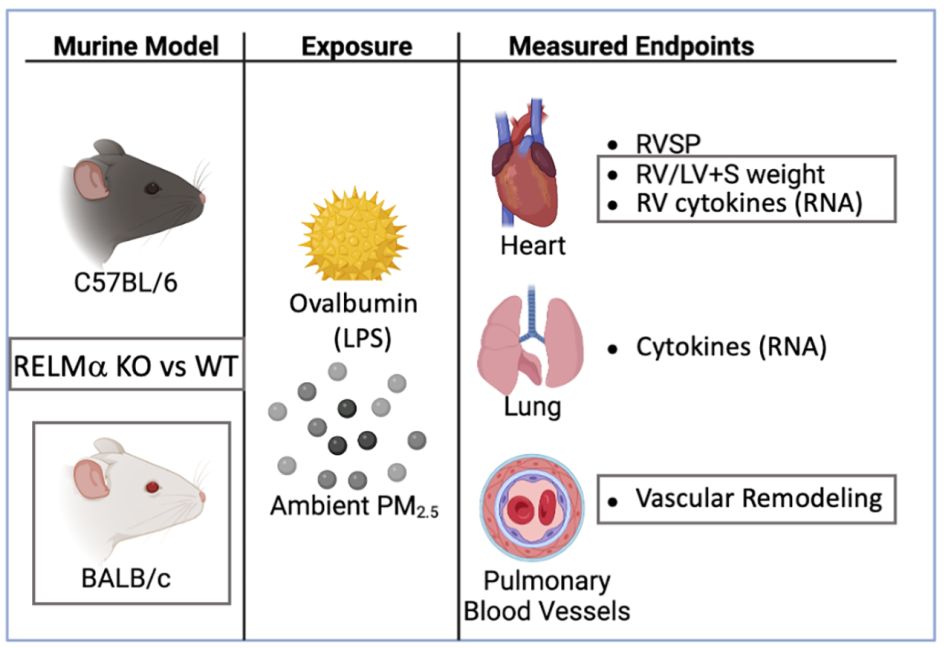
1. Introduction
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) not only has a high mortality but also has limited treatment options [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9]. Our prior work has shown that pulmonary arterial remodeling and subsequent increased right ventricular (RV) systolic pressure (RVSP) could be induced by Th2 response to soluble antigen, and could be exacerbated by urban particulate matter (PM
2.5). [
10,
11] Specifically, CD4+ T cells, B cells, antigen specific antibody, Interleukin (IL)-13 and IL-17A had critical roles in mediating the severe pulmonary arterial remodeling and PH in our C57BL/6 murine model. [
10,
12,
13]
Resistin like molecule α (RELMα) is an intriguing cytokine at the intersection of response to hypoxia [
14,
15,
16,
17,
18] and adaptive immune response and belongs to an ancient mediator family, with Resistin being the oldest member. [
19,
20] In the context of our prior findings, our aim was to identify the mediator down-stream of the adaptive immune response that would induce the PH phenotype. We focused on RELMα because of the intriguing role of this cytokine at the intersection of the immune and the hypoxia response. RELMα was termed ‘found in inflammatory zone 1’ (FIZZ1) because it was originally discovered in inflammatory zones associated with an experimental allergic airway disease model [
15,
21]. Subsequently, RELMα was identified as a biomarker in Th2 asthma models [
22], since it is highly upregulated in epithelial cells and alternatively activated macrophages of the M2 type [
23,
24]. RELMα was also termed hypoxia induced mitogenic factor (HIMF) because it is highly upregulated in lung tissues exposed to hypoxia, specifically in vascular smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells. [
15,
17,
25,
26] HIMF induces cell proliferation and chemotaxis in smooth muscle cells [
14,
18,
27,
28,
29]. RELMα belongs to the resistin family of cytokines which in mice consists of four members: resistin, RELMα, -β, and -γ [
21,
30,
31,
32].
Mechanistically, RELMα has a critical role in hypoxia induced PH phenotype [
17]. With respect to inflammation induced by an adaptive immune response, RELMα has been reported to have either pro-inflammatory [
23,
33], anti-inflammatory [
24,
34], or neutral [
35] roles depending on the experimental model used.
We used mice deficient in RELMα
-/- and measured right ventricular systolic pressure, right heart weight as measure of hypertrophy, pulmonary arterial remodeling and several mediators of immune and vascular responses in the lungs and right ventricle. We compared C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice because BALB/c mice have relatively larger constrictive responses in the airways compared with C57BL/6 mice [
36,
37]. Further, the lung’s immune response in C57BL/6 mice is more of pleiotropic T helper type, while BALB/c mice have a more polarized, type 2 dominant response to antigen exposure [
38,
39]. Taken together, this design allowed us to study the function of RELMα for the PH phenotype induced by an adaptive immune response in the lungs.
2. Materials and Methods
Ethics Statement. All animal experiments were performed according to guidelines outlined by the United States Department of Agriculture and the American Association of Laboratory Animal Care under the supervision and specific approval of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees at New York University, Grossman School of Medicine (IACUC #140812-01).
Mice. RELMα
-/- on a C57BL/6 background (Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Tarrytown, NY) were backcrossed to BALB/c (Dr. Marc E. Rothenberg’s laboratory, Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center) and a breeding pair was kindly provided [
23,
33]. RELMα
-/- mice (KO) were then backcrossed to C57BL/6J for 6 generations. C57BL/6J and BALB/c wild type (WT) mice were purchased (Jackson Laboratory) and adjusted to the environment in our colony for 10 days. Either these mice, or littermates of the backcross strain were used for comparison with RELMα
-/-. Male and female mice 5-7 weeks of age at the start of the experiment were randomized into cages holding up to 4 mice. All mice were housed under pathogen free conditions.
RELMα-/- Genotyping. PCR-based method using ear tissues was used for genotyping. Briefly, for pretreatment of ear tissues, 180 µl of 50 mM NaOH was added into a tube containing ear tissues and incubated at 95°C for 13 min, and stayed at 22°C until use. 20 µl of 1M Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) was added, mixed with vortexing. 5 µl of pretreated sample was used for total 25 µl of PCR reaction. TERRATM PCR Direct Polymerase mix kit (Clontech, Mountain View, CA) was used with primers 5-GTCAGCAATCCCATGGCGTA-3 (forward) and 5-GTCTGTCCTAGCTTCCTCACTG-3 (reverse); 400 bp for KO allele or primers 5-GTCAGCAATCCCATGGCGTA-3 (forward) and 5-ACTTCCCTACCC ACCCATTCC-3 (reverse); 800 bp for WT allele. A gradient PCR method was used with the following conditions: 98°C for 2 min, followed by 2 cycles of 94°C for 10 s, 64°C for 30 s, 72°C for 50 s, followed every 2 cycles with 1°C reduced annealing temperature until annealing temperature go to 58°C, followed 27 cycles of 94 °C for 35 s, 58°C for 30 s and 72 °C for 50 s, followed by 1 cycle of 72°C for 10 min, and followed by a hold at 4°C. The product was run on a gel to distinguish WT, heterozygous, KO mice.
Urban PM (PM
2.5) (<2.5 mm in aerodynamic diameter) was collected from New York ambient air and resuspended as previously described [
40,
41]. PM
2.5 was diluted in phosphate buffered saline(PBS), ultrasonicated before use and mixed with OVA solution so that the final concentration was 25 μg PM
2.5 / 50 µl intranasal dose.
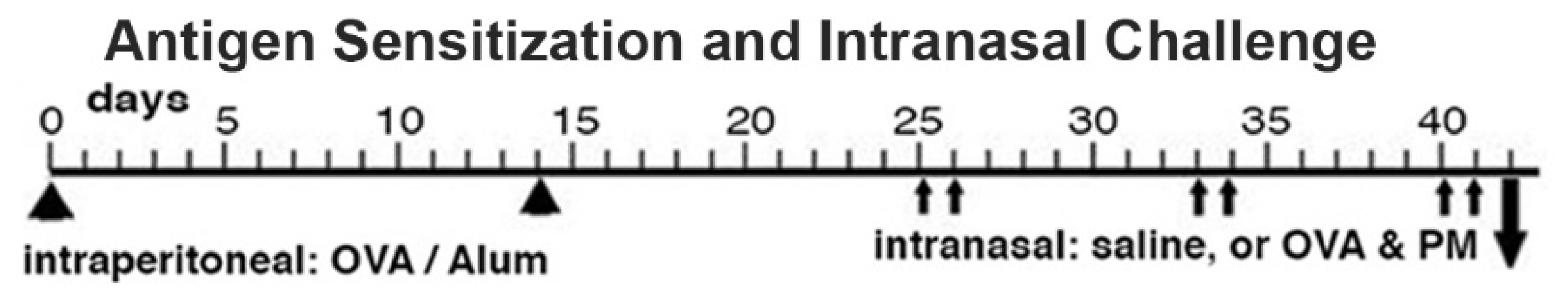
Antigen priming and antigen & PM2.5 challenge (OVA&PM). Animals were primed and challenged with antigen as previously published [
3,
11,
12,
13,
42]. Briefly, mice were injected intraperitoneally with Ovalbumin (OVA) (grade V; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO; 50 µg/dose) adsorbed to Alum (Imject Alum; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Rockford, IL; 2 mg/dose) at a two-week interval. Two weeks later, the mice were intranasally challenged with either PBS, or combined OVA (100 µg/dose) & PM
2.5 (25 μg/dose) for two times each week, for a total of 6 doses given over a three-week period. The mice were analyzed one day following the last intranasal exposure,
Figure 1. This OVA preparation contains lipopolysaccharide (LPS) that contributes to the responses in the airways and lungs to intranasal OVA challenge in this mouse model [
43].
Group comparisons. In a pilot study, we compared sensitized C57BL/6 or BALB/c wild type or KO mice intranasally exposed to either saline, PM2.5, OVA, or OVA&PM2.5. The data of the pilot study showed that as expected [
11] all groups of saline or PM
2.5 exposed mice showed no significant difference in any of our measurements. Therefore, we pooled these two groups. Further, the pilot study showed that the comparison of the responses of WT and KO mice to OVA alone were the same as when WT and KO mice were exposed to OVA& PM
2.5. For these reasons, the data from these two exposure groups were pooled to increase statistical power for the WT vs KO comparisons.
RV Systolic Pressure was measured by inserting a catheter via the jugular vein in anaesthetized, spontaneously breathing mice [
11,
42,
44]. Mice were analyzed without prior knowledge of group identity, and we alternated mice from different cages to eliminate ‘cage effects’. Briefly, mice were anaesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of Avertin (Sigma-Aldrich) made by mixing 5 ml of 2-Methyl-2-butanol and 5 g of 2,2,2-Tribromoethanol; 0.25 ml of the stock solution was diluted with 10 ml of saline solution; the mice were injected according to their weight, 10 μl / g mouse. Once surgical plane of anesthesia was reached, the right jugular vein was isolated. The pressure catheter (F1.4, Millar Instruments, Inc. Houston, TX) was inserted and advanced into the RV to measure the pressure. Then the mice were euthanized with an overdose of barbiturate and lung and heart tissues were harvested. The RV pressure data were analyzed using the LabChart 7 program (ADInstruments, Colorado Springs, CO).
RV Hypertrophy, Fulton's Index [right/(left + septum) ventricular weight]. The RV, and left ventricle plus septum were removed and weighed. The data were used to calculate the right ventricular weight relative to the weight of the left ventricle and septum.
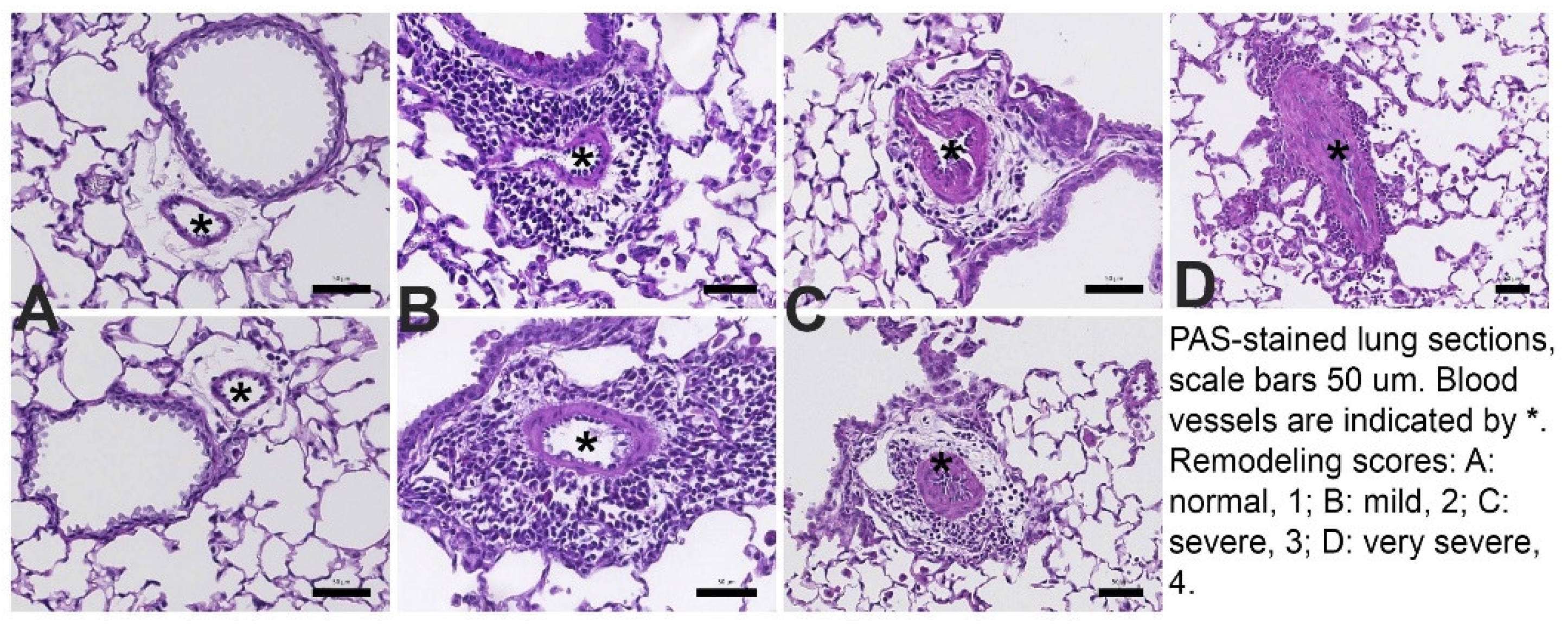
Pulmonary vascular remodeling. The approach was as previously described [
3,
45,
46,
47,
48] and the analysis was performed without knowledge of the group identity of the sample. Briefly, the lungs were placed into formaldehyde for fixation, paraffin embedded and sections stained with H&E (hematoxylin and eosin) or with Periodic Acid Schiff (PAS). The slides were scanned using the Leica Biosystems SlidePath Gateway and the Leica SCN400 (Leica Microsystems Inc., Buffalo Grove, IL) whole slide scanning system at the Histopathology Core of NYU Medical Center. The digital dynamic slide images were analyzed at 200x magnification.
Examples for the pulmonary vascular scoring are shown in
Figure 2: 1- normal, 2 – thickened, but regular, 3- thickened and irregular layers of smooth muscle cells, 4- further thickening and more irregular arrangement of smooth muscle cells. At least 20 consecutive view fields randomly selected in all available lung lobes were evaluated at 200x magnification. All arteries with a diameter of <100μm were scored. For each lung, the remodeling score was calculated as the mean of all scores collected per lung.
Severe remodeling was also determined as percentage of all scored blood vessels per lung. characterized by having severely thickened walls and disorganized layers of smooth muscle cells (smooth muscle cells in the blood vessel wall that assumed a pattern that differs from the lumen) [
10]. For each lung, severe arterial thickening was calculated by the following formula: 100 ÷ number of all scored blood vessels × number of severely remodeled vessels.
mRNA expression: Total RNA from lung tissue was isolated (RNeasy Mini Kit; QIAGEN Inc, Valencia CA) and reverse transcribed using the High-Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA). Real time PCR was performed in duplicate with 20 ng of cDNA using the 7900HT Fast Real-Time PCR system (Applied Biosystems). The qPCR for the detection of the gene expression was performed with SYBR Green (Invitrogen, Grand Island, NY) and primers purchased from Origene (Rockville, MD). RELMα (Retnla), RELMβ (Retnlb), RELMγ (Retnlg), were assayed using TaqMan Gene expression Assay (Applied Biosystems) based on a FAM labeled probe and the corresponding TaqMan gene expression assay for β-actin. The sequences for the primers or probes, respectively, are listed in
Table 1. The following conditions were used: 95 °C for 10 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 15 s and 60 °C for 1 min, followed by a hold at 4 °C. Raw data were analyzed with SDS Relative Quantification Software version 2.3 (Applied Biosystems) to determine cycle threshold (ΔCt). For each sample, ΔCt values were standardized to the housekeeping gene β-actin by calculating 1.98ΔCt ×10,000. Data were expressed as β-actin standardized ΔCt values, or as percent-fold-difference from the mean of the wild type OVA&PM
2.5 group (set at 100U).
Statistical analysis: Statistical analysis and graphs were generated with Prism version 9.2 (Graphpad). Data from multiple groups were analyzed for significant differences using the Kruskal Wallis test (tie corrected). Pair-wise comparisons were conducted with the unpaired, two-tailed Mann-Whitney U test. P<0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
3. Results
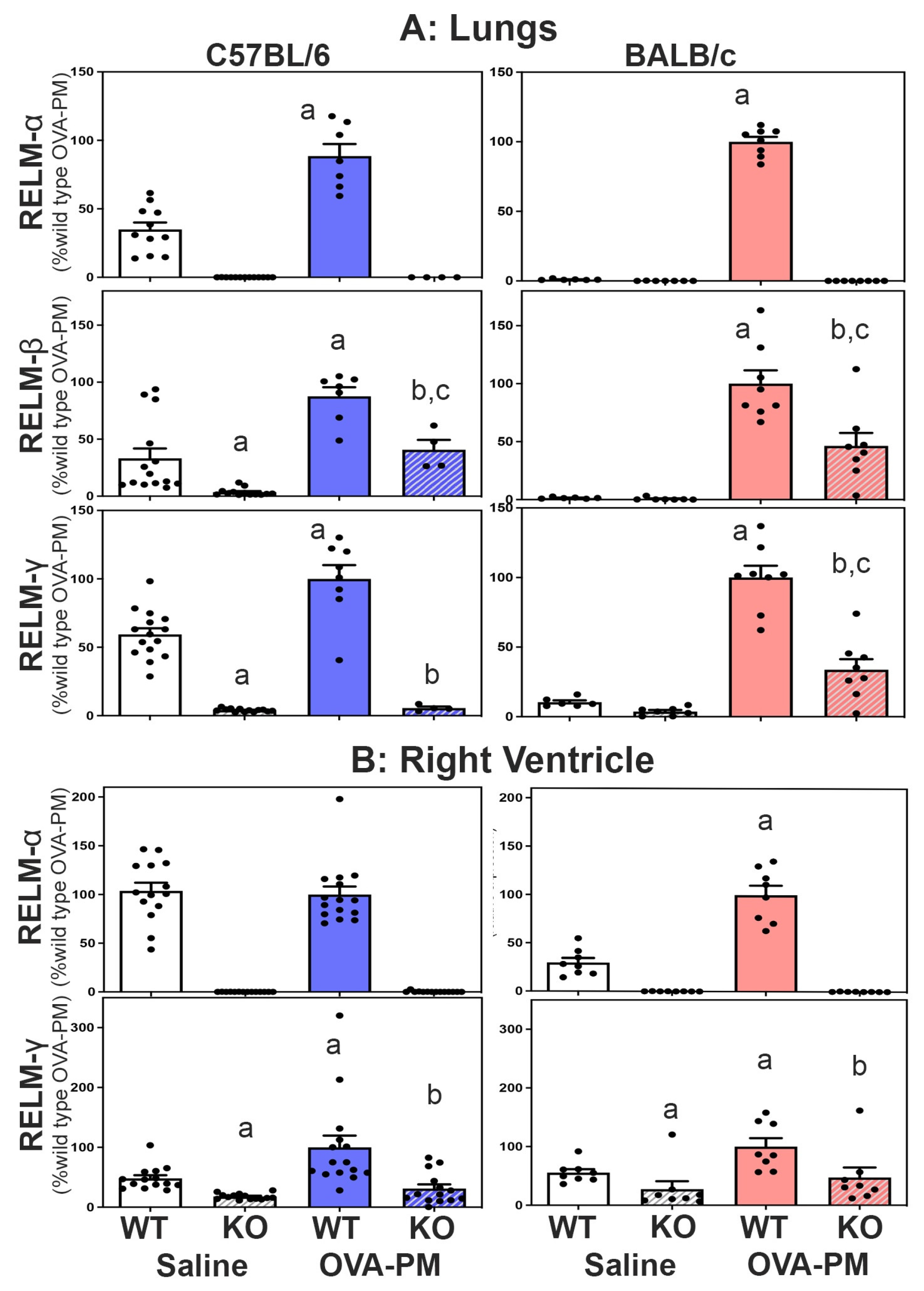
Expression of RELMβ and RELMγ in RELMα-/- mice. All three members of the resistin like molecule family are located on mouse chromosome 16 in the gene-order Retnlb, Retnla, Retnlg. To test the idea that the gene-deletion manipulation in the RELMα-/- mice could have changed the expression of RELMβ and RELMγ, we determined the expression of all three resistin like molecules in the lung and right heart tissues of wild type and KO mice. Figure 3A shows that antigen and PM2.5 exposure significantly increased the expression of RELMα, β and γ in the lungs of WT mice, and that this increase occurred to a larger fold-degree in BALB/C strain mice. Figure 3A also shows that RELMα-/- mice of both strains had no RELMa expression and significantly decreased expression of RELMβ and RELMγ in the lungs compared to wild type mice.
Expression of RELMα and RELMγ, was readily detected in the right ventricle (RV),
Figure 3B. RELMb was not detectible in the right ventricle (data not shown). Exposure with antigen/PM
2.5 significantly increased the expression of RELMα in the RV of BALB/c WT mice and RELMγ in the RV of WT mice from both strains. As in the lungs, the right ventricles of RELMα
-/- mice of both strains had no RELMa expression and significantly decreased expression of RELMγ when compared to WT mice,
Figure 3.
In BALB/c KO mice, decreased RELM expression attenuated pulmonary vascular remodeling induced by exposure to antigen and PM
2.5: Groups of WT and KO mice were given antigen and ambient PM
2.5 (OVA&PM). As expected, [
10,
11,
12,
13,
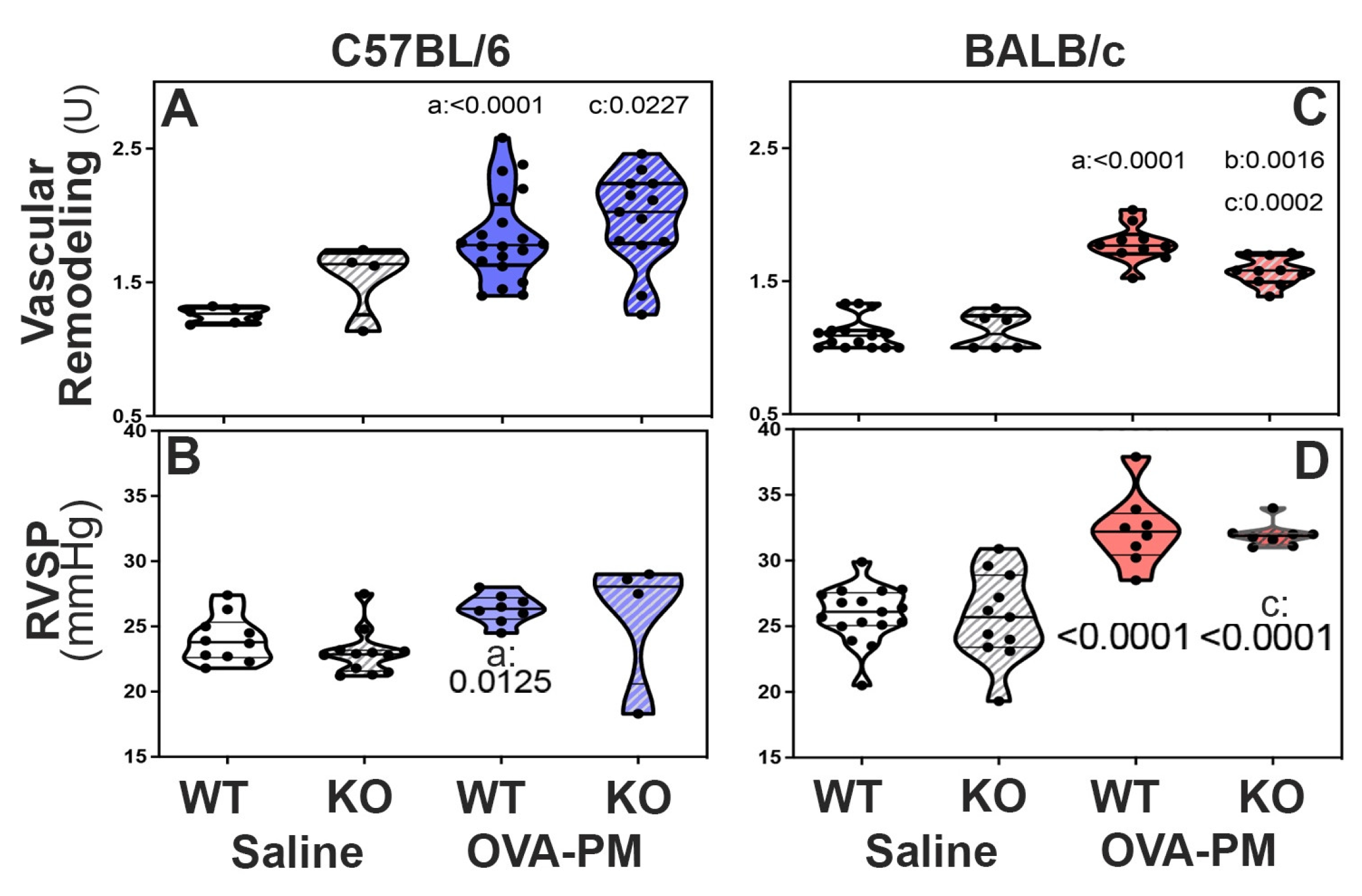
42] WT C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice developed significantly pulmonary vascular remodeling compared to saline, Figure 4A. Figure 2 shows the vascular pathology corresponding to the scores. RELMα KO mice of the BALB/c strain had significantly ameliorated vascular remodeling compared to wild type, Figure 4A. In contrast, RELMα-/- mice of the C56BL/6 strain developed pulmonary vascular remodeling to the same extent as WT, Figure 4A.
BALB/c RELMα KO mice did not develop severe pulmonary arterial remodeling upon exposure to antigenPM2.5. Following exposure to antigen/PM
2.5, the frequency of severely remodeled arteries was higher in C57BL/6 mice when compared to BALB/c mice,
Table 2. In keeping with the data shown in
Figure 4A, the percentage of severely remodeled pulmonary arteries was significantly lower in antigen/PM
2.5 exposed RELMα
-/- BALB/c mice when compared to WT,
Table 2. In contrast, WT and RELMα
-/- C57BL/6 mice had a similar frequency of severely remodeled arteries in the lungs,
Table 2.
RELMα is not necessary for increases in RV systolic pressure induced by exposure to antigen and PM2.5: To understand the role of RELMα for the increase in RV systolic pressures (RVSP), groups of WT and KO mice were given antigen and ambient PM
2.5 (OVA-PM). As expected, [
10,
11,
12,
13,
42] OVA-PM exposed WT C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice developed significantly increased RVSP compared to control,
Figure 4A,B. Unexpectedly, RELMα
-/- mice of both strains showed increases in RV systolic pressure upon challenge with OVA&PM similar to the WT controls,
Figure 4B.
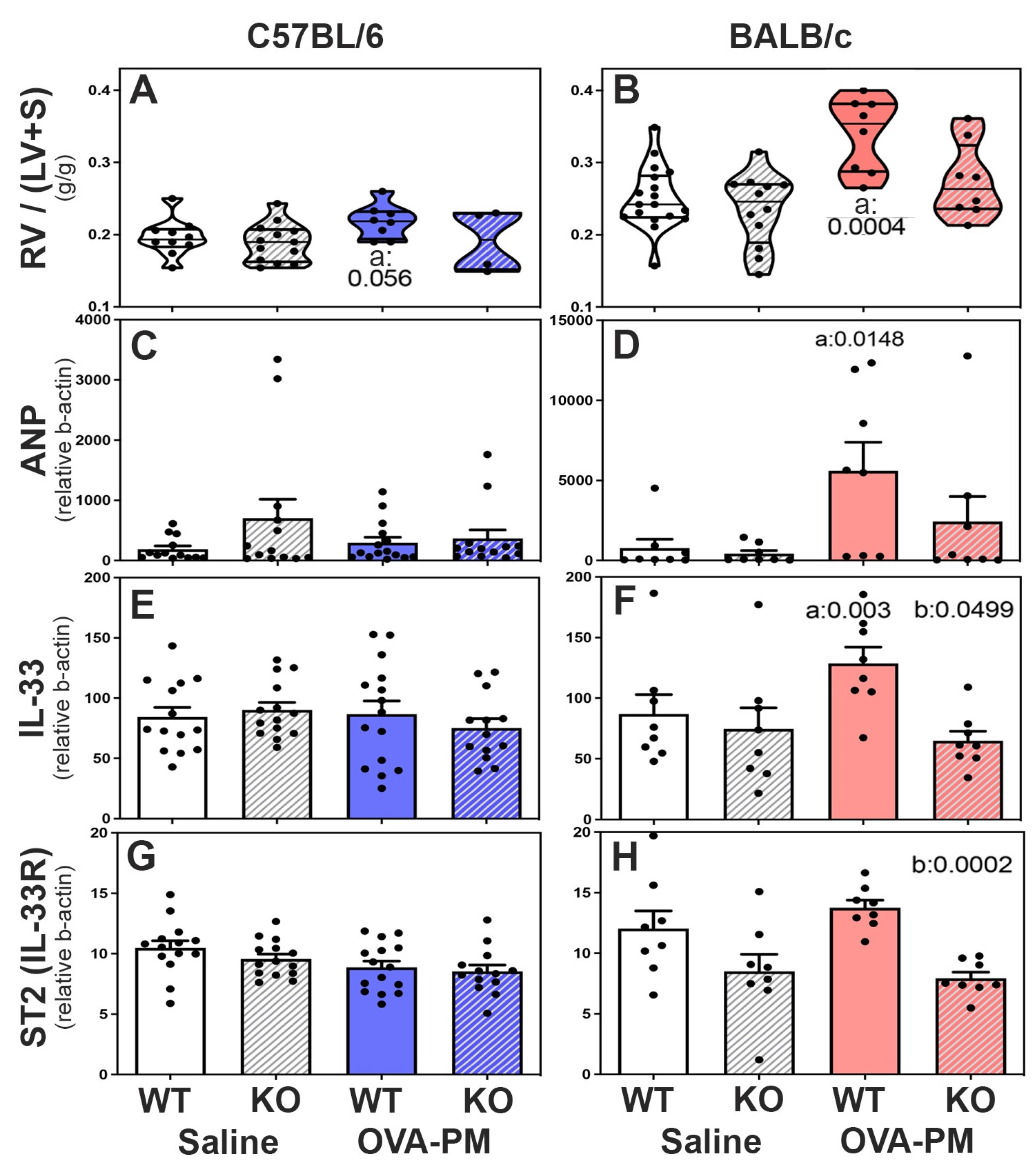
Right heart weights and expression of ANP, IL-33 and IL-33-receptor (ST2) in the ventricles of the right heart of WT and RELMα-/- mice: In PBS treated mice right heart weights were similar in wild type and RELMα KO mice in both C57BL/6 and BALB/c strains, Figure 5A-B. However, the right heart weight was higher in BALB/c strain control mice when compared to C57BL/6 control mice. Upon exposure to antigen and PM2.5, only BALB/c WT mice developed significantly increased right heart weights Figure 5B. Antigen and PM2.5 exposed C57BL/6 strain wild type mice showed a trend to increased right heart weights, Figure 4A. Importantly, RELMα-/- BALB/c mice did not develop significant increases in right heart weight following exposure to antigen and PM2.5, Figure 5B, while RELMα-/- C57BL/6 mice were not different from wild type, Figure 5A.
The mRNA expression of ANP (natriuretic peptide type A) was measured as an indicator of RV stress, [
49]
Figure 5C,D. Only BALB/c WT mice, but not RELMα
-/- BALB/c mice developed increased ANP expression in the RV compared to control groups,
Figure 5D. The mRNA expression of IL-33 and the IL-33-receptor ST2 was measured in right heart tissue because IL-33 and ST2 are thought to have important roles in regulating right ventricular homeostasis [
50]. Antigen and PM
2.5 exposure did not change right ventricular IL-33 or ST2 expression in C57BL/6 mice,
Figure 5E,G. In contrast, BALB/c WT but not BALB/c RELMα
-/- mice had significantly increased right ventricular IL-33 expression following antigen/PM
2.5 exposure,
Figure 5F. The IL-33 receptor, ST2, was expressed at lower levels in the right ventricles of RELMα
-/-BALB/c mice, which reached statistical significance in antigen and PM
2.5 challenged RELMα
-/-BALB/c mice relative to WT,
Figure 5H.
4. Discussion
Our data showed that endogenous RELMα was not necessary for the development of increased right ventricular systolic pressures in mice exposed to antigen and PM
2.5. This conclusion is based on our studies using mice of two different strain backgrounds, C57BL/6 and BALB/c. Based on previous reports showing that RELMα, also called HIMF, was both necessary and sufficient to cause the hypoxia induced increase in right ventricular systolic pressure [
15,
16,
17,
25], our data were unexpected. However, the discrepancy can be explained by the very different experimental systems used.
In our studies comparing WT and RELMα-/- mice, we found distinct differences between C57BL/6 and BALB/c strains. In the C57BL/6 strain, RELMa was redundant. In the BALB/c strain relative to WT, RELMα-/- mice challenged with antigen and PM2.5 did not develop increased right ventricle weight, had ameliorated pulmonary vascular remodeling, and no increase in right ventricle ANP expression together with decreased IL-33 and ST2 expression in the right ventricle.
Cardiac myocytes, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells express IL-33 constitutively [
50]. IL-33 expression is further increased by inflammatory stimuli in cardiac myocytes and fibroblasts. Cardiac endothelial cells express the IL-33-receptor, ST2, while cardiac myocytes and fibroblasts have relatively low level of surface ST2-expression. [
50] The significantly lower expression of these mediators of inter-cellular communication in the right ventricle of RELMα
-/- BALB/c mice may have prevented an increase in right ventricular weight in response to antigen and PM2
.5 exposure despite the right ventricular systolic pressures that were increased to wild type levels.
The RELMα
-/- mice that we studied also had significantly decreased RELMb and RELMg expression in the lungs and right ventricle. Therefore, our study indicates a critical role of these mediators in BALB/c mice for the responses to antigen and PM
2.5, while they were redundant in C57BL/6 mice. The strain difference could be due to differences in the responsiveness of the pulmonary vasculature to proliferative and constrictive cues. In this respect, it is remarkable that C57BL/6 mice have polymorphisms (SNPs) in the 3-prime region of the BMPR2 (bone morphogenetic protein receptor, type II) gene that are not found in BALB/c mice (
https://www.informatics.jax.org/snp/marker/MGI:1095407). Decreased function of the BMPR2 gene is associated with a high risk to develop pulmonary hypertension [
51]. Another possibility is that potential receptors for the RELM molecules, among them toll like receptor (TLR4) or RAGE (advanced glycosylation end-product) [
52,
53] are polymorphic and differ between C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice. There is strong evidence that resistin binds TLR4 [
54,
55], however, little is known about the binding of RELM molecules to TLR4. However, TLR4 is polymorphic between BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice [
56], and this is particularly important because the antigen (OVA) that we used contains lipopolysaccharide which induces inflammation via TLR4. The RAGE gene is located in the MHC locus, H2K, and this locus is highly polymorphic between BALB/c (H2Kd) and C57BL/6 (H2Kb) mice.
There are some limitations of our study: 1) First of all, humans only have one resistin like molecule, RELMβ, and human RELMβ is induced in hypoxia and is mitogenic for vascular smooth muscle cells [
57]. It is thought that mouse RELMα is the homologue of human RELMβ but mouse RELMα may not have the same function as human RELMβ. 2) Secondly, the RELMα
-/- mice of both strain backgrounds that were studied by us have a compound KO phenotype with a deletion of RELMα, and significantly depressed RELMβ and RELMγ. In mice, the three resistin like molecules developed by gene-duplication on chromosome 16 and the compound deficiency is likely due to the deletion of a master regulator of all three resistin like molecules in the KO animals. The compound KO phenotype of our mice may partially explain the different data with respect to the role of RELMα for the pulmonary hypertension phenotype that has been reported in the hypoxia system [
16]. Those studies were conducted with RELMα specific inhibitors in wild type animals. 3) Lastly, our studies used a very low dose of PM
2.5 that does not induce a response intranasally which is different from mice given saline intranasally [
11]. Therefore, the RELMα-dependent responses identified in our studies (e.g. BALB/c strain mice pulmonary arterial remodeling, increased right ventricular weights and mediator expression) were driven by the adaptive immune response to OVA and perhaps the associated lipopolysaccharide. Future dose-response studies are necessary to understand the role of RELMα for cardiovascular and lung responses to PM
2.5 exposure.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, our study demonstrates that the role of RELMα for the pulmonary hypertension phenotype and molecular markers of right ventricular stress is dependent on the mouse background strain that in turn determines clearly distinct adaptive immune response types in the lungs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, ND, AN, GG; Data curation, GG; Formal analysis, ND, WCC, SHP, GG; Funding acquisition, GG; Investigation, WCC, SHP, GG; Methodology, WCC, SHP, LM, AN, GG; Project administration, WCC, AN, GG; Resources, ND, SHP, AN, GG; Supervision, GG; Validation, WCC, SK, GG; Visualization, ND, SK, GG; Writing – original draft, ND, SHP, AN, GG; Writing – review & editing, ND, WCC, LM, SK, AN, GG. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded in part by the National Institutes of Health 1R21HL092370-01 (GG), 1R01 HL095764-01 (GG); American Heart Association, Founders affiliate (0855943D, GG), Stony Wold-Herbert Award (SK), KL2TR001446-07(SK), and U01-OH011855 (AN); core support was by NIEHS center grant (ES00260) and Cancer center grant (5P30CA16087-33).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data supporting reported results can be found in the manuscript. Additional details may be requested from the corresponding author Professor Grunig.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Cogan, J.D.; et al. High frequency of BMPR2 exonic deletions/duplications in familial pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2006, 174, 590–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, R.J.; Morrell, N.W. Molecular mechanisms of pulmonary arterial hypertension: role of mutations in the bone morphogenetic protein type II receptor. Chest 2008, 134, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daley, E.; et al. Pulmonary arterial remodeling induced by a Th2 immune response. J Exp Med 2008, 205, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sztrymf, B.; et al. Clinical outcomes of pulmonary arterial hypertension in carriers of BMPR2 mutation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2008, 177, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crosswhite, P.; Sun, Z. Nitric oxide, oxidative stress and inflammation in pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Hypertens 2010, 28, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldred, M.A.; et al. Characterization of the BMPR2 5'-untranslated region and a novel mutation in pulmonary hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2007, 176, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinovitch, M. Molecular pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Clin Invest 2008, 118, 2372–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.Y.; Loscalzo, J. Pathogenic mechanisms of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2008, 44, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strange, J.W.; et al. Recent insights into the pathogenesis and therapeutics of pulmonary hypertension. Clin Sci (Lond) 2002, 102, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daley, E.; et al. Pulmonary arterial remodeling induced by a Th2 immune response. The Journal of experimental medicine 2008, 205, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunig, G.; et al. Perspective: ambient air pollution: inflammatory response and effects on the lung’s vasculature. Pulm Circ 2014, 4, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; et al. The effects of antigen-specific IgG1 antibody for the pulmonary-hypertension-phenotype and B cells for inflammation in mice exposed to antigen and fine particles from air pollution. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0129910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; et al. IL-13 and IL-17A induced pulmonary-hypertension-phenotype due to inhalation of antigen and fine particles from air pollution. Pulm Circ 2014, 4, 654–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelini, D.J.; et al. Hypoxia-induced mitogenic factor (HIMF/FIZZ1/RELM alpha) recruits bone marrow-derived cells to the murine pulmonary vasculature. PLoS One 2010, 5, e11251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelini, D.J.; et al. Hypoxia-induced mitogenic factor (HIMF/FIZZ1/RELMalpha) induces the vascular and hemodynamic changes of pulmonary hypertension. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2009, 296, L582–L593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, D.J.; et al. Hypoxia-induced mitogenic factor (HIMF/FIZZ1/RELMalpha) in chronic hypoxia- and antigen-mediated pulmonary vascular remodeling. Respir Res 2013, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, X.; et al. FIZZ1/RELMalpha, a novel hypoxia-induced mitogenic factor in lung with vasoconstrictive and angiogenic properties. Circ Res 2003, 92, 1065–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaji-Kegan, K.; et al. Hypoxia-induced mitogenic factor has proangiogenic and proinflammatory effects in the lung via VEGF and VEGF receptor-2. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2006, 291, L1159–L1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Tan, H.; Irwin, D.M. Evolution of the vertebrate Resistin Gene family. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0130188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hue, I.; et al. Recent advances in the crosstalk between adipose, muscle and bone tissues in fish. Frontiers in Endocrinology 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holcomb, I.N.; et al. FIZZ1, a novel cysteine-rich secreted protein associated with pulmonary inflammation, defines a new gene family. Embo J 2000, 19, 4046–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; et al. FIZZ1 plays a crucial role in early stage airway remodeling of OVA-induced asthma. Journal of Asthma 2008, 45, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munitz, A.; et al. Resistin-like molecule alpha enhances myeloid cell activation and promotes colitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008, 122, 1200–1207e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, M.G.; et al. Alternatively activated macrophage-derived RELM-{alpha} is a negative regulator of type 2 inflammation in the lung. J Exp Med 2009, 206, 937–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johns, R.A.; et al. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1alpha Is a Critical Downstream Mediator for Hypoxia-Induced Mitogenic Factor (FIZZ1/RELMalpha)-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2016, 36, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renigunta, A.; et al. Human RELMbeta is a mitogenic factor in lung cells and induced in hypoxia. FEBS Lett 2006, 580, 900–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Johns, R.A. Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) is a binding partner for hypoxia induced mitogenic factor (HIMF/FIZZ1) and mediates myeloid cell chemotaxis. Faseb J 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; et al. Hypoxia-induced mitogenic factor/FIZZ1 induces intracellular calcium release through the PLC-IP(3) pathway. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2009, 297, L263–L270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; et al. S100A11 mediates hypoxia-induced mitogenic factor (HIMF)-induced smooth muscle cell migration, vesicular exocytosis, and nuclear activation. Mol Cell Proteomics 2011, 10, M110 000901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.D.; et al. Disulfide-dependent multimeric assembly of resistin family hormones. Science 2004, 304, 1154–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstmayer, B.; et al. Identification of RELMgamma, a novel resistin-like molecule with a distinct expression pattern. Genomics 2003, 81, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steppan, C.M.; et al. A family of tissue-specific resistin-like molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001, 98, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munitz, A.; et al. Resistin-like molecule alpha decreases glucose tolerance during intestinal inflammation. J Immunol 2009, 182, 2357–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesce, J.T.; et al. Retnla (relmalpha/fizz1) suppresses helminth-induced th2-type immunity. PLoS Pathog 2009, 5, e1000393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munitz, A.; et al. Resistin-like molecule-alpha regulates IL-13-induced chemokine production but not allergen-induced airway responses. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2012, 46, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, K.; et al. Strain dependence of airway hyperresponsiveness reflects differences in eosinophil localization in the lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2001, 281, L394–L402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; et al. Influence of the route of allergen administration and genetic background on the murine allergic pulmonary response. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 1997, 155, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, C.D.; et al. M-1/M-2 macrophages and the Th1/Th2 paradigm. J Immunol 2000, 164, 6166–6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, H.; et al. Innate immune response in Th1- and Th2-dominant mouse strains. Shock 2004, 22, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, T.; et al. A centrifugal particle concentrator for use in inhalation toxicology. Inhal Toxicol 1999, 11, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, T. Linking health effects to PM components, size, and sources. Inhal Toxicol 2007, 19 (Suppl. 1), 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; et al. Modification of hemodynamic and immune responses to exposure with a weak antigen by the expression of a hypomorphic BMPR2 gene. PLoS One 2013, 8, e55180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenbarth, S.C.; et al. Lipopolysaccharide-enhanced, toll-like receptor 4–dependent T helper cell type 2 responses to inhaled antigen. The Journal of experimental medicine 2002, 196, 1645–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.C.; et al. Right ventricular systolic pressure measurements in combination with harvest of lung and immune tissue samples in mice. J Vis Exp 2013, e50023. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, C.; et al. Interleukin-19: a constituent of the regulome that controls antigen presenting cells in the lungs and airway responses to microbial products. PLoS One 2011, 6, e27629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padilla, J.; et al. IL-13 Regulates the Immune Response to Inhaled Antigens. J Immunol 2005, 174, 8097–8105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, J.G.; et al. Il-13 and IFN-gamma: interactions in lung inflammation. J Immunol 2001, 167, 1769–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunig, G.; et al. Requirement for IL-13 independently of IL-4 in experimental asthma. Science 1998, 282, 2261–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, J.C.; et al. Developmental pattern of ventricular atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) expression in chronically hypoxic rats as an indicator of the hypertrophic process. Journal of molecular and cellular cardiology 1994, 26, 753–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanada, S.; et al. IL-33 and ST2 comprise a critical biomechanically induced and cardioprotective signaling system. J Clin Invest 2007, 117, 1538–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.D.; et al. BMPR2 mutations and survival in pulmonary arterial hypertension: an individual participant data meta-analysis. Lancet Respir Med 2016, 4, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; et al. HIMF (hypoxia-induced mitogenic factor) signaling mediates the HMGB1 (high mobility group box 1)-dependent endothelial and smooth muscle cell crosstalk in pulmonary hypertension. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology 2019, 39, 2505–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; et al. RELMα licenses macrophages for damage-associated molecular pattern activation to instigate pulmonary vascular remodeling. The Journal of Immunology 2019, 203, 2862–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarkowski, A.; et al. Resistin competes with lipopolysaccharide for binding to toll-like receptor 4. Journal of cellular and molecular medicine 2010, 14, 1419–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.C.; et al. Human resistin protects against endotoxic shock by blocking LPS–TLR4 interaction. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2017, 114, E10399–E10408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukamoto, H.; et al. Reduced surface expression of TLR4 by a V254I point mutation accounts for the low lipopolysaccharide responder phenotype of BALB/c B cells. The Journal of Immunology 2013, 190, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Johns, R.A. Resistin family proteins in pulmonary diseases. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 2020, 319, L422–L434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the sensitization and challenge protocol.
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the sensitization and challenge protocol.
Figure 2.
Photomicrographs show examples of small <100um pulmonary arteries (*).
Figure 2.
Photomicrographs show examples of small <100um pulmonary arteries (*).
Figure 3.
Expression of RELMa, b, g in the lungs (A) or the right ventricle (B). RELM b was not detected in the right ventricle (data not shown). Bars show means, SEM and individual data points of relative CT values measured to b-actin and calculated relative to the mean of the OVA-PM wild type groups at 100U. Groups were compared by independent, 2-tailed Mann Whitney test, p<0.05 for comparison with a) WT-PBS, b) WT-OVA-PM, c) KO-PBS.
Figure 3.
Expression of RELMa, b, g in the lungs (A) or the right ventricle (B). RELM b was not detected in the right ventricle (data not shown). Bars show means, SEM and individual data points of relative CT values measured to b-actin and calculated relative to the mean of the OVA-PM wild type groups at 100U. Groups were compared by independent, 2-tailed Mann Whitney test, p<0.05 for comparison with a) WT-PBS, b) WT-OVA-PM, c) KO-PBS.
Figure 4.
Pulmonary Vascular Responses to exposure with OVA-PM in C57BL/6 strain (A,B) or BALB/c (C,D) strain mice measured by pulmonary arterial remodeling scores (A,C) and right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP, B,D) . Violin plots show individual data points and data distribution. Pairwise comparisons were with independent, 2-tailed Mann Whitney test. P<0.05 for comparison with a) WT-PBS, b) WT-OVA-PM, c) KO-PBS.
Figure 4.
Pulmonary Vascular Responses to exposure with OVA-PM in C57BL/6 strain (A,B) or BALB/c (C,D) strain mice measured by pulmonary arterial remodeling scores (A,C) and right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP, B,D) . Violin plots show individual data points and data distribution. Pairwise comparisons were with independent, 2-tailed Mann Whitney test. P<0.05 for comparison with a) WT-PBS, b) WT-OVA-PM, c) KO-PBS.
Figure 5.
Right Ventricular Responses in C57BL/6 strain (A,C,E,G) and BALB/c (B,D,F,H) strain mice measured by right ventricular weight (RV/LV+S) (A,B) and expression of mediators that reflect RV stress (ANP-natriuretic peptide type A, IL-33, ST2-IL1RL1-IL-33 receptor). Violin plots (A,B) show individual data points and data distribution. Bars (C-H) show means, SEM, and individual data points. C-H: CT values were calculated relative to b-actin (x1,000). Pairwise comparisons were with the independent, 2-tailed Mann Whitney test. P<0.05 for comparison with a) WT-PBS, b) WT-OVA-PM, c) KO-PBS.
Figure 5.
Right Ventricular Responses in C57BL/6 strain (A,C,E,G) and BALB/c (B,D,F,H) strain mice measured by right ventricular weight (RV/LV+S) (A,B) and expression of mediators that reflect RV stress (ANP-natriuretic peptide type A, IL-33, ST2-IL1RL1-IL-33 receptor). Violin plots (A,B) show individual data points and data distribution. Bars (C-H) show means, SEM, and individual data points. C-H: CT values were calculated relative to b-actin (x1,000). Pairwise comparisons were with the independent, 2-tailed Mann Whitney test. P<0.05 for comparison with a) WT-PBS, b) WT-OVA-PM, c) KO-PBS.
Table 1.
List of primers and probes.
Table 1.
List of primers and probes.
| ANP-F |
nppa |
TACAGTGCGGTGTCCAACACAG |
| ANP-R |
nppa |
TGCTTCCTCAGTCTGCTCACTC |
| IL-33-F |
il33 |
ACTGCATGAGACTCCGTTCTG |
| IL-33-R |
il33 |
CCTAGAATCCCGTGGATAGGC |
| ST2 rtF |
il1rl1 |
GGATTGAGGTTGCTCTGTTCTGG |
| ST2 rtR |
il1rl1 |
TCGGGCAGAGTGTGGTGAACAA |
| β-actin-F |
actb |
GGCTGTATTCCCCTCCATCG |
| β-actin-R |
actb |
CCAGTTGGTAACAATGCCATGT |
| RELMα (TaqMan) |
retnla |
CTTGCCAATCCAGCTAACTATCCCT |
| RELMβ (TaqMan) |
retnlb |
GGAAGCTCTCAGTCGTCAAGAGCCT |
| RELMγ (TaqMan) |
retnlg |
AAACCTGGCTCATATCCCATTGATG |
| Actin, β (TaqMan) |
actb |
ACTGAGCTGCGTTTTACACCCTTTC |
Table 2.
Percentage of severely remodeled pulmonary arteries following exposure to OVA-PM1.
Table 2.
Percentage of severely remodeled pulmonary arteries following exposure to OVA-PM1.
| Severely Remodeled Pulmonary Artery (OVA-PM exposed) |
C57BL/6 |
BALB/c |
| Median |
Quartiles |
Group n |
P-value |
Median |
Quartiles |
Group n |
P-value |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Wild Type |
12.03 |
1.315, 50.460 |
8 |
0.1919 |
7.275 |
0.00, 10.390 |
10 |
0.0126 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| RELMa-/- |
39.13 |
19.790, 41.800 |
9 |
0.000 |
0.00, 3.846 |
10 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).