1. Introduction
As technology and smart devices become more prevalent in all aspects of human lives, power usage has increased dramatically. There is no way the conventional electrical grid can meet the growing demands for energy. It is for this reason that smart grids have become increasingly prevalent in meeting the ever-increasing demand for power. Smart grids (SG) increase the resilience and stability of conventional electrical networks by incorporating information technologies (IT). A smart meter (SM) is employed in SG in order to monitor power and communication. SMs are advanced metering devices that provide two-way communication between utilities and their customers, enabling utilities to measure and monitor energy usage in real-time. The application of SMs in the power grids offers a range of benefits, including:
Improved Accuracy: SMs are able to measure energy usage more accurately than traditional meters, leading to improved billing accuracy and fewer customer disputes.
Improved Efficiency: By providing real-time data, SMs enable utilities to more efficiently manage their power grids, reducing outages and improving reliability.
Reduced Costs: SMs can help reduce operational costs by eliminating the need for manual meter readings and providing more accurate billing information.
Improved Customer Service: SMs enable utilities to offer a range of value-added services, such as energy usage tracking and energy saving tips, to their customers.
Increased Revenue: SMs can help utilities identify opportunities to increase revenue, such as offering time-of-use pricing or demand response programs.
A smart appliance is scheduled using an energy management controller (EMC) installed at a user’s location in the domestic, industrial, and commercial areas. There are a variety of methods applied in demand-side management (DSM) for addressing the problem of power optimization through peak clipping, load shifting, flexible load shifting, valley filling, strategic conservation, and increasing strategic loads. It is possible to transfer load from peak hours to off-peak demand hours with the help of these methods [
1]. DSM provides 2 primary functions: demand response (DR) and load management [
2]. Demand response programs in power grids are designed to reduce the demand for electricity during peak periods, such as summer afternoons when air conditioning is running at full blast. These programs typically involve incentives for consumers to reduce their electricity consumption during peak times, such as providing discounts for customers who reduce their energy use, or providing rewards for customers who participate in demand response programs. Additionally, utilities may use demand response programs to encourage customers to shift their energy use to off-peak hours, such as night-time or early morning, when electricity is cheaper and more abundant. By reducing peak demand, these programs can help utilities avoid having to build additional power plants or buy additional electricity from other utilities. User load management can be called DSM as well. In other words, it involves moving energy consumption from peak demand (at peak) periods to non-peak demand (at non-peak ) times for reducing power costs. Variable price signals cause users to respond with DR. A DR can take 2 forms: reducing power costs or offering incentives to users [1, 2].
Reduced energy bills, lower Peak to Average Ratio (PAR), and lower user dissatisfaction have been the primary goals of energy management systems (EMS). In order to reach the mentioned purposes, a diversity of algorithms are developed. Refs [
3,
4] applied mixed-integer linear programming, non-integer linear programming, convex programming, and mixed integer nonlinear programming to minimize price and power usage. Although the methods have been widely applied, they have a long convergence time, and they are limited to just a few devices. Using meta-heuristic methods, experts solve the power optimization problem by overcoming the shortcomings mentioned above. Ref [
5] presented the genetic algorithm (GA) aimed at minimizing costs. Ref [
6] applied ant colony optimization (ACO) and differential evolution (DE) to minimize costs and aggregate energy usage.
There are a variety of algorithms that experts have developed for SG in order to optimize power efficiency in domestic, industrial, and commercial sectors, which will be of benefit to users and utilities alike. Balanced load and decreased energy costs are the primary objectives of scientists. A variety of factors are taken into account, including price methods, appliance kinds, and consumer demands.
Ref [
7] examined a mix of bacterial foraging algorithm (BFA) and GA-driven DSM designed for intelligent houses. Its goal is to reduce peak loads, minimize costs, maximize consumer satisfaction, and shift loads. Comparing HBG with GA and BFA, PAR, and wait time can be decreased via HBG price. Ref [
8] examined a community-driven method for optimizing energy consumption. By integrating renewable power resources, the paper was able to achieve a high level of satisfaction for consumers and less power consumption by utilizing particle swarm optimization (PSO). Ref [
9] examined the time-limited bio-inspired algorithm-driven system for home energy management (HEM). To diminish power bills and achieve consumers’ high level of satisfaction, GA, moth-flame optimization algorithm and their combination have been examined. Ref [
10] examined a HEM system utilizing cuckoo search. In order to compare the effectiveness of GA and the cuckoo search algorithm, the DAP signal is used to measure power price reductions, PAR, and consumer dissatisfaction. Ref [
11] investigated cuckoo search combined with levy flights for a type of fruit-fly and bird. A cuckoo search has a number of advantages over GA and PSO due to its robustness and genericity. Ref [
12] applied TLBO (teacher learning-based algorithm) algorithm, GA algorithm, TLGO (teacher learning genetic optimization) algorithm and LP (linear programming) algorithm in order to plan appliances. Flexible devices were classified as "time flexible" and "power flexible" to facilitate efficient power usage in SG. It is possible for power users to plan devices to optimize their power usage using the method. As a result of the method, users who have a limited overall power usage can benefit from maximum satisfaction as well. Ref [
13] examined the most effective operating strategies in microgrids using the enhanced swarm optimization algorithms and adaptive evolutionary algorithms. Ref [
14] examined the optimum planning method for domestic devices, utilizing the DAP signals in the smart home. With the algorithm, optimal costs are reduced by 22.6%, and normal prices are reduced by 11.7%. There is no power optimization involved. Ref [
15] examined the shifting of loads, minimizing costs, and the energy storage system (ESS). The suggested system allows users to purchase power at low demand times and sell it back to utilities at peak times.
Ref [
16] examined the gradient-based PSO (GPSO) method applied to demand response (DR) for the smart home, taking into account the uncertainty associated with loads and power costs. Ref [
17] applied heuristic-driven GAs in DR applications in HEM systems for optimum energy planning. Enhanced DE and the newly developed differential teaching learning algorithm were employed to minimize domestic overall power costs and consumer dissatisfaction levels. Ref [
18] examined joint multi-swarm PSO in order to minimize costs without considering PAR. Ref [
19] applied GA alongside the DAP method to schedule the load demands efficiently. Ref [
20] offered load balancing mechanisms for commercial, domestic, and industrial sectors. The energy consumption using GA and not using GA in DSM was investigated. Power consumption at peak times was decreased through GA-driven DSM. Unfortunately, neither PAR nor consumer dissatisfaction were mentioned. Ref [
21] applied PSO to schedule electrical devices to minimize power costs. An experiment was conducted in a smart community using various scenarios involving altering the renewable power usage rates and consumer satisfaction levels. In order to minimize power costs and reduce PAR, the suggested optimization methods sacrificed consumer satisfaction. The study examines and analyzes 2 bio-inspired algorithms to optimize power in the domestic area including grasshopper optimization algorithm (GOA) and BFA. Due to the fact that the algorithms are designed using the optimal optimization methods of naturally-occurring organisms. The simulation shows that by implementing bio-inspired optimization algorithms, the power costs and PAR are minimized in comparison with unplanned loads.
A Smart Energy Management Controller is presented in the present study for residential areas in which each appliance is linked and controlled. In order to find an optimal outcome for a single house, this paper uses 2 heuristic algorithms the BFA and the GOA. BFA is a metaheuristic optimization algorithm that mimics the foraging behavior of bacteria. It is used to search for the optimal solution of complex problems. BFA is an effective tool for energy management of power grids. It is used to optimize the scheduling of power generation and distribution in order to reduce energy consumption and improve efficiency. BFA has the ability to explore the entire search space and identify the optimal solution. It is also capable of dealing with multiple objectives and constraints. On the other hand, GOA is a population-based metaheuristic algorithm inspired by the behavior of grasshoppers. It uses the random search of grasshoppers to explore the search space and the social behavior of the grasshoppers to exploit the promising areas of the search space. GOA has been used to solve various optimization problems related to energy management in power grids. In this study, GOA and BFA schedule each Automatically Operated Appliance (AOA). By planning this way, energy costs and PAR can be minimized. The algorithms take into account the energy cost and peak-to-average ratio (PAR) of the appliances when creating the schedule. The algorithms will adjust the start and end times of the appliances to minimize energy costs and PAR. The algorithms also consider the different energy sources available, such as solar or wind energy, and will prioritize the use of these sources to further reduce energy costs. By using these algorithms, the energy costs and PAR can be minimized, allowing for a more efficient use of energy. In the simulations, GOA and BFA are shown, and their plots demonstrate their efficacy and feasibility for AOA. Moreover, the use of appliance planning in residential houses is a key factor in reducing power price and PAR (peak average ratio) without compromising user comfort (UC). By strategically scheduling the operation of electrical appliances, households can reduce their electricity bills and reduce their peak demand. This can be achieved through the use of smart thermostats, smart power strips, and other energy-saving devices that allow users to set their own comfort levels and reduce their energy consumption. Additionally, appliance planning can help households optimize the use of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind energy, which can further reduce power prices and PAR without compromising user comfort.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows: a detailed explanation of the suggested scheme and optimization algorithm can be found in Part 2. Part 3 describes the DSM structure and requirements. Part 4 discusses the simulation outcomes. Finally, Part 5 provides the conclusion.
2. Suggested Scheme
In smart grids, demand-side management (DSM) performs functions such as energy management and demand control. Demand-side management (DSM) is an approach to managing electricity demand in order to reduce overall energy consumption and improve power grid efficiency. It can be used for both residential and commercial buildings, and involves strategies such as load management, energy efficiency, and peak demand reduction. Load Management Benefits:
Improved Grid Efficiency: Load management helps to reduce the strain on the power grid by allowing electricity to be used more efficiently. This can help to reduce energy costs and improve the reliability of the grid.
Lower Energy Bills: By reducing peak demand, load management can help to reduce energy bills for both businesses and households.
Increased Sustainability: By reducing energy consumption, load management can help to reduce emissions and promote sustainability.
Challenges
Cost: Implementing load management can be expensive, as it requires the installation of smart meters and other equipment.
Complexity: Load management can be difficult to implement, as it requires the coordination of multiple stakeholders and an understanding of the power grid.
Lack of Awareness: Many people are unaware of the benefits of load management, and may not understand the need for it.
Technically, load management is possible for both single and multiple houses using the suggested model. Users and utilities can communicate 2-way through SG. Utility knows existing consumer consumption via SG. This paper proposes to use 2 kinds of devices in the suggested model: non-interruptible, and interruptible. Devices with constant power/load and flexible consumption time fall under the interruptible group, whereas devices with flexible load and constant consumption time fall under the interruptible group. Interrupting them while they are working is not allowed. Time of usage (TOU) has been utilized to calculate the overall early price of consuming power. TOU creates a block for certain periods of time. There is no change in the power cost during these hours (
Table 1). As well as this, the study uses TOU as a cost model to calculate bills. Time of Usage (TOU) is a pricing strategy used by electric utilities to encourage customers to shift their energy consumption to periods of lower demand. This strategy is used to reduce the overall cost of providing electricity to customers and to reduce peak demand on the electric grid. The goal of TOU in Demand Response is to reduce the need for additional power generation capacity and to reduce the cost of electricity for customers. The TOU in demand response pricing strategy works by setting different prices for electricity at different times of the day. During peak demand periods, such as during the middle of the day when people are using the most electricity, the price of electricity is set higher. During off-peak periods, such as in the evening when people are using less electricity, the price of electricity is set lower. This encourages customers to shift their energy consumption to the lower-priced off-peak periods, which reduces the overall cost of providing electricity. The benefits of TOU in demand response are numerous. By shifting energy consumption to off-peak periods, customers can save money on their electricity bills. Additionally, by reducing peak demand on the electric grid, utilities can avoid the need to build additional power generation capacity, which can be expensive and time-consuming. Finally, by reducing peak demand, utilities can also reduce the amount of carbon dioxide emissions released into the atmosphere, which is beneficial for the environment.
This paper aims to minimize the energy price and PAR by minimizing power usage. This study focuses on the decrease of overall costs as a result of using Eq.1 which minimizes PAR (
Table 2).
Peak to Average Ratio (PAR) management in power systems is a critical factor in the efficient operation of power systems. It is the measure of the peak power demand compared to the average power demand over a given time period. The PAR is used to assess the capability of the grid to handle the peak demand and to identify potential areas of improvement that could be made to reduce the peak demand. In order to manage the PAR, it is important to understand the various factors that contribute to the peak demand. In Eq.2, the total is calculated and PAR is computed through applying Eq.3 in the following manner:
The main factors that contribute to the peak demand are the energy consumption of the customers, the power factor, the transmission line capacity, and the load profile. The energy consumption of the customers is the amount of energy consumed by the customers and is usually represented in terms of kilowatt-hours (kWh). The power factor is the ratio between the real power and the apparent power and is usually measured in terms of power factor correction (PFC). The transmission line capacity is the maximum amount of power that can be transmitted through the transmission lines and is usually represented in terms of megawatts (MW). The load profile is the amount of power demand that is expected to be present at any given time and is usually represented in terms of peak load.
In order to manage the PAR, it is important to identify the areas of improvement that could be made to reduce the peak demand. This includes improving the power factor, reducing the transmission line capacity, and reducing the energy consumption of the customers. Additionally, it is important to monitor the load profile and identify any changes that could result in a peak demand. Once these areas of improvement have been identified, they can be implemented to reduce the peak demand and improve the PAR. Additionally, it is important to monitor the PAR on a regular basis to ensure that it remains within the acceptable range.
A. Optimization Methods
The energy management of power grids and residential loads is an important task that has been a focus of research for many years. In recent years, two algorithms have emerged as promising solutions to this problem: the Hybrid Bacteria Foraging Algorithm (BFA) and the Grasshopper Optimization Algorithm (GOA). These algorithms have been applied to a variety of energy management tasks, such as load forecasting, load shedding, and energy optimization. In this article, we will discuss the benefits of using these algorithms in energy management of power grids and residential loads. Both BFA and GOA have been used to solve a variety of energy management problems, including load forecasting, load shedding, and energy optimization. BFA and GOA are both powerful tools for energy management due to their ability to quickly identify optimal solutions and their ability to handle complex problems. In addition, both algorithms are robust and efficient, making them suitable for large-scale problems.
The use of BFA and GOA in energy management of power grids and residential loads can provide numerous benefits. For example, these algorithms can be used to reduce energy costs by optimizing energy consumption. BFA and GOA can also be used to reduce the risk of power outages by accurately forecasting the load and shedding unnecessary loads. In addition, these algorithms can be used to optimize energy storage, which can help reduce the cost of energy storage and improve the efficiency of energy storage systems. Finally, BFA and GOA can be used to optimize the use of renewable energy sources, which can help reduce the environmental impact of energy production.
a) GOA
Grasshoppers are destructive insects commonly referred to as pests since they damage agriculture. The number of grasshopper species is about11000 [
22]. In general, they are regarded to be flying animals. According to
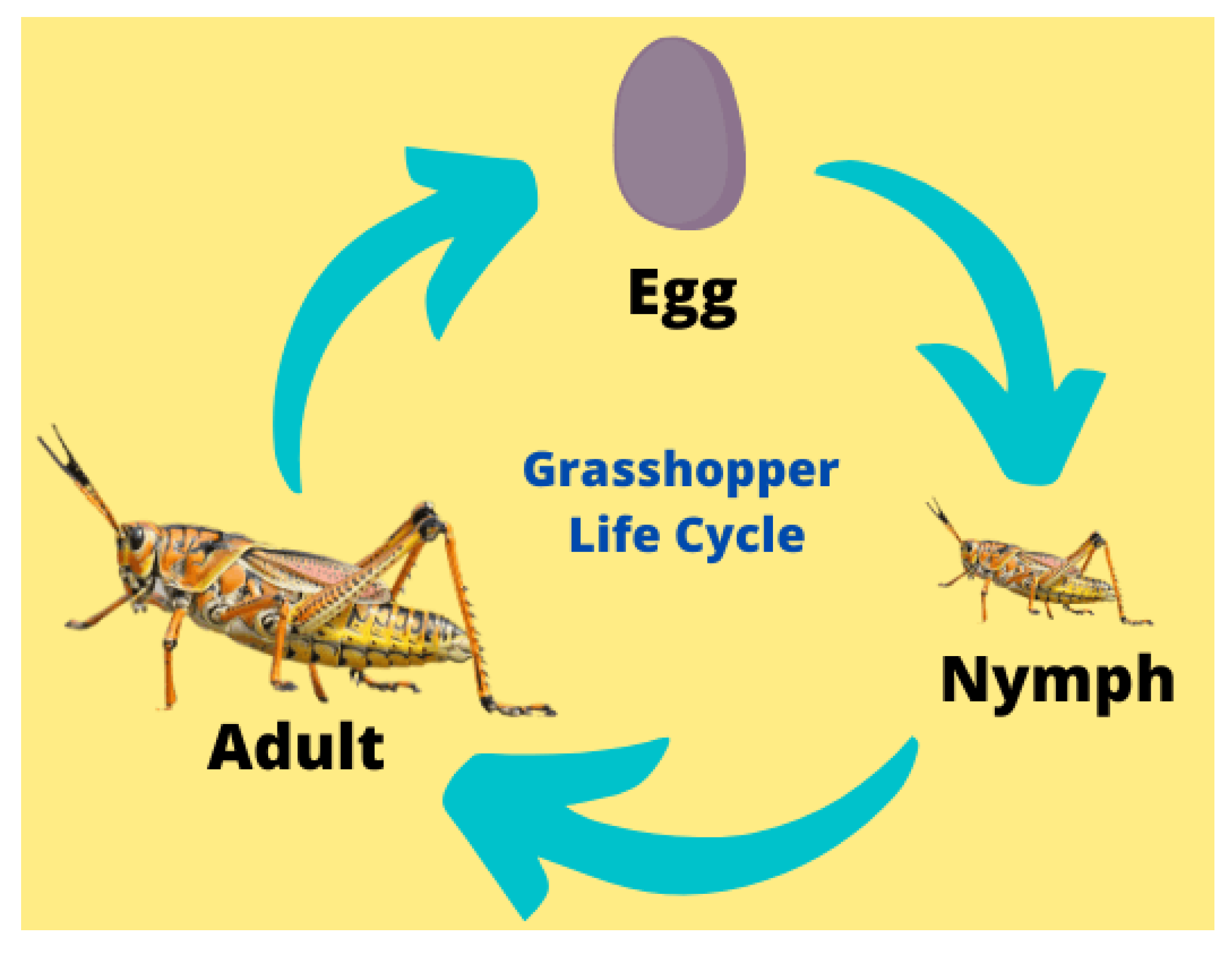
Figure 1, grasshoppers pass through three phases as they reach adulthood: eggs, nymphs, and adults.
In the natural world, grasshoppers are usually observed in swarms. Farmlands are attacked by them and turned into nightmares for farmers. Grasshoppers, both adults, and nymphs display the behavioral trait of swarming. An average grasshopper swarm consists of approximately 5 billion grasshoppers and covers a region of about 60 miles. Algorithms inspired by nature use specific mechanisms for searching for food. Exploration and exploitation are 2 methods involved in this process.
(a) Exploration: This is the method of discovering a novel solution in the quest area by applying the existing solutions.
(b) Exploitation: It involves the search of the surrounding quest area by the algorithm. GOA’s mathematical scheme reflecting grasshopper swarming behavior has been presented like ref [
23].
Here,
is the
grasshopper’s location,
shows the social collaboration,
shows a grasshopper’s gravitational force and
shows the air-advection. In the previous formula, randomness is produced by:
In which,
,
and
would be randomly selected numbers from 0 to 1.
can be shown as follows:
Here, the number of search units has been shown by
,
shows the social relationship among 2 grasshoppers
and
,
represents the corresponding distance among
and
grasshoppers and would be as follows:
represents the vector of the agent from the
grasshopper to the
grasshopper. The equation for calculating social force is described as below:
Here, the attractive force has been represented by
, the distance has been shown by
and attraction’s measure has been shown by
.
component would be:
In which, a gravitational force has been shown by
, and the not-positive sign indicates its direction is toward Earth’s center, whereas agent vector in Earth’s direction is shown by
. Thus,
component would be:
In which, represents the fixed drift in the presence of a wind and represents the wind directional agent vector.
The following results can be achieved by substituting
and
into
:
The simulations show interactions among grasshoppers in a swarm using the previous formula of the swarm in free space.
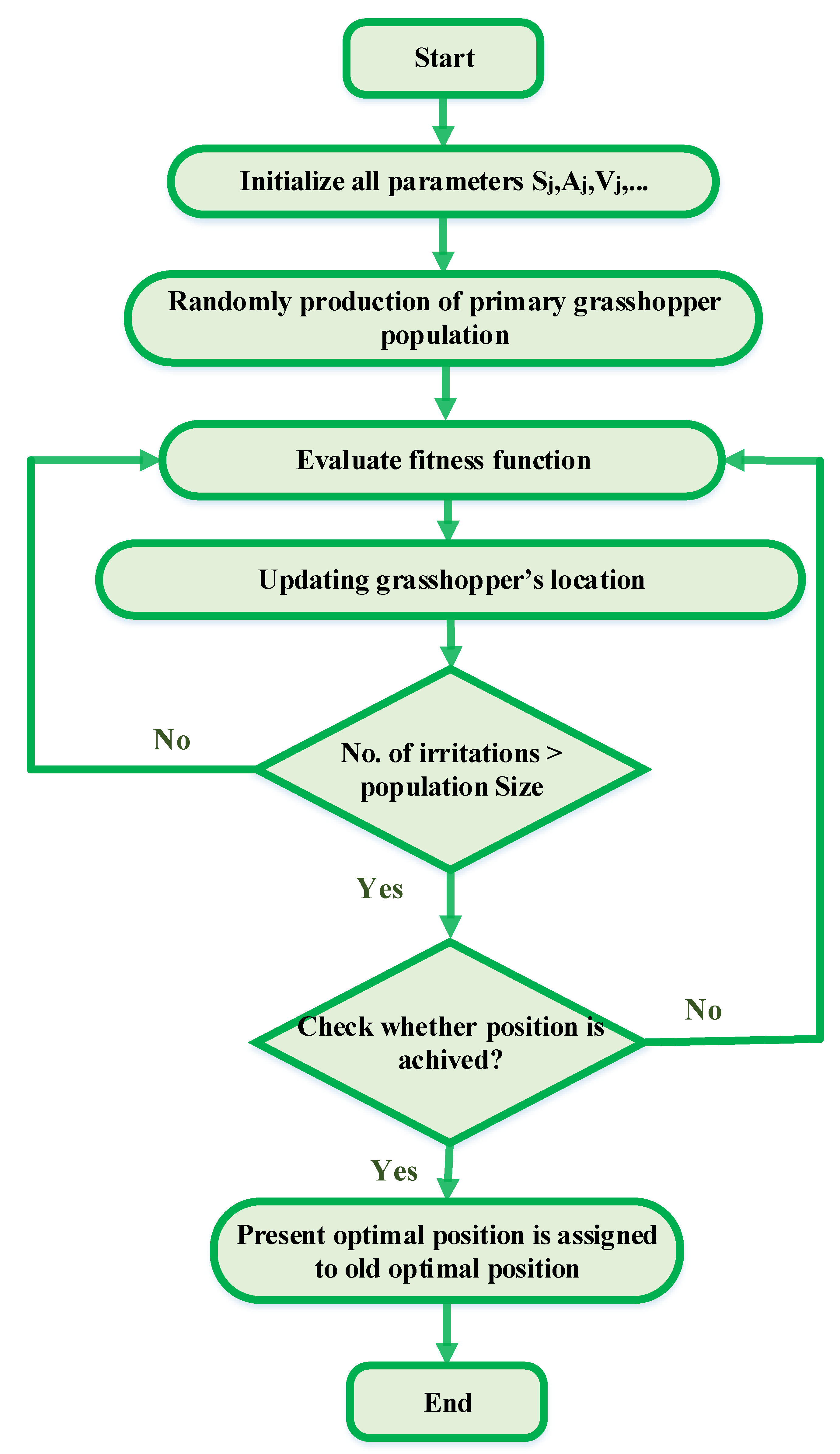
Figure 2 illustrates the procedures of the GOA algorithm.
b) BFA
Kevin Passino introduced BFA in 2002 [
24]. The most important part of the algorithm would be the method of group foraging of Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria. A bacteria’s power per unit time is maximized by foraging for nutrients and food. Signals are also used by bacteria for communication. It is possible for prey to be on the move due to hunters. As a result, the bacterium chases it optimally. The more food a bacterium gets, the more energy it has for other functions such as mating, sheltering, fighting, and so on.
BFA can be explained by the next phases: (a) Chemotaxis (b) Swarming (c) Reproduction (d) Elimination.
i) Chemotaxis
The E. coli move through the chemotaxis phase by using flagella. Biologically, its movement can be described as either swimming or tumbling.
The next formula describes the chemotaxis motion of bacteria:
Here, describes the place for the bacterium for chemotactic, reproductive and dispersal-deletion stage. shows stage bacteria’s size takes in a random direction during tumbling. represents the vector in random direction .
ii) Swarming
The ability to swarm is a characteristic of the E.coli bacterium. As a result of this stage, a ring-shaped framework is formed by bacteria cells and moves to find food. During this phase, the bacteria are released into the environment and begin to explore the search space, seeking out the most promising areas for potential solutions. This is done by the bacteria following the chemotactic signals in the environment, which are generated by the presence of nutrient sources. These nutrient sources act as a reward for the bacteria, as they are attracted to them and will move towards them. As the bacteria move towards these sources, they will also start to interact with each other, forming aggregates and swarms. The swarming behavior of the bacteria allows them to explore the search space more efficiently, as they can cover more ground and identify more potential solutions. The swarming behavior also helps the bacteria to collaborate and share information with each other, which is important for the overall optimization process. As the bacteria move through the search space, they will also start to modify their chemotactic signals, which can help guide the other bacteria towards the most promising areas of the search space. The swarming phase of the BFA is essential for the overall optimization process, as it allows the bacteria to explore the search space more efficiently and identify potential solutions.
iii) Reproduction
The Reproduction phase in the Bacteria Foraging Algorithm (BFA) is an important step in the optimization process. It is the process of creating new bacteria based on the best performing bacteria from the previous iteration. In this phase, the best performing bacteria are selected and cloned to form a new swarm of bacteria. The new swarm is then evaluated in the next iteration of the algorithm. The selection of the best performing bacteria is based on their fitness values, which are calculated based on their performance in the environment. The bacteria with the highest fitness values will be selected and cloned to form the new swarm. The number of cloned bacteria is determined by the reproduction rate, which is a parameter of the algorithm. The selection of the bacteria is done in a roulette wheel selection process, where each bacteria is assigned a probability based on its fitness value.
The new swarm of bacteria is then evaluated in the environment and the process is repeated until a satisfactory solution is found. The reproduction phase is an important part of the optimization process as it ensures that the best performing bacteria are selected and cloned to form the new swarm. This ensures that the new swarm is more likely to find a better solution than the previous one.
iv) Elimination and Dispersal
In the absence of nutrients, bacteria die or disperse into new environments. High temperatures also kill them. Chemotaxis can be facilitated by bacteria locating themselves close to food sources when the environment has poor conditions.
The fitness of all bacteria is calculated as follows:
Here,
represents the bacterium’s fitness and
represents bacteria’s location.
The time-varying objective can be achieved by putting the objective function (OF)
in the real OF
.
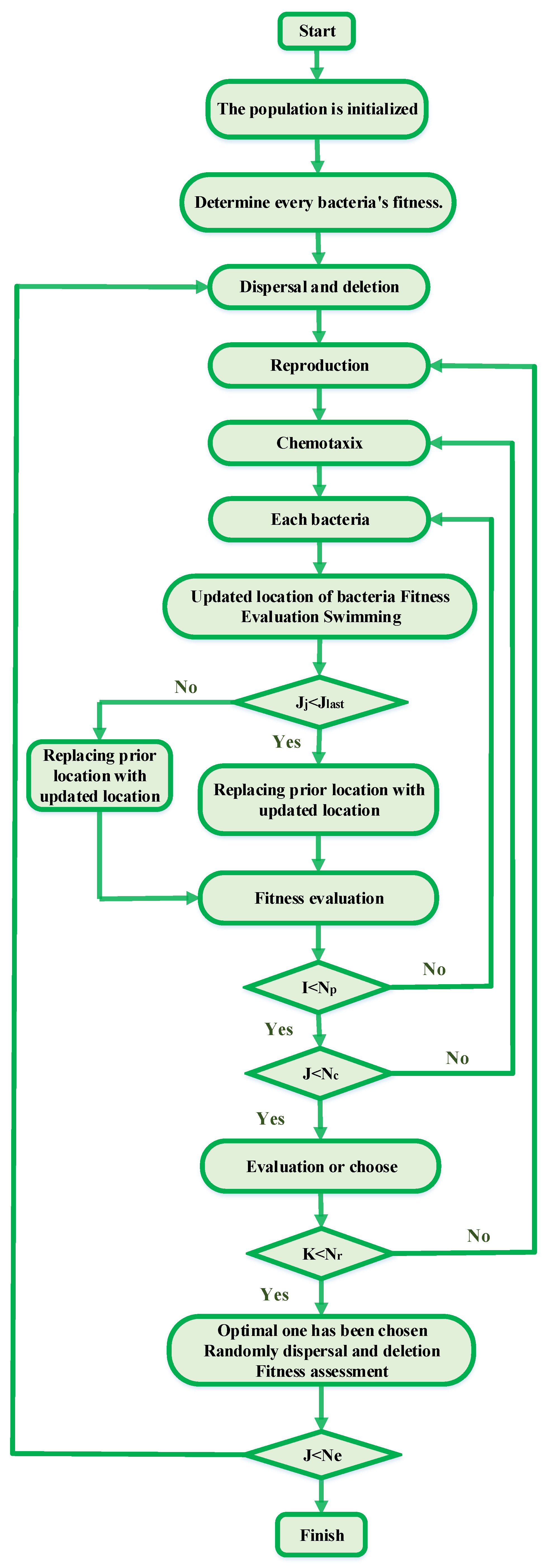
Figure 3 illustrates the stages included in the BFA algorithm.
3. Sustainability and DSM Technological Requirements in Smart Grid
Demand Side Management (DSM) is a technology that enables energy users to manage their electricity consumption in order to reduce their energy costs and improve energy efficiency. This way, it would help the system sustainability effectively. It is a technology that enables energy users to manage their electricity consumption in order to reduce their energy costs and improve energy efficiency. Demand Side Management (DSM) is an important tool in microgrid operations. It is a way to manage the demand for electricity in a more efficient way than traditional methods. DSM enables microgrids to optimize their energy use by taking into account the different types of energy sources available, the cost of each energy source, and the needs of the users. DSM allows smart grids to reduce their energy consumption, reduce their energy costs, and improve their overall efficiency. DSM can be used in a variety of ways. It can be used to reduce peak load, reduce energy costs, and improve the reliability of the smart grid. By reducing peak load, the smart grid can reduce its energy costs. Peak load is when the demand for electricity is highest, and reducing it can reduce the amount of energy needed to meet the demand. This can result in lower energy costs for the smart grid. DSM can also be used to improve the reliability of the smart grid. By using DSM, the smart grid can better manage its energy sources and optimize its energy use. This can help the smart grid to avoid power outages and other disruptions, which can lead to increased customer satisfaction and improved reliability. DSM involves the use of software and hardware systems to control and monitor the use of energy.
Software and hardware requirements for DSM include energy management systems, energy monitoring systems, energy storage systems, and control systems. These systems can be used to monitor energy consumption, identify areas of potential energy savings, and control energy usage to reduce energy costs. In the hardware area, it involves a combination of energy efficiency measures, demand response programs, and other demand-side initiatives. DSM can help reduce energy costs, reduce emissions, and improve energy reliability. To implement DSM, energy suppliers need to have the right hardware and software components in place. Hardware requirements can then be described as below:
1. Smart meters: Smart meters are used to monitor and track energy usage, enabling customers to better manage their energy consumption.
2. Communication networks: Communication networks, such as cellular or Wi-Fi, are used to connect smart meters to the energy supplier’s systems.
3. Data storage: Data storage solutions are needed to store energy usage data collected by the smart meters.
4. Computers and servers: Computers and servers are needed to process the data collected from the smart meters and to run the demand-side management software.
5. Demand response equipment: Demand response equipment, such as thermostats and energy management systems, are used to control energy usage in response to signals from the energy supplier.
6. Sensors: Sensors are used to detect changes in energy usage and to trigger demand response equipment.
In order to successfully implement DSM, there are several software requirements that must be met. These software requirements include:
An energy management system (EMS) that can track and monitor energy usage and identify efficient energy-saving opportunities.
A demand response system (DRS) that can be used to manage peak demand and reduce electricity costs.
A customer engagement system (CES) that can be used to engage customers and ensure they are aware of energy-saving opportunities.
A data analytics platform (DAP) that can be used to analyze energy usage data and provide insights into energy-saving opportunities.
A customer service system (CSS) that can be used to address customer inquiries and concerns.
An energy efficiency system (EES) that can be used to identify and implement energy efficiency measures.
A renewable energy system (RES) that can be used to identify and implement renewable energy sources.
A distributed energy resource management system (DERMS) that can be used to manage distributed energy resources.
A smart grid system (SGS) that can be used to facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources and distributed energy resources.
A MS that can be used to measure and monitor energy usage. The most benefits of DSM include lower energy costs, improved energy efficiency, and improved energy reliability. Lower energy costs can be achieved by reducing energy demand and increasing energy efficiency. Improved energy efficiency can be achieved by using more efficient technologies and systems, and improved energy reliability can be achieved by using energy storage systems to store energy for later use.
Challenges and limitations of DSM include the cost of implementing the technology, the complexity of the technology, and the lack of awareness of the technology. The cost of implementing the technology can be expensive, and the complexity of the technology can make it difficult to use. Additionally, the lack of awareness of the technology can make it difficult to get people to use it. In fact,, DSM has been used for decades to manage electricity demand and reduce the need for costly investments in new power plants and transmission lines. However, the implementation of DSM in the presence of renewable energy sources presents a unique set of challenges. First, the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources makes it difficult to predict when and how much energy will be available for use. This makes it difficult to accurately plan for DSM activities, as the timing and amount of load shifting may need to be adjusted to take advantage of available renewable energy. Second, the cost of implementing DSM programs is often higher than the cost of traditional energy sources. This is due to the need for specialized equipment, additional labor, and other costs associated with the installation and maintenance of DSM programs. Third, the integration of renewable energy sources into the grid can cause disruptions in the electricity supply, which can cause problems for DSM programs. For example, if a DSM program is set to reduce electricity consumption during peak times, but renewable energy sources are producing more electricity than expected, the DSM program may not be successful. Moreover, the current regulatory environment for electricity markets does not always support the implementation of DSM programs. Regulatory policies often favor traditional energy sources, making it difficult for DSM programs to compete in the market.
The role of DSM in the future power system will be to reduce energy costs, improve energy efficiency, and improve energy reliability. DSM will also be used to reduce the amount of energy used, which will help reduce emissions. Additionally, DSM will be used to improve the efficiency of the power system by using more efficient technologies and systems. Finally, DSM will be used to store energy for later use, which will help improve energy reliability. The technical limitations
High Upfront Costs: Implementing DSM programs can be expensive and require significant upfront investments. This can be a barrier for businesses and households that don’t have the financial resources to take part.
Lack of Awareness: Many consumers are unaware of DSM programs and the benefits they can provide. Without the proper education and outreach, potential customers may not be aware of the options available.
Limited Technology: Many DSM programs require the installation of advanced technology, such as smart meters or energy management systems. These technologies can be expensive and may not be available in all areas.
Regulation: In some cases, government regulations can limit the implementation of DSM programs. For example, some states may have restrictions on how utilities can charge customers for energy usage.
Data Security: DSM programs rely heavily on data collection and analysis. This can raise concerns about data security and privacy. It’s important to ensure that any data collected is secure and private.
4. Simulation Outcomes and Discussion
A detailed explanation of the simulation outcomes is provided here. The simulations we conduct in MATLAB are used for manipulating the efficiency of the suggested methods GOA and BFA.
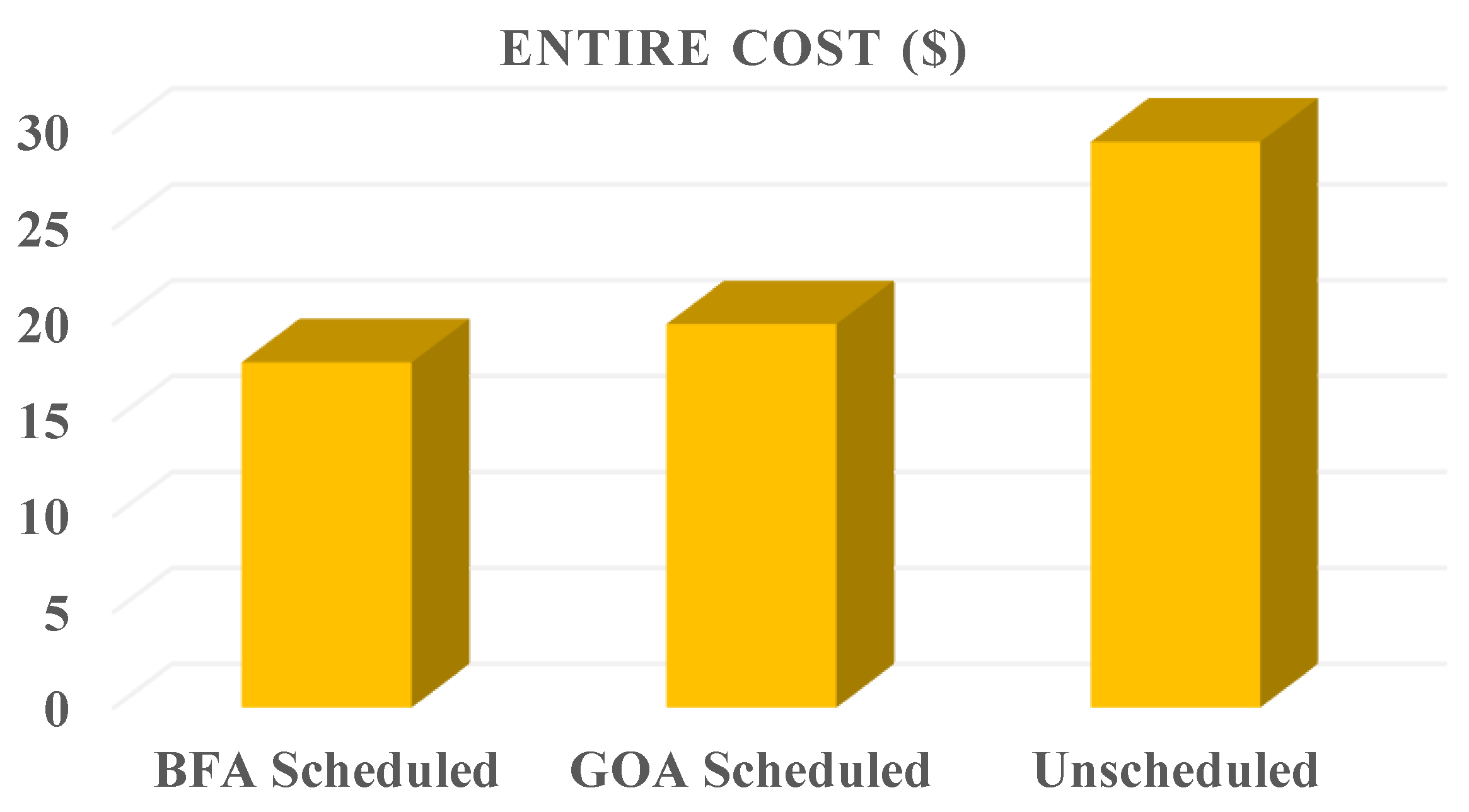
A. Price
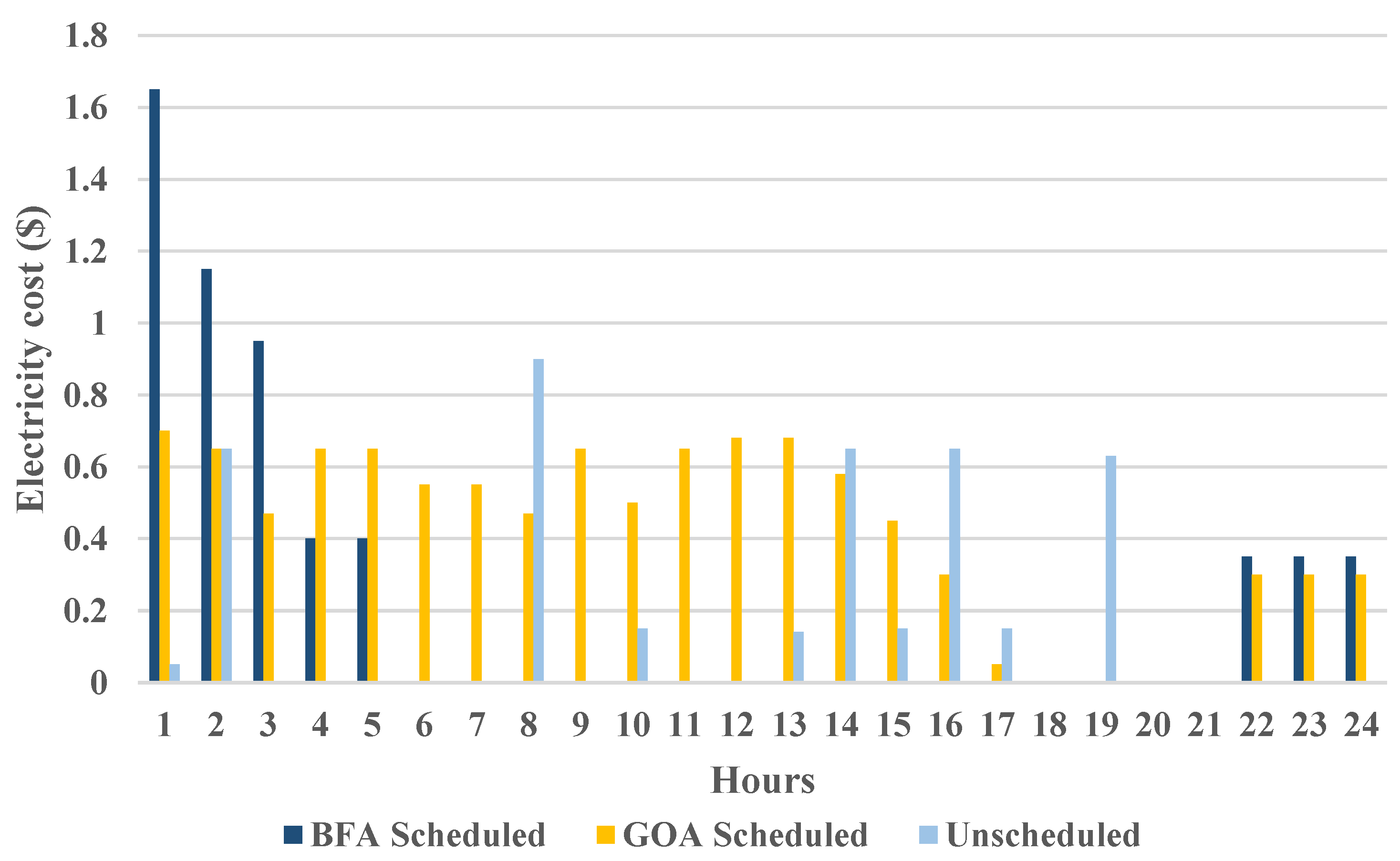
Since the load transferred from peak times to off-peak times, GOA will have fewer energy costs than unplanned and BFA. A maximal electricity bill of 59 cents per hour is obtained from unplanned devices at 8 to 9 compared to lower costs from BFA planned devices and optimal performances from GOA, resulting in a price reduction of 3 cents. GOA always displays more desirable outcomes than BFA, as it displays less uncomfortable outcomes while the unscheduled outcomes are the poorest ones. According to the aforementioned graph, GOA performs more efficiently at all times. At the start of the period, it is high and gradually drops. The BFA reaches a peak between 6 and 7 hours, however, it is controllable and lower than the unplanned (
Figure 4).
GOA nearly decreased the electricity bill to 35%, while BFA nearly decreased it to 20%. GOA decreased energy costs more by delaying the running time of a few devices, which is in accordance with their OF. Compared to others, GOA has a lower and more efficient energy price (
Figure 5).
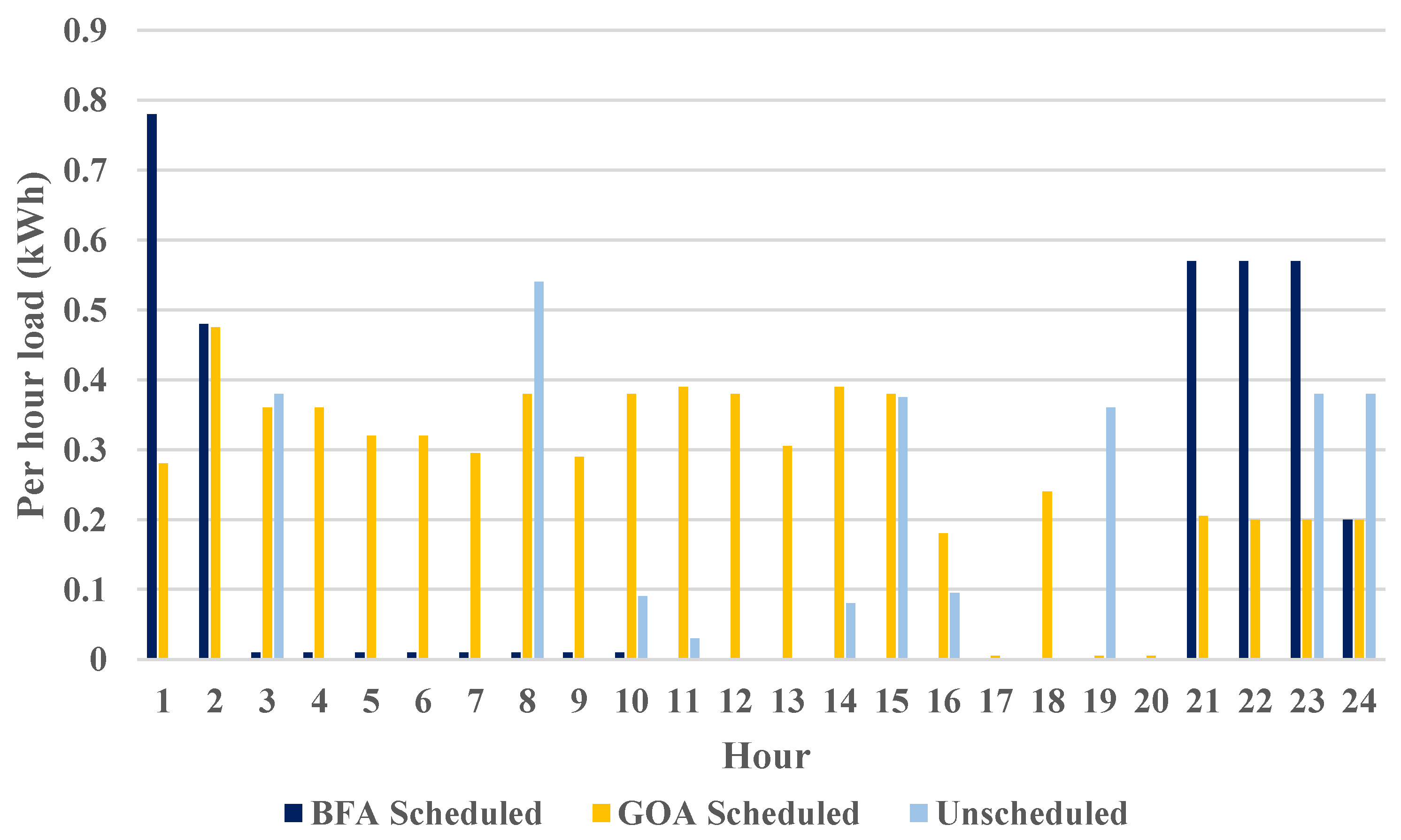
B. Load
The graph shows that the load is kept for GOA and BFA planned devices for 2 to 5 hours. Planned devices in GOA and BFA show an approximately continuous load of 1 kWh, while unplanned devices consume more energy compared to the GOA. BFA shows a larger load during the same period in comparison with non-scheduled. All this is due to the transferring of loads from on-peak to off-peak times. The unplanned devices demonstrate that the usage is not smart, since the load during peak times is a lot higher when compared to during other periods of time, which is caused by the lack of smart methods. Compared to ON peak periods, GOA has lower power usage. While the BFA planned devices and GOA grew to 3 kWh over the period of 18 to 24 hours, the peak load is used during these periods since high energy costs do not threaten, which means that the interruptible devices can take advantage of the periods to the fullest extent possible. Through the use of GOA and BFA algorithms, both non-interruptible and interruptible devices are able to use power efficiently in OFF and ON peak periods.
It is impossible for non-scheduled devices to display the most efficient power usage. As a result of the suggested methods and the categorization of devices into various groups, an improved load arrangement has been achieved. During the day, the load of devices remains constant. However, the GOA method is used to plan the devices so that they can be efficiently used during peak times in order to minimize costs (
Figure 6).
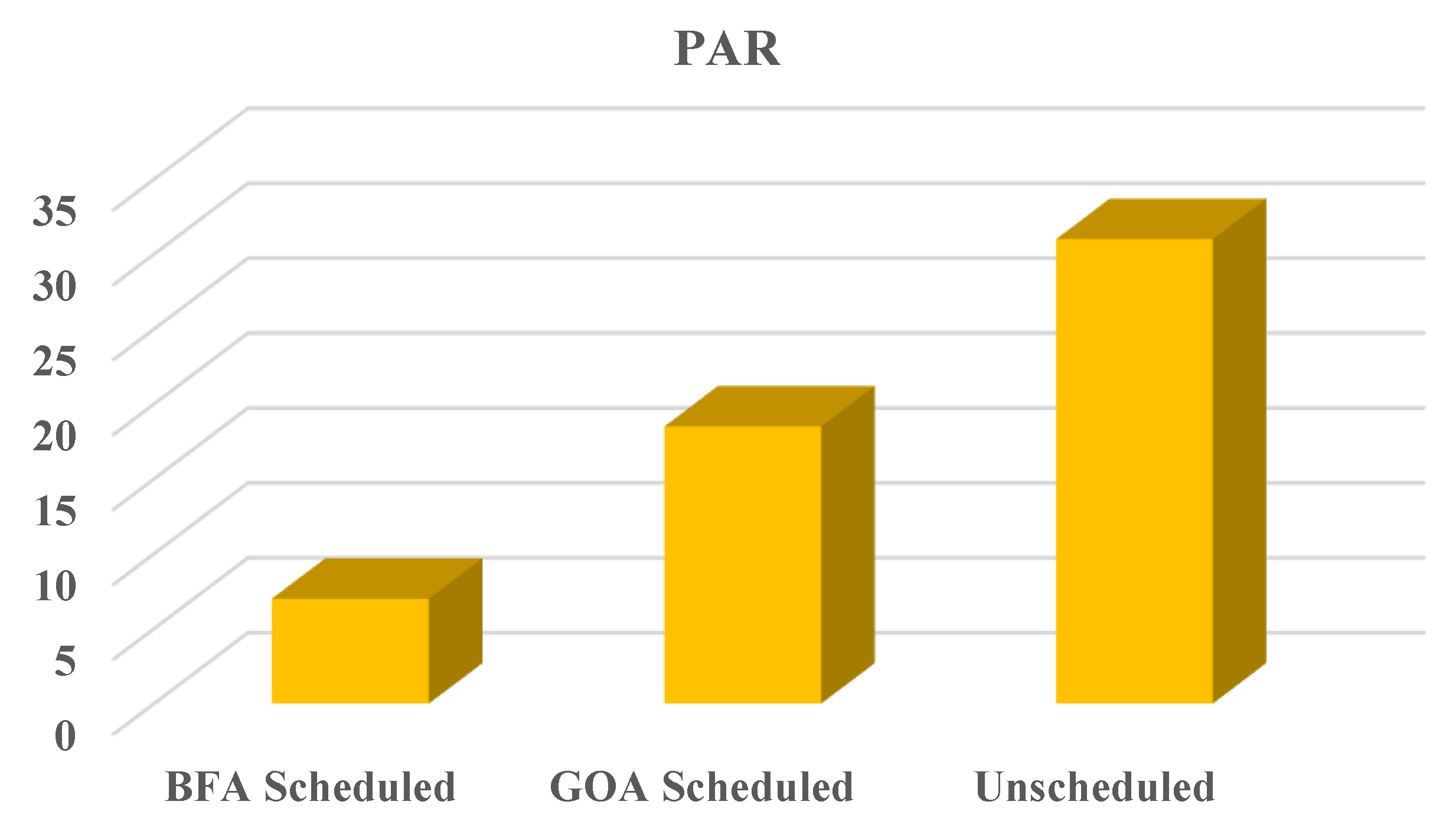
C. PAR
By utilizing the various optimization methods, PAR has been decreased, thereby balancing supply and demand Due to the lack of importance of fixed appliances, interruptible and non-interruptibles were given more priority. The aforementioned graph shows that GOA plans to schedule a PAR load that has been reduced by 50%. Meanwhile, BFA also displays a 40% decrease in PAR. TOU pricing avoids peaking by providing data to users. In comparison to BFA, GOA reduces PAR by almost 50%. There is a significant increase in PAR in the unplanned since smartness techniques were not applied. As a result of the electric capacity factor, the suggested methods performed better because utilities could fill demand from users, thereby reducing energy costs. Unplanned devices perform poorly because they do not address peak formation issues, whereas planned devices prevent creating peaks and are scheduled for 24 hours (
Figure 7).
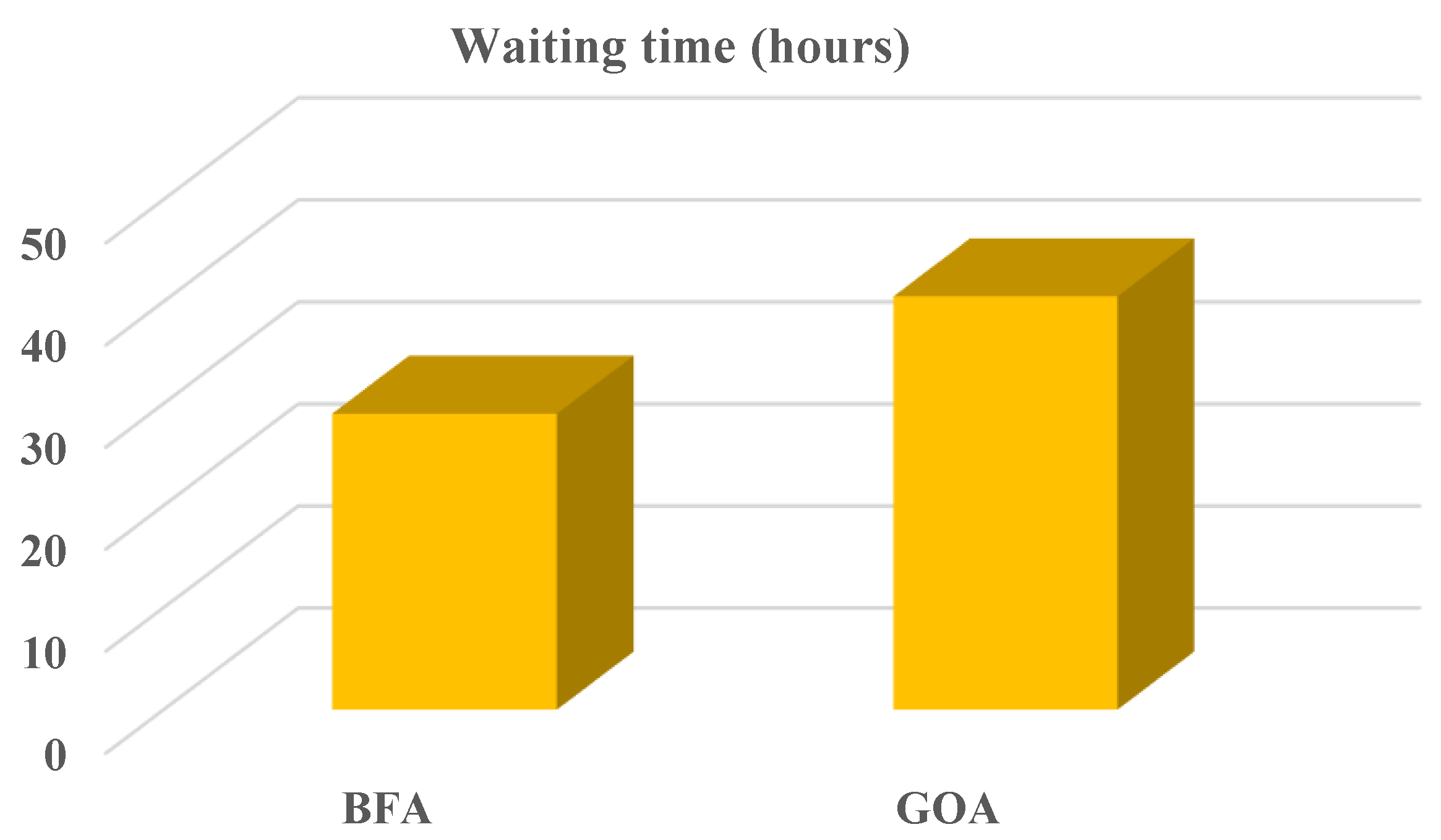
D. Consumer Satisfaction
The energy prices and wait times are balanced, meaning that if one increases, the other will decrease. This ensures that energy production remains efficient and cost-effective. To further optimize energy production, loads are transferred from ON peak times to OFF peak times. This is done with the help of bacteria foraging algorithm (BFA) and grasshopper optimization algorithm (GOA). BFA and GOA as two optimization algorithms which are used to transfer loads from ON peak times to OFF peak times. Both BFA and GOA are used to optimize the load transfer from ON peak times to OFF peak times in order to reduce energy prices and wait times. As a result, energy production is optimized and cost-effective. As seen in
Figure 8, both BFA and GOA are used to transfer loads from ON peak times to OFF peak times. This helps to reduce energy prices and wait times, thereby increasing the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of energy production.
5. Discussion
The discussion of Peak to Average Ratios (PARs) and consumer satisfaction for load management in industrial, commercial, and domestic sectors is an important topic. Demand Side Management (DSM) is a key factor in achieving optimal outcomes from load management. Therefore, understanding the impact of DSM on PARs and consumer satisfaction is essential. In the industrial sector, DSM has been shown to improve energy efficiency and reduce peak demand. This can lead to improved PARs and increased customer satisfaction. It is important to note, however, that DSM may not always be beneficial for industrial customers. Depending on the type of load and the cost of energy, DSM may not be cost-effective. In the commercial sector, DSM can help reduce peak demand and improve PARs. However, customer satisfaction may not be improved significantly due to the complexity of the load. Additionally, the cost of energy may be too high to make DSM cost-effective. In the domestic sector, DSM can help reduce peak demand and improve PARs. Additionally, customer satisfaction can be improved significantly due to the simplicity of the load. Furthermore, the cost of energy is usually low enough to make DSM cost-effective. To sum up, DSM is an important factor in achieving optimal outcomes from load management. In the industrial, commercial, and domestic sectors, DSM can help reduce peak demand and improve PARs. Additionally, customer satisfaction can be improved significantly in the domestic sector. However, it is important to consider the cost of energy when determining whether DSM is cost-effective.
By providing incentives for customers to shift their OPH, the power grid can reduce the strain on the system during peak times, helping to ensure a reliable and consistent supply of electricity. Furthermore, metering devices can be used to help customers save costs by preventing load shifting between high- and low-cost periods. This can be beneficial to both the customer and the power grid, as it can reduce the overall cost of electricity for the customer, while also helping to ensure a more reliable and efficient delivery of electricity. Moreover, it is clear that the use of incentives to motivate customers to shift their OPH from Peak Hours, combined with the use of metering devices to prevent load shifting between high- and low-cost periods, can be beneficial for both customers and the power grid. By providing incentives and metering devices, customers can save costs while the power grid can ensure a reliable and consistent supply of electricity.
6. Conclusions
AOA was controlled by an energy management controller in the present study. The suggested method uses GOA and BFA signals under (TOU) signals to schedule AOA according to the consumer’s preferences. The suggested methods aim to reduce delay time and energy costs. The utilities benefit from the minimization of PAR because it makes them more reliable and flexible. This paper compares the outcomes of the suggested method applying GOA and BFA with the unplanned outcomes. GOA and BFA are more optimal than unplanned costs based on simulation outcomes. Both GOA and BFA have lower PARs than unplanned energy usage. It is clear that the suggested GOA and BFA-driven method provides a stable and affordable solution for energy management systems. he results of the simulation indicate that GOA and BFA are more optimal than unplanned costs. The results of this paper provide a good basis for future research on the efficiency of GOA and BFA in the context of project management. The findings of this paper suggest that GOA and BFA can be used to improve the efficiency of project management. The results of this paper can be used to inform future research on the efficiency of GOA and BFA in project management. Furthermore, the findings of this paper can be used to inform decision makers about the potential of GOA and BFA to improve the efficiency of project management. The results show that the use of an Energy Management Controller (EMC) is a great way to keep track of energy usage, operational time, and costs associated with appliances. Customers of power grids can benefit from incentives offered in Off-Peak Hours (OPH) to shift their energy consumption away from Peak Hours. Additionally, the use of metering devices can help customers save costs by preventing load shifting between high- and low-cost periods. Future research will focus on reducing costs and maximizing consumer satisfaction through other planning methods.
References
- Hashmi MH, Hänninen S, Mäki K. Survey of smart grid concepts, architectures, and technological demonstrations worldwide. In2011 IEEE PES conference on innovative smart grid technologies Latin America (ISGT LA) 2011 Oct 19 (pp. 1-7). IEEE.
- Jokar, H.; Bahmani-Firouzi, B.; Simab, M. Bilevel model for security-constrained and reliability transmission and distribution substation energy management considering large-scale energy storage and demand side management. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 2617–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaeiyan, S.; Nafar, M.; Niknam, T. A novel bio-inspired stochastic framework to solve energy management problem in hybrid AC-DC microgrids with uncertainty. Int. J. Bio-Inspired Comput. 2021, 18, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiasi, M.; Dehghani, M.; Niknam, T.; Baghaee, H.R.; Padmanaban, S.; Gharehpetian, G.B.; Aliev, H. Resiliency/Cost-Based Optimal Design of Distribution Network to Maintain Power System Stability Against Physical Attacks: A Practical Study Case. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 43862–43875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.M.; Akram, R.; Memon, Z.A.; Nazir, M.H.; Javed, W.; Siddique, M. Demand Side Management Techniques for Home Energy Management Systems for Smart Cities. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.-L.; Liu, Q.; Bogle, I.D.L.; Zheng, Z. A Self-Learning Based Dynamic Multi-Objective Evolutionary Algorithm for Resilient Scheduling Problems in Steelmaking Plants. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2022, 20, 832–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan AJ, Javaid N, Iqbal Z, Anwar N, Saboor A, Qasim U. A Hybrid Bacterial Foraging Tabu Search Heuristic Optimization for Demand Side Management in Smart Grid. In2018 32nd International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications Workshops (WAINA) 2018 (pp. 550-558). IEEE. 16 May.
- Wynn, S.L.L.; Boonraksa, T.; Marungsri, B. Optimal generation scheduling with demand side management for microgrid operation. In2021 9th International Electrical Engineering Congress (iEECON) 2021 Mar 10 (pp. 41-44). IEEE.
- Ullah, I.; Khitab, Z.; Khan, M.N.; Hussain, S. An Efficient Energy Management in Office Using Bio-Inspired Energy Optimization Algorithms. Processes 2019, 7, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsmadi, Y.M.; Abdel-Hamed, A.M.; Ellissy, A.E.; El-Wakeel, A.S.; Abdelaziz, A.Y.; Utkin, V.; Uppal, A.A. Optimal configuration and energy management scheme of an isolated micro-grid using Cuckoo search optimization algorithm. J. Frankl. Inst. 2019, 356, 4191–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelidari, M.; Hamidzadeh, J. Feature selection by using chaotic cuckoo optimization algorithm with levy flight, opposition-based learning and disruption operator. Soft Comput. 2020, 25, 2911–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid N, Zarin SS, Ullah I, Kamal M, Latif U, Ullah R. A Hybrid Tabu-Enhanced Differential Evolution Meta-Heuristic Optimization Technique for Demand Side Management in Smart Grid. InConference on Complex, Intelligent, and Software Intensive Systems 2018 Jul 4 (pp. 37-50). Springer, Cham.
- Gao, R.; Wu, J.; Hu, W.; Zhang, Y. An Improved ABC Algorithm for Energy Management of Microgrid. Int. J. Comput. Commun. Control. 2018, 13, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan IU, Ma X, Taylor CJ, Javaid N, Gamage KA. Heuristic algorithm based dynamic scheduling model of home appliances in smart grid. In2018 24th International Conference on Automation and Computing (ICAC) 2018 Sep 6 (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
- Nasir, T.; Bukhari, S.S.H.; Raza, S.; Munir, H.M.; Abrar, M.; Muqeet, H.A.U.; Bhatti, K.L.; Ro, J.-S.; Masroor, R. Recent Challenges and Methodologies in Smart Grid Demand Side Management: State-of-the-Art Literature Review. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Wu, H.; Gu, C.; Hernando-Gil, I. Optimal home energy management under hybrid photovoltaic-storage uncertainty: a distributionally robust chance-constrained approach. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2019, 13, 1911–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madathil, D.; Pandi, V.R.; Nair, M.G.; Jamasb, T.; Thakur, T. Net Zero Energy in a Residential Building Using Heuristic Optimization Solution. J. Control. Autom. Electr. Syst. 2021, 32, 458–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouakkaz, A.; Haddad, S.; Garcã a, J.A.M.; Mena, A.J.-G.; Castaã±Eda, R.J. Optimal Scheduling of Household Appliances in Off-Grid Hybrid Energy System using PSO Algorithm for Energy Saving. Int. J. Renew. Energy Res. 2019, 9, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.U.; Wadud, Z.; Elavarasan, R.M.; Hafeez, G.; Khan, I.; Shafiq, Z.; Alhelou, H.H. An Optimal Power Usage Scheduling in Smart Grid Integrated With Renewable Energy Sources for Energy Management. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 84619–84638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awais M, Javaid N, Shaheen N, Iqbal Z, Rehman G, Muhammad K, Ahmad I. An efficient genetic algorithm based demand side management scheme for smart grid. In2015 18th International Conference on Network-Based Information Systems 2015 Sep 2 (pp. 351-356). IEEE.
- Shi, K.; Li, D.; Gong, T.; Dong, M.; Gong, F.; Sun, Y. Smart Community Energy Cost Optimization Taking User Comfort Level and Renewable Energy Consumption Rate into Consideration. Processes 2019, 7, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meraihi, Y.; Gabis, A.B.; Mirjalili, S.; Ramdane-Cherif, A. Grasshopper Optimization Algorithm: Theory, Variants, and Applications. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 50001–50024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topaz CM, Bernoff AJ, Logan S, Toolson W. A model for rolling swarms of locusts. The European Physical Journal Special Topics. 2008 Apr;157(1):93-109.
- Liu, Y.; Passino, K. Biomimicry of Social Foraging Bacteria for Distributed Optimization: Models, Principles, and Emergent Behaviors. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 2002, 115, 603–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).