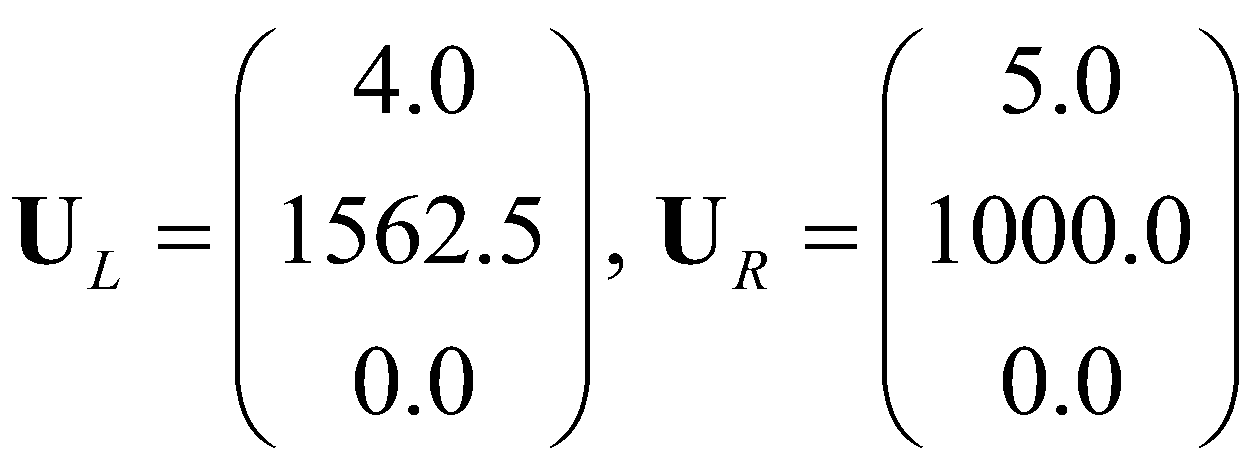 (35)
(35)