1. Introduction
Insulin resistance (IR), an impaired response of peripheral tissues to insulin is considered a major pathogenic factor in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). According to previous studies, one of the major causes of IR is chronic obesity [
1]. Obesity associated IR is closely linked to adipocyte dysfunction [
2], resulting in impairment of glucose and lipid homeostasis as well as inflammatory responses [
3]. Under chronic obese condition, increased free fatty acids induce cellular oxidative stress in adipose tissue through the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) which trigger adipocyte dysfunction and induce production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β from adipose tissue, consequentially potentiating adipose tissue inflammation and obesity related diseases such as T2DM [
4]. Adipose dysfunction in obesity also potentiates insulin resistance and triglyceride storage impairment. These abnormalities lead to increased accumulation of free fatty acids in circulation and increased accumulation of free fatty acids in skeleton muscle, triggering insulin resistance in skeleton muscle [
5]. These findings indicated that therapeutic strategies ameliorating adipocyte dysfunction and related skeleton muscle insulin resistance may be beneficial in the management and treatment of obesity related T2DM.
Catharanthus roseus, an evergreen plant belongs to the apocynacea family, is a chief source of indole alkaloids [
6]. Vindoline, an indole alkaloid found in high concentrations in the leaves of
Catharanthus roseus, is the one of the major compounds behind the anti-diabetic properties of the plant [
7,
8]. The effect of vindoline on IR models have not been yet been examined. Hence, this study focuses on evaluation of the anti-diabetic properties of vindoline in dysfunctional 3T3-L1 adipocytes and in insulin resistant L6 skeleton myoblasts.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals, biochemicals and cell lines
All chemicals and reagents used were of analytical grade. 3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT), oil red O stain, dichloro-dihydro-fluorescein diacetate (DCF-DA), 3-isobutyl-1-methyl xanthine (IBMX), insulin, TRIzol and dexamethasone were purchased from Sigma Aldrich, USA. Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM), fetal bovine serum (FBS) and antibiotic solutions were procured from Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA. 3T3-L1 pre-adipocyte and L6- myoblast cell lines were obtained from National Centre for Cell Science (NCCS), India. All other chemicals and solvents were purchased from SRL, Ranbaxy, Merck and Spectrochem, India.
2.2. Plant material and extraction procedure
Catharanthus roseus leaves were collected from Trivandrum district, Kerala, during the month of October. The specimen was authenticated by an expert (Dr. Valsaladevi, Curator, Department of Botany, University of Kerala) and a specimen voucher number was obtained (KUBH 10135). The washed and air-dried leaves were made into powder in a mechanical blender and subjected to hot methanolic extraction with a soxhlet apparatus. Extract was evaporated to dryness using a rotary flash evaporator.
2.3. Isolation of vindoline
For the isolation of vindoline, methanolic extract of
Catharanthus roseus leaves was subjected to silica gel column chromatography using step gradient elution from 100% dichloromethane (DCM) to 100% methanol and eluted fractions were collected. Based on the thin layer chromatography (TLC) results under dragendroff’s reagent, fraction-3 was subjected to silica sub column chromatography using DCM and methanol and eluted sub- fractions were collected. The presence of vindoline was confirmed by LC-MS/MS analysis (Shimadzu) [
9].
2.4. T3-L1 cell culture, differentiation and induction of dysfunction in adipocytes
Mouse 3T3-L1 preadipocytes were cultured in DMEM supplemented with heat-inactivated 10% FBS plus antibiotic mixture (100U penicillin/ml and 100 µg streptomycin/ml) in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 at 37
0C. Cells at 80% confluence were allowed to differentiate from preadipocytes to fully matured adipocytes following the already established protocol [
10].
For the induction of adipocyte dysfunctions, 12 hours serum starved mature adipocytes were incubated for 48 hours with 1µM dexamethasone and 1µM insulin or 1ng/ml IL-1β
[4] and these dysfunctional 3T3-L1 adipocytes were grouped as follows-
Group 1: Normal mature adipocytes (3T3- control); Group 2: Untreated dysfunctional adipocytes (model); Group 3: Dysfunctional adipocytes + 12.5 µg/ml vindoline (VDL 12.5); Group 4: Dysfunctional adipocytes + 25 µg/ml vindoline (VDL 25); Group 5: Dysfunctional adipocytes + 1mM metformin (Met). The treatment period was 24 hours.
2.5. L6- myoblast cell culture and induction of insulin resistance
Rat skeletal muscle L6 myoblast cells were cultured in DMEM supplemented with heat-inactivated 10% FBS plus antibiotic mixture (100U penicillin/ml and 100 µg streptomycin/ml) in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 at 37
0C. Cells at 80% confluence were processed for differentiation from L6-myoblasts to myotubes under reduced serum concentration, as described previously [
11].
After differentiation, myotubes were incubated in DMEM containing 25mM/L glucose for 4-5 days to induce insulin resistance [
12] and these insulin resistant myotubes (IR-myotubes) were grouped as follows,
Group 1: Normal myotubes (Control); Group 2: Untreated IR-myotubes (Model); Group 3: IR-myotubes + 12.5 µg/ml vindoline (VDL 12.5); Group 4: IR-myotubes + 25 µg/ml vindoline (VDL 25); Group 5: IR-myotubes + 1mM metformin (Met). The treatment period was 24 hours.
2.6. Evaluation of cell viability
Cell viability of 3T3-L1 adipocytes and L6-myotubes treated with different concentrations of vindoline was measured using MTT assay [
13] according to previous reports. Absorbance was read using a plate reader (Bio-Rad, USA).
2.7. Evaluation of glucose consumption activity
The glucose consumption ability of dysfunctional adipocytes and IR-myotubes after vindoline treatment was analyzed according to previously described method [
14]. Briefly, the dexamethasone plus insulin induced dysfunctional adipocytes or IR-myotubes were preincubated with DMEM containing 0.2% FBS for 12 hours and were then incubated with different concentrations (12.5 and 25 µg/ml) of vindoline for 24 hours. The medium was collected and glucose concentration were determined by the glucose oxidase method. The amount of glucose consumption was calculated as the difference between glucose concentrations of blank wells and wells with cells under treatment.
2.8. Evaluation of intracellular lipid accumulation
The fat accumulation in dexamethasone induced dysfunctional adipocyte with and without vindoline treatment was determined using Oil red O assay. Briefly, the dexamethasone plus insulin induced dysfunctional adipocytes plated in 24 well plates were treated with different concentrations of vindoline for 24 hours at 37°C. Cells were washed with PBS twice and fixed with 10% formalin. After 30 minutes fixation, formalin was removed and cells were washed twice with distilled water. To this, freshly prepared oil red O solution (0.5% oil red O in isopropanol) was added and kept for 60 minutes at room temperature. After incubation, cells were washed with PBS to remove extra dye for the capturing the image. Isopropanol was added to extract the stain from cells and absorbance measured at 500 nm using a microplate reader (Bio-Rad, USA).
2.9. Evaluation of ROS production
ROS production in IL-1β induced dysfunctional adipocytes after vindoline treatment was determined by DCF-DA staining assay [
15]. Briefly, the IL-1β induced dysfunctional adipocytes were cultured in 24 well plates were treated with different concentration of vindoline and kept at incubation for 24 hours. After incubation, cells were washed with PBS and incubated with DCF-DA (20μM) for 30 minutes in dark. Cells were washed with PBS to remove extra dye followed by capture of image using a fluorescence microscope with excitation wavelength of 492 nm and an emission wavelength of 520 nm.
2.10. Evaluation of glycogen content
The glycogen content of IR-myotubes after vindoline treatment was estimated according to previous reports [
16]. Briefly, IR myotubes were treated with different concentrations of vindoline for 24 hours. 1mM metformin and 10μL of 10nM insulin were used as positive control and stimulant respectively. After removal of medium, HEPES buffer was added and kept for 2 minutes, followed by addition of 10mM glucose in HEPES buffer and incubated for 30 minutes. After incubation, media was aspirated followed by addition of 30% potassium hydroxide and kept for 5 minutes to lyse the cells. The lysate was heated for 30minutes at 70°C and chilled on ice along with addition of ice cold 95% ethanol and left overnight at 80°C for glycogen precipitation. The content was centrifuged at 8000g for 10 minutes and the glycogen content in the pellet was measured following the anthrone method.
2.11. Gene expression studies
For gene expression studies, total RNA was isolated from mouse 3T3-L1 adipocytes and rat L6-myotubes using TRIzol reagent according to the manufacturer’s instructions and cDNA synthesis was performed using Bio-Rad cDNA synthesis kit (I Script reverse transcription super mix for RT-PCR). The real time qPCR was carried out using Bio-Rad RT-PCR kit (iTaqTM Universal SYBR green super mix) on real time PCR instrument according to manufacturer’s protocol.
The following gene specific primers were used:
Table 1.
List of primers used for quantitative PCR analysis of transcriptional gene expression.
Table 1.
List of primers used for quantitative PCR analysis of transcriptional gene expression.
| Gene |
Forward primer (5’-3’) |
Reverse primer (5’-3’) |
| Rat IRS-1 |
CTGCATAATCGGGCAAAGGC |
CATCGCTAGGAGAACCGGAC |
| Rat GLUT-4 |
GTTGCGGATGCTATGGGTC |
GTATGGGGAGTAAGGGAG |
| Rat β-actin |
CCAACCGTGAAAAGATGA |
TCCAGTAGTGATAGCCGT |
| Mice GLUT-4 |
CTGGCACTTCCACTCAAC |
GAGACTGATGCGCTCTAAC |
| Mice IRS-1 |
TAACTGGACATCACAGCAGAATG |
ACGGATGCATCGTACCATCT |
| Mice TNF-α |
ACCCTCACACTCACAAACCA |
ACCCTGAGCCATAATCCCCT |
| Mice CCL-2 |
TCCCTGCGCATCTTCATT |
TTCGTCCCAAGGAGTAGC |
| Mice adiponectin |
TAAACATTTCCGGCCCCTCC |
GCTCCACTGTGTCAGCTTCT |
| Mice β-actin |
AGGATCACGACTGACAAAGGC |
ATGGAGCCACCGATCCACA |
2.12. Statistical analysis
Values are expressed as mean ± standard error mean (SEM) of triplicate values of three independent experiments for each sample within a parameter. Graphical representation and statistical analysis were carried out on GraphPad Prism 9.5 software (San Diego, CA, USA). Statistical analysis was carried out by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc multiple comparison test. Statistically significant difference for P < 0.05 is indicated by different symbols, as mentioned in figure legends.
3. Results
3.1. Isolation of vindoline
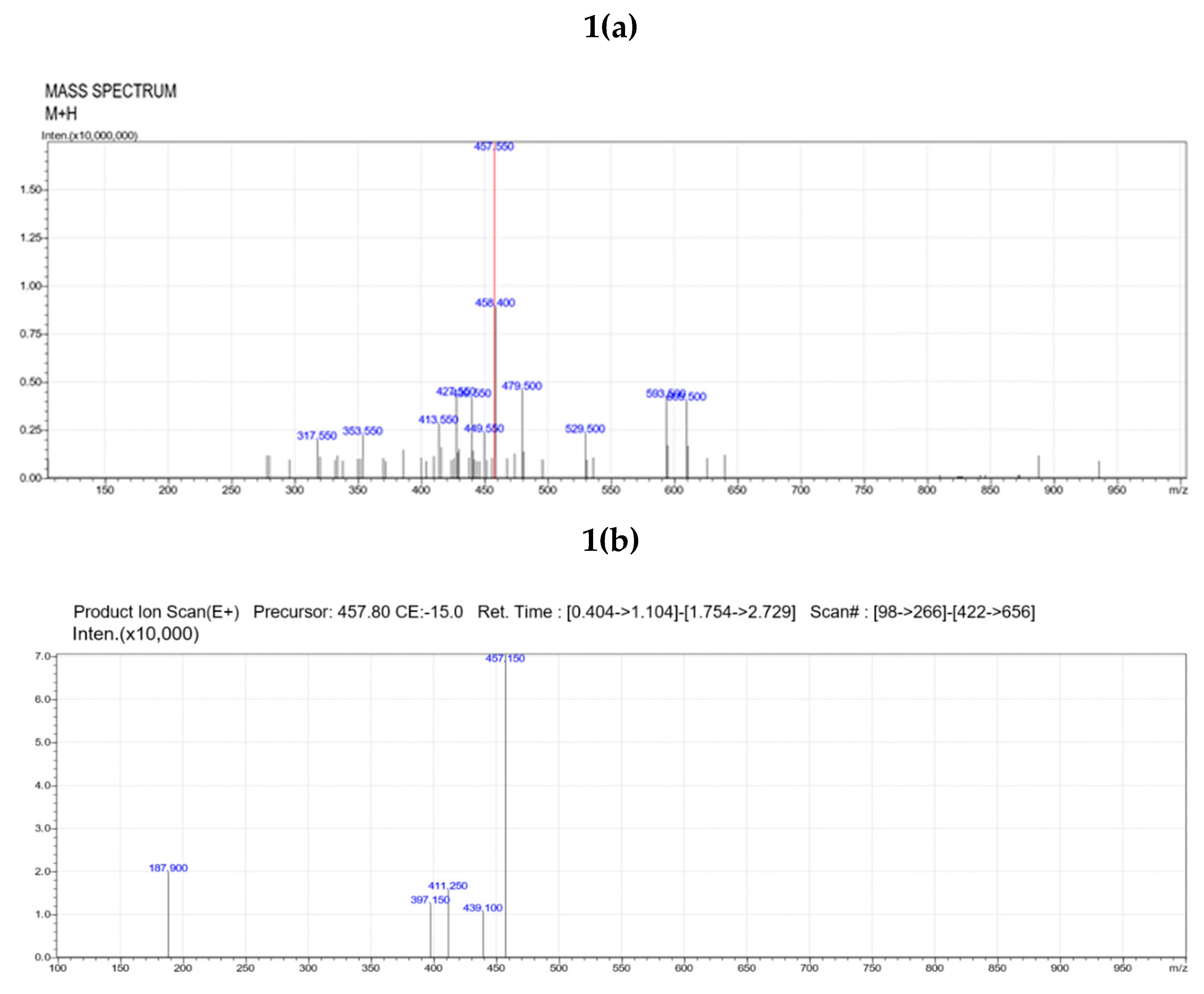
LC/MS-MS analysis of sub-fraction 3 obtained from sub column chromatography showed base peak at 457, indicative of the presence of the indole alkaloid vindoline (
Figure 1a). MS/MS fragmentation pattern of the sub-fraction 3 showed ions at m/z 187.9, 411, 439, 457 etc., related to structure of vindoline (
Figure 2b), confirming that the isolated compound was purified vindoline.
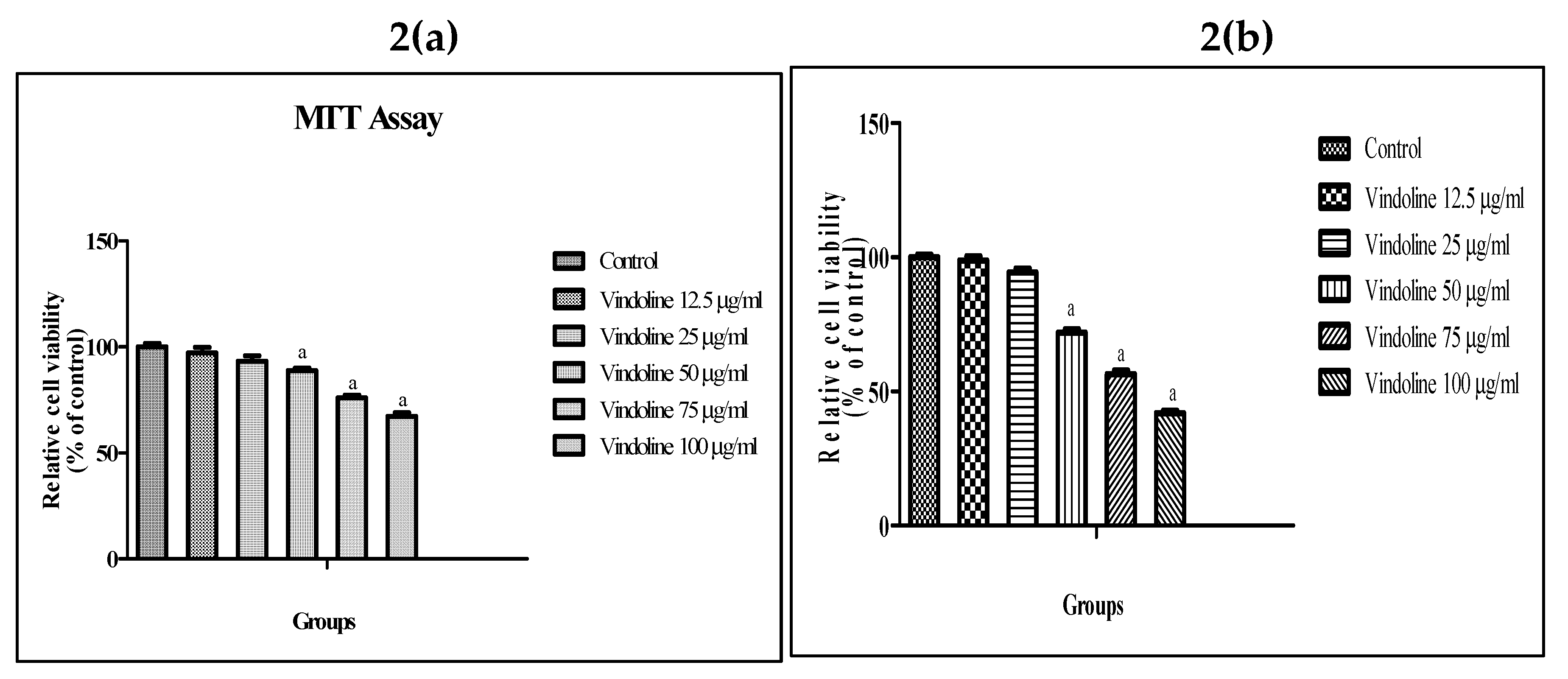
3.2. Effect of vindoline on 3T3-L1 adipocyte and L6 myotube viability
MTT assay results show that vindoline treatment up to 25µg/ml for 24 hours did not exhibit any significant effect on viability of 3T3-L1 adipocytes and L6 myotubes with respect to untreated cells respectively (
Figure 2). Hence, we have used 12.5 and 25µg/ml vindoline for subsequent studies.
3.3. Effect of vindoline on adipocyte dysfunction
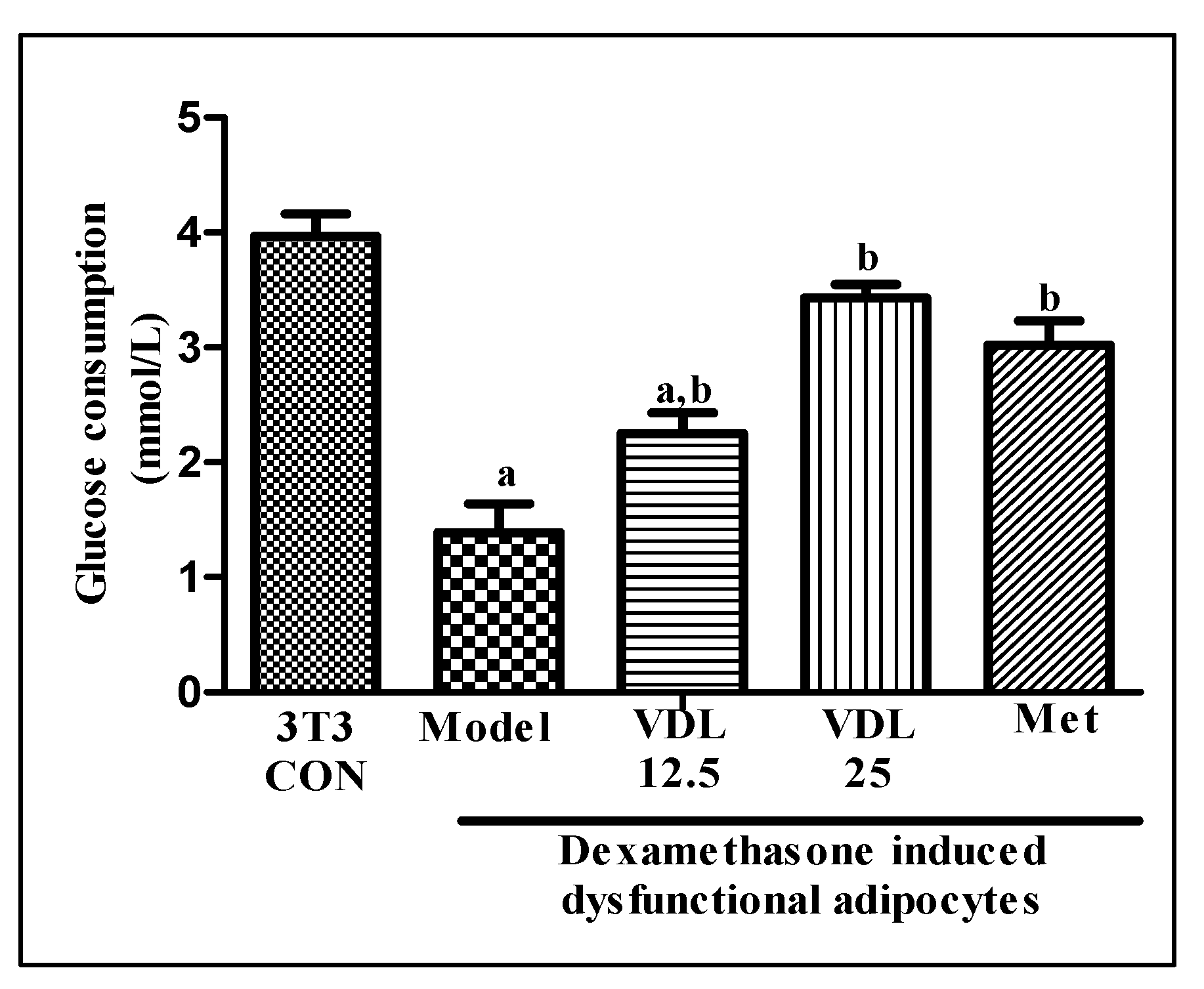
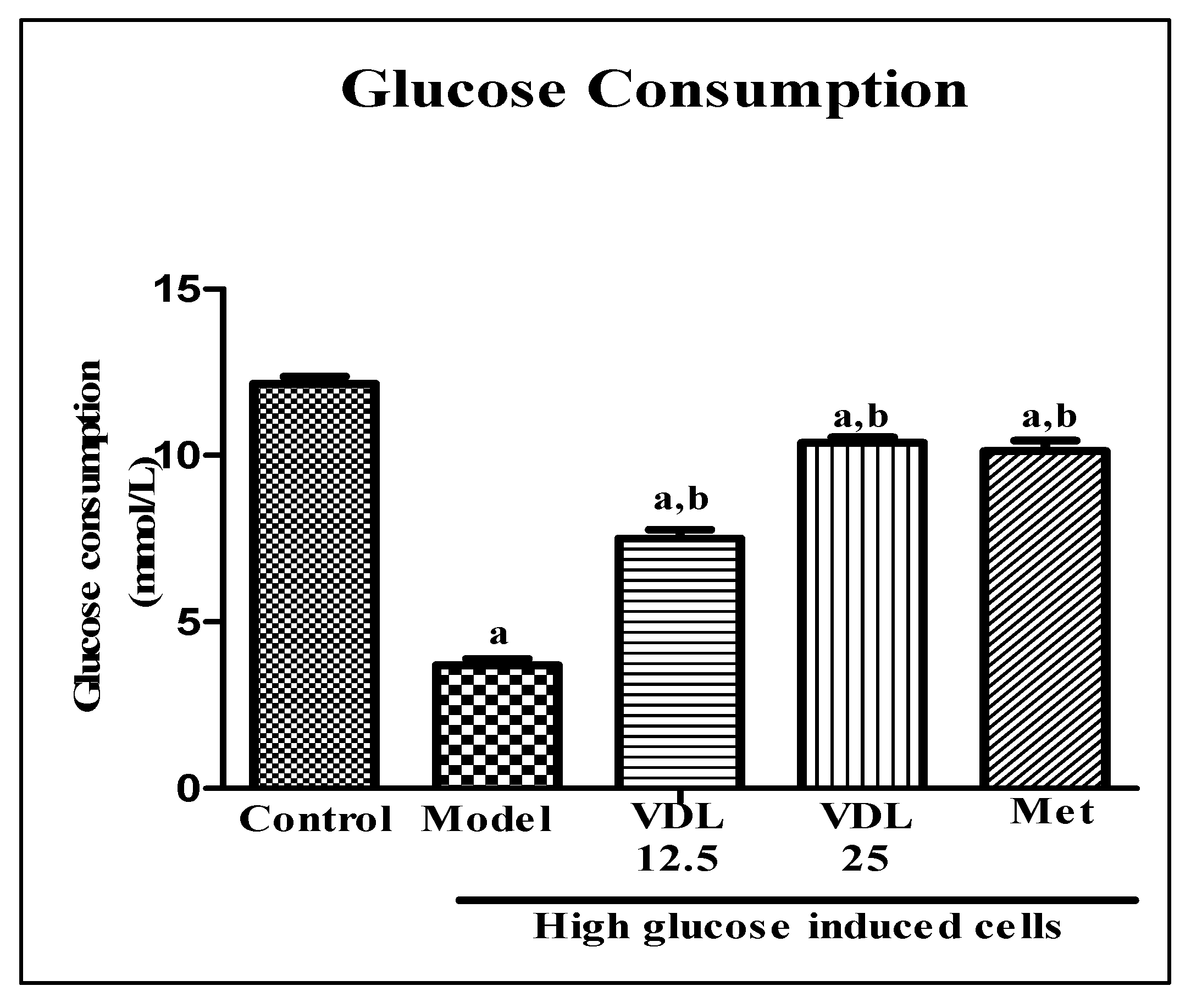
3.3.1. Effect of vindoline on glucose consumption in dysfunctional adipocytes
The glucose consumption of dexamethasone induced dysfunctional adipocytes was decreased significantly with respect to healthy adipocytes. Treatment with vindoline for 24 hours significantly increased the glucose consumption of dysfunctional adipocytes in a dose dependent manner (
Figure 3).
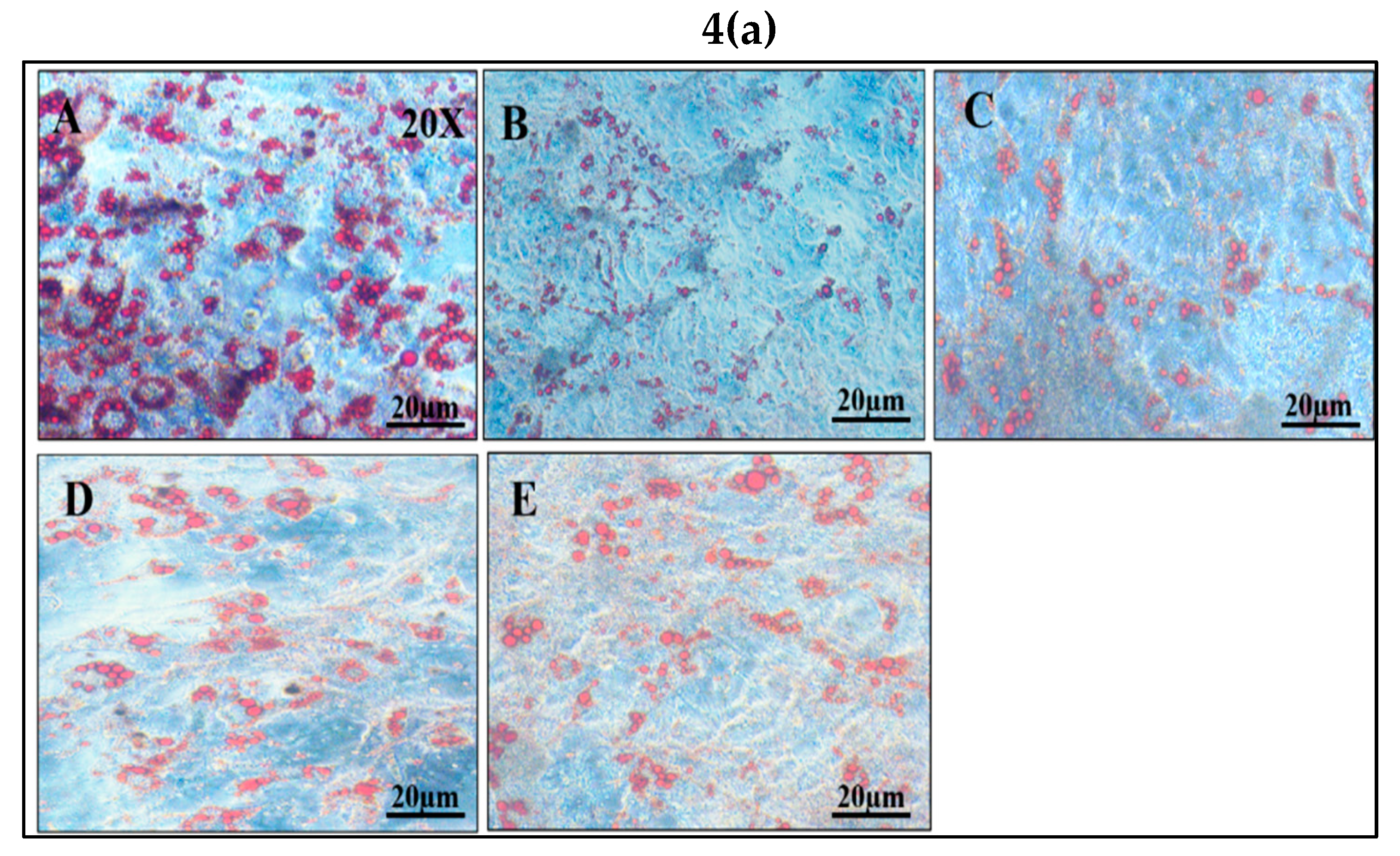
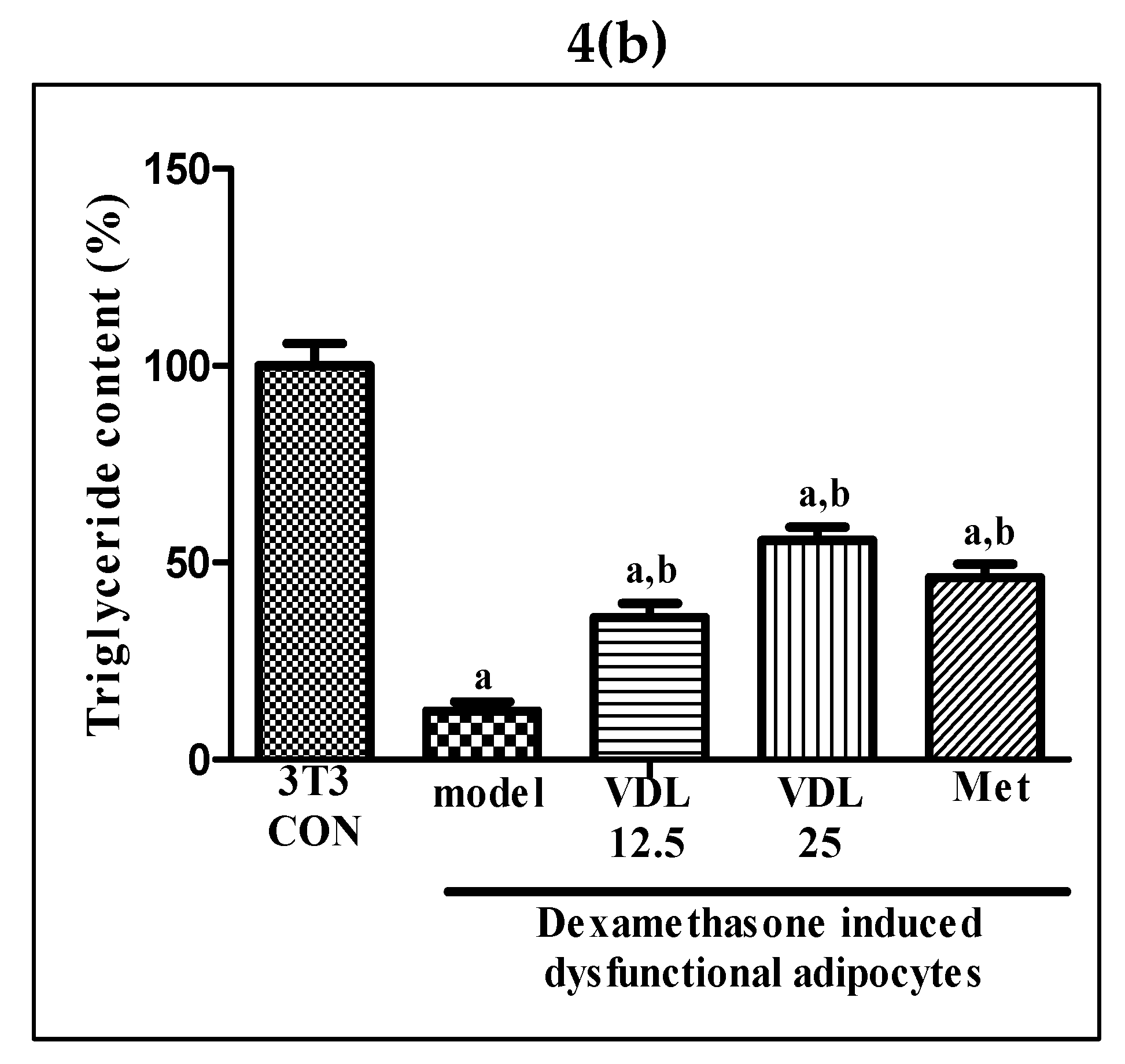
3.3.2. Effect of vindoline on lipid accumulation in dysfunctional adipocytes
Intracellular lipid accumulation, characteristic of mature adipocytes, was found to decrease after the induction of dysfunction with dexamethasone for 48 hours. However, a significant increase in lipid content was observed in dysfunctional adipocytes after vindoline treatment in a dose dependent manner, which is also confirmed by quantification method (
Figure 4a,b).
3.3.3. Effect of vindoline on GLUT-4, IRS-1 and adiponectin expression in dysfunctional adipocytes
The mRNA expression levels of GLUT-4, IRS-1 and adiponectin were significantly lower in dexamethasone induced dysfunctional adipocytes compared with healthy adipocytes. Dysfunctional adipocytes treated with vindoline showed significantly increased expressions of GLUT-4, IRS-1 and adiponectin (
Figure 5)
.
3.3.4. Effect of vindoline on ROS production in IL-1β induced dysfunctional adipocytes
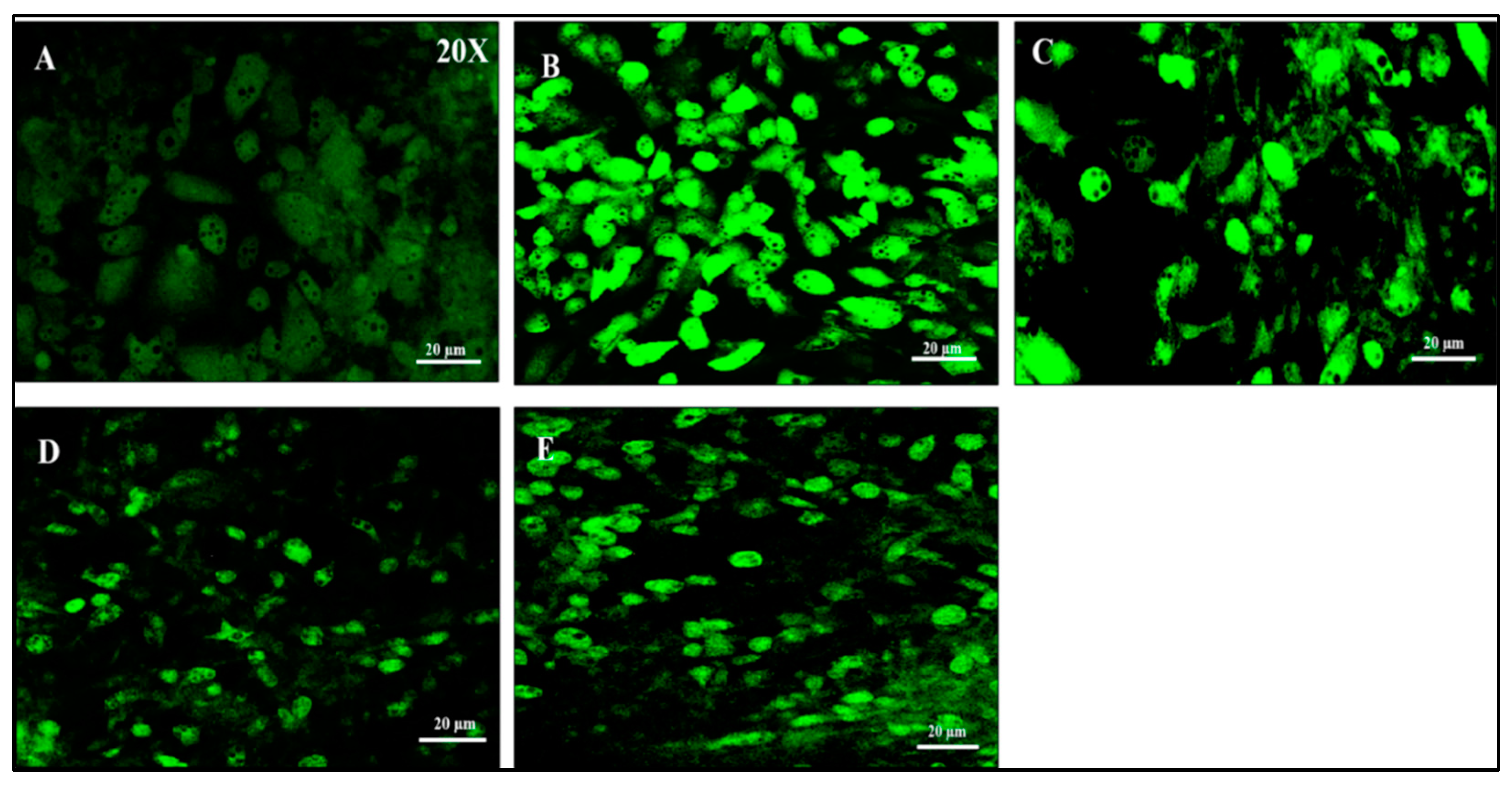
A marked increase in DCF-derived fluorescence was exhibited by IL-1β induced dysfunctional adipocytes, indicating a higher level of intracellular ROS production, when compared to healthy adipocytes. Vindoline treatment for 24 hours resulted in a marked decrease in fluorescence intensity.
Figure 6.
Measurement of ROS production by DCFH-DA staining in IL-1β induced dysfunctional adipocytes after vindoline treatment. A: Control; B: IL-1β induced dysfunctional adipocytes; C: IL-1β induced dysfunctional adipocytes + 12.5 µg/ml vindoline (VDL 25); D: IL-1β induced dysfunctional adipocytes + 25 µg/ml vindoline (VDL 25); E: IL-1β induced dysfunctional adipocytes + Metformin 1mM.
Figure 6.
Measurement of ROS production by DCFH-DA staining in IL-1β induced dysfunctional adipocytes after vindoline treatment. A: Control; B: IL-1β induced dysfunctional adipocytes; C: IL-1β induced dysfunctional adipocytes + 12.5 µg/ml vindoline (VDL 25); D: IL-1β induced dysfunctional adipocytes + 25 µg/ml vindoline (VDL 25); E: IL-1β induced dysfunctional adipocytes + Metformin 1mM.
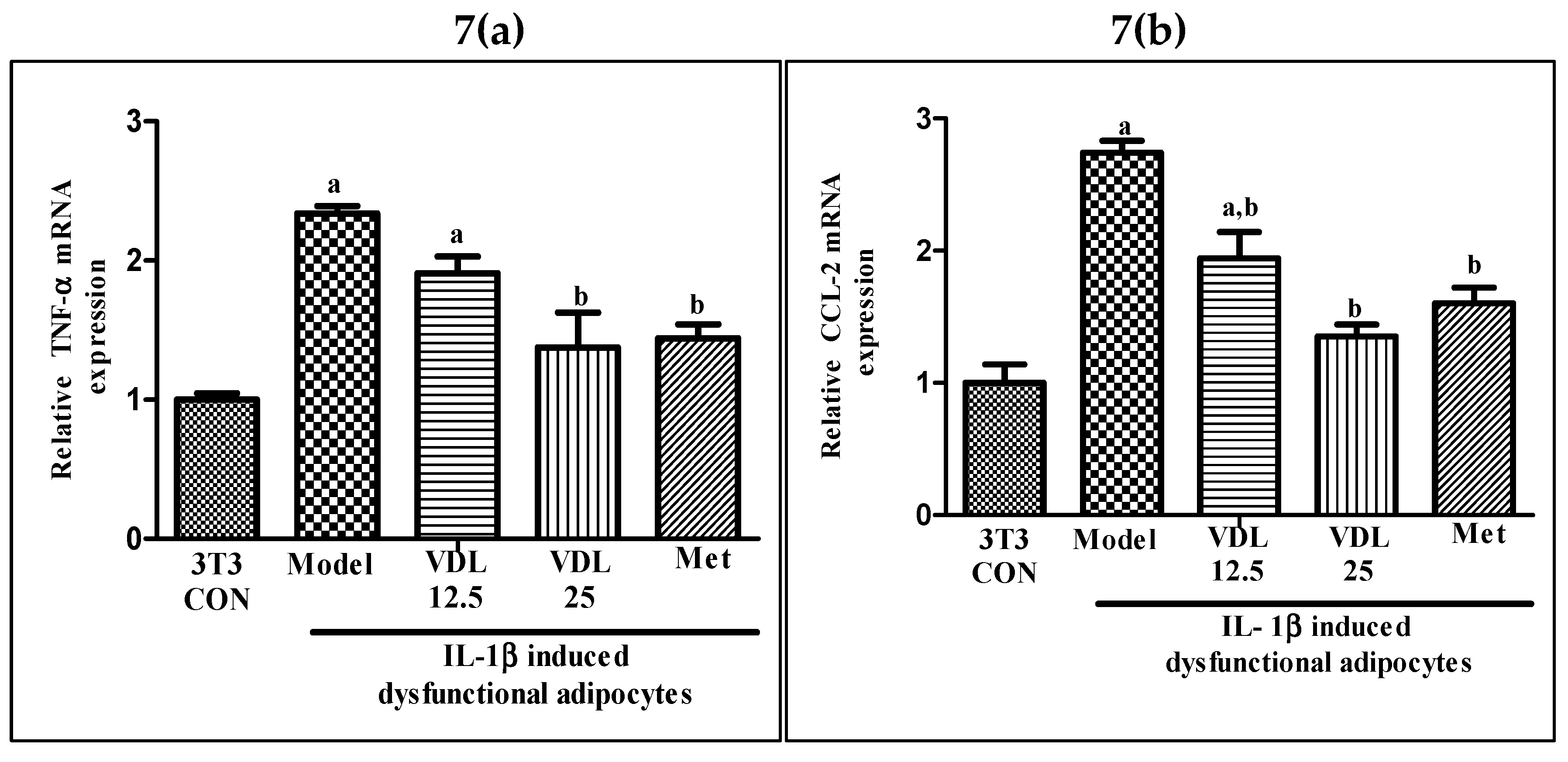
3.3.5. Effect of vindoline on pro-inflammatory gene transcription in IL-1β induced dysfunctional adipocytes
As shown in
Figure 7, the mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory genes such as TNF-α and CCL-2 were significantly upregulated in IL-1β induced adipocytes when compared with the healthy adipocytes. However, treatment with vindoline significantly downregulated the TNF-α and CCL-2 gene transcriptional expression in dysfunctional adipocytes.
3.4. Effect of vindoline on IR- L6 myotubes
3.4.1. Effect of vindoline on glucose consumption in IR-myotubes
Effect of vindoline on glucose consumption in IR- myotubes was estimated by glucose-oxidase method. As shown in
Figure 8, the glucose consumption was significantly decreased in IR model group when compared to control. However, treatment with vindoline for 24 hours significantly increased the glucose consumption of model group in a dose dependent manner.
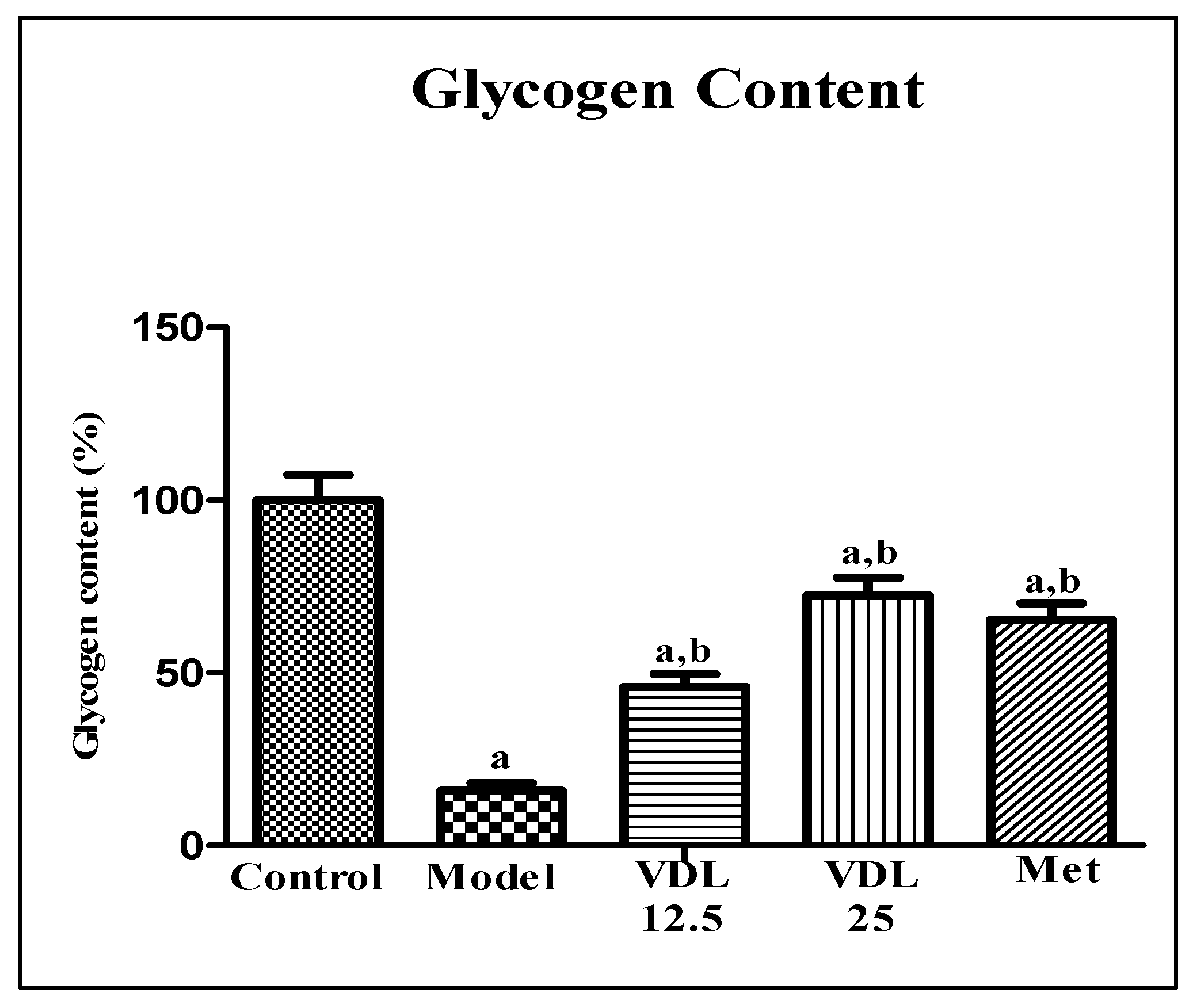
3.4.2. Effect of vindoline on glycogen content in IR-myotubes
The effect of vindoline on glycogen content was estimated by anthrone method. Compared with the control myotubes, the glycogen content in myotubes induced with high glucose decreased significantly. Treatment with different doses of vindoline in high glucose induced myotubes showed a significant increment in glycogen content in a dose dependent manner and which was comparable to the metformin (
Figure 9).
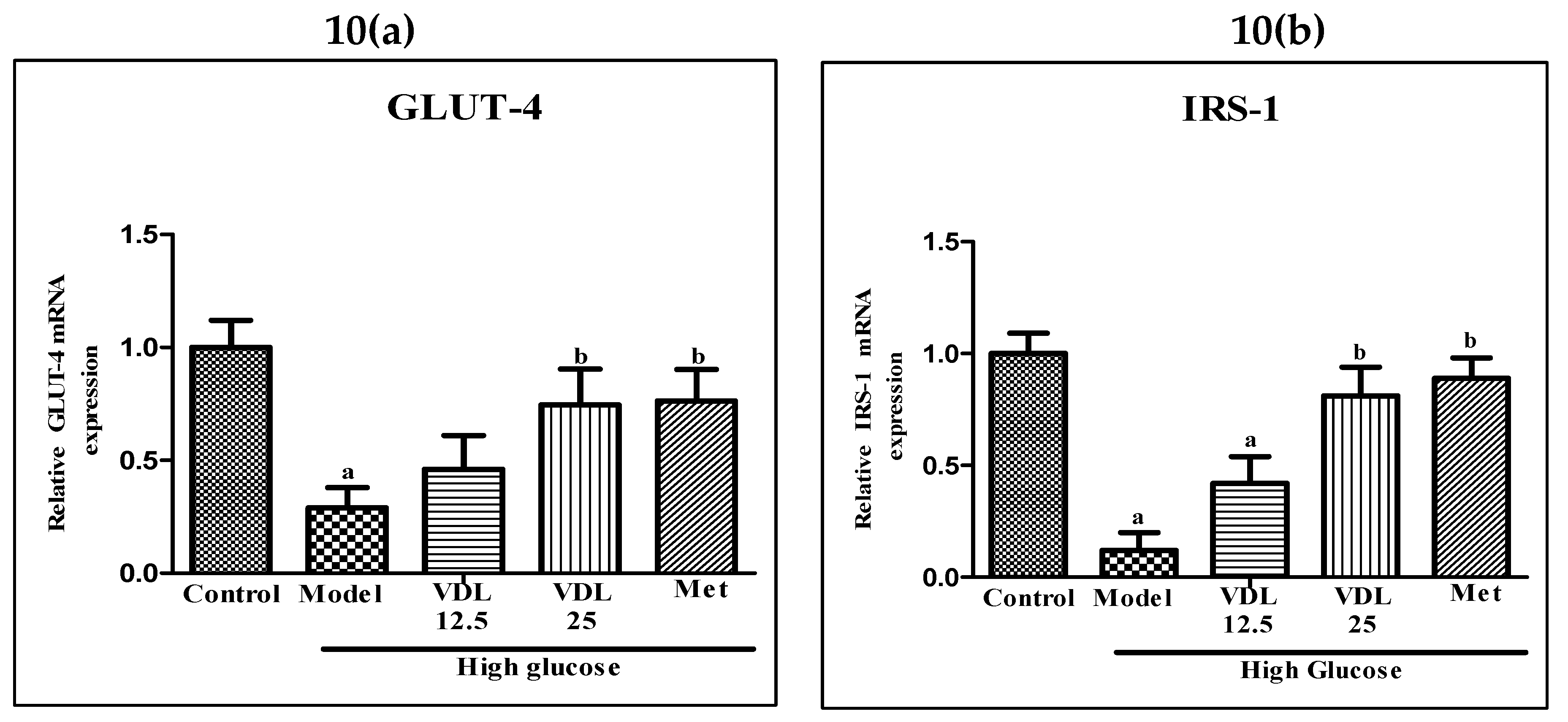
3.4.3. Effect of vindoline on GLUT-4 and IRS-1 expression in IR-myotubes
The mRNA expression levels of GLUT-4 and IRS-1 were significantly lower in glucose induced IR-myotubes when compared with control. On the other hand, IR-myotubes treated with vindoline showed significantly increased expressions of GLUT-4 and IRS-1 (
Figure 10).
4. Discussion
Nutritional overload associated with obesity is associated with the onset of T2DM. One of the first tissues of the body to respond to a nutritional overload is adipose tissue [
17] and the resultant mediators influence the insulin sensitivity of other tissues [
18]. Hence, the main risk factor for insulin resistance is a dysfunctional adipose tissue [
19]. While investigations on several agents with antidiabetic properties have been carried out, very few studies have explored the potential of adipose tissue specific modulatory agents. Vindoline has been demonstrated to possess antidiabetic properties [
20]. However, no systemic work has been carried out on the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-diabetic effect of vindoline in IR models involving adipocytes and skeletal myoblasts. Hence, this study where we have isolated vindoline from
Catharanthus roseus leaves, confirmed its purity by LC-MS/MS analysis, and carried out antidiabetic property evaluation in IR models assumes significance.
In the first phase of this study, we have investigated the role of vindoline on dysfunctional adipocytes using dysfunctional mouse 3T3-L1 adipocytes as in vitro model system. An initial MTT assay evaluation was carried out with different concentrations of vindoline on 3T3-L1 preadipocytes for its effect on cell viability. Assay results confirmed that more than 90% of the cells were viable up to 25µg/ml concentration after 24 hours treatment as compared to untreated control. Hence, two concentrations of vindoline, namely 12.5 and 25µg/ml were selected for the subsequent in vitro studies.
Two adipocyte dysfunction inducers were used in this study, dexamethasone (IR inducer) and IL-1β (adipocyte inflammation inducer). Dexamethasone treatment prevent translocation of GLUT-4 to the cell surface via altering insulin signaling pathway by inhibiting phosphatidylinositol -3- kinase (PI3K) and serine/threonine protein kinase and induces insulin resistance. Dexamethasone treatment also enhances the activity of hormone sensitivity lipase, which leads to increased lipolysis in adipocytes. However, since dexamethasone is a known anti-inflammatory agent, it does not induce inflammation and oxidative stress, another hallmark of insulin resistance in adipocytes. Hence, for the induction of inflammation and oxidative stress in adipocytes, we have used an adipocyte inflammation inducer, IL-1β, which stimulate production of ROS and favoring pro-inflammatory status of the cell, potentiates adipocyte dysfunction of adipocytes [
4].
Obesity linked elevated basal fat cell lipolysis is closely related with insulin resistance. Therefore, inhibition of adipocyte lipolysis is considered as a promising therapeutic goal for treating insulin resistance and obesity associated T2DM [
21]. In the current study, dexamethasone induced dysfunctional adipocytes showed a significant increase in lipolysis as compared with normal adipocytes, but treatment with different concentrations of vindoline inhibited dexamethasone induced lipolysis in a dose dependent manner in dysfunctional adipocytes.
According to previous studies, capacity of adipocytes to respond to insulin depends on expression of IRS-1 and GLUT-4 [
22]. Insulin stimulated adipocytes exhibit increased glucose uptake due to the translocation of GLUT-4, a main insulin regulated glucose transporter, from the cytosol compartment to the plasma membrane via the activation of IRS-1-PI3K-AKT pathway. Increased amount of GLUT-4 in adipose tissue is a good marker of systemic insulin sensitivity [
18,
23] and decreased level of IRS1 has been reported to be involved in insulin resistance [
24]. Adipokines, the physiologically active secretory products of adipocytes, have important role in the metabolism of not only adipose tissue but even the whole body. Hence, these can be used as an indicator for adipose tissue dysfunction and insulin resistance [
25]. Adiponectin, an anti-inflammatory adipokine secreted from adipose tissue also promote recruitment of GLUT-4 to the plasma membrane, thereby maximizing insulin’s ability to mediate glucose uptake, while a low level of adiponectin is associated with obesity, insulin resistance and T2DM [
26]. Our study results showed that dexamethasone induced dysfunctional 3T3-L1 adipocytes treated with different concentrations of vindoline significantly enhanced basal glucose consumption, accompanied by increased expression of GLUT-4, IRS-1 and adiponectin.
Inflammation and insulin resistance in adipose tissue are associated events. In the obese condition, free fatty acids released from adipose tissue trigger production of pro-inflammatory cytokine from adipocytes and induce an inflammatory state and oxidative stress. The elevated expression of pro-inflammatory markers such as CCL-2, IL-6 and TNF-α and infiltration of inflammatory cells in adipose tissue during obesity play a role in the insulin resistance [
27,
28]. Our result showed that IL-1β induction to adipocytes resulted in an enhanced production of ROS and a significant upregulation of pro-inflammatory markers, such as CCL-2 and TNF-α. However, vindoline treatment significantly suppressed the ROS production and transcriptional level of pro-inflammatory cytokines in dysfunctional adipocytes. These results indicate that vindoline treatment can suppress insulin resistance and chronic inflammatory responses in dysfunctional adipocytes.
Previous studies have reported that any alteration of glucose transport in adipocytes results in insulin resistance in skeletal muscle [
29]. Thus, in the next phase of this study, we have investigated the role of vindoline on high glucose induced
in vitro insulin resistant rat skeletal muscle L6 myotubes cells. L6 skeletal muscle cells were treated with different concentrations of vindoline to assess its effect on cell viability. Similar to the observations with adipocytes, the MTT assay results confirmed that more than 90% of the cells were viable up to 25 µg/ml concentration after 24 hours treatment as compared to untreated control. Hence vindoline concentration of 12.5 and 25 µg/ml was selected for the subsequent
in vitro studies with L6 myotubes.
In skeletal muscle of diabetics with insulin resistance, intracellular accumulation of lipid metabolites due to obesity associated adipose tissue dysfunction suppress insulin stimulated IRS-1 tyrosine phosphorylation resulting in inhibition of GLUT-4 translocation to membrane and decreased insulin stimulated skeleton muscle glycogen synthesis [
30]. In our study, the glycogen content was diminished in IR-myotubes, but vindoline treatment to IR-myotubes significantly enhanced glycogen content accompanied by increased upregulation of IRS-1 and GLUT-4.
5. Conclusion
This study shows that vindoline can regulate inflammatory responses and glucose metabolism in dysfunctional adipocytes induced either by dexamethasone or IL-1β and improve insulin sensitivity in high glucose induced IR-myotubes possibly by activation of glycogen storage via IRS-1 and GLUT-4 upregulation. Hence, vindoline can be used as a potent therapeutic agent for the management of obesity associated T2DM.
Author Contributions
Beegum Noorjahan Shijina: Investigation, Experimental analysis, Manuscript writing. Achuthan Radhika: Designing analysis component, Manuscript editing. Sainulabdeen Sherin: Data interpretation, Statistical analysis, Manuscript preparation. Prabath Gopalakrishnan Biju: Experimental design conceptualization, Funding, Data interpretation, Manuscript proof reading.
Funding
The present work was supported by the following funding sources to the authors: Senior Research Fellowship from University Grants Commission, India to BNS and University of Kerala plan fund to PGB.
Institutional Review Board Statement
NA.
Informed Consent Statement
NA.
Data Availability Statement
Data shall be made available on specific request.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the technical and instrumentation support provided by Central Laboratory for Instrumentation and Facilitation (CLIF), University of Kerala for the LC-MS/MS analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors disclose no competing interest in this work.
Abbreviations
CCL2: Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2, DCF-DA: Dichloro-dihydro-fluorescein diacetate, DCM: Dichloromethane, DMEM: Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium, FBS: Fetal bovine serum, GLUT: Glucose transporter, IL: Interleukin, IR: Insulin resistance, IRS: Insulin receptor substrate, LC/MS-MS: Liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry, Met: Metformin, MTT: 3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide, PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, ROS: Reactive oxygen species, T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus, TLC: Thin layer chromatography, TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor- alpha.
References
- Kim, J. N., Han, S. N., Kim, H. K. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Diabetic Effect of Black Soybean Anthocyanins: Data from a Dual Cooperative Cellular System. Molecules, 2021, 26(11): 3363. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.Y., Cui, S.C., Zheng, T.N., Ma, H.J., Xie, Z.F., Jiang, H.W., Li, Y.F., Zhu, K.X., Huang, C.G., Li, J., Li, J.Y. Sarsasapogenin improves adipose tissue inflammation and ameliorates insulin resistance in high-fat diet-fed C57BL/6J mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021, 42(2): 272-81. [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.C., Hsieh, P.S. The role of adipocyte hypertrophy and hypoxia in the development of obesity-associated adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance. Adiposity - Omics and Molecular Understanding. InTech. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Marisol, M. M., Celeste, T. M., Laura, M. M., Fernando, E. G., José, P. C., Alejandro, Z., Omar, M. C., Francisco, A. A., Julio César, A. P., Erika, C. N., Angélica, S. C., Gladis, F., Enrique, J. F., Gabriela, R. Effect of Cucumis sativus on Dysfunctional 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Sci Rep. 2019, 9: 13372. [CrossRef]
- Guilherme, A., Virbasius, J. V., Puri, V., Czech, M. P. Adipocyte dysfunctions linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008, 9: 367-77. [CrossRef]
- Goboza, M., Aboua, Y. G., Chegou, N., Oguntibeju, O. O. Vindoline effectively ameliorated diabetes-induced hepatotoxicity by docking oxidative stress, inflammation and hypertriglyceridemia in type 2 diabetes-induced male Wistar rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019, 112: 108638. [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.G., Chen, F., Li, P., Quan, L., Chen, J., Yu, L., Ding, H., Li, C., Chen, L., Gao, Z., Wan, P. Natural product vindoline stimulates insulin secretion and efficiently ameliorates glucose homeostasis in diabetic murine models. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 150(1): 285-97. [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A., Akhtar, M.A., Islam, M.R., Hossain, M.S., Alam, M.K., Wahed, M.I.I., Rahman, B.M., Anisuzzaman, A.S.M., Shaheen, S.M., Ahmed, M. Antidiabetic and hypolipidemic effects of different fractions of Catharanthus roseus (Linn.) on normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Sci. Res. 2009, 1: 334-44.
- Tiong, S.H., Looi, C.Y., Hazni, H., Arya, A., Paydar, M., Wong, W.F., Cheah, S.C., Mustafa, M.R. and Awang, K. Antidiabetic and antioxidant properties of alkaloids from Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don. Molecules. 2013, 18: 9770-84. [CrossRef]
- Chang, T. H., Polakis, S. E., Differentiation of 3T3-L1 fibroblasts to adipocytes. Effect of insulin and indomethacin on the levels of insulin receptors. J Biol chem. 1978, 253(13), 4693–96. 13. [CrossRef]
- Gao, D., Griffiths, H.R., Bailey, C.J. Oleate protects against palmitate-induced insulin resistance in L6 myotubes. Br J Nutr. 2009, 102(11): 1557-63. [CrossRef]
- Guru, A., Issac, P. K., Saraswathi, N. T., Seshadri, V. D., Gabr, G. A., Arockiaraj, J. Deteriorating insulin resistance due to WL15 peptide from cysteine and glycine-rich protein 2 in high glucose-induced rat skeletal muscle L6 cells. Cell Biol Int. 2021, 45(8): 1698-709. [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983, 65(1-2): 55-63. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L., Yang, Y., Wang, X., Liu, S., Shang, W., Yuan, G., Li, F., Tang, J., Chen, M., Chen, J. Berberine stimulates glucose transport through a mechanism distinct from insulin. Metabolism. 2007, 56(3): 405-12. [CrossRef]
- Pedraza-Chaverrí, J., Reyes-Fermín, L. M., Nolasco-Amaya, E. G., Orozco-Ibarra, M., Medina-Campos, O. N., González-Cuahutencos, O., Rivero-Cruz, I., Mata, R. ROS scavenging capacity and neuroprotective effect of alpha-mangostin against 3-nitropropionic acid in cerebellar granule neurons. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2009, 61(5): 491-501. [CrossRef]
- Issac, P. K., Guru, A., Chandrakumar, S. S., Lite, C., Saraswathi, N. T., Arasu, M. V., Al-Dhabi, N. A., Arshad, A., Arockiaraj, J. Molecular process of glucose uptake and glycogen storage due to hamamelitannin via insulin signalling cascade in glucose metabolism. Mol Biol Rep. 2020, 47(9): 6727-40. [CrossRef]
- Burhans, M.S., Hagman, D.K., Kuzma, J.N., Schmidt, K.A., Kratz, M. Contribution of Adipose Tissue Inflammation to the Development of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Compr Physiol. 2018, 9(1): 1-58. [CrossRef]
- Cignarelli, A., Genchi, V. A., Perrini, S., Natalicchio, A., Laviola, L., Giorgino, F. Insulin and Insulin Receptors in Adipose Tissue Development. Int J Mol Sci. 2019, 20(3): 759. [CrossRef]
- Oliva, M. E., Ferreira, M. R., Chicco, A., and Lombardo, Y. B. Dietary Salba (Salvia hispanica L) seed rich in α-linolenic acid improves adipose tissue dysfunction and the altered skeletal muscle glucose and lipid metabolism in dyslipidemic insulin-resistant rats. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2013, 89(5): 279-89. [CrossRef]
- Goboza, M., Meyer, M., Aboua, Y.G., Oguntibeju, O.O. In Vitro Antidiabetic and Antioxidant Effects of Different Extracts of Catharanthus roseus and Its Indole Alkaloid, Vindoline. Molecules, 2020, 25: 5546. [CrossRef]
- Morigny, P., Houssier, M., Mouisel, E., Langin, D. Adipocyte lipolysis and insulin resistance. Biochimie, 2016, 125: 259-66. [CrossRef]
- Veilleux, A., Blouin, K., Rhéaume, C., Daris, M., Marette, A., Tchernof, A. Glucose transporter 4 and insulin receptor substrate-1 messenger RNA expression in omental and subcutaneous adipose tissue in women. Metabolism. 2009, 58(5), 624-31. [CrossRef]
- Petersen, M.C., Shulman, G.I. Mechanism of insulin action and insulin resistance. Physiol Rev. 2018, 98(4): 2133-223. [CrossRef]
- James, D.E., Stöckli, J., Birnbaum, M.J. The aetiology and molecular landscape of insulin resistance. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22(11): 751-71. [CrossRef]
- Chen, H., Li, J., Zhang, Y., Zhang, W., Li, X., Tang, H., Liu, Y., Li, T., He, H., Du, B., Li, L., Shi, M. Bisphenol F suppresses insulin-stimulated glucose metabolism in adipocytes by inhibiting IRS-1/PI3K/AKT pathway. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022, 231: 113201. [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y., Luo, N., Klein, R.L., Garvey, W.T. Adiponectin promotes adipocyte differentiation, insulin sensitivity, and lipid accumulation. J Lipid Res. 2005, 46(7): 1369-79. [CrossRef]
- Hammerstedt, A., Rotter Sopasakis, V., Gogg, S. Improved insulin sensitivity and adipose tissue dysregulation after short-term treatment with pioglitazone in non-diabetic, insulin-resistant subjects. Diabetologia. 2005, 48: 96-104. [CrossRef]
- Wang, M., Chen, Y., Xiong, Z., Yu, S., Zhou, B., Ling, Y., Zheng, Z., Shi, G., Wu, Y., Qian, X. Ginsenoside Rb1 inhibits free fatty acids-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol Med Rep. 2017, 16(6): 9165-72. [CrossRef]
- Abel, E.D., Peroni, O., Kim, J.K., Kim, Y.B., Boss, O., Hadro, E., Minnemann, T., Shulman, G.I,, Kahn, B.B. Adipose-selective targeting of the GLUT4 gene impairs insulin action in muscle and liver. Nature. 2001, 409 (6821): 729-33. [CrossRef]
- Petersen, K.F., Shulman, G.I. Etiology of insulin resistance. Am J Med. 2006, 119 (5 supp 1): S10-S16. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).